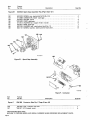
Download Miller Electric SCE-1A Specifications
Transcript
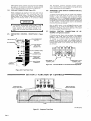
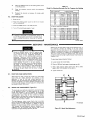
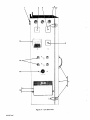
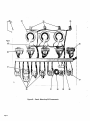
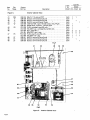
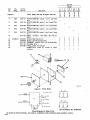
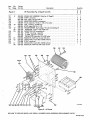
February 1980 FORM: OM-540A Effective With Serial No. HK321565 MODEL SCE-1A SCE-3A SCE-5A SCM-lA SCM-3A SCM-5A .tcc ._ , I. ~ 5 OWN E RS MANUAL I11dIER MILLER ELECTRIC MFG. CO. 718 S. BOUNDS ST. P.O. Box 1079 APPLETON, WI 54912 USA NWSA CODE NO. 4579 PRINTED IN U.S.A. ~% L ~L~ L~ ~ L&P ~ LIMITED WARRANTY EFFECTIVE: JUNE 1. 1979 This warranty supersedes all previous MILLER warranties and is ex clusive with no other guarantees or warranties expressed or implied. ( LIMITED WARRANTY-Subject to the terms and conditions hereof, Miller Electric Mfg. Co., Appleton, Wisconsin warrants to its Distributor/Dealer that all new and unused Equipment furnished by Miller is free from defect in workmanship and material as of the time and place of delivery by Miller. No warranty is made by Miller with respect to engines, trade accessories or other items manufactured by others. Such engines, trade accessories and other items are sold subject to the warranties of their respective manufacturers, if any All engines are warranted by their manufacturer for one year from date of original purchase. . Except specified below, Millers warranty does not apply to components having normal useful life of less than one (1) year, such as spot welder tips, relay and contactor points, as MILLERMATIC parts that come in contact with the welding wire including nozzles and nozzle insulators where failure does from defect in not result workmanship or material. Miller shall be required to honor warranty claims Equipment in the event of failure resulting from on ranted within the ment to following periods the original user: from the date of a war- defect delivery of Equip- As matter of a submitted by the general policy on1y, Miller may honor claims original user within the foregoing periods. In the case of Millers breach of warranty or any other duty with respect to the quality of any goods, the exclusive remedies therefore shall be, at Millers option 11) repair or (21 replacement writing by Miller in appropriate cases, (31 repair or replacement at an authorized Miller service station or 141 payment of or credit for the purchase price (less reasonable depreciation based upon actual use) upon return of the goods at Customers risk and expense. Upon receipt or, where authorized in the reasonable cost of of notice of apparent defect or failure, Miller shall instruct the claimant on the warranty claim procedures to be followed. ANY EXPRESS WARRANTY NOT PROVIDED HEREIN AND ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY, GUARANTY OR REPRESENTA- PERFORMANCE, AND ANY REMEDY FOR BREACH OF CONTRACT WHICH, BUT FOR THIS PROVISION, MIGHT ARISE BY IMPLICATION, OPERATION OF LAW, CUSTOM OF TRADE OR COURSE OF DEALING, INCLUDING lION ANY AS TO IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR OF FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR WITH RESPECT TO PURPOSE, ANY AND ALL EQUIPMENT FURNISHED BY MILLER (S EX CLUDED AND DISCLAIMED BY MILLER. 1. Arc welders, power sources and components 2. Original main power rectifiers (labor - . 1 year onlyl welding guns and feeder/guns - 3. All 4. All other Millermatic Feeders 5. Replacement 6. Batteries or 1 year 3 years EXCEPT WRITING, 90 days 1 year repair parts, exclusive of labor . 60 days 6 months ULTIMATE AS EXPRESSLY MILLER PURCHASE BY that Miller is notified in of the date of such failure. .~, J~ writing within thirty (30) days ARE BY MILLER INTENDED IN FOR COMMERCIAL/INDUSTRIAL USERS AND FOR OPERATION BY PERSONS TRAINED AND EXPERIENCED WELDING IN THE EQUIPMENT USE AND CONSUMER USE. MILLER provided PROVIDED PRODUCTS TO, AND NO RESELLER AND NOT MAINTENANCE FOR CONSUMERS WARRANTIES DO NOT EXTEND IS AUTHORIZED TO EXTEND MILLERS WARRANTIES TO, ANY CONSUMER. ~ J~ OF OR TABLE OF CONTENTS Section No. SECTION 1 1 1 - Page No. INTRODUCTION General 1. 1 2. Receiving-Handling 1 3. Description 1-4. Safety - 1 1 - SECTION 2 1 INSTALLATION 2- 1. Electrical Input Connections 1 2. 2. 2 2 2 - - - Secondary Connections 3. Shielding Gas Con nØctions 1 1 Coolant Connections 4. 2 5. Contactor Control Receptacle 2 2. 6. Emergency Stop Switch Connections 2- 7. Manual Control Connections Of Sequence C SECTION 3 3 - 1. 3- 2. 3 3 3 - - - - - - 3 5. Manual Control Of 3 3 4 Sequence C 4 High-Frequency Control SEQUENCE OF OPERATION Gas 4 Shielded Metal-Arc 4 Tungsten-Arc Welding (GTAW) Welding (SMAW) 3. Shutting Down 1. SECTION 5 5 3 Current Control Weld Switch 4- 2. 4 Sequence Control Function 4. SECTION 4 4 FUNCTION OF CONTROLS 3. Start Switch (SCE/SCM-1A and 2A) 3- 6. 2 2 5 MAINTENANCE 5 High Voltage Capacitors Spark Gap Adjustment 3. Bypass Panel 1. 5- 2. 5 5 6 5 - - Control Circuit Protection 4. 6 SECTION 6 TROUBLESHOOTING SECTION 7 CERTIFICATION FOR HIGH FREQUENCY ARC WELDING EQUIPMENT 7- 1. General 7 7 2. General Information 7 3. Power Service 7 7 7 7 7 - - - - - 4. Welding Machine 7 5. Welding Leads 8 6. Wiring In The Vicinity Of The Welding 7- 7. Grounds 7 8. Metal 9. Individual Installation Certification 7 - - Building 7-10. Check List Area 8 8 8 9 9 SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION - Dime nsions (Inches) Weight (Pounds) Height Width Depth Net Shipping 33-1/4 26-1/4 10-3/4 168 230 Figure 1-1. Specifications 1-1. GENERAL generator manual should be read completely. This will help avoid possible injury due to misuse or improper welding prepared especially for use in familiar izing personnel with the design, installation operation, main tenance, and troubleshooting of this equipment. All informa tion presented herein should be given careful consideration to assure optimum performance of this equipment. applications. This manual has been 1-2. The following definitions apply to CAUTION, IMPORTANT, and NOTE blocks found throughout this manual: RECEIVING-HANDLING Prior to installing this equipment, clean all packing material from around the unit and carefully inspect for any damage that may have occurred during shipment. Any claims for loss or damage that may have occurred in transit must be filed by the purchaser with the carrier. A copy of the bill of lading and freight bill will be furnished by the carrier on request if Under this heading, installation, operating, and main procedures or practices will he found that if carefully followed may create a hazard to per- tenance not sonnel. occasion to file claim arises. I When requesting information concerning this equipment, it is essential that Model Description and/or Stock Number and Serial (or Style) Numbers of the equipment be supplied. 1-3. DESCRIPTION IL 1 U heading, installation, operating, and main tenance procedures or practices will be found that if not carefully followed may result in damage to equip . Under Sequence Controls are specifically designed to be used in conjunction with an electric current controlled welding power source. These Sequence Controls provide five different sequences for either automatic or semi-automatic operation of the various welding processes. The function of each sequence is described in Section 3, FUNCTION OF CON TROLS, in this manual. The SCE Models are equipped with electronic timers in sequences B, C, and D. The SCM Models are equipped with mechanical timers in sequences B, C, and These this ment. NOTE D. U 1-4. SAFETY Before the equipment is put into operation, the safety sec at the front of the welding power source or welding I U heading, explanatory statements will be need special emphasis to obtain the most efficient operation of the equipment. Under this found that I tion SECTION 2 2-1. - INSTALLATION welding power the link for the ELECTRICAL INPUT CONNECTIONS Refer to the Installation Section of the welding power Refer to Figure 2-1 for positioning required operating voltage. source. of source On the SCE/SCM-5A, the control transformer which provides primary power to the control is located in the welding Manual for instructions on connecting electrical input power to the welding power source. the power source. SCE/SCM-1A and 3A Models, inside the cabinet on the lower right corner above the control transformer, is either a three or a five pole terminal block with one jumper link attached. The primary power supply to the Sequence On the 2-2. Control is connected to this block. The jumper link must be connected for the primary power supply voltage that will correspond with the primary power supply voltage of the (Figure 2-2) unit was shipped wh the secondary inte r connecting cables between the Sequence Control and welding power source unconnected. It is therefore necessary to route and secure the secondary inter connecting cables (already attached to Sequence Con trol) to the proper weld output terminals on the welding power source. The secondary welding cables should only be attached to the output terminals on Sequence Control to achieve proper operation of this 230/460 VOLTS ~ 460 230 SECONDARY CONNECTIONS 208/230/460 VOLTS Refer to Owners 208 230 Installation Section of the welding power Manual for proper weld cable size. source 460 The secondary terminals on the Sequence Control are labeled ELECTRODE and WORK. Connect the electrode holder 230/460/575 VOLTS cable to the terminal marked ELECTRODE and the work cable to the terminal marked WORK. 00 000 2-3. 230 460 TA-040 107-4 Figure 2-1. Line SHIELDING GAS CONNECTIONS (Figure 2-2) These front panel and are have a right-hand, 575 Voltage Jumper Link Arrangement labeled connections are IN-GAS-OUT. located The on the connections OM-540 Page 1 2-4. gas 5/8-18 female thread. Connect the hose from the shielding supply to the connection labeled IN. Connect the hose control facilities. Either from the electrode holder to the connection labeled OUT. used in COOLANT CONNECTIONS This (Figure 2-2) 2-6. three-prong, twistlock receptacle provides remote hand or a contactor foot switch can be conjunction with this receptacle. EMERGENCY STOP SWITCH CONNECTIONS 2-3 and 3-2) (Fig ures These connections located on the front panel and are labeled IN-COOLANT-OUT. The connections have a lefthand, 5/8-18 female thread. Connect the hose from the coolant supply to the connection labeled IN. Connect the from hose the are electrode holder to the connection A five-pole terminal block with two jumper links attached, located on the inside lower left corner of the cabinet, provides a means of emergency stop connections of weld sequences B, C, or 0. If it is desirable to connect an emergen cy stop switch in the circuit, remove the jumper link that is connected across the fourth and fifth terminals, counting left labeled OUT. right. Connect a normally-closed switch to the terminals from which the link was removed. to If a portable, self-contained coolant system with this unit, ensure bypass capability to that avoid the coolant possible damage With the WELD switch in the AUTOMATIC position, weld sequences B, C, or D may be interrupted at any time by opening the emergency stop switch. Opening of this switch will initiate sequence E (post-flow time). is used has pump the to when the coolant valve closes and coolant flow motor stops. 2-7. 2-5. CONTACTOR CONTROL RECEPTACLE MANUAL CONTROL CONNECTIONS QUENCE C (Figures 2-3 and 3-2) A five-pole terminal block, with located provides ~ ~ DC AMMETER ~ $ I SE (Figure 2-2) WELD SWITCH OF To HIGH-FREQUENCY SWITCH on the a means connect an two jumper links attached, inside lower left corner of the cabinet, of external switch control of sequence C. external switch for manual control of sequence C, remove the jumper link connected across the first and second terminals counting left to right. Connect a L~ normally-open switch was to the terminals from which the link removed. START SWITCH (ONLY ON SCE/SCM-1 A) GAS CONNECTIONS COOLANT CONNECTIONS C ON TA CTO R CONTROL RECEPTACLE ELECTRODE TERMINAL WORK TERMINAL TA-OlO 566 Terminal Block For External Switch Figure 2-3. Figure 2-2. Front Panel View SECTION 3- FUNCTION CONTROLS OF POST-FLOW OF PRE-FLOW OF GAS & COOLANT ANT GAS & Operation DFINISH CWFLD ~ E ~i~I77~ffl7~A #~ Ui Ui a. S ~ ~START ~ \~ ~ FINISH TIME TA-040 107-6 Figure 3-1. Sequence Time Chart Page 2 3-1. current This Sequence Control is a five sequence automatic control designed for Gas Tungsten-Arc Welding )GTAW). The function of each sequence is as follows: C. the minimum from value (Figure 3-1) SEQUENCE CONTROL FUNCTION range on to welding the the maximum of the selected power source. Slope Weld Amperage Control (Sequence D) The SLOPE control provided for selecting the slope weld adjustable and can be set for any is current value. The control is Sequence Sequence A: B: Sequence C: Sequence D: Sequence E: PRE-FLOW: coolant; adjustable gas mechanical time of 1/4 to 15 seconds. current: START adjustable control and timer preset magnitude of current and time. and value the minimum from current finish the control to the welding the on range be should maximum power set for of the selected For a normal source. a value less than the (sequence C) setting. WELD control and timer adjustable provide exact values of current and time. be manually controlled. Sequence can SLOPE current: adjustable control and timer are preset to determine magnitude and WELD current: time duration of current at end of weld. POST-F LOW: gas and coolant; adjustable mechanical time sequence of 2 seconds to 3 3-3. START SWITCH (SCE/SCM-1A) (Figure 2-2) This switch provides a choice of selecting either fast start of sequence B (START weld). A. a normal or a Normal Position minutes. (Figure 3-2) CURRENT CONTROL the current The welding current for sequences B, C. and D is governed by the setting of the control immediately above each sequence timer. These controls are calibrated in percentages and function as remote controls, in that they are fine amperage adjustments of the AMPERAGE ADJUSTMENT control on the welding power source. The REMOTE AMPERAGE CONTROL switch on the welding power source must be in STANDARD position for proper operation of the the NORMAL position, the starting less than the setting of the START weld amperage control, but will rapidly increase to the setting of the START weld amperage control. With 3-2. B. start the at a value Fast Position With will 3-4. in switch will the in switch the FAST position, the starting current START weld amperage setting. start at the value of the WELD SWITCH (Figure 2-2) Sequence Control. This switch provides a choice of selecting either an automatic or semi-automatic operation of the Sequence Control. NOTE A. AMPERAGE The welding power ADJUSTMENT must source in be control the one on With the switch in the AUTOMATIC position, the Sequence Control will operate automatically through all sequences with the use of a contactor control switch connected to the CONTACTOR CONTROL receptacle. hundred percent (maximum) position for maximum control of the selected range. A. Start Weld Amperage Control B. (Sequence B) The START control is provided for selecting the start weld value. The control is adjustable and can be set for any value from the minimum to the maximum of the selected current current start the Automatic Position the range on the welding power source. For a normal control should be set for a value less than the WELD Manual Position MANUAL position, the timers of removed from the circuit. are However, the weld sequence current value will be controlled by the WELD amperage control on the Sequence Control. Closing the contactor control switch will initiate sequence A With the sequences in switch B, C, the and D )PRE-FLOW). Upon completion of sequence A, the WELD will be initiated automatically. The Sequence (sequence C) setting. sequence B. Weld Amperage Control (Sequence C) The WELD control is provided for selecting the normal weld value. The control is adjustable and can be set for any current Control will continue to operate in the WELD sequence until the contactor control switch is opened. Opening this switch will extinguish the WELD sequence and initiate sequence E (POST-FLOW gas and coolant time). START WELD PILOT LIGHT FOR WELD AMPERAGE CONTROL EACH WELD SEQUENCE AMPERAGE CONTROL PILOT LIGHT FOR GAS AND WATER 1 GAS AND COOLANT GAS AND COOLANT POST-FLOW CONTROL PRE-FLOW TIME SLOPE WELD AMPERAGE CONTROL CONTROL.~~, 2 START WELD TIME CONTROL SLOPE WELD TIME CONTROL .T!~TIME TERMINAL BLOCK FOR EXTERNAL SWITCH OPERATION WELD CONTROL VOLTAGE CHANGEOVER TERMINAL BLOCK FOR CONTROL TRANSFORMER AND EMERGENCY STOP SWITCH CONNECTION I. HIGH FREQUENCV SPARK GAP Figure 3-2. Control Panel View OM-540 Page 3 3-5. MANUAL CONTROL OF SEQUENCE C Provisions allow provided for are Continuous accomplished by welding timing of sequence C to any desired time. This is external switch into the position labeled DIRECT. To decrease the intensity, connect both links in the position labeled AIR. This unit was shipped with the links connected in the DIRECT position. manual for connecting an B. Circuit. Refer to Section 2-7 for information on connecting the external switch. The Sequence Control functions auto matically through sequences A and 3-6. With HIGH-FREQUENCY CONTROL C. (Figure 2-2) labeled START-OFF-CONTINUOUS. position, high frequency is1 be used must Start Position Welding (GTAW). Gas Tungsten-Arc Coupling D. Located on each side of the high-frequency panel are three terminals and one jumper link. The positions of the links are labeled DIRECT and AIR. These links provide facilities for SECTION 4 Continuous Position With the switch in induced is CONTINUOUS position, the high fre weld circuit during all three welding sequences, or as long as the contactor is energized. This method is recommended for AC Gas Tungsten-Arc quency connecting the high-frequency transformer for either direct or air coupling which governs the amount of high-frequency intensity. To increase the intensity, connect both links in the 4-1. OFF the the switch in the START position, high frequency is induced into the weld circuit as an aid in starting the arc. When a welding arc is established, the high frequency will automatically shut off. This method is recommended for DC high frequency is controlled through the Direct-Air coupling jumper links and the HIGH-FREQUENCY switch Direct-Air in With The A. switch the removed from the weld circuit. This position for Shielded Metal-Arc Welding (SMAW). B, but the time duration of sequence C is controlled by the external switch. Closing the external switch will extinguish sequence C and initiate the SLOPE weld time (sequence DL Off Position into the Welding (GTAW). SEQUENCE OF OPERATION - GAS TUNGSTEN-ARC WELDING (GTAW) 14. Close the contactor control and switch commence welding. For Gas Tungsten-Arc Welding controls as follows: 1. (GTAW(. check and adjust the 15. Check that shielding gas and coolant connections described in Sections 2-3 and 2-4. 3. Check that secondary connections Section 2-2. are 4-2. described in as as necessary for proper welding are as 2. Readjust the controls condition. SHIELDED METAL-ARC WELDING (SMAW) For Shielded Metal-Arc Welding as follows: (SMAW) check and adjust the controls Determine the type of welding current required (AC, DCSP, or DCRP(, and position the Polarity switch or Selector switch on the welding power source accord 1. Disconnect or shut off the shielding gas and coolant supplies. ingly. 4. Place the Range switch on the welding power the desired current range. 5. Rotate the the welding AMPERAGE power source source 2. Check that secondary connections Section 2-2. 3. Determine the type of welding in DCSP ADJUSTMENT control on to the maximum position. or Selector are described in as current required (AC, DCRP), and position the Polarity switch or switch on the welding power source accord ingly. 6. control, WELD START weld amperage control, and the SLOPE amperage the control on Sequence Control Rotate the weld amperage the desired to 4. Place the Range switch on the welding power the desired current range. 5. Rotate source in setting. 7. Place the WELD switch in the desired position. The AUTOMATIC position is generally used, but the MANUAL position may be employed. the 6. AMPERAGE the welding source power ADJUSTMENT to control the maximum on position. Rotate the WELD amperage control (sequence C) on Sequence Control for the approximate percentage of weld current desired within the range selected on the 8. On SCE/SCM-1A in the desired Models, place position according the START switch to the the welding power source. welding appli cation. 7. 9. Place the HIGH-FREQUENCY switch in the START for dc welding, and in the CONTINUOUS position position for 10. ac 8. Place the WELD switch in the MANUAL position. On Adjust the shielding gas and coolant pre-flow and post-flow timers for the desired time setting. 9. On in 11. Select the proper size SCE/SCM-1A Models, START adjust the amperage control to approximately the as the WELD amperage control setting. welding. tungsten for the welding same weld setting SCEISCM-1A the desired Models, place the START switch position according to she welding application. application from Table 4-1. 10. 12. Connect normally-open switch TACTOR CONTROL receptacle. a into the 11. to welding, it is imperative that proper protective clothing (welding coat and gloves) and eye protection (glasses and welding helmet) be put on. Failure to comply may result in serious and even permanent bodily damage. Place Page 4 Place the POWER switch in the ON position. on the welding HIGH-FREQUENCY in switch Connect a normally-open switch TACTOR CONTROL receptacle. the OFF into the CON to welding, it is impera ye that proper protective clothing (welding coat and gloves) and eye protection (glasses and welding helmet) be put on. Failure to comply 13. the position. CON may result in serious and even permanent bodily damage. power source I Place the POWER switch in the ON position. 12. on the welding power source Table 4-1 Guide For Selecting Electrode For Gas Tungsten-Arc Welding 13. Close the control contactor switch and commence welding. PURE TUNGSTEN 14. Readjust the controls as necessary for proper weld Electrode Dta. lIn.l condition. 4-3. SHUTTING DOWN Break the 1. arc. CURRENT RANGE DCSP.Argon ACHF-Argon DCSPHelium .010 Up to 15 Up 15 Up to 20 .020 10 to 30 15 to 50 20 to 60 .040 20w 70 25 to 70 30 to 90 1/16 50 to 50 6Oto 150 3/32 100 to 160 1/8 150 to 210 125 to to 135 125 to 225 140 to 250 to 360 240 to 400 - 2. Allow with the welding power applied. source to idle for 3 minutes load no 215 5/32 190 to 280 350 to 450 390 to 500 3/16 250 to 350 450 to 720 500 to 800 1/4 300 to 500 720 to 990 800 to 1100 to 25 Place the POWER switch in the OFF position. 3. 1% AND 2% THOR ATED TUNG STEN 4. Turn off the shielding gas supply if used. I ~ding 0 is performed in a confined area, failure to turn off the gas supply could result in a buildup of gas fumes, endangering personnel reentering the welding .010 Up .020 15to35 .040 20 1/16 50 to 140 to to 20 Up 80 15to50 Up to 30 20to60 25 to 80 30 to 100 50 to 145 60 to 160 3/32 130 to 250 135 to 235 150 to 260 1/8 225 to 350 225 to 360 250 to 400 5/32 300 to 450 360 to 450 400 to 500 3/16 400 to 650 450 to 720 500 to 800 1/4 500 to 800 720 800 to 1100 _______________ area. to 990 _______________ TA-gO I SECTION 5 ~ng not the remove P0 WER power the OFF position d oes of the welding power switch from - all Completely terminate all welding power source by before lockout procedures employing machinery attempting any inspection or work on the inside of the welding power source or the Sequence Control, If the welding power source is connected to a disconnect switch, padlock the switch in an open position. If connected to a fuse box, remove the fuses and padlock the cover in the closed position, If the unit is connected to a circuit breaker, or other disconnecting device without locking facilities, attach a red tag to the device to warn others that the circuit is being internal source electrical worked circuitry. to power the MAINTENANCE Widening of the spark gaps through normal operation may, if not corrected, increase the loading of the high voltage capacitors and thus contribute to their premature failure. Cleaning or dressing of the point is not recommended as the material at the points is tungsten and is impossible to file. The entire points should be replaced when they become extremely pitted or burned to such an extent that little or no tungsten is left. To adjust spark gaps proceed A. Loosen B. Place C. Apply slight an screws (A) on as follows: both sides. .008 inch feeler gauge in spark gap gauge is held area pressure against spark point (B) firmly between the two points, (C). so feeler on. D. Tighten 5-1. 190-3 screws (A), HIGH VOLTAGE CAPACITORS are rarely a source of trouble. Any local radio repair shop Can readily determine the condition of the capacitors. If one of the high voltage capacitors fail, operation may be continued with one capacitor until a new These parts one can be To prevent excessive overload on the the spark gap point setting should about .004 inches. secured. remaining single capacitor, be reduced 5-2. to SPARK GAP ADJUSTMENT (Figure 5-1) can readily be inspected by opening the door Sequence Control. The spark gaps are set at .008 inches when shipped. It will be necessary to periodically readjust these after extended operation. Usually, inspection and adjustment every three to four months will suffice. Readjustment is indicated when intermittent operation of the gaps is noted. Usually this occurs when the gap setting has The spark gaps of the increased to .012 inches or greater. high-frequency output varies directly (up to a certain point) with the spark gap spacing. In extreme cases where the greatest amount of high frequency is needed, it may be The .010 inches TA-020 623 greater. adjust setting necessary This increases the high-frequency radiation; therefore, it is to that consistent with suggested the gap the minimum to gap setting or (.008 good welding operation, be used. inches) Figure 5-1. Spark Gap Adjustment OM-540 Page 5 5-3. 5-4. BYPASS PANEL The Sequence Control is equipped with fuses protecting the control circuit components. The diagram markings and quantity of fuses may vary depending on the model. Normally the fuses can be easily inspected by opening the cabinet door and examining the interior of the unit. Consult the circuit diagram at beginning of welding power source Owners Manual for specific information on this unit. The proper information about specific fuses can be determined from the Parts List. The purpose of the bypass panel is to reduce the high-fre quency feedback into the transformer of the welding power A defective capacitor in this Circuit would reduce source. high-frequency output, and might be evident by loss of oil from the capacitor case. If in doubt as to the condition of the capacitors, have them checked at a radio repair shop. The resistors in the Circuit would show evidence of failure if they are cracked. Failure in this circuit is rare, and would be suspected only as a last resort. SECTION 6 CONTROL CIRCUIT PROTECTION TROUBLESHOOTING - Tt~~i~ internal Cir is connected. It is assumed that proper installation has been made, according to Section 2 of this manual, and that the unit has been functioning properly until this trouble developed. attempting any inspection the Unit. Troubleshooting or work on of internal circuitry should be performed by qualified personnel only. Use this chart in conjunction with the circuit diagram while performing troubleshooting procedures. If the trouble is not remedied after performing these procedures, the nearest I I Hazardous cuitry voltages of this Disconnect Unit are present long as as the on power power before the inside of I Factory Authorized Service Station thould be contacted. In of equipment malfunction, the manufacturers cases recommendations should be strictly followed. all The following remedies for unit. is chart designed to diagnose provide and of the troubles that may develop in this some TROUBLE SUGGESTED CHECK AND/OR REMEDY PROBABLE CAUSE All Fuse F6 open. ~Replace fuse F6 (see Section 5.4). Remote Hand Switch not tight in Ensure that Remote Hand Switch is no inoperative; sequences output. Gas and coolant flows for a brief period and then shuts off (transformer Ti is energized). receptacle Rd. All Fuse F7 open. ~Replace fuse F7 (see Section 5-4). Fuse F8 open. ~RepIace fuse F8 (see Section 5-4). sequences inoperative; no secure in receptacle RC1. output. Gas and coolant does not Ti flow (transformer is energized). Sequence Control entirely moperative Ti (transformer not ener gized). Normal output; no switch High-frequency high OFF in Incorrect spark gap. Check spark gap. Shorted high voltage Normal Place high-frequency switch in proper position. position. frequency. Low output. high capacitor(s). Adjust as required. See Section 5-2. Replace capacitor(s). Incorrect spark gap. Check setting for .008 inch. See Section 5-2. High-frequency Check all connections for high-frequency leaks. frequency. Erratic weld current. Incorrect direct-air coupling. Check that both Poor tungsten. Check tungsten and replace if contaminated. Incorrect polarity. Check polarity. Incorrect welding cable size or not shut off. not at workpiece. Blown control operating voltage of Adjust slider on resistor open-circuit voltage. operating voltage of Adjust slider on resistor R2 welding arc is initiated. in ~Replace fuses F6 F7 ensure that beginning of welding Manual for circuit diagram. I Page 6 a fuse of the proper size is used. power source R2 so so relay CR3 coupling. Owners I~ pulls relay CR3 drops fuses F6 and/or F7 (see Section 5-4). circuitry. if it becomes necessary to replace any fuse in this unit, See and/or same Check for proper weld cable size (see Section 2-2). Tighten Check ground connections. Incorrect pull in. connected for the Poor ground relay CR3. Contactor does are all welding cable connections. relay CR3. Weld current does links loose connections, Incorrect Contactor pulls in. leaks. out in on when SECTION 7- CERTIFICATION FOR HIGH FREQUENCY ARC WELDING EQUIPMENT 7- 1. GENERAL 3. Direct radiation from welding leads. Direct radiation from welding leads, although very pronounced, decreases rapidly with distance from the welding leads. By keeping the welding leads as short as possible, the operator can do the This following information is necessary to make a proper installation of the high frequency arc welding equipment de scribed in this instruction manual. In order to comply with Part 18 of the Rules and Regulations of the Federal Com munications Commission, the certificate in front of this man ual must be filled in completely and signed. The certificate must be kept WITH THE EQUIPMENT AT ALL TIMES to comply with the regulation. The manufacturer of the covered herein has equipment a great deal minimize interference from the source. The intensity and frequency of the radiation can be altered over wide limits by changing the location and rela tive position of the welding leads and work. If possible. loops and suspended sections should be avoided. 4. con ducted approved field tests and certifies that the radiation can reasonably be expected to be within the legal limits if the correct installation procedures, as outlined, are followed. The importance of a correct installation cannot be over emphasized since case histories of interference due to high frequency stabilized arc Welding Machines have shown that invariably an inadequate installation was at fault. Pick-up and reradiation from power lines. Even though welding lead radiation falls off rapidly with distance, the field strength in the immediate vicinity of the welding area may be extremely high. Unshielded wiring and un grounded metallic objects in this strong field may pick up the direct radiation, conduct the energy for some dis tance, and produce a strong interference field in another area. This it The to of the equipment must complete the certification by stating that he has installed the equipment and is using it, according to the manufacturers instructions. The user must user most troublesome source of interfer careful adherences to proper installation pro in this booklet will minimize this type outlined usually the but ence, cedure as of interference. sign the certification notice appearing in front of this instruc tion booklet indicating that he has complied with the require- 7 men ts. In the event that interference with authorized services occurs, in spite of the fact that the radiation from the welding equip is within the specified limits, the user is required to take suitable steps to clear the situation. The factory person nel will assist the user by supplying technical information to clear the situation, ment In lieu of complying with the installation requirements and the certification of each individual installation, the user may elect to certify his entire plant by having a reputable engin eering firm make a plant radiation survey. In such cases, the installation instructions incorporated in this instruction booklet could very well serve as a guide in minimizing inter might be contributed by welding equipment. ference that the high frequency outlined below: Direct radiation from the welding machine. This is radia tion that escapes directly from the Welding Machine case. This is very pronounced if access doors are left open and unfastened and if the Welding Machine case is not pro perly grounded. Any opening in the metal Welding Ma chine case will allow some radiation to escape. The high frequency unit of this certified equipment is adequately shielded to prevent direct radiation of any consequences if proper grounding is carried out. Direct feedback to the power line. High frequency energy get on the power line by direct coupling inside the equipment or the high frequency unit, the power line may then serving as a radiating The specific installation instructions for making the proper primary connections to the equipment as outlined in the in struction booklet furnished with the equipment, should be followed carefully with one exception as notted in the following paragraph. Frequently installation instructions specify that the primary power service shall be run in solid or flexible metallic con duit. Ordinary helically wrapped conduit is designed for mechanical protection and is not suitable for electrical shield ing. Only primary solid metallic conduit or conduit of equivalent should be used to enclose the power service leads. electrical shielding ability Solid metallic shielding shall enclose the primary power ser vice to the equipment from a point 50 feet from the equip ment in a unbroken run. In a high frequency stabilized arc Welding Machine installa tion, interfering radiation can escape in four distinct ways as 2. 3. POWER SERVICE arc 7-2. GENERAL IN FORMATION 1. - This shielding shall be grounded at the farthest point from equipment and should make good electrical contact with casing of the equipment. The ground should be in accor dance with the specifications outlined in the section entitled GROUNDS and as shown in Figure 7-1. Care should be taken that paint or corrosion at the junction of conduit and case, does not interfere with good electrical contact. the the There shall be no gap in this shielding run. This simply means that within 50 feet of the equipment, no portion of the power wires serving the equipment shall be unshielded. If there is any question about the electrical efficiency of the joints between individual conduit sections, outlet boxes and the equipment case, bonding should be carried out by solder ing a copper strap or wire across the joint as shown in Figure 7-2. clean and bolt antenna. Solder N proper shielding and filtering, direct vented in this certified equipment. By coupling ~pPCor Strap Solder is pre lxi Damountable Bonding Strap for conduit Jointt Copper Wire SolE~lder At least 50 feet p Metallic conduit - ~ __________ Good electrical iointt be- ,~ Ibi Solid Bonding with Copper Wire for Conduit Jointt / ____ tween Box and conduit High Frequency Stabilized Weld ing Machine or Otcillator Ground I / Good electrical 1.4 clean metal to Figure 7-4. WELDING MACHINE contact. metal. / 1/7//I /7//f/fl 7-1. Power Service Installation H. F. Stabilized Arc Welding Machine Figure 7-2. Two Recommended Methods For Electrical Bonding Across Poor Conductivity Conduit Joints The location of the equipment should be chosen with respect to nearness to a suitable ground connection. The equipment case, firmly bonded to the power conduit, should be grounded to the work terminal of the equipment with a copper cable or braid with rated current carrying capacity equal to or greater than that of the power service wires. OM-540 Page 7 This work output terminal of the be grounded to a good electrical section entitled GROUNDS) cable of the same capacity with the as equipment should then ground (as a short length work defined in of ,/gfoolrntervaltf 7-3). welding Machine cese firmly ~ ~ work Terminal bonded to Power conduit grounded to driven ground rod or cold water pipe heavy braided strap ot cable with Electrode Source of Holder j Power case grounded Keep ALL unshielded Figure 7-3. Ground Connections At Welding While the equipment is in operation, all access and service doors shall be closed and properly fastened, Spark gap settings shall be maintained at the minimum separ ation consistent with satisfactory welding results. 7-5. WELDING LEADS In order to minimize direct weld lead radiation, the welding leads (electrode lead and work lead) must be kept as short as possible. Certification tests on this machine have been made with leads 25 feet long. Considerable improvement in radia tion minimization can be had by shortening the leads as much as possible. the electrode lead and possible and (See Figure 7-4). the on floor ground serves to or work lead reduce the as grounded wires \ Machine No change in the wiring or the location of parts inside the equipment, other than power service tap changes or other adjustments specifically covered shall be made, The equip ment shall not be modified in any way since changes in the equipment can affect the radiation characteristics and may not be in accordance with the test data upon which the man ufacturer bases his certification. as /7~ Work 77//////////////77//////77/ to Work Terminal Keeping N, Shielded Wires welding (See Figure lead. out and / un of this High Field Intensity zone. ~,_,,, N ~ Figure 7-5. General Requirements To Minimize Reradiation Pick-Up In the Vicinity of the Weld Zone Extreme precaution should be taken to make sure that the location of the zone is chosen so that none of the condjtirns are voided by unshielded wires off the premises but still with in the radial dimensions of the H.F.l. zone. This 50 foot H.F.I. zone is a minimum that is imposed on the installation. Certification tests by the manufacturer are based on this limit. Keeping will zone unshielded wires farther than 50 feet from the weld materially aid in minimizing interference. If it is impossible to relocate unshielded wires, that section within the H.F.I. zone, should be placed in conduit and each end of the conduit section grounded. close NOTE radiation. 1 emphasized that all changes in power and should be made by a qualified electri cian and comply with the National Electrical Code requirements. Any shielding or relocation of telephone or signal wires must be done either by the service com pany concerned or with the specific permission of said It must be Welding J~ Machine Electrode Holder Keep leads or on ground boards and 3/4 to 1 apan k j-c company. Work 7/ /77 Figure lighting wiring Oscillator or Keep leads never in excess of 25 feet. as short as possible 7-4. General Rules For Welding 77. GROUNDS Leads Frequent pretation 7-6. WIRING IN THE VICINITY OF THE AREA WELDING booklet the A As discussed in the general information section, the most serious source of interference is reradiation from wires that are located near the welding area. Any ungrounded electrical conductor in the strong directly radiated field, produced by the welding leads, serves as a pick-up device and may conduct the interference for some distance and reradiate strongly at another location. For purpose of simplification and standardization, the space all around the weld zone at a distance of 50 feet in all direc tions is referred to as the High Field Intensity (H.F.l.) zone. (See Figure 7-5). To minimize radiation of this type all wiring in the H.F.I. zone shall be in rigid metallic conduit, lead covered cable. copper braid or material of equivalent shielding efficiency. Ordinary flexible helically wrapped metallic conduit, com is not satisfactory for shielding. monly referred to as B.X. and should not be used. The shield on all wiring should be grounded at intervals of 50 feet and good electrical bonding between sections shall be maintained. ground least 8 feet shielding requirement applies to all wiring, including tel ephone, inter-communication, signal and control and inciden tal service. Page 8 following specifications apply: connection should be made to long ment to be a driven rod at and driven into moist soil. A cold water pipe can provided it enters the be used in place of the ground rod 10 feet of the equip ground within grounded. connecting the point to be grounded to the rod or pipe should be as short as possible since the lead itself can become an effective radiating antenna. All leads ground ground ground in reducing interference de conductivity. In certain locations it may become necessary to improve the ground conductivity by treating soil around the ground rod with a salt solution. The effectiveness of a pends upon the ground 7-8. METAL BUILDING It is frequently through that operating of high frequency stabilized arc welding equipment in metallic buildings will completely eliminate troublesome radiation. This, however, is a false assumption. structure, if properly grounded, may direct radiation from the weld zone but will have no effect on conducted interference and reradiation. As a result, all installation requirements necessary for certifica tion must be complied with. A metallic serve This reference is made to a good ground in previous is considerable leeway in the inter of this term, for the purpose covered in this Although there sections. building to reduce If the metallic building is not properly grounded, bonding to good electrical grounds placed around the periphery of the building will give reasonable assurance that the build 9. several ing itself is contributing not to the radiation. 10. 11. Any all CERTIFICATION INSTALLATION 7-9. INDIVIDUAL the above installation requirements may be user if he desires to exercise the option of making an individual field survey of the particular unit instal lation (or the complete installation if more than one unit is involved), and certifying on that basis. or by waived of tions Commission, Surveys units or of this nature may include the can cover a unit single complete plant or multiple equipment secondary? case connected to the work terminal Is the wire used for this connection of sufficient size? Is the work terminal connected to good electrical a ground? 12. the This survey shall be made by a competent engineer in accord ance with the test procedure requirements as set forth in Part 18 of the Rules and Regulations of the Federal Communica Is the of the Is the cable or equal the to copperbraid used for this connection current carrying capacity than greater in lead? or welding 13. Is this cable 14, Are the spark-gaps set at .008 access doors closed and bolted? as short possible? as or less? 15. Are all service and 16. Are the 17. Are 18. Are the welding suitable board? 19. Are the 20. Have you visualized the I-f.F.l. zone, a sphere with foot radious centered on the weld zone? 21. Have the unshielded power and light wires originally in this H.F.I. zone been placed in grounded shields or been relocated outside the zone? Have all large metallic objects and any lon9 guy supporting wires in the H.F.I. zone been grounded? welding they as leads less then 25 feet short as long? possible? structure. leads the on floor or placed on a - 7-10. CHECK LIST The following questions may be used by the installer as check to see if all installation requirements have been met: 1. Has the equipment been located be kept short? leads, serving the unit, in conduit? 2, Are the power 3. Is there good electrical contact between power duit and case? con 22, 4. Do the conduit couplin~ make good electrical tact? lIf in doubt, use bonding). con 23. Is there good electrical contact between conduit and switch on service boxes? 6, If approximately 3/4 so that no premises are 1 to apart? a 50 Are the grounds driven ground rods? 25. Is 26. If so, does it connection? 27. Are the connections 28. If operated within properly grounded? a cold water pipe used as or external power or tele within the zone? 24. ground? metallic conduit is not used, is the shielding equivalent shielding efficiency? (Copper sleev used of lead covered cable, etc-, is satisfactory. Spirally wound flexible metallic conduit is not suitable). ing, 8, Have you checked lines off the phone 5, 7. leads that ground leads so can rigid welding a Is the conduit system grounded at feet from the equipment? Is the conduit NFl. zone? run a point complete (without any at least gap) 50 in the enter the ground 10 feet to a or less from the the ground clean and metal building, If your answer is yes to the above questions, fy the installation by signing the certificate, tight? is the you building can certi OM-540 Page 9 February 1980 FORM: OM-540A Effective With Serial No. HK321565 MODEL SCE-1A SCE-3A SCE-5A SCM-lA SCM-3A SCM-5A PARTS LIST 4 7 Figure A OM-540 Page 1 - Left S~de View Item Dia. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. Figure A 1 601 156 2 Si 011 624 3 S3 S2 Oil 610 011 610 4 028 872 5 026 421 023 220 6 S2 011 609 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 SWITCH,toggleSPDTl0ampl25volts SWITCH,toggleSPDTl0ampl25volts CABINET, w/o door & component mtg. panel (consisting of) Both 1 1 Both 1 1 1 Both 2 2 2 1 CATCI-L, door BRACKET, support (S CE/SCM . to machine) SWITCH,toggleSPDTl5ampl25volts DOOR (consisting of) HANDLE, door- pull 8 019 677 9 STRIKE, catch door 013 442 WINDOW, plexiglass 028 868 COVER, terminal board (consisting of) 604 768 FASTENER, SC 1/4 turn No. 5 602 344 RETAINER, screw 018 851 PLATE, cover opening terminal 602 347 RECEPTACLE, rivet type screw 1/4 turn 035 493 RECEPTACLE, twistlock grounded 3P3W 035 493 RECEPTACLE, twistlock grounded 3P3W 026 420 Both ... . . 1 Both 1 Both 1 Both 1 1 Both 1 1 1 Both 2 2 2 1 1 Both 1 1 Both 1 1 1 Both 2 2 2 Both 2 2 2 Both 2 2 2 Both 1 1 . . Both - - 12 RC1 RC2 13 GS1, WS1 - 003 538 025 603 14 A 14 A 025 608 14 A 025 611 14 A 14 A 025 610 025 625 14 A 14 A 14 A 14 A P1 025 025 025 025 025 617 621 618 617 701 1 Both - 003 539 010 295 010 296 . 5A Both 020 916 12 Model hA 13A1 NIPPLE, chase 1-1/4 thick NUT, locking 1-1/4 inch SWITCH, toggle 4PDT 15 amp 125 volts 7 10 11 SCM Description Left Side View 601 152 3 Quantity SCE Or ac 2 way 1/4 lPS port (consisting of) COIL, valve 115 volts ac FITTING, hose brass elbow male 1/4 NPT x 5/8-18 LH (coolant) FITTING, hose brass elbow male 1/4 NPT x 5/8-18 LH (gas) METER, amp dc 5OMV 0-300 scale or METER, amp dc 5OMV 0-500 scale or METER, amp dc 5OMV 0-600 scale or METER, ampdc5OMVO-800 scale VALVE, 115 volts 1 Both 2 2 Both 1 1 1 Both 2 2 2 Both 2 2 Both 1 1 2 . - - ... METER, METER, METER, METER, or amp ac 0-300 scale 0-500 scale ac 0-600 scale or amp amp ac ampac0-800scale METER,ampacO-500 FILTER, high frequency 2 or Both 1 Both Both 1 1 1 1 BE SURE TO PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. OM-540 Page 2 26 27 31 32 Figure B Page 3 - 30 Panel, Mounting W/Components 29 28 Item Dia. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. Figure B 020 918 21 030 922 21 PL1-3 020 920 020 924 020 921 020 925 010 853 010 855 030 653 030 653 019 627 027 603 PL4 027 601 21 21 22 23 R3-5 23 R23-25 24 25 027 602 26 26 26 TD1,5 TD1,5 TD1 ,5 TD1 ,5 034 703 CR1 034 704 034 705 034 706 034 619 27 28 CR1 R2 034 666 030 617 28 R21,22 29 29 30 31 32 CR3 030 617 034 601 034607 033 609 034 615 26 27 CR3 RFC CR2,8 CR5,6, 7,9 33 TD2-4 33 TD2-4 33 33 33 33 33 33 33 TD2-4 TD2-4 TD2-4 TD2-4 TD2-4 TD2-4 TD2-4 Description Quantity Model hA I 3A 5A Panel, Mounting W/Components 21 21 SCE Or SCM 034 613 034 703 PANEL, mounting components (consisting PANEL, mounting components (consisting PANEL, mounting components (consisting PANEL, mounting components (consisting PANEL, mounting components (consisting PANEL, mounting components (consisting FASTENER, screw slotted hd No. 2 RETAINER, screw No.2 RHEOSTAT, WW 150 watt 15 ohm RHEOSTAT, WW 150 watt 15 ohm KNOB, pointer 1/4 bore LIGHT,indicator-redlens6-l25voltsac LIGHT,indicator-greenlens6-l25voltsac BULB, incandescent base 120 volts TIMER, 15 second 115 volts or TIMER, 1 minute 115 volts or TIMER, 3 minute 115 volts or TIMER, 5 minute 115 volts RELAY, 24 volts ac DPDT RELAY,24voItsac3PDT RESISTOR,WWadj25watt2000 ohm . SCE SCM SCE SCM SCE SCM Both 2 2 2 . Both 2 2 2 Both 3 3 Both 3 3 3 Both 3 3 3 Both 1 1 1 Both 4 4 4 Both 2 2 2 Both 1 1 1 1 Both 1 1 Both 1 Both 2 2 Both 4 4 SCM 3 3 3 SCE 3 3 3 - - - - - - - RESISTOR,WWadj25watt2000 RELAY, 24 volts dc DPDT ohm RELAY,llOvoItsdc3PDT CHOKE,filter2amp6ohm RELAY, ll5voItsacDPDT RELAY, 115 voltsac3PDT TIMER, 15 second 115 volts ac or 034 704 TIMER, 1 minute 115 volts ac or 034 705 TIMER, 3 minute 115 volts ac or 034 706 TIMER, 5 minute 115 volts ac 047 277 TIMER, delay 2 sec or 047 278 TIMER, delay 5 sec or 046 157 TIMER, relay 15 sec or 046 158 TIMER, relay 25 sec or 047 279 TIMER, delay 50 sec (Fig D Pg 7) of) of) of) of) of) of) 1 1 1 1 1 1 Both 3 Both Both 1 Both 2 1 BE SURE TO PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. OM-540 Page 4 Quantity SCE Item No. Dia. Factory Mkgs. Part No. 41 CR4 034 615 42 iT 038 639 42 iT 038 622 42 iT 038 646 43 W 44 F8 034 909 034 912 012 639 012 638 010 854 014 491 *012 606 012 640 038 621 038 639 038 639 45 46 48 Description F6 2T 48 5T 48 2T RELAY, 115 volts ac2PDT BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 6 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 5 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 10 pole CONTACTOR, 4 pole 115/230 volts ac (Fig F Pg 9) INTER LOCK, contactor normally open FUSE, cartridge 6 amp 600 volts HOLDER, fuse cartridge 30 amp 600 volts NUT, speed No. 2 BRACKET, door stop FUSE, plug 15 amp 250 volts HOLDER, fuse plug BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 4 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 6 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 6 pole 3A I 5A Both - Figure C - Interior Cabinet View 44 1 1 1 1 Both - 4~3 1 Both - 42 1 Both Both - 41 Both Both 1 Both 1 Both 2 2 2 Both 2 2 2 Both 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 Both 1 Both Both Fig F Page 5 I Interior Cabinet View Figure C 47 Model Or SCM 45 1 Item Dia. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. Figure C 038 620 TE2 038 602 TE2 038 622 50 TE3 038 640 51 iT 036618 51 52 Ti 036 629 101 800 53 018849 54 020 636 54 - - HF PANEL - 56 - 4T 58 BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 5 pole 035 925 TERMINAL ASSEMBLY, power output (consisting of) 038 622 028 865 SCM hA I 3A I 5A TERMINAL BOARD Both 1 1 1 1 Both 2 2 Both 1 1 Both 2 2 Both 1 1 Both 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 Both 2 2 2 Both 2 2 2 Both 2 2 Both 2 2 2 2 Both 6 6 6 Both 4 4 4 Both 1 1 Both 3 Both Both Both Both Both 1 Both Both C21-23 031 610 STUD, brass 1/2-13 x2-5/8 center drilled PIN, spring-carbonsteell/8x3/8 WASHER, flat steel 1/2 SAE WASHER, lock external tooth 1/2 NUT, brass hex jam 1/2-13 NUT, brass-hex fulll/2-13 BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 3 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 2 pole LINK, jumper terminal block CLIP, jiffy conduit 1/2 inch CAPACITOR, electrolytic 40 uf 250 volts dc C24 031 611 CAPACITOR, electrolytic 5 uf 150 volts dc Both 1 034615 RELAY,ll5voltsacDPDT Both 8 RELAY, RELAY, RELAY, RELAY, 115 volts ac 3PDT llSvoltsacDPDT 110 volts dc 3PDT Both CR10 CR1 1 034 613 034 615 034 607 034 601 Both 1 24 volts dc DPDT Both 1 CR12, 14,17 034 612 3 034 615 RELAY, llOvoltsdcDPDT RELAY, 115 volts ac DPDT Both CR18 038 982 010 912 602 247 602 217 601 840 601 839 59 LINK, jumper terminal block BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 3 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 5 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp single pole TRANSFORMER, kva 1/2 30-1 15 duplex TRANSFORMER, kva 1/2 15-30-115 TUBING, steel 5/8 OD x 3/8 ID x 5-1/4 BRACKET, mounting RH HF panel (Fig EPg8) 020 638 HF PANEL (Fig EPg8) 018850 ANGLE, mounting HF 018848 ANGLE, mounting LH HF panel 55 59 Description Model Interior Cabinet View (Contd.) 49 57 Quantity SCE Or 3T 3T 038 602 038617 038 620 601 119 60 - - - - - Both Both 22 Both 2 2 CR2,2B, 4,7,8, 13,15, 16 CR2A, 5,6,9 CR10 F7 R26-29 S R3 SCE 4 1 1 1 SCE FUSE, plug 15 amp 250 volts HOLDER, fuse-plug 604 178 RESISTOR, carbon 2 watt 100 ohm 037 568 RECTIFIER, signal w/mtg. brackets (consisting of) Both 1 1 Both 1 1 RECTIFIER, signal w/mtg. brackets (consisting of) BRACKET, rectifier mounting 601 242 INSULATOR, washer heat sink 037 616 RECTIFIER, selenium Both *t012 606 t012 602 Both Both 4 1 SR21 -24, 26 037 568 102 363 - - SR25 Both 2 5 2 Both 2 2 Both *Recommended Spare Parts. tOptional Parts. BE SURE TO PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. OM-540 Page 6 Quantity Model Item Dia. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. I 2 Description Sec 5 I Sec 15 Sec Figure Timer, Delay (See Fig. B Page 4 Item 33) N N N 030 131 R50 POTENTIOMETER, carbon 1 50 I Sec tfl O~ N ~- N N N CD ~. N ~. 0 0 0 U~ N CD 0 0 71 I N N D 25 Sec I ~. turn 2 watt 50K ohm 71 030 108 R50 POTENTIOMETER, carbon 1 turn 2 watt lOOK ohm 71 028 768 R50 POTENTIOMETER, carbon 1 turn 2 watt 350K ohm 71 R50 030 738 POTENTIOMETER, carbon 1 turn 2 watt 500K ohm 71 028 770 R50 POTENTIOMETER, carbon 1 turn 2 watt 1 meg ohm 72 73 74 75 76 77 047 133 RFC5O,51 052 038 010 047 024 978 839 116 124 366 78 RELAY, enclosed - delay 120 volts time ac DPDT 1 1 1 1 1 CHOKE, 5600 UH 45 ohm BLOCK, terminal 20 amp 5 pole GROMMET, rubber 3/8 ID x 1/2 mounting hole CHASSIS, timer KNOB, pointer line indicator NAMEPLATE (order by model & serial 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1~ 1 1 numbers) 1 1 1 1 1 - 71 72 76 TA-045 216 Figure D - Timer, Delay RFC 50 18 RFC 51 2A~-~~ L~~~5A L_~j~ii B CONNECTION A CONNECTION ID TO ~15 18~ 3A B~ 4A 17~ SA CONNECTION Circuit Diagram No. A-049 250 Circuit Diagram For Delay Timer BE SURE TO PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. Page 7 Dia. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. Quantity Description - Item Figure 121 HF Panel (See E Item 54) 020 623 SPARK GAP ASSEMBLY (See 122 010 886 123 124 125 601 838 STRIP, conductor NUT, brass-hex jam 3/8-16 MOUNTING BOARD, component STUD, brass No. 10-32 x 1-3/8 w/hex collar COIL, coupling-air500 amp STUD, brass3/8-16x2-l/8 TRANSFORMER, high voltage 115 volts (consisting of) RESISTOR, carbon 1 watt lOOK ohm CAPACITOR, HF (consisting of) STRIP, mounting capacitor CLAMP, capacitor 1 inch dia CAPACITOR, metal film 10 uf 220 volts RESISTOR, WWfixed 10 watt 10K ohm CAPACITOR, mica 0.002 uf 5000 volts dc STRIP, conductor CAPACITOR, mica 0.001 uf 6000 volts dc RESISTOR, WWfixed 100 watts 10 ohm 126 G Fig. C Page 6 016 612 T3 038 887 033 601 12 038 891 036 323 127 128 R7 129 130 C3 081 282 131 007 532 132 133 Ri 134 C2 059 887 030 603 031 602 010 884 135 136 030 724 081 291 Cl R6 031 605 030 602 Fig. El Page 9) 123 Fig 127 ,~ ~D ~ C ~ ~ 1 1 44 88 1 1 22 1 1 22 1 - 126 ,o ~,, ~O 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 22 1 1 1 1 44 22 1 1 1~ 1 Fl 121 125 TC-020 636-8 L132 13113O~ 129 Figure E - HF Panel BE SURE TO PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. OM-540 Page 8 Item Factory No. Part No. Figure El 020 623 Quantity Description Spark Gap Assembly (Fig E Pg 8 Item 121) SCREW, cap-steel socket hd 10-24x3/4 CONNECTOR, holder-spark gap 020 622 HOLDER, points 142 602 023 143 010 888 144 4 1 4 145 *020 603 POINT,sparkgap 4 146 010 913 WASHER, flat-brass3/16 IDxl/20D 8 147 020 621 BASE,sparkgap 148 602 204 WASHER, lock steel external tooth No. 10 602 101 SCREW, machine steel round hd 10-24 x 5/8 1 8 - 149 8 - 148 147 149 142 TA-020 623-B 156 Figure El - Spark Gap Assembly 157 57 TB-034 909 Figure Item Factory No. Part No. Figure F 034 909 156 034 910 157 *034 911 F - Contactor Description Contactor (See Fig. C Page 5 Item 43) COIL, contactor 115 volts KIT, contact point - *Recommended Spare Parts. BE SURE TO PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. Page 9 Quantity 1 4