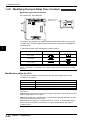
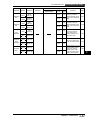
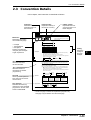
Download Programming - PLC Products Group
Transcript
96M0366 INDEX 1 2 3 Installation Support Software Programming 2. System Installation 3. Access Window 4. KV-D20 Operator Interface Panel 1. Introduction 1. Programming 2. Editor 2. Instructions 3. Simulator 3. Interrupts 4. Monitor 4. High-speed Counters 5. Appendices 5. Positioning Control 6. Interrupts, High-speed Counters, Positioning Control 5. KV-10/80 Hardware 6. Handheld Programmer 7. Serial Communication 7. KV-L2 Serial Interface Module 8. Programming Examples 8. KV-AN6 Analog I/O Module 9. KV-AD4/DA4 Analog I/O Unit 10. Troubleshooting 11. Appendices Specifications are subject to change without notice. AFFILIATED COMPANIES KEYENCE CORPORATION 1-3-14, Higashi-Nakajima, Higashi-Yodogawa-ku, Osaka, 533-8555, Japan PHONE: 81-6-6379-2211 FAX: 81-6-6379-2131 KEYENCE CORPORATION OF AMERICA PHONE: 201-930-0100 FAX: 201-930-0099 KEYENCE (MALAYSIA) SDN BHD PHONE: 03-252-2211 FAX: 03-252-2131 KEYENCE (UK) LIMITED PHONE: 01908-696900 FAX: 01908-696777 KEYENCE (THAILAND) CO., LTD. PHONE: 02-369-2777 FAX: 02-369-2775 KEYENCE DEUTSCHLAND GmbH PHONE: 0711-79 73 71-0 FAX: 0711-797 77 99 KEYENCE THAIWAN CO., LTD. PHONE: 02-2627-3100 FAX: 02-2798-8925 KEYENCE FRANCE S.A. PHONE: 01 47 92 76 76 FAX: 01 47 92 76 77 KEYENCE KOREA CORPORATION PHONE: 02-563-1270 FAX: 02-563-1271 KEYENCE SINGAPORE PTE LTD. PHONE: 392-1011 FAX: 392-5055 © KEYENCE CORPORATION, 1999 NKVP-UM-4-1000 Printed in Japan User's Manual Visual KV Series 3 Programming 1. Configuration and Specifications Visual KV Series 3 Programming How this manual is organized: The Visual KV Series User’s Manual is composed of 3 separate manuals; 1-Installation, 2-Support Software, 3-Programming. Please read each manual relevant to your purpose. Safety Precautions This instruction manual describes the operation and function of the KV Series PLC. Read this manual carefully to ensure safe use and maximum performance from your KV Series PLC. Symbols The following symbols alert you to important messages. Be sure to read these messages carefully. Failure to follow instructions may lead to injury. (electric WARNING shock, burn, etc.) CAUTION Note: Failure to follow instructions may lead to product damage. Provides additional information on proper operation. Conventions This manual describes the operation/function of all Keyence KV Series PLC. Note following conventions when you use. Visual KV (Series) KV-10xx, 16xx, 24xx, 40xx KV-10AR/AT/DR/DT KV-24AR/AT/DR/DT KV-16AR/AT/DR/DT KV-40AR/AT/DR/DT Conventional KV (Series) KV-300 (Series) KV-10/80 (Series) KV-10R(W)/T(W) KV-24R(W)/T(W) KV-80R(W)/T(W) KV-300 KV-16R(W)/T(W) KV-40R(W)/T(W) General Precautions • At startup and during operation, be sure to monitor the functions and performance of the KV Sereis PLC. • We recommend that you take substantial safety measures to avoid any damage in the event a problem occurs. • Do not open or modify the KV Series PLC or use it in any way other than described in the specifications. • When the KV Series PLC is used in combination with other instruments, functions and performance may be degraded, depending on operating conditions and the surrounding environment. • Do not use the KV Series PLC for the purpose of protecting the human body. Note: The built-in display may show the error message "Error 40" blinking the very first time you turn on the power supply to the Visual KV Series. Press any key around the display to cancel this message. The Visual KV Series shows this message when no program is loaded. (1) Note to User When using the Visual KV Series in the following conditions or environments, be sure to use the Visual KV Series with sufficient margin regarding the rating and functions, take appropriate safety precautions such as fail-safe, and contact our sales personnel if any questions arise. • Use in conditions or environments not described in this manual • Use for nuclear power control, railway facilities, air service facilities, vehicles, combustion devices, medical equipment, amusement machines, safety equipment, etc. • Use for applications where large effects are predicted to be given on human lives and properties and safety is especially requested. Restriction on Acquiring the CE Marking ■ Restriction to be compatible with EMC directives • When using a relay output type unit (whose model name ends with "R"), connect spark killers having the appropriate withstand voltage against the load to the output terminals in parallel to contacts (because the unit discharges when a relay contact becomes open and noise is generated). In our experiments, we use the following models of spark killers. XEB0101 0.1 µF-10 Ω manufactured by OKAYA DENKI SANGYO The following 1-turn ferrite core is added to the AC power input circuit of the KV40AR/T, the KV-24AR/T and to the DC power input circuit of the KV-40DR/T. ZCAT3035-1330 manufactured by TDK Note: The contents above do not by themselves ensure that the entire machine manufactured in accordance with the above contents is compatible with EMC directives. You must judge by yourself whether or not the entire machine is compatible with EMC directives because compatibility may change depending on the component configuration, wiring and location inside of the machine. ■ Restriction on compatibility with low-voltage directives (IEC-1010-1) • Use insulated type crimp-style terminals. • For wiring materials, use lead wires whose sheath is 0.4 mm or more. • The Visual KV Series is allowed to be installed in a vertical position only. (Spacers for expansion units are not available.) • Be sure to use the Visual KV Series inside the control panel. (2) Features of the Visual KV Series ● Extremely small The Visual KV Series is the smallest in the world among AC type PLCs equipped with screw terminal blocks, and saves installation space. ● Extremely fast The minimum scan time is 140 µs and minimum instruction execution time is 0.7 µs, which is the fastest control in its class. ● AC power built-in type newly added AC power built-in type units are newly added. This type can be used in small spaces where a switching power supply unit cannot be installed. ● Excellent Access Window An Access Window with two-color backlight is adopted in all models to facilitate changing and monitoring of device data. Changing between RUN mode and PROGRAM mode, checking the error code when an error has occurred, etc. can be performed in a Visual KV Series unit without the need for any handheld programmer. The analog trimmer, which has been popular in the conventional KV Series, is digitized to enable more detail settings. [Digital trimmers] ● User message setting function In the Access Window, 256 different user messages can be displayed. This function can be used to give instructions on works on the production line, indicate abnormalities in the units, etc. ● Program write in RUN mode Ladder programs can be changed even while the system is running. ● Equipped with two serial ports Visual KV Series basic units are equipped with two serial ports to connect peripheral units, improving the debug environment. (The KV-10xx is equipped with only one serial port.) ● Easy Ramp-up/down control function The one-axis motor control function is offered separately from high-speed counters so that feedback control is enabled. ● Equipped with two 24-bit high-speed 30 kHz, two-phase counters The Visual KV Series is equipped with two high-speed counters each with a twopoint comparator output function that enables high-speed encoder input. ● Specified frequency pulse output function High-speed counters can function as pulse oscillators of 50 kHz maximum with easy setting, without creating a complicated ladder program. ● Frequency counter function High-speed counters can function as frequency counters with easy setting, without creating complicated ladder programs. ● Cam switch function High-speed counters can function as cam switches with easy setting, without creating complicated ladder programs. (3) ● Interrupt function The Visual KV Series is equipped with four high-speed interrupt inputs of 10 µs maximum. ● Input time constant change function The time constant can be set in 7 steps from 10 µs to 10 ms. ● Double memory backup functions In addition to a conventional SRAM battery backup function, the Visual KV Series is also equipped with an EEPROM backup function. Compatibility with Conventional KV Series Peripheral Units The Visual KV Series functions as a high-end compatible model of the conventional KV Series. Peripheral units of the conventional KV Series such as the ladder support software "KV IncrediWare (DOS)" and "LADDER BUILDER for KV" and the handheld programmer KV-P3E(01) can be used since they are part of the Visual KV Series. However, it should be noted that the contents have changed as follows. • The internal clock cycle of high-speed counters consists of three types: 1 µs, 10 µs, and 100 µs. • The time constant for an input relay specified by the HSP instruction is 10 µs. • The analog trimmer function is set with the Access Window built into the basic unit. • The available device setting range of the TMIN instruction is from 0 to 65535. [Handheld programmer KV-P3E(01) can display 0 to 9999 .] • The RUN/PROGRAM LED is displayed in the Access Window provided on the front face of the basic unit. • Transistor output is not independent, but is common. • With the transistor type, the output terminal layout is different. • The specifications for output current of transistor outputs Nos. 500 to 502 is 100 mA. • Conventional KV Series expansion units are not available as expansion units for the Visual KV Series. • The channel setting switch is not provided for expansion units. Channels are determined in connection order. • Scans in expansion I/O units are not synchronous with the scan time in Visual KV Series basic units. • Assignment of special utility relays has partially changed. • Data memory device Nos. DM1000 to DM1999 are assigned as special data memories. (4) Cautions when using the previous version of ladder support software Pay strict attention to the following items when using the ladder support software. • • CAUTION When using the ladder support software "KV IncrediWare (DOS)" or "LADDER BUILDER for KV Ver. 1.0x", set the model to "KV-300". DM0 to DM1999 are only available. When the ladder support software "LADDER BUILDER for KV Ver. 1.0x" is used, do not use the monitor’s Change All function. If the Change All function is used, the basic unit may be damaged. Never use the Change All function. Peripheral units and other units incompatible with the Visual KV Series Peripheral units in the conventional KV Series and other units shown below are not compatible with the Visual KV Series. • • Expansion I/O units for the conventional KV Series: KV-8ER/8ET/8EX/16EX/ 8EYR/8EYT/16EYR/16EYT Analog I/O units for the conventional KV Series: KV-AD4/DA4 Cautions when Using the Serial Port The KV-16xx/24xx/40xx units are equipped with two RJ-11 modular connectors for serial communication. When using them, pay strict attention to the following contents: (5) • Programs can be transferred and monitored using either communication port A or B. However, never connect the ladder software and a handheld programmer to the two ports at the same time. • The KV-D20 operator interface panel can be connected to either communication port A or B. However, only one KV-D20 unit can be connected to a single basic unit. • Never leave both the KV-D20 operator interface panel and KV-P3E(01) handheld programmer on simultaneously for a long period of time. (6) How this manual is organized The Visual KV Series User’s Manual is composed of 3 separate manuals; 1-Installation, 2-Support Software, 3-Programming. Please read each manual relevant to your purpose. 1 Installation Chapter 1 Configuration and Specifications [Visual KV Series Only] Describes the system configuration of the Visual KV Series, the names and functions of each part, and the specifications. Chapter 2 System Installation [Visual KV Series Only] Describes the installation and connection of each Visual KV Series unit as well as system maintenance. Chapter 3 Access Window [Visual KV Series Only] Describes the Access Window used for changing and monitoring data. Chapter 4 KV-D20 Operator Interface Panel [Visual KV Series Only] Describes the KV-D20 Operator Interface Panel used for changing, monitoring, and displaying the status of inside relays, timers, counters and data memories. Chapter 5 KV-300, KV-10/80 Hardware [KV-300, KV-10/80 Series Only] Describes the hardware specifications and wirings for KV-300 and KV-10/80 Series. Chapter 6 Handheld Programmer Describes how to use the handheld programmer and memory card. Chapter 7 KV-L2 Serial Interface Module [KV-300 Series Only] Describes the serial interface modules for KV-300 Series. Chapter 8 KV-AN6 Analog I/O Module [KV-300 Series Only] Describes the optional Analog I/O module for KV-300 Series Chapter 9 KV-AD4/DA4 Analog I/O Unit [KV-10/80 Series Only] Describes the optional Analog I/O unit for KV-10/80 Series. Chapter 10 Troubleshooting This chapter describes the error code list, countermeasures against problems, and error indications for each unit. Appendices The appendix includes a list of ladder program applications and the index. 2 Support Software Chapter 1 Introduction Describes the items included in the package, the product outline, the method to connect a personal computer, the installation method, etc. (7) Chapter 2 Editor Describes the operating procedures in Editor mode. Chapter 3 Simulator Describes the operating procedures in Simulator mode. Chapter 4 Monitor Describes the operating procedures in Monitor mode. Appendices Includes instructions list, devices list, sample program list and quick reference for key operation and shortcuts. 3 Programming Chapter 1 Programming Describes basic knowledge including program creation procedures, device configuration, relay assignments, special functions to set and confirm Visual KV Series operations, as well as the extended ladder diagrams. Understand the contents described here completely at first before creating programs. Chapter 2 Instructions Describes the concrete usage of instructions in the KV Series. Refer to "Chapter 3 Interrupts" on page 3-183 for details of interrupt instructions. Refer to "Chapter 4 High-speed counters" on page 3-195 for details of the high-speed counters used in the application instruction. Chapter 3 Interrupts [Visual KV Series Only] The interrupt processing function executes an interrupt program when an external input or request from the high-speed counter comparator (interrupt factor) is encountered during KV operation. This chapter describes the types of interrupt factors as well as inputs and outputs encountered during interrupt processing. Chapter 4 High-speed Counters [Visual KV Series Only] Describes high-speed counters and high-speed counter comparators, which allow highspeed pulse measurement and pulse output, independent of the scan time. Chapter 5 Positioning Control [Visual KV Series Only] Describes ramp-up/down control of stepping motors and servo motors. Chapter 6 Interrupts, High-speed Counters, Positioning Control [KV-300, KV-10/80 Series Only] Describes ramp-up/down control of stepping motors and servo motors. Chapter 7 Serial Communication The KV Series can be connected to an external device with an RS-232C interface to establish communication. This chapter describes communications specifications, how to connect the KV Series to external devices, and how to perform communication. Chapter 8 Programming Examples Describes the typical programming examples for KV-10/80 Series. These programs can be used for Visual KV Series. However, pay attention to the I/O addressing compatibility before use. (8) Contents 3 Programming Chapter 1 Programming 1.1 Before Creating Programs .............................................................................. 3-2 1.1.1 Flow from Introduction to Operation ................................................................... 3-2 1.1.2 Scan Time ........................................................................................................... 3-3 Scan time ..................................................................................................... 3-3 Input response time delay ............................................................................ 3-3 1.2 User Memory .................................................................................................... 3-4 1.2.1 Program Capacity ............................................................................................... 3-4 Maximum number of lines in a program ....................................................... 3-4 Calculating the byte count used ................................................................... 3-4 1.3 Device Configuration ....................................................................................... 3-5 1.3.1 Device List .......................................................................................................... 3-5 Relay list ...................................................................................................... 3-5 List of I/O relays in basic units ..................................................................... 3-5 List of relays in expansion units ................................................................... 3-6 1.3.2 Relay No. ............................................................................................................ 3-7 Address No. ................................................................................................. 3-7 Contact No. .................................................................................................. 3-8 Channel No. ................................................................................................. 3-8 1.3.3 Assigning Relay Nos. .......................................................................................... 3-8 1.3.4 Input Relays ........................................................................................................ 3-9 Basic unit ..................................................................................................... 3-9 Expansion unit ........................................................................................... 3-10 1.3.5 Output Relays ................................................................................................... 3-10 Output operation time ................................................................................ 3-10 1.3.6 Internal Utility Relays ........................................................................................ 3-11 Retentive function of internal utility relays .................................................. 3-11 1.3.7 Special Utility Relays ........................................................................................ 3-12 Description ................................................................................................. 3-12 1.3.8 Special Utility Relay List ................................................................................... 3-14 Special relays and arithmetic operation flags ............................................ 3-14 Special utility relays for high-speed counter(0) .......................................... 3-14 Special utility relays for high-speed counter(1) .......................................... 3-15 Other special utility relays .......................................................................... 3-15 1.3.9 Timers and Counters ........................................................................................ 3-18 Timer/Counter list ....................................................................................... 3-18 Description ................................................................................................. 3-18 1.3.10 Data Memories ................................................................................................. 3-19 1.3.11 Temporary Data Memory .................................................................................. 3-21 1.3.12 Relay Nos. and Functions ................................................................................. 3-22 1.4 Special Functions .......................................................................................... 3-23 1.4.1 Input Time Constant Change Function ............................................................. 3-23 Setting the input time constant for basic units using special utility relays .. 3-23 1.4.2 Modifying the Input Relay Time Constant ......................................................... 3-24 Modification within the CPU ....................................................................... 3-24 1.4.3 Constant Scan Time Mode ............................................................................... 3-25 1.4.4 Output Disabled Function ................................................................................. 3-26 1.4.5 Input Refresh Disabled Function ...................................................................... 3-26 1.4.6 Contact Comment Save Function ..................................................................... 3-27 1.4.7 Special Functions ............................................................................................. 3-28 Constant Scan Time Mode ........................................................................ 3-28 Output Disabled Function .......................................................................... 3-28 Input Refresh Disabled Function ................................................................ 3-28 1.5 1.5.1 1.5.2 1.5.3 (9) Extended Ladder Diagrams .......................................................................... 3-29 Features of Extended Ladder Diagrams ........................................................... 3-29 Advantages of Extended Ladder Diagrams ...................................................... 3-30 Example of an Extended Ladder Diagram ........................................................ 3-31 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Instructions 2.1 2.1.1 2.1.2 2.1.3 2.1.4 2.1.5 Instruction List [Visual KV Series] .............................................................. 3-34 Basic Instructions .............................................................................................. 3-34 Application Instructions ..................................................................................... 3-36 Arithmetic Instructions ...................................................................................... 3-38 Interrupt Instructions .........................................................................................3-41 Function No. List (Alphabetical order) .............................................................. 3-41 2.2 2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.3 2.2.4 Instruction List [KV-300 Series, KV-10/80] ................................................. 3-42 Basic Instructions .............................................................................................. 3-42 Application Instructions ..................................................................................... 3-45 Arithmetic Instructions ...................................................................................... 3-48 Interrupt Instructions .........................................................................................3-54 2.3 Convention Details ........................................................................................ 3-55 2.4 2.4.1 2.4.2 2.4.3 Instruction Details .......................................................................................... 3-56 Basic Instructions .............................................................................................. 3-56 Application Instructions ..................................................................................... 3-95 Arithmetic Instructions .................................................................................... 3-134 2.5 Programming Notes ..................................................................................... 3-189 Interrupts Visual KV 3.1 Interrupt Instructions ................................................................................... 3-192 3.2 3.2.1 3.2.2 3.2.3 3.2.4 Interrupt Processing .................................................................................... 3-194 Interrupt Processing ........................................................................................ 3-194 Types of Interrupts .......................................................................................... 3-195 Interrupt Priority .............................................................................................. 3-196 Interrupt Program ............................................................................................ 3-196 3.3 Direct Input/Output ...................................................................................... 3-197 3.3.1 Direct Input ..................................................................................................... 3-197 3.3.2 Direct Output ................................................................................................... 3-197 3.4 3.4.1 3.4.2 3.4.3 3.4.4 Chapter 4 Applications of Interrupt Programs ........................................................... 3-198 Interrupt with a Signal Converter .................................................................... 3-198 Interrupt with a High-speed Counter ............................................................... 3-199 Measuring the ON Time of High-speed Pulses .............................................. 3-200 Measuring the Period in which a Target Passes between Two Points ........... 3-201 High-speed Counters 4.1 Visual KV High-speed Counter Instructions ............................................................... 3-204 4.2 Outline of High-speed Counters ................................................................. 3-206 4.2.1 High-speed Counters and High-speed Counter Comparators ........................ 3-206 Structure of high-speed counters and high-speed counter comparators . 3-206 Specifications of high-speed counters ..................................................... 3-208 High-speed counter comparators ............................................................. 3-209 4.2.2 Internal Clock for High-speed Counters .......................................................... 3-210 4.3 4.3.1 4.3.2 4.3.3 4.3.4 4.3.5 4.3.6 Setting and Operation of High-speed Counters ........................................ 3-211 Reading the Current Value of the High-speed Counter .................................. 3-211 Preset Value of the High-speed Counter Comparator .................................... 3-211 Comparator Output ......................................................................................... 3-211 Count Input Method ........................................................................................ 3-212 Resetting the High-speed Counter ................................................................. 3-214 Differences with the CTH Instruction between the Conventional and Visual KV Series ................................................................ 3-216 4.3.7 Applications of High-speed Counters ............................................................. 3-217 4.4 4.4.1 4.4.2 4.4.3 4.4.4 4.4.5 Extended Functions of High-speed Counters ........................................... 3-221 24-bit High-speed Counter .............................................................................. 3-221 Changing the Current Value of a 24-bit High-speed Counter ......................... 3-223 Application Example of 24-bit High-speed Counter (single-phase input) ....... 3-224 Ring Counter Function .................................................................................... 3-225 Applications of Ring Counters ........................................................................ 3-226 4.5 Special Functions Using High-speed Counters ........................................ 3-228 (10) 4.5.1 4.5.2 4.5.3 4.5.4 4.5.5 Specified Frequency Pulse Output Function .................................................. 3-228 Applications of the Specified Frequency Pulse Output ................................... 3-229 Frequency Counter Function .......................................................................... 3-231 Applications of Frequency Counters ............................................................... 3-232 Cam Switch Function ...................................................................................... 3-233 Cam switch mode .................................................................................... 3-233 Multi-step comparator mode .................................................................... 3-234 Setting method .........................................................................................3-234 4.5.6 Application of the Cam Switch (Cam Switch Mode) ....................................... 3-236 4.6 Direct Clock Pulse Output ........................................................................... 3-237 4.6.1 Outline of Direct Clock Pulse Output .............................................................. 3-237 4.6.2 Pulse Output Setting with the High-speed Counter Comparator .................... 3-238 Changing the pulse period and width ....................................................... 3-238 Calculating the pulse period and comparator preset value ...................... 3-239 Operation with special utility relays .......................................................... 3-239 4.7 4.7.1 4.7.2 4.7.3 4.7.4 Chapter 5 Examples of Direct Clock Pulse Output .................................................... 3-242 Example of Outputting a Pulse with 1:1 ON/OFF Ratio .................................. 3-242 Example of Outputting a Pulse with Variable ON/OFF Ratio .......................... 3-245 Example of Stopping the Pulse Output at a Specified Pulse Count ............... 3-249 Application of Direct Clock Pulse Output (Ramp-up/down control) ................ 3-251 Positioning Control Visual KV 5.1 Outline of Positioning Control .................................................................... 3-254 5.1.1 Ramp-up/down Control ................................................................................... 3-254 5.2 Parameter Setting and Operating Procedures .......................................... 3-255 5.2.1 Parameter Setting Procedure ......................................................................... 3-255 5.2.2 Operating Procedure ...................................................................................... 3-257 5.3 5.3.1 5.3.2 5.3.3 Chapter 6 Examples of Using the Positioning Control Function .............................. 3-258 Connection Example ....................................................................................... 3-258 Tips .................................................................................................................3-258 Application Examples of the Positioning Control Function ............................. 3-259 Interrupts, High-speed Counters, Positioning Control KV-300, KV-10/80 6.1 Interrupt Instructions ................................................................................... 3-268 6.1.1 Description of Interrupts .................................................................................. 3-268 Input processing for routine program and interrupt routine ...................... 3-268 Types of interrupt ..................................................................................... 3-268 Interrupt priority ........................................................................................ 3-269 Interrupt routine ........................................................................................ 3-269 Direct output ............................................................................................. 3-270 Direct input ...............................................................................................3-270 6.1.2 Interrupt Instructions ....................................................................................... 3-271 6.2 Direct Clock Pulse ........................................................................................ 3-276 6.2.1 Output of Direct Clock Pulse ........................................................................... 3-276 Outline of High-Speed Counters .............................................................. 3-276 Outline of Pulse Output ............................................................................ 3-279 Examples of Pulse Output ....................................................................... 3-284 6.3 Positioning Control ...................................................................................... 3-296 6.3.1 Positioning Control (Ramp-up/down Control) ................................................. 3-296 Outline of positioning control .................................................................... 3-296 Setting and application of parameters ..................................................... 3-297 Examples of stepping motor control ......................................................... 3-300 Chapter 7 Serial Communication 7.1 7.1.1 7.1.2 7.1.3 Communications Specifications ................................................................ 3-306 Communications Specification ........................................................................ 3-306 Connection with the KV Unit ........................................................................... 3-306 Connecting the KV-300 CPU to a Personal Computer ................................... 3-307 7.2 Serial Communication ................................................................................. 3-308 7.2.1 Command Transmission Procedure ............................................................... 3-308 (11) Chapter 8 7.2.2 7.2.3 7.2.4 7.2.5 7.2.6 7.2.7 Format of Commands/Responses .................................................................. 3-309 Communication Command/Response List ..................................................... 3-310 Setting Communication Commands and Responses to Commands .............. 3-311 Other Response Codes .................................................................................. 3-315 Error Code List ................................................................................................ 3-316 Example Program ........................................................................................... 3-317 7.3 7.3.1 7.3.2 7.3.3 Loading Text Data ........................................................................................ 3-318 Receiving Text Data ....................................................................................... 3-318 Transmitting Text Data ................................................................................... 3-319 Sample Program ............................................................................................. 3-320 7.4 ASCII Code List ............................................................................................ 3-321 Programming Examples 8.1 List ......................................................................................................... 3-324 8.2 Details ......................................................................................................... 3-326 8.2.1 Reference Program Examples ........................................................................ 3-326 Basic Instructions ..................................................................................... 3-326 Application Instructions ............................................................................ 3-334 Arithmetic Instructions .............................................................................. 3-343 WARRANTIES AND DISCLAIMERS 1 3-367 Installation Chapter 1 Configuration and Specifications Visual KV 1.1 System Configuration ...................................................................................... 1-2 1.1.1 System Configuration ......................................................................................... 1-2 1.2 Specifications ................................................................................................... 1-4 1.2.1 General Specifications ........................................................................................ 1-4 1.2.2 AC Power Specifications .................................................................................... 1-5 Visual KV Series operation at power interruption ........................................ 1-5 1.2.3 Performance Specifications ................................................................................ 1-6 Data backup function against instantaneous power interruption ................. 1-7 1.3 Common I/O Specifications of Basic Units ................................................... 1-8 1.3.1 Model of a Basic Unit .......................................................................................... 1-8 1.3.2 Common I/O Specifications ................................................................................ 1-8 1.4 KV-10AR/AT(P)/DR/DT(P) (10-I/O Basic Unit) ............................................. 1-10 1.4.1 Part Names and Functions ............................................................................... 1-10 1.4.2 Terminal Layout Drawings and I/O Circuit Diagrams ........................................ 1-11 KV-10AR/DR (Relay output type) .............................................................. 1-11 KV-10AT(P)/DT(P) (Transistor output type) ............................................... 1-13 1.4.3 AC Power Input (KV-10AR/AT(P)) .................................................................... 1-14 1.4.4 Relationship between Continuous Simultaneous ON Ratio and Ambient Temperature 1-15 1.4.5 Dimensions ....................................................................................................... 1-16 1.5 KV-16AR/AT(P)/DR/DT(P) (16-I/O Basic Unit) ............................................. 1-17 1.5.1 Part Names and Functions ............................................................................... 1-17 1.5.2 Terminal Layout Drawings and I/O Circuit Diagrams ........................................ 1-18 KV-16AR/DR (Relay output type) .............................................................. 1-18 KV-16AT(P)/DT(P) (Transistor output type) ............................................... 1-20 1.5.3 AC Power Input (KV-16AR/AT(P)) .................................................................... 1-21 1.5.4 Relationship between Continuous Simultaneous ON Ratio and Ambient Temperature 1-22 1.5.5 Dimensions ....................................................................................................... 1-23 1.6 KV-24AR/AT(P)/DR/DT(P) (24-I/O Basic Unit) ............................................. 1-24 1.6.1 Part Names and Functions ............................................................................... 1-24 1.6.2 Terminal Layout Drawings and I/O Circuit Diagrams ........................................ 1-25 KV-24AR/DR (Relay output type) .............................................................. 1-25 KV-24AT(P)/DT(P) (Transistor output type) ............................................... 1-27 1.6.3 AC Power Input (KV-24AR/AT(P)) .................................................................... 1-28 1.6.4 Relationship between Continuous Simultaneous ON Ratio and Ambient Temperature 1-29 1.6.5 Dimensions ....................................................................................................... 1-30 1.7 KV-40AR/AT(P)/DR/DT(P) (40-I/O Basic Unit) .............................................. 1-31 (12) 1.7.1 Part Names and Functions ............................................................................... 1-31 1.7.2 Terminal Layout Drawings and I/O Circuit Diagrams ........................................ 1-32 KV-40AR/DR (Relay output type) .............................................................. 1-32 KV-40AT(P)/DT(P) (Transistor output type) ............................................... 1-34 1.7.3 AC Power Input (KV-40AR/AT(P)) .................................................................... 1-35 1.7.4 Relationship between Continuous Simultaneous ON Ratio and Ambient Temperature 1-36 1.7.5 Dimensions ....................................................................................................... 1-37 1.8 1.8.1 1.8.2 1.8.3 KV-E4X/E8X/E16X (Expansion Input Unit) .................................................. 1-38 Part Names and Functions ............................................................................... 1-38 Input Specifications ........................................................................................... 1-38 Terminal Layout Drawings and Input Circuit Diagrams .................................... 1-39 KV-E4X (4-I/O expansion input unit) .......................................................... 1-39 KV-E8X (8-I/O expansion input unit) .......................................................... 1-40 KV-E16X (16-I/O expansion input unit) ...................................................... 1-41 1.8.4 Dimensions ....................................................................................................... 1-42 1.9 KV-E4R/E4T/E8R/E8T(P)/E16R/E16T(P) (Expansion Output Unit) ............. 1-43 1.9.1 Part Names and Functions ............................................................................... 1-43 1.9.2 Output Specifications ........................................................................................ 1-43 KV-E4R/E8R/E16R (Relay output type) ..................................................... 1-44 KV-E4T/E8T(P)/E16T(P) [Transistor output type (NPN/PNP)] .................. 1-44 1.9.3 Terminal Layout Drawings and Input Circuit Diagrams .................................... 1-45 KV-E4R [4-I/O expansion output unit (relay output type)] .......................... 1-45 KV-E4T [4-I/O expansion output unit transistor output type)] .................... 1-46 KV-E8R [8-I/O expansion output unit (relay output type)] .......................... 1-47 KV-E8T(P) [8-I/O expansion output unit (transistor output type)] .............. 1-48 KV-E16R [16-I/O expansion output unit (relay output type)] ...................... 1-49 KV-E16T(P) [16-I/O expansion input unit (transistor output)] .................... 1-50 1.9.4 Dimensions ....................................................................................................... 1-51 1.10 1.10.1 1.10.2 1.10.3 KV-E4XR/E4XT(P) (Expansion I/O Unit) ....................................................... 1-52 Part Names and Functions ............................................................................... 1-52 Input Specifications ........................................................................................... 1-53 Output Specifications ........................................................................................ 1-53 KV-E4XR (Relay output type) .................................................................... 1-53 KV-E4XT(P) (Transistor output type) ......................................................... 1-53 1.10.4 Terminal Layout Drawings and Input Circuit Diagrams .................................... 1-54 KV-E4XR (Relay output type) .................................................................... 1-54 KV-E4XT(P) (Transistor output type) ......................................................... 1-56 1.10.5 Dimensions ....................................................................................................... 1-58 1.11 1.11.1 1.11.2 1.11.3 1.11.4 Chapter 2 KV-D20 (Operator Interface Panel) ............................................................... 1-59 Part Names and Functions ............................................................................... 1-59 General Specifications ...................................................................................... 1-60 Functional Specifications .................................................................................. 1-60 Dimensions ....................................................................................................... 1-61 System Installation Visual KV 2.1 2.1.1 2.1.2 2.1.3 Installation Environment ............................................................................... 1-64 Installation Environment ................................................................................... 1-64 Installation Position ........................................................................................... 1-65 Installation Procedure ....................................................................................... 1-66 Expansion unit spacer ................................................................................ 1-66 2.1.4 Cautions on Wiring for Each Unit ...................................................................... 1-67 Wiring procedures for basic units ............................................................... 1-67 Cautions on wiring for I/O units .................................................................. 1-68 Terminal ..................................................................................................... 1-68 Cautions on grounding ............................................................................... 1-69 2.1.5 Contact Protection ............................................................................................ 1-69 2.2 Connecting Visual KV Series Expansion Units .......................................... 1-70 2.2.1 Visual KV Series Expansion Units .................................................................... 1-70 2.2.2 Connecting Visual KV Series Expansion Units ................................................. 1-71 Connection methods .................................................................................. 1-72 Number of connectable units ..................................................................... 1-73 2.2.3 Confirming the Connection Settings of Expansion Units .................................. 1-74 Expansion unit relay list ............................................................................. 1-74 Connection information for expansion units ............................................... 1-75 Input time constant for expansion units ..................................................... 1-76 (13) Clearing the input value when disconnecting ............................................. 1-76 2.2.4 Transferring I/O Information between Expansion Units and the Basic Unit ...... 1-77 When inputting ........................................................................................... 1-77 In the case of output .................................................................................. 1-77 2.3 Inspection and Maintenance ......................................................................... 1-78 2.3.1 Inspection ......................................................................................................... 1-78 2.3.2 Maintenance .....................................................................................................1-78 Chapter 3 Access Window Visual KV 3.1 Overview of the Access Window .................................................................. 1-80 3.1.1 What is the Access Window ............................................................................. 1-80 3.1.2 Access Window Use Examples ........................................................................ 1-80 3.2 3.2.1 3.2.2 3.2.3 3.2.4 3.2.5 Basic Operating Procedures ......................................................................... 1-81 Operation Mode ................................................................................................1-81 Access Window Modes ..................................................................................... 1-81 Part Names and Functions of the Access Window ........................................... 1-82 Selecting Modes and Setting/Resetting Key Lock ............................................ 1-82 Turbo Function .................................................................................................. 1-83 3.3 Digital Trimmer Mode .................................................................................... 1-84 3.3.1 Function and Operating Procedure ................................................................... 1-84 Key operation and screen display .............................................................. 1-84 Function and operating procedure ............................................................. 1-84 3.4 Device Mode ................................................................................................... 1-87 3.4.1 Function and Operating Procedure ................................................................... 1-87 Devices that can be displayed and changed ............................................. 1-87 Key operation and screen display .............................................................. 1-87 Selecting the device and displaying the current value/set value ................ 1-88 Changing a numeric value ......................................................................... 1-89 Holding the setting ..................................................................................... 1-91 3.4.2 Screen Display for Each Device Type .............................................................. 1-91 Data memory (DM) .................................................................................... 1-91 Temporary data memory (TM) ................................................................... 1-91 Timer/counter (T/C) .................................................................................... 1-92 High-speed counter comparator (CTC) ...................................................... 1-92 Trimmer (TRM) .......................................................................................... 1-93 Relay (RLY) ...............................................................................................1-93 3.5 System Mode .................................................................................................. 1-94 3.5.1 Function and Operating Procedure ................................................................... 1-94 Key operation and screen display .............................................................. 1-94 LOAD mode and SAVE mode .................................................................... 1-96 Display in LOAD/SAVE mode .................................................................... 1-96 3.6 Message Display ............................................................................................ 1-97 3.6.1 Error Messages and Error Status ..................................................................... 1-97 3.6.2 User Messages ................................................................................................. 1-97 How to use the user messages .................................................................. 1-98 Chapter 4 KV-D20 Operator Interface Panel Visual KV 4.1 4.1.1 4.1.2 4.1.3 Before Operation .......................................................................................... 1-100 Checking Package Contents .......................................................................... 1-100 Part Names and Functions ............................................................................. 1-101 Details about the KV-D20 ............................................................................... 1-102 General specifications .............................................................................. 1-102 Functional specifications .......................................................................... 1-102 Dimensions .............................................................................................. 1-103 4.1.4 Installation and Environment .......................................................................... 1-104 Use environment ...................................................................................... 1-104 Panel mounting ........................................................................................ 1-105 4.1.5 Inspection and Maintenance ........................................................................... 1-106 Inspection ................................................................................................. 1-106 Maintenance ............................................................................................ 1-106 4.2 Overview and Operation .............................................................................. 1-107 4.2.1 Use Examples for the KV-D20 ........................................................................ 1-107 (14) 4.2.2 Connection with the KV Series ....................................................................... 1-108 Connection ...............................................................................................1-108 Precautions .............................................................................................. 1-108 4.2.3 Overview of the KV-D20 ................................................................................. 1-109 Switching the display mode ..................................................................... 1-109 Overview of each display mode ............................................................... 1-110 Assignment of relays/DM ......................................................................... 1-111 Other functions .........................................................................................1-112 Precautions about screen change function .............................................. 1-115 4.2.4 Operator Mode ................................................................................................1-117 Screen selection in operator mode .......................................................... 1-117 Operator screen ....................................................................................... 1-118 Direct access screen ................................................................................ 1-126 KV-I/O monitor screen ............................................................................. 1-127 Switch comment screen ........................................................................... 1-128 Lamp comment screen ............................................................................ 1-128 Screen change permission in operator mode .......................................... 1-129 4.2.5 Device Mode ................................................................................................... 1-130 Device mode ............................................................................................ 1-130 Operation example for device mode ........................................................ 1-132 4.2.6 System Mode .................................................................................................. 1-134 System mode ........................................................................................... 1-134 4.3 Examples of Ladder Programs ................................................................... 1-135 4.3.1 Basic Ladder Programs .................................................................................. 1-135 Before creating ladder programs ............................................................. 1-135 Basic ladder programs ............................................................................. 1-136 4.3.2 Examples of Ladder Programs ....................................................................... 1-143 Example of displaying user messages ..................................................... 1-143 Example of displaying messages with titles ............................................. 1-145 Example of position control ...................................................................... 1-146 Example of frequency counter ................................................................. 1-149 Example of 24-bit high-speed counter ..................................................... 1-152 Example of cam switch function ............................................................... 1-154 4.4 4.4.1 4.4.2 4.4.3 Chapter 5 Appendix ....................................................................................................... 1-158 Troubleshooting .............................................................................................. 1-158 Available Character List .................................................................................. 1-162 Comment Draft Sheet ..................................................................................... 1-163 KV-300, KV-10/80 Hardware KV-300, KV-10/80 5.1 System Configuration .................................................................................. 1-166 5.1.1 KV-300 ............................................................................................................1-166 5.1.2 KV-10/80 ......................................................................................................... 1-167 5.2 Module/Unit Specifications ......................................................................... 1-168 5.2.1 Wiring: KV-U4 Power Supply Module ............................................................. 1-168 Parts and functions .................................................................................. 1-168 5.2.2 Wiring: KV-U5 DC Power Distribution Module ................................................ 1-169 Parts and functions .................................................................................. 1-169 5.2.3 Wiring: KV-300 CPU ....................................................................................... 1-170 Parts and functions .................................................................................. 1-170 5.2.4 Wiring: KV-C16X/C32X Connector Input Module ........................................... 1-171 Parts and functions .................................................................................. 1-171 5.2.5 Wiring: KV-C32T/B16R/B16S Connector Output Module ............................... 1-172 Parts and functions .................................................................................. 1-172 5.2.6 Wiring: KV-R1A I/O Distribution Module ......................................................... 1-173 Parts and functions .................................................................................. 1-173 5.2.7 Wiring: KV-R8X/R16X/R8R/R16R/R8T/R16T I/O Terminal Modules ............. 1-174 Parts and functions .................................................................................. 1-174 5.2.8 Module Names and Functions ........................................................................ 1-175 5.2.9 Peripheral Equipment Names and Functions ................................................. 1-176 5.3 5.3.1 5.3.2 5.3.3 Module/Unit Connections ............................................................................ 1-178 Environmental Requirements ......................................................................... 1-178 Installation Guidelines ..................................................................................... 1-178 Assembling the System .................................................................................. 1-179 Connecting modules ................................................................................ 1-179 5.3.4 Mounting to the DIN Rail ................................................................................. 1-180 5.3.5 Removing the Terminal Block ......................................................................... 1-181 (15) 5.3.6 Connecting the AC Power Supply Module and DC Power Distribution Module .... 1-182 KV-U4 AC Power Supply Module ............................................................ 1-182 KV-U5 DC Power Distribution Module ..................................................... 1-182 5.3.7 I/O Connectors ................................................................................................ 1-183 KV-300 CPU ............................................................................................ 1-183 KV-C16X/C32X ........................................................................................ 1-184 KV-C32T/B16R/B16S .............................................................................. 1-185 KV-R8X/R16X/R8R/R16R/R8T/R16T ...................................................... 1-186 5.3.8 I/O Terminal Modules: Communication Cables and Power Distribution ......... 1-187 Transmission distance by cable type ....................................................... 1-187 Connection patterns ................................................................................. 1-187 Incorrect wiring patterns ........................................................................... 1-188 Power distribution .................................................................................... 1-188 5.3.9 Connector Assembly Instructions ................................................................... 1-189 5.3.10 KV-300 CPU I/O Indicators ............................................................................. 1-191 5.3.11 KV-10/80 Expansion Units .............................................................................. 1-192 5.3.12 Mounting Environment .................................................................................... 1-194 Chapter 6 Handheld Programmer 6.1 Using the Handheld Programmer ............................................................... 1-196 6.1.1 Outline of the Handheld Programmer ............................................................. 1-196 6.1.2 Precautions ..................................................................................................... 1-198 6.2 Basic Operations ......................................................................................... 1-200 6.2.1 Basic Programming Operation ........................................................................ 1-200 6.3 Functions ...................................................................................................... 1-216 Function Nos. list ..................................................................................... 1-216 ALL CLEAR .............................................................................................. 1-217 HANDHELD PROGRAMMER CLEAR ..................................................... 1-217 COUNTER CLEAR .................................................................................. 1-218 HIGH-SPEED COUNTER CLEAR ........................................................... 1-218 ALL DATA MEMORY CLEAR .................................................................. 1-219 ALL LATCHING RELAYS RESET ........................................................... 1-219 PROGRAM SENT OR RECEIVED .......................................................... 1-220 OFFLINE EDITOR START ...................................................................... 1-221 OFFLINE EDITOR STOP ........................................................................ 1-221 TIMER/COUNTER CURRENT VALUE CHANGE ................................... 1-222 TIMER/COUNTER SETTING CHANGE .................................................. 1-224 RELAY ON/OFF ....................................................................................... 1-226 WRITE INTO DATA MEMORY ................................................................ 1-227 READ TRIMMER SETTING ..................................................................... 1-228 SYNTAX CHECK ..................................................................................... 1-228 PROGRAM CAPACITY CHECK .............................................................. 1-229 6.4 Memory Card ................................................................................................ 1-230 6.4.1 Functions [used with KV-P3E(01)] .................................................................. 1-230 6.4.2 Storage Capacity ............................................................................................ 1-230 CLEAR ..................................................................................................... 1-232 NEW ......................................................................................................... 1-233 ACCS ....................................................................................................... 1-234 ACCS: SAVE ........................................................................................... 1-235 ACCS: LOAD ........................................................................................... 1-236 ACCS: VERIFY ........................................................................................ 1-236 ACCS: DELETE ....................................................................................... 1-237 Chapter 7 KV-L2 Serial Interface Module KV-300 7.1 Outline ......................................................................................................... 1-240 7.1.1 Features .......................................................................................................... 1-240 7.2 7.2.1 7.2.2 7.2.3 Configuration ............................................................................................... 1-241 Parts and Functions ........................................................................................ 1-241 System Configuration ..................................................................................... 1-242 Outline of Operation Modes ............................................................................ 1-244 7.3 7.3.1 7.3.2 7.3.3 Installation .................................................................................................... 1-245 Setting the Operation Mode ............................................................................ 1-245 Communications Protocols ............................................................................. 1-247 Connector Wiring ............................................................................................ 1-248 (16) 7.3.4 Connecting to External Units .......................................................................... 1-249 Connecting to An External Display .......................................................... 1-249 Connecting to an IBM PC-AT Computer .................................................. 1-249 Connecting to the KV-10/16/24/40/80 ...................................................... 1-250 Connecting KV-L2s .................................................................................. 1-250 7.4 Software Setup ............................................................................................. 1-252 7.4.1 Using KV Software [KV IncrediWare (DOS)] .................................................. 1-252 Starting KV IncrediWare (DOS) from the KV-L2 ........................................................ 1-252 7.5 KV Mode Programming ............................................................................... 1-253 7.5.1 Operating in KV Mode .................................................................................... 1-253 Communications protocol ........................................................................ 1-253 7.5.2 Serial Communications Procedure ................................................................. 1-255 Command transmission procedure .......................................................... 1-255 Command/response format ..................................................................... 1-256 Communications commands and responses ........................................... 1-256 Communications commands .................................................................... 1-257 7.5.3 Transmission and Reception of Text Data ...................................................... 1-262 Assigning relay nos. and data memory address nos. .............................. 1-262 Transmitting Text Data ............................................................................. 1-264 Receiving text data .................................................................................. 1-265 ASCII code/binary conversion function .................................................... 1-266 Example program ..................................................................................... 1-269 7.6 Display Interface Mode Programming ....................................................... 1-270 7.6.1 Operating in Display Interface Mode .............................................................. 1-270 Communications protocols ....................................................................... 1-270 Communications control procedure ......................................................... 1-271 7.6.2 Command and Response Format ................................................................... 1-273 7.6.3 Commands and Responses ........................................................................... 1-275 List of commands and responses ............................................................ 1-275 Description of commands and responses ................................................ 1-277 End codes ................................................................................................1-291 7.7 Non-procedure Mode Programming .......................................................... 1-292 7.7.1 Operating in Non-procedure Mode ................................................................. 1-292 Communications protocol ........................................................................ 1-292 Connecting to the KV-L2 .......................................................................... 1-293 7.7.2 Assignment of Relay Nos. and Data Memory Address Nos. .......................... 1-294 Assigning relay nos. and data memory address nos. .............................. 1-294 7.7.3 Transmitting Text Data ................................................................................... 1-297 Data transmission and internal data memory addresses ......................... 1-297 7.7.4 Receiving Text Data ....................................................................................... 1-298 Format of received data and data memory addresses ............................ 1-298 7.7.5 ASCII code/Binary Conversion Function ........................................................ 1-300 7.8 Troubleshooting Guide ............................................................................... 1-304 7.8.1 Troubleshooting .............................................................................................. 1-304 7.8.2 Precautions .....................................................................................................1-305 7.9 Specifications ...............................................................................................1-306 7.9.1 Specifications .................................................................................................. 1-306 General specifications .............................................................................. 1-306 Communications protocol ........................................................................ 1-306 RS-232C connector specifications ........................................................... 1-306 RS-422A terminal block specifications ..................................................... 1-306 7.9.2 Dimensions .....................................................................................................1-307 7.10 Command List .............................................................................................. 1-308 7.10.1 List of Commands and Responses ................................................................. 1-308 7.10.2 List of Commands and Responses in Display Interface mode ....................... 1-309 Chapter 8 KV-AN6 Analog I/O Module 8.1 KV-300 Outline ......................................................................................................... 1-312 Features ................................................................................................... 1-312 8.2 Configuration ...............................................................................................1-313 8.2.1 Parts and Functions ........................................................................................ 1-313 8.2.2 System Configuration ..................................................................................... 1-314 8.3 Installation .................................................................................................... 1-315 8.3.1 Terminal Nos. ................................................................................................. 1-315 (17) 8.3.2 8.3.3 8.3.4 8.3.5 Removing the Terminal Block ......................................................................... 1-316 Example of Voltage I/O Wiring ........................................................................ 1-317 Example of Current I/O Wiring ........................................................................ 1-318 Setting I/O Ranges ......................................................................................... 1-319 8.4 8.4.1 8.4.2 8.4.3 8.4.4 8.4.5 8.4.6 8.4.7 8.4.8 8.4.9 Programming ................................................................................................ 1-320 Input Characteristics (A/D) .............................................................................. 1-320 Calculating Input Data (A/D) ........................................................................... 1-321 Output Characteristics (D/A) ........................................................................... 1-322 Calculating Output Data (D/A) ........................................................................ 1-323 Assigning Data Memory (DM) Addresses ....................................................... 1-324 Reading Analog Input ..................................................................................... 1-325 Measuring Analog Input Average ................................................................... 1-326 Writing Analog Output ..................................................................................... 1-327 Converting Analog Input to Analog Output ..................................................... 1-328 8.5 8.5.1 8.5.2 8.5.3 KV-AN6 Appendices .................................................................................... 1-329 Troubleshooting .............................................................................................. 1-329 Precautions ..................................................................................................... 1-330 Specifications .................................................................................................. 1-331 Environmental specifications ................................................................... 1-331 System specifications .............................................................................. 1-331 8.5.4 Dimensions ..................................................................................................... 1-332 Chapter 9 KV-AD4/DA4 Analog I/O Unit 9.1 KV-10/80 Outline ......................................................................................................... 1-334 Features ................................................................................................... 1-334 9.2 Configuration ............................................................................................... 1-335 9.2.1 Part Names and Functions ............................................................................. 1-335 KV-AD4 .................................................................................................... 1-335 KV-DA4 .................................................................................................... 1-336 9.2.2 Specifications .................................................................................................. 1-337 KV-AD4 .................................................................................................... 1-337 KV-DA4 .................................................................................................... 1-339 9.2.3 System Configuration ..................................................................................... 1-341 9.3 9.3.1 9.3.2 9.3.3 Installation .................................................................................................... 1-342 Installation Procedure ..................................................................................... 1-342 Checking the Installation Environment ........................................................... 1-343 Setting the KV-AD4 Input Mode ...................................................................... 1-344 Setting the input mode ............................................................................. 1-344 9.3.4 Connecting External Instruments .................................................................... 1-345 Wiring ....................................................................................................... 1-345 Wiring diagrams ....................................................................................... 1-346 9.3.5 Connecting to the KV-10 to 80 ........................................................................ 1-348 9.3.6 Maintenance ................................................................................................... 1-349 Inspection and Cleaning .......................................................................... 1-349 9.4 Programming ................................................................................................ 1-350 9.4.1 Programming the KV-AD4 .............................................................................. 1-350 A/D Conversion Mechanism .................................................................... 1-350 About Digital Data after A/D Conversion .................................................. 1-351 Calculating Voltage and Current Values from Digital Data ...................... 1-352 9.4.2 Programming the KV-DA4 .............................................................................. 1-353 D/A Conversion Mechanism .................................................................... 1-353 Converting Digital Data to Voltage or Current Values to be Output ......... 1-354 Writing Digital Data to Data Memory for D/A Conversion ........................ 1-356 9.4.3 A/D and D/A Conversion Tables ..................................................................... 1-357 Voltage Conversion Table ........................................................................ 1-357 Current Conversion Table ........................................................................ 1-358 9.5 Programming Examples .............................................................................. 1-359 Calculating Analog Data Values from Digital Data ................................... 1-359 Writing Data to be Analog-output ............................................................. 1-361 Outputting Analog Trimmer Values .......................................................... 1-364 Outputting Analog Input Data ................................................................... 1-365 Outputting Analog Input from a Pressure Sensor to an Air Valve ............ 1-366 Setting the Minimum and Maximum Voltage Limits and Measuring the Average Voltage ...................................................................................... 1-367 9.6 Troubleshooting ........................................................................................... 1-370 (18) Chapter 10 Troubleshooting 10.1 10.1.1 10.1.2 10.1.3 10.1.4 Error List ....................................................................................................... 1-372 List of Error Codes in Basic Units ................................................................... 1-372 Error indication in Expansion Units ................................................................. 1-374 Program Errors ...............................................................................................1-375 Memory Card Errors and Other Errors ........................................................... 1-376 10.2 Replacing Relays .........................................................................................1-377 Replacement procedure ........................................................................... 1-377 10.3 Troubleshooting ........................................................................................... 1-378 10.3.1 Troubleshooting List ....................................................................................... 1-378 10.4 Error Messages ............................................................................................ 1-380 Appendices Appendix A. Specifications and Dimensions [Visual KV Series] .................... 1-382 A.1 System Specifications [Visual KV Series] ....................................................... 1-382 Hardware ................................................................................................. 1-382 Software and Programming ..................................................................... 1-383 AC power supply unit ............................................................................... 1-384 A.2 Common I/O Specifications of Basic Units ..................................................... 1-384 Input specifications .................................................................................. 1-384 Output specifications (relay output): KV-10AR/DR, KV-16AR/DR, KV-24AR/DR, and KV-40AR/DR .............................................................. 1-385 Output specifications (transistor output): KV-10AT(P)/DT(P), KV-16AT(P)/DT(P), KV-24AT(P)/DT(P), and KV-40AT(P)/DT(P) ............ 1-385 A.3 Expansion Unit Specifications ........................................................................ 1-385 A.4 Dimensions .....................................................................................................1-389 Appendix B. Specifications and Dimensions [KV-300 Series] ......................... 1-392 B.1 System Specifications [KV-300 Series] .......................................................... 1-392 Hardware ................................................................................................. 1-392 Software and Programming ..................................................................... 1-393 AC Power supply module/DC power distribution module ........................ 1-394 B.2 Module Specifications ..................................................................................... 1-398 KV-300 CPU ............................................................................................ 1-398 KV-C16X/C32X Input Modules ................................................................ 1-399 KV-C32T/B16R/B16S Output Modules ................................................... 1-400 KV-R8X/R16X I/O Terminal Modules ....................................................... 1-401 KV-R8T/R16T/R8R/R16R I/O Terminal Modules ..................................... 1-402 KV-R8T/R16T/R8R/R16R I/O Terminal Modules (RUN Output) .............. 1-403 KV-R1A I/O Distribution Module .............................................................. 1-403 B.3 Dimensions .....................................................................................................1-404 Appendix C. Ladder Program List ...................................................................... 1-406 Appendix D. A/D and D/A Conversion Tables [KV-AN6] ..................................... 1-408 Voltage conversion table .......................................................................... 1-408 Current conversion table .......................................................................... 1-409 WARRANTIES AND DISCLAIMERS 2 1-419 Support software Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Items Included in the Package ........................................................................ 2-2 1.2 Outline of the Ladder Builder for KV .............................................................. 2-3 1.2.1 Operating environment and system configuration .............................................. 2-3 1.2.2 Features and functions of the Ladder Builder for KV .......................................... 2-4 Features of the Ladder Builder for KV ......................................................... 2-4 Functions of the Ladder Builder for KV ........................................................ 2-6 1.3 Before Programming ....................................................................................... 2-7 Machines to be prepared ............................................................................. 2-7 1.3.1 Differences from the KV IncrediWare (DOS) ...................................................... 2-8 1.3.2 Differences from the Ladder Builder for KV Ver 1.0 ........................................... 2-8 1.4 (19) Installing the Software ..................................................................................... 2-9 1.4.1 Preparation for installation .................................................................................. 2-9 1.4.2 Installation Procedure ....................................................................................... 2-10 Installation in Windows 95 ......................................................................... 2-10 Installation in Windows 3.1 ........................................................................ 2-12 Chapter 2 1.5 Cautions for Use ............................................................................................ 2-13 1.6 1.6.1 1.6.2 1.6.3 1.6.4 1.6.5 Basic Operations ........................................................................................... 2-14 Program creation flow and available modes ..................................................... 2-14 Starting up and exiting from the software ......................................................... 2-16 Screen .............................................................................................................. 2-18 Mouse operation and keyboard operation ........................................................ 2-21 Online Help ....................................................................................................... 2-23 Editor KV-300 2.1 Outline of the Editor Functions .................................................................... 2-26 2.1.1 Cautions for editing ladder programs ................................................................ 2-26 2.2 Edit Screen .....................................................................................................2-27 2.2.1 Name and function of each part of the screen .................................................. 2-27 2.2.2 Ladder program window screen ....................................................................... 2-28 2.3 2.3.1 2.3.2 2.3.3 2.3.4 2.3.5 2.3.6 2.3.7 File Management ............................................................................................ 2-29 Creating a new file ............................................................................................ 2-29 Setting the automatic file read function ............................................................. 2-30 Setting automatic file save for the file ............................................................... 2-31 Saving and reading files ................................................................................... 2-32 Reading and saving a file in another format ..................................................... 2-33 Saving a ladder diagram in text format ............................................................. 2-36 Verifying files .................................................................................................... 2-36 2.4 2.4.1 2.4.2 2.4.3 2.4.4 2.4.5 2.4.6 Entering/Deleting Symbols and Connection Lines .................................... 2-37 Entering symbols .............................................................................................. 2-37 Deleting symbols .............................................................................................. 2-42 Entering contacts/coils directly ......................................................................... 2-42 Changing the device at the current cursor position .......................................... 2-43 Entering/Deleting connection lines ................................................................... 2-44 Canceling edit operations ................................................................................. 2-45 2.5 2.5.1 2.5.2 2.5.3 Entering Comments/Labels ......................................................................... 2-46 Editing comments/labels ................................................................................... 2-46 Editing line comments ....................................................................................... 2-50 Changing ladder lines into comments ............................................................... 2-51 2.6 Edit and Arrangement .................................................................................. 2-52 2.6.1 Copy, move, and delete .................................................................................... 2-52 2.6.2 Inserting and deleting lines ............................................................................... 2-57 2.7 2.7.1 2.7.2 2.7.3 2.7.4 2.7.5 Jump, Search, and Replace ......................................................................... 2-58 Jump .................................................................................................................2-58 Searching for instruction words/operands ........................................................ 2-62 Searching for the device at the cursor position ................................................. 2-63 Replacing operands .......................................................................................... 2-64 Converting a/b contacts .................................................................................... 2-65 2.8 Editing the Mnemonic List ........................................................................... 2-67 2.8.1 Displaying and terminating a mnemonic list ..................................................... 2-67 2.8.2 Copy, move, and delete .................................................................................... 2-69 2.9 Displaying the Use Status ............................................................................. 2-70 2.9.1 Displaying a use status list ............................................................................... 2-70 2.10 Setting the System .........................................................................................2-71 2.10.1 Setting the system ............................................................................................ 2-71 2.11 Entering and Developing Macros ................................................................ 2-72 2.11.1 Creating a macro file .........................................................................................2-72 2.11.2 Entering and developing macros ...................................................................... 2-74 2.12 2.12.1 2.12.2 2.12.3 Compilation .................................................................................................... 2-75 Executing compilation ....................................................................................... 2-75 Error display ......................................................................................................2-76 Double coil check .............................................................................................. 2-76 2.13 Printing Functions .........................................................................................2-77 (20) 2.13.1 Printing .............................................................................................................. 2-77 2.13.2 Preview display ................................................................................................. 2-81 2.14 Changing the Display Color on the Screen ................................................. 2-82 2.14.1 Changing display colors on the screen ............................................................. 2-82 Chapter 3 Simulator 3.1 Outline of the Simulator Functions .............................................................. 2-84 3.1.1 Outline of the functions ..................................................................................... 2-84 3.1.2 Restrictions in the simulator .............................................................................. 2-84 3.2 Starting up and Exiting from the Simulator ................................................. 2-86 3.2.1 Operating procedure for startup and exit .......................................................... 2-86 3.2.2 Name and function of each part of the screen .................................................. 2-88 Chapter 4 3.3 3.3.1 3.3.2 3.3.3 3.3.4 3.3.5 Ladder Monitor ............................................................................................... 2-89 Outline of the ladder monitor ............................................................................ 2-89 Executing scans ................................................................................................ 2-89 Executing steps .............................................................................................. 2-101 Jump and search ............................................................................................ 2-105 Stop/reset and device all clear ........................................................................ 2-108 3.4 3.4.1 3.4.2 3.4.3 3.4.4 3.4.5 Monitor All .................................................................................................... 2-109 Outline of monitor all ....................................................................................... 2-109 Displaying, saving, and reading the monitor all window ................................. 2-109 Monitor all window .......................................................................................... 2-113 Registering devices ........................................................................................ 2-113 Selecting and changing devices ..................................................................... 2-116 3.5 3.5.1 3.5.2 3.5.3 3.5.4 3.5.5 3.5.6 3.5.7 Registration Monitor .................................................................................... 2-119 Outline of the registration monitor ................................................................... 2-119 Displaying, saving, and reading the registration monitor ................................ 2-119 Registration monitor window ........................................................................... 2-122 Registering devices ........................................................................................ 2-122 Selecting and changing devices ..................................................................... 2-123 Manipulating timing charts .............................................................................. 2-128 Printing out the registration monitor ................................................................ 2-131 Monitor 4.1 4.1.1 4.1.2 4.1.3 Outline of the Monitor Functions ............................................................... 2-134 Outline of the functions ................................................................................... 2-134 Restrictions in the monitor .............................................................................. 2-134 Precautions for communication ...................................................................... 2-135 4.2 Communicating with the PLC ..................................................................... 2-136 4.2.1 Setting the PLC communication parameters .................................................. 2-136 4.2.2 Setting the comment transfer .......................................................................... 2-138 4.3 Starting up and Exiting from the Monitor .................................................. 2-139 4.3.1 Operating procedures for startup and exit ...................................................... 2-139 4.3.2 Name and function of each part of the screen ................................................ 2-143 4.4 4.4.1 4.4.2 4.4.3 4.4.4 4.4.5 4.4.6 4.4.7 Ladder Monitor ............................................................................................. 2-144 Outline of the ladder monitor .......................................................................... 2-144 Displaying the ladder monitor window ............................................................ 2-144 PLC error check .............................................................................................. 2-144 Starting the monitor ........................................................................................ 2-145 Stopping the monitor ....................................................................................... 2-145 Screen displayed while the monitor is running ............................................... 2-146 Setting the PLC operation mode ..................................................................... 2-147 4.5 Monitor All and Registration Monitor ......................................................... 2-148 4.5.1 Functions of the monitor all window ................................................................ 2-148 4.5.2 Functions of the registration monitor .............................................................. 2-148 4.6 4.6.1 4.6.2 4.6.3 (21) Monitor Function .......................................................................................... 2-149 Disabling the input refresh/Disabling the output ............................................. 2-149 Changing the current values all at once ......................................................... 2-150 Device all clear ...............................................................................................2-154 Appendices Appendix A Error Message List ......................................................................... 2-156 A-1 System errors ................................................................................................. 2-156 A-2 Memory errors ................................................................................................ 2-156 A-3 File errors ........................................................................................................ 2-157 A-4 Installation errors ............................................................................................ 2-157 A-5 Errors that occur in the editor ......................................................................... 2-158 A-6 Errors that occur in the monitor/simulator ....................................................... 2-159 A-7 Communication errors (displayed in the monitor) ........................................... 2-159 A-8 PLC errors ...................................................................................................... 2-160 A-9 Errors that occur during compilation ............................................................... 2-161 Appendix B Instruction List ............................................................................... 2-163 B-1 Basic instructions ............................................................................................ 2-163 B-2 Application instructions ................................................................................... 2-164 B-3 Arithmetic instructions ..................................................................................... 2-165 B-4 Interrupt instructions ....................................................................................... 2-166 Appendix C Relay No. List .................................................................................. 2-167 C-1 Relays, timers, counters, and memory numbers for each model ................... 2-167 Appendix D Special Utility Relay List ................................................................ 2-168 D-1 Special relays and arithmetic operation flags ................................................. 2-168 D-2 Special utility relays for high-speed counter (0) .............................................. 2-168 D-3 Special utility relays for high-speed counter (1) .............................................. 2-169 D-4 Other special utility relays ............................................................................... 2-169 D-5 Memory switches ............................................................................................ 2-172 D-6 Special memory list ......................................................................................... 2-172 Appendix E Devices for KV-10R(W)/T(W) to 80R(W)/T(W), KV-300 ................ 2-174 E-1 Special utility relays ........................................................................................ 2-174 E-2 Memory switches ............................................................................................ 2-176 E-3 Special memory list ......................................................................................... 2-176 Appendix F Sample Program List ..................................................................... 2-178 F-1 Description of sample ladder programs .......................................................... 2-178 Appendix G Quick Reference ............................................................................. 2-180 G-1 Editor .............................................................................................................. 2-180 G-2 Simulator ......................................................................................................... 2-188 G-3 Monitor ............................................................................................................ 2-195 Appendix H Notes for Programming ................................................................. 2-201 H-1 Circuits that must be modified ........................................................................ 2-201 H-2 Precautions for programming ......................................................................... 2-202 H-3 Programs which cannot be decompiled .......................................................... 2-203 Appendix I List of Files Used ............................................................................ 2-204 Appendix J Countermeasures for Frequent Communication Errors ............ 2-205 WARRANTIES AND DISCLAIMERS 2-215 (22) WARRANTIES AND DISCLAIMERS See 3-367. Caution • No part of this manual may be reprinted or reproduced in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of KEYENCE CORPORATION. • The content of this manual is subject to change without notice. • KEYENCE has thoroughly checked and reviewed this manual. Please contact the sales office listed at the end of this manual if you have any questions or comments regarding this manual or if you find an error. • KEYENCE assumes no liability for damages resulting from the use of the information in this manual, item 3 above notwithstanding. • KEYENCE will replace any incomplete or incorrectly collated manual. All company names and product names in this manual are registered trademarks or trademarks of their respective owners. (23) Chapter 1 Programming This chapter describes basic knowledge including program creation procedures, device configuration, relay assignments, special functions to set and confirm Visual KV Series operations, as well as the extended ladder diagrams. Understand the contents described here completely at first before creating programs. ➮ For a detailed description of instructions, refer to "2.4. Instruction Details" (p.3-56). 1.1 Before Creating Programs .......................................................... 3-2 1.1.1 1.1.2 Flow from Introduction to Operation ........................................................... 3-2 Scan Time .................................................................................................. 3-3 1.2 User Memory ................................................................................ 3-4 1.2.1 Program Capacity ...................................................................................... 3-4 1.3 Device Configuration ................................................................... 3-5 1.3.1 1.3.2 1.3.3 1.3.4 1.3.5 1.3.6 1.3.7 1.3.8 1.3.9 1.3.10 1.3.11 1.3.12 Device List .................................................................................................. 3-5 Relay No. ................................................................................................... 3-7 Assigning Relay Nos. ................................................................................. 3-8 Input Relays ............................................................................................... 3-9 Output Relays .......................................................................................... 3-10 Internal Utility Relays ............................................................................... 3-11 Special Utility Relays ................................................................................ 3-12 Special Utility Relay List ........................................................................... 3-14 Timers and Counters ................................................................................ 3-18 Data Memories ......................................................................................... 3-19 Temporary Data Memory ......................................................................... 3-21 Relay Nos. and Functions ........................................................................ 3-22 1.4 Special Functions ...................................................................... 3-23 1.4.1 1.4.2 1.4.3 1.4.4 1.4.5 1.4.6 1.4.7 Input Time Constant Change Function .................................................... Modifying the Input Relay Time Constant ................................................ Constant Scan Time Mode ....................................................................... Output Disabled Function ......................................................................... Input Refresh Disabled Function .............................................................. Contact Comment Save Function ............................................................ Special Functions ..................................................................................... 1.5 Extended Ladder Diagrams ...................................................... 3-29 1.5.1 1.5.2 1.5.3 Features of Extended Ladder Diagrams .................................................. 3-29 Advantages of Extended Ladder Diagrams ............................................. 3-30 Example of an Extended Ladder Diagram ............................................... 3-31 3-23 3-24 3-25 3-26 3-26 3-27 3-28 1.1 Before Creating Programs 1.1 Before Creating Programs This section describes what you should know before creating programs and operations for the Visual KV Series. 1.1.1 Flow from Introduction to Operation This section describes an overview of program creation procedures, functions used, and setting items. In the example described below, a latch circuit is created as a program for the Visual KV Series. Introduction ➞ Examining contents of operations Figure 1 shows a latch circuit which operates as follows. Pushbutton switch PB1: ON ➞Pilot lamp (PL) turns on. Pushbutton switch PB2: OFF Fig. 1 PB1 = N.O. contact switch PB2 = N.C. contact switch PB1 PB2 ▲ Pushbutton switch PB1: OFF ➞Pilot lamp (PL) remains lit even if PB1 turns Pushbutton switch PB2: OFF OFF. Pushbutton switch PB1: OFF ➞Pilot lamp (PL) goes out Pushbutton switch PB2: ON when PB2 is set to ON. ▲ 1 RL (Relay) Time chart PB1 contact PB2 contact PL ON OFF ON OFF ON PL OFF Next, a program is created that will use the same operation as this circuit to control a PLC. ➞ Program examination Circuit 1 shows relay symbols for the latch circuit. Examine which contact in the Visual KV Series is used for each pushbutton switch and pilot lamp (Table 1). When many I/O devices are required for control, expansion units should also be considered. Table 1 Circuit 1 RL PB1 PB2 RL Relay (coil) Relay (contact) RL Relay (contact) PL Pilot lamp I/O device Pushbutton switch PB1 (N.O. contact) Pushbutton switch PB2 (N.C. contact) Relay RL Pilot lamp PL Contact No. Input relay (0000) Input relay (0001) Internal relay (1000) Output coil (0500) ➞ Program creation Edit a program using the "LADDER BUILDER for KV" programming support software creation tool. Ladder diagram 0000 0001* 1000 1000 1000 0500 Coding list LD 0000 OR 1000 AND 0001 OUT 1000 LD 1000 OUT 0500 END * Enter "N.O. (AND X001)" to 0001 to use N.C. contact. ➞ Transferring and confirming the program Transfer the created program to the Visual KV Series, perform a test run, and then confirm operations with the actual devices. ➞ Operation 3-2 Chapter 1 Programming 1.1 Before Creating Programs 1.1.2 Scan Time Scan time The Visual KV Series repeatedly executes a ladder based on the sequence circuit as follows. Writes the ON/OFF status of all input terminals to the input memory before executing the program. Input processing Program execution Output processing Reads the ON/OFF status of each device (internal utility relay, timer, counter, etc.) based on the instructions, and performs arithmetic operations. Writes the arithmetic operation result to the output memory. Outputs the contents of the output memory to output terminals. The duration of time required to perform one cycle is called the scan time (or cycle time). The scan time varies based on program size and the instructions used in the program. Input response time delay In addition to the I/O processing time, there is also an input time delay in the Visual KV Series caused by the scan time. The input time delay is generated because the input status can only be read during the input processing time. If the input status is changed after input processing, the changed contents can only be read during the next scan time. In the figure below, 1 and 2 can be read but 3 cannot be read. 1 Input signal 2 3 ON OFF Scan time Input processing Program execution Output processing Input processing Program execution Output processing Program execution Input processing Read Output processing Input processing Program execution Output processing Input processing Output processing Read Scan time Reference: The maximum and minimum values of the input response time are as follows. Maximum value: Input time constant + Scan time x 2 + Output response delay time Minimum value: Input time constant + Scan time + Output response delay time Note 1: When the input time constant is made small by setting the HSP instruction, special utility relay 2813, and data memory DM1940, a signal may not be received if its ON time is shorter than the scan time. Note 2: The INT instruction is independent of the scan time. Note 3: The minimum scan time is 140 µs (with the basic unit). Chapter 1 Programming 3-3 11 1.2 User Memory 1.2 User Memory This section describes the allowable size (capacity) of a program which can be created in the Visual KV Series. 1.2.1 Program Capacity When a user program is created for the Visual KV Series, the maximum number of steps a program can contain using the mnemonic diagram varies based on the byte count of the instructions used. The instruction byte count is determined individually for each instruction. ➮ For more about byte counts for each instruction, refer to "2.1 Instruction List" (p.3-34). Maximum number of lines in a program In the KV-10xx/16xx, a program with approximately 2,000 steps can be written. In the KV-24xx/40xx, a program with approximately 4,000 steps can be written. 1 • Total byte count of the memory used by instructions ≤ 6,000 bytes / 12,000 bytes • Total byte count of the memory used by objects of instructions ≤ 12,000 bytes / 24,000 bytes * In the description above, a value on the left side indicates the byte count for the KV-10xx/16xx, while a value on the right side indicates the byte count for the KV-24xx/40xx. * The memory occupied by objects indicates the memory required to execute a program when operation is started. For example, the allowable number of steps to be written can be calculated from the memory occupied by the instructions as follows. 12,000 bytes / 3 bytes (average byte count of an instruction) = 4,000 steps Note: If either the memory occupied by the instructions or the memory occupied by objects of a program exceeds the specified memory capacity, the program cannot be written or executed. Calculating the byte count used The byte count used in this program can be calculated as shown in the table below. #00020 T000 0000 0500 T000 0500 Line No. Instruction Operand Byte count 00000 LD 0000 3 5 00001 OR 0500 3 4 00002 TMR 000#00020 2 7 00003 ANB T000 3 8 OUT 0500 00004 Total 3-4 Chapter 1 Programming Number of objects 3 8 14 bytes 32 bytes 1.3 Device Configuration 1.3 Device Configuration "Device" is a general name for relays, registers, etc. processed by instructions. This section describes the available devices in the Visual KV Series and their general use. 1.3.1 Device List Relay list Relay No. Normal use High-speed use (1) High-speed use (2) They function as B phase of high-speed counters through specification of utility relays in KV-10. – 0000 0001 0002 Input relays (Direct input allowed area) Interrupt inputs INT0 to INT3 Remarks (Polarity inversion allowed) Input captures 0003 – High-speed counter 0 input High-speed counter 1 input 0004 0005 0006 Input relays 0007 – 0008 0009 0010 to 0415 0502 – A phase input – – B phase input Output relays (Direct output allowed area) 11 – – Preset input – Input relays 0500 0501 High-speed counter 0 High-speed counter 1 High-speed counter 0 High-speed counter 1 High-speed counter 0 High-speed counter 1 – High-speed counter 0 output High-speed Specified frequency counter 1 pulse output output Ramp-up/down control output 0503 70 points – – – – 0504 to 0915 Output relays 76 points 1000 to 1915 Internal utility relays 160 points 2000 to 2815 Special utility relays 144 points 2900 to 2915 Special utility relays HKEY information storage area 3000 to 17915 Internal utility relays 2,144 points Note 1: The ON/OFF status of the set functions is always cleared when the operation mode is changed from PROGRAM to RUN. However, special utility relays 2700 to 2715 are held even when the operation mode is changed from PROGRAM to RUN or when the power is turned off. Note 2: Internal utility relays can be held by setting the MEMSW instruction List of I/O relays in basic units Model KV-10xx KV-16xx KV-24xx KV-40xx Basic input relays 0000 to 0005 0000 to 0009 0000 to 0015 0000 to 0107 Basic output relays 0500 to 0503 0500 to 0505 0500 to 0507 0500 to 0515 Chapter 1 Programming 3-5 1.3 Device Configuration List of relays in expansion units ■ Input units Connection order 1st input module 2nd input module 3rd input module 4th input module KV-E4X KV-E8X KV-40 KV-10/16/24 KV-10/16/24 KV-E16X KV-40 KV-40 KV-10/16/24 100 to 103 200 to 203 100 to 107 200 to 207 100 to 115 200 to 215 200 to 203 300 to 303 200 to 207 300 to 307 200 to 215 300 to 315 300 to 303 400 to 403 300 to 307 400 to 407 300 to 315 400 to 415 400 to 403 400 to 407 400 to 415 ■ Output units Connection order 1st output module 2nd output module 3rd output module 4th output module 1 KV-E4T(P)/R KV-E8T(P)/R KV-E16T(P)/R 600 to 603 600 to 607 600 to 615 700 to 703 700 to 707 700 to 715 800 to 803 800 to 807 800 to 815 900 to 903 900 to 907 900 to 915 ■ I/O units KV-E4XR/T(P) Connection order 1st input module 2nd input module 3rd input module 4th input module 1st output module 2nd output module 3rd output module 4th output module * * 3-6 Input relays Output relays KV-10/16/24 KV-40 100 to 103 200 to 203 200 to 203 300 to 303 300 to 303 400 to 403 KV-10/16/24 KV-40 603 to 606 603 to 606 703 to 703 703 to 703 803 to 803 803 to 803 903 to 903 903 to 903 400 to 403 Relay Nos. of expansion units are automatically assigned in the order of connection. The connection order is counted only for input and output units. When I/O units are connected, they are counted as input units and output units separately. Chapter 1 Programming 1.3 Device Configuration 1.3.2 Relay No. The relay No. configuration is shown below. Channel No. 12515 Contact No. (00 to 15) Address No. (Input: 0 to 4, output: 5 to 9) Address No. Address Nos. are assigned to basic units, input expansion units, output expansion units, and I/O expansion units. Zero to 4 are assigned to input units, while 5 to 9 are assigned to output units. Address Nos. assigned in a unit vary based on the number of I/O terminals and the connection position of the unit. Model Basic units Input expansion units Output expansion units I/O expansion units Address Nos. KV-10xx 0, 5 KV-16xx 0, 5 KV-24xx 0, 5 KV-40xx 0, 1, 5 kV-E4X 1 to 4* KV-E8X 1 to 4* KV-E16X 1 to 4* KV-E4R/E4T(P) 6 to 9 KV-E8R/E8T(P) 6 to 9 KV-E16R/E16T(P) 6 to 9 KV-E4XR/E4XT(P) 1 to 4*, 6 to 9 11 * 2 to 4 in KV-40xx ■ Address No. assignment procedure • The address No. is represented as a number 0 to 9. • Address Nos. 0 to 4 are provided for inputs, while address Nos. 5 to 9 are provided for outputs. Chapter 1 Programming 3-7 1.3 Device Configuration Contact No. • Contact Nos. are input/output terminal Nos. of basic units, input expansion units, output expansion units, and I/O expansion units. • The contact No. is represented as a number 0 to 15. Example In the KV-E4X, with 4 input terminals, the contact Nos. are 0 to 3. In the KVE16T(P), with 16 input terminals, the contact Nos. are 0 to 15. • In a unit with 16 or more terminals, the contact No. of the 17th terminal returns to 0 and its address No. is increased by 1. Example In the KV-40AR, with 40 terminals (24 input and 16 output terminals), address No. 0 is assigned to input terminal Nos. 1 to 16 and address No. 1 is assigned to input terminal Nos. 17 to 24 Channel No. The channel No. is the higher order digit in the contact No. 1 1.3.3 Assigning Relay Nos. When assigning relay Nos., the unit No. is based on the connection position of the unit, and the address No. is determined based on the unit type and I/O contacts. a) KV-16AR Basic unit Input: 10 points Output: 6 points b) KV-E4X Input expansion unit Input: 4 points c) KV-E8R Output expansion unit Output: 8 points With the connections above, the relay Nos. for each unit are assigned as shown in the table below. 3-8 Unit Assigned relay Nos. a) KV-16AR 0000 to 0009 (input) and 0500 to 0505 (output) b) KV-E4X 0100 to 0103 (input) c) KV-E8R 01600 to 0607 (output) Chapter 1 Programming 1.3 Device Configuration 1.3.4 Input Relays Input relays receive ON/OFF signals sent from external input equipment. Note 1: Input relays function as contacts in programs. They cannot be used as relay coils (outputs). Note 2: There is no restriction of the contact type (N.O. or N.C.) used, the order the relay Nos. are used, or the number of relays used. Basic unit ■ Input relay time constant Though the time constant is usually 10 ms ±20%, it can be changed using the following settings. • When the HSP instruction is used: 10 µs ±20% • While special utility relay 2813 remains ON, the time constant can be changed in 7 steps by setting data memory DM1940 as follows. When DM1940 is set to 0: 10µs ±20% 1: 20 µs ±20% 2: 500 µs ±20% 3: 1 ms ±20% 4: 2.5 ms ±20% 5: 5 ms ±20% 6: 10 ms ±20% Never set a numeric value of 7 or larger. ➮ 11 For more about changing the input time constant, refer to "1.4.1 Input Time Constant Change Function" (p.3-23). ■ Hardware input (independent of scan time) • High-speed counter When the time constant is set to 10 µs using the HSP instruction or data memory DM1940 (only while special utility relay 2813 remains ON), the maximum input response of input relays 0004 and 0005 of CTH0 and CTH1 becomes 30 kHz. • INT instruction: 0000 to 0003 This instruction can receive any signal without regard to the scan time as far as the signal ON time is longer than the input time constant. ➮ "HSP instruction" (p.3-86), "INT instruction" (p.3-192), "4.1 High-speed Counter Instructions" (p.3-204) Note 1: While special utility relay 2813 remains ON, the input time constant can be specified for all input relays in a basic unit. Note 2: Never enter a number of 7 or larger to data memory DM1940. Note 3: The input time constant specified by data memory DM1940 becomes effective at the rising edge of special utility relay 2813. To change the input time constant, first change data memory DM1940, then set special utility relay 2813 to OFF and ON again. Or change the operation mode of a KV basic unit from PROGRAM to RUN. Note 4: If the HSP instruction and special utility relay 2813 are used at the same time, priority is given to the HSP instruction. Note 5: Only when a high-speed counter input or INT instruction is given, available input signals do not depend on the scan time. Chapter 1 Programming 3-9 1.3 Device Configuration Expansion unit ■ Input relay time constant By setting special utility relays 2609 to 2612 to ON, the time constant in input expansion units can be set to 10 µs. Special utility relay No. 2609* 2610 2611 2612 * Function Input time constant of input expansion unit with relay Nos. 0100 to 0115 Input time constant of input expansion unit with relay Nos. 0200 to 0215 Input time constant of input expansion unit with relay Nos. 0300 to 0315 Input time constant of input expansion unit with relay Nos. 0400 to 0415 OFF: 10 ms, ON: 10 µs OFF: 10 ms, ON: 10 µs OFF: 10 ms, ON: 10 µs OFF: 10 ms, ON: 10 µs Not available with the KV-40xx 1.3.5 Output Relays Output relays output the program execution results to the outside. There are two types of outputs, relay and transistor. 1 Note 1: Output relays function as contacts and relay coils in programs. Note 2: There is no restriction of the contact type (N.O. or N.C.) used, the order the relay Nos. are used, or the number of relays used. Output operation time • Transistor output OFF ➞ ON: 50 µs or less (10 µs or less in 500 to 502) ON ➞ OFF: 250 µs or less (10 µs or less in 500 to 502, 100 µs or less for other outputs in the basic unit) • Relay output OFF ➞ ON: 10 ms or less ON ➞ OFF: 10 ms or less Transistor output type KV-10AT(P)/DT(P) KV-16AT(P)/DT(P) Relay output type KV-10AR/DR KV-16AR/DR KV-24AT(P)/DT(P) KV-40AT(P)/DT(P) KV-24AR/DR KV-40AR/DR KV-E4T KV-E8T(P) KV-E4R KV-E8R KV-E16T(P) KV-E4XT(P) KV-E16R KV-E4XR Note 1: When programming direct clock pulses, output relays 0500 and 0501 are used to output pulses in a transistor-type output unit. Note 2: When the ramp-up/down control function is used, output relay 0502 outputs positioning pulses in a transistor-type output unit. ➮ "Chapter 5. Positioning Control" (p.3-253) Note 3: When the specified frequency pulse output function is used, output relay 0501 outputs pulses in a transistor-type output unit. ➮ "4.5.1 Specified Frequency Pulse Output Function" (p.3-228) 3-10 Chapter 1 Programming 1.3 Device Configuration 1.3.6 Internal Utility Relays In a relay circuit, when one relay contact is used twice or more inside the circuit, a multi-pole relay with the same number of poles as the number used may be needed. Internal utility relays function only in programs, and eliminate the complexity of relay circuits to facilitate circuit design. Note 1: Internal utility relays function as contacts and relay coils in programs. Note 2: There is no restriction of the contact type (N.O. or N.C.) used, the order the relay Nos. are used, or the number of relays used. Retentive function of internal utility relays Except for internal utility relays, all relays turn OFF when the operation mode is changed or when operation is stopped via a power shutdown. When operation is restarted, all relays remain OFF except relays whose input condition is ON. However, internal utility relays can be set using the MEMSW (memory switch) whether or not they are to be retained. (Internal utility relays 2700 to 2715, however, are always retained.) When an internal utility relay is set to be retained, its ON/OFF status is stored even if the power is turned off. By using the retained relay all clear function (FUN65), all relays which are set to be retained can be set to OFF. ➮ For more about setting the memory switch, refer to "MEMSW instruction" (p.3-92). Application example of a retentive function: Lift vertical movement control Internal utility relays 1000 and 1001 are set to be retained. When the upper/lower limit switch turns ON, the direction of lift movement is inverted. Even if the power is turned off while the lift is moving up (or down), the lift continues to move up (or down) when the power is turned on again. MEMSW $0004 0000 Upper limit switch (0000) 0001 1000 0001 #00010 T000 0000 1001 Lower limit switch (0001) Move-down (0500) 1000 1001 #00010 T001 T000 0501 0500 T001 0500 0501 END Move-up (0501) ENDH Note: The retentive function is effective only when internal utility relays retained by the self-retentive circuit or the SET/SFT/KEEP instruction are also retained by the memory switch. Internal utility relays are not retained in the program shown below. 0000 1001 Chapter 1 Programming 3-11 11 1.3 Device Configuration 1.3.7 Special Utility Relays Each special utility relay has a unique function. By using special utility relays effectively, programs can be simplified and program control improved. Note 1: A special utility relay can be used as many times as desired in one program. Note 2: Special utility relays dedicated for reading can be used as contacts, but cannot be used as outputs. ➮ For more about relays dedicated for reading, refer to "1.3.8 Special Utility Relay List" (p.3-14). Description Relay 2002: Always ON By setting an output relay to ON using relay 2002, the output relay can be used as a "running indicator output". 2002 HSP 0100 2002 00000 LDA DM0000 STA Set the input time constant of relay 0100 to 10 µs. Transfer the ON/OFF status data of channel 0000 to DM0000. 1 Relay 2003: Always OFF. Opposite that of relay 2002, use relay 2003 where it is not required to be turned on. For example, when using only the up function of an up/down counter, use relay 2003 in the DW (down) input. Relays 2004, 2005 and 2006: Clock pulse For each relay, the time ratio is "ON:OFF = 1:1". (Accordingly, the ON time of relay 2005 is 0.05 sec/pulse.) However, because these relays depend on the scan time, error as much as the scan time is generated. • • By combining an output relay, an "intermittent output" can be made. By using relay 2006 as input for a counter, the counter can be used as a longterm timer. 1000 #03600 C000 2006 1000 C000 1000 turns ON at every hour. Relay 2007: Remains OFF during only one scan when operation is started. This relay can be used when a signal needs to be sent after a specific period (equivalent to one scan) after operation is started. This relay can also be used for an initial reset at the start of operation. After one scan, this relay remains ON. 1000 2007 #00100 C005 0000 When operation is started, this relay returns the current value of C005 to 0. 3-12 Chapter 1 Programming 1.3 Device Configuration Relay 2008: Remains ON during only one scan when operation is started. This relay can be used for an initial reset at the start of operation. After one scan, this relay remains OFF. 0000 1000 SFT D 1100 CLK 1100 2008 RES When operation is started, this relay sets all internal utility relays used by the SFT instruction to OFF. 2008 #00000 LDA DM0000 STA When operation is started, this relay returns the current value of DM0000 to 0. Relay 2813: Sets the input time constant of the CPU. While relay 2813 remains ON, the input time constant of a basic unit can be set using the value of DM1940. Chapter 1 Programming 3-13 11 1.3 Device Configuration 1.3.8 Special Utility Relay List Special relays and arithmetic operation flags ➮ "1.3.7 Special Utility Relays" (p.3-12) Relay No. Always ON. 2003* Always OFF. 2004* 0.01-s clock pulse (duty cycle: 50%) 2005* 0.1-s clock pulse (duty cycle: 50%) 2006* 1.0-s clock pulse (duty cycle: 50%) 2007* Remains OFF during first scan after startup. 2008* 2010* Remains ON during first scan after startup. Turns ON when result of arithmetic operation is negative or when an overflow is generated. Turns ON when result of arithmetic operation is 0. 2011* Turns ON when result of arithmetic operation is positive. 2012* Turns ON when an arithmetic operation generates an error. 2009* * 1 Function 2002* Read-only relay. Special utility relays for high-speed counter(0) ➮ "Chapter 4. High-Speed Counters" (p.3-203) Relay No. Function 2100* Internal clock used only for CTH0 (1 µs) 2101* Internal clock used only for CTH0 (10 µs) Internal clock used only for CTH0 (100 µs) Automatic clear of CTH0 when comparator CTC0 2103 turns ON. Prohibits/permits direct output to 0500 when 2104 comparator CTC0 turns ON. Direct output to 0500 is set to OFF when comparator 2105 CTC0 turns ON. Direct output to 0500 is set to ON when comparator 2106 CTC0 turns ON. ON/OFF status of output to 0500 is reversed each 2107 time comparator CTC0 turns ON. Prohibits/permits direct output to 0500 when 2108 comparator CTC1 turns ON. Direct output to 0500 is set to OFF when comparator 2109 CTC1 turns ON. Direct output to 0500 is set to ON when comparator 2110 CTC1 turns ON. ON/OFF status of output to 0500 is reversed each 2111 time comparator CTC1 turns ON. A utomatic clear of CTH0 when comparator CTC1 2112 turns ON. Selects multiplication mode for comparator CTH0. 2113 OFF ON OFF ON 2114 OFF: 1 pulse OFF: x2 ON: x4 ON: 2 pulses Read-only relay. 2102* * Multiplication mode 2113 2114 ON: Cleared OFF: Not cleared ON: Prohibited OFF: Permitted ON: Set to OFF OFF: Not set to OFF ON: Set to ON OFF: Not set to ON ON: Reversed OFF: Not reversed ON: Prohibited OFF: Permitted ON: Set to OFF OFF: Not set to OFF ON: Set to ON FF: Not set to ON ON: Reversed OFF: Not reversed ON: Cleared OFF: Not cleared 1 pulse x2 x4 2 pulses OFF ON OFF ON OFF OFF ON ON Note: Never use special utility relays that are not shown above. 3-14 Chapter 1 Programming 1.3 Device Configuration Special utility relays for high-speed counter(1) ➮ "Chapter 4. High-Speed Counters" (p.3-203) Relay No. 2200* Internal clock used only for CTH1 (1 µs) 2201* Internal clock used only for CTH1 (10 µs) 2202* Internal clock used only for CTH1 (100 µs) Automatic clear of CTH1 when comparator CTC2 turns ON. Prohibits/permits direct output to 0501 when comparator CTC2 turns ON. Direct output to 0501 is set to OFF when comparator CTC2 turns ON. Direct output to 0501 is set to ON when comparator CTC2 turns ON. ON/OFF status of output to 0501 is reversed each time comparator CTC2 turns ON. Prohibits/permits direct output to 0501 when comparator CTC3 turns ON. Direct output to 0501 is set to OFF when comparator CTC3 turns ON. Direct output to 0501 is set to ON when comparator CTC3 turns ON. ON/OFF status of output to 0501 is reversed each time comparator CTC3 turns ON. Automatic clear of CTH1 when comparator CTC3 turns ON. Selects multiplication mode for comparator CTH1. OFF ON OFF ON OFF: 1 pulse OFF: x2 ON: x4 ON: 2 pulses 2203 2204 2205 2206 2207 2208 2209 2210 2211 2212 2213 2214 * Function ON: Cleared OFF: Not cleared ON: Prohibited OFF: Permitted ON: Set to OFF OFF: Not set to OFF ON: Set to ON OFF: Not set to ON ON: Reversed OFF: Not reversed ON: Prohibited OFF: Permitted ON: Set to OFF OFF: Not set to OFF ON: Set to ON OFF: Not set to ON ON: Reversed OFF: Not reversed ON: Cleared OFF: Not cleared Read-only relay. Multiplication mode 2213 2214 1 pulse x2 x4 2 pulses OFF ON OFF ON OFF OFF ON ON Note: Never use special utility relays that are not shown above. Other special utility relays Relay No. 2305 Function External outputs disabled (outputs 0500 to 0915) External refresh inputs disabled (inputs 0000 to 0415) Constant scan time mode (write preset value in TM29) Remains ON for one scan when scan time exceeds preset constant scan time. Start flag for frequency counter operation. 2306 Specified frequency pulse output 2307 2308 Error flag for specified frequency pulse output Stops motor driver when turned ON. Turns ON when motor driver is in operation. Stops motor driver in emergencies when turned OFF by interrupt instruction. Starts motor driver when turned ON (detection at rising edge). Start flag for cam switch operation. Turns ON when an error occurs in cam switch operation. 2300 2301 2303 2304 2309 2310 2314 2315 ON: Disabled OFF: Not disabled ON: Disabled OFF: Not disabled ON: Enabled OFF: Disabled ON: Enabled OFF: Disabled * Read-only relay. Chapter 1 Programming 3-15 11 1.3 Device Configuration Relay No. 2400 2401 2402 2403 2404 2405 2406 2407 2408 2409 2410 2411 2412 2413 2414 1 2415 2500 2501 2502 2503 2504 2505 2506 2507 2508 2509 2510 2511 2512 2513 2515 3-16 Function Timing of CTH0 external signal OFF External preset OFF OFF not used ON At falling edge ON OFF At rising edge ON ON Level Interrupt polarity of INT OFF OFF At rising edge OFF ON At falling edge ON OFF At rising edge ON ON At both edges Interrupt polarity of INT1 OFF OFF At rising edge OFF ON At falling edge ON OFF At rising edge ON ON At both edges CTH0 set as ring counter ON: Set OFF: Not set Ignore phase B input when CTH0 is set to no multiplication mode. ON: Ignore phase B input and always count up. OFF: Use phase B input as usual. Timing of CTH1 external preset OFF External preset OFF OFF not used ON At falling edge ON OFF At rising edge ON ON Level Interrupt polarity of INT2 OFF OFF At rising edge OFF ON At falling edge ON OFF At rising edge ON ON At both edges Interrupt polarity of INT3 OFF OFF At rising edge OFF ON At falling edge ON OFF At rising edge ON ON At both edges CTH1 set as ring counter ON: Set OFF: Not set Ignore phase B input when CTH1 is set to no multiplication mode. ON: Ignore phase B input and always count up. OFF: Use phase B as usual. Customized switch [F1] on KV-D20 operator interface panel is assigned. Customized switch [F2] on KV-D20 operator interface panel is assigned. Customized switch [F3] on KV-D20 operator interface panel is assigned. Customized switch [F4] on KV-D20 operator interface panel is assigned. Customized indicator lamp 1 on KV-D20 operator interface panel is assigned. Customized indicator lamp 2 on KV-D20 operator interface panel is assigned. Customized indicator lamp 3 on KV-D20 operator interface panel is assigned. Customized indicator lamp 4 on KV-D20 operator interface panel is assigned. Permits change between operator OFF: Not mode and device mode of KV-D20 ON: Permitted permitted operator interface panel . Permits the KV-D20 operator interface OFF: Not panel to be shifted between operator ON: Permitted permitted mode and system mode. Specifies the display language for the ON: Japanese OFF: English KV-D20 operator interface panel Sets the beep for the KV-D20 operator ON: Use beep OFF: No beep interface panel Reserved for system Reserved for system Displays a user message (contents of ON: Display OFF: Do not DM1950) in the Access Window message display message Chapter 1 Programming 1.3 Device Configuration Relay No. 2609 2610 2611 2612 2613 Function Input time constant of input expansion unit with relay Nos. 0100 to 0115 Input time constant of input expansion unit with relay Nos. 0200 to 0215 Input time constant of input expansion unit with relay Nos. 0300 to 0315 Input time constant of input expansion unit with relay Nos. 0400 to 0415 Clearing of input at expansion disconnect 2712 Disconnect error OFF: Normal ON: Disconnection in connected unit 2714 Use of high-speed input correction circuit ON: Used OFF: Not used OFF: 10 ms ON: 10 µs OFF: 10 ms ON: 10 µs OFF: 10 ms ON: 10 µs OFF: 10 ms ON: 10 µs OFF: Cleared ON: Not cleared This area is stored even when the operation mode is changed from PROGRAM to RUN, or when the power is turned off (without being affected by the MEMSW instruction). This area is not cleared even if the utility relay All Clear function is activated. However, this area is cleared when an All Clear is executed without registering a program. 2715 ON while cam switch is in operation. 2800 Break signal send to communication port A (remains ON while sending). Receives text data from communication port A, and remains ON during only 1 scan while receiving text data. Communication port A text data acceptance error. Remains ON during only 1 scan ON when text data is received while either relay 2801 or relay 2803 is ON. Communication port A text data receive error Remains ON during only 1 scan when a text data receive error occurs. Communication port A text data send start (remains ON during sending.) Break signal send to communication port B (remains ON while sending). Receives communication port B text data, and remains ON during only 1 scan while receiving text data. Communication port B text data acceptance error. Remains ON during only 1 scan ON when text data is being received while relay 2806 or relay 2808 is ON. Communication port B text data receive error Remains ON during only 1 scan when a text data receive error occurs. Communication port B text data send start (remains ON during sending.) Turns ON when an abnormality occurs with backup battery. 2801 2802 2803 2804 2805 2806 2807 2808 2809 2812 2813 Sets input time constant to all inputs in basic module (except inputs used by HSP instruction). OFF: Sets input time constant to 10 ms. ON: Refers to value stored in DM1940, then determines input time constant. 2814 HKEY instruction: Multiple keys are prohibited. 2815 HKEY instruction: Scan is finished. 2900 to 2915 HKEY information storage area. Note: Never use special utility relays that are not shown above. Chapter 1 Programming 3-17 11 1.3 Device Configuration 1.3.9 Timers and Counters Timers and counters can be set in a program, and their outputs can be used as contacts elsewhere in the program. [There is no restriction on the contact type (N.O. or N.C.) and the order of use.] A same number can be assigned to only one timer or counter. For example, T005 and C005 cannot be used in the same program. Timer/Counter list Name Timer Counter Timer (0.1-s timer) High-speed timer (0.01-s timer) High-speed 1-ms timer (0.001-s timer) Counter Up/down counter Contact T000 to T249 Coil (instruction) TMR000 to 249 TMH000 to 249 TMS000 to 249 C000 to C249 Number 250 in total C000 to 249 UDC000 to 249 Description 1 ■ Timers • When 0.1-s timers (TMR) and high-speed 0.001-s timers (TMS) are used as contacts, the "Tnnn" No. is used for both types. However, the form for setting is different. "TMRnnn#ddddd" is used for 0.1-s timers, "TMHnnn#ddddd" is used for high-speed 0.01-s timers, and "TMSnnn#ddddd" is used for high-speed 1-ms timers (nnn = timer No, ddddd = timer set value). • In a single program, different timer Nos. must be assigned to each of TMRnnn, TMHnnn, and TMSnnn. • When the PLC is stopped, all timers are reset and their current values become equivalent to set values. ■ Counters • When counters (C) and up/down counters (UDC) are used as contacts, the "Cnnn" No. is used for both types. However, the form for setting is different. "Cnnn#ddddd" is used for counters, while "UDCnnn#ddddd" is used for up/down counters. • In one program, different numbers must be assigned to each of the counters and up/down counters. • Even when operation is stopped, each counter stores whatever value it has at that time. ➮ "TMR instruction" (p.3-67), "TMH instruction" (p.3-68), "TMS instruction" (p.3-69), "C instruction" (p.372), "UDC instruction" (p.3-76). ■ High-speed counters and high-speed counter comparators The Visual KV Se ries is equipped with two high-speed counters (CTH0 and CTH1) and four high-speed counter comparators (CTC0, CTC1, CTC2, and CTC3) with a 30-kHz input response speed (frequency), two phases, and size of 16 or 24 bits. Note: When a high-speed counter or high-speed counter comparator will be used as a 24-bit device, a set value is required to be stored in a data memory using the MEMSW instruction. ➮ 3-18 For details about high-speed counters and high-speed counter comparators, refer to "Chapter 4 Highspeed Counters" (p.3-203). Chapter 1 Programming 1.3 Device Configuration 1.3.10 Data Memories Data memories store various types of data. Data memories are not usually used in a program that consists of contacts, coils, timers, and counters. When arithmetic instructions are used, however, data memories can be used to store data for arithmetic operations as well as the results of arithmetic operations. DM No. DM0 to DM999 Description Not specified (can be used by user) DM1000 to DM1099 Text receive port A DM1100 to DM1199 Text send port A DM1200 to DM1299 Text receive port B DM1300 to DM1399 Text send port B DM1400 DM1403 Cam switch function: The first output relay No. Cam switch function: Comparison value in multi-step comparator mode Cam switch function: Pulse count of one cycle of equipment input to CTH0 Not specified (can be used by user) DM1404 Measurement cycle (ms) DM1405 Result of frequency count (Hz) Cam switch function: Set value of angle at which output relay turns ON/OFF Cam switch function: Set value of angle at which output relay +1 turns ON/OFF : Cam switch function: Set value of angle at which output relay +31 turns ON/OFF Reserved by system (cannot be used by user) DM1401 DM1402 DM1406/DM1407 DM1408/DM1409 : DM1468/DM1469 DM1470 DM1471 to DM1479 DM1480 DM1481 DM1482 DM1483 DM1484 DM1485 DM1486 Not specified (can be used by user) Ramp-up/down control function: Startup frequency (Hz) (200 to 50,000) Ramp-up/down control function: Operating frequency (Hz) (200 to 50,000) Ramp-up/down control function: Acceleration time (ms) (0 to 4,000) Not specified (can be used by user) Ramp-up/down control function: Output pulse count (lower digit) (0 to 65,535) Ramp-up/down control function: Output pulse count (upper digit) (0 to 65,535) Ramp-up/down control function: Error code (11 to 17) DM1487 to DM1499 Not specified (can be used by user) DM1565 to DM1569 Not specified (can be used by user) DM1578 and DM1579 Not specified (can be used by user) DM1580 to DM1599 KV-D20 Operator interface panel: Display device No. DM1664 to DM1699 Not specified (can be used by user) DM1670 to DM1675 Reserved by system (cannot be used by user) KV-D20 Operator interface panel: Screen shift permission setting in operator mode DM1676 Chapter 1 Programming 3-19 11 1.3 Device Configuration DM No. DM1680 to DM1699 Description Area for direct access mode for the KV-D20 operator interface panel KV-D20 Operator interface panel: Display device attributes DM1764 to DM1799 Not specified (can be used by user) DM1806 to DM1809 Not specified (can be used by user) DM1826 to DM1899 Not specified (can be used by user) DM1677 to DM1679 1 DM1900/DM1901* 24-bit value read from CTH0 (lower digit/upper digit) DM1902/DM1903* 24-bit value read from CTH1 (lower digit/upper digit) DM1904/DM1905* 24-bit value read from CTC0 (lower digit/upper digit) DM1906/DM1907* 24-bit value read from CTC1 (lower digit/upper digit) DM1908/DM1909* 24-bit value read from CTC2 (lower digit/upper digit) DM1910/DM1911* 24-bit value read from CTC3 (lower digit/upper digit) DM1912/DM1913 24-bit current value written to CTH0 (lower digit/upper digit) DM1914/DM1915 24-bit current value written to CTH1 (lower digit/upper digit) DM1916/DM1917 24-bit current value written to CTC0 (lower digit/upper digit) DM1918/DM1919 24-bit current value written to CTC1 (lower digit/upper digit) DM1920/DM1921 24-bit current value written to CTC2 (lower digit/upper digit) DM1922/DM1923 24-bit current value written to CTC3 (lower digit/upper digit) DM1924/DM1925 CTH0 preset input (lower digit/upper digit) DM1926/DM1927 CTH1 preset input (lower digit/upper digit) DM1928/DM1929* Input capture when INT0 is generated (lower digit/upper digit) DM1930/DM1931* Input capture when INT1 is generated (lower digit/upper digit) DM1932/DM1933* Input capture when INT2 is generated (lower digit/upper digit) DM1934/DM1935* Input capture when INT3 is generated (lower digit/upper digit) DM1936 Specified frequency pulse output function: Set frequency (Hz) DM1937 I/O expansion unit connection information DM1938 Digital trimmer No. 0: Upper limit value DM1939 Digital trimmer No. 1: Upper limit value Input time constant setting 0: 10 µs 1: 20 µs 2: 500 µs 3: 1 m s 4: 2.5 ms 5: 5 ms 6: 10 ms Any other value cannot be set. Reserved by system (cannot be used by user) Number of instructions converted into 1 scan when division conversion is performed Not specified (can be used by user) DM1940 DM1941 to DM1943 DM1944 DM1945 to DM1949 DM1950 DM1951 to DM1999 * Access window error display (0 to 255) Not specified (can be used by user) Read-only relay. Note 1: 16-bit binary data is stored in each of the data memories as for internal registers. Note 2: The data stored in data memories is held even when the power is turned off or when the All Clear function is executed. The backup time is 20 days or more in the KV-10xx, and 2 months or more in other models. Note 3: DM1000 to DM1999 are assigned as special data memories. 3-20 Chapter 1 Programming 1.3 Device Configuration 1.3.11 Temporary Data Memory These data memories are used for temporary storage. When arithmetic instructions are used, temporary data memories can be used to temporarily store the data for arithmetic operations as well as the results of arithmetic operations. TM No. Usage Attribute TM00 Used for arithmetic operations (DIV/MUL) R/W TM01 Used for arithmetic operations (DIV) R/W TM02 to TM27 Not specified (can be used by user) Stores scan time (module: 1 ms) beyond set value while TM28 constant scan time operation is performed. Stores set value (module: 1 ms) of constant scan time TM29 operation TM30 Stores CTC0 value when INT3 interruption is given. Stores measured scan time (mean value of every 10 TM31 scans) (module: 0.1 ms). Attribute * R: Read R/W R* R/W R* R W: Write Both R and W are enabled when special functions are not used. Note 1: Temporary data memories are initialized when the power is turned on. Note 2: TM20, TM30, and TM31 are read-only, so cannot be used for writing. However, TM28 can be used for both reading and writing if special functions are not used. Note 3: TM00 and TM01 are used by the MUL and DIV instructions. Never use them for any other purpose. Chapter 1 Programming 3-21 11 1.3 Device Configuration 1.3.12 Relay Nos. and Functions Assignment of Relay Nos. The components of a relay no. are shown below. 0 7 5 1 5 Channel No. Relay No. (00 to 15) Module No. (07 to 17) Address No. Input (0 to 4) Output (5 to 9) ■ Unit Nos. Unit nos. are assigned to units within the KV-300 system, with the unit connected to the right of the KV-300 CPU (see the figure below) assigned as no. 7. The CPU is assigned as unit no. 0. 1 Power supply unit CPU 0 7 8 9 16 17 ■ Address Nos. Address nos. are assigned to the input units, output units, and I/O terminal units. The following table shows the assignment of address nos. to units. Unit KV-300 CPU CPU 0, 5 KV-C16X 16-input unit 0 KV-C32X 32-input unit 0. 1 KV-B16R 16-output unit 5 KV-B16S 16-output unit 5 KV-C32T 32-output unit 5, 6 KV-R8X 8-input terminal unit 0 to 4 * KV-R16X 16-input terminal unit KV-R8R 8-output terminal unit KV-R16R 16-output terminal unit KV-R8T 8-output terminal unit KV-R16T 16-output terminal unit * 3-22 Address No. 5 to 9 * The KV-R1A I/O Distribution Unit accommodates 5 input units and 5 output units. Addresses are set with address switches. Chapter 1 Programming 1.4 Special Functions 1.4 Special Functions This section describes special functions to set and confirm operations on the Visual KV Series, and useful functions for program debugging and adjustment of external equipment. 1.4.1 Input Time Constant Change Function The input time constant can be changed when a signal is read from an input contact. When connecting external equipment which has no contact in which chattering such as transistor outputs does not occur, and inputting pulses of short width, the input time constant change function can be used to decrease the input time constant. Setting the input time constant for basic units using special utility relays The input time constant for a basic unit can be changed using data memory DM1940 and special utility relay 2813. Though the input time constant is usually 10 ms, it can be changed to a value that corresponds to the number stored in DM1940 by setting special utility relay 2813 to ON. If the HSP instruction and special utility relay 2813 are used at the same time, priority is given to the HSP instruction and the number stored in DM1940 is ignored. ■ Special utility relay 2813 OFF: Sets the input time constant to 10 ms. ON: Refers to the number stored in DM1940, then determines the input time constant. Number stored in DM1940 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 or more Input time constant 10 µs 20 µs 500 µs 1 ms 2.5 ms 5 ms 10 ms Not allowed Note 1: Be sure to set the input time constant to 10 µs when using the 30-kHz high-speed counter input. Note 2: Never enter a number that is 7 or larger to data memory DM1940. Note 3: The input time constant specified by data memory DM1940 becomes effective at the rising edge of special utility relay 2813. To change the input time constant, first change data memory DM1940, then set special utility relay to OFF and ON again. Or change the operation mode of the KV basic unit from PROGRAM to RUN. Note 4: The input time constant for input relays set by the HSP instruction is 10 µs. ➮ For more about the HSP instruction, refer to "HSP instruction" (p.3-86). ➮ For more about setting the input time constant for expansion units, refer to "Input time constant for expansion units" (p.1-76). Note 5: Set the special utility relay using the SET/RES instructions. Note 6: When the input time constant is set to 1 ms or less, connect the output equipment without contacts. If connecting output equipment with contacts, contact bounds may enter. Note 7: Except for interrupts and high-speed counters, signals whose ON time is shorter than the scan time may not be received even if the input time constant is set to a small value. Chapter 1 Programming 3-23 11 1.4 Special Functions 1.4.2 Modifying the Input Relay Time Constant KV-300 PLC Only ■ Modifying with External Switches KV-C32X/C16X KV-R16X/R8X Input time constant selection switch 3 24V 4 1 ms 0 ms 10 ms 2 5V 0 ms 10 ms 1 ms 1 0 As shown in above figures, an external switch can be used to select the input time constant only on the KV-C32X/C16X Connector Input Units and KV-R16X/R8X I/O Terminal Units. 1 In the following table, white represents the switch position. Input time constant KV-C32X/C16X KV-R16X/R8X 0ms 1ms 10ms 25 µs ±20% 0ms 1ms 10ms 0ms 1ms 10ms 1 ms ±20% 0ms 1ms 10ms 10 ms ±20% 0ms 1ms 10ms 0ms 1ms 10ms Note: Connect a solid-state contact output device when the input time constant is set to 1 ms for 25 µs. Connection of a contact output device may result in contact bounce. Modification within the CPU The input time constant for KV-300 CPU input relay nos. 0000 to 0009 can be modified in the program. Input time constant Setting 10 µs ±20% Turn ON special utility relay 2813 (0000 to 0009). 25 µs ±20% Use the HSP instruction. 10 ms ±20% Default Note 1: When using the 30 kHz high-speed counter input, turn ON special utility relay 2813. Note 2: When special utility relay 2813 is ON, the input time constant of input relays 0000 to 0009 is set to 10 µs ±20%. Note 3: The input time constant remains 10 ms ±20% if the HSP instruction is used when special utility relay 2813 is ON. Note 4: When the input time constant is set to 10 µs or 25 µs, a solid-state output device must be connected. Connection of a contact output device may result in contact bounce. 3-24 Chapter 1 Programming 1.4 Special Functions 1.4.3 Constant Scan Time Mode This function executes a program while keeping the scan time at a constant value which usually changes based on the processing contents. This section describes how to set this function. Though the scan time changes usually depending on the processing contents, it can be kept at a constant value by using this function. This function can be used to acquire data from external equipment at a constant time interval. The set value should be longer than the maximum scan time because the scan time is kept at a constant value until the end of processing. ■ Setting procedure Set the desired scan time to temporary data memory TM29. Set special utility relay 2303 to ON. The scan time is written to TM31. The scan time can be set in 1-ms increments. Enter the desired scan time (ms) to the temporary data memory. ■ Setting example In this example, the scan time is kept at 20 ms. 2008 #00020 LDA TM29 STA 11 2303 SET Note 1: Be sure to set the constant scan time value so it is larger than the actual scan time. Note 2: If the actual scan time exceeds the set scan time, special utility relay 2304 turns ON (during the next 1 scan) while the actual scan time is written to TM28 (unit: 1 ms). Note 3: The scan time can be set up to 200 ms in temporary data memory TM29. If a value larger than 200 ms is input, it will be treated as 200 ms. Chapter 1 Programming 3-25 1.4 Special Functions 1.4.4 Output Disabled Function This function disables outputs from each unit in RUN mode without regard to the program used. By disabling external outputs, the program can be debugged while external equipment is connected, even when output of signals to the external equipment is not desired. ■ Setting procedure When special utility relay 2300 turns ON, all outputs from all output relays (0500 to 0915) to the outside are cleared after 1 scan is finished. However, the display in the Access Window and the output indicator lamps are not cleared. ■ Setting example By setting/resetting special utility relay 2300 using the Access Window, the "KV IncrediWare (DOS)" or "LADDER BUILDER for KV" programming support software, or the KV-P3E(01) handheld programmer, the external output prohibition function can be used. External outputs are prohibited while input 0000 is ON. External outputs are permitted, though, while input 0000 is OFF. 0000 2300 1 ➮ For more about operating procedures, refer to the "Chapter 6. Handheld Programmer" (p.1-195). 1.4.5 Input Refresh Disabled Function This function disables the update of inputs from each unit triggered by input signals from external equipment. By disabling external input refresh, inputs from each unit can be set to ON/OFF in monitor status without mechanical operations to enable a program check. ■ Setting procedure When special utility relay 2301 turns ON, input refresh (read of input relays) for all input relays (0000 to 0415 used by the QL Series) is skipped. In this status, inputs can be set to ON/OFF from the Access Window, the "KV IncrediWare (DOS)" or "LADDER BUILDER for KV" programming support software, or the KV-P3E(01) handheld programmer. ■ Setting example By setting/resetting special utility relay 2301 using the Access Window, the "KV IncrediWare (DOS)" or "LADDER BUILDER for KV" programming support software, or the KV-P3E(01) handheld programmer, the external input refresh prohibition function can be used. External input refresh is prohibited while input 0000 is ON. External input refresh is permitted, though, while input 0000 is OFF. 0000 ➮ 2301 For more about operating procedures, refer to the "Chapter 6. Handheld Programmer" (p.1-195). Note: Once external input refresh is prohibited, it can be permitted only by setting special utility relay 2301 to OFF from the Access Window, the "KV IncrediWare (DOS)" or "LADDER BUILDER for KV" programming support software, or the KVP3E(01) handheld programmer. 3-26 Chapter 1 Programming 1.5 Extended Ladder Diagrams 1.4.6 Contact Comment Save Function • This function transfers contact comments to the Visual KV Series using the "KV IncrediWare (DOS)" or "LADDER BUILDER for KV" programming support software. • The Visual KV Series can store not only programs but also comments registered to each contact using the "KV IncrediWare (DOS)" or "LADDER BUILDER for KV" programming support software. A program may not be easy to understand if only device Nos. are used. By registering comments to the contacts, the program can be easily debugged and more efficiently maintained. • The number of contact comments that can be transferred is up to 1,000 for both normal transfer and compression transfer. • The KV-D20 operator interface panel includes the contact comment display function. ➮ For more about operating procedures, refer to "2.5 Entering Comments/Labels" (p.1-46) and "4.2.2 Setting the comment transfer" (p.2-138). Note 1: Line comments cannot be stored. Note 2: The KV-P3E(01) handheld programmer cannot read or write contact comments. Note 3: The KV-D20 operator interface panel cannot display contact comments which have been compressed and transferred. Chapter 1 Programming 3-27 11 1.4 Special Functions 1.4.7 Special Functions KV-300 PLC only Constant Scan Time Mode In this mode, operation can take place according to a preset scan time (in ms). ■ Setting Write the desired scan time into TM29 (temporary data memory), then turn on special utility relay No. 2303. The scan time can also be written into TM31. Specify a scan time in increments of 10 ms (a value of less than 10 ms is invalid). Here, write a value into TM equivalent to 10 times the scan time. Example Set the constant scan time to 20 ms. 02008 #00200 LDA TM29 STA 2303 SET Note 1: The set value for the constant scan time must be greater than the actual scan time. Otherwise, special utility relay 2304 turns on during every scan to disable constant scan time mode. Note 2: If the scan time exceeds the set value, special utility relay no. 2304 turns on during the next scan. 1 Output Disabled Function During checking of a program, this function clears output from output relays regardless of the program currently running. ■ Setting Turn on special utility relay No. 2300. After one scan is completed, all output relays (00500 to 00503, 07500 to 17915) are cleared. Example Use the output disabled function by executing FORCED RESET/RESET to special utility relay No. 2300 from the monitor display. ➮ To execute FORCED RESET or RESET, refer to "Chapter 6 Handheld Programmer" (p.1-195). Input Refresh Disabled Function Set this function if it is desired to turn ON/OFF input relays from the monitor display without activating the machine when checking a program. ■ Setting Turn ON special utility relay No. 2301 to skip input refresh (reading from input relays). Input relays can then be turned ON/OFF with the KV-P3E(01) or with KV IncrediWare (DOS) on the monitor display. Example Set input relay No. 0000 to ON to disable input refresh; set to OFF to enable input refresh. 0000 2301 Note: If input refresh is disabled, it is not enabled until input relay No. 0000 is turned on from the handheld programmer. 3-28 Chapter 1 Programming 1.5 Extended Ladder Diagrams 1.5 Extended Ladder Diagrams This section describes KEYENCE’s unique extended ladder diagram. 1.5.1 Features of Extended Ladder Diagrams The extended ladder diagram is a programming method developed to reduce problems related to design, testing, operation, and maintenance of programs. In a conventional ladder diagram, output instructions can be written only on the right side of a ladder diagram. On the other hand, in an extended ladder diagram, output instructions can be written anywhere except on the left. As the result, the programs shown below can be written. Mixture of input and output circuits Conventional ladder diagram Only input circuits can be written. Only output circuits can be written. Extended ladder diagram Only input circuits can be assembled. Both input circuits and output circuits can be assembled. Only output circuits can be assembled. Connection of two or more instructions on one line Conventional ladder diagram Extended ladder diagram Instructions can be written only from the left end to the right end on one line. Many instructions can be connected. Branch from output coil Conventional ladder diagram Branches can be made only from input contacts. Extended ladder diagram Branches can also be made from output coils. There is only a single line, so the ladder diagram is easier to understand. Three lines are required. Chapter 1 Programming 3-29 11 1.5 Extended Ladder Diagrams 1.5.2 Advantages of Extended Ladder Diagrams The number of lines in a ladder diagram can be reduced. Because both output instructions and input instructions can be written side by side, the number of program lines can be reduced. As the result, the contents of the program can be seen at a glance. Example When DM0000 stores 1000, 0500 turns ON. 2000, 0501 turns ON. 3000, 0502 turns ON. Conventional ladder diagram 1 Extended ladder diagram DM0000 #01000 LDA CMP 2010 0500 #01000 CMP #02000 CMP 2010 0501 2010 0500 #03000 CMP 2010 0502 2002 #02000 CMP 2010 0501 2002 #03000 CMP 2010 0502 DM0000 LDA 2002 2002 In a conventional ladder diagram, operations performed by the program cannot be easily understood. In an extended ladder diagram, operations performed by the program can be understood at a glance. Processing sequence is clear. Ladder symbols can be laid out in processing sequence, so the program flow is easier to understand. In addition, maintainability is considerably improved. Example When the start switch is set to ON, a lamp is lit for three seconds, a buzzer is sounded for two seconds, and then the motor starts to rotate. 0000 1100 DIFU 1100 1000 STG 0500 #00030 T000 T000 1001 JMP 1001 STG 0501 #00020 T001 T001 1002 JMP 1002 STG 0502 0000 1000 SET ENDS Conventional ladder diagram 0000 1000 T000 1001 T001 T001 T002 1001 #00020 T001 #00030 T002 1001 0500 1003 3-30 Chapter 1 Programming Extended ladder diagram 1001 STG 1003 1003 When the start switch (0000) is set to OFF, the motor is stopped and all operations are reset. #00010 T000 1003 1002 When timer 1 turns ON two seconds later, the buzzer is stopped and the motor (0502) starts to rotate. 0000 1002 1002 When timer 0 turns ON three seconds later, the lamp goes out, a buzzer (0501) is sounded, and timer 1 is activated. 1000 DIFU T002 T000 When the start switch (0000) is set to ON, a lamp (0500) is lit and timer 0 is activated. 0501 1000 DIFU 1000 1001 SET 0500 #00010 T000 T000 1002 JMP 1002 STG 0501 #00020 T001 T001 1003 JMP 1003 STG 0500 #00030 T002 T002 1001 JMP 0501 By using an extended ladder diagram as shown above, the program can be executed in the sequence of the processing to be performed. So even a person who uses a relay sequence for the first time can understand the processing contents. By combining the STG instruction, double coils can also be used. 1.5 Extended Ladder Diagrams Note: When an extended ladder diagram is used, the number of lines in ladder diagram may be reduced. However, this may not necessarily reduce the number of mnemonics in the program. Conventional ladder diagram 0000 Extended ladder diagram 0500 0000 0500 0501 0501 LD 0000 OUT 0500 OUT 0501 LD 0000 OUT 0500 CON OUT 0501 The CON instruction for connection is added. (The scan time is not affected.) 1.5.3 Example of an Extended Ladder Diagram ■ Using W-UE Only when inputs are given in the order "0000 ➞ 0001 ➞ 0002", output 0500 turns ON. Conventional ladder diagram 1002 DIFU 0001 0002 1002 1003 DIFU 0000 1000 1000 1001 1000 1003 At the rising edge of input 0001, 1002 turns ON. At the rising edge of input 1003, 1002 turns ON. If input 0000 is ON, 1000 turns ON. Extended ladder diagram 0000 0001 1000 1000 0002 1001 0500 1001 Input 0000 Input 0001 Input 0002 Output 0500 turns ON. turns ON. turns ON. turns ON. If 1000 is ON, 1001 turns ON. 1001 1001 0500 When 1001 turns ON, output 0500 turns ON. Because the program can be written in only one line when an extended adder diagram is used, it is easier to look at and understand compared with a program written using a conventional ladder diagram. Chapter 1 Programming 3-31 11 1.5 Extended Ladder Diagrams 1 3-32 Chapter 1 Programming Chapter 2 Instructions Describes the concrete usage of instructions in the KV Series. Refer to "Chapter 3 Interrupts" on page 3-191 for details of interrupt instructions. Refer to "Chapter 4 High-speed counters" on page 3-203 for details of the highspeed counters used in the application instruction. 2.1 Instruction List [Visual KV Series] ....................................... 3-34 2.1.1 2.1.2 2.1.3 2.1.4 2.1.5 Basic Instructions ................................................................................. 3-34 Application Instructions ........................................................................ 3-36 Arithmetic Instructions .......................................................................... 3-38 Interrupt Instructions ............................................................................ 3-41 Function No. List (Alphabetical order) .................................................. 3-41 2.2 Instruction List [KV-300 Series, KV-10/80] .......................... 3-42 2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.3 2.2.4 Basic Instructions ................................................................................. 3-42 Application Instructions ........................................................................ 3-45 Arithmetic Instructions .......................................................................... 3-48 Interrupt Instructions ............................................................................ 3-54 2.3 Convention Details ................................................................. 3-55 2.4 Instruction Details .................................................................. 3-56 2.4.1 2.4.2 2.4.3 Basic Instructions ................................................................................. 3-56 Application Instructions ........................................................................ 3-95 Arithmetic Instructions .......................................................................... 3-134 2.5 Programming Notes ............................................................... 3-189 2.1 Instruction List Visual KV Series 2.1 Instruction List Visual KV Series The KV Series uses 80 instructions. The instructions are divided into four categories according to their functions: basic instructions, application instructions, arithmetic instructions, and interrupt instructions. The following is an overview of applications and functions. For details, refer to the respective description pages for each instruction. 2.1.1 Basic Instructions Instruction Symbol nnnn LOAD 2 LOAD BAR nnnn AND nnnn Function Exec.time (µs) Bytes Page LD Connects N.O. contact to bus. 0.7 to 1.6 3 (12) 3-57 LDB Connects N.C. contact to bus. 0.7 to 1.6 3 (12) 3-57 0.7 to 0.9 3 (8) 3-58 0.7 to 0.9 3 (8) 3-58 Mnemonic Operand Operand value AND R No. T/C No. Connects N.O. contact in 0000 to 17915 series with previous contact. T000 to T249 C000 to C249 Connects N.C. contact in CTC0 to CTC3 series with previous contact. AND BAR nnnn OR nnnn OR Connects N.O. contact in parallel with previous contact. 0.7 to 0.9 3 (8) 3-60 OR BAR nnnn ORB Connects N.C. contact in parallel with previous contact. 0.7 to 0.9 3 (8) 3-60 0.8 1 (4) 3-61 0.8 1 (4) 3-63 1.5 3 (12) 3-65 1.5 3 (12) 3-65 1.9 to 12.8 3 (14) 3-66 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 17915 Forces R/T/C OFF when input 1.9 to 20.5 T000 to T249 is ON. C000 to C249 CTH0 to CTH1 CTC0 to CTC3 3 (14) 3-66 ANB AND LOAD ANL OR LOAD ORL OUT nnnn Connects in series blocks made of one or more contacts. Connects in parallel blocks made of one or more contacts. OUT R No. OUT BAR SET nnnn nnnn SET OUB 0500 to 1915 2009 2300 to 17915 Forces relay ON and holds T000 to T249 this status when input is ON. C000 to C249 SET R No. T/C No. nnnn RES RES 0.1-s TIMER #ddddd Txxx TMR 0.01-s TIMER #ddddd T Txxx H TMH (FUN49) RESET 3-34 Outputs input ON/OFF status 0500 to 1915 to R coil. 2009 2300 to 17915 Outputs inverted input ON/ OFF status to R coil. T No., # preset value Chapter 2 Instructions 000 to 249 #00000 to #65535 16-bit on-delay T that counts down in 0.1-s decrements. 12.0 to 17.8 2 (6) 3-67 16-bit on-delay T that counts down in 0.01-s decrements. 12.0 to 17.8 2 (6) 3-68 2.1 Instruction List Exec.time (µs) Bytes Page 16-bit on-delay T that T No., 000 to 249 # preset value #0000 to #65535 counts down in 1-ms decrements. 12.0 to 17.8 2 (7) 3-69 #00000 to # preset value, #65535 Sets 16-bit up-counter. C No., counter 000 to 249 input R 0000 to 17915 12.0 to 17.8 4 (7) 3-72 13.0 to 24.0 2 (10) 3-76 3 (10) 3-78 3 (10) 3-78 3 (11) 3-80 (*) 5 (15) 3-82 Reduces input relay time constant to 10 µs for higher input response. 3.8 to 9.4 3 (8) 3-86 MC (FUN24) Selects ON/OFF status of R coils, Ts, or Cs. 0.2 1 (4) 3-89 MCR MCR (FUN25) Represents end of MC. 0.2 1 (0) 3-89 MEMSW $xxxx MEMSW (FUN26) Sets memory switches. –– 3 (0) 3-92 Performs no operation. –– 1 (0) 3-94 END Indicates end of each routine of program. –– 1 (1) 3-94 ENDH Indicates end of entire program. –– 1 (0) 3-94 Instruction Symbol Mnemonic 1-ms TIMER #ddddd T S Txxx TMS (FUN51) COUNTER #ddddd Cxxx nnnn C UP-DOWN COUNTER UP DW #ddddd RES DIFFERENTIATE UP nnnn DIFU DIFFERENTIATE DOWN nnnn DIFD KEEP UDC xxx UDC (FUN52) DIFD (FUN09) KEEP KEEP (FUN22) SET nnnn RES SFT (FUN39) D nnnn CLK RES mmmm HSP nnnn MASTER CONTROL MC MEMORY SWITCH HSP (FUN18) END HI R No. nnnn: 1st R No. mmmm: Last R No. R No. $ constant NOP (FUN30) NOP END C No., # preset value R No. HIGH SPEED MASTER CONTROL RESET Operand DIFU (FUN10) SFT SHIFT Visual KV Series END ENDH • • • • Operand value 000 to 249 #00000 to #65535 1000 to 1915 3000 to 9915 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 17915 Function Sets a 16-bit up-down counter. Turns ON R for 1 scan 11.2 to 13.2 time at rising edge of input. Turns ON R for 1 scan 10.0 to 12.8 time at falling edge of input. Turns ON R and holds this status when SET input is ON. 8.2 to 19.8 Turns OFF R when RESET input is ON. 1000 to 1915 Sets shift register. 3000 to 9915 (KV-10) 0000 to 0005 (KV-16) 0000 to 0009 (KV-24) 0000 to 0015 (KV-40) 0000 to 0107 $ 0000 to $ FFFF Number of bytes represents the memory capacity required for each instruction. Number in ( ) represents the memory capacity required for object code of each instruction. *1 34 + 0.25 + n x 0.25 (n: No. of shift steps) All operand values are shown in normal notation. The corresponding relay numbers in X-Y-M notation are shown below: Normal notation 0000 to 0415 0500 to 0915 1000 to 6915 7000 to 17915 X-Y-M notation X000 to X04F Y050 to Y09F M1000 to M6915 X700 to X174F or Y750 to Y179F Chapter 2 Instructions 3-35 12 2.1 Instruction List Visual KV Series 2.1.2 Application Instructions Instruction Symbol Mnemonic Operand Operand value WAIT ON nnnn ON mmmm W-ON WAIT OFF nnnn OFF mmmm W-OFF 17915 T000 to T249 nnnn: R, T, C C000 to C249 CTC0 to CTC3 Nos. mmmm: mmmm: 1000 to 1915 3000 to 9915 R No. 1000 to 1915 R No. WAIT UP EDGE WAIT DOWN EDGE W-UE nnnn mmmm CON (FUN 06) PUSH MPS READ MRD POP MPP nnnn STG nnnn JMP JMP (FUN 21) END STAGE ENDS ENDS (FUN 14) STEP STEP END STP nnnn STP (FUN 45) STE STE (FUN 43) • • • Page 5 (12) 3-96 5 (12) 3-96 5 (12) 3-98 1 (0) 3-98 1 (4) 3-102 3.2 1 (4) 3-103 6.8 1 (4) 3-103 10.5 to 13.0 3 (10) 3-103 Executes instructions in STG block when R (operand) is ON. 4.5 to 12.5 3 (8) 3-106 1 (4) 3-106 2.5 3 (10) 3-106 5 (12) 1 (0) 3-114 Turns ON 3-114 R (output operand [mmmm]) when R, T, or C (input operand 10.4 to 12.6 [nnnn]) is ON. Turns ON R (output operand [mmmm]) when R, T, or C (input 13.6 to 18.5 operand [nnnn]) is OFF. Turns ON R (output operand [mmmm]) at rising edge of R, T, 13.6 to 18.5 or C (input operand [nnnn]). Reads input status and arithmetic flag stored with PUSH. Reads & clears input status and arithmetic flag stored with PUSH. R, T, C Nos. 3000 to 9915 0000 to 0009 When input is ON, turns R of current stage OFF and moves 4.3 to 7.5 to stage specified by operand. Turns current stage OFF and next stage ON when input is ON. R No. nnnn: 0000 to 0500 to 9915 Executes program between T000 to T249 STP & STE when R (operC000 to C249 and) is ON. CTC0 to CTC3 11.2 to 13.4 Is used with STEP to make program step. Number of bytes represents the memory capacity required for each instruction. Number in ( ) represents the memory capacity required for object code of each instruction. All operand values are shown in normal notation. The corresponding relay numbers in X-Y-M notation are shown below: Normal notation 0000 to 0415 0500 to 0915 1000 to 6915 7000 to 17915 3-36 Bytes Stores input status and arithmetic flag. STG (FUN 44) JUMP Exec.time (µs) Turns ON R (output operand [mmmm]) at falling edge of R, T, 6.8 to 5.3 or C (input operand [nnnn]). Represents series connection of output instruction together with another instruction. W-DE CONNECT STAGE 2 nnnn mmmm Function Chapter 2 Instructions X-Y-M notation X000 to X04F Y050 to Y09F M1000 to M6915 X700 to X174F or Y750 to Y179F 2.1 Instruction List Instruction INTERVAL TIMER 16-BIT COUNTER 16-BIT COUNTER COMPARATOR 16-BIT COUNTER Symbol ITVL PLS DMnnnn PAUSE mmmm RES CTH0 nnnn #ddddd CTCn CTH1 nnnn 16-BIT COUNTER COMPARATOR #ddddd CTCn SUBROUTINE CALL nn CALL Mnemonic CTH Count input R CTC n: Comparator n: 0,1 No. ddddd: #00001 ddddd: to #65535 # preset value 5 (10) 3-117 0004 2100 2101 2102 14.4 4 (6) 3-204 Hardware-based comparator between preset & current values of high-speed counter 2.3 to 3.5 (CTH0). This comparator is turned ON when these values are equal. 2 (6) 3-204 0005 0500 2200 2201 2202 16-bit (0 to 65535) updown counter for clock pulses with input response frequency of 30 kHz. 14.4 4 (6) 3-204 16-bit (0 to 65535) updown counter for clock pulses with input response frequency of 30 kHz. CTC Hardware-based comparator between preset & current values of high-speed counter (CTH1). This comparator is turned ON when these values are equal. 2.3 to 3.5 2 (6) 3-204 CALL (FUN 03) Subroutine No. 00 to 99 Executes subroutine specified by operand. 5.4 to 6.5 2 (8) 3-122 Subroutine No. 00 to 99 Represents beginning of subroutine specified by operand. 2 (4) 3-122 4.3 1 (4) 3-122 12.0 to 18.0 3 (20) 3-125 0.5 1 (4) 3-125 22.1 to 180.0 5 (10) 3-131 RET (FUN 33) REPEAT START FOR nnnn FOR (FUN 16) Represents end of subroutine. # constant, DM No. TMxx #00000 to #65535 DM0000 to DM1999 TM00 to TM29 HKEY (FUN 17) Executes program between FOR & NEXT for number of times specified by operand. Represents end of repetition. NEXT (FUN 29) • 20.0 to 80.0 n: Comparator n: 2,3 No. ddddd: #00001 ddddd: to #65535 # preset value RET • • Page Count input R SUBROUTINE RETURN HKEY nnnn mmmm Bytes CTH SBN (FUN 38) 16-KEY INPUT Exec.time (µs) Function DMnnnn: DM0000 to Measures pulse-to-pulse DM1985 interval & pulse width in mmmm: specified mode. 1000 to 1912 3000 to 9912 ITVL SBN nn NEXT Operand value DMnnnn: DM No. mmmm: R No. SUBROUTINE ENTRY REPEAT END Operand Visual KV Series nnnn: Input R mmmm: Output R nnnn: 0000 to 415 mmmm: 0500 to 915 Reads 16-key data by time-sharing and outputs these data into special utility Rs 2900 to 2915. Number of bytes represents the memory capacity required for each instruction. Number in ( ) represents the memory capacity required for object code of each instruction. All operand values are shown in normal notation. The corresponding relay numbers in X-Y-M notation are shown below: Normal notation 0000 to 0415 0500 to 0915 1000 to 6915 7000 to 17915 X-Y-M notation X000 to X04F Y050 to Y09F M1000 to M6915 X700 to X174F or Y750 to Y179F Chapter 2 Instructions 3-37 12 2.1 Instruction List Visual KV Series 2.1.3 Arithmetic Instructions Instruction DATA MEMORY WRITE TRIMMER SETTING Symbol Mnemonic nnnn DW DMmmmm DW n TMIN TMIN (FUN 50) Operand value nnnn: #/$ constant DMmmmm: DM No. nnnn: #0000 to #65535 $0000 to $FFFF DMmmmm: DM0000 to DM1999 Writes constant into data memory. 0 to 1 Inputs value set by access window’s digital trimmer (0 to 65535) to internal register. Trimmer No. n TMIN nnnn LDA LOAD A nnnn LDA @TMIN @(FUN 50) 0000 to 17915 T000 to T249 C000 to C249 LDA CTH0 to CTH1 (FUN 23) R No., DM0000 to C/T No., DM1999 DM No, TM00 to TM31 TM xx, #00000 to #/$ constant, #65535 @LDA #TMxx $0000 to $FFFF @(FUN 23) #TM00 to #TM29 2 STA (FUN 42) nnnn STA STORE A nnnn STA @STA @(FUN 42) nnnn CMP CMP (FUN 04) nnnn CMP @CMP @(FUN 04) nnnn ADD ADD (FUN00) R No., C/T No., DM No., TM xx, #TMxx 0500 to 1915 2100 to 17915 T000 to T249 C000 to C249 CTH0 to CTC3 DM0000 to DM1999 TM00 to TM29 #TM00 to #TM29 COMPARE ADD nnnn ADD nnnn SUB SUBTRACT nnnn SUB DM0000 to DM1999 TM00 to TM31 @ADD #00000 to @(FUN 00) DM/TM No. #65535 TMxx, $0000 to #/$ constant, $FFFF SUB #TMxx #TM00 to (FUN 46) #TM29 @SUB @(FUN 46) nnnn MUL MUL (FUN 28) nnnn MUL @MUL @(FUN28) MULTIPLY • • 3-38 Function Operand Inputs value specified by operand into internal register or inputs current value when T/C is specified as operand. Transfers content of internal register to location specified by operand, or changes preset value when T/C is specified as operand. Compares content of internal register and value specified by operand. Exec.time (µs) Bytes Page 8.0 5 (8) 3-136 8.9 1 (6) 3-138 20.9 1 (16) 6.4 to 14.0 3 (8) 3-140 18.4 to 26.0 3 (18) 6.6 to 28.5 3 (8) 3-140 18.0 to 40.5 3 (18) 10.8 to 35.6 3 (6) 3-146 22.8 to 47.6 Adds content of internal 9.4 to 34.2 register and value specified by operand and inputs result back to 21.4 to 46.2 same register. Subtracts value specified 10.8 to 35.6 by operand from content of register and inputs result back to same 22.8 to 47.6 register. Multiplies content of 14.4 to 38.1 internal register by value specified by operand and inputs result back to 26.4 to 50.1 same register. 3 (16) 3 (6) 3-150 3 (16) 3 (6) 3-150 3 (16) 3 (6) 3-150 3 (16) Number of bytes represents the memory capacity required for each instruction. Number in ( ) represents the memory capacity required for object code of each instruction. Chapter 2 Instructions 2.1 Instruction List Instruction Symbol nnnn DIV DIVIDE nnnn DIV nnnn ANDA AND A nnnn ANDA nnnn ORA OR A nnnn ORA nnnn EORA EXCLUSIVE OR A nnnn EORA SHIFT RIGHT A SHIFT LEFT A Mnemonic Operand DM0000 to DM1999 TM00 to TM31 R No., #00000 to DM No., #65535 TM xx, $0000 to #/$ constant, @DIV $FFFF #TMxx @(FUN 11) #TM00 to #TM29 DIV (FUN 11) ANDA (FUN 01) 0000 to 17915 DM0000 to DM1999 @ANDA R No., TM00 to TM31 @(FUN 01) DM No., #00000 to TM xx, #65535 #/$ constant, ORA $0000 to #TMxx (FNC 31) $FFFF #TM00 to @ORA #TM29 @(FUN 31) 0000 to 17915 DM0000 to DM1999 R No., TM00 to TM31 DM No., #00000 to TM xx, #65535 #/$ constant, $0000 to #TMxx @EORA $FFFF @(FUN 15) #TM00 to #TM29 EORA (FUN 15) #dd SRA SRA (FNC 41) #dd SRA @SRA @(FUN 41) #dd SLA SLA (FNC 40) #dd SLA @SLA @(FUN 40) #dd RRA RRA (FUN 37) #dd RRA @RRA @(FUN 37) #dd RLA RLA (FUN 35) ROTATE LEFT A #dd RLA @RLA @(FUN 35) • • • Exec.time (µs) Function 17.4 to 43.3 Divides content of internal register by value specified by operand and inputs result back to same 29.4 to 55.3 register. ANDs each of 16 bits of 8.2 to 33.1 internal register and that of value specified by operand, and inputs result 20.2 to 45.1 back to same register. ORs each of 16 bits of 8.2 to 33.1 internal register and that of value specified by operand, and inputs result 20.2 to 45.1 back to same register. EXCLUSIVE-ORs each of 16 bits of internal register and that of value specified by operand, and inputs result back to same register. Moves content of internal register serially right by value specified by operand. Moves content of internal register serially left by value specified by operand. # constant ROTATE RIGHT A Operand value Visual KV Series 8.2 to 33.1 Bytes Page 3 (6) 3-150 3 (16) 3 (8) 3-159 3 (18) 3 (8) 3-161 3 (18) 3 (8) 3-164 20.2 to 45.1 3 (18) 9.3 to 27.6 2 (6) 12 3-166 21.3 to 39.6 2 (16) 9.2 to 27.6 2 (6) 3-166 21.2 to 39.6 2 (16) #01 to #16 10.3 to 28.6 Rotates contents of internal register and carry bit (2009) clockwise by operand value. 22.3 to 40.6 10.3 to 28.6 Rotates contents of internal register and carry bit (2009) counterclock22.3 to 40.6 wise by operand value. 2 (6) 3-169 2 (16) 2 (6) 3-169 2 (16) Number of bytes represents the memory capacity required for each instruction. Number in ( ) represents the memory capacity required for object code of each instruction. All operand values are shown in normal notation. The corresponding relay numbers in X-Y-M notation are shown below: Normal notation 0000 to 0415 0500 to 0915 1000 to 6915 7000 to 17915 X-Y-M notation X000 to X04F Y050 to Y09F M1000 to M6915 X700 to X174F or Y750 to Y179F Chapter 2 Instructions 3-39 2.1 Instruction List Instruction Visual KV Series Symbol Mnemonic COM COM (FUN 05) COMPLEMENT INCREMENT MEMORY DECREMENT MEMORY MULTIPLEXER COM @COM @(FUN 05) nnnn INC INC (FNC 19) nnnn INC @INC @(FUN 19) nnnn DEC DEC (FNC 07) nnnn DEC @DEC @(FUN 07) #n MPX MPX (FUN 27) #n MPX @MPX @(FUN 27) DMX DMX (FUN 12) DMX @DMX @(FUN 12) TBCD TBCD (FUN 47) TBCD @TBCD @(FUN 47) TBIN TBIN (FUN 48) TBIN @TBIN @(FUN 48) Operand DM/TM No. # constant 2 TRANSFER BCD TRANSFER BIN ASC ASC (FUN 02) ASC @ASC @(FUN 02) RASC RASC (FUN 32) RASC @RASC @(FUN 32) ROOT ROOT (FUN 36) ROOT @ROOT @(FUN 36) ASCII CONVERT REVERSE ASCII CONVERT SQUARE ROOT • • • Exec.time (µs) Bytes 5.6 1 (4) 3-171 17.6 1 (14) 9.8 3 (6) 21.8 3 (16) 10.4 3 (6) 22.4 3 (16) DM0000 to DM1999 TM00 to TM29 Adds 1 to content of data memory specified by operand. DM0000 to DM1999 TM00 to TM29 Subtracts 1 from content of data memory specified by operand. 10.1 1 (6) #0 to #3 Converts 4-bit data (specified by operand) of internal register into 16-bit data. 22.1 1 (16) Converts position of highest order bit with 1 in internal register into 4-bit data. 22.6 1 (4) 34.6 1 (14) Converts content of internal register (16-bit binary) into 4-digit BCD data. 5.6 1 (4) 17.6 1 (14) 9.6 1 (4) 21.6 1 (14) 9.7 1 (4) 21.7 1 (14) 9.3 1 (4) 21.3 1 (14) 95.7 1 (4) 107.7 1 (14) Converts content of internal register (4-digit BCD) into 16-bit binary data. Converts content of lower order 8 bytes of internal register into 2-digit ASCII code. Converts 2-digit ASCII code of internal register into 2-digit numerical value. Takes square root of 32bit data (TM00: higher order byte, internal register: lower order byte) and inputs result back to same register. Page 3-172 3-172 3-176 3-176 3-180 3-180 3-183 3-183 3-185 Number of bytes represents the memory capacity required for each instruction. Number in ( ) represents the memory capacity required for object code of each instruction. All operand values are shown in normal notation. The corresponding relay numbers in X-Y-M notation are shown below: Normal notation 0000 to 0415 0500 to 0915 1000 to 6915 7000 to 17915 3-40 Function Inverts content of each bit in internal register. DM/TM No. DEMULTIPLEXER Operand value Chapter 2 Instructions X-Y-M notation X000 to X04F Y050 to Y09F M1000 to M6915 X700 to X174F or Y750 to Y179F (OUTPUT) 2.1 Instruction List Visual KV Series 2.1.4 Interrupt Instructions Instruction Symbol Mnemonic INTERRUPT DISABLED DI DI (FUN 08) INTERRUPT ENABLED EI EI (FUN 13) INT nnnn INT CTCn RETI R No. 000 to 003 Comparator No. CTC0 to CTC3 RETI (FUN 34) • • • Exec.time (µs) Bytes Page Disables execution of interrupt. 2.2 1 (12) 3-193 Enables execution of interrupt. 4.0 1 (10) 3-193 Executes interrupt instructions between INT and RETI at rising/falling edge of input relays 0000 through 0003. 60.0 to 90.0 1 (8) 3-192 Used with comparators CTC0 to CTC3 and executes instructions between INT and RETI. 60.0 to 90.0 1 (8) 3-192 Represents end of interrupt. 18.0 to 22.0 1 (4) 3-192 Function Operand value INT (FUN 20) INTERRUPT RETURN INTERRUPT Operand Number of bytes represents the memory capacity required for each instruction. Number in ( ) represents the memory capacity required for object code of each instruction. All operand values are shown in normal notation. The corresponding relay numbers in X-Y-M notation are shown below: Normal notation 0000 to 0415 0500 to 0915 1000 to 6915 7000 to 17915 X-Y-M notation X000 to X04F Y050 to Y09F M1000 to M6915 X700 to X174F or Y750 to Y179F 2.1.5 Function No. List (Alphabetical order) The following list shows the function Nos. used to enter instructions with the KVP3E(01) handheld programmer. ➮ Function No. Instruction Refer to "Chapter 6 Handheld Programmer" on page 1-195 for details. Function No. Instruction Function No. Instruction Function No. Instruction 00 ADD 13 EI 26 MEMSW 39 SFT 01 ANDA 14 ENDS 27 MPX 40 SLA 02 ASC 15 EORA 28 MUL 41 SRA 03 CALL 16 FOR 29 NEXT 42 STA 04 CMP 17 HKEY 30 NOP 43 STE 05 COM 18 HSP 31 ORA 44 STG 06 CON 19 INC 32 RASC 45 STP 07 DEC 20 INT 33 RET 46 SUB 08 DI 21 JMP 34 RET1 47 TBCD 09 DIFD 22 KEEP 35 RLA 48 TBIN 10 DIFU 23 LDA 36 ROOT 49 TMH 11 DIV 24 MC 37 RRA 50 TMIN 12 DMX 25 MCR 38 SBN 51 TMS 52 UDC Reference: To find function No. assigned to desired function: 1. Press the [FUN] key. 2. When the cursor appears at the position where the function No. is to be entered, press the ON or OFF key and scroll the functions and assigned Nos. to find the desired function. Chapter 2 Instructions 3-41 12 KV-300 KV-300 Series, Series, KV-10/80 2.2 Instruction List 2.2 Instruction List • • • KV-300 Series, KV-10/80 Number of bytes represents the memory capacity required for each instruction. Number in ( ) represents the memory capacity required for object code of each instruction. Abbreviations: R: Relay, T: Timer, C: Counter, #: Decimal, $: Hex. 2.2.1 Basic Instructions KV-10/16/24/40/80 Instruction Symbol KV-10/16/24/40/80 Mnemonic Operand Operand value Operand value Exec.time Bytes KV-10/16 (µs) KV-24/40/80 nnnn LOAD LOAD BAR nnnn AND BAR 2 1.5 to 2.5 3 (4) Connects N.O. contact to bus. 3-57 LDB 2.1 to 3.5 3 (6) Connects N.C. contact to bus. 3-57 AND 1.5 to 2.5 R No. T/C No. ANB 0000 to 2915 T000 to T063 C000 to C063 CTC0 to CTC3 0000 to 6915 T000 to T119 C000 to C119 2.7 to 4.5 CTC0 to CTC3 OR nnnn OR 1.5 to 2.5 OR BAR nnnn ORB 2.7 to 4.5 AND LOAD ANL 1.0 to 1.4 OR LOAD ORL 1.0 to 1.4 nnnn OUT OUT 0500 to 1915 2009 2300 to 2915 nnnn OUT BAR OUB nnnn SET (SET) nnnn RESET (RES) 0.1-s TIMER #ddddd T xxx SET R No. 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 2915 T000 to T063 C000 to C063 CTH0 to CTH1 CTC0 to CTC3 RES 5.2 to 8.4 0500 to 1915 2009 2300 to 6915 6.4 to 10.4 3 (17) ON/OFF status to R coil. 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 6915 T000 to T119 3.1 to 24.0 3 (8) C000 to C119 CTH0 to CTH1 CTC0 to CTC3 TMR 17.0 to 22.0 2 (5) T No., # preset value 000 to 063 #00000 to #65535 #ddddd H xxx TMH (FNC49) 1-ms TIMER #ddddd S xxx TMS (FNC51) COUNTER #ddddd C xxx nnnn C # preset value, C No., clock source R #00000 to 65535 000 to 063 0000 to 6915 UP-DOWN COUNTER UP #ddddd DW RES UDC (FNC52) C No., # preset value 000 to 063 #00000 to #65535 3-42 Connects N.O. contact in series with previous contact. Connects N.C. contact 3 (8) in series with previous contact. Connects N.O. contact 3 (4) in parallel with previous contact. Connects N.C. contact 3 (8) in parallel with previous contact. Connects in series 1 (2) blocks made of one or more contacts. Connects in parallel 1 (2) blocks made of one or more contacts. Outputs input ON/OFF 3 (13) status to R coil. Outputs inverted input 3 (4) 000 to 119 #00000 to #65535 17.0 to 22.0 2 (5) 17.0 to 22.0 2 (5) Chapter 2 Instructions 3-58 3-58 3-60 3-60 3-61 3-63 3-65 3-65 0500 to 1915 0500 to 1915 2009 2009 Forces R ON and holds 2100 to 2915 2100 to 6915 3.1 to 23.0 3 (8) this status when input is 3-66 T000 to T063 T000 to T119 ON. C000 to C063 C000 to C119 0.01-s TIMER UDC xxx Page LD nnnn nnnn AND Function #00000 to #65535 19.0 to 21.0 4 (7) 000 to 119 0000 to 6915 000 to 119 #00000 to #65535 21.0 to 26.0 2 (5) Forces R/T/C OFF when input is ON. 16-bit on-delay T that counts down in 0.1-s decrements. 16-bit on-delay T that counts down in 0.01-s decrements. 16-bit on-delay T that counts down in 1-ms decrements. 3-66 3-67 3-68 3-69 Sets 16-bit up-counter. 3-72 Sets a 16-bit up-down counter. 3-76 2.2 Instruction List Instruction Symbol DIFFERENTIATE UP nnnn DIFU DIFFERENTIATE DOWN KEEP KEEP (FNC22) R No. 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 2915 SFT (FNC39) R No.1st & last R Nos. 1000 to 1915 HSP (FNC18) R No. (KV-10) 0000 to 0005 (KV-16) 0000 to 0009 D nnnn CLK RES mmmm HIGH SPEED HSP MASTER CONTROL MC nnnn SFT nnnn MCR MEMSW $xxxx $xxxx NOP END END HI 1000 to 1915 DIFD (FNC09) SHIFT MEMORY SWITCH DIFU (FNC10) nnnn DIFD SET RES MASTER CONTROL RESET KV-10/16/24/40/80 Operand value Mnemonic Operand Operand value Exec.time Bytes KV-10/16 (µs) KV-24/40/80 R No. KEEP END ENDH KV-300 Series, KV-10/80 1000 to 1915 3000 to 6915 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 6915 1000 to 19153000 to 6915 (KV-24) 0000 to 0015 (KV-40) 0000 to 0107 Page Turns ON R for 1 11.0 to 13.0 3 (5) scan time at rising edge of input. Turns ON R for 1 11.0 to 13.0 3 (5) scan time at falling edge of input. Turns ON R and 9.0 to 26.0 3 (5) holds this status when SET input is ON. 5 (7) Turns OFF R when RESET input is ON. (*) 8.0 to 9.0 MC (FNC24) 1.8 to 3.2 MCR (FNC25) 0.6 to 1.0 MEMSW $ constant (FNC26) Function 3 (4) 3-78 3-78 3-80 3-82 Sets shift register. 3-86 Reduces input relay time 1 (7) constant to 25 ms for higher input response. Selects ON/OFF 1 (2) status of R coils, Ts, or Cs. Represents end of MC. Sets memory switches. 3-89 3-89 –– 3 (0) NOP (FNC30) –– Performs no opera1 (0) tion. 3-94 END –– 1 (3) Indicates end of each routine of program. 3-94 ENDH –– Indicates end of entire 1 (0) program. 3-94 $ 0000 to $ FFFF 3-92 KV-300 KV-300 Instruction Symbol Exec.time Bytes (µs) Function Page LD 0.15 to 0.70 3 (5) Connects N.O. contact to bus. 3-57 LDB 0.15 to 0.90 3 (7) Connects N.C. contact to bus. 3-57 Mnemonic Operand Operand value nnnn LOAD nnnn LOAD BAR nnnn AND AND BAR AND R No. T/C No. nnnn ANB 0000 to 0009 0500 to 17915 T000 to T249 C000 to C249 CTC0 to CTC3 0.15 to 0.50 3 (4) 0.15 to 0.80 3 (8) OR nnnn OR 0.15 to 0.50 3 (4) OR BAR nnnn ORB 0.15 to 0.80 3 (8) AND LOAD ANL 0.55 1 (3) OR LOAD ORL 0.55 1 (3) Connects N.O. contact in series with previous contact. Connects N.C. contact in series with previous contact. Connects N.O. contact in parallel with previous contact. Connects N.C. contact in parallel with previous contact. Connects in series blocks made of one or more contacts. Connects in parallel blocks made of one or more contacts. Chapter 2 Instructions 3-58 3-58 3-60 3-60 3-61 3-63 3-43 12 2.2 Instruction List KV-300 KV-300 Series, Series, KV-10/80 KV-300 Instruction Symbol Mnemonic Operand Operand value Exec.time Bytes (µs) 0500 to 1915 2009 2300 to 17915 0.20 to 0.56 nnnn OUT OUT nnnn OUB OUT BAR nnnn (SET) SET nnnn RESET (RES) 0.1-s TIMER #ddddd T xxx SET RES #ddddd H xxx TMH (FNC49) 1-ms TIMER #ddddd S xxx TMS (FNC51) COUNTER #ddddd C xxx nnnn C UP-DOWN COUNTER UP #ddddd DW RES UDC xxx Forces R/T/C OFF 0.50 to 4.40 3 (12) when input is ON. # preset value, C No., clock source R C No., UDC (FNC52) # preset value 000 to 249 #00000 to 65535 #00000 to #65535 000 to 249 0000 to 0009 0500 to 17915 7.60 to 9.45 000 to 249 #00000 to #65535 8.00 to 11.60 2 (10) Sets a 16-bit up-down counter. DIFU FNC10) DIFFERENTIATE DOWN nnnn DIFD DIFD (FNC09) KEEP KEEP (FNC22) R No. SFT (FNC39) 1st & last R Nos. 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 17915 1000 to 1915 3000 to 6915 (*) 7000 to 9915 HSP (FNC18) R No. 0000 to 0009 R No. SHIFT D nnnn CLK RES mmmm nnnn SFT HSP HIGH SPEED nnnn 16-bit on-delay T that counts down in 0.1-s decrements. 16-bit on-delay T that 5.60 to 10.40 2 (7) counts down in 0.01-s decrements. 16-bit on-delay T that 5.60 to 10.40 2 (7) counts down in 1-ms decrements. 5.60 to 10.40 2 (7) T No., # preset value 3-65 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 17915 T000 to T249 C000 to C249 CTH0 to CTH1 CTC0 to CTC3 nnnn DIFU SET RES Outputs inverted input 0.50 to 1.20 3 (11) ON/OFF status to R coil. 3-65 Forces R ON and holds 3-66 0.20 to 5.70 3 (12) this status when input is ON. DIFFERENTIATE UP KEEP Outputs input ON/OFF status to R coil. Page 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 17915 T000 to T249 C000 to C249 TMR 0.01-s TIMER 2 R No. 3 (8) Function 1000 to 1915 3000 to 6915 (*) 7000 to 9915 4 (7) Sets 16-bit up-counter. 3-66 3-67 3-68 3-69 3-72 3-76 Turns ON R for 1 scan 3 (10) time at rising edge of input. Turns ON R for 1 scan 3 (10) time at falling edge of 6.70 input. Turns ON R and holds 6.10 to 7.90 3 (11) this status when SET input is ON. 3-78 6.40 to 8.20 5 (15) Turns OFF R when RESET input is ON. 3-82 6.70 4.66 to 4.92 3-78 3-80 3 (8) Sets shift register. 3-86 Reduces input relay time 1 (4) constant to 25 ms for higher input response. 3-89 MASTER CONTROL MC MC (FNC24) 0.20 MASTER CONTROL RESET MCR MCR (FNC25) — 1 (0) Selects ON/OFF status of R coils, Ts, or Cs. 3-89 MEMORY SWITCH MEMSW $xxxx $xxxx — 3 (0) Represents end of MC. Sets memory switches. 3-92 NOP (FNC30) — 1 (0) Performs no operation. 3-94 END 0.95 1 (1) Indicates end of each routine of program. 3-94 ENDH — 1 (0) Indicates end of entire program. 3-94 NOP END END HI END ENDH MEMSW $ constant (FNC26) $0000 to $FFFF Note: 14.0 + 3.0 x (n) to 17.0 + 3.0 x (n) (n represents number of times the original data is generated.) 3-44 Chapter 2 Instructions 2.2 Instruction List KV-300 Series, KV-10/80 2.2.2 Application Instructions KV-10/16/24/40/80 Instruction Symbol KV-10/16/24/40/80 Mnemonic Operand Operand value Operand value Exec.time Bytes (µs) KV-10/16 KV-24/40/80 nnnn ON mmmm W-ON WAIT OFF nnnn OFF mmmm W-OFF WAIT UP EDGE nnnn ↑ mmmm W-UE WAIT DOWN EDGE nnnn ↓ mmmm W-D WAIT ON nnnn: 0000 to 2915 T000 to T063 nnnn: C000 to C063 R,T, or C CTC0 to CTC3 No. mmmm: 1000 to 1915 nnnn: 0000 to 6915 T000 to T119 C000 to C119 CTC0 to CTC3 mmmm: 1000 to 1915 3000 to 6915 11.0 to 13.0 11.0 to 13.0 14.0 to 18.0 14.0 to 18.0 CONNECT CON [FNC 06] 0.4 to 0.6 PUSH MPS 11.0 to 14.0 READ MRD 8.0 to 10.0 POP MPP 10.0 to 12.0 nnnn STG STG [FNC 44] 11.0 to 14.0 JUMP nnnn JMP JMP [FNC 21] END STAGE ENDS ENDS [FNC 14] STEP STP nnnn STP [FNC 45] STAGE R No. STEP END STE ITVL SUBROUTINE ENTRY SUBROUTINE RETURN DM0000 to DM1985 1000 to 1912 3000 to 6912 3-96 3-98 3-98 3-102 3-103 Reads input status and 1 (3) arithmetic flag stored with 3-103 PUSH. Reads & clears input status 1 (3) and arithmetic flag stored with 3-103 PUSH. Executes instructions between 3 (7) STG & JMP when R 3-106 (operand) is ON. 1 (3) Turns current stage OFF when 3-106 input is ON. 3.7 to 5.3 Executes program between 3 (7) STP & STE when R (operand) 3-114 is ON. 0.00 DM0000 to DM0985 1000 to 1912 1 (3) Stores input status and arithmetic flag. 3-96 7.0 to 9.0 29.0 to 79.0 Clock source Rs 0004 2100 to 2102 9.0 to 39.0 #ddddd CTCn CTC n: Comparator No. ddddd: # preset value n: 0,1 ddddd: #00000 to #00255 3.0 to 4.0 CTH1 nnnn CTH Clock source Rs 0005 2200 to 2202 8.0 to 48.0 #ddddd CTCn CTC n: Comparator No. ddddd: # preset value n: 2,3 ddddd: #00000 to #65535 3.0 to 4.0 nn CALL CALL [FNC 03] Subroutine No. 00 to 99 8.0 to 10.0 SBN nn SBN [FNC 38] Subroutine No. 00 to 99 0.00 RET RET [FNC 33] CTH0 nnnn SUBROUTINE CALL STE [FNC 43] Turns ON R (2nd operand 5 (7) [mmmm]) when R, T, or C (1st operand [nnnn]) turns ON. When R, T, or C (1st operand 5 (7) [nnnn]) turns OFF, R (2nd operand [mmmm]) turns ON. R (2nd operand [mmmm]) 5 (7) turns ON at rising edge of R, T, or C (1st operand [nnnn]). R (2nd operand [mmmm]) 5 (7) turns ON at falling edge of R, T, or C (1st operand [nnnn]). Represents series connection 301 of output instruction together with another instruction. Turns current stage OFF and 3 (5) next stage ON when input is ON. CTH 8-BIT COUNTER 16-BIT COUNTER COMPARATOR 0000 to 6915 T000 to T119 C000 to C119 CTC0 to CTC3 Page 10.0 to 13.0 DM & R No. PLS nnnn DM PAUSE mmmm RES 16-BIT COUNTER 0000 to 2915 T000 to T063 C000 to C063 CTC0 to CTC3 1000 to 1915 3000 to 6915 ITVL INTERVAL TIMER 8-BIT COUNTER COMPARATOR R, T, C Nos. 1000 to 1915 Function 3-106 1 (0) Is used with STEP to make program step. 3-114 Measures pulse-to-pulse 5 (7) interval & pulse width in specified mode. 3-117 8-bit (0 to255) up-counter for 4 (4) clock pulses with input response frequency of 10 kHz. Hardware-based comparator between preset & current 2 (5) values of high speed counter. This comparator is turned ON when these values are equal. 16-bit (0 to 65535) up-counter 4 (4) for clock pulses with input response frequency of 10 kHz. Hardware-based comparator between preset & current 2 (5) values of high speed counter. This comparator is turned ON when these values are equal. 3-277 3-277 3-204 3-204 2 (6) Executes subroutine specified by operand. 3-122 Represents beginning of 2 (0) subroutine specified by operand. 3-122 4.6 to 6.2 1 (5) Represents end of subroutine. 3-122 Chapter 2 Instructions 3-45 12 2.2 Instruction List Instruction Symbol KV-300 KV-300 Series, Series, KV-10/80 Mnemonic Operand REPEAT START FOR nnnn FOR [FNC 16] REPEAT END NEXT NEXT [FNC 29] HKEY nnnn mmmm 16-KEY INPUT HKEY [FNC 17] # constant, DM No. KV-10/16/24/40/80 Operand value Operand value Exec.time Bytes KV-10/16 (µs) KV-24/40/80 Function Page #00000 to #00000 to #65535 #65535 DM0000 to 5.0 to 20.0 3 (15) DM0000 to DM1999 DM0999 TM00 to TM29 TM00 to TM29 Executes program between FOR & NEXT for number of times specified by operand. 3-125 1 (3) Represents end of repetition. 3-125 5 (7) Reads 16-key data by time-sharing and outputs these data into 3-131 special utility Rs 2900 to 2915. 1.7 to 2.3 I/O R nnnn:0000 to 0009 10000 to 10415 : 17000 to 17415 mmmm:10500 to 10915 : 17500 to 17915 71 to 370 KV-300 KV-300 2 Instruction Symbol Mnemonic Operand WAIT ON nnnn ON mmmm W-ON WAIT OFF nnnn OFF mmmm W-OFF WAIT UP EDGE nnnn ↑ mmmm W-UE WAIT DOWN EDGE nnnn ↓ mmmm W-DE nnnn: R,T, or C No. Operand value nnnn: 0000 to 0009 0500 to 17915 T000 to T249 C000 to C249 CTC0 to CTC3 mmmm: 1000 to 1915 3000 to 6915 (*)7000 to 9915 Exec.time Bytes (µs) Function Turns ON R (2nd operand [mmmm]) when R, T, or C (1st operand [nnnn]) turns ON. When R, T, or C (1st operand 5.00 to 6.10 5 (9) [nnnn]) turns OFF, R (2nd operand [mmmm]) turns ON. R (2nd operand [mmmm]) 6.10 to 7.50 5 (10) turns ON at rising edge of R, T, or C (1st operand [nnnn]). R (2nd operand [mmmm]) 6.10 to 7.50 5 (10) turns ON at falling edge of R, T, or C (1st operand [nnnn]). Represents series connection — 1 (0) of output instruction together with another instruction. 5.00 to 6.10 5 (9) CONNECT CON [FNC 06] PUSH MPS 1.30 1 (9) READ MRD 2.70 Reads input status and 1 (18) arithmetic flag stored with PUSH. POP MPP nnnn STG STAGE STG [FNC 44] R No. JUMP nnnn JMP JMP [FNC 21] END STAGE ENDS ENDS [FNC 14] STEP STEP END INTERVAL TIMER 16-BIT COUNTER 3-46 STP nnnn STP [FNC 45] STE STE [FNC 43] ITVL PLS nnnn DM PAUSE mmmm RES CTH0 nnnn R, T, C Nos. 1000 to 1915 3000 to 6915 (*)7000 to 9915 0000 to 0009 0500 to 6915 (*)7000 to 9915 T000 to T249 C000 to C249 CTC0 to CTC3 ITVL DM & R No. DMnnnn: DM0000 to DM9985 mmmm: 1000 to 1912 3000 to 6912 (*)7000 to 9912 CTH Clock source Rs 0004 2100 2101 2102 Chapter 2 Instructions Stores input status and arithmetic flag. Page 3-96 3-96 3-98 3-98 3-102 3-103 3-103 Reads & clears input status 3-103 and arithmetic flag stored with PUSH. Executes instructions 5.60 to 6.50 3 (10) between STG & JMP when R 3-106 (operand) is ON. Turns current stage OFF and 3.80 to 6.00 3 (7) next stage ON when input is 3-106 ON. 1.40 1 (9) — 1 (0) Turns current stage OFF when input is ON. 3-106 1.30 3 (9) Executes program between STP & STE when R (operand) is ON. 3-114 — 1 (0) Is used with STEP to make program step. 3-114 13.80 to 17.30 3.85 Measures pulse-to-pulse 5 (11) interval & pulse width in specified mode. 4 (7) 3-117 16-bit (0 to 65535) up-counter for clock pulses with input 3-204 response frequency of 30 kHz. 2.2 Instruction List KV-300 Series, KV-10/80 KV-300 Instruction Symbol Mnemonic Operand Operand value Exec.time Bytes (µs) CTC n: Comparator No. ddddd: # preset value n: 0, 1 ddddd: #00000 to #65535 CTH Clock source Rs 0005 2200 2201 2202 CTC n: Comparator No. ddddd: # preset value n: 2, 3 ddddd: #00000 to #65535 — CALL Subroutine [FNC 03] No. 00 to 99 3.16 SBN nn SBN [FNC 38] 00 to 99 — RET RET [FNC 33] REPEAT START FOR nnnn FOR [FNC 16] REPEAT END NEXT NEXT [FNC 29] 16-BIT COUNTER COMPARATOR #ddddd CTCn 16-BIT COUNTER CTH1 nnnn 16-BIT COUNTER COMPARATOR #ddddd CTCn SUBROUTINE CALL nn CALL SUBROUTINE ENTRY SUBROUTINE RETURN 16-KEY INPUT HKEY nnnn mmmm HKEY [FNC 17] Subroutine No. #00000 to #65535 DM0000 to DM9999 TM00 to TM29 — 16-bit (0 to 65535) up4 (7) counter for clock pulses with input response frequency of 30 kHz. 3.85 1.55 — I/O R nnnn:0000 to 0009 10000 to 10415 : 17000 to 17415 mmmm:0500 to 0503 10500 to 10915 : 17500 to 17915 16.50 Page Hardware-based comparator between preset & current 2 (0) values of high speed counter. 3-204 This comparator is turned ON when these values are equal. 3-204 Hardware-based comparator between preset & current 2 (0) values of high speed counter. 3-204 This comparator is turned ON when these values are equal. 2 (17) Executes subroutine specified by operand. 1.15 to 1.45 # constant, DM No. Function 3-122 Represents beginning of 2 (0) subroutine specified by operand. 3-122 Represents end of subroutine. 3-122 Executes program between 3 (19) FOR & NEXT for number of times specified by operand. 3-125 1 (6) 1 (0) Represents end of repetition. 3-125 Reads 16-key data by time5 (9) sharing and outputs these data into special utility Rs 2900 to 2915. Chapter 2 Instructions 3-131 3-47 12 2.2 Instruction List KV-300 KV-300 Series, Series, KV-10/80 2.2.3 Arithmetic Instructions KV-10/16/24/40/80 Instruction DATA MEMORY WRITE Symbol nnnn < DW > DMmmmm n < TMIN > TRIMMER SETTING KV-10/16/24/40/80 Mnemonic Operand Operand value Operand value Exec.time Function Bytes KV-10/16 (µs) KV-24/40/80 #00000 to #0000 to #65535 #65535 #/$ $0000 to $0000 to 3.6 to 6.0 5 (6) Writes constant into constant, DW data memory. $FFFF $FFFF DM No. DM0000 to DM0000 to DM0999 DM1999 TMIN [FNC 50] @TMIN ↑ TMIN > @[FNC 50] Trimmer No. 0 to 1 n nnnn < LDA > LOAD A nnnn ↑ LDA > 2 nnnn < STA > STORE A nnnn ↑ STA > nnnn < CMP > COMPARE nnnn ↑ CMP > nnnn < ADD > ADD nnnn ↑ ADD > nnnn < SUB > 0000 to 2915 T000 to T063 C000 to C063 LDA R No., CTH0 to CTH1 [FNC 23] C/T No., DM0000 to DM/TM DM0999 No., TM00 to TM31 #/$ #00000 to constant, #65535 @LDA $0000 to #TMxx @[FNC 23] $FFFF #TM00 to #TM29 R No., C/T No., DM/TM No., #/$ @STA constant, @[FNC 42] #TMxx STA [FNC 42] CMP [FNC 04] nnnn ↑ SUB > nnnn < MUL > MULTIPLY nnnn ↑ MUL > nnnn < DIV > SUB [FNC 46] @SUB @[FNC 46] ↑ DIV > @DIV @[FNC 11] Chapter 2 Instructions Inputs value specified by operand into internal register or inputs current value when T/C is specified as operand. 3-136 3-138 3-140 Transfers content of internal register to location specified by operand, or changes preset value when T/ C is specified as operand. 3-140 14.0 to 68.0 3 (5) Compares content of internal register and value specified by 26.0 to 82.0 3 (12) operand. 3-146 Adds content of 13.0 to 65.0 3 (5) internal register and value specified by operand and inputs 25.0 to 79.0 3 (12) result back to same register. Subtracts value 15.0 to 68.0 3 (5) specified by operand from content of register and inputs 27.0 to 82.0 3 (12) result back to same register. DM0000 to DM0000 to DM0999 DM1999 TM00 to TM31 TM00 to TM31 MUL #00000 to #00000 to 17.0 to 71.0 3 (5) [FNC 28] DM/TM #65535 #65535 No., $0000 to $0000 to #/$ No., @MUL $FFFF $FFFF 29.0 to 85.0 3 (12) @[FNC 28] #TMxx #TM00 to #TM00 to #TM29 #TM29 DIV 22.0 to 79.0 3 (5) [FNC 11] DIVIDE nnnn 0500 to 1915 2100 to 2915 T000 to T063 C000 to C063 DM0000 to DM0999 TM00 to TM29 #TM00 to #TM29 13.0 to 15.0 1 (4) Converts trimmer rotation angle into 0 to 249 and inputs it 25.0 to 29.0 1 (11) into internal register. 0000 to 6915 T000 to T119 C000 to C119 10.0 to 46.0 3 (5) CTH0 to CTH1 DM0000 to DM1999 TM00 to TM31 #00000 to #65535 22.0 to 60.0 3 (12) $0000 to $FFFF #TM00 to #TM29 0500 to 1915 2100 to 6915 T000 to T119 9.0 to 99.0 3 (5) C000 to C119 DM0000 to DM1999 TM00 to TM29 21.0 to 113.0 3 (12) #TM00 to #TM29 DM0000 to DM0000 to DM1999 DM0999 DM/TM TM00 to TM31 TM00 to TM31 @CMP #00000 to #00000 to No., @[FNC 04] #65535 #65535 #/$ $0000 to $0000 to constant, ADD $FFFF $FFFF #TMxx [FNC 00] #TM00 to #TM00 to #TM29 #TM29 @ADD @[FNC 00] SUBTRACT 3-48 0 Page Multiplies content of internal register by value specified by operand and inputs result back to same register. Divides content of internal register by value specified by operand and inputs 34.0 to 93.0 3 (12) result back to same register. 3-150 3-150 3-150 3-150 2.2 Instruction List Instruction Symbol nnnn <ANDA> AND A nnnn ↑ANDA> nnnn < ORA > OR A nnnn ↑ ORA > EXCLUSIVE OR A SHIFT RIGHT A 0000 to 2915 0000 to 6915 DM0000 to DM0000 to DM0999 DM1999 @ANDA TM00 to TM31 TM00 to TM31 R No., @[FNC 01] #00000 to DM/TM No., #00000 to #65535 #/$ No., #65535 ORA $0000 to #TMxx $0000 to [FNC 31] $FFFF $FFFF #TM00 to #TM00 to @ORA #TM29 #TM29 @[FNC 31] #dd < SRA > SRA [FNC 41] #dd @SRA @[FNC 41] #dd SLA [FNC 40] < SLA > #dd < RRA > #dd RLA [FNC 35] Moves content of internal register serially right, allowing each bit 3-169 that leaves right end to 24.0 to 44.0 2 (11) enter carry bit and then leftmost bit. Moves content of 12.0 to 29.0 2 (4) internal register serially left, allowing each bit 3-169 that leaves left end to 24.0 to 43.0 2 (11) enter carry bit and then rightmost bit. 12.0 to 30.0 2 (4) < COM > COM [FNC 05] ↑ COM > @COM @[FNC 05] 17.0 to 20.0 1 (10) INC [FNC 19] 12.0 to 15.0 3 (5) nnnn < INC > nnnn ↑ INC > nnnn < DEC > nnnn ↑ DEC > #n MULTIPLEXER #01 to #16 @RLA @[FNC 35] COMPLEMENT < MPX > 5.0 to 6.0 DM/TM No. ↑ MPX > 3-171 DM0000 to DM0000 to DM0999 DM1999TM00 TM00 to TM29 to TM29 14.0 to 17.0 3 (5) @DEC @[FNC 07] MPX [FNC 27] @MPX @[FNC 27] Inverts content of each bit in internal register. Subtracts 1 from content of data memory specified by 26.0 to 31.0 3 (12) operand. Converts 4-bit data (specified by operand) of internal 36.0 to 39.0 1 (11) register into 16bit data. 3-172 24.0 to 25.0 1 (4) # constant #n 1 (3) Adds 1 to content of data memory 3-172 24.0 to 29.0 3 (12) specified by operand. @INC @[FNC 19] DEC [FNC 07] 12 Moves content of internal register 3-166 serially left by value 22.0 to 42.0 2 (11) specified by operand. ↑ RLA > #dd 3-166 10.0 to 28.0 2 (4) RRA [FNC 37] @RRA @[FNC 37] < RLA > DECREMENT MEMORY ANDs each of 16 bits of internal register and that of value specified 3-159 by operand, and inputs 23.0 to 78.0 3 (12) result back to same register. ORs each of 16 bits of 11.0 to 63.0 3 (5) internal register and that of value specified 3-161 by operand, and 23.0 to 77.0 3 (12) inputs result back to same register. 11.0 to 64.0 3 (5) Moves content of internal register serially right by value specified by 23.0 to 42.0 2 (11) operand. @SLA @[FNC 40] #dd ↑ RRA > INCREMENT MEMORY Page 11.0 to 28.0 2 (4) # constant #dd ROTATE LEFT A Function 0000 to 2915 0000 to 6915 DM0000 to DM0000 to 10.0 to 63.0 3 (5) EXCLUSIVE-ORs <EORA> DM0999 DM1999 each of 16 bits of R No., TM00 to TM31 TM00 to TM31 internal register and DM/TM No., #00000 to #00000 to 3-164 that of value #/$ No., #65535 #65535 specified by operand, #TMxx $0000 to $0000 to and inputs result @EORA nnnn $FFFF $FFFF 22.0 to 77.0 3 (12) back to same ↑EORA> @[FNC 15] #TM00 to #TM00 to register. #TM29 #TM29 EORA [FNC 15] ↑ SLA > ROTATE RIGHT A KV-10/16/24/40/80 Operand value Operand value Exec.time Bytes KV-10/16 (µs) KV-24/40/80 ANDA [FNC 01] nnnn ↑ SRA > SHIFT LEFT A Mnemonic Operand KV-300 Series, KV-10/80 #0 to #3 Chapter 2 Instructions 3-176 3-49 2.2 Instruction List Instruction Symbol DMX [FNC 12] ↑ DMX > @DMX @[FNC 12] <TBCD> TBCD [FNC 47] ↑ TBCD> @TBCD @[FNC 47] < TBIN > TBIN [FNC 48] ↑ TBIN> @TBIN @[FNC 48] < ASC > ASC [FNC 02] ↑ ASC > @ASC @[FNC 02] <RASC> RASC [FNC 32] TRANSFER BIN ASCII CONVERT REVERSE ASCII CONVERT 2 Function Page 28.0 to 30.0 1 (3) Converts position of highest order bit with 1 in internal register 40.0 to 44.0 1 (10) into 4-bit data. 3-176 Converts content of internal register (16bit binary) into 4-digit 31.0 to 35.0 1 (10) BCD data. 3-180 19.0 to 21.0 1 (3) 18.0 to 20.0 1 (3) Converts content of internal register (4digit BCD) into 16-bit 30.0 to 34.0 1 (10) binary data. 8.0 12.0 to 14.0 ROOT [FNC 36] 3-183 1 (3) Converts 2-digit ASCII code into one byte data. 24.0 to 28.0 1 (10) 3-183 Takes square root of 32bit data (TM00: higher order byte, internal register: lower order 1 (10) byte) and inputs result back to same register. 3-185 102.0 to 103.0 @ROOT ↑ ROOT> @[FNC 36] 3-180 1 (3) Converts content of lower order byte of internal register into 20.0 to 22.0 1 (10) 2-digit ASCII code. @RASC ↑ RASC> @[FNC 32] <ROOT> SQUARE ROOT KV-10/16/24/40/80 Operand value Mnemonic Operand Operand value Exec.time Bytes KV-10/16 (µs) KV-24/40/80 < DMX > DEMULTIPLEXER TRANSFER BCD KV-300 KV-300 Series, Series, KV-10/80 114.0 to 117.0 1 (3) KV-300 KV-300 Instruction Symbol DATA MEMORY WRITE nnnn < DW > DMmmmm n TRIMMER SETTING < TMIN > DW @TMIN ↑ TMIN > @[FNC 50] < LDA > LOAD A nnnn ↑ LDA > nnnn < STA > STORE A nnnn ↑ STA > #/$ constant, DM No. Operand value nnnn: #0000 to #65535 $0000 to $FFFF DMmmmm: DM0000 to DM9999 TMIN [FNC 50] n nnnn 3-50 Mnemonic Operand Trimmer No. LDA [FNC 23] R No., C/T No., DM/TM No., #/$ @LDA @[FNC 23] constant, #TMxx STA [FNC 42] R No., C/T No., DM/TM No., #/$ @STA constant, @[FNC 42] #TMxx Chapter 2 Instructions 0, 1 Exec.time Bytes (µs) 0500 to 1915 2100 to 17915 T000 to T249 C000 to C249 CTC0 to CTC3 DM0000 to DM9999 TM00 to TM29 #TM00 to #TM29 Page 0.60 to 1.40 5 (11) Writes constant into data memory. 3-136 5.10 to 5.60 1 (11) Converts trimmer rotation angle into 0 to 249 and inputs it into 1 (25) internal register. 3-138 2.00 to 5.70 0000 to 0009 0500 to 17915 T000 to T249 C000 to C249 CTH0 to CTH1 DM0000 to DM9999 TM00 to TM31 #00000 to #65535 $0000 to $FFFF #TM00 to #TM29 Function 0.30 to 28.00 3 (12) 2.30 to 30.00 3 (26) 0.20 to 30.00 3 (12) Transfers content of internal register to location specified by 3-140 operand, or changes preset value when T/C 3 (26) is specified as operand. 2.20 to 32.00 Inputs value specified by operand into internal register or inputs 3-140 current value when T/C is specified as operand. 2.2 Instruction List KV-300 Series, KV-10/80 KV-300 Instruction Symbol nnnn < CMP > Mnemonic Operand Operand value Exec.time Bytes (µs) 9.20 to 36.00 CMP [FNC 04] COMPARE nnnn ↑ CMP > nnnn < ADD > @CMP @[FNC 04] ADD [FNC 00] ADD DM/TM No., #/$ constant, #TMxx DM0000 to DM9999 TM00 to TM31 #00000 to #65535 $0000 to $FFFF #TM00 to #TM29 11.20 to 38.00 7.70 to 35.00 9.70 to 37.00 nnnn SUB [FNC 46] 8.40 to 35.00 nnnn @SUB @[FNC 46] 10.40 to 37.00 nnnn MUL [FNC 28] SUBTRACT ↑ SUB > < MUL > MULTIPLY DM/TM No., #/$ No., #TMxx DM0000 to DM9999 TM00 to TM31 #00000 to #65535 $0000 to $FFFF #TM00 to #TM29 9.80 to 37.00 nnnn @MUL @[FNC 28] nnnn DIV [FNC 11] 13.70 to 41.00 nnnn @DIV @[FNC 11] 15.70 to 42.00 nnnn ANDA [FNC 01] 6.90 to 33.00 ↑ MUL > < DIV > 11.80 to 39.00 DIVIDE ↑ DIV > <ANDA> AND A nnnn @ANDA @[FNC 01] nnnn < ORA > ORA [FNC 31] nnnn @ORA @[FNC 31] ↑ANDA> OR A ↑ ORA > R No., DM/TM No., #/$ No., nnnn @EORA ↑EORA> @[FNC 15] #TMxx nnnn EXCLUSIVE OR A EORA [FNC 15] R No., DM/TM No., #/$ No., #TMxx <EORA> 0000 to 0009 0500 to 17915 DM0000 to DM9999 TM00 to TM31 #00000 to #65535 $0000 to $FFFF #TM00 to #TM29 8.90 to 35.00 6.90 to 33.00 8.90 to 35.00 0000 to 0009 0500 to 17915 DM0000 to DM9999TM00 to TM31 #00000 to #65535 $0000 to $FFFF #TM00 to #TM29 6.90 to 33.00 8.9 to 35.00 3 (12) Compares content of internal register and value specified by 3 (26) operand. 3-146 Adds content of internal register and value 3-150 specified by operand 3 (26) and inputs result back to same register. @ADD @[FNC 00] < SUB > Page 3 (12) nnnn ↑ ADD > Function Subtracts value 3 (12) specified by operand from content of register and inputs result back 3 (26) to same register. 3-150 Multiplies content of 3 (12) internal register by value specified by operand and inputs 3 (26) result back to same register. 3-150 Divides content of 3 (12) internal register by value specified by 3-150 operand and inputs 3 (26) result back to same register. ANDs each of 16 bits of 3 (12) internal register and that of value specified by 3-159 operand, and inputs 3 (26) result back to same register. ORs each of 16 bits of 3 (12) internal register and that of value specified by operand, and inputs 3-161 3 (26) result back to same register. EXCLUSIVE-ORs each 3 (12) of 16 bits of internal register and that of value 3-164 specified by operand, 3 (26) and inputs result back to same register. Chapter 2 Instructions 3-51 12 2.2 Instruction List KV-300 KV-300 Series, Series, KV-10/80 KV-300 Instruction Symbol #dd @SRA @[FNC 41] 12.80 #dd SLA [FNC 40] 10.80 < SLA > #dd ↑ SLA > 10.80 @SLA @[FNC 40] 12.80 # constant 12.00 @RRA @[FNC 37] 14.00 RLA [FNC 35] 12.00 ↑ RLA > @RLA @[FNC 35] 14.00 < COM > COM [FNC 05] 6.10 #dd ↑ RRA > #dd < RLA > ROTATE LEFT A #dd COMPLEMENT ↑ COM > 2 nnnn < INC > INCREMENT MEMORY nnnn ↑ INC > nnnn DECREMENT MEMORY < DEC > 3-52 Moves content of 2 (11) internal register serially left, allowing each bit that leaves left end to 2 (25) enter carry bit and then rightmost bit. 3-169 1 (9) 7.70 3 (12) @INC @[FNC 19] 9.70 3 (26) 7.70 3 (12) @DEC @[FNC 07] 9.70 #n MPX [FNC 27] 7.30 Inverts content of each bit in internal register. 3-171 Adds 1 to content of data memory specified by operand. 3-172 Subtracts 1 from content of data memory 3-172 3 (26) specified by operand. ↑ MPX > @MPX @[FNC 27] 9.30 1 (11) Converts 4-bit data (specified by operand) of internal register into 1 (25) 16- bit data. < DMX > DMX [FNC 12] 6.70 1 (9) ↑ DMX > @DMX @[FNC 12] < MPX > DEMULTIPLEXER 3-169 INC [FNC 19] DM0000 to DM9999 TM00 to TM29 # constant #n Chapter 2 Instructions #0 to #3 8.70 3-166 Moves content of 2 (11) internal register serially right, allowing each bit that leaves right end to 2 (25) enter carry bit and then leftmost bit. 1 (23) DM/TM No. Page 2 (11) Moves content of internal register serially left by value specified by 3-166 2 (25) operand. 8.10 DEC [FNC 07] Function 2 (22) Moves content of internal register serially right by value specified 2 (25) by operand. @COM @[FNC 05] nnnn ↑ DEC > MULTIPLEXER #01 to #16 RRA [FNC 37] #dd < RRA > ROTATE RIGHT A Exec.time Bytes (µs) SRA [FNC 41] ↑ SRA > SHIFT LEFT A Operand value < SRA > #dd SHIFT RIGHT A Mnemonic Operand Converts position of highest order bit with 1 in internal register into 1 (23) 4-bit data. 3-176 3-176 2.2 Instruction List KV-300 Series, KV-10/80 KV-300 Instruction TRANSFER BCD Symbol Mnemonic <TBCD> TBCD [FNC 47] @TBCD ↑ TBCD> @[FNC 47] Exec.time Bytes (µs) 13.20 15.20 TBIN [FNC 48] 14.00 ↑ TBIN> @TBIN @[FNC 48] 16.00 < ASC > ASC [FNC 02] 8.50 ↑ ASC > @ASC @[FNC 02] 10.50 <RASC> RASC [FNC 32] 6.80 ASCII CONVERT @RASC ↑ RASC> @[FNC 32] <ROOT> SQUARE ROOT Operand value < TBIN > TRANSFER BIN REVERSE ASCII CONVERT Operand Page Converts content of internal register (16-bit binary) into 4-digit BCD 1 (23) data. 3-180 Converts content of internal register (4-digit BCD) into 16-bit binary 1 (23) data. 3-180 1 (9) 1 (9) 1 (9) Converts content of lower order byte of internal register into 21 (23) digit ASCII code. 3-183 1 (9) Converts 2-digit ASCII code into one byte data. 3-183 8.80 ROOT [FNC 36] 77.70 @ROOT 79.70 ↑ ROOT> @[FNC 36] Function 1 (23) Takes square root of 32bit data (TM00: higher order byte, internal 3-185 register: lower order 1 (23) byte) and inputs result back to same register. 1 (9) Chapter 2 Instructions 3-53 12 2.2 Instruction List KV-300 KV-300 Series, Series, KV-10/80 2.2.4 Interrupt Instructions KV-10/16/24/40/80 Mnemonic Operand Function Page Symbol INTERRUPT DISABLED < DI > DI [FNC 08] 3.0 to 4.6 1 (4) Disables execution of interrupt. 3-193 INTERRUPT ENABLED < EI > EI [FNC 13] 3.0 to 4.6 1 (4) Enables execution of interrupt. 3-193 INT nnn R No. RETI 1 (8) Comparator No. INT CTCn RETURN INTERRUPT 35.0 to 48.0 000 to 003 INT [FNC 20] INTERRUPT 2 KV-10/16/24/40/80 Operand value Operand value Exec.time Bytes KV-10/16 (µs) KV-24/40/80 Instruction Used with comparators CTC0 to CTC3 3-192 and executes instructions between INT and RETI. 35.0 to 48.8 CTC0 to CTC3 RETI [FNC 34] 20.0 to 23.0 Executes instructions between INT and RETI at rising edge of any of input 3-192 000 to 003 or at falling edge of 003. 1 (3) Represents end of interrupt. 3-192 KV-300 KV-300 Mnemonic Operand Exec.time Bytes (µs) Instruction Symbol INTERRUPT DISABLED < DI > DI [FNC 08] 3.20 INTERRUPT ENABLED < EI > EI [FNC 13] 5.80 INT nnn R No. INT CTCn 3-54 000 to 003 Function Page 1 (9) Disables execution of interrupt. 3-193 1 (0) Enables execution of interrupt. 3-193 40.00 to 80.00 1 (0) Executes instructions between INT and RETI at rising edge 3-192 of any of input 000 to 003 or at falling edge of 003. 40.00 to 80.00 1 (0) 60 to 100 1 (0) INT [FNC 20] INTERRUPT RETURN INTERRUPT Operand value RETI Comparator No. RETI [FNC 34] Chapter 2 Instructions CTC0 to CTC3 Used with comparators CTC0 to CTC3 3-192 and executes instructions between INT and RETI. Represents end of interrupt. 3-192 2.3 Convention Details 2.3 Convention Details In this chapter, each instruction is described as follows: Ladder symbol Represents the form of the instruction on a ladder diagram. Instruction key Represents the key or function No. for entry. Instruction Describes the name and brief function of the instruction. SET / RES 2.4 Instruction Details SET: Set Mnemonic Represents the instruction in ladder language. RES: Reset SET 1 RES 0 Example • Example • Timing diagram • Description Perform programming using the given example to gain experience. : nnnn SET : nnnn RES Turns ON specified relay when input is ON and enables this relay to remain ON. Turns OFF specified relay, timer, or counter when input is ON. 0000 0500 SET 0001 0500 RES Coding Line No. Instruction LD 0000 0001 SET 0500 0002 LD 0001 0003 OUB 0500 Description • Output relay 0500 remains ON after input relay 0000 turns OFF. Output relay 0500 turns OFF when input relay 0001 turns ON. SET instruction sets a latch whereas RES instruction resets it. RES instruction not only turns OFF relay coils but serves as a reset signal when a timer or counter is used as an operand. • • 2 0001 #00100 C000 00000 C000 RES 0002 Note Describes the notes for the instruction. 0001 0002 Coding Shows the coding for the given example. #00100 C000 0000 Note: The SET and RES instructions can be entered in any order. Note, however, that priority is given to the instruction that is entered last. In the above example, when both 0000 and 0001 are ON, RES has priority over SET, causing 0500 to remain OFF. Tips Differences between SET/RES and KEEP Basically , SET/RES and KEEP (➮ p. 3-57 and p. 3-71) serve the same purpose. • SET and RES can be used separately. Therefore, RES can be placed before SET. Another instruction may be placed between SET and RES. • KEEP needs only three lines of program, therefore saving memory space when used a number of times. Tips Describes hands-on techniques for efficient programming. Operand Shows operands (element Nos.) that can be used for the instruction. Operand 0000 0000 0500 RES 0001 0500 SET LD RES LD SET 0000 0000 0500 0001 0500 KEEP SET 0500 0001 LD 0000 LD 0001 KEEP 0500 RES Operands NEW KV KV-300 KV-10/16 KV-24/40/80 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 17915 T000 to T249 C000 to C249 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 17915 T000 to T249 C000 to C249 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 2915 T000 to T063 C000 to C063 0500 to 1915 2009 2100 to 6915 T000 to T119 C000 to C119 CTH0 to CTH1 (RES only) CTC0 to CTC3 (RES only) Key operation Describes the basic key operations on the handheld programmer. Set the mode switch to PROGRAM. Key operation SET 1 3-66 Operand ENT R-SRCH RES 0 Operand ENT R-SRCH Chapter 2 Instructions * The above page is created for explanation purposes only. This page may be different from the actual page. Chapter 2 Instructions 3-55 12