Download SmartGLCD User Manual
Transcript
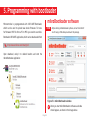
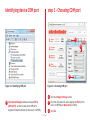
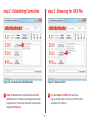
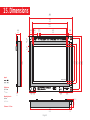
SmartGLCD 240x128 TO OUR VALUED CUSTOMERS I want to express my thanks to you for being interested in our products and for having confidence in MikroElektronika. The primary aim of our company is to design and produce high quality electronic products and to constantly improve the performance thereof in order to better suit your needs. Nebojsa Matic General Manager The PIC®, dsPIC®, PIC24®, PIC32® and Windows® logos and product names are trademarks of Microchip Technology® and Microsoft® in the U.S.A. and other countries. Page 2 Table of Contents What is the SmartGLCD 240x128? 4 step 5 – Uploading .hex file 15 Package Contains 5 step 6 – Progress bar 16 1. Key Features 6 step 7 - Finishing upload 16 7 Tips and Tricks: Speed-up UART data transfer 17 System Specification 2. Power supply 8 6. Programming with mikroProg™ programmer 18 3. PIC18F87K22 microcontroller 10 7. mikroProg Suite™ for PIC® Software 20 Key microcontroller features 10 8. microSD Card Slot 22 4. Programming the microcontroller 11 9. Touch Screen 24 5. P rogramming with bootloader 12 10. RGB backlight 26 mikroBootloader software 12 11. Contrast potentiometer 27 Identifying device COM port 13 12. USB UART 28 step 1 – Choosing COM port 13 13. Buzzer 30 step 2 - Establishing Connection 14 14. Pinout 32 step 3 - Browsing for .HEX file 14 15. Dimensions 33 step 4 – Selecting .hex file 15 What’s next? 34 Page 3 What is the SmartGLCD 240x128? The SmartGLCD 240x128 is a compact smart display, with many on-board peripherals. It’s designed to become a control interface of your device. Main part of the board is a large 240x128 pixel graphical LCD with a 4-wire resistive touch screen. It features RGB backlight, which can greatly improve user experience, but can also be used as a signaling feature. The heart of the board is PIC18F87K22, an 8-bit microcontroller delivering 12MIPS of processing power. Other modules like USB UART, piezo buzzer, microSD slot and connection pads can be found on board as well. The board is preprogrammed with UART bootloader. We have also provided a nice example which will give you a great out-of-thebox experience. Page 4 Package Contains 19122011 www.mikroe.com Copyright ©2011 Mikroelektronika. All rights reserved. Mikroelektronika, Mikroelektronika logo and other Mikroelektronika trademarks are the property of Mikroelektronika. All other tradmarks are the property of their respective owners. Unauthorised copying, hiring, renting, public performance and broadcasting of this DVD prohibited. 01 Damage resistant protective box 02 SmartGLCD 240x128 development board 03 DVD with documentation and examples SmartGLCD SCHEMATICS SmartGLCD 240x128 Pinout ver. 1.51 0 100000 024447 5V power supply Digital I/O SmartGLCD mikroProg GND RST PGD PGC 5V Digital I/O Digital I/O AN4 Digital I/O AN2 AN3 SCK1/SCL1 SDI1/SDA1 SDO1 Analog I/O 240x128 UART lines Interrupt Lines I2C Lines Analog Lines SPI Lines We present you with a complete color schematics for SmartGLCD 240x128 development board. We want you to know what your board is consisted of and how it actually works. 3.3V power supply output Ground 04 SmartGLCD 240x128 user’s guide PWM RA2 RA3 RA4 RA5 RB0 RB1 RB2 RB3 RB4 RC3 RC4 RC5 RD0 RD1 RD2 RD3 RD4 RD5 RD6 RD7 RE0 RE1 RE2 RE3 RE4 RE5 RE6 RE7 NC RF1 RF2 RF3 RF4 RF5 RF6 RF7 RG1 RG2 GND 5V SmartGLCD 240x128 - pinout Digital I/O TX RX UART Ground I2C/SPI I2C/SPI INT SDO2 SDI2/SDA2 SCK2/SCL2 240x128 5V power supply Ground 05 SmartGLCD 240x128 schematic and pinout Page 5 06 USB cable 1. Key Features 01 GLCD 240x128 display 02 RESET button 03 Power supply pads 01 04 I/O pads 05 Pads for mikroProg programmer 06 USB connector 07 Touch panel connector 08 PIC18F87K22 microcontroler 09 Contrast potentiometer 10 microSD card slot 11 USB UART module 12 Buzzer 02 03 Page 6 System Specification 12 04 05 06 power supply Via USB cable (5V DC) power consumption ~350mA in idle state (backlight is ON) 07 board dimensions 140x90cm (5.51x3.24’’) weight ~210g (0.46 lbs) 10 09 08 11 Page 7 2. Power supply The SmartGLCD board can be powered in two different ways: via USB connector (CN1) using MINI-B USB cable provided with the board (Figure 2-1), or via side headers (CN2 or CN4) using external 5V power supply (Figure 2-2 and Figure 2-3). Figure 2-1: connecting USB power supply through CN1 connector Figure 2-2: connecting external 5V power supply through CN2 connector Figure 2-3: connecting external 5V power supply through CN4 connector When the board is powered up the GLCD display will be automatically turned on. The USB connection can provide up to 500mA of current which is more than enough for the operation of all on-board modules and the microcontroller as well. Page 8 CN1 VCC VCC-3.3 VCC USB MINI-B CN4 VCC-MMC E2 10uF FB1 REG1 VCC-3.3 FERRITE BEAD VOUT E1 10uF C11 100nF 2 3 VCC VIN 1 MC33269DT-3.3 C10 E3 100nF 47uF VCC CN2 Figure 2-4: Power supply schematic Page 9 3. PIC18F87K22 microcontroller The SmartGLCD development tool comes with the PIC18F87K22 16 MIPS 8bit Core - nanoWatt - Up to 64M Hz microcontroller. This 8-bit microcontroller is rich with on-chip peripherals and features 128KB of Flash and 4KB of RAM. It can easily handle demanding graphical applications. 31 Level Stack Instruction Data Address Address Decoder Data Key microcontroller features Data/Memor y Bus - Up to 12 MIPS Operation; Flash (Up to 128K - 8-bit architecture; B) - 128KB of Flash memory; RAM (Up to 3.9K B) Data Bus - 3,862 bytes of RAM; - 1024 bytes of EEPROM; PIC18F Program Counter SPI I2C - 80 pin TQFP; - 24 ch, 12-bit ADC; - UART, SPI, I2C; etc. Page 10 I/O Timers Comparators ADC 12-Bit USART CCP MSSP 4. Programming the microcontroller Figure 4-1: PIC18F87K22 microcontroller The microcontroller can be programmed in two ways: 01 Using USB UART mikroBootloader 02 Using external mikroProg™ for PIC, dsPIC, PIC32 programmer Page 11 5. Programming with bootloader Microcontroller is preprogrammed with USB UART Bootloader, which can be used to upload new device firmware. To trans mikroBootloader software note fer firmware .HEX file from a PC to MCU you need to use mikro Bootloader USB UART application, which can be downloaded from: Before starting mikroBootloader software, connect SmartGLCD to a PC using a USB cable provided with the package. http://www.mikroe.com/smartglcd/ Upon download, unzip it to desired location and start the mikroBootloader application: Figure 5-1: mikroBootloader window 01 When you start mikroBootloader software a window should appear, as shown in the image above. Page 12 Identifying device COM port step 1 – Choosing COM port 01 02 03 Figure 5-3: Choosing COM port Figure 5-2: Identifying COM port 01 Click the Change Settings button. 02 From the drop down list, select appropriate Port (in this case it is COM18) and Baud rate (115200). 01 Open Device Manager window and expand Ports (COM & LPT) section to check which COM port is assigned to SmartGLCD board (in this case it is COM18). 03 Click OK. Page 13 step 2 - Establishing Connection step 3 - Browsing for .HEX file 01 01 Figure 5-4: Connecting with mikroBootloader Figure 5-5: Browse for HEX 01 Press the Reset button on SmartGLCD board and click Connect within 5s, otherwise the existing microcontroller program will run. If connected, the button’s caption will be changed to Disconnect. 01 Click the Browse for HEX button and from a pop-up window (Figure 5-6) choose a .HEX file to be uploaded in MCU memory. Page 14 step 4 – Selecting .hex file step 5 – Uploading .hex file 01 01 02 Figure 5-6: Locating and selecting .hex file Figure 5-7: Begin uploading 01 Select .HEX file from the Open dialog window. 01 In order to upload .HEX file click the Begin uploading button. 02 Click the Open button. Page 15 step 6 – Progress bar step 7 - Finishing upload 01 01 Figure 5-8: Progress bar Figure 5-9: Restarting MCU 01 Progress bar enables you to monitor .HEX file uploading. 01 Click OK button after the uploading process has been finished. 02 Press Reset button on SmartGLCD board and wait for 5 seconds. Your program will run automatically. Page 16 Tips and Tricks: Speed-up UART data transfer 02 04 03 01 note If .HEX file transfer from your PC to MCU is too slow, it’s possible to speed up data transfer by setting latency time of COM port to 1 ms. This is done in Device Manager: 01 Right click on the USB Serial Port (COM18) item and then select Properties. 02 Select Port Settings tab. 03 Click the Advanced... button. 04 Set Latency Timer to 1 and click OK. Page 17 6. Programming with mikroProg™ programmer The microcontroller can be programmed with the external mikroProg™ programmer which can be connected to the board via CN3 connector. Before establishing this connection it is necessary to solder 1x5 male header to CN3 connection pads. This can be done in both ways: on the bottom, or the top side, as shown in Figures 6-1 and 6-2. Figure 6-1: The mikroProg can be attached on the back side of the board. Just solder 1x5 header to back side pads (CN3) before connecting it. Figure 6-2: The mikroProg can be also attached on the front side of the board. In this case, solder 1x5 header to front side pads (CN3). note If bootloader program is accidently erased you can upload it again through mikroProg programmer. Program Bootloader18F87K22.hex can be found under Firmware folder (page 12). Page 18 VCC R22 1K VCC PGC PGD mRST# RH2 RH3 RE1 RE0 RG0 RG1 RG2 RG3 MCLR RG4 GND VDDcore/Vcap RF7 RF6 RF5 RF4 RF3 RF2 RH7 RH6 PIC18F87K22 RJ2 RJ3 RB0 RB1 RB2 RB3 RB4 RB5 RB6 GND OSC2 OSC1 VCC RB7 RC5 RC4 RC3 RC2 RJ7 RJ6 PGC VCC PGD VCC C5 100nF VCC RH5 RH4 RF1 ENVREG AVCC AGND RA3 RA2 RA1 RA0 GND VCC RA5 RA4 RC1 RC0 RC6 RC7 RJ4 RJ5 E5 10uF mRST# CN3 VCC RH1 RH0 RE2 RE3 RE4 RE5 RE6 RE7 RD0 VCC GND RD1 RD2 RD3 RD4 RD5 RD6 RD7 RJ0 RJ1 D1 BAT43 Figure 6-3: mikroProg™ connection schematic note Make sure to use only the front row of mikroProg’s IDC10 connector (side with a knob and incision) when connecting it to 1x5 header on your SmartGLCD board. Page 19 7. mikroProg Suite™ for PIC® Software The mikroProg™ programmer requires special programming software called mikroProg Suite™ for PIC®. It can be used for programming all Microchip® microcontroller families, including PIC10®, PIC12®, PIC16®, PIC18®, dsPIC30/33®, PIC24® and PIC32®. The software has intuitive interface and SingleClick™ programming technology. Just download the latest version of mikroProg Suite™ and your programmer is ready to program new devices. mikroProg Suite™ is updated regularly, at least four times a year, so your programmer will be more and more powerful with each new release. Figure 7-1: Main window of mikroProg Suite™ for PIC® programming software Page 20 Software Installation Wizard 01 Start Installation 02 Accept EULA and continue 03 Install for all users 04 Choose destination folder 05 Installation in progress 06 Finish installation Page 21 8. microSD Card Slot Figure 8-1: microSD card slot There is a built-in microSD card slot provided on-board. It enables the expansion of available memory space using microSD cards. Communication between the microcontroller and the card is done through Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI). Page 22 VCC RH1 RH0 RE2 RE3 RE4 RE5 RE6 RE7 RD0 VCC GND RD1 RD2 RD3 RD4 RD5 RD6 RD7 RJ0 RJ1 MMC-CD# R30 3K3 CD CMD VCC CLK GND DAT0 R32 3K3 R31 3K3 CN5 microSD CARD VCC-MMC R29 2K2 C12 100nF VCC-MMC 10uF FB1 MMC-CD# RC4-MISO VCC RC5-MOSI RC4-MISO RC3-SCK MMC-CS# VCC VCC R28 2K2 G RH5 RH4 RF1 ENVREG AVCC AGND RA3 RA2 RA1 RA0 GND VCC RA5 RA4 RC1 RC0 RC6 RC7 RJ4 RJ5 10uF E5 R27 2K2 E2 C5 100nF MMC-CS# PIC18F87K22 RJ2 RJ3 RB0 RB1 RB2 RB3 RB4 RB5 RB6 GND OSC2 OSC1 VCC RB7 RC5 RC4 RC3 RC2 RJ7 RJ6 RC5-MOSI RC3-SCK RH2 RH3 RE1 RE0 RG0 RG1 RG2 RG3 MCLR RG4 GND VDDcore/Vcap RF7 RF6 RF5 RF4 RF3 RF2 RH7 RH6 REG1 VCC-3.3 FERRITE BEAD VOUT E1 10uF C11 100nF 2 1 VCC VCC VIN MC33269DT-3.3 Figure 8-2: microSD Card Slot module connection schematic Page 23 3 R33 1K C10 E3 100nF 47uF 9. Touch Screen The development system features a Graphical LCD in 240x128 pixel resolution. Display is covered with a 4-wire resistive touch panel. Together they form a functional unit called a touch screen, Figure 9-1. It enables data to be entered and displayed at the same time. Figure 9-1: Touch Screen Page 24 C6 100nF VCC BOTTOM Q7 BC546 R20 100K R18 10K DRIVEB GLCD-D7 GLCD-D6 R19 10K TOUCH PANEL CONTROLLER C5 100nF R34 Figure 9-2: Touch Screen connection schematic Page 25 VO GLCD-CD GLCD-RD# GLCD-WR# GLCD-D0 GLCD-D1 GLCD-D2 GLCD-D3 GLCD-D4 GLCD-D5 GLCD-D6 GLCD-D7 GLCD-CE # GLCD-RES# Ve e GLCD-M D GLCD-FS GLCD-CD GLCD-RD# PIC18F87K22 GLCD-MD R14 10K RJ2 RJ3 RB0 RB1 RB2 RB3 RB4 RB5 RB6 GND OSC2 OSC1 VCC RB7 RC5 RC4 RC3 RC2 RJ7 RJ6 GLCD-RES# R17 100K E5 CN6 C9 100nF DRIVEB Q4 BC546 VCC LEFT DRIVEA 10uF TOP R7 10K LEFT BOTTOM Q6 BC556 RH2 RH3 RE1 RE0 RG0 RG1 RG2 RG3 MCLR RG4 GND VDDcore/Vcap RF7 RF6 RF5 RF4 RF3 RF2 RH7 RH6 VCC GLCD-D2 GLCD-D3 VCC GLCD-D1 GLCD-D0 DRIVEA R15 10K VCC TOUCH PANEL R13 10K RH1 RH0 RE2 RE3 RE4 RE5 RE6 RE7 RD0 VCC GND RD1 RD2 RD3 RD4 RD5 RD6 RD7 RJ0 RJ1 R26 10K RIGHT VCC R21 1K Q5 BC546 VCC GLCD-FS 10K GLCD-WR# GLCD-CE# RA6963 GLCD CONTROLLER VCC RH5 RH4 RF1 ENVREG AVCC AGND RA3 RA2 RA1 RA0 GND VCC RA5 RA4 RC1 RC0 RC6 RC7 RJ4 RJ5 Q8 BC556 GLCD-D5 GLCD-D4 VCC GLCD-FS VO VEE R23 10K GLCD-MD VR 10K CONTRAST 10. RGB backlight Graphical LCDs are only capable of showing monochromatic pixel but not color content. The color of the pixel is determined by the color of the backlight which illuminates the display. SmartGLCD has the RGB color backlight - a very useful feature which can give your graphical user interfaces an astonishing look. Display’s backlight module consists of three LEDs: red, green and blue, which can shine simoutaneously. LED can be driven by PWM signals coming from three separate microcontroller pins. Duty ratio of the PWM signal determines the intensity of color (or brightness) of each LED. Combined together they can create more than 16 milion different backlight colors. Figure 10-1: The same graphics with different backlight colors Page 26 11. Contrast potentiometer On the backside of the board there is a small potentiometer which can be used to change Figure 11-1: Constrast potentiometer contrast of the GLCD. The brighter the backlight, the less contrast you will need to properly display the graphical content. Page 27 12. USB UART Figure 12-1: Connecting USB cable to SmartGLCD board Fast on-board FTDI® chip allows you to communicate with a PC or other UART devices using USB UART connection. Before connecting the board to a PC, make sure that you have the appropriate FTDI drivers installed on your operating system. Drivers can be found on the Product DVD: 19122011 www.mikroe.com Av ai Copyright ©2011 Mikroelektronika. All rights reserved. Mikroelektronika, Mikroelektronika logo and other Mikroelektronika trademarks are the property of Mikroelektronika. All other tradmarks are the property of their respective owners. Unauthorised copying, hiring, renting, public performance and broadcasting of this DVD prohibited. lab le on Product D! DVD://download/eng/software/development-tools/universal/ftdi/vcp_drivers.zip DV USB-B connector (CN1) is used for connecting the USB cable, which is delivered with the board package. Plug it in as shown in Figure 12-1. Page 28 VCC RH1 RH0 RE2 RE3 RE4 RE5 RE6 RE7 RD0 VCC GND RD1 RD2 RD3 RD4 RD5 RD6 RD7 RJ0 RJ1 UART-TX PIC18F87K22 RJ2 RJ3 RB0 RB1 RB2 RB3 RB4 RB5 RB6 GND OSC2 OSC1 VCC RB7 RC5 RC4 RC3 RC2 RJ7 RJ6 UART-RX VCC C15 OSCO DTR# OSCI RTS# TEST VCCIO AGND RXD CBUS0 GND CBUS1 NC GND DSR# VCC DCD# RESET# C16 3V3OUT CBUS2 USBDM R9 4K7 R10 10K VCC E4 10uF CN1 USBDP USBDM USBDP VCC C17 100nF Figure 12-2: USB UART module connection schematic Page 29 100nF VCC GND CBUS4 FT232RL VCC NC RI# CTS# 100nF UART-RX UART-TX VCC VCC C5 100nF TXD CBUS3 RH5 RH4 RF1 ENVREG AVCC AGND RA3 RA2 RA1 RA0 GND VCC RA5 RA4 RC1 RC0 RC6 RC7 RJ4 RJ5 10uF E5 RH2 RH3 RE1 RE0 RG0 RG1 RG2 RG3 MCLR RG4 GND VDDcore/Vcap RF7 RF6 RF5 RF4 RF3 RF2 RH7 RH6 VCC VCC-3.3 U12 USB MINI-B 13. Buzzer Figure 13-1: Buzzer module The board is also equipped with piezo buzzer. It is an electric component which can be used to create sound when provided with electrical signal. This is usually a PWM signal coming from a microcontroller pin. Before entering the buzzer itself, the signal is amplified by the on-board buzzer driver circuit. Frequency of the signal determines the pitch of the sound and duty cycle of the signal can be used to increase or decrease the volume. Page 30 VCC RH1 RH0 RE2 RE3 RE4 RE5 RE6 RE7 RD0 VCC GND RD1 RD2 RD3 RD4 RD5 RD6 RD7 RJ0 RJ1 PIC18F87K22 RJ2 RJ3 RB0 RB1 RB2 RB3 RB4 RB5 RB6 GND OSC2 OSC1 VCC RB7 RC5 RC4 RC3 RC2 RJ7 RJ6 VCC C5 100nF VCC RH5 RH4 RF1 ENVREG AVCC AGND RA3 RA2 RA1 RA0 GND VCC RA5 RA4 RC1 RC0 RC6 RC7 RJ4 RJ5 10uF E5 RH2 RH3 RE1 RE0 RG0 RG1 RG2 RG3 MCLR RG4 GND VDDcore/Vcap RF7 RF6 RF5 RF4 RF3 RF2 RH7 RH6 Figure 13-2: Buzzer module schematic Page 31 VCC VCC R37 1K R36 R35 1K 10K BZ1 Q9 BC546 AN4 Digital I/O AN2 AN3 Digital I/O INT SCK1/SCL1 SDI1/SDA1 SDO1 Digital I/O 3.3V power supply output Ground Digital I/O SDO2 SDI2/SDA2 SCK2/SCL2 PWM Page 32 Analog I/O 5V power supply Ground 5V power supply TX RX UART Ground Digital I/O I2C/SPI GND RST PGD PGC 5V RA2 RA3 RA4 RA5 RB0 RB1 RB2 RB3 RB4 RC3 RC4 RC5 RD0 RD1 RD2 RD3 RD4 RD5 RD6 RD7 RE0 RE1 RE2 RE3 RE4 RE5 RE6 RE7 NC RF1 RF2 RF3 RF4 RF5 RF6 RF7 RG1 RG2 GND 5V 14. Pinout I2C/SPI mikroProg Analog Lines Interrupt Lines SPI Lines I2C Lines UART lines 15. Dimensions 140 5512 114 4488 11,6 457 12,7 500 12,7 4000 11,56 455 Legend active surface display margin display Mounting hole size ø 4 mm ø 157 mils 1.6 63 12.57 500 13.12 4.8 516 190 30 1181 2 (79) 12.3 421 Pad hole size ø 1.14 mm ø 45 mils Tolerance +/- 0.5mm 128 5040 Page 33 7 276 90 3543 83 3268 64 2520 74 2913 57.5 2264 7.77 306 14.73 580 16.3 642 2.54 100 107.5 4232 What’s next? Your journey through each and every feature of SmartGLCD board ends here. You got to know it’s modules and organization. Now you are ready to use it. We are suggesting several steps which are probably the best way to begin with. We invite you to join the users of SmartGLCD brand. You will find very useful projects and tutorials and can get help from a large ecosystem of users. Welcome! Compiler You still don’t have an appropriate compiler? Locate PIC® compiler that suits you best on the Product DVD provided with the package: DVD://download/eng/software/compilers/ Choose between mikroC™, mikroBasic™ and mikroPascal™ and download fully functional demo version, so you can begin building your first applications. Projects Once you have chosen your compiler, and since you already got the board, you are ready to start writing your first projects. Visual GLCD software for rapid development of graphical user interfaces enables you to quickly create your GUI. It will automatically create necessary code which is compatible with mikroElektronika compilers. Visual GLCD is rich with examples, which are an excellent starting point for your future projects. Just load the example, read well commented code, and see how it works on hardware. Visual GLCD is also available on the Product DVD. Page 34 DISCLAIMER All the products owned by MikroElektronika are protected by copyright law and international copyright treaty. Therefore, this manual is to be treated as any other copyright material. No part of this manual, including product and software described herein, may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, translated or transmitted in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of MikroElektronika. The manual PDF edition can be printed for private or local use, but not for distribution. Any modification of this manual is prohibited. MikroElektronika provides this manual ‘as is’ without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties or conditions of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. MikroElektronika shall assume no responsibility or liability for any errors, omissions and inaccuracies that may appear in this manual. In no event shall MikroElektronika, its directors, officers, employees or distributors be liable for any indirect, specific, incidental or consequential damages (including damages for loss of business profits and business information, business interruption or any other pecuniary loss) arising out of the use of this manual or product, even if MikroElektronika has been advised of the possibility of such damages. MikroElektronika reserves the right to change information contained in this manual at any time without prior notice, if necessary. HIGH RISK ACTIVITIES The products of MikroElektronika are not fault – tolerant nor designed, manufactured or intended for use or resale as on – line control equipment in hazardous environments requiring fail – safe performance, such as in the operation of nuclear facilities, aircraft navigation or communication systems, air traffic control, direct life support machines or weapons systems in which the failure of Software could lead directly to death, personal injury or severe physical or environmental damage (‘High Risk Activities’). MikroElektronika and its suppliers specifically disclaim any expressed or implied warranty of fitness for High Risk Activities. TRADEMARKS The MikroElektronika name and logo, the MikroElektronika logo, mikroC™, mikroBasic™, mikroPascal™, mikroProg™, mikroBUS™, Click Boards™, EasyPIC and mikromedia™ are trademarks of MikroElektronika. All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their respective companies. All other product and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks or copyrights of their respective companies, and are only used for identification or explanation and to the owners’ benefit, with no intent to infringe. Copyright © MikroElektronika, 2013, All Rights Reserved. Page 35 If you want to learn more about our products, please visit our website at www.mikroe.com If you are experiencing some problems with any of our products or just need additional information, please place your ticket at www.mikroe.com/esupport If you have any questions, comments or business proposals, do not hesitate to contact us at [email protected] SmartGLCD 240x128 Manual ver. 1.51 0 100000 024430