Download ADDER ALIF 2112T User guide
Transcript
AdderLink Infinity 2112T User Guide Experts in Connectivity Solutions KVM Extension Solutions Configuration System and Teaming ports: Initial configuration............................................16 Manual factory reset.....................................................................................16 AdderLink Infinity browser-based configuration utility........................17 A rough guide to configuring TX and RX units......................................18 TX (transmitter) unit configuration....................................................18 RX (receiver) unit configuration..........................................................19 Performing an upgrade.......................................................................................21 Options switches.................................................................................................21 Getting assistance...............................................................................................24 Appendix A - Transmitter (TX) unit configuration pages...........................25 Appendix B - The VNC port: Initial configuration........................................32 Appendix C - Tips for success when networking ALIF units.....................40 Appendix D - Troubleshooting.........................................................................42 Appendix E - Glossary.......................................................................................44 Appendix F - Configuration menus (via VNC).............................................47 Appendix G - VNC viewer connection options...........................................59 Appendix H - VNC viewer window options.................................................62 Appendix I - Java viewer options.....................................................................63 Appendix J - The KVMADMIN utility.............................................................64 Appendix K - Known working video modes................................................65 Appendix L - Hotkey sequences......................................................................66 Appendix M - Cable pinouts, video modes and general specifications...67 Appendix N - Fiber modules and cables........................................................68 Warranty...............................................................................................................69 Safety information...............................................................................................69 Radio frequency energy.....................................................................................70 CONFIGURATION Mounting.................................................................................................................8 Connections...........................................................................................................9 VNC network link.........................................................................................10 Video link........................................................................................................11 Audio links......................................................................................................12 USB link...........................................................................................................12 AUX port........................................................................................................13 Power in..........................................................................................................13 High speed links.............................................................................................14 Further information OPERATION Installation Front panel indicators........................................................................................22 Using the VNC viewer.......................................................................................23 FURTHER INFORMATION Welcome.................................................................................................................2 ALIF features..........................................................................................................3 AdderLink dual 2112T unit features.................................................................5 Supplied items........................................................................................................6 Optional extras......................................................................................................7 Operation Index INDEX Introduction INSTALLATION Contents 1 One-to-many configuration Using multicast techniques, an unlimited number of receivers* can receive video and audio data streams from a single TX unit. * A maximum of thirteen concurrent USB inputs (via multiple RX units) are permitted to a single TX unit. Mixing ALIF and ALIF dual units ALIF 2112T transmitters are complimentary to the standard AdderLink Infinity (1000 series) models which do not support dual DVI channels or fiber optic linking. It is possible to mix ALIF, ALIF dual and ALIF 2112T units on a network. However, whenever the two types are cross connected, the extra abilities of the ALIF dual/ALIF 2112T units will be temporarily disabled. CONFIGURATION One-to-one configuration The simplest configuration links one RX unit to a single TX unit, either by a direct link or over much greater distances via a high speed network. In both cases, Gigabit cable linking and/or fiber can be used. When both are deployed, connection speeds of up to 2 Gigabits are possible. OPERATION Thank you for choosing the AdderLink Infinity dual 2112T transmitter, otherwise known as ALIF 2112T. ALIF 2112T represents a major advance in the capabilities of digital extenders and switches. By encoding high quality DVI video, digital audio and USB connections into Internet Protocol (IP) messages, ALIF dual offers very flexible signal switching and distribution capabilities. Adder’s extensive knowledge of interfacing techniques and high speed networking has allowed us to develop new ways to break the chains of local DVI, USB and audio connections. With ALIF dual, distance is finally no barrier to high specification, high performance computing. Furthermore, since all signals are now IP, the most elaborate and yet simple-to-use switching and multicast techniques make possible a great variety of uses. In concert with a suitable ALIF receiver unit, the ALIF 2112T transmitter supports either two single link DVI video streams or one dual link (very high resolution) DVI video stream. This is in addition to a microphone, speakers and multiple USB peripherals. The distance between them is limited only by the size of your network. ALIF 2112T provides a choice of link connections. Each unit supports both copper-based Gigabit Ethernet cabling as well as Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE). These can be used in parallel to provide up to 2 Gigabit connection speeds with the added benefit of link redundancy that can maintain operation in the event of a failed connection. Additionally, the ALIF 2112T has an in-built VNC server which allows it to stream lowbandwidth versions of its high-resolution output (via a dedicated Ethernet port on the front panel) so that it may be accessed remotely, via a VNC viewer, through any standard network. Low bandwidth VNC connection Up to sixteen remote users can log in via standard networks to view the output from the ALIF 2112T. FURTHER INFORMATION WELCOME INSTALLATION Introduction ALIF and A.I.M. Where multiple ALIF units are used on a network, we have developed the AdderLink Infinity Management (A.I.M.) server to allow comprehensive and secure central control of all transmitters, receivers and users. When using an A.I.M. server to configure ALIF units, it is vital that all ALIF units that you wish to locate and control are set to their factory default settings. Otherwise they will not be located by the A.I.M. server. If necessary, perform a factory reset on each ALIF unit. MANAGEMENT SERVER ADM USR UNC ETH1 ETH2 PWR ADM USR UNC ETH1 ETH2 PWR INDEX AdderLink www.adder.com Please also see Appendix C - Tips for success when networking ALIF units 2 ALIF FEATURES New feature: AFZ+ codec AFZ+ compliments the existing AFZ codec by providing greater compression for increased speed where pixel perfect results are not the primary focus. The transmitter video configuration page allows you to choose the required compression mode. Choices are: • ‘Pixel perfect’ - only uses pixel perfect AFZ, • ‘Adaptive’ - guarantees frame rate, builds to pixel perfect, • ‘AFZ only (pixel perfect), • ‘Smoothest video’ - forces the maximum compression, or • ‘AFZ+ Minimum compression’, • ‘Advanced’ - allows you to choose the mode: • ‘AFZ+ Middle compression’, or • ‘AFZ+ Maximum compression’. ALIF units support the industry standard Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. This offers protection against eavesdropping and tampering by third parties when data are transferred between ALIF transmitters and receivers across networks (and also between ALIF units and AIM servers). INSTALLATION Transport Layer Security (TLS) CONFIGURATION The AFZ compression scheme is primarily focused on improving the performance for “natural” images (i.e. photographs and movies) and is automatically selected whenever there is a benefit to do so. The AFZ codec is lossless and is very low latency (a small fraction of a frame delay). It generally achieves 50% improvement (in compression) over the RLE scheme for any areas of the screen that consist of images, gradients, shadows etc., elements commonly found in modern desktop environments. To maintain compatibility with non AFZ -enabled transmitters and receivers there is an automatic switching method which will revert back to RLE compression when an ALIF (1000) receiver is connected. OPERATION AFZ lossless codec INDEX The Magic Eye feature increases performance and reduces network traffic when ALIF units are used with Apple Macs and other host computers that have dithered video output. It also improves performance if the video source is noisy (e.g. from a VGA-to-DVI converter). Dithering is a technique used by some graphics cards to improve perceived image quality by continuously varying the color of each pixel slightly. This gives the illusion of more shades of color than the display can really reproduce, and smooths the appearance of gradually shaded areas in images. Unfortunately dithering is an issue for KVM extenders such as ALIF because it makes the image appear to be changing all the time even when it is static, thus creating much more network data than can be carried by a Gigabit Ethernet. The result is a reduction in video frame rate, which the user sees as slow mouse response. Magic Eye works by ignoring small variations in the video from frame to frame. It is enabled by default as it is not obvious to the user that his poor mouse behaviour is caused by dithering. In most cases Magic Eye is invisible, but it can produce slight color inaccuracies on the monitor. For full color accuracy, Magic Eye can be disabled for video sources which are not dithered or noisy. FURTHER INFORMATION Magic Eye (anti-dither support added) 3 CONFIGURATION OPERATION ...and also in multicast installations: FURTHER INFORMATION Teaming offers immediate speed improvements in a one-to-one arrangement... INDEX The System and Teaming ports of ALIF units can be used in parallel to produce two important benefits: • Improved connection speeds up to 2 Gigabits per second, and • Important link redundancy that can maintain operation in the event of a failed connection. INSTALLATION Teaming operation 4 ADDERLINK DUAL 2112T UNIT FEATURES The ALIF 2112T units are housed within durable, metallic enclosures with most connectors situated at the rear panel - the Ethernet ports are situated on the front panels. The smart front faces also feature the operation indicators. Front INSTALLATION Rear INDOOR USE ONLY DVI-D-1 OPTIONS DVI-D-2 AUX 1 2 VNC port Teaming port Indicators System (Gigabit Ethernet) port These six indicators clearly show the key aspects of operation: • VNC On when a valid network is present on either the teaming or system port. Flashes to indicate that a VNC connection is present. • SER On when the AUX (serial) port is enabled and active. • AUD On when audio is enabled and active. • USB On when USB is enabled and active. • DVI 2.5A IN 1 2 Power input Options switches (further details) OUT COMPUTER USB port Primary video input Secondary video input Audio line in/out AUX (serial) port OPERATION 5V CONFIGURATION ON On when either or both DVI Video channels are enabled. INDEX FURTHER INFORMATION • PWR Power indicator. 5 SUPPLIED ITEMS INSTALLATION Power adapter (20W) and country-specific power cord Combined DVI-D and USB cable (1.8m) CONFIGURATION Single link DVI-D to DVI-D video cable OPERATION ALIF 2112T transmitter unit Serial null modem cable 2m FURTHER INFORMATION Four self-adhesive rubber feet Quick start guide Safety document INDEX Information wallet containing: 2 x Audio cable 2m (3.5mm stereo jacks) 6 Single mode fiber SFP module Part number: SFP-SM-LC Please refer to the table in Appendix M for information about fiber modules and cables. Single link DVI-D to DVI-D video cable Part number:VSCD1 Combined dual link DVI-D and USB (USB type A to B) cable Part numbers: VSCD3 (1.8m length) VSCD4 (5m length) OPERATION Multi mode fiber SFP module Part number: SFP-MM-LC Active copper SFP module Part number: SFP-CATX-RJ45 USB cable 2m (type A to B) Part number:VSC24 FURTHER INFORMATION Power adapter (20W) and country-specific power lead Part number: PSU-IEC-5VDC-4AMP Audio cable 2m (3.5mm stereo jacks) Part number: VSC22 Serial null modem cable 2m Part number: CAB-9F/9F-NULL-MODEM INDEX Two 19” rack-mount brackets and four screws Part numbers: One unit per 1U rack slot: RMK4S Two units per 1U rack slot: RMK4D CONFIGURATION INSTALLATION OPTIONAL EXTRAS 7 Installation MOUNTING INSTALLATION There are two main mounting methods for transmitter and receiver units: • The supplied four self-adhesive rubber feet • Optional rack brackets Connections OP TIO 1 5V NS LIN E MI IN/ CI N LI NDEV IO -DU T 2 2.5 SAE 1 2 RC ON SO LE FURTHER INFORMATION IN US DOO EO R NL Y AU X US ER LIN E MI IN/ CI N LI N EO CO INDEX Note:The ALIF 2112T and its power supply generate heat when in operation and will become warm to the touch. Do not enclose them or place them in locations where air cannot circulate to cool the equipment. Do not operate the equipment in ambient temperatures exceeding 40oC. Do not place the products in contact with equipment whose surface temperature exceeds 40oC. OPERATION The optional brackets (plus four screws), allow the units to be secured within a standard rack slot. CONFIGURATION Rack brackets 8 CONNECTIONS OPERATION CONFIGURATION INSTALLATION Installation involves linking the ALIF 2112T unit to various ports on the host computer, while an ALIF RX unit is attached to your peripherals: INDEX IMPORTANT: When using an AdderLink Infinity Management box to configure ALIF units, it is vital that all ALIF units that you wish to locate and control are set to their factory default settings. Otherwise they will not be located by the A.I.M. server. If necessary, perform a factory reset on each ALIF unit. Please also see Appendix C - Tips for success when networking ALIF units FURTHER INFORMATION Click a connection to see details 9 2 Connect the other end of the cable to an Ethernet switch. INDEX From your Ethernet switch FURTHER INFORMATION OPERATION To make a VNC link 1 Connect a CAT 5, 5e, 6, or 7 cable to the socket on the front panel of the ALIF unit. CONFIGURATION The ALIF 2112T contains a VNC server that allows you to transmit a low-bandwidth version of the video output across standard networks to authorized remote viewers. The VNC link can either be made over the same network as the main ALIF output or via a separate one. In either case, a separate VNC network port is located on the left side of the ALIF 2112T front panel for the purpose. INSTALLATION VNC network link 10 Video link INSTALLATION ALIF dual units can simultaneously support up to two Single Link high resolution video displays at pixel clocks up to 165MHz; or can alternatively support a single Dual Link very high Resolution video display at pixel clocks up to 330MHz (equating to an example display mode of 2560 x 1600 at 60 Hz refresh). D-1 To primary video output port DV I- D-2 D-1 DV I- D-2 UT ER Note:When using one very high resolution DVI-D dual link display, use a DVI-D Dual Link cable (such as the supplied Adder part:VSCD3) to connect the primary video port of the computer system to the DVI-D-1 connector of the ALIF dual. A dual link cable must also be used at the RX unit. 3 Connect the plug at the other end of the cable(s) to the corresponding DVI-D video output socket(s) of the host computer. CO MP UT ER FURTHER INFORMATION MP DV I- To primary video output port To secondary video output port INDEX CO Note:When using two single link DVI-D displays, connect an additional video input from the secondary video port of the computer system using the supplied secondary DVI-D link cable. OPERATION DV I- CONFIGURATION To make a video link 1 Wherever possible, ensure that power is disconnected from the ALIF and the host computer. 2 Connect either one or two digital video link cables to the DVI-D socket(s) on the TX unit rear panel: 11 Audio links USB link To make audio links 1 Connect an audio link cable between the IN socket on the TX unit rear panel and the speaker output socket of the host computer. To make a USB link 1 Connect the type B connector of the supplied USB cable to the USB port on the TX unit rear panel. TIO 1 AU X 1 NS 2 2 IN Speaker link from host computer OU T USB link from host computer Microphone link to host computer 2 [Where a microphone is to be used]: Connect a second audio link cable between the OUT socket on the TX unit rear panel and the Line In socket of the host computer. CONFIGURATION OP 2 Connect the type A connector of the cable to a vacant USB socket on the host computer. OPERATION D-1 FURTHER INFORMATION DV I- INSTALLATION ALIF dual units act as USB 2.0 hubs and so can provide four sockets at the RX unit with only a single connection at the TX unit. INDEX ALIF dual units support two way stereo digital sound so that you can use a remote microphone as well as speakers. 12 Power in To connect the AUX port 1 Ensure that power is removed from the ALIF unit. 2 Connect a suitable serial ‘null-modem’ cable (see Appendix M for pin-out) between a vacant serial port on your computer and the AUX port on the right hand side of the ALIF dual rear panel. To apply power in 1 Attach the output lead from the power adapter to the 5V socket on the rear panel of the unit. T 1 5V AU X A Power cord from adapter Serial (null-modem) link from your computer 2.5 1 Note: Ensure that Options switches 1 and 2 are both in the ‘OFF’ (up) position to enable normal operation of the unit. See Options switches for details. 2 Connect the IEC connector of the supplied country-specific power cord to the socket of the power adapter. 3 Connect the power cord to a nearby main supply socket. Note: Both the unit and its power supply generate heat when in operation and will become warm to the touch. Do not enclose them or place them in locations where air cannot circulate to cool the equipment. Do not operate the equipment in ambient temperatures exceeding 40oC. Do not place the products in contact with equipment whose surface temperature exceeds 40oC. OPERATION OP FURTHER INFORMATION IN US DOO EO R NL Y CONFIGURATION Each ALIF dual unit is supplied with a power adapter and country-specific power cord. When all other connections have been made, connect and switch on the power adapter unit. INDEX The AUX port is an RS232 serial port that allows extension of RS232 signals up to a baud rate of 115200. The port has software flow control, but no hardware flow control. INSTALLATION AUX port 13 High speed links Optional Fiber Channel or Active Copper SFP module CAT 5, 5e, 6, or 7 link either directly from the other ALIF unit or from a Gigabit Ethernet switch 2 Make your connection(s) between the chosen SFP module and either the other ALIF dual unit or a suitable network switch: Connect the transmit and receive fiber optic links to the sockets on the Fiber Channel SFP module. Then close the latch over the link connectors to lock them into place. Transmit and receive fiber links 2 Connect the other end of the cable either to the other ALIF dual unit or to a Gigabit Ethernet switch, as appropriate. 3 [For connections via a network] repeat steps 1 and 2 for the other ALIF dual unit. Cable and fiber details • For direct links over Ethernet cable, the length of cable should not exceed 100 metres (328 feet). Network cables used for connections may be category 5, 5e, 6 or 7 twisted-pair cable. ALIF 2112T units have an autosensing capability on their network interfaces, so for direct point-to-point connections, no ‘crossover’ Ethernet cable is required. • For direct links via fiber, varying distances can be achieved depending on the module and cable types used. Please refer to the table in Appendix N for detailed information. The fiber links must have crossovers. or Connect a CAT 5, 5e, 6, or 7 cable to the socket on the Active Copper SFP module. CAT 5, 5e, 6, or 7 link CONFIGURATION IT OPERATION To link ALIF dual units using the System port 1 Connect a CAT 5, 5e, 6, or 7 cable to the System port socket on the front panel of the TR AN ALIF dual unit. SM FURTHER INFORMATION 1 Insert the appropriate optional SFP module (SFP-MM-LC, SFP-SM-LC or SFP-CATX-RJ45) into the aperture on the ALIF dual front panel: Please see Appendix C for important tips about networking ALIF units. INDEX To link ALIF dual units using the Teaming port INSTALLATION ALIF dual (inc 2112T) units can be either connected directly to each other or via a high speed network. The connections can be copper-based Gigabit Ethernet as well as Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE). These can be used in parallel to provide up to 2 Gigabit connections speeds. A single System port (Gigabit Ethernet) is provided as standard on the right side of the front panel. Additionally, the Teaming port, located just to the left, allows you to insert either an optional Fiber Channel SFP module or Active Copper SFP module. The chosen module can then allow either a fiber optic or additional Gigabit Ethernet link to be used in parallel with the fixed System (Gigabit Ethernet) port. 14 Configuration The System and Teaming ports Uses the standard Ethernet port on the left side of the front panel and provides lower-bandwidth image video feeds for use across standard networks and the wider Internet. These use either the Gigabit Ethernet or (optional) Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) module, on the right side of the front panel and provide high resolution DVI-D image, audio and peripheral feeds. Please see Appendix B - The VNC port: Initial configuration for details. Please see page 15 for details. INDEX The VNC port FURTHER INFORMATION OPERATION CONFIGURATION INSTALLATION The ALIF 2112T unit consists of two distinct sections (as detailed below) which each have their own separate configuration procedures within this chapter. 15 SYSTEM AND TEAMING PORTS: INITIAL CONFIGURATION ALIF 2112T units are designed to be as flexible as possible and this principle extends also to their configuration. INSTALLATION CONFIGURATION Where ALIF transmitters and receivers (all models) are connected via networked links, you can either configure them individually, or configure them collectively using an A.I.M. server: • Configuring networked ALIF units individually - You need to specify the network addresses of the ALIF units so that they can locate each other. This is done by running the AdderLink Infinity browser-based configuration utility on a computer system linked to the same network as the ALIF units. • Configuring ALIF units collectively - The AdderLink Infinity Management (A.I.M.) server allows you to configure, control and coordinate any number of ALIF transmitters and receivers from a single application. To perform a manual factory reset 1 Remove power from the ALIF unit. 2 Use a narrow implement (e.g. a straightened-out paper clip) to press-and-hold the recessed reset button on the front panel. With the reset button still pressed, reapply power to the unit and then release the reset button. OPERATION Networked linking A factory reset returns an ALIF transmitter or receiver unit to its default configuration. You can perform factory resets using the AdderLink Infinity browser-based configuration utility or by using this direct manual method. IMPORTANT: When using A.I.M. to configure ALIF dual units, it is vital that all units that you wish to locate and control are set to their factory default settings. Otherwise they will not be located by the A.I.M. server. If necessary, perform a factory reset on each ALIF dual unit. Please also see Appendix C - Tips for success when networking ALIF units Use a straightened-out paper clip to press the reset button while powering on the unit FURTHER INFORMATION Where ALIF transmitters and receivers (all models) are directly linked to each other, very little configuration action is required, provided that they have their factory default settings in place. If the standard settings have been changed in a previous installation, you merely need to perform a factory reset on each unit. Manual factory reset After roughly eight seconds, when the factory reset has completed, five of the front panel indicators will flash for a period of three seconds to indicate a successful reset operation. INDEX Direct linking 16 To access the browser-based configuration utility 1 Temporarily connect the ALIF 2112T unit and your computer, as discussed left. 2 Run a web browser on your computer and enter the IP address of the ALIF dual port that you are using. The default settings are as follows: System port Teaming port ALIF 2112T RX units 169.254.1.33169.254.1.32 169.254.1.43169.254.1.42 Note:Where the port addresses of a unit have been changed and are not known, providing it is appropriate to do so, perform a manual factory reset to restore the default addresses. The opening page of the ALIF configuration utility should be displayed: ww w.a d der .co m FURTHER INFORMATION Link from Ethernet switch to the System (Gigabit Ethernet) port on the right side of the front panel OPERATION To connect a computer system for browser-based configuration 1 Connect a suitable network cable to the Gigabit Ethernet port on the right side of the ALIF 2112T front panel. INSTALLATION The browser-based configuration utility within all TX and RX units requires a network connection between the Gigabit Ethernet port of the ALIF 2112T unit and a computer on the same network. The configuration utility allows you to perform all of the following functions: • View/edit the IP network address and netmask, • Configure separate IP network addresses for video, audio and USB, • Configure multicast settings (on RX units), • Configure video bandwidth settings (on TX units), • View the current video output (on TX units), • Perform a firmware upgrade, • Perform a factory reset, • Enable/disable and configure the VNC network port settings. CONFIGURATION AdderLink Infinity browser-based configuration utility Use the menu options to choose the required configuration page You can find further information about the configuration pages within the following appendix later in this guide: • Appendix A - Transmitter (TX) unit configuration pages INDEX Note: It is also possible to gain access to the browser-based utility via the Teaming port. 2 Connect the other end of the link cable to your network. 3 Similarly, link your computer to the same network. 4 If not already switched on, power up your computer and the ALIF 2112T unit.You are now ready to use the browser-based configuration utility. 17 CONFIGURATION OPERATION Setting the TX address and output signal details 1 Display the TX unit System Configuration page. 2 Ensure that the IP address and netmask for the System port and the Teaming port (if used) are correct. The default settings of 169.254.1.33 and 169.254.1.43 for the two ports respectively are their zero config addresses - these are usually changed to some other address suitable for your installation. Indeed, the zero config address for the System port MUST be changed before the Teaming port can be used for network connections. 3 Check that the data streams (Enable Video, Enable Audio and Enable USB - plus Enable Serial, if used) are enabled as appropriate. There are similar options within the RX unit configuration and it is important that the settings in both units are the same. If an option is ticked in one unit but unticked in the other, then that data stream will remain disabled. If you make a change, remember to click the Update Now button. Optimizing the TX video signal Note:Where the ALIF dual system is linked via two Gigabit links with sufficient available bandwidth, there should be no need to alter the default settings on this page. 1 Display the TX unit System Configuration page and then change to the Video Configuration page. 2 Make changes to the controls as necessary for each video port. There is no single combination of adjustments that will suit all installations, but generally: • If moving video images are being shown frequently, then leave Frame Skipping at a low percentage and instead reduce the Peak Bandwidth Limiter and Colour Depth. • Where screens are quite static, try increasing the Background Refresh interval and/or increasing the Frame skipping percentage setting. Make changes one at a time, in small steps, and view typical video images so that you can attribute positive or negative results to the appropriate control. See Video Configuration for individual explanations of the controls. 3Click Update Now to apply each setting change. FURTHER INFORMATION In an ALIF dual system, the majority of configuration settings are dictated by the RX units. Therefore, the local TX unit setup (using its browser-based configuration utility) is usually concerned only with three main factors: Its IP address details, the data streams to enable/disable and video signal optimization. Other TX unit pages, such as USB Settings, System Messages, Firmware Upgrades and Reboot are generally not used or altered during the majority of installations and are discussed elsewhere in this guide. See Appendix A for explanations of all TX configuration page options. INDEX TX (transmitter) unit configuration INSTALLATION A rough guide to configuring TX and RX units 18 CONFIGURATION OPERATION Configuring the RX unit 1 Display the RX unit System Configuration page. 2 In the System Configuration section, ensure that the IP address and Netmask settings for the System and Teaming ports for this RX unit are correct. The default settings of 169.254.1.32 and 169.254.1.42 for the two ports respectively are their zero config addresses - these are usually changed to some other address suitable for your installation. Indeed, the zero config address for the System port MUST be changed before the Teaming port can be used. Enter the new values and click the Update Now button. The System IP Address that is set here will be sent to the TX unit as the destination for transmitted data (when operating in unicast mode). The Gateway entry is only necessary when the TX unit is located on a separate network to the RX unit. 3 Check that the data streams (Enable Video, Enable Audio and Enable USB - plus Enable Serial, if used) are enabled (ticked) or disabled (unticked) as appropriate. There are similar options within the TX unit configuration; If one of these options is ticked in one unit but unticked in the other, then that data stream will remain disabled. If you make a change, click the Update Now button. 4 If necessary, alter the Audio Input Type to match your audio input. The line option is for a stereo line input, mic and mic boost are for mono microphones, the latter benefiting from a +20dB gain boost. FURTHER INFORMATION In an ALIF dual system, it is the RX unit (receiver) that determines where and how data signals are sent (and received) by the TX unit. Although numerous topologies (oneto-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, etc.) are made possible by the ALIF system, they are all dependent on two underlying modes of operation: either Unicast or Multicast transmission. Where multicast transmission is not invoked for video and/or audio data, operation will be automatically served by unicast network transmission technologies. The RX unit setup (using the System Configuration page of its browser-based configuration utility) is concerned with four main factors: Its own IP address(es), the data streams to enable/disable, the IP address(es) of the TX unit and multicast transmission details. Other pages, such as USB Settings, System Messages, Firmware Upgrades and Reboot are generally not used or altered during the majority of installations. For further details about RX unit configuration pages, please see the AdderLink Infinity dual guide. INSTALLATION RX (receiver) unit configuration INDEX continued 19 OPERATION FURTHER INFORMATION • First, tick the Enable Multicast Video / Enable Multicast Audio check box. • Next, enter appropriate Multicast Addresses for the System port Video/ Audio data stream(s). The set of IP addresses between 224.0.0.0 and 239.255.255.255 are specifically reserved for multicast operations. Within a private enterprise network, you merely need to choose a location that is currently unused. However, if your link will pass through public networks, then attention must be given to finding an address within these limits that is not already reserved for special use. The IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) website: iana.org provides a list of publicly reserved addresses. • Next, enter appropriate Multicast Address 2 entries for the Teaming port Video/Audio data stream(s). The video and audio multicast addresses must be different, as must the System and Teaming ports The addresses that you enter will be used by the RX unit to ‘listen-in’ on the video and audio data streams output by the TX unit. The same IP addresses need to be set on every RX unit that will similarly receive the video and audio data streams. 7 Click the Update Now button to save. Repeat the IP addressing and multicast configuration steps for all RX units that will be part of the one-to-many installation. For most installations, the successful implementation of these configuration steps will result in a correctly working system. CONFIGURATION INSTALLATION The two Video and the single Audio Multicast sub-sections are configured in exactly the same way: INDEX 5 In the Target Transmitter Unit Settings section, you need to enter the System port and Teaming port IP addresses for the TX unit that will be supplying the video, audio, USB and serial data streams. This section allows you to determine which peripherals should use the second link. Most often all streams are supplied by the same TX unit, so common System and Teaming port addresses can be applied to all streams. However, it is possible to receive them from different locations, in which case, click the blue arrow to reveal the separate video, audio, USB and serial addresses. For all five peripherals, the System port of the targeted TX unit is always used to carry the respective data streams; your choices involve which of those five should also use the secondary Teaming port link to spread the load(s). For each peripheral, the first IP address is that of the targeted TX unit’s System port. IP Address 2 corresponds to the Teaming port and is used only when the checkbox above is ticked. The default settings for all entries are the standard IP addresses that are factory set within every TX unit (169.254.1.33 and 169.254.1.43). Change these to the appropriate addresses on your transmitter(s) and click the Update Now button to save and activate them. 6 For installations that will include more than one RX unit, for either video or audio or both, then you need to configure the Multicast Settings section. 20 If the upgrade process is interrupted and fails, it may be necessary to switch to the backup firmware image in order to regain operation. See right for details. To upgrade a single unit via network link 1 Download the latest upgrade file from the Adder Technology website. Note:There are separate upgrade files for TX and RX units. 2 Temporarily connect the ALIF 2112T unit and a computer via a network (see AdderLink Infinity browser-based configuration utility section for details). 3 Run a web browser on your computer and enter the IP address of the ALIF 2112T unit to be upgraded. 4 Click the Firmware Upgrade link. Within the Firmware Upgrade page, click the Choose File button. In the subsequent file dialog, locate the downloaded upgrade file - check that the file is correct for the unit being upgraded. 5 Click the Upgrade Now button. A progress bar will be displayed (however, if your screen is connected to the unit being upgraded then video may be interrupted) and the indicators on the front panel will flash while the upgrade is in progress. 6 The indicators should stop flashing in less than one minute, after which the unit will automatically reboot itself. The upgrade process is complete. Finding the latest upgrade files Firmware files for the ALIF dual units are available from the Technical Support > Updates section of the Adder Technology website (www.adder.com). A pair of Options switches are located on the rear panel of every ALIF 2112T unit. Each ALIF 2112T unit retains a backup firmware image which can be used in situations where the primary firmware becomes corrupted (most often through failed upgrade operations). Using the backup firmware will allow you to regain operation of the unit. Option switch 1 OFF Normal operation using the main firmware ON Operate using the backup firmware image Option switch 2 is reserved and must remain in the OFF (up) position for normal operation. INSTALLATION Switch 1 - firmware image select CONFIGURATION WARNING: During the upgrade process, ensure that power is not interrupted as this may leave the unit in an inoperable state. OPTIONS SWITCHES OPERATION ALIF 2112T units are flash upgradeable using the method outlined here. However, for larger installations we recommend that you use the AdderLink Infinity Manager (A.I.M.) to upgrade multiple ALIF dual units. When using the method below, the ALIF dual unit will be upgraded in sequence. IMPORTANT: Upgrades must be performed on both the transmitters and the receivers at the same time. Mixed firmware operation is not supported. FURTHER INFORMATION PERFORMING AN UPGRADE INDEX Note: It is possible to downgrade the AdderLink Infinity firmware. After installing the older firmware, perform a factory reset on each AdderLink Infinity in order to clear the configuration file. 21 In operation, many ALIF dual installations require no intervention once configured. The TX and RX units take care of all connection control behind the scenes so that you can continue to work unhindered. FRONT PANEL INDICATORS CONFIGURATION The six front panel indicators on each unit provide a useful guide to operation: INSTALLATION Operation FURTHER INFORMATION INDEX These six indicators clearly show the key aspects of operation: • VNC On when a valid network is present on either the teaming or system port. Flashes to indicate that a VNC connection is present. • SER On when the AUX (serial) port is enabled and active. • AUD On when audio is enabled and active. • USB On when USB is enabled and active. • DVI On when the DVI Video channel is enabled. • PWR Power indicator. OPERATION Indicators 22 1 On a network connected computer, locate and select the VNC viewer icon A connection details dialog will be displayed: Enter the ALIF 2112T address here and click OK Viewer options (VNC viewer only) Click the VNC icon to view the viewer window options. Ctrl Alt Del Sends the Ctrl Alt Del sequence to the current host computer. Controls Displays a menu of options concerning keyboard, video and mouse operation. Power Click to access the power on/ off options for the current host computer. Dialog area Indicates your username and the host system that you are currently viewing. This area can also display other messages. If required, select the encryption mode INSTALLATION USING THE VNC VIEWER Hosts Click to display a list of computers. Choose an entry to connect to that host computer. Access mode Allows you to choose between Shared and Private access modes. Configure This option is only available to the admin user and provides access to the main configuration menus. When using the viewer window 4 Enter your Username and Password and click the OK button. The viewer window should now open Ü What is the best screen resolution to use? The best resolution for your computer is one that is larger than the screen of the host computer that you are viewing.This will allow you to see everything without scrolling around. Alternatively, the VNC viewer can be set to scale the image to fit your screen, but remember that some pixel dithering effect will be seen when scaling is used. How do I navigate around a larger screen? If the screen that you are viewing has a larger resolution than your viewing window you will need to scroll around to see all items. The viewer window allows you to ‘bump scroll’ (only in full screen mode). This means that when your mouse cursor bumps against the edge of the screen, the screen image will scroll across automatically. How do I escape from full screen mode? Press the F8 button. This button is changeable but is most often set to F8. How do I make the most of a slow connection? The VNC viewer is slightly better suited to slower connections than the browser viewer because it offers more options. Click the Options button of the VNC viewer when entering the ALIF 2112T address during log on. Rate limit mouse events When selected, this mode greatly reduces the mouse movement data that are sent to the host computer. When you move the local mouse, the remote cursor will catch up roughly once per second. OPERATION Auto calibrate This button will calibrate the mouse, but only when relative mouse mode is selected. FURTHER INFORMATION Re-sync mouse Ensures that the mouse pointer which you move and the mouse pointer on the host system are correctly synchronized. INDEX 2 In the ‘Server:’ entry, type the network address that has been configured for the VNC port of the ALIF 2112T unit. 3 Click the OK button. The viewer window may open straight away or the system may require user authentication, in which case an authentication dialog will be displayed: CONFIGURATION Options button Provides a range of viewer and connection settings - MORE [+] 23 Further information • Technical support – www.adder.com/contact-support-form For technical support, use the contact form in the Support section of the adder.com website - your regional office will then get in contact with you. CONFIGURATION • Adder Forum – forum.adder.com Use our forum to access FAQs and discussions. OPERATION • Online solutions and updates – www.adder.com/support Check the Support section of the adder.com website for the latest solutions and firmware updates. FURTHER INFORMATION If you are still experiencing problems after checking the information contained within this guide, then we provide a number of other solutions: INSTALLATION GETTING ASSISTANCE INDEX This chapter contains a variety of information, including the following: • Getting assistance - see right • Appendix A - Transmitter (TX) unit configuration pages • Appendix B - The VNC port: Initial configuration • Appendix C - Tips for success when networking ALIF units • Appendix D - Troubleshooting • Appendix E - Glossary • Appendix F - Configuration menus (via VNC) • Appendix G - VNC viewer connection options • Appendix H - VNC viewer window options • Appendix I - Java viewer options • Appendix J - The KVMADMIN utility • Appendix K - Known working video modes • Appendix L - Hotkey sequences • Appendix M - Cable pinouts, video modes and general specifications • Appendix N - Fiber modules and cables • Safety information • Warranty • Radio frequency energy statements 24 CONFIGURATION OPERATION FURTHER INFORMATION INDEX This section covers the browser-based configuration utility for the AdderLink Infinity TX (transmitter) unit. The TX utility has ten pages, titled as follows: • System Configuration • System Messages • Video Configuration • Statistics • USB Settings • Firmware Upgrade • Security • Reboot • AIM Manager • About INSTALLATION APPENDIX A - Transmitter (TX) unit configuration pages 25 TX System Configuration Enable options These checkboxes allow you to determine which peripheral options will be used:Video, audio, USB and serial. Serial port options These allow you to match the serial configuration being used by the attached PC host. Identify unit When clicked, these buttons cause the front panel indicators to flash to assist with identifying the ALIF unit within a rack. • The Identify Unit (short) button flashes the indicators for five seconds. • The Identify Unit (long) button flashes the indicators for one hour but can be overridden by clicking the Identify Unit (short) button. Target Multicast Configuration The items within this section are required if a multicast group is being arranged i.e. many receivers connected to the one transmitter. For the video port(s) and/or audio channel, you need to enter the multicast IP addresses. In each case, the first address relates to the System (Gigabit Ethernet) port and the second address to the optional Teaming port. In previous revisions of firmware, the destination IP address for video was decided by the RX. If multiple RX units requested the same video source then all had to provide the same multicast destination IP address. In revision 3.3 and above, the TX now decides the destination IP address for video and automatically informs any interested RX units. In a system with a mix of new and old units, both RX and TX units must be configured with the same destination IP address for video. CONFIGURATION Teaming port Determines whether the SFP socket on the right side of the front panel is enabled and which IP address details it should use. The default IP address is 169.254.1.43 which is the zero config IP address that allows the unit to work immediately in point-to-point mode.You are recommended to change this to an appropriate address in the private IP range 192.168.xxx.xxx The default netmask is 255.255.0.0. If you change the IP address to the private range, you are recommended to change this to 255.255.255.0 The default gateway address is 169.254.1.1 Note: Before the Teaming port can be used for connection via a network, you need to ensure that the System port has been configured away from its zero config IP address. OPERATION VNC port Determines whether the port on the left side of the front panel is enabled and which IP address details it should use. The default IP address is 192.168.1.42. FURTHER INFORMATION System port This section determines the IP address, netmask and gateway details for the main Gigabit Ethernet port located on the right side of the front panel. The default IP address is 169.254.1.33 which is the zero config IP address that allows the unit to work immediately in point-to-point mode.You are recommended to change this to an appropriate address in the private IP range 192.168.xxx.xxx The default netmask is 255.255.0.0. If you change the IP address to the private range, you are recommended to change this to 255.255.255.0 The default gateway address is 169.254.1.1 INDEX Unit Description Allows you to optionally add a description of the unit, such as its location. Useful when many ALIF units are being used. INSTALLATION Unit Name Name details that you can alter to distinguish this unit from all others. The name entered here will be read by A.I.M. units (if used) for administration purposes. Note: All multicast addresses for each service endpoint must be unique across the whole ALIF installation. 26 Background Refresh The TX unit sends portions of the video image only when they change. In order to give the best user experience, the TX unit also sends the whole video image, at a lower frame rate, in the background. The Background Refresh parameter controls the rate at which this background image is sent. The default value is ‘every 32 frames’, meaning that a full frame is sent in the background every 32 frames. Reducing this to ‘every 64 frames’ or more will reduce the amount of bandwidth that the TX unit consumes. On a high-traffic network this parameter should be reduced in this way to improve overall system performance. Options: every 32 frames, every 64 frames, every 128 frames, every 256 frames or disabled. Enable Magic Eye This feature, enabled as standard, aims to reduce the effect of dithering - a technique used by some graphics cards to improve the perceived quality and color depth of images by diffusing or altering the color of pixels between video frames. The Magic Eye feature increases the frame rate and eliminates unnecessary network traffic by ignoring the color dithering where it occurs. If the video source is not noisy or dithered then you can switch off Magic Eye to enable full color accuracy. Use Default DDC and Choose Default DDC When the Use Default DDC option is unticked, AdderLink Infinity will use the EDID that is reported by the monitor connected to the receiver unit. However, if you tick the Use Default DDC option, you can then select from a range of preset video resolutions from the Choose Default DDC drop down box. Once selected, the TX will report itself capable of only supporting this one video resolution. Please note that all of the listed video resolutions are single link DVI with a maximum pixel clock of 165MHz and a 60Hz refresh rate. CONFIGURATION Note: All of the following controls are available separately for each video port: OPERATION Peak bandwidth limiter percentage The TX unit will employ a ‘best effort’ strategy in sending video and other data over the IP network. This means it will use as much of the available network bandwidth as necessary to achieve optimal data quality, although typically the TX unit will use considerably less than the maximum available. In order to prevent the TX unit from ‘hogging’ too much of the network capacity, you can reduce this setting to place a tighter limit on the maximum bandwidth permissible to the TX unit. Range: 0 to 95%. INSTALLATION TX Video Configuration Period of Hot Plug Detect signal This is the length of time that a hot-plug detect signal is applied. The default of 25mS is sufficient for the majority of graphics cards, however, a small minority may need to be given a longer a period. Frame skipping percentage Frame Skipping involves ‘missing out’ video frames between those captured by the TX unit. For video sources that update only infrequently or for those that update very frequently but where high fidelity is not required, frame skipping is a good strategy for reducing the overall bandwidth consumed by the system. Range: 0 to 100%. FURTHER INFORMATION Enable Hot Plug Detect... When this option is ticked, every time the monitor is changed at the receiver unit, a hot plug detect message will be sent to the graphics card of the PC attached to the TX unit. Compression Determines the (AFZ and AFZ+) compression method used for video transmission. Choices are: • ‘Adaptive’ - guarantees frame rate, builds to pixel perfect, • ‘Smoothest video’ - forces the maximum compression, or To get here 1 Connect your computer to the Management port on the left side of the front panel. 2 Run a web browser and enter the IP address of the Management port: http://192.168.1.42 If the address is unknown, perform a manual factory reset. 3 If necessary, click the Video Configuration link. • ‘Advanced’ - allows you to choose a fixed compression mode: • ‘AFZ only (pixel perfect), • ‘AFZ+ Minimum compression’, INDEX • ‘Pixel perfect’ - only uses pixel perfect AFZ, • ‘AFZ+ Middle compression’, or • ‘AFZ+ Maximum compression’. 27 Enable Dummy Boot Keyboard When ticked, the TX unit reports a virtual dummy boot keyboard to the attached PC to ensure that a keyboard is always reported when the PC boots up. The dummy boot keyboard uses one of the 13 USB endpoints, therefore if all 13 endpoints are required elsewhere for USB devices (or a KVM switch only supports two HID devices) then it can be disabled by deselecting this option. See also Reserved Port Range below. Disable Hi-Speed This option allows you to force the system to run at the low/full USB speed of 12Mb/s, thus forcing USB 2.0 HiSpeed devices to adapt to the lower rate. INSTALLATION TX USB Settings Control Encryption This setting determines whether encryption should be applied to the control data passed across the link. Note that video data is never encrypted. Secure Web pages with password When ticked, this option enables https security so that the configuration pages are only accessible to the admin user with a password. Change/confirm password These options allow you to change the admin password for the system. To get here 1 Connect your computer to the Management port on the left side of the front panel. OPERATION USB Encryption This setting determines whether encryption should be applied to the USB data passed across the link. Note that video data is never encrypted. FURTHER INFORMATION TX Security INDEX Reserved Port Range For some devices, e.g. touch screens, you may wish to ensure that they are always reported to the same USB port number so that the USB driver will always find the device. This option allows you reserve up to 8 ports for certain devices. At the RX unit, the devices are assigned to the reserved ports. If a port reservation is to be applied, then the dummy boot keyboard should be disabled. The default value for this option is ‘0’, i.e. disabled. See Port Reservation on the RX unit for further details. CONFIGURATION Hub Size Using this option you can select whether the transmitter should report itself as a 13 or a 7 port USB hub. Some USB hosts are only able to support 7 port USB hubs. If this option is set to 7, then only 7 USB devices are supported by the PC. 2 Run a web browser and enter the IP address of the Management port: http://192.168.1.42 If the address is unknown, perform a manual factory reset. 3 Click either the USB Settings or Security links, as appropriate. 28 TX AIM Manager CONFIGURATION INSTALLATION Enable AIM Control Click this button to allow an A.I.M. (Adder Infinity Manager) box to take control of this TX. When the button is clicked, the TX unit will be rebooted to allow the A.I.M. box to discover and control it. Enable system messages Tick to allow the creation of status and error messages by the unit. Send system messages to remote Log Server Choose this option to send the system messages to a remote server via the network. Provide the IP address of a suitable server here also. OPERATION TX System Messages To get here 1 Connect your computer to the Management port on the left side of the front panel. 2 Run a web browser and enter the IP address of the Management port: http://192.168.1.42 If the address is unknown, perform a manual factory reset. INDEX Update Now Click to save and implement any changes that you make. FURTHER INFORMATION Store system messages in unit When ticked, this option will store system messages within the memory of the unit. Click the View messages button to view the list or the Clear messages button to delete the list. 3 Click either the AIM Manager or System Messages links, as appropriate. 29 TX Statistics Note: Only the System port is measured.When the Teaming port is also used, the bandwidth will be shared equally so the figures shown for the System port will apply also to the Teaming port. For instance, if the graph shows 500Mbit bandwidth, then the total bandwidth will be 1 Gigabit. TX Firmware Upgrade Reboot Use this page to perform a reboot or a factory reset. Please see the section Manual factory reset for details. To get here 1 Connect your computer to the Management port on the left side of the front panel. INDEX TX Reboot FURTHER INFORMATION OPERATION Upgrade Use this page to upgrade the main or backup firmware image on the unit. Please see the section Performing an upgrade for details. CONFIGURATION Submit Click this button after ticking the above checkbox to plot the chosen statistics on a pop up graph. INSTALLATION Enable collection of bandwidth statistics The ALIF dual unit can record data transfer statistics from the System port and plot them on a graph for troubleshooting and optimization purposes. When you enable this option, you will first be presented with a pop up from which you can choose which aspects you would like to graph: Data throughput, various packet rates and/or frame rates. 2 Run a web browser and enter the IP address of the Management port: http://192.168.1.42 If the address is unknown, perform a manual factory reset. 3 Click either the Statistics , Firmware Upgrade or Reboot links, as appropriate. 30 TX About To get here 1 Connect your computer to the Management port on the left side of the front panel. OPERATION CONFIGURATION INSTALLATION About This page displays key information about the TX unit that may be requested by Adder Technical Support. INDEX 3 If necessary, click the About link. FURTHER INFORMATION 2 Run a web browser and enter the IP address of the Management port: http://192.168.1.42 If the address is unknown, perform a manual factory reset. 31 APPENDIX B - The VNC port: Initial configuration http://192.168.1.42 The ALIF 2112T welcome screen should be displayed: To download a VNC Viewer To download a (free) VNC Viewer for a desktop or notebook computer, visit the download page of the RealVNC website: http://www.realvnc.com/download/viewer To download a VNC Viewer app for a tablet or smartphone, visit the Apple or Android app store, or look at the RealVNC website (www.realvnc.com) for further information. To use the Java VNC Viewer 1 Connect the ALIF 2112T to an IP network where a suitable computer is available on the same subnet (please see the Installation chapter for connection details). 2 On that computer, open an internet browser and enter the default IP address used by the ALIF 2112T: http://192.168.1.42 The ALIF 2112T welcome screen should be displayed (as shown left). 3 Click the link Connect using built-in Java VNC Viewer. The Java viewer will load and run inside the browser. For more details see Appendix I - Java viewer options. CONFIGURATION Note on viewers The windows VNC viewer supplied by the unit is 4.4.3se4. On the Real VNC website you will find later viewers V5. The V5 viewers support a newer 256 bit encryption technique. However,Virtual media functionality is not supported in V5 viewer. OPERATION To download a Windows VNC Viewer from the ALIF 2112T unit Note:The version of VNC supplied within the ALIF 2112T supports virtual media. 1 Connect the ALIF 2112T to an IP network where a suitable computer is available on the same subnet (please see the Installation chapter for connection details). 2 On that computer, open an internet browser and enter the default local IP address used by the ALIF 2112T: 3 Click the link ‘Download the Windows VNC Viewer from unit’. 4 Once the file is downloaded, run it and follow the on screen instructions to open a VNC connection to the ALIF 2112T. (The VNC Viewer is a single executable file which does not require an ‘installation’ step. Simply put the file in a suitable place (such as the Desktop) and run it from there.) FURTHER INFORMATION Configuration of the VNC port section of the ALIF 2112T is carried out via a network, using a VNC Viewer program running on a computer or mobile device.VNC Viewers are available for most computers, tablets and smartphones. • If you already have a VNC viewer, please follow the Initial configuration instructions given on the next page. • If you do not already have a VNC viewer, there are three options: • You can download a Windows VNC Viewer from the ALIF 2112T itself. • You can download the latest VNC Viewers for most operating systems via the RealVNC website, or for tablets and smartphones from the appropriate app store. • Without downloading anything, you can run a Java version of the VNC Viewer inside your web browser. INDEX Initial connection to the VNC port INSTALLATION This section deals with the initial configuration of the VNC port of the ALIF 2112T unit. For details about the main System and Teaming ports, please see here. The default IP address of the VNC port is 192.168.1.42; it is possible to change this either through the VNC viewer or via the TX System Configuration page. 32 Initial configuration To perform the initial configuration 1 Connect the ALIF 2112T to an IP network (using the VNC port) where a suitable computer is available on the same subnet (please see the section VNC network link for connection details). 2 Use a computer connected to the same subnet of the network. On that computer, locate and select the VNC viewer icon A connection details dialog will be displayed: 5Enter admin as the Username, leave the password entry blank and click the OK button. The viewer window should now open: INSTALLATION To perform the initial configuration, you need to connect the ALIF 2112T to an IP network and use a computer located on the same network to connect to it. Options button Provides a range of viewer and connection settings - MORE [+] 3 In the ‘Server:’ entry, type the address: 192.168.1.42 4 Click the OK button. The viewer window may open straight away (if so continue at step 6) or the system may require user authentication in which case an authentication dialog will be displayed: Use the various options (particularly the ‘Unit Configuration’ and ‘Network Configuration’ options) to arrange the ALIF 2112T to suit your requirements. See Appendix F Configuration menus. Note:To ensure that the Configuration menu is correctly displayed within the VNC viewer, the ALIF 2112T must be connected to the video output of its host computer. OPERATION If required, select the encryption mode FURTHER INFORMATION 6 Click the Configure button to display the Configuration menu: INDEX Enter the ALIF 2112T address here and click OK CONFIGURATION Click the Configure button 33 Controls When clicked, this button reveals a menu of options concerned with keyboard, video and mouse operation. Refresh Screen Click to produce a single mouse click for the left, centre or right mouse buttons Click to produce a continuous mouse click and hold for the left, centre or right mouse buttons button on the menu bar and re-synchronizes This option refreshes the whole screen image to remove any artefacts from moved screen items. This is useful when using very low refresh rates on slow speed communication links. Click to move the remote mouse cursor up, down, left or right INSTALLATION CONFIGURATION This option has the same effect as the the local and remote mouse pointers. This option displays a mouse control dialog and is useful when the remote cursor is failing to respond correctly to your mouse movements, even after using the Resync mouse option. The mouse control dialog allows you to control the remote mouse cursor using a selection of buttons that you click with your local mouse. Click to calibrate the remote mouse Click to display the Advanced Mouse Configuration dialog. See next page. When ticked the unit will attempt to switch to Absolute Mouse mode (recommended). If the computer does not support this then it will display a warning and return to relative mouse mode. OPERATION Resync Mouse Mouse Control FURTHER INFORMATION This mode is for fast network connections where the cursor response is sufficient to provide instant visual feedback on the remote screen. When enabled, the cursor is ‘captured’ within the viewer window until you use the ‘escape’ hot keys. To quit from single mouse mode, press F8 and then P. Alternatively, enable and use the mouse button escape sequences - see Advanced unit configuration for details. The single mouse mode does not require calibration. INDEX Single Mouse Mode 34 Advanced mouse configuration Info When selected, this option displays an information dialog showing the current logged on users, the current host, its video mode and its mouse motion details. OPERATION To switch a system on or off 1 Use the Hosts button to select the required computer. 2 Click the Power button and then select the Switch on or Switch off option, as appropriate. FURTHER INFORMATION The available Change Motion schemes are: Constant, XFree86,Windows Pre-XP,Windows XP,Windows XP SP2, OS/2, Solaris, Solaris 9 and Mac OSX. Most of these offer the Speed setting as the only option, however, the Windows Pre-Xp and XFree86 options contain many other parameters. When the Absolute Mode option is ticked in the main Mouse Control menu, this dialog allows you to adjust the Absolute Offset scale: When configured (and where you have access rights) this option allows you to control the mains power input to the currently selected host computer. Note:This option is generally used to power cycle remote systems that have failed to respond. Before switching a system off, ensure that all attempts have first been made to power it down through normal means. An optional power switch is required to be connected to the AUX port of the ALIF 2112T unit in order to control the mains power input into the associated computer. See also Power switching configuration. INDEX Power switching CONFIGURATION INSTALLATION This dialog allows the mouse acceleration to be configured according to the operating system in use and also permits manual fine tuning for situations where problems are encountered with the Calibrate function. For best results, choose the appropriate Change motion: entry to match the host in use. 35 INSTALLATION This option provides a range of options related to the video configuration. CONFIGURATION Click to send the code Click to send the contents of the clipboard to the host When entering codes: + means press down the key that follows – means release the key that follows +– means press down and release the key that follows * means wait 250ms (note: if a number immediately follows the asterisk, then the delay will equal the number, in milliseconds) It is automatically assumed that all keys specified will be released at the end, so there is need to specify -Ctrl or -Alt if these keys are to be released together. Examples: ‘Ctrl + Alt 12’ would be expressed as: +Ctrl+ Alt+1–1+2 +N means press the ‘N’ key +Scroll means press the Scroll lock key +Space means press the space key Note: If using the Paste Clipboard feature, within the VNC viewer properties, ensure that in the Inputs section, the Share clipboard with server option is enabled. See Appendix G for details. Video source Selects which video input to use. It is possible to display both single head screens (if connected) or select one over the other. If you are viewing Dual-Link video resolutions, only one head will be available. Use Remote DDC Uses the DDC of the monitors connected to the ALIF Reciever. If this option is un-ticked you can select a DDC to use that is reported by the ALIF 2112T. Hot Plug Detect When ticked, allows you to choose one of four hot plug detect periods when, after a display is connected, the DDC information is sought. Ignore Dithering Dithering is a technique used by some graphics cards to improve perceived image quality by continuously slightly varying the color of each pixel. This gives the illusion of more shades of color than the display can really reproduce, and smooths the appearance of gradually shaded areas in images. Unfortunately, dithering is an issue for KVM extenders because it makes the image appear to be changing all the time even when it is static. This means that a great deal of unnecessary network data is sent to the VNC viewer, reducing the video frame rate and making mouse response appear slow. The ‘Ignore Dithering’ option works by ignoring small variations in the video from frame to frame. This increases performance and reduces network traffic when the host computer is an Apple Mac or another computer that has dithered video output. It also improves performance if the video source is noisy (e.g. from a camera or a VGA-to-DVI converter). ‘Ignore Dithering’ is disabled by default to give full color accuracy and the best possible frame rate from non-dithered video sources. Threshold Adjusts the level of dithering noise that is ignored. The ‘Auto’ button attempts to choose a suitable value automatically, but the level can also be adjusted manually using the slider or arrow buttons. The best value is of course a compromise between capturing all the ‘real’ screen changes whilst ignoring the (almost invisible) dithering noise. A good way to choose the value is to watch the Display Activity indicator for a static screen. If the Threshold is too low, the Display Activity will be a high percentage while nothing is really changing. If the Threshold is too high, the Display Activity will be very low (or zero) but some real changes in the screen may be missed. OPERATION Enter the code here Video settings FURTHER INFORMATION This option displays a keyboard control dialog and is useful for sending keyboard combinations (to the host) that are needed regularly or that are trapped by the ALIF 2112T. INDEX Keyboard Control 36 Note:When using Adder Virtual Media features, within the VNC viewer properties, ensure that in the Inputs section, the Share clipboard with server and the Enable file transfer options are enabled. See Appendix G for details. To select and remotely transfer files from the viewer computer 1 On the remote system, log into the ALIF 2112T using the VNC viewer. 2 Invoke the “Send Files” feature of the VNC viewer (called “File Transfer” in later versions), either by clicking the icon on the viewer’s toolbar or selecting from the F8 menu. 3 The viewer will display a window allowing you to select files or a whole folder. Highlight the required files or folders (up to a maximum of 2GB) that you wish to transfer to the host computer and click the Open button. The new disk drive should appear on the host a few seconds later. Note:The Use Entire Folder button provides a quick way to select a whole folder while you are viewing its contents. Note: Remember, at this point the selected files/folders have not yet been transferred to the host system, they are just visible there. 4 On the host computer (via the VNC viewer) locate the new virtual drive (shown as a Removable Disk) and copy the files to the required location on the host computer. CONFIGURATION OPERATION There are several methods of doing this. The easiest method depends on whether: • The files are already on the clipboard of the viewer computer (following an Edit -> Copy operation). See To remotely transfer files from the clipboard >> or • The files still need to be selected. See To select and remotely transfer files from the viewer computer >> Click the Create VM Drive button to announce file availability to the host computer, whereupon a popup will confirm that the new virtual media disk is built. Note: Remember, at this point the selected files/folders have not yet been transferred to the host system, they are just visible there. 4 On the host computer (via the VNC viewer) locate the new virtual drive (shown as a Removable Disk) and copy the files to the required location on the host computer. FURTHER INFORMATION Remotely transferring files to the host as a virtual disk drive To remotely transfer files from the clipboard 1 On the remote system, log into the ALIF 2112T using the VNC viewer. 2 If not already done, use Windows Explorer to locate and copy the required file(s), or folder(s) to the clipboard. 3 Within the VNC viewer window, click the Controls button and then select the Virtual Media option. A popup similar to the following will be displayed: INDEX The Adder Virtual Media feature allows you to remotely make files available to a host computer that is linked to the ALIF 2112T. Disk drives, single files or collections of files and folders up to 2GB in size can be mounted via the VNC link, and appear as a read-only disk on the host. This can prove to be an invaluable tool when upgrading host computers from remote positions. Note:The file transfer is in one direction only, from viewer to host. Note: Adder Virtual Media does not currently work with Apple Mac systems. In order to use the Adder Virtual Media feature, the VM link must be made between the ALIF 2112T and a USB port on the host computer. See USB link for details. There are two main ways to use Adder Virtual Media: • Create a read-only ‘virtual disk drive’ on the host from one or more files chosen at the viewer end. This is useful for copying one or more files from the computer running the VNC viewer to the host computer. See below. • Export a disk drive (e.g. CD, DVD or USB flash drive) from the viewer computer so it appears as a disk on the host attached to ALIF 2112T. A particular use for this is for booting or upgrading the remote host from a CD or other media that you have at the viewer end. See next page. INSTALLATION Virtual Media 37 Remotely exporting a disk drive to the host 3 You can select an entire drive or a disk image (e.g. .iso) file: • Select a disk drive: Click the checkbox adjacent to the listed disk drive that you wish to make available to the host computer, or • Add a Disk Image File: Select the disk image file and click Open. 4 In the Virtual Media dialog box, click the OK button to announce the availability of the drive to the host computer. On the host computer, the new drive will appear in the same way as any removable drive would on your computer. Note: Remember, at this point the selected drive has not yet been transferred to the host system, it is just visible there. 5 On the host computer (either directly or via the VNC viewer) locate the new virtual drive (shown as a Removable Disk) and copy the files to the required location on the host computer. Note:The Remote File or Folder section of this Virtual Media dialog box provides yet another method of creating a virtual drive from some files or folders, as described above. CONFIGURATION OPERATION Remote Files or Folders Click Browse to search for and select single or multiple files/folders to be copied to the host computer. FURTHER INFORMATION When the Create ISO Image option is ticked this creates a bootable disk so that it’s possible to boot the host computer from the virtual media drive. INDEX Remote Drive(s) This section lists any located storage devices on the remote system that are 2GB or less, and which could be copied en masse to the host computer, if desired. INSTALLATION 1 On the remote system, log into the ALIF 2112T using the VNC viewer. 2 Press F8 and then V to display a Virtual Media dialog box: 38 Editing the viewer window menu bar To edit the menu bar via admin 1 Login remotely via VNC viewer as admin user and display the viewer window. 2 Click the Configure button in the top right corner of the viewer window. 3 Click the User Accounts button. 4 Against the entry for the required user, click the Menu Bar Edit button. The following dialog will be displayed: CONFIGURATION To edit the menu bar locally 1 Login remotely via VNC viewer and display the viewer window. 2 Place the mouse pointer on the menu bar and click the right mouse button. A popup will be displayed: INSTALLATION If required, you can customize the menu bar of the viewer window to ensure that it contains only the necessary options. The menu bar can be edited locally by each user or edited singly by the admin or alternatively, the admin can globally alter the menu bar for all users. OPERATION 3 Click on any option within the popup to add it to or remove it from the menu bar. 4 When all changes have been made, click anywhere else within the viewer window. Changes made in this way will affect the individual user only. 5 Select/deselect the items that you wish to appear on the menu bar. As you do so, the Menu bar appearance image will show how the bar will look using your edited settings. 6 Optional: To globally apply your changes, tick the Apply to all users on Save option. 7 Click the Save button. INDEX FURTHER INFORMATION Note: The local menu bar edit popup shown above will only appear if the Enable direct right click Menu editing option is ticked within the Gui Edit Configuration screen (for that user) as shown right. 39 APPENDIX C - Tips for success when networking ALIF units Layer 2 switches are what bind all of the hosts together in the subnet. However, they are all not created equally, so choose carefully. In particular look for the following: • Gigabit (1000Mbps) or faster Ethernet ports, • Support for IGMP v2 (or v3) snooping, • Support for Jumbo frames up to 9216-byte size, • High bandwidth connections between switches, preferably Fiber Channel. • Look for switches that perform their most onerous tasks (e.g. IGMP snooping) using multiple dedicated processors (ASICS). • Ensure the maximum number of concurrent ‘snoopable groups’ the switch can handle meets or exceeds the number of ALIF transmitters that will be used to create multicast groups. • Check the throughput of the switch: Full duplex, 1Gbps up- and down- stream speeds per port. • Use the same switch make and model throughout a single subnet. • You also need a Layer 3 switch. Ensure that it can operate efficiently as an IGMP Querier. Layer 2 (and Layer 3) switches known to work • Cisco 2960 • Extreme Networks X480 • Cisco 3750 • HP Procurve 2810 • Cisco 4500 • HP Procurve 2910 • Cisco 6500 • H3C 5120 • HuaWei Quidway s5328c-E1 (Layer 3) For the latest list of switches known to work with ALIF and setup instructions for them, please go to www.adder.com The recommended layout The layout shown below has been found to provide the most efficient network layout for rapid throughput when using IGMP snooping: INSTALLATION CONFIGURATION Choosing the right switch OPERATION • Choose the right kind of switch. • Create an efficient network layout. • Configure the switches and devices correctly. Network layout is vital. The use of IGMP snooping also introduces certain constraints, so take heed: • Keep it flat. Use a basic line-cascade structure rather than a pyramid or tree arrangement. • Keep the distances between the switches as short as possible. • Ensure sufficient bandwidth between switches to eliminate bottlenecks. • Where the A.I.M. server is used to administer multiple ALIF transceivers, ensure the A.I.M. server and all ALIF units reside in the same subnet. • Do not use VGA to DVI converters, instead replace VGA video cards in older systems with suitable DVI replacements. Converters cause ALIF TX units to massively increase data output. • Wherever possible, create a private network. FURTHER INFORMATION Summary of steps Creating an efficient network layout Note: From firmware version 3.1, tree and hierarchical structures of network switches are also supported.The Transmitter now joins its own multicast group so there is always a route from the querier to the transmitter which was previously missing in earlier firmware versions. • Use no more than two cascade levels. • Ensure high bandwidth between the two L2 switches and very high bandwidth between the top L2 and the L3. Typically 10GB and 20GB, respectively for 48 port L2 switches. continued INDEX ALIF units use multiple strategies to minimize the amount of data that they send across networks. However, data overheads can be quite high, particularly when very high resolution video is being transferred, so it is important to take steps to maximize network efficiency and help minimize data output. The tips given in this section have been proven to produce very beneficial results. 40 CONFIGURATION OPERATION FURTHER INFORMATION INDEX The layout is vital but so too is the configuration: • Enable IGMP Snooping on all L2 switches. • Ensure that IGMP Fast-Leave is enabled on all switches with ALIF units connected directly to them. • Enable the L3 switch as an IGMP Querier. • Enable Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on all switches and importantly also enable portfast (only) on all switch ports that have ALIF units connected. • If any hosts will use any video resolutions using 2048 horizontal pixels (e.g. 2048 x 1152), ensure that Jumbo Frames are enabled on all switches. • Choose an appropriate forwarding mode on all switches. Use Cut-through if available, otherwise Store and forward. • Optimize the settings on the ALIF transmitters: • If moving video images are being shown frequently, then leave Frame Skipping at a low percentage and instead reduce the Peak bandwidth limiter. • Where screens are quite static, try increasing the Background Refresh interval and/ or increasing the Frame skipping percentage setting. Make changes to the ALIF transmitters one at a time, in small steps, and view typical video images so that you can attribute positive or negative results to the appropriate control. • Ensure that all ALIF units are fully updated to the latest firmware version (at least v2.1). INSTALLATION Configuring the switches and devices 41 CONFIGURATION Remedies: • Ensure that IGMP snooping is enabled on all switches within the subnet. • Where each ALIF unit is connected as the sole device on a port connection to a switch, enable IGMP Fast-Leave (aka Immediate Leave) to reduce unnecessary processing on each switch. • Check the video resolution(s) being fed into the ALIF transmitters. If resolutions using 2048 horizontal pixels are unavoidable then ensure that Jumbo frames are enabled on all switches. • Check the forwarding mode on the switches. If Store and forward is being used, try selecting Cut-through as this mode causes reduced latency on lesser switch designs. • Ensure that one device within the subnet is correctly configured as an IGMP Querier, usually a layer 3 switch or multicast router. • Ensure that the firmware in every ALIF unit is version 2.1 or greater. • Try adjusting the transmitter settings on each ALIF to make the output data stream as efficient as possible. See ALIF transmitter video settings for details. FURTHER INFORMATION OPERATION continued INDEX Problem:The video image of the ALIF receiver shows horizontal lines across the screen. This issue is known as Blinding because the resulting video image looks as though you’re viewing it through a venetian blind. When video is transmitted by ALIF units, the various lines of each screen are divided up and transmitted as separate data packets. If the reception of those packets is disturbed, then blinding is caused. The lines are displayed in place of the missing video data packets. There are several possible causes for the loss of data packets: • Incorrect switch configuration. The problem could be caused by multicast flooding, which causes unnecessary network traffic. This is what IGMP snooping is designed to combat, however, there can be numerous causes of the flooding. • Speed/memory bandwidth issues within one or more switches. The speed and capabilities of different switch models varies greatly. If a switch cannot maintain pace with the quantity of data being sent through it, then it will inevitably start dropping packets. • One or more ALIF units may be outputting Jumbo frames due to the video resolution (2048 horizontal pixels) being used. If jumbo frames are output by an ALIF unit, but the network switches have not been configured to use jumbo frames, the switches will attempt to break the large packets down into standard packets. This process introduces a certain latency and could be a cause for dropped packets. • One or more ALIF units may be using an old firmware version. Firmware versions prior to v2.1 exhibited an issue with the timing of IGMP join and leave commands that caused multicast flooding in certain configurations. INSTALLATION APPENDIX D - Troubleshooting 42 Remedies: • Ensure that the ALIF units and the A.I.M. server are located within the same subnet because A.I.M. cannot cross subnet boundaries. • Manually reset the ALIF units to their zero config IP addresses. • Enable portfast on all switch ports that have ALIF units attached to them or try temporarily disabling STP on the switches while A.I.M. is attempting to locate ALIF units. INSTALLATION CONFIGURATION Problem: A.I.M. cannot locate working ALIF units. There are a few possible causes: • The ALIF units must be reset back to their zero config IP addresses for A.I.M. discovery. If you have a working network of ALIF’s without A.I.M. and then add A.I.M. to the network A.I.M. will not discover the ALIFs until they are reset to the zero config IP addresses. • This could be caused by Layer 2 Cisco switches that have Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) enabled but do not also have portfast enabled on the ports to which ALIF units are connected. Without portfast enabled, ALIF units will all be assigned the same zero config IP address at reboot and A.I.M. will only acquire them one at a time on a random basis. You can easily tell whether portfast is enabled on a switch that is running STP: When you plug the link cable from a working ALIF unit into the switch port, check how long it takes for the port indicator to change from orange to green. If it takes roughly one second, portfast is on; if it takes roughly thirty seconds then portfast is disabled. OPERATION Remedies: As per blinding discussed previously. FURTHER INFORMATION Remedies: • Linux PCs Check the video settings on the PC. If the Dither video box option is enabled, disable it. • Apple Mac with Nvidia graphics Use the Adder utility for Mac’s – Contact technical support. • Apple Mac with ATI graphics Enable the Magic Eye dither removal feature. • Windows PCs If you suspect these issues with PC’s, contact technical support for assistance. • Replace old VGA adapters on host computers with DVI video cards. Problem:The audio output of the ALIF receiver sounds like a scratched record. This issue is called Audio crackle and is a symptom of the same problem that produces blinding (see previous page). The issue is related to missing data packets. INDEX Problem:The mouse pointer of the ALIF receiver is slow or sluggish when moved across the screen. This issue is often related to either using dithering on the video output of one or more transmitting computers or using VGA-to-DVI video converters. Dithering is used to improve the perceived quality and color depth of images by diffusing or altering the color of pixels between video frames. This practice is commonly used on Apple Mac computers using ATI or Nvidia graphics cards.VGAto-DVI converters unwittingly produce a similar issue by creating high levels of pixel background noise. ALIF units attempt to considerably reduce network traffic by transmitting only the pixels that change between successive video frames. When dithering is enabled and/or VGA-toDVI converters are used, this can have the effect of changing almost every pixel between each frame, thus forcing the ALIF transmitter to send the whole of every frame: resulting in greatly increased network traffic and what’s perceived as sluggish performance. 43 APPENDIX E - Glossary IGMP Fast-Leave (aka Immediate Leave) When a device/host no longer wishes to receive a multicast transmission, it can issue an IGMP Leave Group message as mentioned above. This causes the switch to issue an IGMP Group-Specific Query message on the port (that the Leave Group was received on) to check no other receivers exist on that connection that wish to remain a part of the multicast. This process has a cost in terms of switch processor activity and time. Where ALIF units are connected directly to the switch (with no other devices on the same port) then enabling IGMP Fast-Leave mode means that switches can immediately remove receivers without going through a full checking procedure. Where multiple units are regularly joining and leaving multicasts, this can speed up performance considerably. INSTALLATION Since its commercial introduction in 1980, the Ethernet standard has been successfully extended and adapted to keep pace with the ever improving capabilities of computer systems. The achievable data rates, for instance, have risen in ten-fold leaps from the original 10Mbit/s to a current maximum of 100Gbit/s. While data speeds have increased massively, the standard defining the number of bytes (known as the Payload) placed into each data packet has remained resolutely stuck at its original level of 1500 bytes. This standard was set during the original speed era (10Mbits/s) and offered the best compromise at that speed between the time taken to process each packet and the time required to resend faulty packets due to transmission errors. But now networks are much faster and files/data streams are much larger; so time for a change? Unfortunately, a wholesale change to the packet size is not straightforward as it is a fundamental standard and changing it would mean a loss of backward compatibility with older systems. Larger payload options have been around for a while, however, they have often been vendor specific and at present they remain outside the official standard. There is, however, increased consensus on an optional ‘Jumbo’ payload size of 9000 bytes and this is fully supported by the AdderLink Infinity (ALIF) units. Jumbo frames (or Jumbo packets) offer advantages for ALIF units when transmitting certain high resolution video signals across a network. This is because the increased data in each packet reduces the number of packets that need to be transferred and dealt with - thus reducing latency times. The main problem is that for jumbo frames to be possible on a network, all of the devices on the network must support them. CONFIGURATION IGMP Querier When IGMP is used, each subnet requires one Layer 3 switch to act as a Querier. In this lead role, the switch periodically sends out IGMP Query messages and in response all hosts report which multicast streams they wish to receive. The Querier device and all snooping Layer 2 switches, then update their lists accordingly (the lists are also updated when Join Group and Leave Group (IGMPv2) messages are received). Jumbo frames (Jumbo packets) OPERATION IGMP Snooping The IGMP messages are effective but only operate at layer 2 - intended for routers to determine whether multicast data should enter a subnet. A relatively recent development has taken place within the switches that glue together all of the hosts within each subnet: IGMP Snooping. IGMP snooping means these layer 2 devices now have the ability to take a peek at the IGMP messages. As a result, the switches can then determine exactly which of their own hosts have requested to receive a multicast – and only pass on multicast data to those hosts. FURTHER INFORMATION Where an ALIF transmitter is required to stream video to two or more receivers, multicasting is the method used. Multicasting involves the delivery of identical data to multiple receivers simultaneously without the need to maintain individual links. When multicast data packets enter a subnet, the natural reaction of the switches that bind all the hosts together within the subnet, is to spread the multicast data to all of their ports. This is referred to as Multicast flooding and means that the hosts (or at least their network interfaces) are required to process plenty of data that they didn’t request. IGMP offers a partial solution. The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is designed to prevent multicast flooding by allowing Layer 3 switches to check whether host computers within their care are interested in receiving particular multicast transmissions.They can then direct multicast data only to those points that require it and can shut off a multicast stream if the subnet has no recipients. There are currently three IGMP versions: 1, 2 and 3, with each version building upon the capabilities of the previous one: • IGMPv1 allows host computers to opt into a multicast transmission using a Join Group message, it is then incumbent on the router to discover when they no longer wish to receive; this is achieved by polling them (see IGMP Querier below) until they no longer respond. • IGMPv2 includes the means for hosts to opt out as well as in, using a Leave Group message. • IGMPv3 encompasses the abilities of versions 1 and 2 but also adds the ability for hosts to specify particular sources of multicast data. AdderLink Infinity units make use of IGMPv2 when performing multicasts to ensure that no unnecessary congestion is caused. INDEX Internet Group Management Protocol 44 CONFIGURATION OPERATION FURTHER INFORMATION INDEX In order to build a robust network, it is necessary to include certain levels of redundancy within the interconnections between switches. This will help to ensure that a failure of one link does not lead to a complete failure of the whole network. The danger of multiple links is that data packets, especially multicast packets, become involved in continual loops as neighbouring switches use the duplicated links to send and resend them to each other. To prevent such bridging loops from occurring, the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), operating at layer 2, is used within each switch. STP encourages all switches to communicate and learn about each other. It prevents bridging loops by blocking newly discovered links until it can discover the nature of the link: is it a new host or a new switch? The problem with this is that the discovery process can take up to 50 seconds before the block is lifted, causing problematic timeouts. The answer to this issue is to enable the portfast variable for all host links on a switch. This will cause any new connection to go immediately into forwarding mode. However, take particular care not to enable portfast on any switch to switch connections as this will result in bridging loops. INSTALLATION Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) 45 carries the data to another user; to complete the picture, consider the transmission medium is Layer 0. In general, think of the functions carried out by the layers at the top as being complex, becoming less complex as you go lower down. As your data travel down from you towards the transmission medium (the cable), they are successively encapsulated at each layer within a new wrapper (along with a few instructions), ready for transport. Once transmission has been made to the intended destination, the reverse occurs: Each wrapper is stripped away and the instructions examined until finally only the original data are left. CONFIGURATION When discussing network switches, the terms Layer 2 and Layer 3 are very often used. These refer to parts of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model, a standardized way to categorize the necessary functions of any standard network. There are seven layers in the OSI model and these define the steps needed to get the data created by you (imagine that you are Layer 8) reliably down onto the transmission medium (the cable, optical fiber, radio wave, etc.) that OPERATION Layer 2 and Layer 3:The OSI model So why are Layer 2 and Layer 3 of particular importance when discussing AdderLink Infinity? Because the successful transmission of data relies upon fast and reliable passage through network switches – and most of these operate at either Layer 2 or Layer 3. The job of any network switch is to receive each incoming network packet, strip away only the first few wrappers to discover the intended destination then rewrap the packet and send it in the correct direction. In simplified terms, the wrapper that is added at Layer 2 (by the sending system) includes the physical address of the intended recipient system, i.e. the unique MAC address (for example, 09:f8:33:d7:66:12) that is assigned to every networking device at manufacture. Deciphering recipients at this level is more straightforward than at Layer 3, where the address of the recipient is represented by a logical IP address (e.g. 192.168.0.10) and requires greater knowledge of the surrounding network structure. Due to their more complex circuitry, Layer 3 switches are more expensive than Layer 2 switches of a similar build quality and are used more sparingly within installations. FURTHER INFORMATION So which one to choose? The Cut-through method has the least latency so is usually the best to use with AdderLink Infinity units. However, if the network components and/ or cabling generate a lot of errors, the Store and forward method should probably be used. On higher end store and forward switches, latency is rarely an issue. INDEX In essence, the job of a layer 2 switch is to transfer as fast as possible, data packets arriving at one port out to another port as determined by the destination address. This is known as data forwarding and most switches offer a choice of methods to achieve this. Choosing the most appropriate forwarding method can often have a sizeable impact on the overall speed of switching: • Store and forward is the original method and requires the switch to save each entire data packet to buffer memory, run an error check and then forward if no error is found (or otherwise discard it). • Cut-through was developed to address the latency issues suffered by some store and forward switches. The switch begins interpreting each data packet as it arrives. Once the initial addressing information has been read, the switch immediately begins forwarding the data packet while the remainder is still arriving. Once all of the packet has been received, an error check is performed and, if necessary, the packet is tagged as being in error. This checking ‘on-the-fly’ means that cut-through switches cannot discard faulty packets themselves. However, on receipt of the marked packet, a host will carry out the discard process. • Fragment-free is a hybrid of the above two methods. It waits until the first 64 bits have been received before beginning to forward each data packet. This way the switch is more likely to locate and discard faulty packets that are fragmented due to collisions with other data packets. • Adaptive switches automatically choose between the above methods. Usually they start out as a cut-through switches and change to store and forward or fragmentfree methods if large number of errors or collisions are detected. INSTALLATION Forwarding modes 46 APPENDIX F - Configuration menus (via VNC) When viewing remotely via VNC, the unit has a main configuration menu through which you can access various sub menus to configure particular items. OPERATION FURTHER INFORMATION INDEX The various configuration pages are covered within this appendix: • User accounts • Gui edit configuration • Unit configuration • Advanced unit configuration • Time & date configuration • Network configuration • Serial port configuration • Host configuration • Power switching configuration • Logging and status CONFIGURATION INSTALLATION To view the main configuration menu 1 Using VNC viewer or a browser, log on as the ‘admin’ user. 2 Click the ‘Configure’ button in the top right corner. The main configuration menu will be displayed: 47 Up to 16 users can be created by the admin user, each with their password. One of the 16 users can be the admin user. This user has access to the units configuration menu. Ticking the ‘IsAdmin’ box creates the Admin user. The admin user can also determine whether the users are allowed access to the power control menu in order to turn servers on and off. User Name All user names must consist of lower case characters or numbers only. No symbols or upper case characters are permissible. The user name can be between 1 and 32 characters in length but cannot contain foreign characters. INSTALLATION User accounts Menu Bar Optionally click to customize the menu bar for each user. See next page. Enable Password Hashing This enables the storing of passwords in an encrypted format, which provides added security. To get here 1 Using VNC viewer or a browser, log on as the ‘admin’ user. 2 Click the ‘Configure’ button in the top right corner. 3 Click the ‘User Accounts’ option. OPERATION Power When ticked, the selected user will be permitted to control the power input to host systems (requires optional power control switch unit(s) to be fitted). FURTHER INFORMATION Remote When ticked, the selected user can gain access via an IP network link (such as a local intranet or the wider Internet, depending on how the ALIF 2112T is connected) and/or Console Server access. INDEX Local This column is greyed out as this feature is not available on ALIF 2112T. CONFIGURATION Password Each password can be between 1 and 16 characters in length. A suitable password is best constructed using a mixture of more than 6 letters, numbers and punctuation characters. 48 Gui edit configuration To edit the menu bar locally 1 Login remotely via VNC viewer and display the viewer window. 2 Place the mouse pointer on the menu bar and click the right mouse button. A popup will be displayed: INDEX To globally edit the menu bar via admin 1 Using VNC viewer or a browser, log on as the ‘admin’ user. 2 Click the ‘Configure’ button in the top right corner. 3 Click on User Configuration 4 Click on the relevant Edit button. FURTHER INFORMATION OPERATION 3 Click on any option within the popup to add it to or remove it from the menu bar. 4 When all changes have been made, click anywhere else within the viewer window. Changes made in this way will affect the individual user only. CONFIGURATION INSTALLATION If required, you can customize the menu bar of the viewer window to ensure that it contains only the necessary options. The menu bar can be edited locally by each user or edited singly by the admin or alternatively, the admin can globally alter the menu bar for all users. 49 New Connections Private Allows you to determine whether new local or VNC connections should be set up as private (when ticked) or as shared (when unticked). Menu Bar Toggle Hot Key Determines the function key that can be used to display/hide the menu bar within the VNC screen. Encryption Four options are available: Always On, Prefer Off, Prefer On, or Maximum. The one to choose depends on the specific details of your installation. The use of encryption imposes a slight performance overhead of roughly 10% but is highly secure against third party intrusion. Maximum selects 256 bit encryption. Firmware Version Indicates the version of the internal software within the ALIF 2112T flash memory. This may be updated using the flash upgrade procedure. Host Keyboard Layout Use the arrow buttons to match the keyboard layout expected by the host system. Admin (Change) Password Click this button to enter/edit the password that will be used to gain administrator access to the ALIF 2112T. Number of simultaneous VNC Users Allows you to restrict the number of concurrent VNC sessions. The maximum number is 16 and the default is 4. VNC Viewer Hot Key Sequence When using the VNC Viewer, you can use key press combinations to select host computers and also to display the host selection menu. This option allows you to choose which keys should be used to form the hotkeys that will precede a switching command. The default setting is CTRL + ALT, so as an example when you press the CTRL ALT and 2 keys, the viewer will change to the host with “Hotkey Host Number” 2 - see Host configuration. Advanced Unit Configuration FURTHER INFORMATION Hardware Version Indicates the version of the electronic circuitry within the ALIF 2112T unit. CONFIGURATION Unit Name The name entered here will be displayed on the local menus and the remote VNC viewer/browser windows. OPERATION To get here 1 Using VNC viewer or a browser, log on as the ‘admin’ user. 2 Click the ‘Configure’ button in the top right corner. 3 Click the ‘Unit Configuration’ option. INDEX This page provides access to a selection of both basic and advanced settings for the ALIF 2112T. Many of the settings displayed here are also accessible through the on-screen menu. INSTALLATION Unit configuration 50 Mouse Rate Defines the rate at which mouse movement data are transmitted to the system.The default option is 20ms, which equates to 50 mouse events per second.This is used to slow down the rate in exceptional circumstances but normally requires no adjustment. Idle Timeout Determines the period of inactivity on a global connection before the user is logged out.The idle timeout period can be set to any time span, expressed in minutes. Session Sleep Timeout Determines the period of inactivity before the viewer screen will blank and a message is displayed. When no hosts are being viewed either because of this time out or if no viewers are active then parts of the video circuitry are powered down reducing power consumption by up to a third. Protocol Timeout Sets the time period by which responses should have been received to outgoing data packets. If the stated period is exceeded, then a connection is considered lost and terminated. Use Quick Mouse Calibration Invokes colord calibration techniques that handle the majority of mouse types. Behaviour for admin connections when limit reached Determines what should occur when the limit on VNC users is reached. Options are: Replace oldest connection, Replace newest connection and Don’t replace. Only non-administrator connections can be terminated in this way. FURTHER INFORMATION Force VNC Protocol 3.3 IMPORTANT: Protocol 3.3 is a legacy version that does not offer any encryption. Hashed passwords are not supported with 3.3 Single Mouse Mode Mouse Switch Select the mouse button combination to exit from single mouse mode (when active). CONFIGURATION Mouse Latency Allowance This option is used during calibration to account for latency delays that may be caused as signals pass through a device. During calibration, the ALIF 2112T waits for 40ms after each mouse movement before sampling the next. If a device adds a significant delay to the flow of data, the calibration process can be lengthened or may fail entirely. The value entered here is added to (or subtracted from) the default 40ms sampling time. Note: You can enter negative values (down to -40) in order to speed up the calibration process when using fast KVM switches. Use this option with caution as it can adversely affect the calibration process. OPERATION Background Refresh Rate Use the arrow keys to alter the background refresh rate used to correct any screen changes missed in normal operation. The options are: Slow, Medium, Fast, Auto or Disabled. The Auto option automatically varies the refresh rate when multiple VNC sessions are active to provide a balance between the sessions. Note:When a low connection speed is detected, the background refresh is automatically disabled, regardless of the settings of this option. Enable Virtual Media When ticked, allows the Adder Virtual Media features to be used. Reset Unit Performs a complete cold boot of the ALIF 2112T unit. INDEX Click this button to display advanced options that do not normally require alteration. INSTALLATION Advanced unit configuration 51 The dst string and [offset] specify the name and offset for the corresponding Daylight Saving Time zone; if the offset is omitted, it defaults to one hour ahead of standard time. The remainder of the specification describes when Daylight Saving Time is in effect. The start field is when Daylight Saving Time goes into effect and the end field is when the change is made back to standard time. The most common format used for the daylight saving time is: Mm.w.d Where: m specifies the month and must be between 1 and 12. The day d must be between 0 (Sunday) and 6. The week w must be between 1 and 5; week 1 is the first week in which day d occurs, and week 5 specifies the last d day in the month. Use NTP When this option is selected, the ALIF 2112T will synchronize its internal clocks using information from the (Network Time Protocol) server listed in the NTP Server IP address field. NTP Server IP address Optionally enter the IP address for a known Network Time Protocol server. Set Time from NTP Server Click to immediately use the time and date information from the listed NTP server. To get here 1 Using VNC viewer or a browser, log on as the ‘admin’ user. 2 Click the ‘Configure’ button in the top right corner. 3 Click the ‘Time & Date Configuration’ option. The time fields specify when, in the local time currently in effect, the change to the other time occurs. If omitted, the default is 02:00:00. Typical examples are: UK: GMT0BST,M3.5.0/1,M10.5.0/2 Central Europe: CET-1CEST,M3.5.0/2,M10.5.0/3 US Eastern: EST5EDT,M3.2.0/2,M11.1.0/2 US Pacific: PST5PDT,M3.2.0/2,M11.1.0/2 For further details • For details of timezone specifier formats, please refer to: http://www.gnu.org/software/libc/manual/html_node/TZ-Variable.html • For details of the Network Time Protocol (main RFC number: 1305; the SNTP subset used as the basis for the ALIF 2112T: 4330) http://www.ietf.org/rfc.html INSTALLATION or EST and 5, respectively. CONFIGURATION std offset dst [offset],start[/time],end[/time] The std and offset specify the standard time zone, such as GMT and 0, or CET and -1, OPERATION Timezone specifier Optionally enter a recognized timezone specifier related to the current position of the ALIF 2112T unit. When an NTP server is used, the specifier will be used to provide the correct real time. The timezone specifier takes the following form: FURTHER INFORMATION This page allows you to configure all aspects relating to time and date within the unit. INDEX Time & date configuration 52 VNC Port This is the logical link through which communications with a remote VNC viewer will be channelled. The default setting is 5900 which is a widely recognized port number for use by VNC software. However, in certain circumstances it may be advantageous to alter this number - see ‘Security issues with ports’ for more details. MAC address Media Access Control address – this is the unique and unchangeable code that was hard coded within your ALIF 2112T unit when it was built. It consists of six 2-digit hexadecimal (base 16) numbers separated by colons. A section of the MAC address identifies the manufacturer, while the remainder is effectively the unique electronic serial number of your particular unit. IP Address This is the identity of the ALIF 2112T within a network. The IP address can be thought of as the telephone number of the ALIF 2112T. Unlike the MAC address, the IP address can be altered to suit the network to which it is connected. It can either be entered manually or configured automatically using the DHCP option. When the DHCP option is enabled, this entry is grayed out. HTTP Port This is the logical link through which communications with a remote web browser will be channelled. The default setting of 80 is an established standard for web (HTTP – HyperText Transfer Protocol) traffic though this can be changed to suit your local network requirements. IP Access Control This section allows you to optionally specify ranges of addresses which will or won’t be granted access to the ALIF 2112T. If this option is left unchanged, then the default entry of ‘+0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0’ ensures that access from all IP addresses will be permitted. See Setting IP access control for details. CONFIGURATION IP Gateway This is the address of the device that links the local network (to which the ALIF 2112T is connected) to another network such as the wider Internet. Usually the actual gateway is a network router and it will be used whenever a required address lies outside the current network. OPERATION IP Network Mask Also often called the subnet-mask, this value is used alongside the IP address to help define a smaller collection (or subnet) of devices on a network. In this way a distinction is made between locally connected devices and ones that are reachable elsewhere, such as on the wider Internet. This process helps to reduce overall traffic on the network and hence speed up connections in general. FURTHER INFORMATION To get here 1 Using VNC viewer or a browser, log on as the ‘admin’ user. 2 Click the ‘Configure’ button in the top right corner. 3 Click the ‘Network Configuration’ option. INDEX This page allows you to configure the various aspects of the IP port. INSTALLATION Network configuration 53 To get here 1 Using VNC viewer or a browser, log on as the ‘admin’ user. 2 Click the ‘Configure’ button in the top right corner. 3 Click the ‘Network Configuration’ option. INSTALLATION Mask Enter an IP network mask that indicates the range of addresses that are to be allowed or denied access. For instance, if only a single specified IP address were to be required, the mask entry would be 255.255.255.255 in order to specify a single location. Access Use the arrow buttons to select either ‘Allow’ or ‘Deny’ as appropriate. CONFIGURATION Network/Address Enter the network address that is to be allowed or denied access. If a range of addresses is being specified then specify any one of the addresses within the range and use the Mask entry to indicate the size of the range. 2 Enter the base network address, the mask and select the appropriate access setting. 3 Click the OK button. To reorder access control entries IMPORTANT:When reordering, ensure that any specific allowed addresses are listed higher in the list than any denied addresses.Take care not to invoke any deny access settings that would exclude valid users. 1 In the access control list, click on the entry to be moved. 2 Click the Up or Down buttons as appropriate. To edit/remove access control entries 1 In the access control list, click on the appropriate entry. 2 Click either the Edit or Remove button as appropriate. OPERATION In the list, access control addresses prefixed by ‘+’ are allow entries while those prefixed by ‘– ‘ are deny entries. To define a new IP access control entry 1 Click the Add button to display a popup dialog: FURTHER INFORMATION The golden rule with this feature is ‘Include before you exclude’ or to put it another way ‘Arrange allowed addresses in the list before the denied addresses’. This is because the positions of entries in the list are vitally important. Once a range of addresses is denied access, it is not possible to make exceptions for particular addresses within that range. For instance, if the range of addresses from A to F are denied access first, then the address C could not be granted access lower down the list. Address C needs to be placed in the list before the denied range. IMPORTANT:This feature should be configured with extreme caution as it is possible to deny access to everyone. If such an error occurs, you will need to perform a reset to factory default settings in order to regain access. INDEX Setting IP access control 54 Serial port configuration INDEX To get here 1 Using VNC viewer or a browser, log on as the ‘admin’ user. 2 Click the ‘Configure’ button in the top right corner. 3 Click the ‘Serial port Configuration’ option. FURTHER INFORMATION OPERATION CONFIGURATION Baud Rate Determines the communication speed of the OPTIONS port. The other communication settings are fixed as: No parity, 8 bit word, 1 stop bit. INSTALLATION This page allows you to configure the baud rate of the ALIF 2112T serial port that is used to control power switch devices. A full range of standard baud rates are available. 55 Host configuration To create a new host entry 1 Click one of the host entries to reveal a Host configuration dialog. To get here 1 Using VNC viewer or a browser, log on as the ‘admin’ user. 2 Click the ‘Configure’ button in the top right corner. 3 Click the ‘Host Configuration’ option. OPERATION FURTHER INFORMATION Erase Host Configuration Removes all hosts from the list. INDEX Sort Allows you to reorder the list of hosts either alphabetically or by entry number. Name Enter the name that will be displayed in the viewer window when you click the Host button. Users Select the users that will be permitted to connect to this host. Either enter * to allow all users or a list of users separated by commas. KVM Switch Macro Declare the hot key sequence that will cause the KVM switch to link with the required host system. See Appendix L - Hotkey sequences for details. Hotkey Host Number Declare the numeric sequence that is pressed together with the VNC viewer hotkeys (usually Ctrl + Alt) to select this host system, which is the same value as the KVM port number. Power On Enter the code required to make an attached power control unit apply power to the host. See Power switching configuration for details. Power Off Enter the code required to make an attached power control unit remove power from the selected host. Reboot Enter the code required to make an attached power control unit remove power and then re-apply it a few seconds later. 2 Enter the required information in each field. 3 Click the OK button. CONFIGURATION INSTALLATION This page provides the opportunity to configure various details for each of the host systems that may be connected to the ALIF 2112T. Each entry can be configured with a name, the permitted users, the hot key combinations required to switch to it and, if required, appropriate power control commands. 56 Where: x is the switch box number, y is the power port number, z is ‘0’ for OFF or ‘1’ for ON r is for Reboot, and \0D represents Enter (or Carriage return). Example 1 To switch ON port 5 of switch box 2, the code would be as follows: • Power sequence: P25=1\0D Example 2 To switch OFF port 8 of switch box 3, the code would be as follows: • Power sequence: P38=0\0D For details about operating this feature, see Power switching control within the Configuration chapter. 6 Enter the Power control sequences in the Power On, Power Off and Reboot fields 7 Click OK to close the dialog and then click the Save button in the main Host Configuration window to store the details. To control two or more ports simultaneously You can control up to four power ports using a single sequence. This is done using the same command structure as shown above, plus a delay command, for each port. Immediately following a port command, insert the characters ‘\*’ before the next port command, and so on up to four ports. For instance, to switch on ports 1 and 2 in the first power switch, the command line would be: P11=1\0D\*P12=1\0D CONFIGURATION /Pxy=z\0D INSTALLATION Notes:The settings given below are for Adder power switches model numbers PSU-8SLAVE and PSU-1GUARD - other power switches may require different settings. Please refer to your power switch documentation for details about codes required by other power switches. The structure of each power sequence (OFF, ON or Reboot) is as follows: OPERATION To configure the power sequences for each host computer 1 Using VNC viewer or a browser, log on as the ‘admin’ user. 2 Click the ‘Configure’ button in the top right corner. 3 Click the ‘Host configuration’ option. 4 Click a host entry to display a Host configuration dialog: 5 If necessary, configure other parameters (Name, Users, Hot Keys - MORE). Power control sequences FURTHER INFORMATION Power switch configuration comprises two main steps: • Configure the OPTIONS serial port to the same speed as used by the power switch box(es), using the Serial port configuration menu. • Configure power ON and OFF strings for each relevant host computer. For each power port there needs to be a valid ‘Power ON string’ and similarly an appropriate ‘Power OFF string’. In each case, the strings are a short sequence of characters that combine a port address and a power on or off value. If a particular computer has more than one power input (and thus requires an equivalent number of power ports to control them), collections of strings can be combined to switch all of the required ports together as a group. INDEX Power switching configuration 57 Date and time the event occurred Type of event, user name and access method or remote IP address To copy and paste the log You can copy the information listed within the log and paste it into another application. 1 While viewing the log screen, press Ctrl and C, to copy the data into the clipboard. 2 In a text application (i.e. Word, WordPad, Notepad) press Ctrl and V, or right mouse click and ‘Paste’. Syslog Server IP Address Logging information can optionally be sent, as it occurs, to a separate system using the standard Syslog protocol. Enter the IP address of a suitable system in the field provided. Click to clear all log entries Click to refresh the list Optionally enter an IP address to which the status log should be sent Click to return to the main menu INDEX To get here 1 Using VNC viewer or a browser, log on as the ‘admin’ user. 2 Click the ‘Configure’ button in the top right corner. 3 Click the ‘Logging and Status’ option. FURTHER INFORMATION OPERATION For further details • For details of the Syslog protocol (RFC number: 3164) http://www.ietf.org/rfc.html CONFIGURATION This screen provides various details about the user activity on the ALIF 2112T unit. INSTALLATION Logging and status 58 APPENDIX G - VNC viewer connection options You can also reduce the four standard tabs to just one that contains only the most commonly used options by clicking the Basic... button in the lower left corner. The resulting page includes all of the Display items shown opposite plus the Connection options shown below: Connection View-only When ticked, no control data (from keyboard or mouse) are sent to the ALIF 2112T. Pass special keys directly to server When ticked, ‘special’ keys (the Windows key, the Print Screen key, Alt+Tab, Alt+Escape and Ctrl+Escape) are passed directly to the ALIF 2112T rather than being interpreted locally. Menu key This feature allows you to select which function key is used to display the VNC viewer options menu. The menu key is the only way to exit from the full screen viewer mode. Note: If you make any changes to the options given here and wish to retain them for successive connection sessions, ensure that the option ‘Use these settings for all new connections’ is ticked. INSTALLATION No Scaling No attempt is made to make the screen image fit the viewer window.You may need to scroll horizontally and/or vertically to view all parts of the screen image. Custom Size Adjusts the server screen image according to the Width and Height settings in the adjacent fields. A drop box to the right of the fields allows you to define the image size by percentage or by pixels, as required. Preserve Aspect Ratio When ticked, maintains a consistent ratio between the horizontal and vertical dimensions of the screen image. Other options CONFIGURATION Scale to Window Size Adjusts the server screen image to suit the size of the viewer window. OPERATION There are four tabbed pages of options: • Display • Inputs • Connection • Expert Scaling Full screen mode When ticked, opens the VNC Viewer in full screen mode. Enable toolbar When ticked, the VNC toolbar will be displayed whenever you hover your mouse near the top centre of the VNC window. Adapt to network speed When ticked,VNC will automatically adjust the image quality to suit the connection speed. When unticked, a slider allows you to choose the balance manually. Always use best available colour quality (not in V5 viewers) When ticked, the VNC Viewer will aim to maximize performance while still maintaining a full color display (even on slower network connections) by affecting other aspects of operation. For instance, by reducing the amount of information sent about the mouse cursor position (which may make the mouse cursor movements appear jerky). FURTHER INFORMATION Click here to access the options Display INDEX Note: If you are using a later version of VNC viewer than that provided with the product originally, some menus may differ slightly from those shown here. When you are connecting to the ALIF 2112T using the VNC viewer, a number of options are available. 59 Inputs Enable mouse input Allows mouse data to be transferred to the ALIF 2112T. Enable 3-button mouse emulation This feature allows you to use a 2-button mouse to emulate the middle button of a 3-button mouse. When enabled, press the left and right mouse buttons simultaneously to create a middle button action.You are advised to generally use a 3-button mouse. Rate-limit mouse move events When ticked, this feature reduces the mouse movement information that is sent to the ALIF 2112T and host system. This is useful for slow connections and you will notice that the remote cursor will catch up with the local cursor roughly once every second. INSTALLATION CONFIGURATION Menu key This feature allows you to select which function key is used to display the VNC viewer options menu. The menu key is the only way to exit from the full screen viewer mode. OPERATION Pass special keys directly to server When ticked, ‘special’ keys (the Windows key, the Print Screen key, Alt+Tab, Alt+Escape and Ctrl+Escape) are passed directly to the ALIF 2112T rather than being interpreted locally. Enable file transfer This permits the “file transfer” method of Virtual Media (see Virtual Media). FURTHER INFORMATION Enable keyboard input Allows keyboard data to be transferred to the ALIF 2112T. Share clipboard with server This permits the “Paste Clipboard” operation (see Keyboard control), and the “Create VM Drive” feature of Virtual Media (see Virtual Media). INDEX Inputs: When set to ‘Enabled’, all primary options below are ticked. The ‘Disabled’ setting unticks all of the primary options (causing ‘view-only mode’ where no control data may be sent to the ALIF 2112T. The ‘Custom’ setting is shown if you choose your own combination of options. 60 Expert OPERATION CONFIGURATION INSTALLATION The options within this section work correctly with ALIF 2112T in their default states and should not require alteration except in special circumstances. FURTHER INFORMATION The options on this page are not relevant to ALIF 2112T connections and should be left in their default states. INDEX Connection 61 APPENDIX H - VNC viewer window options Refresh Screen Requests data from the server for a complete redraw of the screen image, not just the items that change. Virtual Media... Allows files to be transferred from the remote computer to the host. See Virtual Media for details. Send Files to Server... Allows files to be transferred from the remote computer to the host. See Virtual Media for details. New connection... Displays the connection dialog so that you can log on to a different ALIF 2112T or VNC server location. Options... Displays the full range of connection options - see Appendix G for more details. Connection info... Displays various connection and display details. About... Displays information about your VNC viewer. CONFIGURATION OPERATION Ctrl, Alt, Send F8, Send Ctrl-Alt-Del Sends the selected keypress(es) to the ALIF 2112T and host computer. This is necessary because certain keys and key combinations are trapped by the VNC viewer. FURTHER INFORMATION Single mouse mode (P) Used for fast network connections where a second, “predictor” cursor is not required. INDEX Standard window control items Full screen Expands the VNC viewer window to fill the whole screen with no visible window edges or toolbar. Press F8 to re-display this menu. INSTALLATION Click the VNC icon in the top left corner of the viewer window (or press F8) to display the window options: 62 Encoding and colour level Auto select When ticked, this option will examine the speed of your connection to the ALIF 2112T and apply the most suitable encoding method. This option is suggested for the majority of installations. Preferred encoding There are three manually selectable encoding methods which are accessible when the Auto select option is unticked. • ZRLE – This is a highly compressed method that is best suited to slow modem connections. • Hextile – This method offers better performance than the ZRLE when used over a high speed network because there is no need for the ALIF 2112T to spend time highly compressing the data. • Raw – This is a primitive, uncompressed method that is mainly used for technical support issues.You are recommended not to use this method. Colour level The color level is fixed at Medium (256 colors) for almost all browsers. Send clipboard to server This feature is restricted to software server versions of VNC and has no effect on ALIF 2112T installations. Security 512 bits (low security) Selects the lowest level of encoding for communications between the browser and the ALIF 2112T. 1024 bits (medium security) Selects the middle level of encoding for communications between the browser and the ALIF 2112T. 2048 bits (high security) Selects the highest level of encoding for communications between the browser and the ALIF 2112T. Misc Shared (don’t disconnect other viewers) This feature is restricted to software server versions of VNC and has no effect on ALIF 2112T installations. Render cursor locally This feature is restricted to software server versions of VNC and has no effect on ALIF 2112T installations. Fast CopyRect This option should remain enabled. INSTALLATION Accept clipboard from server This feature is restricted to software server versions of VNC and has no effect on ALIF 2112T installations. CONFIGURATION There are four options pages: View only (ignore mouse & keyboard) When ticked, the viewer will not send keyboard or mouse information to the ALIF 2112T or host computer. OPERATION Click here to access the options Inputs FURTHER INFORMATION When you are connecting to the ALIF 2112T using the Java viewer, a number of options are available. INDEX APPENDIX I - Java viewer options 63 CONFIGURATION OPERATION FURTHER INFORMATION INDEX Particularly useful for complex ALIF 2112T configurations and the control of remote installations, KVMADMIN is a powerful administration tool. KVMADMIN is based upon the established VNC viewer and uses the same security system. Rather than a graphical interface such as the standard viewer, KVMADMIN uses command line control to provide the following administration facilities: • Discover and adjust the ALIF 2112T configuration, including host systems, • Save and restore the ALIF 2112T configuration, • Set user names and passwords, • Download the event log, The use of KVMADMIN is strictly limited to the ‘admin’ user and for security purposes it is not possible to retrieve user names or passwords from the ALIF 2112T. To use KVMADMIN you require the IP address and admin password of the ALIF 2112T unit. The command line is as follows: kvmadmin <command> <ip address> [<parameters>] where <command> is one of the following: • -setconfig <config-file> • -getconfig <config-file> • -setusers <csv-file> • -getlog <log-file> • -gethosts <csv-file> • -sethosts <csv-file> • -setmodes <csv-file> For instance, the command line: kvmadmin -getconfig kvm1.cfg 192.168.2.1 ... downloads the current configuration from the ALIF 2112T unit at the given address and stores it in the local file kvm1.cfg. Whereas the command line: kvmadmin -setusers users.csv 192.168.2.1 ... configures the usernames and passwords for the same unit from the local file users.csv. For more information about KVMADMIN, please refer to the user notes supplied with the utility. INSTALLATION APPENDIX J - The KVMADMIN utility 64 CONFIGURATION OPERATION FURTHER INFORMATION INDEX 640x480 @ 60Hz 720x480 @ 60Hz 768x576 @ 60Hz 800x480 @ 60Hz 1024x600 @ 60Hz 1024x768 @ 60Hz 1152x768 @ 60Hz 1152x864 @ 60Hz 1280x720 @ 60Hz 1280x768 @ 60Hz 1280x800 @ 60Hz 1280x854 @ 60Hz 1280x960 @ 60Hz 1280x1024 @ 60Hz 1366x768 @ 60Hz 1400x1050 @ 60Hz 1440x900 @ 60Hz 1440x960 @ 60Hz 1600x900 @ 60Hz 1600x1200 @ 60Hz 1680x1050 @ 60Hz 1920x1080 @ 60Hz 1920x1200 @ 60Hz 2048x768 @ 60Hz 2048x1080 @ 60Hz 2048x1152 @ 60Hz 2048x1536 @ 60Hz 2048x2048 @ 60Hz 2560x1440 @ 60Hz 2560x1600 @ 60Hz 2560x2048 @ 50Hz INSTALLATION APPENDIX K - Known working video modes 65 APPENDIX L - Hotkey sequences ALIF 2112T allows you to enter commands suitable for any KVM switch in order to choose from up to 128 host systems.These switching commands can take the form of hotkey sequences that emulate standard keypress combinations. Examples To send the command Ctrl + Alt 4 you should use the following: +Ctrl+Alt+4. To send the command Ctrl + Alt 12 you should use the following: +Ctrl+ALT+–1+2 (the ‘+–1’ entry causes the 1 key to be pressed and released before the 2 key is pressed). To send the command Scroll lock 1 + Enter (with a 500ms delay) you should use the following: +–Scr*500+1+Ent Main control keys (see ‘Using abbreviations’) Backspace | Tab | Return | Enter | Ctrl | Alt | Win | Shift | LShift | RShift LCtrl | RCtrl | LAlt | AltGr | RAlt | LWin | RWin | Menu | Escape | Space CapsLock | NumLock | PrintScreen | Scrolllock Math operand keys (see ‘Using abbreviations’) Add (Plus) | Subtract (Minus) | Multiply INSTALLATION Function keys Creating macro sequences Hot key macro sequences can be up to 256 characters long. All keys are assumed to be released at the end of a line, however, you can also determine that a key is pressed and released within a sequence. Any of the following three examples will send a command that emulates and a press and release of the Scroll Lock key: +SCROLL-SCROLL +-SCROLL +SCROLLExample: +-SCROLL+-SCROLL+1+ENTER Press and release scroll twice, press 1 then enter then release all keys (equivalent definition is +SCROLL-SCROLL+SCROLL-SCROLL+1+ENTER-1-ENTER) Using abbreviations To reduce the length of the key definitions, any unique abbreviation for a key can be used. For example: “scroll”, “scr” and even “sc” all provide an identifiable match for “ScrollLock” whereas “en” could not be used because it might mean “Enter” or “End” (“ent” would be suitable for “Enter”). Note: Hotkey sequences and abbreviations are not case sensitive. For information about where to enter these codes, please see the sections Host configuration or Keyboard control. CONFIGURATION F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 | F10 | F11 | F12 OPERATION Notes • The entries are not case sensitive. • All characters can be entered using their ASCII codes, from 32 to 126 (i.e. A,B,C, … 1,2,3 etc.) with the exception of the special characters above. • It is not necessary to specify all keys to be released at the end because they are all released automatically after the last code. • A number of KVM switches from alternative manufacturers use hot key sequences that begin with a press/release of either the Scroll Lock or Ctrl keys.These often require a delay between the initial key press and the channel number to allow the switch to respond. A 500ms delay is usually sufficient. KP_Insert | KP_Delete | KP_Home | KP_End | KP_PageUp KP_PageDown | KP_Up | KP_Down | KP_Left | KP_Right | KP_Enter KP_Add | KP_Subtract | KP_Divide | KP_Multiply KP_0 to KP_9 FURTHER INFORMATION Almost any combination of keypresses can be emulated using the following notations: + means press down the key that follows; – means release the key that follows +–means press and then release the key that follows * means add a delay. The standard delay period is 250ms, however, if a number immediately follows the asterisk, this will define an alternate delay period (in milliseconds) Keypad keys (see ‘Using abbreviations’) INDEX Hotkey sequences Central control keys (see ‘Using abbreviations’) Insert | Delete | Home | End | PageUp | PageDown Up | Down | Left | Right | Print | Pause 66 APPENDIX M - Cable pinouts, video modes and general specifications ALIF dual units support all VESA and CEA video modes. INSTALLATION 198mm (7.92”) x 44mm (1.76”) x 145mm (5.7”) 1U compact case, robust metal design 1.11kg (2.44lbs) Rack mount - single or dual units per 1U slot. VESA monitor / wall mount chassis. 100-240VAC 50/60Hz, 0.8A, 5VDC 20W 0ºC to 40ºC (32ºF to 104ºF) CE, FCC CONFIGURATION Casing (w x h x d): Construction: Weight: Mount kits: Power to adapter: Power to unit: Operating temp: Approvals: OPERATION Supported video modes 9pin D-type female FURTHER INFORMATION 9pin D-type female General specifications INDEX RS232 ‘null-modem’ cable pin-out 67 APPENDIX N - Fiber modules and cables OM2 (50/125) OM3 (50/125) OM4 (50/125) OS1 and OS2 (9/125) Multimode (TIA-492AAAA) Multimode (TIA-492AAAB) Multimode (850 nm Laser-optimized) (TIA-492AAAC) Multimode (850 nm Laser-optimized) (TIA-492AAAC) Single-mode (TIA-492C000 / TIA-492E000) Distance Adder part at number for 1Gbps SFP module Bar color Conn. type 220m SFP-MM-LC Black LC Normal Applications Orange Military Applications Slate Suggested Print Nomenclature 62.5/125 Orange Orange 50/125 550m “ “ “ Aqua Undefined 850 LO 50 /125 550m “ “ “ Aqua Undefined 850 LO 50 /125 550m “ “ “ Yellow Yellow SM/NZDS, SM 10Km SFP-SM-LC Blue LC CONFIGURATION (62.5/125) Coding OPERATION OM1 Fiber Type FURTHER INFORMATION Fiber size INDEX Fiber Type INSTALLATION To suit your installation layout, two fiber modules are available for the ALIF dual units to suit various fiber optic cables. The specifications for all are summarized in the table below: 68 CONFIGURATION Adder Technology Ltd warrants that this product shall be free from defects in workmanship and materials for a period of two years from the date of original purchase. If the product should fail to operate correctly in normal use during the warranty period, Adder will replace or repair it free of charge. No liability can be accepted for damage due to misuse or circumstances outside Adder’s control. Also Adder will not be responsible for any loss, damage or injury arising directly or indirectly from the use of this product. Adder’s total liability under the terms of this warranty shall in all circumstances be limited to the replacement value of this product. If any difficulty is experienced in the installation or use of this product that you are unable to resolve, please contact your supplier. INSTALLATION WARRANTY OPERATION For use in dry, oil free indoor environments only. Warning - live parts contained within power adapter. No user serviceable parts within power adapter - do not dismantle. Plug the power adapter into a socket outlet close to the module that it is powering. Replace the power adapter with a manufacturer approved type only. Do not use the power adapter if the power adapter case becomes damaged, cracked or broken or if you suspect that it is not operating properly. • If you use a power extension cord with the units, make sure the total ampere rating of the devices plugged into the extension cord does not exceed the cord’s ampere rating. Also, make sure that the total ampere rating of all the devices plugged into the wall outlet does not exceed the wall outlet’s ampere rating. • Do not attempt to service the units yourself. FURTHER INFORMATION • • • • • • INDEX SAFETY INFORMATION 69 FCC Compliance Statement (United States) This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not installed and used properly, that is, in strict accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, may cause interference to radio communication. It has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class A computing device in accordance with the specifications in Subpart J of part 15 of FCC rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. Operation of this equipment in a residential area may cause interference, in which case the user at his own expense will be required to take whatever measures may be necessary to correct the interference. Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the manufacturer could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment. CONFIGURATION This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class A computing device in accordance with the specifications in the European standard EN55022. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions may cause harmful interference to radio or television reception. However, there is no guarantee that harmful interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment on and off, the user is encouraged to correct the interference with one or more of the following measures: (a) Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna. (b) Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver. (c) Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected. (d) Consult the supplier or an experienced radio/TV technician for help. OPERATION European EMC directive 2004/108/EC FURTHER INFORMATION A Category 5 (or better) twisted pair cable must be used to connect the units in order to maintain compliance with radio frequency energy emission regulations and ensure a suitably high level of immunity to electromagnetic disturbances. All other interface cables used with this equipment must be shielded in order to maintain compliance with radio frequency energy emission regulations and ensure a suitably high level of immunity to electromagnetic disturbances. INSTALLATION RADIO FREQUENCY ENERGY This equipment does not exceed the class A limits for radio noise emissions from digital apparatus set out in the radio interference regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications. Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant les limites applicables aux appareils numériques de la classe A prescrites dans le règlement sur le brouillage radioélectriques publié par le ministère des Communications du Canada. INDEX Canadian Department of Communications RFI statement 70 INSTALLATION www.adder.com/contact-details Support: forum.adder.com CONFIGURATION Contact: OPERATION www.adder.com INDEX FURTHER INFORMATION Web: Documentation by: www.ctxd.com © 2014 Adder Technology Limited All trademarks are acknowledged. Part No. MAN-ALIF2112T • Release 3.3a 71 G Gateway remote setting 53 Gigabit Ethernet 14 Gui editing 39 H Hextile 63 Host computer configuration 56 power switching setup 57 Hotkey sequences 66 codes and macros 66 HTTP port remote setting 53 J Jumbo frames (packets) 44 K Keyboard codes sending 36 Keyboard Control 36 Keyboard layout remote setting 50 L Layers 2 and 3 46 Link cable lengths 14 Logging 58 Log on 23,33 N Network configuration 53 Network layout 40 Network switch choosing 40 Null-modem cable pin-out 67 O Optimization statistics for 30 Options switches 21 OSI model 46 P Password remote logon 33 Power strings for switching 57 Power switching configuration 57 control sequences 57 on & off select 35 user permissions 48 via viewer 35 Private access mode 35 CONFIGURATION M MAC address 52,53 Magic Eye 3,27 Menu bar editing 39 Menu key changing 59,60 Mouse advanced configuration 35 control 34 resync 34 Multicast configuration 20 Q Querier 44 R Rack mounting 8 Raw 63 Receiver configuration 19 Refresh screen 34 Remote configuration advanced unit configuration 51 host configuration 56 logging and status 58 network configuration 53 setting IP access control 54 unit configuration 50 user accounts 48 Reset manual 16 Resync mouse 34 OPERATION C Cable null-modem 67 Cable specifications 66 CODEC 3 Configuration advanced mouse 35 browser-based utility 17 menu bar edit 39 receiver 19 styles 2 switches 21 transmitter 18 Connections TX audio links 12 TX USB link 12 Controls viewer options 34 Control strings power switching 57 Cut-through 46 F Factory reset 16 Fast-Leave 44 Fibre Channel 14 Firmware current version 50 upgrade 21 Forwarding modes 46 Fragment-free 46 Frame Skipping 27 Front panel indicators 22 Full screen mode escape from (F8) 23 I IANA 20 IGMP 44 fast-leave 44 querier 44 snooping 44 Indicators 5,22 Initial configuration 16,32 IP access control 53,54 IP address remote setting 53 IP gateway 53 IP network mask 53 FURTHER INFORMATION B Browser viewer options 32,63 Browser-based utility 17 D Dimensions 67 Dithering 3 INDEX A Access control configuration 54 Access mode shared & private 35 Active Copper 14 Adaptive 46 Advanced unit configuration 51 AFZ 3,27 Anti-dither support 3 Auto select 63 INSTALLATION Index 72 INSTALLATION CONFIGURATION W Warranty 69 Web browser viewer options 32,63 Weight 67 Z ZRLE 63 OPERATION U Unit Configuration 50 Unit name remote setting 50 Upgrade firmware 21 User accounts 48 User configuration 48,49 Username remote logon 33 V Video optimization 18 Video modes 67 Video settings 35,36 Viewer window 23 menu bar editing 39 VNC port remote setting 53 VNC viewer connection options 59 window options 62 FURTHER INFORMATION T Teaming port 14 TX settings 26 Threshold setting 36 Time & date configuration 52 TLS 3 Transmitter configuration 18 Transport Layer Security 3 Troubleshooting 42 INDEX S Safety information 69 Screen best resolution 23 navigation 23 refresh 34 Server configuration 56 SFP module 14 Shared access mode 35 Single mouse mode 34 Slow connections optimizing for 23 Snooping 44 Spanning Tree Protocol 45 Specifications 67 Statistics graphing 30 Store and forward 46 Switch choosing 40 configuring 41 Syslog 58 System port 14 TX settings 26 73













































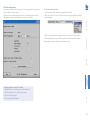





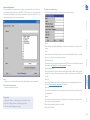


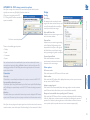


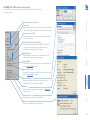
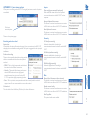




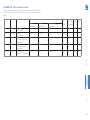

















![010003E - [PROJECT.TOC] - TMG Construction Corporation](http://vs1.manualzilla.com/store/data/006000704_1-51daa2ac67e6ebfb9337b1b072f623df-150x150.png)