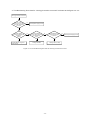
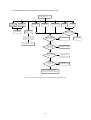
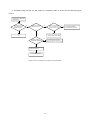
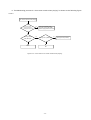
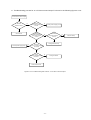
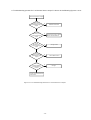
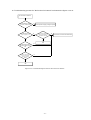
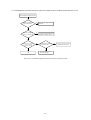
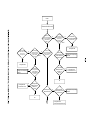
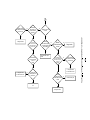
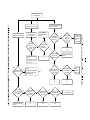
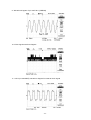
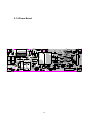
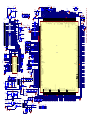
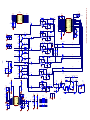
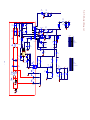
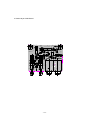
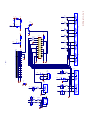
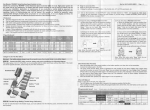
Download service manual DV717 &DV721SI SI
Transcript
DV717 SI &DV721SI service manual Catalog Chapter One About Maintenance 1.1 Safety precautions 1 1 1.1.1 Power supply 1 1.1.2 Precautions for antistatic 1 1.1.3 Precautions for laser head 1 1.1.4 About placement position 2 1.2 Maintenance method 2 1.2.1 Visualized method 2 1.2.2 Electric resistance method 2 1.2.3 Voltage method 2 1.2.4 Current method 2 1.2.5 Cutting method 2 1.2.6 Element substitution method 3 1.2.7 Comparison method 3 1.3 Required device for maintenance Chapter Two Functions and Operation Instructions 3 4 2.1 Features 4 2.2 Control Button Locations and Explanations 4 2.2.1 Front Panel Illustration 4 2.2.2 Rear Panel IIIustration 5 2.2.3 VFD Display Window Illustration 5 2.2.4 Remote Control Illustration 5 2.3 Accessories 7 2.4 FUNCTION SETUP 7 2.4.1 Function Setup 7 2.4.2 Language 7 2.4.3 Image 7 2.4.4 Sound 8 2.4.5 Playback 9 2.4.6 Karaoke 9 2.4.7 Preference 10 2.4.8 Parental control 10 2.4.9 Initial setup 10 2.4.10 Rest to defaults 10 2.4.11 Exit 11 2.5 Specifications 11 Chapter Three Principle and Servicing Section One Principle of the Player 12 12 3.1.1 Block diagramof the player 12 3.1.2 PCB board block diagram of the player 12 3.1.2 PCB board block diagram of the player 13 3.1.3 Introduction to IC of the player 14 Section Two Unit Circuit Principle 15 3.2.1 Laser head pin introduction 15 3.2.2 Disc identification circuit 16 3.2.3 Laser power control circuit 17 3.2.4 Reset circuit 18 3.2.5 Clock circuit 19 3.2.6 Disc in/out circuit 19 3.2.7 Main axis braking circuit 20 3.2.8 Mute circuit and power-off quieting circuit 22 3.2.9 Servo circuit 23 3.2.10 Decode circuit 26 3.2.11 Video circuit 27 3.2.12 Audio circuit 28 3.2.13 Power circuit 30 3.2.14 MIC circuit 31 3.2.15 Headphone circuit 32 3.2.16 panel control circuit 32 3.2.17 AV output circuit 33 Section Three Servicing Cases 35 3.3.1 Servicing cases 35 3.3.2 Troubleshooting flow chart 38 Section Four Waveformdiagram 57 Section Five Function Introduction to IC 65 3.5.1 function introduction to Mt1389 65 3.5.2 function introduction to FLASH 75 3.5.3 function introduction to SDRAM 75 3.5.4 function introduction to D5954 77 3.5.5 function introduction to Cs4360 78 3.5.6 Function introduction to CS5340 78 3.5.7 Function introduction to LM1117MP-1.8 79 3.5.8 Function introduction to HS0038A2 79 3.5.9 Function introduction to 4558/TDA1308 80 3.5.10 Function introduction to U501 (FDSH321) 80 3.5.11 Function introduction to ncp1200 81 3.5.12 Function introduction to U503 (LM431A) 81 3.5.13 Function introduction to U502 82 Chapter Four Disassembly and Assembly Process 83 Chapter Cinque PCB board & Circuit diagramt 84 Section One PCB board 84 Section Two circuit diagram 93 Chapter six BOM List DV721SI Service Manual 100 110 7.1.1 Features 110 7.2.1 PCB board block diagram of the player 111 7.3.1 MIC circuit 112 7.3.2 Control panel circuit 112 7.3.3 Power circuit 113 7.4.1 Troubleshooting flow chart 117 7.5.1 PCB board 120 7.5.2 circuit diagram 127 Chapter One About Maintenance 1.1 Safety precautions 1.1.1 Power supply When maintenance personnel are repairing DVD players, he should pay special attention to the power board with 220V AC and 330V DC which will cause hurt and damage to persons! 1.1.2 Precautions for antistatic Movement and friction will both bring static electricity which causes serious damages to integrated IC. Though static charge is little, when a limited quantity of electric charge is added to largescaleintegrated IC, as the capacitance is very small in the meantime, now the integrated IC is very much easy to be struck through by static electricity or the performance will decrease. Thus static electricity prevention is of extraordinary importance. The following are several measures to prevent static electricity: 1. Use a piece of electric conduction metal with the length of about 2 metres to insert into the earth, and Fetch the lead wire from the top of the surplus metal and connect to the required static electricity device. The length and depth of the metal embedded under the earth should be determined according to the wettability of the local soil. For humid places, it may be shorter, and longer and deeper for dry places. If possible, it can be distributed and layed in terms of “#” shape. 2. On operating table-board, the antistatic table cushion should be covered and grounded. 3. All devices and equipments should be placed on the antistatic table cushion and grounded. 4. Maintenance personnel should wear antistatic wrist ring which should be grounded. 5. Places around the operating position should also be covered with electric conduction cushion or Painted with antistatic paint. 1.1.3 Precautions for laser head 1. Do not stare at laser head directly, for laser emission will occur when laser head is working, which will Hurt your eyes! 2. Do not use wiping water or alcohol to clean laser head, and you may use cotton swab. -1- 1.1.4 About placement position 1. Never place DVD player in positions with high temperature and humidity. 2. Avoid placing near high magnetic fields, such as loudspeaker or magnet. 3. Positions for placement should be stable and secure. 1.2 Maintenance method 1.2.1 Visualized method Directly view whether abnormalities of collision, lack of element, joint welding, shedding welding, rosin joint, copper foil turning up, lead wire disconnection and elements burning up among pins of elements appear. Check power supply of the machine and then use hands to touch the casing of part of elements and check whether they are hot to judge the trouble spot. You should pay more attention when using this method to check in high voltage parts. 1.2.2 Electric resistance method Set the multimeter in resistance position and test whether the numerical value of resistance of each point in the circuit has difference from the normal value to judge the trouble spot. But in the circuit the tested numerical value of resistance is not accurate, and the tested numerical value of integrated IC's pins can only be used for reference, so the elements should be broken down for test. 1.2.3 Voltage method Voltage method is relatively convenient, quick and accurate. Set the multimeter in voltage position and test power supply voltage of the player and voltage of a certain point to judge the trouble spot according to the tested voltage variation. 1.2.4 Current method Set the multimeter in current position and test current of the player of a certain point to judge the trouble spot. But when testing in current method, the multimeter should be series connected in the circuit, which makes this method too trivial and troublesome, so it is less frequently used in reality. 1.2.5 Cutting method Cutting method should be combined with electric resistance method and voltage method to use. This method is mainly used in phenomena of short circuit and current leakage of the circuit. When cutting the input terminal voltage of a certain level, if voltage of the player rises again, it means that the trouble lies in this level. -2- 1.2.6 Element substitution method When some elements cannot be judged good or bad, substitution method may de adopted directly. 1.2.7 Comparison method A same good PC board is usually used to test the correct voltage and waveform. Compared these data with those tested through fault PC board, the cause of troubles may be found. Through the above maintenance method, theoretical knowledge and maintenance experience, all difficulties and troubles will be readily solved. 1.3 Required device for maintenance Digital oscillograph ( 100MHE) TV set SMD rework station Multimeter Soldering iron Pointed-month pincers Cutting nippers Forceps Electric screw driver Terminals connecting cord Headphone Microphone -3- Chapter Two Functions and Operation Instructions 2.1 Features This player has employed the new generation DV decode chip with built-in Dolby Digital decoder which willbring you to a brand-new AV ententainment world. The 2-laser super error-correction mechanism supports CD-R. Brand-new AV Effects 1.Compatible with DivX, MPEG4 discs to produce wonderful pictures. 2.108MHz/12bit video DAC, with more vivid and brilliant pictures. 3.Progressive-scan video outputs to eliminate the flickers hardly ouvercome by interlacing scan and therefore your eyesight will be well-protected. At the same time, the pictures deflnltion Is sharply enhanced and the pictures will be finer, smoother and stabler 4.Brightness, chroma and contrast adjustment functions to render your eyes more comfortable. 5.Digital echo Karaoke to enable your singing easier. 6.Composite Video, S-Video and Component Video outputs. 7.Bullt-In Dolby Digital decoder, separate 5.1Ch Outputs. 8.Dolby output for 2channel(DOWNMIX). 9.DVD-Audio decoding output to reproduce original and realistic sound effects. High Quality Digital Audio 1.Optical and coaxial outputs for Digital audio. 2.DTS, Dolby Digital, PCM Digital audio outputs to satisfy the Fans’Ss acoustic requirements. Many Convenient Features 1.Screen saver protects your TV set carefully. 2.The novel Mp3 playback window GUI provides you a new way to appreciate Mp3 music. 3.Multi-angle playback function makes it possible for you to view a scene from different camera angles. 4.It’ s possible to select the desired beginning, development and ending of a story. 5.Direct entry into desired scenes(title/chapter/track search). 6.Zooming function to zoom up any playing picture. 7.Capable of playing PAL/NTSC discs. 8.Multiple aspect ratios to fit TV sets of various screen ratios. 9.Parental lock function to prevent children from watching unsuitable discs. 10.Multiple dubbing languages and subtitle languages bring you the best entertainment status all the time. Super Compatibility with super VCD, VCD, CD , CD-R , MP3,HDCD,KODAK PICTURE CD etc. 2.2 Control Button Locations and Explanations 2.2.1 Front Panel Illustration -4- 3 2 4 5 6 8 7 1 POWER switch 5 PAUSE button 2 Disc tray 6 STOP button 3 OPEN/CLOSE button 7 IR SENSOR 4 PLAY button 8 Display windows 2.2.2 Rear Panel IIIustration 8 1 Mixed Audio Out jack 5 Video Component/Y Pb Pr Out jacks 2 5.1CH Audio Out jacks 6 S-Video 3 Digital Audio Coaxial Out jack 7 Video Out jack 4 Digital Audio Optical Out jack 8 SCART Outjack 2.2.3 VFD Display Window Illustration 2 3 4 5 PBC SVCD MP3 6 7 ALL 8 9 10 12 11 1 DVD disc 5 DTS 2 PBC 6 VCD、CD、SVCD Disc 10 Repeat 3 Chapter or Track 7 MP3 Disc 11 PAUSE 4 Playback time 8 Playback status indication 12 DOLBY Digital 9 2.2.4 Remote Control Illustration -5- PLAY 1 2 3 4 1 15 16 17 18 2 LANG Button Change the audio language or audio channel 3 6 19 7 20 8 9 10 21 12 13 14 ] Button Open or close the disc tray. 5 11 [ MEMORY Button Save the playing point or jump to the saved point 22 23 24 25 26 4 DISP Button Display or hide disc information. 5 NUMBER Buttons 6 BROWSE Buttons switch new user interface. 27 7 CURSOR Buttons 28 8 SETUP Button Function Setup. 29 9 [ ] Button Open/close the virtual keyboard function. 10 KARAOKE Button Karaoke operation menu. Display DVD menu or open/close PBC. 20 OK Button 21 Cancel Button 22 ZOOM +/-Button Zoom in/out the displayed frame. 23 [ [ 25 [ 13 14 28 PEPEAT Button A-B Button 15 [ ] Button Press once to stand by, Press twice to play. 16 SUBT Button Change subtitle language, Switch JPEG display mode. 17 Q-PLAY Button Set the played image as the power-on logo. Skip the advertisement/warning and play the VOL +/- Button DVD directly. Increase/decrease volume level. 29 ] Button Repeat the select. ] Button CAPTURE Button [ Repeat play. Skip forward. 27 ] Button Skip backward. ]Button Stop playback. 26 [ 12 ] Button Fast forward play. [ Fast backward play. ]Button Play or pause playback. 24 11 18 Change camera angle . MUTE Button Press once to mute, twice to turn off. ANGLE Button 19 -6- MENU Button 2.3 Accessories TV system AUDIO/VIDEO CORD REMOTE AAA SITE BUTTERIES WARRANTY CARD USER MANUAL KARAOKE DISC AUTO TV scan mode 1PCS 1PCS 2PCS 1PCS 1PCS 1PCS IS Video out. Com. TV format LB Sharpness L. Off Gamma 2.4 FUNCTION SETUP Brightness 0 Contrast 0 Hue 0 Saturation 0 High Medium Low 2.4.1 Function Setup 5.Press [LEFT] button if you want to return to the previous setup page. 6.Press [SETUP ]to exit the setup menu. 1.Press the [SETUP] button and the screen displays the selection menu of function setup. 2.4.2 Language Language Setup menu Image DVD menu Sound Soundtrack Playback Subtitle Off Setup menu Russian DVD menu English Ukrainian Soundtrack Karaoke Sbutitles Off Preference Parental control 1.Setup menu: This item is used to set the prompts language on the screen. ◆Optional setting: Russian, English, Ukrainian. ◆Default: English. 2.DVD menu: To set the preference disc menu lang when playing. ◆Optional setting: Russian, English, Estonian, Latvian, Kazakh, Romanian, Byelorussian, Ukrainian, Chinese, Others. ◆Default: English. 3.Sountrack:To set the preference audio language when playing. ◆Optional setting: Russian, English, Estonian, Latvian, Kazakh, Romanian, Byelorussian, Ukrainian, Chinese, Others. ◆Default: English. 4.Subtitles: To set the preference subtitle language when playing. ◆Optional setting: Off, Russian, English, Estonian,Latvian, Kazakh, Romanian, Byelorussian, Ukrainian, Chinese, Others. ◆Default: Off Initial setup Reset to defaults Exit 2.Press the [CURSOR] button to select the menu to be entered and press the [OK] or button to confirm. Or press the [CURSOR] button to Exit item and then press the [OK] button to exit 3.Press [UP/DOWN] arrow to select the desired item you want to set and press [OK]. For example, press [UP/DOWN] arrows to select IMAGE and press [OK]. The Image setting page appears on the screen. TV system TV scan mode AUTO IS Video out. S-Vid. TV format LB Sharpness Gamma AUTO PAL NTSC L. Off Brightness 0 Contrast 0 Hue 0 Saturation 0 2.4.3 Image. TV system TV scan mode 4.Press [UP/DOWN] arrow to select the SHARPNESS item. Press [OK] to confirm it. And then press [UP/DOWN] arrow to select the desired valus.For example: Press[ UP/DOWN] arrow to select “Medium”,then press [OK], the TV screen display. IS Video out. Com. TV format LB Sharpness Gamma -7- AUTO L. Off Brightness 0 Contrast 0 Hue 0 Saturation 0 AUTO PAL NTSC 1.TV system: This item is used to the video output system of this unit. ◆Optional setting: Auto, PAL, NTSC. ◆Default: AUTO. 2.TV scan mode: To set Progressive scan, Interlaced scan mode . ◆Optional settings: Progressive , Interlaced . ◆Default: Interlaced . 3.Video output: To set the types of SCART out connector. ◆Optional setting: S-Video,Component , SCART, ◆Default: Component ◆When using RGB outputs from the SCART interface,please select RGB. Other wise , please select Com-ponent,and when using SVideo output please select S-Video. 4.TVn format: To set the aspect ratio of this player’ s output image. ◆Optional setting: 4:3 Pan-scan, 16:9 letterb., 16:9 TV. ◆Default: 16:9 letterb. 5.Sharpness:Used to set the sharpness of video outputs. ◆Optional setting: High, Medium, Low. ◆Default: Medium. 6.Gamma emendation:This item is used to setup the Gamma value of video output. ◆Optional setting: High, Medium, Low, Off. ◆Default: Off. 7.Brightness:Used to set the brightness of video outputs. 8.Contrast:Used to set the contrast of video outputs. 9.Hue: Used to set the hue of video outputs. 10. Saturation: Used to set the saturation of video outputs. ◆Brightness, contrast, hue and saturation adjusting means: A. Press [UP/DOWN] arrow in the video setup menu to select the desired item you want to adjust. Press [OK] or [RIGHT] button to enter the item's adju-stment. B. Press [UP/DOWN] arrow to adjust the setting value. 1.Mixer... Configuration Digital output Stereo mix Tuning Surr. Mix Low band 5.1 off Surr. Mix FSW. Low band Channels Delays Auto PRO Logic II A.Configuration: To set this player’ s DOWNMIX mode to change multi-channel audio into two channel audio. ◆Optional setting: Stereo, 5.1 ◆Default: Stereo. B.Stereo mix: To set the output means of the left or right audio when playing a Dolby disc with separate two-channel audio. ◆Optional setting: L+R, L, R. ◆Default: L+R. C.Surr. Mix: To set output means of the surround left and right audio when playing a stereo disc. ◆Optional setting: Off, sum, Virt.Surr. ◆Default: Off. D. Low band: select the channel that you desire to output low frequency signal. ◆Optional setting: Front F, Center C, Surround Sr, Subwoofer SW. ◆Default: Front F, Subwoofer SW. E. Channels: To set volume of each individual channel. a. Press [UP/DOWN] navigation keys to select CHANNEL TRIM, then press the [OK] or [RIGHT] navigation key to select ENTER SETUP PAGE as shown in the TV screen: FRONT Volume L 20 0 surround R l r 0 0 0 Center SW 0 0 b. Press [LEFT/RIGHT] navigation keys to select the desired channel to adjust. c. Press [UP/DOWN] navigation keys to raise or lower volume of the channel. d. Press [OK] or [LEFT] to return to the Mix.. setup page. F. Delays: To set delay time of the Center/ Surround/Subwoofer Speaker. St. L+R off FSW Channels Delays PRO Logic II Stereo L+R Stereo mix 2.4.4 Sound Mixer... St. Configuration Off -8- c. Press [OK] or [LEFT] button to return to Audio Setting page after adjustments are done. a. Press [UP/DOWN] navigation keys to select Delays in Channels item, then press [OK] or [RIGHT] navigation key select ENTER SETUP PAGE as shown in the TV screen. 2.4.5 Playback Advertisemenu DVD No VCD/SVCD Files A. P. V Subwoofer 0cm Repeat Off Center 0cm Load effect Off LS/RS 180cm 1.DVD: set whether information ofadvertisement and warnings at the beginning of DVD disc is skipped to play the movie directly. Always skip ads ◆Optional setting: Yes, NO ◆Default: Number 2.VCD/SVCD: To set the PCB status. ◆When playing Super VCD or VCD2.0 discs, if thePCB is ON, the menu image displays. ◆Optional setting: On, Off. ◆Default: On. 3.Files:data disc may probably includes Mp3, JPEG and MPG format files in which you may select DVD player to read the file type. ◆Optional setting: Audio, Picture, Video. ◆Default: Audio, Picture, Video. 4. Repeat : select the repeat playback mode. ◆Optional setting: Off, Single, all. ◆Default: Off. 5. Load effect: set the may to play JPEG image. ◆Optional setting: Off, from top, from bottom. ◆Default: Off. b.Press [UP/DOWN] navigation keys to Select the desired item oup Press [OK] or [RIGHT] button to enter setting. C.Press [UP/DOWN] navigation keys to raise or lower volume. d.Press [OK] or [LEFT] to return to the Delays in channels setting page. G.PRO Logic II: To set PRO Logic II to ON or OFF. If the TITLE does not support this function, we recommend that you set this item to AUTO because it would become worse if the processing effects were added forcibly. ◆Optional setting: Auto, On, Off . ◆Default: Auto. 2.Digital output: select to set the format and stream form of digital audio output. A.SPDIF format: ◆Optional setting: RAW format, SPDIF/PCM. ◆Default: RAW format. B.LPCM ◆Optional setting: 48 kHz 16 bit, 96 kHz 24 bit, 192kHz24bit. ◆Default: 48 kHz 16 bit. 3.Tuning: A.Max volume: set the maximum volume limit. B.Equalizer: To set Equalizer modes. ◆Optional setting: Off, Rock, Pop, Live, Dance, Techno, Classic, Soft. ◆Default: Off. C.Echo: To set different sound field effects. ◆Optional setting: Off, Concert, Living room, Hall,Bathroom, Cave, Arena, Church. ◆Default: Off. D.Tone balance: to set the tone level to match your diapason when you're singing a.Press [UP/ DOWN] cursor buttons to select "tone"item in Audio Setting page, and then press [OK] or [RIGHT] button to enter Adjustment Menu. ◆Method to adjust tone control: B.Press [UP/DOWN] cursor button to adjust setting value. 2.4.6 Karaoke Microphone Kar. help Off On No ast. Off Volume 5 Echo 5 1.Microphone: switch on or off microphone. ◆Optional setting: On, Off ◆Default: Off. 2.Kar. help: select accompany singing means. ◆Optional setting: Channels L, Channels R, Channels No ast, Channels No voc. ◆Default: Channels No ast. 3. Volume: A.In microphone setup page, press [UP/DOWN] cursor to select “Volume”item, and then press [OK] button to enter the adjustment menu. B.Press [UP/DOWN] cursor to adjust the setup value. -9- ◆Optional setting: On, Off. ◆Default: On. C.After adjustment finishes, press [OK] button to return to microphone setup page. 2.4.8 Parental control On Microphone No ast any Volume 4 Kid Echo 4 G Kar. help Allowed.. 4.Echo: A.In microphone setup page,press [UP/DOWN] cursor to select “Echo”item, and then press [OK] button to enter the adjustment menu. B.Press [UP/DOWN] cursor to adjust the setup value. C.After the adjustment finishes, press [OK] button to return to microphone setup page. Microphone Kar. help 1.Allowed..: To set the parental control ratings to prevent children from watching the restricted contents.( In case the discsupports this function.) ◆Optional setting: any, Kid, G, PG, PG-13, PGR, R ,NC-17. ◆Default: any. 2.Set password: To set four digit password to enable you to change the parental control ratings. ◆Default: 7890 Volume 4 2.4.7 Preference On On Gr. equalizer Off Off Background std. Screen saver On PGR NC-17 On LED Control PG-13 R No ast. Echo PG Any Set password Old password New password Verify OK 1.LED Control:This item is used set color of led on the front panel. ◆Optional setting: On, Off. ◆Default: On. 2.Gr. equalizer: This item is used to set wether the Dynamic Spectrum is allowed. ◆Optional setting: On, Off. ◆Default: Off. ◆Dynamic Spectrum display is invalid in Data disc、DVD AUDIO playback. 3.Background: This item is used ti setup the sort of Power-in Logo. ◆Optional setting: Standard, saved. ◆Default: Standard. NOTE The Screen Logo refers that use the image selected by pressing the [CAPTURE] button as the power-on logo. When in the operation of changing screen, if the power-on logo has not set in Screen Logo, the unit will automatically set the power-on logo as Screen Logo. 4.Screen saver: Open or close the screen saver function. Cancel 2.4.9 Initial setup Auto PAL NTSC Press [UP/DOWN] arrow to select the desired option and Press [OK] button to confirm it. NOTE In this setup state, you may not press [LEFT] button to return to the previous menu. 2.4.10 Rest to defaults Load factory settings OK - 10 - Cancel Reset to defaults: To restore all settings to the default value except for the parental control and password settings. 2.4.11 Exit Language Image Sound Playback Karaoke Preference Parental control Initial setup Reset to defaults Exit Press [UP/DOWN] arrow to select the Exit item. Press [OK] button to exit the setup menu. 2.5 Specifications Playable discs DVD-Video,Super VCD,VCD,DivX 3.11,dIVx 4,DivX 5,DivX Pro,XviD,DVD-Audio, CD-DA, CD+DG, HDCD, MP3,WMA,Kodak Picture CD,JPEG Inputs MIC input Audio outputs Outputs Analog audio output: Digital audio output: Stereo,output 5.1CH Coaxial,Optical Composite,S-Video,component Y Cb Cr,progressive scan output Y Pb Pr,RGB/SCART Headphones output Video outputs Vidio characteristics Video amplitude: S-Video amplitude: Component video amplitude: 1.0Vp-p(75Ω) Y:1.0Vp-p(75Ω) C:0.286Vp-p(75Ω) 1.0Vp-p(75Ω) Cb/Cr:0.7Vp-p(75Ω) Audio characteristics Frequency response Signal-to-noise ratio THD 20-20000Hz(±dB) >100(dB) <0.01% Operating voltage ~110-250V,50/60Hz Power consumption 14W General specification Dimensions: Mass: Operating temperature 5-35℃ Operating humidity 15-75(no condensation) 380×258×41.5 mm 2 kg ◆Design and specifications are subject to change without notice. ◆We do not guarantee that all discs can be played smoothly due to the disc quality ,disc recording quality and recording format. - 11 - Chapter Three Principle and Servicing Section One Principle of the Player 3.1.1 Block diagram of the player DV717SI is composed of decode circuit, servo circuit, audio circuit, video circuit, MIC circuit and power circuit. Block diagram is shown as in the following figure 3.1.1.1: KEY U401 (Pt6961) LED Headphone output jack Remote control L H_L U603 TDA1308 R H_R U403 (HS0038A2) U207 (Cs4360) U601 4558 Microphone U219 U220 U221 4580 LT RT LS RS LFT CC A/V OUTPUT BOARD Audio output 2 I C U210 (Cs5340) Video output U201 (Mt1389) Loader 2 I C U302 (D5954) 2 I C 1.8V U205 (HCU04) URST# U214 (FLASH) U211 (SDRAM) U209 (LM1117MP-1.8) Figure 3.1.1.1 Block diagram of the player - 12 - U202 (24LLC02) Loader frame Small bracket Laser head PDAT2 PDAT1 XS307 Xs306 XS301 SPDIF VCC Y C Pr Main panel 4973-21 Y1 IR Decode board 2521S-0 GND XS402 VFDST VFDCK Pb VIEDO XS201 AV board 7717-0 PDAT0 L VFDAT R SL SR XS401 CC LFE Xs403 CN502 Subsidiary panel 9973-2 XS203 XS203 CN502 XS601 Power board 5DV717-0 AC220V +10V MIC and headphone board 6717-0 XS702 XS603 3.1.3 Introduction to IC of the player Introduction to IC of the player is shown as in the following table: Semi-finished PCB name Power board 5DV717-0 Main panel 4973-2 OK board 6717-0 Decode board 2521S-0 IC model name Location Function AZ431 U503 Precise voltage regulator HS817 U502 Photoelectric coupler FSDH321 U501 Power switch IC PT6312 U401 Control panel IC HS0038B3V U402 Remote control receiver KA4558 U601 Operational amplifier (MIC amplifying) TDA1308 U603 Headphone amplifying NJM4558 U219,U220,U221 Operational amplifier (audio amplifying) HCU04 U205 Phase inverter HY57V641620HGT-7 U211 SDRAM LM1117 U209 1.8V voltage regulator IC 24C02 U202 EEPROM MT1389 C version U201 Decode chip D5954 U302 Servo drive CS4360 U207 D/A inverter CS5340 U210 A/D inverter 29LV160BE U214 FLASH - 14 - Section Two Unit Circuit Principle 3.2.1 Laser head pin introduction Laser head pin introduction is shown in the following table: Pin Name Signal flow direction DVD disc CD disc No disc Function description 1 F- Input loader 2.52 2.34 0.46 2 F+ Input loader 2.49 2.49 0.93 Focus error signal is added to two sides of pick-up focus coil 3 T+ Input loader 2.53 2.51 0.94 4 T- Input loader 2.58 2.51 0.93 5 C Input MT1389 2.2 2.25 2.04 Disc data signal 6 D Input MT1389 2.2 3.2 2.04 Disc data signal 7 IOA Input MT1389 0.01 3.2 3.21 Disc identification signal, CD is 3.3V, DVD is 0V 8 RF Input MT1389 2.21 2.53 1.28 The sum of disc data signal 9 A Input MT1389 2.17 2.22 2.04 Disc data signal 10 B Input MT1389 2.19 2.27 2.04 Disc data signal 11 F Input MT1389 2.07 2.44 2.03 Supplementary signal used in trace 12 GND Ground 0.01 0.01 0 Grounding 13 V20 Input loader 2.04 2.06 2.03 Reference voltage 14 Vcc Input loader 5.04 5.04 5.02 Supply voltage for loader 15 E Input MT1389 2.06 2.45 2.03 Disc data signal 16 Blanking haning in air 0.01 0 0 unused 17 VR-CD Input loader 0.21 0.01 0 Through the handling inside loader, make sure MD11 is 180mV when reading CD 18 VR-DVD Input loader 0.01 0.2 0 Through the handling inside loader, make sure MD11 is 180mV when reading DVD - 15 - Trace error signal is added to two sides of pick-up trace coil 19 LD-CD Input loader 0.09 2.1 0 CD laser power control signal 20 MDII Input MT1389 0.21 0.2 0 CD and DVD laser power monitoring signal 21 HFM Input loader 5.04 5.04 5.02 High frequency overlapping signal produces laser with different wave length inside loader 22 Blanking unused 0.01 0.1 0 23 LD-DVD Input loader 2.21 0.1 0 DVD laser power control signal 24 GND unused 0.01 0.01 0 Grounding Note: 1. When reading DVD, there are only A, B, C, D signals. 2. When reading CD, there are A, B, C, D, E, F signals. 3. RFO=A+B+C+D. 4. Focus error signal=(A+C)-(B+D) Trace error signal=E-F. 3.2.2 Disc identification circuit 1. The circuit schematic diagram is shown as the following figure 3.2.2.1: R308 R309 100K 10K R311 AVCC IOA 10K V305 3904-S R310 V303 2SK3018-S 100K V304 2SK3018-S U201 16 Loader MT1389 17 R311 R0 7 DQSO 114 Figure 3.2.2.1 Disc identification circuit 2. Working principle: when reading CD disc, the loader outputs a high level (3.3v) to IOA; when reading DVD disc, the loader outputs a low level (0V) to IOA. When reading CD disc, IOA is high level; V304 and V305 are on; V305 collector electrode is low level;V303 drain electrode is equal to hang in the air (laser receiver pipe inside loader selects CD channel). When reading DVD disc, IOA is low level; V304 and V305 cut off; V303 is on; V304 drain electrode is equal to hang in the air (laser receiver pipe inside loader selects CD channel). Note: V303 and V304 are MOS pipe. - 16 - 3.2.3 Laser power control circuit 1. The circuit schematic diagram is shown as the following figure 3.2.3.1: A B U201 C G Loader D E F Figure 3.2.3.1 Laser power control circuit diagram 2. Working principle: Pin 20 of MT1389 is VCD laser power strong/weak signal input checking pin; pin 21 is DVD laser power strong/weak signal input checking pin; 23 pin is VCD laser power drive control output pin and pin 22 is DVD laser power drive control output pin. When reading VCD disc, if pin 20 of U201 (MT1389) has detected that the laser output power it too strong, after being processed by U201 (MT1389) internal circuit, pin 23 output voltage increases and the on-state degree of V302 decreases to make the voltage supplied for pick-up decrease and the light emitting of laser head become weak. If pin 20 has detected that the laser output power is too low, pin 23 output voltage decreases; on-state degree of V302 increases and the light emitting of laser head become strong to reach the purpose of automatically adjusting laser output power. When reading DVD disc, pin 21 is signal input checking pin and pin 22 is drive control output pin. The working principle is the same with that when playing VCD disc. 3. Key point voltage (unit: V), shown as the following table: Key point Position Voltage when reading DVD Voltage when reading VCD A Emitter electrode of V301 2.9 3.2 B Base electrode of V301 2.2 3.2 C Collector electrode of V301 2.2 0 - 17 - D Collector electrode of V302 0 2.2 E Base electrode of V302 3.2 2.2 F Emitter electrode of V302 3.2 2.9 G one end of R228 0.2 0.2 3.2.4 Reset circuit 1. The circuit schematic diagram is shown as the following figure 3.2.4.1: U207(CS4360) U201 U210(CS5340) Figure 3.2.4.1 Reset circuit schematic diagram 2. Working principle: The two ends voltage of capacitor T217 cannot change suddenly, anode of the capacitor begins charging from 0V and now triode Q204 is on. Pin 5 of phase inverterU205 (HCU04) output port is high voltage and pin 6 of it is low voltage to reset chip U201 (MT1389) and chip U214 (FLASH). When charge of the capacitor is close to 3.3V, triode Q204 cut off; pin 5 of phase inverter input port is low level; phase inverter outputs high voltage from pin 6 and MT1389 reset finishes. After reset of MT1389, reset signal is also given to sound D/A conversion chip CS4360 and sound A/D conversion chip CS5340V for their resetting. 3. Key point voltage (unit: V), shown as the following table: Key Point Position Voltage Remark Cathode of diode VD201 3.3V After pow er-off, TC217 discharge current from this point Point B Anode of diode VD201 After reset finishes, 3.3V After reset finishes, voltage rises from0V up to 3.3V. Point C Pin 5 of phase inverter After reset finishes, 0V After reset finishes, voltage decreases from 3.3V down to 0V. DV33 (pointA) - 18 - 3.2.5 Clock circuit 1. The circuit schematic diagram is shown as the figure 3.2.5.1. Figure 3.2.5.1 Clock circuit Note: Elements marked with “X”symbol are those unused in practice. 2. Working principle: 27MHZ clock provides working clock for system. When powering on, capacitor C275 and C276 will generate a concussion, so a vibration occurs on crystal oscillator. After several times of feedback, a stable 27MHZ clock signal is finally generated on crystal oscillator.The function of phase inverter is to increase feedback coefficient and for isolation. 3. This circuit may probably cause these troubles: power supply not connected; not read disc; colour distortion of picture and no colour of picture. Note: DC voltage of point A and B is 1.47V when in normal working. 3.2.6 Disc in/out circuit 1. The circuit schematic diagram is shown as the following figure 3.2.6.1: 2. Electric current when disc in/out Open disc tray: VCC→ V306CE electrode on→ LOAD+→ Electric machine → LOAD- → V308CE electrode on→R326→Ground When not opening disc tray, pin 51 and 39 of U201 (MT1389) are low level. When opening disc tray, pin 51 of U201 (Mt1389) sends a high level; V308 is on; V308 collector electrode changes into low level; - 19 - Figure 3.2.6.1 Disc in/out circuit LOAD- changes into low level; V306 base electrode changes into low level; V306 is on. V306 collector electrode changes into high level and LOAD+ changes into high level. Close disc tray: VCC→ V309CE electrode on→ LOAD- → Electric machine→ LOAD+ → V307CE electrode on→R326→Ground when closing disc tray, pin 39 of U201 (Mt1389) sends a high level; V307 is on; collector electrode changes into low level; LOAD+ is low level; base electrode through R324 and V309 is low level; V309 is on; V309 collector electrode changes into high level; LOAD- changes into high level. 3.2.7 Main axis braking circuit 1. The circuit schematic diagram is shown as the following figure 3.2.7.1: C307 2200pF OPO R318 0R R317 680K ADIN OP- OP+ R319 R320 150K 150K C308 DNS R322 680K C310 2200pF R321 1 R V1P4 SP- R340 1R Figure 3.2.7.1 main axis braking circuit disgram - 20 - SP+ The equivalent circuit is shown as the following figure: C307 2200pF OPO R318 0R R317 680K ADIN OP- OP+ R319 R320 150K 150K C308 DNS R322 680K R321 1R MT1389 34 47 A/D 37 DMO 35 36 C310 2200pF V1P4 SP- 12 R 3 4 0 1R D5954 SP+ M 5 11 2. Working principle: To prolong the service life of electric machine and decrease the influence of start-up concussion current to the machine, when there is disc in, the development personnel design the main axis electric machine in running state always. Even though “STOP”button is pressed, disc will not stop running immediately. Thus when pressing “OPEN”button, a braking signal is required to make the main axis electric machine stop running to fulfill the completion of opening disc tray in a short period. In the course of playback, Press “OPEN" button and main axis drive signal disappears. For the reason of inertia, the main axis electric machine is still in running state, and now the induced voltage achieved by the induced electromotive force which is generated by electric machine's running on sampling resistor R321 and R340 outputs from pin 34 through resistor E319, R320 and pin 36 of MT1389 after being processed inside MT1389 and magnified, then sends to pin 47 of MT1389 through R13; after A/D conversion and the corresponding processing inside MT1389, an instant electric machine reversal braking signal is outputted from pin 37 of MT1389 to make the main axis electric machine decrease speed. When MT1389 detects the disc stops running, disc tray will open to ensure that disc will not run when disc tray opens. 3. Key point voltage (unit: V), shown as the following table: Key point Position Normal working voltage (V) Voltage change when door is opened (V) SP+ pin 11 of D5954, pin 5 of XS303 3.79 3.79→0.70→1.80 SP- pin 12 of 5954, pin 6 of XS303 1.38 1.38→3.40→1.80 OP+ pin 36/B of MT1389 1.38 1.38→3.10→1.80 OP- pin 35/A of MT1389 1.53 1.53→3.08→1.98 - 21 - OPO pin 34/C of MT1389 2.44 2.44→0.40→2.50 ADIN pin 47/D of MT1389 2.44 2.41→0.41→2.44 DMSO pin 5 of D5954 1.42 1.42 pin 30 of MT1389 1.41 1.41 VIP4 3.2.8 Mute circuit and power-off quieting circuit 1. The circuit schematic diagram is shown as the following figure 3.2.8.1: R21070R(DNS) VOICE-DET MUTEA MUTE1 A MUTE2 B MUTE3 C VCC VD207 1N4148 VD208 1N4148 D VD209 1N4148 +9V R2103 H Q218 1015-S J MUTE-1 VD206 1N4148 VCC 1K R2101 10K R2102 1K TC238 100uF/10V E I R2104 1K G Q211 F 1015-S R2105 -9V 10K Q219 1015-S VD205 Q212 2SC1815-YS 1N4148 R2106 10K k L M TC235 100uF/10V AGND AGND R2108 10K R2109 10K Figure 3.2.8.1 Mute and power-0ff quieting circuit 2. Working principle: under the control of I2 C to MT1389, CS4360 sends 3 mute control signals, MUTE1, MUTE2, MUTE3 from pin 28, 25 and 18 which is added to mute circuit. The generated mute control signal MUTE-1 is added to the base electrode of each switching tubeQ205 - Q210 of 6-path analog channel to make the switching tube and make audio signal bypass into ground to reach the purpose of mute. The working mechanism is that when no audio signal comes to a certain path, CS4360 changes the mute control signal corresponding with this path to high level. After pressing MUTE button, 3-path mute signals all change to high level. When working normally (playing discs), only one path signal of the 3-path signals, MUTE1, MUTE2 and MUTE3 changes into low level, now Q211 is on. The collector electrode of Q211 is high level; Q212 is also on and its collector electrode is low level; Q218 is cutoff; MUTE-1 is low level and sound outputs normally. When muting, MUTE1, MUTE2 and MUTE3 outputted by CS4360 all change into high level. At this time, for the base electrode of Q211 is high level, Q211 is cutoff and Q212 is also cutoff. The emitter electrode of Q218 changes into high level and also is on. +9V voltage is added to MUTE-1 through Emitter Collector of Q218, the outputted high level is added to the base electrode of switching tube Q205~Q210. The switching tube is on and sound is bypassed to ground. - 22 - Power-off quieting: when working normally, because there is no forward bias, Q219 is in cutoff state. When powering off, +9V disappears and the base electrode of Q219 changes into low level. For capacitor TC235 discharge is high level to the emitter electrode, Q219 is on. The discharge of TC235 makes MUTE-1 outputs high level and add to each switching tube through Emitter-Collector of Q219 to make the switching tube on and sound is bypassed to ground to realize the function of power-off quieting. Power-on quieting: when powering on, VCC is connected to power supply, voltage of the two ends of Tc238 cannot change suddenly. The base electrode of Q211 changes into about 5V and then Q211 is cutoff, Q212 is cutoff and MUTE-1 changes into about 1.68 to perform power-on quieting function. The function of -9V voltage in the figure is to ensure the secure cutoff of each switching tube when circuit is working normally. 3. Key point voltage (unit: V), shown as the following table: KEY POINT A B C D E F G H I J K L M NO MUTE 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.53 4.55 5.2 0.84 0.12 -0.15 -4.27 -4.27 5 5 MUTE 5.02 5.02 5.02 5.18 5.23 -3.86 -3.87 1.67 0.81 1.63 -3.87 5 5 INSERT MICROPHO NG 0.02 5.02 0.02 0.53 4.52 5.2 0.64 0.12 -0.15 -4.27 -4.27 5 5 3.2.9 Servo circuit 1. DK1005S adopts SANYO 62 decoder and MTK decode solution (MT1389+FLASH (16M)+ SDRAM (64M)). The servo circuit is mainly composed of front signal processing, digital servo processing, signal processing IC T1389 and drive circuit D5954, in which MT1389 is the main component of decode circuit at the same time. 2. The circuit functional block diagram is shown as figure 3.2.9.1. The Explanation to the block diagram:After powering on or disc in, disc identification circuit identifies the disc inserted into loader, and judges whether the disc is CD or DVD to conduct the corresponding control. At the same time, MT1389 adjusts laser output power through laser power control circuit. Pin 20 of MT1389 is VCD laser power strongness/weakness detecting signal input pin, pin 21 is DVD laser power strongness/weakness detecting signal input pin, pin 23 is VCD laser power drive control output pin and pin 22 is DVD laser power drive control output pin. When reading VCD disc, if pin 20 detects laser output power is too strong, output voltage of pin 23 of MT1389 increases and onstate of V302 decreases to make the voltage provided for pick-up decrease and light emission of laser head become strong. - 23 - TROPEN 39 Disc in/out circuit Disc in/out electric machine and detecting switch 51 TRCLOSE TROUT 48 TRIN 49 DVD laser power control 23 22 20 21 20 VCD laser power control 19 Loader 23 18 Disc identification circuit 17 IOA 114 7 A、B、C、D、E、F(a、b、c、d) 2 1 4 3 Feed electric machine on loader 15 SL+ SL- 14 13 17 12 12 17 18 23 U602 D5954 OPO ADIN OP- OP+ SP- SP+ Main axis braking circuit 35 36 Main axis electric machine on loader 5 Integration circuit 1 Integration circuit MT1389 26 28 47 34 Integration circuit Integration circuit Figure 3.2.9.1 Servo circuit diagram After loader reading disc information, A, B, C, D, E, F signals are sent out to Mt1389 (DVD only has A, B, C, D signals), and then inputted from pin 2~11, 18, 19 of MT1389. After being amplified and processed by the pre-amplifier inside MT1389, now signals are separated to two part s for processing inside Mt1389: After being processed by digital servo signal circuit inside MT1389, one part of signal form corresponding servo control signals and output FOO, TRO, DMO, FMO digital servo control signals from pin 42, pin 41, pin 37, pin 38 of Mt1389 respectively, then change into analog servo control signal FOSO, TRSO, DMSO, FMSO through integration circuit composed by resistor capacitor, and send to driver circuit BA5954 for amplification to bring along focus coil, trace coil, main axis electric machine and feed electric machine after drive amplification. Among these, focus and trace servo are used to correct objective position accurately; feed servo is used to bring along laser head to make radial large-scale move which belongs to the preliminary adjustment to pick-up position;and main axis servo is used to control main axis electric machine to make it read signals in means of constant linear velocity and bring along disc to rotate. - 24 - After processing of amplification by VGA voltage control amplifier and equalization frequency compensation inside MT1389, another part of signals are changed into digital signals through internal A/D converter. When loader is reading CD/VCD signals, these signals are conducted EFM demodulation inside MT1389, and then outputted to latter stage for AV decoding after finishing CIRC (Cross Interleaved Reed-Solomon Code) error correction inside. When loader is readingDVD signals, these signals are conducted ESM demodulation inside MT1389, and then sent to latter stage for decoding after finishing RSPC error correction inside. The other part of servo is open/close disc tray circuit. After panel or remote controller emits open/close disc tray signal toMT1389, in usual conditions, TROPEN and TRCLOSE sent out by pin 39, 51 of Mt1389 are both low level, when signal of “open”comes, after Mt1389 makes disc stop rotating through main axis braking circuit, TRCLOSE is set high to make open/close electric machine on loader frame run to bring along dist tray to eject. After disc tray ejecting to proper Signal of opening to proper position (TR_OUT) is set high level (0V) through the detecting switch on loader frame, MT1389 pulls down TRCLOSE and open/close electric machine stop running. When MT1389 receiving “close”signal, TROPEN is set high level by MT1389, open/clode electric machine tuns conversely to bring along disc tray to close. After disc tray closing to proper position, signal of closing to proper position (TR_IN) is set low level through the detecting switch on loader frame, MT1389 pulls down TROPEN and electric machine stops running to finish “close”process. 3. Explanation to servo terms FOO: when rotating, disc may probably move upwards or downwards slightly to make the focus of laser emitted by pick-up cannot justly fall on data pit of disc, so pick-up is required to move upwards or downwards to make focus aim at data pit justly. When pick-up is moving upwards or downwards, it means that pick-up is making focus acts. TRO: data information is save in disc in form of tracks. The process when pick-up moves from one track to another one to read data is trace. In this process, it is objective, but the entire pick-up, that moves forwards or backwards, and the moving range is very small. FMO: similar to acts of trace, the acts of feed are larger than those of trace. Feed conducts a large scale movement firstly, and then trace moves slightly in this range. Feed moves for a while, and does not move for another while; but trace moves all the time. Feed is rough adjustment and trace is fine. DMO: it is the top that holds up disc. Its rotation speed decides that of disc. Its rotation is generated by an individual DC electric machine, in which rotation speed of DVD is twice over that of CD. Hint: In order to observe these processes, you may take down upper cover of the machine, and then the loader cover board. When power on with no disc in or disc in after disc out, you may observe that pick-up returns to inner ring firstly and then springs back for a little distance, which is feed process. Then pick-up will emit light and you may notice the objective moves upwards and downwards, which is focus process. In face, in the same time of focus, the objective also moves upwards and backwards to - 25 - Make trace acts. Because the range is small, it is not easy to observe, and meanwhile DEMO disc tray also rotates slightly, which is DEMO acts. 3.2.10 Decode circuit 1. Decode circuit block diagram is shown in the following figure 3.2.10.1: PWR SDCLK PRD SDCKE DCS PCE DRAS MT 1389 A0~A20 SWE FLASH DQM0 AD0~AD7 SDRAM DQM1 DQ0~DQ15 URST MA0~MA11 SDA SCL Reset circuit V18 EEPROM 27M 24C02 Clock 1.8V voltage regulating U206 Figure 3.2.10.1 Decode circuit block diagram 2. Working principle: this decode circuit is mainly composed of Mt1389, SDRAM and FLASH. The important conditions for decode circuit working: (1) Reset: refer to reset circuit working principle for details. (2) Clock: this system adopts 27M external clock input and produces the clock signal required inside system through internal frequency doubling circuit. (3) Power: decode chip adopts two groups of power supply: 3.3V and 1.8V, in which 1.8V is provided for internal logic control circuit, so we call care voltage. After power on, reset circuit performs reset to CPU (8032) and FLASH inside Mt1389, decode chip outputs reset signal at the same time to perform reset to other circuit. After system reset, read signal is sent out to FLASH to read the information saved in FLASH and machine displays power on picture. Servo system begins to work to check whether machine closes to proper position and whether switch is turned off, if not, close action is performed. After door detect switch is turned off, the machine begins to carry out the preparation work for reading disc and panel display at the same time. Playback process: laser head picks up disc signal from disc, after being processed by servo system, and sends it to decode circuit for decoding, and signal after being decoded is saved in SDRAM - 26 - Temporarily; when machine needs to replay signal, decode circuit calls the information inside SDRAM for output. Save user's information: information set by user is saved inside EEPROM, if users do not renew ot reset this information, it will be saved inside IC forever. Audio, video output circuit: at present, MT1389 integrates to video D/A converter, MT1389E integrates audio D/A converter inside, and manufactures may select according to their own needs, so when decode audio outputs, part of analog output is digital output. Please refer to circuit diagram and audio circuit introduction for details. 3.2.11 Video circuit 1. The circuit functional block diagram is shown as the figure 3.2.11.1: Y 194 C 196 V-OUT S-VIDEO V-OUT 198 Y1 MT1389 Pb 20 0 203 Pr Component video 20 2 SCART terminal Figure 3.2.11.1 Functional block diagram of video Brightness signal, colour difference signal, CVBS signal and component video signal after being decoded by U201 (MT1389) are sent out to the corresponding terminal for output after lowpass filtering and clipping. Take C signal as an instance, the following figure 3.2.11.2 shows the working principle of filtering limiter circuit. VCC VD210 1N4148 L243 Y2 VIDEO_C 1.8UH R261 75R C289 47pF VD211 1N4148 C290 47pF VGND VGND Figure 3.2.11.2 C signal circuit diagram - 27 - 2. Working principle: R261 is a matched resistor, which makes the signal achieve the maximum power on load. Capacitor C289, C290 and inductor L243,compose a lowpass filter which filters the high frequency interference signals beside useful ones; diode Vd210 and Vd211 compose a limiter circuit. It is known from features of diode that the maximum amplitude of colour difference signal C cannot exceed 5.7V and the minimum one cannot be under -0.7V, thus the high voltage signal from TV set can be avoided burning down the player. Please refer to video signal flow diagram for details. 3. Key point voltage (unit: V) is shown as the following table: Signal Function Trouble No disc In playing Y S-VIDEO brightness S-video has no picture/picture bright/picture dark 0.74/0.65 1.44 C S-VIDEO chroma S-video has no clolr/color distortion 1.48 1.48 VIDEO Compound signal of component video Composite video has no picture/picture bright/picture dark 0.64 0.66 Y1 Brightness signal of component video Component video has no picture/picture bright/picture dark 0.78/0.67 0.56 Chroma signal of component video Component video color distortion 1.76/1.46 0.71 1.5 0.77 Pb Pr Note: In "No disc" column, "/" symbol refers to the data when blue screen is changing into black screen. The above measurement are all those when connecting with load. 3.2.12 Audio circuit 1. The function of connect signal between MT1389 and Cs4360 is shown as the following 213 214 MT1389 215 217 218 219 ALRCK 6 ABCK 5 ACLK 7 ASDATA0 ASDATA1 ASDATA2 2 CS4360 3 4 Figure 3.2.12.1 Diagram about the connection between MT1389 and Cs4360 2. Explanation to signal function is shown as the following table: Signal Name Relevant function ALRCK Left/right bit clock Use to separate left and right signal channels ABCK Bit clock signal ACLK External clock signal Signal Name Relevant function ASDATA0 Digital audio signal includes left/right channel signal Use to ensure the accuracy of signal transmission ASDATA1 Digital audio signal includes surround left/right channel signal working clock of CS4360 ASDATA2 Digital audio signal includes centre/subwoofer channel signal - 28 - 3. Functional block diagram of audio circuit is shown as the figure 3.2.12.2. 222 217 218 219 Mt1389 214 213 215 SDA SCL RST SDATA0 SDATA1 SDATA2 SBCLK 2 3 4 U207 CS4360 7 SW C SR SL R L AUDIO_SW AUDIO_C AUDIO_SR AUDIO_SL AUDIO_R AUDIO_L Operation al amplifier U219 U220 U221 TO AV BOARD TDA1308 28 25 18 U214 153 151 152 158 19 20 23 24 26 27 D/A 6 SACLK 225 10 5 SLRCK ASPDIF 11、12 Head phone Mute circuit SPDIF 158 AMDATA 8 7 2 A/D Cs5340 4 12 OK Q 10 OK L MUTE1 MUTE2 MUTE3 Figure 3.2.12.2 Functional block diagram for audio circuit 4. Working principle: digital audio signals SDATA0, ASDATA1 and ASDATA2 after being decoded by U201 (MT1389) are outputted to pin 2, 3 and 4 of U207 (CS4360) from pin 217, 218 and 219 of U201 (MT1389) respectively, among which the function of 33ohm resistor is to prevent electromagnetic interference. The above three-path digital signals, through CS4360 D/A conversion, output left/right channel analog audio signal from pin 27 and 26; output left/right channel mute control signal MUTE1 from pin 28; output surround left/right channel analog audio signal from pin 24 and 23; output surround left/right channel mute control signal MUTE2 from pin2; output centre subwoofer analog audio signal from pin 20 and 19 and output centre subwoofer mute control signal MUTE3 from pin 28. When a certain path signal has input, the corresponding analog signal of this path has output, and the corresponding MUTE signal is low level, or else it is high level. He used three-path clock signals of U207 (CS4360) are the same with those of U210 (CS5340). U210 (CS5340) is to converse the analog OKA into digital signal and then output from pin 4 of U210 (CS5340), then into pin 224 of MT1389 and form echo with OKA signal which is connected to the operational amplifier after being processed inside U201 (Mt1389). - 29 - 3.2.13 Power circuit 1. The circuit functional block diagram is shown as the figure 3.2.13.1: Bridge rectification and filter circuit 310V DC Start circuit +9V Rectification diode Filter capacitor Rectification diode Filter capacitor +5V Rectification diode Filter capacitor +3.3V Rectification diode Filter capacitor FL+ A Absorption loop SA+5V FLFiltering Rectification diode Rectification diode ~220V Switch module FSDH321 Feedback loop Filter capacitor -21V Q501 Zd502 -9V Figure 3.2.13.1 Power circuit flow chart 2. Working principle A: The working range of this switch power is AC 110V~250V. The voltage value here is 1.414 times of effective AC value. (1) Electromagnetic interference filter circuit: for various electromagnetic radiation exits in surroundings, the inputted current will be disturbed. The function of electromagnetic filter circuit is to remove these interferences by filtration to make those which enter the bridge rectification circuit are relatively pure 220V AC. (2) Bridge rectification and filter circuit: the function of this circuit is to generate a DC about 310V to provide usage for future. (3) Start circuit: when power-on just starts, transformer has not started working, and now the start circuit provides a power supply voltage for FSDH321 to make it work. (4) Absorption loop: The waveform of pin 2 of switch module FSDH321 sometimes is high level, and sometimes is ow level, so a strong self-induction voltage will generate in primary coil of transformer and FSDH321 may probably be caused damage. The function of absorption loop is to form a loop for this self-induction to ensure the normal working of circuit. (5) Rectification diode: The voltage which is just outputted from transformer is pulsating DC. The function of rectification diode is to change pulsating DC into DC together with the later filter circuit. (6) Feedback loop: The length of time of “on’and “off”within the same cycle inside switch module FSDH321 is decided by the feedback loop. Feedback loop samples the +3.3V output port voltage. When the output port voltage is too high, the sampled voltage is on the high side. Through feedback loop, it changes the ratio of occupying space of pin 2 of FSDH321 to decrease the time of on-state. The coupling quantity of transformer decreases and outputted voltage starts decreasing. When the outputted - 30 - Voltage is too low, the sampled voltage is on the low side. Through feedback loop, it makes the ratio of Occupying space of FSDH321 increase. The coupling quantity of transformer increases and outputted voltage starts increasing. Through the function of feedback loop, it makes power board output relatively stable voltage. LM431 used in this power supply is a 2.5V comparison device, which is compared with sampling voltage. When sampling voltage is more than 2.5V (means output voltage is on high side), LM431 is on, and light emitting diode in photoelectric coupler starts emitting light to make the other side of photoelectric coupler starts being on. The light emission of light emitting diode is stronger, the onstate degree is larger. The on time of switch module FSDH321 decreases, the coupling quantity of transformer decreases and the outputted voltage starts decreasing. When sampling voltage is less than 2.5V (means output voltage is on low side), LM431 is cutoff. The on time of FSDH321 decreases, the coupling quantity of transformer decreases and output voltage starts increasing. Through auto control function of feedback loop, it makes power board output relatively stable voltage. (7) Filter circuit: its function is to generate a stable and small-curve DC voltage. “∏" shaped filter is usually adopted in filter circuit. The feature of capacitor filtering is that load resistance is high. When current is small, the function of filtering is obvious. But the feature of inductor filtering is that load resistance is small. When current is large, the function of filtering is obvious. If the capacitor is constructed to “∏" shaped filter, it can perform better filtering effect. 3.2.14 MIC circuit 1. MIC circuit block diagram is shown in the following figure 3.2.14.1: TO U603 +5V Voltage regulating circuit -9V +9V XS601 DET MIC U401 amplifying U401 amplifying TO MPEG OK Figure 3.2.14.1 MIC circuit block diagram 2. Working principle: MIC part: when microphone is inserted into MIC left, DET signal changes from low level to high level, which makes mute circuit of decode part off, no matter disc reading is available, audio signal may output. If this signal has trouble, MIC will have no sound when playback stops. After being filtered, signals inputted in MIC transmit to pin 5 of U601, and signals after discharge output from pin 7 of U601, after being amplified for the second time, they are outputted from pin 1 of U601 to decode board directly for Karaoke signal processing and output overlapped with audio signal to realize Karaoke function. - 31 - 3.2.15 Headphone circuit 1. Headphone circuit block diagram is shown in the following figure 3.2.15.1: R H-R XS603 U603 TDA1308 headphone amplifying H-L L JK601 Headphone socket Figure 3.2.15.1 Headphone circuit block diagram 2. Working principle: H_L/H_R signal of audio output end transmits to headphone amplifying circuit of MIC board through XS603 and headphone amplifying circuit is mainly composed of U603 (TDA1308). Function of main pins of TDA1308: pin 1, 7 is output pin; pin 6, 2 is input pin. After being amplified, audio signals output to headphone socket (JK601) directly. 3.2.16 panel control circuit 1. The circuit functional block diagram is shown as the following figure 3.2.16.1: IR 111 3 HS0038A2 U403 Remote control receiver VCC U201 2 VFDST R415 101 VFDCK VFDAT Subsidiary panel KEY 9973-2 MT1389 99 100 LED2 Indicator light control circuit 15 10 16 11 12 13 9 8 6\5 U401 UPD16312 VFD401 Figure 3.2.16.1 Panel control circuit diagram 2. Working principle: control panel components are composed of VFD screen, drive IC U401 (UPD6312), remote control receiver HS0038A2, buttons and indicator light. U401 (UPD6312) processes the data sent by decode board, and drive display screen displays the corresponding state information; meanwhile,scans panel buttons matrix and sends to U201 (MT1389) after processing buttons information to realize the control to the player by users.Pin 3 of remote control receiver sends the remote control information to U201 (MT1389) to realize remote control function. It has three pin in all, in which pin 1 grounding, pin 2 provides 3.3V voltage and pin 3 IR outputs to decode board. - 32 - 3.2.17 AV output circuit 1. Shown in the figure 3.2.17.1, this board( 7969-5) is mainly composed of output terminal, SCART output switch circuit and filtering circuit. Main functions: output audio and video signals. Video part includes S-video, component video, composite video output. Audio part includes left/right channel, surround left/right, centre, subwoofer and coaxial cable output. SCART terminal integrates cideo and audio output in one. PDAT2 PDAT1 +10V R# L# VIDEO# Y1 Pb Pr RGB_CVBS Mode switch AV_TV SCART Component video output terminal XS701 SPDIF Optical, coaxial terminal SL SR CC LFE Audio output terminal Figure 3.2.17.1 AV output board circuit block diagram 2. SCART terminal SCART terminal is the one that integrates video and audio transmission together, which can transmit video and audio signal, and also the operation is very convenient. There are 21 holes in all locating in the centralpart at the rear side of the player. (1) Explanation to SCART terminal pin function is shown as the following table: Pin Name Signal direction 1 A(B)OUT I 2 A(B)IN 3 A(A)OUT 4 A-COM 5 RETURN 6 A(A)IN 7 BLUE I/O Function description Signal direction Pin Name Audio right channel input 12 NC O Audio right channel output 13 RETURN Pr signal ground I Audio left channel input 14 RETURN Blanking signal ground Audio signal ground 15 RED I/O I/O Pr signalI/O port Pb signal ground 16 BLK I/O I/O Blanking signal I/O port ★ O Audio left channel output 17 RETURN Blanking signal ground I/O Pb signalI/O port 18 TRTURN Composite video signal ground - 33 - Function description Network communication data line 2 8 FUNCSW I 9 RETURN 10 CONT 11 GREEN I/O Function selection jack 19 V-OUT I Composite video signal input Y1 signal ground 20 V-IN O Composite video signal output I/O Network communication data line 2 21 GND I/O Y1 signal I/O port Common (3) SCART terminal function selection is shown as the following table: PDATO PDAT1 PDAT2 Pin 8 of SCART terminal Function 0 × 0 10V AV4:3 0 × 1 7.5V AV16:9 1 × 0 0.90V TV 1 × 1 0.85V TV × 0 × × CVBS MODE × 1 × × RGB MODE Note: PDAT0 and PDAT2 are used to control input voltage of pin 8 of SCART terminal; PDAT1 is used to control voltage change of pin 16 of SCART terminal and the voltage on pin 16 controls SCART terminal to select RGB mode or CVBS mode. - 34 - Section Three Servicing Cases 3.3.1 Servicing cases 【Example 1】Symptom: power on automatically Description: after connecting to power, do not press POWER button, power indicator light is on and machine starts up at the same time. Analysis and troubleshooting: use multimeter to test each channel voltage output of power board and find that there is no CPU3.3V, other channels are normal; check elements in this channel and they are all normal; test pin 9 of transformer and find that there is no voltage output; after checking, open circuit happens between pin 9 and 13 of transformer; after changing transformer, trouble is removed. 【Example 2】Symptom: loader is loud Analysis and troubleshooting: after closing to proper position, loader gives a click sound; check loader and find that after laser head reset is ok, it does not retract quickly, but in reset all the time; push laser head close to main axis electric machine, use multimeter to test pin 3 (LIMIT) of Xs306 and it has open circuit to ground; check feed switch and find that this switch has lost effect; after changing switch, machine is OK. 【Example 3】Symptom: door not open Description: light emission, main axis and feed are all normal; press OPEN button but not any acts happens. Analysis and troubleshooting: use multimeter to test the voltage output of pin 3 of the 5P flat cable XS306 from frame to decode board (open to proper position test) and it is +1.6V, which should be +3.3V; test the resistor from pin 3 to 1389 and it is 330 ohm without trouble, so we doubt that 1389 has trouble; after changing 1389, machine is ok. 【Example 4】Symptom: no picture, no sound and no screen display Step 1: check all voltage of X203, and they are all normal. Step 2: check output voltage of U209 (1.8V voltage regulator) and it is 1.9V, which is normal; check pin 37 of U214 (flash) and it is 3.23V, pin 1 of U211 (SDRAM) is 3.19V, pin 14 of U205 (HCU204); pin 8 of U202 (24LLC02) and it is 3.21V, which is normal. - 35 - Step 3: use oscillograph to test frequency of crystal oscillator X201 and find that there is no waveform; check start-up capacitor C275 and C276 and find that resistance of two ends of C275 is 100 ohm, so this capacitor has electric leakage; after changing it, the machine is ok. 【Example 5】Symptom: component vide has no output Step 1: after checking, we find that composite video is normal, so we can preliminarily determine that component video output part has trouble. Step 2: use oscillograph to test 3 component video output pins of pin 200 (Y4) of U201 (Mt1389), pin 202 (Y5) and pin 203 (Y6, and we find 3 have waveform output, so we may judge that trouble does not lie in Mt1389, but in output circuit. Step 3: in the 3 component video, only when brightness signal has trouble, there is no output, so we directly check the path of brightness signal. Check brightness signal Video-Y4 of pin 11 of flat cable holder XS204 and find that there is no waveform output, so we can judge that trouble lies in decode board. Step 4: check anode of catching diode V216, shown in the figure 3.6.1, and there is still no waveform, so we can confirm that trouble lies in filtering circuit n=matching resistor. R273 is matching resistor, Vd216 and Vd217 are catching diode, and L246, 213, C298, C299 comprise filtering circuit. Step 5: use multimeter to test above circuit elements and no problems are found, but in the above circuit, point A has no waveform; carefully observe L246 and it has rosin joint; after well welding it, component video output resumes normal. 【Example 6】Symptom: color distortion of component video Step 1: use oscillograph to check YpbPr terminal and find that Pb terminal has no signal output. Step 2: use oscillograph to check Y5 signal (pin 202 of 1389 or high level end of R276), and no abnormality is found. Step 3: use oscillograph to check VIDEO-U signal (Vd218 anode) and VIDEO-U and they are normal. Step 4: use oscillograph to check two ends of L247, L214 and find that L247 has open circuit; after changing L247, machine is normal. 【Example 7】Symptom: component video has no output After checking, composite video output is normal, when using oscillograph to test pin 200, 202 and 203 of MT1389, they all have no output; composite video is normal, so we preliminarily judge that trouble does not lie in clock circuit and power supply circuit; change MT1389 directly and component video output resumes normal. - 36 - 【Example 8】Symptom: there is picture but no sound Step 1: all channels have no sound, so trouble is certain to lie in the common part of these channels. Common part of these channels: 1. Power supply voltage of 4558. 2. MUTE-1 signal in mute. 3. CS4360 has trouble. 4. MT1389 has trouble. Step 2: check power supply voltage (土9V) of 4558 from simple steps and it is normal. Step 3: use multimeter to test C electrode of voltage Q218 of MUTE-1 signal and it is high level (1.68V), so trouble may probably lie in mute circuit. Step 4: in mute circuit, to make MUTE-1 be 1.68V, Q212 is sure to be cutoff. To make Q212 cut off, cathode of VD207, VD208, VD209 must be high level; but when using multimeter to test cathode of VD207, it is low level, Q212 should be on in normal conditions; so we decide that Q212 may probably have trouble. Step 5: change Q212 and trouble is removed. 【Example 9】Symptom: mixed right channel has no sound. Step 1: use oscillograph to check R terminal and confirm that there is no output. Step 2: use oscillograph to check pin 26 FR signal of U207 (CS4360) and output is normal. Step 3: check waveform of RT signal (pin 19 of XS204 or C electrode of Q205C) and it is normal. Step 4: check waveform of pin 1 of U219 (4580) and the output is normal. Step 5: use multimeter to check C electrode resistance to ground of Q205 and it is zero, so we doubt Q205 has trouble; after changing Q205, machine is normal. 【Example 10】Symptom: power not on after switching on machine Step 1: check voltage of pin 7 (5V), pin 9 (3.3V) and pin 11 (5V) of Xs203 and it is normal, so ie is estimated that trouble lies in decode board. Step 2: check voltage of pin 2 of U209 and it is 0V (which should be 1.9V in normal condition). Step 3: check R242 and R243 resistance and it is normal, so we estimate that U209 is damaged. Step 4: after changing U209, machine is normal. 【Example 11】Symptom: there is picture but no sound Step 1: each channel has no sound, so trouble lies in the common part of each channel. Step 2: check mute signal MUTE-1 (one end of R2118) and it is -0.98V, which is normal. Step 3: check power supply of U207 (CS4360) and it is normal. Step 4: use oscillograph to test pin 26, 27 of U207 (Cs4360) and find that there is no waveform output; use oscillograph to test pin 2 of U207 (Cs4360) and there is waveform input, so we preliminarily judge that U207 has trouble. Step 5: after changing U207 (Cs4360), trouble is removed. - 37 - 【Example 12】Symptom: not read disc Step 1: check the nerve flat cable socket on Xs301 and no abnormality is found. Step 2: change loader, disc reading is normal and trouble is removed. 【Example 13】Symptom: not read disc Step 1: check Xs301 flat cable and socket and there is no abnormality. Step 2: change loader but trouble still exists. Step 3: check power supply, observe laser head main axis and feed and they are normal, but no focus. Step 4: check D5954 power supply and reference voltage and they are both normal. Step 5: check MT1389 power supply with reference to “MT1389 power supply troubleshooting”. Step 6: check the path between pin 42 (focus error signal output) of MT1389 and pin 1 of D5954, after changing C213, trouble is removed, so it shows that C213 has electric leakage. 【Example 14】Symptom: not read disc Step 1: check flat cable and socket on XS301 and there is no abnormality; change loader and trouble still exists. Step 2: when no disc in, after closing door, we find that when lease head is making focus and trace acts, the emitted DVD light is not strong enough, so we preliminarily judge that laser power control circuit has trouble. Step 3: when using multimeter to test V301 and V302, we find that V301 is stricken through; after changing V301, trouble is removed. 【Example 15】Symptom: machine down in the course of playing According to former experience, this type of trouble may probably occur in MT1389, so change MT1389 directly and trouble is removed. Conclusion: for this type of trouble, firstly change Mt1389, if trouble cannot be removed, change U211 (SDRAM), if it cannot be removed again, change U214 (FLASH). 【Example 16】Symptom: power not on Step 1: check voltage on XS203 flat cable holder and all are normal; check power voltage on U201 (MT1389), U211 (SDRAM), U214 (Flash), U202 (24LLC02) and it is also normal. Step 2: check reset circuit, and reset by force, and power is still not on; check clock circuit and clock frequency is normal. Step 3: change U217 (flash) and trouble is removed. Conclusion: when power supply, reset and clock are all normal, for this type of trouble, firstly change U214 (flash), and then U201 (MT1389) or U211 (SDRAM). - 38 - 3.3.2 Troubleshooting flow chart 1. Troubleshooting process for “Power not on”is shown in the following figure 3.3.2.1: Power not on Check whether voltage of pin 7 (5V), pin 4 (9V) and pin 9 (3.3V) of Xs203 is normal N N Whether output of each path is abnormal Y Y N Check whether power supply loop short circuit over the ground or electrical leakage of filter capacitor appears on decode board N Check whether pin 2 of U209 is short circuit over the ground or resistance gets smaller N Y Whether 1.C237 , TC209.2.C2167\ C254\C2174\C256C25 7\C258 has electric leakage or short circuit N N Check whether pin 5 of U205 (HCU04) is low level N Y A Check whether capacitor C275\C276 has electric leakage and short circuit Change U201 (MT1389) Check whether inductor on 3.3V power supply circuit 1. Change Q204 and check whether it is OK 2. Change VD201 and check whether it is OK N Refer to troubleshooting process of reset circuit Y OK Change U205 N N OK Y Y Change U209 and check whether it is OK Y Change the corresponding element Y Whether two ends of X201 are 27MH frequency when tested by oscillograph Change U209 (LM1117MP-1.8) N Y Check whether pin 6 of U205 (HCU04) has 3.3V Change the corresponding resistor Y Y 1. Check whether pin 37 of U214 (FLASH) has 3.3V. 2. Whether pin 1 of U211 (SDRAM) has 3.3V. 3. Whether pin 14 of U205 (HCU04) has 3.3V. 4. Whether pin 8 of U202 (24LLC02) has 3.3V. Check whether resistance of R242 and R243 are normal Power board troubleshooting Y Refer to troubleshooting process for "power board" for details of power board trouble Check whether pin 2 of U209 has 1.8V voltage Whether power supply pin is short-circuited to ground N Y Change crystal oscillator X201 and check whether it is OK Y Change the corresponding capacitor OK - 39 - N 1. Change U205 and check whether it is OK 2. Check relevant element of reset circuit Change U211 (SDRAM) A N Whether the power is on after restoration by force (note 1) N Whether SDRAM CLOCK is normal Note 1: use a lead to make Y any end of R256 ground for a second N Y N Y Refer to troubleshooting process of reset circuit Program is missing Whether decode chip is normal N Y Change SDRAM Whether firmware upgrading is ok N Change decode chip Y OK Whether SDRAM working is normal Y OK Figure 3.3.2.1 Troubleshooting flow chart for “Power not on” - 40 - Change U201 (MT1389) and check whether it is OK Y OK 2. Troubleshooting process for “Picture has distortion”is shown in the following figure 3.3.2.2: Image distortion Composite video signal distortion Component video distortion All kinds of video output distortion Check whether catching diode VD214 is normal Check whether one path has output in the three paths Restore to default settings Note ① Check catching diode on each component Check whether clock signal is normal Check whether matching resistor R270 and C295, C296, L245 in filter circuit are normal Change MT1389 Change MT1389 Check whether power supply of Mt1389 is OK Change MT1389 Change MT1389 Figure 3.3.2.2 Troubleshooting flow chart for “Picture has distortion” Note: ① Flow chart of restoring to default settings is shown as figure 3.3.2.3: Disc tray open Press SETUP button on remote controller RESET TO Default Press SELECT button twice Figure 3.3.2.3 Operation flow chart for restoring to default settings - 41 - 3. Troubleshooting flow chart for “Having picture but on sound”is shown as the figure 3.3.2.4: Having picture but no sound Check whether power supply I of 4558 and U207 (CS4360) is normal N Check power supply circuit Y Check whether pin 26 of CS4360 has waveform output N Check whether pin 2 of U207 (CS4360) has waveform input N Y Y Check MRTE-1 signal of mute circuit Check whether power supply of MT1389 is normal N Check power supply circuit Y Change CS4360 Change U201 (1389) Figure 3.3.2.4 Troubleshooting flow chart for "Having sound but no sound" - 42 - 4. Troubleshooting process is shown as the following figure 3.3.2.5: Trouble when opening/ closing disc tray Opening disc tray not fully Noise occurs in disc tray door Change frame Close disc tray automatically Open/close disc tray automatically Open disc tray automatically Vibration occurs when disc in/out Disc tray not open Y Disc tray not close Check whether frame is normal N Check whether TC308 and TC309 are normal Check whether flat cable is inserted fully N Well insert flat cable Y Change abnormal capacitor Check whether socket on frame and XS302 has been oxidated N Change socket or use alcohol to clean Y Whether detector switch on frame is normal N Change frame Y Check whether V306 V307 V308 V309 V310 are normal N Change the corresponding triode Y Check whether the resistor and capacitor related to disc open/ close is rosin joint and joint welding Figure 3.3.2.5 Troubleshooting flow chart when opening/closing disc tray - 43 - Change frame 5. Troubleshooting process for “No output for composite video”is shown as the following figure 3.3.2.6: No output for composite video signal Whether it is normal after restoring into default settings N Whether Y3 has video waveform output N Whether U201 (MT1389) power supply and crystal oscillator circuit is normal N Y Y Y OK Change U201 (MT1389) Whether VIDEO_ COMP has waveform N Check whether matching filter circuit has capacitance electric leakage or inductor circuit opening Y Check XS204, XS701 flat cable and socket Y Check filter circuit Figure 3.3.2.6 Flow chart of “No output for composite video” - 44 - 1. Check power supply circuit 2. Check clock signal check and correct flow 6. Troubleshooting process for “On-screen-mosaic when playing”is shown as the following figure 3.3.2.7: On-screen-mosaic when playing Y Check whether power supply and clock signal of U201 (MT1389) is normal N Refer to troubleshooting process of U201 (MT1389) power supply and clock circuit Y Change U201 (MT1389) Ok? Y Finish N Change U211 (SDRAM) N Change U214 (FLASH) Y OK Figure 3.3.2.7 Flow chart of “On-screen-mosaic when playing” - 45 - 7. Troubleshooting process for "No colour of picture" is shown as the following figure 3.3.2.8: No colour of picture Y Check whether clock signal is normal N Check clock circuit Y Check whether U201 (MT1389) is normal N Check clock circuit Y ChangeMT1389 N Check other circuit Y OK Figure 3.3.2.8 Flow chart of “No colour of picture” - 46 - 8. Troubleshooting process for “5.1CH has no sound output”is shown in the following figure 3.3.2.9: 5.1CH has no sound output Whether 1389 power supply is normal N Whether machine mutes N Check power supply circuit Y Y Cancel mute Whether signal outputted by decode chip is normal N Check power supply loop N Y Y N Whether machine setup is normal Change decode chip Whether +9 -9V +5 power supply is normal Y Check whether CS4360 output is normal N Change CS4360 Y Check mute circuit Figure 3.3.2.9 Troubleshooting flow chart for “5.1CH has no sound output” - 47 - Resume setup 9. Troubleshooting process for “Left channel has no output”is shown in the following figure 3.3.2.10: Left channel has no output Check whether pin 27 of CS4360 has signal output N CS4360 has trouble Y Check whether pin 6 of U219 has signal output N Check C2115 C2119 TC225 R2134 R2135 R2148 Y Check whether pin 7 of U219 has signal output N Change U219 Y Check whether C electrode of Q205 has signal output N Check Q205 TC241 Y Check whether XS204 and flat cable is normal N Change Y Check socket and terminal of AV board Figure 3.3.2.10 Troubleshooting flow chart for “Left channel has no output” - 48 - 10. Troubleshooting process when voltage is on high or low side, shown as the following figure 3.3.2.11: Voltage is on high or low side Only one channel is on high or low side On high or low side when multi-channel output Check whether R506, C515, R509 and R508 are normal N Change the corresponding element Y OK N Check whether rectification diode of this circuit is normal Y OK Check the corresponding element of feedback loop Y Check whether C510, TC514 and TC510 are e lectrical leakage or short circuit Check whether filter capacitor is electric leakage or short circuit N Change U503 (LM431) whether it is normal N Change U502(PC817) whether it is normal Y N Change D513 whether it is normal Y OK OK Figure 3.3.2.11 Troubleshooting flow chart for “Voltage is on high or low side” - 49 - Y OK N 11. Troubleshooting process for “Output power of power supply is not enough”is shown as the following figure 3.3.2.12: Output power of power supply is not enough Only one channel’s output power of power supply is not enough Y Change filter capacitor of this channel Several channels’output power of power supply are not enough N Change this channel rectification diode and check whether it is normal Y OK Insert decode board and check whether 310V voltage exists on TC501 N Y Whether it is normal after changing TC501 N Change U501 Y Y OK Change D513 and check whether it is normal Y OK N Change Tc514, C510 and check whether it is normal OK N 1. Check whether earth capacitor, such as C506 is electrical leakage or short circuit 2. Change FSDH321 3. Check feedback loop N Change D506, TC502 and C504 and check whether it is normal Y OK 1. Check rectification diode on bridge circuit 2. Check other circuits Y OK Figure 3.3.2.12 Troubleshooting flow chart for “Output power of power supply is not enough” - 50 - N 12. Troubleshooting process for "No function for buttons" is shown as the figure 3.3.2.13: No function for buttons Check whether voltage of VCC is about 5V N Check power supply voltage of panel Y 检查U401到 解 码 芯 片 的信号是否正常 N Y Check whether D401 D402 has been burnt out Change U401 (UPD6312) and check whether is has been restored N Check other circuit of decode board Y N OK Y Whether it has restored to be normal after changing D401 D402 N Y OK Figure 3.3.2.13 Troubleshooting flow chart for “No function for buttons” - 51 - 13. Troubleshooting process for "No function for remote control”is shown as the figure 3.3.2.14: No function for remote control Whether voltage of VCC is about 5V N Check power supply voltage of panel N Check receiver power supply loop (R415, C405, Tc407 N Check whether remote control is normal Y Whether voltage of U403_2 is about 5V Y Whether it has restored to be normal after changing receiver Y OK N Repair remote control Y Check whether remote control is normal Figure 3.3.2.14 Troubleshooting flow chart for “No function for remote control” - 52 - 14. Troubleshooting process for “No screen display”is shown as the figure 3.3.2.15: No screen display Whether voltage of point B is about 5V N Check power supply voltage of panel Y Check whether signals to decode board are normal N Change U401 (UPD16312) Y Change VFD screen Figure 3.3.2.15 Troubleshooting flow chart for “No screen display” - 53 - No disc Observe when disc is not in Whether pick-up feed is normal (whether pick-up moves forwards and backwards after power on) N Use digital oscillograph to test R209 and check whether the end close to MT1389 has waveform N Check whether C211 has electric leakage or short circuit Note ① N Y Y Change MT1389 Check whether C213 has electric leakage or short circuit over the ground N Use oscillograph to test R211 and check whether the end close to MT1389 has waveform N Note ② Whether pick-up focus is normal (objective will move up and down after power on) Y N Check whether feed signal channel between MT1389 and D5954 is normal N Change the corresponding element Y Y Change MT1389 Change the corresponding element N Change U302 (D5954)and check whether it is normal Check whether the focus signal channel between MT1389 and U302(D5954) is normal N ① Change MT1389 ② Check other circuit Y Y OK ① Change Mt1389 ② Check other circuit N Change U302 (D5954) and check whether it is normal Y Whether pick-up has laser emission OK Y B N Check whether laser power control circuit is normal N Y 1. Change MT1389 2. Check other peripheral circuit Change the corresponding element B Change whether C210 has electric leakage or short circuit N N Check whether the end close to MT1389 of R208 has pulse Y Change MT1389 Check whether the main control channel between MT1389 and U302 is normal Y Check whether main axis braking circuit is normal Y 1. Change MT1389 2. Check other circuit N Change U302 (D5954) and check whether it is Y OK N Whether main axis revolves Y Whether disc rotation speed is normal after disc is being loaded Y Change decode chip or loader N Whether loader laser head is normal N Change loader Y Check whether the end close to MT1389 of R210 has trace signal, and check waveform N Check whether C212 has electric leakage or short circuit N Y 1. Change MT1389 2. Check other circuit Check whether the line from MT1389 to loader is normal Y Change flat cable N Remove one by one No voltage output In which how many channel/channels has/have no voltage output Only one channel has no voltage output Check whether filter capacitor has electrical leakage Find out which channel has no voltage output No voltage output for eacj channel Y Check whether cathode board of D513 has 3.3V N Y Check whether cathode of rectification diode has voltage N Whether it is normal after changing rectification diode 1. Check whether filter inductor has open circuit 2. Change voltage regulator if there is voltage regulator tube, and check whether it is normal Note ① Check whether 310V voltage exits on TC501 N 1. Check fuse 2. Check bridge circuit rectification diode 3. Check element on electromagnetic interference filter circuit Y Y OK Y Y Check whether R508, R509, C515 and R506 are normal OK N Change the corresponding element Y Change U503 (LM431) and check whether it is normal Note ② N Change U502 (Ph817) and check whether it is normal Y Y OK OK Y Check whether R505, C504, D506, are short circuit or electrical leakage Y Change the corresponding element N Change U501 (FSDH321) and check whether it is normal Y OK N Check whether C510, TC510 and Tc514 are short circuit or electrical leakage Change D513 and check whether it is normal N Change U502 (Ph817) and check whether it is normal Y OK N Change U503 (LM431) and check whether it is normal Y OK N Change transformer N Check other relative elements of feedback loop Section Four Waveform diagram This section collects signal waveform diagram of audio, video and each unit circuit with the purpose to help servicing personnel to judge where trouble lies in accurately and quickly to improve servicing skills. For the difference of oscillograph's type, model and tuner, a certain difference may exist, so the servicing personnel are expected to pay more attention to check in daily operation. 1. Waveform diagram for pulse DC of power board D513 anode 2. RFO signal waveform diagram of pin 8 of Xs301 - 57 - 3. A signal waveform diagram of pin 9 of Xs301(B、C、D、E、F) 4. DMO signal (when there is main axis rotation) waveform diagram of pin 37 of U201 (MT1389) 5. FMO signal (when there is feed) waveform diagram of pin 38 of U201 (MT1389) - 58 - 6. TRO signal (when there is trace) waveform diagram of pin 41 of U201 (MT1389) 7. FOO signal (when there is focus) waveform diagram of pin 42 of U201 (MT1389) 8. Waveform diagram of pin 29 (when no disc in) of U214 (FLASH) - 59 - 9. Waveform diagram of pin 38of U211 (SDRAM) 10. Video signal waveform diagram 11. ACLK (12.2878MHZ): waveform diagram for external clock signal - 60 - 12. ABCK (3.07195MHZ): waveform diagram for bit clock signal 13. ALRCK (48KHZ): waveform diagram for left/right channel clock signal 14. SDATAO: waveform diagram for mixed left/right channel digital signal - 61 - 15. SDATA1: waveform diagram for surround left/right channel digital signal (now the disc being played is 2.1CH, and this signal has no output; if 5.1CH, the form is the same with that of SDATA0) 16. SDATA2: waveform diagram for centre subwoofer digital signal 17. 1KHZ analog audio signal output waveform diagram (it is suggested to use test disc, if not, the tested waveform will change at any time to affect judgment. Other waveform is accordant except subwoofer). - 62 - 18. LEF#: waveform diagram for subwoofer channel analog signal 19. AMDAT: waveform diagram for microphone signal after 5340 A/D conversion 20. SPDIF: waveform diagram for optical/coaxial digital audio signal - 63 - 21. 27M clock signal waveform diagram 22. Reset circuit waveform diagram URST# Dv33 - 64 - Section Five Function Introduction to IC 3.5.1 function introduction to MT1389 1. MT1389 (U201) adopts LQFP pin 256 casing and 3.3V/1.8V dual voltage working mode, which is a good performance large-scale CDROM front-end processing CMOS integrated circuit, and CD/VCD/DVD player special-used single chip. It includes focus servo error magnification, trace servo error magnification and horizontal output servo control. The main function are narrated as follows: (1) The main function of front-end RF small signal processing is to process and amplify signals A, B, C, D, E and F transmitted from pick-up, and automatically adjust laser output power, meanwhile fulfil the identification of VCD disc and DVD disc. (2) Digital servo processing may produce focus, trace, feed, main axis servo control signal processing and digital signal processing to realize modulating EFM/EFM+ of Therefore signal. (3) MPEG1/MPEG2/MPEG4/JPEG Video decoder. This chip can decode VCD, DVD, MPEG 4 network video, compatible with “network movie”disc, and also can read JPEG picture to fulfil digital album playback. (4) In audio aspect, AC-3/DTS dual decoding, actively read MP3, compatible with DVD Audio decode, to reach high resolution sound quality restore 1000 times higher than that of CD. (5) By using the built-in 8032 micro-processer of chip, MT1389 may also fulfil the control of the player system to simplify circuit design greatly. (6) Deal with data transferred from tuner and control the tuner. 2. Pin function of MT1389 is shown as the following table: Data Pin Name Function DC voltage Remark direction 1 AGND Analog 0 2 DVDA DVD-RF high frequency AC coupling signal A I 1.72 Signals A, B, C and D from 3 DVDB DVD-RF high frequency AC coupling signal B I 1.72 loader are coupled by capacitor 4 DVDC DVD-RF high frequency AC coupling signal C I 1.72 C201, 5 DVDD DVD-RF high frequency AC coupling signal D I 1.72 6 DVDRFIP I 1.2 DVD-RF high frequency AC coupling signal RFIP input - 65 - C202, C203 respectively unused and DVD-RF high frequency AC coupling signal RFIN 7 DVDRFIN I 1.38 input 8 MA DVD-RAM main beam RF DC signal input A I 2 Signals A, B, C and D from 9 MB DVD-RAM main beam RF DC signal input B I 2 loader are coupled by resistor 10 MC DVD-RAM main beam RF DC signal input C I 2 11 MD DVD-RAM main beam RF DC signal input D I 2 12 SA DVD-RAM assistant beam RF DC signal input A I 1.4 13 SB DVD-RAM assistant beam RF DC signal input B I 1.33 14 SC DVD-RAM assistant beam RF DC signal input C I 1.35 15 SD DVD-RAM assistant beam RF DC signal input D I 1.31 16 CDFON CD focus error inverted input I 1.33 17 CDFOP CD focus error onoinverted input I 1.3 18 TNI 3 beam assistant PD signal interted input I 2 19 TPI 4 beam assistant PD signal noninverted input I 2 20 MDI1 Laser power monitoring input 1 I 0 21 MDI2 Laser power monitoring input 2 I 0 22 LDO2 Laser power output 2 O 3.18 23 LDO1 Laser power output 1 O 3.18 24 SVDD3 Servo 3.3V power supply 3.2 25 CSO/RFOP Main servo signal output/RF noninverted output O 1.3 R2165 is unused, so these two 26 RFLVL/RFON RF level output/RF inverted output O 1.33 pins are unused. 27 SGND Servo ground 0 28 V2REFO Reference voltage 2.8V O 2.74 29 V20 Reference voltage 2.0V O 2.18 30 VREFO Reference voltage1.4V O 1.5 31 FEO Focus error signal output O 1.5 32 TEO Trace error signal output O 1.16 R201, R202, R203 and R204 respectively unnsed E, F signal input directly R2166 is unused Joint welding with capacitor C207 33 TEZISLV Trace zero passage error input I connected with this 1.32 position will cause disc not reading 34 OP_OUT Sensing signal magnifying output - 66 - O 2.55 Input/output of main axis braking circuit 35 OP_INN Sensing signal inverted output I 2 36 OP_INP Sensing signal noninverted output I 1.74 37 DMO Main axis control signal output O 1.37 38 FMO Feed control signal output O 1.38 39 TROPEN PWM Close signal output O 0 I 1.38 unused 40 PWMOUT1/ADIN9 the first path PWM signal output/AD universal input 41 TRO Trace control signal output O 1.38 42 FOO Focus control signal output O 1.38 43 USB_VSS USB ground 0 44 USBP USB data I/O 0 45 USBM USB data I/O 0 46 USB_VDD3 USB 3.3V power supply 3.2 47 FG/ADIN8 Sensing signal input/AD universal input I 2.69 48 TDI/ADIN4 I 3.2 I 0 unused Open-to-position checking signal input/AD universal input Open-to-position checking signal input/AD universal 49 TMS/ADIN5 input 50 TCK/ADIN6 BA5954 signal output/AD universal input O 0 51 TDO/ADIN7 Open signal output/AD universal input O 0 52 DVDD18 Digital 1.8V power supply 1.8 53 IOA2 Microcontroller address bit 2 O 1.96 54 IOA3 Microcontroller address bit 3 O 1.98 55 IOA4 Microcontroller address bit 4 O 1.96 56 IOA5 Microcontroller address bit 5 O 1.69 57 IOA6 Microcontroller address bit 6 O 3.23 58 IOA7 Microcontroller address bit 7 O 3.23 59 HIGHA0 Microcontroller address bit 0 O 1.01 60 IOA18 Microcontroller address bit 18 O 0.05 61 IOA19 Microcontroller address bit 19 O 0 62 DVSS Digital 0 63 APLLCAP Analog phase-locked loop external capacitor 1.8 64 APLLVSS Analog phase-locked loop 0 - 67 - FLASH address signal 65 APLLVDD3 Analog phase-locked loop 3.3V power supply 3.1 output PWR# and change into 66 IOWR FLASH read-write control signal O 3.23 DWR# signal to control FLASH through 0 ohm resistor R297 67 A16 FLASH address bit 16 O 1.3 68 HIGHA7 Microcontroller address bit 7 O 1.18 69 HIGHA6 Microcontroller address bit 6 O 1.99 70 HIGHA5 Microcontroller address bit 5 O 2.9 71 HIGHA4 Microcontroller address bit 4 O 2 72 HIGHA3 Microcontroller address bit 3 O 1.11 73 DVDD3 Digital 3.3V power supply 3.24 74 HIGHA2 Microcontroller address bit 2 O 1.81 75 HIGHA1 Microcontroller address bit 1 O 1.55 76 IOA20 Microcontroller address bit 20 O 0 FLASH address signal FLASH address signal FLASH address signal Output PCE# signal and change into DCE# signal to 77 IOCS FLASH chip selection O 0 control FLASH through 0 ohm resistor R298 78 IOA1 Microcontroller address bit 1 O 2.03 FLASH address signal Output PRD# signal and change into DRD# signal to 79 IOOE FLASH output enable O 0 control FLASH output through 0 ohm resistor R299 80 DVDD3 Power supply 3.23 81 AD0 Microcontroller address/data bit 0 I/O 1.32 82 AD1 Microcontroller address/data bit 1 I/O 1.52 83 AD2 Microcontroller address/data bit 2 I/O 1.16 84 AD3 Microcontroller address/data bit 3 I/O 0.9 85 DVSS Ground 0 86 AD4 Microcontroller address/data bit 4 I/O 1.57 87 AD5 Microcontroller address/data bit 5 I/O 1.57 88 AD6 Microcontroller address/data bit 6 I/O 1.57 89 IOA21/ADIN0 Microcontroller address bit 21/AD universal input O 0.03 FLASH data signal - 68 - FLASH data signal FLASH address signal 90 ALE Microcontroller address enable O 1.18 unused 91 AD7 Microcontroller address/data bit 7 I/O 1.6 FLASH data signal 92 A17 FLASH address bit 17 O 0 93 IOA0 Microcontroller address bit 0 O 2.04 94 DVSS Digital 0 95 UWR Microcontroller write operation 3.22 96 URD Microcontroller read operation 3.26 97 DVDD18 Digital 1.8V power supply 1.92 98 UP1_2 Microcontroller port 0 unused 99 UP1_3 Microcontroller port O 5.15 FLASH address signal unused Panel communication-used clock Panel communication-used 100 UP1_4 Microcontroller port I/O 5.2 data 101 UP1_5 Microcontroller port O 5.2 Panel communication-enable 102 UP1_6 Microcontroller port O 0.3 I2C clock 103 UP1_7 Microcontroller port I/O 3.22 I2C data 104 UP3_0 Microcontroller port O 0 Tuning signal after being managed from SAA6588 105 UP3_1 Microcontroller port O 0.68 106 UP3_4 Microcontroller port I/O 3.8 Serial communication port 107 UP3_5 Microcontroller port I/O 3.23 Serial communication port 108 DVDD3 Power supply 3.24 109 ICE Microcontroller correction mode enable 0 Ground through 1K resistor R213 110 PRST Reset input I 3.3 111 IR Remote control signal input I 5.03 112 INT0 Microcontroller interrupt 0 I 3.6 unused 113 DQM0 DRAM input/output screen-shielded signal O 2.2 114 DQS0 DRAM input/output screen-shielded signal O 3.22 115 RD7 DRAM data I/O 0.9 SDRAM data line 116 DVSS Ground 0 117 RD6 DRAM data I/O 0.4 118 RD5 DRAM data I/O 0.85 SDRAM data line - 69 - 119 DVSS Ground 0.02 120 RD4 DRAM data I/O 1.62 121 RD3 DRAM data I/O 1 122 DVDD18 Digital 1.8V power supply 1.9 123 RD2 DRAM data I/O 1.15 124 RD1 DRAM data I/O 0.92 125 RD0 DRAM data I/O 0.92 126 RD15 DRAM data I/O 0.66 127 DVDD3 Digital 3.3V power supply 3.21 128 RD14 DRAM data I/O 1.2 129 RD13 DRAM data I/O 1.2 130 RD12 DRAM data I/O 1.42 131 RD11 DRAM data I/O 0.85 132 RD10 DRAM data I/O 0.87 133 RD9 DRAM data I/O 0.98 SDRAM data line 134 DVSS Ground 0.01 135 RD8 DRAM data I/O 0.67 SDRAM data line 136 DQS1 DRAM input/output screen-shielded signal O 3.24 137 DQM1 DRAM input/output screen-shielded signal O 2.6 SDRAM data line SDRAM data line SDRAM data line Output WE# signal and change into DWE# to control the write 138 RWE DRAM write enable O 3.17 of SDRAM through 33 ohm resistor Output RAS# and change into DCAS# to control line address 139 CAS DRAM line address selection O 3.11 selection of SDRAM through 33 ohm resistor R267 Output RAS# and change into DRAS# to control row address 140 RAS DRAM row address selection O 3.15 selection of SDRAM through 33 ohm resistor R266 141 DVDD3 Digital 3.3V power supply - 70 - 3.22 Output CS# and change into DCS# to control chip selection 142 RCS DRAM chip selection O 2.7 of SDRAM through 33 ohm resistor 265 143 BA0 DRAM section address 0 O 1.75 144 DVSS Ground 0 145 BA1 DRAM section address 1 O 1.95 146 RA10 DRAM address O 0.04 147 RA0 DRAM address O 0.4 148 DVSS Ground 0 149 RA1 DRAM address O 2.2 150 RA2 DRAM address O 2.25 151 RA3 DRAM address O 1.57 152 DVDD18 Digital 1.8V power supply 1.91 153 RVREF/ADIN3 Reference voltage/AD universal input I 0.01 154 RCLKB DRAM clock O 0.01 155 DVDD3 Digital 3.3V power supply 3.21 156 RCLK DRAM clock O 1.66 157 CKE DRAM clock enable O 1.2 158 RA11 DRAM address O 0.03 159 RA9 DRAM address O 0.07 160 RA8 DRAM address O 0.04 161 DVSS Digital 0 162 RA7 DRAM address O 1.4 SDRAM address line 163 DVSS Digital 0 164 RA6 DRAM address O 1.44 165 RA5 DRAM address O 1.74 166 RA4 DRAM address O 1.63 167 DVDD3 Digital 3.3V power supply O 3.21 168 RD13/ASDATA5 DRAM data/audio serial data I 169 RD30 DRAM data I/O SDRAM address line SDRAM address line unused - 71 - SDRAM address line SDRAM address line 5.04/3.03 Digital potentiometer input (J3) 0.01 Digital potentiometer inpout (J4) CD4052 select signal (AUNIN 170 RD29 DRAM data O 0.01 SL0) CD4052 select signal (AUNIN 171 RD28 DRAM data 0.01 SL1) 172 RD27 DRAM data 0.01 select signal of N4 74HCT125 173 DVDD18 Digital 1.8V power supply 1.91 Output to headphone N12. is not When inserted, output 3.3V, and now the output to headphone from N12 has no waveform. When headphone is 174 RD26 DRAM data I/O 3.6 inserted, this pin outputs 0v, and now only the output to headphone and to left/right channel of AV board of N12 output have waveform, which is headphone select signal. 175 DVSS Digital I/O 0 Ground 176 RD25 DRAM data I/O 3.6 Mute signal 177 RD24 DRAM data I/O 1.68 Resistor R225 is unused, so 178 DQM3 DRAM input/output screen-shielded signal O 0.04 this signal is unused in this model. 179 DQM2 DRAM input/output screen-shielded signal O 0.01 Field sync signal 180 RD23 DRAM data I/O 0.01 unused 181 RD22 DRAM data I/O 0.01 Whether headphone is inserted to detecting signal 182 DVDD3 Digital 3.3V power supply 3.21 When 183 RD21 DRAM data 0.02 selecting tuning function, open power supply loop of tuner. 184 RD20 DRAM data 0.01 unused 185 RD19 DRAM data 0.02 control signal of tuner 186 RD18 DRAM data 0.02 tuner data - 72 - 187 RD17 DRAM data 0.02 tuner clock 188 RD16 DRAM data 0.01 tuner data 189 DACVDDC D/A conversion 3.3V power supply 3.5 190 VREF Reference voltage 1.32 191 FS 1.32 192 YUV0/CIN 1.8 unused 193 DACVSSC D/A conversion 0.01 194 YUV1/Y Video signal YUV1 output/Y signal output O 0.74 Supply Y signal for S-video 195 DACVDDB D/A conversion 3.3V power supply 3.19 196 YUV2/C Video signal YUV2 output/C signal output O 1.47 Supply C signal for S-video 197 DACVSSB D/A conversion 0.01 198 YUV3/CVBS Video signal YUV3 output/CVBS signal output O 0.74 Provide for video output port (VIDEO) 199 DACVDDA D/A conversion 3.3V power supply 3.17 200 YUV4/G Video signal YUV4 output/G signal output O 0.5 Supply Y1 signal for component video output port 201 DACVSSA D/A conversion 0.01 202 TUV5/B Video signal YUV5 output/B signal output O 0.01 Supply Pb signal for component video output port Supply Pr signal for component 203 YUV6/R Video signal YUV6 output/R signal output O 0 video output port 204 DVDD3 Digital 3.3V power supply 3.21 205 VSYNC/ADIN1 Field sync signal output/AD universal input O 0.04 Supply for SCART 206 YUV7/ASDATA5 Video signal YUV7 output/audio serial data 3.79 unused 207 HSYNC/ADIN2 Line sync signal output/AD universal input O 0.2 Supply for SCART 208 SPMCLK I 0.01 unused 209 SPDATA 0.14 unused 210 SPLRCK 3.78 unused 211 SPBCK/ASDATA5 3.86 unused 212 DVDD3 Digital 3.3V power supply 3.21 213 ALRCK Audio left/right channel clock O 1.52 214 ABCK Audio bit clock O 1.6 215 ACLK Audio DAC external clock O 1.59 - 73 - 216 DVSS Digital 0 217 ASDATA0 Audio serial data O 0.01 218 ASDATA1 Audio serial data O 0.01 219 ASDATA2 Audio serial data O 0.01 220 ASDATA3 Audio serial data 0.01 unused 221 DVDD18 Digital 1.8V power supply 1.93 222 ASDATA4 Audio serial data O 3.22 Give audio IC reset signal 223 DVSS Digital 0.01 224 MC_DATA MIC digital audio input I 1.24 225 SPDIF Digital audio signal output O 1.61 226 RFGND18 RF signal 0.01 227 RFVDD18 RF signal 1.8V power supply 0.64 228 XTALO Clock output O 3.18 229 XTALI Clock input I 3.04 230 JITFO RF small signal output O 0.04 231 JITFN RF small signal reversely amplifying input I 2.23 232 PLLVSS Phase-locked loop 0.06 233 IDACEXLP 3.22 234 PLLVDD3 Phase-locked loop 3.3V power supply 0.01 235 LPFON Amplifier loop filter output O 0.01 236 LPFIP Amplifier loop filter input I 0.01 237 LPFIN Amplifier loop filter input I 0.09 238 LPFOP Amplifier loop filter output O 2.24 239 ADCVDD3 D/A conversion 3.3V power supply 3.22 240 S_VCM 0 241 ADCVSS D/A conversion 0 242 S_VREFP 0 243 S_VREFN 0.03 244 RFVDD3 RF 3.3V power supply 3.22 245 RFRPDC DC RF error signal input 0.73 246 RFRPAC AC RF error signal input 1.37 247 HRFZC High frequency RF signal zero passage detect 3.2 - 74 - 248 CRTPLP 1.53 249 RFGND RF ground 0.01 250 CEQP 0.05 251 CEQN 0.02 252 OSP 1.68 253 OSN 1.68 254 RFGC 1.06 255 IREF Reference current 0.92 256 AVDD3 Analog 3.3V power supply 3.22 3.5.2 function introduction to FLASH U214 (FLASH) 16Mbit memorizer, FLASH function pin are shown as follows: Voltage (when no disc) Data direction I Write enable signal, low level is effective 3.23V I Reset, low level is effective 3.23V I 3.23V O 0V I 0V I O +5V I/O I Pin Name 1-9、16-25、48 AO-A19 11 WE 12 RESET 10、13、14 NC 15 RY/BY 26 CE 27、46 VSS Ground 28 OE Output enable signal , low level is effective 29-3、6、38-44 Function 20 bit address bus Blank pin Ready/system busy Chip enable, low level effective DQ0-DQ14 15 bit data bus 37 VCC 45 DQ15/A-1 5V power supply Take word extend mode as data line, and bit extend mode as address line Select 8-bit or 16-bit output mode. High level is 16-bit 47 BYTE output and low level is 8-bit output 3.5.3 function introduction to SDRAM The function of SDRAM (U211) in the player is to save program taken out by Mt1389 from FLASH and information of picture and sound taken out from disc when the player is working to form damping, add the stability of information output and add anti-vibration of the player. The pin function and real voltage are shown - 75 - as the following table: Data Pin Name 1 VDD 3.3V power supply 2 DQ0 I/O 3 VDDQ 4 Voltage Data Name 3.18 28 VSS Ground 0.01 Data bus 0.94 29 MA4 I Address bus 1.65 I/O 3.3V power supply 3.19 30 MA5 I Address bus 1.74 DQ1 I/O Data bus 0.9 31 MA6 I Address bus 1.49 5 DQ2 I/O Data bus 1.3 32 MA7 I Address bus 1.22 6 VSSQ Ground 0 33 MA8 I Address bus 0.05 7 DQ3 I/O Data bus 1.2 34 MA9 I Address bus 0.04 8 DQ4 I/O Data bus 1.5 35 MA11 I Address bus 0.04 9 VDDQ 3.3V power supply 3.18 36 NC Blank pin 0.01 10 DQ5 I/O Data bus 0.7 37 CKE I Clock enable signal 1.22 11 DQ6 I/O Data bus 0.45 38 CLK I System clock input 1.68 12 VSSQ Ground 0 39 UDQM I 13 DQ7 I/O Data bus 0.8 40 NC Blank pin 0.01 14 VDD 3.3V power supply 3.14 41 VSS Ground 0.01 15 LDQM I 2.46 42 DQ8 I/O Data bus 0.6 16 WE I Write control signal 3.17 43 VDDQ 3.3V power supply 3.19 17 CAS I Line address gating signal 3.01 44 DQ9 I/O Data bus 0.91 18 RAS I Row address gating signal 3.13 45 DQ10 I/O Data bus 0.8 19 CS I Chip selection signal 2.95 46 VSSQ Ground 0.01 1.8 47 DQ11 I/O Data bus 0.79 2 48 DQ12 I/O Data bus 1.16 Data in/out screen-shielded signal Section address 0 gating (V) direction Function Voltage Pin direction Function Data in/out screen-shielded signal (V) 2.42 20 SD-BS0 I 21 SD-BS1 I 22 MA10 I Address bus 0.04 49 VDDQ 3.3V power supply 3.19 23 MA0 I Address bus 0.36 50 DQ13 I/O Data bus 1.15 24 MA1 I Address bus 0.35 51 DQ14 I/O Data bus 1.24 25 MA2 I Address bus 2.38 52 VSSQ Ground 0.01 26 MA3 I Address bus 1.59 53 DQ15 I/O Data bus 0.68 27 VDD 3.3V power supply 3.19 54 VSS Ground 0.01 signal Section address 1 gating signal - 76 - 3.5.4 function introduction to D5954 D5954 (U302) is a servo drive IC with built-in 4-channel drive circuit. Digital focus, trace, feed and main axis drive signal outputted by MT1389 is sent to D5954 for amplifying through RC integration circuit. The focus, trace, feed and main axis drive signal being amplified by D5954 is sent to loader to fulfil the corresponding servo work. The introduction to function pin is shown as the following table: Pin Name Voltage when DVD disc CD disc voltage no disc (V) voltage (V) (V) Function 1 VINFC Focus control signal input 1.41 1.4 1.45 2 CF1 External feedback loop 2.3 2.54 2.43 3 CF2 External feedback loop 2.01 2.56 2.43 4 VINSL+ Forward control input, connected to reference voltage 1.41 1.42 1.42 5 VINSL- Main axis control signal input 1.4 1.42 1.42 6 VOSL External feedback resistor 1.4 1.17 1.21 7 VINFFC Focus feedback signal input 1.92 2.59 2.36 8 VCC 5V power supply 5.38 5.04 5.01 9 PVCC1 5V power supply 5.38 5.04 5.03 10 PGND Ground 0.01 0.01 0.01 11 VOSL- Main axis drive reverse voltage output 1.87 3.71 3.54 12 VO2+ Main axis drive forward direction voltage output 1.87 1.24 1.4 13 VOFC- Focus drive reverse voltage output 3.3 2.6 2.33 14 VOSC+ Focus drive forward voltage voltage output 3.3 2.46 2.68 15 VOTK+ Trace drive forward direction voltage output 3.39 2.56 2.51 16 VOTK- Trace drive reverse voltage output 3.52 2.48 2.51 17 VOLD+ Feed drive forward direction voltage output 0.93 2.56 2.5 18 VOLD- Feed drive reverse voltage output 0.93 2.59 2.62 19 PGND Ground 0.01 0.01 0.01 20 VINFTK Trace feedback signal input 3.73 2.5 2.53 21 PVCC2 5V power supply 5.38 5.08 5.07 22 PREGND Ground 0 0.01 0.01 23 VINLD Feed control signal input 1.4 1.41 1.4 24 CTK2 External feedback loop 2.41 2.52 2.53 25 CTK1 External feedback loop 2.51 2.52 2.53 26 VINTK Trace control signal input 1.42 1.42 1.41 27 BIAS 1.4V reference voltage input 1.41 1.42 1.42 28 STBY Enable control signal 0 3.18 3.19 - 77 - 3.5.5 function introduction to CS4360 CS4360 (U207) is a 6CH audio D/A converter produced by CIRRUS LOGIC company, which can realize digital volume adjustment through software. Each step is with 1DB adjustment coefficient, with 9DB decay range and +3.3V or +5V voltage power supply is adopted, 28 pin casing. The main features include 24-bit sampling accuracy, highest sampling frequency, dynamic range of 02DB, SNR of -90DB. When in 3.3V voltage working mode, power consumption is 105MV. Function pin introduction is shown as the following table. Pin Name 1 VLS Function Serial audio power supply, +3.3V Voltage (V) Pin Name 3.22 15 M2 Function Voltage (V) Mode 2 1.3 In-phase feedback voltage output 4.89 External filter of static working voltage 2.42 2 SDIN1 Serial audio data 1 input 0 16 FILT+ 3 SDIN2 Serial audio data 2 input 0 17 VQ 4 SDIN3 Serial audio data 3 input 0 18 MUTEC3 Output 3 mute control 5.03 5 SCLK Bit clock 1.6 19 AOUTB3 Analog audio 3 output 2.44 6 LRCK Left/right channel clock 1.52 20 AOUTA3 Analog audio 3 output 2.44 7 MCLK Main clock input 1.59 21 GND 3.22 22 VA 0 23 AOUTB2 Analog audio 2 output 2.44 0 8 VD 9 GND Ground 10 RST Reset input 3.21 24 AOUTA2 Analog audio 2 output 2.44 11 SCL Serial control clock 0.29 25 MUTEC2 Output 2 mute control 5.03 12 SDA Serial control data 3.22 26 AOUTB1 Analog audio 2 output 2.44 0 27 AOUTA1 Analog audio 2 output 2.44 3.22 28 MUTEC1 Output 1 mute control 5.03 13 14 Digital power supply, +3.3V Ground CS/M1 Chip selection/mode 1 VLC Control port power supply, +3.3 Analog power supply, +5V 5.04 3.5.6 Function introduction to CS5340 Cs5340 (U210) is a kind of complete A/D converter used in digital audio system. It has sampling, A/D conversion and anti-aliasing filtering function, and can generate 24-bit sampling frequency to left and right channels with serial value of each channel up to 2000 KHz. A 5-step multi-bit DELTA-SIGMA modulator is adopted, with digital filtering and simplification function, so external anti-aliasing filter is not needed. It isspecially applicable for audio system required wide dynamic range, Hi-Fi and low noise. Pin Name Data direction Function Remark 1 M0 I Mode selection Decide the operation mode of element 2 MCLK I Main clock Δ-δclock source of adjustor and digital filter 3 VL I Logic power supply Forward power supply of digital input/output - 78 - 4 SDOUT O Series audio data output Two's complement of output series audio data 5 GND Analog 6 VD I Digital power supply Provide forward power supply for digital part 7 SCLK I/O Series clock Provide series clock for series audio interface 8 LRCK I/O Left/right clocl Left/right audio time sequence control clock 9 RST I Reset Element enters a low-consumption state when in low level 10 AINL I Analog input 11 VQ O Static voltage 12 AINR I Analog input 13 VA I Analog power supply Provide forward power supply for analog part 14 REF_GND Reference Provide reference ground for internal sampling circuit 15 FILT+ I Forward reference voltage 16 M1 I Mode selection Decide the operation mode of element 3.5.7 Function introduction to LM1117MP-1.8 LM1117MP-1.8V is 1.8V voltage regulator, locates on decode board to provide 1.8V stable voltage for MT1389. Pin function is shown as the following table: Pin Name Function Remark 1 GND Ground 2 OUT 1.8V voltage output 1.8V 3 IN Voltage input 3.3V 3.5.8 Function introduction to HS0038A2 Infrared receiver HS0038A2 or HS0038B has three pins: power supply anode (pin 2), power supply cathode (pin 1) and data output port (pin 3). If 5V is used for power supply, when keeping the state, voltage of data output port is also 5V (HS0038B requires pull-up resistor). The internal part is composed of infrared receiving diode and amplification circuit. To reduce the interference of visible light to working, diode part of infrared receiving usually adopts black resin casing to filter the beam with waveform length below 700nm. The amplification circuit is composed of an integrated block and elements of resistor and capacitor (including amplification, frequency selection and demodulator circuit), cased inside a screen-shielded box. - 79 - Pin function is shown as the following figure: Pin Name Function Voltage 1 GND Ground 0 2 VCC Power supply 5.1 3 IR Remote control data 5.1 Remark When there is remote control signal, voltage of IR signal changes between 5.1 and 4.1. 3.5.9 Function introduction to 4558/TDA1308 4558/4580 includes two integrated operational amplifiers inside, and pin function is shown as the following table: Function Pin Signal flow Pin Function Signal flow 1 Output of operational amplifier A O 5 Output of operational amplifier B O 2 Cathode input of port operational amplifier A I 6 Cathode input of port operational amplifier B I 3 Anode input port of operational amplifier A I 7 Anode input of port operational amplifier B I 4 minus 9V voltage input I 8 (+) 9V voltage input I 2. U602 (TDA1308) is a headphone drive chip, and pin function is shown as the following table: Pin Name Function Signal flow Pin Name Function Signal flow 1 OUT1 Headphone right channel output I 5 IN2+ Reference voltage input I (2.3V) 2 IN1- Right channel signal input O 6 IN2- Left channel signal input I 3 IN1+ Reference voltage input I (2.3V) 7 OUT2 Headphone left channel output O 4 GND Ground 8 VDD (+) 5V power supply 3.5.10 Function introduction to U501 (FDSH321) Pin 6¡¢7¡¢8 of 5L0380 is controlled by feedback pin 3 to make it on for a while and off for another while to form pulse DC to control coupling quantity of transformer. When secondary output voltage of transformer is on the high side, under the control of pin 3, disconnection time of pin 6¡¢7¡¢8 gets longer and coupling quantity of transformer decreases to make output voltage get lower gradually; when secondary output voltage of transformer is on the low side, disconnection time of pin 6¡¢7¡¢8gets shorter, connection time gets longer (connect inside fsdh321), coupling quantity of transformer decreases and secondary output voltage gets larger gradually. Pin function is shown as the following table: Pin Symbol I/O Description 1 GND Sense FET source terminal on primary side and internal control ground. 2 VCC Positive supply voltage input. - 80 - 3 Vfd The feedback voltage pin is the non-inverting input to the PWM comparator. 4 Ipk Pin to adjust the current limit of the Sense FET. 5 Vstr This pin connects directly to the rectified AC line voltage source. 6 DRAIN The Drain pin is designed to connect directly to the primary lead of the transformer and is capable of 7 DRAIN switching a maximum of 650V. Minimizing the length of the trace connecting this pin to the 8 DRAIN transformer will decrease leakage inductance. 3.5.11 Function introduction to ncp1200 the NCP1200 represents a major leap toward ultra¨Ccompact Switch¨CMode Power Supplies. Thanks to a novel concept, the circuit allows the implementation of a complete offline battery charger or a standby SMPS with few external components. Furthermore, an integrated output short¨Ccircuit protection lets the designer build an extremely low¨Ccost AC/DC wall adapter associated with a simplified feedback scheme. With an internal structure operating at a fixed 40 kHz, 60 kHz or 100 kHz, the controller drives low gate¨Ccharge switching devices like an IGBT or a MOSFET thus requiring a very small operating power. Thanks to current¨Cmode control, the NCP1200 drastically simplifies the design of reliable and cheap offline converters with extremely low acoustic generation and inherent pulse¨Cby¨Cpulse control. When the current setpoint falls below a given value, e.g. the output power demand diminishes, the IC automatically enters the skip cycle mode and provides excellent efficiency at light loads. Because this occurs at low peak current, no acoustic noise takes place. Finally, the IC is self¨Csupplied from the DC rail, eliminating the need of an auxiliary winding. This feature ensures operation in presence of low output voltage or shorts. PIN Symbol I/O Description 1 ADJ I Adjust the skipping peak current 2 FB O Sets the peak current set point 3 CS I Current sense input 4 GND I Ground 5 DRV O Driving pulses 6 VCC I Power supply 7 NC 8 HV I Generates the VCC from the line 3.5.12 Function introduction to U503 (LM431A) U503 (LM431A) is a 2.5V comparator, shown as the figure 3.5.12.1. Compared the inputted voltage of - 81 - R end with 2.5V, when voltage of R end is more than 2.5V, KA end is on and photoelectric coupler starts to send out photocurrent; when voltage of R end is less than 2.5V, KA end is cutoff and photoelectric coupler does not send out photocurrent. CPU+3.3V in power board circuit must be kept in 3.3V, for the function of comparator. No matter more than or less than 3.3V, through on and off status of comparator, it will control the on state of the output end of photoelectric coupler LM431A to adjust the output space occupation ratio of switch module to control the output voltage of transformer and masthead the power supply of the whole system. K R A Figure 3.5.12.1 LM431A outside drawing 3.5.13 Function introduction to U502 U502 (2501) is a photoelectric coupler, shown as the figure 3.5.13.1. The right side is a light emitting diode, which sends out light of different intensity according to the strength of voltage inputted from the right side, generates photocurrent of different intensity on the left side according to light of different intensity, and outputs from position D. The higher of the voltage inputted from the right side, the stronger of the light emitted from light emitting diode and the larger of the photocurrent produced from position D. The lower of the voltage inputted from the right side of photoelectric coupler, the weaker of the light emitted from light emitting diode and the weaker of the current outputted from position D. Figure 3.5.13.1 2501 outside drawing - 82 - Chapter Four Disassembly and Assembly Process DVD players manufactured in BBK are largely identical but with minor differences and are mainly composed of loader components, control panel components, decode and servo board components, power board components, power amplifier board components, MIC board components and AV board components. In order to speed up the compilation of “Service Manual”, we shall not give repeat explanation to model with minor differences in chapter four “Disassembly and Assembly Process”for the later compiled service manuals. For disassembly and assembly process in this chapter, please refer to chapter 4 of “DK1005S Service Manual”or “DK1020S Service”. The pictures of this model are shown as follows: - 83 - Chapter Cinque PCB board & Circuit diagram Section One PCB board 5.1.1 Surface layer of MIC Board JP606 TC615 -9V +9V AGND OK DET JP604 TC605 JP608 JK601 - 84 - + + JP605 R629 TC619 TC614 G603 JP607 TC616 R611 MIC601 JP609 XS601 U601 1 V S JP602 JP603 G602 JP601 G601 TC601 XS603 TC617 TC618 TC620 6717-0 DVD 2006/2/10 R AGND L 5.1.2 Bottom layer of MIC Board R621 C601 R607 R606 C609 R602 R604 L601 C602 C603 Q602 R608 C606 R610 1 R605 R623 R622 R603 C605 Q601R601 R626 C604 C611 U603 R632 C621 C619 R628 C607 R613 R637 R635 C612 C613 R617 C608 R630 C623 ZD601 R625 R627 C616 R633 R631 R636 C620 C622 R638 C617 R634 - 85 - R316 C306 C213 XS302 C309 C2126 R2150 R2149 TC224 R2151 C2127 R2155 C2136 TC229 TC230 R332 R234 R255 R221 R277 L204 R271 V308 25 R256 1 25 RN208 T C2146 TC237 R326 U214 C279 C281 C262 R229 GND TXD C303 C294 TC308 R324 C255 E B C EB C EB C EB C V307 V309 V306 R330 R329 R212 R211R325 U215 R321 R340 R319 V R210 R339 V310 R327 1 R307 R306 R315 R314 C243 L321 L322 D RN203 26 TC303 U203 S2 U302 RN201 R287 27 L249 R248 C2158 C275 R222 L309 L312 L310 R322 C310 R208 C210 R209 C211 RXD TC309 C R245 R246 R247 R249 C277 R254 C278 RN202 1 R304 TC302 C267 C266 L233 L232 C263 L231 C264 L230 50 C265 R230 L229 54 XS301 L323 L301 L305 C312 R302 R305 C201 C202 C203 C204 C205 S1 V305 L314 L317 L319 L316 L318 L320 R301 RN204 TC301 TC209 R201 R202 R203 R204 C206 TC210 U204 C215 R242 V301 V302 R331 XS303 RN207 RN206 O R309 R308 C273 I U209 R311 L226 R285 U201 G C2153 R282 2521S-0 DVD 2005/06/20 B Q204 R2184 U206 26 C327 R289 R279 R288 R278 X201 R295 C233 R227 R244 C219 C235 C220 C229 C227 C226 C323 C325 R2142 R2143 C2120 C2133 R2141 R294 R2153 C2121 C2135 C2124 C2154 R2147 R2145 R2154 R2146 C2143 C2123 C286 R269 C285 R268 C326 R2134 C2114 R2135 R2133 R2148 C2115 C2129 R225 R2139 C2118 C2130 R2137 R2152 R2138 C2142 C2117 C259 C260 R259 C288 R2180 VD207 VD208 VD209 TC204 C272 L236 L224 L228 R252 TC232 RN205 L307 V303 R2101 Q212 R2104 R243 MUTEA L324 Q211 C271 L303 L306 C A C276 TC202 TC207 ASTB R205 AVCC TC235 C225 C224 C223 C240 GND R2102 TC238 R2106 DV33 50 Q219 R2108 Q218 R2109 VD206 C268 VD205 GND TC220 C274 R2159 R250 R251 U205 VD201 U207 28 U210 TC228 R206 C2155 R2156 R207 R226 B C2157 C2156 TC208 C208 TC236 A C2116 R2105 GND R2127 C2139 U220 C217 C216 R214 RN210 C291 C269 -9V VCC U221 R284 R286 GND C296 C2105 C2102 L245 L248 L247 C295 C2104 C2101 U202 TC225 R270 R280 R276 TC226 TC227 OKA R2132 C298 R273 R2107 R283 R2160 R2103 DET +9V C2140 C299 L246 L225 L218 L219 XS203 TC222 TC223 R2122 TC240 C324 TC221 U219 Q209 R2115 R2125 R2113 R2121 Q207 TC233 C290 C293 L243 L244 C289 C292 R261 R274 Q210 R2116 R2128 R236 R237 R2112 R2111 R2120 R2117 Q205 Q206 R2118 C2138 TC241 R2119 R2131 C2122 R2136 C2141 VD211 VD213 VD215 VD221 VD219 VD217 Q208 R2114 R2124 R2123 28 C2152 C2150 C2112 R2129 R2130 C2111 C2151 L205 XS204 C270 R233 VD210 VD212 VD214 VD220 VD218 VD216 R2126 5.1.3 Surface layer of DECODE&SERVO Board D C302 R320 R312 C304 C212 C305 R313 - 86 - DV33 XS202 XS201 U211 TC246 5.1.4 Bottom layer of DECODE&SERVO Board DET OKA GND C343 C261 R260 R2186 R2185 R216 R217 R218 R219 C345 C344 R2187 +9V -9V VD222 VD223 GND VCC GND DV33 C284 C287 GND AVCC ASTB R2181 C222 C239 C218 R215 C232 MUTEA C221 R2182 C238 C237 L234 C248 C250 C2160 C2166 C230 C2174 C283 L308 V304 C329 C328 L203 C2173 C282 R310 R2165 RN209 R232 R264 R263 C2168 C244 C331 C332 C333 C251 C256 C2163 C252 C2171 C280 R213 C257 C2164 L304 C2175 L202 C297 R281 C249 C2172 R303 C311 L311 C301 C254 R2164 R262 C330 R231 C320 C319 C231 C241 R317 C242 C307 C317 R318 C318 C308 C321 C214 C322 C207 L201 C253 R2183 R2166 C247 C2167 C246 R228 C2162 R223 C228 R224 C236 C258 C234 L235 C245 R290 C2170 R297 SL+ R323 SL- C2169 LIM GND R257 R258 SP+ SP- R299 R298 TRIN - 87 - GND TROUT R275 C2145 LOAD+ LOAD- R241 FS0 VSDA VSCK VSTB GND VCC IR TXD RXD DV33 R2140 R239 R240 R238 R272 GND 5.1.5 Surface layer of AV OUT Board - 88 - 5.1.6 Bottom layer of AV OUT Board L707 C716 L709 R708 C702 L702 C701 L701 C703 C707 R709 C718 L708 R710 C721 L712 R713 C720 L711 R712 C719 L710 R706 R711 R715 C727 ZD702 C723 C724 ZD703 R718 - 89 - C726 C728 ZD704 R720 ZD701 C725 L713 R719 L714 R722 R716 C717 D702 R701 C710 R703 L703 C704 C705 C712 C706 C713 C711 C715 D701 C708 R702 5.1.7 Surface layer of Main panel TC407 U403 K403 K402 LED402 O G V K401 K404 TC402 LED401 4973-2 LEI 2004.10.4 VFD401 R418 - 90 - VFDAT VFDCK VFDST GND IR XS402 XS401 5.1.8 Bottom layer of Main panel R406 R407 C435 U401 C433 34 1 R414 R401 C401 R404 C431 R422 DZ402 C429 C428 C427 C426 C425 C424 C423 C422 C421 R410 XS403 C432 SEG2# KEY1 GND LED2 C439 C416 C415 C414 C408 C409 C410 C411 C412 C413 R417 C403 C404 C406 12 R415 - 91 - C438 23 C405 R419 D402 R408 R409 R420 R416 C420 C419 C418 C417 R411 D401 R413 R423 DZ401 C430 R421 R402 V401 44 C437 DZ406 R425 DZ403 R405 C434 R403 R412 DZ404 R424 C436 DZ405 5.1.9 Power Board N C518 JP501 L507 TC504 L509 TC506 C513 G502 R501 C507 R506 - 92 - JP503 B EC L508 TC510 R515 Q501 TC507 C510 R511 C512 JP511 TC512 ZD501 JP518 ZD503 C506 R509 R507 U502 D511 R508 K R A D506 R505 BC501 BC504 R502 BC503 TC502 JP505 C515 U503 C504 F501 TC511 -9V JP510 +9V D512 JP517 R512 CAUTION:FOR CONTIUED PROTECTION AGAINST RISK OF FIRE REPLACE ONLYWITHSAME TYPE F501 T1.6A L250V FUSE TC514 C519 F502 GND +5V GND L501 T1.6AL250V TC508 R504 JP513 ZD502 TC505 R517 D513 U501 D501 D510 SA5V GND +3.3V L503 D504 D502 BCN502 R518 R516 BCN501 D503 ~220V G503 CN501 JP509 C503 D505 R510 JP514 BCN503 ~220V C508 TC503 C502 BC505 D508 T501 CN502 5DV717-0 DVD 2006/03/30 JP520 G505 C514 AGND OKA DET L R503 G501 L505 G504 C511 HIGH VOLTAGE TC501 AGND DET OKA AGND +9V -9V GND +5V GND +3.3V FL+ FL-21V 151 151 151 151 151 151 VCC SEG9 SEG10 SEG11 SEG12 -21V SEG13 SEG14 SEG15 SEG16 GRID6 GRID5 S9 S10 S11 S12/G1 VEE S13/G1 S14/G9 S15/G8 S16/G7 G6 G5 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 KEY2 KEY1 STB CLK VSS DIN DO SW4 SW3 SW2 SW1 U401 UPD16312 G4 G3 G2 G1 VDD LED4 LED3 LED2 LED1 VSS OSC SEG1 SEG2 SEG3 SEG4 SEG5 SEG6 SEG7 SEG8 SEG9 SEG10 SEG11 SEG12 SEG13 SEG14 SEG15 SEG16 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 R411 10K 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 R406 R407 R408 R409 R412 10K R413 10K R414 10K VCC VCC R417 10K R416 10K R410 10K C406 121 C404 121 C403 121 1K 1K 1K 1K LED1 GND VCC C401 TC402 100uF/16V 104 R420 470R VCC LED401 1 VFD-35 KEY4 KEY3 KEY2 KEY1 R405 51K FIL- VFD401 33K 33K 33K 33K R401 R402 R403 R404 VFDST VFDCK GND VFDAT MSW SW2 SW3 SW4 C408 C409 C410 C411 C412 C413 GRID4 GRID3 GRID2 GRID1 VCC 2 1 F1 F1 SEG8 SEG7 SEG6 SEG5 SEG4 SEG3 SEG2 SEG1 VCC GRID6 GRID5 GRID4 GRID3 GRID2 GRID1 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 S8 S7 S6 S5 S4 S3 S2 S1 VDD KEY4 KEY3 FIL+ 2 SEG16 SEG15 121 121 121 121 121 121 SEG14 C420 C421 C422 C423 C424 C425 SEG13 SEG12 SEG11 SEG9 SEG10 121 121 121 121 121 121 SEG8 C414 C415 C416 C417 C418 C419 SEG7 SEG6 SEG5 SEG4 SEG3 SEG1 - 93 - SEG2 RED LED C426 C427 C428 C429 121 121 121 121 VCC C432 104/50V GND R109 1 R423 10K SEG2# 2 R422 1K 1 2 3 R415 100R IR 5 4 3 2 1 SEG2# KEY1 GND LED2 1 2 3 4 C438 151 KEY3 C439 151 K404 KEY4 DZ406 5.1V(DNS) DZ405 5.1V(DNS) DZ404 5.1V(DNS) DZ403 5.1V C430 151 DZ401 5.1V DZ402 5.1V C431 151 C434 151 C435 151 C436 151 C437 151 XS402 XS05 TC407 100uF/16V KEY2 K403 IR GND VFDST VFDCK VFDAT C433 102 C405 104 K402 XS05 VCC R419 10K LED2 KEY1 XS401 470R LED402 LED K401 VCC 5 4 3 2 1 R418 10R 1/4W 1 D402 1N4148 R421 1K U403 HS0038B3V R425 R424 470R D401 1N4148 FIL+ V401 9015CS SEG2 SEG1 LED1 VCC GND -21V FIL- XS403 XS02 Section Two circuit diagram 6G 5G 4G 3G 2G 1G NC NC NC NC NC NC NC P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 P8 P9 P10 P11 P12 P13 P14 P15 P16 35 34 5.2.1 KEY SCAN Board F2 F2 C231 R310 L309 LDO-AV33 FBSMT DV33 V18 V301 2SB1132-S V20 R331 0R F B A RFO IOA D C C230 104 C241 LDO-AV33 C319 C320 105 105 C317 C318 104 C242 104 105 R228 C321 C322 105 105 R313 10K R319 150K V1P4 TRSO FOSO GND GND U302 BA5954 C307 222 R317 680K R320 150K C308 101(DNS) R321 1R OPO R322 680K ADIN OPOP+ 1 2 3 4 5 6 C310 222 C2167 104 C254 104 R2164 10K R281 330R C297 102 V306 8550D C256 104 V307 8050D R326 2.2R\1/4W AGND VGND C258 104 TC309 47uF/16V R212 0R 89V33 L235 FBSMT C244 104 AVDD3 L236 FBSMT C245 104 C246 104 V309 8550D Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y6 Y5 FS0 FS1 ACLK ABCK ALRCK 89V33 RESET# V18 MUTE_DAC ASDAT2 ASDAT1 ASDAT0 ASPDIF AMDAT 474 100K 256 255 254 253 252 251 250 249 248 247 246 245 244 243 242 241 240 239 238 237 236 235 234 233 232 231 230 229 228 227 226 225 224 223 222 221 220 219 218 217 216 215 214 213 212 211 210 209 208 207 206 205 204 203 202 201 200 199 198 197 196 195 194 193 C215 152 C247 104 C248 104 L203 DACVDD3 FBSMTDV33 C249 104 C250 104 U201 MT1389 L202 33R 89V33 C251 104 V308 8050D V310 9014-S R327 510R (TROPEN1) TRCLOSE R339 10K (TRCLOSE1) TROPEN XS302 5P2.0mm 1 LOAD2 LOAD+ 3 4 GND 5 DV33 R330 10K C252 104 C253 104 192 191 190 189 188 187 186 185 184 183 182 181 180 179 178 177 176 175 174 173 172 171 170 169 168 167 166 165 164 163 162 161 160 159 158 157 156 155 -12V 154 153 152 151 150 149 148 147 146 145 144 143 142 141 140 139 138 137 136 135 134 133 132 131 130 129 GND C333 C330 C331 C332 C2175 C2175 105 105 105 105 104 C309 104 104 R221 330R TROUT R277 330R R329 10K C294 C255 102 102 TRIN PWR# PCE# PRD# R297 R298 R299 0R 0R 0R DWR# DCE# DRD# C217 C328 C329 104 105 105 89V33 LOAD+ LOADR325 (TRCLOSE1) 510R TROPEN C257 104 LIMIT DV33 VCC R324 1.5K C2174 104 GND SP+ V1P4 SP- R323 1.5K C214 104 V18 SL+ SL- R340 1R(DNS) TC308 47uF/16V USBVDD ADIN TROUT TDI TRIN TMS STBY TCK TRCLOSE TDO V18 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A18 A19 C212 331 L201 FBSMT R318 0R TRO FOO C213 331 C211 89V33 104 C306 151 18K 20K R210 R211 C210 153 V1P4 R316 20K XS303 XS06 104 DMSO R208 FMSO R209 R315 20K FOSO FEO TEO TEZISLV OPO OPOP+ 10K DMO 15K FMO TROPEN R2166 0R(DNS) C207 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 MDI1 MDI2 RFOP RFON 0R(DNS) R2165 V2P8 V20 V1P4 R307 1R 0R DQ14 TRSO V1P4 STBY 0R 0R 0R 0R DQ2 DQ1 DQ0 DQ15 151 R201 R202 R203 R204 VOICE-DET 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 C304 C305 104 VINFFC VOSL VINSLVINSL+ CF2 CF1 VINFC 105(DNS) DQ4 DQ3 20K PREGND VINLD CTK2 CTK1 VINTK BIAS STBY 105 C205 YUV0/CIN FS VREF DACVDDC RD16 RD17 RD18 RD19 RD20 RD21 DVDD3 RD22 RD23 DQM2 DQM3 RD24 RD25 DVSS RD26 DVDD18 RD27 RD28 RD29 RD30 RD31/ASDATA5 DVDD3 RA4 RA5 RA6 DVSS RA7 DVSS RA8 RA9 RA11 CKE RCLK DVDD3 RCLKB RVREF/V_ADIN3 DVDD18 RA3 RA2 RA1 DVSS RA0 RA10 BA1 DVSS BA0 RCS DVDD3 RAS CAS RWE DQM1 DQS1 RD8 DVSS RD9 RD10 RD11 DR12 RD13 DQ6 DQ5 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 C204 AGND DVDA DVDB DVDC DVDD DVDRFIP DVDRFIN MA MB MC MD SA SB SC SD CDFON CDFOP TNI TPI MDI1 MDI2 LDO2 LDO1 SVDD3 CSO/RFOP RFLVL/RFON SGND V2REFO V20 VREFO FEO TEO TEZISLV OP_OUT OP_INN OP_INP DMO FMO TROPENPWM PWMOUT1/V_ADIN9 TRO FOO USB_VSS USBP USBM USB_VDD3 FG/V_ADIN8 TDI/V_ADIN4 TMS/V_ADIN5 TCK/V_ADIN6 TDO/V_ADIN7 DVDD18 IOA2 IOA3 IOA4 IOA5 IOA6 IOA7 HIGHA0 IOA18 IOA19 DVSS APLLCAP APLLVSS DQM0 DQS0 DQ7 C303 104 GND FMSO R312 D C206 101 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 LDO2 LDO1 DV33 105 SPSP+ DMSO 10K C302 104 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 R314 - 94 - SL+ SLVCC R306 1R VOFC+ VOFCVO2+ VOSLPGND PVCC1 VCC 105 E F 29 30 C243 104 VOTK+ VOTKVOLD+ VOLDPGND VNFTK PVCC2 105 C203 C B A D SUBA SUBB SUBC SUBD DQS0 VCC 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 C202 A TC303 47uF/16V R302 10R R305 1R B RFO V302 2SB1132-S LDO1 C312 104 R304 1R 105 L234 FBSMTRFV18 TC302 47uF/16V LDO2 E C201 URST# IR 0R FBSMT FBSMT FBSMT FBSMT FBSMT FBSMT FBSMT FBSMT FBSMT FBSMT FBSMT R301 10R MDI1 C RXD TXD R303 L312 L314 L316 L317 L318 L319 L320 L321 L322 L323 L324 TC301 220uF/16V 750K R2160 0R(DNS) VSCK FS0 VSDA VSTB SCL SDA FBSMT FBSMT C229 104 C301 104 JITFN HSYNC# VSYNC# AVDD3 100K AVCC V18 L310 L311 104 AD7 A17 A0 FBSMT FBSMT 4.7uH FBSMT FBSMT C237 104 AD4 AD5 AD6 A21 L304 L305 L306 L307 L308 C236 AD0 AD1 AD2 AD3 FBSMT 4.7uH 104 A10 A9 A20 PCE# A1 PRD# C311 104 L301 L303 C235 104 R227 AVDD3 IREF RFGC OSN OSP CEQN CEQP RFGND CRTPLP HRFZC RFRPAC RFRPDC RFVDD3 S_VREFN S_VREFP ADCVSS S_VCM ADCVDD3 LPFOP LPFIN LPFIP LPFON PLLVDD3 IDACEXLP PLLVSS JITFN JITFO XTALI XTALO RFVDD18 RFGND18 SPDIF MC_DATA DVSS ASDATA4 DVDD18 ASDATA3 ASDATA2 ASDATA1 ASDATA0 DVSS ACLK ABCK ALRCK DVDD3 SPBCK/ASDATA5 SPLRCK SPDATA SPMCLK HSYNC/V_ADIN2 YUV7/ASDATA5 VSYNC/V_ADIN1 DVDD3 YUV6/R YUV5/B DACVSSA YUV4/G DACVDDA YUV3/CVBS DACVSSB YUV2/C DACVDDB YUV1/Y DACVSSC 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 V304 2SK3018-S C234 104 C239 104 C240 105 101 R215 1K APLLVDD3 IOWR A16 HIGHA7 HIGHA6 HIGHA5 HIGHA4 HIGHA3 DVDD3 HIGHA2 HIGHA1 IOA20 IOCS IOA1 IOOE DVDD3 AD0 AD1 AD2 AD3 DVSS AD4 AD5 AD6 IOA21/V_ADIN0 ALE AD7 A17 IOA0 DVSS UWR URD DVDD18 UP1_2 UP1_3 UP1_4 UP1_5 UP1_6 UP1_7 UP3_0 UP3_1 UP3_4 UP3_5 DVDD3 ICE PRST IR INT0 DQM0 DQS0 RD7 DVSS RD6 RD5 DVSS RD4 RD3 DVDD18 RD2 RD1 RD0 RD15 DVDD3 RD14 V303 XS301 2SK3018-S 24P0.5mm C238 104 JITFO C233 JITFN C218 JITFO XI XO RFV18 DV33 TC202 10uF/16V C221 105 DV33 C220 473 C219 473 DV33 VREFN 10K V1P4 C222 C223 20pF 102 DV33 VREFN VREFP IOA R223 15K VREFP PWR# A16 A15 A14 A13 A12 A11 V305 3904-S AVCC R224 10K R311 C228 104 C227 104 C226 104 C225 333 C224 104 R309 100K R213 1K V18 Y0 510R R214 FS C216 104 DQ16 DQ17 DQ18 DQ19 DQ20 DQ21 DQ22 DQ23 DQM2 DQM3 DQ24 DQ25 DQ26 DQ27 DQ28 DQ29 DQ30 DQ31 DMA4 DMA5 DMA6 DMA7 DMA8 DMA9 DMA11 DCKE DCLK DCLKB DMA3 DMA2 DMA1 DMA0 DMA10 BA1 BA0 CS# RAS# CAS# WE# DQM1 LIMIT DQ8 DQ9 DQ10 DQ11 DQ12 DQ13 5.2.2 MPEG&SERVO Board 1 R308 SDCLK 35 SDCKE 34 C262 47pF XS201 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 R229 10K L229 FBSMT DCS# R230 10K(DNS) DRAS# 17 XS07 18 DCAS# 16 VCC GND VSTB VSCK VSDA FS0 FBSMT FBSMT FBSMT FBSMT L230 L231 L232 L233 IR DWE# 15 DQM0 14 DQM1 36 33 37 DDQM2 R287 0R(DNS) CLK CKE CS RAS WE DQML DQMH NC NC C265 47pF C264 47pF DV33 C266 47pF L226 FB C280 104 C281 104 C282 104 C283 C2162 104(DNS) 104 R283 330R(DNS) SDCKE 34 DDBA1 18 DRAS# 17 DCAS# 16 DWE# 15 DQM2 R2181 0R(DNS) DDQM2 14 DQM3 R2182 0R(DNS) DDQM3 36 33 37 26 50 CLK CKE CS RAS 7 13 38 44 VCCQ VCCQ VCCQ VCCQ CAS WE DQML NC NC C2163 104 C2164 104 C2166 104 FBSMT(DNS) VCC C2171 104 C2172 104 U209 DCS# DRAS# DCAS# DWE# CLK CKE 19 18 17 16 DQM0 DQM1 C2173 104 C268 104 L225 1K(DNS) C269 104 C270 104 TC204 47uF/16V VGND VCC VD212 1N4148 VIDEO_Y 1.8UH 3 9 43 49 VCCQ VCCQ VCCQ VCCQ C2160 104 VD213 1N4148 C292 47pF C293 47pF VGND VGND 6 12 46 52 VSSQ VSSQ VSSQ VSSQ VSS VSS VSS R274 75R VCC VIDEO_COMP C323 104 R270 75R 1 2 R244 0R(DNS) XI R247 0R R251 10 11 12 R2159 13 C275 X201 27pF 27MHz C295 47pF C296 47pF C274 104 3 XTALI 4 U205B HCU04 R222 Y2 VGND VGND VCC XI Y1 0R VD216 1N4148 R249 10R(DNS) L246 Y4 R248 L249 2.7uH(DNS) U205F VD215 1N4148 DV33 U205A HCU04 R243 91R/1% XO VIDEO_Y1 1.8UH C277 10pF(DNS) R273 75R C298 47pF C299 47pF VGND VGND 0R HCU04 VCC HCU04 C2158 27pF(DNS) U215 AM29F800BT-120SC(SOP)(DNS) TC207 220uF/16V VD217 1N4148 -12V C276 27pF ASPDIF 104 TC208 220uF/16V C290 47pF VD214 1N4148 R245 0R R246 100K 0R C271 VD211 1N4148 C289 47pF VGND SD33 NC NC 0R(DNS) ASTB VIDEO_C 1.8UH R261 75R Y3 R242 200R/1% R205 510R IEC958 VD210 1N4148 L243 L245 C273 104 TC246 47uF/16V VCC U205E GND AVCC MUTE_DAC MUTEA VGND C2150 104 L244 DV33 R250 0R(DNS) L224 FBSMT(DNS) C2151 104 1 14 27 VCC VCC VCC DQML DQMH 54 41 28 DQ0 DQ1 DQ2 DQ3 DQ4 DQ5 DQ6 DQ7 DQ8 DQ9 DQ10 DQ11 DQ12 DQ13 DQ14 DQ15 C2152 104 DQ0 DQ1 DQ2 DQ3 DQ4 DQ5 DQ6 DQ7 DQ8 DQ9 DQ10 DQ11 DQ12 DQ13 DQ14 DQ15 SD33 /CS /RAS /CAS /WE 15 39 LM1117MP-1.8(DNS) L228 FBSMT TC209 220uF/16V AVCC C272 104 SDCLK 38 SDCKE 37 2 4 5 7 8 10 11 13 42 44 45 47 48 50 51 53 1.8UH C2170 104 DV33 +9V A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10/AP A11 BA0/A13 BA1/A12 36 40 VD218 1N4148 UPD[15..0] L247 VIDEO_V VIDEO_Y1 R332 330R(DNS) FS1 VIDEO_U VIDEO_COMP R234 75R Lt AGND C324 102 Rt SL SR Cc +9V AGND R236 LFE 0R(DNS) R237 0R XS28 VGND AGND C2145 104(DNS) DV33 DCE# DRD# DWR# URST# VD201 1N4148 R252 100K R2184 10K 5 R254 1K C325 105 C278 102 33 /BYTE 12 14 43 44 /CE /OE /WE /RESET A21 A20 R241 4.7K(DNS) VD 13 32 GND1 GND2 C2146 104(DNS) 6 VD R256 33R C279 104 URST# TC237 47uF/16V R255 0R R257 0R A16 A15 A14 A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 AA20 AA21 DWR# URST# VP A18 0R(DNS) 23 VCC U205C HCU04 Q204 9015-S 2 A18-U220 R275 A18 DV33 VCC L204 FB(DNS) VIDEO_U 1.8UH A19 A18 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 8M_FLASH(TSOP) 48 A15 A16 47 A14 BYTE 46 A13 Vss 45 A12 DQ15/A-1 44 A11 DQ7 43 A10 DQ14 42 A9 DQ6 41 A8 DQ13 40 A19 DQ5 39 NC DQ12 38 WE DQ4 37 RESET Vcc 36 NC DQ11 35 NC DQ3 34 RY/BY DQ10 33 A18 DQ2 32 A17 DQ9 31 A7 DQ1 30 A6 DQ8 29 A5 DQ0 28 A4 OE 27 A3 Vss 26 A2 CE 25 A1 A0 VD219 1N4148 U214 VD R272 0R(DNS) A19 Y5 UPA[20..0] FS0 VIDEO_C DV33 R271 0R(DNS) AD0 AD1 AD2 AD3 AD4 AD5 AD6 AD7 R258 0R VCC VIDEO_Y 15 17 19 21 24 26 28 30 16 18 20 22 25 27 29 31 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 D11 D12 D13 D14 D15 4.7K HSYNC# VSYNC# A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 A11 A12 A13 A14 A15 A16 A17 NC 4.7K VD XS204 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 3 1 R240 75R A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 A11 A12 A13 A14 A15 A16 A17 C267 104 R2140 R233 IEC958 DV33 RXD TXD GND 4.7K 4.7K 1 2 3 4 XS202 XS04(DNS) R238 R239 - 95 - XS203 XS13 L219 -9V 23 24 25 26 29 30 31 32 33 34 22 35 20 21 26 50 VSS VSS V18 104 OKA GND 5 6 7 8 RN209 33R L205 L218 FBSMT(DNS) 33R 33R 4 3 2 1 CS# RAS# CAS# WE# DCS# R262 0R(DNS) C2169 C2168 104 R231 33R DMA0 DMA1 DMA2 DMA3 DMA4 DMA5 DMA6 DMA7 R232 DMA8 33R DMA9 DMA10 MA11 BA0 #BA1 DCLK R263 DCKE R264 C232 20pF SD33 TC210 47uF/16V VOICE-DET C291 102(DNS) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 0R(DNS) 0R(DNS) 0R(DNS) 0R(DNS) VCC U211 SDRAM 64M 4 10 41 47 VSSQ VSSQ VSSQ VSSQ DQMH RN205 RN206 RN207 RN208 1 25 VCC VCC DQ16 DQ17 DQ18 DQ19 DQ20 DQ21 DQ22 DQ23 DQ24 DQ25 DQ26 DQ27 DQ28 DQ29 DQ30 DQ31 BA1 R2183 0R(DNS) DDBA1 casecade:use RN201,RN202,RN203,RN204,R287,R290,R2183 NC RN205,RN206,RN207,RN208,R262,R2181,R2182 normal mode : use RN205,RN206,RN207,RN208,R262,R2181,R2182 NC RN201,RN202,RN203,RN204,R287,R290,R2183 修改日期:2004-6-10 SD33 0R(DNS) 0R(DNS) 0R(DNS) 0R(DNS) SD33 4 10 41 47 VSSQ VSSQ VSSQ VSSQ VSS VSS DDQM3 R290 0R(DNS) C263 47pF 7 13 38 44 VCCQ VCCQ VCCQ VCCQ CAS RN201 RN202 RN203 RN204 1 25 VCC VCC SDCLK 35 DDQ0 DDQ1 DDQ2 DDQ3 DDQ4 DDQ5 DDQ6 DDQ7 DDQ8 DDQ9 DDQ10 DDQ11 DDQ12 DDQ13 DDQ14 DDQ15 14 C261 102(DNS) VCC 2 3 5 6 8 9 11 12 39 40 42 43 45 46 48 49 DQ0 DQ1 DQ2 DQ3 DQ4 DQ5 DQ6 DQ7 DQ8 DQ9 DQ10 DQ11 DQ12 DQ13 DQ14 DQ15 7 C260 102(DNS) A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 BA/A11 DMA11 SCL SDA DMA0 21 DMA1 22 DMA2 23 DMA3 24 DMA4 27 DMA5 28 DMA6 29 DMA7 30 DMA8 31 DMA9 32 DMA10 20 BA0 19 DDQ0 DDQ1 DDQ2 DDQ3 DDQ4 DDQ5 DDQ6 DDQ7 DDQ8 DDQ9 DDQ10 DDQ11 DDQ12 DDQ13 DDQ14 DDQ15 GND OUT IN C259 104 8 7 6 5 DC/NC VCC RST_/NC RST/WP WP/RST_ SCL VSS SDA R260 680R DQ0 DQ1 DQ2 DQ3 DQ4 DQ5 DQ6 DQ7 DQ8 DQ9 DQ10 DQ11 DQ12 DQ13 DQ14 DQ15 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 R259 680R U204 SDRAM 512*16*2 2 3 5 6 8 9 11 12 39 40 42 43 45 46 48 49 DQ0 DQ1 DQ2 DQ3 DQ4 DQ5 DQ6 DQ7 DQ8 DQ9 DQ10 DQ11 DQ12 DQ13 DQ14 DQ15 R276 A17 GND A0 AD7 AD14 AD6 AD13 AD5 AD12 AD4 VD AD11 AD3 AD10 AD2 AD9 AD1 AD8 AD0 DRD# GND DCE# A1 75R C2101 47pF C2102 47pF VGND VGND VCC VD220 1N4148 L248 Y6 VIDEO_V 1.8UH R280 75R VD221 1N4148 C2104 47pF C2105 47pF VGND VGND 5.2.3 MPEG&SERVO Board 2 U202 AT24C02 A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 BA/A11 BA1 U203 SDRAM 512*16*2 DMA0 21 DMA1 22 DMA2 23 DMA3 24 DMA4 27 DMA5 28 DMA6 29 DMA7 30 DMA8 31 DMA9 32 DMA10 20 BA0 19 DV33 R285 0R(DNS) R284 0R(DNS) RST SDA SCLK LRCK MCLK DIF1 DIF0 DEM0 AVCC 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 MUTEC AOUTA VA AGND AOUTB REF-GND VQ FILT+ MUTE1 LL AVCC AGND RR AGND VQ# FILT+ DV33 24K R2129 C2111 R2132 2 1 3 10uF/16V R2130 R2131 4.7K 4.7K R2136 6.8K AGND AGND C2138 104 C2139 104 C2140 104 6 TC241 7 CH-L 1K 5 10uF/16V -9V AGND Lt AGND Q207 2SC1815-YS AGND 3 1K R2185 10K LFE VD222 1N4148 VD223 1N4148 R2187 20K Q209 2SC1815-YS MUTE-1 R2116 100K TC222 6 5 U220B 4580 -9V 4.7K 4.7K TC223 2 1 3 U221A 4580 10uF/16V -9V R2128 1K RS SR# TC227 10uF/16V LS TC228 10uF/16V R2142 R2143 4.7K 4.7K C2121 102 R2153 6.8K SL# -12V C2133 122 LFE# SW AGND TC229 10uF/16V C# /C R2146 R2147 4.7K 4.7K C2124 102 TC230 10uF/16V R2154 6.8K C2135 122 AGND 8 TC224 6 7 5 R2150 R2151 4.7K 4.7K C2127 102 -9V 4 10uF/16V 104 4580 U221B VD208 1N4148 R2155 6.8K R2101 10K VD209 1N4148 R2102 1K 10K SACLK AMDAT DV33 TC220 47uF/16V SBCLK SLRCK C284 104 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 M0 MCLK VL SDOUT GND VD SCLK LRCLK M1 FILT+ REF_GND VA AINR VQ AINL RST U210 CS5340 104 DV33 OKR OKA# R2180 150R OKL C286 105 C327 105 R216 100K C285 105 C343 104 C344 104 C288 102 OKL R217 100K R218 100K OKR R219 100K ACLK ALRCK ABCK ASDAT2 ASDAT0 R294 ASDAT1 R295 SACLK SLRCK SBCLK SDATA2 33R 33R SDATA0 SDATA1 Q212 2SC1815-YS VCC VD205 1N4148 R2106 10K R2105 10K C345 105 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 RESET# VD206 1N4148 Q219 1015-S TC235 100uF/10V AGND AGND -9V DV33 RN210 33R MUTE-1 R2104 1K Q211 1015-S MUTE3 AGND VGND FS0 C326 R289 TC238 100uF/10V MUTE2 C2136 122 AGND DV33 VOICE-DET 1K MUTE1 +9V R278 0R(DNS) Q218 1015-S R2103 VCC VD207 1N4148 C2126 101 R279 0R(DNS) R2107 0R(DNS) MUTEA +9V CH-C C287 R207 0R +9V DV33 R288 10K(NC) R206 0R R226 R2149 24K R268 0R(DNS) R2152 6.8K C2130 122 C2123 101 Cc R269 0R(DNS) LL AGND C2118 102 R2145 24K 1K CH-SW DV33 RR 101 7 10uF/16V Q210 2SC1815-YS DV33 R2139 U220A 4580 C2120 CH-SL R2127 1K AGND 10uF/16V 24K(DNS) 1K R2126 R2115 100K TC226 +9V 1K R2125 TC232 10uF/16V AGND 1K R2124 OKA# R2138 R2141 24K SL C2157 104 8 - 96 - Q208 2SC1815-YS TC225 R C208 102(DNS) 8 R2114 100K R2186 1K 1 10uF/16V R2123 OKA OKA 10uF/16V L 2 -9V TC233 10uF/16V AGND R225 +9V CH-SR C2156 104 FILT+ C2129 122 101 TC221 1K R2122 R2113 100K U207 CS4360 R282 0R R2148 6.8K C2115 102 AGND 24K C2117 R2121 SR 4.7K 8 C2143 104 C# LFE# MUTE3 VQ# 4 C2142 104 R2135 4.7K 24K(DNS) 1K Q206 2SC1815-YS R2120 1K MUTE1 LL RR MUTE2 LS RS 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 4 C2141 104 R2134 U219B 4580 R2137 R2119 R2112 100K MUTEC1 AOUTA1 AOUTB1 MUTEC2 AOUTA2 AOUTB2 VA GND AOUTA3 AOUTB3 MUTEC3 VQ FILT+ M2 24K(DNS) 101 +9V AGND -9V VLS SDIN1 SDIN2 SDIN3 SCLK LRCK MCLK VD GND RST SCL SDA CS VLC 8 CH-R 1K Q205 2SC1815-YS R2118 R2111 100K 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 4 Rt C2114 4 +9V RESET# SCL SDA R2156 24K R2133 TC236 10uF/16V(DNS) C2155 104 C2154 104 C2122 122 C2112 102 U219A 4580 4 -9V R2117 OKA C2116 102(DNS) +9V TC240 R286 0R(DNS) C2153 104 SDATA0 SDATA1 SDATA2 SBCLK SLRCK SACLK 24K(DNS) 101 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 5.2.4 MPEG&SERVO Board 3 U206 CS4340(DNS) RESET# SDATA0 SBCLK SLRCK SACLK R2108 10K R2109 10K 5.2.5 Power Board L505 10uH/1A D508 HER105 +9V TC503 470uF/25V TC504 470uF/25V C508 104 L509 10uH/1A SA+5V C513 D502 1N4007 R503 39K/2W D503 1N4007 C502 103/1KV ! 15 D510 L507 10uH/2A HER303 14 2 D501 1N4007 D504 1N4007 TC501 47uF/400V D505 HER107 C503 101/1KV(NC) 3 13 4 12 6 11 7 R518 680K 1/2W D506 HER105 C504 104 C511 104 +3.3V TC514 1000uF/10V C510 104 C519 1K(NC) 104(NC) MIC-DET OKA AGND +9V -9V GND +5V GND +3.3V GND SA+5V R504 470R(NC) TC510 1000uF/10V T501 FL+ D512 HER105(NC) L501 JLB1153 33uH +8 -0% TC506 1000uF/10V L508 10uH/2A BCK-28-519S L503 FB ! 10 9 R505 33R TC502 47uF/50V R510 470R(NC) 104(NC) +5V TC505 1000uF/10V C518 R5161K(NC) 104(NC) D513 SF34 R517 ! TC508 1000uF/10V(nc) JP501 0R 16 JP503 0R TC511 100uF/16V(NC) FL- JP513 0R(NC) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 CN502 11P2.0mm To Mpeg Board R512 10K(NC) ! VCC 2 Gnd Vstr Ipk Vfb D511 HER105 3 BC501 ~275V 104 R506 330R - 97 - ZD503 ! U502 PH817 R508 3.3K/1% R507 10K(NC) R502 1K R501 680K 1/2W ! F501 T1.6AL250V ZD501 5.1V/0.5W FL+ C506 104 5.1V/0.5W(NC) ! TC512 47uF/50V C507 473(NC) 1 5 4 D D D 6 7 8 -21V U501 FSDH321 ! F502 T1.6AL250V ! BC503 ~250V 221 ! 2 1 BC504 ! ~250V 221(NC) ! 2 1 BC505 ~250V 221 ! -9V R511 1.5K R TC507 100uF/16V 2.5V R509 10K/1% ! BCN503 ~220V Q501 8550D A BCN502 SW-SPST BCN501 ~220V C515 104 K U503 LM431A AGND MIC-DET OKA AGND +9V -9V GND +5V GND +3.3V FL+ FL-21V R515 220R C514 104 ZD502 10V/0.5W C512 104 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 CN501 13P2.0mm(NC) To Microphone Board H_R TC619 100uF/16V R631 3.9K R633 4.3K A5V R635 10K R629 3.3K AGND C604 R630 3.3K TC614 47uF/16V 1uF 4 3 2 1 3P2.0 H_L R626 1K C619 104(NC) A5V GND IN2+ IN1+ IN2IN1- OUT2 OUT1 VDD XS603 1 2 3 -9V +9V R628 56K C621 104(NC) Q601 8050D A5V AGND R636 10K U603 TDA1308 R632 3.9K AGND R637 22R(NC) R638 22R(NC) C605 104 C620 104(NC) R634 4.3K TC618 47uF/16V TC615 47uF/16V C623 104 C617 101 AGND OK A5V - 98 - Q602 8050D TC605 22uF/16V R623 5.1K R608 1K R610 10K C606 R613 5.1K C607 101 DET 4 3 2 1 C609 R604 560R 6 C611 101 R611 5.1K 7 5 105 105 U601B 4558 2 1 R602 5.1K C603 103 R606 10K OK 3 8 MIC601 PHONEJACK4 R603 22K C612 105 -9VA 4 L601 FBSMT DET OK AGND +9V -9V U601A 4558 +9VA C613 105(DNS) C608 102 R617 100K 1 2 3 4 5 R605 10k +9VA TC601 1000uF/10V ZD601 6.2V/0.5W TC620 100uF/16V C602 104 R621 10R R601 330R C622 104(NC) -9VA TC616 47uF/16V 5 6 7 8 R627 56K R622 10R 2 3 1 TC617 47uF/16V R625 1K JK601 PHONEJACK XS601 5P2.0mm C601 104 R607 10k 5.2.6 MIC Board C616 101 JK704 R717 330R VCC VCC Y1 R705 4.7K R704 4.7K R707 33R PDAT1 V701 8050 R714 V702 8050 2.2K G Y- 1 C716 20pF 2 Pb- 3 C717 20pF 4 Pr- 5 FBSMT AGND L707 B R701 220R 1 R702 2 100R LFE 3 FB C702 102 FBSMT R715 47K C727 C723 102 C710 104 L702 Pb RGB_CVBS R718 L709 TC702 1000uF/16V R709 0R 2.2K PDAT0 SPDIF R708 0R 102 TC703 220uF/16V AGND C708 102 TC704 220uF/16V Pr R JK707 AV_JACK FBSMT VGND AGND L708 C718 20pF R710 0R AV_JACK CC L701 FB AV_TV VGND R719 1K(DNS) SL 1 C701 102 2 L703 3 FB AGND V703 8050(DNS) C725 104 L713 FCM R C724 102(DNS) C726 104 1 L 3 L714 FCM AGND 5 Pb- 7 AGND ZD701 Y- XS701 nCON28 11 ZD702 PDAT2 PDAT1 SPDIF VCC Y C Pr 13 5.1V/0.5W Pr- 15 ZD703 R716 0R(DNS) C707 105 VIEDOR722 0R(DNS) VGND AGND VGND 17 5.1V/0.5W 19 ZD704 21 5.1V/0.5W JK701 A(B)OUT A(B)IN A(A)OUT A-COM RETURN A(A)IN BLUE I/O FUNC SW RETURN CONT GREEN I/O NC RETURN RETURN RED I/O BLK I/O RETURN TRTURN V-OUT V-IN GND 2 AGND JK708 AV_JACK 4 6 AGND 8 AV_TV 10 C728 104 R703 SPDIF 68R C715 104(DNS) 1 VIN VCC JK705 2 C711 104 VCC 3 OPTICAL R L706 VGND 16 RGB_CVBS 1 C706 102 12 14 R# FB GND L 2 L705 L# 3 FB 18 C705 102 R711 0R 20 VIEDO VIEDO- JK702 5 V-OUT VJS3921 TC701220uF L710 FBSMT R706 2.2R Y1 C719 20pF SR 4 L704 5 FB C704 102 6 VGND D701 IN4148 D702 IN4148 AGND 7 Pb VIEDO PDAT0 L SCART 8PIN R SL VGND AGND 9.5V-12V AV 4:3 SCART 8PIN 5.0V-8.0V AV 16:9 SCART 8PIN 0.0V-2.0V TV MODE L# R712 0R SR SCART 16PIN CC LFE +10V XS702 XS03 1 2 3 L AGND R JK709 AV_JACK VGND SCART 16PIN 0 1 CVBS MODE RGB MODE Y TC705 220uF/16V R713 0R L711 FBSMT C720 20pF L712 4 TC706 220uF/16V FBSMT C721 20pF 2 3 JK703 C 1 C712 102 2 - 99 - 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 9 5.1V/0.5W C703 102 3 R# S-VIDEO C713 102 1 PDAT2 R720 2.2K(DNS) VGND VGND AGND 5.2.7 AV OUT Board JK706 AV_JACK +10V Chapter six BOM List MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION DV717SI(RU) SILVER [1389C] AV BOARD PCB SEMI-FINISHED PRODUCT 5448071 0000289 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/4W4.7K±5% SHAPED 10 R704,R705 0000278 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/4W330O±5% SHAPED 10 R717 0000273 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/4W33O±5% SHAPED 10 R707 0000286 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/4W2.2K±5% SHAPED 10 R714 0090001 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 0O±5% 0603 R708~R713 0090002 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 2.2O±5% R706 0090238 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 68O±5% 0603 R703 0090181 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100O±5% 0603 R702 0090008 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 220O±5% R701 0090017 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 2.2K±5% 0603 R718 0090029 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 47K±5% 0603 R715 0310085 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 20P±5% NPO 0603 C716~C721 0310066 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 102±10% 0603 C701~C706,C708,C712,C713,C723,C725,C7 26,C727 0310207 SMD CAPACITOR 50V104±20% 0603 C710,C711,C728 0310234 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 105 +80%-20% 0603 C707 0390057 MAGNETIC BEADS INDUCTOR RH354708 L704,L705,L706 0390095 SMDMAGNETIC BEADS FCM1608K-221T05 L701~L703,L707~L714 0700007 SMD DIODE 1N4148 D701,D702 ① 0700001 SMD DIODE LS4148 D701,D702 ① 0700002 SMD DIODE LL4148 D701,D702 ① 5.1V±5% 1/2W ZD701~ZD704 S8050D V701,V702 0700004 SMD VOLTAGE REGULATOR DIODE 0780050 TRIODE 1090045 ELECTRO-OPTICTRANSFORMER TX179ATW JK705 ② 1090024 ELECTRO-OPTICTRANSFORMER TX179AT JK705 ② 1910132 TERMINAL SOCKET AV2-8.4(WHITE、WHITE) JK707 1910208 TERMINAL SOCKET AV2-8.4(RED、WHITE) JK709 1910133 TERMINAL SOCKET AV2-8.4(RED、BLACK) JK706 1910131 TERMINAL SOCKET AV3-8.4(RED、WHITE、RED) JK708 - 100 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 1860029 SCART SOCKET SCART-01 JK701 1910006 TERMINAL SOCKET S-VIDEO JK703 1910081 TERMINAL SOCKET AV1-8.4-5G-2 YELLOW JK702 1910057 TERMINAL SOCKET AV3-8.4-6G-2 JK704 1940140 CABLE SOCKET 14P 1.0mm STRAIGHT DUAL LINE XS701 PLUG 1940026 SOCKET 3P 2.0mm XS702 2100003 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 7.5mm JP701,JP703,JP705,JP706,JP708~JP713,JP 715,JP724,JP726,JP704 2100010 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 5mm JP702,JP716,JP718,JP720~JP722,JP725 2100004 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 10mm JP707,JP714,JP717,JP719,JP723 AB903 G701,G702 3870115 GROUND CHIP OF POWER BOARD 1564185 PCB 7DV717-0 DV717SI(RU) SILVER [1389C] DECODE BOARD PCB SEMI-FINISHED PRODUCT: 2521S-0 0090001 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 0O±5% 0603 R201~R204,R212,R222,R228,R236,R245,R2 47,R251,R255,R257,R258,R282,R297~R299, R303,R318,R331,R2159,R234,R269,R279,R2 160 0090006 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 75O±5% 0603 R233,R261,R270,R273,R274,R276,R280 0090272 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1O±5% 0603 R304~R307,R321 0090003 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10O±5% 0603 R301,R302 0090005 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 33O±5% 0603 R231,R232,R256,R263,R264,R294,R295,L20 2 0090232 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 150O±5% 0603 R2180 0090009 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 330O±5% 0603 R221,R277,R281 0090013 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 680O±5% 0603 R259,R260 0090014 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1K±5% 0603 R213,R215,R254,R2102~R2104,R2117~R21 28,R2186,L225 0090016 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1.5K±5% 0603 R323,R324 0090249 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 510O±5% 0603 R205,R214,R325,R327,R283 0090019 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 4.7K±5% 0603 R238~R240,R2130,R2131,R2134,R2135,R21 38~R2140,R2142,R2143,R2146,R2147,R215 0,R2151 0090021 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 6.8K±5% 0603 R2136,R2148,R2152~R2155 0090023 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10K±5% 0603 R208,R229,R309,R311,R313,R314,R329,R33 0,R339,R2101,R2106,R2108,R2109,R2164,R 2184,R289,R2105,R2185 0090024 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 15K±5% 0603 R209,R223 0090025 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 20K±5% 0603 R211,R312,R315,R316,R2187 - 101 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0090255 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 24K±5% 0603 R2129,R2133,R2137,R2141,R2145,R2149 0090188 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 18K±5% 0603 R210 0090197 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 150K±5% 0603 R319,R320 0090211 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 680K±5% 0603 R317,R322 0090609 PRECISION SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100O±1% 0603 R243 0090626 PRECISION SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 200O±1% 0603 R242 0090319 PRECISION SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 750K±1% 0603 R227 0090034 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100K±5% 0603 R224,R246,R252,R308,R310,R2111~R2116, R216~R219 0100019 SMD RESISTOR NETWORKS 1/16W 33O±5% 8P RN209,RN210 00003759 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/4W2.2O±5% BELT R326 02604379 CD CD11 16V10U±20%5×11C5 BELT TC202,TC221~TC230,TC232,TC233,TC240, TC241 02601819 CD CD11 16V220U±20%6×12 C5 BELT TC207~TC209,TC301 02600029 CD CD11 16V47U±20%5×11 C5 BELT 02601889 CD CD11 16V100U±20%6×12 C5 BELT TC235,TC238 1940023 SOCKET 7P 2.0mm XS201 0310085 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 20P ±5% NPO 0603 C222,C232 0310190 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 27P ±5% NPO 0603 C275,C276 0310045 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 47P ±5% NPO 0603 C262~C266,C289,C290,C292,C293,C295,C2 96,C298,C299,C2101,C2102,C2104,C2105 0310047 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 101 ±5% NPO 0603 C206,C233,C2111,C2114,C2117,C2120,C21 23,C2126,C288 0310051 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 331 ±5% NPO 0603 C212,C213 0310048 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 151 ±5% NPO 0603 C304,C306 50V104 ±20% 0603 C207,C211,C214,C216,C217,C224,C226~C2 31,C234~C239,C241~C254,C256~C259,C26 7~C274,C279~C282,C301~C303,C305,C309, C311,C312,C323,C2138~C2143,C2150~C21 57,C2160,C2162~C2164,C2166~C2175,C284 ,C287,C343~C345 ③ 0310543 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 104 ±10% X7R 0603 C207,C211,C214,C216,C217,C224,C226~C2 31,C234~C239,C241~C254,C256~C259,C26 7~C274,C279~C282,C301~C303,C305,C309, C311,C312,C323,C2138~C2143,C2150~C21 57,C2160,C2162~C2164,C2166~C2175,C284 ,C287,C343~C345 ③ 0310234 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 105 +80%-20% 0603 C201~C204,C221,C240,C317~C322,C325,C3 28~C333,C326,C327,C285,C286 0310066 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 102 ±10% 0603 C223,C255,C278,C294,C297,C2112,C2115,C 2118,C2121,C2124,C2127 0310231 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 122 ±10% 0603 C2122,C2129,C2130,C2133,C2135,C2136 0310207 SMD CAPACITOR - 102 - TC204,TC210,TC237,TC246,TC302,TC303,T C308,TC309 MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0310067 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 152 ±10% 0603 C215 0310068 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 222 ±10% 0603 C307,C310 0310201 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 153 ±10% 0603 C210 0310055 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 333 ±10% 0603 C225 0310056 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 473 ±10% 0603 C219,C220 0310362 SMD CAPACITOR 16V474 +80%-20% 0603 C218 0390355 SMD INDUCTOR 4.7UH ±10% 1608 L303,L306 0390096 SMD INDUCTOR 1.8UH ±10% 1608 L243~L248 03900579 MAGNETIC BEADS INDUCTOR RH354708 BELT L226 0390095 SMDMAGNETIC BEADS FCM1608K-221T05 L201,L203,L228~L236,L301,L304,L305,L307 ~L312,L314,L316~L324,L218,L219 0960020 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR 27.00MHz 49-S X201 1632368 PCB 2521S-0 0700007 SMD DIODE 1N4148 VD201,VD205~VD223 ④ 0700001 SMD DIODE LS4148 VD201,VD205~VD223 ④ 0700002 SMD DIODE LL4148 VD201,VD205~VD223 ④ 07800509 TRIODE S8050D BELT V307,V308 07800499 TRIODE S8550D BELT V306,V309 0780062 SMD TRIODE 9014C V310 0780063 SMD TRIODE 9015C Q204 0780197 SMD TRIODE C1815 Q205~Q210,Q212 0780198 SMD TRIODE 2SA1015 Q211,Q218,Q219 0780040 SMD TRIODE 3904(100-300) SOT-23 V305 0780193 SMD TRIODE 2SK3018 V303,V304 0780115 SMD TRIODE 2SB1132 V301,V302 0880185 IC NJM4558M SOP U219,U220,U221 ⑤ 0880562 IC 4580 SOP U219,U220,U221 ⑤ 0880361 IC 4558 SOP U219,U220,U221 ⑤ 0880322 IC MM74HCU04M SOP U205 ⑥ 0880513 IC HCU04 SOP U205 ⑥ 0881415 IC HY57V641620HGT-7 TSOP U211 ⑦ 0881872 IC KSV464P4JA-70 TSOP U211 ⑦ 0881182 IC LM1117MP-ADJ SOT-223 U209 - 103 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0881057 IC CS4360 SSOP U207 0882353 IC CS5340 TSSOP U210 0881031 IC 24C02N SOP U202 0882257 IC MT1389FE/C (C VERSION) QFP U201 0881378 IC BA5954FP HSOP U302 1940140 CABLE SOCKET 14P 1.0mm STRAIGHT DUAL LINE XS204 PLUG 1940024 SOCKET 5P 2.0mm XS302 1940005 SOCKET 6P 2.0mm XS303 1940098 SOCKET 11P 2.5mm XS203 1940094 CABLE SOCKET 24P 0.5mm SMD WITH CLASP XS301 DV717SI(RU) SILVER [1389C] MAIN PANEL PCB SEMI-FINISHED PRODUCT 5444529 0090001 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 0O±5% 0603 R403 0310207 SMD CAPACITOR 50V104 ±20% 0603 C401 ⑧ 0310543 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 104 ±10% X7R 0603 C401 ⑧ 0310048 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 151 ±5% NPO 0603 C402,C403 0310376 SMD TANTALUMCAPACITOR NRS10V47U±20%3528(B2) TC401 0700002 SMD DIODE LL4148 VD401,VD402,VD403 ⑨ 0700001 SMD DIODE LS4148 VD401,VD402,VD403 ⑨ 0700007 SMD DIODE 1N4148 VD401,VD402,VD403 ⑨ 0700056 SMD DOUBLE DIODE MMBD4148SE SOT-23 D401~D410 0970003 CERAMIC RESONATOR 455E X401 0881587 IC PT2222A SOP U401 1940150 SOCKET 4P1.0mm SMD XS401 0780129 SMD TRIODE 8550D V401 0090023 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10K±5% 0603 R401 1632060 PCB 4373-3 DV717SI(RU) SILVER [1389C] OK BOARD PCB SEMI-FINISHED PRODUCT 5448072 0090003 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10O±5% 0603 R621,R622 0090009 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 330O±5% 0603 R601 0090012 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 560O±5% 0603 R604 - 104 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0090014 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1K±5% 0603 R608,R625,R626 0090018 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 3.3K±5% 0603 R630 0090224 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 3.9K±5% 0603 R631, R632 0090184 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 4.3K±5% 0603 R633, R634 0090020 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 5.1K±5% 0603 R602, R613, R623 0090023 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10K±5% 0603 R606,R610,R635,R636 0090026 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 22K±5% 0603 R603 0090030 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 56K±5% 0603 R627,R628 0090034 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100K±5% 0603 R617 0310047 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 101 ±5% NPO 0603 C606, C607, C616, C617 0310066 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 102 ±10% 0603 C608 0310072 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 103 ±10% 0603 C603 0310207 SMD CAPACITOR 50V104 ±20% 0603 C601,C602,C604,C605,C623 ⑩ 0310222 SMD CAPACITOR 25V 104 ±20% X7R 0603 C601,C602,C604,C605,C623 ⑩ 0310543 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 104 ±10% X7R 0603 C601,C602,C604,C605,C623 ⑩ 0310234 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 105 +80%-20% 0603 C609,C611,C612 0000339 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W3.3K±5% SHAPED 7.5 R629 0000134 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W5.1K±5% SHAPED 7.5 R611 0260094 CD CD110 16V47U±20%5×11 2 TC614 ~ TC618 ⑾ 0260025 CD CD11 16V47U±20%5×11 2 TC614 ~ TC618 ⑾ 0260200 CD CD11C 16V47U±20%5×7 2 TC614 ~ TC618 ⑾ 0260327 CD GZ16V100U±20%6×12 2.5 TC619, TC620 ⑿ 0260027 CD CD11 16V100U±20%6×12 2.5 TC619, TC620 ⑿ 0260096 CD CD110 16V100U±20%6×12 2.5 TC619, TC620 ⑿ 0260175 CD CD11C 16V100U+20%-15%6×7 2.5 TC619, TC620 ⑿ 0260201 CD CD11C 16V100U±20%6×7 2.5 TC619, TC620 0260021 CD CD11 16V22U±20%5×11 2 TC605 ⒀ 0260037 CD CD11 25V22U±20%5×11 2 TC605 ⒀ 0390095 SMDMAGNETIC BEADS FCM1608K-221T05 L601 0260237 CD CD11 10V1000U±20%8×14 3.5 TC601 ⒁ 0260352 CD GS 10V1000U±20%8×14 3.5 TC601 ⒁ 6.2V ±5% 1/2W ZD601 0700020 SMD VOLTAGE REGULATOR DIODE - 105 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0780085 SMD TRIODE 8050D Q601,Q602 0880124 IC NJM4558D DIP U601 ⒂ 0880308 IC KA4558 DIP U601 ⒂ 0881537 IC TDA1308 SOP U603 1980018 MICROPHONE SOCKET CK3-6.35-24 MIC601 1940024 SOCKET 5P 2.0mm XS601 2121631 FLAT CABLE 3P120 2.0 2 PIN,WITH NEEDLE,TOGETHER DIRECTION XS603 1564176 PCB 6717-0 2100010 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 5mm JP601 ~ JP609 1980046 EARPHONE SOCKET ST-301-030-100 JK601 AB903 G601, G602 3870115 GROUND CHIP OF POWER BOARD DV717SI(RU) SILVER [1389C] POWER BOARD PCB SEMI-FINISHED PRODUCT 5448070 2100010 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 5mm JP503,JP510,JP520 2100003 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 7.5mm JP501,JP505,JP509,JP514,JP518 2100004 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 10mm JP511,JP517 0010337 METAL OXIDE FILM RESISTOR 2W180K±5% SHAPED FLAT 15×7 R518 0000273 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/4W33O±5% SHAPED 10 R505 0000362 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/4W220O±5% SHAPED 10 R515 0000278 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/4W330O±5% SHAPED 10 R506 0000279 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/4W470O±5% SHAPED 10 R510 0000284 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/4W1.5K±5% SHAPED 10 R511 0000283 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/4W1K±5% SHAPED 10 R502 0010115 METAL FILM RESISTOR 1/4W3.3K±1% SHAPED 10 R508 0010064 METAL FILM RESISTOR 1/4W10K±1% SHAPED 10 R509,R512 0010159 METAL OXIDE FILM RESISTOR 2W39K±5%SHAPED FLAT 15×7 R503 0070016 HIGH PRESSURE RESISTOR @1/2W680K±5% VDE R501 0200138 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 50V 104±20% 5mm C504,C508,C510~C512,C515 0210023 TERYLENECAPACITOR 100V 223±10% 5mm C506 0200359 CERAMICCAPACITOR @250V 221±10% 10mm VDE BC503,BC505 ⒃ 0200376 CERAMIC CAPACITOR @250V 221 ±20% 10mm VDE BC503,BC505 ⒃ 0200223 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 1000V 101 +80%-20% 7.5mm C503 ⒄ - 106 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0200228 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 1000V 101±10% 7.5mm C503 ⒄ 0200224 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 1000V 103 +80%-20% 7.5mm C502 0210204 ANTI-JAMMINGCAPACITOR @MKP61 X2 275VAC 104M 15 UL BC501 ⒅ 0210207 TERYLENECAPACITOR @275V 104±20% 15mm VDE BC501 ⒅ 0210206 TERYLENECAPACITOR @275V104±10%15mm VDE BC501 ⒅ 0260557 CD CD11T 16V100u±20%6×12 2.5 TC507,TC511 0260686 CD CD11T 25V220U±20%8×12 C5 TC504 0260559 CD CD11T 50V47u±20%6×12 2.5 TC512 0260564 CD CD11T 50V10U±20%5×11 2 TC502 0260560 CD CD11T 10V1000u±20%8×16 3.5 TC506,TC510 0260341 CD ZT 400V22µ±20%f 16×20 7.5 TC501 0260726 CD CD288H 10V1000U±20%8×16 C5 TC505,TC514 0260659 CD CD288H 35V220U±20%10×12 5 TC503 0410010 CHOKE COIL VERTICAL 10UH 1A 5mm L505,L509 0410011 CHOKE COIL VERTICAL 10UH 2A 5mm L507,L508 0570013 DIODE HER105 D506,D508,D511,D512 0570018 DIODE HER303 SHAPED R 17.5×8mm D510 0570077 DIODE SF34 DO-27 SHAPED R 17.5×8 D513 0570014 DIODE HER107 D505 0570005 DIODE 1N4007 D501~D504 0580006 VOLTAGE REGULATOR DIODE 5.1V 1/2W ZD501 0580032 VOLTAGE REGULATOR DIODE 10V±5% 1/2W ZD502 0882551 IC FSDH321 DIP U501 0880863 IC HA17431VP TO-92 U503 ⒆ 0882041 IC MIK431C TO-92 U503 ⒆ 0882462 IC AZ431AZ-A TO-92 U503 ⒆ 0390057 MAGNETIC BEADS INDUCTOR RH354708 L503 1080011 PHOTOELECTRIC COUPLER HS817 U502 ⒇ 1080006 PHOTOELECTRIC COUPLER PC817 U502 ⒇ 0780049 TRIODE S8550D Q501 1000022 POWER GRID FILTER JLB1153 33uH +∞-0% L501 0460560 SWITCH POWERTRANSFORMER @BCK-25-0091 CQC T501 - 107 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 1940077 SOCKET 11P 2.0mm CN502 1940045 SOCKET 2P 8.0mm 2# BCN501 1940005 SOCKET 6P 2.0mm CN501 2300039 FUSE @T1.6AL 250V VDE F501 (21) 2300049 FUSE @T1.6AL 250V 3.6×10 VDE F502 (21) AB903 G501,G502,G503,G505 3870115 GROUND CHIP OF POWER BOARD 1564298 PCB @5DV717-0 UL DV717SI(RU) SILVER [1389C] REMOTE CONEROLLER 5471656 0310048 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 151 ±5% NPO 0603 C802,C803 0630009 EMISSION PIPE TSAL4400 LED801 0700007 SMD DIODE 1N4148 D801~D803 (22) 0700001 SMD DIODE LS4148 D801~D803 (22) 0700002 SMD DIODE LL4148 D801~D803 (22) 0780130 SMD TRIODE STC3265 Q801 0880220 IC PT2222 SOP U801 (23) 0882379 IC S0102B SOP U801 (23) 0970003 CERAMIC RESONATOR 455E X801 4000038 SELF-TAPPING SCREW PB 2.3×6 COLOR ZINC FOR CONNECTING UPPER COVER AND LOWER COVER 0090272 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1O±5% 0603 R801 1564219 PCB 8516SI-2 3031789 REMOTE CONEROLLERSURFACE RC026-01R BLACK CASING 3041399 BOTTOMCASING OF REMOTE CONTROL RC026 BLACK 2# 3051319 BATTERYCASE DOOR OF REMOTE CONTROL RC026 BLACK 2# 3051273 GLASS OF REMOTE CONTROLLER RC026 MING PURPLE 3850124 ANODE SPRING RC026 3850125 CATHODE SPRING RC026 3850126 ANODE/CATHODE SPRING RC026 4631016 CONDUCT GLUE OF REMOTE CONTROL 5070070 GLUE BAG RC026-01R 3# 85×250 DV717SI(RU) SILVER [1389C] - 108 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS SUBSIDIARY PANE PCB SEMI-FINISHED PRODUCT LOCATION 5445111 1563444 PCB 9973-2 2121417 FLAT CABLE 4P 230 2.0 2 PIN, WITH L NEEDLE,TOGETHER DIRECTION XS901 1340064 LIGHT TOUCH RESTORE SWITCH KFC-A06-2WB L3.8 K901 0200307 POLYPROPYLENECAPACITOR 50V 101±10% SHAPED 5mm C901,C902 2100003 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 7.5mm JP901~JP902 0620076 RADIATION DIODE 3B3HC COLORLESS WITH BLUE LED901 3028526 LED BRACKET(LEFT) DV973 FASTNESS LED901 DV717SI(RU) SILVER [1389C] PROGRAM FLASH ROMDV717SIRU-0A(16M) 0911627 0881650 IC 29LV160BE-70PFTN TSOP U214 (24) 0881651 IC M29W160EB 70N6 TSOP U214 (24) - 109 - DV721SI Service Manual This machine is mainly composed of decode board, power board, AV output board, MIC board and main panel. Decode board: includes decode, servo, audio and video output circuit. Working principle is the same with that of DV717SI. Power board: provides working voltage for each circuit and output voltage has ± 9V +5V +3.3V SA+5V, etc. AV output board: includes SCART, component video, optical and coaxial output terminal, videi output terminal, S-Video. Working principle is the same with that of DV717SI. MIC board: with dual-channel microphone input function, and headphone amplifying circuit deletion. Main panel: button function control, remote control and LCD display. Remark: in order to better know the composition of machine for readers, we have made PCB composition figure, the connecting lines in PCB composition figure are the main control liner, signal line and power cord connected through flat cable, but all connected flat cable are not included. 7.1.1 Features ◆Compatible with DivX, MPEG4 discs to produce wonderful pictures. ◆ 108MHz/12bit video DAC, with more vivid and brilliant pictures. ◆ Digital echo Karaoke to enable your singing easier. ◆ Composite Video, S-Video and Component Video outputs. ◆ Bullt-In Dolby Digital decoder, separate 5.1Ch Outputs. ◆ Dolby output for 2channel(DOWNMIX). ◆ DVD-Audio decoding output to reproduce original and realistic sound effects. ◆ Brightness, chroma and contrast adjustment functions to render your eyes more comfortable. ◆ DTS, Dolby Digital, PCM Digital audio outputs to satisfy the Fans’Ss acoustic requirements. ◆ Optical and coaxial outputs for Digital audio. ◆ Progressive-scan video outputs to eliminate the flickers hardly ouvercome by interlacing scan and therefore your eyesight will be well-protected. At the same time, the pictures deflnltion Is sharply enhanced and the pictures will be finer, smoother and stabler - 110 - Loader frame Small bracket Laser head PDAT2 PDAT1 XS302 Xs303 XS301 SPDIF VCC Y C IR Pr +5V Main panel Y1 GND Decode board CE 4965-2 XS401 CL Pb VIEDO 2521S-0 XS201 PDAT0 DI AV board 7717-0 L DO R SL SR CC XS901 Subsidiary panel XS901 9965-1 LFE XS203 XS402 CPU+3.3V GND IR SW1 GND LED1# LED2# +10V CN502 Power board 5965S-1 AC220V CN503 +5V -9V +9V AGND OK VOICE-DET XS601 MIC board 6965S-0 MIC1 MIC2 As for decode board working principle of this player, it only cancels headphone signal loop on the basis of DV717SI, AV board working principle is the same with that of DV717SI, only PCB board is different. We will mainly introduce differences, and now we will introduce MIC board, main panel and power board working principle of DV721SI. 7.3.1 MIC circuit 1. MIC circuit block diagram is shown in the figure 7.3.1.1: MIC1 MIC2 3 5 U601A U601B 1 1 7 1 Potentiometer Potentiometer 2 2 U602A 1 2 R623 R618 XS601 5 U602B 7 Figure 7.3.1.1 MIC circuit block diagram 2. Working principle: this machine includes two-way MIC input, which adopts 9P MIC holder with quieting function and dual-channel volume adjustment function. After inserting microphone and begin to sing, signals inputted by MIC are inputted to pin 3, 5 of U601 respectively for amplifying and then output from pin 1, 7 of U601 and then twp paths are divided. One path, after volume adjustment through potentiometer, inputs from pin 2 of U602 for mixed amplifying and outputs from pin 1 through flat cable holder XS601 to power board and decode board. The other path, enters the comparator composed by U602B through R623/R618, when input signal is up to a certain range, DET pin has high level output, mute circuit controlled by decode chip does not mute; when input signal is not enough, DET is level. VD601 VD602 in circuit are protection diode and VD603 is rectification diode. 7.3.2 Control panel circuit 1. Control panel block diagram is shown in the figure 7.3.2.1: 2. Working principle: after power on, power board only has 3.3V voltage output, pin 2 of power board standby IC U505 outputs high level and lightens standby light in red, other circuits do not work. After power on, each voltage output is normal, pin 6 of U505 outputs high level, and high level of pin 2 turns off at the same time, standby light turns off, and power board begins to supply power for each circuit. Decode system begins to start up, main panel U402 obtains power supply and outputs high level in P2/S2 end, +5V power, through U404 voltage regulating, outputs 3.5V power from pin 2 to supply power for LED402 LED403 of background light board through V402 to make background light on, at the same time, Sw1 outputs high level Ks1, OSC circuit begins to work, and panel button module enters ready state. If K12 is low level, buttons have no function. - 112 - Display screen background light control circuit U401 LCD COM1~COM4 S5~S20 P2/S2 DO DI DL CE GND +5V IR LED# Blue light P1/SI control circuit PT6554 Subsidiary KSI SW1 OSC control panel K12 circuit 9965-1 KS1~KS6 IR XS 401 KII button Figure 7.3.2.1 Control panel circuit block diagram At the same time, P1/S1 outputs high level to make the blue background light of mirror on and background light may be turned on and off through firmware. Decode chip gives out display data to Pt6554 to make it drive LCD to display. Remote control principle: remote control receiver lies in subsidiary panel, which is supplied power by CPU3.3V, remote control signal IR is divided into two ways: one path arrives at decode board through main panel to realize operation functions; the other way realizes remote control power on through power board standby control circuit. 7.3.3 Power circuit 1. Power circuit block diagram is shown in the figure 7.3.3.1: CPU+3.3V Bridge rectification and filtering circuit Filtering capacitor Rectification diode Filtering capacitor DC310V Switch pipe Sampling winding V502 LM7805 STB SA+5V Rectification diode Filtering capacitor +5V Rectification diode Filtering capacitor +3.3V Rectification, filtering -9V voltage regulating -21V circuit ~220V Switch module NCP1200 U506 +9V Absorption loop Electromagnetic interference filtering circuit Rectification diode Feedback loop Figure 3.2.12.2 Power circuit block diagram - 113 - CPU+3.3V SR160 -9V Standby control circuit 2. Circuit principle: through power socket, protector tube, voltage dependent resistor R501, common mode rejection BC501 and L501, 220V AC is added to the bridge rectification circuit composed by D501-D504. Diode adopts good performance In4007 which has higher voltage resist value than In4001. 310V DC that outputs after bridge rectification, through TC517, C502, C503 filtering, is added to 2-4 winding of transformer YR501 and sent to pin 5 of switch module after rectification. The switch module start voltage is not sent by D506, R505, but taken from 311V of pin 8 and achieved after being processed inside IC. R503, C502, D505 and C503 compose absorption loop to provide discharge loop of reverse electromotive force for transformer 2-4 winding. Transformer 6-7 winding, through D506 half wave rectification, TC502 and R502 filtering, provides about 10V power for pin 6 of NCP1200. Pin 2 of NCP1200 is feedback control pin, which controls the on state of internal field effect tube to make output voltage stable. Pin 4 of NCP1200 is connected to ground, pin 8 HV is connected to high voltage line, pin 5 DRV drives output of external MOSFET, which belongs to current control type, drain electrode max limit current 110mA and working frequency is 40kHz, 60kHz. 3. Five branch circuits are divided for those coupled to secondary level through transformer (1) Voltage outputted by secondary level 16 pin, through D513 half rectification, controllable silicon, TC515 and filtering, outputs CPU3.3V to supply power for CPU; (2) Voltage outputted by pin 15 of transformer, through D508 half wave rectification, TC503, L505 and TC504∏ -type filtering, +9V is achieved, then SA+5V through LM7805 voltage regulating, which supplies power for decode board. (3) After half wave rectification, ∏ -type filtering, pin 12 voltage of transformer outputs 3.3V to supply power for decode board through D515; (4) After D511 half wave rectification, ZD502 voltage regulating, pin 9 voltage of transformer outputs -9V to supply power for audio circuit. We should mention that voltage outputted from secondary level of transformer is pulse DC, so stable DC level may be achieved only through half wave rectification. Diode of half wave rectification adopts quick recovery diode, which works in high frequency state, so we cannot substitute with common diode. Feedback sampling of switch power is from 3.3V (DC power off is from CPU3.3V, power on is from +3.3V) and supplies for photoelectric coupler 2501 through D516 and R506, and sends to R pin of 2.5V comparator through R508 and R509. When 3.3V is on high side, KA pin of comparator LM431A is on, and then sent to pin 4 of switch IC268P through 2501 photoelectric coupling to decrease the on time of inside switch to decrease the coupling of transformer and the outputted 3.3V to reach the purpose of auto control. Vice verse. This machine has DC power on/off function, so switch power has been designed a power management part with main elements U403 12C508A. It is a programmable logic controller responsible for DC power on/off and LED indicator light control. This p-layer is also with this function, no matter - 114 - When the machine is on or in standby, high voltage [art of power board, 3.3V output, sampling and feedback circuit are all in working state. 4. DC power on/off working principle is shown in the figure 7.3.3.2: CPU+3.3V L509 10uH/1A D513 HER105 A U506 MCR100-6 TC515 10uF/25V K D507 1N4148 C516 101 C517 104 R512 22K V502 2N5551 R513 1K R514 10K STB Figure 7.3.3.2 DC power on/off diagram 5. Standby working principle: shown in the figure 7.3.3.3, when working normally, after pressing STANDBY button (or remote controller STANDBY button), SW1 produces a low level, pin 2 of U505 receives the pulse of low level, and outputs a low level signal from pin 5 to make triode V502 cut off; when Tc515 anode is more than 3.3V, it feedback to U503 and make U501 decrease “On”time through U502 and make voltage stabilize in 3.3V, for the winding group of pin 16 of TR501 is most, voltage is highest, when TC515 anode is increasing to 3.3V voltage, other winding voltage is very low, and machine cannot enter working state to realize standby. Standby function of remote control is similar to panel button. CPU+3.3V C522 104 TC514 100UF/10V SW1 10K R523 ASTB R519 10K R521 10K LED1 D518 C519 104 D517 U505 vdd GP5 GP4 GP3 GND GP0 GP1 GP2 8 7 6 5 GND 12C508A LED2 STB R5290R R526 0R(DNS) R524 10K R525 10K 1 2 3 4 R520 R531 10K 10K Q501 R522 10K TC516 22uF/16V 8050 Figure 7.3.3.3 Standby, power on circuit diagram - 115 - 6. Working principle of power on: shown in the figure 7.3.3.3, Sw1 is equal to the input end of Dtype trigger inside U505, each time when Sw1 inputs a triggering level to pin 2 of U505, trigger turns over once, that is pin 3, 5 turn over once. When the player is in standby state, pin 3 LED is defaulted high level to drive panel indicator on; pin 5 STB is defaulted low level, that is V502 base electrode low level. When pressing POWER button on panel (or remote controller), SW1 inputs trigerring low level (or IR inputs power-on signal) to P2 9P7) of U403, pin 3 of U505 changes to low level, panel standby indicator light turns out; at the same time, pin 5 outputs high level to send to base electrode of V502 to make it on, collector electrode changes to low level to make pulse signal of pin 3 of U506 short circuit to ground, controllable silicon cuts off, pin 2 has no output, now CPU+3.3V is provided by +3.3V winding, voltage at this time is low, so voltage increase quickly through feedback loop secondary level winding, and outputs voltage to supply power for each part through rectification, filtering or voltage regulating. - 116 - 7.4.1 Troubleshooting flow chart 1. Troubleshooting process for “CPU3.3V has no voltage output”is shown in the figure 7.4.1.1: CPU3.3V has no voltage output Check whether two ends of Tc501 has 300V voltage N Y Check whether protector pipe is burnt down N Check power cord and filtering circuit Y Check whether power is short circuited to ground N Change protector pipe Y Check whether rectification pipe D501~D504 is stricken through N Check whether U501, U505 are damaged Y Change rectification pipe Check whether cathode of D513 has voltage output N Check whether D513 is normal N Change D513 Y Y Check whether U501, U505 are normal N Change Y Check transformer and U501 peripheral Whether D507 anode voltage output i s normal N Change U506 Y Check filtering circuit Figure 7.4.1.1 Troubleshooting flow chart for “CPU3.3V has no voltage output” - 117 - 2. Troubleshooting process for “No +5V voltage”is shown in the following figure 7.4.1.2: No +5V voltage Whether cathode of D510 has power output N Check D510 and transformer Y Whether pin 7 of CN502 has power output N Check +5V filtering circuit Y OK Figure 7.4.1.2 Troubleshooting flow chart for “No +5V voltage” - 118 - 3. Troubleshooting process for “Voltage output is unstable”is shown in the following figure 7.4.1.3: Voltage output is unstable Check whether pin LM431R has voltage N Check LM431 and sampling resistor Y Check whether LM431R is normal N Change LM431 Y Check whether photoelectric coupler is normal N Change photoelectric coupler Y Change U501 Figure 7.4.1.3 Troubleshooting flow chart for “Voltage output is unstable” - 119 - 7.5.1 PCB board V701 - + - C712 + - TC706 JP712 - 120 - JP710 JP711 JP718 - + TC702 28 + - TC701 L705 JP703 - + - TC705 JK701 JK703 JP704 L710 + TC703 L709 TC704 XS701 JP705 JP701 JP713 JK702 V702 JP715 JP714 R709 JP716 R707 R701 LEI L707 7969-3 2004.4.6 JP717 JP708 JP707 JK705 R708 JP719 L714 R703 JP720 L713 V703 JK706 JP706 JP709 JP702 1. Surface layer of AV OUT Board 2. Bottom layer of AV OUT Board R713 R702 C704 C706 L716 C715 C713 C703 C702 L715 C701 L703 L704 R710 L708 L702 L701 L712 L706 C711 L711 C705 C707 C710 C722 C721 R706 C719 C718 C720 - 121 - C717 C716 R705 R704 R712 R711 R621 R622 C601 DET OK AGND +9V -9V VD601 VD602 VD603 R620 R619 +5V 3. Surface layer of MIC Board G602 C608 R617 TC602 L601 U601 JP603 JP604 JP601 TC603 R607 TC605 TC601 VR601 VR602 - 122 - MIC602 MIC601 R618 R611 R612 R623 C603 L602 R601 R603 R605 R606 C604 C606 TC604 TC616 R610 TC611 R602 1 TC613 XS601 R608 C605 R609 TC606 C607 R604 U602 2003.12.31 6965S-0 LEI R613 G601 JP602 C602 TC615 R616 R615 4. Bottom layer of MIC Board 1 1 - 123 - K U401 XS401 A TC403 LED401 U403 DO DI CL CE GND +5V IR 5. Surface layer of KEY SCAN Board TC402 A LED404 LED405 LED406 LED407 LED408 LED409 K VD401 TC401 K406 4965-2 DVD 2003/8/9 CHENAP R402 K401 K402 - 124 - K403 K404 K405 GND IR SW1 LED# 6. Bottom layer of KEY SCAN Board XS402 R415 OI V402 1 R401 R412 R411 R417 V401 64 C401 R406 17 - 125 - R410 R408 R409 48 R413 V404 R416 V403 R405 R407 R403 C402 U404 C403 R414 C405 R404 C404 G R421 R420 R419 U402 R418 7. POWER Board CN504 R529 R527 R530 TC514 JP501 DVD 5965S-0 3/30/2004 R523 L509 R503 D507 AK G V502 TC503 U506 TC504 L501 D513 HIGH VOLTAGE C502 D501 JP516 L503 BC501 U507 R502 AGND +9V -9V GND GND TC508 2 15 3 14 4 13 5 12 6 11 10 7 T1.6A L250V +5V GND +3.3V C508 C507 C509 L507 L505 ASTB TC505 TC506 D510 L506 TC510 TC509 C515 R507 CAUTION: TC502R505 C506U502 FOR CONTINUED PROTECTION AGAINST RISK OF FIRE REPLACE ONLY WITH SAME TYPE F501 T1.6A L250V FUSE - 126 - R518 R509 C521 R508 +5V GND -21V FLFL+ JP508 1 1 R506 CPU+3.3V CN501 ZD502 U501 JP502 CN505 TC511 ZD501 R510 JP509 D516 D514 TC512 C518 BC503 R504 R516 TC513 R532 D515 C514 U503 D506 JP506 JP511 C511 C501 R515 D519 CPU+3.3V D509 C513 JP504 D511 JP514 GND SA+5V C510 D508 9 D512 C505 BCN501 ~220V JP510 U504 16 R501 F501 DET OK GND IR +5V GND JP503 L508 JP505 CN503 +5V -9V +9V AGND OK JP507 D505 C503 TR501 CN502 D517 TC515 C516 D504 G502 R524 JP513 R528 TC516 R514 D502 B E C D503 LED2# SW1 C519 R517 LED1# JP512 TC501 DET JP515 R511 G501 R607 1K TC605 22uF/16V R609 10K C605 100p -9VA 4 R613 5.1K TC601 4.7uF R603 560R TC603 4.7uF/16V 2 C607 100P R623 1 3 -9VA 10K 4 L602 8 U601A R601 22K C603 103 1 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 R612 4558 R605 10k VR602 4.7K 2 1 10K +9VA TC613 2 MIC602 3 8 3 U602A 4558 4.7uF/16V +5V +9VA - 127 - 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 L601 TC602 4.7u R608 1K 2 C606 100p R604 560R 1 TC606 22uF/16V MIC601 R615 100K R611 4.7K 3 R610 10K U601B 4558 7 6 C608 102 VR601 10K TC604 4.7uF/16V 7 U602B 4558 R621 10ohm1/6W TC615 47uF/16V XS601 R622 10ohm1/6W +9VA C601 104 R619 VD603 1N4158 DET 100 VD602 1N4148 R606 10K R109 1 +9V VD601 1N4148 5 R618 10K C604 103 R616 330 6 5 R602 22K R617 100K -9V -9VA TC616 47uF/16V C602 104 1 2 3 4 5 6 XS06 +5V -9V +9V AGND OK DET TC611 47uF/16V R620 1K 7.5.2 circuit diagram 1. MIC Board OK R704 4.7K +10V R709 CC A+10V 330R R710 2.2K LFE VCC 3 FB V702 8050 V701 8050 SL 4 C703 102 SR 1 A(B)OUT A(B)IN A(A)OUT A-COM RETURN A(A)IN BLUE I/O FUNC SW RETURN CONT GREEN I/O NC RETURN RETURN RED I/O BLK I/O RETURN TRTURN V-OUT V-IN GND 3 L714 FCM 5 AGND 7 9 AGND 11 13 PDAT2 PDAT1 SPDIF VCC Y 15 17 19 C C707 105 21 L704 6 FB R707 JK706 L713 FCM V703 8050 C704 102 2 4 L705 L 6 7 FB C705 102 8 8 10 R 12 L706 9 FB C706 102 14 16 18 10 WHITE 20 11 VJS3921 AGND VGND 12 RED Pb VGND VGND AGND VIEDO PDAT0 L R SL JK702 CC R703 SPDIF VCC 68R LFE +10V 2 C715 224 XS28 G GND SPDIF GREEN 3 BLACK 220R VGND Pb 2 R701 C710 104 JK703B V-OUT5 VGND 1 FBSMT TC702 1000uF/10V VCC TC703 R702 100R 220uF/16V B L707 4 BLUE FBSMT VIEDO TC701 220uF R706 2.2R C721 L710 5 FBSMT C717 104 5 6 104 Pr TC704 220uF/16V R L708 6 FBSMT RED C722 104 7 AGND 3 Y1 L709 RCA-407 VGND C718 104 L711 FBSMT Y TC705 C TC706 220uF/16V L712 220uF/16V 3 AGND VGND C711 104 R713 0R C720 104 JK705 OPTICAL 1 VIN SR VGND L716 FBSMT 2 JK703A S-VIDEO L715 FBSMT 1 FBSMT C712 C713 4 - 128 - Y1 5 A+10V AGND Pr JK701 AV8 L703 FB C716 104 R711 1K XS701 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 2 L702 C702 102 A+10V PDAT2 C701 102 R708 33R AGND R712 2.2K 1 FB R705 75R PDAT0 L701 2. AV OUT Board VCC C719 104 105 105 VGND VGND IN OUT GND 3 2 1 +5V V402 8050D R405 TC402 47uF/16V R412 75R R407 1K 75R R408 R414 1K +5V R413 0R LED403 R403 4.7K +5V LED409 1K P2/S2 KI2 E (DNS) (DNS) C403 C402 2 2 +5V KI1 R417 103 DO CE CL DI 103 1 2 R418 R406 0R 1 LED408 TC401 47uF/16V 2 LED407 C401 103 2 LED406 C404 R404 681 62K 1 LED405 C405 101 V401 8050D 1 LED404 B K C 1 R401 LED402 K R402 470R V404 8050D 1K A +5V R415 1K A REQUIER +4V TO LIGHT TC403 47uF/16V R411 R409 VD401 1N4148 LCD COM1 COM2 COM3 COM4 PT6554LQ 2 2 V403 8550 47R K402 +5V R419 4.7K K404 1 KI2 1 K403 R420 4.7K K405 2 U402 R410 SW1 1 KS5 KS4 KS3 KS2 KS1 COM4 COM3 COM2 COM1 2 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10 S11 S12 S13 S14 S15 S16 S17 S18 S19 S20 K401 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 KS5 KS4 KS3 KS2 KS1 COM4 COM3 COM2 COM1 S39 S38 S37 S36 S35 S34 S33 2 - 129 - S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10 S11 S12 S13 S14 S15 S16 COM1 COM2 COM3 COM4 P1/S1 P2/S2 P3/S3 P4/S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10 S11 S12 S13 S14 S15 S16 R421 4.7K IR +5V GND CE CL DI DO 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 XS401 XS07 S17 S18 S19 S20 S21 S22 S23 S24 S25 S26 S27 S28 S29 S30 S31 S32 U401 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 P1/S1 P2/S2 S3 DI CL CE DO OSD VSS VDD2 VDD1 VDD TEST KI5 KI4 KI3 KI2 KI1 KS6 1 LED# KS1 R416 47R K406 64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 LED401 LED# GND IR SW1 1 2 3 4 XS402 XS04 3. KEY SCAN Board U404 LM117 +5V CPU+3.3V U506 MCR100-6 C516 101 TC515 10uF/25V K G A D507 1N4148 C517 104 R512 22K V502 2N5551 R513 1K TR501 2 D505 HER107 14 3 720K/1W D506 HER105 D510 C509 101 SR360 13 6 11 7 10 D509 SR360 - 130 - 1 2 3 4 L501 UT-20 40mH ADJ HV FB NC CS VCC GND DRV 8 7 6 5 L503 FB SW1 GND LED1# LED2# 1 2 3 4 CPU+3.3V GND IR +5V GND CN503 XS6 1 2 3 4 5 CN505 XS05 D516 +3.3V D515 SR560(JUMP) 1N4148(JUMP) CN504 XS04 CPU+3.3V R518 TC511 100uF/16V R530 10K(DNS) R532 220R/1W -9V C514 101 TC512 47uF/50V R506 150 C518 R502 1/1W 104 R508 3.3K R507 1K C515 104 U502 2501 U503 LM431A C506 102/100V R511 220R/1W C521 104 R510 4.7K FL+ FL-21V GND +5V K R ZD502 9.1V/1W TC513 100uF/16V 5.1V ZD501 ! R501 680K 1/2W R509 2K 1 2 3 4 5 LED1 R527 R528 10K Q503 8550 CN501 10K XS05 CPU+3.3V A F501 T1.6A/250V BCN501 ~220V D514 SR160 TC510 1000uF/10V C513 101 C501 101/1KV R504 BC501 30K ~275V 104 ! C520 104 (OPEN) 300 1 2 3 4 5 6 SA+5V C510 104 D511 HER105 R515 R516 1.5K TC502 10uF/50V L506 TC509 10uH/2A 1000uF/10V D512 HER105 U505 P4NC60 +5V -9V +9V AGND OK VOICE-DET CN502 XS13 CPU+3.3V C505 101 D517 1N4148 TC506 1000uF/10V 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 LED1# U501 NCP1200 +5V C511 101 9 R505 33ohm L508 10uH/1A L507 10uH/2A TC505 1000uF/10V 12 EI128/8-2 ! 100uF/16V VOICE-DET OK AGND +9V -9V GND +5V GND +3.3V GND SA+5V ASTB CPU+3.3V ! ! C522 104 TC514 100UF/10V R519 10K R520 10K R531 10K BC503 ~400V 221 U505 R521 10K LED1 D518 SW1 C519 104 10K R523 D517 ASTB R525 10K vdd GP5 GP4 GP3 GND GP0 GP1 GP2 8 7 6 5 GND LED2 STB R529 0R 12C508A R526 0R(DNS) R524 10K 1 2 3 4 R522 10K Q501 TC516 22uF/16V 8050 IR C503 101/1KV 4 ! ! TC508 15 D504 1N4007 TC501 47uF/400V ! SA+5V 3 OUT U504 LM7805 16 R517 D501 1N4007 IN D508 HER105 ! STB LED2# C502 103/1KV 1 C508 104 2 R503 39K/2W TC504 470uF/25V GND +9V TC503 470uF/25V D503 1N4007 R514 10K L505 10uH/1A C507 101 D502 1N4007 4. POWER Board L509 10uH/1A D513 HER105 LED2