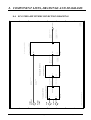
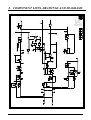
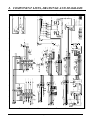
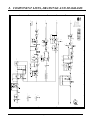
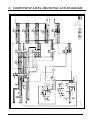
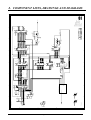
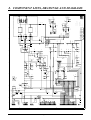
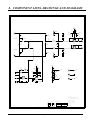
Download 8. component lists, drawings and diagrams
Transcript
FRED MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE (First Responder External Defibrillator Biphasic) Notice technique Version Juillet 2001 Part No. 0-48-0001 FRED MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE Service Manual Revision History Version 1: Art. N° 0-48-0001 Page I July 2001 Vo. Juillet 2001 FRED MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE WARNING This manual shall be considered to form an integral part of the described device. This service manual is intended for qualified personnel. It describes the operating, maintenance and troubleshooting of MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED devices. Compliance with its contents is a prerequisite for correct device performance and the safety of the patient and the operator. The manufacturer shall only be liable for the safety, reliability and performance of the device if: - all assembly, extensions, adjustments, modifications and repairs have been performed by the manufacturer or by persons authorised by the manufacturer. - the electrical system of the premises of use is in accordance with applicable requirements. - the device is used in accordance with the instructions for use. - only original Schiller spare parts are used. This manual describes the device at the time of printing. The provision of this manual shall not in any event constitute permission or approval to modify or repair the device. The manufacturer agrees to supply all the spare parts for a ten-year period. All rights reserved for the devices, circuits, processes and names mentioned in this document. The use of the MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED device shall comply with the description provided in the Operating Manual. The device shall not be put to uses other than as described in the manual, which may be hazardous. Art. N° 0-48-0001 Page II Vo. Juillet 2001 FRED MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE SAFETY INFORMATION • The device bears the following marking: CE-0459 in accordance with the requirements of Council directive 93/42/EEC relating to medical devices, based on the essential requirements of Annex I of the directive. • The device fully meets the electromagnetic compatibility requirements of standard IEC 60601-1-2/EN 60601-2, “Electromagnetic compatibility of Medical Electrical Equipment”. • The device has undergone interference elimination in accordance with the requirements of standard EN 50011, class B. • In order to ensure optimum patient safety, electromagnetic compatibility, measurement precision and device operation, users are advised to use only original Schiller spare parts. Users shall be solely liable for the use of accessories other than original accessories. The manufacturer shall not be liable for any damage due to the use of incompatible accessories or consumable supplies. • The manufacturer shall only be liable for safety, reliability and device performance if: - assembly, configuration, modifications, extensions or repairs have been made by Schiller personnel or personnel that have been duly authorised by Schiller. - the device is used in accordance with the instructions for use. • Users shall be entirely liable for any use of the device that does not comply with the procedures described in the Operating Manual. • This manual describes the device and the technical safety standards applicable at the time of printing. All rights reserved for the circuits, processes, names, software and devices referred to in this service manual. • The quality assurance system applicable in the manufacturer’s facility meets the requirements of international standards EN ISO 9001 and EN 46001. • No part of this document may be reproduced without the written permission of Schiller. Art. N° 0-48-0001 Page III Vo. Juillet 2001 FRED MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE Safety symbols used on the device Danger – High Voltage. Conventions used in the manual G Danger: Warns the user of an imminent hazard. If the warning is not heeded, the user (and/or people and property around the user) could be exposed to death or serious injury. I Caution: Warning describing conditions or actions that could lead to device or software malfunctioning. Note: Remark or note providing useful information to enable the user to get the most from the equipment. F Additional information or explanation about the previous paragraphs. Manufacturer: SCHILLER MEDICAL SA 19, Avenue de la Gare F- 67 162 Wissembourg Tel. Fax : **33 / (0) 3.88.63.36.00 : **33 / (0) 3.88.94.12.82 Art. N° 0-48-0001 Page IV Vo. Juillet 2001 FRED MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE PRECAUTIONS REQUIRED WHILE TESTING THE DEVICE While testing the MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED device, only fixed resistors with high voltage and power ratings that are well insulated from the frame and the earth may be used to simulate the patient. Never use incorrectly insulated systems, systems with loose contacts or systems with components such as sparkers or flash tubes, as they could destroy the device beyond repair. Art. N° 0-48-0001 Page V Vo. Juillet 2001 FRED MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE CONTENTS SERVICE MANUAL REVISION HISTORY.................................................................................................... I WARNING ............................................................................................................................................................ II SAFETY INFORMATION.................................................................................................................................. III-IV PRECAUTIONS REQUIRED WHILE TESTING THE DEVICE.................................................................. V CONTENTS .......................................................................................................................................................... VI-X 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE ............................................. 1-1 1.1. Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 1-1 1.2. Specifications ................................................................................................................................ 1-3 1.3. Optional features ........................................................................................................................... 1-9 1.4. 1.3.1. BUFRDI.................................................................................................................. 1-9 1.3.2. BUFRS.................................................................................................................... 1-9 1.3.3. BUFREC 3.............................................................................................................. 1-9 1.3.4. BUFREC 12............................................................................................................ 1-9 1.3.5. BUFRMAN............................................................................................................. 1-9 1.3.6. FREDVO ................................................................................................................ 1-9 Optional communication features.................................................................................................. 1-9 1.4.1 FREDWARE .......................................................................................................... 1-9 1.4.2 MODEM 1 .............................................................................................................. 1-9 1.4.3 BUFRTC................................................................................................................. 1-10 Art. N° 0-48-0001 Page VI Vo. Juillet 2001 FRED MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE 1.5. 1.6. 2. 1.4.4 SEMA 200 .............................................................................................................. 1-10 1.4.5 READER 0 ............................................................................................................. 1-10 1.4.6 READER 1 ............................................................................................................. 1-10 1.4.7 READER 2 ............................................................................................................. 1-10 Cells, batteries and charger for FRED........................................................................................... 1-10 1.5.1. Mains charger for FRED......................................................................................... 1-10 1.5.2. Vehicle charger for FRED ...................................................................................... 1-10 1.5.3. DG 2002 C2 charger ............................................................................................... 1-11 1.5.4. BT 01 charger - discharger...................................................................................... 1-11 Accessories.................................................................................................................................... 1-11 1.6.1 General accessories................................................................................................. 1-11 1.6.2 Defibrillation accessories........................................................................................ 1-12 1.6.3 ECG accessories...................................................................................................... 1-12 1.6.4 SpO2 accessories .................................................................................................... 1-12 STARTING UP.......................................................................................................................................... 2-1 2.1. Safety instructions ......................................................................................................................... 2-1 2.2. Power supply ................................................................................................................................. 2-2 2.3. Recharging the cadmium-nickel battery........................................................................................ 2-3 2.3.1 Mains charger for FRED®...................................................................................... 2-3 2.3.2 Vehicle charger for FRED ...................................................................................... 2-4 2.3.3 DG 2002 C2 charger ............................................................................................... 2-5 3. OPERATION............................................................................................................................................. 3-1 4. TESTING AND MAINTENANCE .......................................................................................................... 4-1 4.1. Functional inspections ................................................................................................................... 4-1 4.1.1. Art. N° 0-48-0001 Automatic testing upon power up ........................................................................... 4-1 Page VII Vo. Juillet 2001 FRED MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE 4.1.2. Manual testing......................................................................................................... 4-2 4.2. Automatic daily test....................................................................................................................... 4-3 4.3. Systematic check before use.......................................................................................................... 4-3 4.4. Weekly check ................................................................................................................................ 4-4 4.5. Annual check................................................................................................................................. 4-4 4.6. Cleaning and disinfecting .............................................................................................................. 4-4 5. TROUBLESHOOTING............................................................................................................................ 5-1 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS ................................................................................................................. 6-1 6.1. Device disassembly procedure ...................................................................................................... 6-1 6.2. Operations on the upper part ......................................................................................................... 6-2 6.3. 6.2.1. Removing the CPU circuit ...................................................................................... 6-2 6.2.2. Removing the LCD display..................................................................................... 6-3 6.2.3. Removing the BACKLIGHT CONVERTER support circuit ................................. 6-3 6.2.4. Removing the DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP circuit ................................... 6-4 6.2.5. Removing the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP circuit ............................................... 6-4 Operations on the lower part ......................................................................................................... 6-5 6.3.1. Verification of the full discharging of the HV capacitor......................................... 6-6 6.3.2. Removing the DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL circuit ........................................... 6-6 6.3.3. Removing the POWER SUPPLY circuit ................................................................ 6-7 6.3.4. Removing the ECG PREAMP PROTECTION circuit ........................................... 6-7 6.3.5. Removing the HT switching circuit ........................................................................ 6-8 6.3.6. Removing the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT .......................................................... 6-9 6.3.7. Replacing the HV capacitor .................................................................................... 6-10 6.3.8. Replacement of parts............................................................................................... 6-12 Art. N° 0-48-0001 Page VIII Vo. Juillet 2001 FRED MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS ............................................................................................................ 7-1 7.1. General operation .......................................................................................................................... 7-1 7.2. Upper part...................................................................................................................................... 7-2 7.3. 8. 7.2.1. TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP printed circuit board ................................................ 7-2 7.2.2. DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP printed circuit board .................................... 7-4 7.2.3. CPU printed circuit board ....................................................................................... 7-6 7.2.4. BACKLIGHT CONVERTER support PCB .......................................................... 7-11 Lower part ..................................................................................................................................... 7-12 7.3.1. Battery interface printed circuit board .................................................................... 7-12 7.3.2. POWER SUPPLY printed circuit board ................................................................. 7-12 7.3.3. HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT printed circuit board ................................................ 7-13 7.3.4. DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL printed circuit board ............................................ 7-16 7.3.5. HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit board...................................................... 7-21 7.3.6. ECG PREAMP PROTECTION printed circuit board ............................................ 7-22 7.3.7. INSULATION AND SHIELDING printed circuit board ....................................... 7-23 7.3.8. Timing charts of the defibrillator part..................................................................... 7-23 LIST OF COMPONENTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS ............................................................... 8-1 8.1. List of abbreviations and components ........................................................................................... 8-1 8.2. List of signals used in the diagrams............................................................................................... 8-2 8.3. List of different printed circuit boards........................................................................................... 8-7 8.4. ECG preamp interconnection drawing .......................................................................................... 8-8 8.5. Monitor part interconnection drawing........................................................................................... 8-9 8.6. Defibrillator part interconnection drawing .................................................................................... 8-10 8.7. Defibrillator part diagram.............................................................................................................. 8-11 8.8. TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP printed circuit board....................................................................... 8-13 8.9. DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP printed circuit board........................................................... 8-33 8.10. Central processing unit printed circuit board ................................................................................ 8-41 Art. N° 0-48-0001 Page IX Vo. Juillet 2001 FRED MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE 9. 8.11. Backlighting converter support printed circuit board .................................................................... 8-62 8.12. Battery interface printed circuit board........................................................................................... 8-66 8.13. POWER SUPPLY printed circuit board........................................................................................ 8-70 8.14. HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT printed circuit board ...................................................................... 8-75 8.15. DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL printed circuit board .................................................................. 8-82 8.16. HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit board ............................................................................ 8-89 8.17. ECG PREAMP PROTECTION printed circuit board................................................................... 8-94 INDEX ........................................................................................................................................................ 9-1 Art. N° 0-48-0001 Page X Vo. Juillet 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE This section provides a general description of the device, along with the specifications of the various functions and an overview of the optional features and accessories. 1.1. OVERVIEW The MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® device is either a biphasic automated external defibrillator (AED) intended for use by first-aid personnel or a biphasic defibrillator that may be used in the manual mode (optional) by medical personnel. The basic version of MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® includes the following: - a monitor showing the various messages in the semiautomatic mode, an ECG input through adhesive defibrillation electrodes, an automatic VF/VT recognition function, a voice prompt function, a biphasic waveform defibrillation function, a battery slot designed for either a cadmium-nickel battery or a lithium cell, a charging connector for a cadmium-nickel battery, a connector for the PCMCIA memory card. As an option, MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® may be fitted with the following: - a function to display the ECG signal on the monitor, a three-lead ECG acquisition function through the patient cable, a twelve-lead ECG acquisition function through the patient cable, an SpO2 function, manual operating mode, a memory for saving the voices of carers, a function for the telephone transmission of the data saved on the PCMCIA card. The following data are always displayed on the LCD screen: - the time elapsed since the device was switched on, - the number of shocks delivered since the device was switched on, - the messages of the AHA/ERC protocol for AED mode operation. The following data may be displayed on the LCD screen: - the ECG signal, either from the adhesive defibrillation electrodes or from the patient cable, - the heart rate with the heart rate unit, - a systolic indicator, - a battery symbol when the battery charge is low, - a symbol indicating the recording of data on the memory card, - the synchronising mode (only in the optional manual defibrillator mode, in the presence of a QRS signal), - system alarm messages, - defibrillator data: selected energy value, capacitor charging, defibrillator ready, safety discharge (with optional manual defibrillator mode), - the pulse curve and the blood oxygen saturation rate (optional SpO2 feature). Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 1-1 Version July 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE With MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED®, defibrillation is performed easily and safely (all the stages of defibrillation are displayed on the screen) in the semiautomatic mode or in the manual mode (optional). AED mode: the AED or semiautomatic mode can be set up in the factory on the basis of the protocol of the American Heart Association (AHA) or that of the European Resuscitation Council (ERC). The MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® device offers two energy sequences in the AED mode: • standard sequence: when ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia above 180 b/min is detected, an automatic charge of 130 J is started up for shocks 1 and 2, followed by 180 J for any subsequent shocks that may be needed, • upon a request from the customer, the device may be factory-set with the following sequence: when ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia above 180 b/min is detected, an automatic charge of 90 J is started up for shock 1, followed by 130 J for shock 2 and 180 J for any subsequent shocks that may be needed. Manual mode: the energy value is selected through the manual defibrillator keyboard. The energy values available in the manual mode are as follows: 1 J, 2 J, 4 J, 6 J, 8 J, 15 J, 30 J, 50 J, 70 J, 90 J, 110 J, 130 J, 150 J and 180 J. In the manual mode, the selected energy value and the stored energy during the Defibrillator Ready phase are selected on the screen in order to detect any malfunctioning or operator error. Also, a safety system automatically discharges the capacitor within the device if the energy stored is not used. The triggering of the defibrillation pulse by the Shock key may be unsynchronised (semiautomatic mode with ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation) or synchronised (atrial fibrillation and flutters, supraventricular tachycardia in the manual mode). Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 1-2 Version July 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE 1.2. SPECIFICATIONS POWER SUPPLY Battery power supply Battery : Cadmium-nickel: 12 V – 2.4 Ah Cell life : 2.5 hours in the ECG monitoring mode or 110 defibrillation shocks at 180 J Recharge : · DEFIGARD 2002 C2 · with a FRED vehicle charger connected to the battery charge connector · by FRED mains adapter Charging time : · 1 hour with DEFIGARD 2002 C2 · 80% of the capacity after 20 hours through the battery charge connector · 100% of the capacity after 27 hours Recycling frequency : · recommended after every 15 discharge cycles · at least once a month with the recycling schedule label affixed on the battery Lithium cell power supply Cell : Lithium: 18 V – 4.75 Ah Cell life : 5 hours in the ECG monitoring mode or 450 defibrillation shocks at 180 J (at 20°C) : Life after one year of installation in FRED with a daily operating test, without using the device 2 hours in the ECG monitoring mode or 150 defibrillation shocks at 180 J (at 20°C) Life after five years of storage (at +10 to + 20°C) in the original packaging : 4.5 hours in the ECG monitoring mode or 400 defibrillation shocks at 180 J (at 20°C) Recharge : the lithium cell is not rechargeable Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 1-3 Version July 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE MONITOR PART ECG signal Inputs : · insulated – type CF · acquisition through a three-lead patient cable, four-lead · · · · · · · patient cable, ten-lead patient cable or through adhesive defibrillation electrodes leads I, II, III or ECG through the adhesive defibrillation electrodes protection from defibrillation and pacing impedance: > 2.5 MΩ at 10 Hz common mode reject rate > 100 dB noise at the input < 35 µV patient lead current < 0.1µA electrode impedance monitoring Input voltage : · dynamics: ± 5 mV · common mode: ± 1 V · differential mode: ± 1 V Bandwidth : 0.5 Hz - 40 Hz at -3 dB Heart rate range : 10 to 300 b/min Accuracy : ± 5 b/min Minimum QRS width : 5 ms Baseline correction after saturation : after 200 ms QRS indicator : audio and visual VF/VT Recognition Shock recommendation : in the presence of VF/VT at a rate of over 180 b/min Sensitivity : 98.8 % (AHA and MIT) Specificity : 99.97 % (AHA and MIT) Minimum amplitude required for ECG interpretation : ECG amplitude > 0.20 mV Signals with an amplitude < 0.2 mV are interpreted as asystole. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 1-4 Version July 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE LCD Monitor Specifications : · · · · Display : · display of measurement values / alphanumeric settings · ECG curve (optional) · plethysmogram (optional) Scrolling speed : 25 mm/s (for ECG and plethysmogram) Scrolling direction : left to right Technical alarms : · visual and audio Physiological alarms : · visual and audio Recording capacity : 5 hours of ECG records and 500 events maximum for a 2 MB PCMCIA memory card or (optionally) one hour of ECG, one hour of the sound environment and 500 events for a 10 MB PCMCIA memory card. PCMCIA card reading : either with the FREDWARE multimedia system or with the SAED Reader Pro software liquid crystal display (passive matrix), type FSTN black and white dimensions: 130 x 70 mm 2 tracks Alarms Memory SPO2 AND PULSE RATE Inputs : Type CF, protected from defibrillation shocks Sensor : finger sensor or Y sensor Measuring range : 0 to 100% Accuracy : · ± 2 % from 70 to 99 % · ± 3 % from 50 to 69 % Integration period : 8 sec or 16 sec depending on the configuration Signal intensity indicator : bar graph on the monitor Amplitude adjustment : automatic gain Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 1-5 Version July 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE DEFIBRILLATOR PART Electrodes Type of electrode : single-use adhesive defibrillation electrodes Inputs : insulated – type BF Operating modes : · semiautomatic defibrillation (AED mode) · manual defibrillation in synchronised mode · manual defibrillation in non-synchronised mode Energy value selection : · AED mode: semiautomatic function (AED mode) · Manual mode: selection by manual keyboard (optional) Energy values in AED mode : · 130 J – 130 J – 180 J (energy delivered into 50 Ω ) or on Functions request · 90 J – 130 J – 180 J (energy delivered into 50 Ω) · 1 - 2 - 4 - 6 - 8 - 15 - 30 - 50 - 70 - 90 -110 - 130 - 150 – Energy values available in Manual mode : Energy accuracy : · ± 15 % (> 50 J) in 50 Ω · ± 4 J (≤ 50 J) in 50 Ω Energy display : · selected energy value Charge completed indication : · audio message · visual indication Safety : 180 J (energy delivered into 50 Ω) · internal safety discharge displayed on monitor Performance Nominal service Capacitor charging time · with full battery · after 15 discharges at maximum energy : 90 charges at maximum energy with no time gap between two charges (Cd/Ni battery fully charged) · 5 sec with Cd/Ni or lithium cell : · 6 sec with Cd/Ni or lithium cell : Discharge curve: : Biphasic waveform MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE Discharge time into a resistance of 100 Ω : Phase 1 = 4 ms and Phase 2 = 4 ms Idle time = 400 µs between two phases Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 1-6 Version July 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE Discharge time into a resistance of 50 Ω : Phase 1 = 4 ms and Phase 2 = 4 ms Idle time = 400 µs between two phases Synchronised shocks : 25 ms after the R wave Safety discharge : · · · · · 20 sec after charging 160 ms after delivering the shock if insufficient cell/battery charge capacity if technical fault when the device is switched off Discharge curves at 180 Joules Oscillogram of discharge into 40, 60, 80, 100 and 120 Ω resistance at maximum energy 100 1 1. Oh 2. Oh 3. Oh 4. Oh 5. Oh 2 80 3 4 60 Courant (A) 5 R R R R R = = = = = 40 60 80 100 120 40 20 0 -20 -40 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Tem ps (m s) DIMENSIONS AND WEIGHT Dimensions : · Width: 260 mm · Height: 90 mm · Depth: 255 mm Weight : · 2.9 kg (without battery or accessories) · 3.4 kg (with lithium cell) · 3.7 kg (with Cd/Ni battery) Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 1-7 Version July 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENT REQUIREMENTS Transport temperature range : -30 °C to +50 °C : -10 to +50°C Operating temperature range : 0 to +50°C Relative humidity : 30…95%, non condensing Atmospheric pressure : 700…1060 hPa Protection class : · IP 20 without bag, with charger · IP 21 without bag, without charger · IP 23 with bag Storage temperature range Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 1-8 Version July 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE 1.3. FRED ACCESSORIES 1.3.1. BUFRDI Optional ECG display. This option is used to view the ECG taken from the adhesive defibrillation electrodes or ECG electrodes on the monitor. 1.3.2. BUFRS SpO2 module. Optional module including the ECG display (BUFRDI) and that plethysmogram. Supplied with SpO2 sensor and cable. 1.3.3. of the BUFREC3 Optional three-lead ECG module. This option is used to analyse the ECG from a three-lead cable. The BUFRDI module is required for viewing the ECG. Supplied with a three-lead ECG cable and electrodes. 1.3.4. BUFREC12 Optional twelve-lead ECG module. This optional module is used to acquire a twelve-lead ECG for transmission via GSM using special software. Modem (GSM) and software (SEMA 200) for an extra charge. The BUFRDI module is required to display a lead on the screen. Supplied with a ten-conductor ECG cable. 1.3.5. BUFRMAN Optional manual defibrillation function. This optional function is used to operate the defibrillator in the manual mode: the user can select the energy value, set off capacitor charging and deliver the shocks. In the manual mode, shock synchronisation is integrated. The ECG display is also included and configurable. 1.3.6. FREDVO Optional sound environment recording module. This module is used to record the voices of carers (30 min) in addition to the ECG and events. Supplied with 10 MB memory card. The FREDWARE system is required for reading. 1.4. OPTIONAL COMMUNICATION FEATURES 1.4.1. FREDWARE Multimedia system for FRED®. The system includes a multimedia computer for reading (2 or 10 MB) PCMCIA cards directly or through a telephone link. Configured and tested. Supplied with a multimedia PC, 17” monitor, modem, PCMCIA drive and SAED Reader Pro software. 1.4.2. MODEM1 Modem for FRED®. The modem is configured for FRED® and is used to transmit the content of a memory card. The reception system is made up of READER 1 as a minimum. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 1-9 Version July 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE 1.4.3. MODEMGSM Optional feature for transmitting the ECG by GSM. The GSM kit enables the FRED® device with the optional BUFREC12 module to transmit a complete ECG. The SEMA 200 reception software is available for an extra charge. 1.4.4. SEMA 200 Twelve-lead reception software. The SEMA 200 software makes it possible to view and archive the ECG transmitted by FRED® with the optional MODEMGSM and BUFREC12 modules. 1.4.5. READER 0 Memory card data transfer software. This SAED Reader Light freeware is used to transfer the content of the memory card to a PC via a serial link and a PCMCIA card. The software only offers the ECG display function. Compatible with Windows 95, 98 and NT. 1.4.6. READER 1 Memory card data transfer kit. The kit includes a PCMCIA reader, a security key and the SAED Reader Pro software. Installation is available for an extra charge. This complete version is used to transfer the content of the memory card to a PC (series link, PCMCIA, modem). Compatible with Windows 95, 98 and NT. 1.4.7. READER 2 Memory card data transfer kit for laptop PCs with PCMCIA drives. The kit includes a security key and the SAED Reader Pro software. This complete version is used to transfer the content of the memory card to a PC (series link, PCMCIA, modem). Compatible with Windows 95, 98 and NT. 1.5. CELLS, BATTERIES AND CHARGER FOR FRED 1.5.1. Mains charger for FRED® * * 77 592 230-V mains charger, Europe version, for FRED® 79 091 110-V mains charger, US version, for FRED® The FRED mains charger offers slow charging (22 hours) of the cadmium-nickel battery by means of the mains. The FRED mains charger is also used to enable MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® to run in the monitoring mode on the mains power supply. 1.5.2. Vehicle charger for FRED * Art. no. 0-48-0001 W141 2013 Vehicle charger for FRED® Page 1-10 Version July 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE The vehicle charger for FRED offers slow recharging (22 hours) of the cadmium-nickel battery installed in FRED® by means of DC power taken from a vehicle. The vehicle charger is also used to enable MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® to run in the monitoring mode. 1.5.3. DG 2002 C2 charger The DG 2002 C2 charger is used to rapidly recharge one or two cadmium-nickel batteries by means of the mains. The charger makes it possible to have fully charged cadmium-nickel batteries for MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® at all times. 1.5.4. BT 01 charger/discharger The BT01 charger/discharger is used for the rapid charging and recycling of cadmium-nickel batteries by means of the mains. 1.6. ACCESSORIES 1.6.1. Art. no. 0-48-0001 General accessories * U 16006 Ni/Cd – 12 V – 2.4 Ah battery * W141 5323 18 V – 4.75 Ah lithium cell (non rechargeable) * W140 5013 accessory bag * W140 5309 transport bag * W140 5045 Training CD-ROM for FRED® * W741 1927 ECG simulator for training, with electrodes * W140 5046 Training book for FRED® * W141 1876 PCMCIA memory card, capacity 2 MB * W141 1877 PCMCIA memory card, capacity 10 MB * W140 5307 vehicle wall mounting support for FRED® with the transport bag * W140 5367 vehicle wall mounting support for FRED® with no transport bag Page 1-11 Version July 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE * 1.6.2. 1.6.3. 1.6.4. Art. no. 0-48-0001 W141 2108 connecting cable between FRED® and a PC (null modem series) Defibrillation accessories * W141 0241 large single-use defibrillation electrodes for adults * W140 4262 large single-use defibrillation electrodes for children * W140 5424 defibrillation training electrodes, for use on a standard dummy only. These electrodes cannot be used for defibrillation. * W140 4811 Defibrillation cable for demonstration on dummy ECG accessories * W140 9608 three-conductor ECG patient cable with clip (red, green, yellow) and 45° bent connector * U 50063 four-conductor ECG patient cable with clip (red, green, yellow) and 45° bent connector * W140 2037 ten-conductor ECG patient with 45° bent connector * W140 3846 three-conductor ECG patient cable for infants, with no clip (red, green, yellow), with 45° bent connector * 72 365 adhesive ECG electrodes for adults, diameter 34 mm, bag of 50 SpO2 accessories * U 50153 SpO2 finger sensor for adults * U 50106 Oxilink SpO2 sensor (Y type) for U 50105 finger cot * U 50105 finger cot for Oxilink sensor (Y type) U 50106 * U 50072 two-metre SpO2 extension cord Page 1-12 Version July 2001 1. DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED DEVICE Art. no. 0-48-0001 * W140 1977 soft SpO2 sensor for infants, reusable * W140 2254 soft SpO2 sensor for children, reusable * W140 2255 ear SpO2 sensor * W140 2377 single-use SpO2 finger sensor for adults (bag of 10) * W140 2378 adhesive single-use SpO2 sensor for children weighing 15 – 45 kg (bag of 10) * W140 2379 adhesive single-use SpO2 sensor for children weighing 3 – 15 kg (bag of 10) * W140 2380 adhesive single-use SpO2 sensor for infants weighing less than 3 kg (bag of 10) * W140 2852 reusable adhesive tape for SpO2 sensors (bag of 12) * W140 1994 single-use adhesive tape for soft SpO2 sensors (bag of 40) Page 1-13 Version July 2001 2. STARTING UP This section describes the various possibilities of supplying power to the MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® device and charging the cadmium-nickel batteries and outlines some safety instructions to ensure correct device operation. 2.1. SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS Danger! Risk of explosion FRED® has not been designed for use in medical rooms with an explosive atmosphere. Also, the defibrillator may not be used in oxygen-rich environments or in the presence of inflammable substances (petrol) or anaesthetics. Avoid supplying oxygen to the area around the location of the defibrillation electrodes. Shut off any oxygen supply temporarily. Warning! Risk of electrocution The instructions below shall be followed strictly by all users. Any failure to follow the instructions could expose the patient, the user and rescue workers to the risk of death. • MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® is a treatment device that uses high voltages. It may only be used by duly trained and qualified personnel. Any failure to use the device correctly could expose all the people concerned to the risk of death. Follow all the instructions provided in the operating manual. • Before each use, the user shall make sure that the device is safe and in perfect working order (functional check), particularly by inspecting the cables, connections, electrodes and sensors for any sign of damage. Any defective part shall be replaced immediately. • Take care to insulate the patient electrically (no direct contact with the other people present). • Only connect devices to each other or the surrounding equipment if such connection does not jeopardise the safety of the patient, the user and the environment. If the technical specifications of different devices do not offer the certainty that they can be connected to each other safely, the user shall be responsible for contacting the manufacturers or a competent specialist in order to guarantee the safety of the patient, the user and the environment. In any event, the requirements of standard IEC 60601-1-1 / EN 60601-1-1 shall be met. • In view of the requirements relating to devices protected from splashing water of standard IEC 60601 / EN 60601, the device may be used in a humid environment. However, avoid administering defibrillation shocks in very moist or wet environments. • MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® devices may not be used outdoors along with the mains charger or the vehicle charger for FRED. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 2-1 Version July 2001 2. STARTING UP Warning! Risk of disrupting device operation Device operation may be disrupted by the presence of magnetic or electrical fields. While using the device, check if all the other devices operating nearby meet all the relevant electromagnetic compatibility requirements. X-ray equipment, CAT scanners, radio transmitters and mobile telephones etc. may disrupt the operating of other devices as they are authorised to create more powerful electromagnetic fields. Always keep such devices at an appropriate distance and always run a functional check before using the defibrillator. Warning! Risk of disrupting other devices Likewise, energy charging and the delivery of the defibrillation shock could disrupt the operating of other devices. Before proceeding, submit such other devices to a functional check. Warning! Availability MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® is designed for emergency use. As a result, it must be kept ready to operate at all times, regardless of the conditions of use. Always check the charge level of the battery or cell. Warning! Risk of asphyxia Take care to dispose of packaging materials in accordance with the applicable regulations and keep them out of the reach of children. Warning! Risk of device damage • Special care must be taken when HF surgery devices are used at the same time. As a principle, a minimum distance of 15 cm is to be kept between the ECG lead electrodes and the HF surgery or defibrillation electrodes. In the event of doubt, disconnect the patient cables (ECG acquisition) and the defibrillation electrodes while the HF surgery device is in use. • Avoid setting off repeated shocks (in the Manual mode) when the electrodes are not connected to the patient. The internal safety discharge system that dissipates unneeded energy may lead to excess overheating 2.2. POWER SUPPLY MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® may be powered by a rechargeable cadmium-nickel battery with a capacity of 2.4 Ah or by a non-rechargeable lithium cell with a capacity of 4.75 Ah. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 2-2 Version July 2001 2. STARTING UP • • The cadmium-nickel battery offers independent operation for two and a half hours in the monitoring mode or the possibility to deliver 110 defibrillation shocks at 180 Joules. The lithium cell has an operating life of 5 hours in the monitoring mode or the possibility to deliver 450 defibrillation shocks at 180 Joules. Notes MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® cannot be started up without first inserting a correctly charged battery, even when the device is connected to the FRED® mains charger or vehicle charger. MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® automatically monitors the charge capacity of the battery or cell. When the remaining charge level drops to the minimum required (30 minutes of operation or seven shocks at180 J), the BATTERY LOW symbol is displayed on the screen. 2.3. RECHARGING THE CADMIUM-NICKEL BATTERY The cadmium-nickel battery can be recharged in the device itself by the mains charger or the vehicle charger for FRED®. The batteries may also be charged independently from the device with the help of an external DG 2002 C2 charger dedicated to cadmium-nickel batteries. 2.3.1. Mains charger for FRED® Always recharge the cadmium-nickel battery after each use, and leave the FRED® mains charger connected all the time. There is no risk of overcharging the battery. The mains charger offers two functions: • slow recharging (in 27 hours) of the cadmium-nickel battery installed in MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED when the device is off. • ECG monitoring by MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED®. Recharging the cadmium-nickel battery with the mains charger The recharging of the cadmium-nickel battery installed in MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED only operates when the device is off. To charge the cadmium-nickel battery by mean of the FRED® mains charger, start off by switching the device off, connect the charger connection cable to the corresponding connector on MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® and connect the mains charger to the mains. • Art. no. 0-48-0001 A cadmium-nickel battery (2.4 Ah) is recharged to 80% of its capacity in 20 hours, and to 100% in 27 hours via the FRED® mains charger. Page 2-3 Version July 2001 2. STARTING UP ECG monitoring with the mains charger The mains charger for FRED® also enables ECG monitoring with MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED®. For such monitoring, just connect MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® to the mains charger for FRED® and start up the device (which will be powered by the mains). Important notes: When Multipulse Biowave FRED® is powered through the mains charger for FRED®, the defibrillation function is not available and the recharging of the cadmium-nickel battery in place is not guaranteed. Besides, in some conditions of use, the device may generate a low battery alarm message - the message is to be ignored. • • While using MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® in the monitoring mode through the mains charger for FRED®, users are recommended not to charge the high-voltage capacitor: in either of the two modes, manual or AED. However, if you do start charging the high-voltage capacitor, charging will not be effective and the device will either be switched off or display error messages. To cancel the error messages, the device must be switched off with the On/Off key. 2.3.2. Vehicle charger for FRED® The vehicle charger for FRED® also performs two functions: • slow recharging (in 27 hours) of the cadmium-nickel battery installed in MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED®. • ECG monitoring by MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED®. Recharging the cadmium-nickel battery with the vehicle charger The recharging of the cadmium-nickel battery installed in MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® does not depend on the device status. The device is recharged, whether it is on or off. To charge the cadmium-nickel battery by mean of the FRED® vehicle charger, connect the vehicle charger connection cable to the corresponding connector on MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® and connect the vehicle charger to the DC supply of the vehicle (mind the polarity). • A cadmium-nickel battery (2.4 Ah) is recharged to 80% of its capacity in 20 hours, and to 100% in 27 hours via the FRED® vehicle charger. ECG monitoring with the vehicle charger The vehicle charger for FRED® also enables ECG monitoring with MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED®. For such monitoring, just connect MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® to the vehicle charger for FRED® and start up the device (which will be powered by the vehicle). Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 2-4 Version July 2001 2. STARTING UP Important notes: When MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® is powered by the FRED® vehicle charger, the defibrillation function is not available. • • While using MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® in the monitoring mode through the vehicle charger for FRED®, users are recommended not to charge the high-voltage capacitor: in either mode – manual or AED – or when there is no battery. However, if you do start charging the high-voltage capacitor, charging will not be effective and the device will either be switched off or display error messages. To cancel the error messages, the device must be switched off with the On/Off key. 2.3.3. DG 2002 C2 charger The DG 2002 C2 charger is used for rapidly recharging one or two cadmium-nickel batteries. It has been designed specially for such batteries and offers the following advantages: • • optimised charging performance and a longer life for cadmium-nickel batteries. To charge one or two cadmium-nickel batteries with the DG 2002 C2 charger, connect the charger to the mains. Switch on the DG 2002 C2 charger (switch located below the mains cord connector) and insert a battery in one of the two slots. Rapid charging starts as soon as the battery is inserted (the indicator goes on). Recharging a fully discharged battery takes one hour. When the cadmium-nickel battery is fully charged, the console switches to the continuous charge mode (the indicator flashes). A cadmium-nickel battery can be charged to 100% of its capacity in one hour with the DG 2002 C2 charger, which offers a controlled charging facility. Notes: While the battery is being recharged, never expose it to direct sunlight or place it on a radiator. Also, avoid exposing it to temperatures below +5°C. The surrounding temperature may not exceed +40°C as exposure to excessively high temperatures could have an adverse effect on the total life of the battery. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 2-5 Version July 2001 3. OPERATION This section describes the field of use of the device and the basic principles of the chain of survival. For more information about the use of the device and its context of use, it is imperative to refer to the Operating Manual of the FRED® device. In its basic version, MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® is a battery-operated compact biphasic semiautomatic defibrillator. Defibrillation is achieved by means of large single-use adhesive defibrillation electrodes, which also acquire the ECG signal in order to analyse and measure the heart rate. When the device is in use, the user is guided by visual and audio instructions (LCD screen and speaker). For documentation and analysis, the device can save up to 5 hours of the ECG signal and the intervention procedure on its PCMCIA memory card. The use of this device in the semiautomatic defibrillation mode (or AED mode) is only permitted if the legislation of the country of use expressly provides for early defibrillation by non-medical personnel. The personnel shall be trained specially and placed under the control of a physician. A special variant of the device offers the possibility to use the MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® device for manual defibrillation. In principle, the use of this device is part of the “chain of survival” developed by the American Heart Association (AHA) and the European Resuscitation Council (ERC). The chain of survival is represented by a succession of steps taken by different protagonists, all of whom play an essential role in offering continuous care to victims of sudden cardiac arrests. Such care is indispensable in order to improve the chances of survival of such patients. Time is of the essence in the chain of survival. It is generally accepted that the chain of survival includes several complementary integrated steps, which are as follows: 1. Recognition of cardiac arrest 2. Early access 3. Early CPR (cardiac-pulmonary resuscitation) 4. Early defibrillation where required 5. Early advanced life support 6. Hospitalisation in intensive care The people involved in the chain are as follows: • witnesses • first-aid workers • medical teams: paramedics or out-of-hospital medical personnel • hospital teams Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 3-1 Version July 2001 3. OPERATION The effectiveness of the entire chain of survival can be jeopardised if any of its links were to fail. Note relating to biocompatibility The product components and accessories described in this manual that come in contact with the patient during the proper use of the product are designed to fulfil all the requirements of biocompatibility standards. For any questions on this matter, do not hesitate to contact Schiller. F Art. no. 0-48-0001 The correct procedure for using MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® has been provided in the FRED® operating manual. Page 3-2 Version July 2001 4. TESTING AND MAINTENANCE This section describes the testing and maintenance procedures recommended for MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED®. 4.1. FUNCTIONAL INSPECTIONS As regards functional checking, the device offers two different testing possibilities: • Automatic testing upon power up • Manual test 4.1.1. Automatic testing upon power up When the device is switched on, the self test screen appears and the automatic test takes place. The automatic self test upon power up includes the following: • main processor working memory check (read, write) • main processor check (internal memory, arithmetic operations) • program medium check (8-bit CRC) • analogue/digital converter check (verification of power supply voltages) • ECG amplifier module check (internal self test) • VF/VT recognition module test (internal self test) • recording module check (internal self test) • defibrillator check (with no high-voltage capacitor charge) • cadmium-nickel battery or lithium cell charge test If the device does not find any error, it switches to the AED mode and prompts the user to connect the large defibrillation electrodes. On the other hand, if the device detects an error, an audio alarm sounds and an error message is displayed. In that case, switch off the device or the power supply to the device (remove the battery or cell). The device may only be used again after it has been repaired. Note • An error in the data recording module (PCMCIA memory card) does not have any effect on correct device operation. Once the test has been completed, the device switches to the AED mode. To signal the error detected, the recording symbol flashes. • A complete functional check of the high-voltage capacitor discharge circuit (energy discharge test) can only be performed with an appropriate test simulator (see p 4.2). The simulator must generate a fibrillation ECG signal and have a circuit to measure the energy delivered during a biphasic defibrillation shock. Warning! Risk of electrocution • Art. no. 0-48-0001 In addition to a successful self test, remember to visually check all the cables, connections, electrodes and sensors before each use. If the inspection brings out any defects that could reduce the safety of the patient or user, the device may not be used before it is repaired. Page 4-1 Version July 2001 4. TESTING AND MAINTENANCE Precautions required while testing the device While testing the MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED device, only fixed resistors with high voltage and power ratings that are well insulated from the frame and the earth may be used to simulate the patient. Never use incorrectly insulated systems, systems with loose contacts or systems with components such as sparkers or flash tubes, as they could destroy the device beyond repair. 4.1.2. Manual testing Manual tests can be set off at any time while switching on the device, by pressing the On/Off and Contrast keys at the same time. To set off the manual test, switch off the device if it is on. Press the Contrast – key and press the On/Off key with the Contrast – key pressed in. MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® will switch to the manual test mode and the manual test screen will be displayed. First of all, the device runs an internal test of the various functions and then tests the various keypads. Follow the instructions provided on the screen and press the required keys as told. Manual testing includes the following: • main processor working memory check (read, write) • main processor check (internal memory, arithmetic operations) • program medium check (8-bit CRC) • analogue/digital converter check (verification of power supply voltages) • ECG amplifier module check (internal self test) • VF/VT recognition module test (internal self test) • recording module check (internal self test) • defibrillator check (with high-voltage capacitor charge) • cadmium-nickel battery or lithium cell charge test • check of the various keypads (interactive check with the operator) • LCD monitor check If the manual test is successful, the device goes off automatically at the end of the test. If MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® detects an error during the manual test, it transmits an audio alarm till the device is switched off by the operator (pressing the On/Off key or removing the battery). Note • You can interrupt the manual test at all times by pressing the Off key of the device. • Users are advised to run the manual test every time the cell or battery is changed, in order to check the charge level. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 4-2 Version July 2001 4. TESTING AND MAINTENANCE 4.2. AUTOMATIC DAILY TEST In order to ensure that the device is available for use, it runs an automatic functional test every day. Every day at 12.00, MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® runs an automatic daily test even when it is off (monitor off). The automatic daily test procedure is identical to the self test upon power up, with the exception of the defibrillator part test, which includes a charge of the high-voltage capacitor in this case. The automatic daily test includes the following: • main processor working memory check (read, write) • main processor check (internal memory, arithmetic operations) • program medium check (8-bit CRC) • analogue/digital converter check (verification of power supply voltages) • ECG amplifier module check (internal self test) • VF/VT recognition module test (internal self test) • recording module check (internal self test) • defibrillator check with high-voltage capacitor charge • cadmium-nickel battery or lithium cell charge test If the automatic daily test is successful, the device goes off automatically at the end of the test. If MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® detects an error during the automatic daily test, it generates a sound alarm after every two minutes and briefly displays an error message. To stop the alarm, the operator has to start the manual test (see 4.1.2). Note • With a fully charged cadmium-nickel battery, the device can perform this daily check for at least 4 weeks. 4.3. SYSTEMATIC INSPECTION BEFORE USE Before each use, users are advised to visually inspect the device, the cables, the connectors and the electrodes. If any defect or malfunctioning is found that could jeopardise the safety of the patient or user, do not use the device before it is repaired. − Systematic check before each use · device housing condition check · no mechanical damage · no penetration of liquid in the device · soft keypad and connector condition check Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 4-3 Version July 2001 4. TESTING AND MAINTENANCE 4.4. WEEKLY CHECK MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® is an emergency device that must be available for use at all times. The checks below are to be performed at regular intervals: − Weekly inspection · device housing condition check · connector and cable insulator condition check · accessory completeness check 4.5. YEARLY CHECK The after-sales service of Schiller can take charge of checking MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® devices once a year as part of a maintenance agreement. Otherwise, make sure that the checks are performed by personnel who are trained and have the experience and qualifications required for such operations. − Yearly check: · visual inspection of the device to locate any mechanical damage Immediately replace any damaged · · · · · · parts. check of the legibility of safety instructions Replacement of any missing or illegible marking check of the presence and legibility of a brief operating manual. functional device check by means of a manual test leakage current measurement to IEC 60601-2-4 measurement of the energy delivered by the defibrillator (see precautions while testing the device, p. 4.2) careful check of the electrode cables for any mechanical faults, short circuits or cuts Other than the checks and inspections outlined above, MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® does not require any special maintenance. 4.6. CLEANING AND DISINFECTING I Caution: Switch the device off before cleaning it. Remove the battery or cell before starting to clean the device in order to rule out the risk of starting it up accidentally. Disconnect the defibrillation electrode cables from the device before cleaning. No liquid may be allowed to penetrate inside the device. However, if that does happen, the device may not be used before it is verified by the Customer service department. Never clean the device or the electrodes with substances such as ether, acetone, esters or aromatic chemicals. Never use phenol-based agents or agents containing peroxide derivatives to disinfect the surfaces of the housing of the device. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 4-4 Version July 2001 4. TESTING AND MAINTENANCE • Dispose of all single-use electrodes immediately after use in order to eliminate any risk of accidental reuse (hospital waste disposal system). • Before cleaning the sensor and electrode cables, disconnect the cables from the device. For cleaning and disinfecting the cables, wipe them down with a piece of gauze moistened with cleaner or disinfectant. Never immerse the connectors in a liquid. You may use any cleaning or disinfecting solution that is commonly used in hospitals. • Proceed likewise with the housing, with a cloth moistened with cleaner or disinfectant. No liquid may be allowed to penetrate inside the device during this operation. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 4-5 Version July 2001 5. TROUBLESHOOTING This section describes the troubleshooting procedure to be used if MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® fails to operate correctly. If you have trouble locating or correcting the fault, contact the Customer service department of Schiller. Precautions required during troubleshooting While testing the MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED device, only fixed resistors with high voltage and power ratings that are well insulated from the frame and the earth may be used to simulate the patient. Never use incorrectly insulated systems, systems with loose contacts or systems with components such as sparkers or flash tubes, as they could destroy the device beyond repair. PROBLEM CAUSES CORRECTIVE ACTION Battery Battery worn down Test the battery: run 15 charging/discharging cycles at 180 J on an external charge (e.g. a joulemeter) in series of 5 with a five-minute gap. If a charge takes more than 15 seconds, the battery must be changed. The device starts incorrectly and/or does not reach its normal operating mode 1. Exceptional error 2. Operating error 3. Battery too low 4. CPU board 5. TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP board 1. Switch off the device, then on again. 2. Check the instructions and try again. 3. Make sure that the battery is sufficiently charged. 4. Change the CPU board 5. Change the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP board. The device cannot be switched on 1. Battery flat or absent 2. Battery incorrectly inserted 3. Defective On/Off button 4. F1 fuse 5. POWER SUPPLY board 6. High-voltage PCB 7. CPU board 2. Recharge or replace the battery 2. Check the battery connection with the battery interface board 3. Check the On/Off button 4. Change fuse F1 on the high-voltage PCB 5. Change the POWER SUPPLY board 6. Change the high-voltage PCB 7. Change the CPU board The high-voltage capacitor takes more than 15 seconds to charge to 180 J 1. Battery flat 2. Battery worn down 3. High-voltage PCB 4. High-voltage capacitor 5. HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING board 1. Recharge or replace the battery 2. See Battery problem. 3. Change the high-voltage PCB 4. Change the high-voltage capacitor 5. Change the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING board Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 5-1 Version July 2001 5. TROUBLESHOOTING PROBLEM CAUSES CORRECTIVE ACTION The high-voltage capacitor does not charge correctly 1. Battery flat 2.High-voltage and DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCBs 3. CPU board 4. HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING board 1. Recharge or replace the battery 2. Change the high-voltage and DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCBs 3. Change the CPU board 4. Change the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING board The defibrillator does not charge 1. Operating error 2. Battery flat 3. The high-voltage capacitor is incorrectly connected 4. Fuse F3 5. High-voltage and DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCBs 6. HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING board 1. Repeat the operation 2. Recharge or replace the battery 3. Check the connection of the high-voltage capacitor 4. Change fuse F3 on the high-voltage PCB 5. Change the high-voltage and DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCBs 6. Change the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING board The energy delivered is incorrect 1. Operating error 2. The joulemeter is providing an incorrect value 1. Check the instructions and try again. 2. Make sure that the Joulemeter is compatible with pulsed discharge or use an insulated current sensor and measure the defibrillation current. The pulse biphasic waveform is changed 1. High-voltage and 1. Change the high-voltage and DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCBs 2. Change the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING board Loss of date and time 1. Clock upset 2. Backup cell flat: REPLACE AFTER TEN YEARS 3. CPU board Message: 001 : ‘ECG RECEPTION TIMEOUT’ Major error – return the device for repairs Message: 101 : FV RECEPTION TIMEOUT’ Major error – return the device for repairs Message: 102 : ‘SAED AUTOMATON ERROR’ Major error – return the device for repairs Message: 202 : DEFI AUTOMATON ERROR’ Major error – return the device for repairs Art. no. 0-48-0001 DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCBs 2. HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING board Page 5-2 1. Set the clock as instructed in the operating manual and switch on the device. 2. Change the lithium cell on the CPU board 3. Change the CPU board Version July 2001 5. TROUBLESHOOTING PROBLEM CAUSES CORRECTIVE ACTION Message: 301 : DISPLAY AUTOMATON ERROR’ Major error – return the device for repairs Message: 401 : ALARM ID OUT OF RANGE’ Major error – return the device for repairs Message: 501 : ’CMD FIFO SCRATCH ERROR’ Major error – return the device for repairs Message: 502 : MEMORY RECEPTION TIMEOUT’ Major error – return the device for repairs Message: ’605: SPO2 TRANSMISSION ERROR’ Major error – return the device for repairs Message: ’701: ’EEPROM WRITE ERROR’ Major error – return the device for repairs Message: ’801: EXT MODEM TRANS ERROR’ Major error – return the device for repairs Message: ’802: EXT AUTOMATON ERROR’ Major error – return the device for repairs Message: ‘BATTERY LOW’ 1. Battery flat 2. CPU board 1. Recharge or replace the battery 2. Change the CPU board Message: Inappropriate asystole 1. Electrode connection 2. Exceptional error 3. Electrodes 4. ECG PREAMP PROTECTION board 5. Twelve-lead defibrillation ECG amp board 6. CPU board 1. Check the connection between the electrodes and the device. 2. Switch off the device, then on again. 3. Change the electrodes 4. Change the ECG PREAMP PROTECTION board 5. Change the twelve-lead defibrillation ECG amp board. 6. Change the CPU board Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 5-3 Version July 2001 5. TROUBLESHOOTING PROBLEM CAUSES CORRECTIVE ACTION Message: ‘SENSOR’ 1. SpO2 sensor connection 2. Exceptional error 3. SpO2 sensor 4. SpO2 board 5. CPU board 1. Check the connection between the sensor and the device 2. Switch off the device, then on again. 3. Change the SpO2 sensor 4. Change the SpO2 board 5. Change the CPU board Message: ‘ELECTRODE FAULT’ 1. Electrode connection 2. Exceptional error 3. Electrodes 4. ECG PREAMP PROTECTION board 5. CPU board 1. Check the connection between the electrodes and the device. 2. Switch off the device, then on again. 3. Change the electrodes 4. Change the ECG PREAMP PROTECTION board 5. Change the CPU board Message: ‘BATTERY ERROR’ 1. Battery connection 2. Battery flat 1. Check the battery connection 2. Recharge or replace the battery Message: ‘ADC ERROR’ 1. Exceptional error 2. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again. 2. Change the CPU board Message: ‘CPU ERROR’ 1. Exceptional error 2. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again. 2. Change the CPU board Message: ‘DEFI ERROR’ 1. Exceptional error 2. HIGH-VOLTAGE PCB 3. DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL board 4. HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING board 5. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again 2. Change the high-voltage PCB 3. Change the DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCB 4. Change the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING board 5. Change the CPU board Message: ‘ECG ERROR’ 1. Exceptional error 2. TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP board 3. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again 2. Change the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP board. 3. Change the CPU board Message: ‘EEPROM ERROR’ 1. Exceptional error 2. EEPROM problem 3. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again 2. Change the CPU board 3. Change the CPU board Message: ‘EPROM ERROR’ 1. Exceptional error 2. EPROM problem 3. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again 2. Change the EPROM modules 3. Change the CPU board Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 5-4 Version July 2001 5. TROUBLESHOOTING PROBLEM CAUSES CORRECTIVE ACTION Message: ‘MEMORY ERROR’ 1. Exceptional error 2. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again 2. Change the CPU board Message: ‘RAM ERROR’ 1. Exceptional error 2. RAM problem 3. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again 2. Change the CPU board 3. Change the CPU board Message: ‘FV ERROR’ 1. Exceptional error 2. VF microcontroller 3. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again 2. Change the VF EPROM 2. Change the CPU board Message: ‘PULSE’ 1. SpO2 sensor connection 2. SpO2 sensor 3. Exceptional problem 4. SpO2 board 5. CPU board 1. Check the connection between the sensor and the device 2. Change the SpO2 sensor 3. Switch off the device, then on again 4. Change the SpO2 board 5. Change the CPU board Inappropriate or incomprehensible message 1. Exceptional error 2. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again 2. Change the CPU board Inappropriate or incomprehensible audio message 1. Exceptional error 2. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again 2. Change the CPU board No audio messages 1. Exceptional error 2. Device set-up 3. Speaker connection 4.Voice microcontroller 5. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again 2. Check if the sound is on 3. Check the speaker connection 4. Change the Voice EPROM 5. Change the CPU board Incorrect ECG signal 1. Exceptional error 2. Loose contact 3. Electrodes 4. TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP board 5. DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP board 6. ECG PREAMP PROTECTION board 7. CPU board 1. Switch off the device, then on again 2. Check the contact between the electrodes and the device 3. Change the electrodes 4. Change the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP board. 5. Change de DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP board 6. Change the ECG PREAMP PROTECTION board 7. Change the CPU board Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 5-5 Version July 2001 5. TROUBLESHOOTING PROBLEM CAUSES CORRECTIVE ACTION No data stored on memory card 1. The memory card is full 2. The memory card is writeprotected 1. The corresponding icon is flashing: transfer the content of the memory card with the Reader software 2. A crossed-out icon is flashing on the monitor: change the position of the micro switch at the rear of the memory card to set it to the W/P off position When the device is connected to the mains charger, the battery does not charge 1. The device is on 2. Connection with the charger 3. Fuse F2 4. High voltage board wiring 5. High voltage board 1. Switch off the device 2. Check the connection with the charger 3. Change fuse F2 on the high-voltage board 4. Check the wiring of external DC connector 5. Change the high-voltage PCB When the device is connected to the mains charger, the defibrillator does not operate The defibrillator cannot operate with the mains charger when there is no battery. 1. Put in a charged battery When the device is connected to the mains charger, there are alarm messages or the device is switched off when you try to charge the capacitor The defibrillator cannot operate with the mains charger when there is no battery. 1. Switch off the device if it is still on. 2. Put in a charged battery When the device is connected to the vehicle charger, the battery does not charge 1. Connection with the charger 2. Vehicle charger 3. Fuse F2 4. High voltage board wiring 5. High voltage board 1. Check the connection with the charger 2. Check the vehicle charger 3. Change fuse F2 on the high-voltage board 4. Check the wiring of external DC connector 5. Change the high-voltage PCB When the device is connected to the vehicle charger, the defibrillator does not operate The defibrillator cannot operate with the vehicle charger when there is no battery. 1. Put in a charged battery When the device is connected to the vehicle charger, there are alarm messages or the device is switched off when you try to charge the capacitor The defibrillator cannot operate with the vehicle charger when there is no battery. 1. Switch off the device if it is still on. 2. Put in a charged battery Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 5-6 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS This section describes how to dismantle the device in order to replace faulty parts. The warnings below apply to all operations on internal device components. G Warning: MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® is a defibrillator with a highvoltage capacitor that can be charged to a fatal voltage. The device may only be disassembled by specially trained and authorised personnel. I Caution: Before disassembling the device, remove the battery or cell from its slot. I Caution: The device contains circuits sensitive to electrostatic discharge. All operations on MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® shall be performed in accordance with applicable ESD rules. The operations shall be carried out on an antistatic mat connected to the earth, and the operator shall wear an antistatic strap connected to the mat. Remove the antistatic strap while working on the high-voltage part of the defibrillator. I Caution: The device shall undergo a general test every time it is opened. 6.1. DEVICE DISASSEMBLY PROCEDURE Follow the instructions below while disassembling the device: 1. Remove the cadmium-nickel battery or lithium cell from its slot 2. Also remove the mains or vehicle charger cable if the charger is connected to MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED®. 3. Disconnect all the electrode or SpO2 cables. 4. Turn the device over (LCD monitor down) and unscrew the six assembly screws of the bottom and top halves of the housing. 5. After removing the six screws, turn the device over (LCD monitor towards you). 6. The upper and lower halves of the housing can now be separated. Lift off the upper half and place it to the rear of the lower half by clearing the loop of the ribbon cable located inside the CPU shield (18) of the upper half. 7. The two parts can be separated by disconnecting the three cables that connect them: • Disconnect the flat 34-conductor cable with the help of the connector locking clips accessible in the lower half • Carefully disconnect the flat 10-conductor cable from the connector in the top half • Carefully disconnect the shielded 5-conductor cable of the connector that is partly hidden under the insulation piece (25) of the upper half. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 6-1 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS At this point, the two halves are completely separated. Now you can work on the upper part (monitor function) or the lower part (defibrillator function). 6.2. OPERATIONS ON THE UPPER PART While working on the upper part, use the references to the drawing titled “Upper housing assembly”. In order to access the various components in the upper part, you must first remove the shielding cover (18) of the CPU board, which is fixed by six screws. 6.2.1. Removing the CPU circuit After removing the shielding cover (18), the CPU PCB is entirely accessible. Place the upper part flat (LCD screen down) with its rear wall turned towards you (the handle towards the back of the workstation). To remove the CPU board (5) from the upper part, follow the indications below: 1. Carefully remove the flat cable (10 conductors) from its base J3 located close to the rear left corner of the upper part. 2. Also remove the AMP connector connected to the BACKLIGHTING PCB. 3. Lift the CPU board from the side of the notch on the right-hand side of the board and disconnect the connection between cards (with the LCD screen) at that location. 4. Pull the CPU board to the right in order to remove the ejectors of the memory card support from the memory card notch protected by the soft cap (3). 5. Turn the CPU board over so that the side marked Top Side rests on the upper part towards the handle. 6. Remove the various flat jumpers from their respective bases (i.e. J12, J8 and J6 from left to right). MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® devices with an optional manual defibrillation function also have an interconnected jumper at J7. 7. After the above steps have been completed, the CPU board can be removed from the upper part. I Caution: This circuit contains components sensitive to electrostatic discharge. The operation described above shall be performed in accordance with applicable ESD rules. The CPU board has a lithium cell for saving the various settings. The cell continues to power some circuits even when the CPU board is completely disconnected from the device. The backup lithium cell must be replaced after ten years of service. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 6-2 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS 6.2.2. Removing the LCD display Once the CPU board is removed (see relevant section), the LCD display is entirely accessible. Place the upper part flat (LCD screen down) with its rear wall turned towards you (the handle towards the back of the workstation). To remove the LCD display (28) from the upper part, follow the instructions below: 1. Carefully remove the connector connected to the base (CP2) of the BACKLIGHT CONVERTER support board. 2. Unscrew the two monitor fixing pieces (handle side of the upper part). 3. Unscrew the two screen fixing screws (on the side of the patient preamp insulation piece, 25) 4. Once these steps have been taken, the LCD monitor can be removed from the upper part. I Caution: This circuit contains components sensitive to electrostatic discharge. The operation described above shall be performed in accordance with applicable ESD rules. If the LCD monitor is being changed, ensure that the new screen and the protective piece (31) are clean. Never wipe the surface of an LCD monitor with cloth or paper that could be slightly abrasive, as that would scratch the screen. Any dust may be removed by blowing with compressed air. 6.2.3. Removing the BACKLIGHT CONVERTER support circuit In order to gain access to the backlight converter support circuit, you must also remove the CPU board. After removing the CPU board (see relevant section), you have access to the backlight converter support PCB. Place the upper part flat (LCD screen down) with its rear wall turned towards you (the handle towards the back of the workstation). To remove the BACKLIGHT CONVERTER support circuit (9) from the upper part, follow the instructions below: 1. Carefully remove the connector connected to the base (CP2) of the BACKLIGHT CONVERTER support board. 2. Unscrew the three fixing screws of the backlighting converter board. 3. When the steps above have been completed, the BACKLIGHT CONVERTER support circuit can be removed from the upper part. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 6-3 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS 6.2.4. Removing the DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP circuit After the CPU board has been removed (see relevant section), the insulation and shielding enclosure (25) of the ECG preamp circuits is accessible. Place the upper part flat (LCD screen down) with its rear wall turned towards you (the handle towards the back of the workstation). To remove the DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP circuit (6) from the upper part, follow the instructions below: 1. Remove the two adhesive tapes that close the insulation and shielding enclosure (25) of the ECG preamp circuits. 2. After opening the enclosure, remove the insulating piece (24) from the DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP PCB. 3. Unscrew the four screw that hold the DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP PCB. 4. Turn the DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP PCB over and carefully pull flat cable (10 conductors) out of base J1. 5. After the above steps have been completed, the DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP board can be removed from the upper part. I Caution: This circuit contains components sensitive to electrostatic discharge. The operation described above shall be performed in accordance with applicable ESD rules. To replace the DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP PCB, proceed as described above for removal. While reassembling the board, take care to put in the insulation piece (24) before you close the insulation and shielding enclosure (25). Put in place the two adhesive tapes in order to keep the enclosure closed. I Caution: 6.2.5. The impedance setting must be made imperatively with potentiometer P1 of the DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP board. Removing the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP circuit After the CPU and DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP PCBs have been removed (see relevant sections), the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP circuit becomes accessible at the bottom of the insulation and shielding enclosure. Place the upper part flat (LCD screen down) with its rear wall turned towards you (the handle towards the back of the workstation). To remove the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP PCB (7) from the upper part, follow the instructions below: 1. Remove the defibrillator ECG preamp PCB and remove the two tapes remaining on the insulation and shielding enclosure (25) on the left-hand side. 2. Also remove the copper-coated conducting adhesive tape applied along the closing edge of the insulation and shielding enclosure. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 6-4 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS 3. After opening the enclosure, remove the insulation piece (26) from the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP PCB. 4. Unscrew the two screws used to fix the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP PCB (left-hand side of the board). 5. Also unscrew the two fixing pieces of the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP PCB (right-hand side of the board). 6. Remove the cable interconnected with CP1 on the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP PCB. 7. Now you can remove the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP PCB from the upper part. I Caution: This circuit contains components sensitive to electrostatic discharge. The operation described above shall be performed in accordance with applicable ESD rules. If the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP PCB is to be replaced, proceed as described above for disassembly. While reassembling the board, make sure that the insulating piece (26) has been installed correctly. Also make sure that the flat cable (interconnection with the DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP circuit) has been fed through the slot provided before closing the insulation and shielding (25) enclosure. Put it place a copper-coated conducting tape along the edge (left-hand side of the board) and the two adhesive tapes to keep the enclosure closed. 6.3. OPERATIONS ON THE LOWER PART I Caution: Before starting to work on the lower part, make sure that the lithium cell or the cadmium-nickel battery is not in the slot. While working on the lower part, use the references in the drawing titled “Exploded view of biphasic pulse”. In order to have access to the components of the lower part, you must first remove the insulation and shielding circuit (24) that is fixed by seven screws, which covers the entire defibrillator part. While removing the INSULATION AND SHIELDING circuit which is connected to the insulating piece (45), take care to clear the shielded cable. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 6-5 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS G Warning: MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® is a defibrillator with a highvoltage capacitor that can be charged to a fatal voltage. The lower part of the device contains all the components of the defibrillator part. The device may only be disassembled by specially trained and authorised personnel. G Warning: Before disassembling the lower part, it is imperative to make sure that the high-voltage capacitor is fully discharged. Refer to the point below for the discharge. I Caution: While working on a complete defibrillator section assembled in the lower housing (e.g. to remove a board), do not wear an antistatic strap connected to the earth. While working on PCBs of the defibrillator section that are outside the device and disconnected from it, comply with applicable ESD rules. G Warning: After working on the lower part, the energy values are to be tested systematically, followed by a general device test. The energy values shall be located with a tolerance of ± 15% or ± 4 Joules. 6.3.1. Verification of the full discharging of the HV capacitor Caution: The high-voltage capacitor (5) of MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® devices has two capacities – C1 (30 µF/3.6 kV) between terminals C and C1 and C2 (30 µF/1.2 kV) between terminals C and C2. When the INSULATION AND SHIELDING circuit (24) is removed, the components of the defibrillator section become accessible. Place the lower part flat with the handle turned towards you. Connect a voltmeter with a high-voltage probe (or a high-voltage divider) at the terminals of the high-voltage capacitor. Connect the COM pole of the multimeter to the terminal marked (C) of the high-voltage capacitor and the high-voltage probe (or high-voltage divider) to the terminal (C1) of the high-voltage capacitor. Make sure that there is no load voltage at capacity C1. Repeat the operation for capacity C2 between (C) and (C2). 6.3.2. Removing the DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL circuit After removing the shielding cover (24), the DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCB is entirely accessible. Place the lower part flat with the handle turned towards you. To remove the DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCB (42) from the lower part, follow the instructions below: 1. Art. no. 0-48-0001 The DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCB is connected to the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT through a board-to-board connector (J1). Page 6-6 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS 2. I Just pull up the DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL circuit till it is completely separated from the board. Caution: 6.3.3. This circuit contains components sensitive to electrostatic discharge. After disconnecting the PCB from the device, follow applicable ESD rules. Removing the POWER SUPPLY circuit After removing the shielding cover (24), the POWER SUPPLY PCB is entirely accessible. Place the lower part flat with the handle turned towards you. To remove the POWER SUPPLY PCB (16) from the lower part, follow the instructions below: 1. The POWER SUPPLY PCB is connected to the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT through a board-to-board connector (CP14). 2. Just pull up the POWER SUPPLY circuit till it is completely separated from the board. 3. While removing the POWER SUPPLY circuit, take care not to damage the connector (J17) on the HIGHVOLTAGE CIRCUIT located close by. I Caution: 6.3.4. This circuit contains components sensitive to electrostatic discharge. After disconnecting the PCB from the device, follow applicable ESD rules. Removing the ECG PREAMP PROTECTION circuit After removing the shielding cover (24), the ECG PREAMP PROTECTION circuit becomes fully accessible. Place the lower part flat with the handle turned towards you. To remove the ECG PREAMP PROTECTION circuit (25) from the lower part, follow the instructions below: 1. The ECG PREAMP PROTECTION PCB is connected two high-voltage wires (white and orange) to the connector for the large defibrillation electrodes. 2. To disconnect the two high-voltage wires, pull back the insulating sleeves and lugs with flat pliers, taking care not to crush the connector. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 6-7 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS 3. I After the above steps have been completed, the ECG PREAMP PROTECTION board can be removed from the lower part. Caution: This circuit contains components sensitive to electrostatic discharge. After disconnecting the PCB from the device, follow applicable ESD rules. While putting back the ECG PREAMP PROTECTION circuit, make sure that the Faston lugs connected to the two high-voltage wires (orange and white) are installed correctly. Incorrect installation of these lugs can lead to immediate malfunctioning of the defibrillator section or malfunctioning after some time (if the contacts are loose). Make sure that nothing has been forgotten before starting up the device. Every time the board is replaced, remember to set the impedance (see defibrillation preamp board adjustment procedure). 6.3.5. Removing the HIGH-VOLTcircuit Note: It is preferable to use additional marking for high-voltage cables. After the shielding cover (24) and the two high-voltage wires (orange and white) are removed from the ECG PREAMP PROTECTION PCB (25) (see relevant procedures), the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit can be removed. Place the lower part flat with the handle turned towards you. To remove the HIGHVOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit (9) from the lower part, follow the instructions below: 1. Carefully remove the three high-voltage cables (lugs J6, J9 and J2) connected to the high-voltage capacitor. To remove these and the following cables, pull up the insulating sleeves and the lugs with flat pliers. 2. Carefully remove the two high-voltage wires (lugs J10 and J11) connected to the connector for the large defibrillation electrodes. 3. Carefully remove the high-voltage cable connected to lug J12 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT. 4. Carefully remove the high-voltage cable connected to lug J4 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT. 5. Also remove the two cables (red and black) connected to lugs J19 and J20 on the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit. 6. Remove the cable from connector J18 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit. 7. Remove the four high-voltage wires from the high-voltage converter that are connected to lugs J3 (red), J4 (black), J5 (white) and J7 (blue) of the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit. 8. Unscrew the four screws used to fix the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit and take them out. 9. After the above steps have been completed, the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING board can be removed from the lower part. 10. While replacing the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit, also unsolder the (grey) wire soldered to tab J2 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 6-8 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS While putting back the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit, fix it with the two fixing screws and make sure that the high-voltage cables with Faston lugs are installed correctly. Incorrect installation of these lugs can lead to immediate malfunctioning of the defibrillator section or malfunctioning after some time (if the contacts are loose), or even the destruction of several circuits. Also make sure that the wires (black and red, J19 and J20 respectively) are connected and that the cable with AMP connector is connected to J18 of the HIGHVOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit. Put back any cable clamps that may have been removed while disassembling the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit. Make sure that nothing has been forgotten before starting up the device. I Caution: This operation concerns a critical subassembly of the defibrillator section, which carries high voltages. It may only be performed by personnel who have special authorisation and training to work on MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED devices. I Caution: While working on high-voltage wires, take care not to damage the cables. 6.3.6. Removing the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT After removing the shielding cover (24), the DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCB (43) and the POWER SUPPLY circuit (1) (see relevant sections), the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT is accessible. Place the lower part flat with the handle turned towards you. Follow the instructions below to remove the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT (43) from the lower part for repairs: 1. Carefully remove the cable with an Amp connector from base J17 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT. 2. Carefully remove the high-voltage cable connected to lug J16 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT. To remove the cable, pull up the insulating sleeve and the lug with flat pliers. 3. Carefully remove the red and black cables from lugs J7 and J8. Proceed as described. 4. Carefully remove the cable with an Amp connector from base J6 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT. 5. Carefully remove the two high-voltage cables connected to lugs J4 and J12. Proceed as described. 6. Carefully remove the four high-voltage cables from the high-voltage converter connected by Faston lugs to lugs J2, J4, J5 and J7 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit. Undo the corresponding cable clamps to remove the cables. 7. Unscrew the two fixing screws of the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT located close to the insulating wall close to the high-voltage capacitor. 8. Also unscrew the three metal fixing pieces of the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT, close to the rear wall. 9. Now lift the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT vertically till the board-to-board connector formed by base J15 and male connector J1 of the battery interface PCB are fully disconnected. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 6-9 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS 10. Unsolder the grey wire from the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit soldered to pin J2 on the rear of the PCB. 11. The HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT can now be removed from the lower part. I Caution: This circuit contains components sensitive to electrostatic discharge. After disconnecting the PCB from the device, follow applicable ESD rules. Working on the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT is a delicate operation, which concerns a key component for the correct operating of the entire device. All work on this circuit shall be performed with utmost care in order not to damage any component. While putting in place the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT, take care to ensure that the high-voltage cables with Faston lugs are put in place correctly. Incorrect installation of these lugs can lead to immediate malfunctioning of the defibrillator section or the entire device or malfunctioning after some time (if the contacts are loose). Make sure that no cable is stuck anywhere and that the cables are connected to the right location. Also make sure that the various board-to-board connections are made correctly; Put back the various cable clamps so as to restore the original wiring. Do not forget to solder the grey wire to pin J2 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT. While putting in place the fixing piece located nearby, make sure that it is not in contact with pin J2. Make sure that nothing has been forgotten before starting up the device. I Caution: 6.3.7. G Art. no. 0-48-0001 This operation concerns a key component of the device. Failure to put the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT in place correctly could damage the device beyond repair. This operation may only be performed by personnel who have special authorisation and training to work on MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED devices. Replacing the HV Capacitor Warning: This operation concerns the high-voltage capacitor, which can be charged to a fatal voltage. Before starting to work, make sure that the high-voltage capacitor is fully discharged (see relevant section). Never touch the terminals of the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT directly. The high-voltage capacitor may only be replaced by specially authorised and trained personnel. Page 6-10 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS I Caution: The high-voltage capacitor (5) of MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® devices has two capacities – C1 (30 µF/3.6 kV) between terminals C and C1 and C2 (30 µF/1.2 kV) between terminals C and C2. The replacement of the high-voltage capacitor is required extremely rarely, as the capacitor has a very long life. However, if needed, the high-voltage capacitor can be replaced after removing the shielding cover (24). Place the lower part flat with the handle turned towards you. To remove the high-voltage capacitor (5) from the lower part, follow the instructions below: 1. First clear the insulating piece of the high-voltage capacitor (22) by making an incision along the silicone fixing seal between the insulating piece of the high-voltage capacitor (5) and the outer wall of the lower frame. Make the incision with a Stanley knife, taking care to prevent accidental injury. 2. When the silicone seal has been cut fully, remove the insulating piece from the high-voltage capacitor. 3. Repeat the operation with the other silicone seal located between the insulating wall of the lower housing and the high-voltage capacitor itself. 4. When the silicone seal has been cut fully, the high-voltage capacitor must be free in the housing. 5. Remove lug J16 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT, with the black wire connected to the high-voltage capacitor housing. 6. Remove the three high-voltage cables connected to the high-voltage capacitor. To do so, cut the various cable clamps and carefully remove the three high-voltage cables connected to lugs J2, J6 and J9 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit. To remove the cables, pull up the insulating sleeve and the lug with flat pliers. 7. After the above steps have been completed, the high-voltage capacitor can be removed from the lower part. F After removing the (fully discharged) high-voltage capacitor from the lower part, short its three terminals with a conducting wire. While replacing the high-voltage capacitor, wire it before fixing it into its housing. Connect the pole marked (C) of the high-voltage capacitor to lug J6 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit, pole (C1) to lug J2 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit and pole (C2) to lug J9 of the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit. Take care to follow the above polarity instructions and check if the Faston lugs are placed correctly. Incorrect installation of these lugs can lead to immediate malfunctioning of the defibrillator section or malfunctioning after some time (if the contacts are loose). Position the high-voltage capacitor in its slot and glue the high-voltage capacitor housing against the insulating wall of the lower frame with silicone. Put in place a new high-voltage capacitor insulating piece (22) and glue it with silicone. Put back the cable clamps as they were before the operation. Make sure that nothing has been forgotten before starting up the device. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 6-11 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS I Caution: This operation concerns a key component of the high-voltage section. It may only be performed by personnel who have special authorisation and training to work on MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED devices. All operations shall be followed by a test of the delivered energy values. 6.3.8. G Replacement of parts Warning: Parts may only be replaced by personnel who have been specially trained and authorised by Schiller Medical. Also, only original Schiller Medical replacement parts may be used. F Art. no. 0-48-0001 Note: While ordering parts from Schiller Medical, provide the article number of the device and the serial number stated on the bottom of the device. Specify also the article number of the part, the reference, the description in the list of parts and the ECL of the replaced part. Page 6-12 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 6-13 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 6-14 Version July 2001 6. REPLACEMENT OF PARTS Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 6-15 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS 7.1. GENERAL OPERATION From the technical standpoint, MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® is divided into two subassemblies: • The upper part of the device encloses the following: . ECG signal acquisition from adhesive defibrillation electrodes or from the patient cable, . ECG signal analysis, . ECG signal display, . Display of messages in the AED mode . Voice prompt system . Saving of the ECG and events on the PCMCIA memory card, . Optional sound environment recording module . Optional SpO2 module • The lower part of the device encloses the following: . PCB power supply . Pulse biphasic waveform defibrillator section . ECG preamp protection . Cadmium-nickel battery charging The upper part includes the following components: • twelve-lead ECG amplifier for acquiring signals from the patient cable and the interface with the CPU • ECG preamplifier for acquiring signals from the adhesive electrodes • CPU for managing the communication between the various functional parts • VF detection circuit • LCD monitor for viewing traces and messages • Backlight converter for the LCD monitor • Circuit for saving the ECG and events on the PCMCIA card • Control keypads It may also include the following optional features: • SpO2 circuit • Circuit for saving the sound environment in the AED mode on the PCMCIA card (10 MB) The lower part includes the following components: • Control circuit for charging and discharging the high-voltage capacitor • High-voltage capacitor charging circuit • High-voltage capacitor • High-voltage switching circuit to deliver the pulsed waveform • ECG preamp protection circuit • Power supply circuit that generates the power supply voltages from the battery. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-1 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS 7.2. UPPER PART The section below describes the functioning of the various PCBs located in the upper part of the MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® device. The PCBs are as follows: • TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP printed circuit board • DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP printed circuit board • CPU printed circuit board • BACKLIGHT CONVERTER support board 7.2.1. TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMPprinted circuit board The TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP printed circuit board (U3P287) is responsible for acquiring the ECG signal through the patient cable. The PCB also takes charge of transmitting ECG data to the CPU. The PCB is made up of the following: • ECG input circuits • ECG signal amplification, • Pacing and artefact recognition • Microcontroller • Non-floating part • Power supply • Data transmission. OVERVIEW The TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP PCB is made up of an eight-channel hardware amplification chain, a microcontroller for acquiring and processing ECG data, a section for transmission between the floating and the non-floating parts and a power supply. The hardware amplification chains are those of leads I, II and V1 to V6. Leads III and AVR, AVL and AVF are calculated by the microcontroller. The data from all twelve leads are transmitted by a serial bi-directional link to the non-floating part for processing by the HOST CPU. ECG INPUT STAGES The input stages of the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP board include components that offer protection from defibrillation shocks and high-frequency surgical instruments. Protection from defibrillation shocks is provided by resistors R1 to R19 and sparkers E1 to E9. Along with the resistors above, capacitors C1 to C9 form a low-pass filter in order to attenuate the high-frequency components of signals if electrosurgery is used. Poor electrode contact is recognised by polarising the ECG inputs with a voltage source via high resistances. If the electrode contact is loose, the DC component of the ECG signal increases, as does the output voltage of following stages IC10 to IC12. The signals are converted by the ADC via multiplexers IC4 and IC5. A 10-Hz signal may also be injected at each input through input multiplexers in order to check the proper functioning of the amplification chain. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-2 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS ECG AMPLIFICATION CHAIN The paragraph below describes the ECG channel corresponding to lead I (the structure of other channels is identical). Along with IC100, following stages IC10A and IC10B form an instrumentation amplifier with a gain value of 5. The following amplification stage (IC102A) eliminates the DC component of the signal through C110. The lower cut-off frequency of that stage can be modified by analogue multiplexer IC110A. The upper cut-off frequency is determined by capacitors C111 and C112. Stages IC110A, IC110B and C111 form a sample-and-hold device in order to reduce the baseline offset in the case of high-amplitude pulses, e.g. with a pacemaker. The function is active when the two analogue multiplexers have a high impedance. The last amplification stage (IC102B) is identical to the previous stage, but does not include a sample-and-hold function. The total amplification of the chain is 200. The lower cut-off frequency (second order) can be switched from 0.05 Hz to 0.5 Hz, whilst the upper cut-off frequency (fifth order) is fixed and is equal to 150 Hz. PACING AND ARTEFACT DETECTION Pacing pulses and artefacts are recognised by the fact that they have a greater component of higher frequencies. For that purpose, each ECG channel may be selected by the microcontroller via multiplexer IC301. The first amplification stage is made up of IC302A. The higher frequency components of the signal are eliminated by C310 and R310. Components R311, C311 and R313, C311 limit the upper bandwidth. The following stage is built identically (IC302). The two stages make up a band-pass filter that detects and amplifies signal disturbances. Circuits IC302C and IC302D include a window comparator. When the signal disturbance amplitude exceeds a given limit, the comparators set off two monostable components IC303A and IC303B. They control the sample-and-hold stages and supply a signal to the microcontroller. The microcontroller determines if the pulse is an artefact or a pacemaker pulse and can also affect the sample-and-hold stage. MICROCONTROLLER The digital part of the TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP board includes a microcontroller (IC900), an address flipflop (IC903), memory modules (IC901, IC902), address decoding circuits (IC908, IC909), port extension circuits (IC905 to IC907), a reset circuit with power supply voltage monitoring (IC930) and a twelve-bit analogue-digital converter (IC920). The microcontroller is responsible for the following functions: • Mains frequency rejection • Pacing detection source selection • Pacing recognition and suppression • QRS complex detection • Miscellaneous filtering functions • Communication with the HOST CPU • Self test of the analogue part Because these functions are performed by the software, their characteristics are guaranteed over time. The microcontroller can change the lower cut-off frequency of each channel from 0.05 Hz to 0.5 Hz through the “back_x” signal. The function enables the trace to return rapidly in the case of an overrun due to channel saturation. The block signal acts as a sample-and-hold device if pacing or an artefact is recognised. By injecting a 10-Hz signal via multiplexers IC1 to IC3, the microcontroller also runs a self test of the hardware channels. The resulting signal is processed by the microcontroller and the test result is sent to the HOST CPU. Any electrode fault is determined by means of multiplexers IC4 and IC5. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-3 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS NON-FLOATING PART POWER SUPPLY The TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP circuit is powered by a push-pull circuit associated with controller IC700 and switching transistors T700 and T701. The converter secondary supplies two floating power supply voltages: +5V and –5V. Voltage control is applied on the +5V output of the secondary by means of circuit IC701 and optocoupler OPT700. Regulation relies on the principle of pulse width modulation. DATA TRANSMISSION Communication with the HOST CPU takes place through a 115.2 KB bi-directional serial channel. All data transmissions on this PCB operate according to the same principle, so the description is provided for only one channel. The data are applied at optocoupler OPT600 through MOSFET T600. The current limitation of the optocoupler emitting diode is performed by R600. When the current passes through the diode, there is a drop in the voltage at the terminals of R603 on the reception side. As a result, the voltage at the terminals of R603 reflects the flow of information. The signal is differentiated through R604 and C600 before being applied to a Schmidt trigger (IC911A). The output of the Schmidt trigger is connected to the serial port of the microcontroller. The signal amplitude (p2 of IC911A) ought to be greater than twice the hysteresis at p3. The transmission chain for the QRS signal is very similar to the circuit described above. This information is transmitted at a slightly slower speed, with greater hysteresis (1.5 times). 7.2.2. DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMPprinted circuit board The defibrillation ECG printed circuit board (W4P14 1691) is responsible for acquiring the ECG signal taken through the adhesive defibrillation electrodes. This circuit transmits the ECG signal to the floating part of the patient cable ECG preamplifier. The PCB is made up of the following: • Floating power supply • Communication • PWM modulation • PWM demodulation • Amplification and processing • Pacing inhibition • Amplification chain verification OVERVIEW The defibrillator ECG preamplifier is responsible for amplifying and filtering the ECG signals and the contact impedance measurement signal. It is made up of two floating areas. The floating area that is in contact with the patient contains preamplifier U5 and U4, filter R27, R28, C16, R26 and C18, PWM modulator U3 and U8B of the ECG signal and amplifier U2 and U15, filtering C6, R7, C7, R8, C9, R13, C53 and R41 and PWM modulator U3 and U8A of the signal from the contact impedance measurement. The other floating area that is connected to the 12-channel preamplifier contains PWM demodulator U16 and power supplies U9 and U10. Transformer TR1 and optocouplers U11, U12, U13 and U14 are responsible for insulating, supplying power to and ensuring communication between the two floating areas. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-4 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS POWER SUPPLY The power supply of the defibrillator floating part is built around transformer TR1. Oscillator U9 generates a square signal with a cyclical ratio of 1. It is applied through driver U10 to the primary of transformer TR1. The defi_on/off signal is used to switch the power on and off. The voltage at the secondary of TR1 is rectified by D4, D5, D6 and D7 and stabilised by regulators RG1 and RG2. The voltages obtained in this way +VFD and – VFD supply power to the defibrillator floating part. COMMUNICATION Communication between the defibrillator floating part and the patient cable floating part is provided through optocouplers U11, U12, U13 and U14. Communication takes place in the form of digital signals. The pulse width of analogue signals ECG_DEFI and IMP_ELEC_DEFI is modulated before they are applied at optocouplers U11 and U14. Control signals 10HZ_P and INH_PACE are applied directly to the optocouplers. PWM MODULATION PWM modulation is provided by a triangular signal generator built around U3. This reference signal is applied at the same time as the analogue signals to be modulated on the comparators, which supply pulse width modulated signals. These control the optocouplers. PWM DEMODULATION The signals delivered by optocouplers U11 and U14 are applied to the comparators with hysteresis through capacitive links. The modulated signals from the comparators are applied to low-pass filters U16, which return analogue signals. AMPLIFICATION AND PROCESSING OF ANALOGUE SIGNALS The composite signal from the patient contains two types of information. It includes the ECG signal and the (20 KHz) signal of the contact impedance measurement. AMPLIFICATION AND FILTERING OF THE ECG SIGNAL The ECG signal is taken from the composite signal with the filter made up of R102, R103 and C69. After that, it is amplified by the differential amplifier built around U5. A second amplification is provided with U4A. The amplified ECG signal from U4A is applied to modulator comparator U8B. At the same time, at the output of U4A, the ECG signal amplified through the electronic switch is filtered by the low-pass filter made up of R26 and C18 to retain only the DC component of the amplified ECG signal. This DC component of the polarisation voltage given to the ECG signal is brought to detection comparators U17 via U4B and R107. The output of the comparators is applied to transistor T4 which controls electronic switch U7C, which brings a voltage of ~3.5V to modulation comparator U8A. AMPLIFICATION AND FILTERING OF THE IMPEDANCE MEASUREMENT SIGNAL The signal taken from the patient is applied to follower U2 and filtered by high-pass filters C6, R7 and C7, R8 and C9, R13 and C53, R41 in order to eliminate the DC component and the 50 Hz noise. It is then amplified by U2C and U2D. The amplified filtered 20 KHz impedance measurement signal is rectified by U15A and D1 and brought to U15B, which has a P1 adjustment input to adjust the detection limit of the contact impedance. The signal from U15B is applied to the modulator. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-5 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS PACING INHIBITION When a pacing pulse is detected, signal INH_PACE opens a link that monitors the DC component of the ECG signal in order to avoid any drift in the signal as a result of the pacing pulses. AMPLIFICATION CHAIN VERIFICATION The 10Hz_P signal is analysed to verify the validity of the chain of amplification. The 10Hz_P signal, with an amplitude located between +VFD and –VFD, is brought to a voltage compatible with the input of differential amplifier U5 through U6. At the same time, the pulses of 10Hz_P charge capacitor C20 which makes electronic switches U7 conduct and makes it possible to inject the 10Hz_P signal in the differential stage of the amplification chain. 7.2.3. CPU printed circuit board The CPU PCB (W4P141694) makes up the central processing unit of the device and is built around several microcontrollers 80C251. Each microcontroller performs specific tasks. The PCB is made up of the following: • HOST CPU • Video CPU • Recording CPU • VF CPU • Optional SpO2 module OVERVIEW The CPU PCB is built around a structure of four microcontrollers 80C251, which operate in the master-slave mode. The master microcontroller function is performed by the HOST microcontroller (U1). The slave microcontroller function is performed by microcontrollers Display (U100), Recording (U50) and VF (U70). Communication between the HOST microcontroller and the Recording and VF microcontrollers takes place through a serial link via UART (U25). Communication between the HOST microcontroller and the Display microcontroller takes place through a parallel link (D[0-7]) via flip-flop D (U103). Communication with the SpO2 module, external module and PCMCIA modem takes place through a serial link, via UARTs (U25, U26). Communication between the CPU and defibrillation takes place through input and output flip-flops. HOST CPU The HOST CPU is built around a HOST microcontroller (U1), an EPROM (U3), a working RAM (U4), a decoder (U6), input flip-flops (U20, U39, U40, U41) output flip-flops (U103, U18, U33, U34, U35, U36), serial communication UARTs (U25, U26), the device on/off system (D1, D3, D4, T3 etc.),the time stamper (U5), the battery voltage monitoring system (R35, R36, U38, U37), the configuration EEPROM (U7), the analogue-digital converter (U8), the ECG signal amplification-filtering system (U10), the LCD contrast adjustment (U9A), the reset and watchdog circuit (U17), the multiplexer and analogue-digital converter (U38, U37), the audio alarm generator with audio amplifiers (U43, U29, U30). Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-6 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS OUTPUT FLIP-FLOPS Reset Control signals (RAZVID, RAZVF, RAZENREG, RAZSPO2, RAZUART1, RAZUART2) are associations through the OR gate, the signal (Reset) and resetting pulses generated by the HOST microcontroller through output flip-flop U18. Audio alarms The control signals (U33[14-19]) generated by output flip-flop U33 are used to control the form and tone of audio alarms. Spoken messages or audio alarms Control signals (AUDIO [0-2]) generated by output flip-flop U34 control the type of audio emission. Communication with the defibrillator The defibrillator is managed by defibrillator control signals (-SYNCDEF, STARTCONV, SACHARGE, SAWSEL[0-3] and WDUMP) generated by output flip-flops U36 and U35. The signals have been described in detail in the defibrillator part. Signal (-RSTSHOCK) generated by output flip-flop U33 is used to refresh the interrupt flip-flop used to control A/D power conversion of the current delivered during defibrillation shocks. LCD backlight Signal (BACKLIGHT) generated by output flip-flop U35 is used to control the on/off function of the backlighting. Luminous indicator of the defibrillator input Signal (-PATCHLED) generated by output flip-flop U35 is used to control the luminous indicator located above the defibrillator input. Luminous indicators of the analyse key The luminous indicators of the analyse key are controlled by line control signals (LED[1-3]RED, LED[13]GREEN) generated by output flip-flop U35. ECG preamplifier power supply The ECG preamplifier power supply is controlled by signal (-ECG_ON) generated by output flip-flop U35. Communication with the CPU Communication between the HOST CPU and the Display CPU is managed by an interrupt flip-flop that is refreshed by signal (-RSTRDYV) generated by output flip-flop U33. Multiplexing and analogue-digital conversion The channel of the signals to be converted is selected by signals (ADMUX[0-2]) generated by output flip-flop U34. INPUT FLIP-FLOPS Keypad keys The activation of keypad keys via the low-pass filters and the polarisation resistors built around RN1, C80-C87 and RN2 is applied by input flip-flop U40 and read by the HOST microcontroller. Setting jumpers Setting jumpers CH2-CH9 and CH10-CH11 used for setting up the device are taken into account by input flipflops U20 and U41. Communication with the defibrillator The defibrillator status signals (DEFCHARGE, DEFREADY, SECDISCH, -DEFSEC and –CDNI/LI) are applied by input flip-flop U39. The signals have been described in detail in the defibrillator part. Cold start Signal CLDSTRT generated by the voltage supervisor/watchdog circuit is applied by input flip-flop U41. It informs the HOST microcontroller of the reason for the generation of a reset pulse. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-7 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS Communication with the display CPU Display CPU status signals (READY_VID and ERRORVID) are applied by input flip-flop U41. READY_VID is used to synchronise the transfer of data between the HOST CPU and the display CPU and ERRORVID is a signal that monitors the functioning of the display CPU. Besides, signal (READY_VID), which is taken into account by input flip-flop U39 in association with signal (-INTVIDEO), is used to ensure real-time communication between the two CPUs. Voice prompt control Status signal (V_IN_PROGR) from the VF CPU is applied by input flip-flop U39. It is used to prevent conflicts between the transmission of spoken messages and audio alarms. SERIAL COMMUNICATION Communication between the HOST CPU and the VF CPU, the recording CPU, the SpO2 module, the ECG preamplifier, the PCMCIA modem and the external modem takes place through a serial link via U25 and U26. Communication with the external modem alone supports a full RS 232 link. The two quadruple UARTs are controlled by the HOST microcontroller via buses D[0-7] and A[0-2], control signals –PSEN, -WR, reset signals RAZUART[1-2], the selection signals of the various UARTs –CS and interrupt signal –INTUART. The signal occupies an interrupt input on the HOST microcontroller. ON/OFF SYSTEM The device can be switched on in three different ways: 1. Manually with the On/Off key 2. Automatically for the daily test (see the time stamper section below) 3. Switching on by inserting the battery (see the time stamper section below) Pressing the On/Off keypad key forces line ONBYKEY to the low status. The signal becomes –ON/OFF through D1 and U18. It is applied to the power supply switching transistor located on the power supply PCB. At the same time, the ONBYKEY signal is applied through D4 and R12 to input 2 of the HOST microcontroller. In response, the microcontroller puts line KEEPWR of the output flip-flip in the high status. The signal is applied through R9, D3 at the base of T3, which is saturated and keeps the –ON/OFF signal in the low status. Pressing the On/Off keypad key once again forces line ONBYKEY to the low status. That low status is applied to input 2 of the HOST microcontroller, which in turn positions line KEEPWR on the low status. The amplitude of the –ON/OFF signal switches back to +Ubatt voltage and the power supplies are cut off. Switching on with the On/Off button is disabled when the battery voltage is too low (9.5V). When the battery voltage is too low, output 7 of U117 switches to high. The signal is applied to comparator U118, which prevents signal-ON/OFF from switching to zero if the On/Off key is pressed, if the battery is inserted and if the device is trying to run a daily test. Note: When you press the On/Off button with a very low battery, the device switches on normally, but the backlighting does not go on. The device will operate as long as the On/Off key is kept pressed in. TIME STAMPER Time stamper U5 is under the control of the HOST microcontroller through bus D[0-7] and control signals ALE, -CSRTC, -PSEN, -WR. In addition to its conventional function, the time stamper is required to fulfil two specific functions – automatic switching on for the daily test and switching on when the battery is inserted. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-8 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS Automatic switching on for the daily test: When output U5(1) switches to zero, that affects conductor T2, which saturates transistor T3 via D2 and R7, thereby taking the –ON/OFF signal to the ground. The –ON/FF signal controls the power supply switching transistor on the power supply PCB. At the same time, collector signal T3 is transmitted via D1, D4, R12 to HOST microcontroller U1 (12). In its turn, the HOST microcontroller sets signal (KEEPWR) to high. Through R9 and D3, the signal keeps T3 saturated. Switching on when the battery is inserted: When the battery is inserted in its slot, a pulse is generated at the terminals of the differentiator made up by R2 and C27. The pulse is transmitted by the time stamper through T1. In response, output 1 of the time stamper switches to low, which sets off the device switch-on sequence described above. A lithium cell BAT1 is used to save the content of registries and provide buffer power supply for automatically switching on the device for the daily test, through jumper CH1. BATTERY VOLTAGE MONITORING Battery voltage monitoring is performed by dividing bridge R35 and R36. The signal collected (CHECKBAT) is sent to analogue-digital converter U37 via multiplexer U38. SETTINGS EEPROM EEPROM U7 saves some settings and adjustments. It is under the direct control of microcontroller U1 through a serial link made up of control signals CSEEPROM, CLKEEPROM and data signals SERIEL_IN, SERIEL_OUT. DIGITAL-ANALOGUE CONVERSION AND AMPLIFICATION-FILTERING OF ECG SIGNAL Digital-analogue converter U8 shares the serial link and control signals with the settings EEPROM. The analogue signal delivered by the converter first goes through offset-compensated follower U10A followed by 25 Hz filter R23 and C17 and final amplifier U10B with a gain of 1000. LCD CONTRAST SETTING Contrast setting uses the same digital-analogue converter as the settings EEPROM. The signal at the converter output is amplified by U9A and applied to the LCD. RESET AND WATCHDOG The + 5 V voltage supervision and watchdog functions are performed by U17. When the device is operating, the pulses from –CSWDOG constantly refresh the watchdog. When refresh pulses are interrupted, a reset pulse is generated and signal CLDSTRT switches to low. When a reset pulse is set off by the voltage supervisor, the CLDSTRT signal stays high. Signal CLDSTRT is in relation with the HOST microcontroller through input flip-flop U41. MULTIPLEXING AND ANALOGUE-DIGITAL CONVERSION Analogue signals HVMONIT and IPAT from the defibrillator and signal CHECKBAT from the battery voltage monitoring system are applied to analogue-digital converter U37 through multiplexer U38. Signals ADMUX[0-2] of output flip-flop U34 control the selection of multiplexer channels. The analogue-digital converter is controlled by the HOST microcontroller via bus D[0-7] and control signals –CSADC, -PSEN, WR. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-9 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS AUDIO ALARM AND SOUND AMPLIFICATION Audio alarms are generated by microcontroller U43 (PIC16IC54), which is under the control of the HOST microcontroller through output flip-flop U33. The audio alarm signal and the voice prompt signal (VOICE) are applied via multiplexer U31 to audio amplifiers U29 and U30. VIDEO CPU The video CPU is built around the video microcontroller (U100), its EEPROM (U102), output flip-flop (U105) and input flip-flop (U103). The data sent by the HOST microcontroller are received by the video microcontroller through input flip-flop U103. That communication is under the control of signals BUSY_VID and READY_VID. Signal ERRORVID of output flip-flop U105 informs the HOST microcontroller of the status of the video microcontroller. The associated optical link (U104) and status signal TM910OK are not effective. RECORDING CPU The recording CPU is built around the recording microcontroller (U50), its EEPROM (U52), its working RAM (U58), address decoder (U59), output flip-flops (U53, U54, U55 and U56) and the audio message control logic (U62, U61, U60) and the PCMCIA connector support. OUTPUT FLIP-FLOPS Outputs of flip-flops U53, U54, U55 and U56 are used to form the addresses of the flash memory. For making up the flash memory addresses, these flip-flops are addressed one after the other through bus DM[0-7] and CS… signals generated by decoder U59. RECORDING CONTROL LOGIC The audio signals picked up through a microphone (PHONE_IN and PHONEGND) are amplified, filtered and codified by U62. The counter built around U61 and gates U63 and U64 generate the conversion and sampling frequency of ADPCM encoder (U62) and regulates the transfer of data from the encoder to offset register U60. The data output from the offset register are read by the recording microcontroller and saved in the flash memory. The PCMCIA connector support that is screwed onto the CPU PCB receives the flash memory. VF CPU The VF CPU is built around the VF microcontroller (U70), its EEPROM (U72), its working RAM (U80), decoder (U79), voice prompt controller (U73 and U75) and analogue processing system (U90, U91, U92, U93, U94, U95 etc.), which includes A/D and D/A conversion (U78 and U77). VOICE PROMPT CONTROLLER Spoken messages are emitted by the voice prompt controller (U73). It is under the control of the VF microcontroller through DVF[0-7] and signals –RD_VF, -WR_VF and –CSSYNTH. Flash memory U75 contains the various messages. The analogue output of the messages takes place with amplifiers U76B and U66B. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-10 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS ANALOGUE PROCESSING The DC component of signal ECGX1000 is cancelled by capacitor C170. After that, the residual signal is filtered (U91) and rectified (U92). Resulting signal ECGMAX/2 is sent to the ADC. The signal associated with U96 provides automatic gain for the ECGFV signal. The amplitude of the ECGMAX/2 signal, associated with U66A, U93C and U93D, fixes the minimum authorised limit (LIMIT) for an analysis. Signal –DEPASS fixes the maximum authorised limit for an analysis. Signal ECGFV digitised by ADC (U78) is supplied in the analogue form ECGQRS by DAC (U77, U76A). This fixed-gain signal is used to recognise –QRSFV. SPO2 MODULE The SpO2 module is mechanically fixed to the CPU board. The floating power supply of the SpO2 module is provided by PWM controller U112, switching transistors T25 and T26 and transformer TR1. The counter-reaction for voltage stability VSpO2 is provided through U115 and DZ10. Communication between the SpO2 module and the CPU takes place via optocouplers U113, U114 and U116. 7.2.4 BACKLIGHT CONVERTER support printed circuit PCB The BACKLIGHT CONVERTER support printed circuit board (U3 P297) mechanically maintains the LCD monitor backlight circuit. The function includes the following parts: • BACKLIGHT CONVERTER support PCB • backlight converter The backlight converter is powered by the + 12 V voltage generated by the power supply PCB and supplies an output voltage of about 1 kV in order to light the LCD screen by means of a CFL tube included in the display. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-11 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS 7.3. LOWER PART The section below describes the functioning of the various PCBs located in the lower part of the MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® device. The PCBs are as follows: • BATTERY INTERFACE printed circuit board • POWER SUPPLY printed circuit board • HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT printed circuit board • DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL printed circuit board • HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit board • ECG PREAMP PROTECTION printed circuit board • INSULATION AND SHIELDING printed circuit board 7.3.1. BATTERY INTERFACE printed circuit board The BATTERY INTERFACE PCB (W4P14 1682) is responsible for the mechanical and electrical connection between the contacts of the battery inserted in its slot and the electrical circuits of MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED®. The battery interface circuit includes three links via connector J1: • power supply link: + UBATT • earth link: GND • cadmium-nickel battery or lithium cell recognition signal: NTC 7.3.2. POWER SUPPLY printed circuit board The POWER SUPPLY PCB (U3 P296) generates all the power supply voltages required for the monitor section of FRED® to operate. The circuit also includes the On/Off transistor controlled by the CPU. The input voltage of the power supply circuit must be located between 10 and 28 V. The power supply printed circuit generates the following power supply voltages: • + 5 V voltage that powers the logical circuits of the CPU board • + 12 V voltage that powers the analogue circuits of the CPU board, the backlight converter and the radio amplifier. • - 12 V voltage that powers the analogue circuits of the CPU board • - 24 V voltage for adjusting the LCD monitor contrast Transistor T100 takes care of the On/Off function through the ON/OFF control signal. The various power supply voltages are generated by two switching regulators (U800 and IC360), the input voltage of which is switched by transistor T100. + 5V VOLTAGE The + 5 V power supply voltage is provided by switching regulator U800, switching transistors T800, T801, induction coil L800 and freewheel diode D801. The whole system makes up a step-down regulator with peak current limitation (R802 and R805). Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-12 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS + 12 V VOLTAGE The + 12 V power supply voltage is provided by switching regulator IC360, switching transistors T362 and T363, control transistors T360 and T361, transformer TR360 and rectifying diode D361. The system makes up a flyback mode regulator. The current is limited by the network made up of R360, R362 and R363. The voltage is controlled by dividing bridge R368, R369 and R370. - 12 V VOLTAGE The – 12 V power supply voltage is provided through another secondary coil of TR1. After it is rectified and filtered by D500 and C500, the secondary voltage is approximately – 15 V. Linear regulator IC500 regulates the voltage of the – 12 V output. - 24 V VOLTAGE The – 24 V power supply voltage is provided through a third secondary coil of TR1. After it is rectified and filtered by D600 and C600, the secondary voltage is approximately –- 28 V. Linear regulator IC600 and diode DZ601 regulate the voltage of the – 24 V output. 7.3.3. HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT printed circuit board The HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT PCB (W4P14 1721) takes care of the electrical link between the various parts that make up the defibrillator. The POWER SUPPLY and DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCBs are directly connected to the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT. The HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING PCB is connected to the HIGH-VOLTAGE PCB by means of three cables. The HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT is responsible for the transfer of energy between the battery and the high-voltage capacitor, and for battery charging, high-voltage capacitor charging voltage measurement, HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING PCB control and patient relay activation. The high-voltage circuit PCB (W14P14 1721) includes the various parts: • Battery charge circuit via the external DC input • Cadmium-nickel battery or lithium cell recognition circuit • High-voltage generator • High-voltage capacitor safety discharge • Control signal forming circuit of the high-voltage switching PCB • Patient relay activation circuit • High-voltage capacitor charge voltage measurement circuit The defibrillator function is a sequential circuit with four distinct phases: 1) Standby phase: this is when the device is on (monitoring function) and the defibrillator part is standing by (no charging request). 2) Charging phase: phase during which the high-voltage generator charges the high-voltage capacitor (30 µF / 3.6 kV and 30 µF / 1.2 kV). 3) Hold phase: this phase lasts no more than 20 seconds, during which the charged highvoltage capacitor is ready to be discharged. 4) Discharging phase: this is when the high-voltage capacitor is discharging. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-13 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS OVERVIEW The high-voltage circuit associated with the high-voltage capacitor and the high-voltage switching circuit is the power unit of the defibrillator part. The high-voltage PCB has all the components required for charging the high-voltage capacitor and providing the control signals for the capacitor. The high-voltage circuit control signals are generated on the defibrillator control PCB. The power supply of the defibrillator part + UDEF (TP1) is supplied by the power supply board. The power supply is the battery voltage switched by the On/Off transistor of the power supply circuit. Using this power supply voltage, the defibrillator part generates its own source of +5V voltage through regulator RG2 (TP3). STANDBY PHASE During the standby phase, the whole high-voltage circuit (high-voltage generator included) is inactive. Only the high-voltage measuring circuits (U5B), some associated circuits (U3A) and the defibrillator control circuit are powered by the + 5 V voltage generated by RG2 (TP3). The drivers (U1, U2) of the control signals of the insulated gate bipolar transistors of the high-voltage switching circuit are powered by the + 12 V power supply voltage (TP2) generated on the power supply PCB. CHARGING PHASE The high-voltage converter (TR1), which is driven by the high-voltage generator (U4 and associated components) is responsible for the charging phase of the high-voltage capacitor. During the charging phase, safety discharge relay (RL1) is excited by transistor T3 controlled by signal STARTDEF (TP5) in order to enable the high-voltage capacitor to charge. Two conditions must be met to activate the high-voltage generator: • Conditioning of the charging transistor (T10) by the presence of a low level at signal -CHARGEDR • High level at signal GEST (TP6). HOLD PHASE When the high-voltage capacitor is charged to the selected energy value, the defibrillator switches to the hold phase, which lasts no more than 20 seconds. During the hold phase, transistor T11 is made to conduct by a low level at signal –DISCHENDR (TP9). The condition is required in order to validate possible defibrillation, during which the patient relay is activated by the two discharge transistors (T12 and T13). DISCHARGING PHASE The discharging phase is the phase during which the charged high-voltage capacitor is switched to the patient in order to defibrillate. The discharging phase consists in activating the patient relay and controlling the insulated gate bipolar transistors of the high-voltage switching circuit via drivers (U1, U2) in order to generate the pulse biphasic waveform. The discharging phase is always followed by a return to the normally closed position by the safety discharge relay (RL1), after a delay of 160 ms. As a result, high-voltage capacitor discharging can be performed by two different circuits: • Either by the external discharge circuit, i.e. via the high-voltage switching circuit and the patient relay (RL1 and RL2 on the circuit), for defibrillation. • Or by the safety discharge circuit when relay RL1 of the high-voltage circuit is not excited and signal STARTDEF is on low. The safety discharge circuit is made up of the following components: RL1 and power resistor R1 of the high-voltage circuit. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-14 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS Safety discharging of the high-voltage capacitor occurs when signal STARTDEF returns to the low level, in the following cases: • If the energy level is changed to a value below the initial value • When adhesive electrode disconnection is recognised • If no defibrillation occurs after twenty seconds • If a technical fault is found in the defibrillator part • When the device is switched off BATTERY CHARGE CIRCUIT The battery charge circuit is made up of a source of DC current (RG1) associated with R13 and R14. Diode D11 protects the circuit if the external DC connection is reversed. In order to charge a cadmium-nickel battery inserted in the device, the input voltage must be at least 18V. In that case, the battery charging current is 125 mA. If a lithium cell is used, the absence of NTC in the battery housing blocks transistor T5, which disables the battery charge current. CADMIUM-NICKEL BATTERY OR LITHIUM CELL RECOGNITION CIRCUIT The cadmium-nickel battery or lithium cell recognition circuit is made up of U3A, which recognises the presence of NTC in the battery slot. The detection is done by the NTC signal. Comparator U3A outputs the corresponding information for the CPU, signal –CDNI/LI. HIGH-VOLTAGE GENERATOR The high-voltage generator is used to charge the high-voltage capacitor to a preset energy level. The stored energy is measured by measuring the sum of the two charging voltages of the high-voltage capacitor (30 µF / 3.6 kV and 30 µF / 1.2 kV). The high-voltage capacitor is charged by high-voltage converter (TR1), driven by PWM (U4) and associated components T1, T2, T6, T8 and T9. Two conditions must be met to activate the high-voltage generator: • Activation of the charging transistor (T10) by a low level at signal -CHARGEDR • High level at signal GEST (TP6). When transistor T10 conducts, switching regulator U4 is powered, as is the primary of TR1. The presence of a high level at signal GEST unlocks the high-voltage generator, the oscillation of which generates the voltage required to charge the high-voltage capacitor (30 µF / 3.6 kV and 30 µF / 1.2 kV) through the two secondary coils of rectified TR1. The high-voltage generator has a system for controlling the primary peak current formed by R2, R44 and C16 and a triggering circuit after the core formed by T6 and the associated components is demagnetised. The measurement circuit of the charging voltage at the primary of the high-voltage converter used to stop charging is made up of T4 (signal HVMES1). The high-voltage generator has two different charging speeds, depending on the type of power supply used (cadmium-nickel or lithium). Transistor T7 controls the two charging speeds defined by resistors R35, R38 and R30. HIGH-VOLTAGE CAPACITOR SAFETY DISCHARGE CIRCUIT The high-voltage circuit also includes the function for the safety discharge of the high-voltage capacitor. This function includes the safety discharge relay (RL1), which is used to discharge the high-voltage capacitor (30 µF / 3.6 kV and 30 µF / 1.2 kV) into resistor R1. The safety discharge relay is activated by transistor T3, which is driven by signal STARTDEF. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-15 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR CONTROL SIGNAL FORMING CIRCUIT The high-voltage circuit includes two drivers (U2 and U3), which buffer the driving signals of the insulated gate bipolar transistor stages of the high-voltage switching circuit. The driver input signals are generated on the defibrillator control PCB. The driver output signals are connected to the high-voltage switching PCB through connector J6. PATIENT RELAY ACTIVATION CIRCUIT The patient relay activation circuit (RL1 and RL2 on the high-voltage switching circuit) is made up of transistors T11, T12 and T13. The transistors perform the following functions: • T11 : discharge validation transistor driven by signal -DISCHENDR • T12 : patient relay activation transistor driven by signal DISCH • T13 : patient relay activation transistor driven by transistors T14 and T15, which are controlled by signals –SYNCDR and DISCHKEY2 respectively. The patient relay is activated when the entire driving chain is active (simultaneous conduction by all the transistors). Transistors T14 and T15 also drive two pulsed discharge validation transistors through T12 and T15 on the high-voltage switching circuit. HIGH-VOLTAGE CAPACITOR CHARGE VOLTAGE MEASUREMENT CIRCUIT The circuit for measuring the sum of the charging voltages of the high-voltage capacitor (30 µF / 3.6 kV and 30 µF / 1.2 kV) is made up of two dividing bridges R47 / R9 and R48 / R41 referenced to the earth, and differential amplifier U5B. The network of diodes DN3 and DN4 forms a clipping network for protection from any transients during the high-voltage capacitor discharge. The output division factor (signal HVMES2) is 1100. Any insulation fault in the IGBT discharge circuits (high-voltage switching circuit) is also monitored by U5B and the associated components. IGBT insulation faults are detected by resistors R69 and R70 wired on the high-voltage switching circuit. The detection function is performed by the CPU (upper part), which analyses signals HVEMS2. 7.3.4. DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL printed circuit board The DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCB (W4P14 1722) generates all the control signals required for the defibrillator to operate. The PCB makes up the control stage of the power circuit made up of the HIGHVOLTAGE CIRCUIT (W4P14 1721) and the HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit (W4P14 1724). The PCB is made up of the following: • Tension reference and energy selection multiplexer • End-of-charging detection circuit • Input interface circuits • Reset circuit and microcontroller • Output interface circuits • Pulse biphasic waveform control circuit • Safety switching and monitoring circuit Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-16 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS OVERVIEW The DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCB (W4P14 1722) performs the following functions: • monitoring the high-voltage capacitor charging process and the safety discharge function, through microcontroller (U12) • generating the control signals required to drive the IGBTs that make up the pulse biphasic waveform • hardware monitoring of some functions and disabling the defibrillator circuit if a technical fault is found. STANDBY PHASE During the standby phase, the entire defibrillator control circuit is supplied with + 5 V. Microcontroller (U12) timed by Q1 supplies a 16-ms WDCLK signal. Besides, two reference voltages are generated in the circuit: A + 4.00 V reference (DZ1) for selecting the energy values and a + 2.5 V reference (DZ2) for the safety chain comparators. CHARGING PHASE The high-voltage capacitor charging phase is initialised by signal SACHARGE from the CPU PCB (upper part) and interfaced by U10D. Following the control pulse, microcontroller (U12) supplies the following three signals: SECRST, STARTDEF and LOADC. These three signals reset the safety switch, excite the safety discharge relay and activate the high-voltage generator respectively. When the end-of-charging comparator (U3A) generates the –STOP signal, microcontroller (U12) interrupts the charging phase and switches to the hold phase. HOLD PHASE During the hold phase, the microcontroller (U12) supplies signal CFULL in order to make transistor T11 (highvoltage circuit) conduct, by a low level at signal –DISCHENDR. This condition is required to validate defibrillation through the patient relay and the IGBTs of the high-voltage switching circuit. The microcontroller limits the duration of the phase to 20 seconds maximum. During the charging and hold phases, signal STARTDEF activates signals PREPULSE 1 and PREPULSE 2 through U6A, U6B and U6C in order to actively block the IGBTs of the high-voltage switching circuit. These pulses are generated after every 16 ms through U3B and associated components. DISCHARGING PHASE The discharging phase is triggered when the user presses the Shock key on the device. The Shock key supplies two signals, DISCHKEY1 and DISCHKEY2, which generate two control signals for microcontroller U12 through U9A and U9B. When the two signals DISCH and –DISCH2 change status, the microcontroller generates the DISCH and –DISCH signals. The DISCH signal drives transistor T12 (high-voltage circuit), which makes up the first patient relay activation channel (RL1, RL2 of the high-voltage switching circuit). In order to excite the patient relay, the second fully hard channel must also activate transistor T13 of the highvoltage circuit. When the two conditions are met, the patient relay is excited. During that time, signal –DISCH unlocks the 10 KHz oscillator (U7), counter (U5) and the EPROM (U4). After 25 ms, the signals at the EPROM output supply the control pulses of the IGBTs of the high-voltage switching circuit. The resulting 5 KHz switching by the IGBTs of the two phases of 4 ms each generates the pulse biphasic wave. Patient relay activation lasts 160 ms, after which time signal STARTDEF comes back to zero, which makes the contacts of the safety discharge relay return to the normally closed position. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-17 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS The IGBT stages of the high-voltage switching circuit are controlled by four signals, PREPULSE 1, PREPULSE 2, PHASE 1 and PHASE 2 generated by the defibrillator control circuit. Signals PREPULSE 1 and PREPULSE 2 block the IGBTs, while signals PHASE 1 and PHASE 2 make the IGBTs conduct. VOLTAGE REFERENCE AND ENERGY SELECTION MULTIPLEXER The reference voltage for the energy selection stage is made up of DZ1 (TL 1431C) and dividing bridge R68, R69. The fixed reference voltage is + 4.00 V. The energy selection circuit is made up of analogue multiplexer U1. This circuit is addressed by signals SAWSEL0 to SAWSEL3, which are generated by the CPU PCB (upper part). The voltage reference for a given energy value is formed by resistor R70 in association with a base resistance selected by the multiplexer. Stage U2A makes up a follower, the output of which supplies the reference voltage to the end-of-charging comparator (U3A). END-OF-CHARGING DETECTION CIRCUIT The end-of-charging detection circuit is made up of comparator U3A. The reference voltage corresponding to the selected energy is supplied by follower U2A. The measuring voltage (equal to the sum of the two charging voltages) is supplied by signal HVMES1 which is generated on the high-voltage circuit. When the amplitude of signal HVMES1 corresponding to the charging voltage of the high-voltage capacitor (30 µF / 3.6 kV and 30 µF / 1.2 kV) is equal to the reference voltage, the output from comparator U3A (signal –STOP) switches to zero. That stops the high-voltage generator controlled through microcontroller U12, which switches the GEST signal to low. INPUT INTERFACE CIRCUIT The input interface circuits are made up of drivers U10C, U10D, U10E and AOP U9A, U9B. Circuit U10D makes up the interface circuit of signal SACHARGE which triggers the high-voltage capacitor charge. Safety discharging while charging or during the hold phase is triggered by signal WDUMP generated by the CPU PCB and interfaced by driver U10C. Signal SYNCDEF generated by the CPU PCB synchronises the shock in the event of cardioversion through driver U10E. The signal also drives the second discharging channel (hardware) through driver U10F. The shock (first channel) is triggered with the help of two comparators U9A and U9B. The output of U9A is active when high (signal DISCH1). The output of U9B is active when low (signal -DISCH2). Charging is disabled during safety discharging by comparator U11B which checks that there is no voltage at the terminals of the high-voltage capacitor (signal HVMES2) before starting up charging. Signal –HVPRES is active when low. Comparator U2B is used to detect any malfunctioning in the charging transistor (T10) on the high-voltage circuit through the CHARGEN signal. Any short circuit at the charging transistor (T10) is detected during the standby phase and can, if required, block the charging of the highvoltage transistor as T10 is part of the secondary circuit. RESET CIRCUIT AND MICROCONTROLLER All the charge/discharge cycle sequences are driven by microcontroller U12, namely: • Charge triggering • Charge disabling during the safety discharge • Stopping the charge when the selected energy value is reached • Limiting the maximum duration of the charging phase to 20 seconds • Controlling the hold phase, also limited to 20 seconds maximum • Generating a 16-ms clock signal Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-18 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS • • • • • Activating and delaying the discharge phase, duration limited to 160 ms Resetting and setting off the safety discharge Triggering the shock in the direct mode Triggering the shock in the synchronised mode Setting off a battery test cycle. Microcontroller U12 is powered by a + 5 V voltage supplied by the high-voltage circuit. Circuit U18 monitors the power supply voltage and resets the microcontroller (- MCLR) when the device is switched on. If there is any technical fault, U18 also resets the microcontroller through comparator U15A, associated components and the safety switch (U13A). U12 is controlled by quartz (Q1) with an oscillation frequency of 4.0 MHz. Besides, the microcontroller supplies an output signal (WDCLK) that makes it possible to check functioning. Signal WDCLK has an invariable 16-ms period. OUTPUT INTERFACE CIRCUITS The output interface circuits are made up of drivers U10A, U10B, U8A, U8B, U8C, U8D, U8E and U8F. Circuit U14A supplies a high-level output, either through signal STARTDEF or through signal TBAT (in battery test mode). The output of U14A is used to control the charging transistor (T10) on the high-voltage circuit by means of the -CHARGEDR signal via U10B. If a technical fault is detected by the safety circuit (U13A), transistor T1 is saturated, which imposes a low level at the input of U10B, which blocks the charging transistor (T10) of the high-voltage circuit and therefore stops the high-voltage generator (if it is charging the high-voltage capacitor) and leads to a safety discharge of the high-voltage capacitor. Signal STARTDEF (supplied by the microcontroller), which activates the safety discharge relay, is buffered with U8B. The high-voltage generator control signal (GEST) is buffered with U8A. The signal comes from U14B and originates from the LOADC signal output by the microcontroller (U12) during high-voltage capacitor charging or the TBAT signal during the battery test. The discharge validation transistor (T11) on the high-voltage board is activated by U10A, which is controlled by the CFULL signal (hold phase). Transistor (T12) (triggering the shock on the first channel) on the high-voltage PCB (W4P14 1721) is made to conduct by signal DISCH. The defibrillator status signals transmitted to the CPU PCB are as follows: DEFCHARGE, DEFREADY, DEFDISCH and SECDISCH buffered by U8E, U8D, U8F and U8C respectively. The status signal of the safety switch (U13A) is –DEFSEC. PULSE BIPHASIC WAVEFORM CONTROL CIRCUIT The control circuit of the pulse biphasic waveform is made up of circuits U4, U5 and U7, associated with gates U6A, U6B and U6C. During the charging and hold phases, the IGBTs of the high-voltage switching circuit are blocked actively by signals PREPULSE 1 and PREPULSE 2. These blocking signals are generated from signal WDCLK (16 ms) supplied by U12 and differentiated by R71 and C28. The pulses shaped by U3B have a 100µs duration and are switched by U6B, U6A and U6C. During the shock, when signal –DISCH switches to low, oscillator U7, counter U5 and EPROM U4 are activated. The IGBT driving signals (conduction and blocking) are generated by four EEPROM data bits (U4). • Datum D1 of U4 (PHASE1) gives rise to phase-1 IGBT conduction periods through driver (U2) on the high-voltage PCB during the shock • Datum D3 of U4 (PHASE2) gives rise to phase-2 IGBT conduction periods through driver (U2) on the high-voltage PCB during the shock • Datum D4 of U4 gives rise to phase-1 IGBT active blocking periods through U10G, U6C and driver (U1) on the high-voltage PCB • Datum D5 of U4 gives rise to phase-2 IGBT active blocking periods through U10H, U6A and driver (U1) on the high-voltage PCB Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-19 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS SAFETY SWITCH AND MONITORING CIRCUIT The safety circuit deactivates the defibrillator (resets microcontroller U10) and runs a safety discharge of the energy stored in the high-voltage capacitor. The safety functions are as follows: • Monitoring the functioning of the charging transistor (T10) • Monitoring transistor T12 • Monitoring transistor T13 • Monitoring signal WDCLK • Monitoring the insulation faults of the IGBTs of the high-voltage switching circuit • Detecting voltage surges if there is an end-of-charge fault The safety circuit is made up of number of comparators (U11, U16 and U17), which set off the safety switch (U13A) through U15B if a technical fault is detected. When the device is started up, the safety switch (U13A) is triggered by the charging of capacitor C9 and comparator U15B in order to check operation through signal – DEFSEC (active when low). All charging cycles or battery tests are preceded by a reset of the safety switch by the SECRST signal generated by microcontroller U12. The setting off of the safety switch (in the event of a technical fault) stops the high-voltage generator and leads to a safety discharge of the high-voltage capacitor by making T1 conduct. Besides, circuits U15A and U18 reset U12 in the event of a technical fault. MONITORING OF CHARGING TRANSISTOR T10 Charging transistor (T10 on the high-voltage circuit) is monitored by divider R10, R11 (high-voltage circuit) and comparator U2B. MONITORING OF TRANSISTORS T12 AND T13 Patient relay activation transistors (T12 and T13 on the high-voltage circuit) are monitored by window comparators U16A and U16B and circuits U17A, U17D and associated components. MONITORING OF SIGNAL WDCLK Signal WDCLK is monitored by comparator U17B and associated components. MONITORING THE INSULATION FAULTS OF THE IGBTS OF THE HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING CIRCUIT The insulation faults of the IGBTs of the high-voltage switching circuit are monitored by resistors R69 and R70 installed on the high-voltage switching circuit, connected by the grey wire to pin J2 of the high-voltage circuit. If there is any insulation fault in a high-voltage switching IGBT, the amplitude of signal HVMES2 is distorted. In that case, the fault is detected by the CPU PCB (upper part), which switches signal WDUMP to high to activate the safety discharge of the high-voltage capacitor. Besides, the CPU PCB generates an error message on the LCD screen if that happens. DETECTING VOLTAGE SURGES IF THERE IS AN END-OF-CHARGING FAULT Voltage surges if there is a fault in the end-of-charging circuit are detected by comparator U11A, which monitors the amplitude of signal HVEMS2. The triggering limit in the event of a surge is approximately 5.1 kV for the sum of the two charging voltages. The outputs of all the open-collector comparators of the safety circuit are interconnected. If a technical fault is detected, they set off the safety switch through comparator U15B. The reference limit for the comparators of the safety circuit is provided by the voltage reference DZ2, which is itself monitored through U17C. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-20 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS 7.3.5. HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit board The HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING PCB (W4P14 1724) makes up the high-voltage and high-current chopping unit which generates defibrillation by means of a pulse biphasic waveform. The circuit is connected to the HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT (W4P14 1721) and the high-voltage capacitor (30 µF / 3.6 kV and 30 µF / 1.2 kV). The HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING circuit includes control signal interface components, high-voltage switching components (IGBTs) and the patient insulation relay. The HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING PCB is made up of the following: • phase 1 IGBT control circuit • phase 2 IGBT control circuit • IGBT type high-voltage switching circuits • patient insulation circuit with relays OVERVIEW The HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING PCB (W4P14 1724) performs the following functions: • synchronised generation of IGBT control pulses for defibrillation with a pulse biphasic waveform • patient insulation from the high-voltage circuit of the defibrillator section In general, the terms PHASE 1 and PHASE 2 refer to the two phases of the pulse biphasic discharge curve delivered by MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED® (see waveform on pages 1 to 7). PHASE 1 IGBT CONTROL CIRCUIT Phase 1 of the pulse biphasic defibrillation waveform is made up by driving IGBTs T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5, T6, which are connected to the 30 µF / 3.6 kV high-voltage capacitor. The synchronised control of T1 to T6 is performed by the simultaneous induction of the driving cores of grids L1, L2 and L3. Zener diodes (DZ1 to DZ12) make up the IGBT grid clipping components. The grids are driven via the cores by current pulses in the control wire connected to J14 and J16. The current pulses in the control wire are generated by transistors T13 and T14, for the active blocking and conduction of the IGBTs respectively. The control signals of transistors T13 and T14 are PREPHI 1 and PHI 1 respectively, generated on the defibrillator control circuit (W4P14 1722), buffered by the high-voltage circuit (W4P14 1721). T15 is the validation transistor of the pulse biphasic waveform and is controlled by transistors T11, T14 and T15 of the high-voltage circuit. The current in the control wire is limited by R7, R8 and R9. PHASE 2 IGBT CONTROL CIRCUIT Phase 2 of the pulse biphasic defibrillation waveform is made up by driving IGBTs T7, T8, and T9, which are connected to the 30 µF / 1.2 kV high-voltage capacitor. The synchronised control of T7 to T9 is performed by the simultaneous induction of the driving cores of grids L4, L5 and L6. Zener diodes (DZ13 to DZ24) make up the IGBT grid clipping components. The grids are driven via the cores by current pulses in the control wire connected to J15 and J17. The current pulses in the control wire are generated by transistors T10 and T11, for the active blocking and conduction of the IGBTs respectively. The control signals of transistors T10 and T11 are PREPHI 2 and PHI 2 respectively, generated on the defibrillator control circuit (W4P14 1722), buffered by the high-voltage circuit (W4P14 1721). Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-21 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS T12 is the validation transistor of the pulse biphasic waveform and is controlled by transistors T11, T14 and T15 of the high-voltage circuit. The current in the control wire is limited by R7, R8 and R9. IGBT TYPE HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING CIRCUITS The high-voltage and high-current switching circuits are made up by associating IGBTs. The phase 1 switching channel is made up of IGBTs T1, T2, T3, T4, T5 and T6. These IGBTs make up a series assembly of 3 x 2 IGBTs mounted in parallel. The synchronous control of the various IGBTs outputs the first phase of the pulse biphasic waveform by means of the chopping discharge of the 30 µF / 3.6 kV capacitor. Resistors R1, R2 and R3 associated with each pair of IGBTs make up an IGBT potential balancing chain. The phase 2 switching channel is made up of IGBTs T7, T8 and T9. These IGBTs make up a series assembly of 3 IGBTs. The synchronous control of the various IGBTs outputs the second phase of the pulse biphasic waveform by means of the chopping discharge of the 30 µF / 1.2 kV capacitor. Resistors R4, R5 and R6 associated with the IGBTs make up an IGBT potential balancing chain. PATIENT INSULATION CIRCUIT WITH RELAYS The high-voltage switching circuit also performs the function of insulating the patient by means of relays RL1 and RL2. The coils of the two relays are connected in series. The activation of relays RL1 and RL2 is controlled by transistors T11, T12 and T13 of the high-voltage circuit (W4P14 1721). The patient insulation relay (RL1 and RL2) activation duration is 160 ms, which is equal to the duration of the DISCH signal that controls transistor T12. 7.3.6. ECG PREAMP PROTECTION printed circuit board The ECG PREAMP PROTECTION PCB (W4P14 1723) electrically connects the ECG signals from the adhesive defibrillation electrode connector to the defibrillation ECG preamplifier circuit located in the upper part. The PCB is made up of the following: • Stage for protecting the ECG preamplifier from defibrillation shocks • Stage for protecting the patient impedance measurement circuit from defibrillation shocks • Circuit designed to measure the contact impedance of the adhesive electrodes. OVERVIEW The ECG PREAMPLIFIER PROTECTION PCB (W4P14 1723) is made up of two parts: The first part contains the components that protect and clip the defibrillation shock, associated with an oscillator for measuring the patient impedance. The second part contains the components that protect and clip the defibrillation shock, associated with two unit-gain followers for transmitting the ECG signal to the defibrillation ECG preamplifier of the upper part. Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-22 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS CONTACT IMPEDANCE MEASUREMENT The frequency generator dedicated to measuring the contact impedance is built around U2. It delivers a 20-kHz sinus signal. The signal is injected in the patient through R4, R6, R3, C1, C2, R5, C3, C4 and R1, R2. The signal between J1 and J2, which is made up of the ECG signal and the 20-kHz signal that is the patient contact impedance image, is transmitted to the defibrillation preamplifier through R7, R8, R10, R9, L1, L2 and U1A, U1B. The signals at the output of U1 (J3 and J4) are connected to the defibrillator ECG preamplifier in the upper part of MULTIPULSE BIOWAVE FRED®. PROTECTION FROM DEFIBRILLATION SHOCKS The 20-kHz generator is protected by the capacitive coupling of C1, C2, C3 and C4 associated with resistors R7, R8 and sparker E1, then supplemented by a final clipping system built around DZ1, DZ2, R3, R4, and R5, R6. The amplifier chain is protected by power resistors R7, R10 associated with sparker E2. An additional clipping system is built around R8, R9, DN1 and DN2 and is used to bring the residual voltage following a defibrillation shock within the range of power supply voltages +VFD and –VFD. Power supply voltages +VFD and –VFD are generated on the defibrillation ECG preamplifier PCB in the upper part. The two reference voltages DZ5 and DZ6 supply polarising voltages for clipping diodes DN1 and DN2. 7.3.7. INSULATION AND SHIELDING printed circuit board The INSULATION AND SHIELDING PCB (W4P14 1725) provides mechanical protection for the circuits of the defibrillator part, and additional electrical insulation between the high-voltage part of the defibrillator and the upper part. Besides, the insulation and shielding circuit includes conductive coating (connected to the ground by the fixing piece screws) in order to make the upper part more immune to disturbance during defibrillation shocks. 7.3.8. Timing charts of the defibrillator part The pages below provide timing charts relating to the various phases of the defibrillator part. The timing charts are as follows: • Charging phase timing chart • Hold phase timing chart • IGBT control signal timing chart • Discharging phase timing chart Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 7-23 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS Charging phase timing chart -SACHARGE (p15. U10) +5V 0 SECRST (p25. U12) Tmin = 100 ms t +5V 0 5 ms t STARDEF (TP5) +5V 0 t + UCHARGE drain T10 (p2. J9) + UBATT 0 t RL1 Activation on W4P14 1721 Activation or safety discharge relay 0 t GEST (TP6 ) +5V 0 65 ms t Vds T1, T2 70V + UBATT HVMES 1 (TP8) 0 Selected energy reference 180 J VREF = 3,00 V 0 t End of charge - STOP (p1. U3) +5V 0 t HVMES 2 (TP15) + 4,24 V U HT = 4,24 x 1100 U HT = 4664 V 0 Art. no. 0-48-0001 t t Page 7-24 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS Hold phase timing chart STARTDEF (TP5) +5V 0 t GEST (TP6) +5V 0 55 ms 0 55 ms t CFULL p20. U12 Tmax = 20 s Activation of discharge transistor validation T11 (W4P14 1721) Anode of D6 t + UBATT 0 0 t Indication DEF READY t HVMES 2 (TP15) 0 Art. no. 0-48-0001 t Page 7-25 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS IGBT control signal timing chart STARTDEF 0 t 0 t 0 t 16 ms (p7. U3) - DISCH CLK (p10. U7) f = 10 kHz 0 t PHASE 1 (p5. J1) 0 25 ms 4 ms t PHASE 2 (p7. J1) 0 4 ms t PREPULSE 1 (p6. J1) 0 2 ms t PREPULSE 2 (p8. J1) 0 Art. no. 0-48-0001 t Page 7-26 Version July 2001 7. OPERATING EXPLANATIONS Discharging phase timing chart CFULL (p20. U12) 0 t 0 t 0 t 0 t Activation of the shock button DISCH 1 (p1. U9) - DISCH 2 (p7. U9) DISCH (p19. U12) 0 150 ms 160 ms t Pulsed biowave 0 Art. no. 0-48-0001 25 ms Page 7-27 t Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.1. COMPONENT ABBREVIATION LIST Reference BAT BZ Battery – cell Buzzer C CTR Capacitor Cathode ray tube D DN DP DZ Diode Diode network LED display Zener diode – voltage reference E Sparker F FB Fuse Ferrite bead J JP Connector – connection bar – Fast-on lug Jumper L LA LD HP Induction coil - core Lamp - indicator LED (light emitting diode) Speaker P PB PF Potentiometer Pushbutton Fuse-holder Q Quartz R RA RB RG RL RN Resistor – VD resistor Adjustable resistor Rectifying bridge Regulator Relay Resistor network S SP SW Support Solder pin Switch – sectioning switch T TN TP TR Transistor - IGBT Transistor network Test point Transformer U Art no. 0-48-0001 Description Integrated circuit – optocoupler Page 8-1 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.2. LIST OF SIGNALS USED IN THE DIAGRAMS A[0-17] HOST microcontroller address bus AMEM[0 25] Flash memory address bus ANALYSE Analyse/Shock key AVDO LCD monitor controller registry address signal BVDMEM1 Detection of the saving voltage for SRAM memory cards BVDMEM2 Detection of the saving voltage for SRAM memory cards CHARGEN High-voltage capacitor charging enabling signal (active on 1) CHECKBAT Battery voltage monitoring signal CLDSTRT Signal indicating the origin of the RESET signal CONTR_DOWN Decrease contrast key CONTR_UP Increase contrast key CTS_SUBD9 Control signal of the serial link between the HOST microcontroller and the external modem -CDMEM1 Signal of the presence of the flash memory card -CDMEM2 Signal of the presence of the flash memory card -CDNI/LI Cadmium-nickel battery or lithium cell encoding signal -CHARGEDR Control signal of the charge validation transistor (T2) of the high-voltage capacitor (active on 0) -CSADC ADC selection signal (U37) CSAUDIO U33 output flip-flop selection signal -CSDEFI0 U36 output flip-flop and U39 input flip-flop selection signal -CSDEFI1 U35 output flip-flop and U41 input flip-flop selection signal -CSECG_NF UART selection signal, serial link between the HOST microcontroller and the 12-lead ECG preamplifier -CSENREG UART selection signal, serial link between the HOST microcontroller and the recording microcontroller -CSFLASH Flash memory card selection signal -CSKEY U40 input flip-flop selection signal -CSLCD LCD monitor controller selection signal -CSMUX U34 output flip-flop selection signal -CSSpO2 UART selection signal, serial link between the HOST microcontroller and the SpO2 module Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-2 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS -CSSUBD9 UART selection signal, serial link between the HOST microcontroller and the external modem -CSVF UART selection signal, serial link between the HOST microcontroller and the fibrillation detection microcontroller -CSVIDEO Selection signal for communication from the HOST microcontroller to the video microcontroller DCD_SUBD9 Control signal of the serial link between the HOST microcontroller and the external modem DCIN DC input voltage for battery charging DEFCHARGE Signal indicating the high-voltage capacitor charging phase (active on 1) DEFDISCH Signal indicating the defibrillation phase (active on 1) DEFREADY Signal indicating the defibrillator ready phase (active on 1) DISCH Discharge triggering signal from the microcontroller (active on 1) DISCHKEY 1 Signal from the Analyse/Shock key DISCHKEY 2 Signal from the Analyse/Shock key DSR_SUBD9 Control signal of the serial link between the HOST microcontroller and the external modem DTR_SUBD9 Control signal of the serial link between the HOST microcontroller and the external modem D[0-7] HOST microcontroller data bus DMEM[0 7] Flash memory card data bus. DV[0 7] LCD monitor data bus -DEFSEC Signal indicating a technical fault in the defibrillator (active on 0) -DISCHENDR Control signal of the discharge validation transistor (T11) (active on 0) ECG X1000 ECG signal with gain value of 1000 -ECG_ON 12-lead ECG preamplifier power supply control signal -ERRORVID Video microcontroller status signal GEST High-voltage generator control signal (active on 1) HVMES 1 High-voltage capacitor charging voltage measured with the high-voltage converter (TR1). HVMES 2 High-voltage capacitor charging voltage measured with the high-voltage balancing resistors HVMONIT High-voltage capacitor charging voltage amplitude sent to the CPU -INTUART Association of interrupt signals from UARTs -INT1 Association of interrupt signals from video microcontroller and defibrillator Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-3 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS LED1GREEN Analysis indication LED LED2GREEN Analysis indication LED LED3GREEN Analysis indication LED LED1RED Defibrillator Ready indication LED LED2RED Defibrillator Ready indication LED LED3RED Defibrillator Ready indication LED MODE_MEDICAL Manual mode selection key NTC Cadmium-nickel battery or lithium cell recognition signal ONBYKEY Signal from the On/Off key -OEMEM Flash memory card reading signal -ON/OFF Signal from the On/Off circuit (active on 0) PATCHLED Adhesive defibrillation electrode connection indication LED PATRL Patient relay validation by T11 -PATRL Patient relay activation by T12 and T13 PHASE1 Phase 1 control signal PHASE2 Phase 2 control signal PHI1 Buffered control signal for phase 1 IGBTs PH2 Buffered control signal for phase 2 IGBTs PHONE_TRANSM Telephone transmission key PREPHI1 Buffered control signal of the active blocking of phase 1 IGBTs PREPHI2 Buffered control signal of the active blocking of phase 2 IGBTs PREPULSE1 Active blocking control signal for phase 1 PREPULSE2 Active blocking control signal for phase 2 -PSEN Reading validation signal QRS_TRIG QRS complex detection pulse RAZENREG Recording microcontroller reset signal RAZSpO2 SpO2 module reset signal RAZUART1 UART 1 reset signal (U25) RAZUART2 UART 2 reset signal (U26) RAZVID Video microcontroller reset signal RAZVF Fibrillation detection microcontroller reset signal RDYMEM Status signal regulating communication microcontroller and the flash memory card READY_VID Status signal regulating communication between the HOST microcontroller and the video microcontroller Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-4 between the recording Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS RESET Reset signal (active on 1) REVERSE LCD monitor reverse video signal RI_SUBD9 Control signal of the serial link between the HOST microcontroller and the external modem RST_MEM Flash memory card reset signal RST_VID LCD monitor controller reset signal RTS_SUBD9 Control signal of the serial link between the HOST microcontroller and the external modem RXD_ECG_NF 12-lead ECG preamplifier serial link reception signal RXD_ENREG Recording microcontroller serial link reception signal RXD_SpO2 SpO2 module serial link reception signal RXD_SUBD9 External modem reception signal RXD_VF Fibrillation detection microcontroller serial link reception signal -REGMEM Flash memory card registry selection signal -RESET Reset signal (active on 0) -RD_VID LCD monitor controller read signal SACHARGE High-voltage capacitor charge triggering signal (active on 1) SAWSEL0 Energy selection in the AED mode SAWSEL1 Energy selection in the AED mode SAWSEL2 Energy selection in the AED mode SAWSEL3 Energy selection in the AED mode SECDISCH Signal indicating the high-voltage capacitor safety discharge (active on 1) STARTCONV High-voltage generator activation signal in the battery test mode (active on 1) START_CHARGE Defibrillator charging key in the manual mode STARTDEF Charging/discharging cycle control signal (active on 1) SYNCDEF Defibrillation control signal in the direct / synchronised mode +SPEAKER Audio amplifier output signal to speaker -SPEAKER Audio amplifier output signal to speaker -SYNCDR Defibrillation control signal in the buffered synchronised / direct mode TXD_ECG_NF 12-lead ECG preamplifier serial link transmission signal TXD_ENREG Recording microcontroller serial link transmission signal TXD_SpO2 SpO2 module serial link transmission signal TXD_SUBD9 External modem transmission signal Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-5 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS TXD_VF Fibrillation detection microcontroller serial link transmission signal -TESTVF Reserved U_BCKLIGH BACKLIGHT CONVERTER power supply voltage VOICE Analogue signal for voice prompts V_IN_PROGR Status signal transmitted by the fibrillation detection microcontroller informing the HOST microcontroller that a voice prompt is in progress VSMEM1 Flash memory card type recognition. VSMEM2 Flash memory card type recognition. WAITMEM Flash memory card access delay signal WDUMP High-voltage capacitor safety discharge control signal WPMEM Flash memory write protection signal WSEL_DOWN Energy selection key in the manual mode WSEL_UP Energy selection key in the manual mode -WEMEM Flash memory write signal -WR Writing validation signal -WR_VID LCD monitor controller write signal +UBATT Battery power voltage +UBATTF Battery power voltage protected by an 8AT fuse +UDEF Power supply voltage of the defibrillator part -VO LCD screen contrast / polarisation voltage +2,5VREF +2.5V reference voltage +5V Power supply voltage of the circuits of the defibrillator part +5VCPU CPU part circuit power supply +12V Monitor part analogue circuit power supply -12V Monitor part analogue circuit power supply -24V LCD screen contrast / polarisation voltage Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-6 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.3. LIST OF PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARDS Description PCB number Article number of and versions fitted PCB 12-lead U3P287-1 U53287 ECG amp PCB U3P287-2 Defibrillation W4P14 1691A ECG PCB W4P14 1691B CPU PCB W4P14 1694A W141 1901 W141 1904 W4P14 1694C W4P14 1694D U3P297-1 W141 1909 W4P14 1682 W141 1787 U3P296-1 U53296 W4P14 1721 W141 2006 Defibrillator W4P14 1722 W141 2007 control PCB W4P14 1722A High-voltage W4P14 1724 switching PCB W4P14 1724A ECG preamplifier W4P14 1723 W141 2008 W4P14 1725 W141 2010 BACKLIGHT CONVERTER support PCB Battery Interface PCB POWER SUPPLY PCB High-voltage PCB W141 2009 protection PCB Insulation and shielding PCB Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-7 Version July 2001 Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-8 A B C D Version July 2001 8 7 W1411788 J4 J3 7 J5,J6,J7,J8,J9 Protection préampl ( W4P141683. ) Preamp protection (W4P141691) Schema_bloc_preampl_fred.opj Sternum Apex Patient cable Câble patient 8 J2 W1411901 5 J1 Préampl défi ( W4P141691.. ) 4 wire shielded cable 6 5 4 4 3 CP2 CP1 U53287 3 CP3 Préampl 12 canaux ( U3P287 ) 12 canal preamp (U3P287) 10 wire flat cable W1411841 Câble plat 10 fils W1411841 Defi preamp (W4P141691) Câble blindé 4 fils W1411834 12 wire link w1411842 Liaison 12 fils W1411842 6 2 10 wire flat cable (U3P287) Câble plat 10 fils W1411870 2 1 J.MEYER 04.07.2000 CPU ( J3 ) 1 A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.4. ECG PREAMP INTERCONNECTION DRAWING Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-9 A B C D Version July 2001 8 7 7 4 wire shielded cable W1411834 Câble blindé 4 brins W1411834 JP3 Defi pream (W4P141691) W1411901 J2 6 J1 Liaison carte à carte Board to board link 5 5 10 wire flat cable W1411841 Câble plat 10 fils W1411841 Câble plat 10 brins W1411870 10 wire flat cable W1411870 2 separate wire link Liaison filaire 2 fils 34 wire flat cable Câble plat 34 fils W1411840 72960 JP1 Module SpO2 6 Preampli. défi ( W4P141691.. ) Câble filaire 8 fils W1411864 8 separate wire cable W1411864 Scema_bloc_moniteur_fred.opj VERS LE DEFI To the defi VERS LE DEFI To the defi Capteur_SpO2 SpO2 sensor 8 4 CP1 4 12 canal preamp (U3P287) U53287 CP2 CP3 J12 J8 J7 J6 J10 TP5,TP6,TP7 J11 SP1,SP2 Preampli 12 canaux ( U3P287 ) W1411904 J3 J5 J13 J4 J2 J1 2 separate wire Wcable W1411217 CPU ( W4P141694.. ) 3 2 CN1 Ecran LCD W1411909 CP1 3 12 wire cable W1411842 Câble 12 fils W1411842 Clavier W1404924 Clavier W1404923 Clavier W1404926 Clavier W1404925 keyboard 2 Câble plat 9 fils ( CPU version C ): 9 wire flat cable W1411863 Câble plat 9 fils ( CPU version D ): W1412016 Câble blindé 2 fils ( W1411866 ) 1 CCFL 1 J.MEYER 30.06.2000 Patient cable Câble patient On/off keyboard Clavier_M/A Contrast keyboard Clavier_contraste Manual keyboard Clavier_manuel Analyse keyboard Clavier_analyse External keyboard Modem_externe Microphone backlighting Modem_PCMCIA Mémoire_PCMCIA PCMCIA memory CP2 LCD display Rétro-éclairage ( U3P297 ) 2 wire shielded 72939 cable (W1411866) Connecteur carte à carte Board to board connector Câble filaire 2 fils W1411217 Connecteur carte à carte Connecteur carte à carte Board to board connector A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.5. MONITOR PART INTERCONNECTION DRAWING A B C D PLI-00.SCH 8 18V 4,75Ah LITHIUM 12V 1,9Ah Ni/Cd W4P14 1682 INTERFACE BATTERY 332 W4P14 1722A W4P14 1722 7 CONTROL BOARD DEFIBRILLATOR U3P296-1 POWER SUPPLY DEFI PATCH INDICATOR DC INPUT LOUDSPEAKER (Red) (Black) (Grey) (Grey) (Black) (White) Version July 2001 6 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 HVMES1 +5V DISCHKEY1 DISCHKEY2 SAWSEL0 SAWSEL1 SAWSEL2 SAWSEL3 SACHARGE STARTCONV WDUMP SYNCDEF GND GND GND DISCH DEFCHARGE DEFREADY DEFDISCH SECDISCH -DEFSEC -CHARGEDR STARTDEF GEST -DISCHENDR -SYNCDR 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 34 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 N.C N.C N.C N.C PHASE1 PREPULSE1 PHASE2 PREPULSE2 HVMES2 CHARGEN PATRLSEC +UPWR +UPWR +UPWR +UPWR GND GND GND GND +UDEF +UDEF ON/OFF N.C +12V +12V +12V +12V GND GND +5VCPU +5VCPU +5VCPU +5VCPU GND GND GND GND -12V -12V -24V -24V GND GND N.C N.C GND GND GND GND +UBATT +UBATT +UBATT NTC DCIN GND -SPEAKER +SPEAKER GND PATCHLED J1 J18 J15 J17 5 W140 5319 TR1 TRANSFORMER HIGH VOLTAGE W4P14 1721 BOARD HIGH VOLTAGE J8 J7 J6 J12 J4 J2 -HV2 +HV2 -HV1 +HV1 J16 J10 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 1 1 1 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 4 GND +UBATTF PATRL -PATRL N.C PHI1 PREPHI1 PREPHI2 PHI2 2X22M/VR37 (Blue) (Black) (White) (Red) 4 1 1 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 1 ESJC37-10 ESJC37-10 1K/3W J19 J20 J18 J8 J1 J7 1 J4 W4P14 1723 PROTECTION ECG PREAMP 3 J3 J9 3 ECL00 26/03 01 RH DRAWN APPROV HAUTE TENSION J6 J11 J10 J12 J13 J2 2 MODIFICATION 30uF 3640V J2 J1 (White) (Yellow) (Black) (Green) (Brown) HV CAPACITOR 30uF 1250V COMMUTATION W4P14 1724 W4P14 1724A 2 J3 J4 J5 J6 J7 CIRCUIT de J5 1 5 1 6 1 7 1 Page 8-10 1 Art no. 0-48-0001 1 8 1 1 1 1 (Sternum) (Apex) CONNECTOR DEFI-PATCH FLOATING ECG CPU TO HOST SHT NO : 1/1 DSK NO : ........ DWG NO : PRT NO : ART NO : 1 .DG 501 BIPHASIC .PLAN D'INTERCONNEXION .WIRING DIAGRAM (Orange) (White) -VFD FGNF +VFD STERNECG APEXECG +UBATTF ON/OFF GND +12V +12V +12V +5VCPU +5VCPU -12V -24V PATCHLED WDUMP SYNCDEF DISCHKEY1 DISCHKEY2 -CDNI/LI DEFCHARGE DEFREADY DEFDISCH SECDISCH -DEFSEC HVMONIT N.C +SPEAKER -SPEAKER GND GND GND STARTCONV SAWSEL0 SAWSEL1 SAWSEL2 SASWEL3 SACHARGE 1 A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.6. DEFIBRILLATOR PART INTERCONNECTION DRAWING SYN-00.SCH POWER D Art no. 0-48-0001 C B Page 8-11 MAIN CPU A Version July 2001 01 ECL00 22/03 APPROV MODIFICATION PREAMP. ECG DEFI. PROTECTION SHT NO : 1/1 DSK NO : ........ DWG NO : PRT NO : ART NO : .DEFIBRILLATOR BLOCK DIAGRAM .SYNOPTIQUE DEFIBRILLATEUR .DG 501 DEFI.ECG OUTPUT B RH DRAWN ECG PREAMP. DEFI-PATCH CONNECTOR C MONITOR PART HIGH VOLTAGE CIRCUIT 1 CONTROL UNIT TRANSF. HV FLOATING PART D DEFIBRILLATOR GENERATOR HIGH VOLTAGE 6 SUPPLY 2 DEFIBRILLATOR 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.7. DEFIBRILLATOR PART DIAGRAM A 1 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 7 7 8 8 Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-12 A B SYN-01.SCH 8 7 DIGITAL Version July 2001 6 MAIN CPU MONITOR PART INTERFACE SIGNALS DEFIBRILLATOR PUSH-BUTTON 1 2 1 5 GATING BIPHASIC PULSED DRIVERS RELAY (analog) MONITORING CAPACITOR VOLTAGE 2 DISCHARGE BUTTON INTERFACE ANALYSE KEY ANALYSE/DISCHARGE ENERGY SELECTION INTERF. OUTPUT DEFIBRILLATOR DIGITAL VOLTAGE DIVIDER and MULTIPLEXER VOLTAGE REFERENCE STATE MACHINE DETECTION FAILURE DEFIB. HV MONITORING for ENERGY DISPLAY and IGBT DEFAULT DETECTION ESJC 37-10 40M 30uF 1,2KV 4 40M C2 SAFETY DISCH. RELAY 22 1 2 A 2 21 11 A1 SAFETY DISCHARGE POWER RESISTOR 3 INTERFACE IGBT module2 IGBT module1 IGBT HIGH 2 SHT NO : 1/1 DSK NO : ........ PRT NO : ART NO : 1 .DG 501 BIPHASIC .SYNOPTIQUE DEFIBRILLATEUR .DEFIBRILLATOR BLOCK DIAGRAM DWG NO : MODIFICATION PREAMP. PROTECTION ECG CONNECTOR DEFI-PATCH 1 DEFI.ECG OUTPUT TUBE DISCHARGE GAS ECL00 26/03 01 APPROV PREAMP. ECG DEFI. RESISTORS LIMITING CURRENT VOLTAGE 2 RH DRAWN 20M PATIENT RELAY 42 DEFIBRILLATOR CHARGE DRIVER 11 C1 ENERGY CAPACITORS 30uF 3,6KV CIRCUIT HIGH VOLTAGE 3 32 2 A 41 CONTROL UNIT PWM Checking capacitor voltage for End of Charge and desaturat. 3 ESJC 37-10 4 1 A 31 14 A2 END OF CHARGE COMPARATOR TRANS. HV TRANSFORMER 5 13 A1 24 DEFIBRILLATOR 18V LITH.PRIM.BATTERY CHARGE GENERATOR SUPPLY 12V Ni/Cd ACCUMULATOR HIGH VOLTAGE 6 POWER 7 23 C D 8 A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.8. TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMP PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD Article no.: U53 287 Description: 12-LEAD ECG AMP PCB Reference: U3P287-1 or U3P287-2 Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-13 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-14 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-15 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-16 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-17 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-18 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-19 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-20 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-21 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-22 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-23 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS COMPONENT LIST OF TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMPLIFIER PCB 1.1 U3P287-2 POSITION C1 C100 C110 C111 C112 C115 C116 C117 C130 C140 C141 C142 C145 C146 C147 C2 C200 C210 C211 C212 C215 C216 C217 C230 C240 C241 C242 C245 C246 C247 C260 C270 C271 C272 C275 C276 C277 C3 C30 C310 C311 C312 C320 C321 C322 C330 C331 C335 C336 C35 ITEM 45051 21018 22172 21006 21006 22172 21006 21006 21018 22172 21006 21006 22172 21006 21006 45051 21018 22172 21006 21006 22172 21006 21006 21018 22172 21006 21006 22172 21006 21006 21018 22172 21006 21006 22172 21006 21006 45051 8493 21014 21006 21006 21014 21006 21006 21014 20990 21014 21014 21014 Art no. 0-48-0001 DESCRIPTION CAPA CHIP 1206 2.2N 50V NPO 1% CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA CHIP 1206 2.2N 50V NPO 1% CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA CHIP 1206 2.2N 50V NPO 1% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R Page 8-24 MANUFACTURER VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS C4 C40 C400 C410 C411 C412 C415 C416 C417 C430 C440 C441 C442 C445 C446 C447 C460 C470 C471 C472 C475 C476 C477 C48 C49 C5 C50 C500 C501 C51 C510 C511 C52 C53 C6 C600 C601 C602 C603 C610 C611 C660 C661 C7 C700 C701 C702 C703 C704 C705 C706 C707 C708 C709 C710 C711 C712 C713 C715 45051 21014 21018 22172 21006 21006 22172 21006 21006 21018 22172 21006 21006 22172 21006 21006 21018 22172 21006 21006 22172 21006 21006 21014 8493 45051 21014 21014 21002 8493 21014 21002 8493 8493 45051 20996 65496 65496 20983 20996 20983 20998 20983 45051 65496 65496 8493 21014 21006 8493 65496 8493 8493 65496 65496 65496 21006 8493 65496 Art no. 0-48-0001 CAPA CHIP 1206 2.2N 50V NPO 1% CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 2220 1U 63V 20% Z5U CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA CHIP 1206 2.2N 50V NPO 1% CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA CHIP 1206 2.2N 50V NPO 1% CAPA SMD 1206 330P 50V 5% NPO CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA SMD 1206 27P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 330P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 27P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 470P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 27P 50V 5% NPO CAPA CHIP 1206 2.2N 50V NPO 1% CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V Page 8-25 VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SIEMEN SIEMEN VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SIEMEN SIEMEN VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SIEMEN VITRAM VITRAM SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN VITRAM VITRAM SIEMEN Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS C716 C8 C9 C900 C901 C902 C903 C905 C906 C907 C908 C909 C910 C911 C912 C913 C915 C916 C917 C918 C920 C921 C928 C930 C931 C932 C933 CP1 CP2 CP3 CP700 D300 D301 D302 D710 D711 D712 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6 E7 E8 E9 IC1 IC10 IC100 IC102 IC11 IC110 IC12 IC140 IC2 IC202 IC210 IC240 IC260 65496 45051 45051 8493 8493 8493 8493 8493 8493 8493 8493 8493 8493 20983 20983 20983 20994 21018 65496 20990 65496 65496 65496 8493 8493 8493 8493 72998 84306 84306 4384 69251 69251 69251 51589 51589 51589 65947 65947 65947 65947 65947 65947 65947 65947 65947 51685 69964 69964 69964 69964 51685 69964 51685 51685 69964 51685 51685 69964 Art no. 0-48-0001 CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA CHIP 1206 2.2N 50V NPO 1% CAPA CHIP 1206 2.2N 50V NPO 1% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 27P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 27P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 27P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 220P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA SMD 1206 100P 50V 5% NPO CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA ELECT TANTAL SMD 10U 25V CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CN M 13 D PRT CN M 10 S PC CN M 10 S PC CN M 3 D PRT BARSIL H6.7MM DIODE SMD 1206 1% 1N4148 DIODE SMD 1206 1% 1N4148 DIODE SMD 1206 1% 1N4148 DIODE SMD PRLL5819 SOD87 DIODE SMD PRLL5819 SOD87 DIODE SMD PRLL5819 SOD87 SPARKER FUSE 230V SPARKER FUSE 230V SPARKER FUSE 230V SPARKER FUSE 230V SPARKER FUSE 230V SPARKER FUSE 230V SPARKER FUSE 230V SPARKER FUSE 230V SPARKER FUSE 230V IC 4053/MUX CD4053BCM SO16 IC 2274 /TLC2274CD SMD SO D IC 2274 /TLC2274CD SMD SO D IC 2274 /TLC2274CD SMD SO D IC 2274 /TLC2274CD SMD SO D IC 4053/MUX CD4053BCM SO16 IC 2274 /TLC2274CD SMD SO D IC 4053/MUX CD4053BCM SO16 IC 4053/MUX CD4053BCM SO16 IC 2274 /TLC2274CD SMD SO D IC 4053/MUX CD4053BCM SO16 IC 4053/MUX CD4053BCM SO16 IC 2274 /TLC2274CD SMD SO D Page 8-26 SIEMEN VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SIEMEN VITRAM SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM JST LUMBER LUMBER AMP BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN FAIRCH TI TI TI TI FAIRCH TI FAIRCH FAIRCH TI FAIRCH FAIRCH TI Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS IC262 IC270 IC3 IC30 IC300 IC301 IC302 IC303 IC4 IC410 IC432 IC440 IC470 IC5 IC500 IC6 IC600 IC700 IC701 IC900 IC901 IC902 IC903 IC905 IC906 IC907 IC908 IC909 IC910 IC911 IC920 IC930 L1 L2 L600 L701 L900 OPT600 OPT610 OPT660 OPT700 PRT Q900 R1 R10 R100 R101 R102 R103 R104 R105 R11 R110 R111 R112 R113 R114 R115 R116 69964 51685 51685 69964 51685 51953 69964 51676 51953 51685 69964 51685 51685 51953 69958 51953 69964 84126 51832 69968 U06064 51531 69963 51921 51921 51921 69973 69965 69967 69958 69962 69961 14468 21352 14468 21352 14468 84349 84349 84349 84349 U07287 84000 67014 1035 20750 20750 21335 20750 20750 21335 1035 51563 21344 21338 21329 21338 51563 21344 Art no. 0-48-0001 IC 2274 /TLC2274CD SMD SO D IC 4053/MUX CD4053BCM SO16 IC 4053/MUX CD4053BCM SO16 IC 2274 /TLC2274CD SMD SO D IC 4053/MUX CD4053BCM SO16 IC 4051/MUX HEF4051BT SO16 IC 2274 /TLC2274CD SMD SO D IC 4538/CD HEF4538BT SO16 SMD IC 4051/MUX HEF4051BT SO16 IC 4053/MUX CD4053BCM SO16 IC 2274 /TLC2274CD SMD SO D IC 4053/MUX CD4053BCM SO16 IC 4053/MUX CD4053BCM SO16 IC 4051/MUX HEF4051BT SO16 IC 2272 /TLC2272CD SMD SO8 IC 4051/MUX HEF4051BT SO16 IC 2274 /TLC2274CD SMD SO D IC 3525 /SG3525AP SO16 IC 431/VREF TL431CD SO8 SMD IC 80320 /DS80C320 PLCC44 PG ODAM EPROM ECG PROGR. IC 43256/SRAM SOP 28 SMD IC 74573 /SN74AHC573 SMD TSSOP IC 74259/74HC259 SO16 SMD IC 74259/74HC259 SO16 SMD IC 74259/74HC259 SO16 SMD IC 74138 /SN74AHC138 SMD TSSOP IC 7432 /SN74AHC32 SMD TSSOP14 IC 9356 /M93C56 SO8 IC 2272 /TLC2272CD SMD SO8 IC 199 /MAX199 SMD SSOP28 IC 7705 /TLC7705 SMD SO D SELF 18UH RES SMD 0 1% 0.25W 1206 SELF 18UH RES SMD 0 1% 0.25W 1206 SELF 18UH OPTO KOP CNY65 OPTO KOP CNY65 OPTO KOP CNY65 OPTO KOP CNY65 ECG AMP. 12 CHANEL PCB QUARTZ 30MHZ HC49/4H16PF 50PPM 99 RES MET 0414 1% 1W 120K RES MET 121K 1% 0.6W 50PPM RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES MET 121K 1% 0.6W 50PPM RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-27 TI FAIRCH FAIRCH TI FAIRCH PHILIP TI PHILIP PHILIP FAIRCH TI FAIRCH FAIRCH PHILIP TI PHILIP TI MOTORO TI DALLAS EMED NEC TI TI TI TI TI TI STM TI MAXIM TI STETTN BOURNS STETTN BOURNS STETTN TEMIC TEMIC TEMIC TEMIC POLYTR IQD BEYSCH DRALOR BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS DRALOR BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R117 R118 R119 R12 R13 R130 R131 R132 R133 R134 R135 R14 R140 R141 R142 R143 R144 R145 R146 R147 R148 R149 R15 R16 R17 R18 R19 R2 R200 R201 R202 R203 R204 R205 R21 R210 R211 R212 R213 R214 R215 R216 R217 R218 R219 R22 R23 R230 R231 R232 R233 R234 R235 R24 R240 R241 R242 R243 R244 21338 84137 21338 1035 1035 20750 20750 21335 20750 20750 21335 1035 51563 21344 21338 21329 21338 51563 21344 21338 84137 21338 1035 1035 1035 1035 1035 67014 20750 20750 21335 20750 20750 21335 21637 51563 21344 21338 21329 21338 51563 21344 21338 84137 21338 21637 21637 20750 20750 21335 20750 20750 21335 21637 51563 21344 21338 21329 21338 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES CHIP 1206 1% 0.25W 34.8K RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES MET 121K 1% 0.6W 50PPM RES MET 121K 1% 0.6W 50PPM RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES MET 121K 1% 0.6W 50PPM RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES CHIP 1206 1% 0.25W 34.8K RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES MET 121K 1% 0.6W 50PPM RES MET 121K 1% 0.6W 50PPM RES MET 121K 1% 0.6W 50PPM RES MET 121K 1% 0.6W 50PPM RES MET 121K 1% 0.6W 50PPM 99 RES MET 0414 1% 1W 120K RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES CHIP 1206 1% 0.25W 34.8K RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-28 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS DRALOR DRALOR BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS DRALOR BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS DRALOR DRALOR DRALOR DRALOR DRALOR BEYSCH BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R245 R246 R247 R248 R249 R25 R26 R260 R261 R262 R263 R264 R265 R27 R270 R271 R272 R273 R274 R275 R276 R277 R278 R279 R28 R29 R3 R30 R300 R301 R31 R310 R311 R312 R313 R32 R320 R321 R322 R323 R33 R330 R331 R332 R333 R334 R335 R336 R337 R338 R339 R34 R340 R36 R37 R38 R4 R40 R400 51563 21344 21338 84137 21338 21637 21637 20750 20750 21335 20750 20750 21335 21637 51563 21344 21338 21329 21338 51563 21344 21338 84137 21338 21637 21637 67014 21338 20750 20741 21334 21333 21326 20734 21326 21338 21333 21326 20737 21326 21338 21333 21326 21351 21351 21351 21344 21344 20741 20741 53699 21326 21338 21637 21637 21637 67014 21335 20750 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES CHIP 1206 1% 0.25W 34.8K RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES CHIP 1206 1% 0.25W 34.8K RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 99 RES MET 0414 1% 1W 120K RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 82.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 68.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 681 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 68.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 68.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 47.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 99 RES MET 0414 1% 1W 120K RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-29 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BEYSCH BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BEYSCH BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R401 R402 R403 R404 R405 R41 R410 R411 R412 R413 R414 R415 R416 R417 R418 R419 R42 R43 R430 R431 R432 R433 R434 R435 R44 R440 R441 R442 R443 R444 R445 R446 R447 R448 R449 R45 R46 R460 R461 R462 R463 R464 R465 R470 R471 R472 R473 R474 R475 R476 R477 R478 R479 R48 R49 R5 R50 R500 R501 20750 21335 20750 20750 21335 21333 51563 21344 21338 21329 21338 51563 21344 21338 84137 21338 21329 20730 20750 20750 21335 20750 20750 21335 21338 51563 21344 21338 21329 21338 51563 21344 21338 84137 21338 21338 21326 20750 20750 21335 20750 20750 21335 51563 21344 21338 21329 21338 51563 21344 21338 84137 21338 51563 51563 67014 21338 51563 51563 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 68.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES CHIP 1206 1% 0.25W 34.8K RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 332 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES CHIP 1206 1% 0.25W 34.8K RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES CHIP 1206 1% 0.25W 34.8K RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 99 RES MET 0414 1% 1W 120K RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-30 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BEYSCH BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R502 R504 R505 R51 R510 R511 R512 R514 R515 R52 R53 R56 R57 R58 R6 R60 R600 R601 R602 R603 R604 R605 R606 R61 R610 R611 R612 R613 R614 R615 R616 R62 R63 R64 R65 R66 R660 R661 R662 R663 R664 R665 R666 R67 R68 R69 R7 R70 R700 R701 R702 R703 R705 R706 R708 R709 R71 R710 R711 21637 21637 21637 21338 51563 51563 21637 21637 21637 51563 69298 21326 21326 21326 67014 21637 20734 20744 21330 53689 20746 20741 21338 21637 20734 20744 21330 53689 20746 20741 21338 21637 21637 21637 21637 21637 20744 20744 21338 21324 21327 20744 21338 21637 21637 21637 67014 21326 20741 20720 20741 53699 20728 20750 21326 21326 21326 21326 21326 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES CHIP 1206 1% 3.9M RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 99 RES MET 0414 1% 1W 120K RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 681 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.92K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 39.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 274 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 5.62K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 681 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.92K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 39.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 274 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 5.62K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.92K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.92K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 12.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.92K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 99 RES MET 0414 1% 1W 120K RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 56.2 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 47.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 221 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-31 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BEYSCH BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BEYSCH BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R712 R713 R715 R716 R717 R74 R75 R76 R77 R78 R8 R800 R801 R9 R901 R910 R911 R912 R913 R930 R931 R932 R935 R937 R943 R948 R982 RN900 RN905 RN906 RN907 SO901 T600 T610 T660 T70 T700 T701 T71 TR700 20737 21338 21326 20741 21338 21637 21637 21637 21637 21637 67014 72651 986 67014 21352 21637 21338 21326 21338 21338 20747 21338 21338 21338 20737 21326 20720 84061 84061 84061 84061 69969 51471 51471 51470 51470 68375 68375 51470 U21156 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 99 RES MET 0414 1% 1W 120K CAPA CERDI 220PF 6KV R12.5 RES MET 10 1% 0.6W 50PPM 99 RES MET 0414 1% 1W 120K RES SMD 0 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 6.81K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 56.2 1% 0.25W 1206 RES NET SOP16 8X56 2% RES NET SOP16 8X56 2% RES NET SOP16 8X56 2% RES NET SOP16 8X56 2% IC SOCKEL PLCC32 SMD TRANS SMD BSS84 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS84 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS RFD16N05 TO-251AA TRANS RFD16N05 TO-251AA TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 CORE FERRITE MOUNT.U4B156 Page 8-32 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BEYSCH ROEDER DRALOR BEYSCH BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS NUGENT SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN HARRIS HARRIS SIEMEN EMED Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.9. DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD Article no.: W141 1901 Description: DEFIBRILLATION ECG PREAMP BOARD Reference: W4P14 1691A or W4P14 1691B Adjustments: The Defibrillator ECG preamplifier PCB requires one adjustment: 1. setting the patient impedance measurement signal (P1) Adjustment Measuring apparatus Measuring point Adjustable Settings and tolerances Notes Patient impedance measurement signal VDC digital multimeter between pin TP1 (GND) and lug 6 of J10 P1 If Z = 25 Ω the measured voltage must be: The 25-Ω resistor is connected to the adhesive electrode connector. 1.660 V ± 0.050 V Caution: If the defibrillator ECG preamp board or the defibrillator preamp protection board is replaced, this adjustment must be repeated. Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-33 Version July 2001 6 5 Page 8-34 4 3 * A GND VO * 7 6 1 D9 BAS32 VI RG1 79L05 SMD D8 BAS32 5 1 L1 47u L2 47u RG2 78L05 SMD 3 2 8 2 3 6 7 PARTIE FLOTTANTE C41 100n C39 100n * P1691B_1 C37 10u C36 10u D11 BAS32 D10 BAS32 INH_PACE 10HZ_P IMP_ELEC_DEFI T2 D7 BAS85 R47 4.75k D6 BAS85 D4 BAS85 +VFD -VFD BSS138 SMD D5 BAS85 -VFD R72 1k -VFD R46 4.75k +VFD R45 2.21k +VFD R44 2.21k +VFD 15 17 14 18 13 3 4 3 4 2 1 2 1 TR1 MB03422 OPI1264C U13 OPI1264C U12 OPI1264C U14 OPI1264C U11 6 7 8 2 +VD +VD R70 1k R69 1k TP1 PICOT 2 1 2 1 3 4 3 4 C35 470n C34 10u +VD +VD -VD +VREF 100p C49 R56 562 +VREF 100p C44 4 5 + + R53 221k + + C32 22n & RX/CX R CX RX M2 S +VD M1 1 T3 BC860 SMD U9 4047 SMD [2 ,1 2 ,1 14 12 5 4 8 6 3 9 1 2 R95 10k R93 1k C31 22n R58 33.2k C50 10n R83 33.2k C47 10n -VD R94 47.5k C30 1n 2 Version July 2001 1 CK ECL02 10 / 99 JM APPROV 13 12 + 14 2 3 + + 1 U16D TLC2274 SMD + U16A C51 TLC2274 SMD 10n C45 22n C48 10n MODIFICATION defi_on/off -VD +VREF R66 2.74k ECL02 10 / 99 DRAWN +VREF R65 221k R64 221k +VD R62 33.2k R55 33.2k PARTIE NON FLOTTANTE 10 11 13 -VD R57 221k 7 8 U16C TLC2274 SMD U16B TLC2274 SMD 6 5 9 10 R92 100k +VD R63 22.1k C33 10u U10 TSC1428 SMD 2 7 +VD R68 4.75k +VREF R67 4.75k R52 22.1k * -VD C46 22n TP12 PICOT SHT NO : 1/2 DSK NO : DWG NO : W4S141691B PRT NO : W4P141691B ART NO : W1411901 DEFI PREAMPLIFIER 5 8 7 3 +VD PREAMPLIFICATEUR DEFI DG501 DZ7 4.7V C63 10u * R104 82.5R R106 22.1k +VREF ecg_defi 10hz_p imp_elec_defi inh_pace C64 47u 66.5k R105 * 4 VO VI 1 LBO LBI 2 SET OFF 6 GND U/U RG3 MAX884 +VD 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 C62 10u CON10 J1 * +VD C65 22n 2 NE PAS MONTER C38 10u TP11 PICOT TP10 PICOT C40 10u +VFD -VFD APEX STERNUM R71 BSS138 SMD 1k T1 3 TP2 PICOT +VFD -VFD CON5 1 2 3 4 5 ECG_DEFI -VFD +VREF 4 VO Art no. 0-48-0001 7 5 GND 8 6 VI J2 flottant defi B 3 7 6 8 7 C 11 D 4 R51 562 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 1 D C B A 3 * ne pas monter APEX STERNUM R100 1k R101 1k R103 20k R102 20k C67 4.7n C66 4.7n * * C69 4.7n C24 4.7n C23 4.7n * * R54 1k R59 1k + + + 7 1 6 5 + 7 R34 33.2k R33 33.2k + TL062 SMD U5B U2B TL064 SMD R32 100k 6 5 + 11 U2A TL064 SMD 4 2 3 C7 1n C6 1n 2 U5A + # +VFD U7B 4066 SMD # U7A 4066 SMD -VFD R35 100k TL062 SMD 2 3 + + * 11 12 1 13 + 1 C21 100n U2C TL064 SMD -VFD +VFD 9 10 68p C8 R12 100k 6.98k R31 8 1 + 2 Version July 2001 1u C20 -VFD + + +VFD -VFD R39 681k -VFD + +VFD 1 + + R29 6.98k 9 TL064 SMD U2D R38 681k C52 13 12 22n D2 BAS85 R40 1M 2 3 U4A TL062 SMD 2 3 -VFD 22n C54 R30 332k C19 1n R13 10k U6A TL062 SMD C9 1n R14 10k 90.9k R16 C10 33p 7 # U6B TL062 SMD + + R37 100R R28 10k 6 5 8 6 C53 1n U7D 4066 SMD 14 C18 1u R36 681k R26 10M R41 10k + 1 * 330n R25 1.21k * C17 * U15A TL062 SMD + TP7 PICOT 2 3 -VFD +VFD 6 5 + 10HZ_P + 7 -VFD 3 R18 1k -VFD R23 10k 2 3 * * R22 22.1k + 1 100k R107 R86 100k 5 4 C14 100n R85 221k R84 100k C56 22n -VFD +VFD + C11 22u 33.2k R99 U7C 4066 SMD TP8 PICOT +VFD R27 10k C15 100n R17 1M +VFD U3A TL062 SMD C61 330n * R24 100k U4B TL062 SMD BAS85 D1 * TP9 PICOT C58 22n 1 P1 20k 22n C55 5 6 3 2 R88 100k 2 3 1 COMP 7 100n C68 C16 22n U17B TLC393 SMD + - C57 22n +VFD U17A TLC393 SMD + - -VFD COMP +VFD R97 100k R98 47.5k + 7 + R87 10k APPROV CK ECL02 10 / 99 DRAWN JM ECL02 10 / 99 R20 15k + 7 DZ2 3.3V * C12 10n TP5 PICOT * R19 49.9k DZ3 3.3V DZ4 3.3V TP3 PICOT MODIFICATION * DZ1 * 3.3V +VFD -VFD C13 1n R90 100k T4 BC850 SMD +VFD U3B TL062 SMD 6 5 R89 100k R91 10k U15B TL062 SMD + R21 22.1k 1k R109 1k R108 6 5 R42 100k C60 22n + + 1 + + * TP4 PICOT TLC2272 SMD U8B 1 SHT NO : 2/2 DSK NO : 2 DWG NO : W4S141691B PRT NO : W4P141691B ART NO : W1411901 DEFI PREAMPLIFIER ECG_DEFI INH_PACE IMP_ELEC_DEFI PREAMPLIFICATEUR DEFI DG501 PICOT 6 5 7 C59 22n U8A TLC2272 SMD TP6 2 3 -VFD +VFD 3 10 C22 100n R11 100k R10 10k R8 1M R9 10k 8 8 R7 1M 4 4 -VFD 14 Page 8-35 4 7 5 8 6 4 4 A 4 Art no. 0-48-0001 7 5 8 8 6 8 7 4 B 8 8 C 4 D 4 8 # +VFD 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 1 D C B A 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8 6 7 5 4 3 1 2 D D R46 C55 U12 C62 U11 C63 R106 R105 R93 R94 C64 DZ7 R16 C10 R14 R13 C9 R12 C8 R97 R42 R88 R10 R11 R8 R102 C23 * R34 C66 * W4P141691B TOP SIDE R31 R35 U5 TP11 C19 R30 * C16 R28 TP5 U4 R29 U7 C7 R9 R7 C6 R32 R33 R25 * U8 * TP2 TP3 RG1 C39 C40 C37 C38 RG2 D4 D6 D5 D7 U10 C34 C36 C41 TP10 C35 B TP9 * * C17 TP8 R24 * R98 R99 D1 R17 R18 C56 R39 R38 T4 * R72 C33 T3 R71 R91 R27 U9 R89 C68 C58 C12 R22 R20 R45 TP1 C31 E t i q u e t t e U2 U15 U17 U6 T2 T1 C50 C46 R62 R65 C51 R68 R57 R58 C48 R63 R56 C49 * * C14 * U3 TP4 TP12 C P1 C15 R70 * R104 TP6 C44 R66 C30 R92 U14 L2 * RG3 C65 * P C32 C52 S D10 D11 R52 R51 R64 C47 R55 R67 R53 U16 DZ2 C61 * * TR1 TP7 B C60 C54 R69 R83 R44 R21 R37 R36 * * R40 C20 D2 R26 R23 L1 C22 D8 C21 W4P141691B BOTTOM SIDE D9 C69 C R87 C18 R59 * R84 * C59 * R47 D12 C13 R101 1 * C67 J2 R 109 D13 DZ1 C24 R54 R100 R103 C57 C45 R 108 C11 J1 U13 R107 R85 R95 R90 DZ3 DZ4 R86 R19 C53 R41 A A DEFIG ARD 501. PREAMPLIFICATEU R D EFI DEFI PREAM PLIFIER * = pas monté 8 Art no. 0-48-0001 7 6 DRAW N APPRO V MO DIFICATION ECL2 ECL2 10/99 10/99 5 Page 8-36 4 ART N O : W 1411901 PRT N O : W 4P141691B DW G NO : W 4L141691B DSK N O : SH T N O : 1/1 3 BRUKER M EDICAL 2 Version July 2001 1 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS COMPONENT LIST OF TWELVE-LEAD ECG AMPLIFIER PCB W4P14 1691B POSITION C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22 C30 C31 C32 C33 C34 C35 C36 C37 C38 C39 C40 C41 C44 C45 C46 C47 C48 C49 C50 C51 C52 C53 C54 C55 C56 C57 C58 C59 C6 C60 C62 C63 C64 C68 C69 C7 C9 D1 D10 ITEM 20984 51557 21014 21002 72502 72502 21018 51518 21002 72660 72502 72502 21002 21018 21018 51559 51559 22597 51559 51559 51559 72502 51559 72502 20990 21018 21018 21014 21014 20990 21014 21014 21018 21002 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21002 21018 51556 51556 51556 72502 21010 21002 21002 51329 22029 Art no. 0-48-0001 DESCRIPTION CAPA SMD 1206 33P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD TANTAL 22U 20V 20% CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 1U 16V +80/-20% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 20% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 20% CAPA SMD 1812 470N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 20% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 20% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 20% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 20% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 47U 16V 20% CAPA SMD TANTAL 47U 16V 20% CAPA SMD TANTAL 47U 16V 20% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 4.7N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO DIODE SMD BAS85 SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 Page 8-37 MANUFACTURER VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM TDK VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM PHILIP PHILIP Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS D11 D2 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 DZ3 DZ4 DZ7 J1 J2 P1 P1691B R10 R100 R101 R102 R103 R104 R107 R108 R109 R11 R12 R13 R14 R16 R17 R18 R19 R20 R21 R22 R24 R26 R27 R28 R29 R30 R31 R32 R33 R34 R35 R36 R37 R38 R39 R40 R41 R42 R44 R45 R46 R47 R51 R52 22029 51329 51329 51329 51329 51329 22029 22029 51945 51945 51772 84306 72977 51460 W1404663 20750 20737 20737 33927 33927 20722 21335 20737 20737 21335 21335 20750 20750 53697 21347 20737 51750 21325 21327 21327 21335 21637 20750 20750 51763 53690 51763 21335 21329 21329 21335 21345 20724 21345 21345 21347 20750 21335 20741 20741 20745 20745 20733 21327 Art no. 0-48-0001 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS85 SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS85 SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS85 SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS85 SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS85 SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE Z SMD SOD80 3.3V DIODE Z SMD SOD80 3.3V DIODE Z SMD SOD80 4.7V CN M 10 S PC CN M 5 C PRT RES ADJUST 20K 0.25W 1T SMD IC DEF PREAMPLIFIER DG501 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 20K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 20K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 82.5 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 90.9K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 49.9K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 15K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 6.98K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 332K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 6.98K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 681K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 681K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 681K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-38 PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP LUMBER JST BOURNS WUERTH BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R53 R54 R55 R56 R57 R58 R59 R62 R63 R64 R65 R66 R67 R68 R69 R7 R70 R71 R72 R8 R83 R84 R85 R86 R87 R88 R89 R9 R90 R91 R92 R93 R94 R95 R97 R98 R99 RG1 RG2 T1 T2 T3 T4 TP1 TP10 TP11 TP12 TP2 TP6 TR1 U10 U11 U12 U13 U14 U15 U16 U17 U2 21339 20737 21329 20733 21339 21329 20737 21329 21327 21339 21339 20742 20745 20745 20737 21347 20737 20737 20737 21347 21329 21335 21339 21335 20750 21335 21335 20750 21335 20750 21335 20737 53699 20750 21335 53699 21329 22993 22504 51470 51470 51777 51779 42990 42990 42990 42990 42990 42990 W1402079 51582 72268 72268 72268 72268 51675 72941 72272 51545 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 221K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 221K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 221K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 221K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.7K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 221K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 47.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 47.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 IC 7905/VREG MC79L05ACD SO8 IC 7805/VREG MC78L05ACD SO8 TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS SMD BC860C PNP SOT23 TRANS SMD BC850C NPN SOT23 ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM TRANS CONVERTER DG2005D IC 1428/DRV TC1428COA SO8 SMD OPTO COUP OPI1264C OPTO COUP OPI1264C OPTO COUP OPI1264C OPTO COUP OPI1264C IC 062/OP TL062CD SO8 SMD IC 2274 /TLC2274ACD SO14 IC 393/OP TLC393CD SO8 IC 064/OP TL064CD SO14 SMD Page 8-39 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS MOTORO MOTORO SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN MOTORO OXLEY OXLEY OXLEY OXLEY OXLEY OXLEY MICROS TELCOM OPTEK OPTEK OPTEK OPTEK TI TI TI ST Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS U3 U4 U5 U6 U7 U8 U9 51675 51675 51675 51675 51794 69958 51796 Art no. 0-48-0001 IC 062/OP TL062CD SO8 SMD IC 062/OP TL062CD SO8 SMD IC 062/OP TL062CD SO8 SMD IC 062/OP TL062CD SO8 SMD IC 4066/SWI CD4066BM SO14 IC 2272 /TLC2272CD SMD SO8 IC 4047/CD HEF4047BT SO14 SMD Page 8-40 TI TI TI TI HARRIS TI PHILIP Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.10. CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD Article no.: W141 1904 Description: CPU PCB Reference: W4P14 1694A or W4P14 1694C or W4P14 1694D Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-41 Version July 2001 A B C CON4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 CN12 10n CON12 J6 J7 PICOT FOURCHE SP2 SP1 PICOT FOURCHE 5 4 3 2 1 C275 10n 4X100pF * CN17 CON10 J10 4X100pF * CN16 P1694C_5 CPU_FV 4 2 8 +5V 10n C277 R241 100R CN13 10n 5 4 3 2 1 CON5 J8 u_back-light R243 100R R240 100R R217 100R P1694C_6 AVD0 -CSLCD -RD_VID -WR_VID DVD7 DVD6 DVD5 DVD4 DVD3 DVD2 DVD1 DVD0 RST_VID ECGX1000 RAZVF R245 100R 6 2 REVERSE VIDEO onbykey 8 4 TXD_VF RXD_VF VOICE V_IN_PROGR -TESTVF C276 10n +5V 8 * 1 2 3 4 +5V 6 5 7 J14 1 2 3 5 6 CN M DIL20D 7 8 R244 100R R242 100R 100R R216 RAZVID * CN11 10n 1u C261 D[0..7] TM910OK ERRORVID -CSVIDEO -WR BUSY_VID READY_VID CN15 10n 8 2 21 18 12 9 19 20 13 24 23 16 14 1 22 17 11 10 5 6 7 CN10 10n EN1 1 INPUT C1+ C1- 7 U111 MAX239 V- 4 VOLTAGE INVERTER +5V C264 10u 10u C262 C263 1u +12V 3 D 3 4 6 -CDNI/LI DEFCHARGE DEFREADY DEFDISCH SECDISCH -DEFSEC HVMONIT IPAT SPEAKER+ SPEAKER- STARTCONV SAWSEL0 SAWSEL1 SAWSEL2 SAWSEL3 SACHARGE PATCHLED WDUMP -SYNCDEF -ECG_ON TXD_ECG_NF RXD_ECG_NF QRS_TRIG TXD_MODEM RXD_MODEM RST_MODEM RXD_SpO2 TXD_SpO2 RAZUART1 RAZUART2 CHECKBAT A[0..2] CLDSTRT TXD_ENREG RXD_ENREG -RESET -CSSUBD9 -CSVF -INTUART -INT1 -INT1 -INTUART -CSVF -CSSUBD9 -RESET CLDSTRT A[0..2] CHECKBAT RAZSpO2 RAZUART2 RAZUART1 -ON/OFF RAZENREG CN1 10n PICOT FOURCHE TP5 CN2 10n CN4 10n CN3 10n C266 10u +12V TP19 PICOT TXD_MODEM RXD_MODEM RST_MODEM RXD_SpO2 TXD_SpO2 RAZSpO2 Phone shield PICOT FOURCHE TP7 TP6 PICOT FOURCHE 5 4 C235 10u -12V CN6 10n C234 10u 2 10u C233 CN7 10n CN8 10n 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 CON34 J5 4 RSTMEM WAITMEM -REGMEM BVDMEM2 BVDMEM1 -CDMEM2 VSMEM1 VSMEM2 -CSFLASH -OEMEM -WEMEM RDYMEM WPMEM -CDMEM1 AMEM[0..25] DMEM[0..7] 4 6 2 5 1 CN9 10n * 7 3 AMEM[0..25] DMEM[0..7] 2 P1694C_7 RAZSpO2 TXD_SpO2 RXD_SpO2 INTERFACE SpO2 * 3 :NE PAS MONTER RDX_SpO2 RSTSpO2 TDX_SpO2 TXD_MODEM RXD_MODEM RST_MODEM RDYMOD -WEMOD -OEMOD -CEMOD2 -CEMOD1 -CDMOD1 -CDMOD2 WPMOD BVDMOD1 BVDMOD2 -REGMOD WAITMOD RSTMOD DMOD[0..7] ECL02 11 / 99 JM DRAWN +VSpO2 APPROV -CDMOD2 WPMOD BVDMOD1 BVDMOD2 -REGMOD WAITMOD RSTMOD +12V 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 +5V JM JM 2 ECL03 ECL04 ECL06 11 / 99 01 / 00 06 / 00 JM MODIFICATION CON3 J13 CON6 J4 DMOD2 8 4 RAZSpO2 TXD_SpO2 RXD_SpO2 TP4 PICOT 1 140 139 VSMOD1 -CEMOD1 -OEMOD -WEMOD RDYMOD WPMOD -CDMOD1 -CEMOD2 RSTMOD WAITMOD -REGMOD BVDMOD2 BVDMOD1 -CDMOD2 VSMOD2 RSTMEM WAITMEM -REGMEM BVDMEM2 BVDMEM1 -CDMEM2 vsmem1 vsmem2 -csflash -OEMEM -WEMEM RDYMEM WPMEM -CDMEM1 3 DMOD0 5 C232 10u -VEE +UBATT +5V +12V CN5 10n J3 CON10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 P1694C_4 TXD_ENREG RXD_ENREG RAZENREG PHONEGND PHONE_IN CPU_ENREG DMOD1 CN14 10n P1694C_2 START_CHARGE WSEL_DOWN WSEL_UP MODE_MEDICAL LED1RED LED1GREEN LED2RED ANALYSE LED2GREEN LED3RED LED3GREEN CONTR_UP CONTR_DOWN PHONE_TRANSM U_BCKLIGH TXD_SUBD9 DSR_SUBD9 DCD_SUBD9 CTS_SUBD9 RI_SUBD9 RXD_SUBD9 DTR_SUBD9 RTS_SUBD9 +2.5VREF D[0..7] VOICE V_IN_PROGR -TESTVF READY_VID -CSSpO2 -CSECG_NF -CSMODEM -CSENREG -CSADC -CSDEFI0 -CSDEFI1 -CSMUX -CSKEYS -CSAUDIO -WR -PSEN TM910OK ERRORVID TXD_VF RXD_VF IN/OUT P1694C_1 -CSAUDIO -CSKEYS -CSMUX -CSDEFI1 -CSDEFI0 -CSADC -CSENREG -CSMODEM -CSECG_NF -CSSpO2 +2.5VREF RAZVF -PSEN ECGX1000 D[0..7] -CSVIDEO -WR BUSY_VID RAZVID -VO ONBYKEY CPU_HOST 6 6 5 5 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 7 1 3 4 5 6 7 3 4 4 3 CON5 7 8 8 1 2 2 1 J11 5 6 2 1 1 2 4 7 5 6 4 3 3 4 4 3 1 2 6 5 6 5 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 5 6 8 7 5 6 J12 3 4 6 5 7 7 8 Version July 2001 4 DMOD3 8 2 1 2 4 1 3 1 3 5 2 4 6 7 8 DMOD4 1 2 4 3 8 7 1 2 DMOD5 6 C221 10u 1 VSMOD1 VSMOD2 J2 CON80 AMOD[0..25] C231 10u C226 10u C222 10u DSK NO : ........ SHT NO : 0/7 1 DWG NO : W4S141694C PRT NO : W4P141694C ART NO : W1411904 PROCESS UNIT C230 10u J1 69 70 71 CON140 RN 4X33R 10u C220 CENTRALE .CENTRAL .UNITE .DG501 AMOD3 1 2 3 7 2 1 3 8 7 5 6 4 AMOD4 8 8 3 4 DMOD6 AMOD5 4 8 5 6 DMOD7 5 2 4 6 AMOD10 3 8 7 8 AMOD11 5 AMOD9 AMOD12 AMOD24 AMOD7 AMOD25 AMOD6 6 2 2 4 1 3 DMOD3 7 DMOD4 1 2 4 6 8 1 3 5 7 2 4 6 8 1 3 7 2 4 8 1 3 5 7 1 3 5 7 2 4 6 8 AMOD19 AMOD14 AMOD18 AMOD13 AMOD17 AMOD8 2 2 4 6 8 1 3 2 4 AMOD20 7 DMOD5 4 DMOD6 6 AMOD21 1 2 4 6 8 1 3 5 7 6 8 5 7 6 8 1 3 5 7 DMOD7 3 1 3 5 2 4 6 AMOD10 6 Page 8-42 AMOD11 8 AMOD5 5 2 4 6 8 7 8 AMOD6 AMOD25 AMOD7 AMOD24 AMOD12 AMOD23 AMOD15 AMOD22 AMOD16 7 AMOD9 8 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 1 3 5 7 2 4 6 8 AMOD4 3 2 4 AMOD2 AMOD3 AMOD19 AMOD14 AMOD18 AMOD13 AMOD17 AMOD8 1 8 AMOD0 7 6 AMOD1 6 2 2 4 6 8 1 3 5 2 4 6 1 3 5 7 7 8 AMOD20 8 6 8 8 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 1 2 138 137 136 135 134 133 132 131 130 129 128 127 126 125 124 123 122 121 120 119 118 117 116 115 114 113 112 111 110 109 108 107 106 105 104 103 102 101 100 99 98 97 96 95 94 93 92 91 90 89 88 87 86 85 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 3 5 4 6 AMOD21 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Art no. 0-48-0001 DMOD0 5 DMEM1 DMOD1 3 AMEM0 AMOD23 AMOD15 AMOD22 AMOD16 5 DMEM0 DMOD2 1 AMEM1 1 3 5 AMEM21 1 3 5 7 AMEM20 7 AMEM5 2 4 6 8 1 3 5 7 DMEM2 5 7 AMEM2 1 3 5 7 AMEM3 2 AMEM4 1 AMEM16 AMEM22 AMEM15 AMEM23 AMEM12 AMEM24 AMEM7 AMEM25 AMEM6 3 5 7 AMEM9 4 6 8 1 3 AMEM8 AMEM17 AMEM13 AMEM18 AMEM14 AMEM19 5 AMEM11 7 AMEM10 1 3 5 7 DMEM7 5 7 7 DMEM6 1 DMEM5 3 DMEM4 7 DMEM3 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 8 +12VMOD +5VMOD C229 100n 10u C227 C224 100n C223 10u +12V +5V C228 100n C225 100n A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS AMOD2 AMOD1 AMOD0 A B C R37 4.75k 5.6V * : NE PAS MONTER +2.5VREF CHECKBAT -ON/OFF C31 100n DZ12 ONBYKEY +UBATT 8 C27 100n +UBATT R3 10k DZ1 5.1V COMP R15 100k ECGX1000 -VO +5V R36 392k R14 100k U118 LM311 + + S/B B DN G R35 1M 7 6 5 4 TP15 PICOT 7 + + R257 10M U117B TL062 + Version July 2001 * 2 CLDSTRT 1 -WR C16 22n R30 1k R29 10k 7 +5V 3 1 2 3 5 4 3 2 7 6 8 13 R254 249k EEPROM 128X16 256X8 #/ 1 13 7 8 9 11 R32 100R R31 100k C15 22n U8 TLC5620 #,5 REF V BA T CE I O S CI OS CS PFI WDI B A T ON VO CE O RE S RE S PF O WDO L OW L I +5V 5 2 12 16 15 10 14 6 10k U117A TL062 CLDSTRT R28 10k C19 22n 22n C240 R16 2k 2 3 + +UBATT R252 100k RESET -RESET 6 T3 R7 10k + + +5V 2 3 1 + C14 1u 1 TP14 PICOT C241 22n U9A LM358AM + +5V 10k -VEE R20 R9 10k D3 BAS32 T4 * BSS138 R27 475k 8 -12V U10A TL062CD + 10k R19 C238 22n +12V 1 C280 22n +5V 2 3 R8 1k KEEPPWR D2 BAS32 BC850C D1 BAS32 +UBATT R17 +5V U17 MAX691 SMD 10k R18 U7 ST93C56 DZ11 LM385M-2.5 R253 383k C32 100n R38 100k T2 BC860C SERIEL_OUT R6 100k UBAUX BAT1 LITHIUM 3.6V R5 10k V/DETECT +5V 9 10 11 12 [DU] 7 6 M 4 D C279 100n C1 & D3 # &D4 C2 4,D5 +5V EN C A.D.C +5V U16A 74HC32 SMD 1 C21 22n C22 22n R255 1.2M D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 CH1 CHEVRON 23 19 1 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 U5 DS1685S R256 3.32M +UBATT UBAUX VBAUX 7 0 SQW IRQ PWR D 0 A 255 CS ALE WR RD KS RCLR X1 X2 12 CLOCK 16 VBAT TP17 PICOT 6 5 22 13 14 15 17 18 21 -CSWDOG 7 SERIEL_IN LOAD LDAC CSEEPROM CLKEEPROM SERIEL_IN TP16 PICOT U9B LM358AM + CLDSTRT -RESET C20 100n 6 5 -INTUART -INT1 BUSY_VID -WR -PSEN 2 3 1 C281 22n T1 BSS138 R4 100k -CSRTC ALE -WR -PSEN 2 3 20 8 D R2 100k 8 * C239 22n * D5 BAS32 R10 1k R11 100k 9 8 182k 1 5 R13 100k C17 33n 6 5 + 11 7 C3 22n C4 22n 10 Q1 16M PD +5V XTAL1 XTAL2 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 33 32 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 T5 R25 10k R26 10k T6 4 BC860C BC850C R24 2k A16 A17 A8 A9 A10 A11 A12 A13 A14 A15 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 C6 22n C5 22n 4 U1 80C251SB TP12 PICOT uP PB 2 0 T2 0 3 T2EX 4 ECI 5 PA/ 6 A 7 CEX-3 8 9 7 A17 7 10 RST EA 20 X T AL 2 A L E 21 X T AL 1 P S E N 11 RxD 0 0 13 TxD 14 INT0 15 INT1 16 T0 PC/ 17 T1 A+8 18 WR 19 7 7 RD U11E 74HC14 SMD DZ2 5.1V U10B TL062CD + C2 18p C1 18p R39 100k BUSY_VID -WR -INTUART -INT1 RESET XTAL2 XTAL1 TP13 PICOT 10 +5V SERIEL_OUT LDAC LOAD SERIEL_IN CLKEEPROM CSEEPROM R12 1k U32C 74HC02 SMD R23 R40 66.5k R21 100R BAS85 D4 C23 100n 5 44 12 34 1 23 22 32.78KHz 8 C25 12p 5 8 Q2 14 +5V +5V D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 C13 22n 1 2 4 5 EN C1 +5V 1 2 1 5 1 C11 22n 10 3 4 5 +5V U14B 74HC32 SMD 1 9 U13A 74HCT20 SMD 6 6 A15 A14 A13 A12 A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A16 9 10 A8 A9 A10 A11 A12 A13 A14 A15 A16 A17 U15A 74HC4075 SMD 1 C10 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 22n U15B 74HC4075 SMD & U2 1 8 A17 D[0..7] 3 3 A10 A9 A8 A11 A17 A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 A11 A12 A13 A14 A15 A16 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 U14C 74HC32 SMD 74HC573 SMD U14A 74HC32 SMD 4 1 +5V U15C 74HC4075 SMD 6 3 10 TP11 PICOT 2 3 1D 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 +5V 1 2 8 11 12 13 ALE -PSEN ALE C7 22n 14 C26 12p 1 4 20 7 +5V 3 4 4 3 +5V 9 10 12 13 1 2 8 30 22 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 27 26 23 25 4 28 3 31 2 C28 22n A4 A5 A6 A7 C9 22n U11B 74HC14 SMD 4 A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 A11 A12 A13 A14 A15 A16 U18 ECL02 11 / 99 -WR 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 APPROV 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 15 16 17 1 JM JM 2 -CSRTC -CSAUDIO -CSWDOG -CSVF -CSSUBD9 -CSVIDEO -CSSpO2 -CSECG_NF -CSMODEM -CSENREG -CSADC -CSDEFI0 -CSDEFI1 -CSMUX -CSKEYS ECL03 ECL04 ECL06 11 / 99 01 / 00 06 / 00 JM 10 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 -CSWDOG -PSEN RESET U21C 74HC4075 SMD MODIFICATION 11 12 13 U6 74HC154 SMD KEEPPWR 74HC574 SMD U13B 74HCT20 SMD 8 JM -PSEN -CSKEYS -WR 24 D5 D6 D7 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 29 19 20 21 13 14 15 17 18 0 1 2 3 4 5 1 6 2 7 4 8 8 9 10 11 12 13 & 14 EN 15 BIN/ HEX +5V 10 31 1 19 20 21 13 14 15 17 18 U3 27C010 2 U4 IS62C1024L-70Q EN [PGM] [VPP] [5]A [6]A [7]A U21B 74HC4075 SMD 9 18 19 23 22 21 20 DRAWN & EN C1 +5V 0 131071 [0]A [1]A [2]A [3]A [4]A A & [W] [OE] EN [5]A [6]A [7]A 0 A 131071 [0]A [1]A [2]A [3]A [4]A 2 3 1D 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 1 16 0 16 EPROM 128k x 8 SRAM 128k x 8 22 24 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 27 26 23 25 4 28 29 3 2 +5V U106C 74HC32 SMD 9 1 & C12 22n 8 16 0 +5V C8 22n A[0..17] 32 24 14 8 C24 22n 7 4 4 14 C30 22n 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 2 1 1 +5V +5V 10 3 4 5 +5V 6 11 6 11 8 3 -CSVF -CSSUBD9 -CSAUDIO 1 DWG NO : W4S141694C PRT NO : W4P141694C ART NO : W1411904 RN3 8X100k RAZSpO2 RAZENREG RAZVF RAZVID RAZUART1 RAZUART2 CH2 CH6 CH3 CH7 CH4 CH8 CH5 CH9 -CSVIDEO -CSSpO2 -CSECG_NF -CSMODEM -CSENREG -CSADC -CSDEFI0 -CSDEFI1 -CSMUX -CSKEYS PROCESS UNIT DSK NO : ........ NO : 1/7 SHT +5V A[0..2] D[0..7] U21A 74HC4075 SMD 1 U106D 74HC32 SMD 13 U106B 74HC32 SMD 12 1 5 U19D 74HC32 SMD 4 1 13 U19C 74HC32 SMD 12 1 CENTRALE .CENTRAL .UNITE 6 1 U19A 74HC32 SMD 9 1 C29 22n U20 74HC573 SMD 1D EN C1 +5V 1 U19B 74HC32 SMD .DG501 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 5 4 20 6 14 20 10 32 24 7 16 10 7 7 7 12 14 14 Page 8-43 7 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 Art no. 0-48-0001 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS A B C D * C75 100n ECL06 * +5V Version July 2001 : NE PAS MONTER 8 HVMONIT IPAT CHECKBAT DZ6 TL431CD R74 2.21k READY_VID CLDSTRT ERRORVID TM910OK DEFCHARGE DEFREADY SECDISCH -DEFSEC -CDNI/LI V_IN_PROGR +2.5VREF -CSDEFI0 -PSEN R246 0R -CSDEFI1 -PSEN CONTR_UP CONTR_DOWN WSEL_UP WSEL_DOWN START_CHARGE MODE_MEDICAL PHONE_TRANSM ANALYSE -CSKEYS -PSEN TXD_ENREG TXD_VF -CSENREG TXD_ECG_NF -CSVF TXD_SpO2 -CSECG_NF -CSSpO2 R51 10k RN2 8X10k * 1 11 +2.5vref ADMUX0 ADMUX1 ADMUX2 R260 0R 13 12 * U16D 74HC32 SMD D17 BYD37M +5V R247 100k D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 R250 100k 9 C74 22n 13 14 15 12 1 5 2 4 6 11 10 9 BAS32 D13 BAS32 D12 BAS32 D11 BAS32 D10 5 4 +5V 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 EN 0 0 1 G 7 2 # # MUXDX 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 CH11 7 3 U38 4051 SMD -INTVIDEO -INTSHOCK +5V RN1 8X10k 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 U16B 74HC32 SMD 1 6 R251 100k U16C 74HC32 SMD 1 8 +5V 10 -CSADC -PSEN -WR +5V +5V A2 A1 A0 U25 TL16C554 SMD 22n 13 5 TRANS 32 4 MIT. 33 A 3 34 D 0 2 0-7 0-2 35 1 36 XTAL 68 37 RESET 67 18 IOW 66 52 0 IOR 65 38 INTN R XRDY T 39 16 12 11 EN DTR 15 9 CTS I NT 8 DCD RI 10 14 DSR RTS 7 RX TX 17 20 24 25 21 27 28 26 22 29 19 50 46 45 49 43 42 44 48 41 51 54 58 59 55 61 62 60 56 63 53 6 +2.5vref +5V EN C1 R249 0R R77 0R 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 EN C1 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 +5V 1 2 3 9 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 [INT] 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 5 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 U39 74HC573 SMD 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 # 1,2 / U37 ADC0802LCM EN1[CS] 1C2[RD] 1C3[WR] [VREF/2] 7 [VIN-] 6 [VIN+] 19 [CLKR] 4 [CLKC] D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 RXD_ENREG RXD_VF RXD_ECG_NF RXD_SpO2 C71 22n R75 10R EN C1 2 3 1D 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 +5V U40 74HC573 SMD C77 22n C72 22u +5V R73 10k +5V 2 3 1D 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 C80-C87 8X100nF C78 22n U41 74HC573 SMD 2 3 1D 4 5 6 7 8 9 +5V CH10 C73 100p +5V C79 22n 1 11 18p C89 Q3 11.059M 11MHZ C88 18p 10 C51 16 20 30 47 64 23 40 57 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 7 20 +5V 8 20 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 -WR -CSAUDIO -WR -CSMUX -CSDEFI1 -WR D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 -WR -CSDEFI0 QRS_TRIG C68 100n +5V TXD_MODEM -CSSUBD9 CTS_SUBD9 DCD_SUBD9 DSR_SUBD9 TXD_SUBD9 -CSMODEM R52 10k 1 11 C64 22n 2 1 5 1 1 9 3 C54 22n C66 22n C67 22n +5V 8 EN C1 EN C1 C63 22n C65 22n EN C1 6 EN C1 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 C69 22n C70 22n 4 2 1 3 2 4 -RSTRDYV -RSTSHOCK 12 11 13 TP18 PICOT 3 C62 22n +5V -TESTVF backlight -patchled 11MHz -RESET PCI 6 0 7 8 9 PB 10 17 0 11 18 PA 12 1 13 7 2 3 3 RTCC 4 MCLR 16 OSC1 15 OSC2 1 U43 PIC16C54 STARTCONV -RESET -SYNCDEF U11A 74HC14 SMD SACHARGE SAWSEL0 SAWSEL1 SAWSEL2 SAWSEL3 U42A 74HC08 SMD 1 WDUMP RST_MODEM -ECG_ON & +5V 1 1 U32D 74HC02 SMD U32A 74HC02 SMD +5V R55 100k U34 74HC574 SMD 19 18 17 AUDIO0 16 AUDIO1 15 AUDIO2 14 ADMUX0 13 ADMUX1 12 ADMUX2 U33 74HC574 SMD 2 3 1D 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 +5V U35 74HC574 SMD 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 +5V 2 3 1D 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 2 3 1D 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 5 BAS32 D15 BAS32 D14 U11C 74HC14 SMD 74HC574 SMD U36 +5V 2 3 1D 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 R79 475k A2 A1 A0 U26 TL16C554 SMD 13 5 TRANS 32 4 MIT. 33 A 3 34 D 0 2 0-7 0-2 35 1 36 XTAL 68 37 RESET 67 18 IOW 66 52 0 IOR 65 38 INTN R XRDY T 39 16 12 11 EN DTR 15 9 CTS I NT 8 DCD RI 10 14 DSR RTS 7 RX TX 17 20 24 25 21 27 28 26 22 29 19 50 46 45 49 43 42 44 48 41 51 54 58 59 55 61 62 60 56 63 53 6 U27A 74HC32 SMD 6 U27B 74HC32 SMD +5V 5 4 U27C 74HC32 SMD 9 1 8 10 13 12 U11D D16 BAS32 74HC14 SMD R80 1k U27D 74HC32 SMD R54 10k D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 +5V 20 A[0..2] 10 D[0..7] 10 30 47 64 23 40 57 20 14 14 7 7 7 2 C55 22n 3 3 R83 221k R82 392k R81 475k R85 10k R63 10k +12V RI_SUBD9 RTS_SUBD9 RXD_SUBD9 R70 10k T18 BSS138 T17 IRFR9024 RXD_MODEM DTR_SUBD9 +5V 14 -PSEN -WR RAZUART2 RAZUART1 7 R62 10k +5V -INTUART ECL02 11 / 99 JM DRAWN T16 BSS84 R61 1.5k T14 C60 1n JM +5V JM 6 2 4 5 6 7 12 11 10 9 1 16 15 2 C59 100n R72 2R T12 R68 10k 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 # # + 1 8 3 2 +12V DSK NO : ........ SHT NO : 2/7 1 DWG NO : W4S141694C PRT NO : W4P141694C ART NO : W1411904 PROCESS UNIT C53 220n BYPASS CENTRALE U31 DG508 SMD .CENTRAL .UNITE R71 1M R56 1.5k BSS138 T10 C58 22u R69 10k U30 LM380 + C237 22n 8 .DG501 0 G7 2 EN 0 MUX -12V 6 R57 1.5k BSS138 T11 +12V R67 10k 6 U42B 74HC08 SMD & R58 1.5k 5 4 BSS138 U28A 74HC74 SMD C236 22n ECL03 ECL04 ECL06 11 / 99 01 / 00 06 / 00 JM MODIFICATION U29 LM380 + R59 1.5k R66 10k 10 11 12 13 6 5 U28B 74HC74 SMD 9 S C1 1D 8 R 4 S 3 C1 2 1D 1 R C56 22n BSS138 T13 C57 22u R65 10k +5V 14 R60 1.5k 2 7 BSS138 +5V BYPASS + C52 220n 8 3 2 +12V T15 BSS138 APPROV R64 10k R84 475R 7 5 10 10 20 20 4 6 10 5 A[0..2] 1 10 8 14 D[0..7] 8 2 3 6 7 5 13 5 7 14 10 20 14 3 Page 8-44 4 Art no. 0-48-0001 7 8 -INT1 VOICE R78 100k C61 1n SPEAKER+ SPEAKER- PATCHLED LED1RED LED2RED LED3RED LED1GREEN LED2GREEN LED3GREEN U_BCKLIGH DEFDISCH -RSTSHOCK -INTSHOCK -INTVIDEO READY_VID -RSTRDYV A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS A B C D Version July 2001 8 U95B 4538 SMD 10 9 R141 1M C170 1u -12V +12V 15 CX 14 RX/CX 12 1 11 13 R ECGQRS ECGMAX/2 ECGX1000 R196 22.1R R195 22.1R 6 5 + C196 10u C195 10u 7 R143 17.8k +12VF -12VF U90B TL062CD + R142 100k C171 100n R144 17.8k 7 C173 100n R145 17.8k R168 499k 2 3 C247 22n 4 11 + U91A TL064CFP + R146 17.8k R170 619k R169 150k C188 100n 1 C248 22n 14 7 6 5 2 3 +12VF 22n R171 1M R172 130k + 6 U90A TL062CD + 1 -12VF C258 22n + U92B TL064CFP + C180 47p R173 100k 22n C259 2 3 5 + + 1 -12VF C190 47p 100k R175 22n DN1 BAV199 100k +2.5V -2.5V C254 22n R188 10k C249 22n 6 5 2 3 + + + 6 5 100k R177 7 1 + 4 7 22n C253 R189 1k DN3 BAV199 C250 22n U97B TL064CFP + C191 33n U94B LM358AM + U94A LM358AM + -12VF 1 -12VF U92A TL064CFP + +12VF 2 3 +12VF ECG1500 100k 8 8 R176 C260 C183 470n U92C TL064CFP + C181 47n 100k R187 + U91C TL064CFP 9 10 + R174 U97A TL064CFP + 9 10 R151 115k R157 100k +12VF DN2 BAV199 100k R152 562k R186 C178 4.7n R153 115k C177 4.7n C179 4.7n R150 56.2k R149 182k R148 100k R185 100k 7 R154 562k C176 4.7n R184 100k OVERSHOOTING C257 C189 100n + U91D TL064CFP R183 200k + U91B TL064CFP + 13 12 + 6 5 DEPASSEMENT R155 100k R156 10k C175 100n R147 17.8k C174 100n 4 R190 2.4M + 200k 8 R161 U97C TL064CFP 9 10 + R159 221k R158 221k +2.5V + BAS32 + + 4 R180 825k R179 18.2k R178 36.5k 7 R160 4.7M 14 U96B LM358AM + C186 47n R162 100k U93B 4093 SMD & U92D TL064CFP 6 5 D20 6 5 13 12 C182 1u + 3 C185 22n U95A 4538 SMD 1 CX RX/CX R + U66A TL062CD + +5V 2 3 14 22n C255 1 2 4 5 3 R192 5.11k -12VF +12VF U97D TL064CFP C192 1u 13 12 + R181 2.21M -2.5V R164 100k R163 100k +5V +5V C184 100n R191 10k R193 243k +2.5V 3 8 5 4 8 6 11 4 4 -12VF 8 16 +12VF 4 1 + U96A LM358AM + 100k R182 100k & 3 10 R167 1k 2 JM 13 12 2 11 JM U93D 4093 SMD & ECL03 ECL04 ECL06 11 / 99 01 / 00 06 / 00 JM MODIFICATION U93A 4093 SMD APPROV 2 & U93C 4093 SMD +5V 9 8 C256 22n C194 22n 1 C193 68p 1 ECL02 11 / 99 JM DRAWN R165 2 3 -12VF R166 100k C187 47n 6 7 R194 221k C252 22n C251 22n +12VF 8 C172 100n 11 8 R140 200k 7 4 4 Page 8-45 14 Art no. 0-48-0001 7 8 DSK NO : ........ SHT NO : 3/7 DWG NO : W4S141694C PRT NO : W4P141694C ART NO : W1411904 . CENTRAL PROCESS UNIT . UNITE CENTRALE . DG501 1 -QRSFV ECGFV -DEPAS -LIMIT ECGMAX/2 ECGMAX/2 1 A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS A B C Version July 2001 8 :NE PAS MONTER DZ7 R105 1k C122 1u +5V R106 2k 9.1V : MONTER A LA PLACE DE C119 18p C116 Q5 R104 10M + ECL5 C124 1u 11 10 9 12 2k R110 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 7 5 4 6 14 13 15 1 2 3 C117 22n R112 200k R111 200k C123 1u * 3 * 4 10 * C118 18p R108 332R C121 1u U62 MC145540 SMD ECL5 PDI_RESET SCPEN 7 1 5 4 & 6 C101 18p 9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 +5V 1 2 ADPCM CODEC 15 27 26 25 24 23 21 20 19 18 17 16 C120 22n U64A 74HC04 SMD 1 +5V 8 U63C 74HC08 SMD R101 10k TG FSR TIBCLKR TI+ DR VAG C1+ RO C1AXOSPC AXO+ DT VDSP BCLKT VEXT FST PI SCP RX POSCP PO+ TX PDI/RESET SCP SCP EN CLK 22n C113 & U63B 74HC08 SMD 10 Q4 16M U64E 74HC04 SMD ECL5 11 C100 18p U64B 74HC04 SMD 1 10M R107 Q6 20.48M 4060 SMD CT C119 18p U61 -3+ N1/Z2 1 2 - 1 3 R CTR14 U32B SMD 5 74HC02 1 4 6 +5V R109 2k C115 18p R261 10k C125 1u +12V 4.096M BVDMEM1 BVDMEM2 -WEMEM -OEMEM R102 10k +5V 13 12 SCPRX 2 1 C114 22n 6 SCPCLK INT0 SCPCLK 6 11 & +5V 3 22n CKSER 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 33 32 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 9 U64D 74HC04 SMD 5 13 -rdmem 1 12 8 & 11 U42C 74HC08 SMD & -WRMEM -RDMEM 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 LATCHIT U42D 74HC08 SMD 10 9 DM0 DM1 DM2 DM3 DM4 DM5 DM6 DM7 -wrmem 8 ALEMEM -PSENMEM AM8 AM9 AM10 AM11 AM12 AM13 AM14 AM15 DM0 DM1 DM2 DM3 DM4 DM5 DM6 DM7 1 11 +5V 10 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 C103 22n 1 6 AM0 AM1 AM2 AM3 AM4 AM5 AM6 AM7 -PSENMEM U64C 74HC04 SMD AM15 CKSER 5 U51 74HC573 SMD 1D EN C1 20 4 +5V AM15 AM12 AM13 AM14 AM0 AM1 AM2 AM3 AM4 AM5 AM6 AM7 AM8 AM9 AM10 AM11 AM12 AM13 AM14 AM0 AM1 AM2 AM3 AM4 AM5 AM6 AM7 AM8 AM9 AM10 AM11 AM12 AM13 AM14 AM15 DM[0..7] 4 14 10 11 13 12 6 4 5 1 2 3 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 25 24 21 23 2 26 1 22 24 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 27 26 23 25 4 28 29 3 2 +5V +5V EN[CS] C1[OE] C2[WE] 0 32767 A, 1, 2D /A , 2, A & EN BIN/OCT +5V 1D EN3 C2 SRG8 R C1/ 2D 3 2D 3 31 1 19 20 21 C112 22n 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 7 11 12 13 15 16 17 18 19 20 22 27 15 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 +5V * -CSVOICE -CSLOW -CSMID -CSHIGH -CSHUGE -CSFLASH DM0 DM1 DM2 DM3 DM4 DM5 DM6 DM7 DM5 DM6 DM7 DM0 DM1 DM2 DM3 DM4 DM0 DM1 DM2 DM3 DM4 DM5 DM6 DM7 U60 74HC595 SMD ECL5 C110 22n 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 C111 22n 7 0 U59 74HC138 SMD 1 2 4 EN [PGM] [VPP] RAM 32k x 8 U58 43256 14 0 0 13 14 15 17 18 C104 22n 131071 [5]A [6]A [7]A A [0]A [1]A [2]A [3]A [4]A EPROM 128k x 8 U52 27C010 16 0 & +5V 32 C102 U63A 74HC08 SMD U63D 74HC08 SMD & +5V 44 12 34 1 23 22 uP PB 2 0 T2 0 3 T2EX 4 ECI 5 PA/ 6 A 7 CEX-3 8 9 7 A17 7 10 RST EA 20 XT A L 2 A L E 21 XT A L 1 P S E N 11 RxD 0 0 13 TxD 14 INT0 15 INT1 16 T0 PC/ 17 T1 A+8 18 WR 19 7 7 RD PD U50 80C251SB C126 22n 5 3 3 ECL02 11 / 99 JM DRAWN -CSHUGE -CSHIGH -CSMID -CSLOW +5V EN C1 EN C1 +5V 2 1D 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 +5V EN C1 JM +5V 3 C109 22n JM U57 74HC245 SMD 2 G1 1EN2 1EN3 2 U55 74HC574 SMD AMEM16 19 AMEM17 18 AMEM18 17 AMEM19 16 AMEM20 15 AMEM21 14 AMEM22 13 AMEM23 12 C107 22n U54 74HC574 SMD 19 AMEM8 18 AMEM9 AMEM10 17 AMEM11 16 AMEM12 15 AMEM13 14 AMEM14 13 AMEM15 12 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 18 1 DSK NO : ........ SHT NO : 4/7 1 DWG NO : W4S141694C PRT NO : W4P141694C ART NO : W1411904 . CENTRAL PROCESS UNIT . UNITE CENTRALE . DG501 DMEM1 DMEM2 DMEM3 DMEM4 DMEM5 DMEM6 DMEM7 DMEM0 U56 74HC574 SMD AMEM24 19 AMEM25 18 SCPEN 17 SCPRX 16 15 14 13 12 PDI_RESET C108 22n U53 74HC574 SMD 19 AMEM0 18 AMEM1 17 AMEM2 16 AMEM3 15 AMEM4 14 AMEM5 13 AMEM6 12 AMEM7 C106 22n C105 22n ECL03 ECL04 ECL06 11 / 99 01 / 00 06 / 00 JM EN C1 2 1D 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 MODIFICATION 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 APPROV 2 DM0 +5V 2 1D 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 2 1D 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 19 1 DM1 DM2 DM3 DM4 DM5 DM6 DM7 -RDMEM DM0 DM1 DM2 DM3 DM4 DM5 DM6 DM7 DM0 DM1 DM2 DM3 DM4 DM5 DM6 DM7 DM0 DM1 DM2 DM3 DM4 DM5 DM6 DM7 DM0 DM1 DM2 DM3 DM4 DM5 DM6 DM7 2 D MEM[0..7] * + PHONEGND PHONE_IN RXD_ENREG TXD_ENREG RAZENREG WPMEM -CDMEM2 R103 10k 16 -CDMEM1 8 16 14 8 20 20 20 10 10 10 D R100 10k 14 +5V 28 7 22 7 20 7 14 10 28 16 16 AMEM[0..25] 8 Page 8-46 20 Art no. 0-48-0001 10 VSMEM1 VSMEM2 RDYMEM WAITMEM 8 DMEM[0..7] -CSFLASH RSTMEM -REGMEM AMEM[0..25] A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS AM[0..15] A B C D Version July 2001 R121 2.21k 8 1 8 +2.5V * : NE PAS MONTER +5V CT 11 0 10 9 8 3 U81B 74HC393 SMD + CTR4 CT=0 ECGX1000 13 12 RXD_VF TXD_VF -TESTVF RAZVF V_IN_PROGR Q7 7 6 3 2 16M DZ8 TL431CD C140 18p -12V C142 22n R122 1 2 TP9 TP10 +5V -rstsynth 8.25k C141 18p CT 3 0 4 5 6 3 synchro fv 2 3 6 7 -2.5V 7 ECGX1000 P1694C_3 DZ9 TL431CD 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 20 21 11 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 +5V 0 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 33 32 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 ECGQRS ECGMAX/2 ECGFV -DEPAS -LIMIT -QRSFV 7 EA X T AL 2 A L E X T AL 1 P SEN 0 0 RxD TxD INT0 INT1 T0 PC/ T1 A+8 WR 7 7 RD PD U70 80C251SB 7 A17 RST uP PB 0 T2 T2EX ECI PA/ A CEX-3 22n AVF8 AVF9 AVF10 AVF11 AVF12 AVF13 AVF14 AVF15 DVF0 DVF1 DVF2 DVF3 DVF4 DVF5 DVF6 DVF7 6 DVF0 DVF1 DVF2 DVF3 DVF4 DVF5 DVF6 DVF7 C157 1u C144 22n EN C1 10 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 C156 470n ale_vf -psen_vf U71 74HC573 SMD 2 3 1D 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 +5V 20 C143 C155 150P AVF0 AVF1 AVF2 AVF3 AVF4 AVF5 AVF6 AVF7 R120 10k 5 AVF15 AVF12 AVF13 AVF14 AVF0 AVF1 AVF2 AVF3 AVF4 AVF5 AVF6 AVF7 AVF8 AVF9 AVF10 AVF11 AVF12 AVF13 AVF14 AVF0 AVF1 AVF2 AVF3 AVF4 AVF5 AVF6 AVF7 AVF8 AVF9 AVF10 AVF11 AVF12 AVF13 AVF14 AVF15 5 +5V 6 4 5 1 2 3 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 25 24 21 23 2 26 1 22 24 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 27 26 23 25 4 28 29 3 2 1 2 3 9 A +5V EN A, 1, 2D /A , 2, & EN BIN/OCT 7 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 RAM 32k x 8 EN[CS] C1[OE] C2[WE] 0 A 32767 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 -wr_vf -rd_vf -csadc [INT] 1,2 U78 ADC0802LCM EN1[CS] 1C2[RD] 1C3[WR] [VREF/2] / # U79 74HC138 SMD 1 2 4 0 [PGM] [VPP] [5]A [6]A [7]A 131071 [0]A [1]A [2]A [3]A [4]A U80 43256 14 0 C154 47u 19 [CLKR] 4 [CLKC] 7 [VIN-] 6 [VIN+] +5V 16 EPROM 128k x 8 -rd_vf -wr_vf 16 0 & +5V 5 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 7 C153 22n 11 12 13 15 16 17 18 19 20 22 27 C152 22n DVF0 DVF1 DVF2 DVF3 DVF4 DVF5 DVF6 DVF7 -cssynth -csdac -csadc DVF0 DVF1 DVF2 DVF3 DVF4 DVF5 DVF6 DVF7 DVF5 DVF6 DVF7 DVF0 DVF1 DVF2 DVF3 DVF4 U72 27C010 AVF15 31 1 19 20 21 13 14 15 17 18 C145 22n 4 4 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 12 13 -csdac -wr_vf U77 G20 [O1] [O2] 1 2 16 15 DAC7524JS & # 20 [VREF] #/ [RF] C151 22n 1mhz C146 22n 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 A 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 17 36 AO 5 XT1 6 XT2 0 U73 MSM6295 SMD [CS] [WR] 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 #/ # I 7 RD WR CS R SS 7 0 0 +5V 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 2 3 4 8 7 DVF0 DVF1 DVF2 DVF3 DVF4 DVF5 DVF6 DVF7 +5V DVF0 DVF1 DVF2 DVF3 DVF4 DVF5 DVF6 DVF7 DY0 DY1 DY2 DY3 DY4 DY5 DY6 DY7 +5V 17 C158 22n 44 12 34 1 23 22 PARTIE ANALOGIQUE (sheet 2/2) no_analyse U81A 74HC393 SMD + CTR4 CT=0 14 32 TP8 7 6 20 28 16 14 8 10 1 3 out 2,3and6:soft test point 7 8 14 Page 8-47 +5V R123 1k AY0 AY1 AY2 AY3 AY4 AY5 AY6 AY7 AY8 AY9 AY10 AY11 AY12 AY13 AY14 AY15 AY16 AY17 3 3 + + +12VF U76B TL062CD C245 22n 6 5 -enflash ay18 7 + 1 -12VF U76A TL062CD 2 3 + 8 Art no. 0-48-0001 4 C149 ECL02 11 / 99 JM DRAWN C246 22n 100n + R127 332k C159 10n R124 1k 7 JM JM 31 19 20 21 13 14 15 17 18 C160 22n 2 ECL03 ECL04 ECL06 11 / 99 01 / 00 06 / 00 JM ECGQRS U75 29F040 MODIFICATION C150 1u +5V 16 12 EPROM 0 11 512k x 8 10 [0]A 9 [1]A 8 [2]A 7 [3]A 6 [4]A 5 27 0 26 A 524287 23 25 4 [5]A 28 [6]A 29 [7]A 3 2 [WE] 30 1 18 22 & EN 24 U66B TL062CD 6 5 + APPROV R125 100k R126 100k AY0 AY1 AY2 AY3 AY4 AY5 AY6 AY7 AY8 AY9 AY10 AY11 AY12 AY13 AY14 AY15 AY16 AY17 ay18 C147 10u 2 32 8 +5V DY5 DY6 DY7 DY0 DY1 DY2 DY3 DY4 DSK NO : ........ SHT NO : 5/7 1 DWG NO : W4S141694C PRT NO : W4P141694C ART NO : W1411904 . CENTRAL PROCESS UNIT . UNITE CENTRALE . DG501 VOICE 1 A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS A B 1 1 D C 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS +5V +5V 2 AVD15 1 11 U106A 74HC32 SMD DVD0 DVD1 DVD2 DVD3 DVD4 DVD5 DVD6 DVD7 2 DVD[0..7] +5V 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 U105 74HC574 SMD EN C1 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 1D TM910OK ERRORVID 2 C214 22n 3 10 DVD7 DVD6 DVD5 DVD4 DVD3 DVD2 DVD1 DVD0 1 20 1 -WR_VID DVD7 DVD6 DVD5 DVD4 DVD3 DVD2 DVD1 DVD0 7 14 C213 22n +5V C204 22n C202 22n +5V C206 C200 18p C203 22n XTAL2 C205 22n C207 22n BUSY_VID RST_VID READY_VID -WR_VID -RD_VID -WR_VID -RD_VID DVD0 DVD1 DVD2 DVD3 DVD4 DVD5 DVD6 DVD7 AVD[0..15] 4 C208 22n 13 REVERSE 1 AVD0 AVD1 AVD2 AVD3 AVD4 AVD5 AVD6 AVD7 AVD8 AVD9 AVD10 AVD11 AVD12 AVD13 AVD14 AVD15 12 R208 0R U64F 74HC04 SMD U11F 74HC14 SMD 12 13 AVD15 5 -CSLCD AVD0 AVD0 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 27 26 23 25 4 28 29 3 2 0 AVD0 AVD1 AVD2 AVD3 AVD4 AVD5 AVD6 AVD7 EPROM x 8 128k [0]A [1]A [2]A [3]A [4]A A 13 14 15 17 18 DVD0 DVD1 DVD2 DVD3 DVD4 19 20 21 DVD5 DVD6 DVD7 0 131071 [5]A [6]A [7]A [PGM] [VPP] 16 22 24 -PSENVID 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 +5V 32 * 1D U101 74HC573 SMD -PSENVID AVD8 AVD9 AVD10 AVD11 AVD12 AVD13 AVD14 AVD15 U100 80C251SB R207 0R 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 DVD0 DVD1 DVD2 DVD3 DVD4 DVD5 DVD6 DVD7 4 XTAL2 XTAL1 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 7 A17 7 RST EA 35 XT AL 2 A L E 33 32 XT AL1 PSEN 24 0 0 RxD 25 TxD 26 INT0 27 INT1 28 T0 PC/ 29 T1 A+8 30 WR 31 7 7 RD PD 0 & 5 3 RAZVID uP PB 0 T2 T2EX ECI PA/ A CEX-3 16 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 20 21 11 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 D_DVD0 D_DVD1 D_DVD2 D_DVD3 D_DVD4 D_DVD5 D_DVD6 D_DVD7 EN C1 3 44 12 34 1 23 22 XTAL1 1 11 10 20 22n Q8 16M C1201 18p 31 1 +5V EN U102 27010 READY_VID BUSY_VID D[0..7] C209 22n D[0..7] 6 10 6 20 +5V 1 11 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 EN C1 1D 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 D_DVD0 D_DVD1 D_DVD2 D_DVD3 D_DVD4 D_DVD5 D_DVD6 D_DVD7 11 12 1 -WR 13 -CSVIDEO U14D 74HC32 SMD U103 74HC574 SMD D_DVD[0..7] C212 22n 7 7 +5V +5V C211 10u * R206 33.2R TRANSCEIVE Rxd IRED IRED Txd SC 4 .DG501 * U104 TFDT4500 SMD .UNITE CENTRALE .CENTRAL 8 +5V 1 2 3 7 * 6 R205 33.2R PROCESS UNIT JM ECL02 11 / 99 Art no. 0-48-0001 MODIFICATION JM JM Page 8-48 PRT NO : W4P141694C JM ECL03 ECL04 ECL06 11 / 99 01 / 00 06 / 00 B C : NE PAS MONTER D * APPROV DWG NO : W4S141694C DSK NO : ........ NO : 6/7 SHT A DRAWN 8 8 ART NO : W1411904 Version July 2001 A B 1 1 D C 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS +VSpO2 R221 3.32k R220 1k T28 +5V U113 1 4 2 3 R218 BSS84 100k RDX_SpO2 SFH617G +5V 2 RXD_SpO2 2 T27 BSS84 R223 1k +VSpO2 R222 3.32k R219 100k U114 4 TXD_SpO2 1 3 TDX_SpO2 2 SFH617G 3 VSpO2 U116 1 4 2 3 3 R237 3.32k +5V RSTSpO2 SFH617G R239 10k R238 3.32k T29 BSS138 4 4 RAZSpO2 +VSpO2 +12V TP3 PICOT TP2 PICOT D24 BAS32 3 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 T26 IRFR024 R230 2.21k T25 C269 2.2n C278 47u R229 56.2R C271 10n R233 18.2k R234 2.21k C270 100n R235 44.2k U112 SG3525 U115 R224 18.2k 4 6 6 1 2 3 R227 221R R228 1k 1 SFH617G 8 16 14 11 10 9 8 C272 10u ECL3 R225 332R R231 10k INV IN. REF NOINV OUTB SYNC OUTA OSC. SHUTD. CT COMP. RT START DISCHA. 12 C268 47u R232 18.2k C273 10u +12V 15 2 +12V IRFR024 4 D23 BAS32 5 C274 10u 5 D22 BAS32 C267 22u TR1 IMPEDJFS 7 6 5 13 D21 BAS32 DZ10 TL431CD 7 7 7 6 3 2 R226 18.2k . DG501 . UNITE CENTRALE DRAWN JM Art no. 0-48-0001 MODIFICATION JM JM Page 8-49 JM ECL03 ECL04 ECL06 11 / 99 01 / 00 06 / 00 B C D ECL02 11 / 99 APPROV 8 ART NO : W1411904 PRT NO : W4P141694C DWG NO : W4S141694C DSK NO : ........ SHT NO : 7/7 A 8 . CENTRAL PROCESS UNIT Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-50 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-51 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS COMPONENT LIST OF CPU PCB W4P14 1694D POSITION BAT1 C1 C10 C100 C101 C102 C103 C104 C105 C106 C107 C108 C109 C11 C110 C111 C112 C113 C114 C115 C116 C117 C118 C119 C12 C120 C1201 C121 C122 C123 C124 C125 C126 C13 C14 C140 C141 C142 C143 C144 C145 C146 C147 C149 C15 C150 C151 C152 C153 ITEM 72253 20981 21018 20981 20981 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 20981 20981 21018 20981 20981 21018 21018 20981 51518 51518 51518 51518 51518 21018 21018 51518 20981 20981 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 51559 8493 21018 51518 21018 21018 21018 Art no. 0-48-0001 DESCRIPTION LITHIUM CELL 3.6V AA CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R Page 8-52 MANUFACTURER SONNEN VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS C154 C155 C156 C157 C158 C159 C16 C160 C17 C170 C171 C172 C173 C174 C175 C176 C177 C178 C179 C180 C181 C182 C183 C184 C185 C186 C187 C188 C189 C19 C190 C191 C192 C193 C194 C195 C196 C2 C20 C200 C202 C203 C204 C205 C206 C207 C208 C209 C21 C211 C212 C213 C214 C22 C220 C221 C222 C223 C224 51556 20992 22597 51518 21018 21014 21018 21018 21020 51518 8493 8493 8493 8493 8493 21010 21010 21010 21010 20986 72548 51518 22597 8493 21018 72548 72548 8493 8493 21018 20986 21020 51518 20988 21018 51559 51559 20981 8493 20981 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 51559 21018 21018 21018 21018 51559 51559 51559 51559 8493 Art no. 0-48-0001 CAPA SMD TANTAL 47U 16V 20% CAPA SMD 1206 150P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1812 470N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 33N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 4.7N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 4.7N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 4.7N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 4.7N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 47P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 47N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD 1812 470N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 47N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 47N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 47P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 33N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD 1206 68P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R Page 8-53 SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS C225 C226 C227 C228 C229 C23 C230 C231 C232 C233 C234 C235 C236 C237 C238 C239 C24 C240 C241 C245 C246 C247 C248 C249 C25 C250 C251 C252 C253 C254 C255 C256 C257 C258 C259 C26 C260 C261 C262 C263 C264 C266 C267 C268 C269 C270 C271 C272 C273 C274 C275 C276 C277 C278 C28 C29 C3 C30 C31 8493 51559 51559 8493 8493 8493 51559 51559 56394 56394 56394 56394 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 20979 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 20979 21018 51518 51559 51518 51559 56394 51557 51556 21006 21002 21014 51559 51559 51559 21014 21014 21014 51556 21018 21018 21018 21018 8493 Art no. 0-48-0001 CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 35V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 35V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 35V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 35V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 12P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 12P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1812 1U 50V 20% Y4T CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 35V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 22U 20V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 47U 16V 20% CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 47U 16V 20% CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R Page 8-54 VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU SPRAGU SPRAGU SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS C32 C4 C5 C51 C52 C53 C54 C55 C56 C57 C58 C59 C6 C60 C61 C62 C63 C64 C65 C66 C67 C68 C69 C7 C70 C71 C72 C73 C74 C77 C78 C79 C8 C80 C81 C82 C83 C84 C85 C86 C87 C88 C89 C9 CN1 CN10 CN11 CN12 CN13 CN14 CN2 CN3 CN4 CN5 CN6 CN7 CN8 D1 D10 8493 21018 21018 21018 51954 51954 21018 21018 21018 51557 51557 8493 21018 21002 21002 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 8493 21018 21018 21018 21018 51557 20990 21018 21018 21018 21018 21018 8493 8493 8493 8493 8493 8493 8493 8493 20981 20981 21018 79011 79011 79011 79011 79011 79011 79011 79011 79011 79011 79011 79011 79011 22029 22029 Art no. 0-48-0001 CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1210 220N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1210 220N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 22U 20V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 22U 20V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 22U 20V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 100P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 18P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R CAPA RES CER 4X10NF 50V X7R DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 Page 8-55 VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM AVX AVX VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM AVX AVX AVX AVX AVX AVX AVX AVX AVX AVX AVX AVX AVX PHILIP PHILIP Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS D11 D12 D13 D14 D15 D16 D17 D2 D20 D21 D22 D23 D24 D25 D3 D4 D5 DN1 DN2 DN3 DZ10 DZ2 DZ6 DZ7 DZ8 DZ9 J1 J10 J11 J12 J13 J2 J3 J4 J5 J6 J7 J8 P1694D Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q7 Q8 R100 R101 R102 R103 R104 R105 R106 R107 R108 R109 R110 R111 R112 22029 22029 22029 22029 22029 22029 51586 22029 22029 22029 22029 22029 22029 51329 22029 51329 22029 72501 72501 72501 51832 51393 51832 51775 51832 51832 72979 84306 72978 72992 72776 72981 84306 53997 W1411840 72993 77596 77596 W1404667 72529 4372 51925 72529 72702 72529 72529 20750 20750 20750 20750 21637 20737 51734 21637 20730 51734 51734 51736 51736 Art no. 0-48-0001 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS85 SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS85 SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAV199 SOT23 DIODE SMD BAV199 SOT23 DIODE SMD BAV199 SOT23 IC 431/VREF TL431CD SO8 SMD DIODE Z SMD SOD80 5.1V IC 431/VREF TL431CD SO8 SMD DIODE Z SMD SOD80 9.1V IC 431/VREF TL431CD SO8 SMD IC 431/VREF TL431CD SO8 SMD CN M 140 D PRT 53481 SMD CN M 10 S PC CN M 72 D PRT 2X36 BERGSTICK CN F 5 C PRT SERIES 5597 CN M 3 C PRT CN M 80 D PRT 53481 SMD CN M 10 S PC CN M 64 D PRT BARSIL CBL PL LIAISON CI CPU - CI HT CN F 12 C PRT SERIES 5597 CN F 5 D PRT SERIES 5597 CN F 5 D PRT SERIES 5597 CI CPU DG501 QUARTZ 16.000MHZ HC-49/U-S QUARTZ 32.768KHZ QUARTZ 11.0592MHZ QUARTZ 16.000MHZ HC-49/U-S QUARTZ 4.096MHZ HC49/U3H QUARTZ 16.000MHZ HC-49/U-S QUARTZ 16.000MHZ HC-49/U-S RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 332 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 200K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 200K 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-56 PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN TI PHILIP TI PHILIP TI TI MOLEX LUMBER BERG MOLEX JST MOLEX LUMBER PRECID W2652 MOLEX MOLEX MOLEX OD2100 TELEQU SARONI M-TRON TELEQU JAUCH TELEQU TELEQU BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R12 R120 R121 R122 R123 R124 R125 R126 R127 R13 R14 R140 R141 R142 R143 R144 R145 R146 R147 R148 R149 R15 R150 R151 R152 R153 R154 R155 R156 R157 R158 R159 R16 R160 R161 R162 R163 R164 R165 R166 R167 R168 R169 R17 R170 R171 R172 R173 R174 R175 R176 R177 R178 R179 R18 R180 R181 R182 R183 20737 20750 20741 20748 20737 20737 21335 21335 53690 21335 21335 51736 21347 21335 53710 53710 53710 53710 53710 21335 21338 21335 51755 53696 21344 53696 21344 21335 20750 21335 21339 21339 51734 51563 51736 21335 21335 21335 21335 21335 20737 51751 21337 20750 51758 21347 33875 21335 21335 21335 21335 21335 53701 21326 20750 21346 21351 21335 51736 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 8.25K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 332K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 200K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 17.8K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 17.8K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 17.8K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 17.8K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 17.8K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 56.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 115K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 115K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 221K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 221K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 200K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 499K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 150K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 619K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 130K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 36.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 825K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 200K 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-57 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R184 R185 R186 R187 R188 R189 R19 R190 R191 R192 R193 R194 R195 R196 R20 R208 R21 R216 R217 R218 R219 R22 R220 R221 R222 R223 R224 R225 R226 R227 R228 R229 R23 R230 R231 R232 R233 R234 R235 R237 R238 R239 R24 R240 R241 R242 R243 R244 R245 R246 R249 R25 R250 R251 R252 R26 R261 R262 R263 21335 21335 21335 21335 20750 20737 20750 72213 20750 59887 73140 21339 20715 20715 20750 21352 20724 20724 20724 21335 21335 21352 20737 20743 20743 20737 21326 20730 53710 20728 20737 20720 21338 20741 20750 21326 21326 20741 51746 20743 20743 20750 51734 20724 20724 20724 20724 20724 20724 21352 21352 20750 21335 21335 21335 20750 20750 21335 21335 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.4M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 5.11K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 243K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 221K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 0 5% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 0 5% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.32K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.32K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 332 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 17.8K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 221 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 56.2 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 18.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 44.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.32K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.32K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 0 5% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 0 5% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-58 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R264 R266 R267 R268 R269 R27 R270 R271 R28 R30 R31 R32 R35 R36 R37 R38 R39 R4 R40 R5 R51 R52 R54 R55 R56 R57 R58 R59 R6 R60 R61 R62 R63 R64 R65 R66 R67 R68 R69 R7 R70 R71 R72 R73 R74 R75 R77 R78 R79 R8 R80 R81 R82 R83 R84 R85 R9 RN1 RN10 21352 21335 21352 21352 21335 51748 21335 21335 20750 20737 21335 20724 21347 21342 20745 21335 21335 21335 51766 20750 20750 20750 20750 21335 20739 20739 20739 20739 21335 20739 20739 20750 20750 20750 20750 20750 20750 20750 20750 20750 20750 21347 51732 20750 20741 20711 21352 21335 51748 20737 20737 51748 21342 21339 51288 20750 20750 22487 83560 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 0 5% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 0 5% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 0 5% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 475K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 392K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 75K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2 5% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 0 5% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 475K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 475K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 392K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 221K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 475 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES RES 10KX8 2% SOM16 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 Page 8-59 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS RN11 RN12 RN13 RN14 RN15 RN16 RN17 RN18 RN19 RN2 RN20 RN21 RN22 RN23 RN24 RN25 RN26 RN27 RN28 RN3 RN4 RN5 RN6 RN7 RN8 RN9 S102 S3 S52 S72 S75 SP1 SP2 SQ1 SQ3 SQ4 SQ5 SQ7 SQ8 T10 T11 T12 T13 T14 T15 T16 T17 T18 T2 T25 T26 T27 T28 T29 T3 T5 T6 TP10 TP11 83560 83560 83560 83560 83560 83560 83560 83560 83560 22487 83560 83560 83560 83560 83560 83560 83560 83560 83560 51840 83560 83560 83560 83560 83560 83560 72935 72935 72935 72935 72935 21456 21456 72175 72175 72175 72175 72175 72175 51470 51470 51470 51470 51470 51470 51471 51365 51470 51777 51364 51364 51471 51471 51470 51779 51779 51777 42990 42990 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES RES 10KX8 2% SOM16 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES RES 100KX8 2% SOM16 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 RES NET CAT 4X33 SMD 1206 IC SUPPORT PLCC32 SMD IC SUPPORT PLCC32 SMD IC SUPPORT PLCC32 SMD IC SUPPORT PLCC32 SMD IC SUPPORT PLCC32 SMD ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM INSULATING QUARTZ INSULATING QUARTZ INSULATING QUARTZ INSULATING QUARTZ INSULATING QUARTZ INSULATING QUARTZ TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS84 SOT23 TRANS SMD IRFR9024 ROLL TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS SMD BC860C PNP SOT23 TRANS SMD IRFR024N TR TRANS SMD IRFR024N TR TRANS SMD BSS84 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS84 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS SMD BC850C NPN SOT23 TRANS SMD BC850C NPN SOT23 TRANS SMD BC860C PNP SOT23 ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM Page 8-60 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS AMP AMP AMP AMP AMP VOGT VOGT JAUCH JAUCH JAUCH JAUCH JAUCH JAUCH SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN IR SIEMEN SIEMEN IR IR SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN MOTORO MOTORO SIEMEN OXLEY OXLEY Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS TP12 TP13 TP14 TP15 TP16 TP17 TP18 TP19 TP2 TP3 TP4 TP5 TP6 TP7 TP8 TP9 U1 U10 U100 U101 U102 U103 U105 U106 U11 U111 U112 U113 U114 U115 U116 U13 U14 U15 U16 U17 U18 U19 U2 U20 U21 U25 U26 U27 U28 U29 U3 U30 U31 U32 U33 U34 U35 U36 U37 U38 U39 U4 U40 42990 42990 42990 42990 42990 42990 42990 42990 21456 21456 42990 21456 21456 21456 42990 42990 72598 51675 72598 51498 59878 51902 51902 51782 22320 79039 84126 72546 72546 72546 72546 72524 51782 72238 51782 72633 51902 51782 51498 51498 72238 67969 67969 51782 51467 69275 59878 69275 17938 51799 51902 51902 51902 51902 51919 51953 51498 84135 51498 Art no. 0-48-0001 ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM IC 80251/MCU N80C251SB16PLCC44 IC 062/OP TL062CD SO8 SMD IC 80251/MCU N80C251SB16PLCC44 IC 74573/74HC573D SOL20 SMD IC 27010/EPRO 128KX8 PLCC32 IC 74574/SN74HC574DW SOL20CMS IC 74574/SN74HC574DW SOL20CMS IC 7432/SN74HC32D SO14 SMD IC 7414/SN74HC14D SO14 SMD IC 239/DRV MAX239-RS232 SOL24 IC 3525 /SG3525AP SO16 OPTO COUP SFH617G-3 OPTO COUP SFH617G-3 OPTO COUP SFH617G-3 OPTO COUP SFH617G-3 IC 7420/SN74HCT20D SO14 SMD IC 7432/SN74HC32D SO14 SMD IC 4075/SN74HC4075D00 SO14 SMD IC 7432/SN74HC32D SO14 SMD IC 691/MAX691CWE SOL16 IC 74574/SN74HC574DW SOL20CMS IC 7432/SN74HC32D SO14 SMD IC 74573/74HC573D SOL20 SMD IC 74573/74HC573D SOL20 SMD IC 4075/SN74HC4075D00 SO14 SMD IC 16554 /TL16C554 PLCC68 IC 16554 /TL16C554 PLCC68 IC 7432/SN74HC32D SO14 SMD IC 7474/74HC74D SO14 SMD IC 380 /LM380N-8 DIL8 IC 27010/EPRO 128KX8 PLCC32 IC 380 /LM380N-8 DIL8 IC 508/MUX DG508A SO16 8CH-MUX IC 7402/SN74HC02D SO14 SMD IC 74574/SN74HC574DW SOL20CMS IC 74574/SN74HC574DW SOL20CMS IC 74574/SN74HC574DW SOL20CMS IC 74574/SN74HC574DW SOL20CMS IC 0802/ADC0802LCWM SO20 SMD IC 4051/MUX HEF4051BT SO16 IC 74573/74HC573D SOL20 SMD IC 621024 /IS62C1024L-70Q SOP IC 74573/74HC573D SOL20 SMD Page 8-61 OXLEY OXLEY OXLEY OXLEY OXLEY OXLEY OXLEY OXLEY VOGT VOGT OXLEY VOGT VOGT VOGT OXLEY OXLEY INTEL TI INTEL PHILIP AMD TI TI TI TI MAXIM ST SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN TI TI TI TI MAXIM TI TI PHILIP PHILIP TI TI TI TI PHILIP NS AMD NS TEMIC TI TI TI TI TI NS PHILIP PHILIP ISSI PHILIP Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS U41 U42 U43 U5 U50 U51 U52 U53 U54 U55 U56 U57 U58 U59 U6 U61 U63 U64 U66 U7 U70 U71 U72 U73 U75 U76 U77 U78 U79 U8 U80 U81 U9 U90 U91 U92 U93 U94 U95 U96 U97 51498 51466 U06051 72983 72598 51498 59878 51902 51902 51902 51902 22323 51531 51270 51537 51795 51466 51915 51675 69967 72598 51498 59878 51534 79000 51675 51536 51919 51270 84146 51531 51546 33924 51675 51545 51545 51791 33924 51676 33924 51545 W1411839 W1405016 W1404965 34926 21456 42990 Art no. 0-48-0001 IC 74573/74HC573D SOL20 SMD IC 7408/74HC08D SO14 SMD EPROM TM910S PIC16C54 RS3.3 P. IC 1685 TIMER DS168 SOL24 SMD IC 80251/MCU N80C251SB16PLCC44 IC 74573/74HC573D SOL20 SMD IC 27010/EPRO 128KX8 PLCC32 IC 74574/SN74HC574DW SOL20CMS IC 74574/SN74HC574DW SOL20CMS IC 74574/SN74HC574DW SOL20CMS IC 74574/SN74HC574DW SOL20CMS IC 74245/SN74HC245DW SOL20 SMD IC 43256/SRAM SOP 28 SMD IC 74138/SN74HC138D SO16 SMD IC 74154/MC74HC154DW SOL24CMS IC 4060/CD HEF4060BT SO16 SMD IC 7408/74HC08D SO14 SMD IC 7404/MC74HC04AD SO14 SMD IC 062/OP TL062CD SO8 SMD IC 9356 /M93C56 SO8 IC 80251/MCU N80C251SB16PLCC44 IC 74573/74HC573D SOL20 SMD IC 27010/EPRO 128KX8 PLCC32 IC 6295/DSP MSM6295 SMD IC FLASH MEMORY 4MB PLCC32 IC 062/OP TL062CD SO8 SMD IC 7524/AD7524JR SO16 SMD IC 0802/ADC0802LCWM SO20 SMD IC 74138/SN74HC138D SO16 SMD IC 5620 /TLC5620CD SO14 IC 43256/SRAM SOP 28 SMD IC 74393/74HC393M SO14 SMD IC 358A/OP LM358AM SO8 SMD IC 062/OP TL062CD SO8 SMD IC 064/OP TL064CD SO14 SMD IC 064/OP TL064CD SO14 SMD IC 4093/CD HEF4093BT SO14 SMD IC 358A/OP LM358AM SO8 SMD IC 4538/CD HEF4538BT SO16 SMD IC 358A/OP LM358AM SO8 SMD IC 064/OP TL064CD SO14 SMD BACKLIGHT CONVERTER CBL FRONT FIXING PIECE CPU DG501 FIXING PIECE CPU DG501 ACCBL SLVE THERMO B-EX 160/10 ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN TEST SMD D=1.0MM Page 8-62 PHILIP PHILIP OD3200 DALLAS INTEL PHILIP AMD TI TI TI TI TI NEC TI TI PHILIP PHILIP MOTORO TI STM INTEL PHILIP AMD OKI STM TI ANALOG NS TI TI NEC PHILIP NS TI ST ST PHILIP NS PHILIP NS ST W2652 LIP LIP SES VOGT OXLEY Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.11. BACKLIGHTING CONVERTER SUPPORT PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD Article no.: W141 1909 Description: BACKLIGHT CONVERTER SUPPORT PCB Reference: U3P297-1 Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-63 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-64 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8 7 6 5 4 3 1 2 D D C C BC B B A A D EFIG ARD 501. RET RO ECLAIRAG E 8 Art no. 0-48-0001 7 6 D RAW N APPRO V M OD IFICAT IO N ECL0 ECL0 04/99 04/99 5 Page 8-65 4 ART NO : W 1411909 PRT N O : U 3P297-1 D W G N O : W 4L14U 297-1 D SK N O : SH T N O : 1/1 3 B RUK ER M EDIC AL 2 Version July 2001 1 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS BACKLIGHT CONVERTER SUPPORT PCB COMPONENT LIST U3P297-2 POSITION BC C1 C2 CP1 CP2 P297-1 ITEM 72934 31185 8125 5615 84391 U07297 Art no. 0-48-0001 DESCRIPTION CONVERTER FOR LCD SCREEN CAPA MKS 10N 100V 10% R5 CAPA CHIMI AX 100U 25V 6X10 CN M 3 C PRT MODU2 REPLACE BY 72976 DG501 BACKLIGHT SUPPLY Page 8-66 MANUFACTURER TDK WIMA PHILIP AMP JAE POLYTR Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.12. BATTERY INTERFACE PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD Article no.: W141 1787 Description: BATTERY INTERFACE PCB Reference: W4P14 1682 Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-67 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8 6 7 5 4 3 2 1 D D J1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 H1 1 +UBATT C1 100nF C C MOL42376 H2 1 NTC C2 100nF H3 1 B B A DG 501 A INTERFACE BATTERIE BATTERY INTERFACE ART NO : W1411787 DRAWN H 8 Art no. 0-48-0001 7 6 APPROV RH CK ECL00 03 / 99 ECL00 03 / 99 5 Page 8-68 MODIFICATION PRT NO : W4P141682 DWG NO : W4S141682 4 3 DSK NO : SHT NO : 1/1 2 Version July 2001 1 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8 7 6 5 4 3 1 2 D D C C W4P141682 H2 C2 C1 H1 H3 J1 B B A A DEFIGARD 501. INTERFACE BATTERIE BATTERY INTERFACE 8 Art no. 0-48-0001 7 6 DRAW N APPROV M ODIFICATION ECL0 ECL0 04/99 04/99 5 Page 8-69 4 ART NO : W1411787 PRT NO : W 4P141682 DWG NO : W 4L141682 DSK NO : SHT NO : 1/1 3 BRUKER M EDICAL 2 Version July 2001 1 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS COMPONENT LIST OF BATTERY INTERFACE PCB W4P14 1682 POSITION C1 C2 J1 P1682 ITEM 8493 8493 72930 W1404650 Art no. 0-48-0001 DESCRIPTION CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CN M 36 C PRT 0.64X0.64MM BATTERY INTERFACE IC DG501 Page 8-70 MANUFACTURER VITRAM VITRAM MOLEX CIRE Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.13. POWER SUPPLY PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD Article no.: U53 296 Description: POWER SUPPLY PCB Reference: U3P296-1 Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-71 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-72 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8 7 6 5 4 3 1 2 D D C C B B A A D EFIGARD 501. ALIM EN TAT ION POWE R SU PPLY 8 Art no. 0-48-0001 7 6 DRAWN APPRO V M ODIFICATION ECL0 E CL0 04/99 04/99 5 Page 8-73 4 ART NO : U 53296 PRT N O : U 3P296-1 DW G NO : W 4L14U296-1 DSK NO : SHT NO : 1/1 3 B RUK ER M EDICAL 2 Version July 2001 1 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS COMPONENT LIST OF POWER SUPPLY PCB U3P296-1 POSITION CP14 C100 C360 C362 C363 C364 C365 C366 C370 C402 C500 C501 C502 C600 C601 C602 C800 C801 C802 C803 C804 C806 C807 C808 C809 C810 C811 C812 C813 DZ601 DZ800 D360 D361 D500 D600 D800 D801 IC360 IC500 IC600 L100 L400 L500 L600 L800 L801 PRT R100 R101 R359 ITEM 72948 8493 21002 20990 22597 21014 8493 67238 21014 67392 5223 8493 56394 5223 8493 56394 67236 67236 8493 20990 3669 8493 3669 21014 67236 20990 21014 3669 67392 9812 51942 51868 84407 51868 51868 2967 65760 72763 13052 13052 65341 12715 67600 67600 U21147 65341 U07296 21335 21325 20715 Art no. 0-48-0001 DESCRIPTION CN F 34 C MILLI-GRID SMD CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 100P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1812 470N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA CHIMI RAD 100U/25V R5 CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R KOND ELKO AX 100U 25V 6.3X10.5 CAPA ELECT RAD 10U 50V R5 CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 35V 10% CAPA ELECT RAD 10U 50V R5 CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 35V 10% CAPA ELECT RAD 470U/25V R5 CAPA ELECT RAD 470U/25V R5 CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100P 50V 5% NPO CAPA CHIMI RAD ALU 10U 25V R5 CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA CHIMI RAD ALU 10U 25V R5 CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA ELECT RAD 470U/25V R5 CAPA SMD 1206 100P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA CHIMI RAD ALU 10U 25V R5 KOND ELKO AX 100U 25V 6.3X10.5 DIODE Z ZY 12 2W DIODE Z ZY 6.2V 2W DIODE 1N4937 DIODE S SR506 DO201AD 60V 5A DIODE 1N4937 DIODE 1N4937 DIODE 1N4148 DIODE 1N5819 IC 34063/VREG MC34063AD SO8 IC 7912/VREG MC79L12ACP TO92 IC 7912/VREG MC79L12ACP TO92 SELF 1UH 4A SMSC SELF 56UH 1.5A CHOKE IM-2 100UH 10% CHOKE IM-2 100UH 10% CORE FERRITE MOUNT. SELF 1UH 4A SMSC DG501 POWER SUPPLY PCB RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 15K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-74 MANUFACTURER MOLEX VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM PHILIP VITRAM PHILIP NICHIC VITRAM SPRAGU NICHIC VITRAM SPRAGU PHILIP PHILIP VITRAM VITRAM PHILIP VITRAM PHILIP VITRAM PHILIP VITRAM VITRAM PHILIP PHILIP ITT ITT MOTORO INDEG MOTORO MOTORO ITT G.INST MOTORO MOTORO MOTORO FASTRO SIEMEN DALE DALE EMED FASTRO POLYTR BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R360 R362 R363 R364 R365 R366 R367 R368 R369 R370 R500 R600 R800 R801 R802 R805 TR360 T100 T360 T361 T362 T363 T800 T801 U800 69276 20737 20737 69277 20733 20733 20715 20733 20750 20738 21324 21327 21335 20715 69276 69276 U21157 68376 51471 51470 69914 69914 69914 69914 67968 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES WIRE 1% 3W 0.1 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES WIRE 1% 3W 1.8K RES SMD 562 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 562 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 12.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1 1% 0.25W 1206 RES WIRE 1% 3W 0.1 RES WIRE 1% 3W 0.1 CORE FERRITE MOUNT. TRANS RFD15P05 TO-251AA TRANS SMD BSS84 SOT23 TRANS SMD BSS138 SOT23 TRANS RFD16N05L TO-251AA TRANS RFD16N05L TO-251AA TRANS RFD16N05L TO-251AA TRANS RFD16N05L TO-251AA IC 796 /MAX796CSE SO16 SMD Page 8-75 DALE BOURNS BOURNS DALE BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS DALE DALE EMED HARRIS SIEMEN SIEMEN HARRIS HARRIS HARRIS HARRIS TI Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.14. HIGH-VOLTAGE CIRCUIT PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD Article no.: W141 2006 Description: HIGH VOLTAGE PCB Reference: W4P14 1721 Adjustments: The high-voltage PCB offers two adjustments: 1. Adjustment of the energy supplied by the defibrillator (P1) 2. Adjustment of the HV capacitor voltage measurement signal, HVMONIT (P2) Adjustment Measuring apparatus Measuring point Adjustable Settings and tolerances Notes Energy delivered Joulemeter designed for pulsed biphasic waveforms Energy display on the Joulemeter after the shock P1 The value displayed on the Joulemeter must be For a discharge at a selected energy of 180 J VDC digital Signal HVMONIT P2 High-voltage capacitor voltage measurement signal Art no. 0-48-0001 180 J ± 2 J Signal HVMONIT must have an amplitude of Ref.: GND multimeter 4.18 V ± 50 mV Page 8-76 For charge voltage of 4600 V of the high-voltage capacitor (C1 + C2) Version July 2001 Version July 2001 A B C D J7 1 1 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 J3 FV2.8 J16 TB 501 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 MOL87089 J18 J15 MOL4455 1721-H02.SCH FV2.8 J8 FV2.8 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 H1 3.2mm ON/OFF -12V -24V H2 3.2mm +5VCPU +12V +SPEAKER -SPEAKER STARTCONV SAWSEL0 SAWSEL1 SAWSEL2 SAWSEL3 SACHARGE PATCHLED WDUMP SYNCDEF DISCHKEY1 DISCHKEY2 -CDNI/LI DEFCHARGE DEFREADY DEFDISCH SECDISCH -DEFSEC HVMONIT -24V -12V TP08 +5VCPU TP2 +12V ON/OFF +UDEF +UPWR D13 MBRS360T3 ECL02 +UBATT NTC DCIN GND +UBATTF +UDEF MBRS360T3 D15 R69 100K ECL02 F1 8AT TP1 RU1 S10K35 BYD37M U BYD37M D3 ECL01 R18 1M R10 332 R11 681 C10 47nF 7 D5 BYD37M F2 TP6 R45 1K R12 10K R13 20 DZ1 15V T5 IRFL9014 160mAT VO ADJ VI TP8 T10 -CHARGEDR STARTDEF GEST -DISCHENDR -SYNCDR DISCH +5V HVMES2 CHARGEN PATRLSEC HVMES1 IRF4905S R46 10K RN SBE02 J9 R16 20 1 2 RG1 LM317T 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 /40V C2 3300uF J1 +5V 6 7 R4 22.1K R5 22.1K R24 10K R21 100K C7 47pF C8 1nF + U3B LM358AM + MOL87089 6 5 6 PHASE2 R63 15K F3 500mAT 4 R6 22.1K 2 4 2 1 PREPULSE2 10uF/35V C4 U3A LM358AM + 1 +12V R27 10K R39 10K U2 TC4427 +12V U1 TC4427 5 7 5 D7 BAS32 RG2 TP13 TP11 TP10 5 R17 1K R19 3.01K VO ADJ VI PATRL -PATRL TP9 LM317LZ R38 3.32K ECL00 R35 12.1K ECL00 R26 12.1K R29 47.5 C12 22nF R23 22.1K R20 47.5K PHI1 PREPHI1 PREPHI2 PHI2 TP4 TP5 C13 100nF D4 BAS32 T7 BC850C T9 BC860C ECL00 7 T6 BC860C 5 C11 2.2nF R36 10K R30 33.2K R28 4.75K R14 22.1k C18 10uF/35V PREPULSE1 R7 22.1K +5V P1 50K 2 3 + PHASE1 R25 10K R22 10K +UDEF +5V R15 3.32K T4 BC860C 3 D2 BAS32 2 8 7 4 C19 100nF 6 6 C1 100uF/25V D10 BYD37M J6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 DZ3 TVS305 R56 22.1K U4 UC2843AD C U R CO N T 10 VREF OU T 5 R/C S E N S E 1 F EE D C O M P AMP MODU2 R34 XX 14 7 3 C9 47pF 12 11 D11 3 3 8 9 8 TP7 4 C5 10uF/16V TP3 D12 BYD37M R65 22.1K R68 10K T8 BC860C R40 3.01K 100 R32 100 R37 DZ4 ZY91 D9 BYD37M 4 +5V C20 10uF/16V R66 22.1K R67 10K DZ5 15V R8 10K C16 47nF 100 R44 T1 IRF540 DZ6 9.1V R64 100 TP12 D14 BAS32 T14 BC860C T15 BC860C R3 100k T3 IRLL014 R2 0.01 bl bk wh rd R61 22.1K R59 22.1K R51 100K D17 D16 J4 FV2.8 R62 10K R60 10K 3 R33 1K D8 BYD37M R31 22.1K D6 BYD37M D1 BYD37M D16,D17:ESJC37-10 TR1 ETD29 T2 IRF540 11 3 W140 5319 3 1 +5V T13 IRLL014 T12 IRLL014 -PATRL PATRL IRFL9014 T11 RL1 RY16020L5 2 A 21 22 1 A 1 1 12 RS10 R1 27K 30uF 1,2KV 30uF 3,6KV J1 J11 SP +5V R55 10K R49 10K 2 RH ECL01 26/02 01 RH ECL02 26/06 01 DN3 C17 47nF DN4 BAV99 BAV99 C15 47nF J13 SP +5V MODIFICATION RH C14 47nF J10 SP 1x3 BUP309 2x3 BUP309 +5V R57 10K R52 10K +5V MODULE de COMMUTATION R42 511K 2 C3 47nF R43 511K J14 SP R48 40.2M APPROV R41 100K 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ECL00 08/02 01 DRAWN R9 100K SP J2 R47 40.2M J5 SP J12 FV2.8 FV2.8 J9 FV2.8 J8 FV2.8 J7 FV2.8 J6 FV2.8 J5 FV2.8 J4 FV2.8 J3 FV2.8 J2 FV2.8 1 1 U5B 7 SHT NO : 1/1 DSK NO : ........ DWG NO : W4S141721-H02 PRT NO : W4P141721 ART NO : W1412006 .HIGH VOLTAGE CIRCUIT .CIRCUIT HAUTE TENSION P2 50K R58 402K 1 1 C6 100nF HVMONIT HVMES2 PATRLSEC TP14 U5A TLC2272CD TP15 +5V + RL2 JC 2a-6V R54 402K 2 3 + TLC2272CD + .DG 501 BIPH R53 40.2K 6 5 + R50 40.2K DN2 BAV99 DN1 BAV99 R70 10M VR37 R69 10M VR37 RL1 1 JC 2a-6V 8 PATCHLED +SPEAKER -SPEAKER 1 1 1 1 13 A1 4 3 Page 8-77 2 Art no. 0-48-0001 14 A2 1 4 A2 23 1 3 A1 24 24 23 1 J17 AMP MODU2 1 1 A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 1 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8 6 7 5 R3 R4 4 R5 U1 R6 T3 3 1 2 U2 R7 R8 C3 C4 R9 R1 1 R 10 D1 C5 R 12 C6 T4 R1 4 R 15 D2 D C7 R 13 D R 16 R 17 R 18 D3 R 19 R 21 R2 2 T5 C8 D4 E CL01 R2 0 T6 D5 C9 R 24 R25 C 12 R 26 C1 0 R2 3 C11 D6 R 28 D7 R29 U3 T7 R2 7 C 13 T8 R3 1 R 32 R3 3 R 37 D8 R3 0 R3 4 R3 5 R3 8 U4 T9 R3 6 R3 9 D9 R40 C 14 R4 1 C 15 C16 R 43 D1 0 R44 R4 2 C1 7 R 45 T1 0 DZ 1 R 46 C 18 R 51 R52 D Z5 R54 R 56 R57 C R 50 DN3 T1 1 DN1 R4 9 R 53 U5 R 55 C 19 C D N4 T 13 T12 D 11 D N2 E CL02 R 58 R 60 C2 0 R6 1 R 62 R63 DZ 6 R 64 D1 2 D1 4 R66 W 4P14 172 1 R6 7 T15 T14 R 59 D 13 R6 5 R6 8 D 15 R69 TO P SID E J1 TP2 T P8 TP4 TP5 J2 TP9 J3 R4 7 TP6TP10 T P1 4 DZ 3 T P3 R G1 R G2 F3 TP1 5 C1 P1 B J6 P2 J5 B F2 J4 RL 1 C2 F1 T1 T2 R1 J7 J10 DZ 4 R2 J1 1 J12 J13 J8 J9 J14 T P7 R 48 TR 1 J1 5 J16 A A TP1 3 J17 T P12 TP1 J1 8 * = pas monter / not mounted 8 Art no. 0-48-0001 7 DG501 BIPHASIQU E Circuit haute tension Hight voltage circuit R U1 6 T P11 DRAW N A PPRO V CK RH ECL00 06 / 00 E CL00 06 / 00 M O DIFIC AT IO N CK ART : W 1412006 PRT : W 4P141721 DGW : W 4L141721 SHT : 1/1 CK ECL01 E CL02 02 / 01 07 / 01 5 Page 8-78 4 3 2 Version July 2001 1 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS COMPONENT LIST OF HIGH-VOLTAGE PCB W4P14 1721 POSITION C1 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C2 C20 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 DN1 DN2 DN3 DN4 DZ1 DZ3 DZ4 DZ5 DZ6 D1 D10 D11 D12 D13 D14 D15 D16 D17 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 F1 F2 F3 J1 J10 ITEM 1994 72548 21006 21018 8493 72548 72548 72548 72548 56394 8493 58245 51559 72548 56394 51559 8493 20986 21002 20986 51778 51778 51778 51778 72933 39832 51296 72933 51775 51586 51586 51586 51586 79073 22029 79073 11721 11721 22029 51586 22029 51586 51586 22029 51586 51586 2259 35466 35008 79075 59995 Art no. 0-48-0001 DESCRIPTION CAPA CHIMI RAD 100U 63V 10X13 CAPA SMD 1206 47N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 2.2N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 47N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 47N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 47N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 47N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 35V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA CHIMI RAD 3300U 40V 22X25 CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 47N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 35V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 47P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 47P 50V 5% NPO DIODE SMD BAV99 SOT23 DIODE SMD BAV99 SOT23 DIODE SMD BAV99 SOT23 DIODE SMD BAV99 SOT23 DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE TVS305 5V 300W DIODE Z 91V 2W DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80 9.1V DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 DIODE SMD MBRS360T3 403-03 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD MBRS360T3 403-03 DIODE RA 8.5KV 1A DIODE RA 8.5KV 1A DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 FUSE GLASS 5X20MM 8A T 250V FUSE TR5 8X7MM 0.16A T 250V FUSE TR5 8X7MM 0.5A T 250V CN M 38 D PRT MILLI-GRID 2.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK D1.1MM Page 8-79 MANUFACTURER NICHIC VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM ROEDER SPRAGU VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN PHILIP MICROS GENSEM PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP MOTORO PHILIP MOTORO AEG AEG PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP WICKMA WICKMA WICKMA MOLEX VOGT Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS J11 J12 J13 J14 J15 J16 J17 J18 J2 J3 J4 J5 J6 J7 J8 J9 PF'1 PF1 PF2 PF3 P1 P1721 P2 RG1 RG2 RL1 RU1 R1 R10 R11 R12 R13 R14 R15 R16 R17 R18 R19 R2 R20 R21 R22 R23 R24 R25 R26 R27 R28 R29 R3 R30 R31 R32 R33 R35 R36 R37 R38 R39 59995 35779 59995 59995 72931 35779 72156 72972 59995 72143 35779 59995 72157 35779 35779 35893 4915 4915 35012 35012 34811 W1404691 34811 452 18812 51387 72932 72508 20730 20734 20750 51735 21327 20743 51735 20737 21347 8855 72507 53699 21335 20750 21327 20750 20750 21324 20750 20745 73283 21335 21329 21327 20724 20737 21324 20750 20724 20743 20750 Art no. 0-48-0001 ACCBL PIN FORK D1.1MM ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL PIN FORK D1.1MM ACCBL PIN FORK D1.1MM CN F 8 D PRT 4455 PITCH 2.54MM ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT CN M 6 D PRT MODU2 CN M 34 D PRT MILLI-GRID 2.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK D1.1MM CN M 34 D PRT GLSS .LONG F/R ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL PIN FORK D1.1MM CN M 8 D PRT MODU2 ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT CN F 64 D PRT BARSIL R2.54 FUSE SUP PRT 5X20 CLIPS FUSE SUP PRT 5X20 CLIPS FUSE SUP PRT TR5 FUSE SUP PRT TR5 RES ADJUST 50K 0.5W 25T V HV CIRCUIT IC DG501 BIPH RES ADJUST 50K 0.5W 25T V IC 317/VREG LM317T TO220 IC 317/VREG LM317LZ TO 92 RELAY 12V 2XR PRT RES VDR 35V 10% 0.05W R7.5 RES BOB 27K 5% 10W 20PPM RES SMD 332 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 681 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 20 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.32K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 20 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.01K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES BOB 0.01 3% 3W RES SMD 47.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 12.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 47.5 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 12.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.32K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-80 VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT MOLEX VOGT AMP MOLEX VOGT AMP VOGT VOGT AMP VOGT VOGT RN WICKMA WICKMA WICKMA WICKMA BOURNS CIRE BOURNS STM STM KACO SIEMEN DALE BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS DALE BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R4 R40 R41 R42 R43 R44 R45 R46 R47 R48 R49 R5 R50 R51 R52 R53 R54 R55 R56 R57 R58 R59 R6 R60 R61 R62 R63 R64 R65 R66 R67 R68 R69 R7 R8 R9 TR1 T1 T10 T11 T12 T13 T14 T15 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 T9 U1 U2 U3 U4 U5 21327 8855 21335 56375 56375 20724 20737 20750 72179 72179 20750 21327 53700 21335 20750 53700 51745 20750 21327 20750 51745 21327 21327 20750 21327 20750 21325 20724 21327 21327 20750 20750 1034 21327 20750 21335 W1412041 51298 72912 72925 72923 72923 51777 51777 51298 72923 51777 72925 51777 51779 51777 51777 79077 79077 33924 72611 69958 2567 35776 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.01K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 511K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 511K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES MET 40.2M 1% 1W 10000V RES MET 40.2M 1% 1W 10000V RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 40.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 40.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 402K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 402K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 15K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES MET 100K 1% 0.6W 50PPM RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 TRANS CONVERTER HT 81869A TRANS IRF540A NMOS TO220 TRANS IRF4905 S PMOS D2 PAK TRANS SMD PMOS IRFL9014 SOT223 TRANS SMD NMOS IRLL014 SOT223 TRANS SMD NMOS IRLL014 SOT223 TRANS SMD BC860C PNP SOT23 TRANS SMD BC860C PNP SOT23 TRANS IRF540A NMOS TO220 TRANS SMD NMOS IRLL014 SOT223 TRANS SMD BC860C PNP SOT23 TRANS SMD PMOS IRFL9014 SOT223 TRANS SMD BC860C PNP SOT23 TRANS SMD BC850C NPN SOT23 TRANS SMD BC860C PNP SOT23 TRANS SMD BC860C PNP SOT23 IC 4427/DRV TC4427 COA SO8 SMD IC 4427/DRV TC4427 COA SO8 SMD IC 358A/OP LM358AM SO8 SMD IC 2843/PWM UC2843AD SO14 IC 2272 /TLC2272CD SMD SO8 EFX NUT HU M3 ACNI ACCBL SLVE CLIP FASTON 2.8 Page 8-81 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS PHILIP PHILIP BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS DRALOR BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS OD3100 SAMSUN IR IR IR IR SIEMEN SIEMEN SAMSUN IR SIEMEN IR SIEMEN MOTORO SIEMEN SIEMEN TELCOM TELCOM NS MOTORO TI BOSSAR VOGT Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 11588 58061 1708 35965 76015 35772 Art no. 0-48-0001 EFX WASHR VENT M3 INX A2 RADIAT TO218 EFX SCRW TCB CROSS-HEAD M3X8 ACNI ACCBL DUCT THERMO B-EX 480 RADIAT TO220 PRT V ACCBL CLIP FASTON 2.8 0.3-0.6 Page 8-82 BOSSAR THERMA BOSSAR SES THERMA VOGT Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.15. DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD Article no.: W141 2007 Description: DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCB Reference: W4P14 1722 W4P14 1722A Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-83 Version July 2001 A B C D 243 56.2 182 182 511 332 750 8.25K 221 681 4.75K 10K 12.1K R97 R96 R95 R94 R93 R92 R91 R72 R73 R74 R75 R76 R77 J1 R43 22.1K R90 100K R49 22.1K R50 22.1K R80 1M DISCH DEFCHARGE DEFREADY DEFDISCH SECDISCH -DEFSEC -CHARGEDR STARTDEF GEST -DISCHENDR -SYNCDR 8 R44 10K CH7 R47 100K R79 10K 47.5K R86 HVMES1 +5V DISCHKEY1 DISCHKEY2 SAWSEL0 SAWSEL1 SAWSEL2 SAWSEL3 SACHARGE STARTCONV WDUMP SYNCDEF SMD20MOL38H 1722A-01.SCH 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 PATRLSEC HVMES2 CHARGEN STARTCONV SACHARGE SYNCDEF DISCHKEY2 HVMES1 33.2K 30.1K 27.4K 22.1K 9.09K 12.1K 8.25K 4.75K 3.32K 2.74K 2.21K 1.21K 750 +5V +5V D5 BAS32 R31 22.1K R89 22.1K DZ2 TL1431CD R88 22.1K R85 R84 R83 R82 R81 R100 R101 R102 R103 R104 R105 R106 R107 R108 22.1K PHASE1 PREPULSE1 PHASE2 PREPULSE2 HVMES2 CHARGEN PATRLSEC 332 R98 DISCHKEY1 MOL87368 180J 150J 130J 110J 90J 70J 50J 30J 15J 8J 6J 4J 2J 1J R99 22.1K R60 2.21K C29 10uF/16V +5V TP2 R40 121K 7 R1 10K R8 10K +2.5V TP7 C18 100nF U1 4067 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 # EN 0 0 1 G 2 15 3 C25 10uF/16V R87 0 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 10 11 14 13 24 MUXDX 1 +5V R53 10K R56 10K R2 100K +2.5V D7 BYD37M D8 BYD37M 12 # R3 15K R10 20K R9 15K R39 511 R46 10K +5V +5V +5V C20 100nF R51 10K +2.5V R52 100K R54 15K +5V DZ1 TL1431CD C27 10uF/16V R55 100K C30 10nF R70 20K TP1 +5V R67 681 8 R48 22.1K 1 + + U9B LM358 + U9A LM358 + + + + + 5 6 3 2 5 4 9 8 7 6 COMP 7 14 1 15 14 7 1 COMP U16B LM393 + - COMP U16A LM393 + - COMP +5V U11A LM339 + - 6 7 1 2 U11C LM339 +5V C26 2.2uF/35V + - U11B LM339 + - COMP U2B TLC2272CD 6 5 U10D ULN2804LW 4 1 C21 2.2uF/35V U10E ULN2804LW 5 6 5 2 3 +5V U2A TLC2272CD 2 3 +5V 8 C35 100nF R6 10K C33 22pF R78 10K TP6 R45 10K R32 10K R35 1K C34 47nF R38 200K +5V R37 100 R69 3.32K R68 2K COMP +2.5V U3A LM393 + - +2.5V 9 8 5 4 16 U17C LM339 COMP + - U17A LM339 + - U11D LM339 COMP 14 2 C17 22nF R36 100K R42 10K R4 100 R5 475K 13 -HVPRES -CHARGE 5 5 -RST -STOP 11 10 -DISCH U17D LM339 + - COMP C13 22pF Q1 4MHz CH1 C2 470nF +5V +2.5V R30 22.1K C1 10uF/16V +5V -NCHARGE SYNCDEF -DISCH2 R33 1K + - +5V +5V DISCH1 CH2 R34 1K C31 2.2uF/35V COMP +5V 11 10 1 C32 2.2uF/35V C19 2.2uF/35V +2.5V +5V +5V +5V +5V 3 2 +5V U10C ULN2804LW 3 8 2 3 6 7 4 4 4 13 C4 100nF V/DETECT PB PCI RTCC MCLR OSC1 OSC2 7 0 PA PC C15 100nF C14 10uF/16V +5V U18 TL7705AC SENSE RESIN CT REF R29 22.1K +5V 3 0 7 0 6 7 8 9 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 6 5 -DISCH C23 1nF U12 PIC16C57-XT C16 22pF 1 28 27 26 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 L1 1uH 7 2 3 1 +5V 8 2 4 4 +5V 6 4 +5V R57 22.1K 12 5 4 8 6 3 9 1 2 U7 4047 RX/CX R CX RX M2 C6 100nF R28 22.1K +5V 10 1,2[ 11 1,2 13 STARTDEF D9 BAS32 C28 1nF C22 100nF 1 M1 & S D1 BAS32 R15 22.1K +5V C12 10uF/16V TP3 +5V C3 100nF R7 10K WDCLK DISCH CFULL LOADC TBATT STARTDEF WDUMP SECRST 4 14 8 3 8 7 R71 150K R12 10K TP5 D2 BAS32 U13B 4013 S 1D C1 R U15A LM358 + 4 11 + R 5 6 7 6 4040 U5 CT CTR12 +5V +2.5V +2.5V U14C 4075 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 3 9 7 6 5 3 2 4 13 12 14 15 1 U3B LM393 COMP LM339 COMP + - + - 1 7 1 22 24 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 27 26 23 25 4 28 29 3 2 16 0 +5V A 3 4 5 ECL01 30/01 01 RH DRAWN EN [PGM] [VPP] [5]A [6]A [7]A 1 31 07 1 0 [0]A [1]A [2]A [3]A [4]A U15B + 2 1 + 6 +5V R18 10K 6 5 APPROV 1 2 8 +5V 2 3 4 5 MODIFICATION 2 11 12 C9 1uF/35V R63 22.1K 1 R59 22.1K R58 22.1K R17 10K R13 100K 6 R41 1K R64 22.1K +5V +5V +5V U14B 4075 9 C7 100nF T1 BC850C U10H ULN2804LW 8 1 7 U14A 4075 14 U10G ULN2804LW 7 R14 10K R20 10K R62 22.1K +5V R19 22.1K U4 29F010-55JC 31 1 19 20 21 13 14 15 17 18 U6B 4023 & LM358 7 U13A 4013 S 1D C1 R C5 100nF R24 22.1K EPROM 128k x 8 & +5V 16ms R66 10K C10 100nF R21 47.5K R25 22.1K 6 5 3 4 C8 10nF R23 100K +5V R22 22.1K C11 100nF 10 D4 BAS32 D3 BAS32 3 U17B 11 12 13 R26 22.1K 12 13 2 3 +2.5V R11 33.2K TP4 10 + R16 22.1K R27 22.1K 8 9 11 10 1 +5V 8 16 7 12 4 8 14 R65 22.1K SDYSTE1 BURST1 SDYSTE2 BURST2 D6 BAS32 R61 10K U8F 4050 U8C 4050 U8E 4050 U8D 4050 CH4 1 2 8 11 12 13 U6C 4023 & CH3 9 10 13 15 6 12 10 18 2 PRT NO : W4P141722A ART NO : W1412007 SHT NO : 1/1 DSK NO : ........ DWG NO : W4S141722A-01 1 PHASE2 PHASE1 CH6 PREPULSE2 PREPULSE1 -SYNCDR -DEFSEC DEFDISCH SECDISCH DEFCHARGE DEFREADY -DISCHENDR GEST STARTDEF -CHARGEDR CH5 1 .DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL BOARD .COMMANDE DEFIBRILLATEUR U6A 4023 & +5V .DG 501 BIPH +5V +5V U8A 4050 U10F ULN2804LW 6 14 7 11 9 4 17 U8B 4050 +5V C24 100nF U10A ULN2804LW 1 3 5 U10B ULN2804LW 2 1 10 WDUMP 1 12 32 7 8 9 SAWSEL0 SAWSEL1 SAWSEL2 SAWSEL3 8 Version July 2001 2 3 6 7 3 16 Page 8-84 14 Art no. 0-48-0001 7 8 A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8 6 7 5 4 3 1 2 D D R1 R2 R3 C1 R4 R5 R6 R7 C U1 VREF TP1 C5 R19 C22 C21 C26 C16 C19 C6 R20 C13 R57 R37 R45 D2 C10 R54 C23 C14 R21 R46 R15 L1 R38 CH7 D8 C7 R22 R24 C15 R39 C20 R51 R16 D3 R25 R40 R47 R11 R53 R55 R31 C18 R58 C11 R26 D1 C8 R52 R56 R32 R41 D6 R59 R12 R27 R33 D7 C24 C12 R48 R42 C3 R28 R34 R43 R49 R35 C9 C4 D4 R29 R44 R50 R36 C25 R60 R13 R17 R23 R30 D5 C17 R14 R18 CH1 CH2 W4P141722A DZ1 U4 U5 U7 R62 CH3 CH4 R72 R73 R74 CH5 R63 R75 R64 R76 R65 R77 CH6 C32 C33 R66 R71 R78 C28 D9 C34 R79 R67 R68 R69 R70 C30 C27 C29 R61 R81 R82 R83 R84 R85 R86 R87 R88 R89 R90 R80 Q1 * R91 R92 R93 R94 R95 R96 R97 R98 R99 C35 R100 R101 R102 R103 R104 R105 R106 R107 R108 C BOTTOM SIDE U13 T1 U11 U16 C31 U2 TP6 TP7 C2 R8 R9 R10 U14 U8 U3 B U9 U17 U10 B U6 * TP3 J1 DZ2 * TP2 W4P141722A TP4 TP5 WDCLK * * U12 +2.5V U18 U15 * = pas monté / not monted A A DEFIGAR D 501 Commande défibrillateur Defibrillator control 8 Art no. 0-48-0001 7 6 DRA WN APPROV RC RH ECL01 10/ 00 ECL01 10/ 00 MODIFIC ATION 5 Page 8-85 4 ART : W 1412007 PRT : W 4P141722A DGW : W 4L141722A SHT : 1/1 3 BRUKER M EDICAL 2 Version July 2001 1 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS COMPONENT LIST OF DEFIBRILLATOR CONTROL PCB W4P14 1722A POSITION C1 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C2 C20 C21 C22 C23 C24 C25 C26 C27 C28 C29 C3 C30 C31 C32 C33 C34 C35 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 DZ1 DZ2 J1 L1 P1722 Q1 R1 ITEM 51559 8493 8493 51559 20982 51559 8493 20982 21018 8493 72541 22597 8493 72541 8493 21002 8493 51559 72541 51559 21002 51559 8493 21014 72541 72541 20982 72548 8493 8493 8493 8493 8493 21014 72543 22029 22029 22029 22029 22029 22029 51586 51586 22029 72503 72503 79074 79076 W1404692 79082 20750 Art no. 0-48-0001 DESCRIPTION CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 22P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 22P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 22N 50V 10% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 2.2U 35V 20% CAPA SMD 1812 470N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 2.2U 35V 20% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 2.2U 35V 20% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 2.2U 35V 20% CAPA SMD TANTAL 2.2U 35V 20% CAPA SMD 1206 22P 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 47N 50V 5% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 10N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD TANTAL 1U 35V 20% DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 IC 1431/VREF TL1431CD SO8 IC 1431/VREF TL1431CD SO8 CN F 38 C MILLI-GRID SMD SELF SMD BDS3/3/4.6-3S1 DEF CONTROL IC DG501 BIPH QUARTZ 4MHZ SMLB RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-86 MANUFACTURER SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP TI TI MOLEX PHILIP SACEL SARONI BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R10 R100 R101 R102 R103 R104 R105 R106 R107 R108 R11 R12 R13 R14 R15 R16 R17 R18 R19 R2 R20 R21 R22 R23 R24 R25 R26 R27 R28 R29 R3 R30 R31 R32 R33 R34 R35 R36 R37 R38 R39 R4 R40 R41 R42 R43 R44 R45 R46 R47 R48 R49 R5 R50 R51 R52 R53 R54 R55 33927 21324 20748 20745 20743 20742 20741 20738 51516 21327 21329 20750 21335 20750 21327 21327 20750 20750 21327 21335 20750 53699 21327 21335 21327 21327 21327 21327 21327 21327 21325 21327 21327 20750 20737 20737 20737 21335 20724 51736 59889 20724 21336 20737 20750 21327 20750 20750 20750 21335 21327 21327 51748 21327 20750 21335 20750 21325 21335 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 20K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 12.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 8.25K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.32K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.7K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 750 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 47.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 15K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 200K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 511 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 121K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 475K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 15K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-87 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R56 R57 R58 R59 R6 R60 R61 R62 R63 R64 R65 R66 R67 R68 R69 R7 R70 R71 R72 R73 R74 R75 R76 R77 R78 R79 R8 R80 R81 R82 R83 R84 R85 R86 R87 R88 R89 R9 R90 R91 R92 R93 R94 R95 R96 R97 R98 R99 S4 T1 U1 U10 U11 U12 U13 U14 U15 U16 U17 20750 21327 21327 21327 20750 20741 20750 21327 21327 21327 21327 20750 20734 51734 20743 20750 33927 21337 20748 20728 20734 20745 20750 21324 20750 20750 20750 21347 20749 21327 53691 53702 21329 53699 21352 21327 21327 21325 21335 51516 20730 59889 20727 20727 20720 51286 20730 21327 72935 51779 51579 22492 51943 W1405021 51802 51801 33924 51804 51943 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2.21K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 681 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 3.32K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 20K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 150K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 8.25K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 221 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 681 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.7K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 12.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 10K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 9.09K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 27.4K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 30.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 33.2K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 47.5K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 0 5% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 15K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 750 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 332 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 511 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 182 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 56.2 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 243 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 332 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 IC SUPPORT PLCC32 SMD TRANS SMD BC850C NPN SOT23 IC 4067/MUX HEF4067BT SO24L IC 62084/TD62084AF SOL18 IC 339/OP LM339M SO14 SMD PG ODAM 501 DEF CTRL IC 4013/CD HEF4013BT SO14 SMD IC 4075/CD HEF4075BT SO14 SMD IC 358A/OP LM358AM SO8 SMD IC 393/OP LM393M SO8 SMD IC 339/OP LM339M SO14 SMD Page 8-88 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS AMP MOTORO PHILIP TOSHIB NS PIGE PHILIP PHILIP NS NS NS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS U18 U2 U3 U4 U5 U6 U7 U8 U9 51535 69958 51804 W1405391 51494 51800 51796 51798 33924 Art no. 0-48-0001 IC 7705/TL7705ACD SO8 SMD IC 2272 /TLC2272CD SMD SO8 IC 393/OP LM393M SO8 SMD PG ODAM 501 PULSE BIPH IC 4040/CD HEF4040BT SO16 SMD IC 4023/CD HEF4023BT SO14 SMD IC 4047/CD HEF4047BT SO14 SMD IC 4050/CD HEF4050BT SO16 SMD IC 358A/OP LM358AM SO8 SMD Page 8-89 TI TI NS OD3200 PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP NS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.16. HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING CIRCUIT BOARD Article no.: W141 2009 Description: HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING PCB Reference: W4P14 1724 W4P14 1724A Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-90 Version July 2001 A B C J19 FV2.8 1724A-01.SCH R7 12.1 FV2.8 J20 1 1 Page 8-91 8 C3 XX R8 12.1 R9 12.1 1 7 PHI1 PREPHI1 PREPHI2 PHI2 L6 3.3mH 2 4 6 DZ4 15V 4 2 1 3 L5 3.3mH 2 4 BUP309 T4 BUP309 T3 22M VR37 R2 3 1 3.3mH L2 DZ5 15V DZ6 15V DZ7 15V DZ8 15V 4 2 1 3 5 L4 3.3mH 2 4 BUP309 T6 BUP309 T5 3 1 3.3mH L3 DZ9 15V DZ10 15V DZ11 15V 22M VR37 R3 DZ12 15V 4 2 4 4 FV2.8 1 J12 D1 BAS32 C1 1nF J22 SP J21 SP 3 J16 FV2.8 J13 AMP MODU2 J18 FV2.8 J9 FV2.8 J8 FV2.8 J7 FV2.8 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 1 PATRL -PATRL DZ24 15V DZ20 15V 22M VR37 T9 BUP309 R6 22M VR37 RN1 22Kx8 T8 BUP309 R5 DZ19 15V DZ18 15V DZ22 15V DZ23 15V DZ17 15V DZ21 15V 5 DZ16 15V 22M VR37 T7 BUP309 R4 DZ15 15V DZ14 15V DZ13 15V Version July 2001 ECL01 21/11 00 RH DRAWN R13 100 R12 100 R10 100K APPROV 1 1 1 1 1 3 MODIFICATION T12 IRFR024N T11 IRFR024N T10 IRFR024N FV2.8 J17 3 1 3.3mH L1 DZ1 15V DZ2 15V DZ3 15V 6 J15 1 3 BUP309 T2 BUP309 T1 22M VR37 R1 FV2.8 J14 1 1 1 1 1 1 7 FV2.8 1 FV2.8 J6 FV2.8 J5 FV2.8 J4 FV2.8 J3 FV2.8 J2 FV2.8 J1 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 Art no. 0-48-0001 1 D 8 -PATRL PATRL RL2 JC2a T15 2 2 4 C2 1nF R11 100K D2 BAS32 J10 SHT NO : 1/1 DSK NO : ........ DWG NO : W4S141724A-01 PRT NO : W4P141724A ART NO : W1412009 .HIGH VOLTAGE SWITCHING BOARD FV2.8 1 J11 FV2.8 1 .CIRCUIT de COMMUTATION HT .DG501 IRFR024N T14 IRFR024N T13 IRFR024N 3 5 1 6 1 D3 BYD37M 5 3 6 RL1 JC2a 4 2 2 1 1 A B C D 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-92 Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS COMPONENT LIST OF HIGH-VOLTAGE SWITCHING PCB W4P14 1724A POSITION C1 C2 CBL1 CBL2 D1 D2 D3 DZ1 DZ10 DZ11 DZ12 DZ13 DZ14 DZ15 DZ16 DZ17 DZ18 DZ19 DZ2 DZ20 DZ21 DZ22 DZ23 DZ24 DZ3 DZ4 DZ5 DZ6 DZ7 DZ8 DZ9 J1 J10 J11 J12 J13 J14 J15 J16 J17 J18 J19 J2 J20 J21 J22 J3 J4 J5 J6 J7 ITEM 21002 21002 W1412032 W1412032 22029 22029 51586 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 72933 35779 35779 35779 35779 35779 35779 35779 35779 35779 72157 35779 35779 35779 59995 59995 35779 35779 35779 35779 35779 Art no. 0-48-0001 DESCRIPTION CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 1N 50V 5% NPO IGBT CTRL CABLE IGBT CTRL CABLE DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BAS32L SOD80 DIODE SMD BYD37M SOD87 DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V DIODE Z SMD SOD80C 15V ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT CN M 8 D PRT MODU2 ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL PIN FORK D1.1MM ACCBL PIN FORK D1.1MM ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT Page 8-93 MANUFACTURER VITRAM VITRAM OD2100 OD2100 PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT AMP VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS J8 J9 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 P1724A R1 R10 R11 R12 R13 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 R8 R9 RL1 RL2 RN1 T1 T10 T11 T12 T13 T14 T15 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 T9 35779 35779 W1405334 W1405334 W1405334 W1405334 W1405334 W1405334 W1404694 51164 21335 21335 20724 20724 51164 51164 51164 51164 51164 987 987 987 79072 79072 577 79070 51364 51364 51364 51364 51364 51364 79070 79070 79070 79070 79070 79070 79070 79070 Art no. 0-48-0001 ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT ACCBL TAB PL 2.8 PRT TRANS CORE DIAM 16.5 TRANS CORE DIAM 16.5 TRANS CORE DIAM 16.5 TRANS CORE DIAM 16.5 TRANS CORE DIAM 16.5 TRANS CORE DIAM 16.5 HV SWITCHING IC DG501 BIPH RES MET 22M 5% 0.5W 2500V RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES MET 22M 5% 0.5W 2500V RES MET 22M 5% 0.5W 2500V RES MET 22M 5% 0.5W 2500V RES MET 22M 5% 0.5W 2500V RES MET 22M 5% 0.5W 2500V RES MET 12.1 1% 0.6W 50PMM RES MET 12.1 1% 0.6W 50PMM RES MET 12.1 1% 0.6W 50PMM RELAY 6V 1XT PRT RELAY 6V 1XT PRT RES RES 22KX8 2% SIL9 TRANS BUP309 IGBT TO218AB TRANS SMD IRFR024N TR TRANS SMD IRFR024N TR TRANS SMD IRFR024N TR TRANS SMD IRFR024N TR TRANS SMD IRFR024N TR TRANS SMD IRFR024N TR TRANS BUP309 IGBT TO218AB TRANS BUP309 IGBT TO218AB TRANS BUP309 IGBT TO218AB TRANS BUP309 IGBT TO218AB TRANS BUP309 IGBT TO218AB TRANS BUP309 IGBT TO218AB TRANS BUP309 IGBT TO218AB TRANS BUP309 IGBT TO218AB Page 8-94 VOGT VOGT CECLA CECLA CECLA CECLA CECLA CECLA WUERTH PHILIP BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP DRALOR DRALOR DRALOR NAIS NAIS BOURNS SIEMEN IR IR IR IR IR IR SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN SIEMEN Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8.17. ECG PREAMP PROTECTION PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD Article no.: W141 2008 Description: ECG PREAMP PROTECT PCB Reference: W4P14 1723 Art no. 0-48-0001 Page 8-95 Version July 2001 A B 1 1 D C 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS +VFD -VFD +2.5VD R16 100 +VFD1 SP R11 1.21M R7 100K/VR68 R1 2K/RS5 -2.5VD -VFD1 C15 10uF/16V C14 10uF/16V R8 20K R4 R3 1K 3 R5 1K XX J3 2 3 + + 1 1 E2 90V R19 DZ2 8.2V L2 1.5uH R10 100K/VR68 + + 7 1 SP U1B TL062 R13 1M R2 2K/RS5 XX J4 6 5 R6 R9 20K R20 0 C6 XX C4 220pF/6KV SP U1A TL062 C5 XX 1K C3 220pF/6KV L1 1.5uH 1K DZ1 8.2V E1 90V R18 0 4 R12 1M C2 220pF/6KV 8 R17 C1 220pF/6KV 3 2 1 2 R15 100 DN1 BAV199 J1 +2.5VD R14 1.21M J2 4 4 1 DN2 BAV199 SP -2.5VD +VFD +VFD1 5 5 -VFD DZ4 3.9V DZ3 3.9V R22 100 R29 5.1K R23 100 J6 1 + 7 U2B TL062 2 3 8 2 3 6 7 1 4 + DZ6 TL431CD + 1 J7 1 -2.5VD -VFD SP R30 5.1K U2A TL062 C13 1.5nF 8 1 R28 100K -VFD1 7 7 R26 4.22K R27 100K SP 6 C12 1.5nF + J5 2 3 6 7 6 5 8 R24 9.09K 6 C11 100nF C10 100nF +VFD SP DZ5 TL431CD 22.1K C9 220pF R25 4.22K 1 +2.5VD C8 10uF/16V C7 10uF/16V R21 . DG501 . PROTECTION PREAMPLI ECG . ECG PREAMPLIFIER PROTECTION MODIFICATION RH DSK NO : ........ SHT NO : 1/1 B C D Art no. 0-48-0001 DWG NO : W4S141723-00 ECL00 18/10 00 1723-00.SCH Page 8-96 PRT NO : W4P141723 A APPROV 8 8 ART NO : W1412008 DRAWN Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS 8 6 7 5 4 3 1 2 D D U1 R3 C2 W4P141723 E1 E2 R5 J5 J4 J6 * DN2 R19 R20 J7 J3 R13 R14 L2 C6 R9 C12 R25 R26 C13 C3 J2 R10 R2 * DZ2 DZ1 R27 R4 C14 J1 R7 R6 C15 C C1 R1 R11 C5 R12 L1 * R8 * DN1 R17 R18 R30 R16 DZ5 R15 DZ6 R29 C C4 C8 R28 U2 R24 C9 DZ3 DZ4 R21 C11 R23 C10 R22 C7 B B * pas monté / not monted A A DG501 BIPHASIQUE Protection préampli ECG ECG preamplifier protection D RA W N APPROV RC RH 07/ 00 8 Art no. 0-48-0001 7 6 M O DIFICA TIO N ART : W 1412008 PRT : W 4P141723 DGW : W 4L141723 SHT : 1/1 07/ 00 5 Page 8-97 4 3 2 Version July 2001 1 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS COMPONENT LIST OF ECG PREAMP PROTECTION PCB W4P14 1723 POSITION C1 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C2 C3 C4 C7 C8 C9 CBL1 CBL2 CBL3 DN1 DN2 DZ1 DZ2 DZ3 DZ4 DZ5 DZ6 E1 E2 J1 J2 J3 J4 J5 J6 J7 L1 L2 P1723 R1 R10 R11 R12 R13 R14 R15 R16 R17 R19 R2 R21 R22 R23 ITEM 72651 8493 8493 21004 21004 51559 51559 72651 72651 72651 51559 51559 20994 W1411834 W1412042 W1412043 72501 72501 51774 51774 72245 72245 51832 51832 34883 34883 21456 21456 21456 21456 21456 21456 21456 22874 22874 W1404693 72637 72917 21348 21347 21347 21348 20724 20724 21352 21352 72637 21327 20724 20724 Art no. 0-48-0001 DESCRIPTION CAPA CERDI 220PF 6KV R12.5 CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 100N 50V 20% X7R CAPA SMD 1206 1.5N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD 1206 1.5N 50V 5% NPO CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA CERDI 220PF 6KV R12.5 CAPA CERDI 220PF 6KV R12.5 CAPA CERDI 220PF 6KV R12.5 CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD TANTAL 10U 16V 10% CAPA SMD 1206 220P 50V 5% NPO CONNECTING CABLE PREAMP/PREAMP PROTEC CBL WIRE ORG 1 FASTON 2.8-195MM CBL WIRE BC 1 FASTON 2.8-195MM DIODE SMD BAV199 SOT23 DIODE SMD BAV199 SOT23 DIODE Z SMD SOD80 8.2V DIODE Z SMD SOD80 8.2V DIODE Z SMD SOD80 3.9V DIODE Z SMD SOD80 3.9V IC 431/VREF TL431CD SO8 SMD IC 431/VREF TL431CD SO8 SMD SPARKER FUSE SPARKER FUSE ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM ACCBL PIN FORK PRT 1.0MM SELF SMD 1008 1.5UH 10% SELF SMD 1008 1.5UH 10% CI PROT PREAMP ECG DG501 BIPH RES BOB 2K 1% 5W 20PPM RES HT 100K 1% RES SMD 1.21M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1.21M 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 0 5% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 0 5% 0.25W 1206 RES BOB 2K 1% 5W 20PPM RES SMD 22.1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100 1% 0.25W 1206 Page 8-98 MANUFACTURER ROEDER VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM VITRAM SPRAGU SPRAGU ROEDER ROEDER ROEDER SPRAGU SPRAGU VITRAM W2652 OD3100 OD3100 SIEMEN SIEMEN PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP PHILIP TI TI SIEMEN SIEMEN VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT VOGT COILCR COILCR WUERTH DALE PHILIP BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS DALE BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS Version July 2001 8. COMPONENT LISTS, DRAWINGS AND DIAGRAMS R24 R25 R26 R27 R28 R29 R3 R30 R4 R5 R6 R7 R8 R9 U1 U2 20749 51291 51291 21335 21335 59887 20737 59887 20737 20737 20737 72917 33927 33927 51675 51675 3632 Art no. 0-48-0001 RES SMD 9.09K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.22K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 4.22K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 100K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 5.11K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 5.11K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 1K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES HT 100K 1% RES SMD 20K 1% 0.25W 1206 RES SMD 20K 1% 0.25W 1206 IC 062/OP TL062CD SO8 SMD IC 062/OP TL062CD SO8 SMD ACCBL CABLE CLAMP 2.5X89MM Page 8-99 BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS BOURNS PHILIP BOURNS BOURNS TI TI PANDUI Version July 2001 9. INDEX A O Abbreviations, components, 8-1 signals on diagrams, 8-2 Accessories, 1-11 Automated external defibrillator, 3-1 Automatic daily test, 4-2 Automatic test Upon switching on, 4-1 Optional features, 1-9 Ordering parts, 6-12 Overview, 1-1 P Power supply, 2-2 R B Replacement boards, 6-2 parts, 6-12 Battery charge, 2-3 Battery disposal, 1-3 Battery type, 1-3 Biocompatibility, 3-2 S Safety information, III instructions, 2-1 conventions, IV C Chart, 8-11, 8-12 Cleaning, 4-4 CPR, 3-1 T D Technical specifications, 1-3 Temperature, 1-8 Defibrillation waveform, 1-7 Diagrams, 8-13 Dimensions, 1-7 Disassembly, 6-1 V Verification Before use, 4-3 Weekly, 4-4 Yearly, 4-4 E Electromagnetic compatibility, III, 2-2 Electrostatic discharge, 6-1 ESD, 6-1 Exploded views, 6-13, 6-14 Explosive environment, 2-1 W Warning, II F Failures, 5-1 I Interconnections, 8-8 L LCD monitor, 1-5 Liquid penetration, 4-4 Lithium cell, 1-3 M Manual test, 4-2 Manual version, I Memory card, 1-5 Art. no. 0-48-0001 Page 9-1 Version July 2001