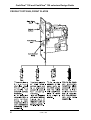
Download Mars CASHFLOW 126 Product specifications
Transcript
The CASHFLOW® 126 AND 129 4-WAY AND 8-WAY SELECTORS DESIGN GUIDE 26043 G3 709623001 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Published by : MEI Internet: http://www.meigroup.com For further information on issues in other languages please write to the Technical Communications Manager at the above address. CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide © , MEI UK International Ltd., 1998. All rights reserved Except as permitted under the relevant local legislation, no part of this publication may be copied, transmitted, transcribed, or distributed in any form or by any means, or stored in a database or retrieval system, or translated in any language (natural or computer), without the prior written permission of MEI. MEI®, CashFlow® and the MEI device are registered trademarks. ©, MEI., 1998. MEI reserves the right to change the product or the product specifications at any time. While every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this publication is accurate, MEI disclaims any liability for any direct or indirect losses (howsoever caused) arising out of use or reliance on this information. This document does not necessarily imply product availability. Part number: 709623001 This edition (February 1998 ) ii Printed in the United Kingdom. ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS SAFETY 1 Warning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Caution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Maximum Operating Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Dangerous Environments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Disposal of Product . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Conformance to International Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 PRODUCT RANGE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 PRODUCT OPTIONS; FRONT PLATES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 PRODUCT OPTIONS; REJECT COVERS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 PRODUCT BUILD OPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 PRODUCT FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 PRODUCT OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Accepted Coins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Inhibited Coins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Rejected Coins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Signals to and from the machine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Multi-Pulse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 PRODUCT OPERATION, ELECTRICAL. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 Validator Connector 1, Machine Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 Validator Connector 2, CF126 / 129 Separator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 Validator Connector 3, Routing Plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 Validator Connector 4, Dynamic Route Inhibit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 Validator Connector 5, Serial Port (Future use only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 Validator Connector 6, (Future use only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 Rotary Data and 4 Way DIL Teach Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 Diagnostic LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 Pre-Gate Strobe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 Post-Gate Strobes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 PRODUCT INTERFACES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 Parallel Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 ........................................................................................... ©, MEI., 1998 iii CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Multi-Pulse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 Coin validation Inhibits A, B, C, D, E, F . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 Parallel Output mode inhibits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 Coin Output Common Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 Binary Coded Output ( BCO ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 Coin Validation Inhibits A, B, C, D, E, F . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 Binary Coded Output Mode Inhibits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 Auto Mode Parallel or BCO Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 ELECTRICAL INTERFACES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 Connector 1, Machine Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 Connector 2, Separator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17 Connector 3, Routing Plug. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 Connector 4, Dynamic Route Inhibit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 Coin Exit Priorities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 Connector 5, Serial Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 Y-chute Interface Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 TYPICAL ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 Coin Output Electrical Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 Output Common Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 Negative Common Voltage Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 Positive Common Voltage Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 Binary Coded Output (BCO) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 Coin Inhibits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 MECHANICAL INTERFACE DRAWINGS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 COIN ROUTING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 Coin Output Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 Route Input Lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 ROUTING CONFIGURATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36 CashFlow® 4-Way Separator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36 CashFlow® 129 8-Way Separator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36 ROUTING CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37 COMPATIBILITY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38 PERFORMANCE STANDARDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39 ELECTRO MECHANICAL CONFORMANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39 COMPLIANCE CLASSIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 Electro-Mechanical Conformance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 iv ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Flammability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 Power Supply Input Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 Mechanical Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 Mean coins between failures (MCBF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 First Year Failure Rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 Coin Acceptance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 Coin Sizes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 Coin Acceptance Rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 Fraud Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 ENVIRONMENTAL PERFORMANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 Humidity Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 Thermal shock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 TRANSPORTATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 LIQUID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 MEI MAIN AND REGIONAL OFFICES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 ©, MEI., 1998 v CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide vi ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide SAFETY Warning Before cleaning, servicing, removing or replacing CashFlow® units, ALWAYS SWITCH OFF or ISOLATE the ELECTRICITY SUPPLY to the machine. Caution This guide is for use only by personnel trained to carry out electrical installation. Dangerous Environments Do not operate the unit in the presence of flammable gasses or fumes, or after the entry of fluid into the machine. Disposal of Product If necessary, always dispose of defective units according to local regulations. Conformance to International Standards When installed and operated according to the instructions provided for the particular unit, CashFlow® products meet the applicable national and international safety standards for any country in which they are used. Safety All electrical connections to the product must be rated according to the requirements for “Accessible SELV” circuits as defined in EN60335-1. The product is therefore suitable for use in a class 2 (non-earthed or non-grounded ) appliance. Over current protection is not included in the product and should be provided as part of the machine. The recommended fuse value at the rated supply of 12V is: 3A Slow blow (to EN60127) Other protection methods may be used providing their over current characteristics remain within the overall operating characteristics of the above fuse. ©, MEI., 1998 1 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide PRODUCT RANGE MEI manufactures coin mechanisms compatible with gaming and amusement machines. The functionality of the range has been enhanced to match market needs while maintaining mechanical compatibility. The product detailed in this book are the CashFlow® 126 and 129 series. Use the following pages to check you have the right product for your application. 2 ©, MEI, 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION Each CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 variant is identified with the use of a profile number. This consists of a twelve digit alphanumeric number located on the validator coinset label. For example: J GB 002 L V 00 T 3 represents a CashFlow® 126 4 way separation system for Great Britain, which is programmed with coinset number 002 and also accepts tokens. Digit Description 1 Product Code 2&3 Country Code 4,5 & 6 Coinset Number Operating 7 Voltage 8 9 & 10 11 12 Mechanical Variant Factory Set Software options Tokens Programmed MEI CashFlow® Series Available Options J = CF126 S = CF129 For example; GB = Britain, DE = Germany, IT = Italy, ZA = South Africa 001 to 999 L = 12v DC L = CF126 4 Way Separator, Side Entry “A” Reject Cover N = CF126 4 Way Separator, Side Entry “C” Reject Cover V = CF126 4 Way Separator, Top Entry “B” Reject Cover G = CF126 4 Way Separator, Top Entry “B” Reject Cover, Single Coin Entry Bezel & Guide Plate H = CF126 4 Way Separator, Top Entry “B” Reject Cover, Dual Coin/Token Entry Bezel & Guide Plate P = CF129 8 Way Separator, Top Entry “B” Reject Cover, Single Coin Entry Bezel & Guide Plate R = CF129 8 Way Separator, Top Entry “B” Reject Cover, Dual Coin / Token Entry Bezel & Guide Plate 00 to 99 (contact MEI for more information) 0 = No T = Yes 3 = CashFlow® Product Series More information is available on the 3 type of reject cover ( A, B and C ) in Product Options; Reject Covers. ©, MEI., 1998 3 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide PRODUCT OPTIONS; FRONT PLATES 4 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide PRODUCT OPTIONS; REJECT COVERS ©, MEI., 1998 5 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide PRODUCT BUILD OPTIONS 6 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide DESCRIPTION & OPERATION Introduction This section describes the CashFlow® 126 with a 4 way separator and the CashFlow® 129 with an 8 way separator system. Description The CashFlow® 126 and 129 system range of products are electronic coin and token handling systems for use in gaming and amusement machines. The CashFlow® 126 can validate up to 14 coins coins and 2 tokens. The 126 product can separate the accepted coins into 4 ways and the 129 product 8 ways. Operation Coin validation parameters are factory programmed for optimum acceptance of up to 14 coins and 2 tokens When a coin or token is inserted the validator senses a range of parameters to see if it recognises the coin/token as part of its pre-programmed set. If variations are required to the programmed coin set please refer to the CashFlow® 126 and 129 Operators Handbook for details. NOTE: In the table below the features of the CF126 Token product are shown separartely from the CF126. In reality this is one CF126 product, but are shown here to indicate the availability of profile options, particularly regarding dual and single coin entry. ©, MEI., 1998 7 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Product Features STD = Available as Standard Feature N/A = Not Applicable OPT = Optional Features CF129 CF126Tkn CF126 Number of Active Coins Up to 16 Up to 16 Up to 16 Number of Active Tokens 2 2 2 Number of Pre-programmed Tokens Up to 16 Up to 16 0 Operating Voltage 12V D.C. 12V D.C. 12V D.C. Number of Coin Outputs 6 6 6 (Parallel mode) Individual Electronic Coin Inhibits 6 6 6 Parallel Interface (Industry standard) STD STD STD Binary Coded Output B.C.O (BACTA STD STD STD Standard) Auto Mode (Parallel / B.C.O. Interface) STD STD STD 4 Way Separator N/A STD STD 8 Way Separator STD N/A N/A Token Teaching STD STD STD Token Group Select STD STD N/A LED Diagnostics STD STD STD Default Route (Programmable) STD STD STD Routing Plug STD STD STD Alarm Output Feature STD STD STD Side Entry N/A OPT OPT Top Entry STD STD STD Coin Only Entry Bezel OPT OPT STD Dual Coin/Token Entry Bezel OPT STD OPT Long Channel Mounted STD N/A N/A Manifold STD N/A N/A Tube Collar STD N/A N/A Coinless Programming STD STD STD Market Application AWP AWP/SWP AWP/SWP 8 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide PRODUCT OPERATION Accepted Coins If a coin or token is recognised by the validator the accept gate will then be activated and the coin/token routed along the accept path to enter the separator which consists of a number of solenoid operated gates to route the coin/token to a pre-programmed exit. The CashFlow® validator has the capability to sense the direction of a coin. An alarm output will be given if a coin does not follow the correct validation sequence. Inhibited Coins Acceptance of one or more coin types can be inhibited, causing them to be rejected. This can be done by using the coin inhibit lines of the validator machine interface connector 1 or by programming the validator to reject specific coin types. Rejected Coins The validator will reject any coin/token that does not match pre-programmed limits, or, if no power is supplied to the validator, the accept gate will remain closed and the coin will be routed via the reject route. If a coin or token jams at the entry point, it can be freed by opening the validator reject flap which releases the coin to the reject path. Side entry mechanisms fitted to the front plates have an in built reject button that opens the validator reject flap when pressed. The host machine is required to provide a suitable mounting facility for top entry versions. Signals to and from the machine Communication between the validator and the machine is made through the validator machine interface and the Y-chute interface connector (dual coin/token entry version only). Once through the validator, the value of the accepted coin is signalled directly to the machine using the appropriate coin output line (or lines in BCO mode). Multi-Pulse Factory set option designed for backward compatibility gives a GB 50p coin output (on a GB profile) four times on validation of a GB £2 coin Only in parallel output mode. ©, MEI., 1998 9 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide PRODUCT OPERATION, ELECTRICAL. Validator Connector 1, Machine Interface The interface to the machine is provided by Connector 1 of the validator. The functions provided are: Coin outputs A, B, C, D, E, F. The unit will operate in one of three Coin Output modes: Fixed Parallel. Fixed Binary Coded Output (BCO). Automatic - Selects BCO or Parallel Interfaces. More detail on these modes are given later. Validator Connector (2), CF126 / 129 Separator This connector is used to connect the validator to the separator. No customer connections are available on this port. ME Series, Active 126 and high security separators are not compatible with this interface and must not be connected, otherwise damage to the validator may result. Validator Connector (3), Routing Plug This connector is used by the customer to control the separator. Once it is fitted to the product all factory set routing will be overridden and all routing will be controlled by the routing plug. The extra two pins on this routing plug allow for additional coin positions, G and H, to be accommodated. Validator Connector (4), Dynamic Route Inhibit This is a 9 pin connector which is an input from the machine to the validator and its function is to divert coin routing. When a specific exit is full with coins, the host machine sends a signal to the validator which will direct future coins to an overflow route. 10 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Validator Connector (5), Serial Port (Future use only) This 10 pin connector, accessible from the bottom of the validator, provides for a potential serial communication to a service tool. At present this connector serves no function. Customers should not connect anything to this connector. Validator Connector (6), (Future use only) A 6-way connector used for a MEI® Route Alpha hand held service tool. At present this connector serves no function. Customers should not connect anything to this connector. Rotary Data and 4 Way DIL Teach Switches In place of the option links used on an ME126 and ME129 a rotary data switch and a 4-way DIL switch have been provided. These are accessible through the opening in the reject cover. The rotary data switch will enable data input to the teach functions i.e. Token Selection. The 4-way DIL switch can be used to enable or disable the alarm by using switch 1 of the DIL switch or various teach functions which are accessed via switches 2, 3 & 4. Diagnostic LED The LED displays a sequence of flash codes to indicate the current operation of the validator, and can be used for fault diagnosis when inserting coin or when teaching functions as shown below. Flash Code Sequence: Constantly ON Validator power on 1 Flash Coin accepted / Reject lever pressed 2 Flashes Coin not recognised and rejected 3 Flashes Coin rejected by validator 4th sensor 4 Flashes Coin recognised but not accepted due to inhibit setting Pre-Gate Strobes This is an integral part of the validator which detects obstructions around the accept gate. If an obstruction is detected then coin acceptance is inhibited. Post-Gate Strobes The strobes are used for added security to the validator. These detect coins which enter the validator using the wrong direction e.g. from the bottom of the validator upwards. If this movement is detected the alarm will sound. ©, MEI., 1998 11 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide PRODUCT CONFIGURATION Using the Rotary Data Switch and the 4-Way DIL Switches the product can be re-configured. Further details regarding the settings shown below can be obtained from the CashFlow® 126 and 129 Operators Handbook. 4-Way DIL Switches 1 2 3 4 OFF ON X X X X X X X X X X X X OFF OFF ON OFF ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON ON X X X X X X ON ON ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF OFF ON ON OFF Configuration Mode Selected Alarm Dis-abled Alarm Enabled Default Overflow Route Machine Interface Type Inhibit Coin/Token Teach Enable Coin/Token Teach Token Group Select for Channel 0 Self Teach a Token into Channel 0 Token Group Select for Channel 1 Self Teach a Token into Channel 1 Discriminator Node ID Select Fraud Defence Teach to Channel 0 Normal Operation Normal Operation Rotary Switch position/s required X X 0-7 C-F 0-F 0-F 0-D E-F 0-D E-F 0-6 E-F X X To commence any changes firstly the power should be removed, the required settings made on the rotary switch, the DIL switch settings are set and then the unit is powered up again. At this point the LED will start flashing. Returning the DIL switches to either all OFF or all ON will commit the changes to non-volatile memory. Tests should then be conducted to confirm that the changes are satisfactory, including the relevant flash sequences of the LED, as described later. If a teach mode is entered inadvertently then either switch off power or just leave for 30 seconds (when the LED will stop flashing), otherwise a teach function may be set that was not intended. 12 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide PRODUCT INTERFACES Introduction The standard interfaces available on CashFlow® 126/129 validators are Parallel and Binary Coded Output (B.C.O.). The validator is supplied in Automatic Mode which senses the type of interface selected by the host machine via pin 8 (Output Mode Select) of the machine interface connector. The product can be taught to ignore the state of this line by changing the machine interface type as above. Parallel Mode This type of interface is a standard 6 coin parallel output interface as used in the ME126/129 (Dual Polarity). For a GB profile the coin outputs are activated as follows: Alarm O/P Coins 5p Token 10p 20p 50p (Old) 50p (New) £1 (1983) £2 Enabled Outputs A 3 Coin Output B C D E F 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Multi Pulse (4 pulses) 3 3 The coin outputs for A and C can be combined ( e.g. A + C, B, D, E, F ) to give compatibility with 5 coin ME126B1 validators. This option is set by programming the validator. The coin outputs are factory defined but can be modified via an MEI service tool, e.g. MEI® Service Alpha. If an alarm condition occurs all coin outputs will be activated simultaneously for >600ms. Multi-Pulse ©, MEI., 1998 13 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide This will only operate when in parallel mode. This factory set option will pulse the GB 50p coin output (of a GB profile) four times on validation of a GB £2 coin. This option can be disabled using the Service Alpha. Coin validation Inhibits A, B, C, D, E, F To inhibit coin acceptance the CashFlow® validator offers six individual inhibit inputs. These inhibits operate for each mode as detailed in the following text. Parallel Output mode inhibits The channels that activate the associated coin output will be inhibited when the inhibit is held High, (e.g. Inhibit A will inhibit coin output A channels). The default settings for the GB profiles are: 14 Inhibit Line Coins Inhibited A 5p B Token C 10p D 20p E 50p old & new £2 F £1 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Coin Output Common Line This line allows for operation with positive or negative common systems. The interface self-configures by sensing the output common voltage supplied by the machine on the coin output common line, (pin 2 for a 15 way machine interface connector, or pin 3 for a 17 way connector). All potentials are relative to the 0 volt return line to the machine. pin 11 for a 15 way connector and pin 12 for a 17 way machine interface connector. Negative common operation is selected when pin 2 output common is 0 volts or negative with respect to pin 11. Positive common is selected when pin 2 is more positive than +7 volts with respect to pin 11. Binary Coded Output ( BCO ) Defined by the validator coin output map. When in BCO mode coin output A is permanently set active to indicate that the BCO feature is available. Coin output A will have a high impedance (approx. 1M Ohm to 0v) if coin output common is allowed to float. If an alarm condition occurs coin outputs B, D, E and F will be activated. Enabled Outputs Coins 5p 10p 20p 50p (Old) 50p (New) A 1 1 1 1 1 £1 (1983) £2 Token Alarm Output 1 1 1 1 Coin Output B C 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 D 0 1 0 0 1 E 0 0 1 0 0 F 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 Coin Validation Inhibits A, B, C, D, E, F To inhibit coin acceptance the CashFlow® validator offers six individual inhibit inputs. These inhibits operate for each mode as detailed in the following text. ©, MEI., 1998 15 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Binary Coded Output Mode Inhibits The channels inhibited, for a given inhibit line going high are factory set by the validators coin inhibit map option. When inhibit (A to F) is active, then coins for the channels specified in the map will be inhibited. The default settings for the GB profile are: Inhibit Line Coins inhibited A £2 B Token C Reserved D 20p E 5p, 10p, 50p old & new F £1 Automatic Mode - Parallel or BCO Selection In this mode the status of the output mode input (on pin 8 of the 17 way connector, or pin 7 for the 15 -way connector of the machine interface) selects either the parallel or the binary coded output interface standards. A logic high signal to this pin will select parallel mode, setting pin 8 to a logic low will select BCO mode. If there is no connection made to pin 8 the interface will default to parallel mode. 16 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide ELECTRICAL INTERFACES Introduction This section gives the pin assignments for all connector interfaces used on the CashFlow® validators and it also includes timing diagrams of the signals appearing on the input and output lines. Connector 1, Machine Interface. The interface to the validator from the machine is exactly the same as those which apply to the MS/ME series validators, with the exception of pin 8 of the 17-way connector. Connector 1 can accept either 15 pin or 17 pin interface connectors. 17 15 Way Way Connector Connector 1 - A Coin Output O (BACTA Standard) Function Definition 1 Ident signal 2 1 B Coin Output O 2 Accept Output 5 3 2 Coin Output Common I 3 Accept Output Common 4 3 F Coin Output O 4 Accept Output 1 5 4 Polarising Key 1 - 5 Polarising Key 6 5 E Coin Output O 6 Accept Output 2 7 6 D Coin Output O 7 Accept Output 3 8 7 Output Mode Select I 8 Select Line 9 8 C Coin Output O 9 Accept Output 4 10 9 C Coin Inhibit I 10 Inhibit 4 11 10 +12V Supply I 11 +12V Supply 12 11 0V Supply I 12 0V Supply 13 12 D Coin Inhibit I 13 Inhibit 3 14 13 E Coin Inhibit I 14 Inhibit 2 15 14 F Coin Inhibit I 15 Inhibit 1 16 15 B Coin Inhibit I 16 Inhibit 5 17 - A Coin Inhibit I 17 Inhibit 6 Functions (Dual Polarity) Input or PIN Output No. Connector types used:- 15 Way Molex SIL 6471 or 17 Way Molex SIL 6471. ©, MEI., 1998 17 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Separator Connector (2) This connector is used for connection to the CashFlow® 126 4 way or CashFlow® 129 8 way separators only. Function Solenoid 3 Pin No. Pin No. Function 1 2 Solenoid 1 Unused 3 4 +12V Unused 5 6 Solenoid 2 Unused 7 8 Unused Data 9 10 Ground Busy 11 12 Ground Reset 13 14 Ground Unused 15 16 Ground V Reference 17 18 + 5V + 12V 19 20 + 12V Connector type used:- 20 way Molex DIL 901-42-0020. WARNING: Do not connect ME129, ME126 Active or ME126 Security separators to this product or damage may result. 18 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Routing Plug Connector (3) A 22 way connector located on the front of the validator. It is used to accept a plug containing wire links or diodes that define the routing and exit path of validated coins. The routing plug is similar to that of the ME126 Active and ME129 products, but with 2 extra pins added toaccommodate coin routing for outputs G & H. NOTE: These outputs must not be confused with the outputs on Conn. 1. Connector type used: Molex 22 - way DIL 90142. NOTE: Neither the 14 nor the 18 pin routing plugs used with the MS/ME series products are compatible with the CashFlow® 126/129 products. However, it is possible for customers to source an adaptor loom, to MEI drawing no. 709856001. For detail please contact MEI Technical Support. Function Pin No. Pin No. Function Route 7 (B) 1 2 Route 7 (B) Route 6 (D) 3 4 Route 6 (D) Route 5 (C) 5 6 Route 5 (C) Route 4 (b) 7 8 Route 4 (b) Route 3 (a) 9 10 Route 3 (a) Route 2 (c) 11 12 Route 2 (c) Route 1 (d) 13 14 Route 1 (d) Coin Output A 15 16 Coin Output B Coin Output C 17 18 Coin Output D Coin Output E 19 20 Coin Output F Coin Output G 21 22 Coin Output H There are 7 exits (pins 1 to 14) labelled route 1 to 7, and 8 coin outputs (pins 15 to 22) labelled coin output A to H. GB Coinset Detail COIN OUTPUT COIN/TOKEN VALUE A B C D E F G H 5P TOKEN 10P 20P 50P old 1P 50p new 2P ©, MEI., 1998 19 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide CashFlow® 126/129 separators provide control over the exit path taken by a validated coin. This is referred to as routing and is accomplished by inserting wire links into a 22 way routing plug which is inserted into connector 3 of the validator. NOTE: Fitting a routing plug to the validator will overide all factory routing settings as long as more than one link is fitted between a coin output and data pin on this connector. 126 ROUTING PLUG 129 ROUTING PLUG PINOUTS AND FUNCTIONS PINOUTS AND FUNCTIONS Function Pin No. Coin H 22 Coin F 20 Coin D 18 Coin B 16 (Exit ‘d’) 14 (Exit ‘c’) 12 (Exit ‘a’) 10 (Exit ‘b’) 8 Exit C 6 Exit D 4 Exit B 2 Pin Function Functio Pin No. n No. 21 Coin G Coin H 22 19 Coin E Coin F 20 17 Coin C Coin D 18 15 Coin A Coin B 16 13 (Exit ‘d’) Route 1 14 11 (Exit ‘c’) Route 2 12 9 (Exit ‘a’) Route 3 10 7 (Exit ‘b’) Route 4 8 5 Exit C Route 5 6 3 Exit D Route 6 4 1 Exit B Route 7 2 Pin Function No. 21 Coin G 19 Coin E 17 Coin C 15 Coin A 13 Route 1 11 Route 2 9 Route 3 7 Route 4 5 Route 5 3 Route 6 1 Route 7 Coin Exit Route Priority Order Highest Lowest Routing Plug Signals The eight coin output signal lines, A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H correspond to up to fourteen possible coin types. The mapping of coin channels is channel set dependent. These lines signal the arrival of valid coins. Links between the coin output signal inputs and the coin route lines specify the exit paths to be taken by the coins. 20 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Route Input Lines - Routes 1-7 The CF129 exit routes are marked as Route (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 & 7) with (8) being the default exit route, as standard. Routes 1-7 on CF129 refer to the coin routes 1 to 7, with 1 having high priority and 7 low priority. Routes 1-7 on CF126 refer to the 4 coin route outputs A, B, C and D as shown in the following table. Note: (d) is the same route as D but has a higher priority. The CF129 exit routes are marked as Route (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 & 7) with (8) being the default exit route. Solenoid 3 Solenoid 2 Solenoid 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 ©, MEI., 1998 129 Route 126 Route 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 (d) (c) (a) (b) C D B A 21 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide ROUTING CONFIGURATION The CF126 exits routes are marked as (B, C & D) with (A) being the default exit route. 129 Separator End View 126 Separator Sol 1 Sol 2 Sol 3 EXITS 1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 EXITS D A (d) B C (a) (b) (c) 5 8 7 Reject 2 1 6 7 8 4 6 3 2 3 5 D C (d) (c) 4 TOP VIEW A (a) B (b) 1 ROUTING CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES When a routing plug is connected the routes will be set up as designated by the plug links and routing plug outputs. Where two or more exit routes are specified for a given coin, the highest priority will be chosen by the validator unless that exit route is being inhibited by a low voltage signal on its position within the dynamic route inhibit connector. P i n P i n Here are listed the three most commonly used routing plug configurations. 1. Single coin to one Exit. 2. Single coin to two Exits. 3. Two coins to the same Exit. 22 Coin H Coin G 21 20 Coin F Coin E 19 18 Coin D Coin C 17 16 Coin B Coin A 15 14 Route 1 (d) Route 1 (d) 13 12 Route 2 (c) Route 2 (c) 11 10 Route 3 (a) Route 3 (a) 9 8 Route 4 (b) Route 4 (b) 7 6 Route 5 (C) Route 5 (C) 5 4 Route 6 (D) Route 6 (D) 3 2 Route 7 (B) Route 7 (B) 1 Routing Plug Viewed From Wire Links End Example 1:Example 1 This shows a single coin to one exit. In this example coin E goes to exit C by linking pin 19 to pin 11 using a wire link. All other coins go to default route. 22 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Example 2:Shows a single coin to two exits. In this example coin E goes to exit D then overflows to exit C. By linking pin 19 to pin 13 & pin 14 to pin 12 using wire links. All other coins go to default. P i n P i n 22 Coin H Coin G 21 20 Coin F Coin E 19 18 Coin D Coin C 17 16 Coin B Coin A 15 14 Route 1 (d) Route 1 (d) 13 12 Route 2 (c) Route 2 (c) 11 10 Route 3 (a) Route 3 (a) 9 8 Route 4 (b) Route 4 (b) 7 6 Route 5 (C) Route 5 (C) 5 4 Route 6 (D) Route 6 (D) 3 2 Route 7 (B) Route 7 (B) 1 Routing Plug Viewed From Wire Links End Example 3:This shows how two coins can be routed to the same exit. In this example coins F and D both are routed to exit C. By linking pin 20 to pin 5 and pin 18 to pin 6 using diode links (the anode of the diode should be connected to the coin pin). Where a default route is required, teaching the default route will alleviate the need to use too many diodes. ©, MEI., 1998 Example 2 P i n P i n 22 Coin H Coin G 21 20 Coin F Coin E 19 18 Coin D Coin C 17 16 Coin B Coin A 15 14 Route 1 (d) Route 1 (d) 13 12 Route 2 (c) Route 2 (c) 11 10 Route 3 (a) Route 3 (a) 9 8 Route 4 (b) Route 4 (b) 7 6 Route 5 (C) Route 5 (C) 5 4 Route 6 (D) Route 6 (D) 3 2 Route 7 (B) Route 7 (B) 1 Routing Plug Viewed From Wire Links End Example 3 23 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Connector 4, Dynamic Route Inhibit This direct input from the machine to the front reject cover of the validator is knows as the Dynamic Route Inhibit. The inhibit placed via this connector indicates that a specific route is full. To Inhibit a route this has to be grounded (i.e. active low to inhibit a route). Connector type used:- 9 pin SIL - AMP 925366. Route Inhibit Connector Pin No. CF129 CF126 8 Way Separator 4 Way Separator Exit Route Exits Coin Exit Priorities 1 Divert to Route 1 Exit (d) = Priority 1 HIGHEST 2 Divert to Route 2 Exit (c )= Priority 2 3 Divert to Route 3 Exit (a) = Priority 3 4 Divert to Route 4 Exit (b) = Priority 4 5 Divert to Route 5 Exit C = Priority 5 6 Divert to Route 6 Exit D = Priority 6 7 Divert to Route 7 Exit B = Priority 7 8 Route 8 is the Default Exit A is the Default 9 Ground Ground LOWEST Coin Exit Priorities If an exit is required to be inhibited, the alternative route/exit must be of a lower priority. For example:If a route inhibit is applied to route 5 ( for the 8 way separator or exit C for the 4 way separator )then routing can only be diverted to routes 6, 7 or 8 the default route on 8 way separators or exits D,B or A for the 4 way separator. If route D is required to be diverted to route C on the 126 product then route 1 (d) should be used, which can then be diverted to any output. Connector 5, Serial Interface Provision has been made for future access to a comprehensive interface facility, but at the present time this connector serves no function. Customers should not connect anything to this connector. 24 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Y-chute Interface Connector Connections to the Y-chute is made with a Molex type 6471 19-way. This connector is fitted to the dual entry (coin and token) system only. It provides an interface for the machine to inhibit acceptance of any coin/token and also gives a signal to the validator to inhibit coins during token input and to inhibit tokens during coin input. This interface is not supplied with the single entry system. Pin No. 1 Function Input / Output Notes 12 Volts Output 12 volts supply to the validator 2 3 4 5 6 7 Inhibit F Inhibit E Inhibit D Inhibit C Polarisation Inhibit B Output Output Output Output Output 8 9 10 Not Used Not Used 0 Volts Output 11 0 Volts Input 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Polarisation Not Used Inhibit B Inhibit C Inhibit D Inhibit E Inhibit F 12 Volts Input Input Input Input Input Input Inhibit signals to the validator Inhibit signals to the validator 0 volts common to the validator 0 volts common input to Y-chute Inhibit signal from the machine 12 volts input to the Y-chute In dual entry systems the Y-chute forms the interface between the validator, Y-chute and the machine. The latter uses the Y-chute interface and the validator interface as its main connection points. The coin outputs are signalled from the validator interface. The coin inhibits are connected ©, MEI., 1998 25 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide to the Y-chute interface, and the inhibit signals are fed back to the validator interface by the host machine interface wiring, as shown below. Dual Entry System ( Coin and Token ) Validator Interface Y - Chute Interface Y-Chute Inhibits and power Machine Coin Inhibits and power Coin Outputs With single entry systems the interface is between the validator and the machine only, with no electronics fitted to the Y-chute. Single Entry System ( Coin Only ) Validator Interface Coin Inhibits and power Machine Coin Outputs NOTE: When an old, (pre-March 1997), Y chute is used with a BACTA standard machine interface (BCO) the mode of operation of the Y chute needs to be changed. (Consult with MEI technical support for further details). 26 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION Voltage Range Current Consumption; 12V (+ 3V maximum, -2V minimum) Quiesent (Idle) - 35mA Coin Flight - 65 mA Accept Gate only - 800 mA 2 Routing Solenoids - 2,300 mA for 320mS 3 Routing Solenoids - 3000 mA for 320 mS Coin Output Electrical Specification A B Logical Outputs C D E F o/p A o/p B o/p C o/p D o/p E o/p F 6X i/p o o/p XOR Polarity Sense Output Driver Block Vcc 4k7 o/p common 1K 10n 56R Output Circuit Block Diagram Absolute Maximum Ratings Output Current (O/PA) - F) Maximum Voltage (O/PA) - F) ©, MEI., 1998 ± 30 mA ± 32 V w.r.t. 0V 27 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Output Common Specification Vcc R ohms (470) Cashflow 126 Outputs A B C Multiplexed D Bus E F A B C D E F OutputCom Rx10 (4k7) I= 6xVcc/R (150mA) Option Switches etc. Strobe 1 Strobe 2 Sample multiplexed implementation - Negative Common Strobe If output common (OPcom) is left floating then it is possible that the output configuration could change. When the OPcom is redefined, then, if the output configuration has to change, then there is a maximum delay of 15us before the coin outputs will be valid. Before this time the outputs will be indeterminate. To prevent this happening a resistor should be added to OPcom to define the level during the multiplexing off period. The value should be large enough so as not to interfere with the normal interplexing operation. In this case the maximum delay between Opcom and coin outputs is 1us. NOTE: Should an alarm situation be detected, all outputs in parallel mode will go true. Any multiplexing device must be capable of sinking or sourcing sufficient current (i.e. 6 x single output current) to keep the output common voltage within the maximum or minimum specification for that configuration. 28 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Negative Common Voltage Range This interface is selected when pin 3 is <2.5V with respect to pin 12. (0V) Negative Common Outputs: On: Maximum current = 30mA O/P saturation voltage (Coin O/P - Opcom) <1.5V Off: 10 uA maximum at 27 volts Pulse Width: (Coin O/P - OPcom) Switched on for between 80 and 120 ms on acceptance of the appropriate coin. Output Common Output to be Set 100 ms 10% + o/p on Other Outputs o/p off T(o/p valid) = 15 micro seconds Negative Output Common Timing Circuit ©, MEI., 1998 29 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Positive Common Voltage Range Positive Common Operation (O/P Common) This interface is selected when pin 3 is greater than +4.5 volts with respect to pin 12. (0V) Output Common Voltage: +7 volts to +26 volts with respect to pin 12. Positive Common Outputs: On: Maximum current = 40mA Saturation voltage (Opcom - Coin O/P) <1.5V Off: 10uA maximum at +27 volts (Opcom - Coin O/P) Pulse Width: Switched on for between 80 and 120ms on acceptance of appropriate coin. 100ms max Vsupply Output Mode Select Output Common Output A T (o/p valid) Coin O/P valid BCO Output Indication from "Power ON" 30 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Binary Coded Output (BCO) BCO mode is indicated by the A output being permanently active. This indicator can take up to 100 milliseconds to be established from power up. In order to ensure reliable operation of the machine the state of this output should be regularly polled (as the coin validator could be reconfigured without the power being removed). As there are often long machine interface leads involved in coin mechanism interfaces, it is recommended that the coin outputs should be de-bounced in software to reduce the effect of glitches. Coin Inhibits Input voltage to enable channels (logic 0) ) <1.0V Input voltage to inhibit channels (logic 1) >4.0V Input impedance 12 Kohms to +5v. ©, MEI., 1998 31 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide MECHANICAL INTERFACE DRAWINGS The following drawings are included in this section: CF126 Front Plate Dimensions Drawing Number 32780 Front plate mounting detail. Drawing Number 32799 Standard front plate dimensions. Drawing Number 35811 Side entry space envelope. CF126 Top Entry Mounting Space Envelope Drawing Number 35812. CF129 Long Channel Mounting Space Envelope Drawing Number 35824 Long channel dimensions. Drawing Number 35954 CF129 system installation dimensions. (Fitted with Long manifold) Drawing Number 35961 CF129 system installation dimensions. (Fitted with Short manifold) 32 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide ©, MEI., 1998 33 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide 34 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide ©, MEI., 1998 35 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide 36 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide ©, MEI., 1998 37 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide 38 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide ©, MEI., 1998 39 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide COMPATIBILITY Compatibility CashFlow® ME126 ME126 Standard Active 126 MS126 & B1 Coin Entry Path Yes Yes Yes Yes Coin Exit Path Yes Yes Yes Yes Mechanical Mounting Yes Yes Yes Yes 12 Volts DC Yes Yes Yes Yes Machine Interface Yes Yes (*) Yes (*) Yes (*) 4 Way Separator (ME or CF126) Yes Yes No Yes 4 Way Separator (ME 126 Active) No Yes Yes No 8 Way Separator (ME129) No Yes Yes No 8 Way Separator (CF129) Yes No No No Parallel Coin Output Yes Yes Yes Yes Serial Output Yes No No No Binary Coded Output (BCO) Yes No No No 18 Way Routing Plug No Yes No Yes 20 Way Routing Plug Yes No Yes No 22 Way Routing Plug Yes No No No NOTE: (*) = Remove polarising pin 8 from your existing machine interface loom 40 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide PERFORMANCE STANDARDS POWER SUPPLY Operating Voltage: +12V tolerance = (+ 3V) (- 2V) Supply Voltage Ripple Within Vmin to Vmax up to 100Hz 250mV pk - pk for F>100Hz Current consumption: Quiescent current: 35mA Max Max current: 2.5A Max (4 solenoids active) COMPLIANCE CLASSIFICATIONS The product is designed to the following standards for sale into European markets and will carry the “CE”mark. Electromagnetic Conformance (EMC) The product is designed to comply with the following European standards: EN50082-1 1992 Electromagnetic Compatibility Generic Immunity Standard EN55022 1995 Limits and methods of measurement of radio disturbance characteristics of information technology equipment. Safety The product is intended for use in machines which are designed to comply with; a) EN60335-1, 3rd Edition, Safety of household and similar electrical appliances, Part 1, General Requirements.” b) BS3456, Safety of household and similar electrical appliances, Part 1, General Requirements. c) BS EN60950 1992, Safety of Information Technology Equipment, including electrical business equipment. The product is suitable for use in a class 2 (non-earthed or non-grounded) appliance as defined in EN60335. All electrical connections to the acceptor must be rated according to the requirements for “Accessible SELV”circuits as defined in EN60335. When used in applications where compliance to BS EN60950:1992 is necessary, the host machine power supply must additionally meet the requirements for SELV limited power supplies as defined in BS EN60950. For these applications, the coin mechanism should be installed so that it is external to any fire enclosure. ©, MEI., 1998 41 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide Flammability All major plastic parts will be moulded in materials with a flammability rating of 94 V-2 / IEC 707 FV2 or better. Some small parts are moulded in materials with a flammability rating of 94 HB / IEC 707 FH2. Power Supply Input Protection Overcurrent protection is not included in the product and must be provided as part of the machine. Recommended fuse rating at the rated supply of 12V is: 3A Slow blow EN60127 Other protection methods may be used providing their over current characteristics remain within the overall operating characteristics of the above fuse. Mechanical Parts The product will not contain mechanically moving parts, or sharp edges, which can prevent a hazard in normal use. Coin Sizes CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 will be able to validate and route coins within the following range: Circular coins, in the range 15mm to 31.5 mm in diameter. Circular coins, in the range 1.1mm to 3.2mm in thickness. Faceted coins within the relevant coinsets will also be handled. Damaged, bent or very distorted coins may not be validated. Coin Acceptance Rate The acceptor will validate coins at up to 3 coins per second, when linearly separated i.e. >330 ms apart. After a coin has been rejected, no further coins will be accepted for a period of 0.5 seconds. Should a further coin be entered during this period, the reject period will be reinitiated. Fraud Performance Dual post gate strobes are fitted to give protection against COAS and Strimmer type frauds. A pre-gate strobe is fitted for protection against “Spoon”fraud. Provision has been made on the PCB for a COAS detector. If the input is seen to go active, the alarm will be sounded. Where machines do not recognise an all outputs ON as an alarm indication the alarm should be disabled by switching option switch 1 to OFF, otherwise false credit may be given in the event of a fraud attack. 42 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide ENVIRONMENTAL PERFORMANCE Temperature Range Normal operational range 10°C to 40°C Full operational range 0°C to 60°C Storage range -10°C to 75°C Max. rate of change 10°C/hr, non condensing Humidity Range Operational10%RH - 90%RH, non condensing Storage 5%RH to 95%RH, non condensing % Relative Humidity 100 - 10,95 35, 95 35, 90 75 S 50 F N 25 F 60, 10 - 10, 10 -20 S 0 20 40 60 75, 10 80 Temperature / Humidity specification Temperature oC N = Normal operating range F = Full operating range S = Storage range Thermal shock Sudden changes of temperature may cause temporary degradation of performance. For continuous operation and specified performance within the full operational temperature range, the rate of change of temperature should not be greater than 10°C per hour, non condensing Vibration (through machine mounting) Vibration 0.25g at 5Hz to 500Hz - pseudo random, flat bandwidth Coin validation will not be affected. ©, MEI., 1998 43 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide TRANSPORTATION The following apply to fully packaged units: Shock Half sine, 30g shock, 18ms dur BS 2011 Part 2.1 EA : 1977 Bump 1000 bumps 6ms duration at 25g BS 2011 Part 2.1 b : 1977 Drop - Free Fall 2 drops from 1m onto each face BS 2011 Part 2.1 ED : 1977 Drop and Topple 50mm drop onto each corner BS2011 Part 2.1 EC : 1977 LIQUID CashFlow® 100 series validators PCB’s are fitted with splash protection shields to protect against fluid intrusion. However, prolonged exposure to a salt laden atmosphere, or liquids which dry onto the surface of the PCB could cause malfunction. 44 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide MEI MAIN AND REGIONAL OFFICES WWW.MEIGROUP.COM ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide INDEX 4-Way DIL Switches, 12 4 Way DIL Teach Switch, 11 4 way Separation, 8, 23 Diagnostic LED, 11 Disposal of Product, 1 Dual Entry System, 25 Dual Entry Systems, 24 Dynamic Route Inhibit, 10, 23 8 E 8-Way Separation, 21 8 way Separation, 8, 23 Electrical Interfaces, 17 Electro-mechanical Conformance, 40 Electromagnetic Conformance, 41 Environmental Performance, 44 4 A Accept Gate, 9 Automatic Mode, 10, 13 F B Binary Coded Output, 10, 13, 15, 30 Binary Coded Output Mode Inhibits, 16 Build Options, 6 C Coin Acceptance Rate, 43 Coin Inhibits, 14, 15, 30 Coin Output, 26 Coin Output Common Line, 14 Coin Output Signals, 20 Coin Routing, 22 Coin Set, 8 Coin Sizes, 43 Coin Validation, 8 Coinset Label, 3 Communications Signals, 9 Compatibility, 39 Conformance to International Standards, 1 D Dangerous Environments, 1 Factory Programming, 8 Flammability, 41 Flash Code Sequence, 11 Fraud Performance, 43 Front Plates, 4 H Humidity Range, 44 I Inhibit Signals, 25 Inhibited Coins, 9 L Liquid Protection, 45 M Machine Interface, 9, 17 MEI® Service Alpha, 13 Maximum Operating Voltage, 1 Maximum Voltage Ratings, 26 Mechanical Interface Drawings, 31 MEI Offices, 51 Multi-Pulse, 9, 14 ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide INDEX N Negative Common Outputs, 28 Negative Common Voltage Range, 28 Safety, 1, 41 Separator Connection, 10 Separator Connector, 18 Single Entry System, 24, 25 T O Temperature Range, 44 Transportation, 45 Operators Handbook, 8, 12 Output Common, 27 Output Common Voltage, 29 V P Parallel Mode, 10, 13, 16, 27 Parallel Output Mode, 13 Parallel Output mode inhibits, 14 Parallel Output Mode., 9 Performance Standards, 40 Positive Common Outputs, 29 Positive Common Voltage Range, 29 Post-Gate Strobes, 11 Power Supply, 41 Power Supply Input Protection, 43 Pre-Gate Strobe, 11 Product Features, 7 Product Identification, 3 Product Interfaces, 13 Product Operation, Electrical, 10 Product Range, 2 Validator, 9 Validator Connector, 10 Validator Connectors, 10, 17, 18, 19, 23 Validator Reject Flap, 9 Y Y-chute, 24, 25 Y-chute Interface Connector, 24 R Reject Covers, 3, 5 Reject Route, 9 Rejected Coins, 9 Rotary Data Switch, 11, 12 Route Input Lines, 21 Routing Plug, 10, 19, 20, 21, 22 Routing Plug Connector, 19 S ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide ©, MEI., 1998 CashFlow® 126 and CashFlow® 129 selectors Design Guide ©, MEI., 1998 Representative