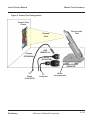
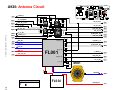
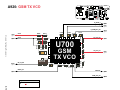
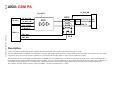
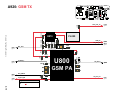
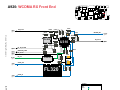
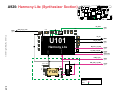
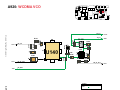
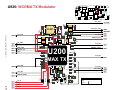
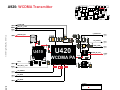
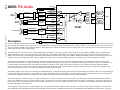
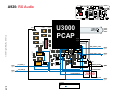
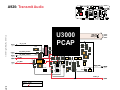
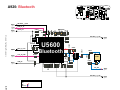
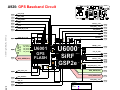
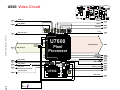
Download Motorola A925 Service manual
Transcript
Level 3 Service Manual Draft 1.1 ™ DIGITAL WIRELESS TELEPHONE Model A920/ A925 UMTS 2100MHz/ PCS 1900MHz/ DCS 1800MHz/ GSM 800MHz Distribution Policy and Copyright Copyright © 2003 by Motorola. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system or translated into any language in any form by any means without the written permission of Motorola. Software License The Agreement sets forth the license terms and conditions for using the enclosed Software. You may use this Software on a single computer, and you may transfer it to another computer as long as it is used on only one computer at a time. You may copy the Software for backup purposes only. You may not rent, sell, lease, sublicense, time-share or lend the Software to a third party or otherwise transfer this License without written consent of Motorola. You shall not decompile, disassemble, reverseengineer or modify the Software. This License is effective until terminated. You may terminate it at any time by destroying the Software together with all copies. The License also terminates if you fail to comply with the terms and conditions of this Agreement. United States copyright laws as well as international treaty provisions protect this Software and accompanying documentation. Any use of the Software in violation of these laws constitutes termination of the License. Limited Liability The Software and accompanying documentation is provided “AS IS” without warranty of any kind. Motorola specifically disclaims all other warranties, expressed or implied, including but not limited to implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. With respect to the use of this product, in no event shall Motorola be liable for any loss of profit or any other commercial damage, including but not limited to special, incidental, consequential or other damages. ii Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Table of Contents 3G Flash Procedures ................................................................................................................. 1-1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................. 1-1 Hardware Requirements ......................................................................................................... 1-1 Power Solution ................................................................................................................................................ 1-1 Interface Solution ............................................................................................................................................ 1-1 PST Software .......................................................................................................................... 1-2 Flash Software Access ........................................................................................................... 1-2 Phone Flashing....................................................................................................................... 1-2 Power Solutions .............................................................................................................................................. 1-2 Hardware Connection Solution ......................................................................................................................... 1-2 Figure 1. PST Hardware Configuration ...................................................................................................... 1-3 PST Flash Procedure ...................................................................................................................................... 1-4 A920/A925 Special Procedures ....................................................................................................................... 1-5 Flash Procedure Summary ..................................................................................................... 1-5 Handset Test Commands ........................................................................................................... 2-1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................. 2-1 Application Installation* .......................................................................................................... 2-1 Figure 1. Launcher Menu ........................................................................................................................... 2-1 Figure 2. Install Window ............................................................................................................................ 2-1 Figure 3. Test Command Icon .................................................................................................................... 2-1 Handset Test Command Mode Entry ....................................................................................... 2-2 Figure 4. Password Prompt ....................................................................................................................... 2-2 Figure 5. Sub Applications ........................................................................................................................ 2-2 Figure 6. Main Entry Screen ..................................................................................................................... 2-2 Figure 6. Input Format ............................................................................................................................... 2-2 Entry Method ........................................................................................................................... 2-3 Opcode entry .................................................................................................................................................. 2-3 Figure 7. Fields entered Separately ........................................................................................................... 2-3 Entering Data .................................................................................................................................................. 2-3 Figure 8. Fields Entered with Delimiter ...................................................................................................... 2-3 Figure 9. Keyboard Entry ........................................................................................................................... 2-3 Figure 10. Stylus Entry ............................................................................................................................. 2-4 Figure 11. Invalid Entry ............................................................................................................................. 2-4 Result Screen ......................................................................................................................... 2-4 Figure 12. Results Screen ......................................................................................................................... 2-4 Table 1. Handset Test Command Summary ............................................................................................... 2-5 Table 2. Standard Response Codes .......................................................................................................... 2-6 Table 3. Field and Parameter descriptions ................................................................................................. 2-7 Table 3. Field and Parameter descriptions - continued ............................................................................... 2-8 Table 3. Field and Parameter descriptions - continued ............................................................................... 2-9 Preliminary Motorola Confidential Proprietary iii Table of Contents A920/A925 Table 3. Field and Parameter descriptions - continued ............................................................................. 2-10 Table 3. Field and Parameter descriptions - continued ............................................................................. 2-11 Manual Test Procedures ............................................................................................................ 3-1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................. 3-1 Call-Processing Tests ...................................................................................................................................... 3-1 Non-Signalling Test Measurements .................................................................................................................. 3-1 GSM/DCS/PCS Call Processing ............................................................................................ 3-2 Hardware Requirements .................................................................................................................................. 3-2 Software Requirements (PCS only) ................................................................................................................. 3-2 Call Origination (GSM and DCS only) .............................................................................................................. 3-3 Figure 10. GSM Signalling Setup .............................................................................................................. 3-3 Figure 11. GSM Connection Control .......................................................................................................... 3-3 Figure 12. GSM Call Connected ................................................................................................................ 3-3 Figure 13. A920 Manual Test Hardware Configuration ................................................................................ 3-4 Call Origination (PCS Only) ............................................................................................................................. 3-5 Figure 14. RadioComm COM Port ............................................................................................................. 3-5 Figure 15. Radio Comm Screen ................................................................................................................ 3-5 Call Test Parameters (GSM/DCS/PCS) ............................................................................................................ 3-6 Table 4. GSM Call Parameters .................................................................................................................. 3-6 Table 5. DCS Call Parameters ................................................................................................................... 3-6 Table 6. PCS Call Parameters ................................................................................................................... 3-6 Figure 16. Burst Output Shape .................................................................................................................. 3-6 Table 7. GSM/DCS/PCS Handover ............................................................................................................ 3-6 WCDMA Call Processing........................................................................................................ 3-7 Hardware Requirements .................................................................................................................................. 3-7 Software Requirements ................................................................................................................................... 3-7 Call Origination (WCDMA) ............................................................................................................................... 3-7 Figure 17. WCDMA Signalling Setup ......................................................................................................... 3-7 Figure 18. Channel Uplink(UE Signal) ........................................................................................................ 3-7 Figure 19. TPC Pattern Type(UE Signal) .................................................................................................... 3-8 Figure 20. WCDMA Call Connected ........................................................................................................... 3-8 WCDMA Call Test Parameters ......................................................................................................................... 3-8 Table 5. WCDMA Call Parameters ............................................................................................................. 3-8 Figure 21. WCDMA Modulation ................................................................................................................. 3-8 Figure 22. ACLR Screen ........................................................................................................................... 3-8 Non-Signalling Test Procedures (GSM/DCS/PCS) ................................................................. 3-9 Hardware Requirements .................................................................................................................................. 3-9 Software Requirements ................................................................................................................................... 3-9 Verify TX Power Output (GSM/DCS/PCS) ....................................................................................................... 3-9 Table 8. TX Power Limits ........................................................................................................................... 3-9 GSM RSSI .................................................................................................................................................... 3-10 Non-signalling Test Procedures (WCDMA) ........................................................................... 3-11 Hardware Requirements ................................................................................................................................ 3-11 Software Requirements ................................................................................................................................. 3-11 Verify TX Power Output (WCDMA) ................................................................................................................. 3-11 Table 9. WCDMA TX Power Output .......................................................................................................... 3-11 Audio/Vibrator Test Procedures............................................................................................. 3-12 Vibrator Test .................................................................................................................................................. 3-12 Handset Mic/Speaker test ............................................................................................................................. 3-13 iv Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Table of Contents Mono Headset Mic/Speaker test ................................................................................................................... 3-13 Stereo Headset Mic/Speaker test .................................................................................................................. 3-14 Melody Speaker test ..................................................................................................................................... 3-14 Software Version Check ........................................................................................................ 3-15 Display Test Procedures ....................................................................................................... 3-15 Display Backlight Test ................................................................................................................................... 3-15 Display Color Test ......................................................................................................................................... 3-16 Figure 23. Eight Color Box Pattern .......................................................................................................... 3-16 Display Linearity Test .................................................................................................................................... 3-16 Figure 24. Grey Scale Block ................................................................................................................... 3-16 Display Flicker Test ....................................................................................................................................... 3-17 Figure 25. Zebra Pattern .......................................................................................................................... 3-17 Display Pixel Defect (Bright) ......................................................................................................................... 3-17 Display Pixel Defect (Dark) ........................................................................................................................... 3-17 LEDS and Keypad Backlight ................................................................................................. 3-18 Status LEDS ................................................................................................................................................. 3-18 Keypad Backlight .......................................................................................................................................... 3-18 Bluetooth Tests (V500/V600 only) ......................................................................................... 3-19 Unmodulated CW TX test .............................................................................................................................. 3-19 Camera Testing ..................................................................................................................... 3-20 Hardware Requirements ................................................................................................................................ 3-20 Camera Test Configuration ............................................................................................................................. 3-20 Figure 9. Camera Test Configuration ........................................................................................................ 3-21 Image Capture ............................................................................................................................................... 3-22 Macbeth Color Chart ..................................................................................................................................... 3-23 Focus Chart .................................................................................................................................................. 3-23 Grey Scale Chart (Shading Test) ................................................................................................................... 3-23 Service Diagrams ....................................................................................................................... 4-1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................. 4-1 Test Point Measurements ........................................................................................................ 4-1 Antenna Circuit ....................................................................................................................... 4-2 GSM Receiver Front End ........................................................................................................ 4-4 Magic LV (Receiver Back End) ............................................................................................... 4-6 Magic LV (Control) .................................................................................................................. 4-8 Magic LV (Synthesizer/Transmitter) ....................................................................................... 4-10 GSM TX VCO ........................................................................................................................ 4-12 GSM Transmitter .................................................................................................................... 4-14 WCDMA RX Front End ......................................................................................................... 4-16 WCDMA Receiver (MAX2309) ............................................................................................. 4-18 Harmony Lite (Receive Section) ........................................................................................... 4-20 Harmony Lite (Control Section) ............................................................................................. 4-22 Harmony Lite (Synthesizer Section) ...................................................................................... 4-24 Harmony Lite (Transmitter Section) ....................................................................................... 4-26 WCDMA VCO ....................................................................................................................... 4-28 WCDMA TX Modulator.......................................................................................................... 4-30 WCDMA Transmitter .............................................................................................................. 4-32 Prelimiary Motorola Confidential Proprietary v Table of Contents A920/A925 PCAP Charger ...................................................................................................................... 4-34 PCAP Regulators ................................................................................................................. 4-36 Receive Audio ...................................................................................................................... 4-38 Transmit Audio ...................................................................................................................... 4-40 PCAP .................................................................................................................................... 4-42 POG ...................................................................................................................................... 4-44 POG Interfaces ...................................................................................................................... 4-46 POG Memory ........................................................................................................................ 4-48 Bluetooth ............................................................................................................................... 4-50 GPS RF Circuit ..................................................................................................................... 4-52 GPS Baseband Circuit .......................................................................................................... 4-54 Video Circuit ......................................................................................................................... 4-56 Helen .................................................................................................................................... 4-58 Helen Interfaces .................................................................................................................... 4-60 Helen Flash Memory ............................................................................................................. 4-62 Helen SDRAM ...................................................................................................................... 4-64 SIM Connector ...................................................................................................................... 4-66 Battery Connector (J5400) .................................................................................................... 4-68 Camera Connector (J7600) ................................................................................................... 4-70 MMC Connector (J3900) ....................................................................................................... 4-72 Keyboard Connector (JPCH) ................................................................................................ 4-74 Display Connector (J5200) ................................................................................................... 4-76 CE Bus Connector (J5000) ................................................................................................... 4-78 Signal Flow Diagram (Side 1) ............................................................................................... 4-80 Signal Flow Diagram (Side 2) ............................................................................................... 4-81 RF Block Diagram ................................................................................................................ 4-82 Baseband Block Diagram ..................................................................................................... 4-83 Parts List ..................................................................................................................................... 5-1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................. 5-1 Electrical Parts List ................................................................................................................. 5-2 vi Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary 3G Flash Procedures Introduction Hardware Requirements This document is intended to describe the flashing (software updates) and procedures for 3G terminals. The 3G terminal described in this document will be limited to the A920/A925. The following hardware will be required to properly flash the phone. Software updates need to be handled in a controlled manner. Carrier software approvals need to be considered before initializing a flashing procedure. Consult a Motorola representative to ensure that the correct software is programmed. 1. Fully Charged battery (SNN5638A) 2. Full-rate Charger (PSM5049A) Software updates allows the service organization to resolve field software issues that customers may be experiencing. Some issues may pertain to specific conditions, therefore, not all units will contain identical software versions. 1. Power Solution Interface Solution USB PST Tool Kit (S8951) USB Cable (SKN6311A) Security Key Adapter kit Power supply (SPN4059A) Motorola Confidential Proprietary 1-1 Flash Procedures PST Software Phone Flashing The Product Support Tool (PST) is used to allow functions such as flashing, flexing, memory transfers, and datalogging. Please contact your local Motorola service representative to obtain user documentation for the PST. Before beginning any flashing procedure, always insure that all hardware connections are secured. Refer to figure 1 for flash connection guides. Any intermittent hardware connections may cause the procedure to fail and result in a nonfunctional (Bricked) 3G terminal. Insure that the Motorola service representative also provides installation documentation, security key requirements, and other related information. The A920/A925 contains a set of Flash EPROMs for the Adjunct Processor and a separate set of Flash EPROMs for the Baseband Processor. Due to this design, the A920/A925 will require separate Flash files for each processor if a “Combo” file is not provided. Flash Software Access A “Combo” file contains the following files, Flash software can be accessed by Motorola personnel only. Contact your local Motorola service representative to obtain updated software releases. In some cases the software may be distributed in ZIP format. The user will need to extract the original (.SHX) file from the ZIP file before is can be used with the PST. WINZIP is the application that can be used to extract the original flash file. For more information on WINZIP, visit, http://www.winzip.com Adjunct Processor Flash Baseband Processor Flash Customer image flex Power Solutions There are two types of power solutions to perform a flashing procedure. 1. Fully Charged Battery Solution 2. Full-Rate Charger Solution (recommended) If the user decides on using the battery solution, he/she must verify that the battery is fully charged. Failing to verify the capacity of the battery may result in battery depletion prior to completing the flash process. This action may cause unrecoverable failures to the 3G terminal. Hardware Connection Solution A920 flash procedures require a USB hardware configuration. Refer to Figure 1 for details. 1-2 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Flash Procedures Figure 1. PST Hardware Configuration PSM5049A SKN6311A Motorola Confidential Proprietary 1-3 Flash Procedures PST Flash Procedure 7. The 3G terminal will be placed in Adjunct flash mode, select the device again to enable the Flash button. 8. Click on the Flash button to begin flashing. DO NOT interrupt any hardware connections during the flash process. Connection interruptions may cause the flashing process to fail and render the 3G terminal non-operational. 9. When flashing is complete, a message will pop up stating,” Flash another phone?”. Select “No” and waiting for 30 seconds before continuing. 10. Power up the 3G terminal to insure that the flash procedure was successful. 11. On the first power up, the user will be prompted to select a language and calibrate the touch screen. Use the listed procedure to complete the flash procedure for a 3G terminal. The baseband processor needs to be flashed first. Once the baseband processor flash is successful, follow up with flashing the adjunct processor. 1. Download the desired flash software into the computer. 2. Launch the PST application by choosing Start/ Programs/Motorola PST/Flash & Test Commands. 3. Attach battery and connect hardware as illustrated in figure 1. 4. Press the Power key and insure that the phone is completely powered on. 5. In the PST application, click on the Browse button and select the desired flash software 6. 1-4 Select the device that will be flashed. Motorola Confidential Proprietary Flash Procedures A920/A925 Special Procedures Flash Procedure Summary There are some variables that need to be considered when updating software for a A920/A925. Improper update procedures may cause the 3G terminal to fail. Always read the release notes for software releases prior to updating the software on a A920/A925. The following is a summary of the procedures for flashing a A920. The user needs to insure that the adjunct and baseband flash files are part of the same build. Also, the user needs to be aware of any step-up procedures. This may require the user to flash an updated bootloader. Step-up procedures can be found in the software release notes. In order to successfully flash a A920, the following sequence is recommended. 1. Backup user data 2. Flash/upgrade the software 3. Perform a “Master Clear” 4. Restore user data 1. Launch PST. 2. Connect USB hardware. Insure 3G terminal remains off. 3. Power up 3G terminal. 4. Use the Browse button to open the “Combo” flash file. 5. Select the device for flashing. 6. Select the device again to enable Flash. 7. Click Flash. 8. Click Yes to all the prompts if the user is certain that software being flashed is correct. 9. When flashing is completed, click “No” when prompted, “Flash another phone?.” 10. Power cycle phone. Verify functionality. Motorola Confidential Proprietary 1-5 Flash Procedures 1-6 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Handset Test Commands Introduction The Handset Test Command mode of the phone is provided primarily for service personnel without access to equipment capable of exercising Test Commands over a computer connection. This mode collects input from the user and packages it in the format required by the Test Command component within the phone. 3. The user will be prompt with a list of software installation files. 4. Highlight Test Command and select Install Figure 2. Install Window Application Installation* The user needs to install the Handset Test Command application before it can be accessed. Obtain the file, “testcmdui.sis”, file from your local Motorola service representative. Use the following procedure to properly install the handset test command application. 1. Copy the testcmdui file into a memory card (SD or MMC) and insure that the card is inserted in the phone. 2. From the App Launcher screen, select Install from the Launcher drop down list Figure 1. Launcher Menu 5. When installation is complete, the Test Command icon will be displayed in the App Launcher screen. Figure 3. Test Command Icon *Test application can only be loaded if application loading is not secured. Preliminary Motorola Confidential Proprietary 2-1 Handset Test Commands A920/A925 Command entry Handset Test Command Mode Entry 5. Figure 6. Main Entry Screen Follow these procedures to launch the handset test command aplication. 1. Under the App Launcher screeen select the Handset test command icon. 2. The user will then be prompt to input a password Choose Handset Test Commands to enter the Test command Opcode screen Figure 4. Password Prompt 6. 3. The password is 0HTCMD# Note: Password is case sensitive 4. Once the application is launched, the user is presented with a list of sub applications Figure 5. Sub Applications 2-2 Before entering any commands, the user will should select the data input format under the Edit menu Figure 6. Input Format 7. The user can select Hexidecimal or decimal. 8. Under the Edit menu, the user can also clear a field or all fields 9. The Back key will return the user to the App Launcher screen Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Handset Test Commands Command entry Entry Method The Back selection will clear the command contents and return the user to the opcode prompt. Once the test command mode is entered, two prompts are used to collect command request information from the user. The opcode entry prompt (Figure 5) allows the entry of either an entire command as described in this section, or entry of a partial command. If a partial command is entered, the user will be prompted to enter the remaining required information via an appropriate number of field entry prompts (Figure 7). Selecting Test with no data entered in the opcode or field entry screen will cause a parse error (unless the field is optional). If the user chooses to enter the entire command with the necessary parameters in the Opcode prompt, “,” delimiters will be used. Figure 8. Fields Entered with Delimiter The comma is used to delimit fields on the opcode entry prompt and is not allowed on the field entry prompt. On the opcode entry prompt, it is not legal to have a comma immediately follow another comma. Opcode entry The opcode entry prompt allows the user to enter the opcode for the test command, or the opcode plus additional parameters delimited by the “,” character. The user may select Test after entering the opcode. If the opcode requires further parameters, the list of Fields shall be shown starting with 1. After all the fields are entered the user shall select Test. The results are then shown on the screen. Entering Data When the User wants to enter the Fields, they shall click the Keyboard Icon at the bottom of the screen to input the values. Figure 9. Keyboard Entry Figure 7. Fields entered Separately Preliminary Motorola Confidential Proprietary 2-3 Handset Test Commands A920/A925 Command Results They can also use the Stylus, depending on the settings selected by the user in the control panel. Figure 10. Stylus Entry If command processing takes more than 2 seconds a message will display, “Running Test...” Result Screen The display of the output shall always be in Hexadecimal Format. Figure 12. Results Screen The user shall enter values in Hex or Decimal. The following values shall be allowed for each entry method: • • Hex: A to F and 0 to 9. (not case sensitive) Decimal: 0 to 9 When the user presses, "Test", the values shall be checked whether they match the values that are allowed. If not, they shall get an Error Message as follows: Pressing the "Back" Key shall always take the user back to the Main Entry Screen as shown in Figure 6 Figure 11. Invalid Entry After the user presses, "Continue", they shall be taken back to the field where the incorrect entry method was found. 2-4 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Handset Test Commands Table 1. Handset Test Command Summary Opcode Opcode Hexadecimal Decimal Opcode Mnemonic 0 0 3 3 AUD_CTRL 4 5 6 4 5 6 AUD_LPB AUD_LVL AUD_PATH 7 0A 12 14 22 2D 36 7 10 18 20 34 45 54 37 55 39 3E C0B 57 62 3083 C0E 3086 Preliminary Key Entry Format AUD_TN_LST 0 *<Action> * <Tone Identifier>OK 3 *<Device/Process> * <Action>OK 4 *<Loopback Type> * <Action>OK 5 *<Get/Set>*<Volume>OK 6 *<Input Path>*<Output Path>*<RX Mute>*<TX Mute>OK CARRIER 7 * <Option> * <Action> OK CP_MODE 10 * <Set/Get> * <Sub-mode> OK INVM 18 * <level> OK LOAD_SYN 20 * <Channel> * 0 OK RESTART 34 * OK SET_RF_PW R 45 * <Power level> OK SUSPEND 54 OK Op Code Description Generate/disable predefined tone Control various audio functions; enable/disable vibrator Enable audio loopback Set audio level Change audio path Enable GSM TX carrier Set Call Processing Mode Master clear or reset Set GSM channel Generate a software restart Set GSM Power level Terminate normal mode and enter test mode TST_DISP 55 * <Parameter> * <Parameter Data> Display predefined patterns OK VERSION 57 *<version Type>OK Retrieve SW version information LEDS 62 * <LED> * <Action> * <Data> OK Control status LEDs W LOAD_SYN 3083 * <RX_FREQ_ID> * Set W CDMA channels <TX_FREQ_ID> OK W _CARRIER 3086 * <Channel ID> * <Action> * <Tx Enable W CDMA TX carrier Pwr> * <Max Pwr> * <Min Pwr> * <Data Pattern> * <Channelization> * <Scrambling> * <DPCCH Spread Factor> * <DPDCH Spread Factor> * <Channelization Code> * <Scrambling Code> OK Motorola Confidential Proprietary 2-5 Handset Test Commands A920/A925 Table 2. Standard Response Codes Opcode Opcode (Hexadecimal) (Decimal) Response Field Definition 0000b (0x00) 0001b (0x01) 0 1 0010b (0x02) 2 0011b (0x03) 3 0100b (0x04) 0101b (0x05) 0110b (0x06) 0111b (0x07) 1000b (0x08) 1001b (0x09) 1010b (0x0A) 1011b (0x0B) 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 parse error (no data follows): invalid data length for command parse error (no data follows): inadequate security level for command/parameter parser error (no data follows): command/parameter not supported for current protocol (CDMA, GSM, TDMA) parse error (no data follows): command/parameter not supported for current mode (normal, test mode, handset test mode) parse error (no data follows): unsupported/invalid opcode parse error (no data follows): unsupported/invalid parameter for opcode command response: generic success (no data follows) command response: generic failure (no data follows) command response: data follows unsolicited/multiple response: data follows (sequence tag is 0) error: couldn’t allocate memory error: internal task error 1100b (0x0C) 12 error: Test Command task timed out waiting for response from another SW component 1101b (0x0D) 13 1110b (0x0E) 14 1111b (0x0F) 15 2-6 CDMA: parse error (no data follows): command/parameter not supported for current submode TDMA: command not supported in current Call Stack Test Mode error: length specified in command header greater than length received by transport layer error: irrecoverable error; phone state has been lost. Phone is being powered down Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Handset Test Commands Table 3. Field and Parameter descriptions Opcode Opcode Field Description (Decimal) Mnemonic 0 AUD_TN_LST Field 1 0 = stop a tone 1 = start a tone Field 2 55 through 64 = DTMF tones, refer to table xx for more tones 3 AUD_CTRL Field 1 0 = Vibrator 2 = Echo canceling 3 = Noise suppressor Field 2 0 = Disable 1 = Enable 4 AUD_LPB Field 1 0 = PCAP loopback 6 = CODEC loopback 7 = VOCODER (speech) loopback Field 2 0 = Disable Audio loopback 1 = Enable Audio loopback Field 3 This field is valid only for VOCODER loopback 0 = AMR 4.75 1 = AMR 5.15 2 = AMR 5.90 3 = AMR 6.70 4 = AMR 7.40 5 = AMR 7.95 6 = AMR 10.20 7 = AMR 12.20 8 = Full Rate 16 = Enhanced Full Rate 32 = Half Rate 5 AUD_LVL Field 1 0 = Set the volume specified Field 2 0 = lowest, 7 = loudest Preliminary Motorola Confidential Proprietary 2-7 Handset Test Commands A920/A925 Table 3. Field and Parameter descriptions - continued Opcode (Decimal) 6 7 2-8 Opcode Mnemonic AUD_PATH CARRIER Field Description Field 1 0 = As is. 1 = Mute input path 2 = Internal (handset) mic 3 = Ext audio input (CE Bus) 4 = Boom (headset) mic 5 = Ext digital audio (USB) 7 = Bluetooth time slot 1 audio input 8 = Bluetooth time slot 2 audio input 9 = Bluetooth time slot 3 audio input Field 2 0 = As is 1 = Mute output path 2 = Internal (handset) Speaker 3 = Alert 4 = Ext audio output (CE Bus) 5 = Speakerphone 6 = Boom (headset) speaker Field 1 0 = All zeroes 1 = All ones 2 = pseudo random sequence w/midamble 0 3 = pseudo random sequence w/midamble 1 4 = pseudo random sequence w/midamble 2 5 = pseudo random sequence w/midamble 3 6 = pseudo random sequence w/midamble 4 7 = pseudo random sequence w/midamble 5 8 = pseudo random sequence w/midamble 6 9 = pseudo random sequence w/midamble 7 10 = RACH BURST 12 = pseudo random sequence w/midamble 0 two time slot 13 = pseudo random sequence w/midamble 0 three time slot Field 2 0 = disable 1 = enable Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Handset Test Commands Table 3. Field and Parameter descriptions - continued Opcode (Decimal) 10 18 20 34 45 54 55 Opcode Mnemonic CP_MODE Field Description Field 1 0=set submode 1=get submode Field 2 5 = GSM 1900 6 = GSM dual band GSM900/GSM1800 8 = WCDMA Region 1 10 = Automatic - Dual mode: WCDMA region 1 and GSM dual band GSM900/GSM1800.a INVM Field 1 0 = Master Reset 1 = Master Clear LOAD_SYN Field 1 Channel number in decimal. Valid channel numbers are: • 1-124 (PGSM 900 MHz) • 0, 975-1023 (EGSM 900 MHz) • 512-885 (DCS 1800 MHz) • 512-810 (PCS 1900 MHz) Field 2 Reserved for future use and TDMA; set to 0. Field 1 As is RESTART SET_RF_PWR Field 1 PA power level (0-19) Field 1 As is SUSPEND TST_DISP Field 1 2 = Display Predefined Pattern 9 = Turn On/Off the Front Light Field 2 Data for 2, (Data) 000 = All pixels off (all black) 001 = All pixels on (all white) 005 = Grey scale block: 16 level, Black to white 006 = Horizontal Zebra Line 014 = Eight Color Box Pattern Data for 9, 000 = Front Light Off 001 = Front Light On, Full Intensity Preliminary Motorola Confidential Proprietary 2-9 Handset Test Commands A920/A925 Table 3. Field and Parameter descriptions - continued Opcode (Decimal) 57 62 3083 2 - 10 Opcode Mnemonic VERSION Field Description Field 1 016000 = DSP Version 017000 = User (login) pf process that created this file 017001 = Build time (universal) in ISO-8601 format 017002 = Clearcase view tag name 017003 = Product base label from Clearcase config spec 017004 = Product ID 017005 = Version Number 017006 = Build commentary 018000 = Flash Booter version number (P2K Booter Only) Field 1 0 = Keypad Backlight LED LEDS 3 = Red LED 4 = Green LED Field 2 3 = Set duty cycle (Red/Green LEDS Only) Field 3 Duty Cycle setup, 000 = Off 012 = ON WLOAD_SYN Field 1 UARFCN for Receive Frequency ID. Valid values are between 0 and 16383. If TX_FREQ_ID is set to 0xFFFF, then RX_FREQ_ID must take values between 190*5 and 16383. Note : If a valid TX_FREQ_ID will be entered, RX_FREQ_ID must be set to FFFF. Field 2 UARFCN for Transmit Frequency ID. Valid values are between 0 and 16383. If it is set to 0xFFFF the TEST_TASK will derive the TX_FREQ_ID from the RX_FREQ_ID. Note : If a valid RX_FREQ_ID is entered, TX_FREQ_ID must be set to FFFF. Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Handset Test Commands Table 3. Field and Parameter descriptions - continued Opcode (Decimal) 3086 Preliminary Opcode Mnemonic W_CARRIER Field Description Field 1 Channel identifier (0-16383). Field 2 0 = Enable carrier. 1 = Disable carrier. Field 3 Initial transmit power (dBm). -128 dBm to 127 dBm Field 4 Maximum transmit power (dBm). -128 dBm to 127 dBm Field 5 Minimum transmit power (dBm). -128 dBm to 127 dBm Field 6 0 = All 0s. 1 = All 1s. 2 = PN9. 3 = PN15. Field 7 0 = Disable spreading. 1 = Enable spreading. Field 8 0 = Disable scrambling. 1 = Enable long scrambling. 2 = Enable short scrambling. Field 9 0 = SF256, slot format 0. 1 = SF256, slot format 1. ... 5 = SF256, slot format 5. Field 100 = SF256, slot format 0. 1 = SF128, slot format 1. ... 6 = SF4, slot format 6. Field 11Channelization Code Number. Field 12Scrambling Code Number. Motorola Confidential Proprietary 2 - 11 Handset Test Commands 2 - 12 A920/A925 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Manual Test Procedures Introduction Non-Signalling Test Measurements The phone allows keypad and computer controlled testing of various digital test parameters. In an event that the phone exhibits RF failures that prevent call processing, the service technician may need to perform some non-signalling tests. These tests will provide information regarding which stage of the phone is failing prior to opening the phone for troubleshooting. The following tests will be described in this chapter. This chapter includes the keypad/computer functions and recommended equipment setup to use when testing a phone manually. Call-Processing Tests Most communications analyzers can simulate a cell site in order to perform automatic call-processing tests. Automatic call processing tests can be performed while the phone is in standby mode. Refer to the communications analyzer’s manual for details about performing call-processing tests. The following call-processing test sequence is recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. GSM Mobile Originated Call WCDMA Mobile Originated Call GSM handover DCS handover PCS handover Preliminary • • • GSM/DCS/PCS TX Power Output GSM RSSI WCDMA TX Power Output The digital phasing parameters are stored in a EPROM on the Transceiver Board. Each transceiver is shipped from the factory with these parameters already calibrated. However, if a board is repaired, these parameters should be measured and, if necessary, adjusted with the GP-Gate System. Checking and adjusting calibration parameters is also useful as a troubleshooting/ diagnostic tool to isolate defective assemblies. Motolora Confidential Proprietary 3-1 Manual Test Procdures A920/A925 GSM/DCS/PCS Call Processing GSM/DCS/PCS Call Processing RF Interface (Everything listed is required) In order to successfully complete a GSM call processing procedure, a test USIM card needs to be available. Test USIM cards have default call parameters that allow users to perform call processing tests through GSM base station simulators. This allows service technicians to perform simulations without accessing the customer’s cellular account. • • • • Hardware Requirements If PCS call processing procedures are necessary, the user will need to send a test command to the phone prior to beginning the test. The command can be initiated through handset test commands or computer test commands. Software requirements for each method is listed below. There are various hardware configurations to perform manual call processing procedures. Below, is a list of the various options. All options require the battery to be attached. A GP-gate system can also be used for manual testing. Refer to the GP-gate user’s manual for details. SMA/N-type Adapter (0-00-00-40042²) SMA Cable 0.5m (0-00-00-40047²) Repair Fixture (5-00-4T-10000²) USIM (0-00-00-40810²) Software Requirements (PCS only) Handset Test Command Power Options • • Computer Test Command Fully Charged Battery (SNN5639B¹ or equivalent) • Full-Rate Power Supply (PSM5049A¹) • Battery Eliminator (5-00-3F-10000²) with 2Wire Adapter (2-00-68-10000²) Note: Requires a single output power supply • No software needed Radio Comm (latest release) Control Interface Options (PCS Only) • • USB Cable (SKN6311A¹) Serial Cable (SKN6315A¹) with CE converter (SYN0279B¹) Note: If handset test commands are being used, a control interface is not needed. ¹Contact your local Motorola dealer for ordering ²Contact AMS Software and Elektronik GmbH for ordering 3-2 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Manual Test Procedures GSM/DCS/PCS Call Processing Call Origination (GSM and DCS only) Figure 11. GSM Connection Control Use the following procedures for call processing. The screen shots are from a Rohde and Schwarz CMU 200. The procedures can be adopted to any other test box that will be used to perform call processing. 1. Install the test USIM in phone. 2. GSM 900 Connection Control Frequency Offset +0 Signal On Single Slot Hz BCCH and TCH Mode BCCH Level - 85.0 RF Channel 37 - 85.0 dBm 975 Ch. 2 GSM1900 Overview Circuit Switched Single Slot Connect Control Menu Select Selection GSM Mobile Station(GSM 1800/Signalling/Overview/P/t Normal GMSK Basic Functions GSM Mobile Station GSM 850 GSM 900 GSM 1800 GSM 1900 3G UMTS User Equipment WCDMA FDD Non-Signalling Signalling 4. AUDIO Analyzer/Generator GSM 850 Analyzer/Generator P/t Normal GMSK GSM 850 Overview P/t Normal GMSK HotKeys Set 1 Timeslot Network AF/RF Sync 1 2 9. Dial a number from the phone and press the send button. 10. The phone is now connected. Figure 12. GSM Call Connected HotKeys Set 2 HotKeys Set 3 GSM1800 Overview Ch. 1 Ch. 2 RUN P/t Norm GMSK 1(28.0 dBm ) Reported Power 25.5 dBm Avg. Burst Power (Current) 25.7 dBm Peak Burst Power Ok Power Ramp - 0.75 RUN Sym. Time Advance Error Ext. Phase Error GMSK - 30 6.2 2.1 HotKeys Assign. Frequency Error Hz Peak Phase Error(Current) RMS MS Receiver Reports Set Broadcast Channel (BCH) to 120 (GSM) or 700 (DCS) 5. Set Broadcast channel level to -85dBm 6. Set Traffic Channel (TCH) to 38 (GSM) or 512 (DCS) 7. Set Traffic channel level to -85dBm Preliminary Hopping Overview GSM 850 Overview P/t Normal GMSK Select RF Channel MHz Wait until the phone indicates a receive signal Hotkeys - Set 1 GSM 850 Analyzer/Generator P/t Normal GMSK Menu BS Signal TCH Level 8. RF Analyzer/Generator Analyzer/Generator MS Signal 1(28.0 Ch. 1 925.2 3 Connection Figure 10. GSM Signalling Setup dB unused Off Note: Control interface doesn’t need to be connected at this time. Setup up the test box for GSM or DCS Signalling - 20.0 dBm used Connect hardware as illustrated in figure 13. 3. Slot Mode 17 ( 0( - 94 to - 93 dBm) RX Level 0.0 to RX Quality Off Discontinuous Transmission(DTX) PCL 0.2 % ) Timing Advance Motorola Confidential Proprietary Circuit Switched Single Slot R P/t Norm, U N GMSK Settings Signalling States MS Capabililties Signalling Info IMSI IMEI Dialled Number Traffic Mode Meas. Control Repetition Stop Condition Display Mode Statistic Count Analyzer Level RF Mode RF Attenuation Triiger Source Trigger Slope MS Signal CIrcuit Switched Timing Advance Single Slot PCL (MS) Connect Control --- -------------123655 Full Rate Version 1 Continuous None Current 100 Bursts Auto Low Noise Signalling Rising Edge Application Analyzer Level MS Signal BS Signal Network 0 Sym. 1 (28.0 dBm) Menus 3-3 Manual Test Procdures A920/A925 Figure 13. A920 Manual Test Hardware Configuration CMU200 Test Box or Equivalent SMA/N-type Adapter 0-00-00-40042 SMA Cable 0.5m 0-00-00-40047 Power Supply (3.6Vdc, 2A) 2-Wire Adapter 2-00-68-10000 A920/A925 RF Fixture 2-00-4E-10000 A830 Battery Eliminator 5-00-3F-10000 P2K USB Cable SKN6311A Control Interface Radio Comm equipped Computer 3-4 RS232 to CE SYN0279B OR Motorola Confidential Proprietary P2K Serial Cable SKN6315A Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Manual Test Procedures GSM/DCS/PCS Call Processing Call Origination (PCS Only) • Before beginning, one of the following test command procedures needs to be completed. Click on AT+/mode, suspend, CP_Mode 1900, respectfully Figure 15. Radio Comm Screen Handset Test Command • • • Power up phone Enter the following key sequence Menu 0 H T C M D * • Enter the following test commands in the Opcode screen 54 ok SUSPEND 10*0*5 CPLOAD, GSM 1900 Power cycle phone • • • • Power cycle phone Repeat steps 1 through 10 in the ,“Call Origination (GSM and DCS only),” section with the following modifications, RadioComm Test Command • • • • Connect as illustrated in figure 13 Power up phone Start RadioComm application Correctly select Settings option for USB or serial Figure 14. RadioComm COM Port • • • Set PCS Signalling BCH = 661 TCH = 512 Once PCS call processing is complete, return the phone to its original state by performing the following procedure, Handset Test Command • • • 54 ok SUSPEND 10*0*10 CPLOAD, Dual mode Power cycle phone Computer Test Command (Radio Comm) • • Preliminary Click on AT+/mode, Suspend, CP_Mode 900/ 1800, respectfully Power cycle phone Motorola Confidential Proprietary 3-5 Manual Test Procdures A920/A925 GSM/DCS/PCS Call Processing Call Test Parameters (GSM/DCS/PCS) Burst Output Shape should fall within the standard limits of the Power Ramp. While the phone under test is in an active call, the parameters for each band should be verified as described. Table 4. GSM Call Parameters Pa ra m e te r Burst Avg Power Out¹ Burst Output Shape Time Advance Error RMS Phase Error Peak Phase Error Frequency Error RX Level Error@-105 dBm² RX Quality @-105 dBm² BER @-105, 10k bits³ Low Lim it 31 1 -1 0 -20 -90 1 0 0 High Lim it 33 1 1 5 20 90 9 4 2 Unit dBm P/F bit/sym deg deg Hz BER measurements is only required if RX Quality reads a value of 4 or greater. dB % High Lim it 32 1 1 5 20 190 10 4 2 PCL: --- 1 / 28.0 dBm / Off Chan. / Meas Slot: 740 / 3 2: --/ Off Current R P/t Norm, U N GMSK Applic. 1 Applic. 2 Analyzer Level -20 -30 Ok -50 25.57 dBm - 0.75 Sym. GSM 0 100 Bursts -70 Unit dBm P/F bit/sym deg deg Hz % BS Signal Avg.BurstPower(Cur.) Timing Adv. Error TSC detected Network Statiatical Counr 0.00 % Out of Tolerance 60 80 Marker 0 20 Overview Table 6. PCS Call Parameters Low Lim it 28 1 -1 0 -20 -190 2 0 0 Low Noise 1: -60 ¹Power Level = 0 ²Set BS TCH level to -103 dBm ³Set BER TCH level to -103 dBm with 10k bits or 128 Frames Pa ra m e te r Burst Avg Power Out¹ Burst Output Shape Time Advance Error RMS Phase Error Peak Phase Error Frequency Error RX Level Error@-104 dBm² RX Quality @-104 dBm² BER @-104, 10k bits³ Auto / Off -10 -80 Pa ra m e te r Burst Avg Power Out¹ Burst Output Shape Time Advance Error RMS Phase Error Peak Phase Error Frequency Error RX Level Error@-103 dBm² RX Quality @-103 dBm² BER @-103, 10k bits³ Max. Level: R: --- +0 Connect Control MS Signal Table 5. DCS Call Parameters High Lim it 32 1 1 5 20 180 11 4 2 Circuit Switched Single Slot Ch. 2 -40 ¹Power Level = 5 ²Set BS TCH level to -105 dBm ³Set BER TCH level to -105 dBm with 10k bits or 128 Frames Low Lim it 28 1 -1 0 -20 -180 3 0 0 Figure 16. Burst Output Shape GSM1800 Overview Ch. 1 40 Power Modulation 100 Spectrum 120 Display 140 Receiver Quality Audio Menus It is recommended that handover procedures be performed as shown in the following table. Table 7. GSM/DCS/PCS Handover Ba nd GSM DCS PCS From Tra ffic Pow e r Cha nne l Control 975 5 512 0 512 0 To Tra ffic Cha nne l 124 885 810 Pow e r Control 19 15 15 Unit dBm P/F bit/sym deg deg Hz % ¹Power Level = 0 ²Set BS TCH level to -104 dBm ³Set BER TCH level to -104 dBm with 10k bits or 128 Frames 3-6 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Manual Test Procedures WCDMA Call Processing WCDMA Call Processing 3. In order to successfully complete a GSM call processing procedure, a test USIM card needs to be available. Test USIM cards have default call parameters that allow users to perform call processing tests through GSM base station simulators. This allows service technicians perform simulations without accessing the customer’s cellular account. Setup up the test box for WCDMA FDD Signalling Figure 17. WCDMA Signalling Setup Ch. 1 Ch. 2 WCDMA FDD Band I Connect Control Spectrum Menu Select Selection GSM Mobile Station(GSM 1800/Signalling/Overview/P/t Normal GMSK Basic Functions GSM Mobile Station GSM 850 GSM 900 GSM 1800 GSM 1900 3G UMTS User Equipment WCDMA FDD Hardware Requirements Non-Signalling Signalling Hotkeys - Set 1 RF Analyzer/Generator Power Spectrum AUDIO Analyzer/Generator GSM 850 Analyzer/Generator P/t Normal GMSK GSM 850 Overview P/t Normal GMSK GSM 850 Analyzer/Generator P/t Normal GMSK Refer to , “Hardware requirements,” under, “GSM/ DCS/PCS Call Processing.” Also Refer to Figure 13. GSM 850 Overview P/t Normal GMSK Menu HotKeys HotKeys Set 1 Set 2 Select HotKeys Set 3 HotKeys Assign. Software Requirements None. 4. Set UE Signal, RF Channel Uplink to 9750 Figure 18. Channel Uplink(UE Signal) Call Origination (WCDMA) WCDMA FDD Connection Control Signal On Setup Use the following procedures for call processing. The screen shots are from a Rohde and Schwarz CMU 200 with WCDMA signalling options installed. The procedures can be adopted to any other test box that will be used to perform call processing. 1. Install the test USIM in phone. 2. Connect hardware as illustrated in figure 4. Analyzer Settings/RF Channel Uplink Default All Settings Analyzer Settings RF Channel Uplink Band [|] Frequency Offset RX/TX Separation Measurement Settings Default Settings UL Scrambling Code Analysis Mode Sync. Mode Measurement Slot Number Correlatoin Mode Threshold UE Power Control Default Settings Connection UE Signal Channel Frequency Downlink 9750 1922.4 MHz + 0.000 kHz 190.000 MHz 2112.4 MHz 0 With Origin Offset All Slots 0 DPCCH - 25 dB BS Signal Network RF Sync. 1 2 Note: Control interface doesn’t need to be connected at this time. Preliminary Motorola Confidential Proprietary 3-7 Manual Test Procdures A920/A925 WCDMA Call Processing 5. WCDMA Call Test Parameters Set TPC Pattern Type to All 1 Figure 19. TPC Pattern Type(UE Signal) WCDMA FDD Connection Control Signal On Setup TPC Settings/TPC Pattern Type - 5.0 dB 3 - 3.0 dB 6 - 7.0 dB 6 0.0 dB 1 PICH PICH Channel Code AICH AICH Channel Code DPDCH DPCH Channel Code Power Offset (DPCCH/DPDH) Secondary Scrambling Code TPC Settings Default Settings TPC Algorithm TPC Step Size TPC Pattern Type Pattern Repeat Pattern Connection 6. UE Signal Table 5. WCDMA Call Parameters Network RF Sync. 1 2 Ch. 2 Dial a number from the phone and press the send button. WCDMA FDD Band I Max. Level: + 30.0 dBm Low Noise Multiple Signal DPCCH+DPDCH 1 CCMode Manual Scr Code 0 The phone is now connected. RMS Magn Error Peak RMS Figure 20. WCDMA Call Connected Ch. 2 WCDMA FDD Band I Connect Control Power Phase Error Peak RMS I/Q Origin Offset I/Q Imbalance Carrier Frequency Error Max. Level: + 30.0 dBm Low Noise Freq/Offset: + 0.000 kHz: Chan. /Freq: 9750 / 1950 MHz R Maximum U N Power Application Waveform Quality Peak Code Dom Error PCDE Code UE Power (Peak) UE Power (RMS) 24.77 24.02 Average dBm dBm 24.73 24.01 dBm dBm Maximum 24.94 dBm 24.09 dBm Minimum 20.69 dBm 10 Statistic Count Power Application Max /Min 22.16 % 8.80 % 14.03 % 5.52 % 12.47 ° 3.95 ° - 32.95 dB - 21.38 dB 4 Hz 0.99226 - 28.12 dB 26.5 % 10.2 % 15.3 % 5.6 % 15.4 ° 4.9 ° - 32.37 dB - 20.07 dB - 76 Hz 0.9897 - 25.49 dB I 0 Analyzer Lev. Trigg UE Signal Ana. Set 0 Slot Number 20.81 dBm UE Power 10 BS Signal Level Ch. 1 BS Signal Settings dBm +40 Ch. 2 Modulation Spectrum Code Dom. Power WCDMA FDD Max. Level: + 30.0 dBm Freq. Offset: + 0.000 kHz Band I +20 +10 Statistic Count Overview Power Modulation Spectrum Low Noise Connect Control R ACLR U N Filter Chan. /Freq: 9750 / 1950 MHz Current 640 Chip Application Meas. Length - 10 ---- - 20 UE Power - 30 10 - 40 Statistic Count - 50 -2 -1 0 - 10.00 MHz - 5.00 MHz - 47.4 - 55.7 - 34.9 - 41.5 - 55.7 - 45.1 - 55.2 - 41.5 - 34.6 - 41.3 Power 3-8 Menus Receiver Quality +0 Menus BS Signal Settings 100.00 % Spectrum +30 100.00 % Receiver Quality BS Signal Level Figure 22. ACLR Screen Analyzer Settings Out of Tolerance Code Dom. Power R Overview U N WCDMA Chan. /Freq: 9750 / 1950 MHz Out of Tolerance Analyzer Lev. Trigg Current Average 20.8 % 8.5 % 15.3 % 5.6 % - 11.5 ° 3.7 ° - 33.06 dB - 21.74 dB 5 Hz 0.9929 - 29.11 dB Q 1 Peak Connect Control Modulation Freq/Offset: + 0.000 kHz: SR1 15 CC1 64 Current Err Vect Magn Ch. 1 Unit dBm Hz % dB dB dB dB Figure 21. WCDMA Modulation Ch. 1 10. High Limit 21.5 195 13.5 -43 -33 -33 -43 ¹Refer to Figure 10 ²Refer to Figure 11 ³Refer to Figure 12 Wait until the phone indicates a signal 9. Low Limit 20.5 -195 0 -100 -100 -100 -100 Parameter Avg. RMS Power Out¹ Avg. Frequency Error² Avg. RMS EVM² Avg. RMS ACLR - 2³ Avg. RMS ACLR - 1³ Avg. RMS ACLR + 1³ Avg. RMS ACLR + 2³ Algorithm 2 1 dB All 1 0000000000000000000000 bin Off BS Signal While the phone under test is in an active call, the parameters for each band should be verified as described. 1 0 MHz + 24.7 + 20.7 dBm dBm All Values in dB Modulation Motorola Confidential Proprietary 2 Ch 100.00 % Out of Tolerance + 5.00 MHz + 10.00 MHz - 34.7 - 41.3 - 51.4 - 57.8 ACLR (Peak) Curr. - 41.3 - 33.7 - 41.0 - 57.8 - 49.0 - 57.4 ACLR (RMS) Avg. Spectrum Code Dom. Power ACLR (RMS) Curr. Analyzer Lev. Trigg Analyzer Settings BS Signal Level BS Signal Settings ACLR (Peak) Avg. ACLR (RMS) Max. Receiver Quality Menus Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Manual Test Procedures Non-Signalling Test Procedures (GSM/DCS/PCS) Non-Signalling Test Procedures (GSM/DCS/PCS) To perform non-signalling test procedures, the user is required to be familiarized with sending test commands to the phone under test. The test commands can be sent using the Handset test command interface or through a computer. Please refer to section, ”Handset Test commands,” for details on how to send test commands through phone keypad entry. In order to successfully send test commands to the phone under test, the phone needs to be in suspend mode. Follow the listed procedure to place the phone in suspend mode. Handset Test Commands 54 ok Handset Test Command • No software needed Computer Test Command • Radio Comm (latest release) Verify TX Power Output (GSM/DCS/PCS) Verify the TX Power output by initiating the commands in this section. Verify that the results fall within the following limits. Table 8. TX Power Limits Suspend Parameter GSM TX Power Out DCS TX Power Out PCS TX Power Out Radio Comm Test Commands Click AT+MODE then SUSPEND (Serial Only) Click PST Initialize and click SUSPEND when initialization is complete (USB Only) Hardware Requirements Refer to page 3-2 for a list of Hardware. Refer to Figure 13 for a configuration illustration. Preliminary Software Requirements Low Limit 31 28 28 High Limit 33 29.5 29.5 Unit dBm dBm dBm Handset Test Commands 54 10*0*10¹ 20*38*0² 45*5³ 7*6*1 Suspend WCDMA/GSM/DCS mode Set Channel 38 Set GSM Power Level 5 Enable Carrier ¹10*0*5 for PCS mode ²20*700*0 for DCS Channel 700; 20*661*0 for PCS Channel 661 ³45*0 for DCS/PCS Power level 0 Motorola Confidential Proprietary 3-9 Manual Test Procdures A920/A925 Non-Signalling Test Procedures (GSM/DCS/PCS) Radio Comm Test Commands GSM RSSI Click on 900/1800 (GSM/DCS) or 1900 (PCS) Verify GSM RSSI by initiating the commands in this section. Verify that the RSSI results are equal to the Broadcast Channel (BCH) level. The user will need to set the RF generator with the following parameters. Enter 38 (GSM), 700 (DCS), or 661 (PCS) and then click Set Broadcast Channel (BCH): Broadcast Channel (BCH) Level: 20 -105 dBm Handset Test Commands No supported test commands Enter 5 (GSM) or 0 (DCS/PCS) and then click Set Radio Comm Test Commands Click on 900/1800 (GSM/DCS) or 1900 (PCS) Select 06 and then click ON Enter Channel 20 Click INIT Click Execute Verify return data is approximately -105 dBm 3 - 10 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Manual Test Procedures Non-signalling Test Procedures (WCDMA) Non-signalling Test Procedures (WCDMA) To perform non-signalling test procedures, the user is required to be familiarized with sending test commands to the phone under test. The test commands can be sent using the Handset test command interface or through a computer. Please refer to section,”Handset Test commands,” for details on how to send test commands through phone keypad entry. Also, refer to, “Computer Test Commands,” for details on how to send test commands through the computer. In order to successfully send test commands to the phone under test, the phone needs to be in suspend mode. Follow the listed procedure to place the phone in suspend mode. Handset Test Commands 54 ok Software Requirements Handset Test Command • No software needed Computer Test Command • Radio Comm (latest release) Verify TX Power Output (WCDMA) Verify the TX Power output by initiating the commands in this section. Verify that the results fall within the following limits. Table 9. WCDMA TX Power Output Parameter WCDMA Power Out Low Limit 20.5 High Limit 21.5 Unit dBm Suspend Radio Comm Test Commands Handset Test Commands Click AT+MODE then SUSPEND (Serial Only) Click PST Initialize and click SUSPEND when initialization is complete (USB Only) Hardware Requirements Refer to page 2 for a list of Hardware. Refer to Figure 4 for a configuration illustration. 54 3086 Field 1 Field 2 Field 3 Field 4 Field 5 Field 6 Field 7 Field 8 Field 9 Field 10 Field 11 Field 12 9750 0 023 027 206 002 1 01 000 000 000 000000000 Suspend W_CARRIER Set Channel Enable Carrier Max Power Out Max TX Power Min TX power PN9 Data pattern Enable spreading Long scrambling SF256, Slot format 0 SF256, Slot format 0 Channelization Code Scrambling Code Note: Enter 1 in field 2 to disable carrier Preliminary Motorola Confidential Proprietary 3 - 11 Manual Test Procdures A920/A925 Audio/Vibrator Test Procedures Audio/Vibrator Test Procedures Radio Comm Test Commands This section describes how to use test commands to verify audio and vibrate functions. Click on WCDMA In order to successfully send test commands to the phone under test, the phone needs to be in suspend mode. Follow the listed procedure to place the phone in suspend mode. For W_CARRIER assign these actions to each field Handset Test Commands Freq ID (Dec) Action Channelization Data Pattern Scrambling DPCCH DPDCH Channelization Code Transmit Power Max Power Min Power Scram Code 54 ok 9750 Enable Enable PN 9 Long SF256, SF0 SF256, SF0 00 15¹ 15¹ 80² 00 ¹0x0015 -> 21 dec -> +21dBm ²0x0080 -> 128 dec -> (128-256 = -128 dBm) Suspend Radio Comm Test Commands Click AT+MODE then SUSPEND (Serial Only) Click PST Initialize and click SUSPEND when initialization is complete (USB Only) Vibrator Test Handset Test Commands 3*0*1 3*0*0 Enable Vibrator Disable Vibrator Radio Comm Test Commands Enable or Disable Vibrator Verification Verfiy vibration function when enabled. 3 - 12 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Manual Test Procedures Audio/Vibrator Test Procedures Handset Mic/Speaker test Mono Headset Mic/Speaker test Handset Test Commands Handset Test Commands 6*2*2 4*7*1*16 6*4*6 Enable internal mic and handset speaker Enable VOCODER loopback at Enhanced Full Rate 4*7*1*16 Enable headset mic and headset speaker Enable VOCODER loopback at Enhanced Full Rate Radio Comm Test Commands RadioComm Test Commands Enable internal mic and headset speaker Enable headset mic and headset speaker Enable Vocoder loopback at Enhanced Full Rate Enable Vocoder loopback at Enhanced Full Rate Verification Verification Speak into the handset mic and listen for undistorted speech in the handset speaker. Preliminary Speak into the headset mic and listen for undistorted speech in the headset speaker. Motorola Confidential Proprietary 3 - 13 Manual Test Procdures A920/A925 Software Version Check Stereo Headset Mic/Speaker test Melody Speaker test Handset Test Commands Handset Test Commands 6*4*8 0*1*245 0*0*245 4*7*1*16 Enable headset mic and headset speaker Enable VOCODER loopback at Enhanced Full Rate Play BACH_INVENTION_1 Stop BACH_INVENTION_1 NOTE: DO NOT issue a Suspend command (54 ok) for this test. RadioComm Test Commands RadioComm Test Commands Enable headset mic and headset speaker Currently not supported Verification Listen for undistorted audio. Enable Vocoder loopback at Enhanced Full Rate Verification Speak into the headset mic and listen for undistorted speech in the headset speaker. 3 - 14 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Manual Test Procedures Display Test Procedures Software Version Check Display Test Procedures Use the following procedures to retrieve software information. Software information can also be retrieved from the phone’s customer User Interface. Refer to the phone’s user manual for details. This section will describe the proper test procedures to determine the functionality of the color display. Any tests that involve displaying a predefined pattern can be returned to the Opcode screen by pressing the right softkey of the phone. In order to successfully send test commands to the phone under test, the phone doesn’t need to be in suspend mode. Follow the listed procedure to configure the phone to accept test commands In order to successfully send test commands to the phone under test, the phone needs to be in suspend mode. Follow the listed procedure to place the phone in suspend mode. Handset Test Commands Handset Test Commands None 54 ok Suspend Radio Comm Test Commands Radio Comm Test Commands Click AT+MODE (Serial Only) Click PST Initialize (USB Only) Click AT+MODE then SUSPEND (Serial Only) Click PST Initialize and click SUSPEND when initialization is complete (USB Only) Test Commands 57*017003 57*017001 Read Software Version Read Build Date Display Backlight Test RadioComm Test Commands Handset Test Commands Select Product Base Label and click “Get” to retrieve software version 55*9*000 55*9*001 Backlight Off Backlight On, full intensity RadioComm Test Commands Select Build Time and click “Get” to retrieve Build Date Click “FL Off” to disable backlight Click “FL On-Full” to enable backlight Verification Verify that the backlights respond for each issued command. Preliminary Motorola Confidential Proprietary 3 - 15 Manual Test Procdures A920/A925 Display Test Procedures Display Color Test Display Linearity Test Handset Test Commands Handset Test Commands 55*2*014 55*2*005 Eight Color Box Pattern Grey Scale Block RadioComm Test Commands RadioComm Test Commands Select Eight Color Box and click “Set” Select Grey Scale and click “Set” Verification Verification Verify that the color pattern on the phone’s display matches the color box in figure 23. Also verify edges (uniform/smooth). Verify that the Grey scale block on the phone’s display matches the Grey scale block in figure 14. This test can also be used to confirm that the color intensity is linear. Figure 23. Eight Color Box Pattern 3 - 16 Figure 24. Grey Scale Block Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Manual Test Procedures Display Test Procedures Display Flicker Test Display Pixel Defect (Bright) Handset Test Command Handset Test Commands 55*2*006 55*2*001 Horizontal Zebra Line All pixels on (all white) RadioComm Test Commands RadioComm Test Commands Select Horizontal Zebra and click “Set” Select All Pixels Off and click “Set” Verification Verification Verify that no noticable flicker exists. Verify that no greater than two pixels are off. Figure 25. Zebra Pattern Display Pixel Defect (Dark) Handset Test Commands 55*2*000 All pixels off (all black) RadioComm Test Commands Select All Pixels On and click “Set” Verification Verify that no greater than two pixels are on. Preliminary Motorola Confidential Proprietary 3 - 17 Manual Test Procdures A920/A925 LEDS and Keypad Backlight Keypad Backlight Use the following procedures to verify status LED and keypad backlight. Handset Test Commands In order to successfully send test commands to the phone under test, the phone doesn’t need to be in suspend mode. Follow the listed procedure to configure the phone to accept test commands. 62*0*1¹ 62*0*0¹ Enable Keypad Backlight Disable Keypad Backlight ¹Leave field 3 blank and press OK RadioComm Test Commands Select Keypad to enable. Deselect Keypad to disable. Handset Test Commands None Radio Comm Test Commands Verification Click AT+MODE then SUSPEND (Serial Only) Click PST Initialize and click SUSPEND when initialization is complete (USB Only) Verify that all keypad backlight LEDs activate. Status LEDS Handset Test Commands 62*3*3*012¹ Enable Red LED 62*4*3*012¹ Enable Green LED ¹000 to disable RadioComm Test Commands Select Red LED or Green LED to enable. Deselect Red LED or Green LED to disable. Verification Verify that the Red and Green status LEDS activate. 3 - 18 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Manual Test Procedures Bluetooth Tests (V500/V600 only) Under Bluetooth, select parameter 01 and enter 2DFC0129 in the “TO Radio” field. Click Execute. Use the following procedures to verify functionality of the Bluetooth device integrated in the phone. In order to successfully send test commands to the phone under test, the phone doesn’t need to be in suspend mode. Follow the listed procedure to configure the phone to accept test commands. None NOTE: The Bluetooth TX signal will activate momentarily once the HCI command is issued. You must have the RF probe positioned for measurement once you click execute. Radio Comm Test Commands Verification Click AT+MODE then SUSPEND (Serial Only) Click PST Initialize and click SUSPEND when initialization is complete (USB Only) Verify that a 2441MHz signal is present. If the phone is closed, use a RF probe to sniff the strongest signal around the “7” key of the keypad. If the phone is open (shields off), verify that -2dBm to +4dBm is read from R320. An high impedance RF probe is required to read this range. Use of lower quality RF probes will result in signal level differences. Handset Test Commands Unmodulated CW TX test Handset Test Commands Not Supported RadioComm Test Commands Under Bluetooth, select parameter 84 and click execute, then select 81 and click execute. Preliminary Motorola Confidential Proprietary 3 - 19 Manual Test Procdures A920/A925 Camera Testing Camera Test Configuration This document is intended to describe the procedures that will determine whether the camera function of a Motorola terminal is under normal operating conditions. Use any color printer to print a hardcopy of the Macbeth color chart. The Focus chart and Grey chart can be printed using any B/W printer. In order to successfully send test commands to the phone under test, the phone doesn’t need to be in suspend mode. Follow the listed procedure to configure the phone to accept test commands. For best results follow this recommended setup, 1. Attach chart to a flat vertical surface (wall) 2. Attach the phone to the desktop charger 3. Attach the control interface to desktop charger 4. If necessary, attach power supply to control interface. Click AT+MODE then SUSPEND (Serial Only) Click USB Initialize and click SUSPEND when initialization is complete (USB Only) 5. Turn on phone. 6. Select Camera option in phone 7. Position Desktop charger so that the camera test chart completely fills the viewfinder. Hardware Requirements Assign a permanent space in the test lab for these test procedures. Always use the same lighting conditions. Also, it’s recommended that a “golden picture” is saved and used for comparison. Handset Test Commands Not supported Radio Comm Test Commands The following hardware will be required to properly test the camera function of the phone. 1. Desktop Charger (SPN5032A or equivalent) 2. USB or RS232 control interface (refer to figure 4) 3. Fast Rate Charger (SPN5078A or equivalent) 4. Hardcopy of Macbeth Color Chart 5. Hardcopy of Focus Chart 6. Hardcopy of Grey Chart 3 - 20 There is a variety of ways the camera test charts can be attached to a vertical flat surface. They can be taped, tacked, attached to flip charts, etc. Use your best judgement. The desktop charger is being used as a fixture to position the phone for test, therefore, it’s recommended that the desktop charger is attached to a countertop to prevent any movement. Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Manual Test Procedures Figure 9. Camera Test Configuration Camera Test Charts Phone under Test Camera View Charger (SPN5049A) USB (SKN6311A) Serial (SYN0279B) Desktop Charger SPN5078A To Outlet (110V/220V) Preliminary To Computer Velcro (or equivalent) Motorola Confidential Proprietary 3 - 21 Manual Test Procdures A920/A925 Image Capture Once the picture is captured, it’ll be displayed on the screen. Click “Save To File” The listed steps should be followed to capture three images (1) the Macbeth color chart, (2) the focus chart, and (3) the grey scale chart. The user will be required to print all images found in Appendix A. Handset Test Commands Not supported Radio Comm Test Commands Under “Common Features” select Camera Click “Take Picture” 3 - 22 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Level 3 Service Manual Manual Test Procedures Macbeth Color Chart Focus Chart 1. From the computer, open the captured color chart image. 1. 2. Compare, the color blocks of the printed Macbeth color chart to the captured image. From the computer, open the captured focus chart image. Block 1-6 Block 7-12 Block 13-18 Verify the focus quality at the center, top-left corner, bottom-left corner, top-right corner, and bottom-right corner. Block 19-24 Follow the listed verifications to determine the quality of the image. Grey Scale Chart (Shading Test) 1. Minimal noise level for Blue, Green and Red on blocks 19 through 24. 1. 2. Uniformity for grey scale blocks 19 through 24. 3. Good white balance on blocks 19 through 24. 4. Good color reproduction on blocks 13 through 18. From the computer, open the captured grey scale chart image. Verify that there is minimal shading deviations on all four corners when compared to the center of the image. Preliminary Motorola Confidential Proprietary 3 - 23 Manual Test Procdures 3 - 24 A920/A925 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Preliminary Service Diagrams Introduction The service diagrams were carefully prepared to allow a Motorola certified technician to easily troubleshoot cellular phone failures. Our professional staff provided directional labels, color coded traces, measurement values and other guidelines to help a technician troubleshoot a cellular phone with speed and accuracy. Because of the sensitivity of RF, measured readings will be greatly affected if they’re taken in certain locations. To get the most accurate readings, take measurements nearest to the labeled measurement on the service diagram. We worked hard in trying to provide the best service diagrams, therefore, to avoid cluttered diagrams, we may exclude some components from the service diagrams. Our professional staff carefully selected to excluded components that are unlikely to fail. Test Point Measurements The measurements labeled on the service diagrams are approximate values and may vary slightly. These measurements are dependent on the accuracy of the test equipment. It is strongly recommended that the test equipment calibration schedule be followed as stated by the manufacturer. RF probes should be calibrated for each frequency in which tests are going to be performed. The types of probes used will also affect measurement values. Test probes and cables should be tested for RF losses and loose connections. Preliminary Motorola Confidential Proprietary 4-1 4-2 A920: Antenna Circuit Int Antenna M001 Ext Antenna Ant Match WCDMA_RX GSM_RX GSM RF SECTION FL001 FEM DCS_RX PCS_RX GSM_TX DCS_PCS_TX N_BAND_0_G GSM_EXC_EN Q902 Motorola Confidential Proprietary N_GSM_EXC_EN N_BAND_1 N_BAND_0 WCDMA RF SECTION FL030 CMOS level shifter Decoder ASIC RX_EN_LIFE MAGIC LV WCDMA_TX FL010 HARMONY LITE HL_TX_EN GSM TX VCO VRF_TX_2_775V Description POG Q901 NB_EXC_EN Q906 N_BAND_0 MAGIC LV All cellular receive bands are fed into either the internal antenna or external antenna. M001 is a mechanical switch which has the internal antenna path connected when a no insertion condition exists. The RF path will switch to external antenna upon insertion of a male SMA connector to M001. The internal antenna path is fed to the FEM(Front End Module) through antenna matching components. The FEM provides band selection and filtering between the EGSM, DCS, PCS and WCDMA receive and transmit bands to a single antenna port. GSM band selection is done by control lines N_BAND_1 and N_BAND_0_G. Mode selection is done by control lines HL_TX_EN, RX_EN_LIFE, N_GSM_EXC_EN, and GSM_EXC_EN. The diplexing arrangement permits reception of WCDMA signals in any FEM switch position. This allows the phone, while in a GSM call in any band, to detect signals from a WCDMA base station. The decision may then be made to hand over to the WCDMA system. Similarly, EGSM base station signals can be detected while the phone is in a WCDMA call to permit a handover decision from WCDMA to EGSM (This is not possible for base station signals in the DCS and PCS bands.). Signals received at the antenna between 2110 - 2170MHz will see the RF switch as an open circuit at any position. Consequently WCDMA Rx signals will go through FL2 to the WCDMA receiver. FL2 should have a maximum insertion loss of ~0.5dB. Outside of the WCDMA Rx band, FL2 behaves as an open circuit, preventing outof-band signals from reaching the WCDMA receiver. GSM, DCS, and PCS receive signals from the antenna port through the FEM should have a maximum insertion loss of -4.4dB. The FEM EGSM transmit path should have a maximum insertion loss of -2.5dB. The FEM DCS transmit path should have a maximum insertion loss of -3.1dB. The FEM PCS transmit path should have a maximum insertion loss of -3.7dB. Q902 is a dual FET package that’s being used to multiplex function of the N_BAND_0 control signal coming from the Magic LV. With the use of Q902, N_GSM_EXC_EN will follow N_BAND_0. GSM_EXC_EN will be the inverted level of N_BAND_0. Q906 is another dual FET package that’s used to prevent simultaneous GSM and WCDMA transmission conditions. During WCDMA transmission conditions, HL_TX_EN will be in a high state. This will open both FETs in Q906, thus, disabling any signal functions from control lines NB_EXC_EN and N_BAND_0. Q901 is used to invert the control signal coming from Q906. A920: Antenna Circuit N_BAND_0 page XX page XX U500 R912 Q906 R903 T650 T660 GSM_EXC_EN GSM_RX N_BAND_0_G DCS_RX page XX T670 PCS_RX RX_EN_LIFE GSM_TX FL001 page XX L825 R812 page XX Q902 page XX E3601 page XX FL001 page XX FL001 page XX N_BAND_0_G Q906 page XX N_GSM_EXC_EN Q902 page XX page XX U810 N_GSM_EXC_EN R900 N_BAND_0 page XX page XX VRF_HV_5V R005 N_BAND_0_G C902 GSM_EXC_EN C004 Motorola Confidential Proprietary FL001 HL_TX_EN LV_EXC_EN C003 U101 page XX C903 page XX page XX Q902 NB_EXC_EN* U500 DCS_PCS_TX page XX GSM_EXC_EN HL_TX_EN C006 U1000 C909 RX_EN_LIFE N_BAND_1 C007 U101 HL_TX_EN Q901 GSM_EXC_EN Q902 page XX HL_TX_EN C010 C005 C030 U700 page XX C008 page XX VRF_TX_2_775V U908 E3503 C908 page XX R904 U1000 C910 TX_RX_ERROR R901 R902 U500 page XX U101 page XX M001 ANTENNA C002 page XX Legend Sig Gen: RX: TX: -20dBm FL030 WCDMA_TX C460 4-3 4-4 A920: GSM RX Front End GSM_RX T650 RF DET DCS_RX T660 RF DET PCS_RX RX_Q+ RX_QRX_I+ RX_I- U625 T670 LIFE ÷2 ÷2 or 4 RX_EN_LIFE ÷5 or 3 Motorola Confidential Proprietary AUX_SPI_CLK AUX_SPI_DATA MAGIC LIFE_CE LP Filter MAGIC SPI DCS PCS GSM RX_VTUNE RX_VCO Description The EGSM, PCS and DCS signals must first pass through baluns before reaching the LIFE IC. Since the LIFE expects differential inputs, the baluns will provide this. Baluns provide the change from an unbalanced to a balanced line condition. By directly connecting to lines together, a possibility might arise where one line might ground a signal and impair the operation of a circuit. This situation is solved through the use of an un-balanced to balanced transformer, a balun. Expected nominal losses is ~.5 - 1.0dBm. The first IC in the EGSM, DCS, and PCS RX line up is U625 (LIFE), which is an LNA, VCO, and down converter mixer. The RX frequency is mixed down to a Very Low Intermediate Frequency (VLIF) of ~ 100KHz. This design is utilized to improve LO leakage causing RF self-mixing, DC offsets, and noise performance. The LIFE IC operates from the MAGIC_LV (tracking regulator), MAGIC_RF_V2_475. and MAGIC_SF (isolated supply for the VCO). LIFE is comprised of four low noise amplifiers (three of which are used) with two quadrature mixer paths for use in receive GSM 900 (925- 960MHz), DCS (18051880MHz), and PCS (1930-1990MHz) frequency bands, all SPI programmable. The RX_VCO signal is fed back to the MAGIC_LV prescaler input. Although the frequency will be dependent of the channel selected, the amplitude signal is ~30dBm. LIFE contains three fully contained VCOs which operate at ~4GHz. These VCOs are internally divided to provide precise quadrature down conversion for the three frequency bands. The input signal RX_VTUNE from the RX backend processor (MAGIC_LV) selects the VCO frequency to operate at. The tune range is .5 - 4.5V. The VCO frequencies for the three technologies are: DCS 3610 - 35759MHz, EGSM 3700 - 3838MHz, and PCS 3859 - 3980MHz. The AGC is provided by a common amplifier section, which is shared by all four LNAs. The AGC amplifier gain control is controlled by the voltage on the AGC pin, utilizing the internal 6-bit D/A to set the AGC via the SPI lines (SPIDATA, SPI_CLK, and SPI_CE). LIFE has an internal RF detector at the input of the AGC amplifier. The detected DC output level will be compared against a reference, which corresponds to the maximum safe input level to the mixer. This reference is SPI selectable so that the threshold can be set to 0dB, 3dB, 6dB, or 9dB below the level, which results in the mixer malfunction. If the detected level is above the reference then AGC_FLAG will go high. The MAGIC_LV will receive this signal as an interrupt and will reprogram the AGC until the level drops below the safe mixer input level as signified by AGC_FLAG returning low. The output signals I / IX and Q / QX are @ ~100KHz IF value for the Very Low IF. The input pin, RX_EN_LIFE controls the on / off state of the receiver and the PLL circuits. For input amplitude at the antenna of -50 to -40dBm the expected nominal output should be an AC rms peak-to-peak voltage of ~4.5 - 14mV. A920: GSM Receiver Front End C537 MAGIC_SF page XX RX_I+ E3552 page XX U500 R508 page XX U630 RX_VCO VLIFE U500 RX_QRX_VTUNE page XX Legend Sig Gen: RX: VCO: C605 C504 C503 R615 -20dBm PCS_RX FL001 AGC C670 T670 DCS_RX FL001 page XX C660 T660 GSM_RX C650 C651 FL001 page XX T650 E530 C505 R503 AUX_SPI_DATA R504 page XX U500 C604 C608 C610 page XX C600 U600 LIFE C609 page XX RX_Q+ L610 C607 U500 R611 page XX C632 L3560 C671 C661 VLIFE page XX VRF_RX_2_775V TP601 C606 U630 RX_I- page XX U500 R610 page XX VRF_REF_2_475V C603 page XX VRF_RX_2_775V R612 Motorola Confidential Proprietary L3560 C602 C631 U500 page XX AUX_SPI_BUS U500 page XX 4-5 4-6 A920: GSM RX Back End (Magic LV) RX_I RX_I_X IFA Σ∆ RX_Q_X Filter Balanced Complex Mod DET PMA IFA AntiAliasing filter Motorola Confidential Proprietary MAGIC LV U500 (RX Section) Σ∆ Filter Prgmable Dig CH Sel and Complex IF Notch or Highpass BFSR RX Serial Interface BDR NB_RX_ACQ POG DET_FLAG RX_Q Description AntiAliasing filter FL500 GSM RX Front End PMA BCLKR Dig Quad Osc The MAGIC_LV (U500) handles the backend processing for the EGSM, DCS and PCS (VLIF: RX_I, RX_I_X, RX_Q, and RX_Q_X) signal lines from LIFE. Simply, the MAGIC_LV performs an analog to digital conversion of I /Q and sends it to the data to the board processor (POG) via the SSI (serial synchronous interface). The MAGIC_LV also has a programmable and phase-able digital IF to improve image rejection. In MAGICLV, each channel is comprised of a Post Mixer Amplifier (PMA), an integrated passive two pole filter, a gain stage (AMP1) followed by an active programmable 2 pole anti-aliasing filter (mainly required to meet the blocking specs). This is followed by a lowpass sigma-delta ADC with a programmable oversampling clock OVSCLK (derived from the reference oscillator) equal to 13MHz for 200kHz channel spacing (13bits). Digital detector circuits are placed on each channel at the output of the sigma delta converters. The outputs of these detectors are compared against a level defined by DET_LVL. If either of the detected levels exceeds the programmed threshold then the pin DET_FLAG is set high. This indicates that the signal level is excessively high for the sigma delta modulator. DET_FLAG is read by the processor, which will respond by re-programming one of the AGC settings to a lower gain until DET_FLAG returns low. The outputs of the sigma-delta modulators are digitally processed through a noise cancellation circuit, comb and decimation filters. A second programmable digital LO based on a look up ROM generates digital quadrature oscillators with programmable gain/phase correction (called balanced complex multiplier) to digitally downconvert the I/Q signals to baseband (digital zero IF) through four quadrature mixers that provide image rejection of adjacent/alternate channels. Gain/ Phase correction at a single baseband frequency is performed on the Digital Quadrature Oscillator to compensate the analog gain/phase mismatch of the quadrature I and Q paths. After baseband downconversion and image reduction, the quadrature I and Q signals are further processed by digital filters that perform channel selectivity and out of band noise rejection. A serial bus consisting of SDFS and SDRX will transmit the RXI and RXQ data in 2‘s complement format. BDR and BFSR are outputs from MAGIC LV. BFSR is a framing signal which marks the beginning of an I,Q transfer. BDR is the serial data. The clock used for the serial transfer is BCLKR. When NB_RX_ACQ goes high MAGIC LV will activate the SSI interface in the digital receiver section. The data transmission over the serial bus will begin at the next normal occurrence of valid I and Q data, as defined internally to the digital receiver. A920: Magic LV (Receiver Back End) Motorola Confidential Proprietary U500 MAGIC LV C540 C534 E975 Y500 C542 TP504 U1000 NB_RX_ACQ page XX U1000 page XX U1000 page XX 4-7 U1000 page XX BFSR BDR BCLKR FL500 E977 FL510 R537 R536 RX_I+ U600 page XX RX_I- U600 page XX RX_Q+ U600 page XX RX_Q- U600 page XX 4-8 A920: MAGIC LV Control Functions RF_TOP MAGIC LV U500 (Control) N_BAND_1 N_BAND_0 TX_KEYM 80 bit Serial Reg MAGIC_DX MAGIC_SPICLK LIFE AUX_SPI_CLK AUX_SPI_DX LIFE_CE T X C o n t ro lle r POG Aux SPI Cntrl R A M P C o n tr o lle r AOC Filter MAGIC_SPI_CS Σ DET_AOC DET_REF GSM TX VRF_RX_2_775V VRF_REF_2_475V VRF_REF_2_475V V5 Superfilter V2 R F _ V 2 _ 2 _ 4 7 5 V S F _ O U T R F _ V 5 _ 2 _ 4 7 5 V MAGIC_DIG_1_875V V4 R F _ V 4 _ 1 _ 8 7 5 V VRF_DIG_1_875V R F _ V 3 _ 1 _ 8 7 5 V Motorola Confidential Proprietary V3 Description AOC_DRIVE The MAGIC LV contains 4 tracking regulators and one superfilter, which will generate the supplies for most of the IC as well as the front end and the main VCO. The tracking regulators derive their internal power from the REG_REF pins. The reference voltages are filtered and buffered for use on the IC. The buffered voltages should track the references within +/-1.5%. A raw supply voltage is provided to the tracking regulators which is higher than REG_REF as specified below for each regulator. A superfilter is needed for the external VCO power supply. This superfilter, cascaded with an external regulator and any filtering in front of the IC, will need to provide 80dB of rejection to a 0.1V step occurring at a 217Hz rate with a risetime of 20us on the raw supply (battery) and a duty cycle of 0.125. The superfilter will use an internal pass transistor that is capable of driving a 30 mA load with a voltage drop of less than 0.4V relative to SF_SPLY from the SF_OUT pin. An external 1uf cap is required on SF_OUT. As the superfilter will track SF_SPLY it will need to sense the power on reset and turn off even though its supply may remain active. All supplies within the IC must be within 5% of their final values after 5msec from the start of POR_LB. The power on reset circuit contained within the crystal reference oscillator is used to aid this functionality. The MAGIC_LV has two sets of SPI interfaces; one set is for handling the control interface for the LIFE IC (AUXSPI lines) and ones for interfacing with POG (SPI lines). AUX_SPI_DX is the serial data input line. AUX_SPI_CLK is the clock input line, where data shifting occurs at the rising edge of this signal. LIFE_CE is the clock enable line, active high, for the LIFE IC. MAGIC_LV will integrate a system of D/As and control logic to generate the power amplifier control ramps. In addition, MAGIC_LV will integrate the op-amps and comparators which receive the detected output of the power amplifier and create the necessary control voltage to drive the power amplifier control port based on the control ramps. When TX_KEYM goes high, the ramp controller receives an positive input. This will cause the AOC_DRIVE pin to linearly rise which in turn will cause the PA output power to rise. The rising PA output power will cause DET_AOC to begin to rise until the DC level on DET_AOC exceeds the DC level on DET_REF by the intentional offset of the RF detector versus it‘s reference. At this point the “Active Detect” comparator will go low and break the input voltage to the integrator with the ramp controller. This will cause the PA power to stop rising and hold the present power level as determined by the 8 bit offset value fed to the ramp controller. The PA control loop is now at a minimal power needed to keep the control system in a closed loop for a controlled ramp up of the power. The MAGIC uses two SPI driven GPO lines which are used to control the operating bands of the GSM RF circuits. They are N_BAND_0 and N_BAND_1. When the MAGIC LV is set to battery save mode it will shutdown the receiver analog sectioins (via RX_EN_LIFE), the AOC, the main synthesizer and the superfilter. A920: Magic LV (Control) C521 VRF_V3_1_875V TP500 C536 TP502 RF_V4_1_875V page XX U510 C546 MAGIC_SF C538 page XX page XX C537 U7704,C603 MAGIC_REG_REF_1_875V C522 C514 page XX VRF_REF_2_475V C523 page XX C506 E3552 Q510 R511 C560 R508 VRF_DIG_1_875V VRF_REF_1_875V_OUT LIFE_CE E528 C3250 page XX U600 C516 page XX MAGIC_REG_REF_1_875V C510 U630 L3560 page XX U510 C521 page XX C514 C517 VRF_V3_1_875V VRF_REF_2_475V C506 page XX E3552 page XX RF_V4_1_875V C522 page XX C546 C520 Motorola Confidential Proprietary VLIFE VRF_RX_2_775V C524 MAGIC LV E3951 page XX page XX C539 U500 C542 page XX R3251 page XX MAGIC_DIG_1_875V VRF_REF_2_475V E3552 page XX TP504 C545 C543 FL510 E529 NB_SPI_CLK page XX C511 U1000 TP501 C544 C540 E976 E975 C534 C542 AUX_SPI_CLK page XX 4-9 U1000 page XX E977 R537 R536 C525 NB_SPI_MOSI MAGIC_CS U600 U1000 page XX 4-10 A920: MAGIC LV (Synthesizers/Transmitter) RX_VCO PRSC TX_VCO_PRSC Mod_sel TX VCO CP_TX Ø 3 Acc FN Seq Gen RX_VTUNE LIFE Σ GSM Look-up Table TXCLK GSM Pre-Distort TX Data Interface DMCS_MAGIC SDTX BFSX Y500 POG AMPS Interpolator Motorola Confidential Proprietary CLK_SEL BB_CLK_13M Description MAGIC LV U500 (Synthesizer Section) 3 Acc FN Seq Gen Σ FL510 Ø PLL_CP The MAGIC_LV receives SSI Tx data at DMCS (digital input to start Tx modulation), TXCLK (clock for serial transfer) and SDTX ( serial Tx data) from POG. The present serial data bit and the three previous data bits are used to set up one of 16 possible waveforms based on the sum of Gaussian pulses stored in a look up ROM. The resulting signal will then be clocked out at a 16x over-sampling rate. This data pattern input to three-accumumalator fractional N synthesizer with a 24-bit resolution. The VCO control lines must have compliance over an output voltage range of 0.3VDC to Vcc-0.3V. The charge pumps will have their own supply pin. The voltage on this pin is expected to be 2.775V typically to obtain sufficient compliance. This will drive external loop filters, which will in turn drive external VCOs. A dual port modulation mode is obtained with a 9 bit D/A which follows the modulation look up table output waveform is output on the GPO3 pin.This signal is then coupled into the loop filter to add in the higher frequency components of the modulation which may have been attenuated in the main PLL path. This will allow the use of a lower bandwidth main PLL to improve the spectral purity of the transmit signal.For EGSM the synthesizer output is 880 - 915MHz, DCS is 1710 - 1785MHz with GMSK modulation and is directly amplified to the transmitter output. The prescaler for the main LO is able to accept input frequencies as high as 2.0GHz. The level of this signal shall be between -20dbm and -10dbm. There are two prescaler inputs to this point each has a 100W resistor in series between the pin and the actual prescaler input. The reference oscillator is a free running 26MHz crystal. AFC is provided through the SPI bus as a programming offset to the fractional N division system. Since the 26MHz crystal is not locked to the AFC, a second fractional divider system is necessary to derive an accurate 200KHz system reference. This reference is then multiplied in a PLL to 13MHz for use as an accurate clock to the logic sections of the transceiver. A920: Magic LV (Synthesizer/Transmitter) VRF_RX_2_775V page XX VRF_HV_5V page XX NB_TX_KEYM C509 page XX R508 R556 BFSX E528 C556 R506 page XX C554 R554 R526 C526 Q510 U500 C528 DMCS_MAGIC C510 C514 page XX U600 page XX U1000 U1000 page XX C517 TX_CLK C546 SDTX U1000 page XX U1000 page XX VRF_REF_2_475V E3552 page XX TP504 C534 C542 E975 Y500 page XX C540 FL510 R537 Legend 4-11 Sig Gen: -20dBm Ref. Freq: VCO: U630 page XX VRF_RX_2_775V page XX VLIFE C525 L3560 U1000 page XX C524 MAGIC LV C527 MAGIC_DIG_1_875V C539 PLLBASE R807 AOC_DRIVE VCORNG Motorola Confidential Proprietary C555 PLLEMIT DET_AOC page XX PLLCP R810 RX_VCO C516 PRSCINT C521 U710 C502 C520 E3601 C507 C535 L3560 R536 BB_CLK_13M U1000 page XX CLK_SEL U1000 page XX 4-12 A920: GSM TX VCO RF_TOP Section GSM_EXC_EN N_GSM_EXC_EN NB_TX_EN POG U700 TXVCO Q700 Decoder N_BAND_0 GSM VCO N_BAND_1 GMSK Look-up Table 9 bit Dual Port D/A Mux Delay FN CP_TX Loop Filter TX_VCO_HB Tank Ckt GPO3 Motorola Confidential Proprietary TX_VCO_PRSC SF_OUT Pre-dist Sys TX_VCO_LB DCS/PCS VCO MAGIC LV Description The VCO frequencies are 897 - 1880MHz, handling the three technology bands. The technology bands are controlled by MAGIC_LV via the data lines: N_BAND_0 and N_BAND_1. CP_TX and GPO3 provides a dual port modulation mode for the TXVCO. N_BAND_0 and N_BAND_1 will select which VCO band will be activated. GSM_EXC_EN and N_GSM_EXC_EN will enable the buffer stage of U570. TX_EN is activated prior to enabling the buffer and PA. TX_VCO_PRSC is fed back to the MAGICLV for proper PLL operation. The output frequency for GSM is TX_VCO_LB and PCS / DCS is TX_VCO_HB. The charge pump output (CPTX) from MAGIC_LV is the input (VT) for the VCO. A920: GSM TX VCO N_BAND_0 N_BAND_1 U500 page XX U500 page XX N_GSM_EXC_EN L701 U1000 C700 C712 MAGIC_SF C711 C708 C701 page XX C706 TX_VCO_LB U800 page XX R700 GSM TX VCO C703 Q700 NB_TX_EN page XX C537 U700 R703 TX_VCO_HB C707 C702 page XX C713 C701 R704 CPTX page XX C5576 U500 C710 Q902 U710 L710 GPO3 page XX R705 Motorola Confidential Proprietary U500 C704 R577 R576 C705 L703 PRSCINT C509 page XX page XX GSM_EXC_EN Q902 page XX Legend Sig Gen: TX: -20dBm 4-13 4-14 A920: GSM PA LV_EXC_EN PA_BATT+ TX_VCO_LB TX_VCO TX_VCO_HB AOC_DRIVE U810 U800 FL020 DCS_PCS_TX RF TOP GSM_TX N_BAND_0 MAGIC LV DET_AOC Motorola Confidential Proprietary DET_REF Description U800 is a tri-band PA module that operates in EGSM, DCS and PCS bands. The nominal expected maximum gain is ~30dB. . The AOC_DRIVE input from MAGIC_LV controls the PA output. The voltage applied at the pin is proportionally related to the output power of the PA, as the voltage increases the gain or power level increases. N_BAND_0 is used to select the operating band. LV_EXC_EN will enable PA operation. The power detector receives the amplified GSM signal at #1 (EGSM_IN), PCS and DCS at pin #12 (DCS_PCS_IN) from the U800. U810 is a dual combination directional coupler and temperature compensated power detector output. The power detector couples the Tx power input and feedbacks an output DET_AOC to MAGIC_LV. A comparator within the MAGIC LV will sample DET_AOC and based on the power amplifier ramps will provide any necessary control voltage adjustments to AOC_DRIVE The DET_REF is a reference voltage to MAGIC_LV. Expected nominal loss is <. 3dB. A920: GSM TX FL001 page XX R814 FL020 R816 C812 R812 DET_AOC L810 C810 R813 GSM_TX LV_EXC_EN FL001 page XX Q902 page XX C805 C800 R810 R815 page XX L832 U500 U810 N_BAND_0 C832 C806 C801 page XX C708 page XX TX_VCO_HB C804 J5400 page XX C802 TX_VCO_LB -20dBm U700 page XX R701 Legend Sig Gen: TX: GSM PA PA_BATT+ C808 AOC_DRIVE R807 R554 U800 VR800 U700 page XX C803 R822 L821 Motorola Confidential Proprietary C830 L825 DCS_PCS_TX 4-15 4-16 A920: WCDMA RX Downconverter (MAX2388) WCDMA RF_LO VCO FL310 U310 FL320 CDMAPOS CDMANEG WCDMA_RX MAX2309 FL300 Motorola Confidential Proprietary MAX2388_SHDN* RX_RF_ATTEN Harmony Lite Description The first IC in the WCDMA Rx line up is U310 (MAX2388), which is an LNA and down converter mixer combination. The RX frequency will be mixed down to an IF frequency of 190MHz. The MAX2388 also has a shutdown mode to power down the IC, via MAX2388_SHDN*, during the front-end receiver‘s idling period to conserve battery life. U310 operates from the PCAP supply voltage RC_VCCA (derived from VRF_RX_2_775V). The nominal gain expect is ~15dB. U310 operates in high gain mode selectable from RX_RF_ATTEN by the HARMONY_LITE . The nominal gain expected while in this mode is 15dB. During high input signal levels the LNA will be off. The receive mixer is a wideband, single-balanced design. The input RF_LO (pin #5) receives the VCO frequency (2330 - 2360MHz) through FL310 from U140 (VCO). The RF input (LNA_IN, pin #10) receives the RX frequency (2110 - 2170MHz) from FL002. The MIX_IN (pin #3) input is connected to LNAOUT (pin #1) through FL300. The function of FL300 is to provide image rejection and out-of-band interferers filtering. The frequency conversion process performed by the mixer / oscillator combination sometimes will allow a frequency other than desired frequency to be fed into the IF and subsequently amplified. The IF mixer output (190MHz) appears on the differential IFPOS (pin #8) and IFNEG (pin #7). These open-collector outputs require an external inductor (L320 & L321) to VCC for DC biasing. The 190MHz IF frequency passes through FL320. The IF SAW filter has a nominal center frequency of 190MHz and a bandwidth of 3.84MHz. Between the input match (C323, C324 & L322), output match (L327, L328, C328, C329, & C325) and the filter (FL320)- the expected nominal losses is ~10dB. C305 U101 RF_RX_ATTEN R305 MAX2388_SHDN R304 page XX U101 page XX R361 RX_VCCA RX_LO page XX C326 C319 WCDMA_RX FL310 C321 RX_VCCA C325 R320 L321 CDMA_IFX C323 C324 R361 page XX page XX FL320 FL010 page XX L320 page XX FL150 U310 C317 L316 R319 L315 Motorola Confidential Proprietary FL300 L303 C303 C302 C313 C304 C307 C314 C310 page XX C315 R301 R315 RX_VCCA R321 R361 L314 C316 A920: WCDMA RX Front End CDMA_IF page XX Legend 4-17 Sig Gen: RX: VCO: -20dBm 4-18 A920: WCDMA RX Demodulator (MAX2309) Harmony Lite ASPI_CLK ASPI_DATA MAX2309_CS RX_I+ RX_I- SPI Interface CDMAPOS MAX2388 RX_STBY* CDMANEG 90° ÷2 AGC Harmony Lite Motorola Confidential Proprietary Description REF_FREQ Bias MAX2309_SHDN* RX_Q+ RX_Q- ÷R Ø Harmony Lite ÷M MAX2309_LOCK Loop Filter Tank Ckt The MAX2309 is an IF quadrature demodulator with the signal paths consisting of a variable-gain amplifier (VGA) and an I/Q demodulator. The IF LO synthesizer‘s reference and RF dividers are fully programmable through the 3-wire serial bus (ASPI_CLK, aSPI_DATA, MAX2309_CS). The 190MHz IF is demodulated to BaseBand differential in phase (I+ / I-) and quadrature (Q+ / Q-) signals to be passed through to the receiver’s backend IC, HARMONY LITE. The IC operates from a pair of supply voltages RX_VCCD & RX_VCCA derived from VRF_RX_2_775V. The MAX2309 VCO output frequency is controlled by an internal phase lock loop (PLL) synthesizer. The external loop filter consists of the components connected to pins #1 and #2 (& pin #26). The VCO output frequency (Tank+ / Tank-) at pins #1and pin #2 are divided down internally, to a desired comparison frequency. The reference signal at pin #7 (REF_15.36MHz) is also divided down to the same comparison frequency. The two divided signals are compared with a three state digital phase detector. The internal phase detector drives the charge pump as well as the lock-detect logic. The charge pump output at pin #26(CP_OUT) is processed by the external loop filter and drives the tunable resonant network, altering the VCO frequency (380MHz) and closing the loop. The AGC ensures that the I/Q inputs to HARMONY LITE are at constant signal level. The IF_AGC line is controlled by HARMONY_LITE with a DC control range of 1.2V to 2.1V. The MAX2309 has a shutdown mode to power down the IC, via MAX2309_SHDN*, during the front-end receiver‘s idling period to conserve battery life. RX_STBY* is used to shut down VGA and demodulator while maintaining the VCO, PLL, and serial interface active. A920: WCDMA RX MAX2309 VRF_RX_2_775V TP340 page XX C361 L3560 R361 RX_VCCA R344,R315 page XX page XX U101 RX_I- U101 RX_QRX_Q+ page XX ASPI_CLK U101 E111 page XX E109 page XX E110 page XX U101 R336 R337 RX_VCCD C349 C330 R331 CR331 R348 R341 C331 R330 C340 Max RX C348 R361 C344 U330 ASPI_DATA page XX R360 R338 RX_VCCA page XX MAX2309_CS MAX2309_LOCK R344 R335 page XX page XX L330 C342 R342 R325 U101 RX_I+ C334 RX_STBY* C326 C327 U101 MAX2309_SHDN R339 C332 R349 REF_FREQ page XX C335 C338 U101 C333 RX_VCCA R347 R346 Motorola Confidential Proprietary R361 page XX R332 CR330 page XX page XX U101 page XX FL320 page XX L325 page XX L3560 RX_VCCD VRF_RX_2_775V page XX 4-19 U101 page XX AGC R360 C360 R348 page XX L324 C325 FL320 page XX Legend Sig Gen: RX: VCO: -20dBm A920: Harmony Lite (RX Section) C113 C114 R152 C157 C156 Q130 C112 C116 C118 C115 T100 RX_SF_BYP E3951 U1000 pageXX U1000 BBIF_RX_DATA(9:0) BBIF_RX_FRAME BBIF_CLK RX_VCC C106 RX_VB2 VRF_RX_2_775V RX_VAG E100 R3560 C107 VHVIO_2_775V LVDD C121 R3560 pageXX ASPI_CLK E111 VRF_DIG_1_875V pageXX C101 RX_VREF Harmony Lite IOVDD_1 pageXX U101 DIG_VDD U330 RX_I+ RX_IRX_Q+ RX_Q- RX_CP_VCC C123 C119 pageXX RX_SF_VCC C102 RX_VREFP C104 R432 R431 C117 L3560 VRF_RX_2_775V C122 Motorola Confidential Proprietary C103 RX_VREFM E110 ASPI_DATA E109 MAX2309_CS E108 MAX2361_CS U330,U200 pageXX pageXX U330,U200 pageXX pageXX U330 pageXX U200 pageXX C120 pageXX TP120 TP119 TP118 TP117 Legend Sig Gen: TX: VCO: -20dBm 4-21 A920: Harmony Lite (RX Section) C113 C114 R152 C157 C156 Q130 C112 C116 C118 C115 T100 RX_SF_BYP E3951 U1000 pageXX U1000 BBIF_RX_DATA(9:0) BBIF_RX_FRAME BBIF_CLK RX_VCC C106 RX_VB2 VRF_RX_2_775V RX_VAG E100 R3560 C107 VHVIO_2_775V LVDD C121 R3560 pageXX ASPI_CLK E111 VRF_DIG_1_875V pageXX C101 RX_VREF Harmony Lite IOVDD_1 pageXX U101 DIG_VDD U330 RX_I+ RX_IRX_Q+ RX_Q- RX_CP_VCC C123 C119 pageXX RX_SF_VCC C102 RX_VREFP C104 R432 R431 C117 L3560 VRF_RX_2_775V C122 Motorola Confidential Proprietary C103 RX_VREFM E110 ASPI_DATA E109 MAX2309_CS E108 MAX2361_CS U330,U200 pageXX pageXX U330,U200 pageXX pageXX U330 pageXX U200 pageXX C120 pageXX TP120 TP119 TP118 TP117 Legend Sig Gen: TX: VCO: -20dBm 4-21 4-22 A920: Harmony Lite (Control Section) Harmony Lite(U101)-Logic Section WB_TX_RAMP 2361LOCK 2361_SHDN TX_STBY* 2361_CS* HL_TX_EN V_DETECTOR WCDMA TX GPI_1 RF_RESET* SMO_15 SMO_21 WCSP PORB WB_ASPI_CE_2 SPI_CE HARMONY_CS SMO_9 SPI_DATA_IN WB_SPI_MOSI SMO_23 SPI_DATA_OUT VGC1 VGC2 VLOAD_SW PABIAS1 SPI/ Sequence Manager WB_SPI_MISO POG WB_SPI_CLK WB_RX_ON WB_RX_SLOT WB_RX_ACQ PABIAS2 WB_TX_PRE_KEY TEMP_COMP WB_TX_SLOT MUX AOC_PWR_UP_DOWN ASPI_DATA ASPI_CLK SMO_5 MAX2388_SHDN SMO_3 WCDMA RX SMO_7 Motorola Confidential Proprietary RF_DETECT MAX2309_LOCK MAX2309_SHDN Description RX_STBY* MAX2309_CS There are several functions that the sequence manager is controlling. 1. Sequence manager outputs to external devices 2. On/Off control of clocks, battery save signals etc… 3. Clock frequency selection for correction paths 4. DCOC register selection coarse, medium and fine modes The HARMONY LITE has two sets of SPI interfaces; one set is for handling the control interface for the transceiver (AUXSPI lines) and ones for interfacing with POG (SPI lines). Further, all SPI interface is generated from POG and written to HARMONY_LITE or parsed through to the MAXIM (U200 & U310) parts. Layer one timing signals control the functionality of the RF section of the transceiver relative to the air interface. There are three signals defined on each transmit and receive section of the transceiver. TX_PRE_KEY and RX_ON are asserted before the need to receive or transmit in order to launch the necessary sequence of events to warm up the required functional blocks. TX_RAMP and RX_AQUIRE are asserted when actual transmission and reception are to begin. RX_SLOT and TX_SLOT are used during continuous transmission and reception to trigger events that must be aligned with slot boundaries. It‘s important to reiterate, the TX_RAMP directly corresponds to the PA turning on and RX_AQUIRE corresponds to data being sent to the WCSP. A920: Harmony Lite (Control Section) Motorola Confidential Proprietary R341 page XX R232 page XX R231 page XX R450 page XX R270 page XX R410 page XX Q420 page XX R455 page XX R454 page XX R339 page XX R342 page XX R304 page XX U420 page XX R347 page XX R203 C113 C112 C114 R152 C115 HARMONY_CS T100 AGC WB_RX_ON MAX2361_SHDN C102 TX_STBY* U101 VGC1 VGC2 VLOAD_SW C101 C106 TEMP_COMP MAX2309_SHDN WB_RX_ACQ RF_RESET* WB_TX_PREKEY ASPI_CLK ASPI_DATA MAX2388_SHDN E109 MAX2309_CS PA_ENABLE E108 MAX2361_CS MAX2309_LOCK page XX TP118 TP117 WB_TX_RAMP AOC_PWR_UP_DOWN Sig Gen: TX: VCO: U1000 U330,U200 page XX page XX U330,U200 page XX page XX U330 page XX U200 page XX C120 TP120 TP119 Legend U1000 page XX E110 C121 U1000 page XX RX_STBY* MAX2361_LOCK U1000 page XX page XX WB_TX_SLOT E111 U1000 page XX E100 Harmony Lite RF_DETECT U1000 page XX WB_RX_SLOT V_DETECTOR U1000 page XX C103 C104 page XX RX_RF_ATTEN C107 R305 C116 C118 C157 page XX SPI_CE SPI_DATA_IN SPI_DATA_OUT SPI_CLK C156 U1000 U1000 page XX U1000 page XX -20dBm 4-23 4-24 A920: Harmony Lite (Synthesizer Section) BLUETOOTH U5600 Harmony Lite U101 BLUE_CLK_EN* U5670 HELEN CODEC_CLK_EN* (Synthesizer Section) 15.36M_CLK_EN* T100 WCDMA TX_LO TX Motorola Confidential Proprietary POG Prescaler TCXO_EN_OUT SPI/ Sequence Manager A/N Counters Q130 REF_OSC_15_36M AFCDAC BLUETOOTH U5600 Y130 FL150 WCDMA RX_LO RX TCXO_EN_IN VRF_RX_2_775V U150 U140 Charge Pump Ø /R REF_OSC_IN Super filter BB_CLK_15.36M REF_H_A WCDMA TX CLK GEN ÷1,2,4,16,32 CLOCK_OUT REF_FREQ WCDMA RX Description The clock source for the Harmony Lite (HLite) is a 15.36Mhz oscillator (TCXO). Y130 is used to generated the 15.36MHz clock source. AFC for Y130 is controlled by the Harmony Lite sequence manager via the AFCDAC line. The 15.36MHz clock source is enabled by an internal SPI bit and external control signal coming from 15.36M_CLK_EN*). The 15.36MHz clock source provides clocks to all A/Ds, DACs, external references and internal digital circuits of the Harmony Lite. In addition, clock references are generated for the POG, RX and TX RF circuits. The WCDMA VCO(U140) has a frequency range of 2.3G thru 2.36GHz, supplying both the receiver and transmitter with an LO. The control range is controlled by HARMONY_LITE with a control range between 0.5 - 2.5V, with an output power @ ~-3 - 3dBm. The WCDMA VCO output frequency is controlled by an internal phase lock loop (PLL) synthesizer. The phase locked loops use a fractional loop divider to permit fast lock times and low phase noise on their output signals. The VCO output frequency is fed into a prescalar and devided down into a desired comparison frequency. The 15.36MHz reference frequency is also divided down into a comparison frequency. The two divided frequencies are then compared with a phase detector. The phase detector will then drive the charge pump. The charge pump output is processed by the external loop filter and drives the tunable resonant network, altering the VCO frequency and closing the loop. The superfilter block is used to provide a filtered supply voltage to the WCDMA VCO. A920: Harmony Lite (Synthesizer Section) RX_PRE C113 C112 C114 R152 Q130 C157 page XX C118 C156 L3560 VRF_RX_2_775V C145 page XX C116 C115 TXCO_EN_OUT RX_CP U101 C117 C102 C101 BB_CLK_15_36M U1000 page XX C104 AFCDAC U140 page XX C106 Harmony Lite R141 page XX RX_SF_OUT REF_OSC_IN R431 C103 C119 Motorola Confidential Proprietary R432 T100 15_36M_CLK_EN* REF_FREQ U1000 page XX C335,R133 page XX page XX RAW_15_36 C5671 page XX R132 REF_OSC_15_36M R130 U130 C133 R134 C130 C131 R131 C132 Y130 U7705 page XX C134 Legend Sig Gen: -20dBm Ref Freq: VCO: 4-25 4-26 A920: Harmony Lite (TX Section) HARMONY LITE U101 (TX section) Mux FIR 10 bits TX_I+ TX_IWCDMA TX PN Seq Gen. Demux S/H Tracking Loop Motorola Confidential Proprietary 10 bits TX_Q+ TX_Q- I/Q Phase and Gain Equal Demux DCOC FIR BBIF_TX (9:0) POG U1000 BBIF_TX_FRAME BBIF_CLK S/H Description The BBIF(BBIF_TX) is the transmit data path for transferring digitally sampled I / Q data from the POG. The demultiplexing unit performs the I/Q deinterleaving function to supply separate I and Q channel data into the transmit FIR filters. The FIR filter design is used to meet 3GPP spec requirements of simultaneous transmission of a pilot channel and of multiple data channels each requiring a different spreading code and each requiring separate power control. The PN sequence generator provides I/Q interleaved 8-bit PN data into the demultiplexing section. The DC correction(DCOC) block is able to correct for DC offsets due to the D/A‘s, anti-aliasing filters, and transmit FIR filters in a feedback control loop. A mixed mode control loop located at the output of the transmit FIR filter is employed to correct DC offsets and I/Q gain imbalances, i.e. DCOC and I/Q Phase and Gain equalizer. The outputs of the I/Q gain equalization unit is fed into 10-bit I and Q DAC‘s. The programmable gain antialiasing filters, or TX smoothing filters, accepts differential I/Q signals of DC to 1.92MHz frequency components from the D/A Converters to attenuate the unwanted clock signals of 15.36MHz and to smooth the signals for the TX modulator(MAX2363). The output of the TX smoothing filters are then fed into a multiplexed 6-bit A/D with sample/hold scheme. This gives the information of the amplitude and the DC common mode voltage from the I / Q Tx filter outputs by a single Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) as the part of digital correction loop. The differential TX I and TX Q signal are finally fed into the TX modulator(MAX2363). A920: Harmony Lite (Transmitter Section) C116 C113 C112 C114 R152 Q130 C157 C156 C118 C115 T100 C119 page XX TX_I+ TX_ITX_Q+ TX_Q- U200 page XX U1000 page XX U1000 AOC_VCC TX_VCC TX_VAG C106 E100 Harmony Lite E111 E110 E109 BBIF_TX_DATA(9:0) TX_FRAME BBIF_CLK TX_VREFP TX_VREF U101 C101 C107 C123 VRF_TX_2_775V C102 C104 C117 HL_TX_EN page XX E3503 TX_VREFM R432 R431 PA_BIAS1 page XX FL001 C103 C122 Motorola Confidential Proprietary U420 page XX U420 PA_BIAS2 E108 C121 C120 page XX TP120 TP119 TP118 TP117 Legend Sig Gen: TX: VCO: -20dBm 4-27 A920: WCDMA VCO RX_LO U101 T100 RX_SF_OUT R150 C150 R147 L153 U140 R146 C148 C151 C146 C282 U150 C145 C140 TX_LO FL150 C142 R140 U101 RX_CP C141 Motorola Confidential Proprietary R141 FL310 R151 L150 RX_SF_OUT RX_PRE Legend 4-29 Sig Gen: VCO: -20dBm U101 4-28 A920: TX Modulator (MAX2363) TX_LO FL150 2361_LOCK TX_STBY* 2361_SHDN IF SAW FL201 2361_CS ASPI_CLK ASPI_DATA 380 MHz TX_I+ TX_I- TX SAW FL401 Σ /2 ¸2 TX_Q+ TX_Q- 1920-1980MHz Motorola Confidential Proprietary MAX2363 U200 IF Gain SPI Harmony Lite U101 Offset IF PLL Synthesizer 760 MHz REF_FREQ Description VGC1 The in phase (I) and quadrature phase (Q) inputs are received at pins #23 (Q+), #24(Q-), #25(I+), & #26(I-) of U200. The expected DC bias levels are 1.30V - 1.40V with a minimum 300mVpp signal upon the DC level. The MAX2363 receives the differential I/Q BaseBand input and converts it up to the IF frequency of 380MHz through a quadrature modulator and IF variable gain amplifier (VGA). The IFINH+ (pin #10) and IFINH- (pin #11) input are connected through off-chip FL201 from IFOUT+ (pin #17) and IFOUT- (pin #16), respectively. The function of FL201 is to provide image rejection and out-of-band interferers filtering. The frequency conversion process performed by the mixer / oscillator combination sometimes will allow a frequency other than desired frequency to be fed into the IF and subsequently amplified. The SAW filter (FL201) has a nominal center frequency of 380MHz and an insertion loss of ~ 3.5dB with a total bandwidth of 5MHz. The IF and RF VGA (VGC1) are common and allow for varying the IF / RF output level . HARMONY_LITE controls the VGC signal with a range of ~1.3 - 2.6V and provides gain a control range of ~75dB. The MAX2363 VCO output frequency is controlled by an internal phase lock loop (PLL) synthesizer. The external loop filter consists of the components connected to pins #33 and #32 (& pin #38). The VCO output frequency (TankH+ / TankH-) at pin #33and pin #32 are divided down internally, to a desired comparison frequency. The reference signal at pin #36 (REF_FREQ) is also divided down to the same comparison frequency. The two divided signals are then compared with a three state digital phase detector. The internal phase detector drives the charge pump as well as the lock-detect logic(2361_LOCK). The charge pump output (IFCP, pin # 38) is processed by the external loop filter and drives the tunable resonant network, altering the VCO frequency (760MHz) and closing the loop. The differential IF output at pins #17 & #16 (IFOUTH+ / IFOUTH-) support high IF operation of frequency of 380MHz. The signal is routed to an off-chip IF SAW filter (FL201) and up-mixed to RF through an image reject mixer and RF VGA. The signal is further amplified with an on-chip PA driver. The RF signal is then routed to an interstage RF SAW filter (FL401). The IF synthesizer (760 MHz VCO) and local oscillator (RF_LO) buffer are both programmable through the 3-wire bus. The sequence manager from HARMONY_LITE programs standby mode(TX_STBY*) and shutdown mode(2361_SHDN). This IC operates from a pair of supply voltages VCC_DIG (isolated supply for IF_CP and 760 VCO) & VCC_ANA derived from VRF_TX_2_775V. A920: WCDMA TX Modulator VGC1 U101 R290 C296 VCC_ANA page XX U101 U101 page XX 4-31 page XX U101 page XX TX_QTX_I+ TX_I- R250 R252 C205 TX_Q+ C298 C299 C244 L243 C223 R205 C221 R213 MAX2361_SHDN page XX U101 R295 C295 VCC_DIG R232 U101 R203 MAX2361_LOCK FL410 L297 page XX R293 C293 U101 VCC_DIG L297 page XX C294 R294 CR200 L297 page XX VCC_DIG C280 R296 page XX page XX page XX MAX TX C290 L298 C292 U200 R270 C270 page XX page XX L298 L280 page XX R200 C282 MAX2361_CS E108 page XX page XX L297 L281 page XX MAX2393_OUT page XX R200,R293 L200 R201 ASPI_DATA C200 VCC_DIG C260 C261 REF_FREQ R133 E110 ASPI_CLK VCC_ANA E3503 page XX REF_FREQ L297 page XX U6003 page XX U101 page XX C222 R215 E111 page XX TX_STBY* C291 L223 page XX R231 CR201 U101 R240 L240 VCC_DIG C297 R291 R292 VRF_TX_2_775V VCC_DIG C201 L241 L297 L201 VCC_ANA page XX L201,R296 page XX page XX R230 C245 C241 Motorola Confidential Proprietary L298 FL201 C243 C242 L242 VCC_ANA L298 C215 C216 Legend Sig Gen: TX: VCO: -20dBm 4-30 A920: WCDMA PA PCAP U3000 RF TOP TEMP_SENSE Temp Sens U440 WCDMA_TX Isolator FL460 Coupler / RF Detector U450 PA U420 PA_ENABLE Variable Attenuator U410 MAX2363 U200 VGC2 Harmony Lite U101 PA BIAS1 PA BIAS2 Motorola Confidential Proprietary VRF_TX_2.775V VLOAD_SW VLD Q401 V_DETECTOR RF_ DETECT Description TEMP_COMP The U410 provides necessary attenuation of the TX carrier before reaching the PA so that it doesn‘t exceed the maximum allowable input of 1dBm of the PA and to control the overall power output of the transceiver. U410 has a 16-18 dB of attenuation depending on the control voltage VGC2 applied at HYBOUT1 and HYBOUT2, which is controlled by Harmony Lite. U420 is a three-stage power amplifier handling the band of WCDMA Tx frequencies between 1920 - 1980MHz. The nominal expected maximum gain is ~30dB. HARMONY_LITE controls the RF biasing of the amplifier at pins #4 (PA_BIAS1) and #5 (PA_BIAS2) with a control range of 0 - 2.5v. HARMONY_LITE also controls pin #12 (VLD) for PA load switching. Although not implemented, the theory of PA load switching in WCDMA is vitally important to conserve battery life and to avoid unnecessary radio interference with base stations. When VLD is at a low state (0v), the transmitter is in high power mode, consuming higher current but with overall better PA performance. When VLD is at a high state, the transmitter is in low power mode, consuming less current with overall poor PA performance. In theory, as the Tx power level increases or decreases beyond a certain power threshold, VLD is enabled or disabled. As Tx power decreases (as requested from a base station) down to ~14.5dBm, VLD will switch high. If Tx power is requested to increase beyond ~19dBm, VLD is switched low. The power detector receives the amplified WCDMA RF signal at RF_IN (pin #6) from the PA. U450 is a combination directional coupler and temperature compensated power detector with a differential output. The power detector couples the TX power input and feedbacks an output RF_DETECT to HARMONY LITE. The TEMP_COMP also obtains the coupled power but removes the RF signal content, leaving a DC level. The DC level is feedback to HARMONY LITE. Expected nominal loss is <. 3dB. The isolator (FL460) provides isolation between Front-End Module (FEM) and transmitter path. Nominal insertion loss is ~ 0. 55dB. A920: WCDMA Transmitter U101 VLOAD_SW page XX VRF_TX_2_775V page XX PA_BATT+ E3503 J5400 U3000 C442 C443 R457 R451 R450 R454 R456 U450 TEMP_COMP C425 WCDMA_RF_OUT page XX U101 PA_ENABLE page XX R431 PA_BIAS1 page XX R432 PA_BIAS2 page XX Legend 4-33 Sig Gen: TX: U101 page XX U101 page XX U101 page XX FL460 page XX C451 C448 C441 RF_DETECT C452 R452 Q420 WCDMA PA V_DETECTOR U440 VRF_REF_2_775V R411 R455 C449 page XX R412 C410 U101 VGC2 U420 C444 U410 R420 C414 C413 FL410 C421 C422 C445 R453 C420 MAX2393_OUT R410 Motorola Confidential Proprietary C200 page XX C453 page XX -20dBm 4-32 A920: Charger CE Conn PCAP U3000 RAW_EXT_B+ EXT_B+ Q3963 R3961 Q3967 OV_SENSE PCAP U3000 OV_GATE ISENSE CHRGC Q3960 MIDRATE_1 Q3966 R5480 MAIN_FET Charger CR3960 BattSense CR3961 Motorola Confidential Proprietary CE Conn BATT+ Q3964 B+ BATT+ Batt Conn BATT_FDBK SPI AD6 BATT_THERM BATT_IO MUX POG Description The majority of the charging circuit is integrated in PCAP. This includes a digital to analog converter, analog to digital converter, battery feedback switch, thermistor switch/pullup, and current control sense. External FETs (Q3966 and Q3954) are provided to enable/disable EXT_B+ and BATTERY supply paths to radio circuitry (B+). An external sense resistor (R3961) and a charging FET (Q3960) are provided to control charging current between EXT_B+ and BATTERY. Due to pin count constraints on the CE bus, the Charger Identification input signal and Battery Feedback output signal share the same accessory connector pin. Software will first detect the Charger ID Voltage (AD6) before enabling the Battery Feedback Voltage via the Battery Feedback Switch in PCAP. The Battery Feedback switch must not be enabled at any time for an accessory that is not a valid Fast Charger. Battery Feedback Voltage provides a reference voltage to the external power supply during charging. The battery feedback switch is needed to remove the battery feedback voltage from the feedback loop of the AC/DC Adapter or VPA when charging is complete or after a fault has occurred. This switch will be enabled before the charger DAC is programmed when charging is to begin. Battery feedback will turn on before the charger is enabled. The charger will be turned off before battery feedback is disabled. A thermistor in the battery package is used to determine cell temperature of the battery pack before charging begins. The battery EPROM (BATT_IO) will contain limit parameters that determine the minimum and maximum temperatures at which charging can occur. PCAP has an integrated over-voltage detection circuit that provides protection against damage caused by external charger voltages exceeding 7.0Vdc. If an over-voltage condition occurs, the EXT_B+ FET (Q3963) will be disabled. This will prevent high voltage (>7Vdc) from being applied to radio circuitry (B+). Mid-rate charging is supported if a valid mid-rate charger and valid battery are detected. A mid-rate charger will source up to 400mA of current to the radio circuitry and charging circuitry during idle mode. The mid-rate charger will supply 5.9Vdc (up to 400mA) to the phone, regardless of the BATT_FDBK voltage. If the phone is in transmit mode, mid-rate current will be supplied to the battery and radio circuitry via the charging path only (EXT_B+ FET (Q3966) will be disabled via the MIDRATE_1 line). Dead battery TX operation or ‘No Battery’ operation is not supported with a mid-rate charger. 4-34 A920: Voltage Regulators B+ PCAP V2 V5 V9 VBOOST_LX VBUCK_LX V_VIB Vsim2 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Vaux3 Vaux4 LX2 HELEN B+ VBUCK_2_25V VBUCK2_1_6V U3910 VCAM_3V PCAP V6_ Drv B+ VUSB VUSB_3_3V V10 VRF_HV_5V Vaux1_ Drv V3 VLVIO_1_95V V4 VRF_REF_1_875V VRF_DIG_1_875V VBLUETH_1_875V VMEM_1_875V V7 V8 V1 B+ Vaux2_ Drv Vaux2 B+ VRF_TX_2_775V VRF_REF_2_775V Q3610 VRF_RX_2_775V U3220 Switcher Supply VOMAP_1_6V VHVIO_2_775V Q3502 Vaux1 Q3980 U3980 Q3403 V6 PCAP VBOOST_5_5V VHOLD_OUT Description CAM_SHUTDOWN VA_2_775V VGPS_RF_2_775V VRF_REF_2_475V V_VIB VSIMC VMMC VAUX4_3V VHOLD_EXT_EN B+ VMAIN_1_55V Q3220 Voltage regulation is provided by the PCAP IC (U3000). Multiple regulators are used to provide better isolation between sensitive load circuitry and noisy circuitry. The regulators and their load circuitry are described below: · VBOOST_LX(VBOOST_5_5V) - VUSB abd V10 input voltage regulator · VBUCK_LX(VBUCK_2_25V) - V1, V3, V4, V7, and V8 input voltage regulator · LX2(VBUCK2_1_6V) - Helen core · V_VIB - Vibrator · Vsim2(VSIMC) - SIM card interface · Vaux1(VRF_TX_2_775V) - RF TX circuits · Vaux2(VRF_RX_2_775V) - RF RX circuits · Vaux3(VMMC_2_8V) - SD/MMC interface · Vaux4(VAUX4_3V) - Image processor, USB xcvrs (Application processor and Bluetooth USB) · VUSB - PCAP USB xcvr · V1(VMEM_1_875V) - Application Processor Flash I/O, Application Procesor DRAM I/O, Baseband Processor Flash Core · V2(VA_2_775V) - Audio · V3(VLVIO_1_95V) - Magic LV I/O, WCSP · V4(VRF_REF_1_875V) - RF reference · V5(VGPS_RF_2_775V) - GPS RF · V6(VHVIO_2_775V) - HV I/O, Display(20), Imager(12), GPS Baseband(8), GPS Flash, Application Processor SDRAM core(200) · V7(VRF_DIG_1_875V) - RF digital · V8(VBLUETH_1_875V) - Bluetooth · V9(VRF_REF_2_475V) - RF Reference · V10(VRF_HV_5V) - RF HV 4-36 A920: RX Audio ST_CMP ST_REF R4395 Stereo Headset J4300 J7700 J7700 ALEFT_OUT Audio Filter Circuit ARIGHT_OUT PGA ARIGHT_IN Audio Filter Circuit SPKR+ A1 SPKR_IN SPKROUT1 Loudspeaker J4200 J4200 ALRT- LOUDSPEAKERLOUDSPEAKER+ Audio Filter Circuit ALRT+ L R SUM SPKR- EARSPKREARSPKR+ ALEFT_IN Audio Filter Circuit PGA AUD MUX Handset Speaker HS_SPKR_R FL4300 HS_SPKR_L 16-bit Stereo DAC 13-bit Phone DAC SSI2 SSI MMSAP_FS MMSAP_CLK MMSAP_TX POG SSI1 SSI ASAP_TX ASAP_RX ASAP_CLK ASAP_FS PCAP A2 ALRT_IN Motorola Confidential Proprietary SPKROUT2 AUDIO_OUT Description EXTOUT R5053 A4 ON2 Receive audio data is transferred from the POG to the PCAP through the ASAP interface for mono audio and the VSAP interface for stereo audio data. The data is then converted into an analog form through a 16-bit Stereo DAC or 13-bit phone DAC. The output of PCAP’s internal DAC drives the internal PGA. The output of the PGA can be routed to one of the four supported outputs via the internal multiplexer. All outputs use the same D/A converter so only one output can be active at one time. The user can adjust the gain of the audio outputs with the volume control buttons. The Handset Speaker is driven by PCAP’s internal SPKR differential amplifier. Following the speaker path from the PCAP pins SPKR- and SPKR+, they are routed through R4004 and R4005 respectively, and then connected to the transducer. Off the SPKR- path, SPKR_IN is routed through C4002 for the inverting input of the speaker amp A1. SPKR_OUT1 from PCAP is routed through C4000 and C4002 to SPKR- which is the DAC output of the CODEC. SPKR_IN and SPKR_OUT1 will output their respective bias voltages on these pins during standby times. This is to maintain the voltage across an external coupling capacitor to avoid audio “pops” when the amplifier is enabled. The headset uses a standard 2.5mm stereo phone jack. The phone will detect the presence of a stereo headset using HS_SPKR_L of the headset jack, which is pulled high by R4395 and connected to the ST_COMP of PCAP (this is an interrupt of PCAP which gets sent to MCU over the SPI bus). This pin will be pulled to a logic low whenever the stereo headset plug is inserted into the jack. The headset may contain a momentary switch, which is normally closed and is in series with the microphone cartridge. When the momentary switch is pressed, the bias current being supplied to the microphone will be interrupted. The phone will detect this action and make an appropriate response to this action, which could be to answer a call, end a call, or dial the last number from scratchpad. The Headset Speaker is driven by PCAP’s internal Left and Right amplifier. Following the speaker path from the PCAP pins ARight_Out and ALeft_Out, they are routed through C4356, R4352 and C4306, R4302 respectively, and then connected to the headset jack. Off the ARight _Out path, AR_IN is tapped off through C4354 for the inverting input of the audio amp ARIGHT. Off the ALeft_Out path, AL_IN is tapped off through C4304 for the inverting input of the audio amp ALEFT. The External Speaker is connected to pin 15 of J5000 (AUDIO_OUT), the accessory connector for the mobile phone. The audio path is routed through R4400 and C4400 and connected to EXTOUT of PCAP. The DC level of this Audio_Out signal is also used to externally command the phone to toggle it’s ON/OFF state. The Audio_Out signal connects to PCAP’s ON2 pin via R5053 to provide this capability. When a DC level of <0.4V is applied by an accessory for a minimum of 700 milliseconds on the Audio_Out line, the phone will toggle it’s ON/ OFF state. The Loadspeaker is driven by PCAP’s ALRT amplifier (A2). The alert path from the PCAP pins ALRT- and ALRT+ are routed directly to the alert transducer. Off the ALRTpath, ALRT_IN is routed through R4201 for the inverting input of the alert amp A2. SPKROUT2 from PCAP is routed through C4200 and R4200 to ALRT- which is the DAC output of the CODEC. A920: RX Audio C3850 R5053 C3650 U3000 PCAP R3055 C3555 C3851 R7654 Y3982 R3951 ST_CMP ST_REF EAR_SPKR+_PCAP page XX J4300 C4355 EAR_SPKR-_PCAP C4002 R4397 R4200 C4008 R4004 page XX C4304 C4390 R5050 C4402 R4400 C4000 C4200 C4202 R4201 C4503 C4501 C4500 C4110 VS4201 R4004 page XX R4393 R4395 HS_SPKR_L VS4200 C4400 J4300 FL4300 C4207 C4198 R4398 R4103 C4114 C4112 R4401 R4396 C4306 C4356 C4394 C4100 C4401 C4113 C4395 Q6051 C4160 U1000 U2000 U5600 C3983 Motorola Confidential Proprietary C3950 C3984 R3851 C5410 ASAP_TX ASAP_FS ASAP_CLK HS_SPKR_R R5052 C4203 STEREO_DETECT J4300 page XX LOUDSPEAKER- page XX LOUDSPEAKER+ J4200 AUDIO_OUT R5053 page XX Legend 4-39 Sig Gen: RX: -20dBm 4-38 A830: TX Audio LOGIC_SENSE EXT_MIC AUDIO_IN HS_MIC J4300 HS_MAKE_DETECT MIC GAIN MIC_OUT NC VAG A3 MIC_BIAS2 MIC AUX_OUT J4100 Audio Filter Circuit AUD MUX Audio Filter Circuit ADC PGA SSI ASAP_RX ASAP_FS ASAP_CLK POG AUX_MIC- Motorola Confidential Proprietary NC MIC_BIAS1 A5 PCAP Description The Internal Microphone is a single ended part. Following the Internal microphone path, the microphone is biased by R4103 to provide a MIC_BIAS of 2.0V from pin MIC_BIAS1 of PCAP. C4198 is connected to MIC_BIAS1 and MB_CAP1 pin on PCAP to bypass the gain from the VAG to MIC_BIAS1 which keeps the noise balanced. From there, the signal is routed through C4100 to AUX_OUT pin on PCAP, bypassing the input to the A5 amplifier. The headset microphone path (HS_MIC) is biased through R4396 and R4392, which is connected to pin MIC_BIAS2 on PCAP and bypassed with C4199 connected to pin MB_CAP2. From here the signal is routed through C4395 and R4388 to MIC_IN- pin on PCAP, which is the input to the A3 Amplifier. The Microphone path is tapped off after R4388 before the MIC_IN- input to R4389 connected to the MIC_OUT pin on PCAP, which is the output of the A3 Amplifier. The HS_MAKE_DET line monitors the presence of a headset by detecting the voltage at A1_INT of PCAP, which passes through R4398. A switching mechanism integrated in the headset jack will open or close the HS_MAKE_DET path to ground, depending on whether the headset is attached or not. The External Microphone input (AUDIO_IN) is connected to the accessory connector for the mobile phone. The path is routed through L4400, C4401 and R4401 to the EXT_MIC pin on PCAP. This signal feeds directly to the input multiplexer without an intervening gain stage. In addition to audio signals, AUDIO_IN supports detection of accessory devices. The accessory attached to the CE bus shall have an output impedance that will load LOGIC_SENSE to a predetermined level. The POG will read the input level of LOGIC_SENSE and configure the audio accordingly. The proper Microphone path is selected by the AUD MUX controller and path gain is programmable at the PGA. The A/D converter willl convert incoming analog signals into 13-bit, 2's compliment, linear PCM words. The digital audio signals are then transferred to the POG DSP through a four wire serial interface (ASAP). A920: Transmit Audio R5482 C4550 C5407 R5480 C5050 R5481 C3983 R4550 C3150 C4355 R4397 C4002 E3153 R4200 C4200 C4202 R4201 C4000 C4402 C4503 C4008 R5050 VS4201 C4401 FL4300 R4393 R4395 R4103 C4198 R4400 C4160 VS4200 C4400 C4112 C4100 C4207 R4398 page XX C4306 C4114 C4501 INT_MIC+ C4500 HS_MIC page XX J4100 Q6051 C4110 L4399 HS_MAKE_DETECT C4394 page XX U1000 U2000 U5600 C4551 C4395 R4306 HS_MAKE_DETECT* R5483 C4210 R4396 page XX R3951 R7654 Y3982 Q4300 C3950 R4401 page XX C3984 VA_2_775V C4113 Motorola Confidential Proprietary E3153 U3000 PCAP ASAP_RX ASAP_FS ASAP_CLK C4304 VA_2_775V C4390 C4203 E3153 page XX R5052 AUDIO_IN L4400 page XX Legend Sig Gen: TX: -20dBm 4-41 4-40 A920: PCAP Speaker Ckts Mic Ckts POG Helen Bluetooth POG Audio Amplifiers SSI Interface Control Logic SPI Interface Motorola Confidential Proprietary Multiplexer Charger Charger Control Helen CE Bus Display Baseband Circuits CODEC Logic Interface CE Bus Touch Screen Interface Overvoltage Protection USB RS232 Bus USB On-the-Go Logic Interface Switching Regulator Regulator Interface Backlight Control Backlight LED Drive Status LEDs Power Cut Power Fail Handling Helen Coin Cell Interface XTAL Stereo Detect Headset A/D U3000 RF Interface Linear Regulators Description The Platform Control Audio Power IC (PCAP), U3000, is a mixed signal IC that contains the following features: · Audio input/output amplification and filtering · Audio path selection · Voltage regulation · Battery charging control · Real time clock · Ringer/vibrator control · RS-232/USB drivers · Back-light control · Status LED control · Multiplexed DAC inputs for temperature and voltage monitoring · Dual SPI control interface to allow access from two independent baseband processors · Stereo DAC · Overvoltage protection · Touch Screen The PCAP IC is controlled and configured by the Baseband Processor IC through a four-wire SPI interface. The Baseband Processor has read/write access to the PCAP IC. Audio data is transmitted/received via the Baseband Processor through a four-wire SSI interface. 4-42 A920: POG Helen Keypad EL1T2 Magic LV (GSM) 1-wire Mux VSAP USB UART1 MQSPI2 Serial BBIF IPCM RISC MCU M341 UART2 MUX DSP Starcore IrDA CKIH UART3 EL1T1 EIM MUX Motorola Confidential Proprietary Harmony Lite (WCDMA) MDI cache MQSPI1 SDRAM WCSP 80kB eDRAM EBIF POG GQSPI 128Mbit FLASH 64Mbit SDRAM PCAP MMC JTAG ASAP GPS LCD Description Nexus GPIO SIM USIM Misc PCAP Codec The POG(baseband processor) integrates a 32-bit RISC Communications Engine (MCU), a 32-bit DSP Core and an Interprocessor Communications Module (IPCM) along with associated peripherals and co-processors. The following provides a brief description of the cores and associated peripherals being used in this design. ·MCU – Micro Controller ·DSP for GSM Signal processing ·EIM(external interface module) interfaces to FLASH and DRAM ·USB/Serial Communications ·GPIO - For A/Ds ·IPCM which provides a multichannel DMA between the Mcore, DSP and peripherals. ·WCSP Interface ·GQSPI - PCAP Interface ·EBIF(External Bus Interface) DMA – WCDMA Data Transportation ·MQSPI1(Qued Serial Peripheral Interface) – WCDMA Control Signals ·EL1T1(Enhance Layer Timer) – WCDMA Event timer ·CKIH - WCDMA 15.36MHz clock ·GPS Interface ·USIM interface ·ASAP interface for PCAP and Bluetooth audio interface ·Serial BBIF(Baseband Interface) – GSM Data Transportation ·MQSPI2(Qued Serial Peripheral Interface) – GSM Control Signals ·EL1T2(Enhance Layer Timer) – GSM Event timer ·CKIH - GSM 13MHz clock In addition to POG’s internal memory system, the architecture provides 128Mbits (16M byte) of external flash memory via two Intel Danali 64M bit parts. The memory bus is 23 address bits and 32 data bits. The flash memory runs at 42-45MHz. A920: POG Legend Ref Freq: E3203 VMAIN_1_55V page XX R1001 page XX POG_LVIO POG_LVIO U1000 page XX R1001 R1061 C1017 page XX C1001 C1020 R1000 page XX E3203 POG_HVIO R1000 C1002 POG_HVIO page XX U3000 page XX R1001 C1027 R3912 C1031 POG_LVIO page XX C1018 TP1021 TP1023 VHVIO_2_775V RESCUE_FLASH_EN POG_HVIO VMAIN_1_55V E3402 page XX U2000 page XX R1000 page XX E3203 page XX TP1024 C1030 AP_DEEP_SLEEP BP_READY RB_RI1 RB_DTR1 RB_DSR1 WIRE_SD0_EN* DCD1B_MUTE* BATT_FB_SWITCH C1003 HKSW_SEL C1012 U2000 page XX U2000 page XX C1007 POG C1033 MIDRATE_2 TP1022 U1000 C1026 VMAIN_1_55V page XX TP1026 C1008 C1150 POG_LVIO E3352 page XX U1150 TP1020 C1019 C1032 C1011 TP1027 Motorola Confidential Proprietary R1001 VLVIO_1_95V TP1025 page XX C1009 U130 RF_OSC_15_36M U1300,U1310 page XX C1021 page XX VLVIO_1_95V C1010 E3352 POG_RESET* BB_CLK_13M C1022 page XX U7705 C525 DATALOG* page XX U5005 page XX U5003 page XX U5004 page XX R2014 page XX U5001 page XX Q5000 page XX U5002 page XX U5004 R1001 4-45 page XX E3203 page XX POG_LVIO VMAIN_1_55V R1101 RF_RESET* U101 page XX C1015 R1103 C1006 C1016 C1005 C1028 C1029 C1034 POG_HVIO page XX C1000 page XX U1000 C1014 E3402 VHVIO_2_775V TP121 C1013 page XX WB_TX_SLOT C1004 U101 R1000 page XX GPS_ON_B VSIM U6002 page XX R3850 page XX page XX A920: POG U6000 page XX U2071 page XX FL500 page XX FL500 page XX FL500 page XX FL500 page XX Motorola Confidential Proprietary U500 page XX U3000 page XX U101 STANDBY U3000 page XX U3000 page XX U3000 page XX U3000 page XX page XX U3000 page XX U1300,U1310 page XX 4-47 U2000 page XX TX_RX_ERROR BCLKR NB_TX_KEYM DET_FLAG SYS_BB_CLK BB_CLK_15_36M MIDRATE_1 U3000 page XX BATT_IO BDR page XX page XX SWB+_EN NB_EXC_EN* BFSR BATT_DETB Q3967 GPS_TX GPS_RX GPS_RESET NB_RX_ACQ page XX U3000 U101 page XX GSP_WAKEUP* GPS_ON_B GPS_BOOT_SEL CLK_SEL NB_TX_EN HL_TX_EN U1000 CLK_32_768K PCAP_RESET* MUX_CTL ADDR(24:0) DATA(31:0) USIM_EN (POG) PCAP_INT POWER_FAIL USIM_CLK USIM_RST USIM_IO HARMONY_CS WB_SPI_MOSI WB_SPI_MISO WB_SPI_CLK BB_SPI_CLK BB_SPI_MISO BB_SPI_MOSI PCAP_CS FLASH_CS* FLASH_ECB* FLASH_OE* FLASH_LBA* FLASH_CLK POR_RESET* FLASH_URW_DQM0 USB_VMOUT USB_VPIN USB_TXEN* RTS_XRXD RXD_VMIN TXD_VPOUT Sig Gen: -20dBm Ref Freq: VCO: WB_RX_ON WB_RX_SLOT WB_RX_ACQ RF_RESET* page XX Q906 page 4-3 R5485 page XX U908 page 4-3 U500 page XX U500 page XX Q700 page XX U101 page XX U1300,U1310 page XX page XX page XX page XX U1300,U1310 U3000 page XX J5500 page XX NB_SPI_CLK MAGIC_CS NB_SPI_MOSI U500 SDTX DMCS_MAGIC TX_CLK BFSX U500 ASAP_TX ASAP_RX ASAP_CLK ASAP_FS U3000 U2000 U5600 BBIF_RX_FRAME BBIF_TX_FRAME BBIF_CLK Legend U5000 BBIF_RX(5:0) BBIF_TX(7:0) WB_TX_PREKEY WB_TX_SLOT WB_TX_RAMP AOC_PWR_UP_DOWN page XX page XX U101 page XX U101 page XX A920: POG Memory U1300,U1310 page XX page XX U3000 page XX R1304 V_FLASH VMEM_1_875V V_FLASH_IO V_FLASH_IO page XX V_FLASH VMEM_1_875V FLASH_12V page XX R1303 page XX TP1300 C1308 page XX C1301 R1300 C1306 C1300 C1303 C1302 R1303 C1307 C1403 C1402 CR1300 V_FLASH_IO R1304 page XX page XX U1400 page XX R1400 page XX E3352 V_SDRAM_IO U1400 U1300 U1310 SDRAM Flash Flash C1401 V_SDRAM DATA(31:0) U1000 ADDR(24:0) page XX U1000 C1309 VLVIO_1_95V V_FLASH_IO FLASH_ECB* FLASH_CLK Legend page XX FLASH_CS* page XX FLASH_OE* Sig Gen: -20dBm Ref Freq: VCO: page XX FLASH_URW*_DQM0 page XX FLASH_LBA page XX POG_RESET* U1000 U1000 U1000 4-49 U1000 U1000 page XX U1310,U1300 page XX page XX U1000 E3352 page XX R1304 U1000 R1304 page XX VLVIO_1_95V page XX page XX V_FLASH_IO R1402 Motorola Confidential Proprietary R1402 V_SDRAM V_SDRAM_IO R1400 U1400 C1400 page XX C1305 U3000 R1304 page XX page XX 4-46 A920: Bluetooth IC BLUETOOTH IC U5600 A5600 U5600 FL5601 uP Unit (UPU) BLUE_HOST_WAKE* BLUE_WAKE* BLUE_CLK_EN* BT_RXBT_RX+ BT_TX+ USB_DP 2.4GHz Transceiver BT_TX- Bluetooth Baseband Core (BBC) Motorola Confidential Proprietary V1 V2 Frequency Synthesizer Power Management Unit (PMU) USB_DM Peripheral Transport Unit (PTU) HELEN POG ASAP_RXD ASAP_TXD ASAP_FS ASAP_CLK PCAP CLK_32_768K REF_OSC_15_36M Description Harmony Lite The BCM2033 has an integrated radio transceiver that has been optimized for use in 2.4 GHz Bluetooth wireless systems. It has been designed to provide low-power, low-cost, robust communications for applications operating in the globally available 2.4 GHz unlicensed ISM band. It is fully compliant with the Bluetooth RF Specification v1.1 and meets or exceeds the requirements to provide the highest communication link quality of service. The receiver has a high degree of linearity, an extended dynamic range, and high order on-chip channel filtering to ensure reliable operation in the noisy 2.4 GHz ISM band. The BCM2033 also features a fully integrated transmitter. Baseband data is GFSK modulated and upconverted to the 2.4 GHz ISM band via an internal mixer. The output Power Amplifier (PA) provides a nominal power output of 0 dBm and has a power control to provide 24 dB of gain control in 8 dB step sizes. Local Oscillator (LO) generation provides fast frequency hopping (1600 hops/second) across the 79 maximum available channels. The uPU runs software from the Link Control (LC) layer, up to the Host Controller Interface (HCI). The microprocessor is an enhanced performance 8051 microcontroller. The BBC manages the buffering, segmentation, and routing of data for all connections. It also buffers data that passes through it, handles data flow control, schedules SCO/ACL TX/RX transactions, monitors Bluetooth slot usage, optimally segments and packages data into baseband packets, manages connection status indicators, and composes and decodes HCI packets. The Peripheral Transport Unit (PTU) handles the Device Interface. The PTU supports three types of devices: USB, UART, and PCM. The PMU provides power management features that can be invoked by either software through power management registers, or “packet handling” in the baseband core. A920: Bluetooth C5671 R5671 page XX R5675 Bluetooth page XX C5623 C5600 R5604 C5612 R5605 C5611 R5603 page XX C5508 R2041 USB_DP C5620 L5600 R5606 C5621 C5650 U5600 L5604 C5651 CLK_32_768K E3451 C5622 L5501 C2618 U3000 R5613 VBLUETH_1_875V Q5600 page XX R5519 E3402 C5604 Motorola Confidential Proprietary C5617 U5623 VHIO_2_775V C5615 R5623 R5608 page XX C5613 C5670 VAUX4_3V R5607 E3900 RAW_15_36 C2614 C132 page XX VBLUETH_1_875V C5818 page XX C5624 E3451 FL5601 L5602 C5607 BT_ANT A5600 page XX VBLUETH_1_875V E3451 page XX Legend 4-51 Sig Gen: -20dBm TX: RX: Ref Freq: 4-48 A920: GPS Harmony Lite GPS ANTENNA PIFA PCAP CLK_32_768K U6002 U6051 RTC FL6050 I Q 24.5535MHz ÷9 X2 A/D AGC 38.194MHz 49.107MHz U6050 SiRF RF to IF SIGN Bias Control SW_VGPS_RF_2_775V Description VGPS_EXTANT_2_775V GPS_RESET* BUS INTERFACE AGCDAT GPS/WAAS DSP ACQCLK U6000 SiRF Baseband POG Motorola Confidential Proprietary ø Y6050 GPS_BOOT_SEL(ED0) MAG IF Filter & IQ Combiner Interface Block ÷41 ÷7 ED(15:0) EXT GPS ANTENNA EA(18:0) M6050 FL6055 U6001 GPS FLASH 1MB REF_FREQ GPS_WAKEUP* GPSCLK GPS_GPIO3 PWRCTL GPS_RX GPIO UNIT DUAL UART U6003 Q6050 GPS_TX GPS_TIME_SYNC VGPS_RF_2_775V VRF_RX_2_775V The 1575.42 MHz satellite signal can be received through the GPS antenna PIFA_Planar Inverted F Antenna) or exernal GPS antenna. GPS signal received through the PIFA will pass through FL6055 and LNA U6051. The signal is then passed to the LNA input of U6050 through FL6050. The input signal at the LNA of U6050 is a Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) signal at 1575.42MHz with a 1.023 Mbps Bi-Phase Shift Keying (BPSK) modulated spreading code. The DSSS signal is then injected into an image reject mixer. The Mixer and on-chip 1565.97 MHz VCO will produce an IF center frequency of 9.45MHz. An IF filter is required between the Mixer and AGC Amplifier to provide an anti-aliasing function before A/D conversion. The IF filter block also contains an I-Q phase shift combiner. This circuit properly phase shifts and sums the I and Q outputs from the image reject mixer to a single channel. The AGC amplifier provides the additional gain needed to optimally load the signal range of the 2-bit A/D Converter. The 2-bit A/D onverter will then provide signal and magnitude output bits to the Interface Block. The outputs of the Interface Block provide clocks and the 2-bit sample data to the CGSP2e/LP(U6000). These signals use single-ended PECL(Positive Emitter-Coupled Logic) signaling to simplify the complexity of this interface. The interface block inputs are the single-wire AGC interface, (AGCDAT) and the Power Control pin (PWRCTL). The GPS DSP within U6000 correlates the incoming MAG and SIGN data. Wide parallel search architecture enables simultaneous search of 1,920 time/frequency bins which enables a powerful combination of very fast reacquisition along with the capability to find and track very weak signals. The UART residing in U6000 is used to interface data information between the GSP2e/LP(U6000) and POG. An integrated GPIO unit provides support for a variety of peripherals. RTC is an ultra-low power implementation of a high precision 32-kHz driven clock derived from the PCAP. It is separately powered by the VDDRTC to allow maximum battery life by maintaining time for the next power on. REF_FREQ is used as an external clock source for U6000. GPS_WAKEUP* is an active low signal from POG to wake up SiRFLoc client from the deep sleep mode. GPS_RESET* is an active low hard reset signal for the SiRF BB IC and Flash. GPS_BOOT_SEL is used by POG to set boot configuration upon reset. GPS_TIME_SYNC is an active high signal to provide time stamping of the precise time aiding that is sent over from POG over the UART. A920: GPS RF Circuit U6000 SIGN page XX U6000 MAG page XX PECLREF page XX VGPS_EXTANT_2_775V page XX C6066 VGPS_RF_2_775V NAND_OUT VRF_RX_2_775V C6082 C6083 M6050 Legend 4-53 Sig Gen: RX: Ref Clk: -20dBm U6051 L6080 L6050 Q6050 C6063 C6080 FL6050 C6084 C6067 C6052 R6063 R6061 C6050 L6053 C6069 GPS_ANT C6055 L6051 page XX C6065 SiRF GRF2e Y6050 GPS_GPIO3 SW_VGPS_RF_2_775V U6050 U3000 page XX U6075 page XX C6060 AGCDAT page XX U6000 C6064 C6062 C6053 U6000 GPSCLK C6057 page XX C6058 U6000 R6060 SW_VGPS_RF_2_775V C6070 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Q6050 C6059 page XX C6061 ACQCLK E6062 U6000 C6051 U6000 L3560 page XX Y6050 page XX A6050 page XX FL6055 A920: GPS Baseband Circuit U1000 page XX R133 page XX U1000 page XX U6000 page XX U6000 page XX U6010 GPS_ON_B REF_FREQ GPS_RESET* JTDI VHVIO_2_775V JTCK VGPS_BB_2_775V VGPS_BB_2_775V GPS_RESET* page XX JTCK U1000 R6059 RTCRST C6010 CLK_32_768K GPS_ON_B page XX U1000 4-55 page XX page XX U6050 U3000 Q6075 GPS_WAKEUP* SW_VGPS_RF_2_775V E3402 page XX Q6050 Q6050 page XX GPS_DATA(15:0) U6001 GPS_ADDR(18:0) U6001 VGPS_BB_2_775V GPS_TX U3000 page XX U1000 page XX TP6004 CS3 GPS_BOOT_SEL GPS_RX page XX R6004 page XX VHVIO_2_775V NAND_OUT page XX U1000 page XX R6004 U6002 page XX U1000 page XX U1000 page XX R6005 C6002 TP6002 SiRF GSP2e VMEM_1_875V RIN C6007 VDD5 C6009 JTDO JTMS JTRST R6003 E6006 C6003 page XX U6010 page XX PWRCTL ECLK GPS_ADDR(18:0) VDDRTC CPIO4 C6001 GPS FLASH E6009 PECLREF U6000 C6004 GPS_DATA(D0) U6003 C6000 GPS_DATA(D1) R6002 page XX GPS_DATA(D7) TP6005 U6000 U6001 GPS_DATA(D8) R6006 page XX GPS_DATA(D15) R6001 TP6008 U6000 R6000 page XX R6004 TP6001 VGPS_BB_2_775V R6008 U6010 GPS_DATA (15:0) Motorola Confidential Proprietary JTDI E3402 page XX page XX U6010 page XX Legend Sig Gen: RX: Ref Clk: -20dBm 4-50 A920: Camera LCD 208x320 TFT 65K color Video Buffer Reset* YUV 4:2:0 to RGB Real Time Data Transmission Motorola Confidential Proprietary Storage FLASH SD MMC Video MPEG4/H.263 Encoding Still Image JPEG Encoding VSYNCO, HSYNCO U7605 Reset* VODATA3 YUV 4:2:2 to YUV 4:2:0 VODATA[7:0] CAM_ICLK U7602 Latch Clock I2C HELEN PCAP VAUX4_3V IrDa_RX GPIO QCIF Qualifier Logic SSCK, SSDA IRDA_Shutdown SUSPEND CAM_ROT_DETECT XIN Vcc Conexant Backend Processor ASIC U7600 PIXCLK PIXVLD Master VSync, HSync DATA[7:0] ICLK I2C Suspend Slave Reset* Vcc Conexant CMOS Imager MSCK, MSDA VAUX4_3V Hall-Effect Switch Description The Conexant imager allows15 fps(frames per second) image readouts at VGA resolution. The Conexant imager will output raw Bayer RGB 8-bit/pixel data to the Conexant backend processor (U7600). The Conexant backend processor will receive the Bayer RGB data from the imager and process the image data into 8-bit YUV uncompressed or compressed data that is send through the VODATA bus to the Helen application processor. U7600 can process the YUV data in VGA(640x480), QVGA(320x240), CIF(352x288), and QCIF(176x144) output resolutions. Control functions for U7600 are done through a 2-wire serial interface(SSCLK and SSDA). The QCIF qualifier logic devices(U7602 and U7603) are used for viewfinder and video capture functions. VSYNC and HSYNC signals provide vertical and horizontal synchronization of the image signals. VSYNC indicates a start and end of a valid video frame while HSYNC indicated the start and end of a valid video line. VODATA sends 8-bit processed image data in YUV 4:2:2 format to the Helen processor. VODATA3 is shared by the camera and IrDA devices. Due to the hardware restrictions, Camera and IrDA wouldn‘t work simultaneously. For this reason, IRDA_SHUTDOWN is used to enable VODATA3 during camera operation. CAM_ROT_DETECT is used to indicate the rotated position of the imager. A magnet integrated in the Conexant imager will activate the Hall effect switch and cause a state change for CAM_ROT_DETECT. The Helen will respond with a horizontal inversion of the image. The image that Helen receives goes through a DSP pre-processing stage where the YUV 4:2:2 is converted to YUV 4:2:0. To display the image on the unit’s display, the YUV 4:2:0 signal passes through a DSP post-processing stage and converts it to RGB. The RGB signal is then passed through a video buffer and to the display. For still image storage cases, the YUV 4:2:0 image passes through JPEG encoding and then transferred to a user selectable storage device(Flash, SD, MMC). For video cases, the YUV 4:2:0 image is passed through MPEG4 or H.263 encoding. The video is then transferred to a user selectable storage device or sent as real time data transmission. A920: Video Circuit U3910 VCAM_3V VSYNC page XX U2000 CAM_RESET* HSYNC C7621 VCAM_3V ICLK CAM_DATA(7:0) U7600 Pixel Processor VODATA7 VODATA6 VODATA3 SENS_DATA(9:0) VCAM_3V SCANMODE U2000 CAM_HSYNC R7635 R7631 CAM_LCLK page XX C7621 C7630 CAM_ICLK_OUT page XX U7602 CAM_SDATA U3910 J7600 J7600 page XX U3910 page XX TP7002 page XX J7600 page XX J7600 page XX U2000 IRDA_SHUTDOWN page XX VHVIO_2_775V page XX VCAM_3V C7631 U2000 page XX VCAM_3V U7605 page XX R7630 U2000 page XX U3910 MSCK MSDA CAM_VSYNC U7603 Motorola Confidential Proprietary page XX J7600 page XX page XX page XX U2000 page XX page XX R7638 R7610 R7611 C7633 R7645 R7612 CAM_ICLK_OUT R7637 C7634 page XX J7600 U2000 E3402 page XX U3910 page XX CAM_VSYNC U2000 page XX Legend 4-57 Sig Gen: -20dBm TX: RX: Ref Freq: 4-52 A920: Helen Helen GPIO uWIRE 1 Wire Bus Battery MMC FLASH FLASH I/F 256 Mbit icache 16KB API SDRAM DMA SDRAM I/F 256 Mbit ARM925 UART3 Bridge RTC MCSI1 icache 12KW MMU Internal XCVR Bluetooth IPCL Single Ended Converter HP0 HP2 HP1 C55x DSP SRAM 48kW USB UART2 DRAM 32kW (host) Motorola Confidential Proprietary PCAP Codec McBSP1 PCAP Stereo Codec (SAP) USB (client) USB Client UART1 CE Bus Description Bluetooth Audio McBSP3 McBSP2 Secondary SPI PCAP IrDA dcache 8KB MCSI2 RAM 1.5Mb POG MMC/SD ULPD LCD I/F Display 32kHz OSC 12MHz OSC 12 MHz Camera IF Backend Pixel Processor I2C Keypad 8x8 Image Sensor Keypad The Helen(adjunct processor) is a dual core processor architecture which incorporates a high-performane TI925T MPU core and a TI TMS320C55x DSP core. The following provides a brief description of the cores and associated peripherals being used in this design. ·Flash I/F, SDRAM I/F - Interfaces to FLASH and SDRAM ·Keypad Interface ·LCD I/F - Display Interface ·UART3 - IrDA interface ·MMC interface ·GPIO - For A/Ds ·Secondary SPI - PCAP interface ·Bluetooth Interface ·Camera IF - Backend Pixel Processor interface ·I2C - Inter-Integrated Circuit Master and Slave interface ·IPCL - Inter-Processor Communications Link for Helen to POG interface ·ULPD - Ultralow-Power Device ·1 wire Communication for Battery EPROM ·USB(client) - Helen USB is used as a client, signals are routed through PCAP’s USB transceiver ·UART1 - RS232 interface to CE bus ·McBSP1 - Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (VSAP) for the PCAP stereo audio interface ·McBSP2 - Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (ASAP) for the PCAP and Bluetooth audio interface A920: Helen U3000 Legend VCC_OUT Sig Gen: RX: VCO: C2001 -20dBm HELEN_VDD2 E2013 page XX HELEN_VDD R2043 MMC_DETECT* U5600 U1140 page XX STO BLUE_HOST_WAKE U3911 page XX E3402 C1140 R2059 R2050 E3402 VHVIO_2_775 R2006 R2002 page XX U3000 page XX R2026 U2000 page XX R2012 page XX 4-59 U3000 page XX HELEN_VDD2 VCC_OUT HELEN_VDD VDDSHV_SUPPLY(VDD3) STANDBY R2097 page XX U2300 HELEN_VDD2 R2097 R2003 C2017 C2006 C2016 C2011 R2320 U2071 C2015 R2055 C2020 R2401 E2013 page XX C2026 C2014 C2028 V_HDRAM_IO R2304 page XX C2018 C2025 R2012 VCC_OUT U3000 page XX HELEN_VDD3 U2000 page XX VOMAP_1_6V C2005 R2304 page XX page XX E2013 page XX E2013 C2019 R2030 VHVIO_2_775V page XX C2090 C2097 CAM_SHUTDOWN C2013 C2003 R2040 page XX U3910 U2000 Helen C2094 R2028 page XX U1000 C2008 C2012 R3902 C2004 BLUE_USB_DM page XX C2022 C2098 U5600 C2021 C1080 C2010 U3000 page XX U3000 page XX CLK_32_768K POWER_FAIL V_HFLASH_IO V_HDRAM_IO C2099 page XX CKIL R2051 C2030 U1000 C2002 C2023 page XX R2011 VHOLD_EXT_EN U1080 U3000 AP_F_CE_0* page XX AP_HKSW R2042 page XX R2041 C2024 page XX R2044 Motorola Confidential Proprietary E3352 U5002 VLVIO_1_95V C2027 Y2000 page XX U2040 E3900 VAUX4_3V HELEN_VDD2 HELEN_VDD2 VDDSHV_SUPPLY(VDD3) STANDBY VLVIO_1_95V PCAP_MCU_RESET* VCC_OUT U3980 page XX U2000 page XX E2013 page XX R2012 page XX U1000 page XX E3352 page XX U3000 page XX U3000 page XX A920: Helen RXD_VMIN TXD_VPOUT RTS_XRXD U3000 page XX U3000 page XX U3000 page XX R3997 page XX U5003 page XX Motorola Confidential Proprietary U5003 page XX U5004 page XX U5003 AP_SD_CKE_HL CR5005 DSEL0 DSEL1 page XX AP_TX AP_RX page XX BP_READY AP_DEEP_SLEEP U1000 page XX U1000 AP_SD_DATA(15:0) U2000 AP_RTS AP_CTS U5005 page XX U5004 AP_SDADD(12:0) BLUE_USB_DP page XX U5002 CAM_LCLK OPT1 HELEN_DCD U5600 page XX CAM_ICLK OPT2 page XX page XX CAM_ROT_DETECT WDI DSEL2 U5001 DITHER_CLK RESET_OUT* page XX U5005 USB_TXEN* SE0_IN USB_VPIN AP_F_ADD(23:0) AP_FDATA(15:0) CODEC_CLK_EN* (Helen) IRDA_TX IRDA_RX IRDA_SHUTDOWN U3000 page XX J5200 page XX 4-61 U1000 page XX LCD_PIXEL(15:0) LCD_PCLK LCD_HSYNC LCD_VSYNC USB_VMOUT USB_VPIN USB_TXEN* LCD_OE LCD_FRONTLIGHT LCD_SHUTDOWN* RTS_XRXD RXD_VMIN TXD_VPOUT page XX R7615 page XX R7620 page XX R7635 page XX U2400 page XX U2400 page XX U2300,U2380 page XX page XX page XX page XX U2300,U2380 U5670 page XX U6500 page XX KBC(6) KBR(4:0) KBC(5:0) Keyboard MMC_CMD MMC_CLK MMC_DAT MMC_WP J3900 ASAP_TX ASAP_RX ASAP_CLK ASAP_FS U3000 U1000 U5600 page XX MMSAP_FS MMSAP_CLK MMSAP_TX U7640 AP_SPI_MOSI AP_SPI_MISO AP_SPI_CLK AP_SPI_CS AP_PCAP_INT page XX page XX U3000 page XX Legend Sig Gen: -20dBm Ref Freq: VCO: CAM_DATA(7:0) CAM_VSYNC CAM_HSYNC CAM_RESET* CAM_SCLK CAM_SDATA U7600 page XX A920: Helen Flash Memory AP_FDATA(15:0) R2304 page XX R2360 U2000 page XX V_HFLASH_IO AP_F_ADD(23:0) V_HFLASH_TRUM_CORE C2306 page XX U2380 U2000 page XX C2350 page XX U3000 page XX U3000 page XX U3000 page XX U3000 D-_PCAP D+_PCAP USB_PU page XX D- page XX D+ PCAP_RESET* J5000 J5000 page XX U3000 page XX R1002 page XX R2360 page XX R3650 C2001 Q3222 Trumble Flash C2303 C1115 TP1003 TP1001 U6010 R6010 C6005 C6019 C6011 C6014 POG_RESET* POWER_FAIL STO POWER_FAIL SYS_BB_CLK VSIM VSIM_OUT GPS_ON_B B+ VHVIO_2_775V V_HFLASH_TRUM_CORE E3352 page XX U1000 page XX Q3222 page XX U1000 page XX U2000,U1000 page XX U7705 V_HFLASH_IO VMEM_1_875V U1000 page XX U3000 page XX U1000 page XX Q3964 page XX E3402 page XX U2300,U2380 page XX U2300,U2380 page XX page XX U3000 page XX TP2300 page XX page XX page XX POWER_FAIL V_HFLASH_TRUM_CORE U2000 page XX VLVIO_1_95V R1127 U1120 R2404 R6011 R3850 U2300 C6008 WIRE_SD0 ASAP_TX R2402 page XX U2000 R2350 C2357 WIRE_SD0_EN* C2302 R2014 VHVIO_2_775V page XX U1000 C2035 V_HFLASH_IO C2099 E3402 C2351 C2356 page XX R2304 page XX V_HFLASH_TRUM_CORE TP2002 Trumble Flash C1112 U2020 R2360 AP_F_CE_1* U2023 page XX R3652 U2000 RST C1113 C2032 C1114 C2034 U3000 page XX BB_RESET* R1002 AP_F_RST* page XX R2304 U2000 C2033 C3651 Motorola Confidential Proprietary U3000 page XX PCAP_RESET* PCAP_RESET* U2000 AP_FDATA(15:0) page XX AP_F_ADD(23:0) page XX U2000 4-63 A920: Helen SDRAM USER_OFF VCC_OUT AP_SD_CS* R2402 VHVIO_2_775V C2401 V_HDRAM_IO page XX U3980 VOMAP_1_6V C3990 C2400 C2402 R2430 page XX TP4504 SDRAM page XX R2098 page XX E3402 V_HDRAM_IO R2402 R2401 VMEM_1_875V page XX U1000 page XX U2400 page XX VHOLD_EXT_EN U3000 R2098 page XX U3000 R2304 U3000 R2401 Motorola Confidential Proprietary Q3981 R2403 page XX R2430 U3000 C2099 R2404 AP_SD_DATA(15:0) U2000 AP_SDADD(12:0) U2000 VCC_OUT AP_SD_CKE_HL AP_SD_CLK page XX page XX U3000 page XX U2000 page XX U2000 page XX 4-65 Parts List Introduction Motorola maintains a parts office staffed to process parts orders, identify part numbers, and otherwise assist in the maintenance and repair of Motorola Cellular products. Orders for all parts listed in this document should be directed to the following Motorola International Logistics Department: To order parts please use the following link: https://wissc.motorola.com/wissc_root/main/BrowserOK.html (Password is Required) For information on ordering parts please contact EMEA at +49 461 803 1638. When ordering replacement parts or equipment information, the complete identification number should be included. This applies to all components, kits, and chassis. If the component part number is not known, the order should include the number of the chassis or kit of which it is a part, and sufficient description of the desired component to identify it. Preliminary ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 6-1 Parts List A920/925 Electrical Parts List Electrical Parts List The following table lists the electrical parts list for the A920/A925 UMTS/GSM handset. Table 10. Electrical Parts List Reference Number A1 A6050DNP C001 C002 C003 C004 C005 C006 C007 C008 C010 C011 C030 C101 C102 C103 C104 C106 C107 C112 C113 C114 C115 C116 C117 C118 C119 C120 C121 C122 C123 C130 C131 C132 C133 C134 C140 C141 5-2 Part Number 3987724N02 3988220M01 2113743N03 0662057C01 2113743N36 2113743N36 2113743N42 2113743N50 2113743N50 2113743N50 2113743N36 2113743N03 2113743N16 2113928P04 2113928P04 2113928P04 2113947C01 2113928N01 2113947H01 2113928P04 2113928P04 2113928P04 2113743L17 2113928N01 2113743M24 2113928C04 2113743M24 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113928N01 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743E07 2113743L25 Description CONTACT CONTACT CAP, 1pF RES, 0 CAP, 27pF CAP, 27pF CAP, 47pF CAP, 100pF CAP, 100pF CAP, 100pF CAP, 27pF CAP, 1pF CAP, 3.9pF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .022uF CAP, 2200pF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C142 C145 C146 C148 C150 C151 C156 C157 C200 C201 C205 C202DNP C203DNP C215 C216 C221 C222 C223 C241 C242 C243 C244 C245 C250DNP C252DNP C260 C261 C270 C280 C282 C290 C291 C292 C293 C294 C295 C296 C297 C298 C299 C302 C303 C304 C305 Preliminary Part Number 2113743N46 2113743N01 2113928C04 2113743N22 2113743N28 2113743N28 2113743N16 2113743N16 2113743N38 2113743N50 2113743L17 2113743N03 2113743N50 2113743E07 2113741F37 2113743N30 2113743N30 2104801Z08 2113743L17 2113743L17 2113743L17 2113743L05 2113743L05 2113947B01 2113947B01 2113743N28 2113743N16 2113743N50 2113743N50 2113743N09 2113743L17 2113947C01 2113743L17 2113743L17 2113743L17 2113743L17 2113743L17 2113743L41 2113743N50 2113743L41 2113743N02 2113743N26 2113743N01 2113743N50 Description CAP, 68pF CAP, 0.5pF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 6.8pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 3.9pF CAP, 3.9pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 100pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 1pF CAP, 100pF CAP, .022uF CAP, 3300pF CAP, 15pF CAP, 15pF CAP, 1.2pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 330pF CAP, 330pF CAP, 10pF CAP, 10pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 3.9pF CAP, 100pF CAP, 100pF CAP, 2pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 100pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 0.75pF CAP, 10pF CAP, 0.5pF CAP, 100pF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-3 Parts List A920/925 Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C307 C310 C313 C314 C315 C316 C317 C319 C321 C323 C324 C325 C326 C327 C330 C331 C332 C333 C334 C335 C338 C340 C342 C344 C348 C349 C360 C361 C410 C413 C414 C420 C421 C422 C425 C444 C445 C448 C449 C451 C452 C453 C460 C502 5-4 Part Number 2113743N50 2113743N26 2409154M60 2113743Q07 2113743L41 2113743N26 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743N34 2113743N34 2113743L17 2113743L17 2113743N23 2113743L29 2113743E07 2113743N28 2113743N28 2113743N18 2113743N16 2113743N28 2113947C01 2113743N50 2113743L05 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L01 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N30 2113743L41 2113928C04 2113743N28 2113743L41 2113743N50 2113743N26 2113743L41 2113743N28 2113947B05 2113743L17 2113743N26 2113743L37 Description CAP, 100pF CAP, 10pF IDCTR, 5.6nH CAP, 1.5pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 10pF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, 22pF CAP, 22pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 7.5pF CAP, 3300pF CAP, .022uF CAP, 12pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 4.7pF CAP, 3.9pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 100pF CAP, 330pF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, 220pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 15pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 12pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 100pF CAP, 10pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 12pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 10pF CAP, 6800pF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C503 C504 C505 C506 C507 C509 C510 C511 C514 C516 C517 C520 C521 C522 C523 C524 C525 C526 C527 C528 C535 C536 C537 C538 C539 C540 C542 C543 C544 C545 C546 C554 C555 C556 C560 C576 C600 C602 C603 C604 C605 C606 C607 C608 Preliminary Part Number 2113740F59 2113743L13 2113741F45 2113743L41 2113743N50 2113743N50 2113743M24 2113928C03 2113743L41 2113928C03 2113743L17 2113928C04 2113928C04 2113928C04 2113928C04 2113743N34 2113743N28 2113743N32 2113743N32 2113743N38 2113928N01 2113743L41 2113928C04 2113928A01 2113743L41 2113947E01 2113947E01 2113928P04 2113928P04 2113928P04 2113947E01 2113743L01 2113743L01 2113743L05 2113743M24 2113743L05 2113743N34 2113928A01 2113743N12 2113743L05 2113743L05 2113743N54 2113743L05 2113743L05 Description CAP, 220pF CAP, 680pF CAP, 6800pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 100pF CAP, 100pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, .01uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 22pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 18pF CAP, 18pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, .01uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, .01uF CAP, 220pF CAP, 220pF CAP, 330pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 330pF CAP, 22pF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 2.7pF CAP, 330pF CAP, 330pF CAP, 150pF CAP, 330pF CAP, 330pF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-5 Parts List A920/925 Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C609 C610 C631 C632 C650 C651 C660 C661 C670 C671 C700 C701 C702 C703 C704 C705 C708 C710 C711 C712 C800 C801 C802 C803 C804 C805 C806 C808 C810 C812 C830 C832 C902 C903 C908 C909 C910 C1000 C1001 C1002 C1003 C1004 C1005 C1006 5-6 Part Number 2113743N54 2113743N36 2113928A01 2113743L41 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N28 2113743N28 2113743N28 2113743N28 2113928N01 2113743L03 2113743L17 0888600M19 2113743N12 2113743N28 2113743N20 2113743N28 2113743N50 2113743N28 2113928C04 2113743E20 2113743E20 2113743N26 2113743E20 2113928N01 2113743E20 2113743L01 2113743N38 2113743P01 0662057M01 2113743N28 2113743N36 2113743N28 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743L41 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 Description CAP, 150pF CAP, 27pF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, .01uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 270pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 3300pF CAP, 2.7pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 5.6pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 100pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 10pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 220pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 180pF RES, 0 CAP, 12pF CAP, 27pF CAP, 12pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C1007 C1008 C1009 C1010 C1011 C1012 C1013 C1014 C1015 C1016 C1017 C1018 C1019 C1020 C1021 C1022 C1026 C1027 C1028 C1029 C1030 C1031 C1032 C1033 C1034 C1110 C1112 C1113 C1114 C1115 C1140 C1150 C1300 C1301 C1302 C1303 C1304 C1305 C1306 C1307 C1308 C1309 C1400 C1401 Preliminary Part Number 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743L41 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 Description CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, .01uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-7 Parts List A920/925 Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C1402 C1403 C2001 C2002 C2003 C2004 C2005 C2006 C2008 C2009 C2010 C2011 C2012 C2013 C2014 C2015 C2016 C2017 C2018 C2019 C2020 C2021 C2022 C2023 C2024 C2025 C2026 C2027 C2028 C2030 C2032 C2033 C2034 C2035 C2070 C2090 C2094 C2097 C2098 C2099 C2302 C2303 C2306 C2350 5-8 Part Number 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743N30 2113743N30 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113743M24 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113743N34 2113743N34 2113928N01 2113743M24 2113928C12 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113743N38 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928C12 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 Description CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 15pF CAP, 15pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 22pF CAP, 22pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C2351 C2356 C2357 C2400 C2401 C2402 C3000 C3001 C3002 C301DNP C3050 C3051 C3052 C3053 C3100 C3101 C3150 C3151DNP C3200 C3201 C3220 C3221 C3222 C3224 C3225 C3226 C3228 C3229 C3227DNP C3250 C3300 C3350 C339DNP C3400 C3401 C3402 C3450 C345DNP C3500 C3501 C3502 C3550 C3555 C3560 Preliminary Part Number 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113947H01 2113928N01 2113928C12 2113928C12 2113928N01 2113743N02 2113928C12 2113928C12 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928C12 2113928C12 2113928C04 2113743N38 2113928C12 2113928C12 2113928C12 2113743L17 2113743N35 2113928C12 2113928C12 2113928C12 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113928C04 2113928C04 2113928C12 2113743N50 2113928C12 2113928C12 2113743M24 2113928C04 2113743L17 2113928C12 2113928C12 2113743M24 2113928C04 2113743N35 2113928C12 Description CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.75pF CAP, 10uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 10uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 24pF CAP, 10uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 100pF CAP, 10uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 10uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 24pF CAP, 10uF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-9 Parts List A920/925 Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C3561 C3562 C3600 C3602 C3601DNP C3650 C3651DNP C3801 C3850 C3851 C3852 C3900 C3903 C3904 C3906 C3901DNP C3902DNP C3910 C3911 C3912 C3914DNP C3950 C3951 C3961 C3962 C3963 C3964 C3965 C3966 C3967 C3960DNP C3980 C3981 C3983 C3984 C3985 C3987 C3989 C3990 C3991 C3993 C3992DNP C3998DNP C4000 5-10 Part Number 2113928C12 2113743M24 2113928C12 2113743N40 2113743N40 2113928C04 2113947B05 2113928C04 2113928C04 2113928C04 2113928N01 2113928C04 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N50 2113947B05 2113743N38 2113928C12 2113928C12 2113928N01 2113743N26 2113928C04 2113743M24 2113928C12 2113743M24 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743L35 2113928C03 2113743N38 2113743N37 2113743N34 2113928C12 2113928C12 2113928P04 2113928C12 2113928C12 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L35 2113928P04 Description CAP, 10uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 39pF CAP, 39pF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 100pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 10uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 10pF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 5600pF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 30pF CAP, 22pF CAP, 10uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 10uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, 5600pF CAP, 1.0uF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C4002 C4003 C4008 C4100 C4110 C4112 C4113 C4114 C4160 C4198 C4200 C4202 C4203 C4207 C4210 C4213 C4301 C4302 C4303 C4304 C4306 C4355 C4356 C4380DNP C4390 C4392 C4393 C4394 C4395 C4400 C4401 C4402 C441DNP C442DNP C443DNP C4500 C4501 C4502 C4503 C4504 C4550 C4551 C5000 C5002 Preliminary Part Number 2113743L13 2113947B05 2113947B05 2113928P04 2113743N38 2113928C04 2113743N26 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113947H01 2113743M24 2113743L13 2113947B05 2113947B05 2113928C04 2113743M24 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113947E01 2311049A89 2113947B05 2311049A89 2113928C04 2113743M24 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743M24 2113928A01 2113743M24 2113743N26 2113743L41 2113743N50 2113743N50 2113743M24 2113743N38 2113928C04 2113743M24 2113928C04 2113743L25 2113743L41 2113743M24 2113743N38 Description CAP, 680pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 10pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 680pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, .01uF CAPP, 22uF CAP, 33pF CAPP, 22uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 10pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 100pF CAP, 100pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 4.7uF CAP, 2200pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 33pF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-11 Parts List A920/925 Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C5003 C5010 C5050 C5053 C508DNP C5100 C5101 C5102 C5103 C5104 C5105 C5106 C5107 C5200 C5202 C5204 C5206 C5208 C5210 C5212 C5213 C5214 C5218 C5220 C5222 C5224 C5226 C5227 C5228 C5229 C5230 C534DNP C5400 C5401 C5402 C5403 C5404 C5405 C5407 C5410 C5411 C5412 C5413 C5501 5-12 Part Number 2113743N38 2113743L41 2113743M24 2113928A01 2113743N28 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113743L41 2113947B05 2113947B05 2113947B05 2113947B05 2113947B05 2113947B05 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113947B05 2113947B05 2113947B05 2113947B05 2113947B05 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113947B05 2113743L25 2113743L25 2113743N34 2113928C12 2113743N22 2113743M24 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743L41 2113928C12 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928P04 2113743N38 Description CAP, 33pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 12pF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, .01uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 2200pF CAP, 2200pF CAP, 22pF CAP, 10uF CAP, 6.8pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 33pF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C5503 C5504 C5505 C5506 C5507 C5508 C5509DNP C5600 C5604 C5607 C5608 C5605DNP C5611 C5612 C5613 C5614 C5615 C5616 C5617 C5618 C5620 C5621 C5622 C5623 C5624 C5649DNP C5650 C5651 C5670 C5671 C5700 C6000 C6001 C6002 C6003 C6004 C6005 C6007 C6008 C6009 C6010 C6011 C6012 C6014 Preliminary Part Number 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113928N01 2113743N38 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743N09 2113743L23 2113743N03 2113743N52 2113743L41 2113743L01 2113743L07 2113743L37 2113743M24 2113743L41 2113743N26 2113743N26 2113743N26 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113743N26 2113743N03 2113743N01 2113928N01 2113743L17 2113743N38 2113743F18 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113947H01 2113743N38 2113743M24 2113743N38 2113743M24 2113743L41 2113928C12 2113743L01 2113928N01 Description CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 2pF CAP, 1800pF CAP, 1pF CAP, 120pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 220pF CAP, 390pF CAP, 6800pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, .01uF CAP, 10pF CAP, 10pF CAP, 10pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 10pF CAP, 1pF CAP, 0.5pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 2.2uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, .01uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 220pF CAP, 0.1uF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-13 Parts List A920/925 Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C6019 C6050 C6051 C6052 C6053 C6055 C6057 C6058 C6059 C6056DNP C6060 C6061 C6062 C6063 C6064 C6065 C6066 C6067 C6069 C6070 C6080 C6082 C6083 C6084 C6090DNP C6091DNP C6500 C6501 C6502 C6503 C6504 C6510DNP C6511DNP C706DNP C7610 C7611 C7612 C7613 C7615 C7616 C7617 C7618 C7620 C7621 5-14 Part Number 2113928P04 2113743N32 2113743L09 2113743N52 2113743N09 2113743N12 2113743L09 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743N03 2113743N42 2113743L13 2113743L41 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743N05 2113743L17 2113743N26 2113743N32 2187893N01 2187893N01 2113743N52 2113743N09 2113743N03 2113928P04 2113928C12 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N03 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113947B05 2113743N38 2113946D02 2113946D02 2113946D02 2113928N01 2113743N30 2113743L09 Description CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 18pF CAP, 470pF CAP, 120pF CAP, 2pF CAP, 2.7pF CAP, 470pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 1pF CAP, 47pF CAP, 680pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 1.2pF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 10pF CAP, 18pF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 120pF CAP, 2pF CAP, 1pF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 10uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 1pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 1.0uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 15pF CAP, 470pF ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number C7630 C7631 C7632 C7633 C7634 C7640 C7641 C7642 C7643 C7644 C7726 C7729 C7721DNP C7730 C7731 C813DNP C901DNP CR200 CR201 CR330 CR331 CR1300 CR3000 CR3050 CR3100 CR3960 CR3961 CR5005 D5101 D5110 D5300 E100 E108 E109 E110 E111 E528 E529 E530 E975 E976 E977 E2013 E2320 Preliminary Part Number 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113928N01 2113743L17 2113743L41 2113743L17 2113743M24 2113743M24 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743N38 2113743M24 2113743N38 2113743M24 4809877C32 4809877C32 4809877C32 4809877C32 4809924D18 4809924D18 4809653F02 4809924D18 4809653F02 4809653F02 4809948D42 4809788E17 4809788E17 4809118D02 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 Description CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 1000pF CAP, .01uF CAP, 1000pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 33pF CAP, 0.1uF CAP, 33pF CAP, 0.1uF SMV1763 SMV1763 SMV1763 SMV1763 RB520S-30 RB520S-30 MBRM120T3 RB520S-30 MBRM120T3 MBRM120T3 RB751V40 EDZ68B EDZ68B LNJ115W8P0MT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-15 Parts List A920/925 Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number E3003 E3050 E3103 E3153 E3203 E3251 E3352 E3402 E3403 E3451 E3503 E3552 E3601 E3900 E3916 E3951 E3965 E6001 E6002 E6003 E6006 E6009 E6062 FL001 FL010 FL020 FL030 FL150 FL201 FL300 FL310 FL320 FL410 FL460 FL500 FL510 FL4300 FL5601 FL6050 FL6055 J001 J3900 J4100DNP J4200DNP 5-16 Part Number SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_BAR0_61 SHORT_BAR0_61 SHORT_BAR0_61 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 4889695L12 9109674L20 9109674L22 9109674L18 5885949K03 9109405J17 9109239M28 fl 9109674L14 9109405J16 9109239M16 fl 5888234M01 9188695K04 bg 4887925N01 4889526L04 bg 9109239M23 9109239M26 9185223E01 0788468M03 0988365M02 c 5085600J01 2888328M01 Description SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORT SHORTING_BAR SHORTING_BAR SHORTING_BAR SHORT SHORT SHORT ASM3201B S0351 74L22 S0350 LDD15A SAFCD380 SAF2G14KB0 LFSG20N25 FLTR SAF1G95KB0 34M01 95K04 FLTR FLTR LE65A 855969 DFM2R1575 CONTACT CONN_J SPKR CONN_P ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Electrical Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number J4300 J5000 J5200 J5400 J5500 J7600 J7700 L003 L005 L010 L150 L152 L153 L200 L201 L223 L240 L241 L242 L243 L280 L281 L297 L298 L302DNP L313 L314 L315 L316 L320 L321 L324 L325 L330 L610 L701 L703 L710 L713 L810 L821 L825 L832 L3000 Preliminary Part Number 0904136G01 0987636K05 0987817K05 3987522K03 3909426M05 0987817K04 0987817K04 2462587P55 2409154M14 2409154M59 2409154M79 2409154M81 SHORT_RES0402 0660076S01 2485793G04 2485793G04 2409377M16 2409377M16 2488289M24 2488289M25 2409154M09 2409154M09 2409377M16 2409377M16 2409154M07 2409154M56 2409154M73 2113743N02 2113743N26 2409646M86 2409646M86 2485793G15 2485793G15 2409377M08 2409154M11 2409154M70 2409154M47 2113743N12 2409154M65 2409154M09 2409154M61 2409154M52 2409154M09 2588866L14 c c c c Description CONN_J CONN_J CONN_J CONTACT BM050406 CONN_J CONN_J IDCTR, 82nH IDCTR, 12.0nH IDCTR, 4.7nH IDCTR, 1.8nH IDCTR, 2.7nH SHORT RES, 0 IDCTR, 10nH IDCTR, 10nH IDCTR, 82nH IDCTR, 82nH IDCTR, 82nH IDCTR, 100nH IDCTR, 4.7nH IDCTR, 4.7nH IDCTR, 82nH IDCTR, 82nH IDCTR, 3.3nH IDCTR, 2.7nH IDCTR, 68.0nH CAP, 0.75pF CAP, 10pF IDCTR, 27nH IDCTR, 27nH IDCTR, 82nH IDCTR, 82nH IDCTR, 22nH IDCTR, 6.8nH IDCTR, 39.0nH IDCTR, 82.0nH CAP, 2.7pF IDCTR, 15.0nH IDCTR, 4.7nH IDCTR, 6.8nH IDCTR, 1.2nH IDCTR, 4.7nH IDCTR, 47uH ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-17 Parts List A920/925 Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number L3050 L3100 L3220 L3560 L4399 L4400 L4401 L5600 L5601 L5602 L5604 L6000 L6050 L6051 L6053 L6080 L7600 L7640 L831DNP M001 M5700 M6050 Q130 Q420 Q510 Q700 Q901 Q902 Q906 Q3220 Q3222 Q3403 Q3502 Q3610 Q3960 Q3963 Q3964 Q3966 Q3967 Q3980 Q3981 Q4300 Q5000 Q5600 5-18 Part Number 2588866L14 2487659M11 2588866L05 2487996L04 2409646M13 2409154M71 2409154M71 2409154M08 2409154M08 2409154M08 2409154M03 0662057M01 2409154M11 2409154M11 2409154M12 2409704K43 2462587Q46 2462587Q59 2409154M65 0987378K01 5909382K09 0987378K01 4809579E24 4809608E03 4862830F01 4809579E16 4809579E58 4809579E48 4809939C34 4809579E43 4809579E02 4809607E04 4809607E04 4809607E04 4862830F01 4862830F01 4862830F01 4862830F01 4809939C39 4809579E49 4862830F01 4809940E03 4809579E58 5109572E39 bga bga bga bga bga bga Description IDCTR, 47uH IDCTR, 47uH IDCTR, 2.2uH EXCML16 IDCTR, 39nH IDCTR, 47.0nH IDCTR, 47.0nH IDCTR, 3.9nH IDCTR, 3.9nH IDCTR, 3.9nH IDCTR, 1.5nH RES, 0 IDCTR, 6.8nH IDCTR, 6.8nH IDCTR, 8.2nH IDCTR, 33nH IDCTR, 820nH IDCTR, 10uH IDCTR, 15.0nH SWITCH MOTOR SWITCH 2SJ347 DTA114YE SI8401DB TN0200T FDG6332C FDC6306P EMB10 FDG6303N 2SK1830 2SB1132 2SB1132 2SB1132 SI8401DB SI8401DB SI8401DB SI8401DB EMD9 SI6467DQ SI8401DB DTC114TE FDG6332C AS179_92 ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number Q6050 Q6051 R009 R1003DNP R1004DNP R1006DNP R1060DNP R1100DNP R1102DNP R1104DNP R1122DNP R1150DNP R1200DNP R130 R131 R132 R133 R134 R1000 R1001 R1002 R1061 R1101 R1103 R1105 R1127 R1300 R1303 R1304 R1301DNP R135DNP R140 R141 R146 R147 R1401DNP R150 R151 R200 R201 R203 R205 R2009DNP R213 Preliminary Part Number 4809579E50 4809579E24 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057N15 0662057M01 0662057M98 0662057N23 0662057M01 0662057M98 0662057M98 0662057M01 0662057M74 0662057N09 0662057N09 0662057M01 0662057N39 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057N23 0662057N23 0662057M01 0662057M74 0662057M98 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M98 0662057M01 0662057M70 0662057M94 0662057M36 0609591M17 0662057M01 0662057M50 SHORT_RES0402 0662057N15 0662057M98 SHORT_RES0402 0662057M43 0662057B27 0609591M37 Description SI1905 2SJ347 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 47K RES, 0 RES, 10K RES, 100K RES, 0 RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 0 RES, 1K RES, 27K RES, 27K RES, 0 RES, 470K RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 100K RES, 100K RES, 0 RES, 1K RES, 10K RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 10K RES, 0 RES, 680 RES, 6.8K RES, 27 RESNET, 220 RES, 0 RES, 100 SHORT RES, 47K RES, 10K SHORT RES, 51 RES, 1.6MEG RESNET, 10K ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-19 Parts List A920/925 Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number R215 R230 R231 R232 R240 R250 R252 R270 R290 R291 R292 R293 R294 R295 R296 R301 R304 R305 R315 R319 R320 R321 R325 R330 R331 R332 R335 R336 R337 R338 R339 R341 R342 R344 R346 R347 R348 R349 R360 R361 R410 R411 R412 R420 5-20 Part Number 0662057V02 0662057N15 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 0662057M26 0609591M01 0609591M01 0662057M50 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 SHORT_RES0402 0662057M85 0662057M50 0662057M26 0662057M26 0662057M26 2113743N22 0662057M26 0662057M70 0662057M01 0662057M98 0609591M37 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M74 0662057N15 SHORT_RES0402 0662057M26 0662057M26 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 0662057M90 0662057M70 0662057M70 0662057M01 Description RES, 10K RES, 47K SHORT SHORT RES, 10 RESNET, 10 RESNET, 10 RES, 100 SHORT SHORT SHORT RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 SHORT RES, 3K RES, 100 RES, 10 RES, 10 RES, 10 CAP, 6.8pF RES, 10 RES, 680 RES, 0 RES, 10K RESNET, 10K RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 1K RES, 47K SHORT RES, 10 RES, 10 SHORT SHORT RES, 4.7K RES, 680 RES, 680 RES, 0 ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number R431 R432 R450 R451 R452 R453 R454 R455 R456 R457 R503 R504 R506 R508 R511 R536 R537 R554 R556 R576 R577 R610 R611 R612 R615 R700 R701 R704 R705 R707 R807 R810 R812 R813 R814 R815 R816 R822 R900 R901 R902 R903 R904 R912 Preliminary Part Number SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 0662057M95 0662057M90 0662057M98 0662057N20 SHORT_RES0402 SHORT_RES0402 0662057M90 0662057N11 0662057M83 0662057M74 0662057N19 0662057M01 0662057N21 SHORT_RES0402 0662057M98 0662057N19 0662057N30 0662057N15 0662057M96 SHORT_RES0402 0662057N30 0662057M58 0662057M01 0662057M28 0662057M38 0662057M64 0662057M76 0662057M56 0662057M39 0662057U95 0662057V02 0662057V02 0662057M43 0662057U98 0662057U60 0662057M01 0662057M98 0662057M98 0662057M98 0662057N15 0662057M01 0662057N15 Description SHORT SHORT RES, 7.5K RES, 4.7K RES, 10K RES, 75K SHORT SHORT RES, 4.7K RES, 33K RES, 2.4K RES, 1K RES, 68K RES, 0 RES, 82K SHORT RES, 10K RES, 68K RES, 200K RES, 47K RES, 8.2K SHORT RES, 200K RES, 220 RES, 0 RES, 12 RES, 33 RES, 390 RES, 1.2K RES, 180 RES, 36 RES, 5.6K RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 51 RES, 7.5K RES, 220 RES, 0 RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 47K RES, 0 RES, 47K ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-21 Parts List A920/925 Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number R1400 R1402 R2002 R2003 R2006 R2011 R2012 R2014 R2026 R2027 R2028 R2029 R2030 R2040 R2041 R2042 R2043 R2044 R2045 R2050 R2051 R2055 R2059 R2056DNP R2070 R2097 R2098 R2304 R2350 R2400 R2401 R2402 R2403 R2404 R2430 R2431 R3004 R3051 R3055 R3056 R3057 R3104 R3205DNP R3221 5-22 Part Number 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M98 0662057M98 0662057M98 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057N11 0609591M37 0662057N23 0662057M50 0662057M50 0662057M98 0662057N23 0662057M35 0662057M35 0662057N03 0662057N03 0662057N23 0662057M82 0662057M01 0662057M98 0662057M98 0662057M98 0662057M50 0662057M26 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057N23 0662057V35 0662057M01 0662057V35 0662057V35 0687874L02 0687874L02 0662057U85 0662057V13 0662057M01 0687874L02 0662057M01 0662057N23 Description RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 33K RESNET, 10K RES, 100K RES, 100 RES, 100 RES, 10K RES, 100K RES, 24 RES, 24 RES, 15K RES, 15K RES, 100K RES, 2.2K RES, 0 RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 100 RES, 10 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 100K RES, 200K RES, 0 RES, 200K RES, 200K RES, 0.1 RES, 0.1 RES, 2.2K RES, 27K RES, 0 RES, 0.1 RES, 0 RES, 100K ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number R3222 R3223 R3224 R3225 R3228 R3400 R3504 R350DNP R3553 R3561 R3650 R3651 R3652 R3850 R3902 R3904 R3910 R3911 R3912 R3961 R3963 R3990 R3995 R3997 R3998 R3999 R3994DNP R4004 R4103 R4200 R4201 R421DNP R4305 R4306 R4393 R4395 R4396 R4397 R4398 R4400 R4401 R4550 R5000 R5001 Preliminary Part Number 0662057N01 0662057N35 0662057V32 0662057V32 0662057N47 0687874L02 0687874L02 0662057M01 0662057M50 0687874L02 0662057M78 0662057M37 0662057M37 SHORT_RES0402 0662057M50 0662057M50 0662057U98 0662057V02 0662057N23 0687874L01 0662057V35 0662057V35 0662057N23 0662057N23 0662057V35 0662057M01 0662057M01 0609591M05 0662057M90 0662057N03 0662057N06 0662057M98 0662057N47 0662057N39 0662057M98 0662057M98 0662057M90 0662057N39 0662057M68 0662057M50 0662057M74 0662057N06 0662057N23 0662057N15 Description RES, 12K RES, 330K RES, 150K RES, 150K RES, 1MEG RES, 0.1 RES, 0.1 RES, 0 RES, 100 RES, 0.1 RES, 1.5K RES, 30 RES, 30 SHORT RES, 100 RES, 100 RES, 7.5K RES, 10K RES, 100K RES, 0.24 RES, 200K RES, 200K RES, 100K RES, 100K RES, 200K RES, 0 RES, 0 RESNET, 22 RES, 4.7K RES, 15K RES, 20K RES, 10K RES, 1MEG RES, 470K RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 4.7K RES, 470K RES, 560 RES, 100 RES, 1K RES, 20K RES, 100K RES, 47K ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-23 Parts List A920/925 Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number R5002 R5003 R5004 R5005 R5006 R5009 R5007DNP R5008DNP R5050 R5052 R5053 R5100 R5101 R5102 R5113 R5114 R5115 R5116 R5117 R5118 R5119 R5120 R5121 R5200 R526DNP R5300 R5301 R5401 R5480 R5481 R5482 R5483 R5485 R5500 R5501 R5502 R5503 R5603 R5604 R5605 R5606 R5607 R5608 R5613 5-24 Part Number 0662057M98 0662057N13 0662057N23 0662057N15 0609591M49 0662057N39 0662057N23 0662057M01 0662057N15 0662057N33 0662057M86 0662057M98 0609591M37 0609591M37 0662057M26 0662057M50 0662057M50 0662057M50 0662057M50 0662057M50 0662057M50 0662057M50 0662057M50 0662057M98 0662057M98 0662057M34 0662057M34 0662057M90 0662057M80 0662057V11 0662057V43 0662057V02 0662057M50 0662057M01 0662057M92 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M78 0662057N08 0662057M96 0655086C39 0662057M80 0662057M80 0662057M96 Description RES, 10K RES, 39K RES, 100K RES, 47K RESNET, 100K RES, 470K RES, 100K RES, 0 RES, 47K RES, 270K RES, 3.3K RES, 10K RESNET, 10K RESNET, 10K RES, 10 RES, 100 RES, 100 RES, 100 RES, 100 RES, 100 RES, 100 RES, 100 RES, 100 RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 22 RES, 22 RES, 4.7K RES, 1.8K RES, 22K RES, 330K RES, 10K RES, 100 RES, 0 RES, 5.6K RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 1.5K RES, 24K RES, 8.2K RES, 2870 RES, 1.8K RES, 1.8K RES, 8.2K ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number R5619 R5610DNP R5623 R5624 R5675 R5683 R6000 R6001 R6002 R6003 R6004 R6005 R6006 R6008 R6007DNP R6010 R6011 R6059 R6060 R6061 R6063 R7610 R7611 R7612 R7613 R7615 R7614DNP R7616DNP R7620 R7630 R7631 R7632 R7635 R7637 R7638 R7641 R7642 R7643 R7644 R7645 R7646 R7654 R7650DNP S2070 Preliminary Part Number 0662057M98 0662057M98 0662057M98 0662057M98 0662057N39 0662057N47 0662057V19 0609591M45 0609591M45 0609591M45 0609591M45 0662057N23 0662057M01 0662057M82 0662057M01 0662057V32 0662057V35 0662057M01 0662057M94 0662057M01 0662057M46 0662057M50 0662057M50 0662057M50 0662057N23 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M01 0662057M50 0662057M82 0662057M82 0609591M29 0662057M46 0662057M98 0609591M37 0662057M78 0662057M92 0662057M98 0662057N23 0662057N23 0662057N23 0662057N39 0662057M01 4085805H02 Description RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 10K RES, 470K RES, 1MEG RES, 47K RESNET, 47K RESNET, 47K RESNET, 47K RESNET, 47K RES, 100K RES, 0 RES, 2.2K RES, 0 RES, 150K RES, 200K RES, 0 RES, 6.8K RES, 0 RES, 68 RES, 100 RES, 100 RES, 100 RES, 100K RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 0 RES, 100 RES, 2.2K RES, 2.2K RESNET, 2.2K RES, 68 RES, 10K RESNET, 10K RES, 1.5K RES, 5.6K RES, 10K RES, 100K RES, 100K RES, 100K RES, 470K RES, 0 SWITCH ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-25 Parts List A920/925 Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number S5100 S5101 S5102 S5103 SH130 SH140 SH150 SH200 SH310 SH330 SH400 SH500 SH700 SH800 SH1000 SH2000 SH3000 SH5600 SH6000 SH6100 SH6200 SH7600 T100 T650 T660 T670 U101 U130 U140 U150 U200 U310 U330 U410 U420 U440 U450 U500 U510 U600 U6004DNP U630 U700 U710 5-26 Part Number 4087635K01 4087635K01 4087635K01 4087635K01 2688976N01 2687472N03 2687476N03 2687475N03 2687473N03 2687474N03 2687471N03 2688037M01 2688036M01 2688035M03 2688975N01 2688974N02 2688727M02 2688038M01 2688033M01 2688031M01 2688034M01 2688089M02 5887510M01 5885949K08 5885949K09 5885949K05 5188450M07 5187634N01 4809283D73 5109940K32 5109817F71 5109944C53 5109817F69 5187970L05 5109908K55 5109768D08 5187970L13 5188450M05 5109522E63 5109940K41 5182159Y04 5109512F47 4809283D97 5887694L17 x x x x bg q q q m bg Description SWITCH SWITCH SWITCH SWITCH SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD SHIELD HHM1520 HHM1409 HHM1410 HHM1525 50M07 KM4110 MQL304 UPC8151TB MAX2363 MC13770 MAX2309 AV122 PA2001_5W LM20 DD02-92 50M05 NC7WZ04 LIFE_30PIN MAX6381 LP3985 83D97 EXB24ATE ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary Service Manual (Level 3) Parts List Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number U800 U810 U908 U1000 U1110 U1120 U1140 U1150 U1300 U1310 U1400 U2000 U2020 U2023 U2040 U2070 U2071 U2300 U2380 U2400 U3000 U3220 U3910 U3911 U3980 U5000 U5001 U5002 U5003 U5004 U5005 U5600 U5623 U5670 U6000 U6001 U6002 U6003 U6010 U6050 U6051 U6075 U6500 U7600 Preliminary Part Number 5109908K74 5885811G11 5109522E83 5199134J02 5109522E53 5109522E60 5109522E53 5162852A59 5199144J01 5199144J01 5109509A55 5189251L05 5109522E60 5109522E53 5109522E25 5109522E16 5109522E60 5199121J01 5199139J01 5109509A45 5188450M06 5187324N01 5109512F46 5164751E01 5187344N01 5109817F58 4889526L02 5109522E82 4889526L01 5109522E82 5109522E82 5189316L01 5109522E82 5109522E60 5109841C70 5199342A01 5186311J23 5186311J23 5109512F46 5187970L16 5105739X12 5109522E17 5162852A33 5189251L01 q bga1 s s b b bg bg s bga bga bga b bga bga mi bga mi mi mi bga1 bga mi mi l Description 08K74 DD05-EN722 NC7SZ11 8 DSPIO NC7SZ125 TC7SZ08FU NC7SZ125 MAX4599EXT 44J01 44J01 K4M64163 OMAP1510 TC7SZ08FU NC7SZ125 TC7SH02FU TC7W74FU TC7SZ08FU 5 28F128K18 5 GE28F256K18 K4S56163LC 50M06 LTC3411 ILC7081 MC74VHC1GT50 LP3983 17F58 0 CSPEMI-307 NC7SB3157 0 CSPEMI-306 NC7SB3157 NC7SB3157 BCM2033A NC7SB3157 TC7SZ08FU 30 GSP2E GT28F800B NC7SZ126 NC7SZ126 ILC7081 GRF2I_LP BGA428 TC7S00FU HSDL3202 CX1164621 ©2003 Motorola, Inc. 5-27 Parts List A920/925 Table 10. Electrical Parts List - cont’d Reference Number U7601 U7602 U7603 U7605 U7640 U7701 U7702 U7703 U7704 U7705 VR800 VR3912 VR3914 VR5500 VS1001 VS1002 VS4200 VS4201 VS4392 VS5000 VS5001 VS5002 VS5003 VS5004 VS5200 VS5400 VS5401 VS5402 VS7600 VS7602 VS7603 VS7604 VS7605 VS7601DNP VS7730 VS7731 Y130 Y500 Y2000 Y3982 Y6050 5-28 Part Number 5109817F66 5109522E16 5109522E82 5186311J23 5109522E16 4889526L01 4889526L01 0662057M50 2409154M66 5109522E82 4809788E17 4809788E17 4809788E17 4809948D44 4809948D44 4809948D44 4809788E06 4809788E06 4809788E17 4809788E08 4813830C29 4809788E06 4809788E06 4813830C29 4809948D44 4809788E06 4809788E06 4809788E06 4809948D44 4809948D44 4809948D44 4809948D44 4809788E17 4809948D44 4809788E17 4809788E17 4809718L14 4809612J43 4809612J45 4809995L13 4885169E03 mi mi bga bga mi bg bg bg bg bg bg bg bg bg Description TLE4913 TC7W74FU NC7SB3157 NC7SZ126 TC7W74FU 0 CSPEMI-306 0 CSPEMI-306 RES, 100 IDCTR, 18.0nH NC7SB3157 EDZ68B EDZ68B EDZ68B CSPESD304 CSPESD304 CSPESD304 UDZTE-176.8B UDZTE-176.8B EDZ68B UDZS8_2B MMSZ5246B UDZTE-176.8B UDZTE-176.8B MMSZ5246B CSPESD304 UDZTE-176.8B UDZTE-176.8B UDZTE-176.8B CSPESD304 CSPESD304 CSPESD304 CSPESD304 EDZ68B CSPESD304 EDZ68B EDZ68B NT5032SA XTAL CX-91F CC5V TX2949 ©2003 Motorola, Inc. Preliminary