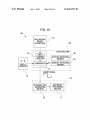
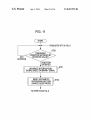
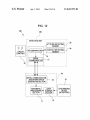
Download Image capturing device and activation method therefor
Transcript
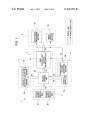
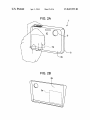
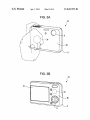
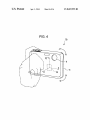
US 8,687,955 B2 Page 2 (56) References Cited US PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,827,347 5,008,497 5,287,138 5,701,527 A A A A 5,708,882 A 5,729,289 A 5,845,161 A 5,900,856 A 5/1989 4/1991 2/1994 12/1997 Bell Asher Shiokama et a1‘ Sakabe et a1‘ V1998 Yokonumaet a1‘ 3/1998 Etoh 12/1998 Schrocket al. 5/1999 Iino et a1. 2004/0240867 A1* 12/2004 Hara ............................. .. 396/55 2005/0219228 A1 10/2005 Alameh et al. 2005/0228320 A1 10/2005 Klinghult 2006/0022955 A1* 2/2006 Kennedy ..................... .. 345/173 2006/0092010 2006/0202925 2007/0030137 2007/0086764 5/2006 9/2006 2/2007 4/2007 Simon etal. Manning et a1. Masters et al. Konicek A1 A1 A1 A1 2007/0257890 A1* 11/2007 Hotelling etal. ........... .. 345/173 2008/0278454 A1 11/2008 Lee etal. FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 5,923,908 A * 7/1999 5,949,484 A * 9/1999 Nakaya etal. . 348/384.1 JP 2000-2094g5 A 7/2000 6,016,407 A * 1/2000 Tsukahara .................. .. 396/302 JP 2000-333055 A 11/2000 JP JP JP JP JP JP 2002_290g02 2003474640 2004-005320 2004420204 2005-072g0g 2006462974 10/2002 9/2003 1/2004 4/2004 3/2005 6/2006 6,148,148 6,298,197 6,459,424 6,492,979 6,519,419 6,558,050 6,628,336 6,888,574 A B1 B1 B1 B2 B1 B2 Schrock et al. ............... .. 396/85 11/2000 10/2001 10/2002 12/2002 2/2003 5/2003 9/2003 Wain et al. Wain etal. Resman Kent etal. Shimada etal. Ishibashi Hamamura 5/2005 Asakura B1 7,102,626 B2 9/2006 Denny, III 7,123,829 B2 10/2006 Ohsuga et a1~ 7,283,738 B2 * 10/2007 Ohsuga et 31' lgg‘rkrllligiet a1‘ """""""" " 348/352 834983531 B2 * A A A A A OTHER PUBLICATIONS Minolta MaXXum Dynax 3X1 Instruction Manual, 1991, Part 1. Minolta MaXXum Dynax 3X1 Instruction Manual, 1991, Part 2. Nikon Digital CameraE300 CoolPiX 300 User’s Manual. 70013 Sakurai ““““““““““““ “ 396/303 Of?ce Action from European Search Report EP 06252534, dated 2003/0063073 A1 4/2003 Geaghan etal. P69212911 2003/0081142 A1* 5/2003 Iijima ......................... .. 348/372 Sony Che Handbook, 2001 2003/0199995 A1 10/2003 Ishiiet al. 2004/0201772 A1 10/2004 Kobayashi * cited by examiner US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 2 0f 16 FIG. 2A FIG. 2B US 8,687,955 B2 US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 3 0f 16 FIG. 3A FIG. 3B US 8,687,955 B2 US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 4 0f 16 FIG. 4 US 8,687,955 B2 US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 6 6f 16 US 8,687,955 B2 FIG. 6 POWER-SUPPLY OPERATION SIGNAL OPERATION SIGNAL OR DETECTION SIGNAL? DETECTION SIGNAL S4 \’\ NO SIGNAL I NORMAL PROCESSING ( BACKGROUND PROCESSING CAPABLE OF IMAGE CAPTURING YES v OPERATIOIIIIPOETIIITAIGCEFSIGNAL ‘85 PROCESSING SECTION SHUTTER OPERATING SIGNAL RECEIVED? IMAGE CAPTURING CI-IANGING TO STATE POWER-SUPPLY SIGNAL RECEIVED IN PREDETERMINED TIME? NO 5S2 ) AWAIT RECEPTION (TIMEOUT MODE) US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 7 0f 16 US 8,687,955 B2 FIG. 7 CONTACT DETECTING SENSOR ATTITUDE DETECTING SENSOR -I;J I ___________I ANALOG SIGNAL A/D CONVERTER —> COMPARATOR INTERRUPTION SIGNAL ARITHMETIC PROCESSING SECTION DATA STORAGE SECTION DATA WRITING DEVICE (IN SHIPPING) / 1s 17 US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 8 0f 16 US 8,687,955 B2 FIG. 8 FROM STEP ST7 IN FIG. 9 ST1 NOT SATISFIED THRESHOLD CONDITION SATISFIED BY DETECTED VALUE? CONDITION SATISFIED GENERATE INTERRUPTION SIGNAL I RESET ARITHMETIC PROCESSING SECTION (CANCEL SLEEP MODE) I TO STEP ST4 IN FIG. 9 5T3 5 US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 9 0f 16 US 8,687,955 B2 FIG. 9 ST8 > CANCEL SLEEP MODE OF ARITHMETIC PROCESSING SECTION FROM STEP ST3 IN FIG. 8 I ST4 POWER SUPPLY OPERATION SIGNAL RECEIVED? i ST9 / II NORMAL PROCESSING BACKGROUND PROCESSING S 8T5 (CHANGING TO STATE CAPABLE) OF IMAGE CAPTURING II ST6 II COMPLETION OF OPERATION 5 $T10 OF SYSTEM COMPONENT POWER-SUPPLY SIGNAL RECEIVED IN PREDETERMINED TIME? NO AWAIT RECEPTION (TIMEOUT MODE) II NO Sm SET ARITHMETIC PROCESSING 5 3T7 SECTION TO SLEEP MODE SHUTTER OPERATING SIGNAL I RECEIVED? TO STEP ST1 IN FIG. 8 IMAGE CAPTURING II ( END ) 5 Sm US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 10 0f 16 US 8,687,955 B2 FIG. 10 12A\ DATADEVICE WRITING / 18 (IN SHIPPING) 1,13A I ‘I j 16 i‘ ' \.\ DATA I \ i DETECTING UNIT i I STORAGE |__ ATTITUDE DETECTING ' T CIRCUIT ' i’ COMPARATOR‘L i CONTACT DETECTING SENSoR k I \\ , | I CoNSTANT - I I \ I L ________________ ._1.5_ ______________________ _I BINARY SIGNAL 19 I | /./ 4b TTTTTT —-—'—'—-—-—-—-—'—-—'—-—-—-—-—-—I : Y i INTERRUPTION i i | GENERATING —> SECTIoN L/ ARITHMETIC I PROCESSING I SECTION : I US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 11 0f 16 US 8,687,955 B2 FIG. 11 FROM STEP ST7 IN FIG. 9 ST20 NOT SATISFIED THRESHOLD CONDITION SATISFIED BY DETECTED VALUE? CONDITION SATISFIED GENERATE INTERRUPTION SIGNAL BASED ON BINARY SIGNAL I RESET ARITHMETIC PROCESSING SECTION (CANCEL SLEEP MODE) I TO STEP ST4 IN FIG. 9 Sm 5 US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 12 0f 16 US 8,687,955 B2 FIG. 12 13B I 1/’ | /'/I DETECTING UNIT I I T i |_ ATTITUDE DETECTING f | I I ' | CIRCUIT CONSTANT SENSOR I CONTACT DETECTING / | ' i l - SERIAL i i SENSOR I —————— —-— \15 I , I I l i _______________________________ __| ------------------- TI ' AND-INTERRUPTION- I GENERATING SECTION I ,, 4b I I’ ! SERIAL-COMMUNICATION- ' . | TTT _ I/ N22 I I 18 X | I I ! ARITHMETIC I I PROCESSING ‘ sTORAGE <—I— DEvICE SECTION SECTION I (IN SHIPPING) DATA i | I' ___________ 3a : COMMUNICATOR \41 i_ _______ __ ' I ! i > COMPARATO\R; ' 3b ______ _'_\x_'_'_: 16 DATA WRITING US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 13 0f 16 US 8,687,955 B2 FIG. 13 FROM STEP ST7 IN FIG. 9 ST30 NOT SATISFIED THRESHOLD CONDITION SATISFIED BY DETECTED VALUE? CONDITION SATISFIED GENERATE SERIAL COMMUNICATION INTERRUPTION SIGNAL 5ST31 I RESET ARITHMETIC PROCESSING SECTION (CANCEL SLEEP MODE) I TO STEP ST4 IN FIG. 9 Sm 5 US. Patent @ t @ I Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 14 0f 16 US 8,687,955 B2 Q @ A E,.OE EV E EE EE g EE E m US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 15 0f 16 US 8,687,955 B2 FIG. 15 FROM STEP ST7 IN FIG. 9 ST40 NOT SATISFIED THRESHOLD CONDITION SATISFIED BY CONTACT DETECTION VALUE? CONDITION SATISFIED ST41 NOT SATISFIED THRESHOLD CONDITION SATISFIED BY ATTITUDE DETECTION VALUE? CONDITION SATISFIED GENERATE INTERRUPTION SIGNAL I RESET ARITHMETIC PROCESSING SECTION (CANCEL SLEEP MODE) I TO STEP ST4 IN FIG. 9 ST43 5 US. Patent Apr. 1, 2014 Sheet 16 0f 16 US 8,687,955 B2 FIG. 16 ( START ) >= FROM STEP ST? IN FIG. 9 !' ___________________ "KT'TTTUSEI _______________ mmmméb??é? DETECTION I DETECTION! ST50 ST53 THRESHOLD CONDITION SATISFIED BY DETECTED VALUE? ' NOT THRESHOLD CONDITION SATISFIED BY DETECTED VALUE? NOT SATISFIED SATISFIED ST51 /\/ GENERATE INTERRUPTION SIGNAL I SATISFIED SATISFIED ST54 GENERATE INTERRUPTION SIGNAL ST52 | ST55 II II /\/ | RESET ARITHMETIC PROCESSING SECTION PROCESSING RESET ARITHMETIC SECTION i (CANCEL SLEEP MODE) (CANCEL SLEEP MODE) i | | L _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ TO STEP ST4 IN FIG. 9 _ _ _ _ __4 L _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ TO STEP ST4 IN FIG. 9 _ _ _ ___| US 8,687,955 B2 1 2 IMAGE CAPTURING DEVICE AND ACTIVATION METHOD THEREFOR release opportunity include a situation in Which, When the CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED APPLICATIONS poWer of the device is off at the time the user ?nds a desired subject, the user fails to capture an image of a subject due to a long time taken after the user holds the device until the For example, cases in Which the user misses a shutter device is ready for image capturing. In other Words, a time necessary for activation after pressing the poWer supply This application is a continuation of Us. application Ser. No. 13/531,967, ?led on Jun. 25, 2012, Which is a continua tion ofU.S. application Ser. No. 12/380,842, ?led on Mar. 4, 2009, Which is a continuation of Us. application Ser. No. 11/434,542 ?led on May 15, 2006 in the Us. Patent and Trademark O?ice Which claims priority from Japanese Patent Application No. JP 2005-142965 ?led in the Japanese Patent O?ice on May 16, 2005, the entire contents of Which are sWitch is no more than approximately one second, even if the activation is fast, so that it is dif?cult to capture an image of a subject (or the like) passing in a moment. This is because it is dif?cult to reduce the activation time to Zero in an actual device. To prevent the user from missing the shutter release opportunity, the system poWer needs to be continuously on or the device needs to be in a suspend state. The suspend state means a state in Which, although an operation of a control unit incorporated herein by reference. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to a technology, used in an 20 image capturing device, for enhancing its activating function such as a CPU (central processing unit) is stopped, the poWer of each portion of the system is on. As described above, to reduce the activation time close to Zero, an increase in poWer consumption is extremely impor tant and necessary in compensation for the reduction. There fore, When a battery-driven portable device is used, it is nec ality so as not to fail to capture a desired image of a subject or essary for a user to carry many charged batteries or to use a the like and preventing unnecessary poWer consumption in a standby state of the image capturing device before it enters an mass storage battery. In a digital camera or the like, a device image capturing mode. A camera-device con?guration (see, for example, Japanese 25 Unexamined Patent Application Publication No. 2003 274640) is knoWn Which shortens an activation time that is necessary from the time a poWer-on operation is performed poWer-saving function is important for capturing as many images as possible. Thus, shortening of the activation time and the need of poWer saving con?ict With each other. Accordingly, it is desirable to satisfy both an improvement in activating functionality and poWer saving in an image capturing device. on a camera device until the camera device is actually 30 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION sWitched on for use. When a poWer supply switch is operated, chattering in Which intermittent opening and closing of a contact is repeat edly performed occurs, thus causing a false operation, etc. Accordingly, after a time passes until effects of the chattering To solve the above problems, according to an embodiment 35 of the present invention, there is provided an image capturing device including ?rst control means for controlling image disappear, a process (so-called “chattering preventing pro cess”) that determines Whether the poWer supply sWitch is capturing, the ?rst control means having a ?rst poWer con opened or closed is performed. In addition, When it is deter mined that the poWer-on operation has been performed, a means for detecting a change to an image capturing mode and system initialiZing process is performed after poWer supplied by a system’s poWer supply unit becomes stable. After that, sumption; operation means including a sWitch; detecting 40 for sending a signal representing the change to the image capturing mode; second control means for monitoring and processing the signal sent from the detecting means, the sec the camera device is in a state capable of processing such as ond control means having a poWer consumption less than the image capturing. In other Words, it is dif?cult to perform an ?rst poWer consumption; and a poWer supply for supplying operation or processing desired by a user unless a time rep resented by “T1+T2+T3” passes after a poWer-supply opera tion time at Which a poWer-supply operation is performed, Where T1 represents a time necessary for the chattering pre venting process, T2 represents a time necessary until the poWer to the ?rst control means, the second control means, 45 ing by supplying poWer from the poWer supply to portions of poWer supplied by the poWer supply unit becomes stable, and T3 represents a time necessary for the system initialiZing 50 process. Therefore, by performing the chattering preventing pro 55 desired by the user is initiated can be shortened. In other Words, by employing a sequence that performs system initial iZation as background processing for the chattering prevent ing process, after the poWer is supplied to the system, the system can be initialiZed Without Waiting for the chattering preventing process to ?nish. For example, When T1<T3, the According to another embodiment of the present invention, there is provided an activation method for an image capturing device having a function of controlling poWer supplying states including a ?rst poWer control state capable of image capturing, the ?rst poWer control state having a ?rst poWer consumption, and a second poWer control state having a 60 poWer consumption less than the ?rst poWer consumption. The activation method includes, in the second poWer control state, monitoring a sWitch operation and a change to an image capturing mode; and, When the change to the image capturing activation time can be shortened to a time represented by “T2+T3” or approximately a time obtained by adding some value to “T2+T3.” HoWever, the image capturing device of the related art has the image capturing device including the ?rst control means When the second control means receives the signal represent ing the change to the image capturing mode from the detect ing means. cess after turning on the poWer supply sWitch and the system initialiZing process in parallel, an activation time from the poWer-supply operation time until the operation or processing and a functional section of the image capturing device. In the image capturing device, a poWer saving state is changed to a poWer supplying state capable of image captur mode is detected in the second poWer control state, changing the second poWer control state to the ?rst poWer control state. 65 Accordingly, in an embodiment of the present invention, at the folloWing problems in its activating functionality and the time a second control means receives a detection signal poWer saving function. representing a change (changing start) to an image capturing US 8,687,955 B2 4 3 mode, power supply control for enabling image capturing is FIG. 4 is an illustration of attitude detection in a camera performed. After changing to a ?rst power control state, image capturing is immediately initiated. In a second power control state, power is supplied only to the second control means and power does not need to be continuously supplied according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 5 is an illustration of examples of screens for activa tion settings; FIG. 6 is a ?owchart showing a system activating process; FIG. 7 is a block diagram showing a main part of a con to the ?rst control means and the second control means. This contributes to reducing power consumption in a standby state ?guration example; before image capturing. FIG. 8 is a ?owchart showing an example of an activation process; FIG. 9 is a ?owchart showing a process ?ow continued According to an embodiment of the present invention, by initiating preparation for image capturing at the time the setting of an image capturing mode is detected, activating from FIG. 8; FIG. 10 is a block diagram showing a main part of another functionality can be enhanced. In addition, it is not necessary to set a power supplying state capable of image capturing at con?guration example; all times. When image capturing is not performed, by setting FIG. 11 is a ?owchart showing a main part of an example of a standby state having low power consumption, a power sav ing effect can be obtained. In other words, since it is di?icult to reduce an activation time itself to Zero, by changing to the ?rst power control state while using, as a start point, the time a system activation process concerning the con?guration shown in FIG. 10; FIG. 12 is a block diagram showing a main part of still another example con?guration; the change to the image capturing mode is detected, both an improvement in activating functionality and power saving 20 For example, after changing to a power supplying state capable of image capturing, when a power supplying opera vation; tion is not performed, or a signal representing a change to an image capturing mode is not detected, by shutting off power 25 supplied to the ?rst power control means to change to the power saving state, power consumption in the standby state can be reduced. In other words, after changing to the ?rst power control state, when a power supplying operation is not performed, or a signal representing a change to an image a system activation process in a case in which a maximum 30 no intention of image capturing or a high probability of no intention, it is preferable to change to the second power con 35 In an embodiment of the present invention, by immediately controlling power supply when detecting setting of an image capturing mode with a detecting unit such as an electrostatic means for detecting the change to the image capturing mode, when it is detected, as a preliminary image capturing step, that the image capturing device is touched by a user, the device 40 according to a con?guration in which a sensor for detecting a change in the attitude of a body of the device is provided as the detecting means, when it is detected, as a preliminary image capturing step, that the image capturing device is held or moved by the user, the device can be changed to the ?rst power control state. Furthermore, by employing a detecting speed mode is set. DETAILED DESCRIPTION trol state (power saving state). can be changed to the ?rst power control state. Alternatively, FIG. 15 is a ?owchart showing a main part of an example of a system activation process in a case in which a high speed mode is set; and FIG. 16 is a ?owchart showing a main part of an example of capturing mode is not detected, by determining that there is In addition, according to a con?guration in which a sensor for detecting contact with a device is provided as the detecting FIG. 13 is a ?owchart showing a main part of an example of a system activation process concerning the con?guration shown in FIG. 12; FIG. 14 is an illustration of examples of settings for acti can be achieved. 45 sensor or angular velocity sensor, image capturing can be initiated after necessary processing such as initialization. For example, at the time a user holds a camera, supplying of power to each portion of a camera system and an initialiZing process are initiated, whereby it takes almost no waiting time after operating a power supply switch until operating a shutter release button. This can prevent occurrence of a situation in which the user misses a shutter release opportunity. An embodiment of the present invention is widely applicable to form that is a combination of these sensors, detection accu still cameras and camcorders, or to various types of image racy can su?iciently be enhanced. In order to obtain a power saving effect in a standby state in capturing devices that can capture still and moving images. which image capturing is not performed, it is preferable that, FIG. 1 shows an example of a basic con?guration of an 50 image capturing device according to an embodiment of the present invention. An image capturing device 1 includes an operation unit 2 including power supply switches and a detecting unit 3 using 55 nals sent from these sensors are sent and processed in a when the second control means receives a signal representing a change to an image capturing mode from detecting means, a power-supply-instruction signal be sent from the second control means to a power supply after a resting state of the second control means is canceled. an electrostatic sensor, an angular velocity sensor, etc. Sig BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an example of a basic con?guration of an image capturing device according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIGS. 2A and 2B are perspective views showing contact 60 detection in a camera according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIGS. 3A and 3B are illustrations of a different example of the contact detection in a camera according to an embodiment of the present invention; system controller 4. The operation unit 2 includes various types of operation buttons and switches provided on the image capturing device 1. In FIG. 1, only power supply switches 2a and 2b are shown. An operation signal from a power supply switch (or a power switch) serves as a trigger signal for supplying power. When an embodiment of the present invention is applied to, for example, a digital still camera, the number of power supply switches is not limited to one depending on a con?guration 65 form, but there is a system including a plurality of power supply switches. In this embodiment, two switches are shown. US 8,687,955 B2 5 6 The detecting unit 3 is provided to detect a change in mode to an image capturing mode. The detecting unit 3 may have the image capturing device 1. In this embodiment, an image signal processing section 511 and an image display section 5b are shoWn as typical examples. The image signal processing the following forms: (I) form using sensor for detecting contact With image cap turing device 1; section 511 includes an image capturing unit, a camera signal processor, and a recording-and-playback-system signal pro (II) form using sensor for detecting change in attitude of cessor, and performs image capturing, and image recording image capturing device 1; and (III) form Using form (I) and form (II). and playback, and, in the image display section 5b, an LCD (liquid crystal display) panel or the like is used. A poWer supply 6 supplies poWer to the ?rst control unit 4a, the second control unit 4b, and the system con?guration unit At ?rst, in form (I), for example, a contact detecting sensor 311 such as an electrostatic sensor is used. The contact detect ing sensor 311 detects contact of a user With the image captur 5. In application of an embodiment of the present invention, a ing device 1, and sends a signal of the detection to the system poWer supply 611 in Which, for example, a battery (primary controller 4. Excessive detection sensitivity causes a situation in Which slight contact With the image capturing device 1 performs poWer supplying for activation, so that the fre quency of false detection increases, etc. Thus, it is preferable battery or secondary battery), a fuel cell, or the like, is used, and a poWer-supply voltage generating section 6b (such as a to appropriately set the detection sensitivity to ensure contact detection. necessary for each circuit are provided irrespective of the circuit con?guration of the poWer supply 6. The poWer-sup DC-DC converter) for generating a poWer-supply voltage attitude detecting sensor 3b detects a change in device attitude ply voltage generating section 6b supplies poWer to each circuit through poWer-supply lines. In this embodiment, When the poWer supply 611 supplies When the image capturing device 1 is held or moved by the poWer to the poWer-supply voltage generating section 6b in a Also in the above form (II), an attitude detecting sensor 3b, such as an angular velocity sensor or gyrosensor, is used. The 20 state in Which a battery pack or the like is installed in the user, and sends a signal of the detection to the system con troller 4. Cases to Which an embodiment of the present inven tion is applied include a form in Which, not only the angular 25 unit 4b can be immediately performed. The second control unit 4b has poWer consumption less than that of the ?rst control unit 4a. This is because, since the second control unit 4b handles monitoring and processing the velocity sensor, but also an acceleration sensor is used as a sensor capable of measuring a change in speed, and a form in Which detection accuracy is enhanced by using a vibration sensor to increase the number of detection axes. Alternatively, in a camera device having an image stabiliZing function, by 30 using an angular velocity sensor and acceleration sensor pro vided for image stabilization to detect a change in device attitude, a detecting unit can be mounted Without increasing the number of components and expense. Improvement of the detection accuracy includes a method 35 that uses a plurality of sensors of the same type in the above forms (I) and (II), and a method that uses sensors of different types in combination, as in form (III). When determination is multilaterally performed, the latter is more effective. In FIG. 1, for brevity of description, form (III) is assumed, 40 and an example of the detecting unit 3 in Which it includes sensors of plural types is shoWn. In addition, forms of trans mission from the detecting unit 3 to the system controller 4 include analog transmission and digital transmission (includ ing binariZation communication and serial communication), 45 second control unit 4b, a consumption current is set to hun dred microamperes or less. Unlike that, an arithmetic operation unit having a ?xed operating frequency, or an arithmetic operation unit in Which poWer control can be performed by variably controlling an operating frequency is used as the ?rst control unit 4a. When acceleration of processing or the like is preferentially per formed, the poWer consumption of the ?rst control unit 411 of image capturing at all times by performing a poWer-supply operation (by the user) to supply poWer to the ?rst and second control units 411 and 4b, and the system con?guration unit 5, a situation in Which the user misses a shutter release oppor tunity can be avoided. HoWever, poWer consumption in the above case is large, thus shortening a time in Which the image capturing device 1 can be battery-driven. Accordingly, in the a second control unit 4b. The con?guration of the system controller 4 has, for example, the folloWing forms: 50 standby state before image capturing, by supplying poWer from the poWer supply 611 to the second control unit 4b having less poWer consumption, a poWer saving effect can be obtained. circuit; and a form in Which the system controller 4 is formed as a single chip and circuit portions having functions of both control units are formed in the single chip. In either form, the ?rst control unit 411 controls image operation signal and the detection signal, unnecessary poWer consumption is prevented in a standby state before image capturing. When, for example, a microcomputer is used as the increases than that of the second control unit 4b. In other Words, if the image capturing device 1 is set in a mode capable Whose details are described later. The system controller 4 includes a ?rst control unit 411 and a form in Which each control unit is formed as a separate image capturing device 1, poWer supply from the poWer supply voltage generating section 6b to the second control In an embodiment of the present invention, in a poWer 55 saving mode in Which poWer is supplied from the poWer capturing, or recording or playback of captured image data, supply 611 to the poWer-supply voltage generating section 6b, and the second control unit 4b monitors and processes an When the second control unit 4b receives, from the detecting unit 3, a signal representing a change in mode to the image capturing mode, the poWer supply 6 supplies poWer to the ?rst control unit 411 and the system con?guration unit 5, and the poWer saving mode subsequently changes to a poWer supply operation input signal from the operation unit 2 and a detec tion signal from the detecting unit 3. For example, a micro computer or the like may be used as the ?rst control unit 4a. 60 For example, an application speci?c IC (integrated circuit), a microcomputer (used as a sub-computer for a main-computer ing state capable of image capturing. Speci?cally, poWer con used as the ?rst control unit 4a), or the like, may be used as the second control unit 4b. In a system con?guration unit 5 under the control of the trol states of the image capturing device 1 include at least the ?rst control unit 4a, various types of components are used depending on the speci?cations and system con?guration of folloWing states: 65 a ?rst poWer control state (hereinafter referred to as “IS”) in Which the image capturing device 1 is capable of image capturing; and