Download Miller Electric SCE-1A Specifications
Transcript
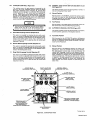
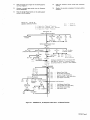
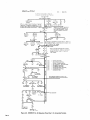
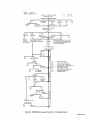
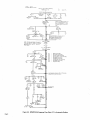
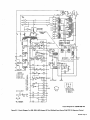
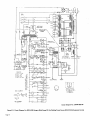
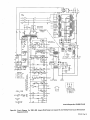
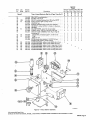
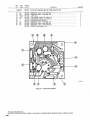
September 1973 FORM: OM-540 Effective with serial No. 71 .576983 MODEL/STOCK NO. SERIAL/STYLE NO. OWNERS MODEL STOCK NO. SCE- 1 A 040 105 SCE-2A 040 107 SCE-3A 040 109 SCE-5A 040 256 SCM-lA 040 104 SCM-2A 040 106 SCM-3A 040 108 SCM-5A 040 255 DATE PURCHASED MANUAL MILLER ELECTRIC MFG. CO. APPLETON, WISCONSIN, USA 54911 NWSA CODE NO. 4579 US ERRATA SHEET After this manual was printed, refinements in equipment design occurred. This sheet lists exceptions to data appearing later in this manual. Item Dia. Part No. Listed Replaced With No. Mkgs. In Parts List Part No. Quantity Description CONTACTOR, size 1-3/44 pole (Eff with S/N HE8O1 243)... 14 W 034820 034 909 16 GS,WS 035 601 003 538 VALVE (Eff with S/N HF854924) 033 050 003 539 039602 035 493 19 012 602 012 640 41 033410 034 910 42 034 825 *034911 COIL, valve 115 volts ac (Eff with S/N HF854924) RECEPTACLE, grounded-twistlock 3P3W (Eff with S/N HE793827) HOLDER, fuse-plug COIL, contactor 115/230 volts (Eff with S/N HE8O1 243).... KIT, point-contact (Eff with S/N HE801243) 031 601 Deleted 17 99 RC1 C3 100 014 159 059 887 BE SURE TO CAPACITOR, HF (consisting of) CAPACITOR, metalfilm 10 uf 220 volts CLAMP, capacitor 1 inch dia 2 - Parts PROVIDE1MODEL~ 1 4 - 007 532 *Recomm~J~dSpare 1 Deleted 081 291 C3 1 AND SER IAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. OM-540 Page A A CERTI FICATE NAME OF EQUIPMENT:_________________________ MODEL NO.. SERIAL NO._~________________________ This equipment has been by the Joint iate Industry less than established by 10 microvolts the Federal on per meter at on the radiation limitations established as The by specified welding equipment identified above only applicable to this model for the purpose for which it ance with the Date Installed. manufacturers as was the conditions Welding mile, the one for equipment book recommended as Machines found to rad limit allowable maximum of this type. be reasonobly Federal Communications Commission, in the instruction expected only to when in provided. CERTIFICATION has been outlined in the intended and instructi~ns. of Commission Arc test the basis of these tests, may USERS structions distance a Communications stalled, operated and maintained field High Frequency Stabilized Installations using this equipment meet under standardized type-tested Committee DATE is installed instruction being in accordance with book furnished. maintained and It the is operated specific being in in used accord TABI-E OF CONTENTS Paragraph No. SECTION 1 1 1 1 - - - INTRODUCTION 1. General 1 2. Receiving-Handling Description 1 Safety 1 3. 1-4. SECTION 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 - - - - - - - 1. 2. 3. 3 3 3 3 - - - - - 1 INSTALLATION Primary Connections Secondary Connections Shielding Gas Connections 5. Con tactor Control 1 1 2 Receptacle 7. Manual Control Connections Of 1. 2 Sequence Control Function 3 3. Normal-Fast Start Switch 3 3 Automatic-Manual Switch 4. 5. Manual Control Of Sequence 4 C 4 High Frequency Control SEQUENCE OF OPERATION 4 Welding (SMAW) Gas Tungsten-Arc Welding (GTAW) 2. SECTION 5 4 MAINTENANCE 11 5-1. Maintenance Safety 5- 2. 5-3. 5- 4. 5- 5. 11 High Voltage Capacitors Spark Gap Spark Air Gap Adjustment By-Pass Panel 11 11 11 TROUBLESHOOTING SECTION 6 SECTION 7CERTIFICATION FOR HIGH FREQUENCY ARC WELDING EQUIPMENT 23 7-1. General - 2 2. Current Control 4. 1. Shielded Metal-Arc 7 2 FUNCTION OF CONTROLS SECTION 4 - 1 Emergency Stop Switch Connections Sequence C 6. 3- 6. 4 1 4. Water Connections SECTION 3 3 Page No. 23 2. General Information 23 7-3. PowerService 7-4. 23 7 24 7 - - Welding Machine 5. Welding Leads 6. Wiring In The Vicinity Of The Welding 7-7. Grounds 7- 8. Metal 7 Individual Installation Certification - 9. Building 7-10. Check List PARTS LIST Area 24 24 24 25 25 SECTION 1 ~Dimensions INTRODUCTION Weight (Pounds (Inches) Height Width Depth Net Shipping 33-1/4 26-1/4 10-5/8 168 230 Figure 1-1. Specifications 1-1. GENERAL 1-4. This manual has been izing personnel with SAFETY Before the equipment is put into operation, the safety sec tion at the front of this manual should be read completely. This will help avoid possible injury due to misuse or improper prepared especially for use in familiar the design, installation, operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of this equipment. All information presented herein should be given careful con sideration to assure optimum performance of this equipment. welding applications. following definitions apply to CAUTION, IMPORTANT, and NOTE blocks found throughout this manual: The 1-2. RECEIVING-HANDLING CAUTION Prior to installing this equipment, clean all packing material from around the unit and carefully inspect for any damage that may have occurred during shipment. Any claims for loss or damage that may have occurred in transit must be filed by the purchaser with the carrier. A copy of the bill of lading and freight bill will be furnished by the carrier on request if occasion to file claim arises. U I Installation, operating, and maintenance procedures. practices, etc., which will result in personnel injury or loss of life if not carefully followed. I I When requesting information concerning this equipment, it is that Model Designation and/or Stock Number and Serial (or Style) Number of the equipment be supplied. IMPORTANT essential I I 1-3. Installation, operating, and maintenance procedures, practices, etc., which will result in damage to equip- DESCRIPTION ment. U U These Sequence Controls are specifically designed to be used in conjunction with an electric current controlled welding power source. These Sequence Controls provide five different sequences for either automatic or semi-automatic operation of the various welding processes. The function of each sequence is described in Section 3, Function of Control, in this manual. The SCE Models are equipped with electronic timers in sequences B, C, and D. The SCM Models are equip ped with mechanical timers in sequences B, C, and D. SECTION 2 2-1. - NOTE Installation, operating, and maintenance procedures. practices, Refer to and the of the Installation Section (Primary correspond with the primary power supply voltage of the welding power source. Refer to Figure 2-1 for positioning of the link for the required operating voltage. Connection para power source Installation, Operation Manual for connecting the primary power Maintenance to the welding power I Control is connected to this block. The jumper link must be connected for the primary power supply voltage that will welding supply emphasize. INSTALLATION PRIMARY CONNECTIONS graph) etc., which it is essential to I source. On the SCE/SCM-5A the control transformer which provides primary power to the control is located in the welding the On the SCE/SCM-1A, 2A and 3A Models, inside the cabinet on the lower right corner above the control transformer, is either a three or a five pole terminal block with one Jumper link attached. The primary power supply to the Sequence power 2-2. source. SECONDARY CONNECTIONS (Figure 2-2) 230/460 VOLTS the Installation Section (Secondary Connection of the welding power source Installation, Opera tion and Maintenance Manual for proper weld cable size. Refer to paragraph) ~ 460 230 The secondary terminals on the Sequence Control are labeled ELECTRODE and WORK. Connect the electrode holder cable to the terminal marked ELECTRODE and the work cable to the terminal marked WORK. 208/230/460 VOLTS _u ~ 208 _u 230 460 2-3. 230/380/460 VOLTS SHIELDING GAS CONNECTIONS These labeled connections are IN-GAS-OUT. (Figure 2-2) located on the front panel and are The connections have a right hand, 5/8-18 female thread. Connect the hose from the shielding supply to the connection labeled IN. Connect the hose gas 230 380 from the electrode holder to the connection labeled OUT. 460 230/460/575 VOLTS 2-4. VtATER CONNECTIONS (Figure 2-2) connections are located on the front panel and are IN-WATER-OUT. The connections have a left hand, 5/8-18 female thread. Connect the hose from the water sup ply to the connection labeled IN. Connect the hose from the These labeled 230 460 575 TA-040 107-4 Figure 2-1. Line Voltage Jumper Link Arrangement electrode holder to the Connection labeled OUT. OM-540 Page 1 EMERGENCY 2-6. I~RT~1 If a portable water coolant system is make the above connections, as possible occur to the coolant system motor. 2-5. CONTACTOR CONTROL Ures 2-3 and used, do damage uences B, C, or 0. If it is desirable to connect an emergency stop switch in the circuit, remove the jumper link that is connected across the fourth and fifth terminals counting left to right. Connect a normally closed switch to the terminals from which the link was removed. (Figure 2-2) This two prong, twistlock receptacle, trol facilities. Either a remote hand used. A two twistlock prong, provides With the AUTOMATIC-MANUAL Switch in the AUTO MATIC position, weld sequences B, C, or D may be inter rupted at any time by opening the emergency stop switch. Opening of this switch will initiate sequence E (post-flow contactor con foot switch can be is supplied with the or plug, (Fig A five pole terminal block with two jumper links attached, located on the inside lower left corner of the cabinet, pro vides a means of emergency stop connections of weld seq not could RECEPTACLE STOP SWITCH CONNECTIONS 3-2) Sequence Control. time). 2-7. MANUAL QUENCE C HIGH FREQUENCY SWITCH CONTROL CONNECTIONS 2-3 and 3-2) OF SE (Figures A five pole terminal block, with two jumper links attached, located on the inside lower left corner of the cabinet, pro vides of external switch control of sequence C. To external switch for manual control of sequence C, remove the jumper link connected across the first and second terminals counting left to right. Connect a normally open switch to the terminals from which the link was removed. a means connect an CABLE TO OUTPUT TERMINALS OF WELDING POWE~ SOURCE EMERGENCY STOP JUMPER LINK TA-040 107-2 Figure 2-2. TA-OlO 566 Front Panel View Figure 2-3. Terminal Block For External Switch Operation SECTION 3 -OPERATION 31. SEQUENCE CONTROL FUNCTION (Figure 3-1) Sequence Sequence Sequence A: B: as follows: Pre-flow of gas and water; adjustable chanical time of 1/4 to 15 seconds. me Sequence Start-current; adjustable control and timer POST-FLOW OF GAS & pre-set magnitude of current and time. Weld Current, adjustable control and timer provide exact values of current and time. Sequence can be manually controlled. Sequence D: Final weld current; adjustable control and timer are pre-set to determine magnitude This Sequence Control is a five sequence automatic control, designed for Gas Tungsten-Arc Welding (GTAW). The func tion of each sequence is C: E: and time duration of current at end of weld. Post-flow of gas and water, adjustable me chanical time sequence of 2 seconds to 3 minutes. PRE-FLOW OF & WATER ~ tA~ 9 ST~RT ~ ~C V WftD I-,/7777777777/7/ /(((~/ /___________________ t7T~\ ~ ~ DI FINISH ISH 1 (((777/7(7 \~ TIME TA-040 107-6 Figure 3-1. Sequence Time Chart Page 2 3-2. CURRENT CONTROL (Figure 3-2) 3-3. NORMAL-FAST START SWITCH (SCE/SCM-1A and 2A)(Figure 2-2) The welding current for each sequence is governed by the setting of the three Amperage Controls which are labeled Start Weld Amperage Control (sequence B), Normal Weld Amperage Control (sequence C), and Slope Weld Amperage Control (sequence D). The control dials are calibrated in percent. These controls act as remote controls, in that they are fine current adjustment of the Fine Current Adjustment Controls on the welding power source. The STANDARDREMOTE Amperage Control Switch on the welding power source must be in the STANDARD position.. This switch provides a choice of selecting either fast start of sequence B (start weld). A. a normal or a Normal Position With the switch in the NORMAL position the starting current will start at a value less than the setting of the Start Weld Amperage Control, but will rapidly increase to the setting of the Start Weld Amperage Control. B. Fast Position With the switch in the FAST position the starting current will the value of the Start Weld Amperage setting. start at Cu rrent Ad ju stme~ trols on the we Iding power source must be in the one hundred percent position for maximum control of the selected range. A. Start Weld Amperage Control on 3-4. Automatic Position A. With the switch in the AUTOMATIC Normal Weld Amperage Control (Sequence C) This control is provided for selecting the normal weld current value. The control is adjustable and can be set for any value from the minimum to the maximum of the selected current range on the welding power source. C. position, the Sequence Control will operate automatically through all sequences with the use of a contactor control switch connected to the Con tactor Control Receptacle. (sequence C) setting. B. (Figure 2.2) This switch provides a choice of selecting either an automatic or semi-automatic operation of the Sequence Control. (Sequence B) This control is provided for selecting the start weld current value. The control is adjustable and can be set for any value from the minimum to the maximum of the selected current range on the welding power source. For a normal start the control should be set for a value less than the normal weld AUTOMATIC-MANUAL SWITCH B. Manual Position range on the welding power source. For a normal finish the control should be set for a value less than the normal weld position, the timers of se quences B, C, and D are removed from the circuit. However, the weld sequence current value will be controlled by the normal Weld Amperage Control on the Sequence Control. Closing the contactor control switch will initiate sequence A. Upon completion of sequence A the weld sequence will be initiated automatically. The Sequence Control will continue to operate in the weld sequence until the contactor control switch is opened. Opening this switch will extinguish the weld sequence and initiate sequence E (post-flow gas and (sequence C) setting. water Slope Weld Amperage Control (Sequence D) This control is provided for selecting the slope weld current value. The control is adjustable and can be set for any value from the minimum to the maximum of the selected current With the switch in the MANUAL time). GAS AND WATER POST-FLOW TIME CONTROL SLOPE WELD NORMAL WELD TIME CONTROL VOLTAGE CHANGE OVER TERMINAL BLOCK FOR CONTROL TRANSFORMER TERMINAL BLOCK FOR EXTERNAL SWITCH OPERATION AND EMERGENCY STOP SWITCH CONNECTION TA-040 107-3 Figure 3.2. Control Panel View OM-540 Page 3 3-5. MANUALCONTROLOFSEQUENCEC Provisions are provided for manual timing of sequence C intensity. To increase the intensity connect both links in the position labeled DIRECT. To decrease the intensity Connect both links in the position labeled AIR. to allow continuous welding for any desired time. This is accom plished by connecting an external switch into the circuit. Refer to paragraph 2-7 for information on connecting the external switch. The Sequence Control functions auto matically through sequences A and B. but the time duration of sequence C is controlled by the external switch. Closing the external switch will extinguish sequence C and initiate the slope weld time (sequence D). 3-6. HIGH FREQUENCY CONTROL The controlled high frequency coupling jumper links and the High is B. With the switch in the OFF position, high frequency is re moved from the weld circuit. This method is recommended for Shielded Metal-Arc Welding (SMAW). C. (Figure 2-2) Direct-Air through the Direct-Air Frequency Switch labeled Coupling D. Located on each side of the high frequency panel are three terminals and one jumper link. The position of the links are labeled DIRECT and AIR. These links provide facilities for connecting the high frequency transformer for either direct or air coupling which governs the amount of high frequency SECTION 4 4-1. Welding, check and Continuous Position With the switch or adjust the shielding gas and water sup Check that secondary connections paragraph 2-2. Check that sdcondary connections described in are as 4. paragraph 2-2. 3. are as described in Determine the type of welding Current required DCSP or DCRP) and position the Polar ity Switch or Selector Switch on the welding power source plies. 2. Tungsten-Arc Welding Con 3. shut-off the fre position high (GTAW). whether Disconnect CONTINUOUS the method is recommended for AC Gas 2. trols 1. in quency is induced into the weld circuit during all three weld ing sequences or as long as the contactor is energized. This SEQUENCE OF OPERATION - SHIELDED METAL-ARC WELDING (SMAW) For Shielded Metal-Arc as follows: Start Position With the switch in the START position high frequency is induced into the weld circuit as an aid in starting the arc. When a welding arc is established the high frequency will automatically shut-off. This method is recommended for dc Gas Tungsten-Arc Welding (GTAW). START-OFF-CONTI NUOUS. A. Off Position (AC, accordingly. Place the Current Range Switch on the welding power in the desired current range. source Determinal the type of welding current required (AC, DCSP or DCRP) and position the Polarity Switch or Current Selector Switch on the welding power 5. Rotate the Fine Current Adjustment Control on the power source to the maximum position. welding source 6. accordingly, Rotate the Start Weld Amperage Control, Normal Amperage Control, and the Slope Weld Amper age Control on the Sequence Control to the desired setting. Weld 4. Place the Current Range Switch on the welding power in the desired current range. source 5. Adjustment Control on the position. 7. Rotate the Normal Weld Amperage Control (sequence on the Sequence Control for the approximate per centage of weld current desired within the range selec ted on the welding power source. 8. Rotate the welding 6. Fine Current power source to C) Place the Automatic-Manual Switch in the MANUAL position. 8. On SCE/SCM-1A and 2A Models, adjust the Start Weld Amperage Control to approximately the same setting of the Normal Weld Amperage Control setting. 9. On SCE/SCM-1A and 2A Models place the NormalFast Switch in the desired position according to the welding application. On SCE/SCM-1A and 2A Models, place the NormalFast Switch in the desired position according to the welding application. 9. 7. Place the Automatic-Manual Switch in the MANUAL position. the maximum 10. Place the High Frequency Switch in the START posi tion for dc welding and in the CONTINUOUS position for ac welding. Adjust the shielding gas and water pre-flow and postflow timers for the desired time setting. Table 4-1 Guide For Selecting Electrode For Gas Tungsten-Arc Welding PURE TUNGSTEN Electrode Dia. (In.) 10. 11. 12. 13. Place the High Frequency Switch in the OFF position. Connect a normally open switch into the Contactor Control Receptacle. Place the On-Off Power Switch source to the ON position. Close the Contactor Control on the welding Switch and power commence welding. 14. Readjust the controls as necessary for proper weld condition. 4-2. GAS TUNGSTEN-ARC WELDING (GTAW) For Gas Tungsten-Arc as follows: 1. Welding, check and adjust the controls Check that shielding gas and water Connections described in paragraphs 2-3 and 2-4. CURRENT_RANGE ACHF-Argon DCSPArgon DCSPHelium 15 Up to 20 10 to 30 15 to 50 20 to 20 to 70 25 to 30 to 90 .010 Up .020 .040 to 15 Up to 70 60 1/16 50 to 125 50 to 135 60 to 150 3/32 100 to 160 125 to 225 140 to 250 to 1/8 150 210 215 to 360 240 to 400 5/32 190 to 280 350 to 450 390 to 500 3/16 250 450 to 720 500 to 800 1/4 300 to 500 720 to 990 800 to 1100 to 350 1% AND 2% THOR IATED TUNGSTEN .010 Up to 20 Up to 25 Up to 30 .020 15 to 35 15 to 50 20 to 60 .040 20 to 80 25 to 80 30 to 100 1/16 50 to 140 50 to 145 60 to 3/32 130 to 250 135 to 235 150 to 260 1/8 225 to 350 225 to 360 250 to 400 5/32 300 to 450 360 to 400 to 500 3/16 400 to 550 450 to 720 500 to 800 1/4 500 to 720 10990 800 to 1100 450 160 are as 800 TA-90 Page 4 190-3 11. 12. 13. Select the proper size tungsten for the welding applica tion from Table 4-1. 14. Connect a normally open switch into the Contactor Control Receptacle. 15. Place the On-Off Power Switch the ON position. the on welding the Close switch control contactor and commence welding. Readjust the controls as necessary for proper welding condition. power source to SCE-IA, 2A SCM-IA. 2A CHART SEQUENCE TIMER FLOW p. S 1 Switch in Manual S 2 Switch in Normal Start S 3 Switch in Start Position picks drops - u. d.c. - up out Position Posit ion Power Switch On Control Transformer I ~oltage Control Energized TO 5 p.u. Begins Time Gas & Water Available On a Operator I Fan On On p Times Out~ ~ On PL4 TO 5 Gas & Water Z U FL 4 Off Closes Maintain Switch RC 1 Thxough I CR1 I I H,F, On Primary (Continuous Position) p.u. Lfi Contacror w p.u. CR2 O.C.V. Closes W 1 P1,2 On p.u. R4 ~ CR CR3 Welding d.o. Welding and at - CR 2 - I Off 1-IF. d.o. d.o. (Continuous Primazy W Position) Sequence Continuous Flow Position Start Position. CR6 Start Time and I-I.E. Off Start Control Start Rheostat Control - Relay Relay Weld Terminated I~1 I- R4 C CR 6 - Weld Rheostat Control CR 7 - Weld and CR 8 -i I. o~ Relay ~onsactot W PL2 Control Relay Secondary Voltage Sensing Relay - d.o. Opens d Point A in Gas and Water Control CR 4 CR2 Times Out Opesator Operator TD1 TD 5 as Point B when H.F. Switch is in CR 1 CR 5 Time established do. CR 3 p.u. Fast Posit ionl Eatablished (Start Positionl TD5 arc Off HF, Begins pu. in (S2 d.o, CR4 I CR5 p.u. I d.o.By d.o. Chart when II.F. Switch is in CR4 CR1 TD5 On p.u. Operative (Weld I~eosat) CR3 PL4 Start I On Position) I Gas&Wate.r CR6 p.u. (No Effect in Manual AvaiLable _______________ TO 1 p.u. I Inoperative CR 9 - Slope Relay Time Control Relay Slope Rheostat Control Relay Stop Sequence Relay ~~5 2 FL 4 Off Gas & Watet Off Figure 4-1. SCM/SCE.1A, 2A Sequence Flow Chart - Si Manual Position OM-540 Page 5 SLM-lA~ ICE-IA. 2A SEQUENCE TIMER 2A p~u. FLOW CHART S 1 Switch in Automatic S 2 Switch in Normal picks dtops - d.c. - up out Position Start Position Power Swiich On Control Transformer Energired f Control .CR S Point E when S 2 Switch at Is operative during preflow. operative after Primary a Gas Stare CR S In Normal Position and R 3 Contacrm pulla up. Operator I P14 p.o. Time Beguts Fan On On ~ TD S Water Off p.u. ~1 TOS On Point 0 when S 2 Switch is io Past at p.u. Position and R 3 is I I Gas& Water Voltage Available ~ Times Out ~ Of f .~. -...-, iomentary Through RC 1 Closes Operation of Switch at Closed Switch Normally a TE 4 will stop the Sequence in the Weld polor Sequence. at any Control will revert to Position A of the Flow p.o. Chart, CR1 TD1 d.o. CR2 Pee Begins by Released p.o. flow Time Operator TO 1 fi.j~mes T02 p.o. Regina Starr itself Through CR 9 TOS Gas & Water Our B ~timary H.F.On (Continuous Arc established Coorlnuous at this when H. F. point Switch in Start position. Position) Time Circuit Open coltage Available ii WI Closes CR3 p.u. NOTE: II CR4 CR5 pa. Position and On H.P. TD 2 polls op ood begins of Plow Chart wheo H.P. Switch p.o. I Start time is at in Point Continuous Point C when H.P. Switch at is io Positioo. __________ (Start R 3 P1. S On Operative Rheostat).~5 (Start A Welding Position) ~ c Established B CR3 d .0. CR S I-. I p.o. Regina Start P11 TD2 Operator - (Start CR3 - Position) CR4 Start Time and H.P. CR 5 Start Rheostat Conuol Time p CR 6 TO 2 Timea Out Gas aod Water Coorrol Relay Secondary Voltage Sensing Relay Weld Relay Relay Relay Weld aod Slope Time Control Relay Slope Rheostat Control Relay Stop Sequence Relay CR 9 Begins Start Coorrol Weld Rheostat Control - CR7 PCI CR6 T03p.u. Relay - Off H.P. On Control CR2 I CR 9 Ott p.ii. I Time F TO 3 Times Out CR5 R 4 d.c. (Weld Rheostat) Operative Switch Inoperative P1 R 3 Off (Start Rheostat) Operarioo Connected to 2 & 3 of TE 4 Provides Manual Coorrol of Weld Time Duration CR7 p.o. CR6 d.o. TO4 Time I R 1 Operative (Slope Rheostat).~ Times Out (Weld Rheostat) P13 On p.o. I TD 4 Inoperative I CR9 p.o. Begins Slope S R4 I I I PL2 Off F S CR 9 P.y. 5 5 5 TD1 P13 CR2 H.P. d.o. Off d.o. B fContlnuoos s TD 5 p~ d.o. Begins Time ~onractor do. B Weld Terminated Opem 5 S Times Our d.o. d W W 1 TO 1 TO 3 I Primary Position) TO 2 CR 7 Off a s P1 4 Off Gas & Water Off .0. I CR8 4.0. I R S Irrnperarloe (Slope Rheostat) T04 d.o. Ch d.o. Make H.P. Ready TOl W P13 Figure 4-2. SCM/SCE~iA. 2A Sequence Flow Chart Page 6 - in Dotted lines show flow sequence with Position. H.F. Switch in p.u. w P14 On do. On Welding S Contacror pa. on Locks Si Automatic Position SCM-3A SCE-3A SEQUENCE TIMER FLOW CHART p.s. Q4 MANUAL POSITION SWITCH S 1 - do. POWER SWITCH - picks drops rip out 0N CONTROL TRANSFORMER ENERGIZED CR5 I Control1vouage pu. I I Gis & Water Available TO S pu. Begins Time I Make R 3 Ready Operative Operator CR1 FL 4 Times Out Off Maintained Cloas Switch Thzou h RC a TD ~ 0f1 0n I I Gas & Water (Star Rheostat) PL 1 Fan FL 4 0n 1 p.s. I TO 1 p.s. Begins Time H. F Primary I CR2 0n . Switch S3 Contactor W p Times Out Manual Make in TO S d.o. On -0 Closes Wi (No Effect ~~1 FL 4 Gas & Water (Continuoul Position) TO1 Pu. a- when O.c~.V. ready to pull up TO 2 welding arc is established Welding Position) arc P.S. CR 4 pu. 0n Start Position) Welding CR3 d.o. CR4 d.o. H.F. Off A at point when position. thu Continuous Dotted lines show flow sequence with H. F. CR3 Switch is HF. established H.F. Switch 53 ii in Avatlable Start posItion. Established (Start Position) FL TO2 1 Start Begins 0n p.u. Time TD 2 Times Out CR1 - CR2 CR6 PL2 CR 5 R 4 Operative (Weld Rheostat) d.o. FL 1 R 3 Off ...s I Inoperative Relay Secondary Voltage Sensing Relay CR4 Starr Time and HF. CR S Start Rheostat Control CR6 - Weld Rheostat Control CR 7 - Weld and CR 8 (Start Rheostat) CR1 Gas and Waler Control CR 3 p.u. Slope Start Control Relay Relay Relay Time Control Relay Slope Rheostat Control Relay Stop Sequence Relay CR 9 do. Operator Control Relay I.. By Operator I U :6 CR2 TD1 Primary do. d.o. Contactor HF. d.o. W 0ff (Continuous Position) W 1 TD 2 d.o. CR 6 PL2 d.o. CR5 PL2 p.u. Off Inoperative (Weld Rheostat) Make Ready PL 1 R3 Operative (Stan Rheostat)...... TO p.u. Begins Post Flow Time TDS Times Out FL 4 Off Gas & Water -ncr- Figure 4-3. SCM/SCE-3A Sequence Flow Chart Si In Manual Position - OM-540 Page 7 M-3A Si ni.L-3A SLQSENCF 1 OdER FLOW CHART SWITCII 5 I IN AVTOhIATIL POSITION pnksu r p.o. R)HER SWPICII OS J. o. . dropt CONTROL TRAhSF~MER Rt1EHCIZEO CO S Control p.u. G~Lstei Voltage Available Make H 3 Ready Opetarice Begins Os. & Water (Stan Rheostat) FI!4 p.c. Tune TD p Pan -On. On FL 4 ~ Times Out Of) - FL 1 TDS SOn Operator ~%_~__ will pu. tlntma lIp Ccrcd a TE 4 will stop tin at peutt CR I of Operation Momentary Switch Through bCl the in truce oe se position S of to uuoi quccic at Id sequence. snip Control lie FInn r Chart. S CR0 do. CR1 P.O. Locks Operator Released by 101 on hsell CR3 Through p.. Prellow Tune Begin. S ID I Ca. & Waier TO S TiniesOui H.P. T02 tn (Switch Cont Peimar1, C H Wnlding Contractor pu. H. F. polls up and of Flow Chart when H. F. and position Srarr at begins Snitch tune at is Circuit ic is Ccnticucus pu. CR4 P.O. Of! H.P. Stan Time Switch Start S CR 1 - H CR2 - H CR3 - Cn 4 - in Position Operator lAnes Out Relay Relay Secondary Voltage Sensing Relay Sraat Time and H. F. Starr Rheostat Control Weld hheoear Control - CR1 J R C, Weld Time Coctrcl Oss and Water Control CBS CR6 TD3p.u. Regina icy. de 102 P1 POSH A;o Established 4j2_kE~) 102 Regma position. scqunocrw oh Stari~ (Stan Position) WeMmg PL~l in P. coltsg. CR3: Oc H.P. CO his poini whnni H Acailable yowl point C when H. F. Switch CR3 Swnch 5 3 at Contlouous in position. on in Doned hires show flow Open ID 2 estabh,hed arc Swiich 53 is 00002 Position) ROTE~ llc 3 ~ Starr Time Begwrs in IL 4 d.c. - Start Ccorrol Relay Relay Relay Weld and CR 8 - CR8 - Slope Time Cnnttcl Selay Slope Rheostat Control Relay Srop Sequence Relay p.o. CR 5 04 do. (Weld Rfstnsrat) PLI Operative 3 R3 ORf leopetarioe (Stan Rheostat) ID 3 Times Out ltinh TB 4 w - Connected 1 & 2) Switch operation connected to 2 & 3 manual control o) weld CR7 CRR 124 Remains do. hegms slope P12 CR8 PL53 Off p.o. On p.R. BS Open Rh 124 htoperar foe lIme. CR9 0ft dv, (Cnsrlitoous d.n. 1 Peimoey W Cootactoe Weld Teemonared d.?. Pnnitlnn) 1D2 Begins 0 pu. P13 CR2 H (Slope Rfiecsrat)4 I H.P. Off I provides S Opera rice Oor I 121 I o) TE4 duration. p.c. CBS (Weld Rfreosrat) ume do. ton FInn Tone 123 I 125 Times Out I CR5 CR8 P.O. do. 104 do.. CR8 do. Make Ready H.P. 101, H PL3 Rb hinperarive (Slope RRt~af) Make Ready B 3 OperatIve ____________ P11 P1.4 ~ff Gas & (bract Rlrensasr) Wares 011 Figure Page 8 4-4. SCM/SCE-3A Sequence Flow Chart - Si In Automatic Position Ii SCMSA sUE-IA SEQUENCE TIMER El r)W (hART Manual PoSition 2 & 3 for Switch Operation Switch) Start Position (H. F. 0N POWER SWITCH I CR S TD S pu. I R 3 I Operative (Start Rheostat) Energize Gas & Water Lights Flow Starts CR 9 pu. PL 1 p.u. Stops I PL4 Circuit Closed By.Pass by.pass 1 before Hl.F. is time 1 on.a off before (Control Safety Relay) Make CR 2 bypals Gas& Water Ott CR 2A CR16 pu. Time W CR I p.u. CR U p.u. Conta :tor Welding Ire TDI pu. 0n HF. to CR 13 CR2B pu. d.o. 1fF. Off Make Times Out Energize Begins TD 2 Times Out - CR 2A - CR 25 - CR 3 - CR4 CR 5 - control relay Interlocking control relay Control relay Control relay Overvoltage sensing relay H.F. signal relay Control relay for start rheostat Welding - CR 8 - CR 9 CR 10 - CR 11 - CR 12 CR 13 CR 14 CR 15 - CR 16 - CR 17 - Slope relay Arc CR Goes d.o O~it R 3 Ino~erative (Released by Operator) ~1 CR2A do, do. do. d.o. Extinguil for weld rheostat ed CR11 d.o. I d.o. CR 10 d.o. d.o. CR6 PC2 relay for slope rheostat Safety control relay H.F. time delay relay Differential voltage sensing relay Contactor drop out time delay relay Interlocking control relay Time delay elay (or CR 2 inrerlock Start 165 volt control relay HF. control relay HF. By Past Time Delay Relay do. Off d.o. Voltage Reducer Open p.u. pu. I 1 TI) 5 CR 9 p.u. p.u. CR 16 U a. Begins p.u. CR 17 CR14 CR2 I TD6 CR12 control Control do. CR28 I CR 7 & CR 11. I TD1 Primary Control Delay HF. I CR 1 W - to hF. pu. Operative ) Contactor CR 6 Ready Time I Fl. 1 CR 2 do. After Time TI) 1 TD2 CR6 Lights Up R4 Operator CR 14 -1 PL 2 p - TDI Closes W 1 Lights Up PU Delay - p.u. Esrabli.ihed By-Pass Open CR 1 pu. I Timer, d.o. After Time CR28 RC 2) Couttactor, TI) 6 Times Out CR 17 Ready Energize Up Energize - I Make PL4 Lights CR 2A - opens. I CR 10 to insure TI) I to Ready to Enet gize High Frequency short I BeginS Ready to itself. and PL 3 Make closed by Operator through pu. (Held Closed I 80 VOC Available I TI) 6 ott of CR 17 insures delay H.F. TDSd.o. lockt NOTE: Goes p.u. Circuit Opens H.F. Out d.o. delay nine CR 2 Contactor ~ CR 10 insures CR9 (provides pu. short CR 17 Gas & Water Flow I I CR 14 pu. Continuously I I CR2 I CR 10 TI) 6 Motor Runt Up Times Out Ready Make so TI) S I I PI. 4 pu. I I Suit 80 Volt Position) (Starr S2 up druipt - in ha pt p.::. Switch Si Time By Pass Closed relay TD S CR5 Timm R4 p.u. Out Inoperative R3 Operative Gas & Water Shuts Off PL 4 Goet Of Figure 4-5. SCM/SCE-5A Sequence Flow Chart-Si In Manual Position OM-540 Page 9 sCM-IA SCE-5A SEQUENCE TIMER FLOW CHART picks drops p.o. Switch Si Link & 1 in A atoms tic for 2 80 S2 Position TDt pu. (H. F 0N PL 4 pu. I R3 Operative (Start Rheostat) P I Gas & Water TO 6 Flow Statti Motor Runs CR 10 CR 9 pu. time CR 17 pu. I Circuit Opens Stoll~. H.P. Pass Circuit Closed By NOTE PL 4 Goes CR 10 insures Out by Make pass closed gize before H.F. is on.a short time delay of lady HF. off before Momentary Through RC 2 1~ CR2 Ecer to Make High Frequency Ready through by-pass - CR 28 TD5 d. do. CR 1 d.o. PL4 by Operator o. Gas CR2B p.u. T01 p.o. CR 14 pu. p Ready to Energize High Ere 13 Lights Up after d.o. Delay TimesOur TDJ Make to relay control relay Time Ready Energize CR &Water TO 1 - Overvoltage sensing relay HF. signal relay Control relay for starr rheostat - CR 5 Make CR9 CRIB Control - CR3 CR 2A Energize Interlocking control relay Control relay - CR 2A Switch Open - Operator CR 1 opens. CR 2 Circuit Available CR 9 so CR2- CR2A p.u. 80 VOLTS pu. and Locks itself on to CR2 locks itself) ott CR4 CR 1 delay insure 3 (Control Safety Relay) OVER WORK Closes TO CR 17 insures WELDING TORCH PRESET Operator so and PL Contactor Flow pu. )Ptovides short Gas & Water PL 1 CR14 pu. Continuously Times Out TD 5 up out Switch) I Lights I Make Ready to Energize o. Position) Volt POWER SWITCH CR3 d. Timer (Start Start Position CR16 p.o. quzuCy Contactor, H.P. Timer&CR11 On High Frequency HF. ~p.u. CR11 Result of H.F. (Secondary Voltage Drops as a Arc. Differential Voltage Pulls Up ~ P CR12 1 Time w pu. I Contacor ~.u. TD2 Begins Time PL 1 Lights Up II TO 6 Times Out CR10 Welding Arc Established TD2 TmmosOut TD3 CR 17 I-I.E. do. After Time Delay BeginaTmme CR6p.u I B 4 CR Arc - CR 10 - Safety relay relay for slope rheostat relay delay relay Differential voltage sensing relay Contacror drop out time delay relay Interlocking control relay Time delay relay for CR 2 interlock Start 165 volt corttrolreIay N.E. control relay N.E. By Pass Time Delay ReLay CR 11 CR 12 - CR 13 - CR13 control H.F. time - - CR 17 ~i 1 Goes Out Inoperative B 3 Switch Operation Outage Connected TD4 CR7 P~U BeginaTime CR10 CR 6 p.u. pu. do. PL 2 Goes Out PL 3 t.U. Remains Control. Tinner TO 2~&R3 Start Operative 4 R4 CR7 Locks CR S Lights WeldCycleReverts to Open Through on Itself WI Inoperative Times Out On Approximately 40 Cycles CR 9 Arc Re-established d.o. CR4 do. I I d.o. cLot d.o. CR2 TO S Welding Arc d.o. Begins CR 2A pu. P I d.o. TD 1 d.o. Time I TO 6 CR. 1~ d.c. I I PL 3 CR 16 Goes ~ d.o. TO 2 d.o. d.c. I Out CR11 TD5TimesOut H.F. Off I By-Pass Open p __p I 2 Gas & Water Shuts Off Ready For HF. CR 17 I By-Pass Closed d.c CR2 p.u. Goes Out Figure 4-6. SCM/SCE-5A Sequence Make P1. ~ I I CR 2B - CR3 CR 10 10 2 & 3 of TE 4. 3 pu. CR4 Page to Provides Manual Control of Weld Time Duration. less) or CR B H.P. CR 9 for weld rheostat relay control Slope Weld Rheostat Tb 3 Times Out (One cycle PL2LightsUp 1 CR 5- d.o. Operative Control Control CR 16 Off By-Pass Open Unintenrior~al - CR14 , d.o. - CR 7 CR 8 CR 11) ~ Begins TO 6 CR 6 T03 do. TD4 P d.c. CR7 do. Voltage Flow Chart Reducer - d.c. Open Si In Automatic Position CR5 CR8 pu. d.c. R3 R5 Operative Inoperative MAINTENANCE SECTION 5 5-1. MAINTENANCE SAFETY 5-4. reiunr.]1 To readjust the spark air gaps, proceed A. Loosen Be sure the branch circuit, or the main disconnect switch has been opened before attempting any inspect B. Place ion or C. performing source or switch on the any work inside the welding Placing sequence control. the power (A) screw follows: Apply slight (Fig. 4-1) both sides. .008 inch feeler gauge in spark air gap an gauge is held power on as against spark point (B) the two points. pressure area so (C). feeler firmly between the welding power source in the OFF posi tion does not remove electrical power from the switch terminals. 5-2. SPARK AIR GAP ADJUSTMENT 0. Tighten screw (A). HIGH VOLTAGE CAPACITORS These capacitors require no attention and are rarely a source of trouble. A defective capacitor, however, is evident usually the by housing or evident of oil leakage in certain cases. Any repair shop can readily determine the condition of capacitors. (If one of the high voltage capacitors should fail, operation may be continued with one capacitor until a local radio the can be secured.I In order to prevent excessive over the remaining single capacitor, the spark gap point should be reduced to about .004. new one load on setting 5-3. SPARK GAP The spark point and air gaps can be inspected by opening the Sequence Control. The spark air gaps are factory set at .008 inch. It will be necessary to readjust the spark air gap setting due to extended operation. Readjustment of the spark air gap is also indicated when intermittent operation of the high frequency is noted. Usually this occurs when the spark air gap setting has increased in excess of .012 inch. door of the TA-020 623 Figure 5-1. Spark Air Gap Adjustment 5-5. ~ning BY-PASS PANEL The purpose of the by-pass panel is to reduce the high fre quency feedback into the transformer of the welding power source. A defective capacitor in this circuit would reduce of the spark & r gaps d ue to n ormal ope ra tion, may, if not corrected, increase the loading of the high voltage, capacitors, thus contributing to their premature failure. Cleaning or dressing the points is high frequency output and might be evident by loss of oil from the capacitor case. If in doubt as to condition of the capacitors, have them checked at a radio repair shop. The resistors in the circuit would show evidence of failure if they recommended as the material at the gap area is tungsten. The entire point should be replaced when the tungsten section has disappeared. not are . SECTION 6 Failure in this circuit is cracked. pected only as a rare and would be sus last resort. TROUBLESHOOTING - The data listed here, discusses some of the common problems which may occur in this sequence control. A little thought will probably solve the problem through the information provided. If after checking the following data the trouble has died, it is recommended that a serviceman be called. The during troubleshooting. not been reme It is recommended that the circuit diagram be used for reference been assumption of this data achieved proper welding condition had trouble developed. In all cases of equipment until malfunction, the strictly followed. is that manufacturers TROUBLE Normal output. a recommendations should be REMEDY PROBABLE CAUSE No high Incorrect spark air gap. Check setting for .008 inch. frequency. High frequency switch Shorted Normal output. Low high in off position. high voltage capacitor.. Check switch position. Replace capacitors. Incorrect spark air gap. Check High frequency Check all connections for for .008 inch. setting frequency. leaks. Incorrect direct-air coupling. Check that both links high frequency leaks. are connected for the same coupling. Erratic weld current. Poor tungsten. Check tungsten and replace if contaminated. Incorrect polarity. Check polarity. Incorrect welding cable Poor ground size or loose Check for proper weld cable size (See cable connections. paragraph 1-2.) Tighten all welding connections. at workpiece. Check ground connections. OM-540 Page 11 TROUBLE REMEDY PROBABLE CAUSE Contactor pulls in. Adjust Incorrect operating voltage of CR3 relay. slider R2 resistor on CR3 relay so pulls in on open circuit voltage. Weld current does not shut off. Contactor does pull in. not Adjust slider when welding voltage of CR3 relay. Incorrect operating R2 resistor is initiated. on arc CR3 relay drops Out so Check fuses. Blown fuses in control circuitry. PCI 32 ~36~7 CR C MAI TEl 52 T1 36 FO LO~O~o----------- B :sEc. ~ L I r~ -- 44 I r ~ B 72 ,., A ~ LO_Z~o~o___s_______ IC TE1 23OVr W ~a3OV WELDING SEQUENCE iii ~ H. i~ III 16 I 22 ~ ID _____________ TE3lj~9 TIMER I!(~TE2 ~? _____ \~ ~ ____ 61* 30V ; h4 1ISv 3 EMERGENCY ~ RC3* Ill A I 23 0000000 ~ 00000 30 IA 230V1 :: I _ MACNINE 1460V B I 460V~ . 44 3 ~ II 251 I 14 14 145R1 14 26 ____ CR1 ~ 1,1 2 PCI ~ 2/1 233 3 CR5 M I ~TP~LOCATED CR9 C~~QQQj WELDING MACHINE CR6 0~ WELD ID, 237 \52 ~~o51CR~,PL C-FAST ~j9 CR3 5 8,8 276 RF 29 ELECT WORK FILTERS l_ 0 CR I IR ~o. Ir~i~Ii3i RD I 3,5031 V8 ~ Ill I 1231 CR9 PAIRS IOPTIONAL-ESTRA( _I l_~:~J. I TWISTED VOLTMETERS I b.NOPMALI CR85 LOPE CR~ I / CR4A START ~+L 28 P7 236 I 20 Pt ~ T~ 8,10 I SIR START OR--- 235 18 22 REV IN 234 CR5 53 5 4 I? 21 2,14,15 HFO~_~ 9 I START CR 220 221 1C3– ~ L__1T1___J 2~,~RFC 8 ___________ T3 5 CR CR31 SEQLI E NC E 1- ~ PRCFLOW-GSW 2- START 3- WELD 1+~~4 TEl2 SA 23 3 2A 256 2 TIME TD2 I TIME 3< 4-SLOPETIME Al 5- PO5TFLOWGIW ~l~l C W R7226 10 CR 8,19,90.20 8 ~E~0 *Op1IONAL..EXIRA WITH t,JUI ~, ~ ELECTRODE 2 WORK ~PL PC3 CR73 - I 8,10,11 .6-In -~ 21,22,22 60 TO RC9 U REMOTE 72 34420 3 iT 13 61* 4 .91 .90 I 0000 - 20 000 251 4 209 000 - ESTRAI GROUND (WNT 1 B-BRASS 249 C - COPPER (VI (5) 2,4 44 2.9039460 21 . CR RHS-2 ~PL 000000 CONTROL IOPTIONAL ..(RE 37322 - ~ ~WL 80 TE2 COM 0 16 II. TE3 CR2 ws1 IS 31 245 7246207208 00000 C Si 6 4T Circuit Diagram No. CB.900 529-13C Figure 6-1. Circuit Diagram For 200, 300 & 400 Ampere DC Arc Welding Power Source Page 12 With SCE-1A Sequence Control 3/ 32 2 3 44 20 000000 IT 87* 7 3730 4 20 23039460 0000 000 2T 245 0 TE2 /246207208 0 0 0 4T 12345 Circuit Figure 6-2. Circuit Diagram For 200, 300 & 400 Ampere DC Arc Welding Diagram Power Source With SCM-lA No. CB-900 529-14C Sequence Control OM-540 Page 13 1.11: 3? ~ IF I LO-~-O~y ~27 CWA~ 12 44 7 45 Si TE1 ?30V, 4A0 V I WELDING FM j 20 MACHINE I~ 2 )OV, SEQUENCE 460V TIMER ~ 38 D _ D L___ 230V 32 ~ SEC 1 L OO B S2 MA1 T~ 43 C C,R ~74 Dcz N ___________ (0 Dc. TE2 TE3~ DI TI ,00U0000 1 87* 4 - 175v -1~- -11 ~ E ME P GE NC ~ 1 CR V 0PTI0NAL~~ CR * ~ EXTRAWITHRC3 RC3* ~T ,SRI 26 24~HUNT \ 2,l~,I5 -~----.- -0 -ASTR REV 2/1 M I CR5 START ~FF 1TP-LOCATEDIN CR9 WELDING TDl~CR4A A WELD CRlO15~~ 1~~III~~f 2141 tH7.cPL 6 5 I 218 ~ CR6 220 CR31 SEOUL NCE 1-PREFLOW 3-WELD TIME TIME 5 ELECT I_ L Ci 29 CR 3 223 06W 2 TIME 4-SLOPE 221 6,17,18 TO TO2 FILTERS ~JITTL WO~ CR3~ WORK C2 ~ 237 29 L~_ ~ RF CR8 SLOPE 2-STARI I TWISTED PAIRS VOLTMETER & (OPTIONAL-EXTRA) ICR5 215M 0 235 20 . 9,9 M ~D / R7 5 I T2 _______ 233 18 CR9 CONT 8,10 234 , 28 CR4 203 MACHINE 1h~J IT ~lQ&QIJ 9 ______________ ________________________ A~1C 5- POSTFLOW-G&W ~ ~CR 223 10 8,19,20,20 ~1 0 L M ELECTRODE CR73 /_~ TO3 ii WOR K I 13 OR B I C 0 CR 8,10,71 2 l,22,22 CR9 12 3 44 20 2 000000 31 32 248, rD4 11 i3~I 81* 4 314/ 30 1 00000 20 23039450 000 2T TE2 44 COW 0 4 205 000 3T 1 245207208 00000 245 RC7 U REMOTE DR RHS-2 ,,PL CONTROL IOPTIONAL-EXTRA) 249 2,4,12 )4~50TD - B - C - GROUND (WHI 1 BRASS (VI COPPER (XI 16 TE3 52 251 TO W5~ 76~1257~:v:~:PL 057 4T Circuit Figure 6-3. Circuit Diagram Page 14 For 200 & 300 Diagram No. CB-900 565-3B Ampere Wide Range DC Arc Welding Power Source With SCE-2A Sequence Control I I 31 32 2 3 44 20 000000 4 1 00000 20 23039460 000 2T 245 TE2 C I REMOTE CONTROL (OPTIONAL-EXTRA) CR C 81* B - OROUNO (WI-IT) B-BRASS(Y) IT 314130 ~ RHS-2 CR - COPPER Cx) 44 COAl 0 TE3 1 246 ~72O8 00000 4T Circuit Diagram No. CB-900 574-4B Figure 6-4. Circuit Diagram For Sequence Control 200 & 300 Ampere Wide Range Low Ampere DC Arc Welding Power Source With SCE-2A OM-540 Page 15 PC 1 CR C 13 \/37 31 TF~ MA_J 11 CWA~~ FRI L0-~-LO-f-0~-r 43 SEC. L~I 45 ~ TE1 52 38 0 S U I 2 230vf 4 60V WELDING ~ L~ACHINE 230V 31 ~0- 460V 44 32 23oVr TIMER TE2 1E3 0 ~Q~Q ~V4 4-114 LI4! 14 1,1 EMFRG~NCY STOP ~ j ~SR1 RC3* 4 26 CR PCI 2 ~aT2082 2,14,15 53 SIR - 3 IWELDI~ ~ C~4 IP-LOCATED IN I CR5 START CR9 o~~T15 MACHINE 4 7 T2 8,10 CR5 235 -~-~.F 18 TD~I~.~r.ot__O_. I 5 I I TWISTED / ~(RS VOLTMETER RF 51 - CR6 WELD I I ~29~ 127 START 12,, 233 & ELECT WORK FILTERS IOFTIONALEXTRA1 214 HTc~J 6 236 START ~237\~ 20 IDC - NORMAL I FAST CR3 218 C3~ 3,~ L~13~1~j CR8 SLOPE c & 21 I Cs8 238 CR6 2391 C3~8j 22 8 29 6,17,18 220 9 254 CR CR31 SEQUENCE - 9 ID 0 A~~~226cR PREFLOW -66W z TIME 2START 9 TIME 3-WELD UI TIME 4-SLOPE 5- PO5TFLOW-G~w 9w 3 102 Si 224 225 II 8,19,20,20 ….. 1~(~ WUI *OPTIONAL.E%TRA WORK ELECTRODE WiTH RC3 - ~ I 13 B C 4 .02 :; 246 4T 32 31 32 2 3 44 20 000000 l3_~f 81* 3~ 4 3130 1 0000 23039460 000 21 TE2 44 COW 0 RCT ~i,22,22 REMOTE CONTROL (OPTIONAL- EIITRA) ,3,PL TO4 IT 10 P P5-2 249 2,4 I4~T5D OR - B - C - GROUND (WHT) BRASS (VI COPPER (XI 16 193 CR2 wS, l5-~ 4 205 000 251 31 245 0 1 246 ~7208 0 0 0 0 OSi 41 12345 Circuit Figure 6-5. Circuit Diagram For 200 & 300 Ampere Wide Range DC Page 16 Arc Welding Diagram No. CB-900 565-6 Power Source With SCM-2A Sequence Control 31 32 3 44 20 2 000000 IT 8M 20 4 1 00000 314130 23039460 000 21 251 4 TE2 44 COld. 0 TE3 205 000 3T 245 0 7 0 246207208 0 0 0 41 12345 Circuit Figure Diagram For 200 & 300 Ampere Wide Range Low Ampere DC Sequence Control 6-6. Circuit Arc Welding Diagram No. CB-900 574-3B Power Source With SCM-2A OM-540 Page 17 7, ~ 36~NGMACHINE FM 2050 I I~ ~~230V ~ ~ ~ 09 4600 ~ SEQUENCE CONTROL _~_.tIi~ L__. Ph 00000 81 1750 0 4 000 ~~.Cn IT EMERCEN R Sro 7 50 T CI 1E3 MET. PCI II WOWE 50 2,13,13 ELECT 217 I21i~~ I 257~~1J 270 Zag WELD CR6~ II CR6 lB ~,22 72~C0R 7 2531 238 SLOPE 212 6 20 1I~9~. CR,d~~~_ 21 5,11,17 313217 739 I 25? ;C~l:PL 4 IlIAC TIME SLOPE TIME 241423920 IT CR7 226 POErLOW-CRA 3-WELD 4 223 - WORK ELECTRODE SEQUENCE I 2- START 2T 205 !,I6,I9,~ 245 7246207209 72345 3? 4 3081 METERS-LOCATED MRCS 34 COAl 42 TE2 wsrp-LOCATEOIN 12 47 ST TE3 TIC Sill1 WELDING MACDINE IN OPT IDNALEVIRG WIro 2 EVA TRANS BALANCE ~ SE CONTROL ONLy :~W CONNECTED TERMINAL BALANCE ~ : ~ 4027 TERMITIA E CONNECTION 20,21121 12 IS W1LA 240 2,3 IS Circuit Diagram No. CC-901 016-26C Figure 6-7. Circuit Diagram For 200, 300 & 400 Ampere AC/DC Welding Power Page 18 Source With SCE-3A Sequence Control 0~& 71~1 ~ 203 Or 223 7281207208 37 308/44720 .4ErEps-LocnrED RCS /N CONTROL OPTIONALEXTAA Circuit Figure 6-8. Circuit Diagram For Diagram No. CC-901 O16~18C 200. 300 & 400 Ampere AC/DC Welding Machine With SCM-3A Sequence Timer OM-540 Page 19 6 I TEl ~I. I 230 460230 SEE INSTRUCTION BOOK ~ PROPER PRIMARY IONS ~NECT 39- __7 1E3 12 ______________ ~5V~ 000093 300 30 2300 2600 2300 TE7 CI 8000000 I ~ P61 B 7900 37 72 TI 131 1,_J Lc!:;.c.~_~~_J B 23.3 ~ SCVII~ 37 SS I- 5,78 234 77 ~ 32 34 2321 CRR U 237 IL__fi- 1;40 CR8 35 ' 210 MT 80 SR CR C ~jr~cn I 9 ~ 297 , ., 36 283 74B~7 2~~J 78 CR I 0 ii~i~1 ~ 34 275 54 R sio CR8 2~ CR6~ a 0 ~ _____________ I CR5 107 CR9 CR12 CR29 / 1 MA3 19 42 72,73,78 263 I I I 258\j,,~ 4,24,27,28 ~ /M B I I ~lERGE 277 4 30,38,47 CR CR2 B~ 4 it;~ RC3 IN SEQUENCE TIMER 20,20 cR~, 6 9 -~ F, 267 CR751 C IC CR7 77- CR73 IN WELDING MACHINE ~? ~ TIMER I- PREFLOW OF 06W 2 START IN SEQUENCE ASLOPE TIME 14 S START - CR73 70 WELDING i 1 78 1~r1 .0 COUPLED ~ 8,31,32,32 42 DIRECT ~R1,j,,T3 7L,4 227 11~1----F CR,9 I ~I 1 S2~ 4 ~ ~I ~~52I ~ COUPAE~ j r AIR L!~ G 223 23 4 CR? 27 I CR77 I _________________________ 20 51 I,-0-,-1 Isi WELDING MACRINE 280 I i TIME COST I 47 TO6IWLOCATEDI7I ClOSED OPEN-BOO 278 CRI8 C6 MACHINE TIMER POSTFLOW 0601W HF.ON 6- 76 CR29 SCaUENCE TIME WELD TIME 3 I~R I 28 CR TIMER ~273 CR3 89 SEQUENCE CR7 I SR 25 - 75,76,25 4~2~32~ oJ E~~~ 37,39 CROAI -1E7,~,-l 5 01 _~~,~1 CR CR~y CT I9,33,34,3~B CR7 -U 22 703 1 CR 23 26 ELECTRODE 9150 246 WORK, 79,27,22 41 CR2 0.~ 34 23,3~,3S,36 aS 26 ~ 249 CR 02 370 032 JOB 03 CR2 70 40 21 037 250 760 020 ~039 CR2 28 ~1E4SPL 091 570 0 890 88051 OS, 257 ~ ~ 2 3 C1~ 245 - 30 287 4 00 31 282 CR,O 420 044 0 7 0 246207208 0 0 41 Circuit Diagram No. CB-900 306-13A 38,42 Figure 6-9. Circuit Diagram For 300 Ampere AC Tungsten Page 20 0 2345 Inert Gas Welding Power Source With SCE-5A Sequence Control 1.0 w LO 275~~V.15L3 ~Q~tE3 TE~ 12 40 a 4~1E~ERLA3S.dIYRC~.Q;~ ~ ~ T~ 1._f:!!!!~:I1!!: ~~ 2 213 36 WE &_.~c~n44yji~ ~i~\ ~c~__ TIME 20 I I ~. iS WELD TIME 3 ~: WELDING MACHINE SEQUENCE ~L~A~~FCtW TIMER C0 I CApE 1 hI I C WEDME -4 OPEN-TOy CR) pp I 01 a U- J I 2 ELECTRODE WORK ~? 21 -fl2 26 $R2 o ~ o-~y-o-- 0 370 : TDT :::TT 21 gIg CR10 30 ~ ~ 2~2 2F2F~ 36,42 Circuit Diagram No. CB-900 306-4A Figure 6-10. Circuit Diagram For 300 Ampere AC Tungsten Inert Gas Welding Power Source Wtih SCM-5A Sequence Control OM-540 Page 21 7- CERTIFICATION FOR HIGH FREQUENCY ARC WELDING EQUIPMENT a SECTION 7- 1. GENERAL 3. This following information is necessary to make a proper installation of the high frequency arc welding equipment de scribed in this instruction manual. In order to comply with Part 18 of the Rules and Regulations of the Federal Com munications Commission, the certificate in front of this man .ual must be filled in completely and signed. The certificate must be kept WITH THE EQUIPMENT comply with the regulation. Direct radiation from welding leads. Direct radiation from the welding leads, although very pronounced, decreases rapidly with distance from the welding leads. By keeping the welding leads as short as possible, the operator can do a great deal to minimize interference from the source. intensity and frequency of the radiation can be altered over wide limits by changing the location and rela tive position of the welding leads and work. It possible. loops and suspended sections should be avoided. The AT ALL TIMES to The manufacturer of the equipment covered herein has con approved field tests and certifies that the radiation can reasonably be expected to be within the legal limits if the Pick-up and reradiation from power lines. Even though welding lead radiation falls off rapidly with distance, the field strength in the immediate vicinity of the welding area may be extremely high. Unshielded wiring and un grounded metallic objects in this strong field may pick up the direct radiation, conduct the energy for some dis tance, and produce a strong interference field in another 4. ducted installation procedures, correct as outlined, are followed. The importance of a correct installation cannot be over emphasized since case histories of interference due to high frequency stabilized arc Welding Machines have shown that invariably an inadequate installation was at fault. The area. This is usually the most troublesome source of interfer ence. but careful adherences to proper installation pro cedure as outlined in this booklet will minimize this type of interference. of the equipment must complete the certification by stating that he has installed the equipment and is using it, according to the manufacturers instructions. The user must sign the certification notice appearing in front of this instruc tion booklet indicating that he has complied with the require user 7 ments. In the event that interference with authorized services occurs, in spite of the fact that the radiation from the welding equip is within the specified limits, the user is required to take suitable steps to clear the situation. The factory person nel will assist the user by supplying technical information to clear the situation. ment - 3. POWER SERVICE The specific installation instructions for making the proper primary connections to the equipment as outlined in the in struction booklet furnished with the equipment, should be followed carefully with one exception as notted in the following paragraph. Frequently installation instructions specify that In lieu of complying with the installation requirements and the certification of each individual installation, the user may elect to certify his entire plant by having a reputable engin eering firm make a plant radiation survey. In such cases, the installation instructions incorporated in this instruction booklet could very well serve as a guide in minimizing inter ference that might be contributed by the high frequency arc welding equipment. 7-2. GENERAL IN FORMATION In a high frequency stabilized arc Welding Machine installa tion, interfering radiation can escape in four distinct ways as outlined below: 1. 2. Direct radiation from the welding machine. This is radia tion that escapes directly from the Welding Machine case. This is very pronounced if access doors are left open and unfastened and if the Welding Machine case is not pro perly grounded. Any opening in the metal Welding Ma chine case will allow some radiation to escape- The high frequency unit of this certified equipment is adequately shielded to prevent direct radiation of any consequences if proper grounding is carried out. Direct feedback to the power line. High frequency energy get on the power line by direct coupling inside the equipment or the high frequency unit, the power line then serving as a radiating antenna. may By proper shielding and filtering, direct vented in this certified equipment. coupling mechanical protection and is not suitable for electrical shield solid metallic conduit or conduit of equivalent electrical shielding ability should be used to enclose the primary power service leads. Solid metallic shielding shall enclose the primary power ser vice to the equipment from a point 50 feet from the equip ment in a unbroken run. This shielding shall be grounded at the farthest point from the equipment and should make good electrical contact with the casing of the equipment. The ground should be in accor dance with the specifications outlined in the section entitled GROUNDS and as shown in Figure 7-1. Care should be taken that paint or corrosion at the junction of conduit and case, does not interfere with good electrical contact. There shall be no gap in this shielding run. This simply means that within 50 feet of the equipment, no portion of the power wires serving the equipment shall be unshielded. If there is any question about the electrical efficiency of the joints between individual conduit sections, outlet boxes and the equipment case, bonding should be carried out by solder ing a copper strap or wire across the LineFuseand Switch Boa - T High Frequency Stabilized Welding Machine or Oscillator Good electrical contact. clean metal to metal. f/)////I/Iflff/t/f/Ifff/fIfffIf/fffI////If I/I/f Page 22 Figure ~ Demountable Bonding Strap for conduit Joints wire IbI Solid Bonding with copper wire for conduit Joints 7-2. Two Recommended Methods For Electrical ~, Ground Figure shown in Sol~E~l~EldE~ Solid Metallic conduit __________________ I / as clean and boll copper Good electrical iointt besween Box and conduit joint 7-2. is pre At least 50 feet __ primary ing. Only lal I the power service shall be run in solid or flexible metallic con duit. Ordinary helically wrapped conduit is designed for Figure Bonding Across Poor Conductivity Conduit Joints 7-4. WELDING MACHINE I/I//f /1//f/Il 7-1. Power Service Installation H. F. Stabilized Arc Welding Machine The location of the equipment should be chosen with respect to nearness to a suitable ground connection. The equipment case, firmly bonded to the power conduit, should be grounded to the work terminal of the equipment with a copper cable or braid with rated current carrying capacity equal to or greater than that of the power service wires. This work output terminal of the equipment should then be grounded to a good (as defined in electrical ground section entitled GROUNDS) cable of the same capacity I short length of welding the work lead. (See Figure with as ,Sroundedalj 7-3). Welding bonded .4r50 foot Machine Case firmly I inservalsj_ Work Terminal grounded to driven wound rod or cold waier pipe wish heavy braided sirap or cable Power conduit to Shielded Wires ~# a Welding Machine Electrode Source of Holder Power ~ Work Case grounded io Work Terminal Figure 7-3. Ground Connections At Keep ALL unshielded and un grounded wires out of this High Field lnsensiiy Zone. Welding Machine change in the wiring or the location of parts inside the equipment, other than power service tap changes or other adjustments specifically covered shall be made. The equip ment shall not be modified in any way since changes in the equipment can affect the radiation characteristics and may be in accordance with the test data upon which the ufacturer bases his certification. not the equipment is in operation, all access and service doors shall be closed and properly fastened. Spark gap settings shall be maintained at the minimum separ ation consistent with satisfactory welding results. 7-5. WELDING LEADS In order to minimize direct weld lead radiation, the welding leads (electrode lead and work leadi must be kept as short as possible. Certification tests on this machine have been made with leads 25 feet long. Considerable improvement in radia tion minimization can be had by shortening the leads as much as possible. Keeping the electrode lead and possible and (See Figure 7-4). as on the floor ground serves to or work lead reduce the as Figure 7-5. General Pick-Up man While / N No Requirements To Minimize Reradiation In the Vicinity of the Weld Zone Extreme precaution should be taken location of the zone is chosen so that make sure that the of the conditions are voided by unshielded wires off the premises but still with in the radial dimensions of the NFl, zone. This 50 foot NFl. is zone installation. Certification on this limit. Keeping zone will a to none minimum that is imposed on the by the manufacturer are based tests unshielded wires farther than 50 feet from the weld materially aid in minimizing interference. If it is impossible to relocate unshielded wires, that section within the H.F.I. zone, should be placed in conduit and each end of the conduit section grounded. close radiation. emphasized that all changes in power and should be made by a qualified electri cian and comply with the National Electrical Code requirements. Any shielding or relocation of telephone or signal wires must be done either by the service com pany concerned or with the specific permission of said be Welding Machine ~jEilator Keep leads - or on lighting wiring Electrode Holder ground boards end 3/4..so1if~ Work Keep lends never as short as possible in eeceas of 25 feet. Figure 7-4. General Rules For Welding company. i 7-7. GROUNDS Leads in previous reference is made to a good ground there is considerable leeway in the inter of this term, for the purpose covered in this Frequent sections. Although pretation 7-6. WIRING IN AREA THE VICINITY OF THE WELDING booklet the following specifications apply: A As discussed in the general information section. the most serious source of interference is reradiation from wires that are located near the welding area. Any ungrounded electrical conductor in the strong directly radiated field, produced by the welding leads, serves as a pick-up device and may conduct the interference for some distance and reradiate strongly at another location. For purpose of simplification and standardization, the space all around the weld zone at a distance of 50 feet in all direc tions is referred to as the High Field Intensity (H.F.l.) zone. (See Figure 7-5). To minimize radiation of this type all wiring in the H.F.I. zone shall be in rigid metallic conduit, lead covered cable, copper braid or material of equivalent shielding efficiency. Ordinary flexible helically wrapped metallic conduit, com is not satisfactory for shielding, monly referred to as tX. and should not be used. The shield on all wiring should be grounded at intervals of 50 feet and good electrical bonding between sections shall be maintained. connection should be made and driven into moist soil. ground least 8 feet A cold water it ment to be provided All leads rod or pipe enters can a driven rod at be used in place of the ground rod feet of the equip ground within 10 the grounded. grounded to the ground possible since the ground effective radiating antenna. connecting the point pipe should be lead itself to long can become as an to short be as The effectiveness of a ground in reducing interference de pends upon the ground conductivity. In certain locations it may become necessary to improve the ground conductivity by treating soil around the ground rod with a salt solution. 7-8. METAL BUILDING It is frequently through that operating of high frequency stabilized arc welding equipment in metallic buildings will completely eliminate troublesome radiation. This, however, is a false assumption. metallic building structure, if properly grounded. may to reduce direct radiation from the weld zone but will have no effect on conducted interference and reradiation. As a result, all installation requirements necessary for certifica tion must be complied with, A serve This shielding requirement applies to all wiring, including tel ephone. inter-communication, signal and control and inciden tal service. OM-540 Page 23 If the metallic building is not properly grounded, bonding to several good electrical grounds placed around the periphery of the building will give reasonable assurance that the build is not ing itself contributing to the radiation. 9. 10. 11. INSTALLATION 7-9. INDIVIDUAL Any all CERTIFICATION the Is the of the equipment secondary? Is the wire used for this connection of sufficient size? Is the work terminal connected to 12.. involved), 13. Is this cable 14. Are the 15. Are all service and 16. Are the by of the and user certifying on that basis. This survey shall be made by a competent engineer in accord ance with the test procedure requirements as set forth in Part 18 of the Rules and Regulations of the Federal Communica tions Commission. Surveys units or of this nature may include the can cover a single complete plant unit or multiple a good electrical ground? above installation requirements may be if he desires to exercise the option of making an individual field survey of the particular unit instal lation (or the complete installation if more than one unit is or waived connected to the work terminal case Is the cable or copperbraid used for this connection equal to or greater the welding lead? as short than possible? as set at .008 access doors closed and bolted? spark-gaps welding carrying capacity current in or less? leads less than 25 feet long? 17. Are 18. Are the welding suitable board? 19. Are the 20. Have you visualized the H.F.I. zone, a sphere with foot radious centered on the weld zone? 21. Have the unshielded power and light wires originally in this H.F.I. zone been placed in grounded shields or been relocated outside the zone? 22. Have all large metallic objects and any long guy supporting wires in the H.F.I. zone been grounded? they as short as possible? structure. leads the on floor or placed on a 7-10. CHECK LIST The following questions may be used by the installer as check to see if all installation requirements have been met: 1. Has the equipment been located be kept short? 2. Are the power leads, 3. Is there good electrical contact between power duit and case? con 4. Do the conduit couplings make tact? (If in doubt, use bonding). con the unit, in conduit? good electrical Is there good electrical contact between conduit and switch on service boxes? 6. shielding used of equivalent shielding efficiency? (Copper sleev is satisfactory. Spirally ing, lead covered cable, etc., rigid 8. Is the conduit system grounded at feet from the equipment? Is the conduit H-Fl. zone? Page 24 1 to apart? a 50 23. or Have you checked so that no external power or tele off the premises are within the zone? 24. Are the 25. Is 26. If so, does it enter the ground 10 feet connection? 27. Are the connections to 28. If a grounds driven ground rods? cold water pipe used a as ground? metallic conduit is not used, is the wound flexible metallic conduit is not suitable). 7. approximately 3/4 phone lines 5. If leads that ground leads so can serving welding a run a point complete (without any at least 50 operated within or less from the the ground clean and metal building, is tight? the building properly grounded? gap) in the If your answer is yes to the above questions, you fy the installation by signing the certificate. can certi September 1973 FORM: OM-540 Effective with serial No. 71 -576983 MODEL/STOCK NO. SERIAL/STYLE NO. DATE PURCHASED PARTS LIST MILLER ELECTRIC MFG. CO. APPLETON, WISCONSIN, USA 54911 NWSACODE NO. 4579 MODEL STOCK NO. SC E-1 A 040 105 SCE-2A 040 107 SCE-3A 040 109 SCE-5A 040 256 SCM-lA 040 104 SCM-2A 040 106 SCM-3A 040 108 SCM~5A 040 255 Quantity SCE Item Dia. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. Figure 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 TD1,5 TD1,5 TD1,5 TD1,5 TD2,3,4 TD2,3,4 034 703 TD2,3,4 TD2,3,4 TD2,3,4 TD2,3,4 TD2,3,4 TD2,3,4 TD2,3,4 TD2,3,4 034 705 034 704 034 705 034 706 034 703 034 704 034 706 ++034 847 ++034 848 ++034 849 ++034 850 ++034 851 -1-4-034 852 030 653 3 R3,4,5 R3,4,5 R23,24,25 4 PL1,2,3 030 653 027 603 5 PL4 027 601 3 030 622 027 602 6 82 Description Main A *011 609 Model or SCM 1A 2A 3A 5A Both 2 2 2 2 SCM 3 3 3 3 SCE 3 3 3 3 Both 3 Assembly TIMER, 15 second 115 volt ac or TIMER, 1 minute 115 volt ac or TIMER, 3 minute 115 volt ac or TIMER, 5 minute 115 volt ac TIMER, 15 second 115 volt ac or TIMER, 1 minute 115 volt ac or TIMER, 3 minute 115 volt ac or TIMER, 5 minute 115 volt ac TIMER, interval-electronic 4.5 sec. or TIMER, interval-electronic 9 sec. or TIMER, interval-electronic 13.5 sec. or TIMER, interval-electronic 18 sec. or TIMER, interval-electronic 30 sec. or TIMER, interval-electronic 50 sec. (See Fig. Page4) RHEOSTAT, WW 150 watt 15 ohm RHEOSTAT, WW 300 watt 36 ohm RHEOSTAT, WW 150 watt 15 ohm LIGHT, indicator-red (consisting of) LIGHT, indicator-green (consisting of) BULB, incandescent base 120 volt SWITCH, toggle SPDT 10 amp 125V spade C . terminal P3i~ ~P5P ~ OM-540 Page Figure A Main Assembly 3 3 Both 3 Both Both 3 3 3 3 Both 1 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 1 Both 1 1 Quantity SCE Item Dia. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. Figure 7 A S2 Description Main *011 610 7 S3 *011 610 8 Si 011 624 9 A 025 603 A 025 608 9 A 025 611 9 A 025 610 9 A 025 625 9 A 025 617 9 A 025 621 9 A 025 618 9 A 025 617 P1 025 701 CR2,4,8 034 615 10 11 601 156 601 152 12 iT 038 639 12 iT 038 622 12 iT 038 646 13 034 821 14 W 034 820 15 CR10 034 615 16 GS,WS 035 601 033 050 Both SWITCH, toggle SPDT (center off) 10 amp spade terminal SWITCH, toggle 4PDT 15 amp 125V screw 010 295 010 296 17 RC1 18 F6 *012 606 18 F6 *012 609 19 039 602 012 602 20 2T 038 621 20 2T 038 622 20 5T 038 639 20 2T 038 639 21 038 620 22 TE2 038 602 22 TE2 038 622 038 617 23 TE3 Ti 23 Ti 036 272 23 Ti 036 629 036 618 101 800 24 25 601 119 26 0i8 849 0i8 848 27 020 636 27 020 638 28 018 850 29 038 642 038 945 038 982 010 912 604 247 602 217 601 840 60i 839 018 851 30 CR1 034 619 30 CR1 034 666 1 125V METER, amp DC 5Omv 0-300 scale or METER, amp DC 5Omv 0-500 scale or METER, amp DC 5Omv 0-600 scale or METER, amp DC 5Omv 0-800 scale METER, amp AC 0-300 scale or METER, amp AC 0-500 scale or METER, amp AC 0-600 scale or METER, amp AC 0-800 scale METER, amp AC 0-500 scale FILTER, high frequency RELAY, medium duty 115 volt AC DPDT NIPPLE, chase 1-1/4 inch NUT, lock 1.1/4 inch BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 6 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 5 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 10 pole INTERLOCK, contactor normally open CONTACTOR, size 1-3/4 3 pole (See Fig. B Both 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 Both 1 Both 1 1 1 Both 3 3 3 Both 1 1 1 Both 1 1 Both COIL 1 1 1 Both Page3) RELAY, medium duty 115 volt ac DPDT VALVE, 115 volt ac 2 way 1/4 IPS port (consisting of) 1 1 Both . . 1A~2Aj3AJ5A amp 125V terminal terminal 9 Model SCM Assembly (Cont.) SWITCH, toggle SPDT (center off) 10 spade or 1 Both 1 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 1 SCE 1 1 1 Both 2 2 2 2 Both 1 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 1 1 ELBOW, brass pipe steel 90 degree 1/4 MPT 5/8-18 LH thread ELBOW, brass pipe steel 90 degree 1/4 MPT 5/8-18 RH thread RECEPTACLE, twistlock 2P2W FUSE, plug 15 amp 250 volt FUSE, plug 20 amp 250 volt HOLDER, fuse-plug BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 4 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 5 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 6 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 6 pole LINK, jumper-terminal block. BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 3 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 5 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 2 pole TRANSFORMER, 1/2 kva TRANSFORMER, 1/2 kva TRANSFORMER, 1/2kva TUBING, steel 5/8 OD x 18 Ga Wall x 5-1/4 CLIP, jiffy-conduit 1/2 inch BRACKET, mounting RH HF panel BRACKET, mounting LH HF panel HF PANEL (See Fig. D Page 6) HF PANEL (See Fig. D Page 6) ANGLE, mounting-HF panel TERMINAL ASSEMBLY, power output (consisting of) 1 Both Both 1 Both 1 1 1 Both Both 1 Both 1 Both 1 1 Both 1 1 Both 1 1 Both 1 Both 1 1 Both 1 1 1 ... Both 2 2 2 Both 2 2 2 Both 1 1 1 Both i 1 1 Both 1 i Both 2 2 2 Both 1 1 1 Both 1 1 i Both 2 2 2 Both 2 2 2 Both 2 2 2 . Both 2 2 2 . Both 6 6 6 . Both 4 4 4 1 1 1 - - . TERMINAL BOARD STUD, brass 1/2-13 x 2-5/8 center drilled PIN, spring carbon steel i/S x 3/8 WASHER, flat steel 1/2 SAE WASHER, lock external tooth 1/2 inch NUT, hex brass 1/2-13 jam NUT, hex brass 1/2-13 full PLATE, cover-opening terminal RELAY, medium duty 24 volt ac DPDT RELAY, medium duty 24 volt ac 3PDT . . . 1 Both .... Both Both Both 1 1 OM-540 Page 2 SCE Item Dia. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. Figure A CR3 034 601 31 CR3 034 607 32 R2 030 617 32 R21,22 030 617 33 RFC 033 609 34 CR5,6,7,9 C4,5,6 C21 ,22,23 031 606 C24 031 611 CR2,2B,4,7, 8,13,15,16 CR,2A,5,6,9 034 615 CR10 034 607 CR11 034 601 CR12,14,17 034 612 CR18 034 615 F7 034 613 031 610 034 613 + *012 606 F7 t012 602 F8 012 639 F8 012 638 R26,27 28,29 030 615 SR3 037 568 SCM Description Main 31 Quantity Model or I l 2A I 3A I SA Assembly (Cont.) RELAY, medium duty 24 volt dc DPDT RELAY, medium duty 110 volt dc 3PDT RESISTOR, WW adj 25 watt 2000 ohm RESISTOR, WW adj 25 watt 2000 ohm CHOKE, HF RELAY, medium duty 115 volt ac 3PDT CAPACITOR, paper-oil 1 uf 400 volt CAPACITOR, electrolytic 40 uf 400 volt dc CAPACITOR, electrolytic 5 uf 150 volt dc RELAY, medium duty 115 volt ac DPDT RELAY, medium duty 115 volt ac 3PDT RELAY, medium duty 110 volt dc 3PDT RELAY, medium duty 24 volt dc DPDT RELAY, medium duty 110 volt dc DPDT RELAY, medium duty 115 volt ac DPDT FUSE, plug 15 amp 250 volt HOLDER, fuse plug 250 volt FUSE, cartridge 6 amp 600 volt HOLDER, fuse cartridge 600 volt - - RESISTOR, WW fixed 25 watt 1000 RECTIFIER, signal (consisting of) ohm 1 1 1 1 1 1 Both 1 1 Both 4 4 Both 1 Both Both 2 Both 4 3 Both Both 3 Both 1 Both S Both 4 Both 1 Both 1 Both 3 1 SCE Both 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 Both 1 1 Both 1 1 4 Both Both 1 Both Both 2 SR21 ,22 23,24,26 037 568 102 363 RECTIFIER, signal (consisting of) BRACKET 601 242 SR25 037 616 4T 038 622 3T 038 602 3T 038 617 038 620 INSULATOR 5 1 Both RECTIFIER, signal BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 5 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 3 pole BLOCK, terminal 30 amp 2 pole LINK, jumper-terminal block 1 Both Both 1 1 1 Both 1 1 1 2 2 2 Both Both 2 1 1 2 T5-034 820 Figure Item Dia. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. Contactor (See 41 033 410 COIL 42 *034 825 B Contactor Description 034 820 Figure B KIT, Fig. A Page 2 Item No. 14) 1 contact Page 4 points *Recommended Spare Parts. tOptional Parts. ++ When ordering timers he sure to specify time value of timer. BE SURE TO PROVIDE STOCK, MODEL, AND SERIAL NUMBERS 3 Quantity WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. Quantity Timers Item Dia. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. 51 104 045 52 039 663 54 CR1 Fl 034 816 *012 652 55 012 637 56 038 772 57 010 116 58 015 384 036 830 59 Tl 60 012 243 61 034 371 BRACKET, mounting-socket SOCKET, relay-8 pin RELAY, enclosed medium duty 120 volt ac DPDT FUSE, miniature glass 1/2 amp slo-blo HOLDER, fuse BLOCK, terminal 20 amp 6 pole screw terminal GROMMET, rubber 3/8 ID x 1/2 hole x 1/16 groove I Th 9 Sec Iseci Sec I-. ~ C) C) C) 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 13.5 Sec Timer, Interval-Electronic (See Fig. A Page 1 Item No. 2) Figure C .53 Description I 4.5 30 50 Sec Sec .2 2 2 2 2 2 CHASSIS 1 1 1 1 1 1 TRANSFORMER, power 12 volt secondary TUBING, nylon .150 ID x .250 OD x 3/8 long CIRCUIT CARD ASSEMBLY (See Fig. Cl Page 5). (consisting of) CAPACITOR, metallized paper 4 uf 150 volt dc 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 4 4 4 4 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 62 C4 604 005 63 VI 027 610 TUBE 1 1 1 1 1 64 027 614 SHIELD, tube 1 1 1 1 1 1 65 024 366 1 1 1 1~ 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 66 67 R5 028 768 67 R5 028 769 67 R5 028 770 67 R5 028 771 67 R5 028 772 67 R5 028 773 1-1/8 OD 1/4 bore NAMEPLATE (order by serial number) POTENTIOMETER, carbon 2 watt 350K ohm 4.5 sec. POTENTIOMETER, carbon 2 watt 750K ohm 9 sec POTENTIOMETER, carbon 2 watt 1 meg ohm 13.5 sec. POTENTIOMETER, carbon 2 watt 1.5 meg ohm 18 sec. POTENTIOMETER, carbon 2 watt 2.5 meg ohm 30 sec. POTENTIOMETER, carbon 2 watt 3.5 meg ohm 50 sec. KNOB, pointer line indicator 1 1 1 1 1 1 TC.038 847 Figure C Timer, Interval - Electronic *Recommended Spare Parts. BE SURE TO PROVIDE STOCK, MODEL, AND SERIAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. OM-540 Page 4 Item Dia. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. Figure Cl Assembly (See Fig. C Circuit Card 1 1 Page R4 030 691 77 R6 030 720 78 VR1-5 027 611 79 Ci,2 031 637 SO C3 031 643 RESISTOR, carbon 1 watt 4700 ohm RESISTOR, carbon 1 watt 10K ohm LAMP, neon CAPACITOR, ceramic .02 uf 500 volt CAPACITOR, ceramic .01 uf 500 volt 038 372 PRINTED WIRING BOARD RESISTOR, carbon i watt 22K ohm RESISTOR, carbon 2 watt 10K ohm RESISTOR, carbon 1 watt 120K ohm SOCKET, tube shielded 7 pin 82 Ri 030 722 83 R2 601 394 84 R3 601 395 039 876 4 Item No. 61) 034 371 76 Si Quantity Description 1 5 2 1 1 1 1 1 TA-034 371 Figure Cl *Recommended Spare Parts. BE SURE TO PROVIDE PageS Circuit Card Assembly STOCK, MODEL, AND SERIAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. Ma. Factory No. Mkgs. Part No. Figure D Description Quantity - Item (0 HF Panel (See Fig. A Page 2 Item No. 27) 92 010 886 93 601 838 (See Fig. Dl Page 7) STRIP, conductor NUT, brass hex jam 3/8-16 94 016 612 MOUNTING 95 038 887 91 96 G T3 97 98 99 020 623 033 601 038 891 T2 036 323 R7 030724 C3 031 601 100 014 159 101 Ri 030603 102 C2 031602 010 884 103 104 Cl 031 605 R6 030602 SPARK GAP ASSEMBLY - BOARD, component STUD, brass 10-32 x 1-3/8 with hex collar COIL, coupling STUD, brass 3/8-16 x 2-i/S TRANSFORMER, high voltage 115 volt (consisting of) RESISTOR, carbon 1 watt lOOK ohm CAPACITOR, paper-oil 10 uf 600 volt dc BRACKET, mounting capacitor RESISTOR, WW fixed 10 watt 10K ohm CAPACITOR, mica .002 uf 5000 volt dc STRIP, conductor CAPACITOR, mica .001 uf 6000 volt dc RESISTOR, WW fixed 100 watt 10 ohm - - ~ 1 1 4 4 S 8 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 4 2 2 1 1 1 1 1-c-o20 636 Figure D BE SURE TO PROVIDE HF Panel STOCK, MODEL, AND SERIAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS. OM-540 Page 6 Item Factory No. Part No. Figure Dl Quantity Description 020 623 Spark Gap Assembly (See Fig. 111 602 023 112 604 772 113 010 888 114 020 622 115 *020 603 116 010 913 SCREW, cap socket head 10-24 x 3/4 WASHER, flat steel No. S SAE CONNECTOR, holder HOLDER, point POINT (set of 4) WASHER, flat brass 3/16 ID x 1/2 OD 0 Page 6 Item No. 91) 4 4 1 4 1 set S 117 020621 BASE 1 118 602 204 S 119 602 101 WASHER, lock external tooth No. 10 SCREW, machine steel round head 10-24-5/S S TA-020 623-Al Figure Dl *Recommended Spare Parts STOCK, MODEL, BE SURE TO PROVIDE Page 7 Spark Gap Assembly AND SERIAL NUMBERS WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS.