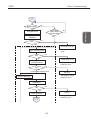
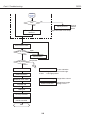
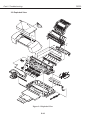
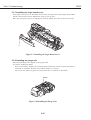
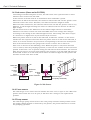
Download S6300 Service Manual
Transcript
REVISION 0 AUG. 2001 COPYRIGHT 2001 CANON INC. CANON S6300 0801 XX 0.00-0 PRINTED IN JAPAN (IMPRIME AU JAPON) 082001 XX 0.00-0 Application This manual has been issued by Canon Inc. for qualified persons to learn technical theory, installation, maintenance, and repair of products. This manual covers all localities where the products are sold. For this reason, there may be information in this manual that does not apply to your locality. Corrections This manual could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors due to improvements or changes in the products. When changes occur in applicable products or in the content of this manual, Canon will release technical information as the need arises. In the event of major changes in the contents of this manual over a long or short period, Canon will issue a new edition of this manual The following paragraph does not apply to any countries where such provisions are inconsistent with local law. Trademarks The product names and company names described in this manual are the registered trademarks of the individual companies. Copyright This manual is copyrighted with all rights reserved. Under the copyright laws, this manual may not be copied, reproduced or translated into another language, in whole or in part, without the written consent of Canon Inc., except in the case of internal business use. Copyright 2001 by Canon Inc. CANON INC. i Printer Technical Support Dept. 11 16-1, Shimonoge 3-chome, Takatsu-ku, Kawasaki, Kanagawa 213-8512, Japan This manual has been produced on an Apple Power Macintosh 7300/180 personal computer and OKI MICROLINE 803 PSIIV laser beam printer; printing films were printed on Agfa SelectSet Avantra 25. All page layouts, logos, and parts-list data were saved with Canon Optical Disc Subsystem mo-5001S™ and Optical Disc Cartridge mo-502M™, and Interface Kit mo-IF2™ for Macintosh. All graphics were produced with MACROMEDIA FREEHAND™ 7.0J. All documents and all page layouts were created with QuarkXpress™ 3.3 Japanese version. I. ABOUT THIS MANUAL This manual consists of four parts containing information for servicing the product. Product Specifications Part 1: Product Specifications Product overview and specifications. Technical Reference Part 3: Technical Reference Block diagrams and information on the hardware's new technologies. Troubleshooting Part 2: Troubleshooting A guide to troubleshooting the product and identifying parts needing replacement. Troubleshooting solutions are listed according to the error indications displayed by the status indicator and by problem descriptions. Appendix Part 4: Appendix Pin configurations. Disassembly and reassembly procedures are not fully covered in this manual. Refer to the illustrations in the separate Parts Catalog as well. I II. TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 1- 1 1- 1 1- 2 1- 2 1- 2 1- 3 1- 3 1- 4 1- 4 1- 4 1- 5 1- 6 1- 6 1- 7 1- 8 Part 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS 1. PRODUCT OVERVIEW 1.1 Product Overview 2. SPECIFICATIONS 2.1 Printer Specifications 2.1.1 Printer specifications 2.1.2 Printer service life 2.1.3 BJ cartridge service life 2.2 Paper Specifications 2.2.1 Paper sizes and weights 2.2.2 Paper types and settings 2.2.3 Printing area 2.3 BJ Cartridge Specifications 2.4 Printer and Scanner Drivers 3. PACKING CONFIGURATION 4. PARTS CODE LIST Part 2: TROUBLESHOOTING 2- 1 2- 1 2- 1 2- 2 2- 2 2- 2 2- 4 2- 5 2- 5 2- 6 2- 9 2 -10 2 -13 2 -13 2 -13 2 -13 2 -13 2 -14 2 -15 2 -15 2 -16 2 -16 2 -17 2 -17 2 -17 2 -18 2 -18 2 -19 2 -19 2 -20 2 -21 2 -22 1. PRINTER OPERATION 1.1 Printer Operation Procedure 1.2 Status Indicator 1.3 Operating the Printer 1.3.1 Cleaning operation 1.3.2 Printing the nozzle check pattern 1.3.3 Roller cleaning operation 2. SERVICING 2.1 Before Troubleshooting 2.2 Detectable Problems from System Start to Exit 2.3 Troubleshooting Problems 2.4 Troubleshooting Error Indications 3. DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY 3.1 Cautions for Disassembly and Reassembly 3.1.1 Cautions for ink stains (Ink path/ink mist) 3.1.2 Damage by static electricity 3.1.3 Deformation of spur tips 3.2 Exploded View 3.3 Disassembly and Reassembly 3.3.1 Carriage lock release 3.3.2 Removing and installing tap screws 3.3.3 Installing and removing the carriage encoder film 3.3.4 Handling encoder film 3.3.5 Removing and installing the control board 3.3.6 Removal of red screws prohibited 3.3.7 Installing the logic board cover 3.3.8 Handling the purge unit 3.4 Adjustments and Settings After Disassembly and Reassembly 3.4.1 Adjustments 3.4.2 Applying grease 3.4.3 Print head position adjustment 3.4.4 Print head seam stripe adjustment II Page 2 -23 2 -24 2 -24 2 -25 2 -25 2 -26 2 -26 2 -26 2 -26 2 -27 2 -27 2 -28 2 -29 2 -30 2 -30 4. 5. 6. 7. 3.4.5 Setting the EEPROM OPERATION CHECK AFTER DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY 4.1 Check Procedure TRANSPORTING THE PRINTER 5.1 Procedure PARTS REPLACEMENT, PERIODIC INSPECTIONS, & TOOLS 6.1 Parts Replacement 6.2 Periodic Inspections 6.3 Tool List SERVICE-RELATED FEATURES 7.1 Service Mode Operations 7.2 Test Printout 7.3 Printing the EEPROM Information 7.4 Resetting the EEPROM 7.5 Setting the Printer Settings in the EEPROM Part 3: TECHNICAL REFERENCE 3- 1 3- 1 3- 2 3- 3 3- 4 3- 5 3- 5 3- 5 3- 5 3- 6 3- 6 3- 6 3- 6 3- 7 3- 7 3- 7 3- 8 3- 8 3- 8 3- 9 3- 9 3- 9 3- 9 3- 9 3- 9 3- 9 3 -10 3 -10 3 -11 3 -12 3 -12 3 -12 3 -12 3 -13 3 -14 3 -14 1. PRINTER CONTROL SECTION 1.1 Printing Data and Control Signal Flow 1.2 Print Drive Method 1.2.1 Print drive control 1.2.2 Print driving method 1.3 Control During Printing 1.3.1 2-dot Pair + Bi-directional printing 1.3.2 Seam stripe control 1.3.3 Rest between scans (Border detection control) 1.3.4 Smear control and rest between pages 1.3.5 Automatic power ON/OFF 1.3.6 Print head protection from overheating 1.3.7 Power motor control 1.4 Detection Functions 1.4.1 Detection by sensors 1.4.2 Paper-end sensor 1.4.3 Ink sensor (Same as for BJ F600) 1.4.4 Cover sensor 1.4.5 Pump sensor 1.4.6 Internal temperature sensor 1.4.7 Head temperature sensor 1.4.8 ASF sensor 1.4.9 Carriage encoder/paper feed encoder 1.5 Other Sensing Features 1.5.1 Waste-ink detection 1.5.2 Print head detection 2. ELECTRICAL DRIVE SECTION 2.1 Block Diagram 2.2 Electrical Section 3. PRINTER'S MECHANICAL PARTS 3.1 Overview of the Printer's Mechanical Parts 3.1.1 Carriage 3.1.2 Purge section 3.1.3 Paper feed section 3.2 Purge Section 3.2.1 Purge section functions III Page 3 -15 3 -17 3 -17 3 -18 3 -18 3 -18 3 -19 3 -22 3 -22 3 -22 3 -23 3 -24 3 -24 3 -25 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 3.2.2 Purge section components 3.3 Paper Feed Section 3.3.1 Paper feed components 3.3.2 Friction separation system 3.3.3 Paper transport section 3.3.4 Paper discharge section LOGIC BOARD COMPONENTS OPERATION WITH A COMPUTER 5.1 Printing Operation with the Basic Settings Sheet 5.2 Using the Utility Sheet INK SUCTION AMOUNT IN THE CLEANING MODE TECHNICAL REFERENCE 7.1 Printing Mode List PRINT HEAD Part 4: APPENDIX 4444- 1 5 7 8 1. CONNECTOR LOCATIONS AND PIN CONFIGURATIONS 1.1 Carriage Board 1.2 Print Head 2. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM IV III. ILLUSTRATION INDEX Page 1- 1 1- 3 1- 3 1- 5 1- 7 Part 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure 11111- 1 2 3 4 5 Printer Exterior 1500 Characters Pattern JIS SCID No. 5 Printable Area Packing Configuration Part 2: TROUBLESHOOTING 2- 1 2- 3 2 -14 2 -15 2 -16 2 -17 2 -18 2 -18 2 -20 2 -21 2 -22 2 -28 2 -29 Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure 2- 1 2- 2 2- 3 2- 4 2- 5 2- 6 2- 7 2- 8 2- 9 2 -10 2 -11 2 -12 2 -13 Operation Panel Nozzle Check Pattern Printout Exploded View Carriage Lock Release Encoder Film Do not Remove the Red Screws Installing the Logic Board Cover Handling the Purge Unit Applying Grease Printing Position Adjustment Pattern Seam Stripe Adjustment Pattern Service/Factory Test Printout (Sample) EEPROM Information Printout (Sample) Part 3: TECHNICAL REFERENCE 3- 1 3- 2 3- 3 3- 4 3- 7 3- 8 3 -10 3 -12 3 -15 3 -16 3 -17 3 -19 3 -22 3 -25 Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure 3- 1 3- 2 3- 3 3- 4 3- 5 3- 6 3- 7 3- 8 3- 9 3 -10 3 -11 3 -12 3 -13 3 -14 Printing Signal Flow Serial Data Print Driving Printing Driving Method Location of Sensors Ink Sensor Block Diagram Printer's Mechanical Parts Purge Section Components Pump Operation Paper Feeding Control Board Basic Settings Sheet (Sample) Nozzle Array Part 4: APPENDIX 4- 1 4- 5 4- 7 Figure 4 - 1 Figure 4 - 2 Figure 4 - 3 Control Board Carriage Board BJ Cartridge V IV. TABLE INDEX Page 1- 9 Part 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS Table 1- 1 PARTS CODE Part 2: TROUBLESHOOTING 2 -10 Table 2- 1 ERROR INDICATIONS Part 3: TECHNICAL REFERENCE 3 -24 Table 3- 1 PRINTING MODE LIST VI Part 1 PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS Page 1- 1 1- 1 1- 2 1- 2 1- 4 1- 6 1- 6 1- 7 1- 8 1. PRODUCT OVERVIEW 1.1 Product Overview 2. SPECIFICATIONS 2.1 Printer Specifications 2.2 Paper Specifications 2.3 BJ Cartridge Specifications 2.4 Printer and Scanner Drivers 3. PACKING CONFIGURATION 4. PARTS CODE LIST Part 1: Product Specifications S6300 I. PRODUCT OVERVIEW 1.1 Product Overview *1: *2: Standard pattern to measure print speed, in use since 1998. Dot-by-dot printing performed at 1,200 x 1,200 dpi on A4-sized paper "Standard Color Printer for Personal Use" Printer(Front) Printer(Rear) Print Head Figure 1-1 Printer Exterior 1-1 Product Specifications “High-Performance Personal and Business Use Color Printer” While emphasizing out-of-box performance, the S6300 offers default setting high-speed and high-quality printing on plain paper. With the same engine as the S600, the printer takes full advantage of the S600’s features, and supports up to A3+ sized paper to function as a high-performance business-use printer. Differences from the S600 are as follows: (1) Supported size of paper Up to A3+ (S600: A4) (2) Print speed (measured with A4-sized paper) Monochrome printing, text (HS): 17 ppm (New monochrome pattern*1) Color printing, DTP (HS): 12 ppm (New color pattern*1) Color printing (for reference): 2.5 ppm (A4 full address pattern*2) (3) Paper eject support function to prevent smearing Part 1: Product Specifications S6300 2. SPECIFICATIONS 2.1 Printer Specifications 2.1.1 Printer specifications Type Paper Feed System Resolution Throughput Desktop serial printer Automatic feed only (No manual feed) 2400 × 1200 dpi (Max. resolution) Bk: 17 ppm Color: 12 ppm Printing Direction HS mode (600 dpi × 600 dpi...): Single-pass bi-directional (Plain/Special HQ mode (600 dpi × 600 dpi/1200 dpi × 1200 dpi): paper) Single-pass unidirectional/double- or triple-pass bi-directional Fine1 mode (1200 dpi × 1200 dpi/As above): 1.2-pass unidirectional/4- or 6-pass bi-directional Fine2 mode (As above/As above): 4-pass bidirectional/4-pass unidirectional or bi-directional Fine3 mode (.../2400 dpi × 1200 dpi): 4-pass unidirectional or 6-pass bi-directional Max. Printing Width 322.2mm (12.7inch) wide Interface IEEE 1284-standard, 8-bit parallel, USB (No HUB function) ASF Capacity Plain paper: Max. 10 mm (Approx. 100 sheets with 75 g/m2 or approx. 110 sheets with 64 g/m2) Sensors Front cover-open sensor, Print Head-loaded sensor, No-ink sensor, Printing position sensor, Paper sensor (paper out detector), Wasteink capacity sensor, Internal temperature sensor, Pick-up roller sensor, Paper-feed roller position sensor, Carriage position sensor, Paper interval sensor Operating Noise (at 39 dB (A) Sound pressure level conforms to ISO 9296. HQ) Ambient Conditions During operation: Temperature 5°C-35°C (41°F-95°F) Humidity 10%-90% RH (No condensation) During non-operation: Temperature 0°C-40°C (32°F-95°F) Humidity 5%-90% RH (No condensation) Power Source Power voltage/frequency Power consumption During standby When Off 100-127 VAC 50/60 Hz Max. approx. 33 W Approx. 3 W Approx. 1 W 220-240 VAC 50/60 Hz Max. approx. 33 W Approx. 3 W Approx. 1 W External Approx. 573 mm (W) × 335 mm (D) × 194 mm (H) Dimensions Weight Approx. 7 kg (excluding Print Head) Certification Radio wave interference: VCCI, FCC, IC, C-Tick, Taiwan/Korea (Printer & adapter) EMC, CCIB (EMC)/CCEE Electrical safety: Electrical appliance regulation, UL, Cul, CE Mark, TUV, FIMKO, SASO, AS, PSB, Korean Electric Commerce, CB/CCIB/CCEE Environmental: Energy Star, Blue Angel Serial No. Location Carriage ribbon cable holder (visible when the access cover is open) 1-2 Part 1: Product Specifications S6300 2.1.2 Printer service life 2.1.3 BJ cartridge service life (1) Service life For monochrome printing (1500-character standard text pattern printing): 30,000 pages For color printing (7.5% duty pattern printing per color): 10,000 pages (2) Ink tank service life (printable pages per tank) Monochrome (black): 695 pages (1500 characters pattern*1/Printing quality: Standard) Color (Cyan): 460 pages (JIS SCID No. 5*2/Printing quality: Standard) (Magenta): 395 pages ( As above ) (Yellow): 300 pages ( As above ) *1 Printing duty: Equivalent *2 Printing duty: Equivalent Equivalent Equivalent to to to to 2.22% 3.68% 5.12% 6.10% pattern (cyan) pattern (magenta) pattern (yellow) pattern Figure 1-2 1500 Characters Pattern Figure 1-3 JIS SCID No. 5 1-3 Product Specifications Whichever comes first: (1) A total of 30,000 sheets printed with 1,500 standard characters in black ink. (2) A total of 10,000 sheets printed with 7.5% duty per color. (3) Five years of use. Part 1: Product Specifications S6300 2.2 Paper Specifications 2.2.1 Paper sizes and weights (1) Paper sizes See the table below. (2) Weight For automatic feeding, the paper's weight should be 64-105 g/m2. 2.2.2 Paper types and settings Type Size Plain paper High-quality paper Photo glossy paper Photo paper Glossy film Transparency film Banner T-shirt transfer Mouse pad Glossy postcard Photo glossy card Japan Post Office postcard Japan Post Office postcard for ink jet printing Pro photo postcard Envelope Sheet Feeder Capacity 64-105 g/m2 A3+/A3/b4/A4+/A4 B5/A5/LGL/LTR HR-101 A3/b4/A4+/A4/B5/A5 LGL/LTR A3+ GP-301 A4+/A4/LTR A3+/B4/LGL PR-101 A4/LTR HG-201 A4/LTR CF-102 A4/LTR BP-101 A4/LTR TR-201 A4/LTR MK-101 --KH-201 148 mm × 100 mm FM-101 118.6 mm × 213.9 mm --148 mm × 100 mm --- 148 mm × 100 mm PH-101 COM#10 DL-size No. 4 No. 6 148 241 220 235 190 mm mm mm mm mm × × × × × 100 mm 106 mm 110 mm 105 mm 98 mm Paper Spacing Less than 10 mm Lever Position Left (Narrow) Less than 80 sheets Left (Narrow) Less than 10 sheets 1 sheet 1 sheet 1 sheet Less than 1 sheet 1 sheet 1 sheet Less than Less than Less than 20 sheets Left (Narrow) 20 20 40 Left (Narrow) Left (Narrow) Left (Narrow) Right (Wide) Right (Wide) Left (Narrow) Left (Narrow) Left (Narrow) Left (Narrow) Less than 40 Left (Narrow) Less Less Less Less Less Left (Narrow) Right (Wide) Right (Wide) Right (Wide) Right (Wide) than than than than than 30 sheets 20 10 10 10 10 If the paper spacing lever is not properly set, problems with paper feeding or printing may occur. 1-4 Part 1: Product Specifications S6300 2.2.3 Printing area ■ A3+,A3,B4,A4+,A4, B5, A5 Paper-feeding direction 28.0 mm 3.0 mm ±1.5 26.5 mm 5.0 mm Recommended printing area: Printable area: 28.0 mm Product Specifications 3.0 mm ±1.5*1 ■ Letter,Leger 26.5 mm 5.0 mm 6.4 mm ±1.5 mm ( 3.4 ) ±1.5 3.4 mm ±1.5*1 ■ Envelope (No. 4/No. 6) mm ( 6.4 ) ±1.5 ■ Glossy postcard/Japan Post Office postcard/ Japan Post Office postcard for ink jet printing/Pro photo postcard 3.0 mm ±3.0 28.0 mm 3.0 mm ±1.5 26.0 mm*2 5.0 mm 26.5 mm 3.4 mm ±2.0 3.4 mm ±1.5 mm ( 3.4 ±2.0 ) ■ Photo glossy card 5.1 mm mm ( 3.4 ) ±1.5 4.1 mm ■ Pro Photo Card PC-101 L: L size PC-101 2L: 2L size PC-101 D: DCS size cut into 4 28.8 mm PC-101 W: 8x10 in. for digital cameras 25.0 mm 29.0 mm 25.0 mm 28.8 mm 25.0 mm*2 3.3 mm 3.3 mm 13.0 mm 13.0 mm 29.0 mm 9.0 mm 9.0 mm 25.0 mm 7.0 mm *1 For recycled paper, it will be 3.0mm ±3 or 3.4mm ±2. *2 If the bottom margin goes beyond the plain paper's printable area, the software application's specifications will apply. The region inside the dotted lines is the printable area where print quality can be guaranteed. Note: The right margins in parentheses indicate that the dimension depends on the paper size. Figure 1-4 Printable Area 1-5 7.0 mm Part 1: Product Specifications S6300 2.3 BJ Cartridge Specifications Configuration Print Head Ink Colors* Ink Tank Weight (Net value) Print Head Detachable ink tanks for each color and BK/Cl (C, M, Y) integrated head BK: 320 nozzles, 2-column vertical array Cl: 256 nozzles/color, 2-column vertical array/color Pigment BK, dyes C, M, Y BCI-3eBK, BCI-3eC, BCI-3eM, BCI-3eY BK: 32 g Cl (C, M, Y): 11 g 2.4 Printer and Scanner Drivers The user interface of the drivers has been greatly improved. See page 3-22 for details. 1 Windows drivers Win95/98/ME BJ raster driver (V. 7.10) Win9NT4.0 BJ raster driver (V. 4.40) Win2000 BJ raster driver (V. 1.40) 2 Macintosh driver Mac BJ printer driver (V. 3.75) 3 Scanner driver None. 1-6 Part 1: Product Specifications S6300 3. PACKING CONFIGURATION After opening the box, make sure all the items below are included. Instruction Manuals Power Cord Printer Ink Tank Print Head Figure 1-5 Packing Configuration There is no storage box for storing the Print Head. 1-7 Product Specifications Paper Support Part 1: Product Specifications S6300 4. PARTS CODE LIST A list of printer parts, consumables, and optional equipment are listed below. The printer's BJ cartridge (print head) will be supplied only as a spare part for servicing. Table 1-1 PARTS CODE Item Printer Print Head*1 Ink tank --- Designation S6300 --Black Cyan Magenta Yellow BJ S6300 --BCI-3eBK BCI-3eC BCI-3eM BCI-3eY Parts Code Q30-3480 (CCSEK) Q30-3482 (HK/TW) Q30-3481 QY6-0034 F47-3131 F47-3141 F47-3151 F47-3161 *1 Supplied only as a spare part for servicing. It will not be supplied as a consumable or optional part. 1-8 Part 1: Product Specifications S6300 Product Specifications This page intentionally left blank 1-9 Part 2 TROUBLESHOOTING Page 2- 1 2- 1 2- 1 2- 2 2- 5 2- 5 2- 6 2- 9 2 -10 2 -13 2 -13 2 -14 2 -15 2 -19 2 -24 2 -24 2 -25 2 -25 2 -26 2 -26 2 -26 2 -26 2 -27 2 -27 2 -28 2 -29 2 -30 2 -30 1. PRINTER OPERATION 1.1 Printer Operation Procedure 1.2 Status Indicator 1.3 Operating the Printer 2. SERVICING 2.1 Before Troubleshooting 2.2 Detectable Problems from System Start to Exit 2.3 Troubleshooting Problems 2.4 Troubleshooting Error Indications 3. DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY 3.1 Cautions for Disassembly and Reassembly 3.2 Exploded View 3.3 Disassembly and Reassembly 3.4 Adjustments and Settings After Disassembly and Reassembly 4. OPERATION CHECK AFTER DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY 4.1 Check Procedure 5. TRANSPORTING THE PRINTER 5.1 Procedure 6. PARTS REPLACEMENT, PERIODIC INSPECTIONS, & TOOLS 6.1 Parts Replacement 6.2 Periodic Inspections 6.3 Tool List 7. SERVICE-RELATED FEATURES 7.1 Service Mode Operations 7.2 Test Printout 7.3 Printing the EEPROM Information 7.4 Resetting the EEPROM 7.5 Setting the Printer Settings in the EEPROM Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 1. PRINTER OPERATION The printer's operation procedures are explained below. You can operate the printer either by itself or with a computer. Both methods are explained below. 1.1 Printer Operation Procedure The printer's operation panel has a POWER button and a RESUME button to cancel printing operation or to cancel an error. With a computer, you can use the printer driver to adjust the print head's position and to change various settings. For details on using the printer driver with the computer, see page 3-22. RESUME button Cancels printing operation or an error. The cleaning and nozzle check pattern can be selected by the number of blinks of the indicator. Figure 2-1 Operation Panel 1.2 Status Indicator When you operate the printer by itself, you can find out the printer's operation status with the indicator. When an error occurs, the nature of the error can be determined by the number of times the indicator blinks. Normal Operation Indicator Display Green light Blinks green (Long/short) Light off Operation Status Power ON Power ON in progress, power OFF in progress, resume operation in progress, cleaning in progress, test printing in progress, front cover open, printing in progress Power OFF Error Indicator Display Blinks orange (Long/short) Green/orange (Toggle blinking) Operation Status The number of blinks differs depending on the error. See page 2-10 for details. The blinking method differs depending on the error. See page 2-11 for details. 2-1 Troubleshooting POWER button Turns the printer ON/OFF and cancels test printing. Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 1.3 Operating the Printer The printer has an offline operation mode that works when the printer is not connected to a computer and the power is on. To conduct the operations below, with the power turned on, hold down the RESUME button until the green indicator blinks for the specified number of times. Operation Cleaning operation Nozzle check pattern printing Roller cleaning operation --- Indicator Blink Count Once Twice 3 times Remarks --Load a sheet of B5 or larger paper. Load no paper or load A4 paper. 4 times Execute no operations. 1.3.1 Cleaning operation To start the cleaning operation, turn on the printer and hold down the RESUME button until the green indicator blinks once. Then let go of the button. Cleaning will then start. The black and color ink nozzles will be cleaned simultaneously by suction. This is the same as using the printer driver to clean all of the ink nozzles. 1.3.2 Printing the nozzle check pattern With the printer turned on, hold down the RESUME button until the green indicator blinks twice. The printer will then start printing the nozzle check pattern. If any printing flaws show up in this test printout, clean the BJ cartridge. Printing the nozzle check pattern requires B5 or larger paper. If the paper's width is narrower than the nozzle check pattern, the printer will print on the bare platen, dirtying the platen with ink. To stop printing of the test pattern midway, press the POWER button. Printing will stop and the paper will be ejected. The printer will remain on. If the problem persists even after cleaning the BJ cartridge three times, Perform Deep Cleaning of from the driver. If that still does not resolve the problem, replace the BJ cartridge. 2-2 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 Troubleshooting Figure 2-2 Nozzle Check Pattern Printout 2-3 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 1.3.3 Roller cleaning operation This is to remove the paper dust adhering to the auto sheet feeder's rollers. With the printer turned on, hold down the RESUME button until the green indicator blinks once. The cleaning of the rollers will then start. There are two cleaning methods: (1) Rotating the rollers without paper Execute roller cleaning without placing any paper on the auto sheet feeder. (The rollers will rotate ten times.) Do this three times. (2) Passing plain paper throughtest Place a sheet of plain paper on the auto sheet feeder and execute roller cleaning. Do this three times. Do not execute the cleaning operation more times than necessary. Excessive cleaning will generate rubber dust which can affect the printer's operation. 2-4 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 2. SERVICING 2.1 Before Troubleshooting Before troubleshooting, check the following and see if any of the applicable problems can be fixed. Problem The printer does not operate at all. No printing. Stripes appear in the printout. 2-5 Troubleshooting Paper feeding does not work. Probable Cause Solution The power outlet is not supplying Connect the AC cord to a power the required voltage. outlet which supplies the required voltage. The power cord is not properly Check that the power cord is connected to the printer or power connected properly. outlet. An internal plug is disconnected. Disconnect and reconnect the plug. The recommended paper is not Use the recommended paper. being used. There is foreign matter in the Remove the foreign matter. paper feed section (sheet feeder, pinch roller, LF roller, platen, spur). The Print Head needs cleaning. Clean the Print Head. The ink cartridge is empty. Replace the ink cartridge. The Print Head has not been Clean the cartridge. If the used for a prolonged period. problem still persists, replace the cartridge. The print head position has not Execute print head position been adjusted. adjustment. See page 2-23. Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 2.2 Detectable Problems from System Start to Exit Errors unresolvable by the user can be checked before system startup is completed. AC power connection CPU & printer controller initialization DRAM check OK? No Yes RAM error EEPROM check Orange lamp lights Checksum Power ON Power LED lights EEPROM error Error check Orange/green toggle blinking 9 times Key input detection prohibited Sensor power ON VSEN ON Cartridge error (a) Interrupt error detection starts Abnormal internal temperature error Head presence detection Paper feed encoder home position obtained Abnormal head temperature error Take the cartridge to the home position. To next page 2-6 Orange blinks 7 times Orange/green toggle blinking 6 times Orange/green toggle blinking 8 times Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 From preceding page 1 No Head present? Yes Reading of head's EEPROM Yes Troubleshooting Procedure within dotted line executed? Head power ON No No OK? Yes 2nd time 1st time execution within dotted line Cartridge error (b) Orange blinks 7 times Purge unit initialization No OK? Yes Purge sensor error Cartridge home position obtained Orange/green toggle blinking 4 times No OK? Yes 1st time No head/2nd time CR error Orange/green toggle blinking 2 times Cap open Reserve discharge Paper feed roller initialization No OK? Yes LF error Paper discharge Orange/green toggle blinking 3 times To next page 2-7 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 From preceding page OK? No Yes Paper jam error Paper feed roller turns slowly Encoder parameter obtained Cover sensor check Open or closed? Closed Head present? Present Ink-low detection Paper spacing lever position detection Waste ink error check I/F power ON Open Move carriage to home position Not present Back to 1 No-ink error No error indication If narrow : Right position from the left edge. If wide : Left edge position. Waste ink warning Orange blinks 8 times Waste ink full error Orange/green toggle blinking 7 times LED lights I/F busy canceled Switch detection prohibit canceled END 2-8 Orange blinks 3 times Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 Faulty Paper Feed Faulty Printout Problem Power does not turn on. After power ON, it immediately turns off. The print head is not recognized. It does not return to the home position. Abnormal noise. Probable Cause / Check Items 1. AC adapter, 2. Logic board Solution 1. Replace faulty parts. 1. Print Head, 2. Print Head contacts, 3. Carriage flex cable 1. Remove and reinstall the Print Head. 2. Replace faulty parts. 1. Dislodged parts, 2. Dislodged pinch roller. 1. Control board 1. Remove foreign matter, 2. Reinstall dislodged parts. 1. Replace faulty parts. Printing stops midway. Multiple sheets 1. ASF (Return tab, faulty are fed at a pressure roller operation) time. Paper is not fed. 1. Foreign matter, 2. PE sensor arm The paper is 1. Paper guide, 2. Foreign matter slanted. adhering to paper feed rollers 1. Replace faulty parts. 1. Remove foreign matter, 2. Replace faulty parts 1. Readjust the paper guide to the correct position, 2. Remove foreign matter. No printing. No color. Scrape marks or white stripes appear even after cleaning. Lines not in the printing data appear. The paper is dirtied. 1. Print Head, 2. Ink tank, 3. Purge unit 1. Print Head, 2. Ink tank, 3. Purge unit, 4. Print Head faulty contacts, 5. Carriage flex cable 1. Replace faulty parts. 1. Ink mist from the paper transport section in the printer. Spur marks appear. Broken vertical lines appear. 1. Deformed spur tips. 1. Pass through several sheets of paper. 2. Use a cloth to clean the paper transport section. 1. Replace faulty parts. Lines are missing. Strange color tones. Overlapping printing 1. Ink tank 1. Set the paper spacing lever to the proper position. 2. Adjust the printing position. 3. Apply the correct amount of grease on the guide shaft. 1. Replace ink tank. 1. Print Head 1. Replace faulty parts. 1. Platen unit (eject roller) 1. Replace faulty parts. 1. Paper spacing lever position not properly set. 2. Improper amount of grease applied on guide shaft. 2-9 1. Remove and reinstall Print Head and check the contacts, 2. Replace faulty parts. Troubleshooting Faulty Operation 2.3 Troubleshooting Problems Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 2.4 Troubleshooting Error Indications 1) Error indication when a user-resolvable error occurs The indicator lights in green, then blinks in orange. This repeats. Check the number of blinks and proceed to correct the error. 2) Error indication when an error not resolvable by the user occurs The indicator toggles between orange and green (orange/green toggle blinking). This repeats. Check the number of toggled blinks and proceed to correct the error. *1: The error code is displayed by the computer. With the iMac and Power Macintosh G3, a "D" or "M" is appended to the beginning of the error code. *2: The waste-ink warning can be canceled by pressing the RESUME button. *3: Press the RESUME button to resume operation. Table 2-1 ERROR INDICATIONS Indicator Blink Count Error Status Code*1 User-Recoverable Errors Orange --Paper feed error 2 blinks Orange 3 blinks --- Paper jam error Orange 4 blinks --- No-ink error*3 Probable Cause and Faulty Parts <Cause> 1. No paper was loaded. 2. During feeding, the paper did not reach the paper-end sensor. 3. During feeding, the paper's bottom edge missed the paper-end sensor. 4. The ASF sensor did not return to its initial position and the paper-end sensor concluded that there was no paper. (ASF motor may be out of sync.) <Suspect Part> Paper feed section, sheet feeder unit, paper-end sensor, control board <Cause> 1. The paper-end sensor still detects the presence of paper even after 23 inches of paper ejection operation. 2. The ASF sensor did not return to its initial position and the paper-end sensor concluded that there was no paper. (Out of sync.) 3. During paper feeding abnormal timing caused the paper-end sensor to still detect paper. <Suspect Part> Paper feed section, paper-end sensor, control board <Cause> The respective ink tank has run out of ink (in the tank and sponge). <Suspect Part> Ink tank 2-10 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 --- BJ cartridge not installed Orange 7 blinks --- Cartridge error Orange 8 blinks --- Waste-ink warning*2 <Cause> Since there is no Print Head installed, the printing and suction that were required could not be executed. <Suspect Part> Print Head, carriage unit <Cause> (a) The print head temperature (output value of the head's internal diode sensor) exceeded the threshold. (b) Print Head EEPROM's checksum <Suspect Part> Print Head <Cause> The total waste ink count recorded in the EEPROM exceeds 95% of the "full" stipulated value. <Suspect Part> Waste ink absorber, control board User-Unresolvable Errors Orange/ 5100 CR error green 2 toggle blinks Orange/ green 3 toggle blinks Orange/ green 4 toggle blinks Orange/ green 6 toggle blinks Orange/ green 7 toggle blinks Orange/ green 8 toggle blinks <Cause> The carriage's encoder signal is abnormal. <Suspect Part> Encoder film, carriage unit, control board, flex cable 6000 LF error <Cause> The carriage's encoder signal is abnormal. <Suspect Part> Encoder film, paper feed sensor unit, control board 5C00 Purge sensor <Cause> error At the sensor's ON timing, it turns OFF. Or vice versa. <Suspect Part> Purge unit, control board 5400 Abnormal internal <Cause> temperature The temperature sensor (TH401) on the control error board is abnormal (disconnected, etc.). <Suspect Part> Control board 5B00 Waste ink full <Cause> error The waste ink absorber has reached 100% of the waste ink capacity. <Suspect Part> Waste ink absorber, control board 5200 Abnormal head <Cause> temperature The print head temperature (output of the diode error sensor in the head) is close to the threshold. <Suspect Part> Print Head, control board 2-11 Troubleshooting Orange 6 blinks Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 Orange/ green 9 toggle blinks 6800 EEPROM error Orange/ lights --- RAM error --- Ink sensor error Internal Error No indications <Cause> An error occurred during the writing to the EEPROM. Checksum error (at soft power ON). <Suspect Part> Control board <Cause> Error at DRAM check (at hard power ON). <Suspect Part> Control board <Cause> No-ink indication is given while there is still ink. External noise (light) has affected the ink sensor. <Suspect Part> Control board, ink sensor, ink tank 2-12 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 3. DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY 3.1 Cautions for Disassembly and Reassembly 3.1.1 Cautions for ink stains (Ink path/ink mist) During servicing, be careful not to touch the ink path and get ink stains on the printer, work table, and your hands and clothing. The ink path includes the Print Head's ink tank supply inlet, the Print Head's ink filter, the ink nozzles, head cap, wiper, and waste-ink absorber. Also, a printer that has seen long-time use or heavy-duty use may have ink mist soiling the platen, inside the front cover, and purge section. The rubbing of clothing can cause a build up of static electricity on the human body. Static electricity can destroy electrical components or alter the electrical characteristics of components. Be extra careful when handling the control board. 3.1.3 Deformation of spur tips Be careful not to deform the spur tips. The spur tips contact the paper after the printing. Since the spur tips' contact area is small, any ink adhering to the spur will be a minuscule amount that can be wiped off by the spur cleaner. It therefore will not dirty the paper. However, if the spur's tips are bent of out of shape, the contact area with the paper will be larger, and any ink adhering to the spur will be a larger amount that the spur cleaner might not be able to wipe off completely. The spur will then stain the paper with a dotted line. 2-13 Troubleshooting 3.1.2 Damage by static electricity Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 3.2 Exploded View Figure 2-3 Exploded View 2-14 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 3.3 Disassembly and Reassembly Supplemental information and cautions for disassembling and reassembling the printer are stated below. As for the disassembly procedure, refer to the Parts Catalog. The illustrations in the Parts Catalog are numbered according to the order of disassembly. 3.3.1 Carriage lock release a b Purge Unit Figure 2-4 Carriage Lock Release 2-15 Troubleshooting Normally, when a cartridge is installed on the carriage and the power is turned off, the printer moves the carriage to the capping position to lock it. When the power is turned on, the carriage lock is normally released. However, if the printer does not operate properly, you can release the carriage lock manually in one of two ways: a) On the back of the printer, push down the purge unit's locking pin. b) On the front of the printer, rotate the gear as shown by the arrow in the illustration below so that the locking pin goes down. Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 3.3.2 Removing and installing tap screws The printer uses tap screws to fasten the printer unit and base. The removed tap screws will have residue from the mold in which the internal thread was made. Since the residue may crush the screw threads, clean off the residue from the tap screws before re-installing or use new tap screws. 3.3.3 Installing and removing the carriage encoder film The carriage encoder film is fixed in place and held taut by the torsion spring. When you install or remove the carriage encoder film, you have to stretch the torsion spring. Be careful not to pull the torsion spring too much in the direction of the arrow. Otherwise, you will not be able to properly install the carriage encoder film the next time. Therefore, when installing or removing the carriage encoder film, be very careful not to pull the torsion spring too much. Figure 2-5 Encoder Film 2-16 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 3.3.4 Handling encoder film (1) Be careful not to get any grease on the encoder film (carriage encoder film and paper feed encoder film). If grease gets on the encoder film, the film's slits will not be read correctly, resulting in error. If grease gets on the film, use alcohol to wipe it off completely. (2) Do not fold or scratch the encoder film. If the film is folded and a white line is created or if a slit is scratched, replace the encoder film. 3.3.5 Removing and installing the control board 3.3.6 Removal of red screws prohibited Since adjustment of the following red screws is very difficult in the field, they must not be loosened or removed. (a) The two paper spacing red screws (one on the right and left). (b) The two screws securing the paper feed motor. a b a Figure 2-6 Do not Remove the Red Screws 2-17 Troubleshooting Remove or install the control board with caution to prevent damage caused by short circuiting. When the printer is turned on and later turned off, the capacitor on the control board will still contain a charge for a while. In this condition, shorting the components on the control board will damage the components. Therefore as a preventive measure, after disconnecting the AC power, wait for 90 sec. Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 3.3.7 Installing the logic board cover If the logic board cover is installed incorrectly, the logic board and paper feed rollers will be obstructed and the ASF motor may go out of sync. Note that prong A is prone to engage incorrectly. Make sure that it fits in correctly. A Figure 2-7 Installing the Logic Board Cover 3.3.8 Handling the purge unit Note the following with regard to the purge unit: (1) Grease soiling the blade Due to the blade's height, the carriage guide shaft may touch it when the shaft is removed or installed. Grease may soil the blade as a result. You must not allow any grease or oily substance to adhere to the blade. Blade Figure 2-8 Handling the Purge Unit 2-18 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 3.4 Adjustments and Settings After Disassembly and Reassembly 3.4.1 Adjustments (1) User Level Timing After BJ cartridge replacement Adjustment Time Required Tools Required Print head printing position 10 min. 2 sheets of A4-size adjustment paper (2) Serviceman Level Adjustment EEPROM setting Time Required Tools Required 2 min. None Print head printing position 10 min. adjustment (including seam adjustment) 2 sheets of A4-size paper Insufficient grease Apply sufficient grease. See --page 2-20 Grease PG-641, FLOIL KG107A, brush 2-19 Troubleshooting Timing After control board replacement or waste-ink absorber replacement After replacement/ disassembly of carriage unit parts Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 3.4.2 Applying grease After disassembly and reassembly, apply the necessary grease on the places shown below. Use a flat brush to spread a thin coat of grease. When applying grease, be careful not to get any grease on the wiper and cap. Back of Guide Rail (Surface Sliding Against the Carriage) PG641: 25 mg Guide Shaft KG-107A: 225 mg Figure 2-9 Applying Grease 2-20 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 3.4.3 Print head position adjustment Figure 2-10 Printing Position Adjustment Pattern 2-21 Troubleshooting The print head has two nozzle arrays for each color. Therefore, it requires the ink landing position adjustments described in (1) and (2) below in addition to the usual bi-directional adjustment described in (3). (1) Landing position adjustment between two same-color arrays • Black-Black array (A) • Cyan-Cyan array (B) • Magenta-Magenta array (C) (2) Landing position adjustment between two different-color arrays • Black-cyan/Magenta/Yellow (F) (3) Bi-directional landing spot adjustment (Same as with previous models) • Black bi-directional (D) • Color bi-directional (E) If the landing spot position is inaccurate, the pattern printing will show overlapping printing or gaps, resulting in black or white stripes. Therefore when doing the adjustment, use a pattern that has no stripes. Load one sheet of A4 paper in the auto sheet feeder, then use the printer driver to execute printing. Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 3.4.4 Print head seam stripe adjustment The print head seam stripe adjustment is done to determine the amount of thinning of the high-duty image portion (indicated by the arrows) comprising the seam (stripe) created between the vertical bi-directional passes. After the CMY printing by the first pass, CMY is printed again in the same way during the second pass. In the case of color printing, there are two feed methods for one pass: 64 and 128. Pattern G was made with 64 nozzles, and pattern H was made with 128 nozzles. When you execute printing with the printer driver, seven patterns with a changing degree of thinning (indicated by the arrows) will be printed vertically. Select the number of the pattern whose seam stripe is the least noticeable. This sets the optimum degree of thinning. Figure 2-11 Seam Stripe Adjustment Pattern 2-22 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 3.4.5 Setting the EEPROM After replacing the control board or waste-ink absorber, reset the EEPROM and restore the printer settings. Then do a test printout to check the results. The procedure is described in 7.1 Service Mode Operations on page 2-27. Once the data in the EEPROM is reset, a test printout cannot be used to check the old data. Be sure to print the data before resetting. All the data, except the printer settings and USB serial number, will be reset. The various settings and waste-ink amount stored in the old EEPROM cannot be written to the new (replacement) EEPROM. The waste-ink full error is expected to occur only when the printer prints more than the number of sheets specified for its service life. However, how soon this error occurs varies depending on how many times the printer has been turned on/off, the number of times the Print Head has been replaced (front cover open/closing), and the operating environment. 2-23 Troubleshooting (1) After control board replacement If the waste-ink absorption amount is over 7 percent (according to a visual check) at the time you replace the control board, also replace the waste-ink absorber. Otherwise, the waste ink amount cannot be counted accurately. Then reset the EEPROM and restore the printer settings. To check the waste-ink absorption amount, you can either check the service/ factory text printout from the old control board or visually check the waste-ink absorber's waste-ink absorption amount. Also, the new control board (EEPROM) does not have the correct data. The EEPROM must be reset. Otherwise, the waste-ink full error will not occur even when the waste-ink absorber's capacity is exceeded and ink could leak. (2) After waste-ink absorber replacement Clear the EEPROM's waste-ink counter. Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 4. OPERATION CHECK AFTER DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY 4.1 Check Procedure After disassembly and reassembly, follow the procedure below to check the printer's operation. 1) Check visually for any grease or foreign matter dirtying the internal parts. Make sure that the encoder film is clean. If there is any grease on the film, wipe it clean with alcohol. 2) Service/factory test printout with the printer alone Check for the following: Missing print in the nozzle check pattern, off-position horizontal lines in the horizontal line pattern, and white stripes in any irregular printing. If any of these occur, clean the print head and adjust the print head position. Then make another test printout. The procedure is described in 7.1 Service Mode Operations on page 2-27. Timing After control board replacement Items to Check The service/factory test printout must show the correct ROM version and product designation. It must also show the printed sheet count and that the total waste-ink amount has been cleared. The printer driver must be able to print the nozzle check pattern (to confirm that the computer is communicating with the printer). After absorber replacement The service/factory test printout must show that the total waste-ink amount has been cleared. Be sure to visually check the encoder film for any grease, foreign matter, etc. If there is any grease, etc., on the film, the printer may malfunction shortly after the repair is completed. 2-24 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 5. TRANSPORTING THE PRINTER The procedure for transporting the printer after completing repairs is described below. 5.1 Procedure (1) Mount the Print Head on the carriage. (2) Turn off the printer so that the carriage locks at the home position. 2-25 Troubleshooting If the Print Head (print head) is not on the carriage, the ink may dry and harden. So even while transporting the printer, leave the Print Head mounted on the carriage. Also, if the carriage is not locked at the home position, it will move while the printer is being transported. This may strain the paper feed encoder film. Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 6. PARTS REPLACEMENT, PERIODIC INSPECTIONS, & TOOLS 6.1 Parts Replacement Level User Serviceman Level User Serviceman Replacement Parts None None Consumables Black BJ cartridge ink tank (Black: BCI-3eBK) Color BJ cartridge ink tank (Cyan: BCI-3eC, Magenta: BCI-3eM, Yellow: BCI-3eY) None 6.2 Periodic Inspections Level User Serviceman Periodic Inspections None None 6.3 Tool List Ordinary Tools Phillips screwdriver Blade screwdriver Needle-nosed pliers Tweezers Flat brush Multi-meter Remarks For the removal and installation of screws. For the removal of plastic parts. For the removal and installation of springs. For the disconnection and connection of flexible cables, etc. For applying grease. For troubleshooting. Special Tools (Part No.) Grease MOLYKOTE PG-641 (CK-0562) Grease MOLYKOTE KG107A (QY9-0057) Remarks To be applied on the specified parts (see Figure 2-20). To be applied on the specified parts (see Figure 2-20). 2-26 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 7. SERVICE-RELATED FEATURES The printer has a service mode for accessing service settings and executing a test printout. You can use the operation panel to switch to the service mode. 7.1 Service Mode Operations Press 0 times Indicator Lights green 1 time 2 times 3 times Lights orange Lights green Lights orange 4 times 5 times Lights green Lights orange 6 times or Lights green more Function Power off (Even if there is no Print Head mounted, the carriage will return to the home position and lock.) Service/factory test printout(Including ink sensor check) EEPROM information printout EEPROM initialization (All the information will be reset to the default, but the printer settings will not be affected.) Clears the waste-ink counter Market area (printer) setting After the power is turned on and a service function is executed, press the RESUME button the stipulated number of times to set the market area setting. (For BJ S6300: Press twice. For S6300: Press once.) Press the POWER button to return to the service function selection mode. 4) After selecting the service function, press the POWER button. The green indicator lights and the service function will be executed. (After the respective function is executed, the printer returns to the service function selection mode.) To cancel printing after it begins, press the POWER button. The Power lamp will blink for a while and then stay lit. You can then select another service function. 2-27 Troubleshooting 1) With the printer turned off, hold down the RESUME button and press the POWER button (the green indicator lights and the desired service function can be selected). 2) While holding down POWER button, let go of the RESUME button and then press the RESUME button twice in succession. Then let go of the RESUME button and POWER button. (Each time you press the RESUME button, the indicator's color toggles between orange and green.) 3) During printer initialization, the green indicator blinks. When the green indicator stops blinking and remains on, press the RESUME button the stipulated number of times to execute the desired service function listed below. (Each time you press the RESUME button, the indicator's color toggles between orange and green.) Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 7.2 Test Printout The service/factory test printout shows the print head's control ROM version, printer settings, total printed sheet count, total waste-ink absorption amount, and other information. Paper Size:A3 Figure 2-12 Service/Factory Test Printout (Sample) 2-28 Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 7.3 Printing the EEPROM Information This prints the contents of the printer's EEPROM and that of the Print Head. With the resulting printout, you can see the settings and data saved in the printer. S6300 P=V1.00 DI=000.00% Page=00032 CH=00005 Bk=(00) Cl=(00) Head TempBK=26.5 Head TempC=27.0 Env Temp=27.0 PF(00 00 00) PC(A=0005 B=0000 C=0000 D=0003) Bk=04214 C=03365 M=01451 Y=01110 WP=0041 IC(BK=0 C=0 M=1 Y=1) Ink tank presence Present: 0 None: 1 Typing count SV0=5700 SV1=5C00 SV2=5C00 Service error (Latest, preceding, further previous) UR(C=000 BK=+02 BK-C=000 Y=000 M=000 G=000 H=+02) User registration adjustment values (From left: B, A, F, none, C, G, H) HDEEPROM V0000 Print head version SN=24AF-418A Print head serial No. LN(03 05 01 15 00 00 03) Print head lot No. DI(BK=+001 CL=+001) Diode sensor (temperature) compensation value (Bk/Cl) IL(BK=-08 C=-08 M=-08 Y=-08) Ejection level WLA=-08 WLB=-08 NGBK=000 NGC=000 NGM=000 NGY=000 Figure 2-13 EEPROM Information Printout (Sample) The error history records the last three (starting with the most recent one) userunresolvable errors that have occurred. It does not include any ROM/RAM errors. Error CR error Abnormal head temperature Abnormal internal temperature error Waste-ink full error Pump sensor error EEPROM Read/Write error 2-29 Error Code 5100 5200 5400 5B00 5C00 6800 Troubleshooting USB=(111111) Part 2: Troubleshooting S6300 7.4 Resetting the EEPROM The printer uses the total waste-ink absorption amount recorded by the EEPROM as the basis for determining whether the waste ink is full. Therefore, after replacing the waste-ink absorber, be sure to reset the total waste-ink absorption amount. Also, after replacing the control board, be sure to reset the new control board's EEPROM and to also replace the waste-ink absorber. 7.5 Setting the Printer Settings in the EEPROM The control board used in the printer is also used in other printers. After replacing the control board, the printer settings for the respective printer must be set. After setting the printer settings, check it with the service/factory test printout. All the logic boards available as a replacement part contain printer settings for the S6300. Therefore, if the logic board was replaced in Japan, be sure to set the correct printer settings. 2-30 Part 3 TECHNICAL REFERENCE Page 3- 1 3- 1 3- 2 3- 5 3- 7 3- 9 3 -10 3 -10 3 -11 3 -12 3 -12 3 -14 3 -17 3 -19 3 -22 3 -22 3 -22 3 -23 3 -24 3 -24 3 -25 1. PRINTER CONTROL SECTION 1.1 Printing Data and Control Signal Flow 1.2 Print Drive Method 1.3 Control During Printing 1.4 Detection Functions 1.5 Other Sensing Features 2. ELECTRICAL DRIVE SECTION 2.1 Block Diagram 2.2 Electrical Section 3. PRINTER'S MECHANICAL PARTS 3.1 Overview of the Printer's Mechanical Parts 3.2 Purge Section 3.3 Paper Feed Section 4. LOGIC BOARD COMPONENTS 5. OPERATION WITH A COMPUTER 5.1 Printing Operation with the Basic Settings Sheet 5.2 Using the Utility Sheet 6. INK SUCTION AMOUNT IN THE CLEANING MODE 7. TECHNICAL REFERENCE 7.1 Printing Mode List 8. PRINT HEAD Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 1. PRINTER CONTROL SECTION The printer control section converts the data created and input by the printer driver into printing data and printer operation signals and it also controls the driving of the print head and electrical mechanisms while referring to feedback from various sensors. 1.1 Printing Data and Control Signal Flow Host computer a Printer controller f c Receiving buffer d e Print buffer Logic section c Print head DRAM b b g g MPU g : Print signal Control ROM Motor driver Sensors : Control signal Figure 3-1 Printing Signal Flow 3-1 Product Specifications The signal flow starting with the printer receiving the printing data and ending with the execution of printing is explained below. a) The printer driver in the computer creates a print file from the image data and compresses the print file. When the printer driver creates the print file, it obtains data concerning the amount of ink to be ejected from the print head. The printer driver refers to this ink ejection amount data. The printer driver can thereby create an optimum print file for the print head. b) The print data, including control signal output from the host computer, moves from the interface controlled by the printer controller (on the logic board) and is captured by the printer controller. The printer controller and DRAM are dedicated buses, and the print data is stored in the DRAM's receiving buffer (ring buffer). c) The print data stored in the receiving buffer is sent to the MPU. The firmware stored in the control ROM is divided into the control command and print data. The control command is processed in the MPU. d) Since the print data is compressed by the printer driver, it is controlled by the printer controller and uncompressed in the DRAM. e) When the printer controller receives a printing start request from the MPU, it obtains the print data in the DRAM print buffer. f) The printer controller converts the print data into serial data and transfers it as the printing signal to drive the print head. In the print head, the print data is converted from a serial signal into a printing data signal and the printing is executed. (See Printing Driving Method.) g) The MPU controls the printer controller, control ROM, and various motor drivers. While monitoring the status of the print head and printer, it also executes overall control of print driving. (See Sensors and Their Functions and Feedback.) Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 1.2 Print Drive Method To print, the printer ejects ink from ink nozzles. To this end, 16-bit serial data is transferred once as a latch signal to each nozzle array (total of 8 arrays: black even/odd-number array, cyan, magenta, yellow/even/odd-number array). This operation is repetitive. The 16-bit serial data includes the following: Data (DATA0 ~ 9) that decides whether or not to heat 10 nozzles, data (BE0 ~ 4) that decides which nozzles to heat, and the dummy heater signal. LTB CLK 0 DATA 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Block Dummy Heat Determination Section Nozzle DATA Section DATA D0 Input Sequence 1 2 3 D2 5 6 7 8 9 10 Description DATA0 DATA1 DATA2 DATA3 DATA4 DATA5 DATA6 DATA7 DATA8 DATA9 Black Even/Odd Array Nozzle Signal DATA 4 BE0 BE1 BE2 BE3 BE4 DHE Input Sequence Data for 10 Nozzles 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Description DATA0 DATA1 DATA2 DATA3 DATA4 DATA5 DATA6 DATA7 Cyan Even/Odd Array Nozzle Signal Data for 8 Nozzles Figure 3-2 Serial Data 3-2 11 12 13 14 15 16 BE0 BE1 BE2 BE4 DHE BE3 DEL0 ~15 = 16 11 12 13 14 15 16 BE0 BE1 BE2 BE4 DHE BE3 DEL0 ~15 = 16 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 1.2.1 Print drive control Print driving is executed as follows: a) The nozzles to be heated are selected in blocks. The nozzles to be heated are selected according to logical blocks of 16 nozzles divided from among the nozzle arrays. In the case of the black nozzles, they are divided into 10 blocks. The top-to-bottom sequence of the ten blocks will be BLE0 to BLE15. For example, in the case of BLE0, it will be as shown in the figure below. Ten nozzles will be selected in this case. b) The nozzles to be heated are selected individually. Among the 10 nozzles selected, the nozzles to be heated or not are selected. This is determined by DATA0 to DADA. c) Determining whether to heat a nozzle or not. The final decision to heat a nozzle or not is decided with the heat enable signal (HE1/HE2). Only the nozzles in the heat block selected by the heat enable signal are heated. Bk EVEN Bk ODD Product Specifications BLE0 BLE1 • • BLE15 HE1 block HE2 block HE1 block • • • • • • • • • • • • • • C1 M1 Y1 Y2 EVEN EVEN EVEN ODD M2 ODD C2 ODD D5 D3 HE1 block HE2 block Signal line D0 D1 D2 D2 Figure 3-3 Print Driving 3-3 D4 D6 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 1.2.2 Print driving method The printer's drive system enables a maximum of 600 × 600 dpi for black and 2400 × 2400 dpi for color. The vertical resolution applies to two nozzle arrays for each color. In the case of black, the two nozzle arrays have 300 dpi. Since their relative position to each other has been shifted by 600 dpi, both nozzle arrays together attain 600 dpi resolution. This enables 600 dpi resolution with single-pass printing. To enable a horizontal resolution of 2400 dpi, 3-dot printing is made possible in 600 dpi intervals. There are a total of eight patterns to enable or disable printing between the 600 dpi dots. Data 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Printing 600 dpi interval 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 Print (1) /No printing (0) 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 Figure 3-4 Printing Driving Method Since it is impossible to heat the nozzles successively in the horizontal direction at 2400 dpi intervals, the heating is broken into four passes. Thus, 2400 dpi printing requires four or more passes to be driven. However, the places that will be printed during a pass are determined by a random mask pattern. Therefore, it is not fixed. 3-4 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 1.3 Control During Printing The printer can produce high-quality printing with no smearing or irregular density with the cartridge, selected media, printing quality setting, printing data, etc., by altering the carriage operation, paper feed operation, etc. By shifting the printing timing with multiple passes during printing, one raster is printed with multiple nozzles. The amount of ink ejected by each nozzle is kept constant to reduce irregular printing density. Also, smearing is less likely to occur since the freshly printed ink is fixed before the next ink is printed. Depending on the paper, up to eight passes can be executed for printing. (For the number of passes allowable in each mode, see 7.1 Print Modes.) 1.3.1 2-dot Pair + Bi-directional printing 1.3.2 Seam stripe control Seam stripe control suppresses the stripes created at the seams between passes. It aims to produce a high-quality image with a single pass. For high-duty images where seam stripes are prone to occur between each pass, a dot-thinning process is executed. The degree of thinning to be implemented is determined when the user executes the print head position adjustment with the printer driver. 1.3.3 Rest between scans (Border detection control) To prevent color smearing and a whitish color cast along the border between a color ink and black ink caused by the inks' differing characteristics, printing can be executed with a rest inserted between scans. During the printer's internal print processing, the border between color and black inks is detected. When color ink is printed along a border with black ink, a wait is added for ink drying. The wait is set for each printing mode and each color. This reduces ink smearing. Since this operation reduces the throughput, the user is able to select a rest between scans (a special setting) for only plain paper or postcards (when smearing is most prone to occur). It is executed if the print data includes borders between black and color inks. 3-5 Product Specifications In the case of conventional bi-directional printing, when for example cyan and magenta are mixed to produce blue, cyan is printed during the first pass and magenta is printed during the second pass. The color printed on the first pass always comes out stronger than the color printed on the second pass. The subtle difference in color between the first and second passes creates irregular printing between scans. To resolve this problem, the printer uses two nozzle arrays for each color to print each pixel at 600 dpi. The image is created with 2 dots, and the sequence of printing each dot is controlled. In other words, the C2+M2 and M1+C1 portions to be printed during the first pass are mixed during a single scan. In the same way, the C1+M1 and M2+C2 portions to be printed during the second pass are mixed. The difference in color caused by the printing sequence still occurs, however, it is not recognized as irregular printing because it changes at 1200 dpi intervals. Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 1.3.4 Smear control and rest between pages Both smear control and the rest between pages are for preventing smearing by the edge of the printed paper sliding against the preceding printed page. If pigment ink is used for high-duty printing, smear control can delay the printing operation right before the next sheet of paper is stacked on the printed sheet. Smear control is executed by the printer controller. As for the rest between pages, the user can set it with the printer driver so that printing stops temporarily after each page is printed, regardless of the printing data. The smear control and rest between pages are independent operations. If both the smear control delay time and rest time between pages are set, a longer time will take effect. 1.3.5 Automatic power ON/OFF The printer incorporates an automatic power ON/OFF feature. The printer turns on when it receives a printing signal from the computer, and it turns off automatically after a certain period of time when no printing signal is received. This feature can be set with the printer driver. With automatic power ON enabled, the printer turns on automatically when 3 or more bytes of data is received continuously. The interface will remain operational even during power OFF. (Set with the EEPROM.) With automatic power OFF enabled, the printer turns off when a set period of time elapses after the last printing data are sent by the computer. The printer does not turn off automatically in the following cases: An error has occurred, paper has been loaded into the manual feed slot, or when the front cover has been opened. 1.3.6 Print head protection from overheating If ink runs out and the printing operation continues, the bubble jet head will overheat. To prevent overheating, overheating protection control takes effect if the head temperature sensor inside the bubble jet head detects an excessively high temperature. 1.3.7 Power motor control Power motor control is for controlling the current to attain the following objectives: (1) Reduction of current consumption during printing The current is controlled so that the AC adapter's maximum output (momentary current) is not exceeded. By increasing the number of passes, current to heat the heater once is suppressed. (2) The head's average current consumption is suppressed to restrain the power source's temperature increase. Since the power source's temperature increases, it cannot be used while the average current is exceeded. 3-6 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 1.4 Detection Functions 1.4.1 Detection by sensors The following sensors detect the printer's condition. Cover Sensor(SW) Internal Temperature Sensor Paper Feed Encoder Purge Sensor Carriage Encoder ASF Sensor Figure 3-5 Location of Sensors 1.4.2 Paper-end sensor The photo interrupter-type, paper-end sensor detects the paper with the paper sensor arm's flag when the edge of the paper passes through the paper feed section. When there is no paper, the sensor is closed by the paper sensor arm. When paper is detected, the sensor is open and paper is thereby detected. 3-7 Product Specifications Paper-end Sensor Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 1.4.3 Ink sensor (Same as for BJ F600) Consisting of an LED and photo sensor, the ink sensor uses optical means to detect whether there is ink in the ink tank. At the bottom of the ink tank is an indentation that works like a prism. When there is ink in the ink tank, the refractive index of the ink and the prism's resin material is about the same. Therefore, the reflected amount of light is small. When the ink is exhausted, the refractive index of the air and the prism's resin is very different, so all the light entering the sensor is reflected and the amount of reflected light is high. The ink sensor detects the difference in the reflected light amount to determine whether or not there is ink in the tank. The MPU detects the voltage that changes according to the change in the reflected light amount. The analog value that is input is converted to a digital value by an internal A/D converter. When the printer detects no ink in the ink tank, it indicates "ink low" on the status monitor for the respective ink tank. After the printer detects no ink in the ink tank, it starts to count the number of ejected dots corresponding to the amount of ink (about 20% of the ink amount) in the sponge and it starts to detect the no-ink error. This error is detected in the following cases: While the power is ON, when the front cover is closed, after the pumping operation, or after the set number of dots have been printed. If the front cover is opened during the ink amount measurement, the external light may prevent an accurate measurement. The presence of an ink tank will also not be detected. If there is no ink tank, there will be no reflected light and the printer will therefore assume that there is ink. Ink Tank Air Ink Refracted Light Reflected Light Incident Light Incident Light Photo Transistor Photo Transistor Ink Sensor Ink Present Prism Reflected Light Ink Sensor (Completely Reflected) No Ink Figure 3-6 Ink Sensor 1.4.4 Cover sensor The switch-type cover sensor detects whether the front cover is open or not. When the printer detects that the cover is open, it will move the carriage to the replacement position. 1.4.5 Pump sensor The switch-type pump sensor detects the tube pump rotation's initial position. From the pump's initial position as detected by the printer, the printer will start to control the pumping operation. 3-8 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 1.4.6 Internal temperature sensor The internal temperature sensor (TH201) on the control board detects the printer's internal temperature in order to control print head driving. When the printer's internal temperature changes, the thermistor's resistance also changes accordingly and the change in the resistance is detected by the MPU as a change in voltage. The analog value that is input is converted to a digital value by an internal A/D converter. 1.4.7 Head temperature sensor The head temperature sensor is in the BJ cartridge's print head. If the head temperature is abnormally high, the sensor detects the head temperature and the abnormal head temperature error is issued to stop printing operation. When the head temperature changes, the diode sensor changes accordingly and the voltage change is detected by the MPU. The analog value that is input is converted to a digital value by an internal A/D converter. 1.4.8 ASF sensor 1.4.9 Carriage encoder/paper feed encoder With the encoder, the light from the LED passes through the encoder film and enters the photo IC. It is converted into a digital electrical signal when the encoder rotates or when the carriage moves. With this feedback signal, the printer controls the driving of the DC motor. 1.5 Other Sensing Features Besides the sensors described above, the printer has the following detection features. 1.5.1 Waste-ink detection For print head maintenance, ink is ejected by the maintenance jet or purged by the recovery operation. The ejected or purged ink is absorbed by the waste-ink absorber. If the waste-ink absorber discharges ink because it contains more ink than it can absorb, the printer may leak ink. To prevent ink from leaking, the waste-ink absorber's full capacity is detected by estimation. The printer calculates the amount of waste ink produced by the maintenance jet and recovery operations by referring to the ink dot counter. While taking ink evaporation into account, if the estimated waste-ink amount exceeds 95% of the waste-ink absorber's capacity, the waste-ink warning is issued when the power is turned on. If the estimated waste-ink amount reaches 100% of capacity, the waste-ink full error occurs. 1.5.2 Print head detection The presence of the print head is detected with the AD value obtained from the head temperature sensor. If the temperature counted in reverse from the AD value is lower than the absolute 0 degree (an impossible value), the printer will assume that there is no print head. 3-9 Product Specifications The ASF sensor detects the ASF paper feed rollers' initial position. It detects the paper feed rollers' position during ASF initial positioning and paper feeding. Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 2. ELECTRICAL DRIVE SECTION The electrical drive section controls the electrical components in accordance with the control signals and control data received from the control section. 2.1 Block Diagram Main PWB 48 (47.5) MHz Ink sensor 2 2 Key Cover sensor Internal temperature sensor CPU 2 EEPROM 2Kbit Carriage unit Amplifier 3 2 Diode sensor 15 Print head 4 Control ROM 8Mbit 3 EEPROM 48MHz 2 USB I/F Carriage encoder 2 IEEE 1284 I/F Purge motor driver 17 6 Printer controller SDRAM 16Mbit 6 2 Color LED Carriage motor driver A3958 Carriage motor Paper feed motor driver A3958 Paper feed motor ASF motor driver MTD2002G ASF Moter 2 7 Paperend sensor 2 ASF sensor Vcc 5V Purge motor Paper feed encoder Purge unit VH VM 16.7V 27V AC adapter Figure 3-7 Block Diagram 3-10 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 2.2 Electrical Section 3-11 Product Specifications To supply a driving voltage to the motor, IC, BJ cartridge, etc., the electrical section converts the AC voltage received from the AC power source into DC voltage. a) AC adapter The AC adapter converts the voltage from the AC power source into three voltages: +27 VDC, +19 VDC, and +5 VDC. The +27 VDC's output is controlled according to the signal (DWCONT) output by the printer controller. The +27 VDC is used as LF, CR, ASF, and PG for the respective motor drive power source. The +19 VDC is the print head's heater driving power source. The +5 VDC is the logic system's power source. It is constantly supplied by the AC adapter. As a result, as long as AC power is being supplied, all the hardware except the sensors, driver IC, and BJ cartridge are in the active state. b) DC/DC converter The DC/DC converter on the control board converts the voltage into +5 VDC and +3.3 VDC and outputs both. The +5 VDC is used for the EEPROM and reset driving power source and the power voltage for the HVDD, VIF, and VSEN. The HVDD, VIF, and VSEN power voltage outputs are controlled by the printer controller. Also, the +5 VDC is used as the power source for the printer controller, MPU, DRAM, and control ROM. It is also used as a pull-up power source for various switches. By using +3.3 VDC as the power source, the power consumption during power off is less than when +5 VDC is used. Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 3. PRINTER'S MECHANICAL PARTS 3.1 Overview of the Printer's Mechanical Parts The printer's mechanical parts consist of the BJ cartridge, carriage, purge section, and paper feed section. Each part is explained below. Carriage Paper Feed Section Purge Figure 3-8 Printer's Mechanical Parts 3.1.1 Carriage The carriage holds one BJ cartridge in place. The carriage belt driven by the carriage motor (DC motor) moves the carriage horizontally back and forth across the paper. Regarding the carriage's position control, the initial position is detected when the carriage goes against the right wall which is the home position. After that, the carriage position is detected by reading the pulse from the encoder film. The paper spacing position is read from the carriage position when the carriage goes against the left wall. 3.1.2 Purge section The purge section, driven by a dedicated purge motor, consists of the wiper, pump, cap, and carriage lock. The wiper maintains the head face surface to ensure high-quality printing. The ink suction feature enables the ink to be readily ejected from the nozzles. When the BJ cartridge is not in use, the nozzles are protected by a cap, and the carriage is locked in place. The motor's running direction controls the ink suction operation or capping/wiping/ valve open/closing operation. 3-12 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 3.1.3 Paper feed section The paper feed section consists of the paper feed components, paper transport section, and paper discharge section. Paper feed Paper is fed automatically by the auto sheet feeder. The auto sheet feeder is driven by the paper feed motor. Paper of various sizes up to legal size can be stacked and fed automatically (the paper is transported to the paper transport section). Paper transport section The paper feed section, driven by the paper feed motor, keeps the sheet of paper flat and horizontal on the platen and rotates the feed roller to move the paper horizontally to and beneath the print head. Paper eject section After printing, paper is ejected onto the discharge tray by the eject rollers. After the sheet of paper leaves the paper feed rollers, the eject rollers take over to eject the paper. Product Specifications 3-13 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 3.2 Purge Section 3.2.1 Purge section functions In order to maintain good printing quality, the purge section maintains the BJ cartridge's nozzles. The purge section's functions consist of capping and cleaning. a) Capping The purge unit's cap is pressed against the print head's face to protect the nozzles from dust, etc., and to prevent the nozzles from drying out. To prevent the capping position from shifting, the carriage is locked in place at the same time. When the cap is open while the printer is on standby for printing and a certain period of time elapses (55 sec. with no paper or 20 min. with paper loaded), the print head will be capped automatically. You can also cap the print head by pressing the POWER button to turn off the printer. b) Cleaning Cleaning executes the following operations: Wiping: Paper residue and dried ink on the print head's face plate are wiped off. Suction: The ink is sucked out of the print head to refresh the nozzles with new ink. Maintenance jet: To eliminate any air bubbles in the head's nozzles and to remove waste particles near the nozzle openings, ink is ejected from the nozzles onto the cap and maintenance jet receptacle. Cleaning is performed at the times below to ensure that the head produces highquality printing. 3-14 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 3.2.2 Purge section components Cleaner Wiper Cap Purge Motor a) Purge driving motor The purge motor drives the wiper, carriage lock, and pump. It is a constant-voltage motor operating with a 1-2 phase drive. b) Wiper The wiper consists of a wiper and wiper cleaner. The wiping operation is executed while the carriage is fixed at the purge section. It wipes the print head's nozzle array in a vertical motion. c) Cap The rubber cap protects the print head (capping operation) and sucks out (pumping operation) the ink in the cap. When the carriage moves to the capping position, the cap is pressed against the print head's face plate. There is a different cap for the black and color print heads. An ink tube connects the rubber cap to the pump and air valve. 3-15 Product Specifications Figure 3-9 Purge Section Components Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 Rotation Direction for Wire/Capping Rotation Direction for Ink Suction To Waste-Ink Absorber Valve Open Valve Closed Rotating Roller (inside) Black Ink Tube Color Ink Tube Figure 3-10 Pump Operation d) Pump This is a tube pump system consisting of two ink tubes (one for black and one for color) pressurized by a rotating roller. A negative pressure is thereby created to suck the ink. Inside, there is a valve dedicated to black ink and one dedicated to color ink. When the valves close or open separately or simultaneously, only the black ink (color valve open) or color ink (black valve open) can be sucked or both inks can be sucked (black and color valves closed). The amount of ink sucked can be high, medium, or low depending on how much the roller rotates. The pumping operation is executed with the rotation of the roller after the carriage is released from the capping position and both valves are opened. The degree of rotation of the pump's roller and the timing of the rotation are controlled by the step count in accordance with the initial position detected by the pump sensor. The two tubes are placed right before the waste-ink absorber. By mixing pigment ink and dye ink, ink hardening is prevented. 3-16 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 3.3 Paper Feed Section 3.3.1 Paper feed components The paper feed components include an ASF incorporating a friction separation system which uses a separation pad. Compared to previous ASF systems, it has a very strong paper feed force. It consists of the following parts: Paper feed roller and separation pad, pressure roller and return corner, pressure plate, motor, and sensor. Nip Paper feed roller (Transports the paper) Chin Pressure plate (Puts the next sheet in position for the paper feed roller) Return pawl (Returns the paper remaining on the separation pad) Separation pad (Separates the paper) Figure 3-11 Paper Feeding The motor is a constant-current stepping motor. It drives the paper feed roller with 12-phase driving. There is a sensor on the paper feed roller to detect the paper feed roller's initial position. The pressure roller and return corner prevent the paper that could not be completely separated by the separation pad from proceeding to the paper transport section. The pressure roller presses down the sheet of paper that is on the separation pad. It prevents multiple sheets from being transported. The paper therefore has a back tension (counteracting force against the feed roller's pulling force on the paper). Also, the return corner is for returning the paper remaining on the separation pad. The timing for returning the paper changes depending on the paper type and length selected with the printer driver. 3-17 Product Specifications Pressure roller (Applies pressure on the paper on the separation pad to prevent transporting more than 1 sheet) Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 3.3.2 Friction separation system The friction separation system's paper separation method is explained below. 1. When the paper feed roller turns, the top sheet of the paper stack is taken to the nip where the pressure roller contacts the paper feed roller. 2. When the top edge of the paper reaches the nip, the paper pushes down the pad by the amount of the paper's thickness. At this point, since the frictional force between the paper and separation pad is less than the frictional force between the paper and paper feed roller, the paper feed roller further transports the paper into the printer. 3. At this time, the next sheet of paper stops at the chin. 4. If the next sheet of paper could not be stopped at the chin in step 3, it will be stopped on the separation pad because the frictional force between the paper sheets is less than the frictional force between the paper and separation pad. Only the top sheet is therefore sent into the printer. 3.3.3 Paper transport section At the printing section, an unchanging gap between the paper and print head is maintained while the paper is pressed against the platen as it goes between the pressure roller and paper feed roller and between the spur and eject roller. For paper transport control during printing, a metallic, high-precision paper feed roller having a coat of ceramic paint and an optical encoder film affixed on it is used. The paper feed roller is driven by a DC motor via a belt. The paper transport is controlled according to the signal read from the encoder film. The paper is transported in 1/1440-inch increments. 3.3.4 Paper discharge section While the sharp-tipped spurs press down the printed side of the paper (without marking it) against the eject rollers, the eject rollers discharge the printed paper. The paper discharge section consists of the eject rollers and spurs. A sheet of paper fed to the print starting position is printed on as it goes over the platen. The paper is transported by the paper feed and pinch rollers. When printing is completed, the paper is ejected by the eject rollers and spurs, with the paper eject support function (*1) enabled to prevent smearing. *1: The function is enabled when B5 or larger sized plain paper is selected and the Print Quality is set to “Standard” or “High” in the printer driver. 3-18 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 4. LOGIC BOARD COMPONENTS Control ROM Stepping Motor Driver IC EEPROM DRAM DC Motor Driver IC Figure 3-12 Control Board a) Printer controller (IC2) The printer controller has the following eight functions. It operates with a 48 MHz external clock (not synchronized with the CPU). 1. I/F control The data is transferred with a serial (USB 1.1 standard) or parallel (IEEE 1274 standard) transmission. Parallel transmissions operate in the compatible, nibble, and ECP modes. 2. Receiving buffer control The ring buffer-type receiving buffer and the straight-type transmission buffer are controlled. 3. System management enabled With the built-in timer, any clock stoppage or suction time is counted. Also the status of the port in the printer controller is sampled. 4. Data decompression The data compressed by the printer driver is restored as print data. In addition, during printing in the HS mode, 300 dpi data is expanded by 2× vertically and horizontally to 600 dpi. The CMY 2-bit data is also distributed to the even/odd buffers for each even/odd array on the print head. 5. Data processing A dot count is executed for power monitoring and smear processing. Also, dot thinning for seam stripe processing is based on the dot count and color tone. 6. Printing control The data received is rearranged in the raster direction. Also, data is processed so that the print head's heaters are heated in the suitable sequence. 3-19 Product Specifications DC Motor Driver IC Printer Controller MPU Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 7. Print head control Serial print data is sent to the print head. The transfer clock is 6 MHz. Since data latch occurs at the clock's start-up and shutdown, the data transfer speed is faster. Also, the print head heater's heating is executed with a single pulse or double pulse. In the case of a double pulse, the first pulse is a press pulse. The pulse following it becomes the main pulse. The print head's temperature is estimated with the dot count. Based on the estimated temperature, suitable heating is executed with the voltage value. 8. Motor control The encoder signals input from the two DC motors are processed, and a signal for the 1-2-phase driving of the auto sheet feeder motor is generated. b) MPU (IC1) The MPU contains a 32-bit CPU, 16 KB work RAM, 21-bit address bus port, 16-bit data bus port, interrupt controller, A/D converter, I/O port, and other built-in components. With the chip select signal, the MPU selects the control ROM, printer controller, and DRAM. Built-in CPU The 32-bit CPU operates in synchronization with a 48 MHz external clock input. Address bus/Data bus This operates in synchronization with a 20 MHz external clock input. An external RAM (16 Mbit) is accessed via the 16-bit data bus. Interrupt controller The MPU receives external interrupts from the POWER button's ON/OFF and I/F. A/D converter The following analog signals are detected after they pass through the built-in A/D converter. Resume key input EEPROM data I/O EEPROM chip select output Door sensor input CSB power input Sensor (purge, paper end, sheet feeder) inputs LED (ERROR/POWER) outputs I/F (Centronics/CSB) pull-up control I/O Print head power control (ON/OFF) (VDD/VH) Ink sensor power control (ON/OFF) Purge motor control (4 ports, A/B/A/B phase) I/O port The I/O port executes the following control operations. c) DRAM (IC4) The 16 Mbit DRAM is controlled by the printer controller and used as a receiving buffer, download buffer, print buffer, and working area. 3-20 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 d) DC motor driver (IC23/24) The motor driver IC is for driving the DC motor (paper feed motor and carriage motor). This driver is a PWM (pulse-width modulation) IC that changes the current's pulse width to control the output. It thereby controls the motor. The pulse-width control is defined by the serial data (10 bit) from the printer controller. e) EEPROM (IC5) The 2 Kbit EEPROM controlled by the printer controller records the waste-ink absorption amount, page count, and BJ cartridge removal/installation count. The printer reads the EEPROM contents when AC power is supplied and records the data when the power is turned off. f) Control ROM (IC3) The 8-bit control ROM is written with a printer control program. 3-21 Product Specifications g) Stepping motor driver IC (IC25) This is a driver IC for constant-current driving of the ASF motor. The driving method is 1-2-phase driving. Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 5. OPERATION WITH A COMPUTER For printer operation with a computer, printing with the printer driver's "Basic Setting Sheet" and setting the "Utility Sheet" are explained below. 5.1 Printing Operation with the Basic Settings Sheet To enable the user to print easily, the printer driver's ease of use has been improved. The Basic Settings Sheet enables the user to set the paper type, paper feed method, and printing quality. Also, the "Print Advisor" is a new feature. When the user does not know which paper is suitable for printing, the Print Advisor gives on-screen instructions so that the optimum settings are selected automatically. 5.2 Using the Utility Sheet This enables the usual operations such as cleaning, print head refreshing, print head position adjustment, nozzle check pattern printing, power OFF, automatic power setting, and special settings (economy cleaning, smear control, ECP, etc.) for status monitor start-up. When printing is executed for a large amount of data and the ECP mode check is off, the printing speed decreases. Figure 3-13 Basic Settings Sheet (Sample) 3-22 Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 6. INK SUCTION AMOUNT IN THE CLEANING MODE The printer has five cleaning modes (A to G). Cleaning is executed for maximum effectiveness and efficiency. The cleaning operation is selected depending on the respective condition. The ink suction operation differs depending on the condition at three occasions: Operation by the user, cover open/closing, and before printing starts. • Operation by the user: Manual ink suction (Including printer driver operation) • Cover open/closing: Cleaning at printer arrival • Before printing starts: Other than manual suction Mode Cleaning A Bk+Cl Bk Bk Cl Cl Cleaning D All colors Bk+Cl Cleaning E Cleaning F Cleaning G Bk Cl All colors All colors All colors Bk Cl Bk+Cl Bk+Cl Bk+Cl *1 If the preconditions overlap, the stronger suction will take priority. Cleaning A < Cleaning D < Cleaning E < Cleaning F < Cleaning G *2 In the case of the boxed preconditions, the suction starts right after the precondition is executed. For other preconditions, suction is executed right before the printing starts or during printing. *3 Ink tank replacement is detected when the ink tank's status changes from H to L. *4 Printing of EEPROM contents, etc., with the printer alone. *5 Purging operations will be performed after 24 hours only the first 5 times, after which purging will occur at 60 to 336 hours intervals. When checking the functions of the purge unit, measure the suction amount for a manual suction. 3-23 Product Specifications All colors Suction Precondition* Amount (g) 0.15+0.36 Dot count suction, Manual suction (All colors) *2, timer suction (Time not set)*4 0.15 Dot count suction, Manual suction (Bk) , timer suction (60*5 ~ 336 h) 0.36 Dot count suction, Manual suction (Cl) , timer suction (120 ~ 336 h) 0.3+0.72 Tank replacement*3 after soft power ON (All colors) 0.3 Tank replacement*3 after soft power ON (Bk) 0.72 Tank replacement*3 after soft power ON (Cl) 0.45+0.72 Long timer suction (336 h ~) 0.45+1.08 When print head is replaced, at printer arrival 1.5+1.08 Head refreshing Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 7. TECHNICAL REFERENCE 7.1 Printing Mode List The printing mode list for the black, color, and photo BJ cartridges is shown below. By setting the printer driver's "Dithering," "Paper Type," and "Printing Quality," the printer will operate in the printing modes below. Table 3-1 PRINTING MODE LIST Monochrome Printing Resolution (dpi) Paper Type Plain Paper Bk=600 × 600 Bk=600 × 600 Bk=600 × 600 Bk=600 × 600 1Pass-Bi PigBk 4pass-Bi PigBk Postcard Ink-jet P.O. Postcard 1Pass-Bi PigBk 2Pass-Uni PigBk 2Pass-Uni PigBk Default (High/Standard/Fast) High/Standard/Fast Standard/ Fast Standard/ Fast 4Pass-Uni PigBk 4Pass-Uni PigBk Color Printing Resolution (dpi) Paper Type Plain Paper OHP Transparency T-shirt Heat Transfer Paper Glossy Paper/ Glossy Postcard Glossy Film High-quality Paper Postcard/ Envelope Pro Photo Paper Photo Card Ink-jet P.O. Postcard Bk : C : M : Y : Bk=600 × 600 Y=600 × 1200 CM=1200 × 1200 1Pass-Bi PigBk Bk=600 × 600 Y=600 × 1200 CM=1200 × 1200 1/4 Pass-Bi PigBk 2Pass-Bi PigBk Bk=600 × 600 Bk=600 × 600 Y=600 × 1200 CMY=1200 × 1200 Y=600 × 1200 CMY=1200 × 1200 CM=1200 × 1200 CM=1200 × 1200 4pass-Bi PigBk 4Pass-Bi PigBk+YMC 6Pass-Bi YMC 4Pass-Bi 6Pass-Bi YMC YMC 4Pass-Bi YMC 6Pass-Bi 4Pass-Bi YMC YMC 3Pass-Bi 4Pass-Bi PigBk+YMC PigBk+YMC 4Pass-Bi YMC 2Pass-Bi 4Pass-Bi YMC YMC Default CMY=1200 × 1200 (High/Standard/Fast) High/Standard/Fast Standard/ High Standard 6Pass-Bi YMC 6Pass-Bi YMC Black PigBk : Pigment black Bi : Bi-directional Cyan YMC : Processed black Uni : Uni-directional Magenta Yellow The shaded specifications are the default for the respective media. 3-24 Standard/ High Standard/ High Standard/ High Standard/ High Standard/ High Standard/ High Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 8. PRINT HEAD The two nozzle arrays for each CMY color are divided symmetrically left and right along the M line. This makes it completely compatible with bi-directional printing. Also, the relative position of the two nozzles is shifted by 600 dpi for black and by 1200 dpi for color. Thus, the two nozzles together on a single pass produce 600 dpi resolution for black and 1200 dpi resolution for color. There is a heater near the nozzle openings and small ink drops are ejected with a strong force. BLE1 Bk EVEN BLE0 Bk ODD 600 dpi HE1 block HE2 block • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • C1 M1 Y1 Y2 EVEN EVEN EVEN ODD M2 ODD C2 ODD 1200 dpi HE1 block HE2 block Signal Line Ink Path (Nozzle) D0 D1 D2 D2 D4 D6 Nozzle Opening Aluminum Heater Board Heater (EVEN) Common Ink Chamber Ink Supply Opening Heater (ODD) Figure 3-14 Nozzle Array 3-25 D5 D3 Product Specifications M HE1 block Part 3: Technical Reference S6300 This page intentionally left blank 3-26 Part 4 APPENDIX Page 4- 1 4- 5 4- 7 4- 8 1. CONNECTOR LOCATIONS AND PIN CONFIGURATIONS 1.1 Carriage Board 1.2 Print Head 2. Circuit Diagram Part 4: Appendix S6300 1. CONNECTOR LOCATIONS AND PIN CONFIGURATIONS J11 J8 SW2 J2 SW3 J5 SW1 J4 J12 J3 J9 J6 J10 J13 J7 J1 Figure 4-1 Control Board Appendix 4-1 Part 4: Appendix S6300 J1 (Parallel Interface Connector) Pin No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Compatible Mode STROBE DATA1 DATA2 DATA3 DATA4 DATA5 DATA6 DATA7 DATA8 ACKNLG BUSY P.E. SELECT AUTO FEED XT N.C GND GND +5.0V STROBE-RET (GND) DATA1-RET (GND) DATA2-RET (GND) DATA3-RET (GND) DATA4-RET (GND) DATA5-RET (GND) DATA6-RET (GND) DATA7-RET (GND) DATA8-RET (GND) ACKNLG-RET (GND) BUSY-RET (GND) P.E.-RET (GND) INIT ERROR GND N.C +5.0V SELECT IN Nibble Mode HostClk Data1 Data2 Data3 Data4 Data5 Data6 Data7 Data8 PrtClk PrtBusy AckDataReq Xflag HostBusy Undefined Gnd Gnd Vcc Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd INIT DataAvail Undefined Undefined Undefined 1284Active J2 (USB Interface Connector) Pin No. 1 2 3 4 Signal PWR D− D+ GND IN/OUT IN ... Function Cable power source Data Data Cable GND 4-2 ECP Mode HostClk Data1 Data2 Data3 Data4 Data5 Data6 Data7 Data8 PeriphClk PeriphAck AckReverse Xflag HostAck Undefined Gnd Gnd Vcc Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Signal Gnd ReverceReq PeriphReq Undefined Undefined Undefined 1284Active Part 4: Appendix S6300 J6 (Paper-Feed Motor Connector) Pin No. 1 2 3 Signal VSNS ... SNS_PE IN/OUT IN ... IN Function GND Signal by paper end lever J7 (Ink Sensor Connector) Pin No. 1 2 3 Signal INK_PWM ... INKS IN/OUT OUT ... IN Function Photo LED drive signal in the ink sensor GND Voltage varies according to the reflected light amount J8 (DC Power Source Connector) Pin No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Signal +5V +5V-GND VH VH-GND VM VM-GND NC IN/OUT IN ... IN ... IN ... ... Function +5VDC GND +19V GND +27VDC GND NC J9 (Pump Sensor Connector)/Carriage Motor Connector Signal VSEN ... SNS_PG CRA CRB IN/OUT OUT ... IN OUT OUT Function Photo LED drive signal in the ink sensor GND Pump sensor sense signal High (sense)/Low Carriage motor phase A Carriage motor phase B 4-3 Appendix Pin No. 1 2 3 4 5 Part 4: Appendix S6300 J10 (LF Motor Connector) Pin No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Signal OUT_A OUT_B GND LF_ECA VSNS LF_ECB IN/OUT OUT OUT IN IN IN IN Function LF motor phase A LF motor phase B GND LF encoder phase A LF encoder phase B J11 (ASF Motor Connector) Pin No. 1 2 3 4 Signal ASFA ASFB ASFA ASFB IN/OUT OUT OUT OUT OUT Function ASF motor ASF motor ASF motor ASF motor phase phase phase phase A B A B J12(Purge Motor Connector) Pin No. 1 2 3 4 5 Signal +27 PGA PGA PGB PGB IN/OUT OUT OUT OUT OUT OUT Function +2VDC PG motor PG motor PG motor PG motor phase phase phase phase 4-4 A A B B Part 4: Appendix S6300 1.1 Carriage Board 1 1 21 21 1 21 33 1 40 8 Figure 4-2 Carriage Board J1 (Carriage Ribbon Cable Connector) See page 4-6 (J3 Carriage Ribbon Cable Connector Pin Description). See page 4-6 (J4 Carriage Ribbon Cable Connector Pin Description). J3 (Carriage Ribbon Cable Connector) See page 4-6 (J5 Carriage Ribbon Cable Connector Pin Description). J4 (Print Head) Pin No. 1~40 Signal IN/OUT Function See page 4-7 (Print Head Pin Description) 4-5 Appendix J2 (Carriage Ribbon Cable Connector) Part 4: Appendix S6300 J3 (Carriage Ribbon Cable Connector) ↔ J1: Carriage Board Pin No. 1 Signal VHT 2~6 7~11 12~16 17~21 B_VH A_VH B_GND A_GND IN/OUT Function OUT Power transistor driving power source (19 V) in the print head OUT Color heater driving voltage (19 V) OUT Black heater driving voltage (19 V) ... GND (for color heater driving voltage) ... GND (for black heater driving voltage) J1 Pin No. Same as J3 pin No. J4 (Carriage Ribbon Cable Connector) ↔ J2: Carriage Board Pin No. Signal 1, 2, SUBH0 3, 7, 9, 11 14, 16, 19 GND 4 H_ENB1 IN/OUT Function OUT Black secondary heater driving signal ... OUT 5 H_ENB2 OUT 6 8 10 12 13 15 17 18 20 21 H_ENB0 H_LATCH H_CLK H_D0 H_D1 ENCA ENCB VSEN DIA0 DIK0 OUT OUT OUT OUT OUT IN IN OUT IN ... Logic ground Color nozzle heat enable signal (Even/odd array's odd block) Color nozzle heat enable signal (Even/odd array's even block) Black nozzle heat enable signal Data latch enable signal Clock signal Black even array nozzle data signal Black odd array nozzle data signal Carriage encoder signal Carriage encoder signal Carriage encoder sensor power source Head temperature sensor's (diode) anode side (black) Head temperature sensor's (diode) cathode side (black) J1 Pin No. Same as J4 pin No. J5 (Carriage Ribbon Cable Connector) ↔ J3: Carriage Board Pin No. 1, 2 3, 7, 11,19 4 5 6 8 9 10 12 13 14 15~18 20 21 Signal IN/OUT Function SUBHO OUT Color secondary heater driving signal GND ... Logic ground H_D2 OUT Cyan even array nozzle data signal H_D3 OUT Cyan odd array nozzle data signal H_D4 OUT Magenta even array nozzle data signal H_D5 OUT Magenta odd array nozzle data signal H_D6 OUT Yellow even array nozzle data signal H_D7 OUT Yellow odd array nozzle data signal H_EEPROM_CS OUT EEPROM chip select signal in the print head H_EEPROM_SK OUT EEPROM serial data clock signal in the print head H_EEPROM_D OUT EEPROM serial data signal in the print head HVDD OUT Logic power source in the print head DIA1 IN Head temperature sensor's (diode) anode side (color) DIK1 ... Head temperature sensor's (diode) cathode side (color) 4-6 J1 Pin No. Same as J5 pin No. Part 4: Appendix S6300 Part 1.2 Print Head 33 40 8 1 Figure 4-3 BJ Cartridge Function GND (for black heater driving voltage) Cyan even array nozzle data signal Yellow even array nozzle data signal GND (for color heater driving voltage) Head temperature sensor's (diode) cathode side (black) Black secondary heater driving voltage Magenta even array nozzle data signal Color nozzle heat enable signal (Even/odd array odd block) Magenta odd array nozzle data signal Head temperature sensor's (diode) cathode side (color) Black even array nozzle data signal Black nozzle heat enable signal Data latch enable signal Color secondary heater driving signal Yellow odd array nozzle data signal Color nozzle heat enable signal (Even/odd array's even block) Black odd array nozzle data signal Black Logic power source Head's EEPROM chip select signal Clock signal Head's EEPROM output data signal Cyan odd array nozzle data signal Color heater driving voltage Black heater driving voltage Head's EEPROM serial data clock signal Head's EEPROM input data signal Head temperature sensor's (diode) anode side (color) Head's power transistor driving power source 4-7 Appendix Pin No. Signal IN/OUT 1, 2 A_GND ... 3 H_D2 IN 4 H_D6 IN 5, 14, 22 6, 7, 8 B_GND ... 9 DIK0 OUT 10 SUBH0 IN 11 H_D4 IN 12 H_ENB1 IN 13 N.C 15 H_D5 IN 16 DIK1 ... 17 H_D0 IN 18 H_ENB0 IN 19 N.C 20 H_LATCH IN 21 SUBH0 IN 23 H_D7 IN 24 H_ENB2 IN 25 H_D1 IN 26 DIA0 OUT 27, 35 HVDD IN 28 H_EEPROM_CS IN 29 H_CLK IN 30 E_D0 OUT 31 H_D3 IN 32, 40 B_VH IN 33, 34 A_VH IN 36 H_EEPROM_SK IN 37 E_DI IN 38 DIA1 OUT 39 VHT IN R1: D(0.5) SW1 SW2 SW3 1 1 1 +3.3V check CP11 check CP10 47K,1/16W 1K,1/16W 9 6 8 +3.3V +3.3V CP13 C105 CP9 A22 A21 A20 SW_POW C107 +3.3V INK_PWM 2D3 SW_DOR 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 25 VDD2 R5 10K,1/16W CP18 1 CP19 2 SK DO +3.3V 1000P,50V 1U,10V C101 C102 DO DI SK CS GND TEST NC VCC IC5 A6 1U,10V MPU IC1 C103 MA3 MA2 MA1 MA0 MA10 MA12 MA13 M_CSX M_LASX M_CASX M_WEX M_LDQM MD7 MD6 MD5 MD4 MD3 MD2 MD1 MD0 5 6 7 8 UPD82830GC-021-7EA EEPROM BR93LC56RF-W CP20 4 DIO CP21 3 CS 24 P03/INTP0 23 P02/PWM0 22 P01/NMI D4 D12 D5 D13 D6 D14 D7 D15 33 A17 34 A16 35 A15 36 A14 37 A13 38 A12 39 A11 21 P00/ADTRG 20 RESET 19 AVSS 18 AVREFM 17 ANI7 16 ANI6 15 ANI5 14 ANI4 INKS 13 ANI3 12 ANI2 THERM0 11 ANI1 DIODE1 SW_RSM VDD D4 D12 D5 D13 D6 D14 D7 9 AVREFP 8 AVDD 7 A23 6 A22 5 A21 4 A20 3 A19 2 A18 10 ANI0 DIODE0 0.1U,25V C2 RESX 3D7 2D3 2B5 2C5 GND2 D15/A1-1 1 VDD1 D[15:0] A[22:1] CSX0 RDX LWRX A16 A15 A14 A13 A12 A11 A10 _BYTE/VPP DIP-42p A19 0.1U,25V C106 +3.3V 0.1U,25V IC3 ROM DILB42P-8J A18 D11 D3 D10 D2 D9 D1 D8 D0 OE GND1 CE A0 A1 A2 A3 1000P,50V 0.1U,25V C3 CP14 check 2 check 2 CP12 check 2 CP8 +3.3V 21 +3.3V 20 D11 19 D10 D3 18 17 16 15 14 13 D2 D9 D1 D8 D0 RDX BK32164S121 12 11 10 4 A23 A15 8 2 CSX07 A31 A4 A5 A17 A17 99 A6 A16 A16 98 INTX128 P05/INTP2 7 A15 A15 97 INTX229 P06/INTP3 6 A14 A14 96 30 P07/PWM1 5 A13 A13 95 31 P10/R TP0/TCLR0 PG0 4 A12 A12 94 32 P11/R TP1/TI0 PG1 FBA1 2 A11 A11 93 33 P12/R TP2/TO0 PG2 A4 2 FB A9 A5 40 A10 FB2 A10 A10 92 34 P13/R TP3/TCLR1 A8 A9 91 A6 A9 VV1-7000000 PG3 A7 A8 90 A7 R12 1 2 41 A9 0,1A/NOTMNT 0,1A FB1 R13 1 2 1 2 FB 1 1 VV1-7000000 35 P14/R TP4/TI1 DIO A7 89 A7 NTCCM16084LG473JC 2 2 2 1 R1 TH1 C1 2 2 1 2 1 10K,1/16W 1 2 RA1 R2 1 R3 8 2 R4 1 10K,1/16W 7 1 2 1 1 6 2 2 3 0.01U,50V 5 4 1 10K,0.0625 A5 A5 86 0.1U,25V C108 +3.3V 40 P21/INTP5 +3.3V 10K,0.0625 RA2 27 VCC2 26 A3 25 A2 24 A1 23 A0 22 A10 21 A12 20 A13 19 CS 18 RAS 17 CAS 16 WE 15 DQML 14 VCC1 13 DQ7 12 VSSQ1 11 DQ6 10 DQ5 1 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D6 69 D5 68 D4 67 D3 66 D2 65 D0 63 7 5 CP26 SM_ENB 3B3 3B3 8 6 4 2 1U,10V C109 3D3 0.1U,25V IFD[7:0] +3.3R HC0 USB_D 128 46 VDD_IN2 45 GND5 44 STB 43 IF_D0 42 IF_D1 41 IF_D2 40 IF_D3 39 IF_D4 38 IF_D5 37 IF_D6 36 IF_D7 C301-305 R1-13 R 1/4W is 3216 X1,2 TH1 SW1-3 IC1-5 RA1,2 R 1/10W is 2125 R 1/2W is 3225 R 1/16W is 1608 LEDA1 FBA1,2,4 C201-204 C101-110 FB1-6 C7xx are bi-pass capacitor for 16.7V C8xx are bi-pass capacitor for 27.0V C5xx are bi-pass capacitor for 5.0V C1-4 C3xx are bi-pass capacitor for 3.3R C2xx are bi-pass capacitor for 3.3U 1 2 22K,1/16W CSTCW4800MX41030 X2 3 R9 CP8-14,16-21,26-37,44,46,47,49-66 CP1-7,15,22-25,38-43,45,48 blank 0.1U,25V C202 +3.3U 52 GND7 51 GND6 50 PT_A3 C1xx are bi-pass capacitor for 3.3V INTX[3:0] D[15:0] check CP30 SNS_ASF49 PT_A2 SNS_PG 48 PT_A1 SNS_PE 47 PT_A0 IFC0 IFD0 IFD1 IFD2 IFD3 IFD4 IFD5 IFD6 IFD7 1 34 BUSY 35 ACK INTX4 124 33 PE IFC2 IFC1 INTX5 125 32 SLCT IFC3 1000P,50V C303 +3.3R D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 WAITX UWRX LWRX RDX CSX2 CSX1 LED_RS 0.1U,25V C203 +5V 0.1U,25V C4 3D7 1000P,50V RESX C304 2B8 2B8 2B3 2F3 USB_PWC 2B8 IF_PWC 2F8 LED_PW CP50 check check CP51 USB_D +3.3U GND12105 GND13106 D5 107 D4 108 D3 109 D2 110 D1 111 D0 112 CPU_WAITX 113 114 CPU_UWRX CPU_LWRX115 CPU_RDX116 CPU_CSX2117 CPU_CSX1118 PT_B0 119 PT_B1 120 PT_B2 121 PT_B3 122 RSTX 123 GND14126 31 FAULT IFC4 VDD_IN5 127 IFC5 UPD89443GD-021-LML 30 AFXT/SCK 29 INIT IFC7 USB_DX129 IFC6 28 SELIN IC2 +3.3R USB_DX HVD_PWC VDD_IN6 130 GND15131 26 GND4 27 VDD_IN1 INTX6 132 HVH_PWC HC1 134 ENCODE0 2F5 SNS_PWC HC[19:0] 2E3 25 RAM_A3 INTX7 133 135 ENCODE1 23 RAM_A1 MA3 24 RAM_A2 22 RAM_A0 MA1 MA2 IFC8 A[22:1] 1000P,50V C302 2E3 3F5 2D3 IFC[8:0] +3.3R 2F8 C301 1000P,50V MA0 HC2 PT_A4 136 MA10 21 RAM_A10 MA4 2F8 HC3 HC4 PT_A5 137 FB5 MA5 PT_A7 139 HC5 18 RAM_CSX PT_A6 138 2 HC6 FB H_ENB0 140 HC7 H_ENB1 141 17 RAM_RASX H_ENB2 142 16 RAM_CASX MA13 19 RAM_A13 +3.3V CP28 CSTCW4750MX01 15 RAM_WEX HC8 8 BK32164S241 FBA4 HC9 H_LATCH 143 HC10 H_CLK 144 HC11 14 RAM_LDQM 13 GND3 H_D0 145 12 RAM_A4 6 4 2 MA4 BK1608HS241 MA12 20 RAM_A12 +3.3V CP27 22K,1/16W X1 3 R7 INTX[3:0] PG[3:0] check check +3.3V VDD3 51 P25/TXD 52 P26/RXD 53 1 MA7 SNS_USB 2A8 CSX0 P27/CLKOUT54 7 FBA2 CSX1 check 5 BK32164S121 3 1 CSX2 D0 3 1 2 HC12 FB H_D1 146 HC13 1 MA5 11 RAM_A5 HC14 FB6 HC15 H_D2 147 10 RAM_A6 MA6 BK1608HM471 HC16 H_D3 148 9 RAM_A7 check MA7 HC17 H_D6 151 H_D4 149 H_D7 152 6 SIN H_D5 150 HC18 H_SUB0 153 5 SMC GND16155 GND17156 0.1U,25V C204 +3.3U 4 AMC ASIC 1 Circuit Diagram 01 8 RAM_A8 MA8 MA6 2 7 SOT MA9 C104 C110 CSZ0 55 2 CP29 check MA8 MA11 M_CKE M_CLKF M_UDQM MD8 MD9 MD10 0.1U,25V P30/CSZ1 56 P31/CSZ2 57 P32/CSZ3 58 RDZ 59 WRZ0 60 WRZ1 61 P33/WAITZ 62 SM_DIR 1 D7 D1 D8 D1 64 D9 D7 70 D10 D8 71 D10 73 D9 72 D11 D11 74 VDD4 75 VSS0 28 A4 29 A5 30 A6 31 A7 32 A8 33 A9 34 A11 35 NC0 36 CKE 37 CLK 38 39 DQMU NC1 40 VSS1 41 DQ8 42 VCCQ243 DQ9 44 DQ10 45 VSSQ2 46 check HC19 check H_SUB1 154 check 3 TEST 2 GND2 MD11 1 GND1 DQ11 47 DQ12 48 0.1U,25V C201 +3.3U VCCQ349 MD12 MD13 IC4 MD14 MD15 DQ14 51 VSSQ3 52 DQ15 53 VSS2 54 2 DQ13 50 DRAM 9 VCCQ1 8 DQ4 7 DQ3 6 VSSQ0 5 DQ2 4 DQ1 3 VCCQ0 2 DQ0 1 VCC0 2 1 2 1 A4 A4 85 41 P22/INTP6 VDD_4 208 53 VDD_1 2 VDD_IN8 207 54 VDD_IN3 1 MA9 RAM_A9 206 55 XT1 CP31 42 A20 CP32 A8 2 N.C CP33 1 2 1 69 A22 A22 3 2 70 A21 A21 A6 87 INTX339 P20/INTP4 VDD_IN7 183 78 VDD_IN4 A8 3.3K,1/16W 71 A20 A20 GND6100 26 GND1 GND19192 72 A19 A19 CP56 MD7 RAM_D7191 73 A18 A18 A3 MD6 RAM_D6190 74 A17 A17 A2 MD5 RAM_D5189 75 A16 A1 MD4 RAM_D4188 76 A15 A16 LWRX D15 D15 80 MD3 RAM_D3187 77 A14 A14 A17 D14 D14 79 GND18182 79 GND10 2 36 P15/R TP5/TO1 CS INTX027 P04/INTP1 80 A13 A13 A18 check 2 D13 D13 78 46 XT1 CP16 MD8 C305 check 1 check D12 D12 77 47 XT2 MD2 RAM_D2186 1000P,50V check A18 check 48 TEST1 49 TEST2 MA[13:0] check A19 R8 81 A12 A12 CP57 82 A11 A11 CP58 83 A10 A10 CP59 84 A9 A9 CP60 85 A8 A8 CP61 1 MD10 2 MD1 RAM_D1185 1 MD0 RAM_D0184 MD[15:0] A7 CP62 2 3D6,3F6 3 A6 CP63 180,1/10W +3.3R A5 CP64 1 4 check D[15:0] R6 1 A3 GND476 50 GND3 2 1 2 1 10K,1/16W GND20201 60 SCK MA11 RAM_A11 205 56 XT2 MD11 CP34 INTX3 2 RAM_CKE204 57 GND8 MD12 LF_ECA 3D5 LF_ECB 3D5 CP35 INTX2 1 RAM_CLK203 58 NTEST1 MD9 RAM_D8200 61 CLK_OUT 3F3 ASF_STB MT_D15 181 3D6 91 A2 A2 1 37 P16/R TP6 SK 2 1 check RAM_D9199 62 GND9 MD13 RAM_D10198 63 ENCODE2 MD14 RAM_D11197 64 ENCODE3 MD15 65 INTX3 RAM_D12196 CP36 INTX1 A4 CP65 92 A1 A1 GND588 38 P17/R TP7 PWC 3E7 check RAM_D13195 66 INTX2 3C6 LF_STB 94 D15 D15 A3 84 42 P23/INTP7 8 1 check RAM_D14194 67 INTX1 3E3 ASF_I1 MT_D14 180 3F3 ASF_I0 MT_D13 179 3F3 ASF_IN4 MT_D12 178 3F3 ASF_IN3 MT_D11 177 3E3 ASF_IN2 3E3 ASF_IN1 MT_D9 175 MT_D10 176 86 A7 CP55 MT_D8 174 87 A6 CP54 MT_D7 173 88 A5 3D6 MT_D6 172 95 D14 D14 A2 83 43 P24/ASCK 7 2 check check 3C6 LF_MODE 96 D13 D13 A[22:1] 2 1 check CP17 2 5 check MT_D5 171 97 D12 D12 6 check 98 D11 D11 R11 +3.3V check 100 D9 A1 82 44 TEST0 6 3 check RAM_D15193 68 INTX0 CP37 INTX0 A0 81 45 GND2 5 4 check check 3D6 LF_CLK MT_D4 170 89 A4 CP53 MT_D0 166 3E6 CR_DATA 165 CR_MDATA 3E6 CR_CLK 3E6 CR_STB CR_STB 163 CR_MCLK164 3E6 CR_ENB CR_ENB161 3E6 CR_MODE 162 CR_MODE 99 D10 D10 7 check LF_DATA MT_D3 169 90 A3 2 1 3D6 LF_ENB MT_D2 168 93 GND11 LF_PHASE MT_D1 167 CP66 A15 2 1 2 1 202 RAM_UDQM 59 NTEST2 CP52 CR_PHASE 3F6 D9 2 VDD_3 157 104 VDD_2 R10 BK1608HS601 LEDA1 M_OSC MOT_OSC158 101 D8 D8 2 1 180,1/10W 2 A CP46 1 4 A K ORANGE 1 2 CP49 FB3 GREEN FB4 K 1 2 FB 3 2 FB 1 SEC2494C BK1608HS601 CR_PHASE160 102 D7 D7 check check CP47 1 CR_BRAKE159 103 D6 D6 4-8 2 K4S641632D-TC1H 1 2 1 check check CP44 8 A B C D E F Part 4: Appendix S6300 2. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM 7 6 5 8 7 6 5 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 IFD1 IFD2 IFD3 IFD4 IFD5 IFD6 IFD7 7 6 5 2 3 4 IFC2 IFC3 IFC4 1 CP115 IFC7 IFC6 check 1B5 1D1 1D1 1D1 5 6 7 8 FB 2 :11 IFD7:DATA8:09 check check R27 2 2 R26 24,1/16W CP1641 check 2 R28 3 8 7 6 5 1 2 3 4 VIF 8 7 6 5 2 3 4 VIF FBA16 1 4 3 2 5 6 7 8 VIF FBA17 1 check RA14 RA16 RA15 3.3K,1/16W 35:+5V 36:SELIN* 17:RET 18:+5V 1.5K,1/16W R25 check 5 4 2 3 617CM-1427 6 J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J9P J9P J9P check 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 GND D+ D- PWR (4P + FG x5) J9P J2 J9P J2 J9P J2 J9P J2 J9P J2 J9P CP173 J2 check 2 1 USB I/F CP172 J2 check RET RET -PE RET -BUSY RET -ACK* RET -D8 RET -D7 RET -D6 RET -D5 RET -D4 RET -D3 RET -D2 RET -D1 RET -STB* RET RET +5V +5V NC NC INIT* AFXT* SELIN* FAULT* SLCT PE BUSY ACK* STB* D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 UBBS-4R-D10 CP171 J2 check 33 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 17 16 35 18 34 15 31 14 36 32 13 12 11 10 1 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 (36P) J1 J1 J1 J1 J1 J1 J1 J1 J1 J1 J1 J1 J1 J1 J1 J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P J36P CP170 J2 check CP161 check CP160 check CP159 check CP158 J1 check CP157 J1 J1 J1 CP156 J1 check CP155 J1 check CP154 J1 check CP153 J1 check CP152 J1 check CP151 J1 check CP150 J1 check CP149 J1 check CP148 J1 check CP147 J1 check CP146 J1 check CP145 J1 check CP144 J1 check CP143 J1 390,1/10W 1 LF1 CP142 J1 check USB I/F 33:RET 34:NC 32:FAULT* 14:AFXT* 15:NC 31:INIT* 13:SLCT 16:RET 30:RET -PE 09:D8 12:PE 26:RET -D7 08:D7 29:RET -BUSY 25:RET -D6 07:D6 28:RET -ACK* 24:RET -D5 27:RET -D8 06:D5 10:ACK* 23:RET -D4 11:BUSY 22:RET -D3 21:RET -D2 03:D2 04:D3 20:RET -D1 02:D1 05:D4 19:RET -STB* CP141 J1 check J36P CENTRONICS I/F 57GE-40360-853(D114B) 6 CP140 J1 check 1K,0.0625 R24 3.3K,0.0625 RA13 3.3K,0.0625 01:STB* R29 CP169 FN1A4P Q12 24,1/16W 47K,1/16W CP1631 SNS_USB CP165 USB_D USB_DX check FB FB14 BK1608HS601 +3.3V IFD6:DATA7:08 IFD4:DATA5:06 IFD3:DATA4:05 IFD2:DATA3:04 IFD1:DATA2:03 IFD5:DATA6:07 USB_PWC CP162 1 5 4 BK32164S601 IFC7:INIT* :31 IFC8:SELIN*:36 6 3 BK32164S601 IFC6:AFXT* :14 :13 7 2 FBA15 8 1 FBA14 RA12 3.3K,0.0625 8 CENTRONICS I/F 33P,50V CA14 VIF BK32164S6013.3K,0.0625 2 IFC5:FAULT*:32 IFC4:SLCT :12 IFC2:BUSY IFC3:PE :10 IFC1:ACK* 33P,50V CA13 VIF BK32164S601 FB13 FB IFD0:DATA1:02 470P,50V C12 :01 1 33P,50V CA12 100,1/16W R23 2 470P,50V CP1361 check check CP137 FN1A4P Q11 100,1/16W BK1608HS601 R22 C11 IFC0:STB* 1K,0.0625 RA11 4 CP118 check 3 CP117 check 2 CP116 check IFC0 IFC8 1 IFC5 FB12 BK1608HS601 8 1 IFC1 FBA13 BK32164S601 check 2 33P,50V CA11 CP1281 BK32164S601 FBA12 8 1 FBA11 BK32164S601 R21 47K,1/16W 7 2 IFD0 check 3 1 2 2 6 3 1 5 4 5 2 8 1 7 FB 1 2 DIODE0 check FB11-19 J1-7 LF1 R 1/10W is 2125 is 3216 is 3225 R 1/4W R 1/2W 2 1U,10V C17 check CP177 SENSOR 3 2 1 7 6 5 4 8 2 check CP2523 check CP2501 VSNS +5V 3 2 1 6 5 4 1 13 IC11 1 11 check R38 2 R64 1 2 check CP185 IC11 2 R48 check 7 IC11 CP166-168,175,176,180,181,199-209 blank CP140-165,169-174,177-179,182-198 CP102-114,119-127,129-135,138,139 blank CP212-218,220-223,236,249 blank CP251,254,256,257 blank check C16 check 15K,1/16W R52 6 5 3 4 C13 1C8 +5V HVD_PWC 6 5 3 4 1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 5 3 4 HC2 check FB FB17 2 3 5 6 7 8 3 2 1 3 2 1 3 2 1 3 2 1 3 2 1 HLAT HENB0 HENB2 HENB1 ENCD0 HD1 HD0 HCLK CP198 check FB FB18 check CP246 check CP245 check CP244 check CP243 check CP242 check CP241 check CP240 check CP239 check CP238 check CP237 check CP235 check CP234 check CP233 check CP232 check CP231 check CP230 check CP229 check CP228 check CP227 check CP226 DIA1 check CP248 check CP247 10K,1/16W R62 ROM_D NNCD5.6G/NOTMNT 2 HVD 4 5 ZDA16 CP225 check ROM_CS HD7 HD6 HD5 CP224 check J21P 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 H-GND H-GND H-GND H-GND H-GND H-GND H-GND H-GND H-GND H-GND HVH HVH HVH HVH HVH HVH HVH HVH HVH HVH HVH 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 S-GND DIA0 S-GND VSNS ENCD1 S-GND ENCD0 S-GND HD1 HD0 S-GND HCLK S-GND HLAT S-GND HENB0 HENB2 HENB1 S-GND SUBH0 SUBH0 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 J21P J5 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 S-GND DIA1 S-GND HVD HVD HVD HVD ROM_D ROM_SK ROM_CS S-GND HD7 HD6 HD5 S-GND HD4 HD3 HD2 S-GND SUBH1 SUBH1 HEAD2 21FMN-BMTTNC-A J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 J21P J4 HEAD1 21FMN-BMTTNC-A J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 J21P J3 1 HEAD0 HVH J3 CP197 check NNCD5.6G/NOTMNT ROM_SK 4 5 ZDA15 HD4 HD3 HD2 NNCD5.6G/NOTMNT 4 5 ZDA13 DIA0 ENCD1 NNCD5.6G/NOTMNT 4 5 ZDA12 NNCD5.6G/NOTMNT 4 5 ZDA11 FBMJ2125HS420-T 47K,1/16W R61 1 21FMN-BMTTNC-A Circuit Diagram 02 HEAD I/F 1 FP1L3N Q16 +3.3V BK1608HS601 1 CP219 6 2 HC3 7 1 8 FBA22 BK32164S601 1 2 3 4 FBA21 BK32164S241 CP211 8 7 6 5 FBA20 BK32164S241 BK32164S121 CP210 check check 8 7 6 FBA19 1 2 3 HC4 HC17 HC16 HC15 HC14 HC19 HC18 HC13 HC12 HC1 HC0 HC11 HC10 HC9 5 7 2 HC5 4 8 1 HC7 HC8 FBA18 HC6 BK32164S241 HC7: HENB2 HC15: HD5 HC6: HENB1 HC14: HD4 HC5: HENB0 HC13: HD3 check Q14 TPC8402 2 750,1W HEAD POWER ON/OFF HC3: ROM_SK HC11: HD1 HC19: SUBH1 HC12: HD2 HC4: ROM_CS check CP195 4 +19.0V 3 check CP194 2 1 0.1U,25V CP196 HC2: ROM_D HC10: HD0 HC18: SUBH0 +5V 1D1 +5V 100,1/16W R53 5 CP192 1 2 0.01U,50V DIODE SENSOR CP210,211,219,224-235,237-248 R50 R49 6 CP191 2 CP190 R44 100,1/16W 0.01U,50V 15K,1/16W C15 check 13.3K,1/16W1 LA6324NML CP250,252,253,255,258-261 check 2 R47-54: D(0.5) 1 R42 R41 1 +5V 22K,1/16W 100K,1/16W C14 7 +19.0V2 HC1: ENCD1 HC9: HCLK HC17: HD7 HC[19:0] INKS +5V CP260 check R45 3 CP187 1 2 DIODE SENSOR R37-46: D(0.5) check Q18 FA1L4M 2 CP186 2 +5V 13.3K,1/16W 1 13.3K,1/16W R39 2 1F1 8 1 RA17 HC8: HLAT HC16: HD6 HC0: ENCD0 check 2 R55 100,1/16W 10K,0.0625 CP193 1 HVH_PWC 1D1 3 INK_PWM 3 CP259 1B8 1C5 1K,1/16W 0.1U,25V 1 +3.3V check 22K,1/16W 1 check 2 CP261 SNS_PE SNS_ASF 1C5 3 CP258 100K,1/16W LA6324NML 1 R40 75K,1/16W CP101,115-118,128,136,137 LA6324NML 10 9 CP189 R47 2 390K,1/16W +5V LA6324NML check 12CP184 check CP183 2 R37 +5V 7 8 2 CP2553 check 1 FBA24 R65 BK32164S601 150,1/4W CP2531 check 390K,1/16W J3P J7 J3P J7 J3P J7 B3B-PH-KBLC-H +5V Q17 FP1L3N FBA23 BK32164S601 INK SENSOR J3P J6 J3P J6 J3P J6 B3B-PH-KBLC-H ZDA11-13,15-16 VSNS VSNS AUTO SHEET FEED IC11 R21-56,61-66 RA11-17 FB FB16 VV1-8000000 1 FP1L3N Q13 +5V 4 39K,1/16W PAPER END SENSOR FB Q11-14,16-18 PS1 IC11 R 1/16W is 1608 FBA11-24 C711 C511 CA11-14 C7xx are bi-pass for 24.0V 8 CP188 0.1U,25V C5xx are bi-pass for 5.0V C3xx are bi-pass for 3.3R C2xx are bi-pass for 3.3U HORIZONTAL SLIT 14 C511 check CP182 check 2 3 FB15 47K,1/16W BK1608HS601 CP174 1 C11-17 DIODE1 C1xx are bi-pass for 3.3V 1C8 1C8 1E1 SNS_PWC 5 2 FB11 8 1 2 7 2 8 7 2 1 6 3 7 1 2 1 5 4 5 6 1 8 2 2 1 2 1 TLP832(CANO) IF_PWCCP101 1 68K,1/16W 1C1 2 check 1 2 R32 2 1 2 1 8 1 8 1 8 1 3 6 3 7 2 7 2 7 2 4 5 4 6 3 6 3 6 3 1 8 1 4 5 4 5 4 2 7 2 390,1/10W 390,1/10W 6 3 6 3 R33 2 CP178 1 1 2 R35 2 3 4 5 4 5 4 check R36 R34 2 1 PS1 39K,1/16W CP179 1 2 1 R63 BK1608HS601 2 68K,1/16W VER TICAL SLIT 2 1 +5V R66 2 1 2 1 IFD[7:0] 1D5 IFC[8:0] 1D5 R30 2 1 R31 1 2 1 1 11 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 1 R43 R51 2 1 110K,1/16W 2 1 R56 2 C711 1 0.01U,50V 7 33K,1/16W 22K,1/16W 22K,1/16W 22K,1/16W 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 4 1 4 1 110K,1/16W R46 R54 11 1 1 4-9 2 4 11 2 4 1 2 2 1 1 1 2 Appendix 8 A B C D E F S6300 Part 4: Appendix J8 J8 J8 J8 J8 J8 +5V C523 7 6 5 4 3 2 CP304 FB 2 VOUT VCC 2 4 5 PST597ENR IC22 GND SUB M/R FB FB33 C721 3 0.1U,25V C131 R72 check CP314 +3.3V RESX PWC check +3.3U+3.3R 3 4 6 5 M_OSC 3 7 6 LF_CLK 1F2 1F2 LF_MODE LF_STB 5 CP316 CP374 check 1 CP327 GND318 REF 13 VREG 24 REF 13 12 STB 5 4 3 2 1 J8-13 LF11-12 R71-88 R 1/10W is 2125 R 1/4W is 3216 R 1/2W is 3225 ZD21,22 FU1-2 R 1/16W is 1608 FBA33-38 FB31-37 C8xx are bi-pass capacitor for 27.0V CP301-307,311-366,369-384 CP308-310 blank C521-525 C801-806 C131-132 C721 C21-39 C5xx are bi-pass capacitor for 5.0V C7xx are bi-pass capacitor for 16.7V 3 4 CM04RC01 +5V CP381 2 CP382 1 check check check 0.1U,25V C36 6 LF12 7 CP335 check check CP334 8 FBA35 BK32164S601 C3xx are bi-pass capacitor for 3.3R check CP332 CP331 check C804 C32 0.22U,50V +5V CP333 0.1U,25V 3 4 CM04RC01 LF11 C2xx are bi-pass capacitor for 3.3U A3958SLB IC24 MODE14 11 CLK NC1 15 9 ENABLE OUT_A 16 SENSE 17 GND318 8 VDD GND419 7 GND2 10 DATA CP330 +27V_A check 0.01U,50V VM 20 OUT_B 21 NC2 22 RANGE23 6 GND1 5 OSC 4 PHASE 3 CP2 2 CP1 1 VCP +5V LF_ECB VSNS LF_ECA check C28 100P,50V CP379 2 CP380 1 check VSNS C29 39K,1/16W C1xx are bi-pass capacitor for 3.3V CP376 check 1B4 2F4 1B4 check CP320 CP319 check C803 LF MOTOR IC A3958SLB IC23 MODE14 12 STB NC1 15 11 CLK 0.01U,50V C525 check CP375 check CP329 check CP328 check +5V 2 C31 GND419 9 ENABLE OUT_A 16 SENSE 17 7 GND2 8 VDD +27V_A 0.01U,50V VM 20 OUT_B 21 NC2 22 0.22U,50V C24 SNS_PG CP318 check +5V VREG 24 RANGE23 6 GND1 5 OSC 4 PHASE 3 CP2 0.22U,50V C30 1C5 CR MOTOR IC 2 CP1 1 VCP 10 DATA 0.01U,50V C524 check CP373 check CP317 check +27V_A FBA34 BK32164S601 2 8 LF_DATA 1 2 LF_ENB 1 8 FBA33 LF_PHASE 7 CP315 0.22U,50V check +5V 2 0.22U,50V BK32164S601 CR_MODE CR_STB CR_CLK CR_DATA CR_ENB M_OSC CR_PHASE 1 C23 0.22U,50V C22 +27V_A 4 1F2 1F2 1F2 1F1 1F2 1F2 1F2 1F2 1F2 1F2 1F1 1F2 CG: Centoronics I/F Ground +27V_B 100U,35V check CP384 check CP383 SG,MG,HG Signal, Motor, Head +27V_A CP313 check 2 2 FB35 FB FB FB34 VV1-7000000 SPEC 1 1 CP312 C802 1B8,1D1 1A7 220U,35V 100K,1/16W C801 2 FU2 2 J FCC3220202 1 1 FU1 FCC3220202 2 1 JNT1 100U,35V C132 +3.3V check CP311 R71 GND OUT IC21 IN 0.1U,25V C522 2 1000U,35V47K,1/16W RESET IC 3 2 1 1000P,50V C21 check 2 FB37 0,2A FB FB36 0,2A FB 2 BK1608HS601 CP307 1 check CP378 check CP377 1 check CP306 check CP305 1 check C521 100U,35V 2 FBMJ3216HS800 +19.0V CP303 1 check 2 FB32 FB FB31 FBMJ2125HS420 +5V CP302 2 1 CP301 1 check 2 1 check 390,1/10W J9 5 4 3 2 B6B-CZHK-B-1 6P, 1.5mm pitch J5P J5P J5P J5P J5P J6P J6P J6P J6P check CP341 check J6P J6P CP343 J10 2 check CP342 J10 1 check CP340 1U,10V C39 check CP339 J10 6 check CP338 J10 5 check CP337 J10 4 check CP336 J10 3 check CP324 check CP326 J9 check CP325 J9 check CP323 check CP322 J9 check 1 B5B-CZHK-B-1 5P, 1.5mm pitch CP321 J9 1A6 1A6 1B5 1F2 1F3 1F3 1F3 1F3 1F3 1F3 VSNS +5V 5 ASF_STB 4 6 5 4 SM_ENB SM_DIR PG3 PG2 PG1 PG0 7 ASF_IN13 PG[3:0] 8 1 ASF_IN22 FBA37 C37 C38 check CP345 check 8 7 6 5 +5V 0.1U,25V C526 check CP366 BK32164S601 1 2 3 4 FBA38 RD3.3SB1 0.01U,50V ZD22 2 +27V_B ZD21 O4 14 15 16 O3 NC1 I3 GND3 TD62064BP-1 9 10 11 12 13 GND4 I4 NC2 IC26 COM2 O2 I2 GND2 GND1 I1 O1 COM1 OUTB 15 MODE14 GND413 GND312 SENS 11 OUTA 10 VBB1 9 2 REF 3 RC 4 GND1 5 GND2 6 VCC 7 PH 8 ENA A3953SLB IC27 VBB2 16 1 BRK 100U,35V C806 +27V_B HS MOTOR IC 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 PG MOTOR IC RD30FM check CP347 check CP346 +27V_B 0.01U,50V C805 NC1 1 OUT1 2 23 IN1 24 VCC2 NC2 3 VMMA4 22 IN2 21 I0 RSA 5 OUT2 6 19 VR 20 VSA GND126 25 GND2 RSB 8 OUT3 7 VMMB 9 17 VSB 18 CR 16 STB NC3 10 OUT4 11 14 IN3 15 I1 VCC1 12 IC25 MTD2002G 13 IN4 1 check J5P J5P check J2P J2P CP372 J13 2 check CP371 J13 1 B2B-PH-KBLC-H 2P, 2mm pitch J5P CP365 J12 5 check CP370 check J5P CP364 J12 4 check CP369 check J5P CP363 J12 3 check CP360 check B5B-PH-KBLC-H 5P, 2.0mm pitch J4P CP362 J12 2 check CP359 J4P CP361 J12 1 check CP358 check J4P CP355 J11 4 check CP357 check J4P CP354 J11 3 check CP356 check +27V_B check CP351 check B4B-PH-KBLC-H CP353 J11 2 check CP350 check 4P, 2.0mm pitch CP352 J11 1 check CP349 check CP348 Circuit Diagram 03 ASF MOTOR IC CP344 3300P,50V BK32164S601 6 3 ASF_I1 ASF_I0 7 8 ASF_IN32 ASF_IN41 FBA36 BK32164S601 3 2 4 2 1 2 0.1U,25V J7P J7P J7P J7P J7P J7P J7P 5 R84 J8 6 R85 SPEC VV1-7000000 R87 7 0.51,1/4W UPC2933T 390,1/10W B7B-XH-2-TV4 2 1 R73 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 1 1 1K,1/16W 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 1 R76 2 2 1 1000P,50V C26 0.22,1W 1 1000P,50V 0.1U,25V C33 C35 2 1 C25 C27 0.1U,25V 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 1000P,50V R77 2 C34 0.22,1W 2 1 R80 1 2 1 2 1 0.22,1W/NOTMNT 0.22,1W/NOTMNT 22K,1/16W 2 1 1 2 R75 2 1 1 1000P,50V R76-79: F(1.0) R80-83: F(1.0) 0.51,1/4W R74 2 2 1 1 R78 R79 R82 R83 2 2 1 1 R81 2 1 9.1K,1/16W 13K,1/16W 9.1K,1/16W 13K,1/16W 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 R88 1 2 1 1 47K,1/16W R86 1 8 2 1 4-10 2 2 1 R86,R87: F(1.0) 7P, 2.5mm pitch A B C D E F Part 4: Appendix S6300 1 The printing paper contains 100% waste paper. PRINTED IN JAPAN (IMPRIME AU JAPON) CANON INC.