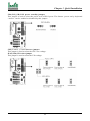
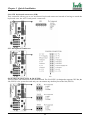
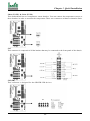
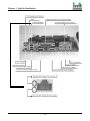
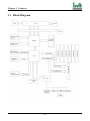
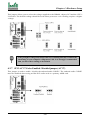
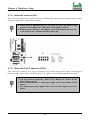
Download Iwill Slot 1 WS133 Motherboard
Transcript
Contents Chapter 1Quick Installation ..................... 3 1.1Layout ....................................................................................... 3 1.2CPU setting ............................................................................... 4 1.3Jumpers ..................................................................................... 5 1.4Expansion Slots / Sockets ........................................................ 8 1.5Connectors .............................................................................. 10 1.6Form Factor ............................................................................ 16 Chapter 2Overview.................................. 17 Chapter 3Features ................................... 20 3.1Motherboard Components Placement................................... 20 3.2Back Panel .............................................................................. 22 3.3Block Diagram ........................................................................ 23 3.4Specifications .......................................................................... 24 Chapter 4Hardware Setup ...................... 26 4.1 Before Installation ................................................................. 26 4.3 Install the Processor .............................................................. 31 4.4 Install Memory Modules ....................................................... 35 4.5 Install PCI Expansion Cards ................................................. 37 4.6 Usage of the AMR slot .......................................................... 38 4.7 Connect Devices and Power Supply ..................................... 39 WS133 Series Rev 1.1B 1 FB2A319201100 Chapter 1 Quick Installation Chapter 5BIOS Setup ............................. 50 5.1 Introduction............................................................................ 50 5.2 Main Menu ............................................................................. 51 5.3 Standard CMOS Features .................................................... 52 5.4 Advanced BIOS Features ..................................................... 54 5.5 Advanced Chipset Features .................................................. 57 5.6 Integrated Peripherals .......................................................... 60 5.7 Power Management Setup .................................................... 65 5.8 PnP/ PCI Configurations ....................................................... 68 5.9 PC Health Status ................................................................... 69 5.10 IWILL Smart Setting .......................................................... 70 5.11 Load Fail-Safe Defaults ...................................................... 72 5.12 Load Optimized Defaults .................................................... 73 5.13 Set Supervisor / User Password Setting ............................ 73 5.14 Save & Exit Setup ............................................................... 73 5.15 Exit Without Saving ............................................................ 73 Chapter 6 Power Installer CD................ 74 6.1 Software Installation ............................................................. 74 6.2 How to use the Power installer CD ...................................... 74 6.3 Installing Operating Systems ................................................ 76 Appendix Install the Suspend to IDE Hard Disk Utility ........................... 78 2 WS133 Series Chapter 1 Quick Installation Chapter 1 Quick Installation Several easy installation steps will be described in this chapter to help the experienced users with quick installation. If you are a beginner, or need to know more about this product, please refer to Hardware Setup. 1.1 Layout WS133 Series 3 Chapter 1 Quick Installation 1.2 CPU setting This motherboard is designed for Intel® Pentium® III, Pentium® II and Celeron™ through a SC242 connector. CPU Model Celeron 266 Celeron 300 Celeron 333 Celeron 366 Celeron 400 Celeron 433 Pentium II 350 Pentium II 400 Pentium II 450 Pentium III 450 Pentium III 500 Pentium III 550 Pentium III 600 Pentium III 533B Pentium III 600B Pentium III 550E Pentium III 600E Pentium III 650E Pentium III 700E Pentium III 533EB Pentium III 600EB Pentium III 667EB Pentium III 733EB Vcore & Package 2.0V, SEPP 2.0V, SEPP 2.0V, SEPP 2.0V, SEPP 2.0V, SEPP 2.0V, SEPP 2.0V, SECC(2) 2.0V, SECC(2) 2.0V, SECC(2) 2.0V, SECC2 2.0V, SECC2 2.0V, SECC2 2.05V, SECC2 2.0V, SECC2 2.0V, SECC2 1.65V, SECC2 1.65V, SECC2 1.65V, SECC2 1.65V, SECC2 1.65V, SECC2 1.65V, SECC2 1.65V, SECC2 1.65V, SECC2 JP3 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 JP3A 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3 2-3 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 “CPU Speed” in BIOS Manual 300Mhz(66x4.5) 333Mhz(66x5) 366Mhz(66x5.5) 400Mhz(66x6) 433Mhz(66x6.5) 350Mhz(100x3.5) 400Mhz(100x4) 450Mhz(100x4.5) 450Mhz(100x4.5) 500Mhz(100x5) 550Mhz(100x5.5) 600Mhz(100x6) 533Mhz(133x4) 600Mhz(133x4.5) 550Mhz(100x5.5) 600Mhz(100x6) 650Mhz(100x6.5) 700Mhz(100x7) 533Mhz(133x4) 600Mhz(133x4.5) 667Mhz(133x5) 733Mhz(133x5.5) This motherboard also can support Socket370 CPUs with Iwill Slocket II transitional card. CPU Model Celeron 300A Celeron 333 Celeron 366 Celeron 400 Celeron 433 Celeron 466 Celeron 500 Celeron 533 Pentium III 500E Pentium III 550E Pentium III 600E Pentium III 650E Pentium III 700E Pentium III 533EB Pentium III 600EB Pentium III 667EB Pentium III 733EB Vcore & Package 2.0V, PPGA 2.0V, PPGA 2.0V, PPGA 2.0V, PPGA 2.0V, PPGA 2.0V, PPGA 2.0V, PPGA 2.0V, PPGA 1.60V, FCPGA 1.60V, FCPGA 1.65V, FCPGA 1.65V, FCPGA 1.65V, FCPGA 1.60V, FCPGA 1.65V, FCPGA 1.65V, FCPGA 1.65V, FCPGA JP3 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 4 JP3A 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 “CPU Speed” in BIOS 300Mhz(66x4.5) 333Mhz(66x5) 366Mhz(66x5.5) 400Mhz(66x6) 433Mhz(66x6.5) 466Mhz(66x7) 500Mhz(66x7.5) 533Mhz(66x8) 500Mhz(100x5) 550Mhz(100x5.5) 600Mhz(100x6) 650Mhz(100x6.5) 700Mhz(100x7) 533Mhz(133x4) 600Mhz(133x4.5) 667Mhz(133x5) 733Mhz(133x5.5) WS133 Series Chapter 1 Quick Installation 1.3 Jumpers JP1 (CMOS) Clear CMOS jumper The jumper is for BIOS setting value. JP3 & JP3A (FSB) CPU FSB select jumper These jumpers allow the selection of the CPU’s based external frequency. The CPU “External Frequency” multiplied by the “Frequency Multiple” equals the CPU’s “Internal Frequency”. Currently, most of the processors have the Frequency Multiple locked, so you only need to select the External Frequency. This motherboard will detect the proper external frequency your CPU used, so you can leave these jumpers on their defaults, and the based external frequency will be determined by CPU automatically. In this case you need not go to BIOS to do setup. If you want to have some further setting, the CPU speed is setup using “IWILL Smart Setting”. This is found in the BIOS setup program by pressing <Del> during the boot up process. WS133 Series 5 Chapter 1 Quick Installation JP6 (PS2_SB) PS/2 power standby jumper This jumper is used to select the power well of PS/2 ports. The feature “power on by keyboard / mouse” can be enabled or disabled by this jumper. JP9 (Vcore+ ) Vcore booster jumper This jumper is used to select the CPU core voltage. JP10 (VIO) VIO select jumper This jumper is used to select the VIO voltage. 6 WS133 Series Chapter 1 Quick Installation JP13 (AC 97) AC97 Codec Enabled / Disabled jumper This jumper is used to enable / disable the onboard audio CODEC. JP15 (LAN) LAN Enabled / Disabled jumper (WS133-N only) This jumper is used to enable / disable the onboard LAN chip. JP16 (FLASH) FLASH protect jumper This jumper is used to select the Flash ROM protected mode. WS133 Series 7 Chapter 1 Quick Installation Do not leave JP16 without any cap. 1.4 Expansion Slots / Sockets J1 (Slot1) Processor connector Slot1 is Single Edge Contact (SEC) CPU slot. J3—J5 (DM0—DM2) 168-Pin DIMM Sockets 8 WS133 Series Chapter 1 Quick Installation Install memory in any combination as follows: Location DM0 DM1 DM2 Support Module Type Single-Side Module Double-Side Module Single-Side Module Double-Side Module Limitation No No DM2 must be empty 1.DM1 must have a single-side module Single-Side Module 2.Must be the same or half memory size of DM1 Double-Side Module DM1 must be empty Total System Memory (Max 512 MB) J12—J17 (PCI 1—PCI 6) PCI expansion slots The connectors are Bus Master PCI Expansion Slots. J27 (AMR) AMR Slot WS133 Series 9 Chapter 1 Quick Installation 1.5 Connectors J28 (IDE0) Primary ATA/66 IDE channels J29 (IDE1) Secondary ATA/66 IDE channels J30 (FDC) Floppy connector J32 (COM2) This is an internal connector for COM2 port. 10 WS133 Series Chapter 1 Quick Installation J36 ATX keyboard connector (KB) This connector allows you to use an internal keyboard connector instead of having to attach the keyboard onto the ATX back-panel connectors. J37 ATX power connector J39 (FCPU) & J40 (FAUX) & J41 (FSYS) There are three fan connectors on this motherboard. The J39 (FCPU) is designed to support CPU fan; the J41 (FSYS) is for system fan used and you can connect any auxiliary fan to the J40 (FAUX). WS133 Series 11 Chapter 1 Quick Installation J40A (TAUX) & J41A (TSYS) This motherboard has two temperature sensor headers. You can connect the temperature sensor to these headers in order to monitor the temperature.These two connectors without orientation limit. J43 This connector is composed of all the headers that may be connected to the front panel of the chassis. J45 (IR) This connector is designed for the SIR/FIR/CIR devices. 12 WS133 Series Chapter 1 Quick Installation J46 (WOL) This is the Wake-on-LAN connector. In order to wake up the system through a plug-in network card, the card must provide a high active wake signal. J47 (WOM) This connector can be connected to MR card or internal modem card to provide the ability of power on by modem device. J48 (SMBUS) This connector provides the connectivity of SMBUS utilization. WS133 Series 13 Chapter 1 Quick Installation J52 (PTI,optional) The flat panel and TV out functions can be supported through this connector. This connector only supports the digital LCD panel. An analog LCD panel comes with a 15 -pin VGA connector can be used on the external VG connector. Iwill PI and TI only use on the Iwill motherboard of WS133 version 1.1 and WA133 version 1.1. J54 (CD_IN) The audio output can be transfered from CD-ROM to the audio system through this connector directly. J31 J33 J35 J38 J49 J55 External COM1 connector External Parallel connector External PS/2 mouse & keyboard connector External Dual USB & RJ45 connector External VGA connector External Game / Line-in / Line-out / MIC connector 14 WS133 Series Chapter 1 Quick Installation WS133 Series 15 Chapter 1 Quick Installation 1.6 Form Factor 16 WS133 Series Chapter 2 Overview Chapter 2 Overview Thank you for purchasing the IWILL WS133 motherboard. This operation manual will instruct you how to configure and install the system properly. It contains an overview about the engineering design and features of this product. Also, this manual provides useful information for later upgrades or configuration changes. Keep this for your future reference. About This Manual This manual will introduce to the user how this product is installed. All useful information will be described in later chapters. Keep this manual for future upgrades or system configuration changes. Chapter 1 Quick Installation Chapter 2 Overview Chapter 3 Features Chapter 4 Hardware Setup Chapter 5 BIOS Setup Chapter 6 Power Installer CD The quick reference for experienced user An overview of this motherboard Information and specifications Information for setting up the motherboard Information for setting up the system BIOS Information for the Power Installer CD Item Checklist You should find the following components when opening the box: [Ô] Iwill motherboard [Ô] This operation manual [Ô] One 40-pin/80-thread ATA/66 IDE cable with three heads [Ô] One 34-pin Floppy cable with four heads [Ô] One 10-pin to 9-pin COM port transitional cable (including a bracket) [Ô] One Iwill Power Installer CD [Ô] Bag of spare jumper caps [Ô] One Customer ATX IO Shield Optional [ ] Thermal Sensor for HDD [ ] Thermal Sensor for System [ ] Iwill Slocket II CPU transitional card - Socket370-to-Slot1 [ ] Iwill SIDE-Pro66 PCI ATA/66 IDE controller [ ] Iwill SIDE-2930C PCI Fast SCSI controller [ ] Iwill SIDE-2930CB PCI Fast SCSI controller [ ] Iwill SIDE-2936UW PCI Ultra Wide SCSI controller [ ] Iwill SIDE-2935LVD PCI Ultra2 SCSI controller [ ] Iwill SIDE-DU280 PCI Dual channel Ultra2 SCSI controller [ ] MR card WS133 Series 17 Chapter 2 Overview Introduction The WS133 series motherboard is the most flexible platform in today’s market based on the newest Intel® i810E chipset. A major advancement in chipset technology, the Intel® i810E integrates 3D graphics engine directly into the chipset to deliver a high-quality 3D experience. Combining Intel® 3D graphics with the onboard audio CODEC, AMR slot and the optional LAN chip results in a comprehensive, compatible platform that offers system integrators a comprehensive and cost-effective solution. This motherboard supports both the current (Deschutes / Katmai) and the next generation of processors (Coppermine) without any headache. With the optional Slocket II transitional card, it even can support the processors that packed as a PPGA or FCPGA type. In other words, no matter what kind of processors you have, the WS133 motherboard always provides you an adequate solution. There are three DIMM sockets on the motherboard, which provide you the most flexibility of DRAM usage. The original investment can be guaranteed by six bus-master PCI slots design. The PC99 compliant colorful connectors and the easy jumper setting provide the user more convenience. Besides that, the robust feature, well-prepared documents and the powerful software CD support make this motherboard the best choice of the value segment. Copyright This manual contains information protected by copyright law. All rights are reserved. No part of this document may be used or reproduced in any form or by any means, or stored in a database or retrieval system without prior written permission from Iwill Corporation. Trademark Intel® / Pentium® / Celeron™ are trademarks of Intel Corporation. Iwill and Iwill logo are trademarks of Iwill Corp. All other product names are trademarks and registered trademarks of their respective owners. Warning Most of the features of this product have passed strict verification tests, and are subject to change at any time without prior notice. If any malfunction occurs due to the future technical changes made by the respective component manufacturers, Iwill assumes no responsibility or liability for it. Notice Information furnished in this manual is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, Iwill Corporation assumes no responsibility for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. Iwill Corporation reserves the right to change product specifications at any time without notice. Applications described in this document for any of these products are for illustrative purposes only. Iwill Corporation makes no representation nor warranty that such applications are suitable for the specified use without further testing or modification. Iwill Corporation assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document. 18 WS133 Series Chapter 2 Overview YEAR 2000 issue All motherboard currently shipped from IWILL contain BIOS capable of handling the year 2000 data correctly. The IBM compatible PC utilizes a Motorola MC146818 compatible Real Time Clock (RTC) chip to maintain the date and time. Unfortunately, the “century” is not manipulated by the RTC. It uses 8-bits of information to report the year, and can only hold the last two digits of a year in packed BCD format. For example, 1997 is reported solely as 97. Since the RTC also contains non-volatile memory, IBM has specified a location in the memory to hold “century” information. By combining the century data with the year data, software can obtain a full 4digit year. When the Year 2000 arrives, the RTC reports the year as ‘00’ and the “century” in RTC memory will contain ’19.’ Combining the full 4-digit year yields 1900, not 2000. Any application which compare dates, or uses relative dates to perform functions will see incorrect dates. All motherboards contain BIOS, which is one of the key ingredients to check for systems designed to handle the year 2000. All motherboards currently shipped from IWILL contain BIOS capable of handling the year 2000 date correctly. Be aware that the BIOS capability alone does not ensure that the system will handle the transition correctly. Other system components such as the operating system and application software also need to be able to handle the year 2000 date, and recognize the date format from other sources. EC Declaration of Conformity We IWILL Corporation No. 10, Wu Chuan 3rd Rd., Hsin Chuang City, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C. Declare under sole responsibility that the WS133 motherboard Meets the intent of Directive 89/336/ECC for Electromagnetic Compatibility. Compliance was demonstrated to the following specifications as listed in the official Journal of the European Communities: EN 50081-1 Emissions: EN 55022 Radiated, Class B EN 55022 Conducted, Class B EN 60555-2 Power Harmonics EN 50082-1 Immunity: IEC 801-2 Electrostatic Discharge IEC 801-3 RF Radiate IEC 801-4 Fast Transient WS133 Series 19 Chapter 3 Features Chapter 3 Features This Iwill WS133/WS133-N motherboard are well designed for the user. Who wants the most stable plat form, best performance/price ratio and convenience. 3.1 Motherboard Components Placement 20 WS133 Series Chapter 3 Features The following are part descriptions for the motherboard parts shown on the opper page. 1: ATX Power Connector 2: SC242 Slot1 Connector 3: Display Cache Memory 4: Intel 810E GMCH 5: Three DIMM Sockets 6: Floppy Connector 7: Primary and Secondary IDE Connectors 8: Intel ICH Chipset 9: Intel FWH Chipset (Programmable BIOS) 10:Multi-I/O Chip 11:COM2 Header 12:LAN Chip 10/100M BaseT (WS133-N only) 13:32bit/33MHz Bus Master PCI Slot 14:AC'97 V2.1 Audio CODEC 15:PTI header (Optional) 16:AMR Slot 17:Joystick, Midi Line Out ,Line in, Microphone In Connector 18:VGA Monitor Connector 19:Parallel Connector 20:COM1 Connector 21:LAN and USB Connector (LAN Optional) 22:PS/2 Mouse, PS/2 Keyboard Connector. WS133 Series 21 Chapter 3 Features 3.2 Back Panel 22 WS133 Series Chapter 3 Features 3.3 Block Diagram WS133 Series 23 Chapter 3 Features 3.4 Specifications Processor Supports one Slot1 connector with pre-installed URM (Universal Retention Mechanism) Supports Intel® Celeron™ (Katmai, SEPP) CPU from 266 MHz to 433 MHz Supports Intel® Pentium® II (Klamath / Deschutes, SECC/SECC2) CPU from 233 MHz to 450 MHz Supports Intel® Pentium® III (Katmai, SECC2) CPU from 450 MHz to 600 MHz Supports Intel® Pentium® III (CuMine-256, SECC2) CPU from 533 MHz to 733 MHz Supports both H/W and S/W setting methods on CPU frequency selection Supports CPU voltage auto detection Supports adjustable CPU core voltage ChipSet Intel® i810E AGPset Support 66/100/133 MHz CPU external frequency Integrated 2X AGP controller supports up to 1600x1200x8bit color at 85 Hz refresh Supports Hardware Motion Compensation for S/W MPEG Decode Supports Software DVD at 30 fps Supports 4MB Dynamic Display Memory Supports 85MHz Flat Panel Monitor interface (optional) Supports Digital Video Output for use with an external NTSC/PAL TV encoder (optional) Main Memory Supports three DIMM sockets Supports 3.3V unbuffered PC100 SDRAM modules Supports Single-sided and Double-sided DIMM modules Supports 16M/32M/64M/128M/256M SDRAM modules Supports up to 512MB memory when using 128M technology Supports up to 256MB memory when using 64M/16M technology Bus Master IDE Supports dual channel IDE interface for up to four IDE devices Supports Ultra DMA Bus Master with 66 MB/s burst data transfer rate Supports PIO mode 0/1/2/3/4 and Multi-word mode 0/1/2/3/4 Supports HDD/Tape drive/CD-ROM/CD-R/CD-RW/LS120/ZIP drive Multi-IO Provides one floppy port to support 1.2M/1.4M/2.8M/3 Mode FDD and QIC-80 tape drive Supports two high-speed 16550A serial ports Supports one SPP/ECP/EPP parallel port Supports one PS2 mouse port Supports one PS2 keyboard port Provides one Game/MIDI port to support two joysticks Supports FIR and CIR infrared communication Supports PS2 mouse and PS2 keyboard auto swapping 24 WS133 Series Chapter 3 Features USB Supports two UHCI Universal Serial Bus ports Supports USB keyboard/mouse/joystick/telephone/modem devices Expansion Slots Supports six Bus Master PCI slots Supports one AMR slot for AR/MR/AMR cards LAN on board (WS133-N only) Build-in Realtek RTL8139B Ethernet LAN controller (10Base-T/100Base-TX) Supports IEEE 802.3u Auto-Negotiation Supports Full-Duplex Flow Control (IEEE 802.3x) Supports Wake-Up on Magic packet, LinkChg and Microsoft wake-up frame (PME#) Sound on board Build-in AC‘97 Sound CODEC Management Supports ACPI 1.0 and APM 1.2 specification Supports Suspend to Ram (STR) Supports extra SMBUS connector Supports Hardware Monitoring for the voltage, temperature and fan control Supports Chassis Intrusion feature Supports Power on by LAN/Ext. Modem/Int. Modem/PS2 Keyboard/PS2 Mouse/RTC Alarm Supports ACPI Blinking LED Supports “AC-Loss Recovery” feature Supports Manually Assign PCI IRQ Supports Auto-reboot function when system hang Supports Remote Power-up using Wake-on-LAN technology Fully Year2000 Compliance BIOS Adopt Award BIOS Supports On-board upgrade ability Supports BIOS ROM Flash protection Others ATX Form Factor 12“ x 7.5” WS133 Series 25 Chapter 4 Hardware Setup Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.1 Before Installation For installation, you may need some or all of the following tools: Medium size flat blade screwdriver Medium size Phillips head screwdriver A 3/16 inch nut driver or wrench Users must follow these guidelines to ensure the motherboard is protected during installation. a. Make sure your computer is powered-off whenever working with inside components. b. The motherboard, like all other electronic equipment, is sensitive to static. Please take the proper precautions when handling it. If possible, ground yourself by touching a metal table or desk. keep the board in its conductive wrapping until it is configured and ready to be installed in your system. c. Keep all magnets away from both your hard and floppy disk drives, especially magnetic screwdrivers. Keep both floppy and hard disks apart if disassembled. d. Keep water and liquids away from your computer and its components. 4.2 Jumper setting 4.2.1 JP1 Clear CMOS jumper (CMOS) To reset the CMOS data, you should turn off the computer first, take the JP1 jumper cap off pins 1-2, place onto pins 2-3, and then place back onto pins 1-2 again. Then, turn on your computer, press <Del> key during boot up and enter the BIOS setup program to re-set your preferences. 26 WS133 Series Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.2.2 JP3 & JP3A CPU FSB select jumper (FSB) These jumpers allow the selection of the CPU’s based external frequency. The CPU “External Frequency” multiplied by the “Frequency Multiple” equals the CPU’s “Internal Frequency”. Currently, most of the processors have the Frequency Multiple locked, so you only need to select the External Frequency. This motherboard will detect the proper external frequency your CPU used, so you can leave these jumpers on their defaults, and the based external frequency will be determined by CPU automatically. In this case you need not go to BIOS to do setup. The CPU speed is setup using “IWILL Smart Setting”. This is found in the BIOS setup program by pressing <Del> during the boot up process. After you setting up these jumpers to assign the “Based External Frequency” you should enter BIOS setup program, select the proper CPU speed within “Iwill Smart Setting”page. The BIOS will display the proper options depends on these jumpers setting. For example, if you choose 66Mhz by setting both JP3 and JP3A to 1-2, then the BIOS will prompt you 66Mhz, 75Mhz and 83Mhz for selecting. The table shows the proper setting for most of the processors in the market. The WS133 is designed for Intel® Pentium® III, Pentium® II and Celeron™ through a SC242 connector. CPU Model Vcore & Package JP3 JP3A “CPU Speed” in BIOS Celeron 266 2.0V, SEPP 1-2 1-2 Manual Celeron 300 2.0V, SEPP 1-2 1-2 300Mhz(66x4.5) Celeron 333 2.0V, SEPP 1-2 1-2 333Mhz(66x5) Celeron 366 2.0V, SEPP 1-2 1-2 366Mhz(66x5.5) Celeron 400 2.0V, SEPP 1-2 1-2 400Mhz(66x6) Celeron 433 2.0V, SEPP 1-2 1-2 433Mhz(66x6.5) Pentium II 350 2.0V, SECC(2) 2-3 1-2 350Mhz(100x3.5) Pentium II 400 2.0V, SECC(2) 2-3 1-2 400Mhz(100x4) Pentium II 450 2.0V, SECC(2) 2-3 1-2 450Mhz(100x4.5) WS133 Series 27 Chapter 4 Hardware Setup Pentium III 450 2.0V, SECC2 2-3 1-2 450Mhz(100x4.5) Pentium III 500 2.0V, SECC2 2-3 1-2 500Mhz(100x5) Pentium III 550 2.0V, SECC2 2-3 1-2 550Mhz(100x5.5) Pentium III 600 2.05V, SECC2 2-3 1-2 600Mhz(100x6) Pentium III 533B 2.0V, SECC2 2-3 2-3 533Mhz(133x4) Pentium III 600B 2.0V, SECC2 2-3 2-3 600Mhz(133x4.5) Pentium III 550E 1.65V, SECC2 2-3 1-2 550Mhz(100x5.5) Pentium III 600E 1.65V, SECC2 2-3 1-2 600Mhz(100x6) Pentium III 650E 1.65V, SECC2 2-3 1-2 650Mhz(100x6.5) Pentium III 700E 1.65V, SECC2 2-3 1-2 700Mhz(100x7) Pentium III 533EB 1.65V, SECC2 2-3 2-3 533Mhz(133x4) Pentium III 600EB 1.65V, SECC2 2-3 2-3 600Mhz(133x4.5) Pentium III 667EB 1.65V, SECC2 2-3 2-3 667Mhz(133x5) Pentium III 733EB 1.65V, SECC2 2-3 2-3 733Mhz(133x5.5) This motherboard also can support Socket370 CPUs with Iwill Slocket II transitional card. CPU Model Vcore & Package JP3 JP3A “CPU Speed” in BIOS Celeron 300A 2.0V, PPGA 1-2 1-2 300Mhz(66x4.5) Celeron 333 2.0V, PPGA 1-2 1-2 333Mhz(66x5) Celeron 366 2.0V, PPGA 1-2 1-2 366Mhz(66x5.5) Celeron 400 2.0V, PPGA 1-2 1-2 400Mhz(66x6) Celeron 433 2.0V, PPGA 1-2 1-2 433Mhz(66x6.5) Celeron 466 2.0V, PPGA 1-2 1-2 466Mhz(66x7) Celeron 500 2.0V, PPGA 1-2 1-2 500Mhz(66x7.5) Celeron 533 2.0V, PPGA 1-2 1-2 533Mhz(66x8) Pentium III 500E 1.60V, FCPGA 2-3 1-2 500Mhz(100x5) Pentium III 550E 1.60V, FCPGA 2-3 1-2 550Mhz(100x5.5) Pentium III 600E 1.65V, FCPGA 2-3 1-2 600Mhz(100x6) Pentium III 650E 1.65V, FCPGA 2-3 1-2 650Mhz(100x6.5) Pentium III 700E 1.65V, FCPGA 2-3 1-2 700Mhz(100x7) Pentium III 533EB 1.60V, FCPGA 2-3 2-3 533Mhz(133x4) Pentium III 600EB 1.65V, FCPGA 2-3 2-3 600Mhz(133x4.5) Pentium III 667EB 1.65V, FCPGA 2-3 2-3 667Mhz(133x5) Pentium III 733EB 1.65V, FCPGA 2-3 2-3 733Mhz(133x5.5) 28 WS133 Series Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.2.3 JP5 PCI compatibility jumper (JP5) This jumper is for the internal use. 4.2.4 JP6 PS/2 power standby jumper (PS2_SB) The computer can be powered on through PS/2 keyboard or PS/2 mouse. In order to support this feature, the standby power must be provided to PS/2 ports. 4.2.5 JP9 Vcore booster jumper (Vcore+) This jumper allows you to select the voltage supplied to the CPU. The default voltage should be used unless processor over-clocking requires a higher voltage. 4.2.6 JP10 VIO select jumper (Vio) WS133 Series 29 Chapter 4 Hardware Setup This jumper allows you to select the voltage supplied to the DRAM, chipset, PCI and the CPU’s I/O buffer. The default voltage should be used unless processor over-clocking requires a higher voltage. Using a higher voltage may help when over-clocking but may result in the shortening of your computer component’s life. It is strongly recommended that you leave these setting on its default. 4.2.7 JP13 AC’97 Codec Enabled / Disabled jumper (AC’97) This jumper is used to enable / disable the onboard audio CODEC. The onboard audio CODEC must be disabled when using an ISA/PCI audio card or a primary AMR card. 30 WS133 Series Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.2.8 JP15 LAN Enabled / Disabled jumper (LAN) (WS133-N only) This jumper is used to enable / disable the onboard LAN chip. 4.2.9 JP16 Flash protect jumper (FLASH) This jumper is used to select the Flash ROM protected mode. Do not leave JP16 without any cap. 4.3 Install the Processor The WS133 motherboard provides one Single Edge Contact (SEC) slot to support Pentium ® III, Pentium® II and Celeron™ processors. WS133 Series 31 Chapter 4 Hardware Setup All of the processors have two categories: OEM version and Boxed version. The OEM version processor has no heat sink, fan and heat sink support, while the Boxed version processor has all of them. Without a fan, the processor could overheat and damage both the processor and the motherboard. If this is the case, purchase a fan before you turn on your computer. This motherboard is shipped with a pre-installed Universal Retention Mechanism (URM), so you can go through to install the processor directly. Universal Retention Machanism Step 1: Lift each of the two retention mechanism brackets so that they stand fully upright. You should hear a soft “click” sound once each bracket is in the correct upright position. Step 2: Insert the CPU horizontally into the retention mechanism, sliding both edges in simultaneously and as “evenly” as possible. Then, press down gently yet firmly so that the CPU is fully inserted correctly into the socket. 32 WS133 Series Chapter 4 Hardware Setup Step 3: Pull the clip beside retention mechanism upward to lock the CPU. UNLOCK LOCK Do not forget to set the correct CPU External Frequency and Multiple (Multiple setting is available only on unlocked processors) for your processor or else boot up may not be possible. Step 4: Finally, attach the fan cable to the CPU fan header FCPU. WS133 Series 33 Chapter 4 Hardware Setup Slocket II (Slocket 370-Slot1 Convertor) Step 1: Lift each of the two retention mechanism brackets so that they stand fully upright. You should hear a soft “click” sound once each bracket is in the correct upright position. Step 2: Insert the CPU horizontally into the retention mechanism, sliding both edges in simultaneously and as “evenly” as possible. Then, press down gently yet firmly so that the CPU is fully inserted correctly into the socket. 34 WS133 Series Chapter 4 Hardware Setup Do not forget to set the correct CPU External Frequency and Multiple (Multiple setting is available only on unlocked processors) for your processor or else boot up may not be possible. Step 3: Finally, attach the fan cable to the CPU fan header FCPU. 4.4 Install Memory Modules The motherboard has three Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM) sockets and supports the maximum memory size up to 512MB. These DIMM sockets only support 3.3V unbuffered SDRAM modules of 16M, 32M, 64M, 128M and 256M. The motherboard also support SPD (Serial Presence Detect) architecture to provide the best choice for performance vs. stability. 1. The chipset does not support ECC. However, the ECC memory modules may still be used, but the ECC function will not be available. 2. No hardware or BIOS setup is required after adding or removing memory modules. WS133 Series 35 Chapter 4 Hardware Setup Memory Configuration Table Location DM0 DM1 DM2 Support Module Type Single-Side Module Double-Side Module Single-Side Module Double-Side Module Limitation No No DM2 must be empty 1.DM1 must have a single-side module Single-Side Module 2.Must be the same or half memory size of DM1 Double-Side Module DM1 must be empty Total System Memory (Max 512 MB) Step 1:Open latches of DIMM socket Step 2:Insert the RAM module into the DIMM Secket Step 3: Press the latches into the notches of the RAM module 36 WS133 Series Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.5 Install PCI Expansion Cards Make sure that you have unplugged the power supply before you adding or removing expansion cards or other component6. Failure to do so may cause damage to both the motherboard and expansion cards. This motherboard provides six bus master PCI expansion slots. You can expand the features of the computer by adding some expansion cards. Before you do that, read the documentation for your expansion card carefully and make any necessary hardware settings on it, such as jumpers or switches. Locate a free expansion slot and remove the bracket plate with screw on the slot you intend to use, carefully align the card’s connectors, press it firmly and secure the card on the slot with the screw you remove above. After installing the necessary software drivers, you can enjoy the features that expansion card provided. Step 1:Place the motherboard onto the Step 2:Secure the motherboard on the chassis chassis by fastening respective screws Step 3:Insert the expansion card into the PCI socket WS133 Series 37 Chapter 4 Hardware Setup Step 4:Secure the expansion card on the chassis by fastening the screw. In the PCI bus design, the BIOS automatically assigns an IRQ to a PCI slot that has a card in it. To check the IRQ map of your system in Windows 98, the Control Panel icon in My Computer contains a System icon, which gives you a Device Manager tab. Double click on a specific hardware device gives you the Resource tab, which shows the IRQ and address. Make sure that no two devices use the same IRQ or your computer will experience problems. If your expansion card must be performed with a specific IRQ, you can enter BIOS setup program to assign the specific IRQ in PnP/PCI Configuration page. 4.6 Usage of the AMR slot This motherboard provides a Audio Modem Riser (AMR) slot to support a specially designed audio and/or modem card called an AMR card. Main audio and/or modem processing is done by system processor to provide an upgradeable audio and/or modem solution at an incredibly low cost. There are two type of AMR card, one defined as primary and another defined as secondary. This motherboard uses the primary channel so that a secondary AMR card can coexist without the need to disable the onboard audio CODEC. The onboard audio CODEC must be disabled when using a primary AMR card. 38 WS133 Series Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.7 Connect Devices and Power Supply All the connectors showed in this section are not jumpers, DO NOT PLACE JUMPER CAPS OVER THE PINS OF THEM. If you do so, you will damage the motherboard permanently. 4.7.1 Primary / Secondary IDE Connectors (IDE0 / IDE1) This motherboard provides two independent Ultra ATA/66 IDE channels, which doubles the ATA/33 burst data transfer rate to 66 MB/s and are 100 percent backward compatible with all existing ATA / ATAPI devices. These connectors also support ZIP and LS-120 devices. The ATA/66 requires a special 40-pin, 80-conductor cable that reduces noise bleed-over and improves signal integrity by providing 40 additional ground lines between each of the standard 40-pin ATA (IDE) signal lines and ground lines. Although a new 40-pin, 80-conductor cable is required for Ultra ATA/66, the chip set pin connector remains the same at 40. The 40-pin, 80-conductor cables will support the Cable Detect feature. The blue (end) connector should be connected to the system board. The black (end) connector is known as the master position. The gray (middle) connector can be used for slave devices. A legacy ATA (IDE) drive can coexist with an Ultra ATA/66 drive. However, for the Ultra ATA/ 66 device to attain Ultra DMA 4 mode, an Ultra ATA/66 capable cable is required. Orient the red markings on the ribbon cable to pin1 of the connector WS133 Series 39 Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.7.2 Floppy Connector (FDC) This motherboard has one floppy connector to support 360K, 720K, 1.2M, 1.44M, 2.88M, 3 Mode floppy drives and QIC-80 floppy tape drive. After connecting the single end to the board, connect the two plugs on the other end to the floppy devices. Orient the red markings on the ribbon cable to pin1 of the connector 4.7.3 Back Panel 40 WS133 Series Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.7.3.1 PS/2 Mouse Connector (Green color) This connector can be used to support a PS/2 mouse. 4.7.3.2 PS/2 Keyboard Connector (Purple color) This connector can be used to support a PS/2 keyboard. The PS/2 mouse and PS/2 keyboard can be auto-detected by this motherboard. That means if you plug the PS/2 keyboard into the mouse connector, it still can work without any trouble and vice versa. It i recommended that you turn off the computer before connecting or disconnecting keyboard and/or mouse. 4.7.3.3 Universal Serial Bus Connectors This motherboard has two USB ports, any USB-compatible peripherals and/or hub can be connected into either USB port. 4.7.3.4 Serial port COM1 Connector (Teal color) One serial port is ready for a modem or other serial devices. A second serial port is available using a serial port bracket connected from the motherboard to an expansion slot opening. 4.7.3.5 Parallel port Connector (Burgundy color) This connector is used for printers, or other parallel devices. 4.7.3.6 VGA Connector (Blue color) This connector is for output to a VGA compatible device. 4.7.3.7 Joystick/Midi and Audio Port Connector (Gold color) You may connect joysticks or game pads to this connector for playing games, or connect MIDI devices for playing / editing professional audio. Line Out (Lime color) can be connected to headphones or powered speakers. Line In (Light Blue color) allows audio sources to be recorded by your computer or played through the Line Out connector. Mic (Pink color) allows microphones to be connected for inputting voice. 4.7.3.8 Ethernet RJ45 Connector (for WS133-N only) The RJ45 connector is optional at the time of purchase and is located on top of the USB connectors. The connector allow the motherboard to connect to a Local Area Network (LAN) through a network hub. WS133 Series 41 Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.7.4 Serial Port COM2 Connector (COM2) The optional serial port bracket can be used to add an additional serial port for serial devices. 4.7.5 CPU, Auxiliary and System FAN Connectors (FCPU, FAUX and FSYS) There are three fan connectors on this motherboard. The J39 (FCPU) is designed to support CPU fan; the J41 (FSYS) is for system fan used and you can connect any auxiliary fan to the J40 (FAUX). Depending on the fan manufacturer, the wiring and plug may be different. In most of the case, the red wire is positive, while the black is ground. Connect the fan’s plug to the board taking into consideration the polarity of the connector. The “Sense” signal is to be used only by a specially designed fan with rotation signal. You may use the hardware monitoring utility to monitor the Rotations per Minute (RPM) of the fan. 42 WS133 Series Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 1. The CPU will overheat if there is no airflow across the CPU heatsink. 2. Damage may occur to the CPU fan and/or motherboard if these pins are incorrectly used. 4.7.6 Auxiliary and System Temperature Sensor Connectors (TAUX and TSYS) This motherboard has two temperature sensor headers. You can connect the temperature sensors to these headers in order to monitor the temperature.These two connectors without orientation limit. The CPU temperature can be monitored by a CPU inside thermal diode. If your CPU does not have this feature, purchase one temperature sensor and connect it to the Auxiliary Temperature Sensor Connector. WS133 Series 43 Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.7.7 Front Panel Connector (J43) This connector is composed of all the headers that may be connected to the front panel of the chassis. Power/Soft-Off Connector (PWR_ON) The system power is controlled by a momentary button connected to this connector. Pressing the button once will switch the system between ON and OFF. Pushing the button for more than 4 seconds will turn the system off. ACPI LED Connector (ACPI) This 2-pins connector is for a ACPI power status indicator. The LED status will depend on the connector. Chassis Intrusion Connector (CASE) This connector is for a chassis designed for chassis intrusion detection. After-market toggle switches may also be installed to the chassis panel or on any removable components. Two wires should be available from the chassis to connect to this connector. When any chassis component is removed, the contact should open and the motherboard will record a chassis intrusion event. If this feature is not used, a jumper cap must be placed over the 2 pins of the connector. IDE LED Connector (ALED) This 2-pin connector connects to the case-mounted IDE LED, which lights when the IDE devices connected to the primary / secondary IDE connectors are working. Reset Connector (RST) This 2-pin connector connects to the case-mounted reset button for rebooting your computer without having to turn off the power supply. System Power LED Connector (PLED) This 3-pin connector connects to the case-mounted system power LED, which lights when the system is powered on. Keyboard Lock Connector (KL) This 2-pin connector connects to the case-mounted key switch to allow keyboard locking. Speaker Connector (SPKR) This 4-pin connector connects to the case-mounted speaker. 44 WS133 Series Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.7.8 Infrared Connector (IR) This connector supports an optional wireless transmitting and receiving infrared device when using the appropriate application software. a. When using a SIR/FIR devices, you need to enter the BIOS setup program and configure the ART Mode Select?field as “IrDA”. b. When using a CIR device, the jumper cap of JP6 should be placed over 1-2 in order to use Consumer Infrared power up. 4.7.9 Wake-On-LAN Connector (WOL) This connector connects to a plug-in network card, which supports the WOL technology to powers up the system when a wakeup packet or signal is received through the LAN card. a. You may need to enable the “Wake Up by Ring/LAN” feature in the BIOS setup program. b. Your system must have a ATX power supply with at least 720mA 5VSB power. c. This motherboard only supports the LAN card with a high-active wake signal. WS133 Series 45 Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.7.10 Wake-On-Modem Connector (WOM) This connector connects to internal modem cards (PCI or AMR) with a Wake-On-Modem output to powers up the system when a ringup packet or signal is received through the modem card. a. For the external Modems, the Wake-On-Modem is detected through the COM port. b. You need to enable the “Wake Up by Ring/LAN” feature in the BIO setup program. c. Your system must have a ATX power supply with at least 720mA 5VSB power. 46 WS133 Series Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.7.11 SMBUS connector J48 (SMBUS) This connector provides the connectivity of SMBUS utilization. 4.7.12 ATX keyboard connector J36 (KB) This connector allows you to use an internal keyboard connector instead of having to attach the keyboard onto the ATX back-panel connectors. 4.7.13 Flat Panel &TV-Out slot J52 (PTI, optional) The flat panel and TV out functions can be supported through this connector. This connector only supports the digital LCD panel. An analog LCD panel comes with a 15 -pin VGA connector can be used on the external VG connector. Iwill PI and TI only use on the Iwill motherboard of WS133 version 1.1 and WA133 version 1.1. WS133 Series 47 Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.7.14 Internal Audio Connector (CD_IN) This connect allow you to receive stereo audio input from such sound sources as a CD-ROM, TV tuner or MPEG card. 4.7.15 ATX Power Supply Connector This connector connects to the ATX power supply. The plug from the power supply will only insert in one orientation because of the different hole sizes. In order to support the power up function other than power/soft-off button, such as Wake-On-LAN, Wake-On-Modem, your ATX power supply must supply at least 720mA 5VSB. 48 WS133 Series Chapter 4 Hardware Setup 4.7.16 Power On Procedures 1. After all connections are made, close the system case over. 2. Be sure that all switches are off. 3. Connect the power cord into the power supply located on the back of your system case (please refer to the manual of your power supply). 4. Connect the power cord into a power outlet that is equipped with a surge protector. 5. Many of the power supply support 110V/220V by a switch setting. Switch your power supply to the correct supply voltage (refer to the power supply’s manual). 6. Turn on your system in the following order: a. The monitor. b. The external devices. c. The computer system. The power LED on the front panel of the chassis will light. After few seconds, the system will then run power-on tests. Some additional messages will appear on the screen during the test. If you do not see anything within 30 seconds from the time you turn on the power, the system may have failed a power-on test. Recheck the jumper settings and connections or call your retailer for assistance. 4.7.17 Power Off Procedures 1. Exit from all the software applications. 2. Shut down your operating system. 3. Switch off the power button. If you are using Windows 95/98, the power supply should turn off automatically after Windows shut down 4. Turn off all the external devices. 5. Turn off your monitor. WS133 Series 49 Chapter 5 BIOS Setup Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.1 Introduction The motherboard uses AWARD BIOS, which is stored in flash memory and can be upgraded using the appropriate software program. The setup program is for viewing and changing the BIOS setting for a computer. These settings are stored in battery-backed RAM so that it retains all the settings after the power has been turned off. 5.1.1 Upgrade BIOS The BIOS can be upgraded from a diskette with the Award Flash utility — AWDFLASH.EXE. The BIOS image file, and update utility are available from IWILL’s WEB site: www.iwill.net 5.1.2 Enter BIOS setup program Power-on the system by either pressing the Power-On button, or by using any of the power-on features provided by the motherboard. Then, press the <Del> key after the Power-On Self Test (POST), and before the scanning of IDE devices. Simply look for the message “Press DEL to enter SETUP” displayed at the bottom of the screen during the boot up process. If the message disappears before you’ve had a chance to respond, you can restart the system by Turning off the system power then turn it on again, or Pressing the “RESET” button on the system case, or Pressing <Ctrl>, <Alt> and <Del> keys simultaneously. 5.1.3 Using BIOS setup program The following table shows the function keys available for each menu screen. áUp âDown ßLeft àRight <Esc> <PgUp> or <+> <PgDn> or <-> <F1> <F2> <F5> <F6> <F7> <F10> Move to the previous field Move to the next field Move to the field on the left hand side Move to the field on the right hand side Quit from setup program without saving changes, or Exit from current menu page and return to main menu page Select the previous value for a field Select the next value for a field General Help Item Help Previous Values Fail-Safe Defaults Optimized Defaults Save the current value and exit setup program 50 WS133 Series Chapter 5 BIOS Setup Generally, the BIOS default settings have been carefully chosen by the system manufacturer to provide the absolute maximum performance and reliability. It is very dangerous to change any setting without full understanding. We strongly recommend that you DO NOT update your BIOS if the system works perfectly. DO NOT change any setting unless you fully understand what it means. If the system does not work smoothly after changing the BIOS settings, follow the procedures described previously, enter the BIOS setup program, then load the original manufacturer default settings. If the system is no longer able to boot after changing the settings, the only way to recover it is to clear the data stored in RTC CMOS. To reset the RTC CMOS data, take the JP1 jumper cap off pins 1-2, place onto pins 2-3, and then place back onto pins 1-2 again. This will return the RTC to the default setting. Then, get into the BIOS setup program , choose Load Fail-Safe Defaults ; Load Optimized Defaults, and select the original manufacturer default settings in your CMOS. 5.2 Main Menu The main menu allows you to select from several setup pages. Use the arrow keys to select among these pages and press <Enter> key to enter the sub-menu. A brief description of each highlighted selection appears at the bottom of the screen. WS133 Series 51 Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.3 Standard CMOS Features 5.3.1 Date This field specifies the current date. The date format is <month>, <day>, and <year>. 5.3.2 Time This field specifies the current time. The time format is <hour>, <minute>, and <second>. The time is calculated based on the 24-hour (military-time) clock. 5.3.3 IDE Primary Master / Primary Slave / Secondary Master / Secondary Slave Press “Enter” to enter next page for detail hard drive setting. 5.3.3.1 IDE HDD Auto-Detection Auto-Detect the HDD’s Capacity, and its parameters. 5.3.3.2 IDE Primary Master / Primary Slave / Secondary Master / Secondary Slave This field specifies the parameter of drive that corresponds to the drive installed in your system. “Manual” lets you set the remaining fields on this screen. Selects the type of fixed disk. Options Auto (*) None Description BIOS automatically fills in the values for the cylinders, heads and sectors fields No disk drives are attached 5.3.3.3 Capacity Your disk drive size 52 WS133 Series Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.3.3.4 Access Mode This field specifies the IDE translation mode. Options Description NORMAL Specifies traditional CHS addressing mode LARGE Specifies extended CHS translation mode LBA Specifies LBA translation mode AUTO (*) BIOS specifies translation method automatically 5.3.3.5 Cylinders Set the number of cylinders for this hard disk. 5.3.3.6 Heads Set the number of read/write heads 5.3.3.7 Precomp Setting a value of 65535 means disable write precompansation feature. 5.3.3.8 Sectors Set the number of sectors per track 5.3.4 Drive A / Drive B This field specifies the type of floppy drives. Options Description None No floppy drive is connected (Drive B default) 360K, 5.25 in. A 360K floppy drive is connected 1.2M, 5.25 in. A 1.2M floppy drive is connected 720K, 3.5 in. A 720K floppy drive is connected 1.44M, 3.5 in. A 1.44M floppy drive is connected (Drive A default) 2.88M, 3.5 in. A 2.88M floppy drive is connected 5.3.5 Video This field specifies the type of the graphics adapters used by the primary system monitor. Options Description EGA/VGA (*) Specifies EGA or VGA adapter CGA 40 Specifies CGA adapter with 40 column mode CGA 80 Specifies CGA adapter with 80 column mode MONO Specifies Monochrome adapter 5.3.6 Halt On This field determines how the system reacts to errors once detected. Options Description All Errors (*) Each time the BIOS detects a non-fatal error, the system will stop and display an error message No Errors The system will not stop for any errors that are detected All, But Keyboard The system will stop for any errors except keyboard error WS133 Series 53 Chapter 5 BIOS Setup All, But Diskette All, But Disk/Key The system will stop for any errors except diskette error The system will stop for any errors except diskette and keyboard errors 5.3.7 Base Memory The amount of base (conventional) memory installed in the system. The value of the base memory is typically 640K. This field has no options. 5.3.8 Extended Memory This is the amount of memory located above 1MB in the processor’s memory address map. This field has no options. 5.3.9 Total Memory Displays the total memory available in the system 5.4 Advanced BIOS Features An asterisk (*) denotes the default setting, whenever appropriate. 5.4.1 Virus Warning When this function is enabled, the BIOS monitors the boot sector and partition table of the hard disk drive for any attempt at modification. If an attempt is made, the BIOS will halt the system and then display an error message. Afterwards, if necessary, you can run an anti-virus program to locate and remove the problem before any damage is done. Many disk diagnostic programs will attempt to access the boot sector table, which can cause the above warning message. If you run such a program, we recommend that you first disable the Virus Warning function beforehand. 54 WS133 Series Chapter 5 BIOS Setup Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.4.2 CPU Internal Cache This field configures the CPU internal cache (L1 cache). Options Enabled (*) Disabled 5.4.3 External Cache This field configures the system’s external cache (L2 cache). Options Enabled (*) Disabled 5.4.4 CPU L2 Cache ECC Checking This field specifies whether the CPU L2 cache supports ECC or not. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.4.5 Processor Number Feature Intel(r) Pentium(r) III processors are equipped with a built-in processor serial number for security purposes. When enabled, you allow reading access to this serial number. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.4.6 Quick Power On Self Test This field allows the system to skip certain tests while booting. This will decrease the time needed to boot the system. Options Enabled (*) Disabled 5.4.7 First / Secondary / Third / Other Boot Device The BIOS attempts to load the operating system from the devices in the sequence selected in these items. Options Floppy (*) LS/ZIP HDD-0 (**) SCSI (***) CD-ROM HDD-1 HDD-2 HDD-3 LAN Disable WS133 Series 55 Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.4.8 Swap Floppy Drive When enabled, floppy drives A and B will be exchanged without the user physically changing the connection on the cable. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.4.9 Boot Up Floppy Seek Seeks disk drives during boot up. Disabling speeds boot up.When enable ,the BIOS will check the flooy drive status during boot up. Options Enabled (*) Disabled 5.4.10 Boot Up NumLock Status This field determines the configuration of the numeric keypad after system boot up. Options Description On (*) Keypad works as number keys Off Keypad works as arrow keys 5.4.11 Gate A20 Option This field configures how the gate A20 is handled. The gate A20 is a device used to address memory above 1 MB. At first, the gate A20 was handled from a pin on the keyboard. While some keyboards still provide this support, it is more common, and much faster, for modern system chipsets to provide support for gate A20. Options Description Fast (*) GateA20 signal supported by core logic Normal GateA20 signal supported by keyboard controller 5.4.12 Typematic Rate Setting This field determines if the typematic rate is to be used. When enabled, the BIOS will report (after a moment) that the key has been depressed repeatedly. When disabled, the BIOS will report only once if a key is held down continuously. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.4.13 Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec) When Typematic Rate Setting enabled, this field specifies how many characters will be displayed in one second when a key is held down continuously. Options 6 (*), 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 24, 30 5.4.14 Typematic Delay (Msec) When enabled, typematic delay allows you to select the time delay between when the key is first pressed and when the acceleration begins. Options 250 msec (*), 500 msec, 750 msec, 1000 msec 56 WS133 Series Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.4.15 Security Option This field configures how the system security is handled. It works conjunction with SETTING SUPERVISOR / USER PASSWORD page to control the security level of the system. Options Description Setup (*) System needs a password to enter BIOS setup program Sys tem System needs a password to boot 5.4.16 OS Select for DRAM >64MB When enabled, this field allows you to access the memory that is over 64MB under OS/2. Options OS/2 Non-OS/2 (*) 5.4.17 Report No FDD For WIN 95 For a floppy diskless system that runs Windows 95, this field should be set to Yes. Options Yes No (*) 5.5 Advanced Chipset Features This setup page is used to specify advanced features available through the chipset. The default settings have been chosen carefully for most operating conditions. DO NOT change the value of any field in this setup page without full understanding. 5.5.1 SDRAM CAS Latency Time This controls the number of clocks between the SDRAM read command and the time that the data actually becomes available. Options 2 3 (*) WS133 Series 57 Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.5.2 SDRAM Cycle Time Tras/Trc This controls the number of SDRAM clocks used per access cycle. Options 6/8 (*) 5/7 5.5.3 SDRAM RAS-to-CAS Delay This controls the number of clocks between the SDRAM active command and the read / write command. Options 2 3 (*) 5.5.4 SDRAM RAS Precharge Time If an insufficient number of cycles is allowed for the RAS to accumulate its charge before DRAM refresh, the refresh may be incomplete and the DRAM may fail to retain data. This controls the idle (delay) clocks after issueing a prechange command to the SDRAM. Options 2 3 (*) 5.5.5 System BIOS Cacheable When enabled, accesses to the system BIOS will be cached. Options Enabled (*) Disabled 5.5.6 Video BIOS Cacheable When enabled, access to the video BIOS will be cached. Options Enabled (*) Disabled 5.5.7 Memory Hole At 15M-16M Some add-in cards need to re-map its resource to a block of main memory address range. Any host cycles that match this memory hole are passed on to the add-in cards. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.5.8 CPU Latency Timer Configuration options: Enabled Disabled (*) 5.5.9 Delayed Transaction When enabled, the south bridge ICH will supports the Delayed Transaction mechanism when it is the target of a PCI transaction. Options Enabled (*) Disabled 58 WS133 Series Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.5.10 On-Chip Video Window Size This field configures the main memory size for AGP graphics data used. Options 32MB 64MB (*) Disabled 5.5.11 Local Memory Frequency The field configures the frequency that onboard display cache memory support. Options 100MHz 133MHz (*) Onboard Display Cache Setting 5.5.12 CAS # Latency Select the onboard display cache memory clock periods. Options 2 / 3 (*) 5.5.13 Paging Mode Control Select the paging mode control. Options Close Open (*) 5.5.14 RAS-to-CAS Override Select the display cache clock periods indicates the RAS-to-CAS Override delay.(i.e., row activate command to read /write command) Options By CAS# LT (*) Override 5.5.15 RAS# Timing This item controls RAS# active to precharge, and refresh to RAS# active delay ( in local memory clocks). Options Slow Fast (*) 5.5.16 RAS# Precharge Timing This item controls RAS# precharge (in local memory clocks). Options Slow Fast (*) WS133 Series 59 Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.6 Integrated Peripherals 5.6.1 On-Chip Primary / Secondary PCI IDE This field enables or disables the onboard IDE controller. Options Enabled (*) Disabled 5.6.2 IDE Primary Master / Slave PIO IDE Secondary Master / Slave PIO These fields configure the PIO (Programmable Input Output) transfer mode for each IDE devices. The maximum transfer rates of each PIO mode are listing as follow: Higher setting may exceed the capability of older IDE device and cause problem. PIO Mode Setting PIO Mode 0 PIO Mode 1 PIO Mode 2 PIO Mode 3 PIO Mode 4 Maximum transfer rate 3.3 MB/sec 5.2 MB/sec 8.3 MB/sec 11 MB/sec 16.6 MB/sec Options Auto (*) Mode 0 Mode 1 Mode 2 Mode 3 Mode 4 Description The BIOS negotiates with device automatically Use Mode 0 timing to access device Use Mode 1 timing to access device Use Mode 2 timing to access device Use Mode 3 timing to access device Use Mode 4 timing to access device 60 WS133 Series Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.6.3 IDE Primary Master / Slave UDMA IDE Secondary Master / Slave UDMA If you select Auto, the IDE controller uses Ultra DMA 33/66 Mode to access Ultra DMA-capable IDE devices. Depend on the resent of negociation with your HDD. The maximum transfer rate of Ultra DMA 66 Mode is 66.6 MB/sec. Options Auto (*) Disabled 5.6.4 USB Controller Select Enabled if your system contains USB peripherals. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.6.5 USB Keyboard under DOS Select Enabled if you want to use USB keyboard under DOS Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.6.6 Init Display First This item allows you to decide which slot to activate first, either PCI slot or AGP slot. Options PCI Slot Onboard AGP (*) 5.6.7 AC97 Audio/Modem Auto” allows the motherboard’s BIOS to detect whether you are using any AC’97 modem/audio device.If a modem/audio device is detected , the onboard modem/audio controller will be enabled ; if no modem/audio device is detected , the onboard modem/audio controller will be disabled. If you want to use different controller cards to connect modem and audio connector , set these fields to disabled”. Options Auto (*) Disabled 5.6.8 IDE HDD Block Mode When enabled, the IDE controller will use the faster block mode to access devices. Options Enabled (*) Disabled 5.6.9 Power-On Function This field configures the Power-On mode of the system. This feature only supports PS/2 keyboard and PS/2 mouse. It does not work with USB keyboard or serial mouse. WS133 Series 61 Chapter 5 BIOS Setup The Power-On button will not function in this mode. Options Description Password You can assign a password string through KB Power-On Pass word field. Typing this password string will power-on your system. Hot KEY You can assign a hot key through the Hot Key Power-On field.Pressing this hot key will power-on your system. Mouse/Password “Double-Clicking” the mouse button or typing the KB poweron password will automatically power-on your system. Mouse/Hot KEY “Double-Clicking” the mouse button or typing the KB hotkey will power-on your system. Button only (*) Simply power-on your system by pressing the Power-On button on the front panel of your PC case. Keyboard 98 Enables Keyboard 98 function. This function is good only for users of Keyboard 98. 5.6.9.1 KB Password Power-On In you wish to use this function, bring the cursor to the field written “Enter”, then press <Enter>. The computer will display the message, “Enter Password”. Type your password and press <Enter>. After the message “Confirm Password” is displayed, re-type your password. The KB Power-On function will be in effect after you save and exit setup. To disable a password, bring the cursor to the “Enter” field again, then press <Enter>. The computer will display the message, “Enter Password”. Press <Enter>. A message will confirm that the password is disabled. 5.6.9.2 Hot Key Power-On This field specifies key selection for the Keyboard-Power-On hot key. Options Ctrl-F1 / Ctrl-F2 / Ctrl-F3 / Ctrl-F4 / Ctrl-F5 / Ctrl-F6 Ctrl-F7 / Ctrl-F8 / Ctrl-F9 / Ctrl-F10 / Ctrl-F11 / Ctrl-F12 5.6.9.3 PS2 MOUSE Button Power on The field specifies key selection for PS2 MOUSE Button Power on. Options Left Right 5.6.10 Onboard FDC Controller This field enables or disables the onboard floppy controller. Options Enabled (*) Disabled 5.6.11 Onboard Serial Port 1 / 2 These fields configure the onboard serial ports. There are several port addresses and IRQ channels to select from. Options Description 3F8 / IRQ 4(*) Port address 3F8h, IRQ 4 2F8 / IRQ 3(*) Port address 2F8h, IRQ 3 3E8 / IRQ 4 Port address 3E8h, IRQ 4 2E8 / IRQ 3 Port address 2E8h, IRQ 3 62 WS133 Series Chapter 5 BIOS Setup Auto Disabled BIOS assigns port address and IRQ channel automatically Disables serial port 5.6.12 COM2 Mode Select This field must be configured in order to use the infrared connector, which supports infrared wireless transmitting and receiving of data between devices when using the appropriate application software. Options Normal (*), IrDA, ASKIR 5.6.12.1 RxD, TxD Active for IrDA and ASKIR functions When setting the field to either IrDA or ASKIR, you must select the active level of receiving and transmission signal. Options Hi, Lo (*) / Lo, Hi / Lo, Lo / Hi, Hi 5.6.12.2 IR Transmission delay for IrDA and ASKIR functions When setting the field to either IrDA or ASKIR, you must select whether or not you require a delay between IR transmissions. Options Enabled (*) Disabled 5.6.12.3 IR Duplex Mode Options Full Half (*) 5.6.12.4 Use IR Pins Options IR-Rx2Tx2 (*) RxD2 , TxD2 5.6.13 Onboard Parallel Port This field configures the onboard parallel port. There are several port addresses and IRQ channels to select from. Options Description 378 / IRQ 7(*) Port address 378h, IRQ 7 278 / IRQ 5 Port address 278h, IRQ 5 3BC / IRQ 7 Port address 3BCh, IRQ 7 Disabled Disables parallel port 5.6.14 Parallel Port Mode This field configures the operating mode of an onboard parallel port. Ensure you know the specifications of your parallel port devices before selecting field. Options SPP (*) / EPP / ECP / ECP+EPP 5.6.14.1 EPP Mode Select When the Parallel Port Mode field is configured as EPP, ECP+EPP mode, the EPP version needs to be specified. Please refer to your peripheral document before selecting field. WS133 Series 63 Chapter 5 BIOS Setup Options EPP1.7 EPP1.9(*) Description Use EPP 1.7 protocol Use EPP 1.9 protocol 5.6.14.2 ECP Mode Use DMA When the Parallel Port Mode field is configured as ECP, ECP+EPP mode, it needs a DMA channel for data transfer. This field specifies the DMA channel for ECP parallel port use. Options Description 1 Use DMA channel 1 3 (*) Use DMA channel 3 5.6.15 AC PWR Loss Recovery The field configures the system activity after experiencing a power failure. Options Description Former-Sts System returns to former status prior to AC loss event Off (*) System remains off after AC loss event 5.6.16 Game Port Address This field configures the onboard game port. There are several port addresses to select from. Options Description 201(*) Port address 201h 209 Port address 209h Disabled Disables game port 5.6.17 Midi Port Address This field configures the midi port. There are several port addresses to select from. Options Description 330(*) Port address 330h 300 Port address 300h 290 Port address 290h Disabled Disables midi port 5.6.18 Midi Port IRQ This field configures the midi port IRQ. There are several IRQs to select from. Options Description 5 (*) Port address IRQ5 10 Port address IRQ10 64 WS133 Series Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.7 Power Management Setup Each power-saving mode has a respective timer. The value of the timer can be assigned or reloaded and it will count down to zero. When the timer equals to zero, the system will be forced into the related suspend or power-saving mode. If any predefined signal or event is detected during the timer counting period, the timer restarts automatically. 5.7.1 ACPI Suspend Type There are several ACPI modes used to save computer’s energy S1 (POS) This is the Power-On-Suspend state, the CPU clock will run at slower speed, when entering the suspend state. S3 (STR) This is the Suspend-To-Ram state, all system data will be saved in system’s memory and all devices except the memory will shut off. 5.7.2 Power Management This feature allows the user to select the default parameters for the power-saving mode. Options Description Min Saving When idle for one hour, the system enters suspend mode Max Saving When idle for fifteen minutes, the system enters suspend mode User Define(*) User can specify the time the system enters suspend mode 5.7.3 Video off Method This field specifies the method that video subsystem used for power saving. Options Description V/H SYNC+Blank Turn off the vertical and horizontal synchronization ports and write blanks to the video buffer Blank Screen Writes blanks to the video buffer only DPMS (*) Initial display power management signaling with DPMS WS133 Series 65 Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.7.4 Video Off In Suspend This determines the manner in which the monitor is blanked. Options Yes (*) No 5.7.5 Suspend Type Select the Suspend Type. Options Stop Grant (*) / PwrOn Suspend 5.7.6 MODEM Use IRQ This determines the IRQ in which the MODEM can use. Options 3 (*)/ 4 / 5 / 7 / 9 / 11 / NA 5.7.7 APM Suspend Timer This field specifies the time the system enters power-saving mode. It is available only when the Power Management field is set to User Define. Options 1 Min / 2 Min / 4 Min / 8 Min / 12 Min / 20 Min 30 Min / 40 Min / 1 Hour / Disable (*) 5.7.8 APM HDD Power Down Timer This field specifies the time the system enters HDD power down. It is available only when the Power Management field is set to User Define. Options 1 Min / 2 Min / 3 Min / 4 Min / 5 Min / 6 Min 7 Min / 8 Min / 9 Min / 10 Min / 11 Min / 12 Min 13 Min / 14 Min / 15 Min / Disable (*) 5.7.9 PWR-Off Mode by PWR-BTTN This field specifies the function of power button. Options Description Instant-Off (*) When power button pressed, the system turns off immediately. Delay 4 Sec. After the power button has been pressed and held for four seconds, the system turns off. 5.7.10 Wake up by PCI card When enabled, you can “wake-up” your system using a PCI rev.2.2 card ,when a “PME” event occuring. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.7.11 Wake up by LAN/RING When Wake up by LAN function is enabled, the PC can power-on or “wake up” through LAN (Local Area Network). When Wake up by RING function is enabled, the PC can power-on through an external modem connected to your PC. 66 WS133 Series Chapter 5 BIOS Setup Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.7.12 CPU Thermal throttling This field specifies the throttling function of CPU Thermal. When the CPU’s temperature attain it’s default protection point, the CPU will run slower in order to descend the heat generation from itself. Options Description 87.5% Keep 87.5% of CPU’s full speed performance 75.0% Keep 75.0% of CPU’s full speed performance 62.5%(*) Keep 62.5% of CPU’s full speed performance 50.0% Keep 50.0% of CPU’s full speed performance 37.5% Keep 37.5% of CPU’s full speed performance 25.0% Keep 25.0% of CPU’s full speed performance 12.5% Keep 12.5% of CPU’s full speed performance 5.7.13 PowerOn/Resume by Alarm When enabled, you can set the date and time to automatically power-on your PC (similar to an alarm clock). Options Description Disabled (*) Disables RTC alarm function Enabled Enter the Date and Time Alarm to power-on the PC. To set alarm for every day, select “0” for Date (of month) Alarm. 5.7.14 Reset APM Timer Events This field enables the system to detect activity, and restart the timer of the power-saving mode. 5.7.14.1 Primary IDE 0 If enabled, timer restarts whenever the master disk of the primary IDE channel is active. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.7.14.2 Primary IDE 1 If enabled, timer restarts whenever the slave disk of the primary IDE channel is active. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.7.14.3 Secondary IDE 0 If enabled, timer restarts whenever the master disk of the secondary IDE channel is active. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.7.14.4 Secondary IDE 1 If enabled, timer restarts whenever the slave disk of the secondary IDE channel is active. Options Enabled Disabled (*) WS133 Series 67 Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.7.14.5 FDD, COM, LPT Port If enabled, timer restarts whenever the floppy disk serial device/parallel device is active. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.7.14.6 PCI IRQ# If enabled, timer restarts whenever any of the interrupts occurs. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.8 PnP/ PCI Configurations 5.8.1 PNP OS Installed The field specifies whether a Plug and Play operating system is installed. Options Yes No (*) 5.8.2 Reset Configuration Data Normally, you leave this field Disabled. Select Enabled to reset Extended System Configuration Data (ESCD) if you have installed a new add-on and the system reconfiguration has caused such a serious conflict that the operating system can not boot. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.8.3 Resources Controlled By The Award Plug and Play BIOS has the capacity to automatically configure all of the boot and Plug and Play compatible devices. However, this capability means absolutely nothing unless you are using a Plug and Play operating system such as Windows(98/95. If you set this field to “manual” choose specific resources by going into each of the sub menu that follows this field (a sub menu 68 WS133 Series Chapter 5 BIOS Setup is preceded by a “>”). Options Auto (ESCD)(*) Manual Description Resources controlled by BIOS automatically Resources controlled by the user 5.8.4 PCI / VGA Palette Snoop This field controls the ability of a primary PCI graphics controller to share a common palette with an ISA/VESA video or MPEG card Options Description Enabled PCI VGA co-works with ISA MPEG card Disabled (*) All cases except above 5.8.5 PCI 1/PCI 5 IRQ Use PCI 2/PCI 6 IRQ Use PCI 3/Onboard LAN IRQ Use PCI 4 IRQ Use These fields set how IRQ use is determined for each PCI slot. The default setting for each field is “Auto” , which uses auto-routing to determine IRQ use. Option Auto(*)/3/4/5/7/9/10/11/12/14/15 5.9 PC Health Status This page is monitoring your status of computer. On the screen displays CPU/System temperature, FAN speed, and voltages. WS133 Series 69 Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.10 IWILL Smart Setting Over-clocking is not guaranteed. Users must have substantial knowledge of proper CPU relative to adjusting CPU speeds. Over-clocking should be done only by experienced engineers who conduct tests. 5.10.1 Auto Detect DIMM/PCI Clk When enabled, the motherboard will automatically disable the clock source for a DIMM socket, which does not have a module on it. This is true for all PCI slots. Options Enabled (*) Disabled 5.10.2 Spread Spectrum This item configures radiation emitted from the system. When enabled, system will release less radiation. Options Enabled Disabled (*) 5.10.3 CPU Speed Options CPU Speed:CPU External Frequency ÑCPU Clock Ratio 70 WS133 Series Chapter 5 BIOS Setup CPU / SDRAM Clock: This field allows user to adjust the CPU frequency. If your CPU external frequency is 66MHz, BIOS will display the following settings: Shown on screen 66 / 100 MHz 70 / 105 MHz 75 / 113 MHz CPU External frequency 66 MH 70 MH 75 MH SDRAM frequency 100 MHz 105 MHz 113 MHz If your CPU external frequency is 100MHz, BIOS will display the following settings: Shown on screen 100 / 100 MHz 107 / 107 MHz 112 / 112 MHz 119 / 119 MHz 124 / 124 MHz 129 / 129 MHz 133 / 133 MHz 138 / 138 MHz 140 / 140 MHz 145 / 145 MHz 150 / 150 MHz CPU External frequency 100 MHz 107 MHz 112 MHz 119 MHz 124 MHz 129 MHz 133 MHz 138 MHz 140 MHz 145 MHz 150 MHz SDRAM frequency 100 MHz 107 MHz 112 MHz 119 MHz 124 MHz 129 MHz 133 MHz 138 MHz 140 MHz 145 MHz 150 MHz If your CPU external frequency is 133MHz, BIOS will display the following settings: Shown on screen 133 / 100 MHz 138 / 100 MHz 140 / 105 MHz 145 / 110 MHz 150 / 113 MHz 153 / 115 MHz CPU Clock Ratio: Options WS133 Series CPU External frequency 133 MHz 138 MHz 140 MHz 145 MHz 150 MHz 153 MHz SDRAM frequency 100 MHz 100 MHz 105 MHz 110 MHz 113 MHz 115 MHz 2/2.5/3/3.5/4/4.5/5/5.5/6/6.5/7/7.5/8 71 Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.10.4 BIOS-ROM Flash Protect The main function of BIOS-ROM Flash Protect prevents the virus of computers to destory the system of computers. When JP16 is set on 1-2 , the Flash ROM pretection mode will be controlled by this field. Options Description Non-Fresh By BIOS Freshable By BIOS When your system booting, you can find the BIOS status on the screen: There are three possible conditions will be shown that indicates your hareware setting respectively (Please refer to JP16 Flash protect jumper): 1. Protected By BIOS 2. Protected By H/W 3. Flashable 5.11 Load Fail-Safe Defaults When you press <Enter> on this item you get a confirmation dialog box with a message similar to: Pressing ‘Y’ loads the BIOS default values for the most stable, minimal-performance system operations. 72 WS133 Series Chapter 5 BIOS Setup 5.12 Load Optimized Defaults When you press <Enter> on this item you get a confirmation dialog box with a message similar to: Pressing ‘Y’ loads the default values that are factory settings for optimal performance system operations. 5.13 Set Supervisor / User Password Setting These setup pages are used for password setting. When a password has been enabled and the Security Option field is set as Setup, you will be required to enter the password every time you try to enter BIOS Setup program. This prevents an unauthorized person from changing any part of your system configuration. Additionally, if the Security Option field is set as Boot, the BIOS will request a password every time your system boot. This would prevent unauthorized use of your computer. In you wish to use this function, bring the cursor to this field, then press <Enter>. The computer will display the message, “Enter Password”. Type your password and press <Enter>. After the message onfirm Password” is displayed, re-type your password. The Supervisor Password function will be in effect after you save and exit setup. To disable a password, bring the cursor to this field, then press <Enter>. The computer will display the message, “Enter Password”. Press <Enter>. A message will confirm that the password is disabled. Once the password is disabled, the system will boot and you can enter setup program freely. The User Password allows you to enter BIOS setup program, but yo cannot change the value of any fields Please keep your password in safe place. 5.14 Save & Exit Setup Saves current CMOS value and exit BIOS setup program. 5.15 Exit Without Saving Abandons all CMOS value changes and exits BIOS setup program. WS133 Series 73 Chapter 6 Power Installer CD Chapter 6 Power Installer CD 6.1 Software Installation The attached Power Installer CD contains all the necessary drivers, utilities for IWILL’s full range of motherboards. It provides an easy way for users to install the needed drivers without going through a complicated process. The Power Installer CD is able to auto-detect and display the drivers, utilities needed for your motherboard. 6.1.1 What’s inside Power Installer CD for this motherboard 1. Drivers Intel INF Installation Utility Security Driver Onboard AGP Driver Software Audio Driver Network Driver Installation Guide 2. Utilities Make Driver Diskettes Hardware Monitor Utility PC-Cillin Anti-Virus Adobe Acrobat Reader 3. Manuals 6.2 How to use the Power installer CD The Power Installer CD supports the Auto Run program under Windows 98/95 and Windows NT operating systems. All the necessary drivers, utilities and manual for this motherboard will show on the screen. Select the one that needs to be installed, then simply follow the messages displayed on the screen to complete setup. IWILL Power Installer does not support a keyboard at this moment. You must use a mouse to install it. 6.2.1 How to view manual This Power Installer CD includes detailed information of all IWILL manuals for every motherboard manufactured by IWILL. Please insert the IWILL Power Installer CD into the CD-ROM drive; Click the “View Manual” item, and select the product that you want to view. 74 WS133 Series Chapter 6 Power Installer CD 6.2.2 How to make driver diskette 6.2.2.1 Without O.S. installed This bootable Power Installer CD also allows you to boot up your system, even when the OS has not been installed. During the boot-up process, you can perform “IWILL Diskette Creator,” which will automatically make the driver diskettes you need. At least one CD-ROM drive and one 1.44M floppy drive are necessary to make “IWILL Diskette Creator” work properly. Follow the instructions below to make your own device driver floppy diskettes if you have a CD-ROM with IDE interface. If you have already installed SCSI CD-ROM, please make sure your SCSI host adapter supports bootable CD-ROM, and then proceed directly to step 8 , and then finish the procedure. 1. First, power-on or “boot” your system. 2. Press <Del> key during boot sequence to enter “ CMOS Setup Utility” 3. Use arrow keys to select “ADVANCED BIOS FEATURES” on the menu, then press “Enter.” 4. Select “First Boot Device” and change the default setting to “CDROM” using Page Up /Page Down key. 5. Press <Esc> key to go back to CMOS SETUP Utility menu. 6. Press <F10> to select “Save and Exit Setup” 7. Press “Y” then “Enter” to complete. Now you are able to boot up the system from the CD-ROM. 8. Insert the Power Installer CD into the CD-ROM drive and re-start the computer. 9. IWILL Diskette Creator will now execute automatically for making your own driver diskettes. 10.Make the desired driver diskettes according to the instructions displayed on screen. 6.2.2.2 Under windows 98/95/NT You may just click on the software Make Driver Diskettes Utility shown on screen, then select the driver you need, follow the messages shown on screen to complete. 6.2.3 How to Install Intel INF Installation Utility You may just click on the Intel INF Installation Utility shown on screen that needs to be installed, then follow the prompts to complete setup. After completing O.S. installation,user must install “Intel INF Installation Utility” first to avoid some problems during installation. 6.2.4 How to install Security Driver You may just click on the Security Driver shown on screen that needs to be installed, then follow the prompts to complete setup. WS133 Series 75 Chapter 6 Power Installer CD 6.2.5 How to install Onboard AGP Driver You may just click on the Onboard AGP Driver shown on screen that needs to be installed, then follow the prompts to complete setup. 6.2.6 How to install Software Audio Driver You may just click on the Software Audio Driver shown on screen that needs to be installed, then follow the prompts to complete setup. 6.2.7 How to install Network Driver (WS133-N only) You may just click on the Network Driver Installation Guide shown on screen . Please follow the istructions to install the network driver. 6.2.8 How to use PC-Cillin Anti-Virus program Simply click on the PC-Cillin Anti-Virus shown on screen that be installed, then follow the prompts to complete setup. 6.2.9 How to use Hardware Monitoring Utility You may just click on the Hardware Monitor Utility shown on screen then follow the prompts to complete setup. 6.3 Installing Operating Systems This section briefly demonstrates how to install a few popular software operating systems. Use this section only as a guide. It is highly recommended that users first refer to the installation manual of their operating system for a more thorough, detailed description on how to install the operating system. 6.3.1 Windows 98 Whenever installing Windows 98, please remember that Setup creates a new folder for Windows 98, and won’t transfer any existing system settings. Windows 98 will become your default operating system, and will use standard system settings. This procedure represents an entirely new installation of Windows, therefore you’ll need to reinstall any existing programs you may want to use. During Setup, your computer will automatically restart several times using the Windows 98 Setup wizard. 76 WS133 Series Chapter 6 Power Installer CD 6.3.1.1 Installing the CD-ROM version of Windows 98 1. Place a Windows 98 Startup Disk into the floppy disk drive. 2. Restart your computer. The Microsoft Windows 98 Startup menu will appear. 3. Place the Windows 98 CD into your CD-ROM drive. 4. Type the number 1 and press <ENTER >. A series of scans is performed, and then the MS-DOS prompt is displayed. 5. Type the word setup at the MS-DOS display, and press <ENTER>. Setup performs a check (A message will be displayed). This message won’t appear if your computer can’t locate your CD-ROM drive. If you haven’t installed the correct CD-ROM driver, please consult your drive’s documentation or contact your hardware manufacturer. 6. Press <ENTER>. Microsoft ScanDisk will check your disk drives for errors. 7. When ScanDisk finishes, press the X key. Setup will initialize. Then, Windows 98 Setup begins. 8. Please follow the instructions that are displayed. Setup may ask you to insert your original Windows 95 or Windows 3.1 disks if you’re using the upgrade version of Windows 98. 6.3.2 Windows NT 5.3.2.1 Installing the CD-ROM version of Windows NT on an IDE system 1. First, power-on or “boot” your system. 2. Press <Del> key during boot sequence to enter “ CMOS Setup Utility” 3. Use arrow keys to select “BIOS FEATURES SETUP” on the menu, then press “Enter.” 4. Select “Boot Sequence” and change the default setting from A, C, SCSI to “CDROM, C, A” using Page Up /Page Down key. 5. Place the Windows NT 4.0 CD-ROM in the drive. 6. Follow all instructions to finish Windows NT installation. WS133 Series 77 Appendix Appendix Install the Suspend to IDE Hard Disk Utility Overview : Suspend to Disk is an energy-saving feature that allows you to temporarily power off your system (i.e. when you step away from your computer for a meeting, errand, etc.), then return to the original screen (when the screen was last on) to resume your work the next time you power-on the system. This feature is fast and efficient, especially if your system is handling a small memory size. Although the Suspend to Disk utility can be installed without an operating system, it is highly recommended that you first install an operating system before installing Suspend to Disk. You must first make a “Suspend to Disk” diskette to use for installation. Insert the Power Installer CD into your CDROM, select Make Driver Diskette from the menu, and carefully follow the instructions to make a driver diskette. More importantly, you must ensure the Suspend to Disk feature has been disabled before installing new devices, or upgrading your system memory. System Requirements for installing Suspend to Disk: 1. Suspend to Disk utility only works with IDE hard disk drives. You cannot use this utility with any SCSI device because the system BIOS controls IDE devices, but cannot control SCSI devices. 2. This feature works fine with Windows 95/98, and Windows NT FAT file systems, but does not work with Windows NT NTFS file system. 3. This feature works fine with APM compatible PCI/AGP VGA and Sound Blaster compatible cards and drivers. 4. The Intel Bus Master IDE driver is not fully compatible with Suspend to Disk. If this causes some problems, please uninstall the drivers, or do not use Suspend to Disk. 5. Whether you select file or partition method, please make sure that you have enough free HDD space for creating this hidden file or partition. Ex: if you have 64MB system memory and 4MB of VGA memory, you need at least 68MB (64MB + 4MB) of HDD space. You also have to reserve some free space for your future memory expansion. For example, if you plan to upgrade you system memory to 128MB in the near future, then you may reserve a 132MB (128MB+4MB) space. 6. The following are just some of the many AGP cards that have been tested and approved to work satisfactorily with Suspend to Disk: 78 WS133 Series Appendix Manufacturer/model Chipset IWILL Adventure II 3Dlabs Permedia 2 Matrox G200 GainWard 3Dfx Banshee View Top Vulcan B 3Dfx Banshee View Top Titan 4000 S3 Trio 3D Prolink 3Dfx Banshee ATI 3D Rage Pro ATI Rage IIC ASUS Sis 6326 Set-Up Suspend to Disk: 1. Before installing Suspend to Disk utility, please make sure your system is running normally. That means you should have all the necessary drivers installed, including: Intel INF Installation Utility (MUST) Graphics and Audio Driver (MUST) Intel Security Driver (if need) Network Driver (if need) 2. The WS100 supports the Suspend to Disk with O.S.’s help; please make sure you enable the ACPI feature under the O.S. For example, you can type command “SETUP /P J” to install Windows 98 with ACPI support. If you have the Windows 98 already installed, refer to the following steps to enable ACPI feature. a. Click "Start","Run", type "REGEDIT.EXE" then press Enter key. b. Change to location ”HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Detect c. Select “Edit”,”New”,”String Value”and add “Acpioption” d. Double click the “Acpioption” then set the value data to 1. Select Control Panel “ Add New Hardware” to add ACPI devices. 3. Perform the Suspend to Disk utility-ZVHDD. EXE (refer to below) 4. After you finish the ZVHDD installation, enter “Control Panel”,select “Power Management” then enable the “Hibernate Support” 5.Return to “Power Management” then enable “Advanced” select “Hibernate”and click “Apply” Enter DOS mode From Windows 95/98/NT : Open your “Programs” file, and select “MS DOS Prompt”. Once you’ve entered DOS from Windows a. Type the following: C:\WINDOWS>lock WS133 Series 79 Appendix Press <Enter> b. The system will ask, “Are you Ready? ” Press “y” for “yes” Press <Enter>. c. Insert your Suspend to Disk diskette into your floppy disk drive. (See above). d. Type the following: C:\>A: Press <Enter> e. Create a file or partition There are two ways to store the data into HDD: Create a file or partition. You must make sure you have enough disk space before selecting either option (Please refer to System Requirements above). Creating a file stores all the necessary information (you may be working on) into a hidden read-only file within the system hard disk. Creating a partition allows further protection for you by storing all the necessary information into partition separate from other files. Create a file on DOS Model You may select the file size, or allow the system to automatically select for you. Automatic Selection Type the following: A:\>zvhdd /c /file (Note one space is between “zvhdd and “/c”,and the space is between “/c”and “/file”) Press <Enter> The system will then automatically select file size. Then, the system will display the following message: “The C:\SAVE2DSK.BIN has been executed” The Suspend to Disk utility has been set up. Enter File Size (Example: You select 100 MB file size) Type the following: A:\>zvhdd /c /file /m:100 (Note one space is between “zvhdd” and “c” between “c” and “file” and between “file” and “m:100”) Press <Enter> In this case, the system will use 100 MB file size that you’ve selected. Then, the system will display the following message: “The C:\SAVE2DSK.BIN has been executed.” The Suspend to Disk utility has been set up. 80 WS133 Series Appendix Create a partition Type the following: A:\>zvhdd /c /partition (Note one space is between “zvhdd” and “c” and one space is between “c” and “partition”) The system will start to create and format a partition. Whether you have selected file or partition options, once the Suspend to Disk utility has been set up, press any key, and you will automatically return to Windows. Then, you must restart your system in order to enable the Suspend to Disk feature. Whether you have selected file or partition options, once the Suspend to Disk utility has been set up, press any key, and you will automatically return to Windows. Then, you must restart your system in order to enable the Suspend to Disk feature. Enter DOS command directly : You may also enter DOS during the re-boot process by pressing the <F8> key after powering on the system, and selecting “Command prompt only.” If your system normally runs from DOS, or you have a DOS diskette, simply boot from DOS. Then, simply follow procedure “c” through “e”(above). Since Windows does not control the system, it will automatically re-boot. How to use Suspend to Disk : Simply press the power-on button located on the front panel of your computer chassis. Note: Do not hold the power-on button more than four seconds, because of the system will shutdown and the Suspend to Disk function will not work immediately, Delete Suspend to Disk from Windows 95/98/NT : Open your “Programs” file, and select “MS DOS Prompt.” 1. Type the following: C:\WINDOWS>lock Press <Enter> 2. The system will ask, “Are you Ready?”Press “y” for “yes”. Press <Enter>. 3. Insert your Suspend to Disk diskette into your floppy disk drive. (See above). 4. Type the following: C:\>A: Press <Enter> 5. To delete file, type the following: A:\>zvhdd /d /file (Note one space is between “zvhdd” and “/d ” and one space is between “/d” and “/file”) 6. To delete partition, type the following: A:\>zvhdd /d /partition WS133 Series 81 Appendix (Note one space is between “zvhdd” and “/d ” and one space is between “/d ”and “/partition” ) 7. Press any key to return to Windows. Then restart your system. Delete Suspend to Disk from DOS Directly : Enter DOS during the re-boot process by pressing the <F8> key after powering on the system, and select “Command prompt only.” Or, if your system normally runs from DOS, or you have a DOS diskette, simply boot from DOS. 1. Insert your Suspend to Disk diskette into your floppy disk drive. (See above). 2. Type the following: C:\>A: Press <Enter> 3. Then, follow procedures “5” through “7” ( See above). Since Windows does not control the system, it will automatically re-boot. 82 WS133 Series