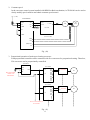
Download Speed Combination/Feed Back Regulator
Transcript
Speed Combination/Feed Back Regulator Operation manual Type:ACE-S08/09 ACE-S Series Auxiliary Controller Type Name Purpose The variation angle, tension, weight and angle bias on two axes detected by synchronization machine can be converted as DC voltage; a converter can be controlled to operate at the same speed, synchronous operation, constant ACE-S02/02B/02C Position Detector tension operation, single-to-synchronous operation. Built-in tilt mechanism can slowly increase or decrease signals set by frequency to reduce the mechanical impact. Can select as a proportional/differential controller. One proportional coupler can connect to six converters and control five proportional (differential) Proportional/Differential couplers. ACE-S04/06 Coupler Built-in tilt mechanism can slowly increase or decrease signals set by frequency to reduce the mechanical impact. The rotational speed of a motor can be converted as converter frequency input through electrical signal by an RPM generator or interceptive pulse generator. Speed Converter/Feed Can be equipped with a potentiometer as constant tension for cloth, line or ACE-S08/09 plastics. Linear and loose conversion can be used with an RPM generator as Back Controller linear control or motor constant control. Built-in tilt mechanism can slowly increase or decrease signals set by frequency to reduce the mechanical impact. ACE-S10 Multi-function Controller ACE-S12 Signal Distributor ACE-S13A/13B Signal Isolation Converter Remote control: Remotely control to start, accelerate, decelerate and stop a converter, and can automatically memorize operation frequency during power failure. Traverse control: Used for transverse equipment, so that can move left or right. PLC multi-step control: Execute procedure control according to the setting phase, and recycle it. Input current can be simultaneously delivered to five sets of output after converted (Current or voltage output can be switched.). For the applications of multiple conversion system, pressure signals can be simultaneously delivered to multiple converters so that achieve constant pressure. Used at a place for output and input conversion (I-I, I-V, V-V and V-I) or isolation. ACE-S13A: The range of current output is DC 0 ~ 20mA. ACE-S13B: The range of current output is DC 4 ~ 20mA. 2 Introduction Thank you for purchasing ACE-S13 controller. Please carefully read this user manual before the installation. In order to correctly operate and use, please attach this user manual on that machine so that can provide the reference of maintenance and service or troubleshooting in the future. Safety Notices Please carefully read this user manual and pay attention to safety notices, symbols or text specified in “DANGER” and “NOTE” prior to performing the installation, wiring, operation, maintenance or troubleshooting. DANGER: Indicates the operation could cause severe injury or death if it doesn’t execute according to instruction on the user manual. NOTE: Indicates the operation could minor injury or product damage if it doesn’t execute according to instruction on the user manual. ※ Although indicates the level of light damage, it could cause severe injury. Only qualified staff can carry out the installation, wiring, trial run or troubleshooting. ※Qualified staff: Those who get familiar with the principle, structure, characteristic, operation procedure and installation of ACE controller to take safety measures and avoid danger as well as carefully read the user manual. 3 Selected power voltage must have the specifications identical to controller input voltage. If wrong voltage is connected, internal control circuit will be burned out. Please pay special attention to that. Wiring between ACE controller and converter should be as short as possible (Heat dissipation should be considered if they are in the same control panel.). Please select appropriate line diameter when wiring main loop power. Ground lines should conform to the third type (ground resistance below 100Ω). Main loop power and control loop lines should be connected to ground point (PE). Signal lines should adopt twisted pair or isolated lines to avoid noise interference, Wiring and and the ground items should be performed. Installation Signal lines should be kept away from high voltage or power lines. Don’t bundle with high power lines. Don’t connect control loop terminals during the power delivery to avoid damage caused by the surge impact. Please confirm power indicators on a panel turn off to perform the removal after the power is disconnected. Please connect according to terminal symbol when wiring, and lock screws to avoid trip. Please recover the upper cover to avoid electric shock after wiring is completed The wiring operations must be performed by the qualified staff. Don’t install at a place where to have high temperature, humidity, oil, lint, iron Ambient Environment powder, copper powder, dust and corrosion. Heat dissipation should be considered when installing in a control panel. The ambient temperature should not be greater than +50℃. 4 Contents Ⅰ. Features ---------------------------- 1 Ⅱ. Specifications ------------------------- 1 Ⅲ. Terminal Definition --------------------- 2 Ⅳ. Terminal Position and Dimension Diagrams -------------- 4 Ⅴ. Connection Diagram ---------------------- 5 Ⅵ. Adjustment ─------------------------ 9 Ⅶ. Installation and Wiring Notices ------------------- 11 Ⅷ. Application Examples ----------------------- 12 5 I. Features: The RPM of a motor is converted as electric signal by a RPM generator or photo-interception pulse generator, which can be used for input signal of converter frequency or provide RPM feedback signal to achieve the effects of converter constant speed and linear speed. A feedback regulator can be equipped with a potentiometer as constant tension for cloth, line or plastics as well as constant linear speed and rolling control of loose conversion. Built-in tilt mechanism can slowly increase or decrease signals set by frequency to reduce the mechanical impact. II. Specifications: Item Power Voltage Power Consumption Frequency Input Description AC 100 ~ 230V, 50/60Hz About 5VA DC 0 ~ 10V input, input impedance 20kΩ Tilt Time Adjustment (adjustable range of acceleration and deceleration) 0 ~ 36 seconds, adjustable (The default is 0 second.) Input adjustment (R) (VR7) adjustment: 0 ~ 3 times (the default is 1 time.) (VR5) and (JP1) adjustment: JP1 is adjusted to L. The adjustable range of VR5 is 0 ~ 2 times. Instantaneous Compensation (P)(=1/proportional zone) (setting when equipped with a generator) JP1 is adjusted to H. The adjustable range of VR5 is 0 ~ 10 times. (setting when equipped with a potentiometer) JP1 is adjusted to H; VR5 is adjusted to 2 times. Delay Compensation Time (I)(= integral time) (VR6) adjustment: 5 ~ 70 seconds. The default is set as 35 seconds AC generator input: Output voltage will be within AC 25V ~ 75V when a RPM generator is at max RPM. Output frequency will be over 60Hz when an RPM generator is at min RPM. Magnetic polarity of an RPM generator needs 24 polarities or more (When a RPM is 1800RPM, output frequency needs over 360Hz.) Speed Feedback Input DC generator input: Output voltage will be within DC 40V ~ 110V when a RPM generator is at max RPM. Input impedance for RPM generator is 30kΩ±2kΩ. Photo-interception generator: Input of pulse frequency: 0 ~ 3.5kHz, 0 ~ 4.5kHz. 0 ~ 9kHz, 0 ~ 50kHz. For frequency input, please refer to Table (1). Voltage level: The Hi and Low level needs over 8.4V and below 1.4V. Input impedance of photo-interception pulse generator is 47kΩ. 1 Remark Item Description Remark Frequency setting output: Frequency output (CMD): DC 0 ~ 10V, 7.5mA (15 converters can be simultaneously connected in parallel.) Output Signal RPM feedback output: RPM feedback output (O/P): DC 0 ~ 10V, 7.5mA (15 converters can be simultaneously connected in parallel.) RPM feedback output (FBK): DC 0 ~ -10V, 1mA Regulating power output: DC 0 ~ 12V, 100mA (max) can be adjusted, and over-current protection loop is equipped. The default is DC10V±0.5V. The range of frequency can be adjusted according to frequency setting when actually operated. Operating location: Installed at a place where no corrosive or conductive gas, liquid and dust exists. Ambient temperature: -10℃ ~ +50℃ (no condensation and freeze) Operating Environment Storage temperature: -20℃ ~ +60℃ Humidity: 90%RH Vibration: Below 5.9m/sec (0.6G) Altitude: Below 1000m (3280ft) III. Terminal Definition: Terminal Name AC1. AC2 PE P15 SET-GI CMD-GI PHI-GI Description Remark Power input terminal: Input voltage AC 100 ~ 230V, 50/60Hz Ground terminal for equipment Power terminal of frequency setting input: If the power of frequency setting input is supplied by converter signal, this terminal will not be connected. Output current ≦15mA. (A potentiometer is connected to P15-SET-GI terminal. The potentiometer impedance needs ≧1kΩ) Frequency setting input terminal: Frequency set at 1kΩ and 1.5W, DC 0 ~ 10V input, input impedance 20kΩ. Frequency setting output terminal: Signal voltage DC 0 ~ 10V; output current ≦7.5mA (15 converters can be simultaneously connected in parallel.) Input terminal of photo-interception pulse generator: Signal voltage level: The Hi and Low level needs over 8.4V (max input voltage Note 1 12V) and below 1.4V. For frequency input, please refer to Table (1). Terminal input impedance 47kΩ 2 Terminal Name TGI-GI FBK-GO Description RPM generator (voltage) input terminal: Remark AC generator input: Output voltage will need within AC 25V ~ 75V when a RPM generator is at max RPM. Output frequency will need over 60Hz when a RPM generator is at min RPM. Magnetic polarity of an RPM generator needs 24 polarities or Note 1 more (When a RPM is 1800RPM, output frequency needs over 360Hz.) DC generator input: Output voltage will be within DC 40V ~ 110V when a RPM generator is at max RPM. Terminal input impedance is 30kΩ±2kΩ. RPM feedback output terminal, signal output from DC 0 ~ -10V, output current ≦1mA. (Output load resistance needs ≧10kΩ.) PM feedback output terminal, signal output from DC 0 ~ 10V, O/P-GO VP. VN output current ≦7.5mA. (15 converters can be simultaneously connected in parallel.) Power output terminal for potentiometer: VP: 7V ~ 15V, internal limit resistance 470Ω VN: -7V ~ -15V, internal limit resistance 470Ω A potentiometer is connected at VP – PI– VN terminals. (Potentiometer resistance needs ≧1kΩ.) PI-GI Error input terminal, voltage input: DC -10V ~ 10V CMB-GI Bias input terminal, voltage input: DC -10V ~ 10V VO-GO RPM feedback output terminal, signal output from DC 0 ~ 10V, output current ≦7.5mA. (15 converters can be simultaneously connected in parallel.) VRP-GO Internal output terminal of regulating power: DC 0 ~ 12V, 100mA (max) can be adjusted, and over-current protection loop is equipped. The default is DC10V±0.5V. The range of frequency can be adjusted according to frequency setting when actually operated. VRI and VRO External output terminal of regulating power Note1: When photo-interception pulse signals are input to PHI-GI, DSW1 will be switched to D; When RPM generator signals are input from TGI-GI, DSW1 will be switched to A. 3 IV. Terminal Position and Dimension Diagrams: Terminals at lower layer Terminals at upper Unit: mm Screw M4-2 Unit: mm Fig. (1) 4 V. Connection Diagram: AC 100 - 230V 50/60HZ R R U S S V T T W 變壓比 Transform ratio 1:1 FWD ACE-S08/09 PE AC1 VR8 ACC P15 SMPS 電位器 SET CMD Signal tilt circuit 信號傾斜電路 GI VR7 R-GAIN JP1 變頻器 Converter VR9 DEC VR10 GAIN VN P15 COM Tilt 傾斜電路調整 circuit adjustment VP Frequency頻率設定輸入 setting input 1k ohm 1.5W 1K ohm 1.5W Potentiometer REV AC2 VR5 P-GAIN HP GI Setting 設定 Vin Gnd 比例帶 Proportion band CMB LP PI VO VR6 I-GAIN GI GO 積分 Integral TS VR3 BIAS DSW2 ON VR1 PH-GAIN PHI 1 FBK 2 Pulse脈波頻率信號 frequency signal 輸入範圍切換 Input switch F/V F/V D DSW1 A O/P GO GI VR2 TGI VRP Level conversion TAC-GAIN 位準轉換 可調式穩壓電源 Regulating power V-ADJ. REG. 0~12V VR4 V-REG VRI VRO GO 雙隔離線 Double-isolation Fig. (2) Connection diagram of speed controller For a converter setting frequency 5 IM TGI GI AC 100 - 230V 50/60HZ R R U S S V T W T 變壓比 Transform ratio 1:1 1:1 FWD ACE-S08/09 PE AC1 VP VR8 ACC P15 VR9 DEC VR10 GAIN P15 VN SET Signal tilt circuit 信號傾斜電路 GI CMD VR7 R-GAIN JP1 COM Tilt傾斜電路調整 circuit adjustment SMPS Frequency 頻率設定輸入 setting input 1k ohm1K1.5W ohm 1.5W Potentiometer 電位器 REV AC2 設定 Setting VR5 P-GAIN HP Converter 變頻器 GI Proportion band 比例帶 CMB LP FBK GO PI VO VR6 I-GAIN GI GO Integral Vin Gnd 積分 TS DSW2 ON PHI GI VR1 PH-GAIN 1 at zero speed FBK 脈波頻率信號 Pulse frequency signal 輸入範圍切換 Input switch F/V F/V D DSW1 A O/P GO 信號 TGI VRP PI 2 轉速發電機 RPM generator signal 零速時短路 Short circuit VR3 BIAS Level 位準轉換 conversion GI VR2 TAC-GAIN Regulating power 可調式穩壓電源 V-ADJ. REG. 0~12V VR4 V-REG VRI VRO GO 雙隔離線 Double-isolation lines Fig. (3) Connection diagram of speed combination Close loop control of motor RPM (RPM generator speed feedback) (DSW1 selects A) 6 TG (PG) IM Photo-interceptiv 光遮斷式脈波 e pulse產生器 generator PHI GI AC 100 - 230V 50/60HZ R R U S S V T T W 變壓比 Transform ratio 1:1 1:1 AC1 頻率設定輸入 1k ohm1K1.5W ohm 1.5W Potentiometer 電位器 COM Tilt 傾斜電路調整 circuit adjustment VR8 ACC P15 SMPS Frequency setting input REV AC2 VP IM FWD ACE-S08/09 PE Encode VR9 DEC VR10 GAIN P15 VN SET Signal tilt circuit 信號傾斜電路 GI CMD VR7 R-GAIN HP JP1 Setting 設定 VR5 P-GAIN 變頻器 Converter GI Proportion band 比例帶 CMB LP FBK GO PI VO VR6 I-GAIN GI Vin GO Gnd 積分 Integral ON 光遮斷式脈 Photo-interceptiv e pulse signal 波信號 GI VR1 PH-GAIN 1 Short circuit at 零速時短路 zero speed VR3 BIAS DSW2 PHI TS FBK 脈波頻率信號 Pulse frequency signal 輸入範圍切換 Input switch F/V F/V D DSW1 A O/P GO TGI VRP PI 2 Level conversion 位準轉換 GI VR2 TAC-GAIN Regulating power 可調式穩壓電源 V-ADJ. REG. 0~12V VR4 V-REG VRI VRO GO 雙隔離線 Double-isolation lines Fig. (4) Connection diagram of speed combination Close loop control of motor RPM (photo-interception pulse generator speed feedback) (DSW1 selects D) 7 AC 100 - 230V 50/60HZ R R U S S V T W T 變壓比 Transform ratio 1:1 1:1 FWD ACE-S08/09 PE AC1 AC2 VP SET VR8 ACC P15 COM VR9 DEC VR10 GAIN VN CMD Signal tilt circuit 信號傾斜電路 GI VR7 R-GAIN JP1 REV Tilt 傾斜電路調整 circuit adjustment SMPS P15 IM HP 設定 Setting VR5 P-GAIN GI Proportion band 比例帶 CMB LP PI VO VR6 I-GAIN GI GO 變頻器 Converter Integral 積分 TS VR3 BIAS DSW2 ON PHI VR1 PH-GAIN 1 FBK 2 脈波頻率信號 Pulse frequency signal 輸入範圍切換 Input switch F/V F/V D DSW1 A GO GI TGI VRP Frequency 頻率設定輸入 setting input 1k ohm 1.5W 1K ohm 1.5W Potentiometer 電位器 O/P VR2 Level conversion TAC-GAIN 位準轉換 Regulating power 可調式穩壓電源 V-ADJ. REG. 0~12V VR4 V-REG VRI VRO GO GO Vin Gnd 雙隔離線 Double-isolation lines Fig. (5) Connection diagram of regulating power setting frequency (VRO output can connect 50 converters in parallel.) 8 VI. Adjustment: 1. Tilt circuit adjustment: 1.1. Built-in tilt mechanism can increase (decrease) the tilt time for frequency setting signals by adjusting VR8 (ACC) and VR9 (DEC) to reduce the mechanical impact. 1.2. VR10 (GAIN) is used to adjust the voltage level between frequency setting input (SET) and frequency setting output (CMD). The gain is adjusted from 0.5 to 1.5. The default for gain is 1. (When frequency setting input is DC 10V, frequency setting output is DC 10V.) 2. Selection of RPM feedback signal (DSW1): 2.1. When RPM feedback signals are input by an RPM generator or other analog signal, DSW1 will be switched to A. 2.2. When RPM feedback signals are input by photo-interception pulses, DSW1 will be switched to D. 3. Selection of photo-interception pulse input frequency (DSW2): 3.1. When photo-interception pulse signals are input, DSW2 will be switched to the appropriate gear in accordance with the full scale of RPM feedback frequency to ensure resolution of RPM feedback signal. 3.2. Table (1) shows DSW2 setting and input frequency when photo-interception pulses are input. Table (1): ACE-S08/09 photo-interception pulse input frequency DSW2#1 DSW2#2 Input Frequency ON ON 0 ~ 3.5 kHz (default) OFF ON 0 ~ 4.5 kHz ON OFF 0 ~ 9 kHz OFF OFF 0 ~ 50 kHz 4. RPM feedback bias VR3 (BIAS): 4.1. It is recommended for bias setting to adjust VR3 (BIAS) and set output terminal O/P or FBK bias when an RPM generator or photo-interception pulse generator stops. 4.2. Bias is adjusted as DC±3V. The default is DC 0V±0.1V. 5. RPM feedback gain VR1(PH-GAIN) or VR2 (TAC-GAIN): 5.1. When RPM feedback signals are input by an RPM generator or other analog signals (DSW1 is switched to A), VR2 (TAC-GAIN) can be used to adjust RPM feedback gain. The default is TGI. When DC 60V is input, O/P output signal is DC 10V±0.1V. 5.2. When RPM feedback signals are input by photo-interception pulses (DSW1 is switched to D), VR1 (PH-GAIN) can be used to adjust RPM feedback gain. The default is PHI. When 1.6 kHz is input (DSW2 selects 0 ~ 3.5 kHz input frequency.), O/P output signal is DC 10V±0.1V. 9 6. Standard speed [R] [VR7]: The adjustment is from 0 to 3 times. The default is 1 time (no adjustment). 7. Proportional band [P gain =1/proportional band] [VR5]: Clockwise rotate to narrow the proportional band. If the proportional band is narrower, the control will hugely change when the feedback value has minor change. With the narrowness of the proportional band, the response will be better. However, the excess and vibration will take place as well stability becomes worse; when adjusting P [VR5], minor rotation will take place so that the control will not occur instability; the proportional band is adjusted from 0 to 2 times and 0 to 10 times by [JP1]. The default is 2 times. 8. Integral time [I] [VR6]: Clockwise rotate to reduce the integral time. The integral time is the time that reaches the same control with proportional action when performing integral action. With the shorter integral time, the time that reaches the setting value will be faster. However, poor stability as described in 7 will be easily occurred. The default is 35 seconds. 9. When actually operating, the larger initial proportional band and longer integral time can be set. You can observe the system to adjust the proportional band and integral time after starting. 10. If the feedback value tested is not stable, the proportional band will be increased; the integral time is increased, so that the full-domain operation and feedback value are stable. If the feedback value tested is stable after starting, the proportional band and integral time can be reduced. However, the full-domain operation and feedback value are kept stable, as shown in Fig. (6). Error Setting value Feedback value Fig. (6) Step-response diagram of PI action 10 Speed setting Motor RPM Motor RPM Motor RPM Motor RPM Fig. (7) Speed characteristics 11. When you set as load, the speed arbitrarily selected will operate. The speed is rapidly changed to observe the rotational response. Because the status changes owing to speed, the optimal setting is selected within high, intermediate and low speed. If speed is greatly and rapidly changed, maximum speed will change below 2 ~ 3% owing to the current limit, as shown in Fig. (7). 11.1. The response of A and B is normal. 11.2. The situation of C is under damping, which should increase the proportional band [P] [VR5 counterclockwise rotate]. If the normal value can’t be obtained, the integral time [I][VR6 clockwise rotate] should be increased to extend response. 11.3. The situation of D is over damping which should decrease the proportional band [P] [VR5 clockwise rotate]. If the normal value can’t be obtained, the integral time [I] [VR6 counterclockwise rotate] should be reduced to respond the time in advance. VII. Installation and Wiring Notices: 1. Notices of potentiometer installation: 1.1. A place where less vibration impact occurs. 1.2. A place where no oil, water and metal powder exists. 1.3. A place where easily maintains a potentiometer. 1.4. Coupling with potentiometer machinery can’t have overload. 2. Swing angle when using a potentiometer: When the distance moves from the lower limit to the upper limit, the swing angle of a potentiometer should be within 60 degrees. When potentiometer resistance is half, it will be used as the central point between the upper and lower limit. 3. Swing direction when using a potentiometer: 3.1. Adjustment at rolling side: When the distance moves from the lower limit to the upper limit, a potentiometer should clockwise rotate. At this time, resistance between pin 1 and 2 of a potentiometer should increase. 3.2. Adjustment at sending side: When moving from the lower limit to the upper limit, a potentiometer should counterclockwise rotate. At this time, resistance between pin 1 and 2 of a potentiometer should decrease. 4. Each RPM input terminal (TGI, PHI and GI) absolutely can’t be connected to local power. Otherwise, internal circuit could be burned out. 5. In order to avoid voltage drop and interference, the wiring distance of each RPM input signal should be as short as possible and isolated lines should be used, so that can correctly detect the speed and position change. 6. If output voltage from an RPM generator has large ripple voltage, ripple voltage of speed feedback output (terminal O/P and GO) will become large. At this time, converter speed will become instable as well. 7. If the number of polarity is less than that of specification when using AC generator as speed feedback, ripples of frequency setting output voltage will become large as well. 8. The length of output signal terminal [VO, GO] and converter frequency terminal [Vin, GND] should be within 3m. 11 VIII. Application Examples: 1. RPM detected by the motor axis side as coupling control: (A) 連動側馬達 Motors at coupling side Main 主速馬達 speed motor 變 頻 器 變 頻 器 IM 變 頻 器 IM Converter Main speed 主 converter 速 IM Converter TAC (PG) 變 Converter ACE-S08/09 IM 頻 器 Fig. (8) Note: If the acceleration and deceleration time of main speed converter is greater than that for inverters at the coupling side, the acceleration and deceleration time of converter at the coupling side will be based on main speed converter, so that can obtain the consistent acceleration and deceleration characteristics. (B) 連動側馬達 Motors at coupling side 主速馬達 Main speed motor Main speed 主 converter 速 變 頻 器 變 頻 器 No.1 No.1 IM1 變 頻 器 No.2 No.2 IM2 變 頻 器 No.3 No.3 IM3 Converter IM Converter Converter TAC (PG) ACE-S08/09 變 Converter 頻 器 No.4 IM4 No.4 ACE-S04/06 變 頻 器 No.5 No.5 Converter IM5 Fig. (9) Note: If the acceleration and deceleration time of main speed converter is greater than that for inverters at the coupling side, owing to the different proportion of each converter, the acceleration and deceleration time of converter at the coupling side will be based on main speed converter, so that can obtain the consistent acceleration and deceleration characteristics set by different frequencies. 12 2. Constant speed: In the converter control system installed with RPM feedback mechanism, ACE-S08/09 can be used to slowly modify speed variation and obtain constant speed control. +5V (+10V) ACE-S08/09 SET Vo Vin GI Go Gnd CMB TS PI UVW IM TG (PG) 變頻器 Converter Short circuit at 零速時短路 zero speed FBK (Power for PG) (PG用電源) VRP GO (PHI) TGI GI Fig. (10) 3. Proportional operation of main speed setting converter: Each proportional controller can be connected with five converters for proportional setting. Therefore, 250 converters can be proportionally controlled. ACE-S08/09 主 速 設 定 Main speed setting 1K 1.5W 1k ohm 1.5W 電位器 Potentiometer ACE-S04/06 VRP VRI Vin VRO GO GI VO1 GO1 VO2 GO2 VO2 GO3 變 Vin Converter Gnd 頻 器 IM 變 Vin Converter Gnd 頻 器 IM ACE-S04/06 Vin GI 50 sets of最多可接50台 ACE-S04/06 can be ACE-S04/06 connected. Fig. (11) 13 VO1 GO1 VO2 GO2 VO2 GO3 4. Application examples of rolling control: 4.1. The sending side is the standard side. The rolling side is the track side. Frequency 頻率設定輸入 setting input 1k ohm 1.5W1.5W 1K ohm Potentiometer 電位器 Converter 1K 1kohm ohm 1.5W 1.5W 電位器 Potentiometer 10kohm ohm1.5W 1.5W 10K Potentiometer 電位器 零速時短路 Short circuit TS Converter at zero speed Fig. (12) 4.2. The sending side is the track side: TS Converter 零速時短路 Short circuit at zero peed 1K ohm1.5W 1.5W 1k ohm 電位器 Potentiometer Frequency setting input 1k 頻率設定輸入 ohm 1.5W 1K ohm 1.5W Potentiometer 10kohm ohm1.5W 1.5W 10K Potentiometer 電位器 電位器 Converter Fig. (13) 14 4.3. Constant speed feedback: Frequency setting input 1k ohm 1.5W 頻率設定輸入 Potentiometer 1K ohm 1.5W 電位器 TS Converter 零速時短路 Short circuit at zero peed FBK Fig. (14) 4.4. No differential speed control: Main converter 頻率設定輸入 1K ohm 1.5W 電位器 Frequency setting input 1k ohm 1.5W Potentiometer TS 零速時短路 Short circuit at zero peed Fig. (15) 15 Converter at following side