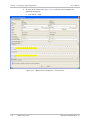
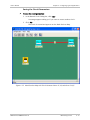
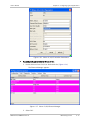
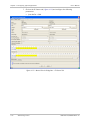
Download RADview-SC/TDMoIP - RADProductsOnline
Transcript
RADview-SC/TDMoIP Network Management System for TDM Pseudowire Gateways IPmux-24 © 1994–2008 RAD Data Communications Publication 05/08 Contents Chapter 1. Introduction 1.1 IPmux-24 Overview .................................................................................................... 1-1 1.2 RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Overview ..................................................................... 1-1 Overview of the RADview FCAPS Model ................................................................... 1-2 Overview of the IPmux-24 Management Functions .................................................. 1-3 Chapter 2. Installation and Setup 2.1 Pre-Configuring IPmux-24 for Network Management................................................... 2-1 Configuring the IP Parameters ................................................................................. 2-1 Configuring the Manager List .................................................................................. 2-2 2.2 Connecting IPmux-24 to the Management Station ...................................................... 2-3 2.3 Launching RADview IPmux-24 ..................................................................................... 2-3 2.4 Using the GUI ............................................................................................................. 2-4 Selecting the Device or a Port ................................................................................. 2-5 Status Indicators..................................................................................................... 2-5 Common Dialog Buttons ......................................................................................... 2-6 System Level Menu Options .................................................................................... 2-6 Port Level Menu Options ......................................................................................... 2-8 Chapter 3. Configuration Management 3.1 Setting the System Parameters .................................................................................. 3-2 Configuring System Parameters............................................................................... 3-2 Configuring System Information .............................................................................. 3-4 Maintaining the Manager List .................................................................................. 3-6 Changing an Entry in the Managers List .............................................................. 3-7 Removing an Entry from the Managers List ......................................................... 3-7 Viewing the Host .................................................................................................... 3-7 Configuring the System Clocks ................................................................................ 3-8 Configuring Bridge Parameters .............................................................................. 3-10 Viewing Bridge Ports ............................................................................................. 3-11 Changing Bridge Port Parameters...................................................................... 3-12 Configuring the MAC Table .................................................................................... 3-12 Adding a New Entry .......................................................................................... 3-14 Removing a Static Entry from the MAC Table .................................................... 3-14 Deleting the MAC Table .................................................................................... 3-15 Configuring the Static MAC Table........................................................................... 3-15 Adding a New Entry to the Static MAC Table ..................................................... 3-17 Removing an Entry from the Static MAC Table................................................... 3-17 Removing all Entries from the Static MAC Table ................................................ 3-17 Configuring VLAN Membership (Egress) ................................................................. 3-18 Adding a VLAN Membership (Egress)................................................................. 3-19 Changing a VLAN Membership (Egress) ............................................................. 3-20 Removing a VLAN Membership (Egress) ............................................................ 3-20 Configuring VLAN Parameters ................................................................................ 3-20 Adding a VLAN ................................................................................................. 3-21 Changing VLAN Parameters............................................................................... 3-22 Removing a VLAN ............................................................................................. 3-23 Configuring QoS Classification ............................................................................... 3-23 RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 i Table of Contents User's Manual Configuring QOS Mapping ..................................................................................... 3-24 802.1P Mapping ............................................................................................... 3-24 DSCP Mapping .................................................................................................. 3-25 ToS Mapping .................................................................................................... 3-27 Port Default Priority Mapping ........................................................................... 3-28 Configuring Quality of Service (Rate Limitation)..................................................... 3-29 3.2 Setting the Operational Parameters.......................................................................... 3-30 Configuring IPmux-24 Ports at the Physical Layer................................................... 3-30 Configuring the E1/T1 Ports.............................................................................. 3-30 Configuring the Ethernet Ports ......................................................................... 3-35 Configuring the Internal Ethernet Ports............................................................. 3-36 Assigning Timeslots to Bundles ............................................................................. 3-38 Selecting an Available Time Slot ........................................................................ 3-40 Selecting all Available Time Slots....................................................................... 3-40 Removing all Selected Timeslots from a Bundle ................................................. 3-40 Managing Bundle Connections............................................................................... 3-40 Creating Bundle Connections ............................................................................ 3-40 Removing Bundle Connections .......................................................................... 3-41 Removing a Bundle........................................................................................... 3-43 3.3 Additional Tasks ....................................................................................................... 3-44 Displaying Ethernet Interface Information ............................................................. 3-44 Displaying Ethernet SFP Information...................................................................... 3-45 Displaying Ethernet Optical SFP Information .......................................................... 3-46 Resetting IPmux-24 to the Default Configuration................................................... 3-47 Polling the Agent .................................................................................................. 3-47 Resetting IPmux-24............................................................................................... 3-48 Chapter 4. Configuring Typical Applications 4.1 Configuring the IPmux-24 Units .................................................................................. 4-3 Configuring the Host IP Parameters ......................................................................... 4-3 Configuring the Manager List .................................................................................. 4-4 4.2 Connecting IPmux-24 to the Management Station ...................................................... 4-4 4.3 Configuration Sequence ............................................................................................. 4-4 4.4 Creating Circuits ......................................................................................................... 4-5 Creating a Mesh Service Circuit ................................................................................ 4-6 Defining the E1 Parameters ................................................................................ 4-6 Creating a Circuit .............................................................................................. 4-10 Saving the Circuit Parameters ........................................................................... 4-13 Displaying the Circuit Parameters ..................................................................... 4-14 Creating a Normal Service Circuit ........................................................................... 4-15 Defining the E1 Parameters .............................................................................. 4-16 Creating a Circuit .............................................................................................. 4-18 Saving the Circuit Parameters ........................................................................... 4-23 Displaying the Circuit Parameters ..................................................................... 4-24 Chapter 5. Security Management 5.1 Setting Management Access Authorizations................................................................ 5-1 5.2 Unix Users and Permissions ........................................................................................ 5-2 Chapter 6. Performance Management 6.1 Introduction ............................................................................................................... 6-1 6.2 Setting the Polling Interval ......................................................................................... 6-2 ii RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 Viewing Viewing Viewing Viewing Viewing Viewing Viewing Table of Contents Bundle Statistics............................................................................................ 6-3 HDLC Statistics .............................................................................................. 6-5 Bundle Current Statistics ............................................................................... 6-6 Bundle Intervals Statistics .............................................................................. 6-8 E1/T1 Port Current Statistics ......................................................................... 6-9 Port Intervals Statistics ................................................................................ 6-11 Ethernet Port Statistics................................................................................ 6-13 Chapter 7. Fault Management 7.1 Monitoring Object Status............................................................................................ 7-1 Masking Traps ......................................................................................................... 7-1 Viewing Active Alarms ............................................................................................. 7-3 Viewing the History Log .......................................................................................... 7-4 Clearing the History Log .......................................................................................... 7-6 Viewing Self Test Results ........................................................................................ 7-7 7.2 Performing Loopback Tests ........................................................................................ 7-7 RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 iii Table of Contents iv User's Manual RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Chapter 1 Introduction This chapter provides an overview of the IPmux-24 version 1.0 device, as well as the RADview Service Center TDMoIP IPmux-24 functions. This chapter contains the following sections: • IPmux-24 Overview • RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Overview • Overview of the RADview FCAPS Model • Overview of the IPmux-24 Management Functions. 1.1 IPmux-24 Overview IPmux-24 offers a solution for extending traditional E1/T1 or serial data services transparently over packet switched networks (PSNs) such as IP, Ethernet, and MPLS networks. IPmux-24 converts the data stream coming from its TDM ports into configurable-sized packets that are extended over Gigabit or Fast Ethernet network ports, and vise versa. 1.2 RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Overview IPmux-24 includes an SNMP agent that enables full management from the network via SNMP, for example, by means of RADview network management stations. In addition, IPmux-24 includes the following additional management capabilities via both out-of-band and inband communication: • Supervision terminal (ASCII terminal or a PC running a terminal emulation program), connected either directly or through a modem or any other type of full-duplex data link. This terminal can perform all of the IPmux-24 supervision and configuration functions, including preliminary system configuration. • Telnet, from any host capable of IP communication with IPmux-24. The functions available via Telnet are similar to those available from a supervisory terminal. • Web browsers, using ConfiguRAD. ConfiguRAD is a user-friendly Web-based element management system that is embedded in IPmux-24 and provided at no extra cost. ConfiguRAD can be accessed from any standard Web browser. This manual discusses configuration via RADview, RAD’s SNMP-based network management application for PC or Unix. To configure IPmux-24 via ASCII terminal, Telnet, or Web browser, see the IPmux-24 Installation and Operation Manual. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Overview 1-1 Chapter 1 Introduction User's Manual Overview of the RADview FCAPS Model RADview provides a complete solution for monitoring and controlling IPmux-24. The RADview solutions conform to ITU-T Telecommunication Management Network (TMN) recommendations for SNMP management systems, known as the FCAPS model: 1-2 • Fault management – detects and correlates faults in network devices, isolates faults and initiates recovery actions. • Configuration management – tracks configuration changes, configures, installs and distributes software and configuration files over the network. • Accounting management – collects accounting data and generates network usage reports. • Performance management – continuously monitors network performance (QoS, CoS) and resource allocation. • Security management – controls and restricts access to network resources. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Overview RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 1 Introduction Overview of the IPmux-24 Management Functions Table 1-1 lists the operations that you can perform via RADview, and their locations in this manual. Table 1-1. Management Functions Operation Location in User’s Manual Configuration: Chapter 3 • Configuring System Parameters • Configuring System Information • Maintaining the Manager List • Viewing the Host • Configuring System Clocks • Configuring Protection • Configuring Bridge Parameters • Configuring Bridge Ports • Configuring the MAC Table • Configuring the Static MAC Table • Configuring VLAN Membership (Egress) • Configuring VLAN Parameters • Configuring Ethernet Ring • Configuring QoS Classification • Configuring QoS Mapping • Configuring Quality of Service (Rate Limitation) • Deleting the LAN Table • Configuring IPmux-24 Ports at the Physical Layer • Configuring the Internal Ethernet Ports • Assigning Timeslots to Bundles • Managing Bundle Connections • Removing Bundle Connections • Displaying Ethernet Interface Information • Displaying Ethernet SFP Information • Displaying Ethernet Optical SFP Information • Displaying Bundle Connection Information • Resetting IPmux-24 to the Default Configuration • Polling the Agent • Resetting IPmux-24 Chapter 5 Security: • Telnet and Web Access Chapter 6 Peformance: • Setting the Polling Interval • Viewing Bundle Statistics • Viewing Bundle Current Statistics • Viewing Bundle Intervals Statistics • Viewing E1/T1 Current Port Statistics • Viewing Port Intervals Statistics • Viewing Ethernet Port Statistics RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Overview 1-3 Chapter 1 Introduction 1-4 User's Manual Operation Location in User’s Manual Fault: Chapter 7 • Masking Traps • Viewing Active Alarms • Viewing the History Log • Clearing the History Log • Viewing Self Test Results • Performing Loopback Tests RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Overview RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Chapter 2 Installation and Setup This chapter describes how to configure IPmux-24 for management and connect them to the management station, and includes the following sections: • Pre-configuring IPmux-24 for Network Management Configuring the IP Parameters Configuring the Manager List • Connecting IPmux-24 to the Management Station • Launching RADview IPmux-24 • Using the GUI Selecting the Device or a Port Status Indicators Common Dialog Buttons System Level Menu Options Port Level Menu Options. 2.1 Pre-Configuring IPmux-24 for Network Management To remotely manage IPmux-24 via a network management station (NMS), it is necessary to first configure some basic parameters via an ASCII terminal session to the control port. The following steps are required: 1. Configuring the host IP parameters (IP address, IP mask, default gateway) 2. Defining the network management station in the manager list. For more detailed information about configuring IPmux-24 for network management, see Chapter 4 of the IPmux-24 Installation and Operation Manual. Configuring the IP Parameters The IPmux host IP parameters may be assigned automatically via DHCP or they may be configured manually. ³ To manually configure the host IP parameters: 1. Display the Host IP menu (Configuration > System > Host IP). 2. Disable the DHCP mechanism. 3. Save the changes. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Pre-Configuring IPmux-24 for Network Management 2-1 Chapter 2 Installation and Setup User's Manual 4. Enter the new host IP parameters for IPmux: Host IP address IP mask Default gateway 5. Save the changes. Configuration>System>Host IP 1. IP address 2. IP mask 3. Default gateway 4. DHCP 5. DHCP Status ... (192.168.10.1) ... (255.255.255.0) ... (0.0.0.0) (Disable) > > Please select item <1 to 5> ESC-prev.menu; !-main menu; &-exit 1 Mngr/s Figure 2-1. Configuring the Host IP Parameters for IPmux-24 Configuring the Manager List ³ To configure the Manager List: 1. Display the Manager List menu (Configuration > System > Management > Manager List). 2. Enter the IP address of the network management station. 3. Save the changes. Configuration>System>Management>Manager list 1. Manager IP address ... (192.168.10.100) 2. Link up/down trap (Disable) 3. Alarm trap (Disable) 4. VLAN tagging (Disable) > Please select item <1 to 4> ESC-prev.menu; !-main menu; &-exit 1 Mngr/s Figure 2-2. Configuring the Manager List 2-2 Pre-Configuring IPmux-24 for Network Management RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 2 Installation and Setup 2.2 Connecting IPmux-24 to the Management Station IPmux-24 can be managed by a network management station (NMS) that is located on the LAN (hub or switch) connected to the one of the unit’s Ethernet ports. ³ To connect IPmux-24 to the network management station: 1. Connect a network management station to the LAN (hub or switch). 2. Connect one of IPmux’s Ethernet ports to the LAN. 2.3 Launching RADview IPmux-24 The RADview IPmux-24 management application can be opened from the SNMPc Management Console (PC version), HPOV (Unix version), or Network Elements Tree windows. A separate RADview IPmux-24 management window can be opened for each IPmux-24 unit. Note ³ In order to launch the Element Manager, you must first ensure that the server is running and start the client. If it is not already in the NMS database, you must also add the IPmux object to the NMS as a managed element. For additional details on launching and using RADview please refer to the RADview-SC/TDMoIP User's Manual. To open the IPmux Element Manager from the SNMPc Management Console window (PC version): • Double-click the IPmux-24 icon located in the map view. The RADview IPmux Element Manager window appears. ³ To open the IPmux Element Manager from the EMS HPOV window (Unix version): • Select the IPmux-24 icon located in the map view and then click the zoom icon ( ). The RADview IPmux Element Manager window appears. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Launching RADview IPmux-24 2-3 Chapter 2 Installation and Setup 2.4 User's Manual Using the GUI Figure 2-3. Element Manager – IPmux The RADview IPmux Element Manager window provides a dynamically updated representation of the IPmux-24 network element, allowing you to monitor and manage the IPmux device. The Element Manager window displays the device hardware configuration, represented as a list of rows, showing the existing slots and ports. IPmux is managed by selecting a row and then selecting the desired function from the menus. In many cases, this will open a sub-window or dialog box, allowing further selection and manipulation. The status of each port is indicated by the background color of its row, according to the following table. Table 2-1. Element Manager Port Status Colors Row Color Status White/Gray Normal Purple Fail Blue Test Each row in the Element Manager window contains three columns: 2-4 • The Object column (Interface Name) represents the system or slot object. • The Interface Type column represents the type of interface port installed in this slot. • The Connector Type column represents the type of physical connector on this port. Using the GUI RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 2 Installation and Setup Selecting the Device or a Port By selecting a row, you can manipulate or manage the selected system or port. When selected, a light blue frame is displayed around the selected window, and the background color of the selected row is dark gray. Only one row can be selected at a time. There are two IPmux user interface object levels: ³ • System (whole device) – contains all of the parameters and functions that are common to the whole device. • Port – contains all of the parameters and functions of the selected port. To select the entire device (system): • ³ In the Element Manager window, click the System row. To select a port: • In the Element Manager window, click the row of the desired port. Status Indicators At the top of the window, the title bar displays <element name>:<status>, where status is either Connected or Disconnected, according to the current connectivity of the network element to the NMS. At the bottom of the Element Manager window, there is also a communications status bar. Sometimes, congestion in the network handling the management traffic causes significant delays during polling, transfer of large data tables, etc. When feasible, a progress bar is used to inform the operator of the ongoing process status. Otherwise, a message is displayed in the status bar at the bottom of the screen, according to the following table. Table 2-2. Element Manager Status Bar Messages Message Status Working... Displayed from the moment when a request is sent to the network element (IPmux-24), until data is received or a certain time expires (around 5 seconds). Waiting... Displayed while the RADview station waits more than a few seconds for the network element response, but less than the time-out time. Interrupted When all attempts to communicate with network element failed (timeout), or when the response was an SNMP error. Ready Displayed after the process has been successfully completed. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Using the GUI 2-5 Chapter 2 Installation and Setup User's Manual Common Dialog Buttons Function buttons, located in a sub-window or dialog box, each initiate the execution of an operation. The most common buttons, and their respective functions, are listed in the following table. Table 2-3. Common Dialog Buttons Button Function Set Confirm and activate the selections made in the dialog box and close the box. Apply Confirm and activate the selections made in the dialog box without closing the box. Cancel Cancel the selections made in the dialog box and close the box. Close Close the dialog box without any other effect. OK Confirm the message displayed in an information box, and close the box. Add Open a new dialog box that is used to add a new item to the list or table displayed in the dialog box. Change Open a new dialog box that is used to change an item selected in the list or table displayed in the dialog box. Delete Delete a selected item from the list or table displayed in the dialog box. Refresh Poll the managed unit to retrieve again the information needed to display the current dialog box. This action updates the displayed information. System Level Menu Options The following tables list the RADview tasks that are available on the system level. Table 2-4. System Management Options Tasks – Configuration Dialog Box and Parameter Location Path Configuring System Information System Information dialog box See Configuring System Information Configuration ´System Info… Configuring System Parameters System Parameters dialog box See Configuring System Parameters Configuration ´System Parameters… Viewing Bundle Connection Table Bundle Connection Table See Configuring Bundles Configuration ´Bundle ´Bundle ConnectionTable… Configuring Bridge Parameters Bridge Parameters dialog box Configuration ´Bridge ´Parameters… See Configuring Bridge Parameters. 2-6 Using the GUI RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 2 Installation and Setup Tasks – Configuration Dialog Box and Parameter Location Path Viewing Bridge Ports Bridge Ports Table Configuration ´Bridge ´Ports… See Viewing Bridge Ports. Configuring the MAC Table MAC Table dialog box See Configuring the MAC Table Configuration ´Bridge ´MAC Table… Configuring VLAN Membership (Egresss) VLAN Membership (Egress) dialog box See Configuring VLAN Membership Configuration (Egress) Configuring 802.1P Mapping 802.1 Mapping See 802.1P Mapping. Configuring DSCP Mapping DSCP Mapping See DSCP Mapping. Configuring TOS Mapping TOS Mapping See TOS Mapping. Configuring Port Default Priority Mapping Port Default Priority Mapping Configuring Quality of Service (Rate Limitation) Rate Limitation dialog box See Configuring Quality of Service See Port Default Priority Mapping (Rate Limitation) Configuring Ethernet Ring Ethernet Ring dialog box See Configuring Ethernet Ring. ´Bridge ´VLAN Membership (Egress)… QoS ´Mapping ´802.1P… QoS ´Mapping ´DSCP… QoS ´Mapping ´TOS… QoS ´Mapping ´Port Default Priority… Configuration ´QoS ´Rate Limitation… Configuration ´ETH Ring… Deleting LAN tabel Delete LAN Table dialog box See Deleting LAN Table Configuration ´System Commands ´Delete LAN Table Restoring default configuration Default Configuration dialog box See Resetting IPmux-24 to the Default Configuration ´System Commands ´Default Configuration Configuration Resetting the IPmux-24 device Reset Agent dialog box See Resetting IPmux-24 Configuration ´System Commands ´Reset Polling the Agent See Polling the Agent Configuration ´System Commands ´Poll Agent Configuring the System Clocks System Clocks dialog box See Configuring the System Clocks Configuration ´Clocks… Tasks – Fault Dialog Box and Parameter Location Path Viewing active alarms Active Alarm List Fault RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Using the GUI 2-7 Chapter 2 Installation and Setup Tasks – Configuration User's Manual Dialog Box and Parameter Location Path See Viewing Active Alarms ´Alarms… Viewing the history log System Log Buffer See Viewing the History Log Fault ´History Log ´List… Clearing the history log See Clearing the History Log Fault ´History Log ´Clear Viewing self test results Self Test Results dialog box See Viewing Self Test Results Diagnostics ´Self Test Results… Tasks – Options Dialog Box and Parameter Location Path Viewing the Host configuration Host dialog box See Viewing the Host Configuration. Options ´Host Interface IP List… Establishing link between IPmux-24 and manager Manager List dialog box See Maintaining Manager List Options ´Manager List… Masking traps Masking Traps dialog box See Masking Traps Options ´Masking Traps… Setting Telnet and Web Access Access dialog box See Enabling or Disabling Telnet and Options ´Access… Web Access Tasks – Statistics Dialog Box and Parameter Location Path Setting polling interval Polling Interval dialog box See Setting the Polling Interval Statistics ´Polling Interval… Viewing bundle statistics Bundle Statistics dialog box See Viewing Bundle Statistics Statistics ´Bundle Statistics… Port Level Menu Options The following tables list the RADview tasks that are available on the port level. Table 2-5. Port Level Management Options Tasks – Configuration Dialog Box and Parameter Location Path Viewing Interface Information Interface Information dialog box See Viewing Ethernet Interface Configuration ´Interface Info… (for Ethernet only) Configuring port parameters Information Interface Parameters dialog box See Configuring the E1/T1 Ports, Configuration ´Parameters… Configuring the Ethernet Ports, Configuring the Serial Port, Configuring the Internet Ethernet Ports. Configuring bundles 2-8 Using the GUI Bundle dialog box See Configuring Bundles Configuration ´Bundles… RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 2 Installation and Setup Tasks – Diagnostics Dialog Box and Parameter Location Path Initiate a loopback Loopback State dialog box See Performing a Loopback Test Diagnostics ´Loopback… Tasks – Statistics Dialog Box and Parameter Location Path Interface Statistics dialog box See Viewing Ethernet Port Statistics Statistics ´Interface Statistics… Viewing current statistics Port Current Statistics dialog box See Viewing Current Statistics Statistics ´Current… Viewing intervals statistics Port Intervals Statistics dialog box See Viewing Intervals Statisitics Statistics ´Intervals … Ethernet Interface Viewing Ethernet interface statistics (only for Ethernet) E1/T1 Interface RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Using the GUI 2-9 Chapter 2 Installation and Setup 2-10 Using the GUI User's Manual RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Chapter 3 Configuration Management This chapter describes how to configure IPmux-24 on all levels, including system and port, and contains the following sections: • • • Setting the System Parameters Configuring System Parameters Configuring System Information Maintaining the Manager List Viewing the Host Configuring the System Clocks Configuring Bridge Parameters Viewing Bridge Ports Configuring the MAC Table Configuring the Static MAC Table Configuring VLAN Membership (Egress) Configuring VLAN Parameters Configuring QoS Classification Configuring QOS Mapping Configuring Quality of Service (Rate Limitation) Setting the Operational Parameters Configuring IPmux-24 Ports at the Physical Layer Configuring the E1/T1 Ports Configuring the Ethernet Ports Configuring the Internal Ethernet Ports Assigning Timeslots to Bundles Managing Bundle Connections Additional Tasks Displaying Ethernet Interface Information Displaying Ethernet SFP Information Displaying Ethernet Optical SFP Information Resetting IPmux-24 to the Default Configuration RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-1 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Polling the Agent Resetting IPmux-24 3.1 Setting the System Parameters Configuring System Parameters The System Parameters command enables you to view and set major system parameters for the IPmux-24 device. You can configure parameters such as the Default Gateway, DHCP Client Mode, Aging Time, and Transmit Clock Source, and the External Clock User Quality. ³ To set system parameters for the selected IPmux device: 1. Select Configuration > System Parameters…. The System Parameters dialog box appears (see Figure 3-1). System Parameters differ, depending on the different port combinations. Table 3-1 describes the different system parameters. 2. Configure the desired parameters. 3. Click <Set> to implement the changes. Figure 3-1. System Parameters Dialog Box 3-2 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Table 3-1. System Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Default Gateway IP Address DHCP Mode DHCP Client Mode Enabled - Enables DHCP Client action for IPmux-24 Disabled - Disables DHCP Client action for IPmux-24 Default: Enabled Aging Time (sec.) Aging Time, in seconds Checked, Unchecked 0..4080 Default: 300 Note: When the checkbox is checked, the Aging Time parameter is enabled and its value can be changed. Transmit Clock Source The source of the transmit clock Internal - Local clock source is used External - Recovered from the other interface network and used for data transmission on this interface Loopback - Transmit clock recovered from received data Adaptive - Adaptive clock regeneration Note: Field is disabled if an activate circuit is connected. External Clock User Quality Allows the user to mark the quality level of the clock ST1 - Stratum-1 PRC (Primary Reference Clock) Rec. G.811 (0x10) ST2 - Stratum-2 SSU-T (Sync. Source Unit-Transit) Rec. G.812 Transit (0x70) ST3 - Stratum-3 SSU-L (Sync. Source Unit Local) Rec. G.812 Local (0xA0) ST3E - Stratum-3 Enhanced Clock (0xD0) Default: ST1 The quality is encoded according to SSM (Synchronization Status Messages) encoding. The binary bits in positions 8765---- of the byte are encoded in the following manner (Bit 8 is the left-most and most significant bit (MSB); bit 5 is the least significant bit (LSB)): Bit No. 8765 Description 0010 - Stratum-1 / PRC (Primary Reference Clock) Rec. G.811 0100 - Stratum-2 / SSU-T (Sync. Source Unit-Transit) Rec. G.812 Transit 1000 - Stratum-3 / SSU-L (Sync. Source Unit Local) Rec. G.812 Local [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-3 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Configuring System Information The System Info command enables you to view and set system information for the IPmux-24 device. This information is useful for identifying multiple IPmux-24 units and for tracking their locations and administrative contacts. You can also use the System Information dialog box for setting the system Date and Time and for viewing the DHCP client status. ³ To set system information for the selected IPmux device: 1. Select Configuration > System Info…. The System Information dialog box appears (see Figure 3-2). 2. Enter the required settings as described in Table 3-2. 3. Click <Set> to implement the changes. Figure 3-2. System Information Dialog Box 3-4 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Table 3-2. System Information Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Description Description of the system Object ID Object ID Name System name Contact System contact Location System location System Up Time System up time Date System date Time System time Number of Interfaces Number of interfaces on the system Read only DHCP Status Server ID DHCP Server IP address Read only Lease Expiration Time The time left, in minutes, until lease expiration Status DHCP Status [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-5 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Maintaining the Manager List In order to remotely configure IPmux-24, the IP address of the NMS must be listed in the Manager List. The Manager List command enables you to display and configure the Manager List, where you designate the destination NMS stations for SNMP traps. The Manager list has 10 static entries for 10 Managers. ³ To display the manager list: • Select Options > Manager List.... The Manager List appears. Figure 3-3. Manager List Dialog Box Note An entry where IP Address = 0.0.0.0 is considered “no manager” entry. To add an entry, see Changing an Entry in the Managers List. Table 3-3. Manager List Parameters Parameter Possible Values/Remarks Manager ID The Manager List ID. IP Address IP address of the Network Management System IP Mask The IP Mask. Mask Traps Indicates whether or not traps are masked by the system. Yes, No [Change…] Click to change an entry in the Managers List [Remove] Click to remove an entry from the Manages List [Close] Click to apply the Managers List parameters and close the dialog box [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. 3-6 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Changing an Entry in the Managers List ³ To change an entry in the Manager List: 1. Select an entry in the Manager List and click <Change…> The Change Manager dialog box appears (Figure 3-4). 2. Change the desired parameters. The Change Manager parameters are the same as the parameters for the Manager Table (see Table 3-3). 3. Click <Set> to implement the changes. A message appears, warning about possible disconnection of the manager. 4. Click <OK> to continue. Figure 3-4. Change Manager Dialog Box Removing an Entry from the Managers List ³ To remove an entry from the Manager List: 1. Select a row from the Manager List (Figure 3-3) and click <Remove>. A message appears, warning about possible disconnection of the manager. 2. Click <OK>. Viewing the Host ³ To view the host: • Select Options > Host Interface IP List…. The Host Interface IP List dialog box appears (see Figure 3-5). The parameters are described in Table 3-4. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-7 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Figure 3-5. Host Dialog Box Table 3-4. Host Interface IP List Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks IP Address Host IP Read only VLAN Tagging VLAN Tagging No, Yes Note: If VLAN Tagging = Yes, the VLAN ID and VLAN Priority values will be used for the bundles. VLAN ID Host VLAN ID 1…4095 VLAN Priority Host VLAN frame priority. 0..7 [Close] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Configuring the System Clocks The System Clocks command enables you to configure the Master and Fallback clocks that keep the IPmux-24 communications lines synchronized with external devices. You can also use this command to mark the Clock Quality (Stratum) Level. ³ To configure the system clocks: 1. Select Configuration > Clocks…. 2. The System Clocks Dialog Box appears (see Figure 3-6). 3. Configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-5, and click <Set>. Note 3-8 Master and Fallback clocks cannot be set to the same port. 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Figure 3-6. System Clocks Dialog Box Table 3-5. System Clocks Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Current Clock Indicates the current source of the system clock (read only). Master Fallback Master Clock Source Adaptive Internal Rx Port Station (External) Port 1 Fallback Clock Source Adaptive Internal Rx Port Station (External) Port 1 [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-9 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Configuring Bridge Parameters ³ To configure bridge parameters: 1. Select Configuration > Bridge > Parameters…. The Bridge Parameters Table appears (see Figure 3-7). 2. Configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-6. 3. Click <Set>. Figure 3-7. Bridge Parameters Dialog Box Table 3-6. Bridge Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks VLAN Mode Aware, Unaware Default: Unaware Note: When chaning the VLAN Mode, the following message appers: “Changing VLAN Mode may disconnect the Agent” Forwarding Mode Bridge forwarding mode Filter – filter frames received according to MAC Address Transparent – forward all frames received (not dependent on VLAN) Default: Filter Aging Time (sec.) Aging Time, in seconds Checked, Unchecked 0..4080 Default: 300 Note: When the checkbox is checked, the Aging Time parameter is enabled and its value can be changed. [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. 3-10 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Viewing Bridge Ports ³ To view bridge ports: 1. Select Configuration > Bridge > Ports…. The Bridge Ports Table appears (see Figure 3-8). 2. Configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-7. 3. Click <Close>. Figure 3-8. Bridge Ports Table Table 3-7. Bridge Port Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Port The selected port. Read only Ingress Filtering Enable, Disable Read only Accept Frame Type All, Tag Only Read only Port VID/Stacking VID 1..4094 Default: 1 Default Priority Tag Default frame priority of the VLAN added by the port. 0..7 Read only Tag Handling Indicates how the Ingress VLAN Tag is processed. None, Stacking Read only Note: This field only exists when Bridge VLAN Mode = Unaware and is only enabled for USER ports. [Change…] Click to change the parameters of the Bridge Port. [Close] Click to apply the settings and close the window. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-11 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Parameter Possible Values / Remarks [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Changing Bridge Port Parameters ³ To change bridge port parameters: 1. From the Bridge Ports Table just described, select a row. 2. Click <Change…>. The Change Bridge Port Table appears (see Figure 3-9). 3. Configure the desired parameters. The Change Bridge Port parameters are the same as the parameters for the Bridge Port Table (see Table 3-7). 4. Click <Set>. Figure 3-9. Change Bridge Port Dialog Box Configuring the MAC Table The Mac Table command enables you to manually configure Virtual (VLAN) Bridged Local Area Networks, port-based VLANs (per IEEE 802.1Q), where VLAN membership of a data frame is determined based upon the bridge port on which the frame is received and the frame's destination MAC address. The mappings of Received Bridge Ports and destination MAC Addresses to VLAN IDs are stored in the MAC Table. ³ To configure the MAC Table: 1. Select Configuration > Bridge > MAC Table…. The MAC Table dialog box appears (see Figure 3-10). 2. To sort the information in the MAC Table, click on the column you wish to sort it by. 3. Configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-8. 4. Click <Close>. 3-12 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Figure 3-10. MAC Table Dialog Box Table 3-8. MAC Table Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks VLAN ID 1…4094 Read only Note: This parameter appears when VLAN Mode = Aware. MAC Address The destination MAC address in a frame to which this entry's filtering information applies Note: The second nibble in the MAC Address must be an even number. Read only Received Bridge Port The port number of the port from which a frame must be received in order for this entry's filtering information to apply NET–ETH 1 NET/USER–ETH 2 USER–ETH 3 Read only Status Learned Static Read only [Add…] Click to add a new entry to the table. [Remove] Click to remove an entry from the table. [Remove All] Click to delete the table. [Next] Click to display the next 500 entries. [Close] Click to apply Static MAC Table parameters and close the window. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-13 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Parameter Possible Values / Remarks [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window Adding a New Entry ³ To add a new entry: 1. From the MAC Table just described, click <Add…>. The MAC Table: Add Entry dialog box appears (see Figure 3-11, Figure 3-15). 2. Configure the desired parameters. The Add Entry parameters are the same as the parameters for the Mac Table (see Table 3-8, Table 3-9). 3. Click <Apply>. The new entry is added to the table. 4. Click <Close>. The Add Entry dialog closes and the Static MAC Table dialog box displays the updated table. Figure 3-11. MAC Table: Add Entry Dialog Box Removing a Static Entry from the MAC Table ³ To remove a static entry: 1. From the MAC Table just described, select one or multiple static row(s) you wish to remove from the table. 2. Click <Remove>. A confirmation message appears. Figure 3-12. Removing a Static Entry Confirmation Box 3. Click <OK>. The static entries are removed from the table. 3-14 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Deleting the MAC Table ³ To delete the MAC Table: 1. From the MAC Table just described, click <Remove All>. A confirmation message appears. Figure 3-13. Remove All Confirmation Box 2. Click <OK>. All of the entries are removed from the table. Configuring the Static MAC Table The Mac Table command enables you to manually configure Virtual (VLAN) Bridged Local Area Networks, port-based VLANs (per IEEE 802.1Q), where VLAN membership of a data frame is determined based upon the bridge port on which the frame is received and the frame's destination MAC address. The mappings of Received Bridge Ports and destination MAC Addresses to VLAN IDs are stored in the Static MAC Table. ³ To configure the MAC table: 1. Select Configuration > MAC Table…. The Static MAC Table dialog box appears (see Figure 3-14). 2. To sort the information in the Static MAC Table, click on the column you wish to sort it by. 3. Configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-9. 4. Click <Close>. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-15 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Figure 3-14. Static MAC Table Dialog Box Table 3-9. Static MAC Table Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks VLAN ID 1..4094 MAC Address The destination MAC address in a frame to which this entry's filtering information applies Received Bridge Port The port number of the port from which a frame must be received in order for this entry's filtering information to apply User1 User2 Network [Add…] Click to add a new entry to the table. [Remove] Click to remove an entry from the table. [Remove All] Click to remove all entries from the table. 3-16 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Adding a New Entry to the Static MAC Table ³ To add a new entry: 1. Click <Add>. The Static MAC Table: Add Entry dialog box appears (see Figure 3-15). 2. Configure the desired parameters. The Add Entry parameters are the same as the parameters for the Static Mac Table (see Table 3-9). 3. Click <Apply>. The new entry is added to the table. 4. Click <Close>. The Add Entry dialog closes and the Static MAC Table dialog box displays the updated table. Figure 3-15. Static MAC Table: Add Entry Dialog Box Removing an Entry from the Static MAC Table ³ To remove an entry from the Static MAC table: 1. Select the rows of entries you wish to remove from the table. 2. Click <Remove>. A confirmation message appears. 3. Click <OK>. The entries are removed from the table. Removing all Entries from the Static MAC Table ³ To remove all entries from the Static MAC Table: 1. Click <Remove All>. A confirmation message appears. 2. Click <OK>. All of the entries are removed from the table. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-17 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Configuring VLAN Membership (Egress) The VLAN Membership (Egress) Configuration command enables you to configure the list of virtual LANs (VLANs) for IPmux-24. A VLAN is a logical (virtual) network of devices that behave as if they are on the same physical LAN segment, even if they are physically connected to different network segments. In addition, multiple VLANs can co-exist on the same switching hardware, providing a form of logical network segmentation. Note ³ VLAN Membership (Egress) is only enabled when VLAN Mode = Aware. To view VLAN Membership (Egress): 1. Select Configuration > Bridge > VLAN Membership (Egress)…. The VLAN Membership (Egress) Table appears (see Figure 3-16). 2. Configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-10. 3. Click <Close>. Figure 3-16. VLAN Membership (Egress) Table Table 3-10. VLAN Membership (Egress) Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks VLAN ID The VLAN ID 1...4094 Read only VLAN Name The name of the VLAN name. Read only NET-ETH 1 Tagged, Untagged, None Read only 3-18 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Parameter Possible Values / Remarks NET/USER-ETH 2 Tagged, Untagged, None Read only USER-ETH3 Tagged, Untagged, None Read only [Add…] Click to add a new VLAN Membership (Egress). [Change…] Click to change the parameters of a VLAN Membership (Egress). [Remove] Click to remove a VLAN Membership (Egress). [Close] Click to apply changes and close the window, [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Adding a VLAN Membership (Egress) ³ To add a VLAN Membership (Egress): 1. From the VLAN Membership (Egress) Table just described, click <Add…>. The Add VLAN Membership (Egress) dialog appears (see Figure 3-17). 2. Configure the desired parameters. The Add VLAN Membership (Egress) parameters are the same as the parameters for the VLAN Membership (Egress) Table (see Table 3-10). 3. Click <Apply>. The new VLAN Membership (Egress) is added to the table. 4. Click <Close>. The VLAN Membership (Egress) dialog closes. Figure 3-17. Add VLAN Membership (Egress) Dialog Box Note The number of VLANs cannot exceed 64. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-19 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Changing a VLAN Membership (Egress) ³ To change a VLAN Membership (Egress): 1. From the VLAN Membership (Egress) Table just described, select the row you wish to change and click <Change…>. The Change VLAN Membership (Egress) dialog appears (see Figure 3-18). 2. Configure the desired parameters. The Change VLAN Membership (Egress) parameters are the same as the parameters for the VLAN Membership (Egress) Table (see Table 3-10). 3. Click Apply. The VLAN Membership (Egress) is changed. 4. Click Close. The VLAN Membership (Egress) dialog closes. Figure 3-18. Change VLAN Membership (Egress) Dialog Box Removing a VLAN Membership (Egress) ³ To remove a VLAN Membership (Egress): 1. Select a VLAN Membership (Egress) in the VLAN Membership (Egress) Table. 2. Click <Remove>. The selected VLAN Membership (Egress) is removed from the table. Configuring VLAN Parameters The VLAN Configuration command enables you to configure the list of virtual LANs (VLANs). A VLAN is a logical (virtual) network of devices that behave as if they are on the same physical LAN segment, even if they are physically connected to different network segments. In addition, multiple VLANs can co-exist on the same switching hardware, providing a form of logical network segmentation. ³ To configure VLAN parameters: 1. Select Configuration > VLAN Configuration…. The VLAN Configuration dialog box appears. 3-20 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management 2. Configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-11. 3. Click <Close>. Figure 3-19. VLAN Configuration Dialog Box Table 3-11. VLAN Configuration Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks VLAN ID 1..4094 VLAN Name The name of the VLAN Network Port Yes, No Bundle No, Yes Manager No IP Address [Add…] Click to add a new VLAN. [Change…] Click to change the parameters of a VLAN. [Remove] Click to remove a VLAN. [Close] Click to apply the VLAN parameters and close the dialog box. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the dialog box. Adding a VLAN ³ To add a new VLAN: 1. In the VLAN Configuration dialog box just described, click [Add…]. The Add VLAN dialog appears (see Figure 3-20). 2. Configure the desired parameters. The Add VLAN parameters are the same as the parameters for the VLAN Configuration Table (see Table 3-11). RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-21 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual 3. Click Set. The VLAN is added and the screen is refreshed. Figure 3-20. Add VLAN Dialog Box Note • The Add button will be disabled if there are already 16 VLANs in the table. • The VLAN ID must be different from any already in the table. Changing VLAN Parameters ³ To change VLAN Parameters: 1. In the VLAN Configuration dialog box just described, click the row of a VLAN, to select it. 2. Click <Change…>. The Change VLAN dialog appears (see Figure 3-21). 3. Configure the desired parameters. The Change VLAN parameters are the same as the parameters for the VLAN Configuration Table (see Table 3-11). 4. Click <Set>. The VLAN parameters are changed. Figure 3-21. Change VLAN Dialog Box 3-22 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Removing a VLAN ³ To remove a VLAN: 1. In the VLAN Configuration dialog box just described, click the row of a VLAN to select it. 2. Click <Remove>. A warning message appears: “Removing VLAN may disconnect the Agent for 30 seconds“. 3. Click <OK>. The VLAN is removed. Note The Remove button is only enabled for disconnected VLANs; if the selected VLAN is used by a bundle or a Manager, then the Remove button will be disabled. Configuring QoS Classification ³ To configure QoS classification: 1. Select Configuration > QoS > Classification. The QoS Classification dialog box appears (see Figure 3-22). 2. For each of the bridge ports, select the QoS classification, as described in Table 3-12. 3. Click <Set>. Figure 3-22. QoS Classification Dialog Box Table 3-12. QoS Classification Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Network 802.1p, DSCP, TOS, Per Port User 1 802.1p, DSCP, TOS, Per Port User 2 802.1p, DSCP, TOS, Per Port TDM PW 802.1p, DSCP, TOS, Per Port [Set] Click to set and save the information. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-23 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Parameter Possible Values / Remarks [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Configuring QOS Mapping 802.1P Mapping ³ To configure 802.1P mapping: 1. Select Configuration > QoS > Mapping > 802.1P…. The 802.1P Mapping dialog box appears (see Figure 3-23). 2. Select one or multiple cells (see Table 3-13 for a description of the parameters). 3. Click <Set>. Figure 3-23. 802.1p Mapping Table 3-13. 802.1P Mapping Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks 1 User Priority 0…7 (cells titles) st: Read only 2 :Traffic Class nd 0…3 Read only [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Traffic Class>] Click to update the Traffic Class. [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. 3-24 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Updating the Traffic Class ³ To update the Traffic Class: 1. In the 802.1P dialog just described, select one or multiple cells. 2. Click <Traffic Class>. A submenu appears (see Figure 3-24), displaying available Traffic Class values. 3. Select a Traffic Class value. The submenu closes. 4. Click <Set>. The Traffic Class value is updated. Figure 3-24. Updating Traffic Class Menu DSCP Mapping ³ To configure DSCP mapping: 1. Select Configuration > QoS > Mapping > DSCP…. The DSCP Mapping dialog box appears (see Figure 3-25). 2. Select one or multiple cells (see Table 3-14 for a description of the parameters). 3. Click <Set>. Figure 3-25. DSCP Mapping RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-25 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Table 3-14. DSCP Mapping Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks 1 User Priority DSCP value of the incoming IP packet. st: 0…63 (cells titles) Read only 2 :Traffic Class nd The regenerated priority level the incoming DSCP value is mapped to. 0…3 Read only [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Traffic Class>] Click to update the Traffic Class. [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Updating the Traffic Class ³ To update the Traffic Class 1. In the DSCP dialog just described, select one or multiple cells. 2. Click <Traffic Class>. A submenu appears (see Figure 3-26), displaying available Traffic Class values. 3. Select a Traffic Class value. The submenu closes 4. Click <Set>. The Traffic Class value is updated. Figure 3-26. Updating Traffic Class Menu 3-26 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management ToS Mapping ³ To configure ToS mapping: 1. Select Configuration > QoS > TOS…. The TOS Mapping dialog box appears (see Figure 3-27). 2. Select one or multiple cells (see Table 3-15 for a description of the parameters). 3. Click <Set>. Figure 3-27. TOS Mapping Table 3-15. TOS Mapping Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks 1 User Priority DSCP value of the incoming IP packet. st: 0…7 (cells titles) Read only 2 :Traffic Class The regenerated priority level the incoming DSCP value is mapped to. nd 0…3 Read only [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Traffic Class>] Click to update the Traffic Class. [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Updating the Traffic Class ³ To update the Traffic Class: 1. In the TOS dialog just described, select one or multiple cells. 2. Click <Traffic Class>. A submenu appears (see Figure 3-28), displaying available Traffic Class values. 3. Select a Traffic Class value. The submenu closes RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-27 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual 4. Click <Set>. The cell or cells Traffic Class value is updated. Figure 3-28. Updating Traffic Class Menu Port Default Priority Mapping ³ To configure Port Default Priority mapping: 1. Select Configuration > QoS > Port Default Priority…. The Port Default Priority Mapping dialog box appears (see Figure 3-29). 2. Select one or multiple cells (see Table 3-16 for a description of the parameters). 3. Click <Close>. Figure 3-29. Port Default Priority Mapping Table 3-16. Port Default Priority Mapping Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks 1 User Priority A unique port index. st: 0…7 (cells titles) Read only 2 :Traffic Class nd The Traffic Class level of this port. 0…3 Read only [Close] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. 3-28 1BSetting the System Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Configuring Quality of Service (Rate Limitation) The Rate Limitation command enables you to configure rate limits for IPmux-24, in order to maintain Quality of Service (QoS) during times of high network traffic. You can select Ingress Rate Boundaries to define the rate limiting ranges for the ingress traffic. The actual data rate of the incoming traffic is selected from the rates limited by the boundaries. These boundaries are applied to the regular and flooded Rate Limits. You can also select regular or flooded Rate Limits, to be applied to all frames. ³ To configure Quality of Service (Rate Limitation): 1. Select Configuration > QoS > Rate Limitation…. The Rate Limitation dialog box appears (see Figure 3-30). 2. For each Ethernet port, configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-17 and click <Set>. Figure 3-30. Rate Limitation Dialog Box Table 3-17. Rate Limitation Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Egress Rate Limitation (Mbps) The maximum rate permitted to transfer via this port (per Ethernet port: NET–ETH 1/USER-2 /USER–ETH 3) No Limit, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 41, 50, 60, 83, 125, 250 Ingress Rate Limitation The maximum rate permitted at ingress of this port with this Traffic Priority (per Ethernet port: NET–ETH 1/USER-2 /USER–ETH 3) No Limit, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 41, 50, 60, 83, 125, 250 Ingress Burst Size (Kbytes) The burst size that the port can support beyond the rate limitation determined by value selected in Egress Rate Limitation. 12, 24, 48, 96 Note: This parameter is only available is Ingress Rate Limitation <> No Limit. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BSetting the System Parameters 3-29 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Ingress Limit Packet Type The packet type that will be rate limited. Rate limitation is determined by value selected in Egress Rate Limitation. All – all packet types are rate limited Broadcast, Multicast and Flooded Unicast – Broadcast, Multicast and Flooded Unicast are rate limited Broadcast and Multicast – Broadcast and Multicast packets are rate limited Broadcast – Broadcast packets are rate limited [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. 3.2 Setting the Operational Parameters Configuring IPmux-24 Ports at the Physical Layer Configuring the E1/T1 Ports The E1/T1 Interface Parameters command enables you to configure the various parameters of the E1/T1 port (the port’s software configuration). The parameters vary according to the port type. ³ To display or configure E1/T1 parameters: 1. Click an E1/T1 port. 2. Select Configuration > Parameters.... The E1 or T1 Interface Parameters dialog box appears (see Figure 3-31 and Figure 3-32). 3. Configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-18 and click <Set>. 3-30 2BSetting the Operational Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Figure 3-31. E1 Interface Parameters Dialog Box RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 2BSetting the Operational Parameters 3-31 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Figure 3-32. T1 Interface Parameters Dialog Box Table 3-18. E1/T1 Interface Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Port E1, T1 Admin Status Enable, Disable Transmit Clock Source Source of the transmit clock Adaptive - Adaptive clock regeneration Loopback - Transmit clock recovered from received data Internal - Local clock source, either the internal clock or an external clock that is directly attached to IPmux-24 System - Recovered from the other interface network and used for data transmission on this interface. This option is only available when the external clock is operational. Default: Adaptive 3-32 2BSetting the Operational Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Parameter Possible Values / Remarks User Clock Quality Marks the quality level of clock ST1 - Stratum-1 Clock (0x10) ST2 - Stratum-2 Clock (0x70) ST3 - Stratum-3 Clock (0xA0) ST3E - Stratum-3 Enhanced Clock (0xD0) Default: ST1 Note: If Network Type = Type A, only ST1 and ST2 are available. The quality is encoded according to SSM (Synchronization Status Messages) encoding. The binary bits in positions 8765---- of the byte are encoded in the following manner (Bit 8 is the left-most and most significant bit (MSB); bit 5 is the least significant bit (LSB)): Bit No. 8765 Description 0010 - Stratum-1 / PRC (Primary Reference Clock) Rec. G.811 0100 - Stratum-2 / SSU-T (Sync. Source Unit-Transit) Rec. G.812 Transit 1000 - Stratum-3 / SSU-L (Sync. Source Unit Local) Rec. G.812 Local Rx Sensitivity Determines the maximum attenuation of the receive signal that can be compensated for by the interface receive path Long Haul - -32 dB Short Haul - -10 dB Line Type Line type affects the number of bits per second that the link can reasonably carry. It also affects the interpretation of the port performance statistics. For E1 ports: Framed (G.704), Framed-CRC, Framed-MF, Framed-CRC-MF Unframed (G.703) - Use when the data being transmitted is unframed. For T1 ports: ESF - Extended SuperFrame D4 - AT&T D4 format Unframed - Use when the data being transmitted is unframed. Note: Line Type is grayed out and can't be changed when a bundle is defined over the selected interface. Line Code Type of Zero Code Suppression used on the link (only applicable for T1 ports) B7ZS, B8ZS, AMI Idle Code Byte pattern of the data transmitted in the E1/T1 Framer idle timeslots (not applicable when the Line Type is unframed) 0 to FF Signaling Mode Type of signaling used on the link (only applicable for T1 ports) None, Robbed Bit Line Interface T1 device operation mode DSU, CSU Note: Only applicable for T1 ports RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 2BSetting the Operational Parameters 3-33 Chapter 3 Configuration Management Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Line Length (feet) 0-133, 134-266, 267-339, 400-533, 534-655 User's Manual Note: Only applicable for T1 ports with Line Mode DSU Line Buildout (dB) Transmit line gain for T1 CSU line mode 0, -.5, -5, -2.5 Note: Only applicable for T1 ports with CSU Line Mode Restore Time (sec) Used to change the sync. Algorithms to reduce the time required for the port to return to normal operation after a RED (LOF - loss of frame synchronization) alarm. 1, 10 Note: Only applicable for T1 ports. Not applicable when the Line Type is Unframed. OOS Signaling Defines the value to be sent as a signal after alarm detection: Space - Both A and B signaling bits are forced to '0' during out-of-service periods Mark - Both A and B signaling bits are forced to '1' during out-of-service periods Space_Mark - A and B bits are forced to '0' for 2.5 seconds; then they are switched to '1' until out-of-service condition disappears Mark_Space - A and B bits are forced to '1' for 2.5 seconds; then they are switched to '0' until out-of-service condition disappears Space Signaling Code Space Signaling Code – value to be sent as a signal during the first 2.5 seconds after alarm detection E1, T1-ESF: 1..F T1-SF(D4): 1..4 Mark Signaling Code Trunk conditioning signal value after alarm detection E1, T1-ESF: 1..F T1-SF(D4): 1..4 OOS Code Trunk conditioning data pattern to be sent upon a DS0 fail Note: When Line Type is set to Unframed, OOS Code is grayed out and its value cannot be changed. AIS Transmit Enable, Disable Trail Mode Enables the end-to-end transfer of TDM OAM in framed mode, when theirTDMoIP Payload Format is set to V2. Termination - Trail mode is disabled Extension - Trail mode is enabled Network Type The network layer from which the clock is derived. Type A = 12 Type B = 13 Note: This parameter is only applicable when Transmit Clock Source = Adaptive. Note: If Network Type is set to Type A and User Clock Quality is set to ST3, ST3E or Other, the following message is displayed in the status bar: “For Network Type A the only valid values of User Clock Quality are ST1, ST2”. [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Cancel] Click to close the window. 3-34 2BSetting the Operational Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Parameter Possible Values / Remarks [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Configuring the Ethernet Ports The Ethernet Interface Parameters command enables you to configure the various parameters of the Ethernet port (the port’s software configuration). ³ To set configuration parameters for the Ethernet interface: 1. Click the User or Network Ethernet port. 2. Select Configuration > Parameters... The Ethernet Interface Parameters dialog box appears (Figure 3-33). 3. Configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-19 and click <Set>. Note The User Ethernet rate is the smaller value of User Rate Limit and (100–TDMoIP traffic). Figure 3-33. IPmux-24 Interface Parameters Dialog Box – Network/User Port Table 3-19. Ethernet Interface Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Port The selected port. NET–ETH 1, NET/USER–ETH 2, USER–ETH 3 Read only Type ETH Name Port name NET–ETH 1, NET/USER–ETH 2, USER–ETH 3 Read only for internal ETH RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 2BSetting the Operational Parameters 3-35 Chapter 3 Configuration Management Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Adminstrative Status The desired state of the link. User's Manual Down, Up Operational Status The actual link status. Up, Down, Testing Auto Negotiation Checked (enabled), Unchecked (disabled) Note: Disabled for fiber optic Ethernet interface. Notes: This parameter is not available for internal ETH. Max Capability Advertised Defines the maximum capabilities of the interface. 10BASE-T half duplex mode, 10BASE-T full duplex mode, 100BASE-TX half duplex mode, 100BASE-TX full duplex mode Note: Working in half duplex mode is not optimal and might cause communication problems. Disabled for fiber optic Ethernet interface. Notes: This parameter is not available for internal ETH. This parameter is read only for SFP connector. Default Type 10BASE-T half duplex mode, 10BASE-T full duplex mode, 10BASE-TX half duplex mode, 10BASE-TX full duplex mode Notes: This parameter is read only for internal ETH. This parameter is read only for SFP connector. [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Note • Changing the Boundaries parameter automatically changes the set of values that may be selected for the User1 and User2 ports in the Rate Limit and Flooded Rate Limit combo-boxes. For Network ports, it only changes the set of values that may be selected in the Flooded Rate Limit combo-box. When the set of selectable values for a combo-box is automatically changed, its parameter value is set to Disable. • For user ports (User1, User2), Flooded Rate Limit is only available when Rate Limit is set to Disable. If Rate Limit is not set to Disable, then Flooded Rate Limit is grayed out, and its value is not used. • If Flooded Rate Limit is not set to Disable then Rate Limit is grayed out, and its value is not used. Note When Auto Negotiation is disabled and Max Capability Advertised is different from the capabilities of the LAN, for example, when Max Capability is 100BaseT full duplex, while the LAN is in 10BaseT half duplex, the NMS will disconnect. Configuring the Internal Ethernet Ports The Internal Ethernet Interface Parameters command enables you to configure the various parameters of the Internal Ethernet port. 3-36 2BSetting the Operational Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management ³ To set configuration parameters for the Internal Ethernet interface: 1. Click the Internal Ethernet port. 2. Select Configuration > Interface... The Internal Ethernet Interface Parameters dialog box appears (see Figure 3-34). 3. Configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-20 and click <Set>. Figure 3-34. Internal Ethernet Interface Parameters Dialog Box Table 3-20. Internal Ethernet Interface Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Port The selected port. Read only Type ETH IP Address The host interface IP address. IP Mask The host interface subnet mask. Default Next Hop The host interface default Next Hop address. This address is used as the default next hop for every Bundle mapped to this host. Encapsulation VLAN Tagging VLAN Tagging No, Yes Note: If VLAN Tagging = Yes, the VLAN ID and VLAN Priority values will be used for the bundles. VLAN ID Host VLAN ID 1…4095 RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 2BSetting the Operational Parameters 3-37 Chapter 3 Configuration Management Parameter Possible Values / Remarks VLAN Priority Host VLAN frame priority. User's Manual 0..7 [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Assigning Timeslots to Bundles Bundles are groups of timeslots. The Bundle Table displays the details of each bundle in the upper section of the table, and a representation of each timeslot with the bundle assigned to it in the lower section of the table. Each bundle can be assigned to multiple timeslots, but each time slot can only have one bundle assigned to it. The Bundles command enables you to assign timeslots to bundles, and to remove the timeslot assignments from bundles. ³ To view bundles for an E1/T1 port: 1. Click an E1/T1 port. 2. Select Configuration > Bundles... The Bundles Table appears (see Figure 3-35). 3. Configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-1 and click <Close>. 3-38 2BSetting the Operational Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Figure 3-35. Bundles Table – Port Level Table 3-21. Bundle Configuration Table Parameters – Port Level Parameter Possible Values/Remarks Port The selected port. Read only Type ETH Bundle No. Bundle Number Bundle Name Name of the selected bundle Empty Bundle When checked, indicates the bundle has not been assigned to any TSs (timeslots) Bundle Status Status of the bundle Connected, Disabled, Remote Fail, Local Fail, Unavailable, Validation Fail, Sequence Error, Buffer Underflow, Buffer Overflow Time Slots The timeslots and the bundles assigned to them. Timeslots with bundles assigned to them are marked with a dark blue box, while unassigned timeslots are marked with a gray box. A T1 port has 24 timeslots that can be assigned to a bundle; an E1 port has 31 (without MF) or 30 (with MF). [Edit] Click to select an available time slot for a selected bundle. [Select All] Click to select all available time slots for a selected bundle. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 2BSetting the Operational Parameters 3-39 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Parameter Possible Values/Remarks [Clear All] Click to remove all selected time slots from a selected bundle. [Apply] Click to apply changes. [Close] Click to apply Bundle Configuration Table Parameters and close the dialog box. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Selecting an Available Time Slot ³ To select an available timeslot: 1. From the Bundles Table just described, select a bundle and click <Edit…>. 2. Click the square beneath the timeslot number. The selected timeslots appear yellow. 3. Click <Apply>. Selecting all Available Time Slots ³ To select all available timeslots for the selected bundle: • From the Bundles Table just described, select a bundle and click <Select All>. Removing all Selected Timeslots from a Bundle ³ To remove all selected timeslots from the selected bundle: • Note From the Bundles Table just described, select a bundle and click <Clear All>. You cannot edit a bundle that has already been used to define a connection in the Bundle Connection Table (Figure 3-37). To edit such a bundle, first delete the bundle from the Bundle Connection Table (Figure 3-37), and then return to the Bundle Table to select new parameters. Managing Bundle Connections Bundles are groups of timeslots. The Bundle Connection Table command displays the detailed technical parameters of each bundle in the system. Although you can use the Element Manager to view the bundle connections and to remove them, complete management of bundle connections is accomplished using the Service Center map. For information on managing bundle connections using the Service Center map, refer to Chapter 5 of the RADview SC/TDMoIP System Manual. Creating Bundle Connections For information on creating and managing bundle connections using the Service Center map, refer to Chapter 5 of the RADview SC/TDMoIP System Manual. 3-40 2BSetting the Operational Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Removing Bundle Connections For information on removing bundle connections using the Service Center map, refer to Chapter 5 of the RADview SC/TDMoIP System Manual. In cases where a circuit is broken, you may use the Bundle Connection Table to manually remove a bundle connection. ³ To display the bundle connection table: 1. Select Configuration > Bundle Connection Table…. The Bundle Connection Table appears (see Figure 3-36 and Figure 3-37). 2. Configure the desired parameters as described in Table 3-22 and click <Close>. Figure 3-36. Bundle Connection Table (left side) Figure 3-37. Bundle Connection Table (right side) Table 3-22. Bundle Connection Table Parameters Parameter Possible Values/Remarks Slot No. 1 Channel No. 1..4 Bundle No. 1..31 Note: A maximum of 16 bundles is allowed Bundle Name RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Bundle name of the selected channel. The Table displays one bundle name per line. 2BSetting the Operational Parameters 3-41 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Parameter Possible Values/Remarks Admin. Status Down, Up Oper Status Connected, Disabled , Remote Fail, Local Fail, Unavailable, Validation Fail, Standby, Sequence Error, Buffer Underflow, Buffer Overflow Dest. IP Logical name or IP address of the destination IPmux Next Hop IP address to which the Ethernet frame will be sent when the Dest. Name IP is not in the device subnet Dest. Bundle Bundle number in the destination IPmux device 1..496 Jitter Buffer (tens of μsec) Depth of the jitter buffer (per-link, elastic buffer, whose size is configurable in units of 10 micro seconds (μs). E1: 0..37..3200 T1: 0..37..2400 ToS IP ToS (Type of Service) assigned to this channel: 0..255 Configures the IP ToS field in the IP frames transmitted by the device. Configures the entire byte – not only the 3 ToS bits. ToS assignment applies to all TDM packets leaving IPmux. TDM Bytes in Frame UDP payload (one-eight) length enabling reduction of Ethernet throughput. E1/T1: 48..1440 (steps of 48) T3/E3: 240..1440 (steps of 48) SAToP: 1..45 CESoPSN: 1..1440 Note: Applicable only when Connection Mode is TDMoIP (CE). VLAN Tagging No, Yes VLAN ID VLAN ID 1..4094 VLAN Priority VLAN priority 0..7 OAM Connectivity Disabled Enabled Bundle Thoughput Throughput in bps PSN Type Bundle encapsulation MPLS/ETH - Multi-Protocol Label Switching / Ethernet UDP/IP Connection Mode SAToP – Valid for Line Type = Unframed CESoPSN – Valid for Line Type = Framed HDLCoPSN Outound Label Tagging Outbound labels: Disabled, Enabled Note: Available only when PSN Type is MPLS/ETH. 3-42 2BSetting the Operational Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Parameter Possible Values/Remarks Outbound Tunnel Label MPLS transmit label: 0..1048576 Note: Available only when PSN Type is MPLS/ETH. Outbound EXP Bits The MPLS Network priority (EXP bits) used for this bundle 0..7 Inbound Label Tagging Inbound labels: Disabled, Enabled Note: Available only when PSN Type is MPLS/ETH. Inbound Tunnel Label MPLS receive label: 0..1048576 Note: Available only when PSN Type is MPLS/ETH. [Remove] Click to remove a bundle. [Close] Click to apply changes and close the dialog box. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Removing a Bundle ³ To remove a bundle: 1. Select a bundle in the Bundle Connection Table. 2. Click <Remove>. A warning message appears. Figure 3-38. Remove Bundle Connection 3. Click <Yes> to confirm. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 2BSetting the Operational Parameters 3-43 Chapter 3 Configuration Management 3.3 User's Manual Additional Tasks Displaying Ethernet Interface Information The Ethernet Interface Information command enables you to display the various parameters of the Ethernet port. You can use this information as a troubleshooting aid, to ensure that the Ethernet cable is working properly and that the connection is at the appropriate speed at half/full duplex. ³ To display information about the Ethernet interface: 1. Click the Ethernet port. 2. Select Configuration > Interface Info.... The Interface Information table appears (see Figure 3-39). For a description of the parameters, refer to Table 3-23. Figure 3-39. Interface Information – Network/User Port Table 3-23. Interface Information Table Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Port NET–ETH 1, NET/USER–ETH 2, USER–ETH 3 Type ETH Mode Transmission mode: Full Duplex, Half Duplex Rate (Mbps) Transmission rate: 10, 100, 1000 Status Status of the link: Connected, Not Connected Interface Type According to wavelength and laser mode 1300nmSM or 1300nm (single mode/multimode) Note: This parameter only appears for fiber optic Ethernet interface [Close] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. 3-44 3BAdditional Tasks RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Displaying Ethernet SFP Information ³ To display information about the Ethernet SFP: 1. Click the Ethernet port. 2. Select Configuration > SFP Info…. The SFP Information table appears (see Figure 3-40). For a description of the parameters, refer to Table 3-24. Figure 3-40. SFP Information Dialog Box Note SFP information is not available for Internal ETH port. Table 3-24. SFP Information Table Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Port NET–ETH 1, NET/USER–ETH 2, USER–ETH 3 Connector Type The specific port or interface. Fiber optic connectors: LC Copper connectors: RJ-45 Vendor Specific Manufacturer Name SFP port manufacturer name. Typical Max. Range The maximum range supported by the SFP port in meters. For Optical SFP: • Values <= 1km are displayed in meters with 10 meter resolution, Example: 320 m • Values > 1kmare displayed in Km with 0.1 Km resolution. Example: 3.7 Km For Copper SFP: • Values are displayed in meters with 1meter resolution, Example: 238 m RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 3BAdditional Tasks 3-45 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Wavelength (nm) The wavelength of an Optical interface/port in nm, as well as an indication if it is LASER. 850, 1310, 1310 LASER, 1550 LASER, 1470 LASER, 1490 LASER, 1510 LASER, 1530 LASER, 1570 LASER, 1590 LASER, 1610 LASER Note: This parameter is only enabled if the SFP is Optical. Fiber Type The laser mode of an Optical Laser interface/port. SM, MM Note: This parameter is only enabled if the SFP is Optical. [Close] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Displaying Ethernet Optical SFP Information ³ To display information about the Ethernet Optical SFP: 1. Click the Ethernet port. 2. Select Configuration > Optical Parameters... The Optical SFP Information table appears. For a description of the parameters, refer to Table 3-25. Note Optical SFP information is not available for Internal ETH port. Table 3-25. Optical SFP Information Table Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Port The selected Ethernet port. NET–ETH 1, NET/USER–ETH 2, USER–ETH 3 A vertical bar graph is displayed for each of the optical paramaters indicating the actual levels. Tx Optical Power (dBm) A vertical bar graph representing the transmitted optical power level. Beneath the bar graph, the current, maximum and minimum values are displayed as well. -40.0…8.2 LASER Bias Current (mA) A vertical bar graph representing the LASER bias current level, Beneath the bar graph, the current, maximum and minimum values are displayed as well. 0.0…131.0 LASER Temp (℃ / A vertical bar graph representing the LASER temperature level. ℉) Beneath the bar graph, the current, maximum and minimum values are displayed as well. For ℃: 0.0…100.0 For ℉: 32.0…212.0 Rx Optical Power (dBm) A vertical bar graph representing the received optical power level. Beneath the bar graph, the current, maximum and minimum values are displayed as well. -40.0…8.2 3-46 3BAdditional Tasks RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 3 Configuration Management Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Supply Voltage (Volt) A vertical bar graph representing the supply voltage. Beneath the bar graph, the current, maximum and minimum values are displayed as well. 0.0…+6.5 [Close] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Resetting IPmux-24 to the Default Configuration The Default Configuration command enables you to reset the Agent’s configuration back to the factory defaults. Use this command when you wish to reconfigure all of the parameters from a clean starting point. This is useful when IPmux-24's current configuration is completely unsatisfactory, such as when moving a device to another site, or if the configuration database has become corrupted or the device's software has been upgraded. ³ To set the selected IPmux-24 to the default configuration: 1. Select Configuration > System Commands > Default Configuration. A confirmation message appears (Figure 3-41). 2. Click <OK> to confirm reset of the default configuration. The default configuration replaces the current configuration. Figure 3-41. Default Configuration Dialog Box Polling the Agent RADview periodically and automatically reads (polls) IPmux-24 variables. You can force RADview to immediately poll the Agent and update the display by polling IPmux-24 manually. The Poll Agent command is useful if you configure the device NOT to perform periodic polling of the Agent. ³ To poll the agent: • Select Configuration > System Commands > Poll Agent. RADview polls IPmux-24 and updates any displayed information. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 3BAdditional Tasks 3-47 Chapter 3 Configuration Management User's Manual Resetting IPmux-24 The Reset command enables you to reset the Agent’s hardware to re-initialize the main board CPU of the IPmux-24 unit. Use this command to reset IPmux-24 in the unlikely event that the device is unresponsive (has locked up) or is behaving erratically. ³ To reset IPmux-24: 1. Select Configuration > System Commands > Reset. A confirmation message appears (Figure 3-42). 2. Click <OK> to confirm. The Agent’s hardware resets; the IPmux-24 unit is re-initialized and its active software is decompressed and loaded into the RAM. Figure 3-42. Reset Agent Dialog Box Note 3-48 The reset operation implements any changes made to the IPmux-24 configuration. 3BAdditional Tasks RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications This chapter provides detailed instructions for setting up a typical application using two IPmux units, and contains the following sections: • Configuring the IPmux-24 Units Configuring the Host IP Parameters Configuring the Manager List • Connecting IPmux-24 to the Management Station • Configuration Sequence • Creating Circuits Creating a Mesh Service Circuit Defining the E1 Parameters Creating a Circuit Saving the Circuit Parameters Displaying the Circuit Parameters Creating a Normal Service Circuit Defining the E1 Parameters Creating a Circuit Saving the Circuit Parameters Displaying the Circuit Parameters This chapter provides detailed instructions for configuring two IPmux-24 units operating opposite each other (see Figure 4-1). RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BConfiguring the IPmux-24 Units 4-1 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications User's Manual E1 PBX Internal Clock E1 IPmux-24 (A) Adaptive Clock 172.18.94.127 Ethernet Switch IPmux-24 (B) Loopback Clock 172.18.94.128 PBX Receive Clock 172.18.159.33 Network Management Station Figure 4-1. IPmux-24 Units Operating Opposite Each Other Certain guidelines are relevant to this application. In general, there are four basic configuration steps (described below) that need to be followed when deploying any IPmux unit. 1. IP Configuration – Setting the device host IP address and the manager IP address. 2. Physical layer configuration – Setting the TDM parameters (line type, clocking, etc.) according to the application requirements and topology. 3. Creating a circuit via the Service Center. Table 4-1. Configuration Summary Device E1 Parameters IP Parameters Bundle Parameters Bundle Connection IPmux-24 (A) • Transmit clock source: adaptive Line type: Framed G.704 CRC-4 enabled CAS: disabled Host IP address: 172.18.94.127 Bundle 1 Timeslots in bundle: 1–10 Bundle 1 of IPmux-24 (B) Transmit clock source: Loopback Line type: Framed G.704 CRC-4 enabled CAS: disabled Host IP address: 172.18.94.128 Bundle 1 Timeslots in bundle: 1–10 Bundle 1 of IPmux-24 (A) • • IPmux-24 (B) • • • 4-2 1BConfiguring the IPmux-24 Units RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications 4.1 Configuring the IPmux-24 Units This section explains how to configure the IPmux units. The configuration procedure is similar for both units, except for defining different host IP addresses, different clocking modes and different destination IP addresses for the bundle connection. Configuring the Host IP Parameters The host IP parameters are configured via the terminal application. ³ To configure the host IP parameters: 1. Display the Host IP menu (Configuration > System > Host IP), and configure the IP address and mask of the host: IPmux-24 (A) host IP address – 172.18.94.127 IPmux-24 (B) host IP address – 172.18.94.128 2. Save the changes. Configuration>System>Host IP 1. IP address 2. IP mask 3. Default gateway 4. DHCP 5. DHCP Status ... (172.18.94.127) ... (255.255.255.0) ... (0.0.0.0) (Disable) > > Please select item <1 to 5> ESC-prev.menu; !-main menu; &-exit 1 Mngr/s Figure 4-2. Configuring Host IP Parameters for IPmux-24 (A) RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BConfiguring the IPmux-24 Units 4-3 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications User's Manual Configuring the Manager List ³ To configure the manager list: 1. Display the Manager List menu (Configuration > System > Management > Manager list), and enter IP parameters for the network manager station: NMS IP address – 172.17.10.100 Manager location – Network-Eth1. 2. Save the changes. Configuration>System>Management>Manager List 1. Manager IP address ... (172.18.159.33) 2. Manager location > (Network-Eth1) 3. Link up/down trap (Disable) 4. Alarm trap (Disable) 5. VLAN tagging (Disable) > Please select item <1 to 5> ESC-prev.menu; !-main menu; &-exit 1 Mngr/s Figure 4-3. Configuring Network Manager 4.2 Connecting IPmux-24 to the Management Station IPmux-24 can be managed by a Network Management Station (NMS) that is located on the LAN (hub or switch) connected to the one of the unit’s Ethernet ports. ³ To connect IPmux-24 to the Network Management Station: 1. Connect a Network Management Station to the LAN (hub or switch). 2. Connect one of the IPmux’s Ethernet ports to the LAN. 4.3 Configuration Sequence Several basic configuration steps need to be followed when deploying any IPmux unit: 1. IP Configuration – Setting the IPmux-24’s host IP address and the manager IP address 2. Physical layer configuration – Setting the TDM parameters (line type, clocking, etc.) according to the application requirements and topology 3. Creating circuits via the Service Center. 4-4 3BConfiguration Sequence RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications IPmux-24 can be managed by a network management station that is located on the LAN connected to the one of the unit’s Ethernet ports. In order to establish a proper connection, it is necessary to configure IPmux with a basic configuration. ³ To perform the preliminary IPmux-24 configuration: 1. Connect an ASCII terminal to the IPmux-24 RS-232 control port. 2. Log in as Superuser (su). 3. Assign an IP address to IPmux-24. 4. Assign a subnet mask and a default gateway. 5. You can also enable or disable the IPmux-24 DHCP client. 6. Set read, trap, and read/write communities to public. 7. Set a manager IP address and location. Note Make sure that you save your settings at each configuration screen. 4.4 Creating Circuits In the Service Center application, circuits can be created for Mesh and Normal Services. Both processes are outlined below. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 4BCreating Circuits 4-5 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications User's Manual Creating a Mesh Service Circuit Figure 4-4. Mesh Services Map Defining the E1 Parameters ³ To configure the E1 parameters for the source IPmux-24 (A): 1. Double click on IPmux-24 (A) (172.18.94.127) in the Mesh Services Map (Figure 4-4). The Element Manager appears. 4-6 4BCreating Circuits RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications Figure 4-5. IPmux-24 (A) Element Manager 2. Select CH1. 3. From the Configuration menu, select Parameters... The Interface Parameters dialog box appears (Figure 4-6). 4. Select the following parameters: Transmit Clock Source = Adaptive Line Type = Framed-CRC. 5. Click <Set>. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 4BCreating Circuits 4-7 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications User's Manual Figure 4-6. IPmux-24 (A) E1 Interface Parameters ³ To configure E1 parameters for IPmux-24 (B): 1. Double click on IPmux-24 (B) (172.18.94.128) in the Mesh Services Map (Figure 4-4). The Element Manager appears. Figure 4-7. IPmux-24 (B) Element Manager 4-8 4BCreating Circuits RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications 2. Select CH1. 3. From the Configuration menu, select Parameters... The Interface Parameters dialog box appears (Figure 4-8). 4. Select the following parameters: Transmit Clock Source = Loopback Line Type = Framed-CRC. 5. Click <Set>. Figure 4-8. IPmux-24 (B) E1 Interface Parameters RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 4BCreating Circuits 4-9 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications User's Manual Creating a Circuit ³ To create a circuit between IPmux-24 (A) and IPmux-24 (B): 1. On the Services Map, select the source for the circuit. In this example it is the IPmux-24 (A). 2. While holding down the CTRL key, right click the mouse and drag a line between the source IPmux-24 (A) and destination IPmux-24 (B). The Manual Circuit Configuration dialog box appears. Figure 4-9. Manual Circuit Dialog Box – General Parameters Tab 3. Click on the General tab (Figure 4-9) and configure the following parameters: Connection Type = E1 Connection Bandwidth = 10xTs 4. Click on the Primary Circuit tab (Figure 4-9) and configure the following parameters: 4-10 Line Type = Framed-CRC TDM Bytes in Frame = 48 OAM Connectivity = Enabled (checked). 4BCreating Circuits RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications Figure 4-10. Manual Circuit Dialog Box – Primary Circuit Tab RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 4BCreating Circuits 4-11 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications User's Manual 5. Click on the EP Param tab (Figure 4-11), scroll down and configure the following parameters: Jitter Buffer = 500. Figure 4-11. Manual Circuit Dialog Box – EP Param Tab 4-12 4BCreating Circuits RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications Saving the Circuit Parameters ³ To save the circuit parameters: 1. In the Manual Circuit Dialog Box, click <Set>. A message appears asking you if you want to create another circuit. 2. Click <No>. The circuit is created and appears on the Mesh Services Map. Figure 4-12. Mesh Services Map with Circuit between IPmux-24 (A) and IPmux-24 (B) RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 4BCreating Circuits 4-13 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications User's Manual Displaying the Circuit Parameters ³ To display the circuit parameters: 1. Click on the link in the Services Map (Figure 4-12). 2. Right click and select Circuit List… The Circuit List appears. Figure 4-13. Circuit List 3. Click <Parameters…>. The Manual Circuit Parameters dialog box appears. 4. Verify that the parameters are correct. 4-14 4BCreating Circuits RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications Creating a Normal Service Circuit Normal Services have Branch and Central Sites. Double-clicking on the Branch and Central Sites opens the site windows. In our example, IPmux-24 (A) is located in the central site and IPmux-24 (B) is located in the branch site. Figure 4-14. Normal Services Map RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 4BCreating Circuits 4-15 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications User's Manual Defining the E1 Parameters ³ To configure the E1 parameters for IPmux-24 (A): 1. Double click on IPmux-24 (A) at the central site (Figure 4-14). The Element Manager appears. Figure 4-15. IPmux-24 (A) Element Manager 2. Select CH1. 3. From the Configuration menu, select Parameters... The Interface Parameters dialog box appears (Figure 4-6). 4. Select the following parameters: Transmit Clock Source = Adaptive Line Type = Framed-CRC. 5. Click <Set>. 4-16 4BCreating Circuits RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications Figure 4-16. IPmux-24 (A) E1 Interface Parameters ³ To configure E1 parameters for IPmux-24 (B): 1. Double click on IPmux-24 (B) at the branch site (Figure 4-14). The Element Manager appears. Figure 4-17. IPmux-24 (B) Element Manager 2. Select CH1. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 4BCreating Circuits 4-17 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications User's Manual 3. From the Configuration menu, select Parameters... The Interface Parameters dialog box appears (Figure 4-8). 4. Select the following parameters: Transmit Clock Source = Loopback Line Type = Framed-CRC. 5. Click <Set>. Figure 4-18. IPmux-24 (B) E1 Interface Parameters Creating a Circuit ³ To create a circuit between IPmux-24 (A) and IPmux-24 (B: 1. On the Central Site, select the source for the circuit. In this example it is the IPmux-24 (A). 2. While holding down the CTRL key, right click the mouse and drag a line between IPmux-24 (A) and IPmux-24 (B). A circuit is created between the two sites and appears with a dotted line. 4-18 4BCreating Circuits RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications Figure 4-19. Normal Services Circuit Creation ³ To configure circuit parameters: 1. Select the circuit by clicking on its line in the Normal Services Map. 2. Right click and select Circuit List… The Circuit List dialog box appears. Figure 4-20. Circuit List 3. Click <Create…>. The Manual Circuit Configuration dialog box appears. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 4BCreating Circuits 4-19 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications User's Manual Figure 4-21. Manual Circuit Dialog Box – General Parameters Tab 4. Click on the General tab (Figure 4-21) and configure the following parameters: Connection Type = E1 Connection Bandwidth = 10xTs. 5. Click on the Primary Circuit tab (Figure 4-22) and configure the following parameters: Line Type = Framed-CRC TDM Bytes in Frame = 48 OAM Connectivity = Enabled (checked). 6. Select Central and Branch Sites. 4-20 4BCreating Circuits RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications Figure 4-22. Manual Circuit Dialog Box – Primary Circuit Tab RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 4BCreating Circuits 4-21 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications User's Manual 7. Click on the EP Param tab (Figure 4-23) and configure the following parameters: Jitter Buffer = 500. Figure 4-23. Manual Circuit Dialog Box – EP Param Tab 4-22 4BCreating Circuits RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications Saving the Circuit Parameters ³ To save the circuit parameters: 1. In the Manual Circuit Dialog Box, click <Set>. A message appears asking you if you want to create another circuit. 2. Click <No>. The circuit is created and appears on the Normal Services Map. Figure 4-24. Normal Service with Circuit RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 4BCreating Circuits 4-23 Chapter 4 Configuring Typical Applications User's Manual Displaying the Circuit Parameters ³ To display the circuit parameters: 1. Click on the link in the Services Map (Figure 4-24). 2. Right click and select Circuit List… The Circuit List appears. Figure 4-25. Circuit List 3. Click <Parameters…> The Manual Circuit Parameters dialog box appears. 4. Verify that the parameters are correct. 4-24 4BCreating Circuits RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Chapter 5 Security Management This chapter discusses how to manage IPmux-24 security, and includes the following sections: • Setting Management Access Authorizations • Unix Users and Permissions. 5.1 Setting Management Access Authorizations The Access command allows you to enable or disable management via Telnet and Web access. Use this command to tighten security or to enable access, when necessary. ³ To enable or disable Telnet and Web access: 1. Select Options > Access…. The Access dialog box appears (Figure 5-1). 2. Configure Telnet and Web access and click <Set>. Figure 5-1. Access Dialog Box RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Setting Management Access Authorizations 5-1 Chapter 5 Security Management User's Manual Table 5-1. Telnet and Web Access Parameters Parameter Possible Values/Remarks Telnet Access Enable/Disable accessing the device via Telnet Disable - No one is allowed to access the device via Telnet. Enable - All users are allowed to access the device via Telnet Access. Managers Only - Only manager stations listed in the manager's list are allowed to access the device via Telnet. Secured Mode Only - All users are allowed to access the device via Telnet Access and only Secure data is accepted. Secured Mode Manager List Only - Only manager stations listed in the manager's list are allowed to access the device via Telnet and only Secure data is accepted. Note: Secured Mode Only and Secured Mode Manager List Only are only available for IPmux-14/24. Web Access Enable/Disable accessing the device via Web browser Disable - No one is allowed to access the device via Web. Enable - All users are allowed to access the device via Web. Managers Only - Only manager stations listed in the manager's list are allowed to access the device via Web. Secured Mode Only - All users are allowed to access the device via Telnet Access and only Secure data is accepted. Secured Mode Manager List Only - Only manager stations listed in the manager's list are allowed to access the device via Telnet and only Secure data is accepted. 5.2 Unix Users and Permissions RADview/HPOV, when running on a Unix-based operating system, supports the users and permissions security feature. Only an Administrator can add or remove nodes from the Service Center map. For further details, refer to the RADview-SC/TDMoIP system manual. 5-2 Unix Users and Permissions RADview -SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Chapter 6 Performance Management This chapter discusses how to monitor IPmux-24 performance. 6.1 Introduction IPmux-24 continuously collects performance statistics for its various ports and for bundle connections. The collected data enables network administrators to monitor the transmission performance, and thus the quality of service provided to users. RADview can display Intervals Statistics, information and graphs that aggregate the statistics over 15 minute intervals. RADview can also display Current Statistics, information and graphs displaying a more immediate view of the statistics counters. The Current Statistics window is refreshed periodically, according to the Polling Interval, or manually, whenever you click the <Poll> button. This chapter explains how to perform the following tasks: • Setting the Polling Interval • Viewing Bundle Statistics • Viewing HDLC Statistics • Viewing Bundle Current Statistics • Viewing Bundle Intervals Statistics • Viewing E1/T1 Port Current Statistics • Viewing Port Intervals Statistics • Viewing Ethernet Port Statistics. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BIntroduction 6-1 Chapter 6 Performance Management 6.2 User's Manual Setting the Polling Interval RADview updates displayed statistical data by polling IPmux-24 at set intervals. The Polling Interval command allows you to set the number of seconds between polls. ³ To set the polling interval: • Select Statistics > Polling Interval…. The Polling Interval dialog box appears. Figure 6-1. Polling Interval Table 6-1. Polling Interval Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Polling Interval (sec) Number of seconds between polls Polling Enable Selecting the checkbox enables polling when a Statistics dialog box is open. After each poll, RADview automatically updates the information in the dialog box. If polling is disabled, RADview does not automatically update a Statistics dialog box. Note: Polling is always enabled when a Statistics graph is open. [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Cancel] Click to close the window. 6-2 2BSetting the Polling Interval RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 6 Performance Management 6.3 Viewing Bundle Statistics The Bundle Connection Statistics command enables you to view statistics for all bundle connections. This information is useful for assessing quality of service, for network troubleshooting and planning purposes. ³ To display Bundle Connection Statistics: • Select Statistics > Bundle Statistics.... The Bundle Statistics dialog box appears. Figure 6-2. Bundle Statistics Table 6-2. Bundle Statistics Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Slot 1 CH CH1..CH4 Bundle No. 1..496 Bundle Name Bundle name for selected channel. Table will display one bundle name per line. Admin. Status Desired state of the link Down, Up Oper. Status Actual state of the link Connected, Remote Fail, Local Fail, Disabled, Unavailable, Validation Fail, Sequence Error, Buffer Underflow, Buffer Overflow Dest. Name Logical name or IP address of the destination IPmux RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 3BViewing Bundle Statistics 6-3 Chapter 6 Performance Management User's Manual Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Sequence Errors (sec) Number of seconds that the sequence number of an incoming frame caused a transition from the 'sync' state to the 'out of sequence' state. Out of sequence frames are dropped because the frames were received from the network with Sequence Numbers not equal to the last Sequence Number + (1 or 2). Buffer Underflow (sec) Number of seconds that the receive (Eth to TDM) buffer underflowed. When a continuous underflow is caused by a loss of frame flow, a single buffer underflow is counted. A buffer undeflow indicates that frames were dropped because the receive buffer was in an underrun state. The buffer enters underflow state when: • Sequence errors occur • Flow underrun takes place due to PDV expiration • An overflow condition occurs. Buffer Overflow (sec) Number of seconds that the receive (Eth to TDM) buffer overflowed. A buffer overflow indicates that frames were dropped because the receive buffer exceeded the maximum allowed depth. PSN Sequence Errors Number of times that the sequence number of an incoming frame indicated Loss of Frame or that Out of Order occurred in the PSN PSN Reordered frames Number of times that Frames had been reordered in the PSN [HDLC Statistics] Click to view HDLC statistics. [Bundle Current Statistics…] Click to view Bundle Current statistics. [Bundle Intervals Statistics…] Click to view Bundle Intervals statistics. [Reset Counters] Select a row in the table and click <Reset Counters> to reset the Bundle Connection Statistics Counters. [Close] Click to close the Bundle Statistics window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the Bundle Statistics window. 6-4 3BViewing Bundle Statistics RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 6 Performance Management 6.4 ³ Viewing HDLC Statistics To view the HDLC Table: 1. Select Statistics > Bundle Connection Statistics... The Bundle Statistics dialog box appears (Figure 6-2). 2. Select the bundle for which you wish to display the statistics. 3. Click <HDLC Statistics…>. The Bundle HDLC Statistics dialog box appears (see Figure 6-4). Figure 6-3. Bundle HDLC Statistics Dialog Box Table 6-3. Bundle HDLC Statistics Parameters Parameter Remarks Bundle No. The number of the selected bundle. Read only Bundle Name Bundle name for selected channel . Read only Tx Frames Number of HDLC frames that were transmitted. Read only Rx Frames Number of HDLC frames that were received. Read only CRC Error Frames Number of received HDLC frames with CRC errors. Read only Alignment Error Frames Number of received HDLC frames with alignment errors. Read only RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 4BViewing HDLC Statistics 6-5 Chapter 6 Performance Management User's Manual Parameter Remarks Oversize Frames Number of HDLC frames received which are longer than 1470. Read only Undersize Frames Number of HDLC frames received which are shorter than 4. Read only Abort Frames Number of HDLC frames received with abort indication. Read only [Close] Click to close the Bundle HDLC Statistics dialog box. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the Bundle HDLC Statistics dialog box. 6.5 Viewing Bundle Current Statistics The Bundle Current Statistics command enables you to view current statistics for the selected bundle connection. Statistics are displayed in both table and graph formats. This information is useful for assessing quality of service, for network troubleshooting and planning purposes. ³ To view the Bundle Current Table: 1. Select Statistics > Bundle Connection Statistics.... The Bundle Statistics dialog box appears (Figure 6-2). 2. Select the bundle for which you wish to display the statistics. 3. Click <Bundle Current Statistics…>. The Bundle Current Statistics dialog box appears. 6-6 5BViewing Bundle Current Statistics RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 6 Performance Management Figure 6-4. Bundle Current Statistics Table 6-4. Bundle Current Statistics Parameters Parameter Remarks Bundle No. For E1: 1 to 496 For T1: 1 to 384 Bundle Name Bundle name for selected channel Time Elapsed (sec) Amount of time that has passed since the beginning of the current 15-minute interval 0..899 Sequence Errors (sec) Number of seconds in the current interval that the sequence number of an incoming frame caused a transition from the 'sync' state to the 'out of sequence' state. Out of sequence frames are dropped because the frames were received from the network with Sequence Numbers not equal to the last Sequence Number + (1 or 2). RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 5BViewing Bundle Current Statistics 6-7 Chapter 6 Performance Management User's Manual Parameter Remarks Buffer Underflow (sec) Number of seconds in the current interval that the receive (Eth to TDM) buffer underflowed. When a continuous underflow is caused by a loss of frame flow, a single buffer underflow is counted. A buffer undeflow indicates that frames were dropped because the receive buffer was in an underrun state. The buffer enters underflow state when: • Sequence errors occur • Flow underrun takes place due to PDV expiration • An overflow condition occurs Buffer Overflow (sec) Number of seconds in the current interval that the receive (Eth to TDM) buffer overflowed. A buffer overflow indicates that frames were dropped because the receive buffer exceeded the maximum allowed depth. Max. Delay Variation (10 μsec) Maximum size of the buffer (in 10s of μsec) in the selected interval Min Jitter Buffer Level (msec) Minimum jitter buffer level (in msec) for the current interval Max Jitter Buffer Level (msec) Maximum jitter buffer level (in msec) for the current interval [Close] Click to close the Bundle Current Statistics dialog box. [Poll] Click to refresh the data in the Bundle Current Statistics dialog box. 6.6 Note: This parameter is used for a CES E1/T1 card whose hardware version is greater than 5.00. Viewing Bundle Intervals Statistics RADview can display Intervals Statistics, information and graphs that aggregate the statistics over 15 minute intervals. The Bundle Intervals Statistics command displays intervals statistics for the selected bundle connection, in both table and graph formats. This information is useful for assessing quality of service, for network troubleshooting and planning purposes. ³ To view a list of statistics from previous intervals: 1. Select Statistics > Bundle Connection Statistics.... The Bundle Statistics dialog box appears (Figure 6-2). 2. Select the bundle for which you wish to display the statistics. 3. Click <Bundle Intervals Statistics…>. The Bundle Intervals Statistics dialog box appears. 6-8 6BViewing Bundle Intervals Statistics RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 6 Performance Management Figure 6-5. Bundle Intervals Statistics The Bundle Intervals Data parameters are the same as the Bundle Current Data Parameters (Table 6-4) with the addition of information regarding Interval No. and its duration. 6.7 Viewing E1/T1 Port Current Statistics The Current statistics command enables you to view current statistics for the selected E1 or T1 port. Statistics are displayed in both table and graph forms. This information is useful for assessing quality of service, for network troubleshooting and planning purposes. ³ To view a list of current error statistics for an E1/T1 port: 1. Click an E1/T1 port. 2. Select Statistics > Current... The Port Current Statistics dialog box appears. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 7BViewing E1/T1 Port Current Statistics 6-9 Chapter 6 Performance Management User's Manual Figure 6-6. Port Current Statistics Table 6-5. Port Current Statistics Parameters – E1/T1 Parameter Remarks Slot 1 Port CH1..CH4 Type E1, T1 Current Data Each parameter displays the number of seconds of that particular type of error encountered by the E1/T1 interface during the current 15-minute interval Time Elapsed (sec) Amount of time that has passed since the beginning of the current 15-minute interval 0..899 6-10 7BViewing E1/T1 Port Current Statistics RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 6 Performance Management Parameter Remarks ES Errored Seconds A second containing one or more of the following events: CRC error, SEF (OOF), or AIS. Note: • An OOF defect is the occurrence of a framing bits error. If SES also occurs at the same time, ES will stop after 10 seconds. SES Severely Errored Seconds 320 or more CRC error events, one or more SEF (OOF), or AIS. OOF defect indicates a framing bits error. UAS Unavailable Seconds Number of seconds that the interface is unavailable. The system is unavailable after 10 continuous SES. LCV Line Code Violations For T1: The sum of BPV and EXZ defects that occurred in a second. BPV is the occurrence of a zero string greater than 15 (for AMI) or 7 (for B8ZS). EXZ is the occurrence of a pulse of the same polarity as the previous pulse. For E1: The number of code violations. (Two consecutive bipolar violations of the same polarity). [Close] Click to close the Port Current Statistics dialog box. [Poll] Click to refresh the data in the Port Current Statistics dialog box. 6.8 Viewing Port Intervals Statistics RADview can display Intervals Statistics, information and graphs that aggregate the statistics over 15 minute intervals. The Interval statistics command displays intervals statistics for the selected E1 or T1 port, in both table and graph formats. This information is useful for assessing quality of service, for network troubleshooting and planning purposes. ³ To view a list of statistics from previous intervals: 1. Click an E1/T1 port. 2. Select Statistics > Interval... The Port Intervals Statistics dialog box appears. The results of the previous intervals are displayed in the Port Intervals Statistics table, below the graph. Note • If system is running less than fifteen minutes, the following message is displayed: “System is up less than 15 min. No intervals data.” • After 900 or more Unavailable Seconds, the Ratios (AR, ESR, and SESR) display 0. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 8BViewing Port Intervals Statistics 6-11 Chapter 6 Performance Management User's Manual Figure 6-7. Port Intervals Statistics Table 6-6. Port Intervals Statistics Parameters – E1/T1 Parameter Remarks Slot 1 Port CH1 Type E1, T1 Number of Intervals Number of intervals sampled Inv No. Interval Number From (hh:mm) Starting time of the interval To (hh:mm) Ending time of the interval ES Errored Seconds A second containing one or more of the following events: CRC error, SEF (OOF), or AIS. Note: • An OOF defect is the occurrence of a framing bits error. • If SES also occurs at the same time, ES will stop after 10 seconds. 6-12 8BViewing Port Intervals Statistics RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 6 Performance Management Parameter Remarks SES Severely Errored Seconds 320 or more CRC error events, one or more SEF (OOF), or AIS. OOF defect indicates a framing bits error. UAS Unavailable Seconds Number of seconds that the interface is unavailable. The system is unavailable after 10 continuous SES. LCV Line Code Violations For T1: The sum of BPV and EXZ defects that occurred in a second. BPV is the occurrence of a zero string greater than 15 (for AMI) or 7 (for B8ZS). EXZ is the occurrence of a pulse of the same polarity as the previous pulse. For E1: The number of code violations. (Two consecutive bipolar violations of the same polarity). AR Availability Ratio ESR Errored Seconds Ratio SESR Severely Errored Seconds Ratio [Close] Click to close the Port Intervals Statistics dialog box. 6.9 Viewing Ethernet Port Statistics The Ethernet Interface Statistics command enables you to view statistics for the selected Ethernet port. The aggregate statistics for the port are displayed in a dialog box. This information is useful for assessing quality of service, for network troubleshooting and planning purposes. ³ To view Ethernet interface statistics: 1. Click the User or Network Ethernet interface. 2. Select Statistics > Interface Statistics... The Ethernet Interface Statistics dialog box appears. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 9BViewing Ethernet Port Statistics 6-13 Chapter 6 Performance Management User's Manual Figure 6-8. Interface Statistics Dialog Box Table 6-7. Interface Statistics Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Port Net 1, Net/User 2, User 3 Type ETH Received from Ethernet Frames The total number of packets received (including bad packets, broadcast packets, and multicast packets) Octets The total number of octets of data (including those in bad packets) received on the network (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets) 6-14 9BViewing Ethernet Port Statistics RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 6 Performance Management Transmitted to Ethernet Frames Total number of frames successfully transmitted Octets Total number of octets successfully transmitted [Close] Click to close the Interface Statistics dialog box. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the Refresh dialog box. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 9BViewing Ethernet Port Statistics 6-15 Chapter 6 Performance Management 6-16 9BViewing Ethernet Port Statistics User's Manual RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Chapter 7 Fault Management This chapter describes how to manage IPmux-24 alarms and how to run a loopback test, and contains the following sections: • • Monitoring Object Status Masking Traps Viewing Active Alarms Viewing the History Log Clearing the History Log Viewing Self Test Results Performing Loopback Tests 7.1 Monitoring Object Status This section discusses monitoring the status of network objects including managing alarms. Masking Traps The Masking Traps command enables you to select which SNMP traps should be masked (disabled). You can mask a trap in order to prevent a known problem from causing repeated alerts at the network monitoring station and to enable focusing on new problems that may arise. All traps can be selected or deselected for masking as a group, or they can be selected individually. ³ To manually select traps for masking: 1. Select Options > Masking Traps…. The Masking Traps dialog box appears (see Figure 7-1). 2. Select which traps to mask (for an explanation, see Table 7-1), and then click <Set>. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BMonitoring Object Status 7-1 Chapter 7 Fault Management User's Manual Figure 7-1. Masking Traps Dialog Box Table 7-1. Masking Traps Parameters Parameter Possible Values/Remarks Authentication Failure Selecting this checkbox disables the Authentication Failure trap. LOS Selecting this checkbox disables the LOS trap. LOF Selecting this checkbox disables the LOF trap. AIS Selecting this checkbox disables the AIS trap. RDI Selecting this checkbox disables the RDI trap. FEBE Selecting this checkbox disables the FEBE trap. External Clock Selecting this checkbox, if available, disables the External Clock trap. Note: This parameter is only enabled when an external clock is operational. Bundle Connection Bundle Connectivity Selecting this checkbox disables the Bundle Connectivity trap. [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. 7-2 1BMonitoring Object Status RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 7 Fault Management Viewing Active Alarms The Alarms command enables you to view agent alarms from the time that the selected IPmux-24 was turned on or from the last time the active alarm list was cleared. Use this command to locate problems and as a troubleshooting aid. ³ To view the Active Alarm List: • Select Fault > Alarms.... The Active Alarm list appears (see Figure 7-2). For a description of the parameters, refer to Table 7-2. Figure 7-2. Active Alarm List RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BMonitoring Object Status 7-3 Chapter 7 Fault Management User's Manual Table 7-2. Active Alarm Parameters Parameter Possible Values/Remarks Slot 1 Port The type of port T1/E1 Alarm The type of Alarm Port alarms: Far End LOF, Far End Sending AIS, Near End LOF, Near End Loss of Signal, Near End Sending TS16 LOMF [Print] Click to print the Active Alarm list. [Save to File…] Click to save the Active Alarm list to a file. [Close] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. Viewing the History Log The History Log command enables you to display a history of alarms (up to 512 entries) that were sent from the selected IPmux-24 to the network management station. Use this command to locate problems and as a troubleshooting aid. ³ To view the History Log: • Select Fault > History Log > List…. The System Log Buffer table appears (see Figure 7-3). For a description of the parameters, refer to Table 7-3. 7-4 1BMonitoring Object Status RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 7 Fault Management Figure 7-3. System Log Buffer Table 7-3. System Log Buffer Parameters Parameter Possible Values/Remarks No. The number of the alarm in the log buffer Description Brief description of the alarm Up to 80 characters [Print] Click to print the System Log Buffer. [Save to File…] Click to save the System Log Buffer to a file. [Next] Click to view the next 20 entries. [Start From…] Click to view entries starting from a specific index number in the History Log. [Close] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. ³ To view entries, starting from a specific number, in the History Log: 1. Click <Start From…>. 2. Select the starting number. 3. Click <Set>. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 1BMonitoring Object Status 7-5 Chapter 7 Fault Management ³ User's Manual To print all the entries in the History Log: • Click <Print>. Clearing the History Log The History Log > Clear command enables you to erase all of the entries in the alarm history. This command is helpful for clearing out large numbers of entries for repeated alarms resulting from problems that have already been corrected or noted. ³ To clear the History Log: 1. Select Fault > History Log > Clear. A confirmation box appears. 2. Click <OK> to confirm. Figure 7-4. Clearing the Log Buffer Confirmation Message 7-6 1BMonitoring Object Status RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 User's Manual Chapter 7 Fault Management Viewing Self Test Results The Self Test Results command enables you to view the results of the IPmux-24 self-test. When the device is turned on, it checks itself. In case a fault is detected, this is noted in the Self Test Results log. Use this command as a troubleshooting aid to help determine the cause of an apparent device hardware or software failure. ³ To view Self Test results obtained when the selected IPmux-24 was powered up: • Select Diagnostics > Self Test Results.... The Self Test Results dialog box appears displaying descriptions of detected faults (see Figure 7-5). Figure 7-5. Self Test Results 7.2 Performing Loopback Tests The Loopback diagnostics command enables you run loop tests on an E1 or T1 port, to troubleshoot data loss on a link and locate where the data is being lost in order to correct the problem. ³ To initiate a loopback test for an E1/T1 interface: 1. Click an E1/T1 port. 2. Select Diagnostics > Loopback... The Interface Loopback dialog box appears (see Figure 7-6). 3. Set the desired loopback test, as described in Table 7-4 and click <Set>. RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 2BPerforming Loopback Tests 7-7 Chapter 7 Fault Management User's Manual The loopback test is performed. Figure 7-6. Interface Loopback State Dialog Box Table 7-4. Interface Loopback Parameters Parameter Possible Values/Remarks Port Port number of the interface. Type E1, T1 Current Loopback Current loopback status Internal, External, Disable Loopback Type of loopback test Internal, External, Disable [Set] Click to set and save the information. [Cancel] Click to close the window. [Refresh] Click to refresh the information in the window. 7-8 2BPerforming Loopback Tests RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 Index —A— Agent resetting IPmux-24, 3-48 Agent mode system level menu options, 2-6 Alarms active viewing, 7-3 —B— Bridge port parameters changing, 3-12 Bundle Connections creating, 3-40 managing, 3-40 removing, 3-41 Bundles bundle connection table, 3-40 configuring, 3-38 removing, 3-43 removing time slots, 3-40 selecting all available time slots, 3-40 selecting and available time slot, 3-40 viewing current table, 6-6 intervals table, 6-8 statistics, 6-3 —C— Clocks system configuring, 3-8 Configuration Management, 3-1 —D— Default Configuration resetting, 3-47 Device, 1-1 —E— E1/T1 parameters configuring, 3-30 statistics viewing current, 6-9 intervals, 6-11 Element Manager, 2-4 Ethernet RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24 interface information displaying, 3-44 parameters configuring, 3-35 statistics viewing, 6-13 Ethernet optical SFP displaying, 3-46 Ethernet SFP displaying, 3-45 —F— Fault Management, 7-1 FCAPS model, 1-2 —H— History Log clearing, 7-6 viewing, 7-4 —I— Installation and Setup, 2-1 Internal Ethernet parameters configuring, 3-36 Introduction, 1-1 IPmux-24 Introduction, 1-1 —L— Loopback Tests performing, 7-7 —M— MAC Table adding a new entry, 3-14 configuring, 3-12, 3-15 removing an entry, 3-14 Management configuration, 2-1, 3-1 connecting to the NMS, 2-3 fault, 7-1 functions, 1-3 options, 1-1 performance, 6-1 security, 5-1 setting access authorizations, 5-1 Manager List, 3-6 Managers List changing an entry, 3-7 removing an entry, 3-7 I-1 Index Masking Traps, 7-1 Menu Options system level, Agent mode, 2-6 —P— Performance Management, 6-1 Polling Interval setting, 6-2 Polling the Agent, 3-47 Port Level Management Options, 2-8 Port Level Menu Options IPmux-14, 2-8 IPmux-24, 2-8 —Q— QoS Classification configuring, 3-23 QoS Mapping 802.iP, 3-24 configuring, 3-24 DSCP, 3-25 port default priority, 3-28 TOS, 3-27 QoS,configuring, 3-29 Quality of Service,configuring, 3-29 —R— RADview launching, 2-3 RADview, using, 2-4 Rate Limitation,see QoS,configuring, 3-29 Resetting Agent, 3-48 —S— Security, 5-1 Unix users and permissions, 5-2 Security Management, 5-1 Self Test Results viewing, 7-7 Static MAC table adding an entry, 3-17 removing all entries, 3-17 removing an entry, 3-17 Statistics bundle, 6-3 Ethernet, 6-13 I-2 User's Manual System clocks configuring, 3-8 System Commands resetting Agent, 3-48 default configuration, 3-47 System Information configuring, 3-4 System level menu options Agent mode, 2-6 System Level Operations, 2-6 System management options Agent mode, 2-6 System Management Options, 2-6 System Parameters configuring, 3-2 —T— Telnet Access, 5-1 Traffic class updating, 3-25, 3-26, 3-27 Traps masking, 7-1 Typical Applications configuration sequence, 4-4 configuring, 4-1 connecting IPmux-24 to the NMS, 4-4 creating circuits, 4-5 —U— User interface, 2-4 —V— VLAN Adding, 3-21 changing, 3-22 configuring parameters, 3-20 removing, 3-23 VLAN Membership (Egress) adding, 3-19 changing, 3-20 configuring, 3-18 removing, 3-20 —W— Web Access, 5-1 RADview-SC/TDMoIP IPmux-24