Download Miller Electric GPS-1000 Specifications
Transcript
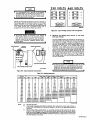
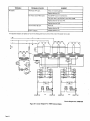
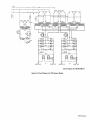
August 1979 FORM: OM-267A Effective With Serial No. HJ199959 MODEL G PS-bOO G PS-1500 OWNERS fullER MANUAL ~ MILLER ELECTRIC MFG. CO. 718 S. BOUNDS ST. P.O. Box 1079 APPLETON, WI 54912 USA ADDITIONAL COPY PRICE 55 CENTS NWSA CODE NO. 4579 PRINTED IN U.S.A. ~\ . t, t~% L&~ ~ L L~ LIMITED WARRANTY EFFECTIVE: JUNE 1. 1979 This warranty supersedes all previous MILLER warranties and is ex clusive with no other guarantees or warranties expressed or implied. LIMITED ( WARRANTY-Subject to the terms and conditions hereof, Miller Electric Mfg. Co., Appleton, Wisconsin warrants to its Distributor/Dealer that all new and unused Equipment furnished by Miller is free from defect in workmanship and material as of the time and place of delivery by Miller. No warranty is made by Miller with respect to engines, trade acother items manufactured by others. Such cessories or engines, trade accessories and other items are sold sublect to the warranties of their respective manufacturers, if any All engines are warranted by their manufacturer for one year from date of original purchase, . Except as specified below, Millers warranty does not apply components having normal useful life of less than one (1) such as spot welder tips, relay and contactor points, MILLERMATIC parts that come in contact with the welding As a of general policy only, Miller may honor claims by the original user within the foregoing periods. matter submitted In the case of Millers breach of warranty or any other duty with respect to the quality of any goods, the exclusive remedies therefore shall be, at Millers option Ii) repair or (21 replacement writing by Miller in appropriate cases, 13) repair or replacement at an authorized Miller service station or 14) payment of or credit for the purchase price Iless reasonable depreciation based upon actual use) upon return of the goods at Customers risk and expense. Upon receipt of notice of apparent defect or failure, Miller shall instruct the claimant on the warranty claim procedures to be followed. or, where authorized in the reasonable cost of ~ to year, including wire not nozzles and nozzle insulators where failure does result from defect in workmanship or material. Miller shall be required to honor warranty claims on warEquipment in the event of failure resulting from a defect within the following periods from the date of delivery of Equipment to the original user: ranted ANY EXPRESS WARRANTY NOT PROVIDED HEREIN AND WARRANTY, GUARANTY OR REPRESENTAPERFORMANCE, AND ANY REMEDY FOR BREACH OF CONTRACT WHICH, BUT FOR THIS PROVISION, MIGHT ARISE BY IMPLICATION, OPERATION OF LAW, CUSTOM OF TRADE OR COURSE OF DEALING, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED TION ANY AS TO IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR OF FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH RESPECT TO ANY AND ALL EQUIPMENT FURNISHED BY MILLER IS EX CLUDED AND DISCLAIMED BY MILLER. 1. 2. Arc welders, power sources and components Original main power rectifiers Ilabor 3. 4. .. 1 year only) feeder/guns - 5. Replacement Batteries or repair parts, exclusive of labor EXCEPT AS 90 . days 1 year 60 days 6 months EXPRESSLY MILLER WRITING, All welding guns and All other Millermatic Feeders 6. 1 year 3 years ULTIMATE PURCHASE BY EXPERIENCED WELDING IN THE EQUIPMENT USE AND CONSUMER USE. MILLER TO, of the date of such failure. MILLERS ,)-, .r ARE BY MILLER INTENDED IN FOR COMMERCIAL/INDUSTRIAL USERS AND FOR OPERATION BY PERSONS TRAINED AND provided that Miller is notified in writing within thirty 130) days ,~ PROVIDED PRODUCTS AND NO RESELLER AND MAINTENANCE NOT FOR CONSUMERS OF OR WARRANTIES DO NOT EXTEND IS AUTHORIZED WARRANTIES TO, ANY CONSUMER. TO EXTEND ? TABLE OF CONTENTS Page Section No. SECTION 1 1 1 - - 1. SAFETY RULES FOR OPERATION OF ARC WELDING POWER SOURCE Introduction 2. General Precautions 1-3. ArcWelding 1 4. Standards Booklet Index - SECTION 2 2 3. SECTION 3 3 4 5 Receiving-Handling Description 2-4. Safety - 1 1 INTRODUCTION 2-1. General 2- 2. No. 5 5 5 INSTALLATION 3-1. Location 6 3- 2. Electrical Input Connections 6 3 - 3. Weld Output Connections SECTION 4 4 4 - - 1. 8 OPERATION Power Control Switch 2. Overload Protection 8 9 4-3. Pilot Light 4-4. Meters 9 4-5. 9 SECTION 5 Duty Cycle 9 MAINTENANCE 5-1. FanMotor 9 5- 2. Internal 9 Cleaning 5- 3. Control Circuit Protection SECTION 6 TROUBLESHOOTING 9 S 1-SAFETY RULES FOR OPERATION OF ARC SECTION 1-1. learn by experience. Learning safety through personal experience, like a child touching a hot Stove (S harmful, wasteful, and unwise. Let the experience of others teach you. We Metals coated with or containing materials that emit toxic fumes should not be heated unless coating is removed from the work surface, the area is well ventilated, or the operator Safe practices developed from experience in the use of weld ing and cutting are described in this manual. Research, devel opment, and field experience have evolved reliable equipment and safe installation, operation, and servicing practices. Acci dents occur when equipment is improperly used or main tained. The reason for the safe practices may not always be given. Some are based on common sense, others may require technical volumes to explain. It is wiser to follow the rules. wears an and, if necessary, while a a wearing an confined space should be avoided. Leaked gas large quantities can change oxygen concentration danger ously. Do not bring gas cylinders into a confined space. Leaving confined space, shut OFF gas supply at source to prevent possible accumulation of gases in the space if down stream valves have been accidently opened or left open. Check to be sure that the space is safe before re-entering it. to Vapors from chlorinated solvents heat of the and These - - Reference standards: Published Standards on safety are Electrical Code, Occupational Safety and Administration, local industrial codes, and local in spection requirements also provide a basis for equipment in stallation, use, and service. National Health to form can be decomposed by the PHOSGENE. a highly toxic C. Fire and Explosion Prevention Causes of fire and explosion are: combustibles reached by the arc, flame, flying sparks, hot slag or heated material; misuse of compressed gases and cylinders; and short circuits. BE AWARE THAT flying sparks or falling slag can pass through cracks, along pipes, through windows or doors, and through wall or floor openings, Out of sight of the goggled operator. Sparks and slag can fly 35 feet. GENERAL PRECAUTIONS Burn Prevention leather (or asbestos) gauntlet protective clothing gloves, hat, and high safety-toe shoes. Button shirt collar and pocket flaps, and wear cuffless trousers to ~ioid entry of sparks and slag. Wear (Or flame) radiant energy can penetrate to atmospheres containing even minute amounts of trichloroethylene or perchloroethylene. also available for additional and more complete procedures than those given in this manual. They are listed in the Standards Index in this manual. ANSI Z49.1 is the most complete. arc other lung and eye irritating products. The ultra gas, violet (radiant) energy of the arc can also decompose tn chloroethylene and perchloroethylene vapors to form phos gene. DO NOT WELD or cut where solvent vapors can be drawn into the welding or cutting atmosphere or where the safe practices are divided into two Sections: 1 General Precautions, common to arc welding and cutting; and 2 Arc Welding (and Cutting)(only). A. being ventilated air-supplied respirator. confined space only while it is Work in observe these safe practices may cause serious in. jury or death. When safety becomes a habit, the equipment can be used with confidence. 1-2. air-supplied respirator. in Gas leaks in Read and understand these safe practices before attempting to install, operate, or service the equipment. Comply with these procedures as applicable to the particular equipment used and their instruction manuals, for personal safety and for the safety of others. The POWER SOURCE~ harmful concentrations of toxic fumes. Adequate local exhaust ventilation must be used, or each person in the area as well as the operator must wear an air-supplied respirator. For beryllium, both must be used. INTRODUCTION Failure WELDING - To prevent fires and explosion: Keep equipment clean and operable, free of oil, grease, and (in electrical parts) of metallic particles that can cause short circuits. glasses with side shields underneath, appropriate filter lenses or plates (protected by clear cover glass). This is a MUST for welding or cutting, (and chipping) to protect the eyes from radiant energy and flying metal. Replace cover glass when broken, pitted, or spattered. Wear helmet with safety goggles or See 1-3A.2. If combustibles are in area, do NOT weld or cut. Move the work if practicable, to an area free of combustibles. Avoid paint spray rooms, dip tanks, storage areas, ventilators. If the cannot Out ignition Avoid oily or greasy clothing. A spark may Hot metal such as electrode stubs and never be handled without gloves. Medical first aid and eye ignite be of shields. them. workpieces should First aid facilities and treatment. moved, move combustibles at least 35 feet reach of sparks and heat; or protect against with suitable and snug-fitting, fire-resistant covers or work away a qualified first aid person should be available for each shift unless medical facilities are close by for immediate treatment Walls touching combustibles on opposite sides should not be welded on (or cut). Walls, ceilings, and floor near work should be protected by heat-resistant covers or shields. Fire watcher must be standing by tinguishing equipment during and for ing or cutting if: with some suitable fire ex time after weld of flash burns of the eyes and skin burns. appreciable combustibles (including building construc tion) are within 35 feet b. appreciable combustibles are further than 35 feet but can be ignited by sparks c. openings (concealed or visible) in floors or walls within 35 a. Ear plugs should be wom when working on overhead or in a confined space. A hard hat should be worn when others work overhead. Flammable hair preparations should to weld or cut. not feet may expose combustibles to sparks be used by persons d. intending combustibles partitions B. Toxic Fume Prevention with oxygen. Lead -, cadmium similar -. zinc -, adjacent to walls, ceilings, roofs, or metal ignited by radiant orconducted heat. be Hot work permit should be ensure Adequate ventilation. Severe discomfort, illness or death can result from fumes, vapors, heat, or oxygen enrichment or depletion that welding (or cutting) may produce. Prevent them with adequate ventilation as described in ANSI Stan dard Z49.1 listed 1 in Standards index. NEVER ventilate and can mercury -, materials, when welded and beryllium - bearing (or cut) may produce supervisors obtained before operation to approval that adequate precautions have been taken. After work is done, check that embers, and flames. area is free of sparks, glowing An empty container that held combustibles, or that can pro. duce flammable or toxic vapors when heated, must never be welded on or cut, unless Container has first been Cleaned as described in AWS Standard A6.O, listed 3 in Standards index. OM-267 Page 1 thorough steam or caustic cleaning (or a washing, depending on the combustibles solubility) followed by purging and inerting with nitrogen or carbon dioxide, and using protective equipment as recom mended in A6.0. Waterfilling just below working level may substitute for inerting. includes: This solvent a water or unknown contents should be cleaned (see Do NOT depend on sense of smell or sight to determine if it is safe to weld or cut. A container with Protect cylinders particularly valves from bumps, falls, objects, and cylinders. weather. Replace Stuck Do NOT use valve. cylinder valve that supplier. a hammer not be can falling securely when moving caps or wrench to open opened by hand. Notify a your paragraph above). castings cutting. They Hollow or or can containers must be vented before welding gases. Never try to mix any gases in Mixing a cylinder. Never refill any cylinder. explode. Cylinder fittin~ should Explosive atmospheres. Never weld or cut where the air may contain flammable dust, gas, or liquid vapors (such as gaso line). 3. never be modified or exchanged. Hose Prohibited D. use. Never use hose other than that designed for the specified gas. A general hose identificatidn rule is: red for fuel gas, green for oxygen, and black for inert gases. Compressed Gas Equipment Standard precautions. Comply with precautions in this manual, and those detailed in CGA Standard P-i, PRECAU TIONS FOR SAFE HANDLING OF COMPRESSED GASES IN CYLINDERS, listed 6 in Standards index. Pressure 1. Use ferrules or clamps designed for the hose (not ordinary or other substitute) as a binding to connect hoses to wire fittings. No copper Regulators tubing splices. Use only standard brass fittings to splice hose. relief valve is designed to protect Only the regula from overpressure; it is not intended to protect any downstream equipment. Provide such protection with one or Regulator tor relief devices. more Never connect a regulator to a cylinder containing gas other than that for which the regulator was designed. Remove faulty regulator from service immediately for repair (first close cylinder valve). The following symptoms indicate a Avoid long runs to prevent kinks and abuse. Suspend hose off ground to keep it from being run over, stepped on, or other wise damaged. Coil excess hose to prevent kinks and tangles. Protect hose from damage by sharp slag, and open flame. edges, and by sparks, Examine faulty regulator: tions. Leaks if gas leaks externally. Excessive Creep if delivery pressure continues to rise with downstream valve closed. if gauge pointer does not move off stop pin Faulty Gauge when pressurized, nor returns to stop pin after pressure release. - hose regularly for leaks, wear, and loose connec Immerse pressured hose in water; bubbles indicate teaks. - - Repair. Do NOT attempt repair. Send faulty regulators for repair to manufacturers designated repair center, where special techniques and tools are used by trained personnel. 2. Cylinders Cylinders must be handled carefully to prevent teaks and damage to their walls, valves, or safety devices: Avoid electrical Circuit contact with cylinders including third rails, electrical wires, or welding circuits. They can produce short circuit arcs that may lead to a serious accident. (See Repair leaky or 4. hose by cutting worn (1-2D3). Do NOT use area Out and splicing tape. Proper Connections Clean cylinder valve outlet of impurities that may clog orifices and damage seats before connecting regulator. Except for hydrogen, crack valve momentarily, pointing outlet away from people and sources of ignition. Wipe with a clean lintless cloth. Match regulator to cylinder. Before connecting, check that the regulator label and cylinder marking agree, and that the regulator inlet and cylinder outlet match. NEVER CON NECT a regulator designed for a particular gas or gases to a cylindercontaining any other gas. 1-3C.) Tighten DOT marking must be on each cylinder. It is assurance of safety when the cylinder is properly handled. ICC or an Use only cylinders with name of gas Identifying gas marked on them; do not rely on color to identify gas con tent. Notify supplier if unmarked. NEVER DEFACE or alter connections. When assembling threaded connections, clean and smooth seats where necessary. Tighten. If connec tion teaks, disassemble, clean, and retighten using properly fitting wrench. content. name, number, or other markings on a cylinder. It is illegal Adapters. Use a CGA adapter (available from your supplier) between cylinder and regulator, if one is required. Use two wrenches to tighten adapter marked RIGHT and LEFT and hazardous. HAND threads. Empties: Keep valves closed, replace caps securely;mark MT; keep them separate from FULLS and return promptly. Regulator outlet (or hose) connections may be identified by right hand threads for oxygen and left hand threads (with grooved hex on nut or shank) for fuel gas. Prohibited use. Never use a cylinder or its than its intended use, NEVER as a support Locate or secure Passageways where and cylinders work so areas. they contents or cannot be Keep cylinders for other 5. roller. knocked over. clear of areas they may be struck. Transporting cylinders. With a crane, use a secure support as a platform or cradle. Do NOT lift cylinders off the ground by their valves or caps, or by chains, Slings, or mag such nets. Pressurizing Steps: Drain regulator of residual gas through suitable vent before opening cylinder (Or manifold valve) by turning adjusting screw in (clockwise). Draining prevents excessive compression heat at high pressure seat by allowing seat to open on pressur ization. Leave adjusting screw engaged slightly on single-stage regulators. Stand to side of regulator while opening cylinder valve. Open cylinder valve slowly so that regulator pressure in slowly. When gauge is pressurized (gauge reaches regu lator maximum) leave cylinder valve in following position: For oxygen, and inert gases, open fully to seal stem against possible leak. For fuel gas, open to less than one turn to permit quick emergency shutoff. creases Do NOT expose cylinders to excessive heat, sparks, slag, and etc. that may cause rupture. Do not allow contents to exceed 130F. Cool with water spray where such exposure exists. flame, Page 2 operation with low-reflective, non-combustible screens or panels. Allow for free air circulation, particularly at floor Use pressure charts (available from your supplier) for safe and efficient, recommended pressure settings on regulators. level. Check for leaks on first pressurization and regularly there or after. Brush with soap solution (capful of Ivory Liquid equivalent per gallon of water). Bubbles indicate leak. Clean off soapy water after test; dried soap is combustible. E. User F. Leaving Equipment Unattended source are wearing flash Before B. starting are in area. to weld, make Rope Staging-Support with precautions be used for welding or screen flaps or bay C. Fire and Explosion Prevention Comply with precautions Equipments equipment. Burn Protection Protective welding rated capacity. Do not overload arc It may overheat cables arid cause a fire. or flash and cause a Never strike an arc on a cylinder or other pressure vessel. It brittle area that can cause a violent rupture or lead to such a rupture later under rough handling. creates a D. in 1-2. Compressed Gas Equipment Comply with precautions The welding arc is intense and visibly bri~t. Its radiation can damage eyes, penetrate lightwei~t clothing, reflect from light-colored surfaces, and burn the skin end eyes. Skin burns resemble acute sunburn, those from gas-shielded arcs are GET BURNED; COMPLY more severe and painful. DONT WITH PRECAUTIONS. in 1-2C. Loose cable connections may overheat fire. standards referenced in index. Comply with precautions in 1-2B. cut Comply with precautions in 1-1, 1-2, and this section. Arc Welding, properly done, is a safe process, but a careless opera tor invites trouble. The equipment carries high currents at significant voltages. The arc is very bright and hot. Sparks fly, fumes rise, ultraviolet and infrared energy radiates, weld- E. in 1-2D. Shock Prevention Exposed hot conductors or other bare metal in the welding circuit, or in ungrounded, electrically-HOT equipment can fatally shock a person whose body becomes a conductor. DO NOT STAND, SIT, LIE, LEAN ON, OR TOUCH a wet sur face when welding, without suitable protection. Clothing To protect Wear long-sleeve clothing (particularly for gas-shielded arc) in addition to gloves, hat, and shoes (1-2A). As necessary, use additional protective clothing such as leather jacket or sleeves, flame-proof apron, and fire-resistant leggings. Avoid outergarments of untreated cotton. against shock: Keep body and clothing dry. Never work in damp area with out adequate insulation against electrical shock. Stay on a dry duckboard, or rubber mat when dampness or sweat can not be avoided. Sweat, sea water, or moisture between body reduces and an electrically HOT part or grounded metal the body surface electrical resistance, enabling dangerous and possibly lethal currents to flow through the body. - Bare skin protection. Wear dark, substantial clothing. Button collar to protect chest and neck and button pockets to pre vent entry of sparks. 1. 2. that Generator engine exhaust must be vented to the outside air. Carbon monoxide can kill. ARC WELDING 1. sure closed. Toxic Fume Prevention Comply meats are hot, and compressed gases may be used. The wise operator avoids unnecessary risks and protects himself and others from accidents. Precautions are described here and in A. See that all persons doors and drain gas. Rope staging-support should not ting operation; rope may burn. 1-3. persons who manual. Close gas supply at C. all Others working goggles. Responsibilities Remove leaky or defective equipment from service immed iately for repair. See User Responsibility statement in equip ment Viewing the weld. Provide face shields for looking directly at the weld. will be Grounding the - Equipment Eye and Head Protection installing, connect the frames of each unit such as welding power source, control, work table, and water circula tor to the building ground. Conductors must be adequate to carry ground currents safely. Equipment made electrically HOT by stray current may shock, possibly fatally. Do NOT GROUND to electrical conduit, or to a pipe carrying ANY gas or a flammable liquid such as oil or fuel. When Protect eyes from exposure tric arc without to arc. NEVER look at an elec protection. Welding helmet or shield containing a filter plate shade no. 12 or denser must be used when welding. Place over face before striking arc. Protect filter plate with a clear cover plate. Three-phase connection. Check phase requirement of equip before installing. If only 3-phase power is available, connect single-phase equipment to only two wires of the 3-phase line. Do NOT connect the equipment ground lead to the third (live) wire, or the equipment will become electri a dangerous condition that can shock, possibly cally HOT fatally. ment Cracked radiation or broken helmet can pass through or shield should NOT be worn; to cause burns. Cracked, broken, or loose filter plates must be replaced IM MEDIATELY. Replace clear cover plate when broken, pitted, or spattered. - Before side shields MUST be worn under the helmet to give some protection to the eyes should the helmet not be lowered over the face before an arc is struck. Looking at an arc momentarily with unprotected eyes (particularly a high intensity gas-shielded arc) can cause a retinal burn that may leave a permanent dark area in the field of vision. Flash 3. goggles with Protection of Nearby Personnel welding, check ground for continuity. Be sure conduc touching bare metal of equipment frames at connec tors are tions. line cord with a ground lead is provided with the equip connection to a switchbox, connect the ground lead to the grounded switchbox. If a three-prong plug is added for connection to a grounded mating receptacle, the ground lead must be connected to the ground prong only. If the line cord If a ment for with a three-prong plug, connect to a grounded mating receptacle. Never remove the ground prong from a plug, or use a plug with a broken off ground prong. comes Enclosed room or For production welding, a separate enclosed bay is best. In open areas, surround the welding area. Trademark of Proctor & Gamble. OM-267 Page 3 2. Do Electrode Holders not If, in open power circuit or change polarity while welding. emergency, it must be disconnected, guard against an flash from switch Fully insulated electrode holders should be used. Do NOT holders with protruding screws. shock burns, 3. connect all power to or arcing. use Leaving equipment unattended. Always equipment. Connectors Fully insulated lock-type welding cable lengths. connectors should be used to Power disconnect switch join power 1-4. 4. must shut OFF be available near and dis the welding source. STANDARDS BOOKLET INDEX Cables inspect cables for wear, cracks and damage. IMMEDIATELY REPLACE those with excessively worn or lethal shock from damaged insulation to avoid possibly bared cable. Cables with damaged areas may be taped to give resistance equivalent to original cable. Frequently For more information, their latest revisions and refer to the comply as following standards applicable: or - 1. ANSI Standard Z49.1, SAFETY IN WELDING AND CUTTING obtainable from the American Welding Society, 2501 NW 7th St., Miami, Fla. 33125. 2. ANSI Standard Z87.1, SAFE PRACTICE FOR OCCUPA TION AND EDUCATIONAL EYE AND FACE PROT~C TION, obtainable from American National Standards Institute, 1430 Broadway, New York, N.Y. 10018. 3. American Welding Society Standard A6.0, WELDING AND CUTTING CONTAINERS WHICH HAVE HELD COMBUSTIBLES, obtainable same as item 1. ELectrode wire becomes electrically HOT when the power switch of gas metal-arc welding equipment is ON and welding gun trigger is pressed. Keep hands and body clear of wire and other HOT parts. 4. Standard 51, OXYGEN-FUEL GAS SYSTEMS FOR WELDING AND CUTTING, obtainable from the Fire Protection Association, 470 Atlantic National Avenue, Boston, Mass. 02210. 7. 5. NFPA Standard 518, CUTTING AND WELDING PRO CESSES, obtainable same as item 4. 6. CGA Pamphlet P-i. SAFE HANDLING OF COM PRESSED GASES IN CYLINDERS, obtain~Ie from the Compressed Gas Association, 500 Fifth Avenue, New York, N. V. 10036. 7. OSHA Standard 29 CFR, Part 1910, Subpart 0, WELD ING, CUTTING AND BRAZING. Keep cable dry, free of oil and grease, and protected from hot metal and sparks. Terminals And Other Exposed Parts 5. Terminals and other exposed parts of electrical units should have insulating covers secured before operation. Electrode Wire 6. Safety Devices Safety devices such not be disconnected as or interlocks and circuit breakers should shunted out. Before installation, inspection, or service, of equipment, shut OFF all power and remove line fuses (or lock or red-t~ switches) to prevent accidental turning ON of power. Discon nect all cables from welding power source, and pull all 115 volts line-cord pIu~. Page 4 NFPA SECTION 2- INTRODUCTION Input At Rated Rated Model 1000 1500 Welding Current Amperes 100% Duty Cycle 1000@76 Volts 1500@76Volts 60 Hz. Three-Phase Open- Weight Amperes At Circuit Voltage Output Load Max. 230 Volts 85 224 330 85 (Pounds) Dimensions kva f460_Volts kw (Inches) Net Height-41-1(8 112 85 89 Width -27-1/4 896 Width -27-1/4 986 t Height-41-1/8 123 131 I I Depth -46 165 I Ship t 106811158 Depth -46 Figure 2-1. Specifications TB-080 172 Figure 2-1. 2-2. Functional This will help avoid possible iniury welding applications. GENERAL This manual has been prepared especially for use in familiar izing personnel with the design, installation, operation, main tenance, and troubleshooting of this equipment. All informa tion presented herein should be given careful consideration to assure optimum performance of this equipment. 2-2. Diagram due to misuse or improper The following definitions apply to CAUTION. IMPORTANT, and NOTE blocks found throughout this manual: RECEIVING-HANDLING Prior to installing this equipment, clean all packing material from around the unit and carefully inspect for any damage that may have occurred during shipment. Any claims for loss or damage that may have occurred in transit must be filed by the purchaser with the carrier. A copy of the bill of lading and freight bill will be furnished by the carrier on request if occasion to file claim arises. When requesting information concerning this equipment, it is essential that Model Description and/or Stock Number and Serial (or Style) Numbers of the equipment be supplied. I Under this heading, installation, ope rating, and main procedures or practices will be found that if carefully followed may create a hazard to per tenance not . sonnel. 1~A~1 U Under this heading, installation, operating, and main procedures or practices will be found that if carefully followed may result in damage to equip tenance 2-3. DESCRIPTION This incorporates a three phase Delta (CP) type main power connected, constant potential transformer to provide the constant voltage output required to operate the resistance grid welding stations connected to welding power source not I SAFETY Before the equipment is put into operation, the safety sec tion at the front of this manual should be read completely. I m the unit. 2-4. ment. I I Under this heading, explanatory statements will be found that need special emphasis to obtain the most efficient operation of the equipment. I OM-267 Page 5 SECTION 3 - INSTALLATION ELECTRICAL INPUT CONNECTIONS 3-2. Electrical Input Requirements A. welding power source is designed to be operated from a three-phase, 60 Hertz, ac power supply which has a line volt age rating that corresponds with one of the electrical input voltages shown on the nameplate. Consult the local electric utility if there is any question about the type of electrical This system available at the installation site or how proper tions to the welding power source are to be made. connec Input Conductor Connections B. m It is recommended that a line disconnect switch be input circuit to the welding power This would provide a safe and convenient source. means to completely remove all electrical power from the welding power source whenever it isnecessary to perform any internal function on the unit installed lncludlng 2-7/8 in the Uftlng Eye CAUTION TB-079 823 Figure 3-1. Overall Dimensions And Hole Layout 3-1. LOCATION Base Mounting making electrical input connections to the lockout welding power source, machinery procedures should be employed. If the connection is to be made from a line disconnect switch, the switch should be padlocked in the open position. If the (Figure 3-1) connection is made from a fuse box, remove the fuses from the box and padlock the cover in the closed position. If the unit is connected to a circuit breaker, A proper installation site should be selected for the welding power source if the unit is to provide dependable service, and remain relatively maintenance free. other disconnecting device without locking facilities, attach a red tag to the device to warn others that the circuit is being worked on. or A proper installation site permits freedom of air movement into and out of the welding power source, and also least subjects the unit to dust, dirt, moisture, and corrosive vapors. A minimum of 18 inches of unrestricted space must be main tained between the source front and rear Also,the underside of the be welding power kept completely free of obstructions. The installation site should also permit easy removal of the welding power source Outer enclosure for maintenance functions. panels and the welding power CAUTION nearest obstruction. source must ~ct source power IMPORTANT place any filtering device over the intake air passeges of the welding power source as this would restrict the volume of intake air and thereby subject the welding power source internal components to an to the welding power Supply. Table 3-1. condition and subsequent failure. War ranty is void if any type of filtering device is used overheating base for dimensions and input conductors The input conductors should be covered with an insulating material which conforms to local electrical standards. Table 3-1 is provided only as a guide for selecting the proper size input conductors and fuses. Do not Holes are provided in the welding power mounting purposes. FIgure 3-1 gIves overall the base mounting hole layout. the before making connections to the three.phase Input Conductor and Fuse Size Input Conductor Size- AWG source Model 11000 460 Volts 575 Volts 230 Volts 460 Volts 4/0 (2) 2 (8) 4 (8) 350 115 125 400 MCM (1/0) 2/0 (4) 1/0 (6) 500 250 225 Ampere j~OO Ampere Fuse Size In Amperes 230 Volts 575 Volts On for most welding power sources a lifting device is provided moving the unit. However, if a fork lift vehicle is used for lifting the unit, be sure that the lift forks are long enough to extend completely under the base. .fl~TA~ The use of lift forks too short to extend out of the opposite side of the base will expose internal com ponents to damage should the tips of the lift forks penetrate the bottom of the unit. Page 6 lnput conductor sizes are based on allowable ampacities of insulated copper conductors, having a temperature rating of 75C, with not more than three conductors in a raceway or cable. Numbers in ( ) are equipment ground conductor sizes. Insert the three input conductors plus one ground conductor the access hole on the rear panel. This hole will accept standard conduit fittings. See Figure 3-2 for hole loca through tion and size. 230 VOLTS It is recommended that a terminal lug of adequate amperage capacity be attached to the ends of the in put and ground conductors. The hole diameter in the terminal lug must be of proper size the line and ground terminal studs. to U accommodate . Connect the three input conductors to the line terminals on the contactor. Connect the ground conductor to the terminal labeled GROUND on the frame near the contactor. The 460 VOLTS ~0I 16 01 10 0IF~6I 10 l0 o o 01 O 10 01 10 61 tO 61 0 0 ~1 remaining end of the ground conductor should be connected a proper ground. Use a grounding method that is acceptable to the local electrical inspection authority. to 059 530 Figure 3-3. Input Voltage Jumper Link Arrangement ~ou nd power source on!y. Do terminal is chassis and not connect C. connec ted to the we Iding grounding purposes conductor from the ground a is terminal to any one of the line terminals as this will result in an electrically energized welding power source chassis. Matching The Welding Power Source To The Avail Voltage able Input for The input voltage jumper links provided on the primary ter minal board permit the welding power source to be operated from various line voltages. The various voltages from which this unit may be operated are stated on the nameplate and on . the input voltage label. The input voltage jumper links are positioned for the highest of the voltages stated on the nameplate. If the welding power source is to be operated from a line voltage which is lower than the highest voltage for which the unit was designed, the jumper links will have to be moved to the proper positions before operating the unit. Figure 3-3 shows the various positions of the jumper links on the standard welding power source. If the input voltages on the nameplate differ from those shown in Figure 3-3, the input voltage jumper links must be positioned as shown on the input voltage label. NOTE If only one jumper link is required on each of the grouped terminals, it is recommended that the unused jumper links be placed across the terminals which are to be used. This will prevent losing the jumper links which are not required for this connection. TB-079 825 Figure 3-2. Input Conductor Connections Table 3-2. Welding Total Amperes, DC 50 Welding Cable Lengt h 100 150 Size Of Cable I Copper) In W eld Circuit 200 250 300 350 400 100 4 4 2 2 2 1 1/0 1/0 150 2 2 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/b 3/0 200 1 1 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-2/0 250 1/0 1/0 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 300 2/0 2/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 350 3/0 3/0 4/0 400 3/0 3/0 3/0 500 4/0 4/0 3/0 4/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-2/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-3/0 2-3/0 24/0 600 4/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 700 4/0 4/0 2-3/0 800 2-2/0 2-2/0 900 2-3/0 2-3/0 2-3/0 2-3/0 2-4/0 2-4/0 2-4/0 500MCM 2-3/0 2-4/0 1000 1250 2-4/0 2-4/0 2-4/0 500MCM 2-3/0 2-4/0 2-4/0 1000MCM 500MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 500MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM I000MCM I000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 500MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1500 500MCM 500MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1750 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 2000 1000MCM 1000MCM 1000MCM 2-4/0 2-3/0 TA-052 764 NOTE: A. 50 FEET OR LESS. B. CABLE SIZE IS BASED ON DIRECT CURRENT (DC), 100% DUTY CYCLE AND EITHER A 4 VOLTS OR LESS DROP OR A CURRENT DENSITY OF NOT OVER 300 CIRCULAR MILS PER AMP. C. WELD CABLE INSULATION WITH A VOLTAGE RATING TO WITHSTAND THE OPENCIRCUIT VOLTAGE (OCV) OF THE WELDING POWER SOURCE MUST BE USED. WHILE MOST WELDING POWER SOURCES HAVE AN OPEN-CIRCUIT VOLTAGE OF LESS THAN 100 VOLTS, SOME WELDING POWER SOURCES OF SPECIAL DESIGN MAY HAVE HIGH ER OPEN-CIRCUIT VOLTAGE. OM-267 Page 7 3-3. WELD OUTPUT CONNECTIONS (Figure 3-4) To obtain the full rated output from this unit, it is necessary select, install, and maintain proper welding cables. Failure in any of these areas may result in loss than to comply ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' A B A B '~ ~ ~l to satisfactory welding performance. DC Nog~ti~e DC Po~iti~a DC Nog~tivo DC Positive B A A 079 746 1000 Ampere Models - B 1000 AMP POSITION 500 AMP POSITION U Ensure that the unit is completely shut down before making any weld output connections. DC DC Positive ' ' DC Positive Negative ' ' oc Negative ' ' __ A. Location The POSITIVE and NEGATIVE weld output terminals located on the lower portion of the front panel. B. are ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' A B A B A B A B 750 AMP POSITION Welding Cables were not followed ordered with this unit, the steps to the best welding ensure is C. recommended that and condition 2. Use Table 3-2 the of as a anticipated great extent dependent on the use and connections that are in good adequate size. to a guide for selecting maximum weld Output Connections Simultaneously, 500 amperes of weld output is available between one B Positive and B Negative output terminals of the 1000 ampere models. 750 amperes of weld output is available from the 1500 ampere models when similiar connections are made. When the weld output terminals are bused together, 1000 amperes of weld output is available between the A Positive and A Negative or B Positive and B Negative output terminals of the 1000 amperes models. 1500 amperes of weld output is available from the 1500 ampere models when similiar connections are made. These units are shipped with the bus bar in place. which is added to the voltage of the arc. Excessive cable resistance may result in overloading as well as reducing the maximum current output capability of this Unit. Prªper operation is welding cables Weld Output Connections When the weld output terminals are not bused together. 500 amperes of weld output is available between one A Positive and A Negative output terminals of the 1000 ampere models. the welding cables be kept as short as possible, be placed close together, and be of adequate current carrying capacity. The resistance of the welding cables and connections causes a voltage drop of Weld Figure 3-4. performau~ce: It 059 539 1500 Ampere Models if welding cables listed should be 1. 1500 AMP POSITION cable size for which will be from the welding correct current used, Table 3-2 shows total cable length power source to the resistance grid welding station. Select the size cable that is recommended for the maximum weld current that is to be used. 3. Do not 4. Use correct Iugs on the weld cables to connect them to the weld output terminals. 5. Ensure that all connections use damaged or frayed cables. ~05 it ive tput te rm inal of one sect ion of th is connected to the negative output terminal of the other section, two times the normal output voltage will exist between the remaining two terminals, Consult applicable safety codes. power are clean and source ou is ~output tight, SECTION 4 - OPERATION 4-1. POWER CONTROL SWITCH (Figure 4-1) Ammeter B B Voltmeter ~ssing not the POWER CONTROL STOP button does power from all of the welding power internal circuitry. Completely terminate all remove source electrical to the welding power source by power lockout procedures before employing machinery attempting any inspection or work on the inside of the unit. If the welding power source is connected to a disconnect switch, padlock the switch in an open position. If connected to a fuse box, remove the fuses and padlock the cover in the closed position. If the unit is connected to a circuit breaker, or other disconnecting device without locking facilities, attach a is red tag to the device to being worked on. Depressing DC Positive DC Negative TB-079 824 Figure Page 8 4-1. Front Panel the POWER warn others that the circuit CONTROL START button will energize the welding power source and place the unit in a ready-to-weld status. The START button must be held in momentarily to ensure that the fan is running at operating speed. Depressing the POWER CONTROL STOP button will shut the welding power source down. 4-2. OVERLOAD PROTECTION Thermostat TP1, located in the main transformer, is wired into the contactor W coil circuit. Should overheating occur, TP1 would open causing the contactor to drop out thereby suspending all operations. If TP1 opens, allow the unit to cool before resuming operations. Circuit breaker CB protects the welding power source from excessive secondary current draw. Current transformer CT1 and CT2, located in the secondary of the main transformer, sense the secondary current draw. Should overloading occur, CB would open causing the contactor to drop Out thereby suspending all operations. 2000 MODEL 1500 GPS-1500 U UI < 0 z 0 -J UI GPS -10 00 1000 To place the welding power source in a ready-to-weld status should this circuit breaker trip, the circuit breaker should be manually reset. Should the circuit breaker continue to trip after each reset, an internal problem in the circuitry is most probably present. Do not attempt any further welding until the trouble has been remedied. 40 4-4. welding 70 80 90 100 B.079 809 Figure 4-2. Duty Cycle Chart DUTY CYCLE The duty cycle of a welding power source is the percentage of a ten minute period that a welding power source can safely be operated at a given output. This welding power source is rated at 100 percent duty cycle. This means that the welding power source can be safely operated at rated load contin uously. Figure 4-2 enables the operator to determine the safe output of the welding power source at various duty cycles. PILOT LIGHT The pilot light PL1 indicates when the is in a ready-to-weld status. 60 % DUTY CYCLE 4-5: 4-3. 50 power source METERS The meters They are are provided intended for not to monitor the I welding operation. exact current or voltage IMPORTANT measure These meters are internally connected to the output terminals. The voltmeters will indicate the voltage at the output terminals, but not necessarily the actual voltage at the welding arc (due to cable resistance, poor connections, etc.). The ammeters will indicate the current output of the unit. ments. Exceeding the heating and indicated duty cycle thereby damage to will cause over- the welding power source. SECTION 5- MAINTENANCE factured with lifetime-lubricated sealed ball bearings and I attention should be 5-2. the POWER CONTROL STOP button does remove power from all of the welding power no required. INTERNAL CLEANING Depressing not internal circuitry. electrical power to the source Completely terminate Occasional blowing out or vacuuming of the dust and dirt from around the internal components is recommended. This should be done periodically depending upon the location of the unit and the amount of dust and dirt in the atmosphere. The welding power source outer enclosure should be removed and a clean, dry air stream or vacuum suction should be used for this cleaning operation. all welding power source by lockout procedures before machinery attempting any inspection or work on the inside of the unit. If the welding power source is connected to a disconnect switch, padlock the switch in an open position. If connected to a fuse box, remove the fuses and padlock the cover in the closed position. If the unit is connected to a circuit breaker, or other disconnecting device without locking facilities, attach employing a red tag to the device to worked on. warn 5-3. The entire control circuit of the welding power source is protected by a 600 volt, 3 ampere, cartridge type fuse Fl. This fuse is located under the top cover beside contactor W. Should this fuse open, the welding power source would completely shut down. others that the circuit ~~ing 5-1. CONTROL CIRCUIT PROTECTION FAN MOTOR All models are equipped with an exhaust fan and rely on forced draft for adequate cooling. The fan motor is manu SECTION 6 U I- - TROUBLESHOOTING volta~ Hazardous the internal on present circuitry of the welding power source as long as power is connected to the unit. Disconnect power before attempting any inspection or work on the inside of the unit. Troubleshooting of internal circuitry should be performed by qualified personnel only. The following remedies for welding power is designed to diagnose and provide of the troubles that may develop in this chart some It is proper installation has been made, 3 of this manual, and that the welding has been functioning properly until this trouble assumed according that to Section power source developed. Use this chart in conjunction with the circuit diagram while performing troubleshooting procedures. If the trouble is not remedied after performing these procedures, the nearest Factory Authorized Service Station should be contacted. In all of equipment malfunction, the manufacturers cases recommendations should be strictly followed. source. OM-267 Page 9 TROUBLE PROBABLE CAUSE No output. Thermostat TP1 open. REMEDY Allow unit a cooling period. Replace defective TP1. . Fan motor switch FMS is open. Hold START button in momentarily. Fan motor rpm is too slow due to low input Replace defective fan voltage. motor FM. Replace defective FMS. Circuit breaker CB open. Reset CB. Replace defective CB. Fuse Fl is blown. 1f it becomes necessary to replace any fuse in the welding Replace defective Fl. power source, ensure that a fuse of the proper size is used. Circuit Figure 6-1. Circuit Diagram For 1000 Ampere Models Page 10 Diagram No. B-080 675 POSITIVE Circuit Diagram No. CB-902 388-lA Figure 6-2. Circuit Diagram For 1500 Ampere Models OM-267 Page 11 August1979 FORM: OM-267A Effective With Serial No~ HJ199959 MODEL GPS-1000 GPS-1500 PARTS LIST 13 Figure A OM-267 Page 1 Left Side View Quantity Item No. Dia. Mkgs Figure 1 059572 059592 4 W 4 W Wi 036630 059720 *079 507 079506 004104 *004258 004259 034821 *6()4259 5 6 Fl 7 SR1,11 VS 1,2 D1-6, 079827 024 471 11-16 037 157 Cl -6 11-16 031 689 SR1,11 059 685 7 1000 1500 Description Left Side View 2 T2 ________ Part No. A 3 Model Factory 012638 COVER, opening exit cable PANEL, rear TRANSFORMER, control 100VA 115-230/460 CONTACTOR, 120 amp 3 pole 600 volts (consisting of) KIT, contact point COIL, contactor 120/240 volts CONTACTOR, 210 amp 3 pole 600 volts w/ 115 volts ac (consisting of) KIT, contact point COIL, contactor 120 volts ac INTERLOCK, contactor normally open FUSE, cartridge 3 amp 600 volts HOLDER, fuse cartridge 30 amp 600 volts RECTIFIER, silicon diode (consisting of) SUPPRESSOR, 1 uf 2.7 ohm - - - . . DIODE, rectifier 275 amp 250 volts straight polarity 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 12 CAPACITOR, ceramic0.01 uf500voltsdcw/3/16&1/4terminals 6 RECTIFIER, silicon diode (consisting of) 2 Cl -6 11-16 031 689 . CAPACITOR, ceramic 0.01 uf 500 volts dc w/3/16 & 1/4 terminals 6 Dl -6 11-16 8 9 9 10 11 12 Vl,2 A1,2 Al,2 PB1 PL1 CB 13 15 16 DIODE, rectifier 275 amp 250 volts straight polarity METER, volt dc 0-100 scale METER, amp dc 5OMV 0-800 scale METER, amp dc 5OMV 0.1K scale SWITCH, push button start stop 60 amp 110 volts BULB, incandescant slide base 120 volts 2 2 - HOUSING, light - slide base 125 volts LENS, light 034945 CIRCUIT BREAKER, manual reset 2P 5 amp 240 volts BAFFLE, air top rectifier red clear - ac - 059616 BRACKET, mounting terminal board 079388 SHUNT, meter5oMV800amp 030635 SHUNT, meter 5OMV 1000 amp 059567 TERMINAL ASSEMBLY, power output 601841 NUT, brass-hexjam 5/8-11 601842 NUT, brass hex full 5/8-11 059566 TERMINAL BOARD, power output 038909 .STUD,brass5/8-11 x3 602249 WASHER, flat steel SAE 5/8 602219 WASHER, lock steel external tooth 038032 BUS BAR 059983 BUS BAR, jumper secondary - Shunt Shunt - 18 2 2 - 027 628 059563 14 15 037 157 025638 059118 059 120 011 636 *027 629 027 631 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 (consisting of) - - - - - 1 16 8 2 8 1 16 82 8 8 8 8 4 4 8 2 *Recommended Spare Parts. BE SURE TO PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. OM-267 Page 2 -31 ~1 1 Figure Page3 B Right Side View Quantity Item Dia. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. Figure 28 R1,11 R2,12 SR2,12 C8,18 C7,17 29 TEl TE2 30 31 32 FM FMS 33 34 Ti 34 Ti 35 35 CT1,2 CT1,2 TP1 **Replace Right Side B 27 at Model Description 009139 059 605 030 691 604288 037 513 031 640 601 375 031 683 059 555 038 897 602 221 010 910 601837 038 621 038804 038 898 038 620 059585 014 425 032616 032 633 011 850 052 613 059676 079 718 059 575 **079 719 **059 576 **079 529 059 574 080075 036612 026 181 059 559 003 107 010014 026 627 Factory or 100011500 View VISOR,front-top 1 1 PANEL, front 1 1 RESISTOR, carbon 2 1 watt4700 ohm RESISTOR,WWfixedl0watt2ohm RECTIFIER, selenium control CAPACITOR, electrolytic 500 uf 200 volts dc RING, mounting capacitor CAPACITOR, paperoiiO.5uf200voltsdc TERMINAL ASSEMBLY, primary (consisting of) TERMINAL BOARD, primary WASHER, lock steel internal tooth 3/8 WASHER, flat steel SAE 3/8 .NUT,brass-hex3/8-16 BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 4 pole .STUD,brass3/8-16x2-1/2 LINK, terminal connecting LINK, jumper terminal block 30 amp WINDTUNNEL,20inch BAR, support windtunnel BLADE,fan60Hz20inch3wing2l degree MOTOR, 1/4 hp 230 volts ac 1625 RPM (consisting of) SWITCH, centrifugal (GE Motor) or SWITCH, starting (Emerson Motor) 2 2 2 2 - . - . - . . - . - . - . . BASE . 1 1 1 12 12 12 12 36 36 1 1 12 12 6 1 6 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (consisting of) 1 main (consisting of) TRANSFORMER SUBASSEMBLY TRANSFORMER SUBASSEMBLY 1 TRANSFORMER, TRANSFORMER, . 2 1 power power - main 1 - COIL, primary/secondary COIL, primary/secondary TRANSFORMER, current300/5 TRANSFORMER,current800/5 THERMOSTAT, normally closed (located in coils) PANEL, side COVER, top . 1 6 6 . 2 2 6 2 1 CLAMP GASKET, lifting eye 6 2 1 2 - cover 1 1 Factory Authorized Service Station. BE SURE TO PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. OM-267 Page 4