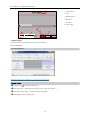
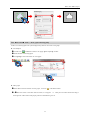
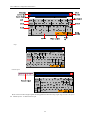
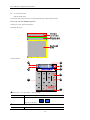
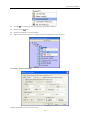
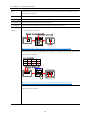
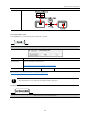
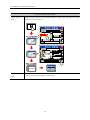
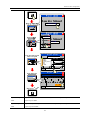
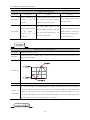
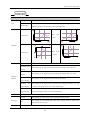
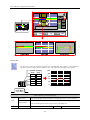
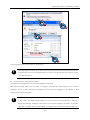
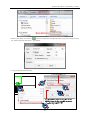
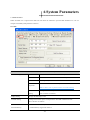
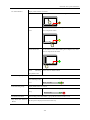
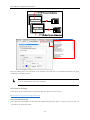
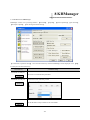
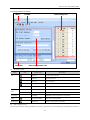
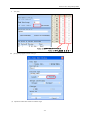
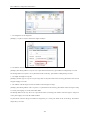
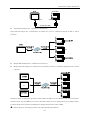
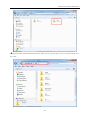
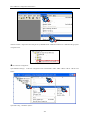
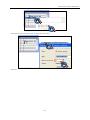
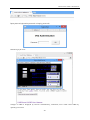
Download Kinco HMIware User Manual
Transcript
Safety Precautions Read this manual and related manuals that mentioned in this manual carefully before you use the products, at the same time operate the products under the premise of full safety attention. In order to use the products safely, we use the following icons and graphic symbols to represent precautions, and there is some important safety content for the precautions icons, please be sure to observe them. Danger If rated precautions are not taken, it may cause personal injury or death. Warning If rated precautions are not taken, it may cause personal injury. Be Care If rated precautions are not taken, it may cause slightly personal injury Notice If rated precautions are not taken, it may cause undesirable result or state. Forbidden Some instructions, processes and remove operations are forbidden to ensure correct use of product Put away this manual after reading, so that you can read it anytime. Note when using the product: The following places should be avoided when using MT series HMI: The place that the temperature and humidity exceeds the range of the specifications The place with high humidity that may cause condensed water The place that the temperature changes acutely The place that is shined by ultraviolet ray The place with heavy dust The place that is polluted by chemicals The place that is polluted by oily substance The place with heavy shock and vibration The place that is exposed to sunshine and wind directly. The communication cables that connect HMI and PLC should be kept far from equipments that may generate interference, like VFD, motor at the same time. At the same time do not put the control cable, power cable and high line in the same wireway or nearby, or the interference may causes the malfunction of the equipment. Please ensure the security of the system before you power on the HMI. The proper configuration program is must when you want to use HMI to control PLC. Please install the USB driver before you use USB cable to download user data Please use finger or professional touch pen to operate the HMI The input operation may fail if the HMI is touched rapidly and continuously. Please input the content after the previous operation is input successfully. If the backlight is off or the HMI has no display, do not touch it by mistake. Please confirm the safety of the system and then operate it. If the dip switches are changed, the operation takes effects after the restart button is pressed or the HMI is powered off and on. When you change the 3V battery in HMI, please choose the right model and install it correctly. Copyright©2008 Kinco Automation Ltd. All Rights Reserved Kinco Automation Ltd. 2 Preface Thank you for choosing Kinco MT series HMI. Before you use the MT series products, please read this manual carefully and understand it fully to ensure the personal and equipment safety. About this manual This manual is for the usage and design way of Kinco HMIware configuration software (“Kinco HMIware” for short). You can download it at our official English web site: http://www.kinco.cn/en/ ! The content in this manual may not be updated in time because of the improvement of products or other reasons. We advice customer to pay attention to the information at our web site in order to ensure the right timely information of product specifications and accessories When you use this manual, some rated manuals and supporting details maybe involved. They are: Communication Connection Help This manual provides some information of rated communication setting, supported registers and communication cables when the MT series HMI communicate with the PLC that it supports. Product documents Like catalog, products parameter list, order explanation, installation explanation manual, warranty and so on. Examples Some demo programs at our site. Range of Application This manual provides guides to Kinco HMIware, so that you can develop the project in HMI. Target Population This manual is for the people, commissioning engineers, technical support and Maintenance engineers who use Kinco MT series HMI and has basic knowledge in automation area. If necessary, they should have the ability to program with C language. How to use this manual This manual introduce the process, components, configuration methods, operation details and using skills from easy to difficult and step by step. It has three parts: introductory part, junior part and senior part. The new starter can start form introductory part, the one who has experience with Kinco HMIware just need to run over the introductory part, the engineer with rich experience in Kinco HMIware can start from the third part directly. The icons and terms in this manual 1 Safety icons and terms Danger If rated precautions are not taken, it may cause personal injury or death. Warning If rated precautions are not taken, it may cause personal injury. Be Care If rated precautions are not taken, it may cause slightly personal injury Notice If rated precautions are not taken, it may cause undesirable result Forbidden Some instructions, processes and remove operations are forbidden to ensure correct use of product General information of icons and items ! Provide tips or added information for using product correctly Link to the rated information of other manuals ※ The items with explanation and footnotes。 ☞ Content for tips Link to the rated information of this manual Items The following are the items in this manual: Items used in this manual Meaning Kinco HMIware The software for Kinco MT series HMI: Kinco HMIware configuration software HMI Kinco MT series HMI PLC Programmable Logic Controller PC Personal Computer External Storage Device The U disk or SD card that Kinco MT series HMI supports. 2 The following items are different from the official trade mark or name Items used in this manual Official trade mark or name Windows 98 Microsoft® Windows® 98 Operation System Windows Me Microsoft® Windows® Me Operation System Windows 2000 Microsoft® Windows® 2000 Operation System Windows XP Microsoft® Windows® XP Operation System Windows Vista Microsoft® Windows® Vista Operation System Windows 7 Microsoft® Windows® 7 Operation System Windows Server 2003 Microsoft® Windows Server® 2003 Operation System The following items describe the operation of mouse: Item Operation Step Click Do not move the mouse; press the left button, then release. Right Click Do not move the mouse; press the right button, then release. Double Click Drag Move Input Operation Do not move the mouse; press the left button two times quickly, this operation only takes effect on left button. Hold pressing the left button and move the mouse, release the left button at the target position. Move the mouse to the target position and stop. Press the left button in the input box, then release. When there is a cursor in the input box, input the content. Click, double click or right click the blank 3 Picture Precautions when using the software Install the proper Kinco HMIware according to the language of the OS, if you install the Chinese version in English OS, some function may be abnormal, because there is no Chinese character library in English OS. Kinco HMIware is backward compatible, but not the reverse. That is to say, the project that compiled by the higher version software cannot be opened and compiled by lower version, but the project that compiled by lower version software can be opened and compiled by higher version. The *.pkg file that compiled by the version that earlier than EV5000 V1.3.0 cannot be decompiled Please remember the password if you use the project password, upload password and decompilation password, we cannot provide the reset the password service or any universal password. The display difference between the Kinco HMIware and HMI: (1) When you configure the project, there are some grids as the aligning reference in Kinco HMIware configuration area, there is no grids in HMI screen. (2) The following size difference maybe happen when using dial scale and dial axis. (3) If the graphic uses the gradient color as fill color, the following display difference maybe happen. Product Support Online support If you have any question when using the product, you can contact our overseas technical engineers; they can support you online or by email. 4 Technical Training If you have any question about the product described in this manual, you can contact our company directly or local distributors. About the technical training, please pay attention to the information at our site or consult the sales manager. Contact us Kinco Automation Ltd Email: [email protected] 5 Index Part1 Basic Part 1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................................................................ 1 1.1 About Kinco HMIware ............................................................................................................................................... 1 1.2 Features List of Kinco HMIware ................................................................................................................................ 1 2 Starting ................................................................................................................................................................................. 13 2.1 How to use Kinco HMIware..................................................................................................................................... 13 2.2 How to get Kinco HMIware software....................................................................................................................... 13 2.3 Kinco HMIware Installation and Operating Environment Requirement................................................................... 13 2.4 Install/Uninstall ........................................................................................................................................................ 13 2.4.1 Install Kinco HMIware................................................................................................................................. 13 2.4.2 Uninstall Kinco HMIware ............................................................................................................................ 14 2.5 Start/Quit .................................................................................................................................................................. 14 2.5.1 Start Kinco HMIware ................................................................................................................................... 14 2.5.2 Quit Kinco HMIware.................................................................................................................................... 15 2.6 System Language Change ........................................................................................................................................ 15 2.7 F1 Help..................................................................................................................................................................... 16 2.8 Upgrade/Update........................................................................................................................................................ 16 2.9 Software Compatibility............................................................................................................................................. 16 2.10 Install USB Driver.................................................................................................................................................. 17 2.11 Software Application Program Introduction ........................................................................................................... 19 3 Make Project......................................................................................................................................................................... 21 3.1 Project Requirement ................................................................................................................................................. 21 3.2 System Analysis ....................................................................................................................................................... 22 3.3 Make Project............................................................................................................................................................. 24 3.3.1 Create Project ............................................................................................................................................... 24 3.3.2 Device Selection, Connection and Parameters Setting ................................................................................. 25 3.3.3 Edit Frame.................................................................................................................................................... 27 3.3.4 Save Project.................................................................................................................................................. 46 3.3.5 Project Simulation ........................................................................................................................................ 46 3.3.6 Download Project......................................................................................................................................... 47 3.4 Project Folder Introductions ..................................................................................................................................... 47 Part2 Advanced Part 1 User Interface ....................................................................................................................................................................... 51 1.1 Interface Layout ....................................................................................................................................................... 51 1.2 Menu ........................................................................................................................................................................ 51 1.2.1 File Menu ..................................................................................................................................................... 51 1.2.2 Edit Menu..................................................................................................................................................... 52 1.2.3 View Menu ................................................................................................................................................... 52 1 1.2.4 Screen Menu................................................................................................................................................. 52 1.2.5 Draw Menu................................................................................................................................................... 53 1.2.6 Components Menu ....................................................................................................................................... 53 1.2.7 Tools Menu................................................................................................................................................... 53 1.2.8 Option Menu ................................................................................................................................................ 53 1.2.9 Window Menu .............................................................................................................................................. 53 1.2.10 Help Menu.................................................................................................................................................. 53 1.3 Toolbar...................................................................................................................................................................... 54 1.3.1 Basic Toolbar................................................................................................................................................ 54 1.3.2 Draw Toolbar................................................................................................................................................ 54 1.3.3 Page Switch Toolbar..................................................................................................................................... 54 1.3.4 Position Toolbar ........................................................................................................................................... 54 1.3.5 Line Width Toolbar....................................................................................................................................... 55 1.3.6 Line Style Toolbar ........................................................................................................................................ 55 1.3.7 System Toolbar............................................................................................................................................. 55 1.3.8 Database Toolbar.......................................................................................................................................... 55 1.3.9 Code Edit Toolbar ........................................................................................................................................ 55 1.3.10 Fill Effect Toolbar ...................................................................................................................................... 55 1.3.11 Label Position Toolbar................................................................................................................................ 56 1.3.12 State Switch Toolbar................................................................................................................................... 56 1.3.13 Font Toolbar ............................................................................................................................................... 56 1.3.14 Status Bar ................................................................................................................................................... 56 1.3.15 Tip Text ...................................................................................................................................................... 56 1.3.16 Toolbar Options.......................................................................................................................................... 56 1.4 Software window...................................................................................................................................................... 56 1.4.1 Graph Element Window ............................................................................................................................... 57 1.4.2 Project Files Window ................................................................................................................................... 58 1.4.3 Project Sstructure Window ........................................................................................................................... 58 1.4.4 Message Window ......................................................................................................................................... 59 1.4.5 Component List Window.............................................................................................................................. 60 1.5 Configuration Edit Area............................................................................................................................................ 61 1.5.1 Construct Window........................................................................................................................................ 61 1.5.2 HMI Edit Window ........................................................................................................................................ 62 1.5.3 Graphic Edit Window................................................................................................................................... 62 1.5.4 Macro Edit Window ..................................................................................................................................... 63 1.5.5 Edit Initial Window ...................................................................................................................................... 63 2 Basic Design Method............................................................................................................................................................ 64 2.1 Window screen ......................................................................................................................................................... 64 2.1.1 Specification of window screen.................................................................................................................... 64 2.1.2 Window Display Methods ............................................................................................................................ 64 2.1.3 Display Position ........................................................................................................................................... 67 2.1.4 Display Order ............................................................................................................................................... 67 2.1.5 Copy/Delete Windows.................................................................................................................................. 68 2.2 Draw......................................................................................................................................................................... 69 2 2.2.1 Image Format ............................................................................................................................................... 69 2.2.2 Vector ........................................................................................................................................................... 69 2.2.3 Geometric Figures Attribution...................................................................................................................... 72 2.2.4 About Fountain Fill ...................................................................................................................................... 73 2.2.5 Bitmap.......................................................................................................................................................... 74 2.2.6 About Transparent Color .............................................................................................................................. 74 2.3 Text........................................................................................................................................................................... 75 2.3.1 Font Type...................................................................................................................................................... 76 2.3.2 Dot Matrix Font............................................................................................................................................ 76 2.3.3 Vector Font ................................................................................................................................................... 76 2.3.4 Graph Font ................................................................................................................................................... 77 2.3.5 Text Attribute Edition ................................................................................................................................... 78 2.3.6 Notes for Using Vector Font......................................................................................................................... 78 2.4 Keyboard .................................................................................................................................................................. 79 2.4.1 Keyboard Type ............................................................................................................................................. 79 2.4.2 NUM Keyboard............................................................................................................................................ 81 2.4.3 ASCII Keyboard........................................................................................................................................... 83 2.4.4 HEX Keyboard............................................................................................................................................. 83 2.4.5 Create your Own Mumber Keyboard ........................................................................................................... 84 2.4.6 Create your Oown Unicode Keyboard ......................................................................................................... 86 2.4.7 Call Keyboard in the Group Component Library ......................................................................................... 87 2.5 Code Type................................................................................................................................................................. 88 2.5.1 BIN............................................................................................................................................................... 88 2.5.2 BCD ............................................................................................................................................................. 89 2.5.3 LSB .............................................................................................................................................................. 89 2.6 Language Switching ................................................................................................................................................. 89 2.7 RTC Set .................................................................................................................................................................... 91 2.7.1 Through Special Registers............................................................................................................................ 92 2.7.2 Calibrate System Time in System Setup Screen ........................................................................................... 93 2.7.3 System Time and PLC Time Synchronization.............................................................................................. 93 2.8 LOGO Screen(Logo)........................................................................................................................................... 96 2.8.1 LOGO Screen Specification ......................................................................................................................... 96 2.8.2 Init Screen Setting ........................................................................................................................................ 96 2.8.3 Note for Using Init Screen............................................................................................................................ 98 2.9 Exchange Serial........................................................................................................................................................ 98 2.10 Replace Devices ..................................................................................................................................................... 99 2.10.1 Replace HMI ............................................................................................................................................ 100 2.10.2 Replace PLC............................................................................................................................................. 101 2.11 Index Function...................................................................................................................................................... 102 2.11.1 Index Register........................................................................................................................................... 102 2.11.2 Index Station Num.................................................................................................................................... 103 2.12 Buzzer................................................................................................................................................................... 105 2.12.1 Touch Beep............................................................................................................................................... 105 2.12.2 Alarm Beep............................................................................................................................................... 106 3 2.13 Screen Saver ......................................................................................................................................................... 107 2.14 Password Setting .................................................................................................................................................. 108 2.14.1 Project Protection ..................................................................................................................................... 108 2.14.2 Screen Protection...................................................................................................................................... 108 2.14.3 Component Protection.............................................................................................................................. 109 2.15 Data Encryption.................................................................................................................................................... 110 2.16 Animation Effects................................................................................................................................................. 112 2.17 Multi-Copy ........................................................................................................................................................... 115 2.18 Group.................................................................................................................................................................... 116 2.19 Find /Replace........................................................................................................................................................ 119 3 Window .............................................................................................................................................................................. 121 3.1 Window Types ........................................................................................................................................................ 121 3.2 System Default Window......................................................................................................................................... 123 3.3 Edit Window........................................................................................................................................................... 124 3.3.1 Window Add............................................................................................................................................... 124 3.3.2 Window Opening........................................................................................................................................ 125 3.3.3 Window Copy/ Multi-Windows Copy ........................................................................................................ 126 3.3.4 Window Deletion/ Multi-Windows Deletion.............................................................................................. 127 3.4 Window Attribute ................................................................................................................................................... 128 3.4.1 Open Window Attribute Box ...................................................................................................................... 128 3.4.2 Window Attribute Descriptions .................................................................................................................. 129 3.5 Components Related to Window ............................................................................................................................ 132 4 Component ......................................................................................................................................................................... 133 4.1 Common Setting of Component ............................................................................................................................. 133 4.1.1 Create and Delete Component.................................................................................................................... 133 4.1.2 Execution Order of Components ................................................................................................................ 134 4.1.3 Methods to Open Attributes Window ......................................................................................................... 135 4.1.4 Basic Setting............................................................................................................................................... 136 4.1.5 Tag Setting.................................................................................................................................................. 138 4.1.6 Graphics Setting ......................................................................................................................................... 139 4.1.7 Control Setting Option ............................................................................................................................... 140 4.1.8 Display Setting ........................................................................................................................................... 143 4.1.9 Touch Sound Control.................................................................................................................................. 145 4.1.10 Save Historical Data................................................................................................................................. 145 4.2 Button/Switch Components.................................................................................................................................... 147 4.2.1 Bit State Setting.......................................................................................................................................... 147 4.2.2 Bit State Switch.......................................................................................................................................... 150 4.2.3 Multiple State Setting................................................................................................................................. 152 4.2.4 Multiple State Switch ................................................................................................................................. 155 4.2.5 Combination Operations............................................................................................................................. 157 4.2.6 Function Key.............................................................................................................................................. 158 4.3 Lamp Component ................................................................................................................................................... 164 4.3.1 Bit State Lamp............................................................................................................................................ 164 4.3.2 Multiple State Display................................................................................................................................ 166 4 4.4 Number Components.............................................................................................................................................. 167 4.4.1 Number Input ............................................................................................................................................. 169 4.4.2 Number Display ......................................................................................................................................... 170 4.5 Text Components.................................................................................................................................................... 170 4.5.1 Text Iput ..................................................................................................................................................... 174 4.5.2 Text Display ............................................................................................................................................... 174 4.5.3 Note Book .................................................................................................................................................. 175 4.6 Graph/Meter Components ...................................................................................................................................... 175 4.6.1 Trend Curve................................................................................................................................................ 178 4.6.2 XY Plot....................................................................................................................................................... 190 4.6.3 Oscillograph ............................................................................................................................................... 194 4.6.4 Meter .......................................................................................................................................................... 196 4.6.5 Bar Picture.................................................................................................................................................. 198 4.7 Alarm Component .................................................................................................................................................. 201 4.7.1 Event Display ............................................................................................................................................. 203 4.7.2 Historical Event Display ............................................................................................................................ 207 4.7.3 Event Bar.................................................................................................................................................... 208 4.7.4 Alarm Display ............................................................................................................................................ 210 4.7.5 Alarm Bar ................................................................................................................................................... 210 4.8 Window Component ............................................................................................................................................... 211 4.8.1 Direct Window ........................................................................................................................................... 211 4.8.2 Indirect Window......................................................................................................................................... 213 4.9 Graphic Components .............................................................................................................................................. 214 4.9.1 Vector Graph .............................................................................................................................................. 214 4.9.2 Bitmap........................................................................................................................................................ 214 4.9.3 Free Plotting ............................................................................................................................................... 214 4.9.4 Dynamic Graph .......................................................................................................................................... 215 4.9.5 GIF ............................................................................................................................................................. 215 4.10 Video Input Component........................................................................................................................................ 216 4.10.1 Video ........................................................................................................................................................ 216 4.10.2 Camera ..................................................................................................................................................... 218 4.11 Multiple State Neon Lamp.................................................................................................................................... 219 4.11.1 Bit State Neon Lamp ................................................................................................................................ 219 4.11.2 Bit State Neon Lamp ................................................................................................................................ 220 4.12 Animation Components ........................................................................................................................................ 221 4.12.1 Animation................................................................................................................................................. 221 4.12.2 Moving Component.................................................................................................................................. 222 4.12.3 Pipeline..................................................................................................................................................... 226 4.13 Grid Components.................................................................................................................................................. 227 4.13.1 Grid .......................................................................................................................................................... 227 4.13.2 Historical Data Display ............................................................................................................................ 228 4.13.3 User Info Display ..................................................................................................................................... 233 4.13.4 Operation Log .......................................................................................................................................... 234 4.13.5 Data Report .............................................................................................................................................. 236 5 4.14 Data Transmission Component............................................................................................................................. 245 4.14.1 Recipe....................................................................................................................................................... 245 4.14.2 Data Transmission .................................................................................................................................... 246 4.15 Project Database ................................................................................................................................................... 248 4.15.1 Text Library.............................................................................................................................................. 249 4.15.2 Address Tag .............................................................................................................................................. 250 4.15.3 Event Information .................................................................................................................................... 251 4.15.4 Alarm Information.................................................................................................................................... 255 4.15.5 PLC Control ............................................................................................................................................. 257 4.15.6 Sound Lib ................................................................................................................................................. 264 4.15.7 Data Logger.............................................................................................................................................. 265 4.15.8 Schedule List ............................................................................................................................................ 267 4.16 Auxiliary Component ........................................................................................................................................... 271 4.16.1 Scale ......................................................................................................................................................... 271 4.16.2 Timer ........................................................................................................................................................ 272 4.16.3 Scroll Bar ................................................................................................................................................. 275 4.16.4 Date/Time................................................................................................................................................. 276 4.16.5 Note Pad................................................................................................................................................... 276 4.16.6 File List .................................................................................................................................................... 277 4.16.7 Trigger Touch ........................................................................................................................................... 277 5 Better Understanding of Library......................................................................................................................................... 279 5.1 Text Library ............................................................................................................................................................ 279 5.1.1 Create a Text Library.................................................................................................................................. 279 5.1.2 Export/Import Text Library ........................................................................................................................ 281 5.1.3 Set the Language of Text Library ............................................................................................................... 281 5.1.4 Text Library Application ............................................................................................................................ 282 5.2 Address Tag Library ............................................................................................................................................... 284 5.2.1 Build a Address tag Library........................................................................................................................ 284 5.2.2 Address Tag Application............................................................................................................................. 284 5.3 Graphic Library ...................................................................................................................................................... 285 5.3.1 Import Graphics.......................................................................................................................................... 285 5.3.2 Build New Graphics ................................................................................................................................... 289 5.3.3 Edit Graphics.............................................................................................................................................. 298 5.3.4 How to Use the Graphics............................................................................................................................ 301 5.4 Sound Lib Application............................................................................................................................................ 303 5.4.1 Import Audio File ....................................................................................................................................... 303 5.4.2 How to Use Audio File............................................................................................................................... 305 6 System Parameters.............................................................................................................................................................. 307 6.1 HMI Attributes ....................................................................................................................................................... 307 6.1.1 HMI............................................................................................................................................................ 307 6.1.2 Task Bar ..................................................................................................................................................... 308 6.1.3 HMI Extended Attributes ........................................................................................................................... 310 6.1.4 HMI System Information Text ................................................................................................................... 313 6.1.5 Security Levels Setting............................................................................................................................... 314 6 6.1.6 User Permissions Setting............................................................................................................................ 314 6.1.7 Historical Events Storage ........................................................................................................................... 315 6.1.8 Print Setting................................................................................................................................................ 316 6.1.9 Serial Port Setting....................................................................................................................................... 317 6.1.10 Extended Memory .................................................................................................................................... 319 6.2 PLC Attribute ......................................................................................................................................................... 319 7 Compile/Simulate/Download/Upload................................................................................................................................. 321 7.1 Compilation............................................................................................................................................................ 321 7.1.1 Methods of Compilation............................................................................................................................. 321 7.2 Simulation .............................................................................................................................................................. 321 7.2.1 Modes of Simulation .................................................................................................................................. 321 7.2.2 Exit Simulation........................................................................................................................................... 322 7.3 Download ............................................................................................................................................................... 322 7.3.1 Download Method Selection ...................................................................................................................... 322 7.3.2 Download via U disk or SD card................................................................................................................ 324 7.3.3 Download Selection ................................................................................................................................... 324 7.4 Upload/ Download/Compile Project via KHManager ............................................................................................ 328 8 KHManager ........................................................................................................................................................................ 329 8.1 Introduction to KHManager ................................................................................................................................... 329 8.2 Methods of Open KHManager ............................................................................................................................... 330 8.3 Download ............................................................................................................................................................... 330 8.4 Upload .................................................................................................................................................................... 331 8.5 System Operation ................................................................................................................................................... 331 8.6 Get Version ............................................................................................................................................................. 331 8.7 Decompile Operation.............................................................................................................................................. 331 8.8 Data Decryption ..................................................................................................................................................... 332 9 Macro.................................................................................................................................................................................. 333 9.1 Macro Editing Environment ................................................................................................................................... 333 9.2 Macro Edit.............................................................................................................................................................. 333 9.2.1 Build Macro ............................................................................................................................................... 333 9.2.2 Delete Macro.............................................................................................................................................. 334 9.2.3 Rename Macro ........................................................................................................................................... 334 9.2.4 Program Macro........................................................................................................................................... 335 9.2.5 Execute Macro............................................................................................................................................ 338 9.3 Macro Application .................................................................................................................................................. 338 9.4 Local Variable Function.......................................................................................................................................... 340 9.5 Array Application ................................................................................................................................................... 341 9.6 Some Notes on the Macro ...................................................................................................................................... 344 10 Password........................................................................................................................................................................... 345 10.1 Project Protection ................................................................................................................................................. 346 10.1.1 Project Password Protection ..................................................................................................................... 346 10.1.2 Upload Password Protection and Prohibit Uploading............................................................................... 346 10.1.3 Decompilation Password Protection and Prohibit Decompiling............................................................... 348 10.1.4 Download Password Protection................................................................................................................ 349 7 10.2 Window Protection ............................................................................................................................................... 350 10.2.1 Window Password Setting........................................................................................................................ 350 10.2.2 Security Level Setting of Window............................................................................................................ 351 10.2.3 System reserved registers related to security level ................................................................................... 352 10.2.4 Security level password input window ..................................................................................................... 352 10.2.5 Modifying Password Online..................................................................................................................... 353 10.2.6 Application of Passwords Required for Switching Windows ................................................................... 354 10.3 Component Protection .......................................................................................................................................... 355 10.3.1 Security Level Protection for Components............................................................................................... 355 10.3.2 User Permission Protection for Components............................................................................................ 355 10.3.3 System Reserved Registers Related to User Permissions ......................................................................... 356 10.3.4 System Reserved Registers Related to Add/Delete Users and User Permissions Online.......................... 356 10.3.5 Window for User Permission Password Input .......................................................................................... 357 10.3.6 Application of Security Level Protection for Components ....................................................................... 358 10.3.7 Application of User Permission Protection for Component...................................................................... 359 11 Recipe/ RecipeEditor ........................................................................................................................................................ 367 11.1 Register Related to the Recipe.............................................................................................................................. 367 11.2 Method for Checking the Recipe Size .................................................................................................................. 368 11.2.1 Method for Checking the RW Size ........................................................................................................... 368 11.2.2 Calculation for Recipe Address Range ..................................................................................................... 369 11.3 Usage of Recipe.................................................................................................................................................... 370 11.3.1 Absolute Address ...................................................................................................................................... 370 11.3.2 Index Address ........................................................................................................................................... 370 11.3.3 Application of Recipe ............................................................................................................................... 371 11.4 RecipeEditor ......................................................................................................................................................... 373 11.4.1 Recipe Editor Start-up .............................................................................................................................. 374 11.4.2 Recipe Editor User interface..................................................................................................................... 375 11.4.3 Usage of RecipeEditor.............................................................................................................................. 377 11.5 Recipe Uploading/ Downloading/ Clearing .......................................................................................................... 384 12 KHMonitor ....................................................................................................................................................................... 385 12.1 Descriptions of KHMonitor.................................................................................................................................. 385 12.2 Start KHMonitor................................................................................................................................................... 385 12.3 KHMonitor Interface ............................................................................................................................................ 385 12.4 How to Use KHMonitor ....................................................................................................................................... 386 13 Print .................................................................................................................................................................................. 389 13.1 Type of Printer supports local printing ................................................................................................................. 389 13.2 Printing-related Components ................................................................................................................................ 390 13.3 Pictbridge Print..................................................................................................................................................... 392 13.4 Print Function Setting Method.............................................................................................................................. 394 13.4.1 Local Print: HMI serial is connected directly to the Printer ..................................................................... 394 13.4.2 Local Print: HMI USB Slave is connected directly to the Printer ............................................................ 395 13.4.3 Network Print (remote print): Through Network Printer to Print HMI Screen......................................... 396 13.4 Print Page Application Skills ................................................................................................................................ 401 13.5 Print Error............................................................................................................................................................. 402 8 14 HMI Communication........................................................................................................................................................ 403 14.1 Serial Communication .......................................................................................................................................... 403 14.1.1 HMI and PC Serial Communication......................................................................................................... 403 14.1.2 HMI and PLC /Controller Serial Communication .................................................................................... 403 14.1.3 Serial Communication Related Settings ................................................................................................... 410 14.2 Network Port Communication.............................................................................................................................. 410 14.2.1 HMI and PC Network Port Communication............................................................................................. 410 14.2.2 HMI and HMI Port Communication Network.......................................................................................... 411 14.2.3 HMI and PLC/Controller Network Port Communication......................................................................... 412 14.2.4 FTP Function............................................................................................................................................ 415 14.3 Field Bus Communication .................................................................................................................................... 418 14.3.1 CAN Communicate .................................................................................................................................. 418 14.3.2 DP Communicate ..................................................................................................................................... 419 14.4 MPI Communicate................................................................................................................................................ 424 14.5 MODBUS Protocol Applications(Master-slave mode).................................................................................... 428 14.5.1 MODBUS Protocol Overview.................................................................................................................. 428 14.5.2 MODBUS Protocol Communication Format ........................................................................................... 430 14.5.3 MODBUS Protocol in the HMI Application ............................................................................................ 436 15 VNC.................................................................................................................................................................................. 442 15.1 Various client-sides............................................................................................................................................... 442 15.2 Access via LAN.................................................................................................................................................... 442 15.2.1 Remote control HMI by PC via LAN....................................................................................................... 442 15.2.2 Remote control HMI by mobile via LAN................................................................................................. 445 15.2.3 Remote control HMI by browser via LAN............................................................................................... 446 15.3 Access via WAN ................................................................................................................................................... 448 16 Register............................................................................................................................................................................. 452 16.1 Local Registers of HMI ........................................................................................................................................ 452 16.1.1 Bit Address ............................................................................................................................................... 452 16.1.2 Word Address ........................................................................................................................................... 452 16.2 System Special Registers of HMI......................................................................................................................... 453 16.2.1 Parameter Setting of Hardware................................................................................................................. 454 16.2.2 System Setting.......................................................................................................................................... 455 16.2.3 Components Setting ................................................................................................................................. 460 16.2.4 Security Leve l and User Permission........................................................................................................ 462 16.2.5 Data and Project Management.................................................................................................................. 463 16.2.6 Communication ........................................................................................................................................ 465 Part3 Hardware Part 1 Name and Specification...................................................................................................................................................... 470 1.1 Name of Each Part......................................................................................................................................... 470 1.2 Specifications of Each Part............................................................................................................................ 471 2 Connection with Preiferal Equipments ............................................................................................................................... 476 2.1 Connection via Serial Port............................................................................................................................. 476 2.2 Connection via USB Interfaces ..................................................................................................................... 478 9 2.3 Connection via LAN Interfaces..................................................................................................................... 479 3 System Setting Mode.......................................................................................................................................................... 481 3.1 Methods to Display System Setting Mode .................................................................................................... 481 3.2 System Setting............................................................................................................................................... 481 4 Touch Screen Calibrate Mode............................................................................................................................................. 483 4.1 Methods to Display Touch Screen Calibrate Mode ....................................................................................... 483 4.2 Touch Screen Calibrate Setting ..................................................................................................................... 483 5 Firmware Update Mode ...................................................................................................................................................... 484 5.1 Methods to Display Firmware Update Mode ................................................................................................ 484 5.2 Firmware Update Setting............................................................................................................................... 484 6 Maintenance and Tending ................................................................................................................................................... 485 6.1 Maintenance .................................................................................................................................................. 485 6.2 Tending.......................................................................................................................................................... 485 Appendix 1 Regular PLC Used for HMI ............................................................................................................................... 487 Appendix 2 List of Error Information.................................................................................................................................... 491 Appendix 3 List of System Prompt Message......................................................................................................................... 496 10 Basic Part 1 Introduction This chapter mainly introduces the features and functions of Kinco HMIware Configuration Software. 1.1 About Kinco HMIware Kinco HMIware Configuration Software(Hereinafter referred to as “Kinco HMIware”)is a human-machine interface(HMI) configuration software developed by Kinco Electric (Shanghai) Ltd. (Hereinafter referred to as “Kinco”),it is special for MT4000/5000 series HMI. Kinco HMIware provides a powerful integrated development environment for users. Products are widely applied in various kinds of fields such as medical, chemical industry, electric power, printing, textile, food, national defense and engineering machinery, intelligent household, high speed railway and so on. 1.2 Features List of Kinco HMIware Edit operation functions Functions Diagrams Notes ☞Details Batch to modify font please refer to 【 Advanced Part 2.3.5 Text properties Attribute Edition】 ☞Details Batch to modify graph 【 properties please Advanced refer Part to 2.2.3 Geometric Figures Attribution】 ☞Details please refer to 【Advanced Part 3.3.3 Window Batch to copy windows Copy /Multi-Windows Copy】 ☞Details Crossing projects to 【 copy components please Advanced refer Part to 2.1.5 Copy/Delete windows】 ☞Details Batch to set components please refer to 【 Advanced Part 1.2.2 Edit alignment Menu】 1 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ☞Details Batch to set components please refer to 【 Advanced Part 1.2.2 Edit same size Menu】 ☞Details Batch to set components please refer to 【 Advanced Part 1.2.2 Edit same space Menu】 ☞Details Overlay windows please refer to 【Advanced Part 2.1.2 Windows Display Methods】 ☞Details Group components please refer to 【Advanced Part 2.18 Group】 ☞Details Multi-copy components 【 please Advanced refer Part to 2.17 Multi-copy】 ☞Details please refer to 【Advanced Part 2.9 Exchange Exchange serial ports Serial】 ☞Details please refer to 【Advanced Part 2.10 Replace Devices】 Exchange devices Functions of Components Switch and lamp Functions Diagrams 2 Notes Basic Part Introduction Lamps for displaying OFF ON states of device’s ☞Details please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.3 Lamp address Component】 Switches for changing ☞Details states of device’s 【 address please Advanced refer Part to 4.2 Button/Switch Component】 Switches for changing ☞Details the value of device’s 【 address Button/Switch Component】 please Advanced refer Part to 4.2 Number/Text input and display Functions Diagrams Notes ☞Details Number input please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.4.1 Number Input】 ☞Details Number display please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.4.2 Number Display】 ☞Details please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.5.1 Text Text input Text display Input】 ☞Details D100 4 D 4 8 M H D101 2 0 4 9 Space I please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.5.2 Text HMI Display】 ☞Details System time display 【 Advanced Date/Time】 3 please Part refer to 4.16.4 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ☞Details Text annotations please refer to 【Advanced Part 2.3 Text】 Data transmission Functions Diagrams Notes ☞Details Transmit data by timing please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.16.2 Timer】 ☞Details Transmit data by touch please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.14 Data Transmission Component】 ☞Details Transmit data by trigger please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.14.2 Data ... ... Transmission】 ☞Details please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.14.1 Recipe Data transmit by recipe Data】 Meter and Graph Functions Diagrams Notes ☞Details Display data as meter refer to 【Advanced Part 4.6.4 Meter】 D100=75 Display data as bar please 100 ☞Details 50 【 Advanced Part 4.6.5 Bar graph Picture】 0 4 please refer to Basic Part Introduction ☞Details please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.6.1 Trend Display data as trend Curve】 curve ☞Details please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.6.1 Trend Display data as dot Curve】 graph. ☞Details please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.6.1 Trend Display data as Curve】 projection graph ☞Details Zoom in please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.6.1 Trend Curve】 Zoom of trend curve Normal Zoom out Alarm Functions System Diagrams Notes ☞Details alarm please refer to 【 Advanced Part 6.1.4 HMI information System Information Text】 5 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software User-defined system ☞Details PLC No Response PLC disconnect please refer to 【 Advanced Part 6.1.4 HMI alarm information System Information Text】 Display ☞Details user-defined refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.7 Alarm alarm information when Component】 alarm happen Display please alarm ☞Details please refer to infromation in popup window when 【 Advanced Part 4.7 Alarm alarm Component】 happen The buzzer will peal ! 2 2011/06/23 15:22:54 15 1 2011/06/23 14:01:00 14:44:20 14 0 2011/06/23 10:50:01 11:40:10 10 Beep... ☞Details please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.7 Alarm when alarm happen Component】 ☞Details Obtain the alarm time of event please refer to 【 Advanced Part 2.7.3 System information time from external clock. and PLC CPU time synchronization】 ☞Details please refer to Query historical event 【Advanced Part 4.7.2 Historical records by inputting Event Display】 date or file number ☞Details Import/Export alarm/event logon please to 【 Advanced Part 4.7 Alarm information Component】 Conditional control Functions refer Diagrams 6 Notes Basic Part Introduction ☞Details please refer to Components are limited 【Advanced Part 4.1.7 Control by user security level. Setting Option】 ☞Details please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.1.7 Control Setting Option】 Components are limited by user permission. ☞Details please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.1.7 Control Components are limited by the status Setting Option】 of registers. ☞Details please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.1.7 Control Notification operation Setting Option】 Conditional Display Functions Display according Diagrams ☞Details components to Notes please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.1.8 Display user Setting】 security level. 7 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ☞Details please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.1.8 Display Display Setting】 components according to user permission. ☞Details Display please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.1.8 Display components Setting】 according to the status of registers. Data Storage Function Functions Diagrams Save historical event Notes ☞Details please refer to information. 【 Advanced Part 6.1.7 Historical Events Storage】 Save sampling data of ☞Details SD trend curve. please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.1.10 Save SAVE SRAM Save operation records Historical Data】 ☞Details please refer to 【 Advanced Part 6.1.3 HMI Extended Attributes】 Save recipe data ☞Details please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.14.1 Recipe】 Data Clear Function 8 Basic Part Introduction Functions Diagrams Notes ☞Details please refer to Clear historical event 【 Advanced Part 4.7 Alarm records. Component】 ☞Details Clear historical data 【 records of trend curve. please Advanced 8.3 please refer to SRAM Clear historical recipe Part to Download】 ☞Details data. refer 【 D100 150 D100 0 D101 125 D101 0 Advanced Part 8.3 Download】 Window Changing Function Functions Diagrams Notes ☞Details Change window by to Key】 D0:0 10 window refer 【Advanced Part 4.2.6 Function touch button. Change please ☞Details Frame 0 Frame 10 by PLC control. please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.15.5 PLC Control】 ☞Details please refer to Popup other window in 【 Advanced Part 4.8 Window current window. Component】 Password Protection Function Functions Diagrams 9 Notes Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ☞Details please refer to Password protection for 【 Advanced Part 10.1 Project project. Protection】 ☞Details please refer to Password protection for 【 Advanced Part 10.1 Project uploading project. Protection】 ☞Details please refer to Password protection for 【 Advanced Part 10.1 Project decompiling project. Protection】 ☞Details please refer to Password protection for 【Advanced Part 10.2 Window user security level. Protection】 ☞Details please refer to 【 Advanced Part 10.3.2 User Permission Password protection for Protection for Components】 user permission. CSV file encryption ☞Details CSV file CSV file Encrypt Decrypt please to 【 Advanced Part 2.15 Data Encryption】 External Input/ Output Functions refer Diagrams 10 Notes Basic Part Introduction ☞Details please refer to【HMI Read data from barcode and PLC connection guide 】 reader. manual Obtain image ☞Details from please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.10 Video video. Input Component】 Printout the screen ☞Details image or data. 【Advanced Part 13 Print】 please refer to Connect keyboard and mouse. Print Function Functions Diagrams 15:25:54 Abnormal T 14:01:00 Abnormal T 10:50:01 Abnormal T Trigger printing event information. 2 2011/06/23 15:22:54 15 1 2011/06/23 14:01:00 14:44:20 14 0 2011/06/23 10:50:01 11:40:10 10 Notes ☞Details please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.15.3 Event Information】 ☞Details please refer to Touch button to print 【Advanced Part 4.2.6 Function screen image. Key】 ☞Details Print trend curve real please refer to 【 Advanced Part 4.6.1 Trend time. Curve】 Frame 10 D0:0 10 ☞Details please refer to Print screen image by 【 Advanced Part 4.15.5 PLC PLC control. Control】 Frame 0 Upload/Download Functions Diagrams 11 Notes Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ☞Details please refer to Download project from 【 Advanced Part 7 Compile PC. /Simulate/Download/Upload】 ☞Details please refer to Upload project from 【 Advanced Part 7 Compile HMI to PC. /Simulate/Download/Upload】 ☞Details Download project from please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.2.6 Function external memory. Key】 Upload project from ☞Details HMI 【Advanced Part 4.2.6 Function to external memory. please refer to Key】 Script Function Macro Functions Diagrams Notes ☞Details Execute data operation please refer to 【Advanced Part 9 Macro】 or control the display in HMI by macro. Other Function Functions Diagrams Notes ☞Details Customize logo. please refer to 【 Advanced Part 2.8 Logo Screen (Logo)】 12 Basic Part Introduction ☞Details please refer to 【Advanced Part 2.6 Language Change Switching】 languages online ☞Details Clock setting refer to 【Advanced Part 2.7 RTC Set】 ☞Details Save please screen please refer to by 【 Advanced Part 4.15.5 PLC screenshot function Control】 ☞Details Index for register please refer to 【 Advanced Part 2.11 Index address(Offset) Function】 ☞Details please refer to 【 Advanced Part 2.11 Index Index for PLC station Function】 number.(Offset) 13 2 Starting 2.1 How to use Kinco HMIware The procedure for using Kinco HMIware is shown in following figure. 2.2 How to get Kinco HMIware software Users can download Kinco HMIware software from download center in Kinco’s website: http://www.kinco.cn/en/ 2.3 Kinco HMIware Installation and Operating Environment Requirement ! Note for using Windows Vista/Windows 7 OS: When using Windows Vista/Windows 7 OS, don’t install Kinco HMIware in system disk(C:). When using Windows Vista/Windows 7 OS, Kinco HMIware must run as administrator. Right click the icon of Kinco HMIware.exe, and then select “Run as administrator” as following figure: 2.4 Install/Uninstall There are two versions of Kinco HMIware (Chinese version and English version). 2.4.1 Install Kinco HMIware The procedure of installation is as following: Double click“Setup.exe”file to run the installation program. Enter welcome window. Select installation directory, the default directory is “D:\Program Files” and it will create “Kinco HMIware” folder automatically. Click【Browse】to change the installation directory. Confirm installation. It will appear installation statues of Kinco HMIware, click【Install】to start installing software. 13 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Install successfully If the software install successfully, then it will appear the information. Click【Finish】to finish installation. After finishing installation, Kinco HMIware will create a complete startup directory in【Start】menu, and create the shortcut of Kinco HMIware and EVManager in desktop of operation system. In above installation process, the user can click【Cancel】to quit installation. 2.4.2 Uninstall Kinco HMIware Please quit Kinco HMIware firstly before uninstalling. Run uninstall. Method 1:Uninstall from【Start】menu. 【Start】【All Programs】【Kinco】【Kinco HMIware】【Uninstall】 Method 2:Uninstall from【Control Panel】【Add/Del Programs】 Uninstall procedure Select “Remove”, click【Next】to start uninstalling process. Modify Select new program features to add or select currently installed features to remove. Repair Reinstall all program features installed by previous setup. Remove Remove all installed features. If there are some files or folders added in the install directory of Kinco HMIware, please delete these contents by manual after uninstalling the software. 2.5 Start/Quit 2.5.1 Start Kinco HMIware Method 1:Start in【Start】menu. 【Start】【All Programs】【Kinco】【Kinco HMIware_ENU】【Kinco HMIware】 Method 2:Double click the shortcut of Kinco HMIware in desktop to start software. When it is first time to start Kinco HMIware, it will display window as following: When it is not the first time to start Kinco HMIware, then it will open the last operated project automatically. 14 Basic Part Starting 2.5.2 Quit Kinco HMIware After starting Kinco HMIware software, there are several ways to quit the software as follows: Click the【Close】button on the upper right side of the window. Click the icon of Kinco HMIware on the upper left of the window, then select “Close” in the control menu. Click Kinco HMIware【File】menu, then select “Quit” in the pull-down menu. Press【Alt】key and【F4】key on the keyboard at the same time. 2.6 System Language Change Kinco HMIware supports switching multiple languages, user can switch the software language by the System Language of Option(O) in the software menu bar. It supports Chinese, English, Korean and Russian switching at this moment. Switch the Chinese version to English version Switch the English version to Chinese version 15 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 2.7 F1 Help When user use the Kinco HMIware software, there are there methods to use the F1 help. Press the F1 on the keyboard Click the [Help] button on the component attribute Click the [Help] menu 2.8 Upgrade/Update Note 1. To ensure the product working properly, it is forbidden to update, modify, uninstall and reinstall before the software is closed. 2. Before updating software, to ensure the product working properly, please uninstall the old version software completely. 3. Please backup the project made by old version software before using the new version software to update the project made by old version software. The latest software or upgrade package can be downloaded from the download centre in Kinco’s website : http://www.kinco.cn/en 2.9 Software Compatibility ! In Kinco HMIware, projects made by old version software can be opened by new version software, but project made by new version software can’t be opened by old version software. 16 Basic Part Starting 2.10 Install USB Driver ! USB driver must be installed by manual, can’t be installed automatically. When it is first time to use Kinco HMIware, it need to install the USB driver for downloading HMI project. Users can install USB driver by manual as following procedure: Use USB cable to connect the USB SLAVE port of HMI to USB HOST port of PC, and connect the power supply of HMI correctly and power on, then it will popup dialog box of【Update Driver Software】,then click “Browse my computer for driver software”: Following dialog box will display. Click【Browse】: Set the route to the driver folder in the install directory of Kinco HMIware, then click【OK】: 17 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software After finishing installation, it will popup the dialog box of “The best driver software for your device is already installed”, then click【Close】to quit. If PC doesn’t popup【Installing device driver software】automatically in the first step, but there is a balloon tips in the toolbar as following figure: Then open【Device Manager】【Universal Serial Bus Controllers】,there is a detection icon of unknown device. Right click The icon and select “Update Driver Software” as following figure: At this time, it will popup【Update Driver Software】automatically: 18 Basic Part Starting Select “No,” and click【Next】,then continue the installation procedure of USB driver as above. After finishing installation, there is a balloon tip of “Kinco HMI USB” on the toolbar as following figure: After that, open【Device Manager】,the unknown device will change to “Kinco HMI USB” in【Universal Serial Bus Controllers】.It means the USB driver installation is successful. If the USB driver can’t be installed correctly, there is a balloon tips on the toolbar of operation system as following figure: Then there is an icon of unknown device in【Device Manager】.For this problem, please select the right directory to reinstall USB driver. 2.11 Software Application Program Introduction Kinco HMIware software is integrated with Kinco HMIware.exe, EVManager, EVPLCAddressView, RecipeEditor.exe and PDOManager and so on. Additionally, there are two manuals integrated in Kinco HMIware software. Users can find the shortcuts of these functional units in【Start】【All Programs】【Kinco】【Kinco HMIware_ENU】.Their descriptions are shown in following table: Functional Unit Descriptions 19 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Main software which is used to create, edit, compile, simulate and download project. User’s Manual Guide manual about communication between Kinco HMI and supported control devices. Auxiliary software, it is used to upload, download, decompile, HMI firmware update, obtain HMI system information an so on. Auxiliary software, it is used to configure the CAN communication parameters. Auxiliary software, it is used to create, view or edit recipe data file and external memory data file. Auxiliary software, it is used to monitor the HMI and PLC registers. Uninstall software; it is used to uninstall Kinco HMIware software. 20 3 Make Project This chapter takes PH value of neutralization pond control system for example to explain the process of making project by Kinco HMIware. 3.1 Project Requirement The project requires auto-control mode and manual control mode. In full-automatic control mode, after pressing “Start” button, the system will detect the water level of first neutralization pond automatically. When the liquid meter(LIT03) detect that the water level reaches preset height, then it will enter automatic circulation process: close electric valve(AV01),open electric valve (AV02),and start air blower(B01) and circulating pump(P01) to aerate and circulation stir. After stirring uniform, it will start acid metering pump(P02) or alkali metering pump(P03).When the PH value detected by AIT01 satisfies effluent standard (6≤PH≤9),then stop P02 or P03,open AV01 and close AV02,then let off the qualified water to the second neutralization pond. If the water level detected by LIT04 reaches the preset height, then it will detect the PH value of AIT02 automatically. If it satisfies 6≤PH≤9, then close AV04 and open AV03.Let off the water until the water level detected by LIT04 is lower than lower limit, then close AV03.If it doesn’t satisfy the requirement, then it will close AV03 and open AV04 to continue processing. When detecting the water level of the first neutralization pond lower than lower limit, then stop B01 and P01, herein this process finish. When the water level of the first neutralization pond reach preset height, then continue to next process. 21 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software In the circulation process, LIT01 and LIT02 real time monitor the liquid level of acid storage jar and alkali storage jar. If it is lower than lower limit, then it will show alarm information. In manual control mode, every process is controlled separately by manual according to the value of AIT01 and AIT02 instead of being triggered by the water level of neutralization pond. 3.2 System Analysis According to project requirement, this control system can be consisting of upper computer, PLC and instrumentation. PLC is mainly used to sample data (data of liquid meter and PH meter), control device (air blower, circulating pump, electric valve).Here we use HMI as upper computer to communicate with PLC by RS-232C. The configuration and parameters are shown in following table. Upper computer system configuration: Software Kinco HMIware software Hardware One PC with Windows XP/Vista/7 operation system and Kinco HMIware software. One MT series HMI(Herein we choose MT5320T) One PLC(Herein we choose Kinco CPU306EX) One DC24V power supply for HMI One AC220V power supply for PLC One specified USB download cable(Herein we choose USB port for downloading program) One RS232C cross cable for communication between HMI and PLC.(Herein we choose RS232C communication) PLC address allocation Device Address Device Address Start switch SW01 I 0.0 Liquid meter LIT01 AIW 4 Emergency stop switch I 0.1 Liquid meter LIT02 AIW 6 Air blower B01 Q 0.0 Liquid meter LIT03 AIW 8 Circulating pump P01 Q 0.1 Liquid meter LIT04 AIW 10 Metering pump P02 Q 0.2 Electric valve AV01 Q 1.0 Metering pump P03 Q 0.3 Electric valve AV02 Q 1.1 PH meter AIT01 AIW 0 Electric valve AV03 Q 1.2 PH meter AIT02 AIW 2 Electric valve AV04 Q 1.3 Auxiliary relay AR01 M 0.0(Turn on when the liquid Auxiliary relay AR05 M 0.4(Turn on when the liquid SW02 Auxiliary relay AR02 level of LIT01 is lower than lower level of LIT03 is lower than limit) lower limit) M 0.1(Turn on when the liquid 22 Auxiliary relay AR06 M 0.5(Turn on when the liquid Basic Part Make Project Auxiliary relay AR03 Auxiliary relay AR04 level of LIT01 is higher than level of LIT03 is higher than upper limit) upper limit) M 0.2(Turn on when the liquid Auxiliary relay AR07 M 0.6(Turn on when the liquid level of LIT02 is lower than lower level of LIT04 is lower than limit) lower limit) M 0.3(Turn on when the liquid Auxiliary relay AR08 M 0.7(Turn on when the liquid level of LIT02 is higher than level of LIT04 is higher than upper limit) upper limit) HMI frame Auto Control a. Bar Graph b. Bit State Lamp c. Multiple State Display d. Number Display e. Date/Time f. Event Bar g. Bit State Switch h. Text i. Function Key j. Timer Manual Control a. Bit State Switch b. Text c. Number Display d. Event Bar e. Date/Time f. Function Key Alarm Display 23 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software a. Event Display b. Text c. Bit State Switch d. Date/Time e. Event Bar f. Function Key 3.3 Make Project Following are the procedure for making project in Kinco HMIware. 3.3.1 Create Project Start Kinco HMIware ☞Details please refer to【Basic Part 2.5.1 Start Kinco HMIware】 Create Project Click the icon in toolbar to create project. Input project name.(Herein the project name is set as “PH control system”) Select path of saving project.(Herein we use the default path) Click【OK】to finish creating project. 24 Basic Part Make Project After creating project, it will popup grey grid working area. This area is named “Construct Window”. 3.3.2 Device Selection, Connection and Parameters Setting Device selection——select communication method Drag “Serial Port” in【Graph element window】—【Connector】to construct window. Device selection——select HMI model Drag “MT5320T”in【Graph element window】—【HMI】to construct window. When you release the mouse after dragging HMI icon, it will popup【Display Mode】dialog box as following figure. There are “Horizontal” and “Vertical” option in it.(Herein we select “Horizontal”), then click【OK】 25 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Device selection——select PLC mode(or communication protocol) Drag “Kinco PLC Series” in【Graph element window】—【PLC】to construct window. Device connection Drag HMI icon to make “COM” port approach to the left side of connector(herein we choose COM0) until the connector moving together with HMI. Then connect PLC and connector by the same way. Parameters setting——HMI setting Double click HMI,it will popup window of【HMI Attribute】 Click【Task Bar】option Cancel the option of “Display Task Bar” in【Task Bar】(Herein we don’t need to use "Task Bar”) Click【COM0 Setting】option and set the corresponding parameters of COM0 according to the communication parameters of PLC. Others all set as default. 26 Basic Part Make Project Parameters setting——slave station no. setting Double click PLC,it will popup【PLC Attribute】window. Set “Station No.” according to PLC’s actual station no. (Herein the PLC’s station no. is 1) 3.3.3 Edit Frame Open HMI edit window 27 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Right click HMI icon Click “Edit” in the popup menu as following figure. It will open HMI edit window as following figure(It will open Frame0 by default) Edit frame——Create new frame 28 Basic Part Make Project System will create frame 0~9 automatically when creating HMI. Therein, frame 1~9 are specified system windows. Only Frame0 can be used freely by user. According to the system analysis, we need to create two windows. Procedure for adding frame: Click【Screen】menu, select “Add Frame”. System will popup【New Frame】window, therein “Frame Name” can be defined freely(Herein we use system default name “Frame10”).Then click【OK】.And then create Frame11 by the same way. After creating new frames, they will show in 【 Project structure window】as shown in left figure. Edit “Auto Control” frame——Change background color The initial background color of windows is black(RGB:0,0,0).User can change the background color according to actual requirement(Herein we set the background color as light grey color (RGB:182,182,182)) 29 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Operation procedure is as following: Double click background area, it will popup【Window Attribute】dialog box. Click “Use Background Color” Click “Fill Color” Click “Custom Color”, it will popup【Select color】window Choose the desired color or set RGB value in Red(R),Green(G)and Blue(B). Finally click【OK】 Edit “Auto Control” frame——Edit frame title 30 Basic Part Make Project Click icon in toolbar, it will popup【Text Attribute】window Type “Auto Control” in【Content】area. Select【Vector Font】 Setting in “Font Attribute”: Font Times New Roman Size 16 Alignment Center Color Black After finishing setting font attribute, then click【OK】 Then there is a red box in the edit window. Choose and put on a suitable place. Create title of” Manual Control” and “Alarm Display” by the same way. Edit “Auto Control” frame——Draw the operation flow chart of PH control system Draw the operation flow chart of PH control system by using line, rectangle and polygon. 31 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Take the graph in red box in the figure above for example, the procedure of drawing is as follows: Click icon in “Draw Toolbar”. ~Move mouse to edit area, it will appear “+”.Then click 7 times on the related position. Right click mouse to finish drawing polygon. ☞More drawing methods please refer to【Advanced Part 2.2 Draw】 Double click polygon to open the “Graphic Attribute” window. Set graphic attribute of polygon as follows: Line Color Black Line Width 2 pound Background Fill Color White 32 Basic Part Make Project Edit “Auto Control” frame——Draw graph of metering pump If there is no desired graph in the system image library, then user can create a new graph. New Graphics Click the icon in Database Toolbar, it will popup【New Graphics】window Set the attribute as following figure Click【OK】to enter edit window of vector graph Draw graph Select state0 in the edit window of vector graph,click icon in the Draw Toolbar ~Move the mouse to the black edit area below, it will appear “+”.Then press left mouse button and drag to lower right side. Then release at the proper position to finish drawing a circle. 33 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Select state1 and draw a graph by the same way as drawing state0. ☞More details about new graph please refer to【Advanced Part 5.3 Graphic Library】 Set graphics attribute Double click the graph to open【Graphics Attribute】window,then set the attribute of state0 and state1. state0 Graphics Attribute state1 Graphics Attribute Line Color Black Line Color Black Line Width 2 Pound Line Width 2 Pound Background Fill Color White Background Fill Color Red Save graph After finishing drawing graph of metering pump, click icon in Basic Toolbar to save file pump.vg Click the icon on the upper right of graph edit window to quit the window. 34 Basic Part Make Project Create a new graph and draw graph of electric valve named valve.vg as shown in left figure. Edit “Auto Control” frame——Add Bit State Lamp components (metering pump, circulating pump and electric valve) Add 7 “Bit State Lamp” components for state indication of metering pump, circulating pump and electric valve. The procedure is as follows: Select “Bit State Lamp” from【Graph element window】—【PLC Parts】,then press left mouse button and drag to HMI edit area. Release mouse and it will popup attribute box of【Bit State Lamp】 35 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Set the components attribute as follows: Circulating pump P01/Metering pump P02/ Metering pump P03 Q0.2 Electric valve AV01/AV02/AV03/AV04 Read Q0.3 Q1.0 Q1.1 Q1.2 Read Address Q0.1 Function Normal Address Tag Use;0:M;1:M Function Normal Font Type Vector Font Tag Not use Font Attribute Arial,11,Black,Bold Graph Vector Graph:valve.vg Graph Vector Graph:pump.vg Q1.3 After finishing setting the components, the screen will show as following figure: Finally add text in the screen. The procedure of adding text is the same as【Edit frame title】,show as following: 36 Basic Part Make Project Edit “Auto Control” frame——Add Bit State Switch components(Start, emergency stop) Add two “Bit State Switch” as “Start” and “Emergency stop” button as shown in following figure: Add two “Bit State Switch” and set the attribute as follows:Start/Emergency stop Read/Write I0.0 I0.1 Address Switch Type Reset Tag Use ; 0 : Start/Emergency stop;1:Start/Emergency stop Graph Vector Graph; Button3-15.vg* Button3-12.vg* *Button3-12.vg/Button3-15.vg are imported from 【System Image Library】—【VG】—【Button】 Edit “Auto Control” frame——Add Function Key components Add two “Function Key” from【Graph element window】—【Function Parts】,which are used to change window to “Alarm Display” and “Manual Control”. 37 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Set the attributes as follows: Manual Control Alarm Function Key Change window[Frame10] Function Key Change window[Frame11] Tag Use;0:Manual Control;1: Tag Use;0:Alarm;1:Alarm Manual Control Graph Vector Graph:CONFIRM.vg Graph Vector Graph:CONFIRM.vg Edit “Auto Control” frame——Add Event Information Logon 38 Basic Part Make Project 1 3 2 4 Click icon in Database Toolbar to open【Event log object list】window Click【Add】button, it will popup【Event】window Add one event information logon as follows: Address M0.0 Event Trigging On Text The liquid level of alkali storage jar is below lower limit! Click【OK】button to close【Event】window and finish the first event information logon. By the same way, add second event information logon. Address M0.2 Event Trigging On Text The liquid level of acid storage jar is below lower limit! Then click【OK】button to close【Event log object list】 39 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Edit “Auto Control” frame——Add information bar Information bar include current system time and current alarm display. Firstly add a rectangle graph and two line as background of information bar as following figure: Set the attributes as follows: Rectangle Line Line Color White Background Fill Color Black Line Color White ☞More drawing methods please refer to【Advanced Part 2.2 Draw】 Add “Date/Time” from【Graph element window】—【Function Parts】for displaying current system time. 40 Basic Part Make Project Set the attributes as follows: Date Display:YYYY.MM.DD Time Display:HH:MM:SS Font Type Vector Font Font Attribute Arial,8,White Graph No use Finally add a text of “Time” as shown in left figure: Add “Event Bar” from【Graph element window】—【Function Parts】for rolling displaying alarm information Set the attributes as follows: Format Event Trig Time Standard Time Format Extended Date Format Event Trig Date Finally add a text of “Alarm” as shown in left figure: Edit “Auto Control” frame——Add Number Display component Add 4 “Number Display” from 【Graph element window】—【PLC Parts】for display the liquid level of alkali(acid) storage jar and the PH value of first(second) neutralization pond. Set the attributes as follows: 41 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software PH meter AIT01/AIT02 Read Address AIW 0 Data Type Liquid meter LIT01/LIT02 AIW 5 Read Address AIW 4 AIW 6 Unsigned int Data Type Unsigned int Integer/Decimal 2/2 Integer/Decimal 1/1 Min/Max 0/1400 Min/Max 0/50 Graph No use Graph No use Edit “Auto Control” frame——Add Bar Picture components Add 2“Bar Picture” from【Graph element window】—【PLC Parts】for displaying the liquid level of alkali(acid) storage jar Set the attributes as follows: Acid storage jar/Alkali storage jar Read Address AIW 4 Border Color Black Normal Color Green/Blue Alarm Lower/Upper Red/Yellow Minimum/Maximum 0/50 Alarm Lower/Upper 5/45 Graph No use AIW 6 Edit “Auto Control” frame——Add Multiple State Display and Timer components Add one “Multiple State Display” from【Graph element window】—【PLC Parts】for displaying the rotary of fan blade of air blower. Set the attributes as follows: Read Address LW 0 State Num. 3 Graph Bitmap:fan-05.bg* *fan-05.bg is imported from 【 System Image Library】—【BG】—【Fan】 Add one “Timer “component from【Graph element window】—【Function Parts】for changing the state value of “Multiple State Display” component. 42 Basic Part Make Project Edit “Manual Control” frame——Add Bit State Switch components Click “10:Frame10”in【Project structure window】to change window to frame10 as shown in following figure: Add 8 “Bit State Switch” components from【Graph element window】—【PLC Parts】for controlling the start and stop of electric valve, metering pump, circulating pump and air blower. Set the attributes as follows: Electric valve AV01/AV02/AV03/AV04 Air blower/Circulating pump/Acid metering pump/Alkali metering pump Read/Write Address Q1.0 Q1.1 Q1.2 Read/Write Q1.3 Address Q0.0 Q0.1 Q0.2 Q0.3 Switch Type Toggle Switch Type Toggle Tag Use Tag Use Graph Vector Graphics:Button3-15.vg Graph Vector Graphics:Button3-15.vg Edit “Manual Control” frame——Add Number Display components Add 4 rectangles as the background graph of “Number Display” components 43 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Set the attributes as follows: Line Color White Background Fill Color Black Add 4“Number Display” components from【Graph element window】—【PLC Parts】for displaying the liquid level of acid(alkali) storage jar and the PH value of first(second) neutralization pond Set the attributes as follows: PH value of first neutralization pond / PH value of Acid storage jar / Alkali storage jar second neutralization pond Read Address AIW 4 Unsigned int Data Type Unsigned int Integer/Decimal 2/2 Integer/Decimal 1/1 Min/Max 0/1400 Min/Max 0/50 Graph No use Graph No use Read Address AIW 0 Data Type AIW 2 AIW 6 Edit “Manual Control” frame——Add information bar The information bar in “Manual Control” frame is the same as “Auto Control”fram. Therefore we can copy the information bar from “Auto Control” frame to “Manual Control” frame. Select all information bars in “Auto Control” frame and right click. Click【Copy】 Change to “Manual Control” frame and right click. 44 Basic Part Make Project Click【Paste】 Edit “Manual Control” frame——Add “Emergency stop” button and “Change window” button Copy the “Emergency stop “button, “Alarm” button and “Manual Control” button in “Auto Control” frame and paste in this frame. Double click “Manual Control” button to open the attribute box of【Function Key】and modify as follows: Function Key Change window[Frame0] Tag Use 0:Auto Control 1:Auto Control Edit “Alarm Display” frame——Add Event Display component 45 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Change window to Frame11。 Add one “Event Display” component from【Graph element window】—【PLC Parts】for displaying the triggered alarm information which have logined in “Event Information Logon” Set the attributes as follows: Read Address Format LW1 Sequence No. Event Trig Time Acknowledge Time Return to Normal Time Standard Time Format Extended Date Format Event Trig Date Edit “Alarm Display” frame——Add information bar The procedure is the same as【Edit “Manual Control” frame——add information bar】 Edit “Alarm Display” frame——Add “Emergency stop” button and “Change window” button Copy the “Emergency stop” button, “Alarm” button and “Auto Control” button in “Manual Control” frame and paste in this frame. Double click “Alarm” button to open the attribute box of【Function Key】and modify as follows: Function Key Change window[Frame10] Tag Use;0:Manual Control; 1:Manual Control 3.3.4 Save Project Click the icon in Basic Toolbar to save the project. 3.3.5 Project Simulation After finishing project, user can simulate the project by “Off-line simulation”. The procedure is as follows: Click the icon in System Toolbar to compile the project. After compilation succeed, click the icon in System Toolbar to popup the dialog box of【EVSimulator】 46 Basic Part Make Project Select the HMI need to compile and then click【Simulate】button to start simulation as shown in following figure: 3.3.6 Download Project The procedure of downloading project is as follows: Choose download way. Click the icon in System Toolbar to open the dialog box of【Project Setting Option】 Select “USB”in【Download Device】(Herein we use USB for downloading) Click【OK】button to close the dialog box of【Project Setting Option】 Click the icon in the System Toolbar, it will popup the dialog box of【EVDownload】 Select the HMI need to download and then click【Download】button to start downloading 3.4 Project Folder Introductions When we create a new project, it will generate specified folders automatically. In these folders, it will generate some files corresponding to the operation. The instructions of the files are as following table. Name HMIn Instructions “n” indicates number. All HMI used in one project will generate independent folder. This folder is used to store macro file and project file. image It is used to store initial picture of bitmap in project. ProjBK It is used to store the old project which is backuped by new software. sound It is used to store the initial file and convert file of the sound in project. tar It is used to store data files for project compilation. temp It is used to store the project which is stored at the last time. vg It is used to store the vector graphics and bitmap in project. EVWindows.dat System file PLCGEDefaultProperties System file name.wpj Project management file, opened by Kinco HMIware. name.bak Data file backup by system automatically 47 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software name.pkg Data package file generated by compilation, it is used for downloading to HMI. 48 Advanced Part 50 1 User Interface 1.1 Interface Layout After opening Kinco HMIware, the main interface displays as below: a. Menu bar b. Toolbar Project construct window c. Configuration edit area d. Component library window g. Compile information window h. Component list window e. Project file window f. i. Status bar The main interface of Kinco HMIware is composed by the following parts: Menu Toolbar Software window Edit area 1.2 Menu 1.2.1 File Menu Save as:Save project to a new path. Project password:Set password for opening project. 4 files recently opened:The software automatically remembers most recently opened 4 files’ name in the “File” menu to facilitate user open project directly. Quit:Close the software, then software will prompt users to save unsaved project. 51 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 1.2.2 Edit Menu Undo: Cancel the latest operation, and return to the state before this operation; redo: Redo the latest operation which has been undone by the Undo operation. ! Can only undo or redo one step, multiple steps of undo and redo is not supported. Find/Replace: Find/Replace component address or tag. Nudge: Left/Right/Up/Down: Move the selected component left/right/up/down by one pixel. Align: Left/Right/Top/Bottom/Vertical Midline/Horizontal Midline: Align the selected components. Size: Width/Height/Both: Set the selected components to the same width/height/ size. Layer: Set Top Layer/Set Bottom Layer/Previous Layer/Next Layer: Adjust the sequence of the multiple overlapped components. Group/Ungroup: Group/Ungroup multiple components. Same Horizontal/Vertical Space: Implement the equal horizontal/vertical space between multiple selected components. Align Horizontal/Vertical Center: Place multiple selected components in the horizontal/vertical center of the window. Flip Horizontally/Vertically/Rotate 90 Degree: Set the selected component to flip horizontally/vertically/rotate 90 degree. Select All Components: Select all the components in the frame. Show Grid: Display screen grid; Alignment Grid: Move by grid; Define the Grid Spacing: Self-define the screen grid space. Lock Component: Lock the components, then the components cannot be moved again. The locked components support copy and paste. Reset Toolbar: The toolbar restore to default state. 1.2.3 View Menu Language:Quickly switch language 1,2,3,4. State:Quickly switch state 0,1,2,3. Zoom:25%~300%;Normal Size: Display in proportion of 1:1. Display Component’s Name: Whether or not display component’s name. Attribute:Attribute of window or component. 1.2.4 Screen Menu Add Frame:Add configuration window. 52 Advanced Part User Interface Delete Frame:Delete configuration window. Frame Attribute: Open the attribute page of the current window. Copy/Delete Windows: Copy/Delete configuration windows. Edit Init Window: Edit starting up logo. 1.2.5 Draw Menu Static Text: Add static text New Graphics: Add new graphics; Import Graphics Library: Import graphics of the system default image library. Group components:Use the group element; Save the group element: Save the group component to system library. components; Load Image: When creating a new bitmap graphic, single click【Load Image】to browse and import pictures. Transparent Color: To make the bitmap transparent. Multicolor-Gray switch: Single click【Multicolor-Gray switch】to switch between multicolor image and grayscale image. 1.2.6 Components Menu ☞More details about components please refer to【Advanced Part 4 Component】 1.2.7 Tools Menu Download Way: Selectable download way: USB/Serial port/Ethernet Recipe Editor: Open recipe editing window. 1.2.8 Option Menu Project Path: Set the default save path for project. Compress big graph: Compress large bitmap size to reduce project size when quantities of bitmaps are used in the project. 1.2.9 Window Menu Cascade:Arrange current opened windows in cascade sequence. Tile Horizontally: Tile current opened windows horizontally. Tile Vertically: Tile current opened windows vertically. Construct Window: Users configuration connection of HMI and PLC, as well set communication parameter in the window. HMI Edit Window:User editing window. Close All Window:Close the current opened project. 1.2.10 Help Menu Kinco HMIware Manual:Kinco HMIware user manual. Communication Connection Guide:Connection guide of Kinco HMIware communicating with various PLCs and controllers. 53 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Version Information:Version information of the software. 1.3 Toolbar 1.3.1 Basic Toolbar 1.3.2 Draw Toolbar Select: Single click【Select】icon to cancel the selected objects. 1.3.3 Page Switch Toolbar 1.3.4 Position Toolbar a b c d a:Nudge Left/Right/Up/Down by one pixel b:Align Left/Right/Top/Bottom/Vertical Midline/Horizontal Midline c:Make Same Width/Height/Size d:Set Top/Set Bottom/Previous Layer/Next Layer e:Group/Ungroup f:Same Horizontal Space/Same Vertical Space g:Align Horizontal Center/Vertical Center h:Flip Horizontally/Vertically/Rotate 90 Degree 54 e f g h i Advanced Part User Interface i:Lock Component Position 1.3.5 Line Width Toolbar 1.3.6 Line Style Toolbar 1.3.7 System Toolbar Compile Compile All Clear Build Result Download Decompile Direct Online Simulation Indirect Online Simulation Offline Simulation Download Method 1.3.8 Database Toolbar 1.3.9 Code Edit Toolbar Code Edit Toolbar: Do not support currently. 1.3.10 Fill Effect Toolbar Filled Style 0~26:when check【Window Attribute】-【Use Background Color】,there are 26 filled styles selectable. Filled style 0 indicates unfilled. 55 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Unfilled: When【Use Background Color】 is checked, single click 【Unfilled】to cancel fill color and filled style. 1.3.11 Label Position Toolbar 1.3.12 State Switch Toolbar 1.3.13 Font Toolbar 1.3.14 Status Bar 【Status Bar】:Shows the current X, Y coordinate values of mouse position, width/height of the target object. 1.3.15 Tip Text 【Tip Text】:When mouse is hovering over toolbar icon, the responding tip text will display. 1.3.16 Toolbar Options 【Toolbar Options】:Single click the down arrow【Toolbar Options】, 【Display/hide panel】 will display for user to start closed toolbars. 1.4 Software window Kinco HMIware software windows include: Graph element window, Project files window, Project structure window, 56 Advanced Part User Interface Message window, Component list window. 1.4.1 Graph Element Window Graph element window is one of the most indispensable windows, which is mainly for supply configuration with devices, components and other design elements. Graph element window is composed of the following 6 element libraries: Connector HMI PLC/Controller PLC Parts Function Parts Project Database 1. Right click on the Graphic Element Window to switch between big icon and small icon of parts: 57 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 2. Hover mouse over icons of HMI or PLC to view information of the corresponding devices: 1.4.2 Project Files Window Project files window is for displaying all graphic libraries, macro files, recipe files and other information include in the current project. 1. Double click macrocode file in Project files window to open macro edit window and edit corresponding macrocode. 2. Double click graphic files in Project files window to open graphic edit window and edit corresponding graphic. 1.4.3 Project Sstructure Window Project structure window is for displaying all the elements in the current project by tree diagram or previews. Tree structure: Displaying all the elements in the current project by tree diagram: 58 Advanced Part User Interface Component 0 Frame 0 Component 1 HMI0 Frame 1 Component2 HMI1 Frame n Project Name HMI HMIn PLC0 PLC PLC1 PLCn Click the project name in Project structure window to expand the topological structure; Click “HMIn” or “Frame n” to display the responding configuration window of the certain HMI; Click component to display configuration window which the component belongs to. Preview:Display the frames of the configuration project in the form of thumbnail. 1.4.4 Message Window Message window displays information of the loaded projects and compilation results, in order to facilitate users accurately search the errors in the project. 59 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Users could delete or export compilation information in Message window by right click. Clear message: clear all the compilation information shown in Message window. Export message: export all the compilation information shown in Message window to the current project file, the exported file name is log.txt by default. 1.4.5 Component List Window Component list window is for check information of all the components used by current projects, including affiliated HMI/PLC,Frame No., component ID, address type, address and so on. 1. Open Component list window from the drop list of【View】 Menu. 2. Double click the line of a component, then configuration edit window will change to the frame which the component belongs to. 60 Advanced Part User Interface 1.5 Configuration Edit Area The windows can be opened in configuration edit area areas follows: Construct Window Open Construct window by clicking “Construct Window” in 【Window】menu or clicking project name in Project structure window. HMI Edit Window Drag a HMI into the Construct Window, and then open HMI Edit Window by right clicking on the HMI icon and select “Edit”, or clicking “HMI n” or “Frame n” in Project structure window. Graphic Edit Window Open Graphic Edit window by creating a new graphic or by double clicking one graphic file in Project files window. Macro Edit Window Open Macrocode Edit Window by creating a new macro or by double clicking macro files in Project files window. Edit Init Window Enter the Edit Init Window by selecting HMI and clicking the clicking the icon of the Database Toolbar in Construct Window, or by in HMI Edit Window. When multiple edit windows are opened, you can arrange the windows by “Cascade”/ “Tile Horizontally”/ “Tile Vertically” in 【Window】menu. 1.5.1 Construct Window Users can configure communication connection between devices and set communication parameter in Construct Window. Communication connection configuration Drag devices and cables from 【Connector】【 / HMI】【 / PLC】list of Graph element window into the Construct Window. Drag devices to connect with wire ends. To make sure the connection is established, drag devices, then the properly attached wire ends will move with the mouse. 61 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Communication parameter setting Double click icon of HMI or PLC to open 【HMI Attribute】or【PLC Attribute】. Serial communication Set serial communication parameter in 【COMX Setting】—【HMI Attribute】;Set communication parameters of PLC/Controller in 【PLC Attribute】. Ethernet communication Set communication parameters of HMI or PLC/controller in【HMI Attribute】—【Network Device Setting】. Field Bus communication Set communication parameters of HMI or PLC/controller in【HMI Attribute】—【Field Bus Setting】. ☞More details about communication please refer to【Advanced Part 14 HMI Communication】 1.5.2 HMI Edit Window Design and edit project frames in the HMI Edit Window. 1.5.3 Graphic Edit Window Users could edit vector graphics (.vg) and bitmap graphic (*.bg) in Graphic Edit Window. ☞More details about graphics edit please refer to【Advance Part 5.3 Graphic Library】 62 Advanced Part User Interface 1.5.4 Macro Edit Window In Macro Edit Window, users could write source code to realize such functions as operation and logic by using standard C language. ☞More details about Macro please refer to【Advance Part 9 Macro】 1.5.5 Edit Initial Window In Edit Initial Window, users could replace or edit the default initial window of HMI. ☞More details about initial window please refer to【Advanced Part 2.8 LOGO Screen (Logo)】 63 2 Basic Design Method 2.1 Window screen This chapter mainly introduces the specification of basic windows in Kinco HMIware , and how to use and display them. 2.1.1 Specification of window screen Specification of new basic window: Size (pixel)(width × height) Max size(pixel) (width × height) Min size (pixel)(width × height) 320×234 320×234 320×240 320×240 480×234 480×234 480×272 480×272 640×480 640×480 800×480 800×480 800×600 800×600 1024×768 1024×768 10×10 Number 1~32768 2.1.2 Window Display Methods Change window Window change is to shut down the current window (including the sub window) and open another appointed one. This operation can be finished by the following two methods: Use function key Function key:[change window],fill a number in [window number] You can change window though touch the function key. ☞More information refers to【Advanced Part 4.2.6 Function Key】 Use plc control “PLC control”:[change window],determine a control address, You can change window by changing the value in this address. 64 Advanced Part Basic Design Method ☞More information refers to 【Advanced Part 4.15.5 PLC Control 】 Window overlay Window overlay is to integrate some windows into one screen. This function can be realized with two methods: Bottom window Double click at the space on the basic window, you can see [window attribute] frame. Once chosen as a bottom window, all the components on it will also show on the basic window. Default common window:[1:Common Window],users also can define any other one freely. All the components on the common window will show on all the basic windows. ☞More information refers to【Advanced Part 3 Window】 1. 3 bottom windows can be used by one basic window at most 2. only one common window 3. Only components of bottom window or common window are shown on the basic window, excluding attribute settings like background color or frame color. Window overlay Window overlay is to integrate some windows into one screen. 65 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software This function can be realized with following methods: Direct window You can switch on or off to open or close popup the window. Its size is determined by the one of direct window. Keyboard window is direct window. ☞More information refers to【Advanced Part 4.8.1 Direct Window】 Indirect window By changing the value, you can open or close the specific window. Its size is determined by the one of indirect window. ☞More information refers to 【Advanced Part 4.8.2 Indirect Window】 Function key Function key:[Popup window] to open the specific window,[close window] to close it.Its size is determined by none but itself. ☞More information refers to【Advanced Part 4.2.6 Function Key】 Fast selection window Default fast selection window [2:Fast Selection], users also can define any other one freely. By click [Menu] on task bar, the fast selection window will display and it will shut down after click again. it. Its size is determined by none but itself. ☞More information refers to 【Advanced Part 3 Window】 1. No limit of popup window .But it`s better to use much fewer or much RAM will not be released. 2. only one fast selection window Window move The place will be changed by using “control bar” of function key. ☞More information refers to【Advanced Part 4.2.6 Function Key】 Basic window cannot be moved ,only popup windows can. 66 Advanced Part Basic Design Method 2.1.3 Display Position Different types of windows display in different styles: Popup window by “direct window” or “indirect window” According to component position The popup window will display where the “direct window”or “indirect window” is put. According to setting value Set [variable display coordinate], values or addresses determine the position of popup window (coordinate of top left corner point. Function key [popup window] Set values of “X”,”Y” in [window attribute]-[position], they are the coordinates of the popup window. Its position cannot be changed when the screen is a basic window and it can only display full screen. 2.1.4 Display Order Different types of windows display on a screen in its order. 67 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 2.1.5 Copy/Delete Windows (1)copy window Copy in Same project or different projects Same project Same project: same HMI or different HMIs Same HMI Copy things from frame A to frame B: Right click [copy] Right click the component on frame A , choose[copy],then change to frame B and paste it on it. By this way, only component is copied, not window attribute. [copy/delete window] Click[frame]-[copy/delete window] , set “count”, “source window”, “destination windows”, click “OK”. By this way, all the components and window attribution are copied. Copy across HMI Copy across HMI can only realized by right click [copy]. ! [Screen]—[copy/delete window]: this copy operation across the HMI windows are not supported Copy across project When copy across different projects, you should open the related two projects with Kinco HMIware, and then right click [copy]. (2)delete window You can delete windows as belows: 68 Advanced Part Basic Design Method Right click [delete] Right click the frame you want to delete under [project structure window], then it will be delete. Windows are deleted one by one, multi-deletion is not supported. [copy/delete windows] Click HMI you want to handle, click [screen]-[copy/delete windows-[delete window],[delete single window]can delete an appointed window,[delete multi-windows]can delete continuous-number windows. ☞More information refers to【Advanced Part 3.3 Edit Window】 2.2 Draw This chapter introduces Kinco HMIware image format and picture drawing and using. 2.2.1 Image Format Kinco HMIware mainly supports two format vg and bg. When createing a vector graph, its default format is vg, while createing a bit map, its default format is bg. Differences between vector graph and bitmap is shown as below: Specification of created graph: Graph format Max size(pixel) Min size(pixel) (width × height) (width × height) line, Vector graph (vg) Graph types round-corner State limit rectangle, rectangle, ellipse, sector, broken 320×240 2×2 Bitmap (bg) line, curve, polygon and so on 1~256 Jpg, bmp, gif, png and so on 2.2.2 Vector [vector],in short, enlarge or narrow without distortion. Geometric figures which can be infinitely enlarged without color change and blurred are mostly in this form 69 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software In Kinco HMIware, you can create vector graph through in two ways: Import from image library Import graph you need from [image library]-[vector graph]. ☞More information refer s to [Advanced Part 5.3.1 Import Grahpics] Use drawing tools in Draw in picture edit window Use component [vector graph].open window edition, draw as you need with drawing tools, save, exit edit window, a new vector graph is finished. ☞More information refers to [Advanced Part 5.3.2 Build New Graphics] Draw in configuration window Draw in the edit window with drawing tools, right click the graph done, choose “save to the VG map”, a new vector graph is finished ☞More information refers to [Advanced Part 5.3.2 Build New Graphics] Now we will introduce how to use drawing tools: Choose an icon, drag in the edit area : line Graphic instrument Drawing step ~move mouse into edit area,”+”shows up, press left on mouse and drag release at the position you prefer a line is finished curve Graphic instrument Drawing step move mouse into edit area,”+”shows up, press left on mouse and drag ,press left on mouse and drag release the mouse you can see a circle click at the start point click at the finishing point ,a curve is finished 70 Advanced Part Basic Design Method rectangle Graphic instrument Drawing step move mouse into edit area,”+”shows up press left on mouse and drag release at the position you prefer a rectangle is finished roundrectangle Graphic instrument Drawing step move mouse into edit area,”+”shows up, click to set the starting point press left on mouse and drag to the position you want release the mouse, a roundrectangle is finished Point at the small green block on the bottom right corner, when the arrow turns two-ways, press left on mouse and drag, ou can change its radius. polyline Graphic instrument Drawing step move mouse into edit area,”+”shows up, click to set the starting point click at the set points right click to finish drawing polygon Graphic instrument Drawing step 71 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ~ move mouse into edit area,”+”shows up, click 7 times at 7 points right click to finish drawing ellipse Graphic instrument Drawing step move mouse into edit area,”+”shows up, click to set the starting point press left on mouse and drag to the position you want release the mouse, a ellipse is finished With the same width and height ,a ellipse turns to be a circle sector Graphic instrument Drawing step move mouse into edit area,”+”shows up, click to set the centre point press left on mouse and drag to the position you want release the mouse ,a closed circle shows up click at starting point click at the ending point ,a sector is finished 2.2.3 Geometric Figures Attribution Attributions as below: graphics Graphic samples Setting attribute 72 Advanced Part Basic Design Method line color, line style、line width、arrow Line style Curve line color、line style、line width line color 、 background fill color 、 foreground fill color 、 pattern fill 、 Rectangle fountain fill、line style、line width line color 、 background fill color 、 foreground fill color 、 pattern fill 、 RoundRectangle fountain fill、line style、line width line color、line style、line width PolyLine line color 、 background fill color 、 foreground fill color 、 pattern fill 、 PolyGon fountain fill、line style、line width line color 、 background fill color 、 foreground fill color 、 pattern fill 、 Ellipse fountain fill、line style、line width line color 、 background fill color 、 foreground fill color 、 pattern fill 、 Sector fountain fill、line style、line width Users can modify attribute in two ways: Attribution frame Double click the graph,modify in [graphics attribute] Tools bar Choose the graph, modify its attribute through[drawing tools]/[ line width]/[line style].In this way, you can only set line color\filled color\line width and line style. 2.2.4 About Fountain Fill The closed graphics can be set fountain fill. Double click the graph,choose[fountain fill]choose the foreground fill color, background fill color line color . 73 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Example: Fountain Foreground Background Fill Line Fill Fill Color Color Color Horizontal ■ □ ■ Vertical ■ □ ■ Oblique ■ □ ■ ■ □ ■ ■ □ ■ ■ □ ■ Under Oblique Corner of Radiation Centre for Radiation Deformation 2.2.5 Bitmap [bitmap],in short,structured with pixel,enlarger or narrow with distortion. Bitmap is structured with pixel array and each has its own information. We can change the graph by dealing with every pixel. In Kinco HMIware, bitmap is created in two ways: Import from image library Import from[image library]-[BG] ☞More information refer s to [Advanced Part 5.3.1 Import Grahpics] 5 Import pictures in forms of jpg、bmp、gif、png Bitmap, open the edit window ,import pictures in forms of jpg, bmp, gif, png and so on, save, exit ,a new bitmap is created. ☞More information refers to [Advanced Part 5.3.2 Build New Graphics] 5 2.2.6 About Transparent Color If a picture influences the aesthetic, users can deal with the pure color with[transparent] tool in drawing tools 74 : Advanced Part Basic Design Method 1 2 “Transparent” can only deal with simple actions, not suggested to use. Besides,bitmap supports PNG format, so you can edit a picture with another editor and convert it into PNG form before import. ! GIF and PNG form picture doesn`t support transparent action 2.3 Text User can add the text for the component by the following way in Kinco HMIware. Set in Draw Toolbar. Click the [A] icon in Draw Toolbar, and input the needed text content in [Text Attribute]-[Display Setting]. Position free Set [Use Tag] or [Use TextLib] in the component attribute. Select [Use Tag] in the [Tag] option in component attribute, and input the needed text contents in [Tag Contents], or select [Use TextLib], if there are TextLib logon in the project. Only shown on the component 75 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 2.3.1 Font Type Kinco HMIware provides 3 available fonts, i.e. dot matrix font, vector font and graph font. The advantages and disadvantages of these three fonts will be described as follows; users can select the suitable font type according to its characteristics. 2.3.2 Dot Matrix Font Dot Matrix font saves the bitmap for each character of the required Chinese character set. Each primitive (small picture) is spliced together to form a character string when it is used. Disadvantages of dot matrix font: Only SimSun is supported. The scaling effect is poor. For each character, 3 kinds of bitmaps (8×8, 16×8, 24×16 (height*width)) are reserved respectively, so the effect is very poor when the larger font is displayed, as shown below: full-width deal only for unASCII characters Kinco HMIware deals with ASCII characters as half-width ones, while unASCII as full-width ones. So if each character has different width, the intervals may be different: advantages of dot matrix font: A smallest storage space is occupied by dot matrix font. 2.3.3 Vector Font Vector font intercepts the characters that are used by the user from the corresponding font library through checking the setup of the user-set fonts, and then makes them into TrueType font file (*.ttf format) for HMI to use. Disadvantages of vector font: Only Support the TrueType installed in the operating system (*.ttf format). Without selecting “Vector Fonts Edge Blur”,the font is displayed with some projections, and comparison results as shown below: 76 Advanced Part Basic Design Method “Vector Fonts Edge Blur” can be set in [HMI Attribute]-[HMI Extended Attributes]. Advantages of vector font: A smaller storage space is occupied. It adopts the method of intercepting the matrix from the font file, thus reducing the size of the font file. For the same character in the same font, only one matrix needs to be intercepted regardless of the size, color, bold/italic styles. The font size can be set freely without any deformation Support the alignment method for multiple-line text. Text library can support the vector font. System default vector font setting User can define the default vector font in [System Default Vector Font] in [Option]. [Example] Set System Default Font as “Arial”, when using tag or text and select “Vector Font”, it will select “Arial”by default automatically. 2.3.4 Graph Font Graph font treats the whole character string as a whole, and intercepts the whole bitmap and saves it in the project. 77 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Disadvantages of graph font: A larger storage space is occupied. Because the character string saves as bitmap, so it needs a larger space. For example: Four characters “configuration”displayed in zero SimSun needs 1824 bytes, as shown below: In addition, the graph font should be intercepted again if the content, size or colors vary slightly, thus causing a linear increase in the occupied space. Text library can’t support the graph font. Advantages of graph font: Support all installed fonts in current operating system. The scaling effect is good. 2.3.5 Text Attribute Edition User can modify the font attribute through the following two methods: Modify in the component attribute dialog box Double-click component /text to set the font attributes in [Component Attribute]-[Tag] or [Text Attribute]. Modify in Font Toolbar Selected component/ text, and then set the font attributes in [Font Toolbar]. This method can support multi-modify font attribute. Different font types support different font attribute to be modified, specific as below: : Support;--: Unsupport Font Attribute Common Bold Italic Underline strikeout Size Color Graphic A A A A A AA A AAA Dot Matrix Font Vector Font Graph Font -- -- -- -- -- -- 2.3.6 Notes for Using Vector Font Based on the special treating method for the vector font, the following conditions should be paid attention to when the vector font is used: 1. Some fonts may not support some characters, or have poor support effects. 78 Advanced Part Basic Design Method For example, the Chinese characters can be displayed by using Arial font, because there are no corresponding Chinese characters in Arial font library. Otherwise the effect will as shown below: 2. Because the dot matrix font and graph font have many disadvantages in the storage space and scaling etc, therefore, use the vector font as much as possible when it can meet the project requirements. 3. Avoid using too many fonts as much as possible. It too many types of vector fonts (e.g. dozens or more) are used by the user, the number of font files will be too many, thus affecting the compilation speed, downloading speed and screen switching speed. 4. Use the common fonts in operating system as much as possible. If a certain project uses “Microsoft Elegant Black” font when it is edited on PC, and when it is transferred to another PC where no “Microsoft Elegant Black” font exists for editing, then all the “Microsoft Elegant Black” characters used in the project will be changed to “SimSun” automatically. 2.4 Keyboard This chapter describes keyboard type and methods of calling keyboard in Kinco HMIware. 2.4.1 Keyboard Type Kinco HMIware support three keyboard for users: NUMERAL Keyboard、ASCII Keyboard and HEX Keyboard. And users can make own keyboard or use external USB keyboard. NUM Keyboard:NUM Keyboard for number input component. Window control bar Max value* Max:AAAAAAAAAAAA Min:AAAAAAAAAAAA Min value* AAAAAAAAAA Shut down Input display clear CLR 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 . ENTER backspace _ minus enter ※ 1. The values shown here are max and min in Max/Min Value Setting in [Number Input Component Attribute]-[Numeric Data], Keyboard permission input value range is limited by the value. 2. If [Proportion Conversion] is selected, the values shown here are max and min after proportion conversion. ASCII Keyboard:ASCII Keyboard for text input component or number input component. Lowercase: 79 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Caps: Chinese Input: ※Set Chinese Font Box Height in [HMI Attribute]-[HMI Extended Attributes], height range from 24 to 99 (pixel). HEX Keyboard:for HEX character input 80 Advanced Part Basic Design Method ※1. The values shown here are max and min in Max/Min Value Setting in [Number Input Component Attribute]-[Numeric Data], Keyboard permission input value range is limited by the value. 2. If [Proportion Conversion] is selected, the values shown here are max and min after proportion conversion. ☞More information refers to [Advanced Part 4.2.6 Function Key] 2.4.2 NUM Keyboard Through the following three methods, Number Input Component will pop up NUM Keyboard in Kinco HMIware. Use public windows keyboard This method is system default. Open [Number Input Component Attribute] - [Keyboard Setting] dialog box, and then select [Public Windows Keyboard], as shown below: Put two “direct window” components respectively on the left and right side of [Frame 1:Common Window],choose [Frame 3:NUM Keyboard] in frame ID. Take apart in the middle of a screen, when the components on the left side is triggered, the direct window on the right side will pop the keyboard, It`s the same with the other side. Use Specified Keyboard This method can pop up keyboard made by user self. 81 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Use specified keyboard. Only after setting window attribute as “keyboard page” can you find the page in [input attribute]-[keyboard setting]-[specified keyboard]. Use external keyboard This method need connect USB Host keyboard. Open [Number Input Component Attribute] - [Keyboard Setting] dialog box, and then select [Not Use Pop-up Keyboard], as shown below: No keyboard will pop up, while user can input things through circumscribed keyboard. It is only applicable to the HMI supporting the USB HOST. 82 Advanced Part Basic Design Method 2.4.3 ASCII Keyboard Through the following two methods, Text Input component / Note Book component will pop up ASCII Keyboard in Kinco HMIware. Use Specified Keyboard This method is system default. Default keyboard:[Frame 4:ASCII Keyboard] If you want to us your own keyboard, you should set it as a keyboard page ,and choose the frame ID of the keyboard window. Use external keyboard Same as number input,No keyboard will pop up, while user can input things through circumscribed keyboard. 2.4.4 HEX Keyboard When input hex number, you should make it with two methods as below: Use Specified Keyboard [number input attribute]-[keyboard setting]-[specified keyboard],choose[Frame 8:HEX Keyboard]. If you want to us your own keyboard, you should set it as a keyboard page, and choose the frame ID of the keyboard window. 83 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Use external keyboard Same as number input No keyboard will pop up, while user can input things through circumscribed keyboard. 2.4.5 Create your Own Mumber Keyboard Num keys0-9, enter, delete and backspace Determine the layout: Create keyboard: function key,move the window,attribute setting: Function Switch Window: Popup window title bar Graphics Select Vector Graphics: function key,close the window,attribute setting: Function Keyboard Function:Escape 84 Advanced Part Basic Design Method Graphics Select Vector Graphics: text display,display the characters, attribute setting: Read address LW 9070*1(special register) Data width 6 function key,delete,attribute setting: Function Keyboard Function:Clear Tag 0:CLR;1:CLR Graphics Select Vector Graphics: function key,backspace,attribute setting: Function Keyboard Function:Back Space Tag 0:;1: Graphics Select Vector Graphics: function key,enter,attribute setting: Function Keyboard Function:Enter Tag Sselect;0:ENTER;1:ENTER Graphics Select Vector Graphics: function key,character input,attribute setting:take Function Keyboard Function:Unicode Tag 0:1;1:1 for example Graphics Select Vector Graphics: number display,display min value, attribute setting: Read address LW 9190*2(special register) Data width 6 number display,display max value, attribute setting: Read address LW 9180*3(special register) Data width 6 ※ 1.LW9060 ~ LW9075 special registers,cache the latest input 85 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 2. LW9190 ~ LW9197 special register,min value display 3. LW9180 ~ LW9187 special register,max value display 2.4.6 Create your Oown Unicode Keyboard Unicode uses two bytes to form a character,often used to display characters cannot display by ASCII, kanji for example. Take Russia as an example: 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 4 5 8 7 6 function key,move the window,attribute setting: Function Switch Window: Popup window title bar Graphics Select Vector Graphics: function key,close the window,attribute setting: Function Keyboard Function:Escape Graphics Select Vector Graphics: text display,display the characters, attribute setting: Read address LW 9060(special register) Data width 16 Unicode choose function key,character input,attribute setting:take Function Keyboard Function:Unicode Tag 0:И;1:И Font vector:Arial Unicode MS for example Graphics Select Vector Graphics: function key,enter,attribute setting: Function Keyboard Function:Enter 86 Advanced Part Basic Design Method Tag 0:вВОД;1:вВОД Font vector:Arial Unicode MS Graphics Select Vector Graphics: function key,delete,attribute setting: Function Keyboard Function:Clear Tag 0:СБР;1:СБР Font vector:Arial Unicode MS Graphics Select Vector Graphics: function key,backspace,attribute setting:: Function Keyboard Function:Back Space Tag 0:BS;1:BS Font vector:Arial Unicode MS Graphics Select Vector Graphics: function key,space,attribute setting: Function Keyboard Function:Unicode Graphics Select Vector Graphics: 2.4.7 Call Keyboard in the Group Component Library Kinco HMIware provides 21 default keyboards in Group Components Library, the method of calling the keyboard in Group Components Library is as follows: 【example】number input calls a keyboard made of group(text input/note book)。[Example] Createe a new window named Frame10, and select [Keyboard Page] from [Special Attribute] in Window Attribute. Right-click the mouse in the blank area in the Frame10 window to select [Group]-[Use the group element], then select [keyboard] from [Group Components] in [Edit Box of Group Components Library], and select the right keyboard from [Preview] and click [Place Group Components] button, then the keyboard will appear in Frame10. 87 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Modify the window size of Frame 10 to the same size as the specified keyboard. Place one number input component (LW0) in Frame0, and select [Specified Keyboard] in [Keyboard Setting] in [Number Input Component Attribute], select [10:Frame10]. Save, compile, and run the project. Then click the number input component (LW0) to make the specified num keyboard pop up in the middle of HMI screen. 2.5 Code Type Kinco HMIware can support code type: BIN, BCD and LSB. User can select the correct encoding type according to the actual encoding type of data process. 2.5.1 BIN BIN(Binary)is binary code type. Most digital systems are based on BIN code to process the data Code Type Word data range Dword data range Signed BIN -32767~32767 -2147483648~2147483647 Unsigned BIN 0~65535 0~4294967295 [Example] Convert binary data 1001 0100 to decimal data: 88 Advanced Part Basic Design Method 1001 0100 = 1×27+0×26+0×25+1×24+0×23+1×22+0×21+0×20 = 148 2.5.2 BCD BCD (Binary Coded Decimal) is two-decimal code. The encoding type represents a decimal number 0 to 9 with 4-bit binary number. Example 9 (Decimal) =1001 (Binary). As easy to deal with,often use for BCD switch and BCD nixie tube display 由 Code Type Word data range Dword data range BCD 0~9999 0~99999999 [Example] Decimal data is +123,the binary data is 0000 0000 0111 1011 (64+32+16+8+2+1=123). But BCD data is #123,it can be simply expressed as 0000 0001 0010 0011 Decimal data is -413,the binary data is 1111 1110 0110 0011(complement for negative number,negation adding 1). But BCD data is #F413,it can be simply expressed as 1111 0100 0001 0011 2.5.3 LSB LSB is the acronym of Least Significant Bit. This encoding type first converts the data in the buffer to binary data, and then determines the current state of component based on the number of consecutive “0”at the least significant bits of the binary dat. [Example] Take the data with word address for example: Decimal Binary State 0 0000 0000 0000 0000 All bit are 0, the state is 16 1 0000 0000 0000 0001 The number of consecutive “0”at least significant bits is 0, the state is 0 2 0000 0000 0000 0010 The number of consecutive “0”at least significant bits is 1, the state is 1 3 0000 0000 0000 0011 The number of consecutive “0”at least significant bits is 0, the state is 0 4 0000 0000 0000 0100 The number of consecutive “0”at least significant bits is 2, the state is 2 5 0000 0000 0000 0101 The number of consecutive “0”at least significant bits is 0, the state is 0 6 0000 0000 0000 0110 The number of consecutive “0”at least significant bits is 1, the state is 1 7 0000 0000 0000 0111 The number of consecutive “0”at least significant bits is 0, the state is 0 8 0000 0000 0000 1000 The number of consecutive “0”at least significant bits is 3, the state is 3 2.6 Language Switching User can pre-register the content written in multiple languages to text library in Kinco HMIware. The switching display among the multiple languages contents can be realized by modifying the value of special register, which refers to LW9130 in Kinco HMIware. 89 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ☞ For details about text library, refers to [Advanced Part 5.1 Text Library] There are two following usages for switching display among the multiple languages by LW9130. Use Multiple State Setting and Multiple State Display components. Createe one Multiple State Display component, the attribute is: Read Address LW9130(HMI system special register) State Num. 3 Tag No Graphics Use vector graphic, createe one vector graphic with 3 state Three multiple state settings stack up upon a multiple state display in corresponding order, attribute settings: Write Address LW9130(HMI system special register) Setting Mode Set Constant Set Value 0/1/2 Tag No Graphics No ☞ For details about component attribute, refer to [Advanced Part 4 Component] When running, the effect is as shown below: 90 Advanced Part Basic Design Method Use Multiple State Switch Createe one Multiple State Switch component, the attribute is: Read/ Write Address LW9130(HMI system special register) Control Mode Dropdown List State Num. 3 Select/Background/Border Color bright green/gray /lack Tag Use;0:Chinese;1:English;2:Japanese Graphics No When running, the effect is as shown below: Equipment operate abnormally 设备运行异常 Language Chinese Chinese English Language Chinese 不具合ままの稼動 Language English Japanese Chinese Chinese English English English Japanese English Japanese Chinese English English Japanese 2.7 RTC Set MT series HMI has real time(RTC)function, BIN coded format,for real time and date display. Once HMI is power off, battery is backup 91 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software In Kinco HMIware,components with real time clock:time, event display, event bar, historical event display, historical data display, operation log, trend curve ,XY plot. So when using components above, you should ensure the accuracy of time or you may get wrong information 2.7.1 Through Special Registers LW10000~LW10006: Special Register Address Type Code Type Descriptions LW10000 Second, LW10001 Minute, the effective value range from 0 to 59 LW10002 Hour, LW10003 WORD BIN Day, LW10004 Month, LW10005 Year, LW10006 Week, the effective value range from 0 to 59 the effective value range from 0 to 23 the effective value range from 1 to 31 the effective value range from 1 to 12 the effective value range from 2000 to 2037 the effective value range from 0 [Sun] to 6 [Sat] [Example]set year, month, date, minute, second, use 6 number input components as shown : attributes: Read/Write LW10005(HMI system LW10004(HMI system LW10003(HMI system Address special register) special register) special register) Integer 4 2 2 Min/ Max 2000/2037 1/12 1/31 Alignment Left Leading 0 Leading 0 Font Color Black Graphics No attributes: Read/Write LW10002(HMI system LW10001(HMI system LW10000(HMI system Address special register) special register) special register) Integer 2 2 2 Min/ Max 0/23 0/59 0/59 Alignment Leading 0 Font Color Black Graphics No Input the real time to get the right time information: 92 Advanced Part Basic Design Method 2011 / 10 / 18 19 : 57 : 01 / 2011 10 / 19 : 57 : 01 18 Max:AAAAAAAAAAAA Min:AAAAAAAAAAAA 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 0 . 9 CLR Max:AAAAAAAAAAAA Min:AAAAAAAAAAAA 57 _ 1 ENTER 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 . 0 CLR _ ENTER 2 2.7.2 Calibrate System Time in System Setup Screen Switch to system setting mode, modify time on this interface. Take one HMI for example: ☞More infermationrefers to[Hardware Part 3.1 Methods to Display System Setting Mode】 2.7.3 System Time and PLC Time Synchronization There are two following way to make the system time and PLC CPU time synchronization: Use Data Transmission function of Timer component In this way, we will use the Timer component to transfer the data in the time register of PLC to HMI system special register LW10000~LW10006. ☞ For details about Timer component, refers to [Advanced Part 4.16.2 Timer] ! Minimum execution cycle is 100ms,so there is an inevitable time deviation between HMI and PLC. Use The External Clock for Event Only for trigger time and return to normal time of event (HMI time for acknowledge time ). Choose “use external time for event”- [HMI attribute]-[HMI extended attributes ],related time will read from special 93 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software registers: LW9010~LW9017 ,which get time by timer receiving from PLC CPU clock. LW9010~9017: Data Type Code Type Address LW9010 LW9011 WORD BIN LW9012 LW9013 ! Descriptions Address Second, the effective value range from 0 to 59 Minute, the effective value range from 0 to 59 Hour, the effective value range from 0 to 23 Date, the effective value range from 1 to 31 LW9014 LW9015 LW9016 LW9017 Descriptions Month, the effective value range from 1 to 12 Year, the effective value range from 1980 to 2079 Week, the effective value range from 0[Sun] to 6[Sat] Millisecond, the effective value range from 0 to 999 Minimum execution cycle is 100ms,so there is an inevitable time deviation between HMI and PLC. [Example] Take FX2N PLC for example: FX2N CPU clock Addr. Type D8013 D8014 Descriptions Addr. Type Second, the effective value range from 0 to D8017 59 Minute, the effective value range from 0 to D8018 59 D8015 Hour, the effective value range from 0 to 23 D8016 Date, the effective value range from 1 to 31 D8019 Descriptions Month, the effective value range from 1 to 12 Year, the effective value range from 1980 to 2079 Week, the effective value range from 0[Sun] to 6[Sat] Select “Use External Time for Event” in [HMI Attribute]-[HMI Extended Attributes]. 94 Advanced Part Basic Design Method Add the needed event to Event Information List. ☞ For details about event information logon, refers to [Advanced Part 4.15.3 Event Information] use a event display to display information written in event information list. attribute: Read Address LW 0(HMI Local Register) Format Sequence No. Event Trig Time Acknowledge Time Return to Normal Time Standard Time Format(H:M:S) Extended Date Format(Y/M/D) use a timer to transport data from PLC to HMI attribute: Execution Cycle 1×100ms Data Transmission Source Address Destination Address SD 8013*(PLC register) LW 9010(HMI system special register) Data Type Word 95 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Data Transmission 6(word) ※ FX2N PLC D8000~D8255 corresponding to HMI SD8000~SD8255。 value in D0 is larger than 100: 2.8 LOGO Screen(Logo) LOGO screen is the screen that appears during the startup of HMI. LOGO screen can be customized by users. 2.8.1 LOGO Screen Specification The specification of LOGO screen HMI models MT4424T/TE Max size(pixel) (Width×Height) Picture format 800×480 MT4414T/TE Jpg, bmp, gif and so on MT4620TE 800×600 Others Width×Height<131000 2.8.2 Init Screen Setting Change initial window: Graph instrument step 96 Advanced Part Basic Design Method Select the HMI to be set LOGO screen in Construct Window. 2 Click the icon in Toolbar. 1 Right-click in the editing space after entering the LOGO screen setting window. Select “Load Image” There are will pop up [Open] dialog box, user can find the path of picture to be imported and select the picture. Click [Open] button. 97 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software LOGO Screen is set successfully. HMI Click the icon in the toolbar, and pop up the [KHDownload] dialog box, then select the HMI to be downloaded the LOGO screen. Select the [LOGO file] and click the [Download] button that means the LOGO screen will be downloaded to the HMI. The method for not showing LOGO: Open [KHManager]-[Download Operate] and select “Unshow LOGO”, then click the [Set] button. If the setting is successful, [Set Successfully] dialog box will appear. And then LOGO screen will not appear during the startup of HMI next time. ☞ For details about KHManager, refer to [Advanced Part 8 KHManager]. 2.8.3 Note for Using Init Screen Pictures for initial screen should keep in allowed size. 2.9 Exchange Serial By “exchange serial 0 and serial 1”,all the devices connected to these two ports along with their parameters will be exchanged without bothering to reset. In Kinco HMIware construct window select the HMI which to exchange serial, right-click and select "Exchange serial 0 and serial 1 ", as shown below: 98 Advanced Part Basic Design Method ! Exchange serial function is only applicable to COM0 and COM1, are not suitable for COM2 2.10 Replace Devices In the industrial field, we often need to change devices. Kinco HMIware has shortcuts to make it. Note HMI replacement must be carried out through the [Replace HMI Type] option, and if it is done by getting the original HMI deleted and then a needed HMI type created, the original project screen will be lost. 99 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Note PLC replacement must be carried out through the [Replace PLC Type] option,and if it is done by getting the original PLC deleted and then a needed PLC type created, the PLC address type set in the original project will be replaced by the HMI local address. 2.10.1 Replace HMI Select a HMI icon and right-click it in the Construct Window of Kinco HMIware, and then click “Replace HMI Type”, as shown below: 1 2 Then, the [Replace HMI Type] dialog box will pop up: 100 Advanced Part Basic Design Method Choose the HMI you want in []new HMI]-[HMI type],If resolution ratio of the two differ a lot ,it is suggested to choose all the special windows ,or the old ones are in use. Click OK to finish. ! 1. Replace a HMI with 3 serials with one with 2,you should connect the device to COM0 or COM1 if it is once connect to COM1.Otherwise ,replacement won`t be allowed. 2. HMI with Ethernet can only replaced by one has too 3.Once the new HMI type doesn`t support components in the old ones, all them will disappear automatically. 4. If resolution ratio of the two types are different size of component will be enlarged or narrowed, excluding word size.. 2.10.2 Replace PLC Select a PLC icon and right-click it in the Construct Window of Kinco HMIware, and then click “Replace PLC Type”, as shown below: Then, the [Replace PLC Type] dialog box will pop up: 101 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software The user can select the replace PLC type in the pull-down list of the destination PLC type, and the user select new address types in address type mapping list according to the address type relationship between source PLC type and destination PLC type. 2.11 Index Function 2.11.1 Index Register We can change operator address by changing value of a register .In this way, we call this register index register. Real address=initial address + value of index register. After using index register, only the real register value will be modified, not the initial one. ! Some backgrounders including event information logon, alarm information logon, PLC control, macro ,trend curve, XY plot, oscilloscope do not have this function. [Example] Number Input component, the attribute is: Read/Write Address LW 0(HMI local register) Number Display component, the attribute is: Read Address D 100(PL C register) 102 Advanced Part Basic Design Method Index Register select:LW 0 Number Display component, the attribute is: Read Address D 200(PLC register) Index Register select:LW 0 You can check all the product indicator data by input line number 2.11.2 Index Station Num When HMI communicates with more than one PLC through one port, it usually needs to drag many PLCs on the screen. If there are a lot, it will be a little crowd. In order to avoid it, user can make it by [change station num. When editing a project, only one PLC is dragged out, by change choose [change station num] in component attribute, you can switch to different station PLCs. 0 ~ 255 station ID,special registers LW9416 ~ LW9431 103 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ! 1. Some backgrounders including event information logon, alarm information logon, PLC control, macro, trend curve, XY plot, and oscilloscope do not have this function. 2. Special register index station ID, 16 different number devices to max on one screen . [Example] Number input, attribute: read/write address LW 9416(special register) Number display, attribute: Read address D 100(PLC register) Change station num Index0:LW9416 Number display, attribute: Read address D 101(PLC register) Change station num Index0:LW9416 You can check all the product indicator data by input line number 104 Advanced Part Basic Design Method Station 2 Production line Station 1 1 Production cycle 150 Product count 210 D100 D101 Production line 150 210 2 Production cycle 200 Product count Station 2 Station 1 Station 3 D100 D101 200 320 Station 3 320 2.12 Buzzer Buzzer is built HMI body, and can issue a "beep" sound device. The buzzer is usually used for touch and alarm. 2.12.1 Touch Beep Touch beep means that when user touches the screen components, the buzzer will issue a "beep" sound. Enabling and disabling the touch beep can be achieved through the following three ways: Set in [HMI Attribute]-[HMI Extended Attributes]: Check the "User buzzer" means that enable the buzzer sounds, as shown: 105 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Save, compile and download to the HMI, then setting can take effect. Set in system setting mode Switch to system setting mode, and set the buzzer enable or disable. Take a HMI for example: 2011 / 10 / 18 19 : 57 : 01 MTxxxx SETUP Option Startup Window NO. 0 Backlight Saver Time: 10 Buzzer Disabled Enable Reset HMI after set the buzzer! 2011 / 10 /18 19 : 57 : 01 MTxxxx SETUP Option 0 Startup Window NO. 10 Backlight Saver Time: Buzzer Disabled Enable Reset HMI after set the buzzer! ☞More information refers to [Hardware Part 3 System Setting Mode] Change the value of LW10012 to make buzzer enable or disable. LW10012 Specific instructions as shown in table: System Register Descriptions LW 10012 0:buzzer disable; 1: buzzer enable 2.12.2 Alarm Beep When item logon in the alarm information or event information is triggered, HMI will beep. 106 Advanced Part Basic Design Method Choose “buzzer” as below: Users can choose buzzing time raging from 1 to 65535, unit: second User should set value of LB9141 to shut off the buzzer: Special register address LB 9141 Specification ON:shut off buzzer,reset to 0 2.13 Screen Saver Use a screen saver function can effectively prevent the screen in a important frame by inadvertently touch screen causes disoperation. Screen saver function is enabled in the [HMI Attribute] - [HMI extended attributes]: When the HMI screen in the set period of time without touched, the screen will switch to the specified window that screensaver window. If the screen saver window is a non-fixed value, you can change the value of the special register LW9532 to change 107 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software screensaver window number. 1. Screen saver time range from 1 to 65535, unit is minute; if set to 0, it means does not use the screen saver function. 2. Check the "Return to original window when screensavers ends", which means that when the system enters screen, if there are touch-screen operation, the system will switch back to the previous window into screensavers. Uncheck it means to continue to stay in the screensaver window, you need to set window switching element to switch screen. 2.14 Password Setting Kinco HMIware security function includes project protect, screen protect and component protect. 2.14.1 Project Protection project protection:before you can open a project ,you should input password Project password protection: Upload protect:before uploading ,you should input a password Project upload projection: After input upload password Project decompile protection::when turning pkg into wpj, you should input a password Project decompile protection: PKG file WPJ file After input decompile password 2.14.2 Screen Protection You can set security levels or user permissions to limit operator from entering some important windows. 108 Advanced Part Basic Design Method security levels to protect screen Set number of security levels and relevant password in [HMI attribute]-[security levels]. There are two ways: Take window A switching to window B for example: Window security level Window security level is set to 0(default), Window B security level is set to 1, then window A can be switched to window B when the system security level is equal or up to 1. So user must input the 1 or up 1 level password before switching the window. About password window: User can pop password window with the help of direct window, while function key will be used to switch the state of it. User can also create a new window or call the system one[Frame9:Login Window]. Set the control authority Set control setting to the component changing window. Choose “conditional enable” in [attribute]-[control setting]-[Touching enabled setting], select “security level”, set minimum level:1(or higher than 1).Then only users whose level is not less than 1can operate this component. screen protection through user permission You need first to assign authority in [HMI attribute]-[user permissions setting] Then you can set control setting of a component to implement this function. Choose “conditional enabling”in [HMI attribute]-[control setting]-[touching enabled setting],select “permission control”, “select permission”:1 (for example). Only user who has permission 1 can use this component. User can input its name and password to get the permission. About login window: User can also create a new window or call the system one [Frame9: Login Window]. 2.14.3 Component Protection In Kinco HMIware, you can limit others to operate some important components by set security levels or user permissions. In two following ways you can protect components from being used without allowance: 109 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Through Security Level Through Permission Control ☞For details about password, refers to [Advaced part 10 Password] 2.15 Data Encryption For the data stored in the external memory – USB disk\ SD card, data encryption function can be used to limit the user to make modification, editing and so on to the data files as CSV format. 1. If the [data decryption] operation is not performed to the CSV file generated for the component using [Data Encryption], the illegible characters will be displayed in the opened CSV file. 2. If the data is decrypted through KHManager, the CSV file can only be opened for viewing instead of modifying or editing. 3. If the encrypted file is modified by someone intentionally, the error prompt will appear during the [Decompile] operation in KHManager, making the damage of source file informed to the user. 4. The components supporting [Data Encryption] function are trend curve, XY plot, historical data display components. Take the setting method of [Data Encryption] for sampling data file of the Trend Curve as example: (1) [Trend graph component attribute] - [Save historical data] - Select [Save to external device] - Select [Data Encryption]. (2)The illegible characters will be displayed in the generated CSV file after the encryption if it is directly opened. 110 Advanced Part Basic Design Method (3)Open the KHManager software to decrypt CSV file. 111 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software The following dialog box will pop up after the successful decryption. The display effect of the CSV file decrypted successfully is as shown below. 2.16 Animation Effects In Kinco HMIware, user can make the screen more vivid by using animation effects in three ways: using multiple state display component By frequently switching some static pictures ,you can see a continuous effect . [Example]multiple state display making animation effect of an air blower 112 Advanced Part Basic Design Method multiple state display,making animation effect of an air blower,attribute: Read address LW 0 (HMI local register) Move type 3 Graphics Vector graphics: timer,change values of multiple state display,attribute: Execution Cycle 1×100ms State Setting Mode Periodical JOG++ (circle) Date Type word Asc value 1 Upper 2 Addr. Type LW 0 (HMI local register) When the project is run, the effect is as shown: ☞More information refers to [Adcanced Part 4.3.2 Multiple State Display] Animation By changing values, component can move from one position to another, so user will see a continuous action effect. [Example]ambition making conveyer belt effect 113 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ambition, attribute: Read address LW 0(HMI local register) Graphics Vector graphics: timer,change values of presupposed path, attribute: Execution Cycle 1×100ms State Setting Mode Periodical JOG++ (circle) Date Type word Asc value 1 Upper 3 Addr. Type LW 1(HMI local register) When the project is ran, the effect is as shown: ☞More infermation refers to [Advanced Part 4.12.1 Animation Components] Moving component By changing values, component can move from one position to another ,so user will see a continuous action effect. [Example] moving component making ball moving effect 320px 1 50px 50px 2 240px 3 Moving component property is set to: Read address LW 0 (HMI local register) Move type X & Y axis Graphics Vector graphics: Timer element, used to change the X-direction coordinate values of moving element, property is set to: Execution Cycle 2×100ms 114 Advanced Part Basic Design Method State Setting Mode Periodical Bounce(turnover upon limit) Date Type word Step 1 Upper 0 Lower 270(320-50) Addr. Type LW 1(HMI local register) Timer element, used to change the Y-direction coordinate values of moving element, property is set to: Execution Cycle 3×100ms State Setting Mode Periodical Bounce(turnover upon limit) Date Type word Step 1 Upper 0 Lower 190(240-50) Mode LW 2(HMI local register) When the project is ran, the effect is as shown: 2.17 Multi-Copy The method of multi-copy: Select components, click the right mouse button and select [Multi-Copy], pop up multiple copies Properties window. 115 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software a:Interval makes the right border of the component as the start point to perform the copy. Pitch makes the 1st point in the upper-left corner of the component as the start point to perform the copy. Interval Pitch b:Copy quantity:Duplication elements quantity c:Interval:The distance between the duplicated elements, in pixels d:Increase/ Decrease:Address Increase or decrease e:Address auto change:Integer bit register address auto increase or decrease f:After address auto change:The register address after the decimal point auto increase or decrease 2.18 Group Several components or the graphics are combined together and saved into the Group Components Library, thus making them called by other projects conveniently. The format of Group Components Library is *.pgl. How to open [edit box of group components library] Click [Draw] menu-[Group components]-[use the group element] Right-click the mouse in the blank space of the window, select [Groups]- [use the group element], then the [edit box of group components library] dialog will pop up, as shown below: 116 Advanced Part Basic Design Method Name Export Library Description Make the [Group Components Library] saved in the path defined by the user for convenient import. Import Library The default path of group components library is the userlib directory under the installation path of Kinco HMIware, and the user can also import the group components library from the self-defined path. Click [Import Library], and select the required group components library in the path corresponding to the saved group components library, then click [Open] to add this group components library to the group components library of the current project. New Library Click [New Library] button will make the dialog pop up, and the user can put the name of this new created group components library in it. The default path to save the group components library is the userlib directory under the installation path of the software. Delete Library Delete the group components library opened currently. Delete All Groups Delete all the graphics in the group components library opened currently. Delete Group Components Delete the selected graphics in the group components library opened currently. Place Group Components Place the selected group graphics in the group components library opened currently into the screen edited currently. [Example]: How to add group graphics to a new created group components library is described as follows: (1) Click [use the group element] in [Group components] in [Draw], and click [New Library] after the Edit Box of Group Components Library pops up, and input “group” as the name of the group components library in the group component library name dialog box, as shown below: 117 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Click [Enter] to create an empty group components library as shown below: (2)Place 3 rectangles in the screen, as shown below: Selected these 3 rectangles, and right-click the mouse to select [Group]-[Save the group elements], and then click the [Save Group Components] button in the Edit box of Group Components Library dialog box to make the following dialog box pop up. 118 Advanced Part Basic Design Method (3)Input “graph 1”in the Part Group Name dialog box, and then click [OK] button, then these 3 rectangles with the name of [graph 1] will be added into the new created group components library with the name of [group], as shown below: (4)If there are other group components to be added into the group components library with the name of [group], the operation method is the same as that mentioned above. And you just need to select [group] in the Group Components Library list as the path to save it. 2.19 Find /Replace Click [edit] menu-[find/ replace] Click the Press the PC keyboard shortcuts “CTRL” + “ F” icon on toolbar The following dialog box will pop up: Name Find Range Description Current Project All the frames, macros, background database in HMI will be searched. Background Only the background database components, such as event information logon,alarm 119 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Database information logon,trend carve etc. will be searched. All HMI Frames and Macros All the frames and macros in current project will be searched. All Frames All the frames in current project will be searched. All Macros All the macros in current project will be searched. Frames and Macros All the frames and macros in the selected HMI will be searched. All Frames All the components in all the frames in the selected HMI will be Current HMI searched. Current Frame All the components in the current frame in the selected HMI will be searched. Find Register All Macros Only all the macros in the current HMI will be searched. Register Type It means to find the device with Bit type or Word type. Addr. Type It represents the device type and device address in the controller where the search is performed. Checking “Range” means the search will be performed in the set range of address. Text Unselect match It means the judgment of the case of the characters and the case/ full match consistency in the whole text will not be done during the search. Match Case It means the match of the case of the characters in the text to be searched is required. Full Match It means the match of the text to be searched in the whole text is required. Replace After this option is set, the device type and address found according to the set conditions will be replaced by the specified device type and address. “Automigration by Cor. Address” in the Replace part will take effect once the “Range” in Find part is selected. If “Automigration by Cor. Address”is not selected, the replace address is the same; while if “Automigration by Cor. Address”is selected, the replace address is the consecutive address which will automatically deviate by making the set replace address as the start address. When the above parameters are set, if the “Find” button in the dialog box is clicked, the search of address meeting the condition will be performed the window locating in the Find Range. If the component is found, then No., Location, Name and Data will be displayed in the bottom white box. When the component meeting the requirements is found, the screen will automatically switch to the position where this component locates and the attribute dialog box for this component will pop up after this component is double-clicked. Clicking “Replace” or “Replace All” means the found component meeting the conditions will be replaced by the component with the address type and address set in the “Replace” part. 120 3 Window Window is the basic element for HMI project, each screen is made of some windows. With window, you can place the various components, graphics, texts displayed on the HMI screen. 3.1 Window Types According to the different of the function or using ways, there are 3 types of windows: Basic Window, Common Window and Fast Selection Window. The Basic Window after its size is changed can also be used as pop-up window. All the windows can be used as the bottom window. Specific descriptions are shown as below: Window Types Basic Window Descriptions This window is the most commonly used window. When Basic Window is changed by using [Function Key]-[change window] or [PLC Control]-[change window] function, the current screen will be cleared (All the windows rather than Common Window and Fast Selection Window will be cleared.), and the Basic Window to be changed will be displayed in the current screen. When the component in Basic Window calls the pop-up windows, the Basic Window is always on opening status, and the original information will be reserved, and the called pop-up window will be attached to the current Basic Window. The master-slave relationship is between Basic Window and all of related pop-up windows. When Basic Window N is switched to Basic Window M, all of the sub-windows of Basic Window N will be closed while Basic Window M and is sub-windows will be displayed. Fast Selection This window is the window called by the operation buttons, is generally used to place the commonly Window used buttons. And it will be always displayed in the screen until the operation button makes it hidden. The default Fast Selection Window is Frame 2. You can modify the other window as Fast Selection Window in [HMI Attribute]-[HMI Extended Attributes]-[Fast Selection Window]. Common The components in this window will be displayed in the other window, but does not include Pop-up Window Window. Usually each window shared or the same components will be put in Common Window. The default Common Window is Frame 1. You can modify the other window as Common Window in [HMI Attribute]-[HMI Extended Attributes]-[Public Window]. Bottom Window This window is generally used to put some common components such as background graphics, charts, and titles and so on. Using this window, you needn’t to edit the some components repeatedly. The components in Bottom Window will be inserted into the general window during, and in fact window isn’t displayed at all. Pop-up Window All the Pop-up windows are attached to the current Basic Window. The windows closed by the function key only can close Pop-up window, direct window or indirect window, can’t close Basic Window. The direct window, indirect window, [Event Information Logon]-[Pop-up window] and [Function 121 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Key]-[Popup window] all belong to the Pop-up window. One screen can include Basic Window, Fast Selection Window, Common Window, while every Basic Window or Common Window can include many Bottom Windows and Pop-up Windows. The relationship between them is shown as below: ※ The pop windows by Event information logon and Function key setup The number of windows in each project is limited as follows: Window Type Default Window No. The largest number of windows Basic Window 0 The window No. ranges: basic window 0, 10 to 32767 Common Window 1 1 Fast Selection Window 2 1 Bottom Window -- Up to 3 bottom windows can be set for each window. Pop-up Window -- Unlimited until the memory runs out ! 1.As once opened,the popup window won`t release the RAM unless closed,it is suggest to use it as few as possible. 2. The same window can be opened once by one related window, therefore you can’t open the same window by 2 or up direct window/ indirect window in the basic window. 3. All the Pop-up windows are attached to the current basic window, so when the current window is switched to the other Basic Window, the Pop-up window will be closed. In this case, if the window is switched back to this Basic Window, you will find that the Pop-up window originally attached to this window still exist; otherwise you use the [Close window] function of function key. 4.A popup window in the common window does exist until shut down with the Function key [Close window] 5. Fast Selection Window supports the Pop-up window. 6. Use Basic window rather than Popup window, Indirect window or direct window which may slow down the communication speed. 7. The actual largest number of Basic window and Popup window is related to HMI`s RAM. 122 Advanced Part Window 3.2 System Default Window A new project has 10 default windows as seen in the Project structure window as follows: Default windows description: Window number 0 Window name Frame0 Description Basic window,default initial window Common window,two popup windows used to pop default keyboard. Do not 1 Common Window delete these two windows or the keyboard is unavailable. Attention: Devices used in every window can be put in it 2 Fast Selection Fast Selection,used in coordinate with [Fast selection window] in HMI attribute 3 NUM Keyboard NUM Keyboard,default keyboard 4 ASCII Keyboard ASCII keyboard,backup 5 File List Window File List Window,used in coordinate with [Input/Export] in Function key 6 Password Window Password Window,used in coordinate with File List Window 7 8 Confirm Action Confirm Action Window,pop up when [Control setting]-[Operator confirm] is ☞For details,refer to【Advanced Part 4.1.7 Control Setting Option】 Window chosen HEX Keyboard HEX Keyboard, backup Login Window,pop up when [Control setting]-[Conditional enable]-[Security 9 Login Window level]-[auto show login window] is chosen ☞More information refer to【Advanced Part 10 Password】 123 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 1. Default Frame 0~9 no deletion 2.Device address and attribute in Frame1-9 cannot been modified, or they may not be in normal use. You can only change the text set 3.3 Edit Window 3.3.1 Window Add A new project has 10 system default windows. User can add some new windows, and there are 3 methods to create a new window. Click the [Add Frame] in [Screen] menu. Click the Select the HMI0 to right click in Project Structure Window and select [Add Frame], icon of [Add Window] in [Page Switch Toolbar]. Click [Add Frame], and the [New Frame] dialog box will pop up. 124 Advanced Part Window Specific descriptions are shown as below: Name Frame Vacant Position Descriptions When the existing windows are not in a continuous order, the new window will automatically insert in the first vacant place. End The new frame will automatically be numbered next to the existing last number. Default choice. Custom The new frame number can be defined freelyfrom10 to 32767 without duplicating the existing number. Frame ID New frame number. When the Frame position is [Vacant]or[End],this option is unavailable. Only when it is [Custom], you can modify it. Frame Name Ether default or custom After [New Frame] setting,click【New】,a new frame is created. 3.3.2 Window Opening There are 4 methods to open the window after the window is created. Select the window in the pull-down menu in [Page Switch Toolbar]. Click the icon of [Previous page]/[Next page] to open the window. The previous window can be displayed by clicking the icon, and the next window can be displayed by clicking the incon. Click the window ID in [Project Structure window]-[Tree View]. Double-click the window ID in [Project Structure window]-[Windows Preview]. 125 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 3.3.3 Window Copy/ Multi-Windows Copy Window support the function of copy and multi copy. Click the [Copy/Delete windows] in [Screen] menu to copy window. Click [Copy/Delete windows] and the following dialog box will pop up: Specific descriptions are shown as below: Name Descriptions Operation Type Copy window:count Select the function of Copy window and set the count Source Windows Copy Single Window Set the starting source copied window ID 126 Advanced Part Window Param Setting Copy Multi-Windows Set the starting source copied window ID and the end source window ID, from window M to window N will be copied at the same time. Set the starting destination windows ID. The end destination window ID Destination windows ID Setting will increase automatically according to the copied number and the number of the source window, can’t be modified. The destination window ID mustn’t be the existing window ID. 3.3.4 Window Deletion/ Multi-Windows Deletion Delete the current window There are 4 methods to delete the current window: Click [Delete Frame] in [Screen] menu. Click the icon of Delete Frame in [Page Switch Toolbar] Right click the selected window in [Project Structure window]-[Tree View], select [Delete]. Selected the window in [Project Structure window]-[Tree View], and press the [Delete] key of PC keyboard. Delete custom window Click the [Copy/Delete windows] in [Screen] menu to delete window. 127 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Click [Copy/Delete windows] to pop up the [Copy/Delete windows] properties dialog box,and select [Delete Window]. Specific descriptions are shown as below: Name Descriptions Operation Type Delete Window Select the function of delete window. Delete Window Delete Single Window Set the starting deleted window ID Operation Delete Multi-Windows Set the starting source deleted window ID and the end source window ID, Setting ! from window M to window N will be deleted at the same time. 1. After delete window, all components in this window will lost and can’t be recovered. Be careful with using this function. 2. The windows from Window 0 to window 9 are system default window, unable to delete. 3.4 Window Attribute 3.4.1 Open Window Attribute Box There are 5 methods to change the window attribute in Kinco HMIware software. Click [Frame Attribute] in [Screen] menu. 128 Advanced Part Window Click the Directly click the Double-click the blank in the current window. Right click the selected window to set in [Project structure window]-[Tree View], select [set]. icon in the [Current Frame Attribute] in [Page Switch Toolbar]. icon. 3.4.2 Window Attribute Descriptions Window attribute descriptions are shown as below: 129 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Window attribute descriptions Name Assign the name for each window for convenient differentiation. No. The window No. ranges from 0 to 32767. Window No. can be set when the new window is created, and it can’t be changed after it has been created. Security Level Set the security level for the current window ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 10 Password] Switching to the lowest security This function is used with security level. level when window closed ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 10 Password] Position X/Y This function is only valid for using “popup window” function of the function key. When the window is set this attribute, the vertex in the upper-left of the window will be displayed in the special X/Y position. Width/Height Set the width and height of the window. If the special attribute features [Print page], the width and height both can be larger than the fact screen size, but do not exceed 1024. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 13 Print] Bottom Window Set the corresponding bottom windows for the current window. The bottom window is in the bottom of the edit window as background graphics. The window to be set as the bottom window must be the created window, where the components used by the multiple windows together can be put. Frame Set the width and the color of frame. The frame width ranges from 0 to 16. If the width is not 0, the color can be selected for the frame. Shielding public window If the shielding public window keyboard mapping is selected, it will shield the keyboard keyboard mapping in the common window. This function is only valid for the self-keyboard HMI. Special Attribute Keyboard page: Set the current window as keyboard window, and use with the specified keyboard of the keyboard setting in component attribute. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.4 Keyboard] Print page: Set the current window as print window. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 13 Print] Video page: Set the current window as video window. It is set when video component is put in pop-up window. Use Background Color [Fill color] is the background color, [Background] is the filling graphics color. If the fill 130 Advanced Part Window style is 0, only fill color is displayed in this window. Transparence It is only valid for the pop-up window and the fast selection window. Transparence is 0%, 20%, 50%, 80%, 100% Pop Window Type The Pop Window Type shows the relationship between one pop-up window and its adjacent window. If one window features “Monopoly”, its parent window will be frozen Monopoly after it pops up, and it will always be displayed in the Top layer。 If one window features “Clipping”, the border of this window will be Clipping restricted by its parent window, i.e. the part displayed out of the border of its parent window will be cut off. If one window features “Tracking”, it will move together when its parent Tracking window moves. Coherence Window A and Window B are both attached to the Basic Window. Generally, Window A will be displayed in the Top layer when it is touched. But if “Coherence” is selected, it will not be displayed in the Top layer even if it is touched, but it will always be attached to its parent window. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 3 Window] Note: If “Clipping” is selected, “Tracking” must be selected simultaneously. Timer List descriptions Timer List Show all the timers. If there is none,it won`t display. Special setting element list descriptions Special setting Show all the timers and setting components with window attribute. If there is none ,it won`t display element list 【Example】Pop Frame10,11,12 over Frame0,transparence are respectively0%,20%,80%.Moreover,initial coordinate are respectively(0,0),(110,0),(220,0). Popup frame10 Popup frame11 131 Popup frame12 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software frame0:3 function keys to pop frame10,11,12: function Change window:pop frame10 pop frame10 pop frame10 Tag Use tag;0:Pop frame10 Use tag;0:Pop frame11 Use tag;0:Pop frame12 Graphic Vector graphic: Frame10,11,12attribute settings: Initial coordinate 0 110 220 transparence 0% 20% 80% Background color choose,fill color:yellow Save, compile and download. In operation,click function key, you can see frame as bellow Popup frame10 Popup frame11 Popup frame12 Popup frame10 Popup frame11 Popup frame12 3.5 Components Related to Window Components directly related to the window are: Direct window, indirect window, and function key (Change window, Goto Prev, Change common window, Change fast selection window, Popup window, Close window, Popup window title bar and Minimize). Functions directly related to the window are: Change Window, Write Data to PLC (Current Base Window), Change Window (Ignore the window 0) of PLC Control. ☞ For details about contents of these components, refer to [Advaced part 4 Component] 132 4 Component Components are the objects by which user inputs and operate data; user can execute some operations by operating these objects. The attribute of component must be set correctly according to actual application. Different attributes influence the component operating and executing result directly. This chapter will introduce the detail of component attribute. 4.1 Common Setting of Component 4.1.1 Create and Delete Component (1)Create component There are two ways to create component: Create from the Graph element window In the PLC parts/Function parts/projects database of Graph element window, drag the component to the edit area, then the attribute window will pops up automatically, there will be a “+” cursor when you click the OK of attribute window, then move the cursor to appropriate position and click left button to put the component, click right button to cancel creating component. As shown in following picture: 2 1 Create from Menu Click the components(I) menu, chose a wanted component, then the attribute window will pops up automatically, there will be a “+” cursor when you click the OK of attribute window, then move the cursor to appropriate position and click left button to put the component, click right button to cancel creating component. 133 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Text library, address tag and sound lib are in the Option(O) menu (2)Delete component There are two ways to delete the components that have created Delete by right click menu Chose the component, right click then click the Delete to delete the selected component Delete by Delete key on the key board Chose the component, then press the Delete key on the keyboard to delete component 4.1.2 Execution Order of Components In some application, there is a chance that one touch to trigger multiple components execution, so the customer stacks several components together. At this time, if there is a touch operation, the stacked components are not executed at the same time but executed according to the order of components. The top component is executed first, then the following components. As shown in the following picture: Besides, customer can check the layer position of the stacked components Right click the stacked components; you can see the following options: 134 Advanced Part Component You can use the tool bar (set top/set bottom/ previous layer/next layer) to adjust the layer position of the stacked components ! 1. If there is a component that executes Change window operation in the stacked components, the components that under this Change window component will not be executed. 2. The number of stacked components should be less than 32. 4.1.3 Methods to Open Attributes Window The attributes window will pop up automatically when the component created, and there are three methods to open attribute 135 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software window of the created component. Double click to open attribute window Chose the component, right click, chose the Attribute operation in the menu Chose the component, click the icon on the tool bar How to open attributes window of stacked components When multiple components stacked together, the lower component can be selected by right click, then open attributes window by above methods. ! Multiple attribute windows can not be open at the same time 4.1.4 Basic Setting In the Basic Attributes option, customer can set the operation object, address type and other related attributes Detail description of Basic Attributes Priority Reserved 136 Advanced Part Component Write Address The register address to which the status value or data that writes. If it is unavailable, the component is read-only component, the display status depends on the value and data in the Read Address HMI The HMI number; the number is distributed automatically in order when the HMI is built PLC No. The PLC controller number; the number is distributed automatically in order when the PLC controller is built Change Station Num When HMI communicate with multiple PLC controllers, you can use this option to connect corresponding PLC controller. This option is used in the application that uses one HMI-multiple PLCs or ,multiple HMIs-multiple PLCs but only one PLC in the program ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.11.2 Index Station Num] Addr. Type Chose the address type of the PLC register or HMI local register Bit registers in HMI : LB、LW.B、RB、RBI、FRB、FRBI Word registers in HMI: LW、RW、RWI、ERW0~2、ERWI0~2、FRW、FRWI ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 15.1 Local Register of HMI] 5 PLC/Controllers’ address type is different according to different PLC/controller device Refer to the Communication Connection Guide for more details about PLC/controller address type Address Set the register address of the command or data Code Type BIN, BCD or LSB ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.5 Cdoe Type] Word Length The register number that the component takes up, It is usually 1, it also changes according to different components and address type. System Register The registers in HMI which have special use ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 15.2 System Special Registers of HMI] Format The format of the address type in PLC/controller or HMI Use Address Tag Use the addresses that have been defined in the Address Tag ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 5.2 Address Tag Library] Use register Read Address the index Use a certain register as the index register of the component ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.11.1 Index Register] The register address from which the status value or data read. If it is unavailable, the component is 137 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software write-only component; the display status cannot display the data or state of read address. Description The reference name of this component. 4.1.5 Tag Setting In the Tag option of component attribute, set the display text of each state. Detail description of Tag Use Tag Use the tag Use Graph Font Use graph font mode in tag text ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.3.4 Grahp Font] Tag Cross-border Checked Check Adjust the component size automatically according to the tag content, as following picture: Uncheck Do not adjust the component size automatically according to the tag content, the tag content that cross border will be cut, as following picture: 138 Advanced Part Component Use Textlib Use the text in the textlib as tag content ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 5.1 Text Library] Tag List The comment text corresponding to each state Tag Content Input the comment text of each state here Copy Contents to All State Front Type Chose one state in the Tag list, click this option to copy the tag content of this state to all the state Use vector font or dot matrix font in tag content ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.3 Text] Font Attribute Set the attributes of the tag content, like font, size, alignment, color and so on. The current font attributes can be copied to each state or tag content of each language The steps to set tag: Add tag content of state 0 Step Check the “Use Tag Chose the state 0 in Tag List Input comment text in the Tag Content Add tag content of state 1 Chose the state 1 in Tag List Input comment text in the Tag Content 4.1.6 Graphics Setting Set the graphic of each state in the Graphics option of component attribute, the graphic can be vector or bit map. Detail description of Graphics 139 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Vector Graphics Use vector graphic to display Bitmap Use bitmap to display Use original size This option is effective when chose bitmap as graphic, if it is checked, component will display the original size of the graphic Save to System Library Save the checked graphic or graphic of some state to the system library in the UserselPath file folder Import Graphics Import vg or bg format graphic from system library or external Graphics Status Preview the graphic of the checked state. For some stateless control component, like Vector Graph and Bitmap, The graphic display in Vector or Bitmap is the picture checked here. ☞Refer to Advanced Part 5.3 Graphic Library for more details 4.1.7 Control Setting Option Set the control conditions and security in the Control Setting, also can set the trigger macro and trigger register operation here. Detail description of Control Setting 140 Advanced Part Component Touching Always valid The touch is enabled always the time. The operator can operate is all the time Enable Always invalid The touch is never enabled. The operator cannot control operator it Setting Conditional Security Level: If clicked means the current security level must higher than the set Enabling security, so the operator can operate this component to set the state value or data to the corresponding register. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 10.3.1 Security Level Protection for Components] Permission Control: If clicked means the operator must has corresponding permission so he can operate this component to set the state value or data to the corresponding register. 141 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 10.3.2 User Permission Protection for Components] Register Control: if clicked means the specified bit register or word register must satisfy the setting conditions, so that operator can operate this component to set the state value or data to the corresponding register. Auto show login window If clicked means when touch the component but the current user security level or permission cannot satisfy the setting security level or permission, the password input window (Frame9: Login window) will pop up automatically. Show Element Invalid Tag If clicked means when the component is touch invalid, the component will display touch invalid tag. This function is optional only when the Always Invalid or Conditional Enabling is selected. The color of touch invalid tag can be set in HMI Extended Attributes of HMI Attributes Security Min Press Time Setting The minimum time of a hold pressing to make touch effective. The unit is 100ms, when it is set to 0, it means do not set this option. Operator If clicked means when touch the component, the Confirm Window (Frame7:Confirm Confirm Action Window) will pop up. Click YES to make this touch effective and if click Cancel or do not click YES during the wait(s), the touch operation will be canceled 142 Advanced Part Component automatically. Record If clicked means the operation event will be recorded , this event can be displayed in the Operations Operation Log , and saved in csv file in the external storage Min Time Interval(Second) The minimum time interval between two touch operations of one same component or two different components. 0 means do not set the Min time Interval Notificatio Trigger Macro Execute the specified macro when the operation to the component is successful n Trigger Register Word Write the “Write Value” to the specified register before the Written Notice After operation is executed successfully Written Notice Bit operation is executed successfully Write the On/Off signal to the specified register before the Written Notice After Notice Write the “Write Value” to the specified register after the operation is executed successfully Written Write the On/Off signal to the specified register after the operation is executed successfully 4.1.8 Display Setting Set the display condition, display size, position in the Display Setting. Detail description of Display Setting 143 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Lock If clicked means the component is locked, the position of component cannot be changed by mouse or moving keys on keyboard X/Y The coordinate value of the top left of component Width/Height The width and height of component(The unit is pixel) Always Display If clicked means the component is displayed all the time Never Display If clicked means the component is hidden, the hidden component cannot touch Conditional Security Level Control: Clicked means the component is displayed only when the current security level Display is higher than the setting level. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 10.3.1 Security Level Protection for Components] User Permission Control: If clicked means the component is displayed only when the operator has corresponding permission ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 10.3.2 User Permission Protection for Components] Register Control: Click means he component is displayed only when the specified bit register or word register satisfies the condition 144 Advanced Part Component . 4.1.9 Touch Sound Control In the Sound option, set the sound when the component is touched Detail description of Sound Use Sound Set the sound when the component is touched. Sound Library Open the sound library attributes box. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.15.6 Sound Lib] Play Play and listen the audio Stop Stop the audio ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 5.4 Sound Lib Application] ! “The sound function is only suitable for the HMI with audio output port. 4.1.10 Save Historical Data Detail description of Save Historical Data 145 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Save to Recipe Save sampling data to the recipe register (RW) of HMI Data Field The end address = the start address + 20 +sampling page number*(4+ channel number). If the data exceeds the storage limit, the sampling data will cover the previous data Save to External Save the sampling data to the external device Device Storage Devices SD card, USB DISK1*、USB DISK2* are optional Outage keep in If the HMI is powered off and restart, the information can be regained Export to csv Save the sampling data to external device in CSV file. This CSV file is saved in File /trend/subdirectory/file name Data Encryption Encrypt the sampling data ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.15 Data Encryption] Save MS Save the sampling time to ms level and record in CSV file Subdirectory Set the subdirectory name of CSV file when it is saved in external device, customer can change this name The default subdirectory name of History Data is History Data, Trend Curve is History Trend, XY plot is XY-CHART Storage Type Daily File Save the sampling data by days, and the name of CSV files is in “yyyy mmdd” form 146 Advanced Part Component Single File Save the sampling data by items, and the name of CSV file is the Subdirectory Bulk Storage Provide a buffer storage mode, Only when the data is up to the bulk storage setting, and then write the data to SD card or U disk. The “Default” means don’t use buffer storage mode, as soon as there is sampling data, write this data to SD card or U disk Max Storage Set the limit of the storage: if it is by Daily File, the unit is day, if it is by Single File, the unit is item. If chose the “Daily File”, the file name is as “yyyymmdd”, The Max Storage means the maximum csv file number under this routine, if csv file exceeds the max storage number; the previous files will be deleted. If chose the “Single File” in Storage Type, the CSV file named by the Subdirectory name, The Max Storage means the maximum items in this csv file, if the items is up to the limit, the data will not be saved Variable Subdirectory The Subdirectory is read from specified registers, the maximum register number is 16 ※ If a HMI has two USB host, the number of U disk depends on the sequence they plug in HMI. That is to say the first U disk that plug in HMI is USB DISK1, and the second U disk that plug in HMI is USB DISK2. It does no matter with the slot position. ! When the sampling data is saving to external storage device, the special system register should set OFF before removing the external storage device, or the data will be damaged or lost. They are LB9153(SD card)、LB9154(USB disk1)、LB9155(USB disk2) 4.2 Button/Switch Components They are Bit State Setting, Bit State Switch, Multiple State Setting, Multiple State Switch, Combination Operations, and Function Key and so on. 4.2.1 Bit State Setting The Bit State Setting defines a touch area. When this area is active, this button can set the HMI bit address or PLC bit address On or Off. The display status of this component will not be changed by the input value. 147 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Detail description of Bit State Setting Type Function description Press to set specified address ON, still ON if released or pressed again On Press to set bit address OFF, still OFF if released or pressed again Off Press to set specified address ON, still ON if released; Press again to set address OFF, Still OFF if released Toggle Only when this component is hold pressing, the specified address is ON, change to OFF if released Reset When the window which contains this component opens, the specified address is set ON Set On when Window Open Set Off when Window Open When the window that contains this component opens, the specified address is set OFF 148 Advanced Part Component When the window that contains this component closes, the specified address is set ON Set On when Window Close When the window that contains this component closes, the specified address is set OFF Set OFF when Window Close When the window that contains this component is maximized, the specified address is set ON Set ON when Window Maximized When the window that contains this component is maximized, the specified address is set OFF Set OFF when Window Maximized When the window that contains this component is minimized, the specified address is set ON Set ON when Window Minimized Set OFF when Window Minimized When the window that contains this component is minimized, the specified address is set OFF 149 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software When window minimized M0:OFF M0 When the backlight of the window that contains this component is off, the specified address is set ON Set On when Backlight Off When the backlight of the window that contains this component is off, the specified address is set OFF Set On when Backlight Off In the window which contains this component, when a Number Input component inputs successfully, the specified address is set ON Set On when Input Success In the window which contains this component, when a Number Input component inputs successfully, the specified address is set OFF Set OFF when Input Success Map the component to the F1~F12 of external keyboard or F1~F8 of the HMI which Key has keys itself. This function is suitable for the HMI with USB host or HMI with keys itself 4.2.2 Bit State Switch The Bit State Switch is a combination of Bit State Lamp and Bit State Setting component, it defines a touch area, if this area is active, this component can switch HMI or PLC bit address between on and off, at 150 Advanced Part Component the same time, the display state of component will change according to the value of read address. Detail description of Bit State Switch Switch Type Function description Press to set specified address ON, still ON if released or pressed again On Press to set specified address OFF, still OFF if released or pressed again Off Press to set specified address ON, still ON if released; Press again to set address OFF, Still OFF if released Toggle Only when this component is hold pressing, the specified address is ON, change to OFF if released Reset Key Map the component to the F1~F12 of external keyboard or F1~F8 of the HMI which has keys itself. This function is suitable for the HMI with USB host or HMI with keys itself 151 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 4.2.3 Multiple State Setting The Multiple State Setting component defines a touch area, if this area is active; this component writes a setting value to a specified register in HMI or PLC. The display status of component will not be changed by the value of read address. Write data“125” to D100 D100=125 Detail description of Multiple State Setting Setting Mode Set Press component to set the setting constant to a specified register Constant Set at Window When the window with this component opens, set the setting constant to a specified register automatically Open Set at Window When the window with this component closes, set the setting constant to a specified register automatically Close Set at Window When the window with this component is maximized, set the setting constant to a specified register automatically Maximized 152 Advanced Part Component Set at Window When the window with this component is minimized, set the setting constant to a specified register automatically Minimized Set at Backlight When the backlight of the window that contains this component is off, set the setting value to a specified register automatically Off Set at Enter In the window which contains this component, when a Number Input component inputs success successfully, set the setting value to a specified register automatically D100=125 #### 123 Input is accepted 120 123 D100 Set at Enter In the window which contains this component, when a Number Input component inputs Fail unsuccessfully, set the setting value to a specified register automatically D100=125 #### 123 Input is not accepted 120 120 D100 Add value The value in specified register will be added “Addend” every time presses this button, the result will not exceed the Upper limit 153 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Sub value The value in specified register will be subtracted “Subtrahend” every time presses this button; the result will not exceed the Lower limit Jog++ If hold pressing the button exceeding the “Delay Time”, the value in specified register will be added “Addend” in a “Jog Speed” time. The result will not exceed the Upper limit If the “Immediate Execution of Increase/Decrease Progressively” is checked, the value in specified register will be added “Addend” immediately at every press. If hold pressing the button, the value in specified register will be added “Addend” in every “Jog Speed” time until reaches the Upper limit Jog-- If hold pressing the button exceeding the “Delay Time”, the value in specified register will be subtracted “Subtrahend” in a “Jog Speed” time. The result will not exceed the Lower limit If the “Immediate Execution of Increase/Decrease Progressively” is checked, the value in specified register will be subtracted “Subtrahend” immediately at every press. If hold pressing the button, the value in specified register will be subtracted “Subtrahend” in every “Jog Speed” time until reaches the “Lower” limit Jog++(Circ If hold pressing the button exceeding the “Delay Time”, the value in specified register will le) be added “Addend” in a “Jog Speed” time until reaches the Upper limit, then adds addend from the Lower limit 154 Advanced Part Component If the “Immediate Execution of Increase/Decrease Progressively” is checked, the value in specified register will be added “Addend” immediately at every press. If hold pressing the button, the value in specified register will be added “Addend” in every “Jog Speed” time until reaches the Upper limit, then adds addend from the Lower limit Jog--(Circl If hold pressing the button exceeding the “Delay Time”, the value in specified register will e) be subtracted “Subtrahend” in a “Jog Speed” time until reaches the Lower limit, then subtract subtrahend form the Upper limit If the “Immediate Execution of Increase/Decrease Progressively” is checked, the value in specified register will be subtracted “Subtrahend” immediately at every press. If hold pressing the button, the value in specified register will be subtracted “Subtrahend” in every “Jog Speed” time until reaches the “Lower” limit, then subtract subtrahend form the Upper limit Variable The parameters, like Set Value, Addend, Subtrahend, Upper, Lower, are read from specified registers Parameters Key Map the component to the F1~F12 of external keyboard or F1~F8 of the HMI which has keys itself. This function is suitable for the HMI with USB host or HMI with keys itself 4.2.4 Multiple State Switch The Multiple State Switch is the combination of Multiple State Display and Multiple State Setting. It displays the mapping status according to the value of Read Address (the maximum mapping status is 256). At the same time, it defines an area, when this area is touched, this component writes the mapping value to the Write Address. The Write Address and Read Address can be the same or different. 155 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Detail description of Multiple State Switch Control Add The State No. adds 1 every time press this button, and the mapping value is write to the Write Address, at the same time this component displays corresponding graph according to the value of Read Address. Unloop unchecked: Unloop checked: Sub The State No. subtracts 1 every time press this button, and the mapping value is write to the Write Address, at the same time this component displays corresponding graph according to the value of Read Address. Unloop unchecked: Maximum State 6 Beep...Beep... state5 state4 state3 state0 state1 state2 Unloop checked: List Display the state in list, and the current selected state is in Select Color 156 Advanced Part Component State Num. Dropdown Display the state in dropdown list, but only display the current selected state. Click the List dropdown list to display all the states The maximum state number is 256.(The BIN or BCD encoding supports 256 states at most, and the LSB encoding supports 17 states at most.) Map Value When the value in Read Address equals one of the values in the Map Value list, the component displays the corresponding graph and tag. When the component switches to one state, the corresponding Map Value is write to the Write Address Line Spacing If chose the List or Dropdown List as control mode, this option is used to set the line space between each tag. The unit is pixel Key Map the component to the F1~F12 of external keyboard or F1~F8 of the HMI which has keys itself. This function is suitable for the HMI with USB host or HMI with keys itself 4.2.5 Combination Operations The Combination Operations is used to combine multiple bit state setting and multiple state setting as one component. So the operator can execute bit state setting and multiple states setting operation by 0nly one button. 157 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Detail description of Combination Operations basic attributes Component List Add multiple Bit State Setting and Multiple State Setting components by right click. Write Address Set the Write Address of the components in the Component List Setting Mode Bit State Setting supports On, Off, and Toggle mode only. ☞For details about Bit State Setting, refer to [Advanced Part 4.2.1 Bit State Setting] Multiple State Setting components support Set Constant, Add and Sub mode only. ☞For details about Multiple State Setting, refer to [Advanced Part 4.2.3 Multiple State Setting] Exiting when If checked means that the execution will stop if one of the components fails during the sequence component execution, the next component will not be executed. If unchecked means the Combination execution Fail Operation executes from top to bottom, if one of the components fails during the sequence execution, then jump to execute the next component. 1. When add the components, use the “Insert before” and “Insert behind” option to set the order of the components 2. Use the Move UP and Move Down to change the order in component list 3. Use the Delete option to delete components 4.2.6 Function Key The Function Key provides functions like Switch Window, Keyboard Function, Clear Event, Touch Calibration, save Screenshot to Extended Memory, Execute Macro, and Print and so on. It also can be used to design the key board, and Function Key does not have control register, it executes functions by touch. Switch Window Description of Switch Window function Change Window Press the function key to close the current window (sub windows in this window included) and switch to the window with specified window No. 158 Advanced Part Component Press the function key to close the current basic window, and come back to the previous window. For example, switch fram0 to frame 10, press this function key in frame 10 to back to frame 0. This function is only suitable for basic window Goto Prev If pressed, the Common Window (The default is Frame 1) will be replaced by the specified window as the new Common Window Common Window Frame 1 Frame 0 Frame 0 Change Common Common Window Frame 10 + + Frame 0 Frame 0 Window If pressed, the Fast Selection Window (The default is Frame 2) will be replaced by the specified window as the new Fast Selection Window Change Fast selection window Pop up window If pressed, the specified window will pop up, and displayed above the current window, the current window will not close 159 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Use this option to close the pop-up window, but cannot close the Direct Window and Indirect Window, because they are controlled by the bit or word register. The Close Window function can close the pop up window only, but cannot control data in Close Window register Hold pressing this function key to move the pop up window. This function is suitable for pup up window, direct/indirect window only Pop up window title bar If pressed, the pop up window will be minimized in the task bar. Press the window icon on task bar to reset the window to original position. This function is suitable for pup up window, direct/indirect window only Minimize Map Keyboard Use this function to make virtual keyboard. Function description of keyboard Enter The same function as the Enter on the keyboard Backspace The same function as the Backspace on the keyboard Clear Clear the content in the Number Input and Text Input component Escape Cancel operation, the same function as the ESC on the keyboard Unicode Set the input characters in the “Number Input” and “Text Input” component. The number (0, 1, 2…) or 160 Advanced Part Component ASCII and Unicode (a, b, c…) are operational Move the cursor according to the mode, like Move up, Move down, Move left, Move right, Line head, Cursor Line tail, First position, Last position. This function is suitable for the Note Book component only Select text operation, Start select and Finish select included. This function is suitable for the Note Book Select Text component only Text Operation Set the text operation, includes Copy, Cut, and Paste. This function is suitable for the Note Book only Execute Macro Chose the macro Press function key to execute the existing macro. This function can set function for the F1~F8 of HMI, includes Along, Backwards, ESC, Enter and so on. This function is suitable for MT4201T HMI only. Touch Calibration Press function key with this option checked to enter the touch calibration screen. Customer can calibrate the touch panel. Enter the calibration screen without set the DIP switches Clear Event Press function key to clear the event information in the Event Display component. Save Screenshot to The Extended Memory. Press function key to save the screenshot to the extended memory in bmp picture. So the customer can print or check the screen of HMI. ☞For details about Save Screenshot to the Extended Memory, refer to [Advanced Part 4.15.5 PLC Control] Import/Export Press function key to import/export project or recipe data. ! This function must works with the File List Window and only the HMI with USB host or SD card supports it 161 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Description of Import/Export function Import project to HMI Export Project from HMI Import the project (pkg file) from extended memory to HMI. After that, HMI will restart automatically and run the project. Export the project(pkg file) in HMI to extended memory 162 Advanced Part Component Pop up Frame 5 and select save path Pr oj ect upl oad Cu r r e n t p a t h : ..\ event \ exmem\ hi st or yst or e\ l og\ scr \ t r end\ Pr oj ect upl oad Cu r r e n t p at h : Fi l e n a me : Tr ee / di sk/ usb1/ ..\ event \ exmem\ hi st or yst or e\ l og\ scr \ t r end\ Test . pkg HMI 0: Test . pkg OK Cu r r e n t p a t h : Pr oj ect upl oad / di sk/ usb1/ Fi l e n a me : Pr oj ect Tr ee Pr oj ect Test . pkg OK OK ..\ 1 \2 3 4 event exm em\ Clear w q e hi st or yst or e\r l og\ a s d f Caps scr \ x c = t r| end\ ? z + _ Fi l e n a me : Tr ee / di sk/ usb1/ ESC HMI 0: HMI 0: Pr oj ect upl oad Input file name ..\ event \ exmem\ hi st or yst or e\ l og\ scr \ t r end\ Test . pkg Test . pkg Fi l e n a me : Cu r r e n t p a t h : Tr ee / di sk/ usb1/ > < pr oj ect Test . pkg 5 6 t g vv 7 y 8 u i h HM I 0:j b n CH 9 0 o BACK p k l ENT m ; { Page Up } Page Down OK After press OK Import Recipe to Import the recipe file (.rcp) in extended memory to HMI. The operation steps are the similar with HMI Import Project to HMI Export Recipe from Export the recipe file (.rcp) in HMI to extended memory. The operation steps are the similar with HMI Export Project from HMI 163 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Message Board This function works with the Message Pad; it can be used as an assistant tool of Message Pad. Description of Message Board Tool Pen Press the function key to set the tool as a pen for Message Pad Erase Press the function key to set the toll as a eraser for Message Pad Clear Block Press the function key to clear the selected area of the Message Pad Pen Color Set color of pen Pen Width Set width of pen, 1~8 pixel are optional Clear Press function key to clear all content on Message Pad Print Press function key to print the current screen. ☞For details about print, refer to [Advanced Part 4.15.5 PLC Control] Map Keyboard Map the function key to the F1~F12 of the keyboard. This function is suitable for HMI with USB host only. 4.3 Lamp Component 4.3.1 Bit State Lamp The Bit State Lamp is used to indicate the state (0 or 1) of bit register in HMI or PLC. It can display tag text and graphic. Detail description of Bit State Lamp Function Description Display the corresponding graphic according to the state. This graphic isn’t blinking Normal 164 Advanced Part Component The blinking frequency (Rate) can be set. Value 1 Blinking on state 0, value0 Showing state 0 The blinking frequency (Rate) can be set Value 1 Blinking on state 1, value0 Showing state 0 Value 1 switch Blinking on state 1 and 0, value0 Showing state 0 The blinking frequency (Rate) can be set. Value 0 Blinking on state 0, value 1 Showing state 0 The blinking frequency (Rate) can be set Value 0 Blinking on state 1, value 1 Showing state 0 Value 0 switch Blinking on state 1 and 0, value 1 Showing state 0 The blinking frequency (Rate) can be set Value 1 Blinking on state 0, value 0 Showing state 1 Value 1 Blinking on state 1, The blinking frequency (Rate) can be set value 0 Showing state 1 165 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Value 1 switch Blinking on state 1 and 0, value 0 Showing state 1 The blinking frequency (Rate) can be set Value 0 Blinking on state 0, value 1 Showing state 1 The blinking frequency (Rate) can be set Value 0 Blinking on state 1, value 1 Showing state 1 Value 0 switch Blinking on state 1 and 0, value 1 Showing state 1 4.3.2 Multiple State Display The Multiple State Display displays the mapping state according to the value in the specified HMI register or PLC register. It supports 256 mapping states at most. Description of Multiple State Display State Num. Set the state number of Multiple State Display, it is up to 256. (The BIN or BCD encoding supports 256 state at most, and the LSB encoding supports 17 states at most) 166 Advanced Part Component Set the mapping value of each state. When the value in specified register equals the setting value, Data Mapping the component displays corresponding state 4.4 Number Components Number components include Number Input Component and Number Display Component. They are used to write data to a specified register or read data from a register and display this value. Common Attributes of Number Component. Description of number signed int unsigned int Hex Data type Bin Password Float Double Display the data in signed decimal integer (0~9) format.16 bits data range: -32768~32767; 32 bit data range: -2147483648~2147483647 Display the data in unsigned decimal integer (0~9) format.16 bits data range: 0~65535; 32 bit data range: 0~4294967295 Display the data in hex (0~F) format. The integer part can be set, no decimal. 6 bits data range: 0~65535; 32 bit data range: 0~4294967295 Display the data in binary (0, 1) format. The integer part can be set, no decimal. 6 bits data range: 0~65535; 32 bit data range: 0~4294967295 Display data in “*” format. Only the data type and date width can be set, other options are ignored Transform the 32 bits IEEE float data to decimal data and display in decimal. The default data width is DWORD Transform the 64 bits IEEE float data to decimal data and display in decimal. The default data width is 4-DWORD Data Width Set the data width of the register 16 bits or 32 bits(WORD or DWORD) Integer/Decimal Set the display bit number before and behind decimal dot Show plus sign When the data type is signed int, click this option to display the “+” symbol before positive number Set input/display range for Number Input/Display Component. “Variable Max/Min Value” checked means that the Max/Min Value is variable, and set read register of this variable. The word length of this Max/Min Value register depends on the data width of component. For example, the Max/Min Value is LW0, if the word Setting width is WORD, the LW0 is minimum value register, LW1 is Maximum value register; and if the word width is DWORD, the LW0 and LW1 are minimum value registers, LW2 and LW3 are the maximum value registers Off normal upper/lower If the data is exceeds the Max/Min Value range, the component will display the data in the setting color. 167 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Flash If the value in certain register exceeds the upper limit or lower limit, the data in the component will be flashing to enhance the alarm effect. The data will be displayed after calculating by proportion, the Min Value and Max Value is must be set in the function. For example, the original data is A, and the displaying data is B. Then the relationship between is as followings: B= Min Value+(A-Min)*Proportion and the Proportion=( Max Value -Min Value)/( Max-Min) For example the original data is 20, according to the following setting, the displaying data is 15+(20-0)*(55-15)/(100-0)=23. So the component displays 23 Proportion Conversion ※ For signed/unsigned int, if the Decimal is set, the original data will be displayed after left shift the Decimal bits, but also set the original data to the register. Description of Font Set the display position of data,, it has for methods , they are Left, Right, Leading 0, Center. For example, the Integer is 5, Decimal is 0, input value is 123, then the following are the displaying in four different methods: Alignment Font Adjustment Add the width of display area, the units is pixel 168 Advanced Part Component Horizontal Increased 0 pixel Horizontal Increased 60 pixel ##### ##### 60px Map the component to the F1~F12 of external keyboard or F1~F8 of the HMI which has keys Key itself. This function is suitable for the HMI with USB host or HMI with keys itself Related Attributes Setting of Numeric Data Other Related Attributes Set the Cursor Color when Numeric Data is triggered in the HMI Extended Attributes of HMI Attributes. Cursor 4.4.1 Number Input Number Input Component write the data in value to the certain HMI or PLC register, at the same time display the written date on HMI. Attributes Description of Keyboard Setting Public Windows Keyboard Use the Public Windows Keyboard It is the default setting , and use the keyboard in Frame3: NUM Keyboard Use the specified keyboard in designated window. If use the self-made keyboard, the window Specified Keyboard where the keyboard is should set the Keyboard Page in Window Attribute, so the window number can be displayed in the Specified Keyboard list Keyboard Pop-Up Position Do not Use Pup-Up Set the keyboard pop-up position on HMI When the Number Input Component is triggered, do not pup up keyboard. The HMI supports 169 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Keyboard USB can use the external keyboard The popped-up keyboard can input data to the components continuously by order. During the input operating, the keyboard will not disappear when press ENTER, and the input cursor will flash among the component in circle. The keyboard will be closed by press Close button Use Input Order Input Order Set the input order number for the component For multiple groups of components that need input the data continuously, the first triggered component decides where the cursor circles Group ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.4 Keyboard] 4.4.2 Number Display Number Display is used to display the value in specific HMI or PLC register on HMI. 4.5 Text Components The text components contain Text Input, Note Book, Text Display, they are used to decode the data by ASCII then write it to specific register in character string or read data from specific register then display it in character string after the data decoded by ASSIC Common Attributes Setting of Text Components 170 Advanced Part Component Common Attributes Description of Text Component Swap the high byte and low byte, then display the high byte on the left and low byte on the right High byte and low byte swaps If checked, the text content is decoded by Unicode and displayed. It is usually used to display Unicode multiple languages This mode can display the extended ASCII character between 0X80~0XFF. If checked, the text Extended ASCII cannot display Chinese character; the Unicode and Extended ASSCII cannot be chosen at the same time Word Length The word length is 1~16 optional. Each word contains 2 ASCII characters Description of Font Attribute Use the Vector Font or Dot Matrix Font to display character string Note: Generally speaking, if it is not ASCII character, it cannot be displayed by vector font, but the Unicode character input by Unicode keyboard with sane character tag can be displayed by vector font. For example: Font Type 171 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Add the display area width at the right side, the Set the displaying position of character string, including two methods: Left, Right. Align Font units is pixel. Adjust ment ment Map the component to the F1~F12 of external keyboard or F1~F8 of the HMI which has keys itself. This function Key is suitable for the HMI with USB host or HMI with keys itself Description of Keyboard Setting Attributes Public Windows Keyboard Use the public windows keyboard, the default keyboard is the [Frame3:NUM Keyboard] Use the keyboard in specified window. The default keyboard is the [Frame 4:ASCII Keyboard] If Specified Keyboard you use the self-regulating keyboard, you should set the Special Attribute in HMI Attribute to Keyboard Page, then you can select the Window’s number in Specified Keyboard list Keyboard Pop-up Position Not Use pop-p Keyboard Set the position of the pop-up window in the screen Do not pop up keyboard when trigger text input or text book component, but use the external USB keyboard if the HMI supports the USB host Input the component continuously when the keyboard is popped up, the keyboard will not be closed Use Input Order when press the ENTER key during the inputting, the input cursor will flash in cycle among the components that set the Input Order, the keyboard will be closed when click the Close button 172 Advanced Part Component Input Order Set the input order for the components Sort the components that need to input continuously in different groups, the first triggered component decides which group the cursor will flash among Group D100 HMI 5 Group 2 Group 1 D102 PLC D104 OK D200 100 D202 50 D204 180 ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.4 Keyboard] Related attributes settings about the Text component Description of related attributes Set the cursor color when the Text Input component or Note Book component is triggered in Cursor Color the HMI Extended Attributes of HMI Attributes ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 6.1.3 HMI Extended Attributes] Cursor Move Text Operation Use the Keyboard Function in the function key to move the cursor Refer to Advance Part 4.2.6 Function Key for more information. Use the Keyboard Function in the function key to select, copy, cut, and paste the text content. 173 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ☞Refer to Advanced Part4.2.6 Function Key for more information. 4.5.1 Text Iput The Text Input decodes the data according to ASCII, and then writes it to the HMI or PLC register in character string, at the same time displays the written data in character string on HMI. The written data is saved in the continuous registers that begin from “Read Address”. When displaying the data, the low byte characters are displayed on the left and the high byte characters are displayed on the right. The Text Input component cannot display the multiple rows text content 4.5.2 Text Display The Text Display component displays the HMI or PLC data in character string on HMI after decoding it according to the ASCII. D100 4 D101 2 D 4 M 8 H 0 Space 4 D100(Word No.:2) 9 I HMI The Text Display component cannot display the multiple rows text content 174 Advanced Part Component 4.5.3 Note Book The Note Book is the same as the Text Input; they decode the data according to ASCII, and then write it to the HMI or PLC register in character string, at the same time displays the written data in character string on HMI. The written data is saved in the continuous register that begins “Read Address”. When displaying the data, the low byte characters are displayed on the left and the high byte characters are displayed on the right. The Note Book component can display the multiple rows text content Description of Note Book attributes Total Lines The Word The total lines of input text Register Number of Per Line Display Line Display area line The most data length per line, the unit is word. A length of a ASSIC character is a byte, and 1word = 2 bytes 4.6 Graph/Meter Components In Kinco HMIware, customer can display the data in chart/graph. The graph/meter components contain Trend Curve, XY plot, Oscillograph, Bar Picture, Meter and so on. The Trend Curve, XY plot and Oscillograph are graphs; they are usually used to display data in a single or a series of continuous registers in graph on HMI. The customer can use them according to their function and actual application. The common attributes of graph setting. 175 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Description of Basic Attributes Component Read Address Trend Curve XY Plot Set the sampling register Set the sampling register address of the address of the first channel It depends on the type of XY plot depends on the sampling channel number, Word Length if the m,(m<17), first channel. The address assigning channel the is word length is m The word length depends on the channel number, sampling points, XY plot type and the read register type. The user can not change this Oscillograph Set the sampling register address of the first channel It depends on the channel number and sampling rate. If the channel number is m(0<m<17) and sampling rate is n(0<n<256), the word length is m*n Detail description of channel attributes. Line Width Display the width of the curve Set the data format of sampling data. It contains 16-bit signed, 16-bit unsigned, 32-bit signed, 32-bit Data Type unsigned, float and double Set the display range of sampling data on X axis and Y axis Y max/Y min Color Set the color of curve The Y max/Y min value is from specified registers. In multiple channel application, user can set specified Channel use variable limit registers for Y max/ Y min of each channel. Trend Curve: if the Specified Address is Y min; the Specified Address+1 is the Y max. XY plot: if the Specified Address is Y min, the Specified Address+1 is the Y max, the Specified Address+2 is the X min and the Specified Address+3 is the X max. Oscillograph: if the Specified Address is Y min, the Specified Address+1 is the Y max 176 Advanced Part Component Detail description of extended attributes Channel Properties Chose a channel to edit. The available channels depend on the channel number set in Trend Graphics or XY Curve Graphics or Scope Chart page. And set the line style and line width Connect Style Line Dot X Y axis projection projection Chose the graph of nodes, axis the following six types are available Node Graph ●▲■○ᇞ□× Node Size Set the size of node Use Grid Variable Period ! Node Color Set the color of node The curve use the background and grid, users can set the line and row number, as well as the line width , color and type When use the Time sampling, the Circle time can be read from specified register. Note: The Oscillograph does not support variable period Number of points The number of sampling points can be read from specified register If the circle period and sampling point number use the variable value, the variable value will be used in priority. And the default value will be used if the variable value cannot be got because of the communication problem ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.1.10 Save Historical Data] ! The Trend Curve and Historical Data Display can be used at the same, but when the trend curve and historical data display sample the same register and the data is saved in external device, the Subdirectories should be different, or the only save historical data in just one of the component About the display of curve. 177 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software The Trend Curve and XY plot run at the backstage, the trend curve and XY plot will not be cut off when changing the frame. On the other hand, the Oscillograph does not support running at backstage; the data sampling and curve will be cut off when changing the frame. The special attributes of these curves are as follows. 4.6.1 Trend Curve The Trend Curve reads a series specified continuous registers (in HMI or PLC) in period and display them in curve. The new data will be read from specified registers and displayed at the right/left/top/down side of curve, it is a real-time curve. 178 Advanced Part Component Detail description of trend curve attributes Single page Only display the sampling value in current page, there is no extended curve Type Multiple pages There is extended curve. When the curve goes on, the previous sampling data will not disappear. The historical data will be stored in the buffer area Start Start from left Attributes from right Y O Start Start from top from bottom X Time sampling OFFON trigger sampling ONOFF trigger Sampling Methods sampling OFFON trigger sampling OFFON reset trigger sampling ONOFF reset trigger sampling Cycle The sampling will be triggered when specified register changes from OFF to ON The sampling will be triggered when specified register changes from ON to OFF The sampling will be triggered when specified register changes The sampling will be triggered when specified register changes from OFF to ON. And the specified register will be reset to OFF automatically The sampling will be triggered when specified register changes from ON to OFF. And the specified register will be reset to ON automatically The time interval between two sampling points. The unit could be 1s or 100ms Continue Sam.Type Once Sampling Sample the date timely The sampling will continue even the all sampling points are finished The sampling will stop automatically when all the sampling points are finished, the sampling executes only once Sampling points on each page 179 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software points PageNum This option is valid in the Multiple Page type Channel The number of the channel, it is 16 channels at most This option is valid in the trigger sampling .Take the following picture for example, the LB100(bit register in the HMI) is the trigger register, when the LB100 satisfies the setting condition in the Sampling Method , the sampling will be triggered Control Register Setting Set the Pause and Clear register, the default word length is 2, the set address is used to stop the curve, and the set address +1 is used to clear the curve. The Pause function just stops the change of curve, but not stops the sampling. The Clear function will clear the curve on the Trend curve. Take the following picture for example, the LB0(bit register in HMI) is set to control the Pause-Clear function, when the LB0 is ON , curve will stop refreshing, when the LB0 is OFF , the curve will continue to display, when the LB1 is ON the curve on the Trend Curve will be cleared Pause-Clear Set the register to turn the page of Multiple Page curve, default word length is 3. This option is valid when the Multiple Page is chosen. Use this function to browse multiple page curves, and this function can be SCRO used with Scroll Bar. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.16.3 Scroll Bar] Take the following picture for example, if the specified register is LW0(word address in HMI), so the LW0 is the current browsing index value of scroll bar, the LW1 is the start browsing index value, and the LW2 is the max browsing index value 180 Advanced Part Component This option is used to save the start sampling time and end sampling time of current page, this option is valid when the Save Time option is chosen. Default word length is 12. Take the following picture for example, if the specified address is LW70(word register in HMI), the start time of current time (second, minute, hour, day, month, year) are LW70, LW71, LW72, LW73, LW74, LW75. The end time of current page (second, minute, hour, day, month, year) are LW76, LW77, LW78, LW79, LW80, LW81 Time ! If “Use scroll bar” is selected in [Trend Graph Component Attribute]-[Scale], the [Scroll] cannot be selected in [Trend Graph Component Attribute]-[Trend Graphics]. Description of Scale attributes Use Scroll Bar The trend curve uses the system scroll bar, user can set the scroll bar width, the width range is 20~120, units is pixels. Use Vertical Axis Scale The trend curve uses the system vertical axis scale. Scale color Set the color of vertical color. Display Scale Frame Display the scale frame or not. 181 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Major Scale Number Set the major scale number. Major Scale Length Set the major scale length, the unit is pixels. Minor Scale Number Set the minor scale number. Minor Scale Length Set the minor scale length, the unit is pixels. Label Font Set the label font Integer The integer number of scale (User cannot adjust it ). Decimal The decimal number of scale (User cannot adjust it ). Use Scale Label Use Horizontal Time Scale Axis Trend Curve displays the horizontal scale. Scale Color Set the vertical scale color. Display Scale Frame Display the scale frame or not. Time scale interval The time interval between two time scale point, the unit is sampling circle, for example, if the Time scale interval is 3, the time interval between two scale point is three sampling circles’ time. So the displayed scale number depends on the sampling points number and time scale interval. Length Mark Set the length of time scale, the unit is pixel. each sampling Mark a scale on each sampling point point scale Length Set the length of each sampling points, the unit is pixel. Use Scale Label Label Font Set the scale label font Time Display and set the time format, there are three formats: HH:MM:SS、 HH:MM、HH:MM:SS:MS Date Display and set the date format, there are three formats: 182 Advanced Part Component DD*MM*YY、MM*DD*YY、YY*MM*DD. Separator: /、—、. Vertical Axis Scale Channel Reference Channel The max/min of vertical axis is based on the max/min of specified channel. History Data Query Select “History Data Query” in [History Data Query] of [Trend Graph Component Attribute], then set Query Address and Query Trigger Address to make history data query function for trend graph. Description of History Data Query attributes History data query address, the word length is 8. Start Date: Specified address, word length is 2, input year and date in this address. Start Time: Specified address+2, word length is 2, input time (hour, minute and second) in this address. End Date: Specified address+4, word length is 2, input year and date in this address. End Time: Specified address+6, word length is 2, input time (hour, minute and second) in this address. Take the following picture for example, the specified address is LW200, and user wants to query the data between 9:30:40 14th, Aug, 2012 and 14:16:30 15th, Aug, 2012. Query Address So the Specified address are as follows: Start Date: LW200=20120814 Start Time: LW202=93040 End Date: LW204=20120815 End Time: LW206=141630 Query Trigger Address When the specified address status is on, the trend will trig query function. 183 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software If the Open printing option is checked, the trend curve can be printed in real-time. ! The real-time printing in Trend Curve only supports micro printer Description of printing attributes Print per point Print per page Mode Print whole Trigger by register The printing is triggered by every sampling point The printing is triggered when all the sampling points on a whole page is finished The printing is triggered after all the sampling points on all pages are finished in multiple page trend curves The printing is triggered when the specified register satisfies the setting condition Paper Width Set the paper width according to the printer Step The pixel between two small grids Vertical axis scale Set the standard channel of vertical axis scale. That is to say set the upper limit and lower limit of reference channel Time Mode vertical axis Set the display time mode of horizontal axis. Two modes are optional: HH:MM、HH:MM:SS OFFON ONOFF OFFON Trigger Style OFFON(Reset) If chose the Trigger by register in the Mode, the printing will be triggered when specified register changes from OFF to ON If chose the Trigger by register in the Mode, the printing will be triggered when specified register changes from ON to OFF If chose the Trigger by register in the Mode, the printing will be triggered when specified register changes its state If chose the Trigger by register in the Mode, the printing will be triggered when specified register changes from OFF to ON, then the register will be reset to OFF automatically If chose the Trigger by register in the Mode, the printing will be triggered ONOFF(Reset) when specified register changes from ON to OFF, then the register will be reset to ON automatically Print axis Print The horizontal axis and vertical axis of printing. The line type, line width and axis color can be set horizontal The display time interval (show time), font size and color can be set. The show time means the 184 Advanced Part Component axis(time) display interval between the previous printing time and the next printing time, the unit is sampling points Print vertical axis(scale) Print vertical axis has two forms: Percentage and Sampling value. The font size and color of vertical axis are changeable The baseline is the standard line in horizontal direction. Two baselines can be printed at most. The Print baseline base line value, baseline type, line width and baseline color can be set. The baseline value is suggested not to exceed the limit of standard channel ! This function is valid only when the Open Printing is checked Description of Print Trigger Line Attribute When value of specified register changes, print a trigger line Trigger Register Line Type/Width/Color Set the type, width and color of trigger line Set the time and scale of trigger line Print line scale/time Print state description Font Size Set the font size of trigger line time and scale font Font Color Set the font color of trigger line time and scale font Set the comments information of print trigger line Trigger Line State Set the state number and corresponding value of trigger state description, Num 1~256 are optional. For example, set the trigger line state Num to 3, the 185 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software corresponding value are 0, 1, 2. And the value 0 corresponds to description “temperature rise”, the value 1 corresponds to description “temperature unchanged” and value 2 corresponds to description “temperature descend” When the value of specified register is 2, the trigger line and corresponding description will be printed 100 Trigger line(D100: 10>>3) Temperature descend Description 0 Top: Position description of Bottom 【Extend application of Trend Curve】 View and zoom function Use the LB9110 to open or close the zoom function. When the LB9110 is ON, the zoom function will be opened. Zoom out view: In multiple pages trend curve and the page number is more than 1. When LB9110 is ON, double click on the trend curve screen to zoom out the curve. Zoom in view: When LB9110 is ON, drag the mouse to select a section curve to view the zoomed in curve. 186 Advanced Part Component Zoom in Normal Double Click Zoom out Click Drag Release Cursor function The system special register LB9111 can enable the cursor function. When LB9111 is on, user can touch and trag the cursor to the data point that user want to select. ! The priority of LB9111 is higher than LB9110. If LB9111 is on, the zoom function will be disabling. Sampling time and sampling coordinates query function. When the LB9110 is ON, customer can query the sampling time and sampling coordinates by system registers. Related system registers are as follows:: Description of related system registers Special register address LW9200~LW9205 Function Description Display the viewed sampling These registers are second, minute, hour, day, month, and point time of trend curve year. The Code Type is BIN N means the channel number, display the Y coordinates of viewed sampling point in each channel. For example the LW9210~LW9210+N Display the coordinates of viewed sampling point channel is 2, the LW9210 displays the Y coordinate value of current viewed sampling point in channel 1, and the LW9211 displays the Y coordinate value of current viewed sampling point in channel 2 Take the following picture for example 187 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software a. Number Display,LW9205 b. Number Display,LW9204 c. Number Display,LW9203 d. Number Display,LW9202 e. Number Display,LW9201 f. Number Display,LW9200 g. Number Display,LW9210 h. Number Display,LW9211 Take MT5320T communicating with SIEMENS S7-200 for example, sample the data in VW0, VW2, VW4 and draw them in a curve, at the same time the sampling points scale can be viewed. Build a new Trend Curve component, the component attribute is as followings: Basic Attribute Read Address VW 0(PLC register) Trend Graphics Type Multiple Pages PageNum 10 Channel 3 SCR0 Checked, address: LW 0(HMI local register) Channel No. 0 Y Min/Max: 0/500 Color:■(Red) No. 1 Y Min/Max: 0/500 Color:■(Yellow) No. 2 Y Min/Max: 0/500 Color:■(Green) 188 Advanced Part Component Extended Attributes Use Grid Checked, Lines/Columns: 3/3, Background color: ■(blue-gray), Grid color: □(white), Grid Line Style:- - - Save Historical Data Save to recipe data field Checked, Start address: 0 Add a Scroll Bar component to turn page of the historical curve, the setting is as followings: Basic Attributes Write address LW 0 (HMI local register) Scroll Bar Background Image Vector Graphics, CONFIRM.vg Button Image Vector Graphics, CTRL_BAR001.vg Scroll Bar Extended Attributes Max/Min Value Setting 0/100 Variable Max/Min Value Unchecked Add a Bit State Switch to zoom the curve, the setting is as follows: Read/Write Address LB 9110(special system register in HMI) Switch Type Toggle Tag Use Tag checked; 0: View; 1: Cancel Font Use Font Graph: Times New Roman, Size 12, Center, Blue. Graphics Vector Graphics checked: CONFIRM.vg Add three Number Display components to display the value of current sampling points, the setting is as follows: Read Address LW 9210/LW 9211/LW 9212(special system register in HMI) The effect is as follows: 189 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 4.6.2 XY Plot XY Plot read a series of continuous registers from specified HMI local registers or PLC/Controller registers in a period, and plots them in dual axle curve, it can reflect the relationship of two variables. (X-axis) (Y-axis) D100 D101 1st 5 30 100 80 2nd 10 40 60 3rd 15 50 40 4th 20 40 20 5th 25 30 0 0 10 20 30 Detail explanation of XY Plot attributes Single Page Type Multiple Pages Attributes Standard Only display the data change information of current page, there is no curve extension. There is XY plot extension, each channel can be saved, when the XY plot extends, the historical sampling data will not be lost, but save in the buffer area. Invalid Track 190 Invalid Advanced Part Component Hor Trend izo Vertical ntal Time Sampling OFFON trigger sampling ONOFF trigger Sampling Method sampling OFFNO trigger sampling OFFON reset When specified register changes from OFF to ON, then trigger the sampling. When specified register changes from ON to OFF , then trigger the sampling. When specified register changes its state , then trigger the sampling. When specified register changes from OFF to ON, then trigger the sampling. The trigger sampling specified register will be reset automatically after being triggered. ONOFF When specified register changes from ON to OFF, then trigger the sampling. The reset trigger sampling Cycle Sample data periodically. specified register will be reset automatically after being triggered. The time interval of the two pages or two sampling points. The unit can be s or 100ms. Sampling multiple points every time or in each period, with X and Y components. The register number is related to the channel number and sampling number. For example, there is m channels and n sampling points, that is to say, the register number is m*n*2. XY Type Plot Standard (X-axis) (Y-axis) D100 D101 30 1st 5 D102 D103 40 2nd 10 D104 D105 50 3rd 15 D106 D107 40 4th 20 D108 D109 5th 25 30 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 10 20 30 One Cycle Example, suppose the Read Address is D100, and there is 1 channel, 5 sampling points in each page; so this XY plot will take 10 registers. They are D100, D101, …, D109 which corresponding to the X11, Y11, X12, Y12, …, X15, Y15. Sampling one point each time, with X and Y components. The register number is related Track to the channel number. For example, the channel number is m, sampling points is n, so 191 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software the register number is m*2. 100 (X-axis) (Y-axis) D100 D101 1st 5 30 2nd 10 40 3rd 15 50 4th 20 40 5th 25 30 80 60 1 40 2 3 4 5 20 0 0 10 20 30 One Cycle Example, suppose the Read Address is D100, and there is 1 channel, 5 sampling points in each page; so this XY plot will take 2 registers. They are D100 and D101 which corresponding to the X1 and Y1. Sampling multiple points every time or in each period, with Y components, but no X components. The register number is related to the channel number and sampling number. For example, there is m channels and n sampling points, that is to say, the register number is m*n. (Y-axis) D100 1st 30 D101 2nd 40 D102 3rd 50 D103 4th 40 D104 5th 30 Trend 100 80 60 40 D100 20 D102 D104 D101 D103 0 One Cycle Example, suppose the Read Address is D100, and there is 1 channel, 5 sampling points in each page; so this XY plot will take 5 registers. They are D100, D101, …, D104 which corresponding to the Y11, Y12, …Y15. Sampling Points The sampling points displayed on each page PageNum This option is valid only when the Multiple Pages is chosen. Channel Displayed curve number. Trigger This option is valid when use the trigger sampling in the Sample Methods. Take the following picture for Register example, set the LB100 (HMI local register) as the trigger register, the sampling will be triggered when the Setting state in LB100 satisfies the setting in Sampling Method. 192 Advanced Part Component Pause/Cle Set the register that controls the Pause and Clear function, the default word length is 2, the [set register] ar controls the Pause, and [set register+1] controls the Clear. The Pause function only stops the change of curve, but not stops the sampling. The Clear function clears the curve displayed on the XY plot. Take the following picture for example, set LB0 (HMI local register) as the register to control Pause and Clear. When LB0 is ON, the screen on XY Plot will stop refreshing; when LB0 is OFF, the screen on XY Plot will continue to display the change of curve. When LB1 is ON, the curve on XY Plot will be cleared. Set the register to turn page of multiple pages of XY Plot, the default word length is 3. This option is valid when the Multiple Pages is chosen. Use this function to scroll the multiple pages XY plot, and can be used with the Scroll Bar. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.16.3 Scroll Bar] Take the following picture for example, the specified register is LW0 (HMI local register), so the LW0 is the current index value of scroll bar, LW1 is start index value of scroll bar, LW2 is the maximum index value of SCR0 scroll bar. Use this function to save the start time and end time of current page. This function is valid when the “Save Time Time” is checked. The default word length is 12. Take the following picture for example, the specified address that is used to save time is LW70(HMI local register), the start time (Second, Minute, Hour, Day, 193 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Month and Year) of current page are LW70, LW71, LW72, LW73, LW74 and LW75. the end time (Second, Minute, Hour, Day, Month and Year) of current page are LW76, LW77, LW78, LW79, LW80 and LW81. 4.6.3 Oscillograph The function of Oscillograph component is similar to the Trend Curve. They read continuous registers form specified HMI local registers or PLC/Controller registers periodically, and plots them in single axis curve. Detail explanation of Oscillograph attributes Single Type Property page Only display the data change information of current page, there is no curve extension. Multiple There is XY plot extension, each channel can be saved, when the XY plot extends, the Pages historical sampling data will not be lost, but save in the buffer area. The direction that Oscillograph curve starts. Start from Start from Left Right 194 Advanced Part Component O Y Start from Start from Top bottom X Cycle The time interval of every 2 sampling points. The unit can be s or 100ms. When use the rate sampling, the Oscillograph reads [Sampling Rate number] groups data each time. For example, the Read Address is LW10 (HMI local register), Sampling Rate is 2, Channel is 3, so the read Sampling address is LW10~LW15. The address distribution is as follows: three channels’ data of the first group are Rate saved in LW10, LW11 and LW12; three channels’ data of the second group are saved in LW13, LW14, and LW15. If the sampling cycle is 1s, the Oscillograph reads these two groups data every second. The rate sampling makes the curve more smooth and accurate Sampling points Sampling points number displayed on each page PageNum This option is valid when the Multiple Pages is checked Channel Displayed curve number Set the register that controls the Pause and Clear function, the default word length is 2, the [set register] controls the Pause, and [set register+1] controls the Clear. The Pause function only stops the change of curve, but not stops the sampling. The Clear function clears the curve displayed on the Oscillograph. Take the following picture for example, set LB0 (HMI local register) as the register to control Pause and Clear. When LB0 is ON, the screen on Oscillograph will stop refreshing; when LB0 is OFF, the screen on Oscillograph will continue to display the change of curve. When LB1 is ON, the curve on Oscillograph will Pause/Clear be cleared. Set the register to turn page of multiple pages of Oscillograph, the default word length is 3. This option is valid when the Multiple Pages is chosen. Use this function to scroll the multiple pages Oscillograph, and SCR0 can be used with the Scroll Bar. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.16.3 Scroll Bar] Take the following picture for example, the specified register is LW0 (HMI local register), so the LW0 is the current index value of scroll bar, LW1 is start index value of scroll bar, LW2 is the maximum index 195 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software value of scroll bar. Use this function to save the start time and end time of current page. This function is valid when the “Save Time” is checked. The default word length is 12. Take the following picture for example, the specified address that is used to save time is LW70(HMI local register), the start time (Second, Minute, Hour, Day, Month and Year) of current page are LW70, LW71, LW72, LW73, LW74 and LW75. the end time (Second, Minute, Hour, Day, Month and Year) of current page are LW76, LW77, LW78, LW79, LW80 and LW81. Time 4.6.4 Meter Meter component displays the data of HMI or PLC/Controller in instrument chart. Detail explanation of Meter attributes Dial Style Pie, Circularity(point up), Circularity(point 196 down) Advanced Part Component Hand color Chose the color of the meter hand Length Set the length of the meter hand, the maximum is the radius of the actual circle Width Set the width of meter hand Hand Style Chose the style of meter hand Scale color Chose the color of meter scale Set to display the scale frame or not Show Scale Frame The Number of Main Scale The Length of Main Scale The Number of Minor Scale The Length of Minor Scale Set the number of main scale, 0~50 are optional Set the length of main scale, the maximum cannot exceed the radius length of actual circle Set the number of minor scale, 0~10 are optional Set the length of main scale, the maximum cannot exceed the radius length of actual circle Use Scale Tag Set to display the scale tag or not Tag Font Click the Tag Font to set the font of tag Integer The integer number of scale tag (Can not be set, it will change according to the maximum of meter ) Decimal Set the decimal number of the scale tag, 0~8 are optional Use Dial Axis Checked to set the axis size and color Axis Width Set the size of meter axis, the maximum cannot exceed the radius length of actual circle Axis Color Set the color of meter axis Explanations of Meter Extended Attributes Maximum/Minimum Set the display range of meter. 197 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Variable Min/Max Set the registers where variable Minimum and Maximum are stored. Set the color of the Upper/Lower Limit. Upper Limit/Lower Limit Set the thickness of the circle color block. The maximum can not exceed the radius of meter Fan Thickness circle, and should be equal to or smaller than the Fan External Radius. Set the radius of circle color block. The maximum can not exceed the radius of meter circle, and should be equal to or larger than the Fan External Radius. Fan External Radius Lower Limit/Upper Limit Variable Lower/Upper Limit Set the alarm range of the meter component. Set the register where the alarm range be stored. 4.6.5 Bar Picture Bar Picture displays the data in HMI local register or PLC/Controller register in percentage of bar picture , that is to say the bar picture displays the percentage of actual value compared to the set maximum/minimum value. ! Bar Picture does not support the float data format 198 Advanced Part Component Detail Explanation of Bar Picture Attributes Display the percentage of actual value compared to the set maximum/minimum value in bar picture. Standard Bar Type Display the offset value of actual value compared to the original data in bar picture. Offset Bar Shape Art direction Up Bottom Left Right Rectangle Clockwise Counter clockwise Circle If the value in specified register is in the permissible range, the bar picture displays specified color in filling area. Target Value 199 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Diameter of Fan Set the diameter of fan when the Bar Shape is Circle, the unit is pixel. Start Angle Set the start angle of fan when the Bar Shape is Circle. End Angle Set the end angle of fan when the Bar Shape is Circle. Color Set the color for Normal state, Upper/Lower Limit, Frame and Background. When the value in specified register exceeds the Alarm Upper, the filling area in bar picture flashes. Over Upper Limit Flashing When the value in specified register exceeds the Alarm Lower, the filling area in bar picture flashes. Over Lower Limit Flashing Set the upper/lower limit of bar picture. Maximum/ Minimum The percentage of filling area of Bar Picture can be calculated by the following formula: The percentage of filling area of Bar Picture= (Value in specified register-[Minimum])/([Maximum]-[Minimum])*100% Variable Min/Max The Maximum and Minimum are read from specified registers. Set the alarm range, when the value in specified registered is larger than Alarm Upper or smaller than Alarm Lower, the filling area of bar picture displays the specified Alarm Color. Alarm Upper/Lower Variable Alarm The Variable Alarm Upper/Lower are read from specified registers. 200 Advanced Part Component Upper/Lower Detail Explanation of Scale Attributes Scale Color Set the scale color Set to display scale frame or not. Show Scale Frame Use Scale The Number of Main Scale Set the number of main scale The Length of Main Scale Set the length of main scale, unit is pixel. The Number of Minor Set the number of minor scale The Length of Minor Scale Scale Set the length of minor scale, unit is pixel. Left Scale Right Up Bottom Display Position Use Scale Tag Tag Font Set the font of tag Integer Integer of scale cannot be set by user. Decimal Decimal of scale, can be set by user. 4.7 Alarm Component Alarm component is used to display user alarm or user event information. Inco HMIware provides components of event display, historical event display, event bar, alarm display and alarm bar for displaying alarm information. ! 1.The event information displaying in components of event display, historical event display, event bar must be preset in【Event Information Logon】in project database. 2. The alarm information displaying in components of alarm display, alarm bar must be preset in【Alarm Information Logon】in project database. 3. Alarm information can’t be saved, and alarm display component can only display the unrecovered alarm information. 201 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 4. Event information can be saved, and event display component can display both unrecovered event information and recovered event information. Related attribute of event information setting Event information storage Set the storage of event information in【HMI Attribute】—【Historical Events Storage】. (1)Save to Recipe Data Field It is used to save event information to recipe memory of HMI (RW register). 1.”Save Count” must be greater than 0.If “Save Count” is 0, then system won’t save event to recipe data field. 2.”Start Addr.” can be user-defined. The length of one event information is 16 words. System will set “End Addr.” Automatically according to “Save Count”. 3. Event information which saves to recipe data field cannot display in historical event display component. (2)Save to External Device It is used to save event information to external device. When “Storage Type” is set as “Daily File”, then the event information will save to path “event/Subdirectory name/yyyymmdd.csv”.When “Storage Type” is set as “Single File”, then the event information will save to path “event/Subdirectory name/ Subdirectory name.csv”.(Therein,yyyymmdd is event execution date such as 20110101) 202 Advanced Part Component 1. Only the HMI with USB HOST or SD Card support saving to external device. 2. Only the event information which is saved to external device can query by date or order sequence and display in “Historical Event Display” component. 3.Event information can save to recipe data field and external device at the same time. ☞For details about historical event storage, refer to [Advanced Part 6.1.7 Historical Events Storage] 5 Event information clear There are four ways to clear event information which displaying in event display component. (1)Set LW10015 as 0 and restart HMI. This way is used to clear all the event information which are saved in recipe data field. (2)Tick【Clear History Event Data】in【EVDownload】when downloading project. The event information will be clear after downloading. This way is used to clear all the event information which are saved in recipe data field and external device. (3)Use【Clear Event】function in function key. This way is used to clear all the event information which are saved in recipe data field. (4)Use【Clear History Event】function in【KHManager】. This way is used to clear all the event information which are saved in recipe data field and external device. System Scroll Bar Width setting When the information in Event Display component cannot totally display horizontally, then system will provide scroll bar automatically. The width of system scroll bar can be set in 【HMI Attribute】—【HMI Extended Attributes】,the range is 20~120(Pixel). 4.7.1 Event Display Event display is used to display event information logon in “Event Information Logon”. The displaying events will be sorted by triggered time. 203 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ! 【Read Address】in Event Display component is used to scroll the event information(Up or down). Related setting descriptions for event information Display Type Range This event display component can only display the event within this type range. The event type is set in “Event Information Logon”. Row Space The space between two rows or two Columns. Acknowledge Type Set the acknowledge method for triggered event. Click or Double Click. Color Acknowledge Color The color of event information after affirming. Back to Normal Color The color of event information after event back to normal. Select Area Color The color of dotted line for indicating user information. The format of event information. All the format information display in front of event information. Format Sequence No. Sequence No. of events, it starts from 0. Event Trig Time The time when event triggered Acknowledge Time The time when event acknowledged Return to Normal Time The time when event returns to normal Extended Time Format(D/H:M) Time format is Day/Hour: Minute 204 Advanced Part Component Short Time Format(H:M) Time format is Hour: Minute Standard Time Format(H:M:S) Time format is Hour:Minute:Second Precise Time Format(H:M:S:MS) Time format is Hour:Minute:Second:Millisecond Extended Date Format(Y/M/D) Date format is Year/Month/Day Event Trig Date(M/D) Date format is Month/Day Tick it indicate that the events display by ascending order of sequence Time Ascending Order Display No. and time. Or the event display by descending order of sequence No. and time. Only show the Event which doesn’t Tick it to only show the event which doesn’t recover. Or it will display recover all the events. 【Example】Take the serial communication between MT5320T and SIEMENS S7-200 for example, when the temperature is higher than 80℃ or the pressure is higher than 120Mpa,then the HMI will display alarm and output buzzer alarm, then it can display and query historical event record. Text NO. Trig. Time Acknowledge Return to Time Normal Time Event Multiple State Setting Event Display Temperature/Pressure VW0 VW2 #### #### Create new project [Event], and then add two windows Frame10 and Frame11 which are used for temperature alarm and pressure alarm. Set the attributes as follows: Name Alarm window_1/Alarm window_2 X/Y 80/80 Width/Height 200/100 Use Background Color Tick, Fill Color:■(Yellow) Frame Width:2 Pop Window Type Monopoly: tick Frame Color:■(Gray-50) Add two texts and function keys in Frame10 and Frame11, and then draw a alarm symbol. Set attributes of text as follows: Content Abnormal Temp./Abnormal Pressure Font Type Vector Font Font Attribute Font:Arial Black Size:12 Color:■(Red) 205 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Set attributes of function key as follows: Switch Window Close window Graphics No use Set the size of function key to the same as the size of window. Add event information in【Project Database】—【Event Information Logon】.Set event information as follows: Temperature Alarm: Data Type Word Address VW 0(PLC register) Condition >80 Pop-up window Tick,[10:Alarm window_1] Use buzzer Tick,1 second Text Abnormal Temp.! Pressure Alarm: Data Type Word Address VW 2(PLC register) Condition >120 Pop-up window Tick,[10:Alarm window_2] Use buzzer Tick,1 second Text Abnormal Pressure! Add “Event Display” component in Frame0,set its attribute as follows:: Read Address LW 0(HMI local register) Format Tick Sequence No., Event Trig. Time, Acknowledge Time, Return to Normal Time, Standard Time Format (H:M:S). Add two “Multiple State Setting” components in Frame0, and set their attributes as follows: Write Address LW 0(HMI local register) Setting Mode Sub/Add Subtrahend/Addend 1/1 Lower/Upper 0/100 Graphics Use vector graphics,Button6-27.vg/Button6-28.vg Historical events storage setting 206 Advanced Part Component Open【HMI Attribute】—【Historical Events Storage】,tick【Save to Recipe Data Field】, set【Save Count】to 100,set 【Start Addr.】as 0,means events will be saved in the registers start from RW0. When the value of VW0 is larger than 80℃: NO.2 Return to Normal Trig. Acknowledge Event 15:22:54Time 15:25:13 Abno Time Time 1 14:01:00 14:44:20 14:44:23 Abno 0 10:50:01 11:40:10 10:54:20 Abno Beep... Temperature/Pressure VW0 90 VW2 100 Return to Trig. Acknowledge Normal NO. Event Time Time Time 15:25:13 2 15:22:54 Abnornal T 1 14:01:00 14:44:20 14:44:23 Abnornal T 0 10:50:01 11:40:10 10:54:20 Abnornal T Temperature/Pressure VW0 90 VW2 100 4.7.2 Historical Event Display Historical event display is used to query the triggered historical event information, which are added in “Event Information Logon”, and display them as form format. ! 1.【Read Address】in “Historical Event Display” component is used to query historical event. Word length is 2 by default. 2.It must tick the option “Save to External Device” in【HMI Attribute】—【Historical Event Storage】and set the subdirectory when using “Historical Event Display” component. Descriptions for Table Display Attribute Time Date Table Display Background Setting It is used to set whether display time for trigger, acknowledge and recovery events and time format. Therein, YY means year, MM means month, DD means day. It is used to set whether display date for trigger, acknowledge and recovery events and time format. Therein, YY means year, MM means month, DD means day. Separator Choose the separator for date, there are three format options. Such as 11/06/24. Sequence No. Set whether display the sequence no. of event information Ascending Selecting it indicates the event information is sequenced by ascending order Order according to time. Or it is sequenced by descending order. Set the border width and the color of background, title bar and border of Historical Event Display 207 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software component. If selecting it, then when the value of the specific register is 0,it means to display the historical event information of today or the latest day. When the value is 1,it means to display the historical event information of the previous day. And by Historical Query by File parity of reasoning. Order For example, there are two files in extended memory, 20110621.csv and 20110624.csv.When the value of the specific register is 0, then it will display the Event historical event in Jun.24th, 2011.When the value is 1, then it will display the Query events in Jun.21st, 2011. If selecting it, then when input the date in the specific register, it will display the historical event in this day. The format of inputting date is yyyymmdd (yyyy Query by Date means year, mm means month, dd means day). For example, when input 20110624 in the specific register, then it will display the historical events in Jun.24th, 2011. Set the color, line style, line width of separator line, and row space and column space. The unit of Separator Setting row space and column space is pixel. Tick “Horizontal Line” to display horizontal separator line. Tick “Vertical Line” to display vertical separator line. Trigger Status display Confirm Resume Title Bar Setting Set the status information which is used to display in status column of the table when event is triggered. It is set as 0 by default. Set the status information which is used to display in status column of the table when event is confirmed. It is set as 1 by default. Set the status information used to display in status column of the table when event is resumed. It is set as 2 by default. Set the name and font attribute of title bar. 4.7.3 Event Bar Event Bar is used to display and roll the triggered information from right to left which is already set in “Event Information Logon”. 208 Advanced Part Component Attribute Descriptions of Event Information Display Type Set type range of event information, only this type range will display in the Event Bar. The type of event Range information is set in “Event Information Logon”. Moving Step Moving Rate Gap Space Set the moving step of event information. The unit is pixel. The bigger the value, the faster the moving speed. Set the interval time of moving the event information. The unit is 100ms.The bigger the value, the slower the moving speed. Set the space between two events ranging from1-7 pixel. Set the display format of event information. All the format information will display in front of event information. Format Event Trig. Time The time when event is triggered. Extended Time Format (D/H:M) Time format is Day/Hour: Minute. Short Time Format (H:M) Time format is Hour: Minute. Standard Time Format (H:M:S) Time format is Hour: Minute: Second. Precise Time Format (H:M:S:MS) Time format is Hour: Minute: Second: Millisecond. Extended Date Format (Y/M/D) Date format is Year/Month/Day. Event Trig. Date(M/D) Date format is Month/Day. Selecting it to display the event information by time ascending Time Ascending Order Display order. For example,2011/06/23 15:22:54 Event 1 209 2011/06/23 16:20:40 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Event 2 Cancel it to display the event information by time descending order. For example, 2011/06/23 16:20:40 Event 2 2011/06/23 15:22:54 Event 1 4.7.4 Alarm Display Alarm Display component is used to display the triggered alarm information which is already set in “Alarm Information Logon”. The alarm information will not remove until the alarm condition is cleared. Logon Display ! Abnormal Temp.! Abnormal Temp.! Alarm Remove Recovery 【Read Address】in Alarm Display component is used to roll the alarm information(Upward or downward) Attribute Descriptions for Alarm Display Row Space Set the interval between two alarm information. The unit is pixel. Column Space Set the interval between two characters or words in the alarm information. The unit is pixel. Display Type Range Set the type range of alarm information, only this type range will display in the alarm display. The type of alarm information is set in “Alarm Information Logon”. 4.7.5 Alarm Bar Alarm Bar is used to display and roll the triggered alarm information which is already set in “Alarm Information Logon”. 210 Advanced Part Component Attribute Descriptions of Alarm Bar Set the moving step of alarm information. The unit is pixel. The bigger the value, the faster the Moving Step moving speed. Set the interval time of moving the alarm information. The unit is 100ms.The bigger the value, the Moving Rate Display slower the moving speed. Type Range Set type range of alarm information, only this type range will display in the Alarm Bar. The type of alarm information is set in “Alarm Information Logon”. 4.8 Window Component Kinco HMIware provides two window components, Direct Window and Indirect Window, which are used for popup window. The main differences between the two window components and 【Popup Window】in Function Key are as follows: Component Read Address Control Method Window No. Direct Window Bit According to the state of Read Address Specify in the attribute Indirect Window Word According to the value of Read Address According to the value of Read Address Function Key None Touch Specify in the attribute 4.8.1 Direct Window Direct Window is used to define a display area and display the specific window in this area according to the state of Read Address. 211 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 1. Direct Window’s open or close depends on the state of Read Address, it means that it will popup window when the state of Read Address is ON, and close window when the state is OFF. 2. Generally the size of Direct Window should be set the same as the size of specific popup window. 3. There is no limit for the quantity of Direct Window. Attribute Descriptions of Direct Window Frame ID Specify the window which will display in the display area of Direct Window Select it to set the coordinates of Direct Window as variable. [Address] is used for X coordinate,[Address+1] is used for Y coordinate. Variable Display Coordinates Cancel it to set the coordinates of Direct Window as constant. ! Direct Window can be closed by the “Close Window” function in Function Key 212 Advanced Part Component 4.8.2 Indirect Window Indirect Window is used to define a display area and display the window whose number is the same as the value of Read Address. 1. It will close window when the value of Read Address is 0.And it will popup window 0 when the value is-1. 2. Generally the size of Indirect Window should be set the same as the size of specific popup window. 3. There is no limit for the quantity of Indirect Window. Explanation of Indirect Window attributes Select it to set the coordinates of Indirect Window as variable. [Address] is used for X coordinate, [Address+1] is used for Y coordinate. Variable Display Coordinates Cancel it to set the coordinates of Indirect Window as constant. 213 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 4.9 Graphic Components Kinco HMIware provides Vector Graph and Bitmap which can be used to display vg or bg pictures in system graph library and graph library in project files window. ☞For details about how to build and edit Bitmap and Vector Graph, refer to [Advanced Part 5.3 Graphic Library] 4.9.1 Vector Graph Vector Graph component is used to display vg pictures in system graph library and Project Files Window graph library. There is no register control in Vector Graph component, and graph doesn’t support multiple states switching display. If you want to control vector graph by register, you can chose corresponding vector graphics-Graphics option of other components, like Bit State Switch, Multiple State Setting etc. ☞For details about vector graphics in graphics option, refer to [Advanced Part 4.1.6 Graphics Setting] 4.9.2 Bitmap Bitmap component is used to display bg pictures in system graph library and Project Files Window graph library. There is no register control in Bitmap component, and graph doesn’t support multiple states switching display. If you want to control bitmap by register, you can chose corresponding bitmap in Graphics option of other components, like Bit State Switch, Multiple State Setting etc. ☞For details about bitmap in graphics option, refer to [Advanced Part 4.1.6 Graphics Setting] 4.9.3 Free Plotting Free Plotting component plots graph according the states of specified bit or word register. This component doesn’t open to ordinary customer. 214 Advanced Part Component 4.9.4 Dynamic Graph Dynamic Graph can change the position and size of rectangle, ellipse or line according to value in the specified HMI/ PLC register. Attribute explanation of Dynamic Graph Graphic Type Chose the graph type, rectangle, ellipse and line are optional Line Set the frame line color, line width and line type Filling Set the filling color and picture of rectangle and ellipse Attribute explanation of Dynamic Graph Position The Upper-left Corner of Variable Unchecked Checked The Width/Height of Variable Unchecked Checked The dynamic graph position(X, Y) are constant. The dynamic graph position(X, Y) read from specified register. X position=specified register, Y position = specified register +1. The dynamic graph width and height are constant. The dynamic graph width and height read from specified register. Width=specified register, Height= specified register +1. The component takes the upper-left as base point, X direction moving means increasing towards right. Y direction moving means increasing towards down. The moving unit is pixel 4.9.5 GIF GIF component is used to display the gif picture, and the switching frequency of gif picture can be controlled. 215 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Description of GIF Attributes Use Start Address If checked, when the specified register is ON, GIF displays animation, when register is OFF, GIF displays static picture. Use GIF Default Freq Use the default frequency of gif picture. Use defined Freq User set frequency for the gif picture. Switching Different frequencies mean different switching speed of gif picture; the larger Frequency value means the slower switching speed. Unit: 100ms. Use Variable The switching frequency is read from specified register. Unit: 100ms. Frequency Note: If the specified register is PLC register, but the HMI does not communication successfully with the PLC all the time, the gif use the default frequency. If the communication is cut off, the gif uses the latest historical value in the specified PLC register. Load GIF Load the gif picture from PC, and preview the loaded gif picture in Preview area. GIF Preview Preview the loaded gif picture in this area. Use Original Size If checked, the component size is the same as the gif original size. GIF component only support the gif format picture. 4.10 Video Input Component 4.10.1 Video Video component is used to monitor the industrial site picture in real time, supporting the CVBS signal. ! 1. Only the HMI with BNC connector can support the Video component 2. Supports PAL and NTSC format. And the video mode are optional in HMI Attribute>>HMI Extended Attributes 3. If the video is displayed in pup up window, the pop up window should be set Video Page in Window Attribute>> Special Attribute 216 Advanced Part Component The default Word Length of Read Address is 4, each word corresponds to different function attribute as follows: Explanation of Video component Read Address Read Address Function Description Switch channels, if the value is 0 , the component displays the video Specified Address Switch channel image from channel 0 ; if the value is 1 , the component displays the video image from channel 1; Specified Address+1 Adjust brightness Adjustable range: 0~255 Specified Address +2 Adjust contrast Adjustable range: 0~255 Specified Address +3 Adjust chromaticity Adjustable range: 0~255 [Example] Take MT5620T for example, build a new project. Multiple State Setting component, it is used to switch the channels (There are only 2 CVBS port on MT5620T), its attributes are as followings: Write Address LW 0(HMI local register) LW 0(HMI local register) Setting Mode Jog++; Addend:1; Upper:1 Jog--; Subtrahend:1; Lower:0 Tag Use Tag; 0: Channel+; 1:Channel+ Use Tag; 0: Channel-; 1:Channel- 217 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Graphics Use Vector Graphics Multiple State Setting component, it is used to adjust brightness, it attributes are as followings: Write Address LW 1(HMI local register) LW 1(HMI local register) Setting Mode Jog++; Addend:1; Upper:255 Jog--; Subtrahend:1; Lower:0 Tag Use Tag; 0: Brightness+; 1: Brightness + Use Tag; 0: Brightness-; 1: Brightness Graphics Use Vector Graphics Multiple State Setting component, it is used to adjust contrast, it attributes are as followings: Write Address LW 2(HMI local register) LW 2(HMI local register) Setting Mode Jog++; Addend:1; Upper:255 Jog--; Subtrahend:1; Lower:0 Tag Use Tag; 0: contrast+; 1: contrast + Use Tag; 0: contrast-; 1: contrast - Graphics Use Vector Graphics: Multiple State Setting component, it is used to adjust chromaticity, it attributes are as followings: Write Address LW 3(HMI local register) LW 3(HMI local register) Setting Mode Jog++; Addend:1; Upper:255 Jog--; Subtrahend:1; Lower:0 Tag Use Tag; 0: chromaticity +; 1: chromaticity + Use Tag; 0: chromaticity-; 1: chromaticity Graphics Use Vector Graph: The Video component, its attributes is as followings: Read Address LW 0(HMI local register) 4.10.2 Camera Camera component is also used to monitor the industrial image as the Video component, and the Camera component supports the USB camera video input. 218 Advanced Part Component Camera component uses the Read Address to open, close, switch the camera. For example, suppose the Read Address is LW0 (HMI local register), when LW0 is 0, the camera is close; when LW0 is 1, the camera on USB HOST1 is open; when LW0 is 2 , the camera on the USB HOST2 is open. ! 1. The Camera component is only suitable for the HMI with USB HOST port. 2. If there are cameras on both USB HOST1 and USB HOST2, the two cameras can not be open at the same time. That is to say when one camera is open, the other is closed automatically. 4.11 Multiple State Neon Lamp The Multiple States Neon Lamp component displays text content circularly in neon. Knico HMIware provides Bit State Neon Lamp and Multiple State Neon Lamp, their differences are as followings: Component Control Address Code Type State Number Bit State Neon Lamp Bit BIN 1~2 Multiple State Neon Lamp Word BIN、BCD or LSB 1~256 4.11.1 Bit State Neon Lamp The Bit States Neon Lamp component displays tag content circularly in neon, supports tag content in state 0 and state 1. Change the states of Read Address to switching display the tag content in corresponding states. 219 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Detail Description of Bit States Neon Lamp Moving Style From left to right The text moves from left frame to right frame circularly. From right to left The text moves from right frame to left frame circularly. From top to bottom The text moves from top frame to bottom frame circularly. Form bottom to top The text moves from bottom frame to top frame circularly. Step Length The distance of each movement, the unit is pixel point. Speed The time interval between previous moving text and next moving text, the unit is ms. 4.11.2 Bit State Neon Lamp The Bit State Neon Lamp component displays tag content circularly in neon, supports 256 states tag content at most. Change the value of Read Address to switching display the tag contents corresponding to the value. Detail Description of Multiple State Neon Lamp From left to right The text moves from left frame to right frame circularly. Moving From right to left The text moves from right frame to left frame circularly. Style From top to bottom The text moves from top frame to bottom frame circularly. Form bottom to top The text moves from bottom frame to top frame circularly. Step Length The distance of each movement, the unit is pixel point. Speed The time interval between previous moving text and next moving text, the unit is ms. State Num Set the state number of Multiple State Neon lamp, 256 states at most. 220 Advanced Part Component Data Set the mapping value of each state. When the value in Read Address equals to the corresponding value, the Mapping component displays the corresponding tag content of this value. 4.12 Animation Components In Kinco HMIware, the Animation and Moving Components are used to realize animation effect and make the HMI picture more vivid. 4.12.1 Animation Animation component can preset the trace of moving component, and change the component state and preset trace position according to value of the HMI register or PLC register. Steps to preset the Animation trace: Drag the Animation component to the edit area, there will be a “+”icon, press the left mouse button at appropriate position, so a moving position is preset. Press the right mouse button to end the presetting after all the all the positions are set. The default word length of Animation component is 2, each word corresponding to the different control function , see the details follows: Read Address description of Animation Component Read Address Control Function Description 221 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Specified Address Component State When the value in control address equals to the state number of component, the Animation Component display corresponding tag or picture. Specified Number of preset When the value in control address equals to the number , the Animation Component Address +1 trace moves to corresponding position. Attribution Description of Animation Component. No. Moving Node List and Set the coordinate position of the moving node on HMI. coordinates The number 0 means the first moving node, the number 1 means the second moving node. Add Node Add a moving node at the end of preset trace Insert Node Insert a moving node after the selected moving node Delete Node Delete the selected moving node Shift Up Exchange the position of the selected node and the previous node Shift Down Exchange the position of the selected node and the next node Size(Width, Height) Set the display size of Animation component State Num: Set the state number of Animation component. 4.12.2 Moving Component The Moving Component can change the display state and position according to the value of HMI register or PLC register. 222 Advanced Part Component The default word length of Moving Component is 3, each word corresponding to the different control function, see the details follows: Read Address Description of Moving Component Type Specified Address Specified Address +1 Specified Address +2 X Axis Only Y Axis Only X&Y Axis Component State Component State Component State 256 states at most 256 states at most 256 states at most X axis displacement (pixel Y axis displacement (pixel point) point) Reserved Reserved X axis displacement (pixel point) Y axis displacement (pixel point) Moving Type Description The component moves along the X axis horizontally Type X axis only The component moves along the Y axis vertically Y axis only The component moves along the X and Y axis at the same time. X & Y axis The component moves along the X axis horizontally, but the relative moving position can be set by the input value and proportional value. X Scaling 223 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software The component moves along the Y axis vertically, but the relative moving position can be set by the input value and proportional value. 0 When the value in register that controls Y movement is 1000 Y Scaling (Proportional) Min Proportional Max 50 Maximum 1000 Y It is similar with the X Scaling, but with the reverse direction. When the value in register that controls X movement is 1000 X Reverse Scaling X 1000 Maximum 50 0 Proportional Min Proportional Max It is similar with the Y Scaling, but with the reverse direction. Y 1000 Maximum Y Reverse Scaling 50 When the value in register that controls Y movement is 1000 0 Proportional Maximum (Proportional) Minimun The component moves along the X and Y axis at the same time, the relative moving position can be set by the input value and proportional value. X Scaling, Y Scaling X Scaling, Y Reverse The component moves along the X and Y axis at the same time, and the 224 Advanced Part Component Scaling relative moving position can be set by the input value and proportional value, but in reverse direction in Y axis. Y 500 Maximu m Proportional Maximum 50 (Proportional) Minimum 0 When the value in register that controls X movement is 1000 , controls Y movement is 500 X 0 50 Proportional Minimum 1000 Proportional Maximum Maximum The component moves along the X and Y axis at the same time, and the relative moving position can be set by the input value and proportional value, but in reverse direction in X axis. X Reverse Scaling, Y Scaling The component moves along the X and Y axis with reverse direction, and the relative moving position can be set by the input value and proportional value Maximum Proportional Maximum 1000 X Reverse Scaling, Y Reverse Scaling X When the value in register that controls X movement is 1000 , controls Y movement is 500 50 Proportional Minimum 0 0 Proportiona Minimum 50 Proportional Maximum 500 Y Status Number Set the status number that can be switching display. 225 Maximum Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Variable According to different Type, the Maximum/Minimum of X, Maximum/Minimum of Y, Proportional Min/Max Upper/Lower Limit of X and Proportional Upper/Lower Limit of Y are read from specified registers. ※1.X Scaling or Y Scaling Suppose the read data is A, and the actual display position is B. You can get the B according to the following formula: B=Current Position + (A-Minimum)*Proportional Value, and Proportional Value=(Proportional Upper Limit – Proportional Lower Limit )/(Maximum-Minimum) 2. X Reverse Scaling or Y Scaling Suppose the read data is A, and the actual display position is B. You can get the B according to the following formula: B=Current Position + (Maximum-A)*Proportional Value, and Proportional Value= (Proportional Upper Limit – Proportional Lower Limit )/(Maximum-Minimum) 4.12.3 Pipeline Pipeline component is used to build pipeline effect in the HMI program. Basic Attributes of Pipeline Basic Attributes Default Effect Flow Radius Set the radius of pipeline. Thickness Set the thickness of pipeline border. Body color Set the color of pipeline(the first color) Border color Set the color of pipe border. Body Color Changeable If checked, the pipeline color can be changed by specified register. Body color 2 Set the second color of pipeline Body color 3 Set the third color of pipeline Default color View the display effect of pipeline Flicker If checked, use specified register to switch on/off the flicker effect. Use Flow Effect If checked, use specified register to control the flow effect. Symbol Select the flow symbol Copy Symbol to All Pipe Copy the current flow symbol to all the pipes Symbol Color Set the color of flow symbol. Copy Color to All Pipe Copy the current flow symbol color to all the pipes Display Length Set the length percentage of flow symbol in the pipe, 1~100 are optional. Copy Length to All Pipe Copy the length percentage to all the pipes User Flowinfo to All Pipe Copy the flow effect to all pipes. 226 Advanced Part Component Not use Flowinfo to All Pipe Control Address All the pipes do not use flow effect. If the bit1 of specified register is ON, Pipeline uses the second color; if the bit2 is ON, Pipeline uses the third color; Bit3 is on, Pipeline starts to flicker(when the Flicker is checked), that is to say the pipeline switching displays the first color , second color(bit1 is ON) or third color(bit 2 is ON). If the bit3 is ON, the pipeline display the flow effect(the Use Flow Effect is checked). Note: if the bit1 and bit2 are ON or OFF at the same time, pipeline displays the first color, the flicker is invalid. For example, the Control Address is LW0 (HMI local address), word length is 1. When the LW0 =1 or LW.B0.0 is ON, the Pipeline display the second color; When the LW0 =2 or LW.B0.1 is ON, the Pipeline display the third color; When the LW0 =5 or LW.B0.0 and LWB0.2 are ON at the same time, the Pipeline switching display the first color and the second color. When the LW0 =8 or LW.B0.3 is ON, the Pipeline display the flow effect. Description of Pipe Info Pipe List Number Number 0 is the first pipeline; Number 1 is the second pipeline and so on. Coordinates The start coordinates of the pipeline component. Type Display the current pipe type, there are HLNE (Horizontal), Bend Node (Bend), VLINE (Vertical). Pipe Setting Follow Effect Select the corresponding pipe number, and set its parameters. Type Set the type of current pipe. Coordinates Set coordinates of current pipe. Select the corresponding pipe number, and set its flow effect. Symbol Set the flow symbol of current pipeline. Color Set the color of flow symbol Display Length Set the display percentage of current pipeline. 4.13 Grid Components 4.13.1 Grid The Grid can be selected in row, column or cell. User can set the row number , column number, Select Color, Background Color, Border Color, and the Grid writes the column number and row number to the specified HMI or PLC register. 227 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Grid component takes different register number according to the different Type, see the detail as follows: Type Row register Column register Register number Select in row Specified address — 1 Select in col — Specified address 1 Select in cell Specified address Specified address +1 2 Description of Grid Attributes Set the select type. Type Row/Column Set the row number and column number. Color Set the Select Color, Background Color and Border Color. 4.13.2 Historical Data Display Historical Data Display component read data from specified HMI or PLC continuous registers periodically, and display them in grid. ! 1. The Read Address of Historical Data Display component is register address of the first channel. 2. The Word Length of Historical Data Display depends on the channel number, if the channel number is m (0<m<17), the Word Length is m. 3. When use the Historical Data Display component, one of the Save to Recipe Data Field and Save to 228 Advanced Part Component External Device option, or both must be checked. Detail Description of Display Properties ※If the information in Historical Data Display component cannot be displayed entirely, the scroll bar will be built automatically to make user to view the whole information. And the width of system scroll bar can be set in HMI Attributes >> HMI Extended Attributes, ranges from 20~120 pixel. Channel The continuous register number, 16 channels at most. Sequence No. Display the sequence number or not. Checked means the sampling data information is arranged in ascending order, that is to say the latest Ascending Order sampling data is displayed at bottom; Unchecked means the sampling data information is arranged in descending order, that is to say the latest sampling data is displayed at top. Checked means to display the sampling date, and choose the date format, three Date formats are optional, in the date format, YY means year, MM means month, DD means day. Date/Time Display Date Separator Choose the date separator; three formats are optional, for example 11/06/24. Checked means to display the sampling time, and choose the time format, three Time formats are optional, in the date format, HH means hour, MM means minute, SS means second, MS means millisecond. Color Setting Set the color for grid background and tile bar. Border Setting Set the border color and border line width of grid. Set the separator color, style and width of each row and column in grid, the unit of Row Space and Separator Setting Column Space is pixel point. And check the Horizontal Line means to display horizontal line, check the Vertical Line means to display vertical line. Historical Query Data The data that is saved to the external device can be queried by specified register in Historical Data Query. The default length of specified register is 2. 229 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Check the “Query by file order”, when the value in specified register is 0, it means to query today or the latest day’s historical data, 1 means to query the Query by file order previous day’s historical data and so on. For example, there are two csv file in the external device, when the value in specified register is 0, the historical data file saved on 24th, June, 2011 is queried and displayed, when the value in specified register is 1, the historical data file saved on 21st, June, 2011 is queried and displayed. Check the “Query by date” and input the date to the specified register, then the historical data in corresponding date is queried and displayed. The format of Query by date inputting date is yyyymmdd, yyyy means year, mm means month, and dd means day, for example, input 20110624 in the specified register, the historical data sampled on 24th, June, 2011 is queried and displayed. Variable Circle ! The sampling circle is read from specified register in Time Sampling mode. If the Variable Circle is configured, the Variable Circle value will be used preferentially; and the preset value is called when the Variable Circle value cannot not be read because of losing communication.. Detail Description of Background Attribute Sampling Methods Time Sampling Sample the data periodically. OFFON Only when the specified register changes from OFF to ON, the sampling is trigger sampling triggered. ONOFF Only when the specified register changes from ON to OF, the sampling is trigger sampling triggered. OFFNO trigger sampling Cycle Sam. Type Only when the specified register changes its status, the sampling is triggered. OFFON reset Only when the specified register changes from OFF to ON, the sampling is trigger sampling triggered, and the specified register resets automatically. ONOFF reset Only when the specified register changes from ON to OFF, the sampling is trigger sampling triggered, and the specified register resets automatically. Time interval between every two sampling points, the sampling points can be second or hundred milliseconds. Continuous The sampling will continue after all the sampling points are finished. 230 Advanced Part Component Once Sampling Points Trigger Register Setting The sampling will stop after all the sampling points are finished, the sampling is executed once. In the “Once”Sam.Type , the sampling will stop after all the Sampling Points are finished It is the specified register in the “Trigger Sampling” Sampling Method. The default word length is 2. The pause function is used to stop the sampling, the pause address is the specified address. The clear function is used to clear the sample data saved in the flash, the clear Pause address is the specified address+1. Note: If “Historical Data Query”is selected, the display data is from external device, at the time the clear function is disable. Description of Channel Properties Display Checked means displaying this channel data information in grid. Set the data format of sampling data, supporting format is 16-bit signed, 16-bit unsigned, 32-bit Data Type signed, 32-bit unsigned, float, double. Min/Max Limit N/A Integer N/A Decimal N/A ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.1.10 Save Historical Data] ! Historical Data Display component and Trend Curve can be used together, but when they sample the same registers and save the data in external device, the sub routine of saving file must be different, or chose only one historical data (Historical Data Display component or Trend Curve.) to save. Select [Use Background Data Print] to enable realtime print historical data. If [Net Print] is select, historical data can be printed in network. Description of Background Data Print Use Background Data Print Enable the background data print 231 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Print Type Net Print Real-time Print every sampling data in real-time. Batch Trigger printing when the sampling point number equals the set value. Point Set the sampling points number in batch printing Trig Trigger printing when the specified register satisfies the set condition. Enable the Net Print, download the program to HMI, and then run the Net Print.exe to connect the network printer to print historical data. Note: If the Net Print is checked, the local printing is invalid. Even if the local printer is connected to HMI, the HMI still cannot print via local printer. Print Content Print Serial Print serial number of each sampling point. Number Print Table Header Print the table header of Historical Data Display component. Print Grid Pint the grid ground of Historical Data Display component. Print Date Print date of each sampling data, and select the date format and separator. There are three date format and separator, YY means year , MM means month, DD means day. Print Time Print time of each sampling data, and select the time format and separator. There are three date formats and separators, HH means hour, MM means minute, SS means second, MS means millisecond. Grid Set the line type, line width and color of grid background. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 13.3.2 Network Print] 5 User can set the title name a font in this page, see as follows: 232 Advanced Part Component 4.13.3 User Info Display When configure the “User Permission Setting” function, use the User Info Display component to dispay the user information(system registered or added on line.) in table format. User Permission registered in system User Name Permission Permission Permission 2 3 1 ... Permission 32 User1 User2 NO. User Name 1 User2 111000000000000000 0 User1 100000000000000000 Permission ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 10.3.2 User Permission Protection for Components] 5 Description of Table Display Attributes *1. Users that registered in User Permission Setting of HMI Attribute cannot be deleted on line, so the Editable option in the User Infor Display component is “NO”. *2. When the user information cannot be wholly displayed in vertical or horizontal direction, system will provide scroll bar automatically. The width of system scroll bar can be set in HMI Extend Attributes of HMI Attributes, the width are optional from 20 to 120(pixel). Table Attributes Display Checked means displaying sequence number before each item. 233 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Back Ground Setting Set the background, title bar, frame color and frame width of table. Set the separator color, line style, width and row space, column space. The unit of row space and Separator Setting column space are pixel point. Check the “Vertical Line” means displaying the vertical separator line, and check the “Horizontal Line” means displaying the horizontal separator line. Set the display name and font attribute of table title bar. Title Bar Setting ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.13.2 Historical Data Display] 4.13.4 Operation Log The Operation Log component recode the all the operations on the HMI and display them in table, these recode can be saved as CSV file in external memory device. ! 1. The Read Address of Operation Log is the specified register that is used to query the operation log, the default word length is 2. The Operation Log can display operation result of Bit State Setting, Number Input , Text Input component and so on. 3. The Operation Log component is only suitable for HMI with SD card or U disk. Description of Table Display Attributes 234 Advanced Part Component * When the operation log cannot be wholly displayed in vertical or horizontal direction, system will provide scroll bar automatically. The width of system scroll bar can be set in HMI Extend Attributes of HMI Attributes, the width are optional from 20 to 120(pixel). Table Display Time Checked means displaying the operation time and chose the time format, three formats are operational. HH means hour, MM means minute, SS means second, MS means millisecond. Date Checked means displaying the operation date and chose the time format, three formats are operational, YY means year, MM means month, DD means day. Date Separator Choose the date separator, three formats are operation, for example 11/06/24 Sequence No. Checked mean displaying sequence number of each operation log. User Name* Checked means displaying operation user name. Ascending Order Checked means that the operation logs are arrange in ascending time order, that is to say the latest log is at the bottom; unchecked means that the operation logs are arrange in descending time order, that is to say the latest log is on the top. Background Set the background, title bar, frame color and frame width of operation log table. Setting Historical Query Logs Query by Order File If the “Query by File Order” is checked, 0 in specified register means to call today’s log or latest day’s log; 1 means to call the previous day’s log and so on. For example, there are two operation log csv file in external memory device, they are 20110621.csv and 20110624.csv, when the value in specified register is 0, the csv file that is saved on 24th , June, 2011 is called, when the value in specified register is 1, the csv file that is saved on 21st , June, 2011 is called and displayed. Query by Date If the “Query By Date” is checked, input date in specified register to call the corresponding operation log. The inputting date format is yyyymmdd, yyyy means year, mm means month, dd means day. For example, input 20110624 to specified register, the operation log that is saved on 24th, June, 2011 is called and displayed. 235 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Separator Setting Set the separator color, line style, width and row space, column space. The unit of row space and column space are pixel point. Check the “Vertical Line” means displaying the vertical separator line, and check the “Horizontal Line” means displaying the horizontal separator line. Title Bar Setting Set the display name and font attribute of table title bar. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.13.2 Historical Data Display] *When using the User Permission function, the User Name column displays the current user name. Related attributes settings of Operation Log. >> Operation Recode Storage Setting User needs to set the storage path for Operation Log storage file in HMI Attributes>> HMI Extended Attributes>> Operation Recode Storage Setting. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 6.1.3 HMI Extended Attributes] If the CSV file is stored by Daily File type, the storage path is log/subdirectory/yyyymmmdd.csv; if the CSV file is stored by Signal File type, the storage path is log/subdirectory/subdirectory.csv. Note: yyyymmdd is the date on which the operation log is built, for example 20110101. Recode Operations setting in component attributes. The components whose operation log needs recoding must check the Recodes Operations in Control Setting of component attributes and input description information in the text frame. 4.13.5 Data Report Data Report is used to display the data that is logged in the Data Logger and stored in external memory device on the HMI in report. The logged registers can be continuous or discontinuous registers. Detail Description of Data Report Data Report mode Report Attribute Report type Real time Update the report data timely according to the settings. History Input the time range to query the historical report. Trigger Report In the user defined time interval, trigger the sampling to get the instant 236 Advanced Part Component data. Free Report Display all the data in the user defined time interval. Note: In the real-time Report Mode, if the Free Report exceeds the user defined length, the earliest data will be deleted, then the whole report moves up Daily Report Display the data of one day. Note: In the real-time Report Mode, the Daily Report is displayed in circle. The new data is displayed at the bottom of report. If the report exceeds the length of row number, the newest data displays at the top of report, and all the data in previous circle will be deleted, only the newest row data is reserved, and then start a new circle. Monthly Report Display the data of the moth Quarterly Report Display the data of three months Annual Report Display the data of a year. By Order The sampling data is sequenced by time order; the newest data is at the bottom. Dis. Order Reverse The sampling data is sequenced by reverse time order, the newest data is at the top Set the displaying lines of report, this parameter is only suitable for the Trigger Report and Free Report. Note: 1. Report Line The line number of Daily Report is created automatically according to the Timer Interval, for example, the time interval is 1 hour, so the line number is 24. 2. The line number of Monthly Report is 31, Quarterly Report is 3, and Annual Report is 12. 3. In the “History” Report mode, the line number of Free Report and Free Report depends on the user defined time interval. There are five options; they are Instantaneous Value, Min Value, Max Value, Average Value Get Value Type and Added Value. When the Get value Type is one of Min Value, Max Value, Average Value or Added Value, the report displays the min value, max value, average value or added value of all the sampling values in a circle. Time Record Empty Data There are Begin Time, Mid Time, and End Time. The time that displayed in the report can be begin time, middle time or end time. Specified Value When there is no value in sampling register, the report displays specified 237 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software value, the default value is 0. Process Last Valid Value When there is no value in sampling register, the report displays the last valid value. The time interval of report, there are two options, they are minute and hour. Time Interval Note: This option is only suitable when the Free Report and Daily Report are selected. Because the time interval of Monthly Port and Quarterly Report are month, and time interval of Annual Report is year. History History Inquire Address, the word length is 8. Inquire Start Date: specified address, word length is 2, input year and date in this address. Address Start Time: specified address +2, word length is 2, input time (hour, minute and minute) in this address. End Date: specified address +4, word length is 2, input year and date in this address. End Time: specified address +6, word length is 2, input time (hour, minute and second) in this address. Take the following picture for example, the specified address is LW200, and user wants to query the data between 9:30:40 14th, Aug, 2012 and 14:16:30 15th, Aug, 2012. Trigger Report So the specified addresses are as follows: Start Date:LW200=20120814 Start Time:LW202=93040 End Date:LW204=20120815 End Time:LW206=141630 Start Date: specified address, word length is 2, input year and date in this address. Start Time: specified address +2, word length is 2, input time (hour, minute and minute) in this address. End Date: specified address +4, word length is 2, input year and date in this address. Trigger Report End Time: specified address +6, word length is 2, input time (hour, minute and second) in this address. Take the following picture for example, the specified address is LW200, and user wants to query the data between 9:30:40 14th, Aug, 2012 and 14:16:30 15th, Aug, 2012. 238 Advanced Part Component So the specified addresses are as follows: Start Date:LW200=20120814 Start Time:LW202=93040 End Date:LW204=20120815 End Time:LW206=141630 The specified address, word length is 2, and input year and date in this address. Take the following picture for example, the specified address is LW200, and user wants to query the data on 14th, Aug, 2012. Daily Report So the specified address is as follows: LW200=20120814 The specified address, word length is 2, and input year and month in this address. Take the following picture for example, the specified address is LW200, and user wants to query the data in Aug, 2012. Monthly Report So the specified address is as follows: LW200=201208 Quarterly Report The specified address, word length is 2, and input year and quarter number in this 239 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software address. Take the following picture for example, the specified address is LW200, and user wants to query the data of the third quarter 2012. So the specified address is as follows: LW200=201203 The specified address, word length is 2, and input year in this address. Take the following picture for example, the specified address is LW200, and user wants to query the data of 2012. Annual Report So the specified address is as follows: LW200=2012 When the specified register satisfies the set condition, output report data. Trig history inquire OFFON Only when the specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI outputs report data. ONOFF Only when the specified register changes from ON to OFF, HMI outputs report data. OFFON Only when the specified register changes its status, HMI outputs report data. OFFON(reset) ONOFF(Reset) Only when the specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI outputs report data, and then reset the specified register automatically. Only when the specified register changes from ON to OFF, HMI outputs report data, and then reset the specified register automatically. Detail Description of Data Report Channel 240 Advanced Part Component Data Logger Click this button to pop up Data Logger library. Click this button pop up the dialog box to choose channels. Data Report Channel List Data report channel. Data Sample List Display all the sampling data in the Data Logger library. Data Sample Channel Display all channel information of one sampling data. The data-report channel list Display the selected channels of current report. Set the title, integer and decimal of report channel. Details of Data report display attributes Serial number Display the serial number of sampling data or not. If checked, report displays the sampling time, and chooses the time format and separator. Display time There are three formats optional, HH means hour, MM means minute, SS means second, MS means millisecond. Back color Set the background color and title bar color. Date Format Display sampling date, and choose the date format, there are three formats optional, YY means year, MM means month and DD mans day. Display date Separator Select the date separator, three formats are optional, for example 12/07/19. Set the color, type and width of separating line, and set the width of each row and column, Separator border settings the unit is pixel If the Horizontal Line is checked, report displays horizontal separator, if the Vertical Line is checked, report displays vertical separator, Title bar settings Set the display name and font of title bar. Details of Data Report Control attributes Pause Address Data clear address In real-time report mode, use a bit register to pause data sampling, ON means pause, OFF means outputting data. In real-time report mode, use a bit register to clear the sampling data in Data Report Display. OFFON ONOFF Only when the specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI clears the sampling data in Data Report Display. Only when the specified register changes from ON to OFF, HMI clears the 241 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software sampling data in Data Report Display. Only when the specified register changes its status, HMI clears the sampling OFFON data in Data Report Display. Only when the specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI clears the OFFON(Reset) sampling data in Data Report Display, and then reset the specified register automatically. Only when the specified register changes from ON to OFF, HMI clears the ONOFF(Reset) sampling data in Data Report Display., and then reset the specified register automatically. Export Dir The subroutine name of the exported sample data file in the external memory device, the default name is ReportToCSV, user can modify it himself and the detail routine in external memory device is :\external memory device\export\Export Dir, the file name is named according to the saving time: year-month-day, hour: minute: second: millisecond, for example 20120903-110552.csv File format: csv. Save Disk Save the exported data to the external memory device: SD card, USB1 or USB2. Export data When the specified register satisfies the set condition, HMI exports data. Trigger Param. Sample Data Export Only when the specified register changes from OFF to OFFON ON, HMI exports report data. Only when the specified register changes from ON to ONOFF OFF, HMI exports report data. OFFON Only when the specified register changes its status, HMI exports report data. Only when the specified register changes from OFF to OFFON(reset) ON, HMI exports report data, and then reset the specified register automatically. Only when the specified register changes from ON to ONOFF(Reset) OFF, HMI exports report data, and then reset the specified register automatically. 242 Advanced Part Component 1. Do not put multiple free reports in a same window, it will affect the communicate speed. 2. Do not add too many data channels in a signal Free Report. 3. If there are multiple free reports or multiple channels report in a same window, please use the minute or hour as Time Interval. 4. If you want to plug off the external memory device when HMI is in operation, we suggest using the safe mode, but not plug it off directly. Safe Mode: set the LB9153 (SD card), LB9154 (USB1), LB9155 (USB2) OFF first, then plug of the corresponding memory device. 5. When you download the project again, check the Clear data report option in KHDownload, or the residual information may cause the data error for the new sampling data. Take the MT4522T for example, suppose the sampling address is Dword0, three channels’ data, and the sampling data is stored in SD card, user can query the data in any time interval. Build a new project, and add a Data Logger, the parameters are as follows: Data Sample HMI HMI0 Sample Point 10 Sample Type Circling Sample Get Data Type Sample Continue Channel 3 Sample Circle 10 Sample channel Data Type 16-bit signed/32-bit signed/float Description Channel 0/Channel 1/Channel 2 Data Sample Control Sample Address D0 Sample Data Save Save Disk SD Card Save Dir SampleDataStore Build a Data Report in Frame0 to display data in the Data Logger , the attributes setting is as follows:: Data report attribute Report mode History Report type Trig type Disp.type By order Get value type InstantantaneousValue Empty data process 0 History inquire address LW0 Trig history inquire LB0,Trigger type: OFF>>ON, Reset Data report channel: The data-report channel list Add channel 0 and chann2 to this list 243 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Data report Channel Integer 4 Decimal 2 Data report display attribute Serial Number Checked Display time Checked, the format is HH:MM:SS Back color Back: Display date Date format:YY*MM*DD;separator:/ (light yellow);title: (light blue) Separator/border setting Title Bar Setting Default setting. Put 4 Number Input components and a Bit State Switch in frame0: Start Date LW0,DWORD Start Time LW2,DWORD End Date LW4,DWORD End Time LW6,DWORD Inquire Trigger LB0;Switch Type: toggle. Put 3 Timer components in frame0 to simulate the change of D_Word registers, the attributes setting are as follows: Mode Periodical Jog++(circle) Data Type Word Asc Value 1/6/3 Upper 100/150/200 Addr.Type D_word Address 0/1/3 Value Type Unsigned Int (word length 1)/Signed Int (word length 2)/float (word length 2) Timer Trigger mode: All time, Execution Cycle:10 After a period of time, suppose the HMI system time is 2012/11/09, 16:50:00, we want to query the data between 16:40:30 and 16:41:00, the operation is as follows. 244 Advanced Part Component 事件信 息 4.14 Data Transmission Component Data Transmission component is used to exchange the data between HMI and PLC or controller. In Kinco HMIware, the following components can be used to exchange data: Recipe Data, Data Transmission, Data Transmission function in Timer and General PLC control in PLC Control component. 4.14.1 Recipe Recipe Data component can transmit HMI data that can be stored even powered off to specified PLC/controller registers, or transmit data in PLC/controller data to HMI registers that can be stored even powered off. FRW0 FRW1 FLASH D100 D101 20 120 ... 78 ... ... 98 20 ... 120 ... 78 98 ... ... ... SRAM ERW0 0 ERW0 1 20 ... 120 ... 78 98 ... ... USB RW0 RW1 20 120 ... ... 78 98 SD The Write Address of Recipe Data is the start register of transmitting PLC/controller 245 ... ... Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Detail description of Recipe Data Upload from PLC to Recipe Download from Recipe to PLC Upload from PLC ERW0*1 Download from ERW0 to PLC Upload from PLC to ERW1*1 Function Download from ERW1 to PLC Upload from PLC to ERW2*1 Download from ERW2 to PLC Upload from PLC to FRW*2 Download from FRW PLC Data Length Key Transmit data in specified PLC/controller registers to HMI RW registers Transmit data in HMI RW registers to specified PLC/controller registers Transmit data in specified PLC/controller registers to external memory device(the default is SD card) Transmit data in external memory device (the default is SD card) to specified PLC/controller registers. Transmit data in specified PLC/controller registers to external memory device(the default is USB DISK1) Transmit data in external memory device (the default is USB DISK1) to specified PLC/controller registers. Transmit data in specified PLC/controller registers to external memory device(the default is USB DISK2) Transmit data in external memory device (the default is USB DISK2) to specified PLC/controller registers. Transmit data in specified PLC/controller registers to HMI FLASH memory FRW. Transmit data in HMI FLASH memory FRW to specified PLC/controller registers. The length of transmitting data, unit is word. Map the function to the external keys (F1~F2) or HMI keys (F1~F8). The HMI with USB host slot or keys supports this function. The HMI with USB host or keys supports this function. *1.ERW0, ERW1, ERW2 are special registers for the external memory device, users can distribute them to U disk or SD card in the Extended Memory of the HMI Attributes 2. FRW is a special register type for the HMI flash memory. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 11 Recipe/ Recipe Editor] 4.14.2 Data Transmission Data Transmission component transmits data in specified HMI or PLC/controller registers to the other HMI or PLC/controller registers. The transmission can be triggered by touching or change of specified register. 246 Advanced Part Component Basic Attributes of Data Transition Data Type Key Set the transmitting data type: bit or word Data Length Map the function to the external keys (F1~F2) or HMI keys (F1~F8). The HMI with USB host slot or keys supports this function. The HMI with USB host or keys supports this function Source Address Set the source address of transmitting data Destination Address Set the destination address of transmitting data Variable Parameters Set the transmitting data length The offset of Source Address, Destination Address and Data Length are read from specified registers Take the following picture for example, the Source Address, Destination Address and Data Length use variable parameters, set the D register (PLC register) for Source Address, and the LW100 (HMI register) controls the offset of Source Register; Set LW register (HMI register) for Destination Address, and the LW101 (HMI register) controls the offset of Destination Register; LW103 controls the Data Length. 247 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Check the “Use Trigger Address” in Trigger Address page to trigger the transmission by status of specified register. If use the trigger address to trigger the transmission but not by touch, user can set the Always Invalid in the Control Setting page. Detail Description of Trigger Address Trigger Type Description OFFON When specified register changes from OFF to ON, the transmission is triggered ONOFF When specified register changes from ON to OFF, the transmission is triggered OFFON When specified register changes its status, the transmission is triggered OFFON (Reset) ONOFF (Reset) When specified register changes from OFF to ON, the transmission is triggered, at the same time reset the trigger address When specified register changes from ON to OFF, the transmission is triggered, at the same time reset the trigger address 4.15 Project Database In Kinco Builder, user can put the repeat information or background function in the specified area, in this way, it is easy to 248 Advanced Part Component control and call this information and function, at the same time it can reduce the data redundancy. The specified area are in the project Data Base components, they are: Text Library, Address Tag, Alarm Information, Event Information, PLC Control , Sound Lib and so on. 4.15.1 Text Library Text Library component is used to store the text content in the project, so that it can avoid the input the same text tag many times. Text Library supports multiple language, it makes the HMI can switch the display languages. Kinco HMIware supports 32 languages switching at most. Text Library Interface Display the text content Import csv file*1 Export csv file*2 Open【Language Setting】 *1. Import csv file (text library file) to Text Library of current project 2. Export the Text Library to the CSV file, User can use Microsoft EXCEL to open and edit this CSV file. Language attributes Click the Language in the Text Library to open the Language Setting dialog box, in this dialog box, user can set the font attributes of each language, refer to the following table for details: Description of Language Setting Max Lang Num Text Library supports 32 different languages setting at most; the default max language number is 8. Note: If customer needs to display more than 8 languages, he should set the Max Lang Num. Current Lang Choose the current language. Font Type Choose the data type for current language: Vector Font or Dot Matrix Font. Font Attribute Set the font attributes of current language: Size, Alignment, Color, Italic/Bold and so on. Copy Font Attribute to All Language Language Copy the current font attributes to the font of all the languages. It is related to the OS and input method, take Windows XP for example, if user wants to add the English (America) and Japanese language, click the 249 on the system language bar, then choose Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software the “set” to add English(America) and Japanese as the following picture. 1 2 3 4 After add the English(America) and Japanese languages, user can finde the English(America) and Japanese in the dropdown menu of Language ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 5.1 Text Library] 5 4.15.2 Address Tag Address Tag component can be used to store the address information , and user can add description to these addresses. Tag Address Interface 250 Advanced Part Component *1. Import the address information (CSV file) to the Address Tag. 2. Export the address information of Address Tag to a CSV file, user can use Microsoft EXECEL to pen an edit this CSV file. Build Address Tag attributes Click the Add in Address Tag to open the Build Address Tag box, see the following table for details: Description of Build Address Tag Tag Name Set the name of this address tag. HMI Choose the HMI number of this address tag. PLC NO. Choose PLC/controller number of this address tag. Data Type Choose the data type: word or bit. Address Type Choose the address type of address tag, it can be HMI register or PLC/controller register. Address Set the address of address tag. Code Type Display the code type of address tag: BIN or BCD Format(range) Display the address format and address range. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 5.2 Address Tag Library] 5 4.15.3 Event Information Event Information is used to configure the event content and trigger conditions; it is used with the Event Display and Event Bar together. Event Information supports bit register and word register to trigger event. ☞For details about Event Display and Event Bar, refer to [Advanced Part 4.7 Alarm Component] Event Information Interface *1. Import the event information (in CSV file) to the Event Information library. 2. Export the event information to a CSV file, user can use Microsoft EXECEL to pen an edit this CSV file. 251 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Event Attributes Click the Add in the Event Information to open the Event attributes dialog box, see the following table for details: Triggered HMI Type In multiple HMI program, set the HMI where the Event Display or Event Bar displays this event information. Set the event type: 0~255 are optional. Event Display and Event Bar can display the event information conditionally according to the event type. Address Set the read address of trigger register, choose the bit or word type in Data Type. Attributes On When specified bit register’s status changes from OFF to ON, an event log will be generated. Off When specified bit register’s status changes from ON to OFF, an event log will be generated. < When the value in specified register smaller than the specified value, an event log will be generated. > When the value in specified register larger than a specified value, an event log will be generated. Bit When the value in specified register equals the specified value, an event log will be generated. Value Range: When the value in specified register equals is in the specified value range, an event log will be generated. Take the following picture for example, check the “Value Range”, set 5 to the Min Value and 10 to == Max Value , suppose the data in specified register is N , if 5<=N<=10, an event log will be generated. Word When the data in specified register is not equal to the set value, an event log will be generated. For example, check the “Value Range”, set the Min Value to 15, set the Max Value to 30, suppose the data in specified register is N , if N<15 or N>30, an event log will be generated. <> <= When the data in specified register is less than or equal to the set value, an event log will be generated. >= When the data in specified register is more than or equal to the set value, an event log will be generated. Print Configure the Event Printing in the Printing Setting of HMI Attributes. 252 Advanced Part Component ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 6.1.8 Print Setting] On Trigger Print the event when event is triggered. Return to Normal Print the event when the event returns to normal. Trigger Function Execute Macro The specified macro is triggered when the event happens. Confirm Pop When the event is touched in the Event Display component, pop up specified window. 2 2011/06/23 15:22:54 15 1 2011/06/23 14:01:00 14:44:20 14 0 2011/06/23 10:50:01 11:40:10 10 ! Pop-up Window 2 2011/06/23 15:22:54 15 1 2011/06/23 14:01:00 14:44:20 14 0 2011/06/23 10:50:01 11:40:10 10 2 2011/06/23 15:22:54 15 1 2011/06/23 14:01:00 14:44:20 14 0 2011/06/23 10:50:01 11:40:10 10 Note: please use the “Close window” function in Function Key to close the pop-up window. Trigger Pop When the event is triggered, pop up specified window. 253 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Note: please use the “Close window” function in Function Key to close the pop-up window. Write Data Word length is 3. Write (Trig) address is the specified address; Write (Confirm) address is the specified address+1; Write (Resume) address is the specified address+2; Write(Trig) Write(Confirm) Write(Resume) 0 When the event happens, set OFF to specified register. 1 When the event happens, set ON to specified register. Not When the event happens, reverse specified register status. 0 When the event confirm, set OFF to specified register. 1 When the event confirm, set ON to specified register. Not When the event confirm, reverse specified register status. 0 When the event resume, set OFF to specified register. 1 When the event resume, set ON to specified register. Not When the event resume, reverse specified register status. When the event happens, trigger the buzzer. Buzzing Time ranges from 1 to 65535, the units is second. User Buzzer Text Input text content that needs to be displayed in Event Display after event happens, click the Font to set the font attributes. Data in LW register can be displayed in the event information, user can configure it according to the following format: ^xxxx^: Print header, which means print this content when the event is triggered the first time or a different event is triggered. For example, print “water” as a header, the format is ^water^ %h:mm:s#: Print time; %y:mm:d#: Print date; %nnfmd: Print variable, % means the start sign, nn means register number of LW, ranges from 00 to 99, that is to say , it is from LW0 to LW99, f means there is decimal in the data , d means the end sign. If there is no decimal in the data, the format can be %nnd. Take printing the data in LW20 for example; there is a decimal in this data, use the %20f1d in the Text of the Event Information. Note: If customer wants to print data in PLC register, use the Timer to transmit the dat to LW0~LW99. Use Text The Text content reads from the text library, but not writes in the text box. Library ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.15.1 Text Library] Use Graph Font Set the graph font for the text content in event display, user can set the font attribute after the “Use Graph 254 Advanced Part Component Font” is checked. When multiple languages is used in Text Library, user can choose language then set the font attributes of this Language language. Sound Play selected audio file when this event is triggered. Select Sound Note: Only the HMI with audio output port supports this function. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.15.6 Sound Lib] Open Text Open the Text Library dialog box. Library Open Address Open the Address Tag dialog box. Tag Library 4.15.4 Alarm Information Alarm Information is used to configure the alarm content and trigger conditions; it is used with the Alarm Display and Alarm Bar together. Alarm Information only supports bit register to trigger alarm. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.7 Alarm Component] Alarm Information *1. Import the alarm information (in CSV file) to the Alarm Information library. 2. Export the alarm information to a CSV file, user can use Microsoft EXECEL to pen an edit this CSV file. 255 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Alarm Attributes Click the Add in the Alarm Information to configure the alarm information, see the following table for details: Triggered HMI In multiple HMI program, set the HMI where the Alarm Display or Event Bar displays this alarm information. Set the event type: 0~255 are optional. Type Alarm Display and Alarm Bar can display the event information conditionally according to the event type. PLC Address Set the read address of trigger register, supports bit address only. Use Address Tag Use the address in the Address Tag library. Address Tag Library Open the Address Tag library dialog box. Attributes Trigger On When specified bit register changes from OFF to ON, an alarm log is generated. Off When specified bit register changes from ON to OFF, an alarm log is generated. When the alarm is triggered, the buzzer will be buzzing. Buzzing Time: 1~65535 are optional , the units is second. User Buzzer Text Input the displaying constant when the alarm is triggered; click the Font to set the font attributes. The Text content reads from the text library, but not writes in the text box. Use Text Library Use Graph Font Language ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.15.1 Text Library] Set the graph font for the text content in event display, user can set the font attribute after the “Use Graph Font” is checked. When multiple languages is used in Text Library, user can choose language then set the font attributes of this language. Sound Play selected audio file when current alarm is triggered. Select Sound Note: Only the HMI with audio output port supports this function. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.15.6 Sound Lib] 256 Advanced Part Component Text Library Open the Text Library dialog box. 4.15.5 PLC Control PLC Control is used to log in the trigger condition of some functions, when specified register satisfies the setting condition, the corresponding function will be executed. The function in PLC Control will not be limited by window, the function will execute as soon as the condition is satisfied. PLC Control Interface *1. Import the control file constant (in CSV file) to the PLC Control library. 2. Export the control file constant to a CSV file, user can use Microsoft EXECEL to pen and edit this CSV file. Alarm Attributes PLC Control Attributes Click the Add in the PLC Control to open the dialog box, chose the control function in the Control Type and set the control register and trigger condition. The control type that PLC Control supports are as followings: Change Window (Ignore the window 0), Write Data to PLC (Current Base Window number); Report Printout; Screen Hard Copy; General PLC Control; General PLC Control(Extended); Backlight Close; Backlight Close (Write Back); Execute Macro Program; Backlight Open; Backlight Open(Write Back); Sound Ctrl; Save Screen Shoot Data to Extended Memory. See the following for details of the control type. (1) Change Window When the value in specified register changes to a valid window number, HMI will switch to the window with this window 257 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software number automatically. And write the new window number to the specified register+1 address. For example, Suppose the current window number is 0, specified register address is D100, when the D100 is 10, the HMI switches to the window 10, and return the new window number 10 to D101. If the “Change Window” in PLC Control and “Change Common Window” in Function Key are used at the same time, user can set an invalid window number to the control register by “Set at Window Close” of Multiple State Setting component, in this way to avoid inputting the same window number, but cannot change the window at the next time. (2)Change Window (Ignore the window 0) Change common window function, when the value in specified register is 0, HMI will not change to Window 0. (3)Write Data to PLC (Current Base Window) When switching common window, write the window number to specified register. (4) Report Printout Print the HMI screen according to the value in the specified register. When value in specified register changes and this value is a valid window number, the constant in this window will be printed out. 1. HMI will not switch to the printed window when printing out this window in Print Out function. 2. The data in specified register will be reset to 0 automatically after printing. 3. Report Printout cannot print the constant in window 0. 258 Advanced Part Component User can set the printing constant by the following two methods: Method 1: Check the Custom Print Options Attributes of Custom Print Options Custom Print Attributes Printer Color Monochrome Detail Description Only the color printer supports switching printer color. Color Magnification Ranges from 0.1 to 5.0(Zoom-out printing may causes anamorphous, we do not advice zoom-out printing.) Current Page Start the printing at the first paper in printer. Change page to print Print a blank paper first, and then start the HMI screen printing. Print the screen horizontally. Horizontal print Print Page Print the screen vertically. Vertical print Automatically Take The Paper Print Text Print a whole paper automatically when finishing the printing. This option is only suitable for the stylus printer, micro printer does not support, and laser printer has this setting itself, user needs not to set on HMI. Print Text Print the static text and tag text of current window. Print Meter Print meter component in current window. Print Trend Curve Print trend curve component in current window. Print Bit Map Print bit map component in current window. Print All The Vector Graph Print all vector graph component in current window. Print Background Color Print meter component in current window. Method 2: Do not check the Custom Print Options; use the bits of LW9054 and LW9055 to set the print. LW9054 Setting Bit No. Name 0(OFF) 1(ON) Bit0 Print Text Do not print Print Bit 1 Print Meter Do not print Print Bit 2 Print Trend Curve Do not print Print 259 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Bit 3 Print Bit Map Do not print Print Bit 4 Print All The Vector Graph Do not print Print Bit 5 Print Background Color Do not print Print Use the Multiple States Setting component to set the value of LW9054, if all the constant needs printing, put the Multiple State Setting component in the common window(frame 1) and the setting mode is Set at Window Open, set value is 255. LW9055 Setting 0(OFF) 1(ON) Each bits means zoom out 0.1 Each bits means zoom in 0.1 times (LW9055 times ranges from 1 to 50, which means 0. 1 to 5 times.) Bit NO. Name Bit 0~ Bit 7 Magnification Bit 8 Printer Color Color Monochrome Bit 9 Print page Current page Change page to print For example, if the Magnification is 0.3, Monochrome printing and print current page, that is to say, set the LW.B9055.0, LW.B9055.1, LW.B9055.8 and LW.B9055.9 On. User also can set the above configuration by LW9055 directly, set LW9055 to 259(bit 0, 1, 8 and 9 on means 259) ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 13.3 Print Function Setting Method] 5 (5)Screen Hard Copy Screen Hard Copy is used to print current screen: when the specified bit register changes from OFF to ON, the current screen is printed. The Custom Print Options setting is the same as the Report Printout. (6)General PLC Control General PLC Control is used to transmit data between PLC/controller registers and HMI local registers. When the Control Type is General PLC Control, system will distribute 4 registers to control transmit type, transmit data length, offset of PLC/controller register address and offset of HMI register address. See the following table for details: Address Specified address Function Description Store the transmit type code, different There are 4 transmit type, see details in table 4.15.5_5, codes when the register is write new code, HMI executes mean different transmitting direction. corresponding transmit and the register will be reset to 0 260 Advanced Part Component after the transmitting finishes. Specified address+1 Data length The transmitting data length, units is word. Specified address+2 offset of PLC/controller register address This offset is for the “specified address +4”. Specified address+3 Set the start address of HMI recipe register(RW) or local offset of HMI register address register(LW). See the following table for details of transmit type. Code Data transmit type Code Data transmit type 1 PLC RW(HMI Recipe register) 2 PLC LW(HMI local register) 3 RW(HMI Recipe register) PLC 4 LW(HMI local register) PLC For example: Transmit the data in D100~D104 (PLC register) to the RS100 ~RW104 (HMI recipe register). Set D0 as the specified address in PLC Control, that is to say, D0 controls the Transmit Type, D1 controls the Transmit Data Length, D2 controls the offset of data source register (PLC) and D3 controls the offset of destination register (HMI). According to the example, D0=1 means transmit data from PLC to RW; D1=5 means there are 5 words (D100~D104) needs transmitting; D2=96 which means PLC source address is D100=(96+0)+4, 0 means the start address in General PLC Control. As the D0 to D3 are used for control register, so the source address is D4 , and the offset(96) is also for D4 , so the PLC source register address is D2+ start address in General PLC Control(D0)+4. D3=100 means that the start address of destination register is RW100. (7)General PLC Control (Extend) General PLC Control (Extend) is similar as the General PLC Control, it is also used to transmit data between PLC/controller register sand HMI registers; the difference is that it distributes 6 registers to transmit type, transmit data length, offset of PLC/controller register address and offset of HMI register address. See the following table for details Address Function Description Store the transmit type code, There are 4 transmit type, see details in table 4.15.5_5, when the different codes mean different register is write new code, HMI executes corresponding transmit transmitting direction and the register will be reset to 0 after the transmitting finishes Specified Address+1 Data length The transmitting data length, units is word Specified Address+2 offset of PLC/controller Specified Address+3 register address Specified Address Specified Address+4 Specified Address+5 offset of HMI register address This offset is for the “specified address +6” Set the start address of HMI recipe register (RW) or local register(LW) (8)Backlight Close When the specified bit register changes from OFF to ON, HMI turns off the backlight, and the backlight will be on again if the screen is touched. 261 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software (9)Backlight Close(Write Back) When the specified bit register changes from OFF to ON, HMI turns off the backlight, and reset the specified register to OFF. The backlight will be on again if the screen is touched. (10)Execute Macro Program When the specified register satisfies the execute method, the specified macro will be executed. The execute methods are as follows: Execute Method Description ONOFF When the status of specified register changes, HMI executes specified macro OFFON When the status of specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI executes specified macro ONOFF When the status of specified register changes from ON to OFF, HMI executes specified macro ON When the status of specified register keeps ON, HMI executes specified macro OFFON, reset ONOFF, reset When the status of specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI executes specified macro At the same time reset the specified register to OFF automatically When the status of specified register changes from ON to OFF, HMI executes specified macro At the same time reset the specified register to ON automatically (11)Backlight Open When the specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI will turn on the backlight. (12)Backlight Open (Write Back) When the specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI will turn on the backlight. At the same time HMI resets the register to OFF. 262 Advanced Part Component (13)Sound Control When the specified register satisfies the setting condition, HMI plays specified audio file. Execute Method Description ONOFF When the status of specified register changes, HMI plays specified audio file OFFON When the status of specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI plays specified audio file ONOFF When the status of specified register changes from ON to OFF, HMI plays specified audio file OFFON, reset ONOFF, reset When the status of specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI plays specified audio file At the same time reset the specified register to OFF automatically When the status of specified register changes from ON to OFF, HMI plays specified audio file At the same time reset the specified register to ON automatically ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 5.4 Sound Lib Application] ! Only the HMI with audio output port supports this Sound Control function (14)Save Screenshot Data to Extended Memory. When specified register changes from OFF to ON, save the current screen constant to the extended memory in picture. ! 1. Only the HMI with USB host and SD card supports this function 2. This function supports offline simulation, indirect online simulation and direct simulation. The screenshot pictures are saved in the \disk\sd(usb1 or usb2)\scr file folder of Kinco HHMIware installation route User needs to set the extended device in the HMI Attributes>> HMI. 263 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software The bmp pictures are named as year-month-day, hour: minute: second: millisecond, for example: 2010-09-01, 10:12:50:203.bmp. User also can define the picture name by system special register. The LW9470~LW9485 define the prefix of file name, for example the constant in LW9470~LW9485 is “Version Num .20100001-”, then the screenshot picture name is Version Num .20100001-2010-09-01,10:15:28:421.bmp. ! After the save screenshot is executed, please do not plug out the extended memory device in 1 minute, or the picture may cannot be saved. 4.15.6 Sound Lib Sound Lib is used to save the wav or mp3 audio file. The system will transfer the audio file to snd format file automatically, and user can call this file, the original audio file (WAV or mp3 file) are saved in the sound file folder of current project. Display the audio file Import from extended memory ! 1. One imported audio file must be smaller than 256KB, but the audio file from the Using audio from extended memory does not limit the file size. 2. Supports WAV, MP3 format audio file. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 5.4 Sound Lib Application] 264 Advanced Part Component 4.15.7 Data Logger Data Logger is used to sample data and set sampling method, these data can be displayed on Data Report component. ●Interface of Data Logger Display logged data 1. Import: .Import the data sampling information in CSV file format to the Data Logger 2. Export: Export all logged in sampling data to a CSV file; this file is editable by Microsoft EXCEL. Data Logger Attributes Click the Add to open the Data Logger attributes dialog window, the detail attributes are as follows: Detail Description of Data sampling properties. Sample Point The total sample point number, it ranges from 1~999999 Circle Sampling Sample the data periodically. Trigger Sampling Trigger sampling when the specified register satisfies the condition. Sample Continue The sampling continues even if all the sampling points are finished. Sample Once The sampling stops when all the sampling points are finished, that is to say , the Sample Type Get Datatype sampling is executed only once. Channel The continuous sampling registers number, 16 channels at most. It is invalid if the Sampling Type is Circle Sampling. Circle Sample Param Trigger Type Sample Circle The time interval between each two sampling points, the unit is millisecond. Viable Circle Read sample circle from specified register in circle sampling. It is invalid if the Sampling Type is Trigger Sampling. OFFON ONOFF Only when the specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI triggers the sampling.. Only when the specified register changes from ON to OFF, HMI triggers the sampling.. 265 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software OFFON OFFON(reset) ONOFF(Reset) Data Type Only when the specified register changes its status, HMI triggers the sampling.. Only when the specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI triggers the sampling, and then reset the specified register automatically. Only when the specified register changes from ON to OFF, HMI triggers the sampling, and then reset the specified register automatically. Set the display data format for the sampling data, there are six formats , they are Sample 16-bit signed, 16-bit unsigned, 32-bit signed, 32-bit unsigned, float, double and Channel string. Description Set the description name for the channel If the Variable Circle is checked, the variable value is used preferentially, if the variable value cannot be get because of communication lost , HMI uses the default value(the Sample Circle) . Detail Description of Data Sample Control Set the start address of sampling data, the word length depends on the channel and data type. Take the following picture for example: there are 4 channels, their data types are 16-bit signed, 32-bit signed, float and double. So the word length is 9, because the 16-bit signed is one word, 32-bit signed is two words; float is two words and double is 4 words. Sample Address Save Disk The external memory device of HMI, the SD Card, USB1 and USB2 are optional. Save Dir Sample Data The subdirectory where sampling data is saved in the external memory device. The default name is SampleDataStore, customers can change this name Save themselves, and the detail route of this file is \external device\database\subdirectory name\export file name.db. The file format is .db. Variable Dir Sample Data Clear The subdirectory name is read from specified register, the max word length is 16. Use a bit register to clear the sample data and delete the file in the database. OFFON ONOFF Only when the specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI clears the sample data. Only when the specified register changes from ON to OFF, HMI clears the sample data. 266 Advanced Part Component OFFON Only when the specified register changes its status, HMI clears the sample data. Only when the specified register changes from OFF to ON, HMI clears the OFFON(reset) sample data. and then reset the specified register automatically. Only when the specified register changes from ON to OFF, ONOFF(Reset) HMI clears the sample data., and then reset the specified register automatically. Use a specified bit register to pause the sampling, ON means HMI stops sampling and OFF means HMI starts sampling. Pause Sample Note: In Sample Once mode, this register will be set ON automatically when the sampling is finished, user can set this register OFF to trigger the sampling again. 4.15.8 Schedule List Schedule List is used to configure the operation which will be executed in specific time. 【Schedule List】Interface ※1.Import the CSV file which include schedule list format into【Schedule List】in the current project. 2.Export all the schedule information in current project to specific directory and saved as CSV file.This file can be open by Microsoft EXCEL. 【Schedule List】Setting Click 【Add】 in【Schedule List】to open the setting window of【Schedule List】,its attributes are shown as follows. Descriptions Execute HMI List Select the HMI which will execute the schedule. Basic Pro. Execute when power on Select If HMI power on after the setting time of schedule, then it will execute the “Begin 267 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software item param” automatically. If HMI power on before setting time of schedule and select “End item param”,then it will execute the “End item param” automatically. If HMI power on after setting time of schedule and select “End item param”, then it won’t execute “Begin item param” automatically,but it will execute the end item param automatically.If “End item param” is not selected,then no item will be executed. Unselect If HMI power on before setting time of schedule and not select “End item param”,then it will execute Trig Beep.It is used to set the buzzer when start executing preset operation.The range of buzzer is 1~65535s. When selecting this option,then the begin date and end date can be different,but there can only select one begin date and one end date. For example, begin date is 9:00:00 Sunday,end date is 17:30:00 Tuesday. Date and Time UseSingleDate Begin item param End item param 9:00 17:30 Sunday Tuesday 268 Advanced Part Component When unselecting this option, then the schedule is executed within one day(means from the begin date to end date is within 24 hours) ,but it can set multiple begin date and end date. Note:If the time of end date is earlier than the time of begin date,then the end item param will be executed in next day. Set Begin Date time and day for begin item param.Format is HH:MM:SS (Hour:Minute:Second).Range:hour(0~23),minute(0~59),second(0~59) End Date When selecting [Use end date],the time of end date can be set. When selecting[UseSingleDate],the day of end date can be set. It is used to set schedule time and date by local or PLC address. If unselecting [Use end date],it will occupy 4 words,these addresses are only used for begin date. The variable date addr.=Week. Bit0:Sunday(0:Invalid, 1:Valid)……Bit6:Saturday (0:Invalid, 1:Valid).The format is as following figure. Variable Addr. Date The variable date addr.+1=Hour The variable date addr.+2=Minute The variable date addr.+3=Second Exammple 1:The variable date addr. is LW0,then Week=LW0,Hour=LW1, Mintue=LW2,Second=LW3. If selecting [Use end date],it will occupy 8 words,then these addresses are used for begin date and end date. Example 2:if the variable date addr. is LW0,then the begin date is:Week=LW0, Hour=LW1,Minute=LW2,Second=LW3.End date is:Week=LW4,Hour=LW5, Minute=LW6,Second=LW7. 269 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Descriptions Control Info. Execute Type Descriptions as follows. On: it will set the specific bit address as on at the beginning time. For example, beginning time is 9:30:00. Off:it will set the specific bit address as off at the beginning time. For example:beginning time is 9:30:00 Bit Set Toggle:it will switch the status of the specific bit address at beginning time.If the orginal status of the bit address is off,then it will switch to on.Or it will switch to off. For example,beginning time is 9:30:00 Set Constant:it will write a constant to specific register at the beginning time. For example:beginning time is 9:30:00,constant value is 100 and specific register is 4x1. Word Set Add Value:it will use the original value of specific register to add an addend at the beginning time,and its final value will not exceed the upper limit. For example:beginning time is 9:30:00,addend is 3,upper limit is 80 and specific register is 4x1. 270 Advanced Part Component Sub Value: it will use the original value of specific register to subtract a subtrahend at the beginning time,and its final value will not exceed the lower limit. For example:beginning time is 9:30:00,subtrahend is 3,lower limit is 9 and specific register is 4x1. Data type It is used to select the data type of setting value.It supports 16-bit signed\16-bit unsigned,32-bit signed\32-bit unsigned,float,double. Write Address Set the address which is used for execution. Variable Param Use variables to change the set value(for set constant),Addend,upper(for add),subtrahend and lower(for Address sub) ! 1. If the write addresses are the same in schedule list,it is forbidden to set the same time and date to them. 2. Every time in schedule list only executes once.When it reaches execution time,the specific address will be written a value once. 3. Because it needs to read the data of [Word Set] and [Control Setting],the execution maybe delay according to the data communication. 4. When selecting [Variable Date Address],system will read the address cyclically,the cycle time depends on the busyness of system. 5. When the value of the variable date address exceeds the range of standard time,then the setting schedule will be wrong. 4.16 Auxiliary Component 4.16.1 Scale Scale Component is used to set equal scale label for some components, like Bar Picture, Meter and so on. So components has scale itself, they also can use the Scale component. 271 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Description of Scale component Horizontal Vertical Arc Circularity Style Equal Division Set the equal division number Line Length Set the scale length of Arc and Circularity style Start/End Angle Set the start and end angle of Acr style Line Color Set the line color 4.16.2 Timer When the setting time is up, Timer will execute corresponding functions, like macro, setting parameters, data transmission and so on. Description of Timer Attributes. Timer function will be executed as soon as the timer is initialized, and stopped All time automatically after the Repeat Count. Then the timer will not be triggered till the next initialization. If the Repeat Count is 0, that means the function is executed all the time. Timer function will be executed as soon as the frame is initialized, and stopped Initial frame automatically after the Repeat Count. Then the timer will not be triggered till the next initialization. It is the almost the same the “All time” Trigger Mode. Trigger Mode Close frame Timer function will be executed when the frame is close. The function will be triggered according to the Trigger Address. When the Repeat Count By is 0, it means that the function will be executed till the trigger condition is canceled. re-address When the repeat Count is N, it means that the function will be executed N times if address is triggered, then it will stop automatically. Execution Cycle Response Mode The execution cycle of timer, the unit is hundred milliseconds. The timer executes the Timer Function one time in every execution cycle. Immediate Timer executes the function immediately when the condition is triggered. 272 Advanced Part Component Delay Trigger State Repeat Count Trigger Address Timer executes the function in the next execution cycle when the condition is triggered. That is to say, there will be one circle delay. In the By reg-address mode, the Trigger State is On or Off. The execution number of timer function. If the Repeat Count is 0, it means the function will be executed all the time. In the By reg-address mode, set the register address for trigger register. Execute Macro Execute the specified macro program. That is to say, when the timing time is up, the macro will be executed Data Transmission Transmit the data in batch. When the timing time is up, timer transmits corresponding length data from Source Address to Destination Address Source Address Set the source address of data Destination Address Set the destination address of transmitting data Data Type Set the type of transmitting data, bit or word Data Length Set the number of transmitting data State Setting Change the state or value of specified register. When the timing time is up, timer changes the state of corresponding bit register or write value to the word register. Bit Set Value When the “Execution Cycle” time is up, set the bit register to 0 or 1. Periodical Toggle When the “Execution Cycle” time is up, toggle the bit register between 0 and 1. Periodical Add an Asc value (K) to the data (V) of specified register automatically in every execution JOG++(circle) circle. When the data reaches to the Upper limit, it will start from 0 again. Periodical Subtract a Desc value (K) from the data (V) of specified register automatically in every JOG--(one way) execution circle. When the data reaches to the Lower limit, the data will stop at the lower Word limit. 273 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Add an Asc value (K) to the data (V) of specified register automatically in every execution circle. When the data reaches to the Upper limit, it will stop at the Upper limit. Periodical JOG++(one way) Add a Step value (K) to the data (V) of specified register automatically in every execution circle. When the data reaches to the Upper limit, subtract a Step value (K) in every execution circle till 0, then start add Step a value (K) to the data again, repeat the above Periodical process circularly. Bounce(turnover Lower limit upon limit) T V+K Upper limit NO YES YES NO Lower limit V-K Add a Step value (K) to the data (V) of specified register automatically in every execution circle, when the data reaches to the Upper limit, it will be reset to the Lower limit, then start to add step value again from the Lower limit. Step Up(circle) Step Subtract a Desc value (K) from the data (V) of specified register automatically in every Down(circle) execution circle, when the data reaches the Lower limit, it will be reset to the Upper limit, then start to subtract step value again from the Upper limit. Set Constant When the timing time is up, the preset constant will be written to the specified register. 274 Advanced Part Component 4.16.3 Scroll Bar Scroll Bar is used to change the value of HMI or PLC register by moving the slider, and the scaling relation between actual value and Min/Max is displayed by the position of slider. Description of Scroll Bar Attributes Word Length of Index Number Word and Double Word are optional. Direction Set the direction of scroll bar, there are four directions; they are From Left To Right, From Right To Left, From Up to Down and From Down to UP. Background Image Set the background image of scroll bar, there are three options; they are Not Used, Vector Graphics and Bitmap. Import Image Import the background image from the system image library. Button Image Set the button image of scroll bar, there are three options; they are Not Used, Vector Graphics and Bitmap. Import Image Import the button image from the system image library. Description of Scroll Bar Extended Attributes Slider Width Set the width of slider, ranges from 1 to 99. Uncheck means that the slider uses the default width, which is 10 pixels. Max/Min Value Setting Variable Max/Min Set the start value and max value of scroll bar. Value Set the variable for the Min and Max for the scroll bar, and set the register address, the Setting specified address is the Min, and the specified address+1 is the Max. Set Scroll Mode Ranging from 1 to 100, each time user clicks scroll bar , it adds or subs the setting value. ! The Scroll Bar will not takes 3 words after V1.4.0.0, because the Min and Max can be set as constant, if the Min and Max use variable, user can set the register separately. 275 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 4.16.4 Date/Time Date/Time component is used to display HMI system date and time in specified format. Description of Time attributes Display Date Set the component to display date or not Date format Four formats are optional. DD means day, MM means month, YY means year. Date Separator Three formats are optional, for example, 2011.01.01. Year Checked means Timer displays year in 4 numbers, for example 2011; unchecked 4-digital Display means Timer displays year in 2 numbers, for example 11. Zero suppress for Checked means there is not a 0 before year and month take June for example, when Year and Day this option is checked, Timer displays 6, if unchecked, and Timer displays 06. Display Week Set the component to display week or not, the week is displayed in abbr. Display Time Set the component to display the time or not. Time Two formats are optional: HH means hour, MM means minutes, SS means second. 12-hour System Checked means Time is displayed in 12-hour system, take the three o'clock in the (AM/PM) afternoon for example, if this option is checked, it displays 3:00 PM , if unchecked , it displays 15:00. The Date/Time component can read the RTC time in the HMI, but cannot change it. If user need to change the date or time, they can change it in HMI SETUP screen or via system special registers(LW10000~LW10006) ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.7 RTC Set] 5 4.16.5 Note Pad Note Pad is the message board function; it is used together with the Message Board function in the Function Key. 276 Advanced Part Component 4.16.6 File List File List is used to display the file information in the external memory device. It is divided into three area: the left part displays the file folder information of current catalog. Upper right part displays the file information of current catalog; the Lower right part displays the chosen project file (.pkg file) or recipe file (.rcp file) of current catalog. ..\ event\ exmem\ historystore log\ \scr\ trend\ Test.pkg File information of current catalog HMI0: Chosen file HMI information of current catalog File folder information of current catalog File list component is a special component; it is usually used together with the Import/Export function of Function Key. System also provides [Frame5: File List Window] as file list when user import/export project file or recipe file in the SETUP screen. And the File Browser Window can be changed in the HMI Attributes. 4.16.7 Trigger Touch Trigger Touch is used to trigger multiple components without touching them, when the specified address satisfies the setting Trigger Type condition, all the components in the Trigger Touch area will be triggered. Take the following component for example: The components (1, 3 and 4) are in the Trigger Touch area. 277 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software The component 2 is not in the Trigger Touch area. When the specified address satisfies the setting Trigger Type condition, the 1, 3 and 4 will be trigged, but 2 will not be triggered, because it is out of the Trigger Touch area. Detail Description of Trigger Touch Trigger Touch OFFON ONOFF OFFON OFFON (reset) ONOFF (reset) Description When the specified register changes from OFF to ON, the components in the Trigger Touch area will be triggered. When the specified register changes from ON to OF, the components in the Trigger Touch area will be triggered. When the specified register changes its state, the components in the Trigger Touch area will be triggered. When the specified register changes from OFF to ON, the components in the Trigger Touch area will be triggered. At the same time, reset the specified register to OFF. When the specified register changes from ON to OFF, the components in the Trigger Touch area will be triggered. At the same time, reset the specified register to ON. 278 5 Better Understanding of Library In Kinco HMIware, user can load the text, address tag, graphic and sound in the database, when they need to use this information, they can call it from the database directly, this database is called library in Kinco HMIware. This chapter will give you a detail description of how to use library. 5.1 Text Library We will describe how to use Text Library in this section. 5.1.1 Create a Text Library (1) Click on the Option (O) menu>>Text Library (T) or the icon in the tool bar or the Text Library in the Project Database of Graph element window to open the Text Library dialog box. (2) Click on the Add to pop up the Add Text dialog box. For example, build a text item named “Start Motor”, the State Num is 2, each text supports 256 states at most. Click on the Ok to finish building the text, and click on the Cancel to give up this text. ! The Name of text cannot be modified after it is built After setting the Name and State Num, click on the OK to the next step. (3) The text named “Start Motor” has been added to the Text Library, click on the icon before “Start Motor” to view the states of this text, there are two states: 0 and 1. Click on the blank area under the each language to input text content. In this example , we input “启动” in the language1 of state 0,and “停止”in the language1 of state 1; Input “Start” in the language2 of state 0,and “Stop” in the language2 of state 1. 279 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Besides, user can add/delete/modify the text state by right click option, take the following picture for example: (4) Click on the OK to close the Text Library dialog box after editing. Check the “Use Textlib” in Tag option of a component and then select a already built text in list. 280 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library 5.1.2 Export/Import Text Library The built text library can be exported in a csv file, and the csv file also can be import into the Text Library. ! Import/export the whole text library, but cannot import/export a single text item (1) Export text library The exported csv file can be edit by Microsoft Excel. (2) Import text library 5.1.3 Set the Language of Text Library Click on the Language Setting in the HMI Extended Attributes option of HMI Attributes or the Language in the Text Library dialog box to open the Language Setting dialog box, and then set the global font attributes of each language. 281 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 1. The font attributes in Language Setting is global, and the font attributes in the tag option is only for the tag content of current component. 2. If the font attributes in Language Setting change, it will not affect the font attributes of the tag which has already used the text in text library, if user want this font attributes to be the same as the Language Setting, they can cancel the “Use Textlib”in the tag and then recheck it, so the font attributes is refreshed. 5.1.4 Text Library Application Edit the Text Library quickly When there is a lot of text content in text library, user can export the text library in a csv file , then edit it in the Microsoft excel, it is very conveniently to edit in this way. Firstly, build a text library, and then set the state number and text content. Export the text library to a csv file in your PC, and then open and edit it by Microsoft Excel, you can edit the text name, state number, text content and add new text item. ! The Name, Status, Language1~32 are fixed formwork, if they are modified, there will be problem when the csv file is imported to the Text Library. Save the csv file before close it: 282 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library At last, import the text library file (textlib.csv) to the project. ! When importing the text library file, if there is a text in the project text library has the same name as the text in the file, there will be a tip to warn that whether you want to cover the same name text or not, the covered text cannot be regained. Use Text Library to switch multiple languages Use the special system register LW9130 to switch the languages in text library When LW9130=0, HMI displays the text content in Language1; when LW9130=1, HMI displays the text content in Language2….and so on, When LW9130=31, HMI displays the text content in Language32; if the LW9130>31, HMI displays the text content in Language1. ! The Number of Language in the HMI Extended Attributes of HMI Attributes will limit the language number in Text Library. The default language number is 8 in Text Library, even if the LW9130>8 , HMI only displays the Language1~Language8. If user wants to use more than 8 languages, he needs to set the Max Lang Num in Language Setting, and the Number of Language must be smaller than Max Lang Num. The 283 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Default Language means the default language that HMI displays, for example, the language2 is English in Text Library, if the Default Language is 2, HMI will display the text content in English till LW9130 changes. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.6 Language Switching] 5.2 Address Tag Library We will describe how to use Address Tag library in this section 5.2.1 Build a Address tag Library (1) Click on the Option (O) menu>>Address Tag (A) or the icon in the tool bar or the Address Tag in the Project Database of Graph element window to open the Text Library dialog box. (2) Click on the Add to pop Build Address Tag dialog box For example, build an address tag named “Start Motor”, the address is M0. Click on the OK to finish building this address tag, and click on Cancel to give up this address tag. 5.2.2 Address Tag Application After building the address tag in Address Tag Library, check the Use Address Tag, and chose the corresponding address tag name. Take the following picture for example: 284 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library Bit component can only use the bit address tag; and the word component can only use the word address tag. The Address Tag library supports being imported and exported; the import/export operation is the same as the Text Library. 5.3 Graphic Library Kinco HMiware provides user rich vector graphic and bit map. User can draw vector graphics, like, switch, lamp and so on. User also can import external pictures to bit map. We will describe how to use the Graphic Library in this section. 5.3.1 Import Graphics (1) Import Graphics There are three methods to open the Import Graphic dialog box 1. Click on the icon 2. Click on the Import Graphics Library in Draw (D) menu. 3. Click on the Import Graphics in the Graphics option of a component attributes. a. Switch the states of selected graphic. b. When all graphic are not displayed in above area, click on Refresh to display them all. c. Choose a wanted graphic in above area, click on the Import to load this graphic (vg or bg) to current project. d. Close the Import Graphic dialog box e. Set the graphic type that needs displaying in following area. f. Open the route selection dialog box. There are two sources for graphic library System graphic library: The graphic library in software, it is in the vg_bg_lib file folder of Kinco HMIware installation file folder. 285 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software There are two parts for graphic display area, the upper half displays all thumbnail in graphic library, the lower half displays all states’ preview graphic of selected graphic Import graphic from system graphic library, for example, import the button named “Button1-00.vg”from the System Graphic Library>>Vg>> Button, the operation steps are as follows: 286 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library If the imported vector graphic (vg) or bit graphic (bg) has the same name as the graphic in current project graphic library, there will be a Modify Image Name dialog box to input a new name. User-defined Library Path: user can import a vg or bg from a specified route, that is , user can import the graphics from the vg file folder of other project files. For example , import graphic from D:\Program Files\Kinco\Kinco HMIware\ project \control system\ vg, the steps are as follows: Image Liarary System Image Library User-Defined Library Path ...... Type All graphs(.vg,.bg) 2 1 Image Library State State System Image Library User-Defined Library Path ...... 3 Image Library State State Refresh 287 Import Exit Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Multiple vg/ bg cannot be imported/exported at the same time 2. Export Graphic The imported vg/bg from system library or the new build vg/bg graphics are stored in the vg file folder of project file folder. There are two methods to save the graphic in current project to system graphic; they are stored in vg_bg_lib>>vg /BG >>UserselPath file folder of Kinco HMIware installation file folder. So user can use these graphics in the other project. 1. Project File Window>> Vector Graph 2. Graphic option of component attributes 288 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library 5.3.2 Build New Graphics If the vg/bg in system graph library cannot satisfy user’s application, he can build new vg/bg himself. (1) Build a new vector graph The New Graphics button For example, draw a indicator light name “Lamp” and has two states: Click on the icon Draw (D) menu to open the New Graphics dialog box: 289 or New Graphics (N) of Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software New Graphics dialog box Name The name of new graph State Num Set the state number of new graph, it is 256 at most Type The type of new graphic: vector graph or bit map Width/Height Set the width and height of new graph, the unit is pixel File Name The store route of new graph Description The note information for new graph ! The width and height cannot be modified after being built. Choose the Vector Graph type, input “Lamp” as its name and set 3 to State Number, use the default width (100) and height (100). Click on OK to enter the graphics edit window: View Area Edit Area Draw the graphics for State0 and State1; see the drawing steps as follows: Example Draw a base for the lamp 290 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library 1.Choose State0 2. Choose the Ellipse in the draw tool bar. 3. Move the mouse to edit area, and left click when the + icon appears. 4. Draw a ellipse ☞For details about how to draw a ellipse, refer to [Advanced Part 2.2 Draw] Example Set the graph attributes 2 1. Double click the ellipse to open 1 graphic dialog box. 2. Set the ellipse attributes as follows: Example Line Color RGB(230,230,250) Filling Color RGB(230,230,250) Draw lamp and flashing effect 1. Draw a ellipse which is smaller than the base. 2. Set the ellipse attributes as follows: Line Color RGB(0,255,0) Filling Color RGB(0,255,0) 3. Draw a short line on lamp as the flashing effect. ☞For details about how to draw a line, refer to [Advanced Part 2.2 Draw] Example Draw graph for State1 291 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 1. Select all the graphics of State0 and state0 state1 copy(Ctrl+A and Ctrl+C) state0 2. Select the State1, paste the graphics state1 to state1(Ctrl+V) 3. Set the lamp attributes of Stae1 as 1 2 state0 state1 follows: Line Color RGB(255,0,0) Filling Color RGB(255,0,0) 3 After drawing the lamp graphics, click on the Save in File menu or icon the to save the new graphic, at last click on icon to close the graph edit window. The new vector graphics will be saved as vg format file, they are in the vg file folder of current project file folder User can only use the draw bar to draw pictures on vector, but cannot add some text or external picture to vector graph. Save to the VG map User also can draw vector graphics in project edit window and then save them as VG map. For example, draw a vector graph named “button”, and has two states. The drawing steps are as follows: Example Draw graphics for State0 1. Draw a polygon in HMI Edit Window 2. Double click the polygon, setits attributes as follows: Line Color RGB(0,0,0) Filling Color RGB(165,165,165) 3. Copy (Ctrl +C) and paste (Ctrl +V) the polygon. 4. Rotate the polygon2 horizontally and then vertically. 5. Double click the polygon2 to set its 292 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library attributes as follows: Line Color RGB(0,0,0) Filling Color RGB(255,255,255) 6. Draw a rectangle, and double click to set its attributes as follows: Line Color RGB(0,0,0) Filling Color RGB(0,255,0) Now finish drawing the graphics of State0. ☞For details about how to draw a rectangle, refer to [Advanced Part 2.2 Draw] Example Save the graphics of State0 1. Select all the graphics of State0, then right click. 2. Choose the Save to the VG map in the right click option 3. Set a name for this vector graph in the popped up dialog box, and then click on OK to save. Example Draw graphics for State1 1. Select all he graphics of State0, and then copy (Ctrl +C) and paste (Ctrl +V) 2. After pasting , exchange the two polygon, and set the rectangle’s attributes as follow: Line Color RGB(0,0,0) Filing Color RGB(255,0,0) Now finish drawing the graphics of State1. Example Save the graphics of State1 293 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 1. Select all the graphics of State1, then right click. 2. Choose the “Save as VG map” in right click options. 3. Choose the “Save to VG map” in the popped up dialog box. 4. Choose the “New State” in the Graphics States. The New States in Save VG map dialog box means add a new state to the vg, Update Current State means replace a specified state. User can view the saved vg in Vector Graph of Project file window. (2) Build a new bit map For example, build a new bit graph named “Button”, and it has two states. Click on the New Graphics (N) of Draw (D) menu or icon to open the New Graphic dialog box. 294 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library Choose the Bit Map type and input “Button” as its name, set the State Num to 2, and then click on the OK to enter the graph edit window Import a picture for State0: Import a picture for State1 295 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software After import pictures to bit map, click on the Save in the File menu or the icon icon to save bit map, at last click on the to exit the graph edit window. The new build bit graph will be saved as bg format file, it is saved in the vg file folder of current project file folder. The imported original bmp, jpg, gif pictures are saved in the image file folder of project file folder. ! 1. Do not delete any file in the vg file folder, or the vg/bg cannot display normally in the project. 2. User can only load external picture to bit graph, but cannot use draw tool to draw pictures or add text on it. 3. If user load gif format picture to bit graph, the gif cannot be controlled by component state, for example, if the Bit State Switch uses the gif picture, the component displays the gif animation effect, no matter the component is ON or OFF. Kinco HMIware supports reading the pictures from extended memory devices to bit map; it can save the HMI memory. Only the HMI with USB host and SD card port support reading picture from extended memory device. Example: Put a picture (background.bmp) in the U disk or SD card (It is USB1 in this example), the HMI project read this picture (background.bmp) in the U disk. 1. Copy the picture (background.bmp) to the U disk. 296 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library 2. Build a new bitmap: Click on the icon or the New Graphics(N) in the Draw(D) menu to pop up New Graphics dialog box: Name: background, State Num: 1, Type: Bitmap. 3. Using picture from extended memory 297 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 1. The File Name must be the same as the picture name in the extended memory. 2. The picture can be bmp, jpg or gif or png format. 3. The picture must be in the root directory of extended memory. After above setting, click the icon to save the bitmap, and click on the icon at the upper right to close the graph edit window. 5.3.3 Edit Graphics How to open the Graph Edit Window Open the Graph Edit Window as shown in following picture: Delete the graph Delete the vg/bg graph in current project as shown in following picture: Click on the Yes to delete the chosen vg/bg, and click on the No to cancel this operation. Add/delete states for graphics User can add/delete graphics states in the Graph Edit Window. 298 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library Add state (1) Add States in the right click options state0 state1 state0 1 state1 2 3 state0 (2) The icon state1 in the tool bar: choose one state, and then click on the icon Delete States (1) Delete States in the right click options. 299 to add state. state2 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software (2) The icon in the tool bar: choose one state, and then click on the icon to delete this sate. Delete States The icons and are used to add/delete window in HMI Edit Window, and add/delete graph states in Graph Edit Window. Zoom in/Zoom out edit area In the graph edit window, it is not easy to edit graph if the edit area is too small, user can use the zoom in function to zoom in the edit area. In the graph edit window, click on the icon the icon to zoom in the work space, the maximum is 300%; In the same way, click on to zoom out the work space, the minimum is 25%. See the 200% effect as follows: Gray level of graph Click on the icon to switch the gray level of current graph. 300 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library The transparent color of bit graph ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.2.6 About Transparent Color] 6 5.3.4 How to Use the Graphics (1) How to use the vector and bit graphics. Take the lamp, button and background pictures for example: Add a Bit State Switch to the edit window, and use the Bitmap in Graphics option. Add a Bit State Lamp, and use the Vector Graph in Graphics option. 301 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Add a Bitmap component as a background picture. The bitmap which uses the picture from extended memory device does not support the “Use Original Size” function; user needs to adjust the size according to the original size himself. The simulation effect is as follows: (2)Optimize the bitmap 302 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library The bitmap supports the multiple formats picture, like BMP, JPG, JPE, JPEG, GIF, and PNG. But the color and size of imported pictures will affect the HMI project size and execution speed. Please note the following issues when you import a picture to the bitmap: The resolution of imported picture cannot be higher than HMI’s resolution, for example the HMI’s resolution is 640*480, and the imported picture’s resolution should be lower than 640*480. User can edit the picture to the same size as component by picture edit tool before importing this picture to the project, for example, a bitmap is used in a component with the width and height 100*100, and user can edit the picture to resolution 100*100 before importing this picture to bitmap. If you do not need the high resolution display, edit the picture as small as possible before importing, and then zoom in the program. The pictures saved in HMI are lossless compression in BMP format, if the imported pictures are loss compression in JPG, the pictures will be larger after compiling, and the resolutions will loss. That is, when using bit map. Please optimize the picture size, and chose compression format according to the actual application. Relatively Speaking, the vector graph takes much smaller size than bit map. That is, do not use too many bit maps in the program, use vector graphics as possible, it also can make HMI execute faster. 5.4 Sound Lib Application Kinco HMIware supports sound files, like WAV, MP3 formats. They can be used for touch sound or Event/Alarm sound. 1. The audio output port does not support OPAMP function; user needs to connect a loud speaking to this port. 2. A signal imported sound file must be smaller than 256K, but if the sound file is saved in extended memory, the size is not limited. 3. Supports WAV and MP3 formats only. 4. Only the HMI with audio output port support Sound Lib function. 5.4.1 Import Audio File Click on the icon or Graph element window>>Project Database>>Sound Lib to open the Sound Library box. 303 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Name Size(Byte) Current Sound: Sound Processing 2 Import... play Using audio from Delete 1 3 The system will convert the imported sound file to snd file automatically; the original sound file is saved in the sound file folder of current project file. The sound file also can be read from extended memory, which can save HMI’s memory. [Example]: Read the sound file named “sound4.mp3” from U disk. First, save the sound4.mp3 file to the root catalog of U disk. Root directory Choose the “Using audio from extended memory” in Sound Library. 304 Advanced Part Better Understanding of Library 1. The File Name must be the same as the name of sound file in the extended memory. 2. The audio file read from extended memory must be mp4 format, the wav is not supported. 3. The audio file must be saved in the root catalog of extended memory. 4. The size of audio file is not limited , it depends on the memory size of extended memory device. 5.4.2 How to Use Audio File (1)How to use audio file Only the HMI with audio output port has the Sound option in component attributes. The audio file will be played till the it is over when the component is touched, and this sound cannot be paused. The Alarm/Event Information also can use the sound as the alarm sound. 305 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software (2)Adjust the audio volume User can use the system register LW9464 to adjust the volume, if LW9464=0, it means sound off. The value of LW9464 is from 1 to 100, which means the volume is larger. 306 6 System Parameters 6.1 HMI Attributes Double the HMI icon or right click the HMI icon and choose the Attribute to open the HMI Attributes box. User can configure some HMI system parameters in this box. 6.1.1 HMI Detail description of HMI Attributes option Network Setting IP Set the IP address for the HMI with Ethernet port Subnet Mask Set the subnet mask for the HMI with Ethernet port Default Gateway Set the gateway of LAN which HMI is connected to Enable the FTP function and set a password. Open FTP ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 14.2.4 FTP Function] Network Device Configure the Ethernet protocol when HMI communicates with Setting PLC/controller via Ethernet Display Setting Display the HMI display mode Field Bus Setting Configure the field bus protocol and parameters when HMI communicates with PLC/controller via field bus Save Screenshots to The Extended Memory Choose the extended memory device where the screenshots are saved. Only the HMI with extended memory supports this function 307 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Description Input description for HMI , this description will distinguish different HMI when downloading and simulating 6.1.2 Task Bar The display effect on HMI is as follows: a. Fast Selection Window button b. Task Bar button c. Task Bar d. Touch Indicator Indicator g. Fast Selection Window Detail Descriptions of Task Bar Display Task Bar Display the task bar on HMI or not 308 e. CPU Indicator f. Alarm Advanced Part System Parameters Use Touch Indicator Display touch indicator on tool bar. Undefined Area Color Set the indicator color when touching the undefined area. Touch Set the indicator color when touching the blank area, where there Nonclient Color are no components orders. Touch Client Color Set the indicator color when touching the workplace area, where there are components and orders. Touch Indicating Set the color for indicator frame. Lamp Frame Color CPU Indicating Lamp Display CPU indictor on task bar. CPU Indicating Lamp Set the color for CPU indicating lamp. Color Alarm Indicating Lamp Display alarm indictor on task bar. Alarm Indicating Set the color for alarm indicating lamp. Lamp Fast Selection Window Only Show Fast Selection Button When clicking on the Menu button , pop up the fast selection window or not. Set this option to display fast selection button only. 309 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Button Area Size Set the size of buttons on fast selection window and task bar, the unit is pixel. Font Size/Color Set the font size and color of text on fast selection window and task bar, the unit is pixel. Button Position Set the position of buttons on fast selection window and task bar. Text Align Set the align method of text on fast selection window and task bar. Hide the buttons of fast Delete the text in the text box to hide the buttons. section window and task bar 6.1.3 HMI Extended Attributes 310 Advanced Part System Parameters Back Light/Screen Saver Setting Backlight HMI turns off the backlight if there is no touch within set time, and the backlight will turn on when the HMI screen is touched again. The unit of set time is minute, and the default time is 10 minutes. Screen Saver Backlight automatically turns when In the backlight off state, The backlight will turn on alarm/event occurs. automatically if alarm or event is triggered. HMI displays the screen saver window if there is no touch within set time, user can set the screen saver window in the Window of Screensavers. HMI will display the normal screen again if the screen is touched in screen saver mode. The default screen saver time is 10 minutes. The Window of Screensavers Select a window as screensaver screen picture. Return to Original Window when If this option is checked, the HMI returns to original Screensaver Ends. window when screensaver ends, if it is not checked, HMI goes to the screensaver window when screensaver ends. Upload/Decompile function settings Allow Upload Allow user uploads the project in HMI to PC, the default password is 888888. Note: the Password can not be empty or 0. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 8.4 Upload] Allow Decompile Allow user decompile the pkg file to wpj file, which Kinco HMIware can edit, the default password is 888888. Note: the Password cannot be empty or 0. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 8.7 Decompile Operation] Use Download Allow user download the pkg file to HMI, the default password is 888888. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 10.1.4 Download Password Protection] Video function settings Video Mode Set the signal format of video input, the PAL and NTSC are optional. Only the HMI with BNC port supports this function, and uses the Video component in the program. Text library settings Number of Set the language number in the Text Library, there are 32 languages at most. This function is used Language together with Text Library. Default Language Language Setting The default display language of the texts which use text library. This function is used together with Text Library. Open the Language Setting dialog box .This function is used together with Text Library. System function setting 311 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Use INIT Macro Trigger the macro when HMI is powered on. Use Buzzer Enable the buzzer in HMI Screen Flip Display Display a 180 degrees turn over screen. Auxiliary parameters setting System Scroll Bar Width. Set the width of system scroll bar, it ranges from 20 to 120, the unit is pixel. Chinese Font Box Set the height of Chinese character input box, it ranges from 24 to 99, and the unit is pixel. This Height function is used when input Chinese character to Text Input component. Invalided Set the color of invalid components, this function is used together with component which is set the Components Color Conditional Enabling option. Cursor Color Set the cursor color in the input status of Number/Text Input component. Use External Time Set the time source of the data sample in Datalogger and Data Report. for Datalogger ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.7.3 System Time and PLC Time Synchronization] Use External Time Set the time source of Event Trig time and Return to Normal Time in the Event Display and Event for Event Bar. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 2.7.3 System Time and PLC Time Synchronization] User defines datalogger’s Set the description in created *.db file same as the sample channel description. channel description Operational Storage Devices The SD, USB DISK1*, USB DISK2* , HMI are optional. Records Storage Save MS Save the millisecond of operation log and save them in the CSV file. Settings Subdirectory Set the subdirectory where CSV file is storage, user can modify it. The default subdirectory is Record. Storage Type Daily File Save the daily operation log in CSV file, the file name is named by date,“yyyy mmdd”. Single Save the every recodes of operation log in CSV file, the File Bulk Storage filename is the Subdirectory. Select a cache mode, when the data in buffer memory reaches the set size; write data to SD card or USB drive. The Default means no buffer memory, data is write to SD card or USB drive directly. Max Storage Set the upper limit of storage. The unit of Daily File is Day , and the unit of Single File is item If the Storage Type is Daily File, the CSV file is named as 312 Advanced Part System Parameters “yyyymmdd”and the Max Storage is upper limit of CSV file number in this route. The early file will be delete if the file number exceeds the Max Storage; If the Storage Type is Single File, The file is named as Subdirectory, the Max Storage means the upper limit of the item number in this file, if item number exceeds the Max Storage , the data will not be stored any more.(yyyymmdd means the date when the operation log happens) Related Settings of Window Public Window Attributes Display Public Window above the basic window or below the basic window Pop_up Window Attributes Display pop-up window on the top or not Initial Window Set the first window when HMI is powered on. The default is [0:Frame0] Public Window Set a window as Public Window. The default is [1: Common Window] Fast Selection Window File Brower Window Operation Confirmation Window Set a window as Fast Selection Window, The default is [2:Fast Selection]. The Fast Selection is used together with the fast selection button in the task bar. Set a window as File Brower Window, The default is[5:File List Window]. The File Brower Window is used together with the Import/Export in Function Key. Set a window as Operation Confirmation Window, the default is [7: Confirm Action Window].The Operation Confirmation Window is used together with Operator Confirm of a component. Set a window as Login Window of User Permission and Security Level, the default is Login Window [9:Login Window]. The Login Window is used together with the User Permission and Security Level function. ※Some models have two USB Host ports; the number of USB DISK is according to the sequence when the USB drives are plugged in HMI, but not the position of the USB slot. The USB drive which is plugged in first is the USD DISK1 and the second one is USB DISK2. 6.1.4 HMI System Information Text User can define the display content for the system error information in the User-Defined System Information. When the error happens, if user defines the display content for system error, HMI will display the user-defined content, or HMI displays the default system error information. 313 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Select the default system error information in the red frame, then check the Use User-Defined Information and input user-defined content in the input box. User can define multiple system error information 6.1.5 Security Levels Setting In this option, user can set the security levels and their passwords. There are 16 levels at most ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 10 Password] 6.1.6 User Permissions Setting In this option, user can configure user name, password, logoff time and permission and so on. There are 32 users at most, and each user has 32 permissions at most. 314 Advanced Part System Parameters ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 10 Password] 6.1.7 Historical Events Storage In this option, user can set the route where the historical events are stored; this function is used together with Event components. ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 4.7 Alarm Component] Descriptions of Historical Events Storage Save to Save the historical event information in the recipe memory. Recipe Save Count Data Field Set the item number of historical events, which are saved in recipe memory. If the event item is larger than the set Save Count, the early information will be deleted, and save new information. Note:If the Save Count is 0, the historical event will not be stored. Start Addr Set the start address from which the historical events are stored in recipe memory. End Addr Software will calculate the End Address according to the Save Count and Start Addr. Save to Save the historical event information to external devices. External Storage Devices The SD card, USB DISK1*, and USB DISK2* are optional. Device Outage Keepin When HMI is restarted by power outage,HMI can recover 1024 items historical event which are triggered before power outage, and display them in the Event Display component. 315 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Export to CSV file Save the historical event information in CSV file, and save this CSV file to external memory device, the storage route is :/event/subdirectory name/file name Save MS Save the millisecond of operation log and save them in the CSV file. Subdirectory Set the subdirectory where CSV file is storage, user can modify it. The default subdirectory for historical event is Event. Storage Type Daily File Save the daily historical event information in CSV file, the file is named by date, “yyyy mmdd”. Single File Save the every recodes of operation log in CSV file, the filename is the Subdirectory. Bulk Storage Select a cache mode, when the data in buffer memory reaches the set size; write data to SD card or USB drive. The Default means no buffer memory, data is write to SD card or USB drive directly. Max Storage Set the upper limit of storage. The unit of Daily File is Day , and the unit of Single File is item If the Storage Type is Daily File, the CSV file is named as “yyyymmdd”and the Max Storage is upper limit of CSV file number in this route. The early file will be delete if the file number exceeds the Max Storage; If the Storage Type is Single File, The file is named as Subdirectory, the Max Storage means the upper limit of the item number in this file, if item number exceeds the Max Storage , the data will not be stored any more.(yyyymmdd means the date when the operation log happens) 6.1.8 Print Setting In the Print Setting option, user can enable print functions and set its parameters. 316 Advanced Part System Parameters Descriptions of Printing Setting Enable Print Enable print function of HMI Printer Select a communication protocol for printer ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 13 Print] Net Print port Select a communication port for HMI and printer Baud Rate/Data Bit/Parity If the printing port is serial port, set the corresponding parameters of Check/Stop Bit serial port IP The IP address of the PC which connects to the network printer Setting Print Setting of in the LAN Port The port of the PC which connects to the network printer in the LAN Print Date Print the date when the event is triggered and returns to normal. Event Display Format:mm/dd Print Standard Time(h:m:s) Print the standard time when the event is triggered and returns to normal, If this option is checked the Print Time will be checked automatically. Format: h:m:s Print Sequence NO. Print sequence NO. of event Print Extended Date(d:h:m) Print the extended date when the event is triggered and returns to normal, If this option is checked the Print Date will be checked automatically. Format: yyyyy/mm/dd Print Precise Time(h:m:s:ms) Print the precise time when the event is triggered and the returns to normal, If this option is checked the Print Time will be checked automatically. Format: h:m:s:ms Print Time Print the time when the event is triggered and the returns to normal. Format: m:s Print Extended Time(d:h:m) Print the extended time when the event is triggered and the returns to normal, If this option is checked the Print Time will be checked automatically. Format: h:m:s:ms. Format: d:h:m Check Window Error Check if there is error in this window when printing Network Printing Enable the Network Printing function ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 13 Print] 6.1.9 Serial Port Setting In the CMO0/1/2 Setting, user can set the HMI communication parameters when HMI communicates with PLC. 317 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Descriptions of COM0/1/2 Setting Type Select a communication type when HMI communicates with PLC, the RS232 (RS-232C), RS485-2(RS-485), RS485-4(RS-422A) are optional. Note: the COM2 only supports the RS232(RS232C) Baud Rate/Data Bit/Parity Set the HMI communication parameters when HMI communicates with PLC Check/Stop Bit ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 14 HMI Communication] Device No. When HMI works as a slave device, set the HMI station number. Broadcast When HMI works as MODBUS RTU master, HMI only sends command to PLC, but ignores any response from PLC. The Broadcast can only be 0. PLC Communication Time The time HMI waits response from PLC/controller, unit is millisecond or second. If Out PLC/controller has no response within this time, it is time out; HMI gives up this request and try the next request. If there is no response after several requests, HMI display PLC no response. Do not suggest customers to modify this parameter. Protocol Time Out1(ms) Time out of character. The protocol takes this time as time interval to cut frame; In other words, it is the max time interval between each character. If the communication is not stable, user can increase this value to improve the communication. It ranges from 1to 500. This parameter is set when you connect a PLC to HMI port in the software. Do not suggest customers to modify this parameter. Protocol Time Out2(ms) E5time out, the communication speed will be slow, but the communication error and error package will also be reduced. This value cannot exceed 100. Do not suggest customers to modify this parameter. Max Inter of bit/word block These parameters decide that how many registers can be read in a package when the pack registers are not continual. Do not suggest customers to modify this parameter. 318 Advanced Part System Parameters Max word block word/bit package size Use Default Setting These parameters decide the max length of package. That is, how many the registers that can be read as one frame at a time. Do not suggest customers to modify this parameter. If users modify the default communication parameters, and HMI and PLC does not communicate successfully, they can use this button to set the parameters to default value. 6.1.10 Extended Memory In the Extended Memory option, user can define address type ERW0, ERW1, ERW2 in the extended memory devices, USB drive or SD card. The ERW data will stored in the extended memory in erp file, its route is /exmem/erw.erp, (x=0, 1, 2) 6.2 PLC Attribute In the Construct window, double click PLC icon or right click PLC icon and choose the Attributes to open the PLC Attribute option. User can configure PLC communication parameters PLC Attribute Description 319 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Station No. When PLC/controller works as slave device, set the station No. for PLC/controller. Network Device Setting When HMI communicates with PLC/controller via Ethernet, configure the Ethernet protocol and communication parameters here. IP Address Set the IP address for PLC/controller. Port No. Set the port No. for PLC/controller. PLC Communication Time ☞For details, refer to [Advanced Part 6.1.9 Serial Port Setting] Out……Use Default Setting 320 7 Compile/Simulate/Download/Upload 7.1 Compilation Compilation can be divided into:【Compile】,【Compile All】,【Clear Build Result】. 7.1.1 Methods of Compilation icons in toolbar,or select 【Compile】/【Compile All】/【Clear Build Result】in the【Tools】 Click the menu. Name Description When there are Macro files in the project, click【Compile】will do not compile the Macro files that has Compile been compiled Compile All Compile all the files Clear Build Result Clear all the compiled files, including .pkg files, Macro files .so/.dll, .hmi files, .logo files 7.2 Simulation Kinco HMIware supports 3 modes of simulation: Offline Simulation, Indirect Online Simulation, Direct Online Simulation Name PLC/Controller HMI Description Connections with PLC and HMI are not needed, so the time for each Offline — Simulation — download is shortened significantly. But the program cannot acquire data from the PLC, only read data from the local address. Therefore all data displayed on the configuration windows are static data Need to connect PLC and HMI. PLC data can be obtained Indirect Online √ Simulation √ dynamically. The operating environment of the program is the same as downloaded into HMI, but does not need to download the project to HMI repeatedly, which is quickly and convenient Only PLC needs to be connected, while HMI doesn’t. PLC data can be Direct Online √ Simulation — obtained dynamically. This mode can be used to check whether communication is normal without connecting with an HMI 7.2.1 Modes of Simulation Click the icons in toolbar,or select 【Offline simulation】/【Indirect Online Simulation】/【Direct Online Simulation】in the【Tools】 menu. Select an HMI to be simulated, and click 【Simulation】to start simulation. ! 1. The maximum test time for the direct online simulation is 15 minutes. After 15 minutes, the system will prompt “Online Simulation overtime and Program is end, if want, Please Simulate again.” 2. Mostly only the RS232 communication mode can be used for direct online simulation. Some PLCs 321 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software communicating through Ethernet port can execute direct online simulation through Ethernet port. 3. Connection of direct online simulation for RS232 communication: program cable of PLC connects with the serial port of PC directly. Connection of direct online simulation for Ethernet port communication mode: connect directly through cross-over cable or through a Switch. 4. The port used for direct online simulation cannot be used by other programs, otherwise, communication will fail when simulating. 7.2.2 Exit Simulation To exit simulation by the space key of the keyboard, or click the right mouse button in the simulation box blank, select 【Close】to exit simulation. 7.3 Download Kinco HMIware provides 3 ways of download: USB, Serial port, Ethernet port (Download via Ethernet port is only suitable for HMIs with Ethernet ports). 7.3.1 Download Method Selection Click the icon in toolbar, or select from【Tools】menu—【Download Method】 : The Properties dialog box of【Project Setting Option】pops up, the default download method is via USB port, single click the drop-down list of【Download Method】to select download way. ! 1. Download way is saved according to HMI. For example: there are 2 HMIs in a project, HMI0 and HMI1. The download way of HMI0 is via serial port before closed, and HMI1 is via USB cable before closed. Then open the project again, download way of HMI0 is still via serial port, and HMI1 is still via USB cable. 2. When USB downloading cable is used for the first time, the USB device driver should be installed manually. ☞For more details about the installation of USB driver, please refer to【Basic Part 2.8 Install USB Driver】 3. For downloading through serial port, users should weld the cable by themselves. ☞For more details about welding downloading cable for serial port, please refer to the manual of 【Communication Connection Guide】 322 Advanced Part Compile/Simulate/Download/Upload Notes for downloading through Ethernet and setting of IP: The IPs of PC and HMI should be in the same section. That means the first three digits should be the same and the last digit should be different. If the devices are connected in local area network, then the IPs should not conflict with other device in the local area network. Modify the current IP and PORT of HMI Click【HMI Attribute】—【HMI】, set the target IP to HMI, compile and download into HMI, then the IP of HMI is in line with the set value in project. Set IP in SETUP Interface ☞For more details about setting IP in SETUP interface,please refer to【Hardware Part 3 System Setting Mode】 323 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Set IP via【Update IP/PORT】in KHManager ☞For more details about setting IP via【Update IP/PORT】in KHManager,please refer to【Advanced Part 8 KHManager】 7.3.2 Download via U disk or SD card ☞For more details about downloading via U disk or SD card,please refer to【Hardware Part 3 System Setting Mode】 7.3.3 Download Selection In the property box of 【KHDownload】,select the related options in 【Select Section】 to download the files needed. Detailed description for【Select Section】 Name Description Data file Download user project files in .pkg format Recipe file Download recipe files in .rcp format LOGO file Download Initial Start Window in .logo format Clear recipe Clear recipe data saved in RB/RBI/RW/RWI Clear history event data Clear the record in【Event Display】/【Historical Event Display】parts Clear history record data Clear the record in【Historical Event Display】/【Trend Curve】/【Trend Curve】parts Clear data report Clear data saved in【Data Report】parts Clear ERW data Clear the data saved in external register ERW/ERWI Clear FRW data Clear the data saved in FLASH register FRB/FRBI/FRW/FRWI Download to USB1 Download the project files to external register USB1 Download to USB2 Download the project files to external register USB2 324 Advanced Part Compile/Simulate/Download/Upload Download to SD Download the project files to external register SD Timeout Set the timeout time of download, the unit is millisecond, and it ranges from 0 to 65535 Download recipe files Recipe files should be imported before downloading. Single click icon in toolbar or single click 【Options】menu — 【Import Recipe】,then dialog box of 【Open】pops up,select the recipe files to be downloaded and single click【Open】 to load the recipe files: Compile and then download, select 【Recipe File】as shown in the below figure: Kinco HMIware will record the directories of recipe files, when the selected recipe files is loaded into HMIKinco HMIware. If the directories of recipe files changed, warning information will appear in the compilation message window, the recipe files will no longer be selected when download again. 325 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Download LOGO file (Initial Start Window) ☞For more details about【LOGO file】,please refer to【Advanced Part 2.8 LOGO Screen(LOGO)】 Clear data when download When download project, user could select【Clear recipe】【 , Clear history event】【 , Clear history record】【 , Clear data report】, 【Clear ERW data】,【Clear FRW data】. Select the data to be deleted, then the related data in HMI will be deleted when downloading. Project runs directly in external storage devices When there are too many pictures in project, then the project will be too big to download into HMI. Prompt: When compress bitmap of large size, users could download the project to external devices. Select【Download to USB1】,【Download to USB2】,【Download to USB3】when download as shown in the below picture: 326 Advanced Part Compile/Simulate/Download/Upload Single click【Download】,the project will be downloaded to external memory device. ! 1. The function that project runs directly in the external storage device is only applicable for HMIs supporting external storage devices. 2. The projects copied directly into external storage devices cannot run. 3. The external storage devices cannot be removed during running, otherwise, the project stored in external device will be abnormal. The timeout time of KHDownload can be set by user If the timeout option is checked, user can set the timeout time of download, the unit is millisecond, and it ranges from 0 to 65535.The function can improve download timeout error of serial port, USB and Ethernet port. 327 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 7.4 Upload/ Download/Compile Project via KHManager ☞For more details about upload, download, compile project, please refer to【Advanced Part 8 KHManager】 328 8 KHManager 8.1 Introduction to KHManager KHManager consists of six processing modules: 【Download】, 【Upload】, 【System Operation】, 【Get Version】, 【Decompile Operate】, 【Pass Through Communication】. 【Communication parameter setting】:The current download way selected in KHManager will be displayed. Click 【Set】 to modify the current download way. Download way Parameter setting Download via USB port No need to set communication parameters Download via serial port Choose the current used serial port NO. Download via network Set the IP address and port number of the current HMI 329 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 【PageUP】/【PageDown】:Click 【PageUP/PageDown】to skip among the 6 processing modules. 【Exit】:Exit KHManager. 【Pass Through Communication】is not supported temporarily 8.2 Methods of Open KHManager Open from the【Start】menu of PC. Double click the shortcut of KHManager on desktop. Open from【Tools】menu of Kinco HMIware software. Click【Tools】menu—【System Manager】/【HMI Version Manager】/【Upload Manager】/【Upload Init Window】/ 【Download Init Window】/【Upload project】/【Decompile Manager】to open【KHManager】 Double click【KHManager.exe】in the installation directory of Kinco HMIware software. 8.3 Download Detailed descriptions of【Download】 Download Download User Data Download .pkg files to HMI Section Download LOGO Download Initial Start Window of .logo files to HMI Download Recipe Download .rcp files to HMI Recipe Editor Open【Recipe Editor】 Download FRW Data Download .frp files to HMI Initial Start Show LOGO Window setting Area Clear Section UnShow LOGO Clear Recipe Clear FRW Data Clear ERW Data Select【Show LOGO】,click【Set】,HMI will display Initial Start Window when boots up. Select【UnShow LOGO】,and click【Set】,HMI will do not display Initial Start Window when boots up, but keeps white screen until project window displays. Select【Clear Recipe】,and click【Execute】,to clear the data that is saved in physical storage area of SRAM RB/RBI/RW/RWI. To clear the data that is saved in physical storage area of FLASH FRB/FRBI/FRW/FRWI. To clear the data that is saved in physical storage area of external memory 330 Advanced Part KHManager ERW/ERWI. To clear the displayed history data that is recorded in【History Data Display】 Clear History Data 【Trend / Curve】 【XY / Curve】parts, at the same time the history data and files that are saved in recipe memories and external memories will also be cleared. To clear the displayed history events that are recorded in【Event Display】/ Clear History Event 【Historical Event Display】, at the same time the history data and files that are saved in recipe memories and external memories will also be cleared. 8.4 Upload Detailed descriptions of【Upload】 Upload User Data Upload project files of .pkg format Recipe Editor Open【Recipe Editor】 Upload Recipe Upload .rcp files in HMI Upload FRW Upload .frw files in HMI Upload LOGO Upload .logo files in HMI 8.5 System Operation Detailed descriptions of【System Operation】 Get HMI IP / PORT Information Area Update IP/PORT Area Jumping Section Area Obtain the IP address and port number information of the target HMI Update the IP address and port number to the set value Return to User Application Status HMI jumps to run the configuration program Return to Set Application Status HMI changes to the embedded SETUP interface Update firmware of HMI Update Operation Area ☞For Update the kernel/ file system more details please refer to [Hardware Part 5 Firmware Update Mode] 8.6 Get Version User could view firmware version information of HMI through 【Get Version】 in KHManager, click 【Version Get】, HMI firmware version information will be displayed. Otherwise please check whether the current communication mode is correct or other reasons. 8.7 Decompile Operation The configuration screen edited by Kinco HMIware is saved as wpj files. Compile to generate pkg files which are required for running in HMI and download into HMI. So the files uploaded from HMI are in pkg format. Before open the projects uploaded from HMI, users should decompile the pkg files by KHManager to generate a project file in which wpj file and other files are included, then users can open wpj file and edit. 331 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software a b c d a. Select the target pkg files to be decompiled b. Delete the redundant pkg files no need to be compiled. c. Select a saving path for the decompiling project files. d. Execute decompilation operation Regardless of whether the file allow decompiling or not, upload password dialog box will pop up and request for decompilation password. If decompilation is prohibited, user cannot move to the next step. While if decompilation is allowed and no password is set, and then enter the default password 888888 to move to the next step. 1. When there are more than one (2 or more) HMIs in a project, users need to add all the pkg files of each HMI to execute decompilation operation. 2. When there are more than one (2 or more) HMIs in a project, all the pkg files uploaded from the HMIs must be compiled at the same time, otherwise, the the pkg files cannot be decompiled. 8.8 Data Decryption To decrypt the encrypted CSV files. ☞For more details about [Data Encryption], please refer to [Advanced Part 2.15 Data Encryption] 332 9 Macro Macro uses C language to release logic and arithmetic calculation. User can use macro and other components together to release some complex calculation and make HMI strong function. The macro instructions in Kinco HMIware are compatible with standard C language(ANSI C89). 9.1 Macro Editing Environment There are three parts in this edit environment, they are macro edit window, Macro variables window and macro file list in the project files window. The detail description of macro edit environment detail description of macro edit environment Macro edit window User writes C language code in this window, the variables are defined in the Parameters list; you can use them in the C code. Macro variables window Macro file list The write and read variables in this macro, which are external variable of this macro. User can rename and delete macro in this list. If there are multiple macro, user also can switch macro among different macro. 9.2 Macro Edit 9.2.1 Build Macro There are two ways to build macro: Click on the icon 333 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Click on the “Option”>>Macrocode…(M) There is a New Macrocode dialog window when you build the macro: 1. Choose the HMI where the macro is build, for example HMI0. 2. There is a default macro name(macro_0.C) in the File Name, user can rename it . 2. Click on OK to enter the macro edit window. 9.2.2 Delete Macro Right click the macro in the Project files window; choose the delete to delet the macro. As shown in the following picture: Note that the delete operation of macro does not support undo operation, 9.2.3 Rename Macro Right click the macro in the Project files window; choose the Rename Macro to rename the macro. As shown in the following picture: 334 Advanced Part Macro 9.2.4 Program Macro 1 Define the macro variables before program the macro. Macro Variables In macro, the unit whose value can be changed is called variable, each variable has a name and a initial value, it takes a memory unit in the memory. Variable name When user builds a new variable, the default name is Param and user can modify the name. The definition of macro name must follow the principle of C language, the following are exceptional case: 1. Cannot use the reserved word of language C code. 2. The variable name is not case sensitive(not C language standard) 3. The variable name must start with 26 English letters 4. The variable name only supports 26 English letters, number and underline. 5. The number of group data must be from 2 to 1024, but the number of (unsigned) shot group data cannot be 4, the number of int/float group data be 2.( (not C language standard)) The type of macro variable There are internal variables and external variables in the macro variables Internal variables: they are the registers in HMI. The internal variables can be defined in the Parameters window; it also can be defined in the macro edit window directly. External variables: they are the registers in the PLC/controller which is connected to HMI. The external variables must be defined in the parameters window, and then they can used in the macro edit window. The data type which is supported in macro variable Data Type Bit Data Length 1bit Description Bit variable, 0 and 1 335 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Signed short 1word(16bits) Signed short integer variable, -215~(215 -1) Unsigned short 1word(16bits) Unsigned short integer variable,0~(216-1) Signed int 2word(32bits) Signed integer variable,-231~(231-1) Unsigned int 2word(32bits) Unsigned integer variable,0~(232-1) Float 2word(32bits) Single float variable Double 4word(64bits) Double float variable The write & read type of macro variable write & read Description Read Read the register before the C code is executed, the register will not be read when the C codede is running. Write Write the register after the C code is executed, the register will not be write when the C Read/Write Read the register before the C code is executed and wirte it after the C code is executed. Usually, we define the registers which only need reading as Read type; the registers which need writing have read operation too, so we define them as Read/Write. Regarding some special registers, which are write only, but cannot be read, we can define them as Read. Therefore , in the assignment instruction, the variables at the left side of“=”icon are usually defined as Read/Write and variables at the right side of “=”icon are usually defined as Read Operation of macro variable Right click variable list in the macro variable window, user can choose the add/delete/modify/export/import macro operations. Detail descriptions of variable operations Detail descriptions of variable operations Add Variable Add the new variable to the macro Delete Variable Delete the selected macro Modify Variable Modify the attributes of selected macro 336 Advanced Part Macro Export Variable Export the defined variables to PC in a CSV file. Import Variable Import the variable CSV file to the macro variable window. The notes of macro variable (1) When defining the variable, make sure that there is no overlap in the address range, for example, the LW1000 is defined as a float variable A (double words), that is A takes two addresses: LW1000 and LW1001. If user defines another variable which uses LW1001, there will be error in the macro calculation. (2) The macro only supports the logic and arithmetic operation, but do not supports char type operation. (3) When the variable uses variable station number, especially when the special registers are used as index, the value in the index registers must be modified before macro execution, so the modified station number can be effective in the macro. If the index value is set in the macro, the modified station number can be effective in the next execution of macro. (4) The Export/Import operation only supports export/import all the variables, but not supports export/import a single variable. (5) When user uses Excel to edit exported variable CSV file, note that the ParamName~StationNumID are default formwork, do not modify them or there will be error when you import the CSV file to the macro variable window. Program the C code in the Macro Edit Window ………… ……………… 337 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 1. Add the note information in the macro, so you can check and modify the code conveniently in the future. 2. Use the tab and line break to make the macro a good structure. 3. Do not delete or modify the default code in the macro edit window, press the Enter before “return” to add your code. 3. After the macro is build, save and compile the HMI program , then check if there is any error information in the Message Window . 9.2.5 Execute Macro There are 6 methods to execute the macro in Kinco HMIware, user can choose one method according his application. 1. Triggered when the HMI system starts. Set initialization macro in HMI Attributes>>HMI Extended Attributes, this macro will be trigged when the HMI starts, user can use this macro to set the initialization value of some parameters and transmit some recipe value. 2. Triggered by Function Key Use the Execute Macro function in the Function Key, when the function is pressed , the macro will be triggered once 3. Triggered by Timer There are many trigger method in the Timer, it is very flexible to trigger macro by timer. 4. Triggered by PLC Control When the certain register satisfies the setting condition, the macro will be triggered. 5. Triggered by Event The macro is triggered when the event is triggered 6. Triggered by Notification User can use notification in Control Setting to trigger macro. 9.3 Macro Application For example, we use the value of D100 (PLC register) to change the state of M0 (PLC register), we make this in a macro as an example: when the value of D100 is 123, M0 is 1, or the M0 is 0. 338 Advanced Part Macro First, build a macro, set the macro name “ouput status.c” Then define the variable D100 and M0 in the Parameters Window in macro. Write the following macro code in the macro edit window. Save the project, close the macro edit window then switch to the HMI program edit screen, make the program as follows: Bit State Lamp, which is used to display the state of M0. Its attribute are as follows: Read Address M0(PLC register) Graphics Use Vector Graphics, Number Input Component, which is used to input the value of D100, its attributes are as follows: Read/Write Address D100(PLC Registers) Graphics User Vector Graphics, Timer Component,which is used to execute the macro, its attributes are as follows: Exectution Cylcle 1×100ms Execute Macro Output status Save, Compile and Execute: 339 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 123 0 123 9.4 Local Variable Function When you use the internal (local)l variable, you do not need to define the variable in the macro parameters window, you can define it macro directly, that is to use the local variable of HMI. The advantage of using local variable is that the local variable in the macro can be read/write in real time and the execution speed is faster, performance is better. At the same time, it also saves the time of defining variables in the macro parameters window. In the macro edit window ,there is demo code(example) to read/write the local variable, user can write the macro code to read/write local variable according the demo code, see as follows In this demo code, we transfer the values in LW200 and LW201 to the LW202 and LW203. We will explain to you how to use the local variable function in the following example. For example, use the macro to achieve the addition calculation: LW100(HMI local register) adds LW101(HMI local register) and transfer this result to LW102(HMI local register), the macro code is as follows: 340 Advanced Part Macro In this example , ReadLocal ("LW", 100, 2, (void*)buf, 0) means read the value in LW100 and LW101 and give this value to buf[0] and buf[1]. buf[0]=buf[0]+buf[1] means addition calculation WriteLocal ("LW", 102, 1, (void*)buf, 0) means write the calculation result to the LW102. Save, Compile and Execute: 9.5 Array Application Array is a group of variables, who has the same data type and name. These variables are called element of array. Each element has its own serial number in the array, this number is called index. User can distinguish these elements by their index. The total number of the element of an array is also called the array length. We explain the array to you in the following example: For example, use macro to assign values to 100 continuous registers which starts from D100(PLC register), if we do not use array , we need to define 100 registers in macro parameters window and assign value one by one in the macro code. See as follows: Macro code: 341 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software In the above macro code, the variable name has no unified rule, at the same time , it also takes too much time on define the variables. If users use the array, they can define these variables in one array, see as follows: Macro code: User can use a name and index to representation a variable in the array. For example, data [0] means the first variable in a array, data[1] means the second variable in a array. The data is the variable name of this array, the number after data is the index of this array, we need to put the index to a []. 342 Advanced Part Macro For example, the following example is to define a array variable, then use loop statement to assign 10~15 to the array elements, these data will be displayed on the Number Display Components. The variable is defined as follows: Macro code: Save , compile and execute: Actually, array is a list of data which has the same data type in the memory. Take the above array for example; a[i] starts from the number 100 in the memory. The content and value of this array are as follows: Variable a[0] a[1] a[2] a[3] a[4] a[5] Value 10 11 12 13 14 15 343 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Memory Unit D100 D101 D102 D103 D104 D105 1. When users visits or assign array variable, they need to according to the defined data type. 2. The indexes of array are inter, which starts from 0, not 1. The index n means the (n+1) variable 3. The array a[n] has n elements, but there is no a[n] in these elements. If user uses the nonexistent elements in macro, there will be a overflow error. 9.6 Some Notes on the Macro The values of external variables in the macro are read once when the macro is triggered. The macro will not read it again or in real time in the macro execution process. So the macro result will not be changed if the registers are changed from outside during the macro execution process. When we use the macro, we need to make sure that all the input value are ready before we trigger the macro, or we may cannot get the expect result. The macro result is output once when the macro is finished. The external variable value will not be changed during the macro execution process When we use the macro , we need to make sure that the macro is finished and all the outputs are updated, then we can get the right result.. It is meanness to write the Read Only variable and it is meanness to read the Write Only variable. If the variable needs to be read and write, please define it as R/W. Besides, user must assign value to the variable which has write operation attributes(Write Only or R/W variable) User can define the temporary variable in the macro according to the C language, but can not set the global variable and static variable. If the global variable is needed, please use the LW, LB register. One macro can not call other macros in Kinco HMIware, if user wants to use the Function Call as the C language, they can use a trigger bit in one macro to trigger other macros. 344 10 Password Kinco HMIware provides powerful password function for users, to ensure the security of user’s intellectual property. The passwords are used for project protection, window protection, and important component protection. Project protection functions: Password protection for opening project Password protection for uploading project from HMI Prohibit uploading project from HMI Password protection for decompiling project Prohibit decompiling project Operation window protection: To protect important windows, passwords must be entered when accessing important windows. Component protection: To avoid disoperation, user name and password must be entered to access some important components. ! 1. When project password, uploading password and decompilation password are used, please keep the passwords in mind. The manufacture does not provide factory recovery and universal password service. 2. The system default passwords for decompiling and uploading are 888888. 3. When the password is 0 or Null, system will automatically default to not using password. When passwords begin with 0, 0 is invalid. Differences between User level and User permission: Difference Security Level User Permission Level Range 16 levels(0~15), level 0 is invalid 32 users, 32 operation permissions, User 0 is valid User Name None Available Logout time None Available Not support Support Support Not support Users with low security level password A user can possess multiple operation permissions, cannot access high security levels; and different users can possess the same operation high security level is the “authority”. permission. There is no hierarchy of user Add/Delete levels or permissions in HMI Modify password in HMI Access Restriction 345 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software System reserved register Users with high level password can permissions, access low security level windows or password are needed to execute corresponding components. operation. only user name and correct The involved system reserved registers are different. 10.1 Project Protection 10.1.1 Project Password Protection To prevent unauthorized access and protect user’s intellectual property, passwords are required to open project file of .wpj. Set project password for first time Open the software, single click【File】—【Project Password】, then attribute box of 【Project Password Setting】will pop up,input the password and confirm it. The project password will take effect when open the project next time. Enter password to open project Once project password is set, password entry box will pop up when opening the project again. Enter correct password to open the project, otherwise, error prompt box will pop up. If entering password wrong continuously for 3 times, it would pop up a dialog box showing【Invalid Password. Project cannot be opened!】,then user needs to single click【File】menu—【Open】. Modify or cancel project encryption Open the encrypted project, single click【File】menu—【Project Password】,the attribute box of 【Setting Project Password】 will pop up. To modify password, users need to enter old password, and at the same time set new password. To cancel the password, users only need to enter the old password, leave the new password box blank. Single click 【OK】button., then the modification will take effect when opening the project next time. 10.1.2 Upload Password Protection and Prohibit Uploading Upload Password setting Project allows uploading by default, but upload password is required to prevent unauthorized operation. Default password is “888888”. 346 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor Upload Password setting: Check the option of 【Allow Upload】in 【HMI Attributes】—【HMI Extended Attributes】page. After upload password is set, dialog box of 【Password input】will pop up when uploading, as shown in following pictures: 1. Upload password cannot be null. 2. Data package loss may occur during uploading, then restart the HMI and upload again. 3. Project allows uploading by default, but upload password is required to prevent unauthorized operation. Default password is “888888”. Prohibit uploading: prohibit uploading project from HMI. The specific setting is: 【HMI Attribute】—【HMI Extended Attributes】,do not select the option of【Allow Upload】. When prohibit uploading is set, prompt box will pop up if forcibly upload: 347 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 10.1.3 Decompilation Password Protection and Prohibit Decompiling Decompilation setting Decompilation is used to convert the pkg files running in HMI to wpj files, which can be opened and edited by Kinco HMIware. For new project, system allows decompilation by default, and the default password is“888888”. Setting of decompilation: Select“Allow Decompile”in 【HMI Attribute】—【HMI Extended Attributes】, and set password. For projects that decompilation passwords have been set, when clicking decompilation, password entry box will pop up as shown in following picture: Prohibit decompilation Prohibit decompiling: Prohibit decompiling project from HMI. Do not check the option of【Allow Upload】in【HMI Attribute】—【HMI Extended Attributes】 page, to prohibit user decompiling.pkg file to wpj. 348 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor The pkg files that are set to prohibit decompiling can still be downloaded into HMI. When prohibiting decompilation is set, prompt box will pop up if forcibly decompile: 10.1.4 Download Password Protection Set download password to HMI, to prevent user project saved in HMI being covered by unauthorized operation. Do not use download password Projects do not use password by default. Settings of no use of password: Do not select the option of【Use Download Password】in【HMI Attribute】—【HMI Extended Attributes】 page to do not use password. If download password is not set, the dialog box of download password will not pop up the next time when you download project into HMI. Users can download project into HMI directly. 349 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Use password Use password: Select the option of【Use Download Password】in【HMI Attribute】—【HMI Extended Attributes】 page and set password. The default password is “888888”. When project running in HMI is set to use download password, then【Download Password Dialog】box will pop up next time when user download project into HMI, as follows: If input password is wrong, password error prompt will pop up. Only enter password correctly then project can be downloaded into HMI. 1. When set or modify download password in HMI attributes, users have to download project into ! HMI for the first time and restart HMI, then download password will take effect. 2. After the password is set, please keep it in mind, otherwise, configuration project download will fail. Manufacture does not provide factory recovery and universal password service. 10.2 Window Protection For windows with important parameters or components, user could protect these important windows by security level function. 10.2.1 Window Password Setting Set the number of security levels and corresponding passwords in【HMI Attribute】—【Security Levels Setting】, and system default passwords are“888888”. 350 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor ! 1. Support at most 16 security levels from 0 to 15. Level 0 indicates that there is no password; Level 15 is the highest security level. The bigger the number is the higher the level. 2. The password cannot be zero or empty; when passwords begin with 0, 0 is invalid. 3. The maximum value of password is 99999999. 4. Security level is valid only for base window and not available for other windows. 5. Users with high security level can access low security level windows; While users with low security level cannot access high security level windows. 10.2.2 Security Level Setting of Window Access【Window Attribute】page—【Security Level】and choose the corresponding security level. 351 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ! Software will remember the password input for the first time by default, as long as HMI is powered continuously, do not need to enter the password again when enter into the window next time. If the option of 【Switching to the lowest security level when window closed】is checked, then the password need to be entered again when accessing the window next time. 10.2.3 System reserved registers related to security level Address Description LW9040~9041 Double words, is for inputting password of 【Security Level】 LW9042 Display the security level of current base window LW9043 Force to lower the security level 10.2.4 Security level password input window 【Frame9:Login Window】is provided by the system for security level password input. 352 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor [Frame9:Login Window] is for inputting passwords of security levels and user permissions. User using security level function only need to input appropriate password of security level. 1. The system reserved registers referred in【Frame9:Login Window】could be found in 【Chapter 14 Registers】of this manual 2. User could move the window by the control bar on the top of 【Frame9:Login Window】 10.2.5 Modifying Password Online Kinco HMIware supports security level password modifying online. ! User permission password does not support online modification System reserved registers for modifying security levels Addresses of system reserved registers Addresses of system Description reserved registers Description LW10024~10025 Level 1 password. Double word LW10026~10027 Level 2 password. Double word LW10118~10119 Level 3 password. Double word LW10120~10121 Level 4 password. Double word LW10122~10123 Level 5 password. Double word LW10124~10125 Level 6 password. Double word LW10126~10127 Level 7 password. Double word LW10128~10129 Level 8 password. Double word LW10130~10131 Level 9 password. Double word LW10132~10133 Level 10 password. Double word LW10134~10135 Level 11 password. Double word LW10136~10137 Level 12 password. Double word LW10138~10139 Level 13 password. Double word LW10140~10141 Level 14 password. Double word LW10142~10143 Level 15 password. Double word 353 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 10.2.6 Application of Passwords Required for Switching Windows The following example describes how to protect the window by the security level function. 【Example】Switch the window from window 0 to window 10 by switch window function of “Function Key” component, the window will switch only when the password is entered correctly. In this example, set security level of window 0 to 0, set security level of window 10 to 1 and the password is 123456. Set security level password In the attribute page of【HMI Attribute】—【Security Level Setting】,set level 1 password to 123456. Create a Function Key component in window 0, and the attributes setting is as follows: Function Switch Window: Chang window【10:Frame10】 Tag Use Tag; State 0: Switching window 10; State 1: Switching window 10. Graphics Use vector graphics: Control Setting Select【Conditional Enabling】;Check【Permission Control】; Check 【Select Permission:1】;Check【Auto show login window】. Set the attributes of window 10 and create a Function Key component to switch to window 0. Double click at the blank area of window 10 to open the 【Window Attribute】, and set its attributes as follows: Security Level 1 Switching to the lowest security Check level when window closed* ※ When the option is checked, the current window will be set to the lowest security level when window closed. Password is required to input again when access high level windows; When the option is not checked, there is no need to input password when access windows with the same security level. Set the attributes of Function Key as follows: Function Switch Window: Chang window【0:Frame0】 Tag Use Tag; State 0: Switching window 0; State 1: Switching window 0. 354 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor Graphics Use vector graphics: Save and compile During running, touch Function Key component in window 0 to pop up password input window 【Frame9:Login Window】, and input “123456”to the【LEVEL PASSWORD】box to switch to window 10. 10.3 Component Protection Some important components are set with permission /security level control. Only users with higher or equal permission/ security level could operate to prevent wrong operation. There are two ways for component protection: security level protection, user permission protection. 10.3.1 Security Level Protection for Components Settings of Security level protection for components are similar with window protection. ☞For more details about components using [Security level protection],please refer to [Advanced Part 10.2.6 Application of passwords required for switching windows] 10.3.2 User Permission Protection for Components When【Permission control】is set to a component,then only users with corresponding permission can operate this component. User name and access password setting Open【HMI Attribute】—【User Permissions Setting】,in the box of 【User Permissions Setting】,select 【Enabled】and input User Name,Password, Logoff Time and Permissions. 355 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ! 1. Password only supports number, but does not support other characters. The range of password is 0~2147483647. When password is set to 0, indicating no password in use. 2. Range of logout time is 0~2147483647 minutes. 0 indicates that do not log off and permission remains in effect. The logoff time is timed from the last time operation finished after login. 10.3.3 System Reserved Registers Related to User Permissions Besides set user permission in【HMI Attributes】—【User Permissions Setting】 ,the following system reserved registers can also be used for user permissions setting: Address Function Description LW9486~LW9501 Input user name for login 32 characters at most LW9502~LW9503 Input user password for login Double word LW9504~LW9505 Display permission of current user LB9165 User login confirmation LB9166 User logout confirmation Double word , read only, display 32 bits corresponding permission Set ON to execute login operation, then set OFF automatically Set ON to execute logoff operation, then set OFF automatically 10.3.4 System Reserved Registers Related to Add/Delete Users and User Permissions Online Besides add/delete users and user permissions in 【HMI Attributes】—【User Permissions Setting】,user also can add/delete users and user permissions online. See the table below for system reserved registers related to add/delete users and user permissions online: 356 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor Address Function Description LW9486~LW9501 Input user name for login 32 characters at most LW9502~LW9503 Input password Double word corresponding to user name LW9506~LW9507 User permission assignment Double words, readable/writable, 32 permissions assignment, LW 9506~9507 corresponds to permission 0~31 separately. LW.B corresponds to bits of LW 9506~9507. For example: LW.B 9506.0 indicates permission no. 0. LW.B 9506.A indicates permission no. 10 LW9508~LW9509 Logout time for user Double words, in minutes permission LW9510~LW9511 Confirm password for Double word adding/deleting user LB9167 Confirm to add user Set ON to execute adding user, then set OFF automatically LB9168 Confirm to delete user Set ON to execute deleting user, then set OFF automatically LB9190 Executive mark of user The bit will be set to ON when execute operations of Add/Delete management users Operation failure of user The bit will be set to ON when operation of user management fails LB9191 management ! 1. Only users and user permissions added online can be deleted online. 2. User permissions do not support modify passwords online, but user could modify password through adding/deleting users online. 10.3.5 Window for User Permission Password Input 【Frame9:Login Window】 is provide by the system to input user permission password. 357 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software If user permission function is use, users only need to input corresponding “USER NAME” and “ACCESS PASSWORD” then click “Login”. 1. System reserved registers referred in【Frame9:Login Window】can be found in 【Chapter 14 Registers】. 2. User could move【Frame9:Login Window】by the control bar on the top of the window. 10.3.6 Application of Security Level Protection for Components 【Example】Correct password required before operation of “Bit State Switch” component. In the example, security level is used to protect component, and set minimum level at least 2 to operate this component. Open 【HMI Attributes】—【Security Levels Setting】. Detailed settings are as follows: Create a bit state switch component in window 0, and set its attributes as follows: address LB0. Switch Type: Toggle. 【Control Setting】—【Conditional Enabling】—【Security Level】—【Minimum level: 2】—【Auto show login window】. Read/Write address LB 0(HMI local register) Switch Type Toggle Graphics Use Vector Graphics: Control Setting Select【Conditional Enabling】;Check【Permission Control】; Check 【Select Permission:2】;Check【Auto show login window】 Save and compile During running, when touch the bit state switch component, password input window【Frame9:Login Window]】will pop up, then input level 2 password“222222” or level 3 password “333333” in the password level box. After confirm, user could operate the bit state switch component; If input level 1 password or wrong password, then the operation will fail. 358 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor 10.3.7 Application of User Permission Protection for Component 【Example】Set 3 users: Administrator,Engineer,Operator. The 3 users have different permissions. Operator can operate number input component; Engineer can operate bit state switch component; Administrator can operate both the number Input component and bit state switch component. User ID User Name Password Logoff Time Permission User 0 Operator 111111 10 minutes Operator permission User 1 Engineer 222222 10 minutes Engineer permission User 2 Administrator 333333 1 minutes Operator permission and engineer permission Registered user and corresponding permission in【HMI Attribute】—【User Permission Setting】, the settings are as follows: User 0: Enable User 1: Enable User 2: Enable User Name Operator Password 111111 Logoff Time 10 Permission Permission 0:Operator permission Check Permission 1:Engineer permission Uncheck User Name Engineer Password 222222 Logoff Time 10 Permission Permission 0:Operator permission Uncheck Permission 1:Engineer permission Check User Name Administrator Password 333333 Logoff Time 1 Permission Permission 0:Operator permission Check Permission 1:Engineer permission Check 359 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Set user permission control for components Create a number input component and a bit state switch component, and the attribute setting is as follows: Number input component Read/Write address LW 0(HMI local register) Graphics Use vector graphics: Control Setting Select【Conditional Enabling】;Check【Permission Control】,Select Permission:0 Operator permission; Check【Auto show login window】 Bit state switch component Read/Write address LB 0(HMI local register) Graphics Use vector graphics: Control Setting Select【Conditional Enabling】;Check【Permission Control】 ,Select Permission:1 Engineer permission; Check【Auto show login window】 Save and compile During running, touch number input component to pop up password input window 【Frame9:Login Window】, and input “Operator” to the 【USER NAME】box and“111111”to the【ACCESS PASSWORD】box. Then click 【login 】 to login Operator permission. Now user can operate the number input component. Operations for other components are similar. 360 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor 1. Logoff time: it is the valid time after login,user permission will be lapsed automatically after the time limit. 2. User name is case sensitive. 【Example】Add/Delete user permissions: Take MT5420 for example: (1)Window 0 1 3 Function key component is used to pop up window 10, and attribute settings are as follows: Function Switch window: popup window Graphics Use vector graphics: Tag Use Tag: Add user Function key component is used to pop up window 11, and attribute settings are as follows: Function Switch window: popup window 361 2 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Graphics Use vector graphics: Tag Use Tag: Add user User info display component is used to display user’s information, and attribute settings are as follows: Separator Setting Color: Black; Style: ------ Background Setting Background Color: White; Title Bar Background Color: Green; Border Color: Black Border Width 2 (2)Window 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Function key component is used to close keyboard, and attribute settings are as follows: Function Keyboard Function: Escape Graphics Use vector graphics: Function key component is used to move keyboard, and attribute settings are as follows: Function Switch Window: Popup window title bar 362 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor Graphics Use vector graphics: Text input component is used to input user name, and attribute settings are as follows: Read/Write address LW9486 Word Length 10 Graphics None Number input component is used to input password, and attribute settings are as follows: Read/Write address LW9502 Numeric Data Word Length:2 words;Data Type: 【password】; Data Width【DWORD】 Graphics None Number input component is used to confirm password, and attribute settings are as follows: Read/Write address LW9510 Numeric Data Word Length:2 words;Data Type: 【password】; Data Width【DWORD】 Graphics None Number input component is used to set logout time, and attribute settings are as follows: Read/Write address LW9508 Numeric Data Word Length:2 words; Data Type【unsigned int】,Data Width【DWORD】 Graphics None Bit state switch component is used to select user permissions, and attribute settings are as follows: Write address LW.B9506.0 Switch Type Toggle Tag None LW.B9506.1 LW.B9506.2 LW.B9506.3 Graphics Use vector graphics: Bit state setting component is used to confirm to add users, and attribute settings are as follows: Write address LB9167 Switch Type On Tag Use Tag, 0: Add Graphics Use vector graphics: (3)Window 11 363 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 2 1 3 4 5 6 Function key component is used to close keyboard, and attribute settings are as follows: Function Keyboard Function: Escape Graphics Use vector graphics: Function key component is used to move keyboard, and attribute settings are as follows: Function Switch Window:Popup window title bar Graphics Use vector graphics: Text input component is used to input user name, and attribute settings are as follows: Read/Write address LW9486 Numeric Data 10 Graphics None Number input component is used to input password, and attribute settings are as follows: Read/Write address LW9502 Numeric Data Word Length:2 words;Data Type: 【password】; Data Width【DWORD】 Graphics None Bit state switch component is used to confirm password, and attribute settings are as follows: Read/Write address LW9510 Numeric Data Word Length:2 words;Data Type: 【password】; Data Width【DWORD】 Graphics None Bit state setting component is used to confirm to delete users, and attribute settings are as follows: Write address LB9168 Switch Type On Tag Use Tag; 0: Delete 364 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor Graphics Use vector graphics: Delete user permission is only valid for the users added in HMI. Users set in the configuration project cannot be deleted (4)Save, compile and offline simulation Touch the 【Add User】button, add user dialog box will pop up. Input the user name to be added and the corresponding password, confirm it, then click “Add” to complete the operation. Touch the【Delete User】button, delete user dialog box will pop up. 365 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Input the user name to be deleted and the corresponding password, confirm it, and then click “Delete” to complete the operation. 366 11 Recipe/ RecipeEditor Recipe data is saved on the HMI and can be stored inside the area power down. Recipe data can be stored in the RW and FRW register. For with USB HOST interface or SD card slot on the HMI, the recipe data can also be stored in the ERW register. RW, FRW and ERW distinction as follows: Recipe Register RW Description RW is specially designed for HMI recipe memory SRAM physical storage area that is defined by the address type. When the HMI is powered down, SRAM backup battery sustains by the HMI, but back-up battery power is low, or when no electricity, RW data will be lost. SRAM no endurance limit FRW FRW is dedicated to the physical storage area HMI FLASH address type definition. The data stored in FLASH FRW, not because of HMI powered off or HMI backup battery power and loss of data. But there are erasing times limit FLASH ERW0~2 ERW0 ~ 2 is dedicated to the physical storage area defined in the external memory address type. The data stored in the ERW, not because of HMI powered off or HMI backup battery is dead and losing data RW, FRW, ERW using methods similar, the following content mainly RW, for example, no longer on the FRW and ERW additionally described. 11.1 Register Related to the Recipe Register/ Component Descriptions RB The absolute addresses of the recipe bit addresses saved in the SRAM. RBI The index addresses of the recipe bit addresses saved in the SRAM. FRB The absolute addresses of the recipe bit addresses saved in the flash. FRBI The index addresses of the recipe bit addresses saved in the flash. RW The absolute addresses of the recipe word addresses saved in the SRAM. RWI The index addresses of the recipe word addresses saved in the SRAM. FRW The absolute addresses of the recipe word addresses saved in the flash. FRWI The index addresses of the recipe word addresses saved in the flash. ERW0~2 The absolute addresses of the recipe word addresses saved in the external memory. ERWI0~2 The index addresses of the recipe word addresses saved in the external memory. LW9000 The data in LW9000 is the offset of the index address Data Transmission Transfer the data in recipe data to the data in PLC or HMI. Timer Recipe Data 367 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software General PLC Control/ General PLC Control (Extend) 11.2 Method for Checking the Recipe Size 11.2.1 Method for Checking the RW Size The SRAM capacity (RW size) is different from different types of HMI. Through the following ways user can check the RW size. For example: Take MT5320T for example: Check in Kinco HMIware software Move the mouse to the MT5320 icon in HMI in Graph element window, the system will automatically display the relevant information of this HMI. The [Recipe Size] is the RW size. The recipe size of MT5320T is 256k words that are 512 K Bits. Check in selection guide Check the recipe file attribute after uploading the recipe by KHManager 368 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor Click [Upload Recipe] in [KHManager], and input [File Name], then click [Save]. Recipe is uploading until the “Upload Success” dialog box pop up. Check the size of recipe file uploaded. 11.2.2 Calculation for Recipe Address Range There are two following ways for calculating HMI recipe address range. Calculation based on recipe size [Example]: Take MT5320T for example, the recipe size is 256K words, that 256Kword= 512K Byte, and 1k byte is occupied by the system. The calculation is (512-1)×1024 Byte=523264 Byte. Because Kinco HMIware are addressed in words, so bytes divided by 2 becomes the word address, and then the last three digits become 0,finally get 261000 words. View through the element address range [Examples] For example create a new model for the MT5320T HMI configuration, in the Configuration Editor to create a new screen number input component, set the address type is RW, the user can view the MT5320T in the [address range], RW register address range is: 0 ~ 261000. 369 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 11.3 Usage of Recipe 11.3.1 Absolute Address The recipe memory is battery-backed SRAM (static RAM), in words for units as a storage area, each memory cell has an address corresponding recipe absolute addressing (It is assumed that the initial value of illustration only, to actually quasi) as shown: 11.3.2 Index Address Because absolute address too much, find it very difficult, so the index provides a virtual address of a temporary storage area RWI0, ..., RWIn and an index register LW9000 (occupies 2 words) by changing t LW9000 to find RW. 370 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor [Example] If the value of LW9000 is equal to 105, then the RWI0 will point to the data in address RW105. 11.3.3 Application of Recipe For example: We take the address 4x of Modbus RTU protocol for example, save the value of 4X1~4X5 to 0 recipe file and 1 recipe file. The address range of 0 recipe file is RW0~RW4, The address range of 1 recipe file is RW5~RW9. 371 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Configuration screen as shown: Text: PLC address, recipe 0, recipe 1 Multiple State Switch component used to change the value of LW9000, its attribute are: Read/ Write address LW9000 (HMI system special register) Function Control Mode: add, State Num.: 2, State No. 0 map value 0, State No. 1 map value 1 372 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor Graphics Use vector graphic: Tag Use Tag:recipe 0, recipe 1 Recipe Data component transferring the value of PLC to RW, its attribute are: Write Address 4X 1 (PLC register) Function Recipe Data: Upload from PLC to Recipe, Data Length: 5 words Graphics Use vector graphic: Tag Use Tag;0:Execute Recipe Number Input component inputting the value of the PLC register, its attribute are: Read/ Write address 4X 1 4X 2 4X 3 4X 4 4X 5 Number Display component displaying the value of RW0~4, its attribute are: Read/ Write address RW0 RW1 RW2 RW3 RW4 Number Display component displaying the value of RW5~9, its attribute are: Read/ Write address RW5 RW6 RW7 RW8 RW9 Run and input 0~4 in the PLC address 4X1~4X5, then press [Execute Recipe] button, the value of RW0~RW4 will display 0~4. Press [recipe 0] button and switch to [recipe 1], and modify the value of PLC address 4X1~4X5 to 5~9, then press [Execute Recipe] button, the value of RW5~RW9 will display 5~9. 11.4 RecipeEditor RecipeEditor is a tool in Kinco HMIware, and it is mainly used for the user to create, check, or edit the recipe file in *.rcp, *.csv, *.erp and *.frp format. 373 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software The data file in *.rcp, *.erp and *.frp format can save as *.csv file, and can open, check, edit or print by Excel. File Format Descriptions HMI own the recipe memory corresponding recipe file format, using KHManager tool can upload and rcp download files to the format of the recipe (which, file size depends on the HMI recipe memory size) It is the file format which can be identified by HMI It usually means the file format is based on the configuration settings and automatically saved to an csv external storage device or through the recipe editor to save. This particular binary file format, you can use Microsoft Excel software to open and can be to edit, save and print, and other related operations, but can not be freely modified template format, otherwise the recipe editor and HMI can not be resolved erp The file format only supported that the HMI with external memory, can be saved in USB DISK, SD card The recipe file format corresponding to the FLASH address, HMI will be only generated while used, supports a maximum address is 2G Bits, 2 × 1024 × 1024 × 1024/16 Words = 134217728 Words, when configuration, placed a number input element, the address type selection FRW, will see the range is frp 0-134217727. The number of FLASH recipe address using as the same as the HMI is open, when not in use will be released. Usually used to save the more important and not always erase the data, because the HMI powered off or battery power is not lost, but erasing times is limited. using KHManager tool can upload and download the recipe file format (upload FRW, download FRW) 11.4.1 Recipe Editor Start-up Open from the [Start] menu in the PC operation. Open from the [Tools] menu in Kinco HMIware. Click [Recipe Editor] in the [Tools] menu. Double-click [RecipeEditor.exe] in the [RecipeEditor] file document in Kinco HMIware installation directory. The RecipeEditor folder is copied to another location can be used alone. Click [Recipe Editor] button in [KHManager]-[Download Operate]. 374 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor 11.4.2 Recipe Editor User interface Menu ToolBar Status Bar Data editing area Data configuration area Menu Bar/ Toolbar Name Icon File Toolbar name Descriptions New File Create a new recipe file Open File Open a recipe file Save File Save recipe file Save As Save as a recipe file Exit Exit recipe editor ToolBar Start/ Close Toolbar Status Bar Start/ Close Status Bar File Merge File Merge HMI Merge some recipe files to a recipe file Help About RecipeEditor The version of RecipeEditor Bit Browser Bit Browser Display word register in bit format View Data configuration area There are [Read Address Setting], [Dataformat Operation], [The detail of current dataformat] and [Dataformat Operation 375 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Usage] in data configuration area. Name Read Address Setting Descriptions The Start Address The start address of the reads data segment Read Data Array The number of groups to read data Cur Format length The sum length of each data type× the number of groups RefreshData Click【Refresh Data】,display data as a new setting Select the current data format Dataformat Operation The detail of current dataformat Add Dataformat Click【Add Data format】to add the data format Delete cur Dataformat Click【Delete cur Data format】to delete the current data format Select an entry, double click, pop [Data Type Editor] dialog; - blank right-click menu, you can add, modify, delete data type Auto use dataformat After modify the data format, automatically read the current file Use Dataformat With the same effect [Refresh Data] Dataformat Operation Usage Data editing area Data editing area according to [data configuration area] set the start address, the number of data and data types to display the corresponding register address, and the user can view and modify data area data corresponding to these addresses. Hide / Show [Data Configuration area] Move the mouse to the control bar when the mouse is displayed as , pulling the control bar or click the left mouse button, you can hid [Data Configuration area]. At this moment move the mouse to place the control bar when the mouse is displayed as , pulling the control bar or click the left mouse button, you can restore the display [Data Configuration area]. 【Data editing area】to view, modify, and bit browser Directly input data in the data field [Desc1] (eg.RW1-RW9 are input 1-9), select the data bar required to bit browser, the data bar turns blue, right-click or click on the toolbar, can pop [bit browse] properties box. 376 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor [Examples] For example RW9 value is 9, bit browser form RW9: 03,00 bit address can be seen in red: ON, decimal 9 to binary form as 0000 0000 0000 1001. 11.4.3 Usage of RecipeEditor (1)Add a new recipe file: If you use the RecipeEditor in the first time, you can click icon in the toolbar and then can create a new recipe file. (2)Add Dataformat: Click [Add Dataformat] and input the new format name: e.g. “Mydata”, then click [OK] button. (3)Add Data Item The procedure of adding data type is shown as below: 377 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Data Type can be [Single data] or [Array data]. In 【The detail of current dataformats】, if each ID entry is a single data, data area address only corresponds to one column, if each ID entry is array data, and the array length is N, then the address of the data area corresponding N columns. If the [read address set area] is M, then the address of the data area corresponding to M lines. The entire data area of the format is M rows × (N0 + ... + Nx) columns, where Nx represents the x-th ID entry length of the array, if a single data, Nx = 1, if the array data, and the length of the array number N, the Nx = N Single data Value of RW0~RW9 378 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor Array data [String Data] support Unicode code type (4)Adjustment of Data Start Address and Data Length 379 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software (5)Save: Click icon, and save the current data to recipe file. After the completion of number modify, it would be click [save], otherwise the previous data will be lost after RefreshData button is pressed. (6)Modify data item (7)File Merge HMI can only download a recipe file every time. If you download the second recipe file will overwrite the first file. If you need to use a different recipe file, you can merge all recipe files to one file, then download the file to HMI. Create a 1.rcp file, default setting, and input 1~10. 20~29 Create a 2.rcp file, the start address: 20, and input 2~29. 380 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor Merge 1.rcp and 2.rcp: Click [File Merge] menu-[File Merge]. a:Select merged file type: The merged file will download to 128k words HMI or 256k words HMI. The files size of merge depends on the file type after the merger, if it is 4000 series, then the size is 256KB, if it is 5000 series, then the size is 512KB. Note: The recipe size of MT4522T is 512KB, this time the file types after merger to choose 5000 Series. b:Select the path: Select the file needed to merge. 381 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software c:File Length: the size of merged file [Example]: 1.rcp file is 20 bytes, then the file length is 20 Bytes. d:The address of the file begins to read: the starting address of recipe file. [Example]: The starting address of 1.rcp file is 0, so [The Param of the first file] –[The Address in Merged file] is 0 words. The starting address of 2.rcp file is 20, so [The Param of the second file] –[The Address in Merged file]: 20 words. e:File length: the length of recipe file. [Example]: the data type of 1.rcp and 2.rcp are single data, so the [The Param of the first file]/ [The Param of the second file]-[File length] is 10 words. f:The Address of the file begins to read: The Address of the file begins to merge. [Example]: The Starting address of the 1.rcp file is 0, so [The Param of the first file]-[ The Address of the file begins to read] is 0 words. [File length] is 10 words, that is RW0~RW9. The Starting address of the 2.rcp file is 20, so [The Param of the second file]-[ The Address of the file begins to read] is 20 words. [File length] is 10 words, that is RW10~RW19. So [The Param of the first file]-[ The Address in merged file] is 0 words, [The Param of the second file]-[ The Address merged file] is 10 words. 382 Advanced Part Recipe/RecipeEditor The Address merged file in the Param of the second file must be greater than the sum of the Address merged file and the Address of the file begins to read in the Param of the first file. g:The path for merged file: Set the name and path for the merged recipe file. h:Merge file: Execute the [Merge file] operation. The size of the 12.rcp merged file. Open the 12.rcp merged file in RecipeEditor, and the data will display in [RecipeEditor] as below: 383 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 11.5 Recipe Uploading/ Downloading/ Clearing ☞For details about, refers to [Advaced Part 8 KHmanager] 384 12 KHMonitor 12.1 Descriptions of KHMonitor KHMonitor is used to monitor the data in HMI and PLC registers through HMI. 12.2 Start KHMonitor Click【Start】-【All Programs】-【Kinco】-【Kinco HMIware v2.1】-【Tools】-【KHMonitor】 In the installation directory of Kinco HMIware,double click【KHMonitor.exe】 12.3 KHMonitor Interface Menu/Toolbar Menu File Edit View Toolbar Icon Toolbar Description Open Open an exist monitor file Save Save the monitor configuration file Save as Save as another configuration file,its format is *.khm Exit Close KHMonitor Select All Select all the monitor items in monitor window Add Add a monitor item Del Delete the selected monitor item Run Execute selected monitor register Stop Stop the status of selected monitor register Toolbar Open/Close Toolbar Status Bar Open/Close status bar 385 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software About KHMonitor Help Version information Monitor Window Monitor Window is used to display information such as Name, Value, Status, HMI/PLC, Address, Address type, Update Cycle (ms). Double click the monitor item in Monitor Window to change its setting. 12.4 How to Use KHMonitor 1) Create new monitor item: When it is first time to use KHMonitor, click in toolbar to create data monitor. 2) Enter monitor name: Enter monitor name in the popup window when creating new monitor.Default name is New Monitor0, if create another item, the No. will increase automatically. 3) Set Communication Type: Set the current connection type between HMI and PC. Set Communication Type as following figure: Communication Manager include function such as【Add】,【Modify】,【Remove】,【Remove all】,【OK】 Add: to add a new communication type between HMI and PLC. Modify: to modify the current communication type. Remove: to remove the selected communication type. Remove all: to remove all the communication 386 Advanced Part KHManager Descriptions of Communication Type Settings. Communication Type Serial Parameters Setting Select Selectcurrent currentPC PCCOM COMport. port. Ethernet Set current HMI IP. USB No need to set parameters. 4) PLC: to select the communication protocol between HMI and PLC. Descriptions of【PLC】 Drop down menu for PLC Select the corresponding communication protocol between HMI and PLC. Station PLC’s station No. HMI Device Port Select the HMI port which is used to communicate with PLC 5) Address: to set the address which needs to be monitored Descriptions of【Adderss】 Address Batch Set the address of HMI/PLC which needs to be monitored Batch Count Set the number of address which will be copied, its range is 1~1000 Address Auto Change Mode Copy by address increment/decrement. Forward Address Auto Change Increment/decrement for the address of the register After Address Auto Change Increment/decrement for the address of the register in accordance with the decimal point Note: Batch is only valid in the first time to add monitor items. 6) Address Type: to select the data type of the address, including bit, number and string. It will display the data according to selected data type when monitoring. 7) Run/Stop monitor 【Run】:Select monitor item and click icon in toolbar to run it. Press ctrl/shift icon to select more items. The data will display in “Value” after run the item. 387 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 【Stop】:Select monitor item and click icon in toolbar to stop it. Press ctrl/shift to select more items. 388 13 Print Kinco HMIware support 2 type of printing method: Local print: Printing via serial or USB interface, HMI is connected directly to the printer to print the HMI screen. Network print (remote print): Through network printer to print HMI screen. Network printing needs hardware configuration: HMI with Ethernet port and connect to the LAN, the LAN with a PC, printer, and the printer is no direct link between the HMI, and HMI does not need any drivers. Enthernet Cable 13.1 Type of Printer supports local printing Kinco HMIware supported printer models as follows: Kinco HMIware Printer Models Printer Driver Printer Interface Manufacturer Printer method Dot Matrix WH4008A31-0 WH-A52Z20-30E125 Serial Pin micro-printing 240 pixels / line 53 WH-A52Z20-40E125 Serial Pin micro-printing 240 pixels / line WH-A62R10-41E725 Serial Thermal micro-printing 192 pixels / line WH-A93RG0-00E725 Serial Thermal micro-printing 192 pixels / line Serial Thermal micro-printing 192 pixels / line WH-A62R10 WH-E173R90-00E11720 GA WH-A93RG0-00E825 Serial Thermal micro-printing 384 pixels / line 0E825 WH-T2AR10-30E82B Serial Thermal POS 384 pixels / line WH-E191RB0- WH-E191RB0-00E11820 00E1182055 55 Serial Thermal micro-printing 576 pixels / line SP-E4004SK Serial Impact dot matrix 240 pixels / line MY-POS80K Serial Thermal POS 240 pixels / line E, F MY-POS80K http://www.b rightek.com.c n WH-A93RG0-0 Siupo SP-M, D, information 389 http://www.si upo.com http://www. mypos.cn Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 13.2 Printing-related Components In Kinco HMIware, you can use the print function of specific components as follows: Components name Trigger Support Support Network Local Print Print Print Current Screen Print the specified screen Print Current Screen Print Content Register Function Key — PLC Control(Report Printout) Word PLC Control(Screen Hard Copy) Bit Event Information Logon Word / Bit Print the contents of trigger event Trend Curve Word / Bit Print trend curve ☞ For more details about the print-related elements settings, please refer to [Advanced Part 4 Compent] Report Printout You control the specified window screen printout by changing the value of the specified word registers. When the value of the specified register word changed, and is a valid window number, the window number corresponding window contents will be printed. Printing is completed; the value of the specified register address automatically changes to 0. Example:Set as shown below, when the value of LW0 is equal to 10, print the contents of the window 10. Printing is completed,the value of LW0 automatically change to 0. When the value of LW0 is equal to 11, print the contents of the window 11. [Report] function using output only execute print function does not perform the function of switching window, will not switch to the print window. Using the [Report Printout] function performs only print function and will not switch to the printed window. 390 Advanced Part Printer Event Print In the [Event Information Logon], set the print log events, when the set condition is triggered, it will print out the event contents. Example: Set as shown below, selecting [On Trigger] and [Return to Normal]: when LB0 is ON, print "temperature is too high!” When LB0 returns to OFF, print "Temperature is too high!". 391 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software If you need to print the time, check the contents in [HMI Attribute] - [Print Settings] - [Print Settings of Event Display]. ☞ For more details about Print Settings of Event Display, please refer to [Advanced part 6.1.8 Print Setting] ! [Print] - check the [Print Relative Time], if no printer is connected, HMI will be prompted to an error message "Print Error" ☞ For more details about [Trend Print], please refer to [Advanced Part 4.6.1 Trend Curve] 13.3 Pictbridge Print Pictbridge is a direct connection and picture printing standard, the devices which support this protocol can be connected 392 Advanced Part Printer together and print pictures directly. In Kinco HMIware V2.2, customer can use Pictbridge to connect HMI directly with printer and print the screen directly. This standard supports connecting devices to printer directly but do not need to connect the device to PC to print, it is very convenient for different applications. MT4000 serial HMI supports all the printers which support PictBridge protocol, user can connect HMI and this printer with USB cable on HMI USB slave port. Then they can print HMI screen and data on this printer. HMI ! 1. MT4210T、MT4220TE、MT4310C、MT4300C、MT4300CE、MT4403T\TE、MT4512T\TE、 MT4523T\TE、MT4404T、MT4424TE、MT4522T\TE、MT4620TE,MT4414T\TE,MT4513T\TE. The HMI which are produced after Dec 2013 support Pictbridge printing. 2. MT4210T、MT4220TE、MT4310C、MT4300C、MT4300CE、MT4403T\TE、MT4512T\TE、 MT4523T\TE, MT4404T, MT4424TE、MT4522T\TE、MT4620TE, MT4414T\TE ,MT4513T\TE.The HMI which are produced before Dec 2013 will support Pictbridge printing after updated the kernel and rootfs in Kinco HMIware v2.2(build131108). 3. Kinco HMIware v2.2(build131108)or higher version supports Pictbridge printing When user downloads program from Kinco HMIware or U disk to HMI, if there is information of “Please update Kernel and Rootfs”, which means user needs to update the Kernel and Rootfs. Version Information: Kinco HMIware Version Kernel Roots Need to update or not Enable PictBridge V2.1(build130805) 1828 1895 Yes Do not support V2.2(build131108) 1958 1971 No Support If customer does not need the print function in Kinco HMIware V2.2, please disable the “Enable Pint” in HMI Print Setting and then compile the program again before downloading Flow chart of update printing function 393 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Different modes of HMI USB slave port. Enable Print in HMI Attribute in Kinco HMIware Setting Items Enable Printer Function HMI in Checked Setup Window Unchecked Checked Unchecked Print Mode, can print from USB Print Mode, but cannot print from slave port, but cannot download USB slave port, because there is no program. compiled files for printing. Download Mode, cannot print Download Mode, cannot print To sum up,user must check the Enable Printer Function in setup window and Enable Print in Kinco HMIware to enable the print function in HMI. 13.4 Print Function Setting Method 13.4.1 Local Print: HMI serial is connected directly to the Printer [Example 1] MT5320T connect to WH-A93RG0-00E825 printer, print the current screen by function key. First create a new project. Enable Print and select Printer driver: [HMI Attribute]-[Print Setting]-[Enable Print] 1 3 2 Select the printer driver "WH-A93RG0-00E825" from the [Printer] list. Select the printer port connected with HMI, in this case choose "COM0". ! Same port cannot be set to print port and communication port [Baud rate / data bits / parity / stop bits] recommend using the default settings, and printer parameters must be consistent. In this case [baud] / [data bits] / [Parity] / [stop bits] are the default. You place a function key on screen0, and select [Print] - select All [Print Text]. Compile and download to HMI. 394 Advanced Part Printer The COM0 wiring connection instructions about WH-A93RG0-00E825 printer and MT5320T, please refer to [Communication Manual] Through press the function key to print current screen. Because micro-printer are monochrome printers, when editing HMI configuration project, recommended window fill color is white, the text color is black, try not to use the color pictures, so as to avoid the printing effect is not clear 13.4.2 Local Print: HMI USB Slave is connected directly to the Printer Example of how to use PictBridge function: 1. Enable the “Enable Print” in Print Setting of HMI Attributes. Choose the PictBridge as the Printer.。 2. Set the small dip switches SW1 and SW2 to ON then restart, HMI will display the set up screen, check the “Enable Printer Function” to enable the printing protocol Enable Printer Function in set up screen: 395 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 3. Set the DIP switches SW1 and SW2 to OFF then restart, HMI display the normal operation screen. 4. Use USB cable to connect HMI (USB Slave) to printer to print HMI screen and data. ! a) The USB slave port on HMI is used to download/upload program in default setting, if chick the “Enable Printer Function” in HMI setup screen, the USB port is configured as printing port, It does not support program download/upload or other functions in this mode. b) In rewrite Kernel and Rootfs mode (SW1 ON, SW2 OFF and restart), the USB slave port is always configured as download mode, the above setting can not affect this function in this mode. c) The printer may not work normally after HMI is repowered or restarted, please restart the printer if this problem happens. 13.4.3 Network Print (remote print): Through Network Printer to Print HMI Screen. Element to enable network printing setup method as follows: Components name Function Key PLC Control(Report Printout) PLC Control(Screen Hard Copy) Trigger Register — Word Bit Enable Network print Print Content Print Current Screen Print the specified screen Print Current Screen 396 Advanced Part Printer Event Information Logon rend Curve Word/ Bit Word Print the contents of trigger event Print trend curve [Example]: requirements through remote printer to print the HMI Screens. Preparation before printing: a PC, a HMI with network interface, a printer can be directly connected to the PC This example uses the HP USB printer which model is HP LaserJet P2014, HMI model is MT5320T, and use the [PLC Control] - [Report Printout] function to print the specified screen. Installed printer driver on the PC, then in the operating system [Control Panel] - [Printers and Faxes] to find the appropriate printer, and through the right-click menu to set as the default printer Run the print program on PC【NetPrint.exe】 [NetPrint.exe] program is stored in Kinco HMIware software installation directory, if the user did not change the installation directory, the default installation path is【D:\Program Files\Kinco\Kinco HMIware】。 397 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Double click to run [NetPrint.exe], if the firewall prompts [you want to keep this process?], Select [Unblock]. When printing, [NetPrint.exe] need to keep running, [NetPrint.exe] during operation will be minimized to the tray In the [HMI Attribute] - [Print Settings], set the PC IP address and port which run [NetPrint.exe]: In the [HMI Attribute]-[HMI], set the HMI IP address 398 Advanced Part Printer ! 1. The PC which connect to the printer and the PC which run the [NetPrint.exe] program can be the same, and it can also be any PC within the LAN 2. The PC which connect the printer, the PC which run the [NetPrint.exe] program and HMI are connected to the same LAN, IP address must be on the same subnet, IP address must be the same in front of three, the last one is not the same Enable network printing PLC Control] property in the [[control type] is set to "Report Output" to specify the address of the register LW0; then check [custom printing options]] and [network printing and check all the options] [print content. And then you place a "Numeric Input" component on screen 0. [Read / Write Address] is set LW0. Save and compiled, then downloaded to HMI. 399 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 1. Use [network printing] function, you need to enable the print function in related components,while local print only need to enable print function in [HMI attribute]-[Print setting] 2. Select the [Network Printing], printer color cannot be modified, the default is monochrome Cable The HMI through cross or direct network cable access network. Setting print properties Click [NetPrint.exe] icon to pop up the properties window. As shown: Property described as follows: NetPrint property descriptions Tool Print Setup Paper Direction set portrait/landscape Print Position set align left/mediate [alone]:Printers print in real time, immediately upon receiving the print job Print Print Method [merge]: After receiving the print job is not printed immediately, but covered with a total content of paper to print the print job again, this function is mainly used to save paper 400 Advanced Part Printer Checked, and choose the path, upon receiving the print job, you can save the Save to local screen pictures on your PC instead of printing. Picture format. JPG, picture naming names is the time, yyyymmdd-hhmmss, such as 20120903-110552.jpg Printer Setup Print Preview View print effect Exit Exit [NetPrint.exe] Help About [NetPrint.exe] version information HMI IP address。If the HMI with the PC connected to the same LAN, NetPrint will automatically IP address detect Change on the value of LW0, it will print the contents of the corresponding window 13.4 Print Page Application Skills When the HMI window larger or smaller than the actual width of print paper, you can set the current window to 【Print Page】, by changing the HMI window width and height to achieve print paper more or less than the actual width of the HMI window. This feature is only available for [Report printout] 1. Select [Print page], the window maximum width and height can be set to 1024 x 1024 pixels / line. 2. Once the height of the window is set to exceed the actual height of the HMI window, if the HMI runs the window, over the part will not show up. Recommended to use [Report printout], that only need to print this window, no view on the HMI. If you want to view, you can do a normal screen identical to the user. [Example] HMI model: MT5320T, the width of window is 320 pixels / line. WH-A62R10-41E725 printer support 192 pixels / line. If MT5320T connect to WH-A62R10-41E725, the HMI is wider than the width of the paper, so the window to the right of HMI 128 pixels printed out. Create a new project of MT5320T [HMI Attribute]—[Print Setting]—select[Enable Print]. [Printer]: WH-A62R10 [Port]:COM0 [Baud Rate]/ [Data Bit]/ [Parity Check]/ [Stop Bit] are default. 401 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Double-click screen0,[Window Attribute]-choose [special attribute]-[print page], and set the width is 192, height is 1024. Set control type: [Report printout] ☞ For more detail about [Report printout], please refer to [Advanced part 4.15.5 PLC Control] Cable For more details about the printer connection cable, refer to [communication connection Manual] 13.5 Print Error The following dialog box will be displayed when the printer error: When this error occurs, please check the printer power, cable, printer port, etc. are normal. ☞ For more details about shielding print error messages and modify the print error information content, please refer to [Advanced part 6.1.4 HMI System Information Text] 402 14 HMI Communication This chapter introduces the HMI supports communication and various communication configurations. 14.1 Serial Communication Serial interface that is referred to is a bit of data sent in the order. Serial communication is common in industrial control communication, which is characterized by a communication line as simple as a pair of transmission line can be two-way communication, thereby reducing costs, especially for long-distance communication, the communication distance can be from a few meters to several thousand m, the transfer speed is slow. HMI supports RS-232C, RS-485, and RS-422A three kinds of serial communication connection. 14.1.1 HMI and PC Serial Communication HMI via RS-232C serial cable to connect the PC side serial interface for user projects, recipes and other data upload / download and HMI firmware update. ☞For more details about uploading and downloading via the serial port on the HMI, please refer to [Advanced Part 8 KHManager] 14.1.2 HMI and PLC /Controller Serial Communication Single HMI via the serial port with single PLC communication, but also support multiple serial communication protocol to use the same or a different serial communication protocols PLC / controller communication. In the same COM port, can connect multiple serial communication protocol and uses the same multi-point communication PLC / controller can connect up to 255 devices. The serial communication protocols using different PLC / controller needs were connected to the HMI different COM port, and can simultaneously and use three different serial communication protocols PLC / controller communications, depending on the hardware configuration of the actual HMI decision. ! COM0 and COM1 port supports RS485 interface mode, respectively simultaneously with multiple serial communication protocol to use the same PLC / controller communication; The RS232 interface COM2 port supports only way, it does not support multiple PLC / controller communication 403 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software single HMI with a single PLC / controller communication [Example] Below a MT5320T with a SIEMENS S7-200 communication, for example, requires the HMI monitor PLC M0.0 output state. (This example uses the HMI COM0 port to connect PLC communication) Configure the device in the topology window and set the communication parameters Configuring HMI COM0 client communications parameters: [HMI Attribute]-[COM0 Setting] set the serial communication parameters ! HMI serial communication parameters with the actual PLC communication port parameters consistent Configure the PLC station number: [PLC Attribute] – [station NO.] setting 2 404 Advanced Part HMI Communication ! [PLC Attribute] – [station NO.] consistent with the actual PLC station number Edit the configuration screen Double-click the HMI in the topology window icon to open the Configuration Editor window, From the[ Graph Element window] - [PLC Parts], select "Bit State Lamp" component added to the Configuration Editor window, and set the component Attribute are: Read Address M.B 0.0(PLC Register) State0 State1 Graph Using vector graphics, After setting, save the project, compile and download. Using RS-485 communication cable for connecting the HMI and the PLC,After successful communication can be established on the HMI monitor the state of M0.0 single HMI with multiple PLC / controller communication Single HMI with multiple PLC / controller (different communication protocols) communication 405 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software [Example] Below a MT5320T with a SIEMENS S7-200 (hereinafter referred to as PLC 0), a MITSUBISHI FX2N (hereinafter referred to as PLC 1), a OMRON CP1H (hereinafter referred to as PLC 2) communication, for example, Requirements were monitored on the HMI PLC 0 of VW 100, PLC 1 of D100 data and PLC 2 in Q 0.0 outputs. (This example uses the HMI COM0 port to connect PLC 0, COM1 connected PLC 1, COM2 communication connection PLC 2) Configure the device in the topology window and set the communication parameters In the [HMI Attribute] - [COM0/COM1/COM2 Setting] According to the serial communications port of the connected PLC actual parameters were set to HMI serial communication parameters, Parameters are set as follows: HMI serial Serial communication parameters COM0 RS485-2,9600,8,Even parity,1 COM1 RS485-4,9600,7,Even parity,1 COM2 RS232,9600,7,Even parity,2 In the PLC 0, PLC 1, and PLC 2 [PLC Attribute], in accordance with the actual [PLC station number] to each station number setting: PLC Number Station number PLC 0 2 PLC 1 0 PLC 2 0 Connected to the serial port on a different HMI PLC / controller can be set to the same or a different station number, setting the station number to be connected with the actual PLC / controller station number the same. Edit the configuration screen Double-click the HMI in the topology window icon to open the Configuration Editor window, Respectively, from the [Graph 406 Advanced Part HMI Communication Element window] - [PLC Parts] select two "Number Display" and a "Bit State Lamp" component added to the Configuration Editor window, Component Attribute are set to: Number display element _1 PLC Number* 0 Read Address VW 100(PLC Register) Graph Using vector graphics, Number display element _2 PLC Number* 1 Read Address D 100(PLC Register) Graph Using vector graphics, Bit State Lamp PLC Number * 2 Read Address CIO _bit 100.00(PLC Register) State0 State1 Graph Using vector graphics, ※A multi-machine HMI by changing the components Attribute required of the [PLC number] to distinguish PLC control object. After setting, save the project, compile and download. Use the appropriate communication cable are connected HMI and PLC 0, PLC 1, PLC 2, after the success of communication is established on the HMI monitor VW 100, D100 data as well as the state of Q 0.0 Single HMI with multiple PLC / controller (the same communication protocol) communication 407 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software [Example] Below a MT5320T with three MODBUS device (hereinafter referred to as PLC 0, PLC 1, PLC 2), a MITSUBISHI FX2N (hereinafter referred to as PLC 3), a OMRON CP1H (hereinafter referred to as PLC 4) communication is cases, Requirements were monitored on the HMI PLC 0, PLC 1, PLC 2 of 4X 100, PLC 3 of D100 data and PLC 4 of Q 0.0 outputs. (This example uses the HMI COM0 port to connect PLC 0, PLC 1, PLC 2, COM1 connected PLC 3, COM2 communication connection PLC 4) Configure the device in the topology window and set the communication parameters In the [HMI Attribute] - [Serial 0/1/2 setup] According to the serial communications port of the connected PLC actual parameters were set to HMI serial communication parameters, the parameters are set as follows: HMI Serial ports Serial communication parameters COM0 RS485-2,9600,8,Even parity,1 COM1 RS485-4,9600,7,Even parity,1 408 Advanced Part HMI Communication RS232,9600,7,Even parity,2 COM2 In the PLC 0, PLC 1, PLC 2 [PLC Attribute] , in accordance with the actual [PLC station number] to each station number setting : PLC Number Station number PLC 0 1 PLC 1 2 PLC 2 3 PLC 3 0 PLC 4 0 Connected to a serial port on the HMI with PLC / controller must be set to a different station number and station number set to be connected with the actual PLC / controller station number consistent Edit the configuration screen Double-click the HMI in the topology window icon to open the Configuration Editor window, respectively, from the [Graph Element window] - [PLC Parts] selected four "Number Display" and a "bit status indicator" component added to the Configuration Editor window, element attributes are set as follows: Number display element _1/2/3 PLC Number* 0 1 Read Address 4X 100(PLC Register) 2 Graph Using vector graphics, Number display element _4 PLC Number* 4 Read Address D 100(PLC Register) Graph Using vector graphics, Bit Lamp PLC Number* 5 Read Address CIO_bit 100.00(PLC Register) State0 State1 Graph Using vector graphics, ※A multi-machine screen by changing the components required Attribute of the [number] to distinguish PLC control object. 409 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software After setting, save the project, compile and download. Use the appropriate communication cable are connected HMI and PLC 0, PLC 1, PLC 2, PLC 3, PLC 4, after the success of communication is established on the HMI monitor VW 100, D100 data and Q 0.0 state. 14.1.3 Serial Communication Related Settings (1)Kinco HMIware allowed through "Exchange serial 0 and serial 1 " option will COM0 and COM1 serial port communication parameters and settings in these two serial ports to connect devices on the exchange. ☞ For details about serial to exchange, refer to [Advanced Part 2.9 Exchange Serial] (2)Users in making redundant communication, it can provide a system through Kinco HMIware special register to mask the corresponding fault site communications. ☞ For details about the Station No. Shield, refer to [Advanced Part 15 Register] (3)When the HMI and PLC / controller serial communication failure occurs, the system will automatically prompt the corresponding fault error message. Fault error message contains information about the PLC station number in hexadecimal data display. Meanwhile, the user can customize the system to provide fault error message content or special registers through the system to mask the corresponding fault error message. ☞ For details about the System Information screen, refer to [Advanced Part 15 Register] ☞ For details about the system customization, refer to [Advanced Part 6.1.4 HMI System Information Text] 14.2 Network Port Communication Ethernet has a high transmission speed, low power, easy to install and good compatibility and other advantages, it is widely used in industrial automation control system. HMI via Ethernet communication mainly in the following two ways: One is through the ends of the Straight through Cable RJ45 connector or Crossover Cable, via a hub or switch communications; Another is through the RJ45 connectors at both ends of the Crossover Cable, not through a hub or switch communications, this approach only applies to one pair of a communication. 14.2.1 HMI and PC Network Port Communication HMI via RJ45 connectors at both ends of the Crossover Cable and PC-side network interface connector for user projects, recipes and other data upload / download and HMI firmware update. 410 Advanced Part HMI Communication ☞ For more details about HMI via Ethernet port on uploading and downloading, refer to [Advanced part 7 Compile / Simulate / Download / Upload] 14.2.2 HMI and HMI Port Communication Network HMI and HMI port communication network are the following two ways: Single HMI and single HMI communication Single HMI and single HMI via a network port communication, through both ends of the cross UTP RJ45 connector is connected directly communicate. Multiple (two or more) HMI group network communication Multiple HMI via the network port communication, need to communicate through the Hub or Switch connection. [Example] Below two MT5320T communication, for example, requires HMI0 screen control HMI1 of LB100 status output to ON. Configure the device in the topology window and set the communication parameters In the [HMI Attribute] - [HMI] - [Network Configuration Settings], click [Add] Configuring the HMI network port 411 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software communication parameters: HMI Number Communication protocol IP Address HMI0 Kinco 192.168.100.240 HMI1 Kinco 192.168.100.241 Once configured, the topology diagram and bus configurations are listed below: Edit the configuration screen In the topology window, double HMI0 icon to open HMI0 Configuration Editor window, from the [Graph Element window] - [PLC Parts], select “ Bit State Setting” added to the Configuration Editor window, the component property is set to: HMI* 1 Write Address LB 100(HMI Local register) Switch Type toggle Graphics Using vector graphics, ※In Multi-screen network, elements required by changing the properties of the [number] to distinguish between the touch screen control object. After setting, save the project, compile and download Use a crossover cable to connect HMI0 and HMI1, after the communication is established successfully, you can touch on the HMI0 Bit State Setting Part, Can be HMI1 LB100 state turns ON. 14.2.3 HMI and PLC/Controller Network Port Communication HMI and PLC communications network ports are the following ways: Single HMI and single PLC communication network port Single HMI and single PLC communication via Ethernet port,through the ends of the cross UTP RJ45 connector is connected directly communicate. 412 Advanced Part HMI Communication HMI Controller LAN port LAN port Crossover Cable Single HMI and multiple PLC network port communication Single HMI and multiple PLC communication via Ethernet port, need to communicate through the Hub or Switch connection. Multiple HMI and multiple PLC communication network port Multiple HMI and multiple PLC communication via Ethernet port need to communicate through the Hub or Switch connection. [Examples] Below two MT5320T (hereinafter referred HMI0 and HMI1) and one MODBUS TCP device (hereinafter referred to PLC0), and one OMRON CJ series PLC (hereinafter referred to PLC1) communications as an example. Require to monitor the data of PLC0 4x100 in the HMI0, and to monitor the data of PLC1 D100 in HMI1. Configure the device in the topology window and set the communication parameters 413 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software In【HMI Attribute】—【HMI】—【Network Device Settings】,Click【Add】configuring the HMI network port communication parameters。 Setting HMI: HMI NO. HMI0 IP Address 192.168.100.240 Communication protocol Kinco Modbus TCP Omron CJ Series Ethernet(TCP) HMI1 192.168.100.241 Kinco Modbus TCP Omron CJ Series Ethernet(TCP) Setting PLC:The IP address set here with the actual IP address of the PLC consistent PLC NO. IP Address Communication protocol PLC0 192.168.100.2 Modbus TCP Slave PLC1 192.168.100.201 Omron CJ Series Ethernet(TCP Slave) After configuration, the topology diagram and field bus setting are listed below: Edit the configuration screen In the topology window, double HMI0 icon,opens HMI0 configuration Editor window,from【Graph element window】— 【PLC Parts】choose “Number Display” element add to Configuration Editor window,Element attribute is set to: HMI* 1 Read Address 4x 100(PLC Register) 414 Advanced Part HMI Communication Graphics Using vector graphics, Then opens the Configuration Editor window of HMI1,from【Graph element window】—【PLC Parts】choose “Number Display” element add to Configuration Editor window, Element attribute is set to: HMI* 0 Read Address D 100(PLC Register) Graphics Using vector graphics, ※Multi-screen network elements required by changing the properties of the [number] to distinguish between the touch screen control object. After setting, save the project, compile and download. Using crossover or straight-through cable through the Hub or Switch are connected HMI0, HMI1, PLC0, PLC1, after successful communication can be established to monitor the PLC0's 4x100 data in HMI0 and to monitor the PLC1 D100 data in HMI1 14.2.4 FTP Function Kinco HMIware open the FTP functions,can transport files of external storage device to the PC via the LAN, or transport files of PC to external storage device. ! FTP function is only available with USB HOST or SD card interface and an HMI with Ethernet port. 【Examples】Through the LAN to access MT5320T U disk file, HMI's IP address is 192.168.100.241. In【HMI Attributes】—【HMI】open the property page FTP function。 Select【open FTP】,setting password:123456。 1. FTP default password is 888888. 2. FTP password are not supported characters, cannot be empty, only digits. 415 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software In【HMI Attributes】—【HMI】configure the HMI network parameters. Set the IP address of the current HMI: 192.168.100.241,,Not to modify the subnet mask and default gateway。 Save, compile, then downloading the project. Use cross or straight-through cable via Hub or Switch to access the HMI LAN. Open the IE browser or Explorer, in the address bar, enter the IP address of the HMI: ftp://192.168.100.241, Enter the system will automatically pop-up dialog [Login identity], Enter the user name: root, Password: 123456, you can log into the FTP server. 416 Advanced Part HMI Communication Open usb1 folder, internal documents can browse. But also can be copy their files to a PC or copy files from the PC to the U disk. 417 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 14.3 Field Bus Communication Fieldbus is a kind used in the production site, between devices in the field, between field devices and control devices implement two-way, string-shaped, multi-node digital communication technology. Kinco HMIware Supports field bus communication with CAN and Profibus-DP. 14.3.1 CAN Communicate Kinco HMIware provided CANOpen Node Slave HMI communication protocol can be realized as a slave device with CANOpen communication between the master devices. [Examples] Take one MT5320T-CAN screen and one CAN communications equipment for example. In Kinco HMIware topology window to configure the device and set the communication parameters Double-click the HMI icon in the topology window,in【HMI Attribute】—【HMI】—【Field bus setting】,Click【Add】 configuring the HMI communication parameters. Setting【Protocol】for"CANOpen Node Slave";The remaining parameter settings and the connected CAN device communication parameters are consistent. After configuration, the topology diagram and bus configurations are listed below: Edit the configuration screen Place the “number input/display” in configuration screen, Address Range LW8000~8031. Save and compile and download the project. Configuration of the CAN device 418 Advanced Part HMI Communication For more information on the CAN device configuration, see [Communication connection instructions]CanOpen Node Slave(CANOpenSlave protocol) related content Communications configuration and communication cables are set up, after successfully established communication, HMI can read and write operations on the CAN devices. 14.3.2 DP Communicate The DP of PROFIBUS-DP is Decentralized Periphery,is a field bus. It has the characteristics of high-speed low-cost,Used for device-level control systems and distributed I / O communications. In Kinco HMIware ,HMI software provided by the communication protocol Profibus Slave ,HMI as a slave device and supports Profibus-DP communication protocol PLC / controller communications. HMI as a slave device,HMI local address LW is mapped to PIW(D)/PQW(D),Written to or read from the PLC. The correspondence relation table of registers below: ! PLC Register Address Local address range corresponding HMI PIW(D) LW8500~8615 PQW(D) LW8000~8115 With PLC / controller communication via Profibus DP HMI must be extended with Fieldbus interfaces and the DP model [Examples] Below a MT5320T-DP and a SIEMENS S7-300 communication, for example, requires the HMI monitor PLC PQW256 data. Installing the GSD file by STEP7 software Slave devices need to have a device description file, is used to describe the characteristics of DP the device,This file is called GSD file,This file usually contains device-specific parameters: Such as baud rate, the input / output data length, IO data definition. It is an ASCII text file format,Usually provided by the device manufacturer. Kinco provided "kinco.gsd" File can find In Kinco HMIware installation directory fieldbus folder or “http://www.kinco.cn/Search.aspx?type=product&par1=1&par2=8&nodeid=45&lang=cn” “kinco MT5020 series ProfibusDP GSD file” 419 download Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software GSD file installed,Right in the HW Config directory PROFIBUS DP / Additional Field Devices / MMI find the appropriate configuration file: PLC hardware configuration Open SIMATIC Manager, in the block configuration Insert included OB1、OB82、OB86、OB100、OB121、OB122 tissue blocks: 2 1 3 Open HW Config,add Master System: 420 4 Advanced Part HMI Communication After appears the main rail station system, Configure the master system Add a slave: 421 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ! DP master system and the slave device address number cannot be the same; In addition slave device transfer rate adaptation, without setting Configuring the slave input and output resources:This example configure 16 Words Input,16 Words Output,PIW address from 256~287,PQW address from 256~287 422 Advanced Part HMI Communication Setting User_Prm_Data(0):Double-click the slave station device icon,in【DP slave】—【Parameter assignment】set User_Prm_Data(0)为 1 When LW using double word, only with SIEMENS products through DP communication, only need to User_Prm_Data (0) is set to 1; If communicate with a master device support other DP protocol, User_Prm_Data (0) defaults to 0. In Kinco HMIware topology window to configure the device and set the communication parameters Double-click the HMI icon in the topology window,in【HMI Attribute】—【HMI】—【Field bus setting】,Click【Add】 configuring the HMI communication parameters. Setting【Protocol】for “Profibus Slave”; 【Input/output Modules】Are set to 16 Words,should match with HW Config Slave device input and output resources;Slave address should match with HW Config. 423 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Input/ Output Modules should match with Master configuration, The max length are 116 words. After configuration, the topology diagram and bus configurations are listed below: Edit the configuration screen Double-click the HMI icon in the topology window,and open the Configuration Editor window,in【Graph element window】 —【PLC Parts】Select "Number Display" component added to the Configuration Editor window,Element attribute is set to: Read Address LW 8000(HMI Local address) Graphics Using vector graphics,, After setting, save the project, compile and download. Using DP communication cables are connected the HMI and PLC,After successful communication established , can monitor PQW256 data on the HM. 14.4 MPI Communicate MPI is the multi-point interface (Multi Point Interface) for short,is developed for PLC communication by Siemens. MPI communication when the communication rate is less demanding, communication data is not used when a cheap and easy means of communication. The main advantage of MPI communication CPU can establish communications with multiple 424 Advanced Part HMI Communication devices,Such as PG / PC programming, HMI device (PC) and the other PLC can be connected together to run simultaneously. MPI interface using RS-485 physical interface mode, the transmission rate can be 19.2kbit / s or 187.5kbit / s. In Kinco HMI ware in, HMI software provided by SIEMENS S7-300/400 (MPI Direct) communications protocol, as the master station and HMI MPI communication protocol support PLC / controller communications. ! With PLC / HMI controller via MPI communication must be extended with Fieldbus Interface and is-MPI model. [Examples] Below two MT5320T-MPI (hereinafter referred HMI0 and HMI1) and two SIEMENS S7-300 (hereinafter referred to PLC0 and PLC1) communications, for example, requires HMI0 monitoring PLC0 data on data block variables DB10.DBW 10. In STEP7 Software Configure PLC side communication parameters Create a New Project , Under this project insert two PLC stations , are STATION1(CPU315-2DP) and STATION2(CPU315-2DP),Respectively, to complete the hardware configuration into the CPU,Establish MPI network and configure the MPI station address and baud rate,In this example, the MPI station addresses are set to No. 2 and No. 3, and communication rate 187.5kbit / s. ! 1. Throughout the MPI network communication rate must be consistent and MPI station addresses cannot conflict. 2. When the PLC with 4 or 4 above HMI communication, Need to set the [attributes] - [Communications] to change the parameters of PG communication. For example , CPU 315-2DP,CPU default PG communication number is 1 , OP communication for the 1, S7 standard communication is 12, while the maximum number of connection resources 16; The number of the previous three together is always more than the maximum number of connection resources 16 less two, that means there are two shared an office for the first three, So S7 300 CPU is always maximum and three HMI communication, cannot be even the first four,If you need to increase the number of connecting HMI, just to reduce the number of S7 standard communication to further increase the number of PG communication and keep three of the total does not exceed the maximum number of 16 connection resources can be. To increase communication between the PLC, will have to increase the number of OP communication. Configure DB data block In the SIMATIC Manager to add the data block DB10, in this case the data required to monitor DB10.DBW 10, the definition of a variable data block DB10, the need to define DB10.DBW 0 ~ DB10.DBW 14 or more variables. 425 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ! 1. Define data block variables, note: the variable data type to be set in the HMI data type. Such as data type REAL, then the values in the HMI device data types required to single-precision floating-point 2. Ensure that the data defined in the PLC HMI block variable than the actual use of the data block variables and more. For example, used in the HMI DB5.DBW32, the PLC cannot be defined only to DB5.DBW32, but defined to DB5.DBW34 or DB5.DBW36 or more In Kinco HMIware topology window to configure the device and set the communication parameters Double-click the HMI icon in the topology window,in【HMI Attribute】—【HMI】—【Field bus setting】,Click【Add】 configuring the HMI communication parameters. Setting HMI:in【Device Name】select the appropriate configuration object, and set【protocol】 “MPI”,【Baud Rate】should be match with the actual PLC communication port consistent. ! MPI network connecting multiple master devices, pay attention to the 【master station number】 setting and cannot be the same. Setting PLC:in【Device Name】select the appropriate configuration object, 【Target Address】should be match with the actual PLC station number consistent. 426 Advanced Part HMI Communication After configuration, the topology diagram and bus configurations are listed below: Edit the configuration screen Double-click the HMI icon in the topology window,and open the Configuration Editor window,in【Graph element window】 —【PLC Parts】Select "Number Display" component added to the Configuration Editor window,Element attribute is set to: PLC No.*1 0 Read Address DBn_DBW 1000010(PLC Register)*2 Graphics Using vector graphics, ※1. A multi-screen or multi-screen multi-machine, Need to change element attributes 【PLC No.】to distinguish control object. 2. In the HMI, the address type DBn_ DBX, DBn_DBW, DBn_DBD as custom data block address. The first three data formats for the data block number, later five for the address, address less than five to the previous zero padding. After setting, save the project, compile and download. Using MPI communication cables are connected HMI0, HMI1, PLC 0, PLC 1, after the success of communication is established to monitor DB10.DBW10 in HMI0. 427 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 14.5 MODBUS Protocol Applications(Master-slave mode) MODBUS protocol is a common language applied on the electronic controller. Over this protocol, between the controller, the controller through the network (such as Ethernet), and other devices can communicate. Today, MODBUS protocol has become a common industry standard by which different manufacturers of industrial control equipment can be connected into the network, thereby performing centralized monitoring. 14.5.1 MODBUS Protocol Overview Modbus is a request / response protocol, and provide services required by the function code. Modbus protocol including ASCII, RTU, TCP, etc., does not require the physical layer. Protocol defines the controller can recognize and use the message structure, regardless of what network they are communicating. The Modbus ASCII, RTU protocol provides news, data structures, commands, and fluent manner , Data communication using Maser / Slave mode , Master station data request message, the slave receives the correct data can be sent after a message to the master station in response to the request ; master can also be directly send message modify the data from a slave, two-way read and write. MODBUS stipulates that only master station has the initiative, only a passive response from the slave, including answering error message. MT Series HMI Modbus protocol communications to achieve, follow the standard Modbus communication process: Common data frame format is as follows: Address code Address field of a message frame contains two characters (ASCII) or 8Bit (RTU). Possible from the device address is 0 ... 247 (decimal). Single device address range is 1 ... 247. To contact master device through the slave device address into the address field of the message to select from the device. When a message is sent from the device to respond, he put his address in response to the address field in order to know which device is the master device to respond. Address 0 is used as the broadcast address and all slave devices will recognize. Function code In the HMI system, commonly used function codes are as follows: Modbus Function code Name Function Corresponding address type 01 Read Coil Status Read bit(Read N Bits) 0x 02 Read input discrete Read bit 1x 03 Read multiple registers 04 Read Input Registers Reading integer, status word, float 3x 05 Write Single Coil Write bit(Write a Bit) 0x 06 Write Single Register Write integer, character, status word, float(Write a Word) 4x Reading integer, character, status word, float(Read N Words) 428 4x Advanced Part HMI Communication 15 16 Write multiple coils Write Multiple Registers Write bit(Write N Bits) 0x Write integer, character, status word, float(Write N Words) 4x Data Area Data area contains the specific function of the terminal data needed to respond to queries or the terminal to collect data. These data may be numeric, reference address or set values. For example:Function code tells terminal reads a register the data area from which you need to specify the beginning and read the number of register data, the embedded addresses and data types according to the contents of the slave varies. Error correction code Modbus protocol data needs to checksum, in addition to the serial protocol parity outside, ASCII mode uses the LRC parity, RTU mode uses a 16-bit CRC checksum, TCP checksum mode without additional requirements. Parity Users can configure the controller is an odd or even parity, or no parity. This will determine the character of each parity bit is how to set up. If you specify an odd or even parity, "1" digit will count to the number of bits in each character (ASCII Mode 7 data bits, RTU, 8 data bits). For example RTU character frame contains the following eight data bits:1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1;The whole "1", the number is four。Such as the use even parity, the parity frame bit will be 0, so that the entire "1" bits remain is four. If the odd parity, the parity frame bit will be 1, so that the entire "1" bits is 5. If no parity bit, no parity bit is transmitted, nor checksum testing. Additional padding instead of stop bits to be transmitted character frame. LRC Detect Using ASCII mode, messages include methods based LRC error detection domains. LRC field testing except the beginning of the message field colon and end carriage return line numbers outside content. LRC field is a binary value that contains an 8-bit byte. LRC value calculated by the transmission device and into the message frame, the receiving device receiving the message in the process of calculating LRC, and place it in the message received LRC field value, and if the two values are unequal, there is an error. LRC is the message of the continuous accumulation of bytes 8Bit, discarding the carry bit. LRC Simple function as follows: static unsigned char LRC(auchMsg,usDataLen) unsigned char *auchMsg ; /* Message to be calculated */ unsigned short usDataLen ; /* LRC number of bytes to be processed */ { unsigned char uchLRC = 0 ; /* LRC Byte Initialization */ while (usDataLen--) /* Send Message */ uchLRC += *auchMsg++ ; /* Cumulative */ return ((unsigned char)(-((char_uchLRC))) ; 429 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software } CRC Detect Use RTU mode, the message including the method based on the CRC error detection fields. CRC field test the entire contents of the message. The CRC field is two bytes that contains a 16 bit binary value. Calculated by the transmission equipment was added to the message. Receives the message receiving device recalculates the CRC, and with the received CRC value in the field, and if the two values are different, then an error. CRC added to messages, the low byte of the first to join, and then the high byte. CRC simple function as follows: unsigned short CRC16(puchMsg, usDataLen) unsigned char *puchMsg ; /* the message to be CRC checksum */ unsigned short usDataLen ; /* The number of bytes in the message */ { unsigned char uchCRCHi = 0xFF ; /* High CRC byte initialization */ unsigned char uchCRCLo = 0xFF ; /* Low CRC byte initialization */ unsigned uIndex ; /* CRC cycle index */ while (usDataLen--) /* Transmitted message buffer */ { uIndex = uchCRCHi ^ *puchMsgg++ ; /* Calculate the CRC */ uchCRCHi = uchCRCLo ^ auchCRCHi[uIndex} ; uchCRCLo = auchCRCLo[uIndex] ; } return (uchCRCHi << 8 | uchCRCLo) ; } 14.5.2 MODBUS Protocol Communication Format Following through several examples, and use the serial debugging tools to send and receive data frames HMI listen to learn more about the Modbus protocol communication format. The following examples are primary device HMI, PLC done from the device, and use the RTU transmission mode is described: Topology diagram is shown below: (1)01 Function Code Application Function Code 01 reads 0x10, 0x11, 0x12, 0x13, 0x14, 0x15 Bit of these six states. Placed six "bit state lamp" parts in the HMI configuration, the read address are set to 0x10 ~ 0x15. 430 Advanced Part HMI Communication Running, the host (HMI) Request Station Function First address First address no. code (High byte) (Low byte) 01 01 00 09 Read Bit Number Read Bit Number (high byte) (low byte) 00 06 CRC CRC High byte low byte 6C 0A Slave (PLC) response Station no. Function code Byte count Single byte of data CRC High byte CRC low byte 01 01 01 3A D1 9B HMI debugging tools from the serial port to send data packets HMI display 01H 01H 01H 3AH D1H 9BH 0x15 HMI reads as ON, 0x14 is ON, 0x13 is ON, 0x12 is OFF, 0x11 is ON, 0x10 is OFF. 3A hexadecimal number is covert into binary to 111,010, corresponding exactly. (2)02 Function Code Application Function Code 02 reads 1x999 this Bit state. In the HMI configuration to place a "bit state lamp" part, the read address is set to 1x999。 Running, the host (HMI) Request Station Function First address First address Read Bit Number Read Bit Number CRC CRC no. code (High byte) (Low byte) (high byte) (low byte) high byte low byte 01 02 03 E6 00 01 58 79 Slave (PLC) response Station no. Function code Byte count 01 02 01 01 02 01 Data (single-byte) CRC high byte CRC low byte 00 A1 88 01 60 48 HMI debugging tools from the serial port to send data packets 01H 02H 01H 00H A1H 88H 01H 02H 01H 01H 60H 48H (3)03 Function Code Application 431 HMI display Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Function Code 03 reads 4x 208 ~ 215 this 8 Words value. Placed on the HMI configuration 8 "Number Display" component, the read address are set to 4x 208 ~ 215. Running, the host (HMI) Request Station Function First address First address Read Word Read Word Number no. code (High byte) (Low byte) Number (high byte) (low byte) 01 03 00 CF 00 08 CRC CRC high low byte byte 74 33 Slave (PLC) response Station Functio Byte no. n code count 01 03 10 Data(5) Data(5) Data(1) Data(1) Data(2) Data(2) Data(3) Data(3) Data(4) Data(4) High low High low High low High low Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte 00 01 00 02 00 03 00 04 CRC CRC high byte low byte 72 98 Data(6) Data(6) Data(7) Data(7) Data(8) Data(8) High low High low High low High low Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte 00 05 00 06 00 07 00 08 HMI debugging tools from the serial port to send data packets HMI display 01H 03H 10H 00H 01H 00H 02H 00H 03H 00H 04H 00H 05H 00H 06H 00H 07H 00H 08H 72H 98H (4)04 Function Code Application Function Code 04 reads 3x 1023 the value of the Word. Placed on the HMI configuration 8 "Number Display" component, the read address are set to3x 1023. Running, the host (HMI) Request Station Function First address First address Read Word Read Word Number no. code (High byte) (Low byte) Number (high byte) (low byte) 01 04 03 FE 00 01 CRC high byte CRC low byte 50 7E Slave (PLC) response Station Function no. code 01 04 Byte count 02 Data High Byte Data low Byte 04 D2 432 CRC CRC high byte low byte 3B AD Advanced Part HMI Communication HMI debugging tools from the serial port to send data packets HMI display 01H 04H 02H 04H D2H 3BH ADH (5)05 Function Code Application Use 05 Function code to modify 0x 1 Bit state. Place a "Bit State Setting” component in HMI, the write address is set to 0x 1, switch type is set to "Toggle." Runtime on the HMI click "Bit State Setting" component to switch to the ON state, the serial debugging tools for the data received 01 05 00 00 FF 00 8C 3A; Be switched to the OFF state, the serial debugging tools for the data received 01 05 00 00 00 00 CD CA;(Among them, the hexadecimal value 0XFF00 requests coil to ON. Hexadecimal value 0X0000 request coil is OFF)Meanwhile, the serial debugging tools to reply to the same data. The host (HMI) Request CRC Station Function First address First address Write Bit Number Write Bit Number no. code (High byte) (Low byte) (high byte) (low byte) 01 05 00 00 FF 00 8C CA 01 05 00 00 00 00 CD CA high byte CRC low byte Slave (PLC) response CRC Station Function First address First address Write Bit Number Write Bit Number no. code (High byte) (Low byte) (high byte) (low byte) 01 05 00 00 FF 00 8C CA 01 05 00 00 00 00 CD CA HMI debugging tools from the serial port to send data packets high byte CRC low byte HMI display 01H 05H 00H 00H FFH 00H 8CH 3AH 01H 05H 00H 00H 00H 00H CDH CAH (6)06 Function Code Application Use 06 Function code writes 4x 1 this Word value. In the HMI configuration to place a "multiple state setting" component, the write address is set to 4x 1, set the mode to "set constant", set the value to 88. 433 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Runtime on the HMI click on the " multiple state setting " component, the serial debugging tools received data to 01 06 00 00 00 58 88 30; while serial debugging tools To reply to the same data. the host (HMI) Request Station Function First address First address Write Word Write Word no. code (High byte) (Low byte) Number (high byte) Number (low byte) 01 06 00 00 00 58 CRC high byte 88 CRC low byte 30 Slave (PLC) response Station Function First address First address Write Word Write Word no. code (High byte) (Low byte) Number (high byte) Number (low byte) 01 06 00 00 00 58 HMI debugging tools from the serial port to send data packets CRC high byte 88 CRC low byte 30 HMI display 01H 06H 00H 00H 00H 58H 88H 30H (7)15 Function Code Application Use 15 Function code modify the 0x 10 ~ 25 this 16 Bit state. In the HMI configuration to create a macro code: 15 function code. C, variables are defined as follows: Code is as follows: And then placed on a configuration screen "function key" component, the function is set to "execute macro code: 15 function code. C". Running, click on the function keys on the HMI, the serial data received on debugging tools for the 01H 0FH 00H 09H 00H 10H 02H FFH FFH E3H 09H, while serial debugging tools, the reply data 01H 0FH 00H 09H 00H 10H 84H 05H. The host (HMI) Request 434 Advanced Part HMI Communication First First Station Function address address no. code (High (Low (high byte) byte) byte) 00 09 01 0F Write Write Bit Bit Number Number (low byte) 00 10 Write Bit Bit Bit Data Data Byte High low count Byte Byte 02 FF FF CRC CRC High low Byte Byte E3 09 Slave (PLC) response First Station Function address First address Write Bit Write Bit CRC no. code (High (Low byte) Number (high byte) Number (low byte) High Byte 09 00 10 84 byte) 01 0F 00 CRC low Byte 05 (8)16 Function Code Application Use 16 Function code writes 4x 10 ~ 25 these 16 Words value. In the HMI configuration to create a macro code: 16 function code. C, variables are defined as follows: Code is as follows: And then placed on a configuration screen "function key" component, the function is set to "execute macro code: 16 function code. C". Running, click on the function keys on the HMI, the serial data received on debugging tools for the 01H 10H 00H 09H 00H 10H 20H 00H 01H 00H 02H 00H 03H 00H 04H 00H 05H 00H 06H 00H 07H 00H 08H 00H 09H 00H 0AH 00H 0BH 00H 0CH 00H 0DH 00H 0EH 00H 0FH 00H 10H 88H 37H.while serial debugging tools, the reply data 01H 10H 00H 09H 00H 10H 11H C7H。 The host (HMI) Request Station Function no. code First First Write Word Write Word address address Number (high Number (low (High (Low byte) byte) 435 Write Word Byte count Data(1) Data(1) High low Byte Byte Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 01 10 byte) byte) 00 09 00 10 20 00 01 Data(3) Data(3) Data(4) Data(4) Data(5) Data(5) Data(6) Data(6) Data(7) Data(7) High low High low High low High low High low Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte 00 03 00 04 00 05 00 06 00 07 Data(9) Data(10) Data(10) Data(11) Data(11) Data(12) Data(12) low High low High low High low Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte 09 00 0A 00 0B 00 0C Data(8) High Byte 00 Data(13) Data(8) low Byte 08 Data(13) Data(9) High Byte 00 Data(14) Data(14) Data(15) Data(15) Data(16) Data(16) CRC CRC High low High low High low High low High low Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte Byte 00 0D 00 0E 00 0F 00 10 88 37 Slave (PLC) response Station Function First address First address Write Word Write Word no. code (High byte) (Low byte) Number (high byte) Number (low byte) 01 10 00 09 00 10 CRC CRC High low Byte Byte 11 C7 14.5.3 MODBUS Protocol in the HMI Application In the HMI interface design applications, often encountered need to design their own microcontroller control board communication situation. In this application environment, the MCU control system designers want a simple, stable and reliable means of communication with the HMI to exchange data. The MODBUS protocol is achieved between the HMI and the equipment master-slave communication mode most commonly used way. Below microcontroller (hereinafter referred to as MCU) and HMI through MODBUS protocol (RTU transmission mode in case) communication, for example, explains how to use MODBUS protocol communication between the HMI and the MCU. Between the HMI and the MCU communication through MODBUS protocol mainly have the following two Master-slave ways: Master / Slave HMI as Master device MCU as Slave device Using protocol Modbus RTU Advantage Disadvantages HMI direct access to the MCU MCU as a slave device must constantly mapped out 0X, 1X, 3X, 4X respond to queries the HMI, CPU 436 Advanced Part HMI Communication registers. occupancy rate is high; MCU interrupt response shall be used, programming is relatively difficult. HMI as Master device Modbus RTU MCU as the master device can MCU as Slave device Slave initiate communication; do not take modified, you must regularly check the LW on the HMI configuration data is up too much CPU time. MCU can be read out to achieve them HMI local address LW, LB is inconvenient. mapped to 4X, 0 X register, write or MCU can only access the HMI local read by the MCU. word (LW), the position (LB) (1)HMI as Master, MCU as Slave (using the Modbus RTU protocol) MCU and HMI using standard Modbus RTU protocol for communication, HMI as master, MCU for the slave side, the MCU, you need to write the interrupt service routine to handle communication requests from HMI. MCU must support the standard Modbus RTU protocol, while MCU must map out 0X, 1X, 3X, 4X registers (where 0X, 1X is bit register; 3X, 4X for the word register) The recommended communication parameter is 19200, data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity. In addition to seven data bits protocol support all settings other than combinations. Baud rate range from 1200-115200, with the flexibility to choose. Communication processes First, HMI sends a request to the MCU, MCU accepts the request, a response back to the HMI. MCU can access the HMI, 4X, 3X, 0X, 1X register; the address range is 1 to 65535. ! 1. MODBUS protocol is relatively complex, demanding overtime 2. In the communication process, HMI continuously sends request packets to MCU; MCU accepts the request, the need to continue to give a response to the HMI. MCU's response is given using interrupt mode; therefore, MCU's CPU usage is high. Most of the MCU's CPU resources consumed during the communication response. Therefore, in practical applications need to be taken into account, if the MCU is used in addition to doing communication functions, there are other response functions, HMI (Master) MCU (Slave) using Modbus RTU protocol solution is not recommended, it is recommended to use HMI (Slave) MCU (Master), using Modbus RTU Slave protocol solutions HMI Power communication processes When the HMI after power (1)If the configuration page does not place any project component, the HMI will not send any communication packets External (2)If the configuration page placed engineering components and these components address types are local types (LW, RW, RWI, LB, RB, RBI, LW.B), the HMI will not send any communication packets External 437 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software (3)If the configuration page to place the component works, and these elements are not the local address type for 0X, 1X, 3X, 4X, the HMI constantly scanning configuration page of these registers, and constantly sends communication data packets (4)When using the timer device batch write bit components (consecutive addresses transmission number greater than one) when, HMI will be issued by the packet encapsulation function code: 0x0F (5)When using the timer components word element bulk write (consecutive address transfer number greater than one) when, HMI will be issued by the packet encapsulation function code: 0x10 (6)Using recipes components download operation (that is, the local word register in HMI RW data downloaded to the MCU in the appropriate register, such as 4X). When the download operation data length is greater than 1, HMI will be issued by the packet encapsulation function code: 0x10 Data communications package Assuming HMI configuration screen is placed 25 0X register address type, starting address: 20, HMI station number is 1. HMI send packets: ("H" indicates hexadecimal form) 01H 01H 00H 13H 00H 25H XXH XXH(Wherein: "XX" indicates LRC / CRC) MCU Return packets: 01H 01H 05H CDH 6BH B2H 0EH 1BH XXH XXH(Wherein: "XX" indicates LRC / CRC) HMI Communication parameter configuration HMI Port parameter settings: According to the actual physical connection mode selection set [Communication type]. Baud rate, data bits, parity, stop bits setting must be connected to the MCU and the corresponding parameters consistent. Other parameters are described below: Parameter Explanation PLC Communication HMI wait MCU response, if the MCU to set the time interval in which the response is not given, timeout the HMI that communication timeout, and then continue to send request packet, continue to wait 438 Advanced Part HMI Communication Protocol timeout 1 Inter-character timeout. HMI communication with the MCU in the process, if the communication frame characters and the time interval between characters exceeds the set time interval, the HMI think this communication process is completed, then, to deal with the communication data frame, parse packets. For Modbus protocol, baud rate calculation within the program should be based on an estimate. As follows: Protocol timeout 1 = 1.5*1000000*(1 + data bits + parity + stop bits) / baud + set adjust time bps (baud rate); Sample code (standard C language): int speed_arr[] = { B115200, B57600, B38400, B19200, B9600, B4800, B2400, B1200, B300,B150, B134, B110, B75 }; int name_arr[] = {115200, 57600, 38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, 300, 150, 134, 110, 75 }; int adjust_time_bps_arr[]={1000,4000,10000,11000,25000,40000,70000,140000, 600000,0,0,0,0}; Function: Set a baud rate adjustment values check time Parameter: baud_rate Returns: the current baud rate of the checksum time adjustment value int set_adjust_time_bps(int baud_rate) { int adjust_time; int i; for(i=0;i<sizeof(speed_arr)/sizeof(int);i++) { if(baud_rate==name_arr[i]) { adjust_time=adjust_time_bps_arr[i]; break; } } return adjust_time; } Protocol timeout 2 Reserved (users do not set) Max interval of word Occurs mainly in the HMI read data phase, in order to improve communication efficiency, (bit) block pack relatively tight group of registers connected to pack together to form a bulk read, for example, D1, 439 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software D2, D4, group packet interval is set to 10, these three registers will be taken a bulk read (read from D1 from the bulk 4 registers). Note: The group packet interval must be less than the maximum length of batch read. Max word (bits) block Protocol supports the largest number of registers to read and write batch. This function is used to package size achieve data transmission components to achieve PLC Station number setting: (2)MCU as Master, HMI as Slave (using Modbus RTU Slave protocol) MCU and HMI using standard Modbus RTU protocol for communication, MCU for remote, HMI for the slave side, the MCU, just write a simple communication read / write programs without having to write the interrupt service routine. HMI local address LW, LB is mapped to 4X, 0X register, write or read by the MCU. Registers the correspondence table is as follows: Modbus Register address range Local address range corresponding HMI 0X(1---9000) LB(0---8999) 4X(1---9000) LW(0---8999) The recommended communication parameter is 19200, data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity. In addition to seven data bits protocol support all settings other than combinations. Baud rate range from 1200-115200, with the flexibility to choose from. Communication processes First, MCU sends a request to the HMI, HMI accepts the request, a response back to the MCU. ! 1. MODBUS protocol is relatively complex, demanding overtime 2. In the communication process, MCU as the initiator of communication, initiate communication. When the HMI device accepts the request, a response back to the MCU. Therefore, MCU without constantly interrupt, do not take up too much CPU time Therefore, in practice, if the MCU is used in addition to doing communication functions, there are other response functions (recommended to use this solution). 3. HMI configuration on LW, LB data is modified, you must regularly check the MCU can be read out and realize it is not very convenient. Therefore, the actual application, the MCU written communication read / write process, you should consider requesting the HMI data interval stated in the program to give much time to wait for a communication request 440 Advanced Part HMI Communication HMI Power communication processes In this scheme, the user edit the configuration project, the component type can only select local word address register LW and the local register LB. When powered on the HMI, HMI does not take the initiative to send out a packet communication, HMI is waiting to receive state. After the MCU send request, HMI resuming a response. HM Communication parameter configuration HMI Port parameter settings: Them from the device number for the HMI station number, other communications parameters set according to specific circumstances. 441 15 VNC VNC (Virtual Network Computing) is a kind of software for screen sharing and remote operation via RFB protocol. The VNC software could transfer mouse and keyboard operation and real-time screen. VNC system is composed of client-side, server-side and protocol. The server side shares screen with client-side, while the client-side interacts with server side by monitoring and controlling server-side. VNC is OS independent. Users could use the VNC system to remote control HMI via PC, mobile and so on. 15.1 Various client-sides Kinco does not provide the VNC software. Users could download from the internet: VNC software for PC: VNC Viewer Browser: IE, Firefox… VNC software for mobile terminal: most mobile system support VNC software, for example: VNC/RDP. 1. JAVA plugin tool is required by browser access. Generally, PC has the JAVA plugin. Please refer to Java.com to install if there is no JAVA plugin on PC. 2. You can open multiple VNC Viewer clients to access to multiple HMI at the same time. 15.2 Access via LAN 15.2.1 Remote control HMI by PC via LAN 【Example 1】Remote control MT4414TE by PC. MT4414TE works as server, while PC as client. 1. Only the HMI models with Ethernet port support VNC function for the VNC function is realized via Ethernet. 1) Tools required for Client-side: 2) The related system registers of HMI are as follows: Register Function LB9290 Open VNC function. Set to “1” to open the VNC function. LB9291 Mask user operation. Set to “1” to mask user operation(check only, cannot operate) LB9292 Operation password enabled. Set to “1” to enable operation password. LB9293 Inquiry password enabled. Set to “1” to enable inquiry password. 442 Advanced Part HMI Communication LW10146~LW10147 Operation password LW10148~LW10149 Inquiry password 3) Parameter settings for HMI: Set IP of HMI as follows: 1. Take the default gateway in LAN. Set the VNC related registers: 4) Parameter setting on PC Input IP of the target HMI: 443 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Input Password (Operation password or inquiry password) Monitoring on PC: Changes on HMI is displayed on PC simultaneously, meanwhile, user could control HMI by operating on PC. 444 Advanced Part HMI Communication 1. If input inquiry password on PC side, then users only could check HMI information, but cannot operate. 2. If input operation password on PC side, then users could check HMI information and operate HMI on PC, but cannot operate. 3. If there is no password set on HMI, then no passwords required for monitoring or operating HMI. 15.2.2 Remote control HMI by mobile via LAN 【Example 2】Remote control MT4414TE by an android mobile. MT4414TE works as server, while the android mobile as client. 1) Tools required for mobile 2) Parameter setting of HMI is the same with 【Example 1】 3) Parameter setting on mobile 1. Input IP in the Address box. 2. The default port is 5900, please do not change it, otherwise, may not get connection. 3. Nickname and User name can be omitted. 4. Input operation password or inquiry password. 445 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Monitoring on mobile: Changes on HMI is displayed on mobile simultaneously, meanwhile, user could control HMI by operating on mobile. 15.2.3 Remote control HMI by browser via LAN 【Example 3】Remote control MT4414TE by browser. 1) Parameter setting of HMI is the same with 【Example 1】 2) Open the browser, input IP and port of the target HMI in the website box: http://192.168.130.8:5800 446 Advanced Part HMI Communication Input password (Operation password or inquiry password) Monitoring by browser: Changes on HMI is displayed by browser simultaneously, meanwhile, users could control HMI by operating on browser. 447 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 1. The remote control by browser is realized by a JAVA plugin running on the website. Please make sure that JAVA software has been installed on PC. 2. Default port for browser access is 5800. Please do not change it, otherwise may not get connection. 3. Only after updated kernel and Rootfs by v2.2 (build140314) software or above, the HMI can support the remote control by brower. 15.3 Access via WAN For remote access via WAN, users need to set port mapping of HMI by router. For remote access by VNC Viewer on PC via WAN, users need to map IP of target HMI to port number 5900. 【Example 4】The IP of the remote HMI is: 192.168.4.39 1) Port mapping:Choose menu“Forwarding->Virtual Servers”,click the Add New…button 2) Parameter setting of HMI: 3) Assumed that the WAN IP of the local network where the HMI located is 192.168.100.14, then, users need to input IP 192.168.100.14 into VNC Viewer and mobiles of external network to remote control HMI. Choose menu ”Network->WAN” 448 Advanced Part HMI Communication For remote access by browser via WAN, users need to map the HMI IP to port number 5800. 【Example 5】 The IP of the remote HMI is: 192.168.4.39 1) Port mapping: Choose menu“Forwarding->Virtual Servers”,click the Add New…button 2) Parameter setting of HMI is the same with 【Example 4】 3) Assumed that the WAN IP of the local network where the HMI located is 192.168.100.14, then, use the browser of the external network to visit website: http://192.168.100.14:5800 to remote control HMI. 1. The Gateway must been set in the same network segment for access via WAN. 2. The firewall and antivirus software are suggested to be closed, for it may affect the VNC function. Router mapping method: If the DMZ host is opened on PC, then users could remote control HMI by VNC without port mapping. 【Example 6】 The IP of the remote HMI is: 192.168.4.39 1) Router mapping:Choose menu ”Forwarding->DMZ” 449 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 2) Parameter setting of HMI is the same with 【Example 4】 3) Assumed that the WAN IP of the local network where the HMI located is 192.168.100.14, then,users need to input IP 192.168.100.14 into PCs of external network to remote control HMI. If users need to access multiple HMIs by VNC via WAN, then the router is required for supporting port self-definition of external network port. The model TL-WR841N (TP-LINK) supports port self-definition of external network. 【Example 7】IP of remote HMI1 is 192.168.100.35, IP of remote HMI2 is 192.168.100.36. 1) Port setting of router: add two new items in [transfer rule]-[Virtual server] 1. For access by VNC Viewer, the internal port must be set to 5900 by router, and serve port can be set as casual value. Input IP and internal port for access by VNC Viewer via WAN. 2. For access by browser, the internal port must be set to 5800 by router, and serve port can be set as casual value. Input IP and internal port for access by 450 Advanced Part HMI Communication browser via WAN. 2) Parameter setting of HMI: HMI1: HMI2: 3) Assumed that the WAN IP of the local network where the HMI located is 203.110.174.214, then, users need to input 203.110.174.214:5900 and 203.110.174.214:5901 into PCs and mobiles of external network to remote control HMI. 1. The firewall and antivirus software are suggested to be closed, for it may affect the VNC function. 451 16 Register The registers supported by HMI include local registers and external PLC or the registers of control devices. Local registers include Local Word(LW),Local Bit(LB),Recipe Word(RW) and so on. External registers include M,D,S, etc. 16.1 Local Registers of HMI 16.1.1 Bit Address Description Local bit, Local word address, local registers of HMI, don’t save data after power off. Bit extended from local word,Bit addresses extended from local words. Address Type Address Range LB 0~9999 Format DDDD:Decimal system DDDDD.H LW.B 0~10255.F No. “H” bit of the no. DDDDD word, range of H:0~f Recipe bit,Recipe bit address, local registers of HMI, save data after power off, don’t save 0~261000.F RB DDDDDD.H data when run out of batteries. Recipe bit index,Recipe bit index addresses, indirect addressing mode is adopted, save data after power off, don’t save data when run out DDDDDD.H 0~261000.F RBI 【Example】RBI50 RB address=50+[LW9000] of batteries. Flash recipe bit,Flash recipe bit addresses, using FLASH to save the data that is Erased /Written infrequently, save data after power FRB 0~134217727.F DDDDDDDDD.H FRBI 0~134217727.F DDDDDDDDD.H off even when run out of batteries, but the “erease/write”times are limited. Flash recipe bit index,Flash recipe bit index addresses, using FLASH to save the data that is Erased /Written infrequently, save data after power off even when run out of batteries, but the “erease/write”times are limited. 16.1.2 Word Address Description Local word,Local word addresses. Address Type Address Range LW 0~10255 452 Format DDDDD Hardware Part Name and Specification Recipe word , Local recipe word addresses, indicating the local register of HMI, save data after power off, don’t save data when run out of RW 0~261000 DDDDDD batteries. Recipe word index,Recipe word index addresses, local register of HMI, indirect addressing mode is adopted, save data after power off, don’t save data DDDDDD RWI 0~261000 when run out of batteries. 【Example】RWI50 RW address = 50 + [LW9000] Extended Recipe word,Extended recipe word addresses, usually for HMI external storage devices access, such as SD card, U disk and so on, when more than one external storage devices are ERW0~ERW2 0~2147483647 DDDDDDDDDD 0~2147483647 DDDDDDDDDD FRW 0~134217727 DDDDDDDDD FRWI 0~134217727 DDDDDDDDD used, ERW0/ERW1/ERW2 will be used for indentifying. Extended Recipe word index,Extended recipe word index addresses, usually for HMI external storage devices access, such as SD card, U disk ERWI0~ and so on, when more than one external storage ERWI2 devices are used, ERW0/ERW1/ERW2 will be used for indentifying. Flash recipe word,Flash recipe word addresses, using FLASH to save the data that is Erased /Written infrequently, save data after power off even when run out of batteries, but the “Erease/Write” times are limited. Flash recipe word , Flash recipe word index address, using FLASH to save the data that is Erased /Written infrequently, save data after power off even when run out of batteries, but the “Erease/Write” times are limited. 16.2 System Special Registers of HMI The system has reserved some Local Word(LW),Local Bit(LB) addresses for special purpose, the users must use the addresses according to related description. 453 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software ! When local registers are used, users need to pay special attention to making sure that the local registers cannot conflict with the special registers, otherwise the registers will not be able to be used normally or unexpected results will be lead. 16.2.1 Parameter Setting of Hardware Address Description Read/Write Screen saver indication for entering. When the system enters screen saver/backlight and energy LB9018 saving state, the bit is automatically set to ON; when the system exits screen saver state, it is R set to OFF. Screen saver indication for exiting. When the system enters screen saver/backlight and energy LB9019 saving state, the bit is automatically set to OFF; when the system exits screen saver state, it is R set to ON. LB9045 LB9051 LB9091 LB9092 LB9093 LB9094 LB9120 LB9121 LB9141 LB9145 Restart touch screen. Restart HMI when this bit is set to ON. Enable/disable touch function when backlight is closed. Set this bit to ON will disable the touch function when backlight is closed. Increase LCD contrast. The system will execute the function of increasing LCD contrast by setting the bit to ON, upon completion, the bit will be cleared automatically. Decrease LCD contrast. The system will execute the function of decreasing LCD contrast by setting the bit to ON, upon completion, the bit will be cleared automatically. Increase backlight brightness. The system will execute the function of increasing backlight brightness by setting the bit to ON, upon completion, the bit will be cleared automatically. Decrease backlight brightness. The system will execute the function of decreasing backlight brightness by setting the bit to ON, upon completion, the bit will be cleared automatically. Trigger long sound of buzzer. Set the bit to ON to trigger long sound of buzzer once, upon completion, the bit will be cleared automatically. Trigger short sound of buzzer. Set the bit to ON to trigger short sound of buzzer once, upon completion, the bit will be cleared automatically. Turn off the current sound of buzzer alarm. Set the bit to On to turn off the current sound of buzzer alarm, upon completion, the bit will be cleared automatically. Automatically restart after system crash. Set the bit to ON, to make HMI will restart automatically after it crash for 5 seconds. W R/W W W W W W W W R/W LB9160 Switch bit of CPU light. Set the bit to ON to turn off CPU light, and forbid blinking. R/W LB9163 Screen flip display. Set the bit to ON to flip vertical display the HMI screen. R/W LW9140 Display screen brightness level. R LW9141 Display screen contrast level. R 454 Hardware Part Name and Specification Note:as for KM5303,the value of LW9141 indicates the brightness of the buttons. LW9464 LW9532 Audio volume register. Range: 0~100, 0 indicates mute, from 1 to 100, the volume increases gradually. Number of the screen saver window. Display and set the number of the screen saver window. R/W R/W 16.2.2 System Setting System parameter Setting Address LW10010 LW10011 Description Initial window number, range: 0~65535. Read/Write R/W Screen saver/backlight and energy saving time setting. 0: Disable screen saver; 1~65535: Enable screen saver (take effect without restart). Time unit: minute. R/W Buzzer sound. 0: Disable; 1: Enable (take effect without restart, non-zero value enables the function) LW10012 Note: LW10012 is only used for closing buzzer, not for closing the buzzer sound triggered by R/W alarms and events. For the buzzer sound triggered by alarms and events, the function is prohibited. LW10013 Pop-up window attribute. 0: Normal;1: Display above other windows. R/W LW10014 Common window attribute. 0: Display below base window; 1: Display above base window. R/W LW10015 Number of stored events. Range: 0~65535 R/W LW10016 RTC source. 0: PLC(Local Word);1: Internal RTC R/W LW10017 Default language. Range: 0~7. R/W LW10018 System reserved. For HMI internal use. R/W LW10019 Exchange communication ports. Set the bit to ON to exchange com0 and com1 of HMI. R/W Taskbar control Address Description Read/Write LB9040 Hide/display Fast selection window. Set the bit to ON to hide; Set the bit to OFF to display. R/W LB9041 Hide/display taskbar. Set the bit to ON to hide; Set the bit to OFF to display. R/W LB9042 Hide/display task buttons. Set the bit to ON to hide; Set the bit to OFF to display. R/W LB9043 Hide/display all (Fast selection window, taskbar, task buttons). Set the bit to ON to hide; Set the bit to OFF to display. R/W Keyboard control Address LB9060 LB9061 Description Read/Write Keypad popup indication. Keypad popup is controlled by the component in the left part of the window. When numeric input or text input function is enabled by users, HMI will set the bit to ON automatically, and pop up a direct window including a keypad. After successful entry or 455 R Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software pressing [Esc], this bit will be set to OFF, and the keypad window will be closed automatically. LB9062 LB9063 Keypad popup indication. Keypad popup is controlled by the component in the upper left part of the window. Keypad popup indication. Keypad popup is controlled by the component in the bottom left part of the window. LB9064 Keypad popup indication. Keypad popup is controlled by the component in the right part of the LB9065 window. LB9066 LB9067 Keypad popup indication. Keypad popup is controlled by the component in the upper right part of the window. Keypad popup indication. Keypad popup is controlled by the component in the bottom right part of the window. LB9068 Keypad popup indication. Keypad popup is controlled by the component in optional position of LB9069 the window. LB9080 LB9081 Keypad popup indication. Keypad popup is controlled by the component in the upper half part of the window. Keypad popup indication. Keypad popup is controlled by the component in the bottom half part of the window. R R R R R R R R Pinyin input method Address Description Read/Write This bit is used to switch input method of Chinese and English. When the bit is set to LB9100 ON, the system switches to Pinyin input method; when it is set to OFF, the system R/W switched to English input method. The value is the serial number of the current window in which Chinese characters are LW9150 displayed, the value is used for page turning. LW9152~9167 Display the currently entered Pinyin characters. R/W R Touch Address LB9053 LW9030 LW9031 Description Touch status. The bit will be set to ON when press, OFF when lose. Touch coordinate. Record the touch coordinate of X position that takes the upper-left corner of the screen as origin. Touch coordinate. Record the touch coordinate of Y position that takes the upper-left corner of the screen as origin. LW9540 Position of the touch component (component position). The values are the coordinates (x, y, w, ~9543 h) of the touch component relative to the window coordinates. 456 Read/Write R R/W R/W R Hardware Part Name and Specification LW9544 ~9547 Position of the window which the touch components are in (window position). The values are the coordinates (x, y, w, h) of the window which the touch components are in relative to the R screen coordinates. Cursor Address LB9135 Description Cursor lock. When the bit is set to ON, the cursor is locked in the current input component, it will switch to other input components only after the current input is completed. Read/Write R/W LW9520 Cursor position. X position of the cursor in the input component. R LW9521 Cursor position. Y position of the cursor in the input component. R LW9530 Cursor semi-transparent display. When the value are not set to 0,the cursor will display semi-transparently, the range of the value is 20~100. R/W Change Base Window Address Description Read/Write Disable the return value function of 【PLC Control】—【Change Base Window】. ON: Disable; OFF: Enable. 【Example】: To switch from Base Window 10 to Base Window 12 with the 【PLC Control】 LB9052 —【Change Base Window】 function,and the reading address is D12, the switchover will be R/W implemented when the value of D20 is 12. After the system switches to Base Window 12, PLC will automatically return the number 12 to the address D21. If the return value function is disabled, the system will not return the number 12 to D21. LB9139 LW9050 The bit will be set when change Base Window. The bit will be set to ON when change Base Window display. Displaying Base Window Number. Slave machine can maintain the same Base Window with master machine according to the word. R R Print control Address LB9016 Description Printer error indication. The bit is set to ON in case of printer error and to OFF if printer is normal. Read/Write R Printer control. Set it to ON to disable print function; set it to OFF to enable print function. LB9017 Note: 【HMI Attributes】—【print Setting】—【Enable print】must be selected, otherwise the R/W function of this bit will be invalid. LB9123 LB9132 Event printing setting. Set the bit to ON to separate event content from other information such as serial number, time and so on. Printing indication. The bit will be set to ON when printing, OFF when finished. 457 R/W R Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software LB9133 Printing preprocessing. Set the bit to ON to execute printing preprocessing operation to R/W improve the printing results. LB9143 USB printer connection status. Set the bit to ON for connection, OFF for disconnection. R LW9800 Error code register, word length:2 R LW10254 Enable Pictbridge print. Set it to 1 to enable pictbridge print; set it to 0 to disable pictbridge R/W print. HMI System Version Information Register Description Read/Write LW9640 Hardware Version R LW9641 Kernel Version R LW9642 Rootfs Version R LW9643 GUI Version R LW9644 Comserver Version R LW9645 Servo Version R HMI Time Address Description Read/Write LW9034~9035 Stopwatch, double word, display the time in unit of 0.1 second. LW10000 BIN code,System time (Second), range:0~59 R/W LW10001 BIN code,System time (Minute), range:0~59 R/W LW10002 BIN code,System time (Hour), range:0~23 R/W LW10003 BIN code,System time (Date), range:0~31 R/W LW10004 BIN code,System time (Month), range:0~12 R/W LW10005 BIN code,System time (Year), range:0~9999 R/W LW10006 BIN code,System time (Week), range:0~6 R/W ! R The system time should be downloaded into HMI for debugging, it will call the system time of PC when run in offline simulation mode on PC. External time Address Description Readable/Writable LW9010 Local time(Second), Range:0~59 R/W LW9011 Local time(Minute), Range:0~59 R/W LW9012 Local time(Hour), Range:0~23 R/W LW9013 Local time(Date), Range:0~31 R/W LW9014 Local time(Month), Range:0~12 R/W 458 Hardware Part Name and Specification LW9015 Local time(Year), Range:0~9999 R/W LW9016 Local time(Week), Range:0~6 R/W LW9017 Local time(Millisecond), Range:0~999 R/W ! 1.When 【HMI Attributes】—【Use The External Clock for Event】 is selected, the events will read the values of LW9010~9017 rather than adopt system time of HMI. 2. Before this function is used, the values of PLC time registers must be transmitted to LW9010~9017. VNC Address Description R/W LB9290 VNC enable, set on,start VNC function RW LB9291 VNC operation disable, set on,no VNC operation RW LB9292 VNC operation password enable,set on, password valid RW LB9293 VNC check password enable, set on, password valid RW LW10146~10147 VNC operation password RW LW10148~10149 VNC check password RW Others Address LB9124 LB9162 LB9164 LB9240 LB9260 LB9261 Description Times of alarm setting. Set the bit to ON to display alarm times in the front of the massages. TTF font optimization display. Set the bit to ON to optimize the display effect of the edge of the TTF font. Video mode selection. ON: NTSC mode; OFF: VPAL mode. ON: When he number input component which read address same as write address is input ENT, the new value will display immediately. Speed selection switch pages. ON: Switch page displays fast. OFF: Switch page displays slow. Switch page data display selection. ON:Keep original data. OFF:Page data first brush cut to zero, and then display valid data. Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W Open the function of exporting event to csv file including date. ON:Open.After setting ON,the LB9270 format of csv file in external device(USB,SD Card)will change,it can’t be used together with R/W the function “Save to external device” like USB and SD Card. OFF: Close. LB9280 LB9910 LB9911 Identifier bit of unconfirmed event. ON: there are events which are unconfirmed; OFF: there is no event which is unconfirmed. Open WebServer. Set the bit to ON to open WebServer function; while OFF to close this function. Brower display mode. Set the bit to ON to display HMI image with gray mode in browser; while OFF to display actual HMI image. 459 R/W R/W R/W Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software LW9616 Record the current number of events triggered. Word length:1 LW9370 Operation acknowledgement mode. Operator acknowledgement mode: 1: Confirm; 2: Cancel. LB9915 Set on,with key, KM5303 switch disable RW LB9920 Set on, instead invalid float number NAN of former value RW ! R/W R 1. The above functions will take effect after restart. 2. The values of the local words above will be saved after power off. 16.2.3 Components Setting Input Components Address LB9129 LB9131 LB9140 LB9142 LB9161 Description Trigger input components in basic window. Set the bit to ON to trigger input components in basic window. Input components trigger automatically. Set the bit to ON to make the input components triggered automatically after open window. Caps Lock. Set the bit to ON to make English letters input in capital format; the bit will be set to OFF automatically after input finished. Trigger input components in popup window. Set the bit to ON to trigger input components in the popup window in top layer. Components left alignment display. Set the bit to ON to make the display component(LW9060~9075) on the keyboard displays left alignment when input. LW9002 Display the maximum of numeric input. When numeric input component is activated, it will ~9003 display the maximum of the numeric component. Otherwise, it will be set to 0. LW9004 Display the minimum of numeric input. When numeric input component is activated, it will ~9005 display the minimum of the numeric component. Otherwise, it will be set to 0. LW9060 ~9075 LW9180 ~9187 LW9190 ~9197 LW9380 ~9395 Read/Write W R/W R/W W R/W R R Number/Text input procedure display. The words will display the input procedure when Number/Text input components are activated. LW9075 display the latest input data. Usually R text components are used for displaying. Display the maximum of number input, usually by text components. R/W Display the minimum of number input, usually by text components. R/W Display the historical data of number input components, usually by text components. Text components 460 R Hardware Part Name and Specification Address Description Read/Write Display the bytes of text display component in inverted order. Set the bit to ON, then the high LB9137 bytes and low bytes of text component will exchange to display, the low bytes will display on R/W the right side of the text component. LB9138 LW9130 LW9170 Mask text characters. Set the bit to ON to make text component only display characters in code R/W 33~127. Other characters will be replaced by space character. Switch text library contents online. The value indicates the text library index. R/W Display the page number of note book component. The value indicates the initial row of the R input area. It is used for page turning of note book component. Trend Curve Address Description Read/Write LB9110 Active view and zoom function of trend curve. R/W LB9111 Active cursors function of trend curve. R LW9200 Time value of the browsed points of trend curve, year. BIN code. R LW9201 Time value of the browsed points of trend curve, month. BIN code. R LW9202 Time value of the browsed points of trend curve, date. BIN code. R LW9203 Time value of the browsed points of trend curve, hour. BIN code. R LW9204 Time value of the browsed points of trend curve, minute. BIN code. R LW9205 Time value of the browsed points of trend curve, second. BIN code. R Display the value of every channel of every browsing dot in trend curve. According to the LW9210~ channels of trend curve, the registers will display the current value of each channel. LW9210 R displays the value of channel 0; LW9211 displays the value of channel 1; … Register decoding in Modbus Slave driver Address LW9810 LW9811 Descriptions R/W Adjust the decoding sequence of 16bits integer R/W Value Sequence Descriptions For example:0x0001 0 12 High byte and low byte are normal Means 1 (0x0001) 1 21 High byte and low byte swap Means 256 (0x0100) Adjust the decoding sequence of 2bits integer R/W Value Sequence Descriptions For example:0x0000 0001 0 1234 High byte and low byte,high word and low Means 1 (0x0000 0001) word are Normal 1 2143 High word and low word are normal,but Means 256(0x0000 0100) high byte and low byte swap. 2 3 3412 4321 High word and low word swap,but Means 65536 high byte and low byte are normal. (0x0001 0000) High word and low word,high byte Means 16777216 461 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software and low byte swap. LW9812 (0x0100 0000) Adjust the decoding sequence of 2bits float R/W Value Sequence Descriptions For example:0x3F80 0000 0 1234 High byte and low byte,high word and Means 1.0(0x3F80 0000) low word are Normal 1 2 3 2143 3412 4321 High word and low word are normal,but Means -5.78564e-039 high byte and low byte swap. (0x803F 0000) High word and low word swap,but Means 2.27795e-041 high byte and low byte are normal. (0x3F80 0000) High word and low word,high byte Means 4.60060e-041 and low byte swap. (0x0000 803F) 16.2.4 Security Leve l and User Permission Security Level Address LB9046 Description Lower security level. The bit will be set to ON when system switches from a lower security level to a higher level. Read/Write R LW9040~9041 Password of security level. Double word. W LW9042 Security level. Display security level of current base window. R LW9043 Switch security level by force. Force to switch from higher level (for example, level 2) to lower level (for example, level 0). W Mapping of Security Level Address Description Read/Write LW10024~10025 Level 1 password. Double word R/W LW10026~10027 Level 2 password. Double word R/W LW10118~10119 Level 3 password. Double word R/W LW10120~10121 Level 4 password. Double word R/W LW10122~10123 Level 5 password. Double word R/W LW10124~10125 Level 6 password. Double word R/W LW10126~10127 Level 7 password. Double word R/W LW10128~10129 Level 8 password. Double word R/W LW10130~10131 Level 9 password. Double word R/W LW10132~10133 Level 10 password. Double word R/W LW10134~10135 Level 11 password. Double word R/W LW10136~10137 Level 12 password. Double word R/W LW10138~10139 Level 13 password. Double word R/W LW10140~10141 Level 14 password. Double word R/W 462 Hardware Part Name and Specification LW10142~10143 ! Level 15 password. Double word R/W 1. The value of the local word above could be saved after power off. 2. Online modification of passwords is supported by the function. 3. Passwords could be modified online, while offline simulation does not support passwords modification. User Permission Address Description ReadWrite LB9165 User login. Set ON to execute logining operation, then set OFF automatically. W LB9166 User logoff. Set ON to execute logoff operation, then set OFF automatically. W LB9167 Add user. Set ON to execute adding user operation, then set OFF automatically. W LB9168 Delete user. Set ON to execute deleting user operation, then set OFF automatically. W LB9169 Modify password. Set ON to modify password operation, then set OFF automatically. W LB9190 LB9191 Executive mark of user management. The bit will set to ON when execute operations of Add/Delete users. Operation failure of user management. The bit will be set to ON when operation of user management fails. R R LW9486~9501 User name for login. Input user name for login, 32 characters at most. R/W LW9502~9503 User password. Input user password for login. R/W LW9504~9505 Display user permission of the current user. Display the user permission with 32 bits corresponding to the current user. R LW9506~9507 Set user permission. Set user permission with 32 bits when adding user information. W LW9508~9509 Set automatic logoff time. Set automatic logoff time when adding user information. W LW9510~9511 LW9650~9665 Password confirmation. Input password again to confirm the consistency when adding user information. Display login user name W R 16.2.5 Data and Project Management Recipe operation Address LB9010 LB9011 LB9012 Description Recipe downloading indication. The bit will be set to ON in downloading status, and set to OFF automatically after download is finished (Download from recipe to PLC). Recipe uploading indication. The bit will be set to ON in uploading status, and set to OFF automatically after uploading is finished (Upload from PLC to recipe). Recipe Download/Upload indication. Set to ON in downloading/uploading status, and set to OFF automatically after downloading/uploading is finished. 463 Read/Write R R R Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software LW9000~9001 Index address for recipe data. RWI and RBI access recipe data by this index address. LW9000 is low word, LW9001 is high word. R/W LB9130 Clear RW register. Set the bit to ON to trigger RW clearance. R/W LW9260~9261 Initial address for RW clear operation. R/W LW9262~9263 Word length for RW clear operation. R/W External memory operation Address LB9153 LB9154 LB9155 Description Safety removing setting of SD card. Set the bit to ON before inserting SD card; Set to OFF before removing to make sure safety removing. Safety removing setting of U disk 1. Set the bit to ON before inserting U disk 1; Set to OFF before removing to make sure safety removing. Safety removing setting of U disk 2. Set the bit to ON before inserting U disk 2; Set to OFF before removing to make sure safety removing. Read/Write R/W R/W R/W LB9156 Clear files in SD card. Clear all the files that generated in SD card. W LB9157 Clear files in U disk 1. Clear all the files that generated in U disk 1. W LB9158 Clear files in U disk 2. Clear all the files that generated in U disk 2. W LB9220 HMI is reading SD card indication. ON: reading operation R LB9221 HMI is reading U disk1 indication. ON: reading operation R LB9222 HMI is reading U disk2 indication. ON: reading operation R LB9230 HMI is writing SD card indication. ON: writing operation R LB9231 HMI is writing U disk1 indication. ON: writing operation R LB9232 HMI is writing U disk2 indication. ON: writing operation R LW9470~9485 Prefix title of the copied file. Prefix character strings of the file name which is copied to SD card or U disk. R/W File list box operation Address LB9150 LB9151 LB9152 LB9265 Description Execute import/export operation of project or recipe. Set the bit to ON to execute import/export operation. Protection bit of export project. Uploading password is input correctly when export project, then the bit will be set to OFF, otherwise, it will be set to ON. Switch folder type between tree type and list type. Set the bit to ON to display folders in tree type, while set it to OFF to display folders in list type. Open import/export logo function.ON: Open import/export logo function. OFF: Open import/export project function. 464 Read/Write W R R/W R/W Hardware Part Name and Specification LW9300~9331 LW9332~9363 LW9364 LW9366 Route name of the browsed file. Display the route name which is browsed currently in file list component. Current selected file. Display the file name which is browsing currently in file list component. Import/ export selection of project or recipe. 1: project import; 2: project export; 3: recipe import; 4: recipe export. Copy/cut/ paste operation of files. With file browse component to execute: 1: copy; 2: cut; 3: paste. R R/W R/W W 16.2.6 Communication PLC communication information Address LB9136 LB9144 LB9180 Description Read/Write Filtrate communication of the non-response PLC. Set the bit to on to filtrate communication of the non-response PLC. Hide the component which failed in communication. Set the bit to ON to hide the component which failed in communication. Notification bit of PLC access error, when PLC communication error occurs, the bit will be set to ON. R/W R/W R Mask off code of PLC station NO. (COM port 0). Each bit corresponds to one station no. LW9264~9279 of port 0 (9264.0 corresponds to station no. 0, … , 9279.F corresponds to station no. 255), set the corresponding bit to ON to mask the communication of the corresponding R/W station. Mask off code of PLC station NO. (COM port 1). Each bit corresponds to one station no. LW9280~9295 of port 1 (9280.0 corresponds to station no. 0, … , 9295.F corresponds to station no. 255), set the corresponding bit to ON to mask the communication of the corresponding R/W station. Mask off code of HMI no.. Each bit corresponds to one HMI no. in the network (9400.0 LW9400~9415 corresponds to HMI no. 0, … , 9415.F corresponds to HMI no. 255), set the R/W corresponding bit to ON to mask the communication of the corresponding HMI. Register for communication status indication (COM 0). Each bit corresponds to one LW9432~9447 station no. (9432.0 corresponds to station no. 0, … , 9447.F corresponds to station no. 255). When PLC communication timeout and no response, the corresponding bit will be R/W set to ON, otherwise, the bit will be set to OFF. Register for communication status indication (COM 1). Each bit corresponds to one LW9448~9463 station no. (9448.0 corresponds to station no. 0, … , 9463.F corresponds to station no. 255). When there is no response and PLC communication timeout, the corresponding bit 465 R/W Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software will be set to ON, otherwise, the bit will be set to OFF. Mask off code of error message. Each bit corresponds to one error message. Set the bit LW9296~9299 to ON to mask the corresponding error message indication. For example:“PLC No Response” corresponds to 9296.2, “Socket Connect Error” R/W corresponds to 9296.4 Indication code of error message. Each bit corresponds to one error message, when an LW9550~9553 error indication occurred, the corresponding bit will be set to ON automatically. R For example : “PLC No Response” corresponds to 9692.2 , “Socket Connect Error”corresponds to 9296.4 Mapping of communication parameters Address LW10030~10033 LW10034 Description Read/Write IP address. Each section occupies one word, range 0~255. R/W Download port number. It is download port number rather than communication port R/W number. LW10035 Reserved. R/W LW10110 Gateway. Each section occupies one word, range 0~255. R/W LW10114 Subnet mask. Each section occupies one word, range 0~255. R/W LW10036 Work mode of COM0. 0:232;1:485-4w;2:485-2w R/W LW10037~10038 Baud rate of COM0. Double word.. R/W LW10039 Data bit of COM0. R/W LW10040 Check bit of COM0. R/W LW10041 Stop bit of COM0. R/W LW10042 Slave station no. of COM0 (HMI station no.) R/W LW10043~10044 PLC time-out constant of COM0. R/W LW10045~10046 Protocol time-out constant 1of COM0. R/W LW10047~10048 Protocol time-out constant 2 of COM0. R/W LW10056 Work mode of COM1. 0:232;1:485-4w;2:485-2w R/W LW10057~10058 Baud rate of COM1. Double word.. R/W LW10059 Data bit of COM1. R/W LW10060 Check bit of COM1. R/W LW10061 Stop bit of COM1. R/W LW10062 Slave station no. of COM1 (HMI station no.) R/W LW10063~10064 PLC time-out constant of COM1. R/W LW10065~10066 Protocol time-out constant 1of COM1. R/W 466 Hardware Part Name and Specification LW10067~10068 Protocol time-out constant 2 of COM1. R/W LW10182 Work mode of COM2. 0:232; R/W LW10183~10184 Baud rate of COM2. Double word.. R/W LW10185 Data bit of COM2. R/W LW10186 Check bit of COM2. R/W LW10187 Stop bit of COM2. R/W LW10188 Slave station no. of COM2 (HMI station no.) R/W LW10189~10190 PLC time-out constant of COM2. R/W LW10191~10192 Protocol time-out constant 1of COM2. R/W LW10193~10194 Protocol time-out constant 2 of COM2. R/W ! 1. The above functions will take effect after restart. 2. The value of the local words above will be saved after power off. Variables of station number Address Description LW9416 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 0 of variable of station number. R/W LW9417 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 1 of variable of station number. R/W LW9418 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 2 of variable of station number. R/W LW9419 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 3 of variable of station number. R/W LW9420 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 4 of variable of station number. R/W LW9421 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 5 of variable of station number. R/W LW9422 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 6 of variable of station number. R/W LW9423 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 7 of variable of station number. R/W LW9424 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 8 of variable of station number. R/W LW9425 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 9 of variable of station number. R/W LW9426 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 10 of variable of station number. R/W LW9427 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 11 of variable of station number. R/W LW9428 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 12 of variable of station number. R/W LW9429 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 13 of variable of station number. R/W LW9430 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 14 of variable of station number. R/W LW9431 Variable register of station number. It corresponds to index 15 of variable of station number. R/W Read/Write Error code of bus Address Description 467 Read/Write Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software LW9145 Record error codes of Profibus. R LW9146 Record error codes of Canopen. R Description Read/Write Macro code operation Address LB9116 Macro reading input registers indication. The bit will be set to ON when Macro is reading input R registers, set to OFF automatically after finish reading. LB9117 Macro writing output register indication. The bit will be set to ON when Macro is writing input R registers, set to OFF automatically after finish writing. LB9118 Macro working indication. The bit will be set to ON When Macro is running (read and write R register operation are included), set to OFF after finish. LW9465 Time magnification of Macro time-out. If it is set to N, then the allowable maximum running time for once of Marco is N times as long as the default value. 468 R/W Hardware Part 469 1 Name and Specification This chapter mainly introduces names and specifications of the universal parts of MT series HMI. Names and specifications of the special parts of MT series HMI, please refer to related selection manual. 1.1 Name of Each Part Names of the universal parts of MT series: Front: a PWR CPU COM a. Screen display /Touch control area b. PWR indicator c. CPU indicator Back: 470 b c d d. COM indicator Hardware Part Name and Specification a. Input terminal of power supply DC24V b. 1A Fuse c. LAN interface d. USB HOST(USB type A interface) SLAVE(USB type B interface) f. COM1(female) g. COM0&COM2(male) h. RESET Button i. DIP Switch e. USB j. SD CARD interface k. One-time button type lithium battery 1.2 Specifications of Each Part 1.2.1 Screen display/Touch control area The touch panel is for input/output and display. Caution In the case of personal safety may be endangered or significant losses may be leaded, please do not use the input function of HMI touch switch as emergency stop switch. 1.2.2 LED indicator Indicator Description PWR When the power supply of HMI is ON/OFF, the yellow indicator is ON/OFF. CPU When CPU works normally, the green indicator is ON. When HMI communicates with PLC and such controllers normally, the red indicator will frequently COM ! flick or be normally ON. COM indicator only indicates the communication states of PLCs connected to COM0 and COM1. 1.2.3 Power Supply Input voltage:DC24V±15% 24V:Connect to 24V+ terminal of the power supply. GND:Connect to COM terminal or 0V terminal of the power supply. 24V GND FG FG:Earthing terminal 1.2.4 Fuse Fast fuse with rated current 1A is used. Notice Fast fuse offers protection when the power supply voltage is too high or power polarity is connected reversely, but it cannot ensure the internal electronic components shall not be damaged. 1.2.5 Serial ports 471 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Notice Please do not hot plug communication cable with charged, to avoid the communication interface being damaged. Serial port COM0 COM0 is a 9-pin D-SUB male connector, it supports communication functions of RS-232C/RS-485/RS-422A, and its pin assignment is as follows: Pin# Function Signal RS-232C RS-485 RS-422A 1 RX-(B) -- RS485B Receive data 2 RXD Receive data -- -- 3 TXD Send data -- -- 4 TX- -- -- Send data 5 SG 6 RX+(A) -- RS485A Receive data 7 NC -- -- -- 8 NC -- -- -- 9 TX+ -- -- Send data Signal Ground Serial port COM1 COM1 is a 9-pin D-SUB female connector, it supports communication functions of RS-232C/RS-485/RS-422A, and its pin assignment is as follows: Pin# Function Signal RS-232C RS-485 RS-422A 1 RX-(B) -- RS485B Receive data 2 RXD Receive data -- -- 3 TXD Send data -- -- 4 TX- -- -- Send data 5 SG 6 RX+(A) -- RS485A Receive data 7 CTS Clear to send -- -- 8 RTS Request to send -- -- 9 TX+ -- -- Send data Signal Ground Serial port COM2 COM2 shares physical interface with COM0, is 9-pin D-SUB male connector, this port only supports communication function of RS-232C, and its pin assignment is as follows: 472 Hardware Part Name and Specification Pin# Function Signal RS-232C 1 NC -- 2 NC -- 3 NC -- 4 NC -- 5 SG Signal Ground 6 NC -- 7 RXD Receive data 8 TXD Send data 9 NC -- COM2 can connect with controllers supporting RS-232C, also can be used to upload/download program and debug. 1.2.6 USB interfaces USB HOST USB HOST is a USB A type interface,can connect with peripheral equipments such as USB storage device, keyboard, mouse and so on. Its pin assignment is as follows: Pin# Signal Function 1 VCC +5V power supply 2 D- Data- 3 D+ Data+ 4 GND -5V Earthing USB SLAVE USB SLAVE is a USB B type interface,can connect with the USB port of PC, and is used to upload/download program and debug. Its pin assignment is as follows: Pin# Signal Function 1 VCC +5V power supply 2 D- Data- 3 D+ Data+ 4 GND -5V Earthing 1.2.7 LAN interface LAN port is a 10M/100M transmission speed auto-adapted RJ-45 type interface, can be used to upload/download program and debug; Multiple HMIs equipped with LAN interfaces can be networked at will via this port and communication with controllers supporting Ethernet communication is also supported by this port. Its pin assignment is as follows: 473 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Pin# Signal Function 1 TX+ Send data + 2 TX- Send data - 3 RX+ Receive data + 4 NC -- 5 NC -- 6 RX- Receive data - 7 NC -- 8 NC -- 1.2.8 SD CARD interface SD CARD port is suitable for connecting with ordinary plug of which the size is 32mm×24mm×2.1mm. It can be used to save data and quick upload/download user projects, recipes and such files. Its pin assignment is as follows: Pin# Signal Function 1 CD/DAT3 Card checkout / Data 3 2 CMD Command 3 VSS1 GND 4 VDD Power supply (+3V) 5 CLK Clock 6 VSS2 GND 7 DAT0 Data 0 8 DAT1 Data 1 9 DAT2 Data 2 1.2.9 DIP switch DIP Switch is used to set the HMI system in different working modes, the corresponding working modes of the setting are as follows: SW1 SW2 OFF OFF ON OFF Working mode Normal working mode ☞ More details about Firmware Update Mode, please refer to 【Hardware Part 5 Firmware Update Mode】 OFF ON ☞More details about Touch Screen Calibrate Mode, please refer to【Hardware Part 4 Touch Screen Calibrate Mode】 ON ON ☞More details about System Setting Mode, please refer to 【Hardware Part 3 System Setting Mode】 474 Hardware Part Name and Specification 1.2.10 RESET switch Press the RESET button,HMI will restart. 1.2.11 Button battery Non-rechargeable button type LI-Mn battery is used, and the standard voltage is 3V. (CR series) 475 2 Connection with Preiferal Equipments To meet users’ requirements for multifunction screens of intelligence, information, humanity, MT series HMIs have equipped with kinds of interfaces. The equipments supported by the interfaces are described in turn as follows. 2.1 Connection via Serial Port (1) Connect with PLC and other controllers via serial ports to communicate HMI can connect with the serial ports of PLC and such controllers to communicate via RS-232C/RS-485/RS-422A serial cable. Requirements for connection The PLC and such controllers communicate with HMI must be of the types supported by Kinco HMIware, or support the serial communication protocols supported by Kinco HMIware. Cable production Users can make the connection cable by themselves according to the types of controllers and communication modes. (2) Upload/download data via serial ports HMI can connect with the serial ports of PC to upload/download user projects, recipes and such data via RS-232C serial cable. Requirements for connection Install and run the HMIware configuration software of Kinco on PC, select download ways through the 【Tools】menu of the 476 Hardware Part Connection with Preiferal Equipments software. ☞More details about download please refer to【Advanced Part 7.3 Download】 Cable production Users can make the connection cable by themselves. (3)Connect with scanner and such equipments via serial ports HMI can connect with scanner via RS-232Cserial cable to receive banner code and such data. Requirements for connection The scanners communicate with HMI must be of the types supported by Kinco HMIware, or support the serial communication protocols supported by Kinco HMIware. Cable production Directly use the RS-232C communication cable provided by the scanner manufacturer. (4)Connect with miniprinter via serial ports HMI could connect with miniprinters to print screen or data report via RS-232C serial ports. Requirements for connection The miniprinters communicate with HMI must of the types supported by Kinco HMIware, or support the serial communication protocols supported by Kinco HMIware. More details please refer to the manual of 【Communication Connection Guide】. Cable production Users can make the connection cable by themselves. 477 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 2.2 Connection via USB Interfaces (1) Connect with USB mouse, USB keyboard and such equipments via USB HOST Connect with USB mouse HMI connects with USB mouse, then the USB mouse can execute input operation to the HMI screen. Connect with USB keyboard HMI connects with USB keyboard, then the USB keyboard can execute input operation to the HMI screen via the 【Map Key】function of Function Key components. Connect with USB mass storage device Connection between HMI and USB mass storage device can be used for: Quick upload/download user projects, recipes and such files between HMI and USB mass storage devices via import/export functions; A physical storage area (ERW) is divided up from the USB mass storage device, users take access to ERW registers to read/write data directly on HMI. Historical data of Trend Curve and XY Curve, historical events, operation log and such data can be saved in USB mass storage devices. Connect with USB printer HMI can connect with USB printers via USB cable to print screen and data report. The USB printers communicate with HMI mush be of the types supported by Kinco HMIware, or support the printer communication protocols supported by Kinco HMIware. 478 Hardware Part Connection with Preiferal Equipments Details about the supported printers please refer to the manual of 【Communication Connection Guide】. Connect with USB camera HMI can connect to camera with drive type USB to display the video pictures input by USB camera via camera component. ☞More details please refer to 【Advanced Part 4.10.2 Camera】 (2)Upload/download data via USB SLAVE HMI can connect with the USB interfaces of PC to upload/download projects, recipes and such data via USB cable. Requirements for connection Install and run the HMIware configuration software of Kinco on PC, select download ways through the 【Tools】menu of the software. Cable production Users can make the connection cable by themselves. Details about cable production please refer to the manual of 【Communication Connection Guide】. 2.3 Connection via LAN Interfaces (1)Connect with PLC and such controllers to communicate 479 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software HMI can connect to PLC and such controllers to communicate via an interconnection cable (RJ45 Crossover Cable). Requirements for connection The PLC and such controllers communicate with HMI mush be of the types supported by Kinco HMIware, or support the Ethernet communication protocols supported by Kinco HMIware. Cable production Users can make the connection cable by themselves. (2)Upload/download/monitor data via LAN interface Via interconnection cable (RJ45 Crossover Cable), HMI can connect with the LAN interface of PC to upload/download user projects, recipes and such data; meanwhile users can monitor the data of HMI or PLC and such controllers on PC. Requirements for connection Install and run the HMIware configuration software of Kinco on PC, select download ways through the 【Tools】menu of the software. Cable production Users can make the cable for connection by themselves. (3)Connect HMI to a Local Area Network via Hub/Switch HMI can be connected to a HUB or SWITCH to access a Local Area Network via a standard Ethernet cable (RJ45 straight-through cable) or interconnection cable (RJ45 cross-over cable). This is mainly used for multiple HMIs links or HMI network with multiple PLC and such controllers. ☞ More details please refer to【Adavanced Part 14 HMI Communication】 (4)linking via LAN interface HMI can link to another HMI via interconnection cable (RJ45 Crossover Cable). Requirements for connection All HMIs online are with LAN interfaces, and set 【HMI Attributes】—【Networking Device Setting】in the software. Cable production Users can make the connection cable by themselves. More details please refer to the manual of 【Communication Connection Guide】. 480 3 System Setting Mode In this mode, users can set such items as system time, Startup Window, IP address. 3.1 Methods to Display System Setting Mode Enter the System Setting Mode by the following steps: Set the DIP switch SW1 and SW2 to “ON”; Press the “RESET button, then HMI restarts and enters the SETUP interface. 3.2 System Setting Take the SETUP interface of MT5320T for example: In the SETUP interface of MT5320T,the following items can be set: Startup Window No.:Startup window. It is the displayed window when start HMI, the default value is 0. Backlight Saver Time:Screen saver time, in minutes. The default value is 10. Screen saver is unavailable when the value is 0. Buzzer Disabled/Enabled:Enable/Disable the buzzer. For MT5000/4000 series HMI, select “Mute” to close the buzzer. Network parameter setting: set the network parameters such as IP Address, Port, Subnet Mask, Gateway of a target screen equipped with Ethernet port. Brightness adjustment: Adjust brightness(Brightness Up/Down)to achieve the best visual effect. Brightness adjustment is not supported by some HMI models. Calibrate Time: Check whether the year, month, day, hour, minute and second are the current time, otherwise, calibrate manually. 481 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Import/Export: Quick upload/download user project files or recipe files. The function is only supported be HMIs equipped with USB HOST/SD Card ports. Upload the user project files (.pkg)saved in HMI to USB or SD Card. Upload password is required when upload, the default password is 888888 if it has not been set in the HMI attributes dialogue box. Download the user project files (.pkg)saved in USB or SD Card into HMI. Upload the recipe files (.rcp)saved in HMI to USB or SD Card. Download the recipe files (.rcp)saved in USB or SD Card into HMI. ! The SETUP interface may not be displayed in full size in a single screen, then click “Next” or “” to enter the next page and click Back” or “” to return the previous page. 482 4 Touch Screen Calibrate Mode When the screen touch is not accurate after firmware update, users can calibrate HMI screen under this mode. 4.1 Methods to Display Touch Screen Calibrate Mode There are two methods to enter the Touch Screen Calibrate Mode: Method 1: Enter Touch Screen Calibrate Mode by set DIP switches. Set the DIP switch SW1 and SW2 (on the back of the HMI) to “ON”; Press the “RESET button, then HMI restarts and enters the Touch Screen Calibrate interface. Method 2:Enter Touch Screen Calibrate Mode by the “Touch Calibration” function of【Function Key】. Method 2 is directly completed on the HMI screen, users do not need to manipulate the DIP switches and without bothering to open the control cabinet. ☞More details please refer to【Advanced Part 4.2.6 Function Key】 4.2 Touch Screen Calibrate Setting Follow the “+”sign to touch the screen until you hear a click sound and the“+”sign disappears, then “TP Adjust Success!”is showing, which indicates that Touch Screen Calibrate is successed. Then, set DIP switch 1 and 2 to “OFF” and press 【Reset】button, restart HMI to exit Touch Screen Calibrate Mode. 483 5 Firmware Update Mode In firmware update mode, users can update the version of the Kernel and Root files system (It is strongly recommended that the users use the function under the guidance of Manufacturer). 5.1 Methods to Display Firmware Update Mode Enter the Firmware Update Mode by the following steps: Set the DIP switch (on the back of the HMI) SW1 to “ON” and SW2 to “OFF”; Press the “RESET button, then HMI restarts and enters the Touch Screen Calibrate interface. 5.2 Firmware Update Setting Open KHManager, enter【System Operation】to update the Kernel and Root files system. ☞More details please refer to ! 【Advanced Part 8 KHManager】 Please backup the configuration projects, recipe data and so on before update Kernel/Root files system, to avoid data loss during update. 484 6 Maintenance and Tending This chapter mainly introduces the maintenance and inspection methods to prevent errors occur, so as to ensure the normal use of the products. Caution Do not disassemble the host or touch any internal component in a powered state, otherwise electric shock accidents may be leaded. 6.1 Maintenance To ensure the HMI in an optimal state, please maintain the following items regularly: Engineering data backup Regularly backup engineering data and store it to safe place, to prevent engineering data loss when HMI malfunctions and in need of repairment and parts replacement. Backlight replacement When the backlight darkens and is difficult to see clearly, then, the backlight should be replaced. The users cannot replace the backlight privately. When you need to replace the backlight, please contact your local dealer or representative offices. Battery replacement Some HMI models use button type Li-Mn batteries to save recipe data and system time when HMI powers off, when the voltage of the battery is lower than 2.5V, then the battery should be replaced. Users could buy and replace the batteries according to the specified specifications by themselves. 6.2 Tending Screen tending When the screen gathers dust or dirt, please disconnect the power supply for HMI, then, soak a piece of soft cloth in neutral detergent and wring it to dry, and then wipe the screen gently. ! Prohibition 1. Do not use paint thinner, organic solvent or strong acid mixture to clean the screen. 2. Do not use hard or sharp objects to operate or wipe the screen, otherwise, screen surface will be damaged. Periodic inspection To ensure the HM in an optimal state, please inspect the following items regularly: 485 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Working environment Whether the temperature or humidity of HMI working environment is in the specified range? Whether there is corrosive or flammable gas in the working environment of HMI? Electrical performance Whether the power supply input voltage is in the specified range? Others Has any of the power cable or power cord of the power supply terminals been loosened? Whether all the installed fasteners are locked tight? 486 Appendix 1 Regular PLC Used for HMI Connecting device Brand description ABB AC31/ AC500 (Rockwell)Allen-Bradley MicroLogix PLC AB SLC500/PLC5/MicroLogix SLC500 PLC Series(DF1) PLC-5 PLC AB SLC500/PLC5/MicroLogix Series Ethernet(TCP Slave) CompactLogix PLC AB CompactLogix/ControlLogix ControlLogix PLC Series(DF1) AB CompactLogix/ControlLogix Series Ethernet(TCP Slave) (Advantech)ADAM ADAM-4015/ ADAM-4017 Baldor NextMove ES Controller Baumuller BM4413-ST0-02200-03 Bosch Rexroth KVFC+ Inverter PPC-R Series Controller IndraLogic L Series Controller Bosch Rexroth Bosch Rexroth Ethernet (CAN)CANOpen Node Kinco k4 Slave Other company devices which support CANOpen Danfoss FC-300 Delta DVP PLC DVP Emerson EC10/ EC20 Series PLC Facon FBs/ FBe/FBn Fuji SPB Series PLC/ NB Series PLC GE Fanuc Series 90-30 Series PLC GE Fanuc Series SNP/GE SNP-X Fanuc Series 90-70 Series PLC Modbus TCP Facon FB/Modbus RTU VersaMax Series PLC VersaMax Micro&Nano Series PLC PACSystem RX7i Series PLC Hitachi H Series PLC 487 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software EH-150 Series PLC MICRO-EH Series PLC SJ300 Inverter Hollysys LM Series PLC LK Series PLC Hollysys LK Modbus RTU Hollysys LK Modbus TCP Slave IDEC Micro Smart Series PLC Inovance H2U Series PLC Inovance H2u Modbus RTU Kinco Kinco K3 PLC ED Series Servo CD Series Servo EB-MOD2P-01 Modbus RTU Kinco EB-MOD2P-01 EB-MOD2P-11 Keyence KV-16DT/ KV-1000/ KV-3000/ KV-5000 Lenze Lecom A/B Series Inverter LS Master-k Series PLC LS K-Master Cnet LS K-Master CPU Direct LS K-Master Modbus RTU XGT Series PLC LS XGT Cnet LS XGT CPU Direct GLOFA Series PLC LS GLOFA Cnet LS GLOFA FEnet LUST CDE34.008 ServoOne junior Mitsubishi FX Series PLC Q Series PLC FX Series Link Module QJ Series Link Module Modbus Modbus RTU Modbus RTU Extend Modbus RTU Slave Modbus RTU MT500 Compatible Modbus ASCII 488 Appendix 1 Regular PLC Used for HMI Modbus TCP Modbus TCP Slave Modbus UDP Modbus UDP Slave Omron C Series PLC C Series Link PLC CJ2 Series PLC CJ1 Series PLC CS1 Series PLC CJ Series Link Module CS Series Link Module E5EZ-R3 Controller OPTO SNAP Panasonic FP Series PLC Parker Compax3 Series SLVD Series 6K4 Series Profibus DP Slave Siemens S7-300/ Siemens S7-400 Other company devices which support PROFIBUS DP Master Schneider Micro Series PLC Modbus RTU Premium Series PLC Schneider Modicon Uni-TelWay Nano Series PLC Twido Siemens S7-200 SIEMENS S7-200 SIEMENS S7-200 Ethernet(TCP Slave) S7-300 SIEMENS S7-300/400(PC Adapter Direct) SIEMENS S7-300/400(MPI Direct) Profibus Slave SIEMENS S7-300 Ethernet(TCP Slave) S7-400 SIEMENS S7-300/400(PC Adapter Direct) SIEMENS S7-300/400(MPI Direct) Profibus Slave SIEMENS S7-400 Ethernet(TCP Slave) S7-1200 489 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Thinget XC3-32R-E Modbus RTU Thinget Controller Trio Euro Trio Modbus RTU Extend Vigor VH series PLC/ VB0 series PLC Yaskawa V Inverter MP Series Yaskawa MP2300 Yaskawa Ethernet(UDP Slave) ∑Ⅱ/∑Ⅱ Plus Servo Yokogawa FA-M3 Yokogawa FA-M3 Yokogawa FA-M3 Ethernet(TCP Slave) YuDian AI Series PLC 490 Appendix 2 List of Error Information No. Error information Description Compilation failed! No compiled PKG files are Macro code or other reasons result in compilation failing, generated! no compiled PKG files are generated. Warning: Init. Start Window does not exist, the The initial start picture saved in the original project possibly software will add the default Init. Start Window has been lost, the system will automatically replace it with automatically! Kinco initial start picture. Logo's size is too big, please adjust it! Logo's The bitmap imported for Initial Start Window is bigger than size is out of limit: Width*Height > 2097152 the software restriction. 4 Logo file error! HMI0.lg file went wrong. 5 HMI%s logo compile failed! 6 Current HMI can not support this component! 1 2 3 7 9 Unable to parse file, import failed! 12 13 14 15 16 17 The current HMI does not support the component. it? Unable to write file, export failed! 11 picture used by logo does not exist. Export file already exist, do you want to replace 8 10 HMI0.lg corresponding to Logo does not exist, or the The same file is exported to the same path repeatedly. The exported file name is possibly illegal. The file to import does not exist or the file format is discrepant. The project is existed in your selected content, The new project is of the same name with the already replace the old one? existing project in the path. Project has been opened, can not open repeatedly! Kinco HMIware cannot open one project repeatedly. The new version project can not be opened by Software of low version cannot open the project edited by the old version software! Please update your new version software. The software is upward compatible, software! please use the new version software. Can not save project. Please check the following The project is set to read only and cannot be modified and files permission! saved again. Save project error, please resume you project The project saved last time will be backupped automatically from \"temp\" directory in your project directory! in the \"temp\" directory. The project had been modified, please save and After modifying, the project should be saved and compiled compile first! again. Can not find compiled file, please compile first! PKG file is wrong or lost. A same name project already exists in this folder, please select another folder! Projects of the same name cannot be saved in the same path. 491 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 18 Software was closed abnormally last time, whether restore the unsaved project? The 19 project is created by old Prompt when reopen the project after abnormal close. version software .Do you want to backup and update the Prompt for backuping when use high version software to project now?\n\nWarning:the updated project can open the project edited by low version software. not be opened by old version software! 20 System default window, unable to delete! 21 Rename variable error! 22 Project incompleted! 23 24 25 26 27 Frame0~9 are the system default windows, cannot be deleted. The variable names possibly include “?”, “、”, “/” and such illegal characters. There are only serial port cables or PLCs in the Construct Window. Project error: some HMIs, PLCs or connectors HMIs, PLCs and communication cables do not be are not be connected! connected properly in the Construct Window. After delete, all related pictures will lost and can not be recovered! Do you want to continue? When delete the HMIs in the Construct Window, all the configuration pictures will be deleted and cannot be recovered, please be cautious with this operation. After delete, all related register address for the When delete PLCs, all the registers related with PLC will be plc items will be set default value and can not be changed to HMI default registers, and cannot be recovered, recovered! Do you want to continue? please be cautious with this operation. If remove all, all objects will be deleted and can Prompts of 【Delete all】in the attribute box of BUS, events, not be recovered! Do you want to continue? alarms, text libraries, address labels, PLC control. After replace, some parts of the HMI will change When replacing HMI models, the different screen sizes will position, size or colour, and can not be lead recovered! Do you want to continue? automatically in the configuration project. to some components’ attributes be adjusted When replacing HMI, some components not supported by 28 Element or the special function of the element. It the new HMI will be automatically deleted due to different has been deleted! hardware, for example Video, Historical Event Display and such components. Project contains some HMIs which are not The discontinued HMI models have been deleted in the supported by current version software. These configuration software of higher version, the discontinued HMIs had been auto updated to some available HMI model will be replaced automatically when open the HMIs:\n\n project edited by low version software. 30 Error: address cross-border The addresses exceed the allowed range. 31 Error: address format error The address format does not match with the actual format of 29 492 Appendix 2 List of Error Information Error: address input error component, possibly decimal number is written to octonary system, or entered characters are illegal. Address type not supported by the driver protocols is used 32 Invalid address type! 33 The files are damaged or deleted, can not play! Audio files faulted. Load system word library error!/ Vector font files If the font library used in the project does not exist in the used in project does not exist, please close the computer, then song typeface will be taken as default when project, install the missing font files opening the project. 34 35 36 37 38 Copy error: the destination window ID already exists! windows or projects, the component size should be smaller than target window. Audio file imported into audio library should be less than can not be added to sound library! 256k. The fieldbus device is already defined, do you If a fieldbus or network device is already defined in HMI, it want to replace it?/ Network device is already will prompt when you add the same fieldbus or network defined,do you want to replace it? device again. 40 The Invalid Path!/ The Invalid ProjectName! Prompt when the same protocol is added repeatedly in the same fieldbus device. Prompt when saving project as or opening project but there is no path or project name checked. Bottom Window Error: the frame can not be used as both parent window and bottom window! Two windows cannot be used as mutual bottom window. Window size settings failed, please adjust parts The width and height values of the modified window should position first, then reset the windows size! be bigger than its coordinate values. Image of GIF/PNG format or with alpha channel 43 component across The size of File %s is larger than 256K, the file Only one protocal can be defined in a device! 42 Source windows cannot be copied to the existing windows. Copy Size too large, can not be pasted! 39 41 in the project. do not support the additional transparent color treatment! In picture editing window, transparent color treatment is invalid for image of GIF/PNG format or with alpha channel. Error: Please select at least one display 【Conditional display】of component is chosen,but no condition! display condition is checked and click【OK】. Part size error: Width and height of part can not The width and height values should both be bigger than 1 less than 1! when modifying component size. 46 Error: The content cannot be empty! When static text is used, it must not be empty. 47 Error: Text size must less than screen size! 44 45 The input content of static text is too long and exceeds the screen size. 493 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 Same item exists in the text library, whether or Prompt when import text library and there is item of the not to replace? same name already existed. The Fonts are too big that exceed the display area of the Error: Text size must less than screen size! components and windows. The HMI does not support the HistoryDataDisp KW5300T/KM5303T/KG5509T/KG5300T do not support components! historical data display. MT4220TE/4414TE/4424/4522/4523/4620TE are equipped HMI cannot support USB2! with only one USB host. IP address is already defined, please check it/ IP address conflict, please check it! When there are multiple HMIs in the configuration and network communication protocol is used to network, the IP addresses cannot repeat. The station NO. is already defined, please check When adding new PLC, there is the same station no. already it! existing in the same protocol. The window id is incorrect or the window exists, The number for the new frame is illegal or the number is please input another id! already existed. The current screen does not support the property of sound ! The hmi %s dosn't support the property of Save screen shots to extend memory! The target HMI does not support audio. The target HMI does not support external storage devices. 57 Failed to open file File error when uploading. 58 Cannot open Serial Port Serial port may be occupied already. 59 Open usb handel fail USB cable is not connected or the USB port is broken, or the USB driver is not installed successfully. Errors appear during downloading, so data received by HMI 60 Send data error/read data error/Data checkSum is inconsistent with data sent by upper machine, please error/file checksum fail unplug the communication cable between HMI and PLC, restart HMI and try again. 61 Recipe file size error 62 No download option was be selected 63 Unsupport HMI, download failed! 64 Recipe size is larger than HMI recipe registers. Click the【Download】button when no download option is chosen in The model of the HMI is not supported by the used software, high version software should be used. Please use method of big BMP zipped or simplify configuration project KHDownload dialog box. The project is too large to be downloaded, please check whether lots of bitmaps or vector fonts are used in the project and simplify the project and download again. 494 Appendix 2 List of Error Information 65 create file fail 66 Save file fail 67 Upload password Cannot download to external storage device, possibly there are illegal characters included in the file name. Prompt when download to external storage device and the memory is insufficient. must contain nonzero The password cannot be zero when setting upload password character! in【HMI Attribute】page. 68 Invalid Password, please Input Password again! Upload password entry failure. 69 password checksum fail Prohibiting upload is set in the target HMI program. 70 Invalid Password. Project cannot be opened! 71 password error, please reset system and try again After the project is encrypted, password input is wrong when open project. Password for decompilation is input wrong repeatedly. Data package lost when uploading file, please unplug the 72 Failed to upload file communication cable between HMI and PLC, restart HMI and try again. 73 Click【Decompile】button when no PKG file or target No select decompile PKG file project for decomilation is chosen. Number of PKG Files wrong , can not 74 decompile!/ PKG file is not generated by the same project and same build, can not decompile! 75 76 77 78 79 80 When multiple HMIs are networked, decompilation is not supported. PKG file does not allow decompile! Prohibit decompiling is set in the【HMI Attributes】page. PKG file edited by configuration software Only the PKG files edited by software version higher than version lower than1.2.3.0 cannot be decompiled! version 1.2.3.0 can be decompiled. Another decompile process has not ended, please Prompt when starting a new decompilation while there is a closed it first! decompilation in process. Target project file cannot be saved in the same directory A same directory exists, delete it and continue? with the original PKG file. Online Simulation overtime and Program is end, Maximum duration for direct online simulation is 15 if want, Please Simulate again minutes, after the time run out users need to simulate again. An instance of software already exists, please close it first! Only one simulation process can be executed at one time. 495 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software Appendix 3 List of System Prompt Message Edit/Mask Mask address Prompt message Description Allow LW.B9296.0 [0]System Error System error (Possibly file system fault) mask/edit LW.B9296.1 [1]PLC Response Error Communication with PLC error, possibly the selected driver protocol do not support the current connected PLC (Read/write error) LW.B9296.2 [2]PLC No Response :xx-xx-x PLC no response:xx-xx-x(HMI No.-PLC station No. –Port No.) (Communication with PLC fail, please check communication cable and whether the communication parameters of PLC AND HMI are consistent) LW.B9296.4 [4]Socket Connect Error Connect to server failed. (Connect to local or remote server failed. Usually network communication faulted or PLC driver faulted, very occasionally may communication cable of PLC fault) LW.B9296.5 [5]Socket COMM Error Communication with server error LW.B9296.6 [6]MacroCode Error:xxxx Macro code xxxx execution error (Check marco code, possibly there are memory access cross-border or dividing by zero errors in marco code) LW.B9296.7 [7]Print Error Print error (communication with printer error. Please check printer connection, make sure that whether the current printer is supported by selected printer protocol) LW.B9296.8 [8]Send Package Error Send network massage failed. LW.B9296.9 [9]Memory Shortage Run out of memory (Possibly open two many popup windows or components occupying too much resources, check whether use too many popup windows, direct windows, indirect windows, trend curves, oscillograghs, XY plots, alarms and events in project) LW.B9296.A [10]BCD Transform Overflow BCD conversion outflow. Check whether BCD settings of component are correct. 496 System Parameters LW.B9296.B [11]MacroCode Timeout:xxxx Marco code xxxx executing timeout (Macro execution time is too long or there is an endless loop) LW.B9296.E [14]RW Access Overflow Recipe memory access cross-border(The accessed recipe address is beyond current allowable range of HMI) LW.B9296.F [15]Waiting to Print Waiting for printing. Printing dada is under processing (This is a normal prompt during printing) LW.B9297.0 [16]Servo Not Ready Server data is not ready (possibly server error), or possibly firmware error or PLC driver error. LW.B9297.2 [18]Transmit Data Failed Data transmission failed. LW.B9297.3 [19]Data Input Failed Number input failed, the input value exceeds the minimum/maximum values of number input component. LW.B9297.4 [20]Device Error Device fault (Access to input/output devices error, possibly file system or firmware fault) LW.B9297.5 [21]Copying File ... File is in copy (This is a normal prompt during project export or screen shoot) LW.B9297.6 [22]Copy File Failed File copy failed (Project export or screen shoot fail) LW.B9297.7 [23]Invalid File Import file is invalid(Filename invalid) LW.B9297.8 [24]Password Error Input password wrong LW.B9297.9 [25]SD Card Full SD card is full LW.B9297.A [26]USB Disk1 Full U disk 1 is full LW.B9297.B [27]USB Disk2 Full U disk 2 is full LW.B9298.0 [32]RTC Device Error RTC clock fault (possibly RTC chip fault) LW.B9298.2 [34]Invalid UserName Invalid user name (The input user name is invalid when login or add/delete user) LW.B9298.3 [35]Operation Complete Prompt of operation success (This is normal prompt during printing when adding/deleting user or modifying password) Do not allow edit/mask No DOWNLOAD/SIM MODE Enter download mode corresponding STRAIGHT MODE Enter straight mode mask bits SIMULATION MODE Enter indirect online simulation mode 497 Kinco HMIware Configuration Edit Software LOAD PKG OK! Project download success. LOAD PKG ERROR! Project download fail. TP adjust success! Touch screen calibration success. TP adjust fail, try again! Touch screen calibration fail, calibrate again. DOWNLOAD/SIM MODE There is no project in HMI, download project User Data invalid, please again. redownload! Kinco HMIware version too low! The software version is too low, please use the Please compile with new version! newest version, compile and download project again. System Crash HMI system crash, possibly project is too large or firmware error. 498