Download CES EduPack Manual and Getting Started Guide
Transcript
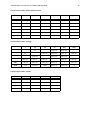
CES EduPackTM 2014 CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide April 2014 CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide 8 4 Getting Started with CES EduPack The following exercises give an overview of CES EduPack and will teach you how to use the core functionality. The exercises in Chapter 5 go into further detail and explore some of the software’s more specialized features. There is also comprehensive help file within the software that gives more detailed guidance, as well as case studies with loadable project files. 4.1 Brief Description of CES EduPack The main tools in CES EduPack are: • BROWSE Explore the database and retrieve records via a hierarchical index or tree. • SEARCH Find information via a full-text search of records. • SELECT The central hub of CES EduPack, used to apply the Rational Material Selection methodology. A powerful selection engine that identifies records that meet an array of design criteria and enables trade-offs between competing objectives. • CHART Create charts and add formatting and labels to illustrate your point. The following exercises cover the use and functionality of these tools. CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide 9 4.2 Browsing and Searching Exercise 1 Opening the Database If you have more than one database installed, CES EduPack will show the Databases dialog. The following exercises use the MaterialUniverse and ProcessUniverse tables, which are part of every Granta database. The Edition Homepage will open, showing a list of the available tables and a graphic for each subset. Click on a subset name to show its description. Use the information icon next to the database name to show a detailed description. • Swap between the available subsets and see how they have different applications and data Click on a subset in the Edition Homepage to select it. The information displayed is for the currentlyselected subset. Notice that the Browse tree in the left pane updates to the currently selected subset. • Change to the PROCESSUNIVERSE table Click on ProcessUniverse and notice that the Browse tree in the left pane updates to show the new table. • CLOSE the HOMEPAGE Click on the cross at the top of the Homepage tab. This page can be reopened at any time from View menu - Home. CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide 10 • Change to the MATERIALUNIVERSE table With the Homepage closed, navigate to different tables using the Table drop-down in the Browse pane. Browse Search Table: MaterialUniverse Subset: All materials Select There are also links to online resources, for both students and educators, from the homepage. CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide 11 Exercise 2 Browse Materials Browse Search Table: MaterialUniverse Subset: All materials Select MaterialUniverse Ceramics and glasses Fibers and particulates Hybrids: composites, foams etc. Metals and alloys Polymers: plastics, elastomers Select the Table MaterialUniverse and the Subset All materials. • Find a record for STAINLESS STEEL • Find a record for CONCRETE • Open the GENERIC record for POLYPROPYLENE Generic records are records at the folder level and give general information on the material, rather than data on a specific variant. Generic records have their own icon . Double-click to open. • Open a POLYPROPYLENE record Double-click on the record name in the tree Click on hyperlinked attribute names. In Level 1 and Level 2 databases, this will bring up a Science Note, giving details of the underlying science and calculations for the attribute. In Level 3 databases, this will bring up the design note, which provides background information on properties, test notes, and selection guidelines. From a design note, there will also be a link to the corresponding Science Note. Right-click on the datasheet to see a context menu with further actions e.g., locate in Browse tree, copy the datasheet, print the datasheet, export the data to an FE package format. CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide 16 4.3 Material Selection Exercise 5 Selection Using a Limit Stage • Find materials with: MAX. SERVICE TEMPERATURE > 200 °C THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY > 25 W/m.°C ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY > 1e15 μohm.cm Browse Search Select 1. Selection Data Limit stage MaterialUniverse: All bulk materials Mechanical properties 2. Selection Stages Thermal properties Graph/Index Limit 3. Results X out of Y pass Tree Min Max Max. service temp. 200 °C Thermal conductivity 25 W/m.K J/kg.K Specific heat capacity Rank by: Property A Material 1 2130 Material 2 2100 Material 3 1950 Material 4 1876 etc. Electrical properties Min Electrical resistivity 1e15 Max ohm. cm Ceramics and glasses Limit guidance bars Composites Metals and alloys Polymers and elastomers 1 1E+8 1E+20 Use the limit bars for guidance on suitable values. Enter the limits – minimum or maximum as appropriate – and click Apply. If a reference record is set, its values for each property will be shown to the right of the min/max entry boxes. Example results: Aluminum nitride, Alumina, Silicon nitride. Some properties have discrete values, rather than numeric ranges. • Edit this limit stage and search for materials with non-opaque TRANSPARENCY. Under Optical Properties, refine by transparency using the drop-down and tick Translucent, Transparent, and Optical quality. Click Apply. Example results: Alumina (translucent) and Diamond. • DELETE THIS STAGE CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide 17 Exercise 6 Selection Using a Graph Stage When plotted on a Graph Stage, records can also be filtered using the charting Box and Line Selection tools. This provides a more qualitative approach to filtering. • Make a BAR CHART of YIELD STRENGTH (σy) Set the y-axis to Yield strength (elastic limit). Browse Search Select 1. Selection Data Bar chart MaterialUniverse: All bulk materials Graph/Index Limit Tree Yield strength 2. Selection Stages Bubble chart Rank by: Property A Material 1 2130 Material 2 2100 Material 3 1950 Material 4 1876 Yield strength 3. Results X out of Y pass Box selection Line selection Density etc. • Use a BOX SELECTION to find materials with high values of YIELD STRENGTH Click Box Selection , then click-drag-release to define the box. • Add DENSITY (ρ) to the other axis Either: highlight Stage 1 in Selection Stages, right-click and choose Edit Stage from the menu; or double-click the axis to edit. • Use a BOX SELECTION to find materials with high STRENGTH and low DENSITY • Use a LINE SELECTION to find materials with high values of the specific strength σy / ρ Click Gradient-Line Selection , then enter slope in the dialog, in this case 1. Click on the graph to position the line through a particular point. Click above or below the line to select an area, in this case above the line for high values of σy / ρ. Drag the line upwards to refine the selection to fewer materials. CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide Selection box Selection line, slope 1 Selection line, slope 1 • Rank the results by specific strength (YIELD STRENGTH / DENSITY) Rank by Stage 1: Performance Index and click on results column to reverse the order. Example results: CFRP, Titanium alloys, Magnesium alloys. • DELETE ALL STAGES Using a Tree Stage, records can be filtered based on their links to records in other data tables, or based on the database hierarchy (tree). 18 CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide 19 Exercise 7 Selection Using a Tree Stage • Find materials that can be MOLDED In the Tree Stage window, select ProcessUniverse, navigate to Molding, and click Insert followed by OK. Browse Search Select 1. Selection Data MaterialUniverse: All bulk materials Tree stage for material Ceramics Steels 2. Selection Stages Graph/Index Limit Tree Material Hybrids Al alloys Metals Cu alloys Polymers Ni alloys... 3. Results X out of Y pass Tree stage for process Cast Material 1 Material 2 Material 3 Material 4 etc. Join Process Shape Surface Deform Mold Composite Powder Prototype • DELETE THIS STAGE • Find processes to join STEELS Select Processes: Joining processes. In the Tree Stage window, select MaterialUniverse, expand Metals and alloys in the tree, select Ferrous, and click Insert followed by OK. • DELETE THIS STAGE CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide 33 5 Toolbars and General Information Standard Toolbar Estimates the environmental impact of products Select entities using design criteria Browse the database tree Perform a search over the database Search for information on the Web Open CES Help Predicts the performance of hybrid materials and structures Favorites, and other options Graph Stage Toolbar Line selection tool Cancel selection Box selection tool Zoom in Add text Family envelopes Normal size File Types *.gbd Granta Database file *.ces CES EduPack Project file *.cet Selection Template file *.frl Favorites file *.prd Eco Audit Product Definition file Hide failed records Results intersection Show reference record Show favorites Show user defined records Show synthesized records CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide 34 Physical Constants and Conversion of Units Absolute zero temperature Acceleration due to gravity, g -273.2°C Avogadro’s number NA 6.022 x 1023 2.718 9.807 m/s2 base of natural logarithm, e Boltzmann’s constant, k 1.381 x 10-23 J/K Faraday’s constant, k 9.648 x 104 C/mol 8.314 J/mol/K Gas constant, R Plank’s constant, h 6.626 x 10-34 Js Velocity of light in a vacuum, c 2.998 x 108 m/s Volume of perfect gas at STP 22.41 x 10-3 m3/mol Angle, Density, Diffusion coefficient, D 1 rad 1 lb/ft3 1 cm3/s 57.30° 16.03 kg/m3 Power, P 1.0 x 10-4 m2/s See below 9.807 N 4.448 N 1.0 x 10-5 N 304.8 mm 25.40 mm 0.1 nm 1000 kg 908 kg 1107 kg 0.454 kg See below Stress, See below Energy, U Force, F Length, l Mass, M Specific Heat, Cp Stress Intensity, K1c Surface Energy, Temperature, T Thermal Conductivity, Volume, V Viscosity, 1 kgf 1 lbf 1 dyne 1 ft 1 inch 1Å 1 tonne 1 short ton 1 long ton 1 lb mass 1 cal/gal.°C 1 Btu/lb.°F 1 ksi in 4.188 kJ/kg.°C 4.187 kJ/kg.°C 1 erg/cm2 1°F 1 cal/s.cm.°C 1 Btu/h.ft.°F 1 Imperial gall 1 US gall 1 mJ/m2 0.556°K 418.8 W/m.°C 1.731 W/m.°C 1 poise 1 lb ft.s 0.1 N.s/m2 0.1517 N.s/m2 1.10 MN/m3/2 1.546 x 10-3 m3 3.785 x 10-3 m3 CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide 35 Conversion of Units - Stress and Pressure MPa dyn/cm2 lb/in2 kgf/mm2 bar long ton/in2 1 107 1.45 x 102 0.102 10 6.48 x 10-2 10-7 1 1.45 x 10-5 1.02 x 10-8 10-6 6.48 x 10-9 6.89 x 10-3 6.89 x 104 1 703 x 10-4 6.89 x 10-2 4.46 x 10-4 kgf/mm2 9.81 9.81 x 107 1.42 x 103 1 98.1 63.5 x 10-2 bar 0.10 106 14.48 1.02 x 10-2 1 6.48 x 10-3 long ton/in2 15.44 1.54 x 108 2.24 x 103 1.54 1.54 x 102 1 J erg cal eV Btu ft lbf J 1 107 0.239 6.24 x 1018 9.48 x 10-4 0.738 erg 10-7 1 2.39 x 10-8 6.24 x 1011 9.48 x 10-11 7.38 x 10-8 cal 4.19 4.19 x 107 1 2.61 x 1019 3.97 x 10-3 3.09 eV 1.60 x 10-19 1.60 x 10-12 3.38 x 10-20 1 1.52 x 10-22 1.18 x 10-19 Btu 1.06 x 103 1.06 x 1010 2.52 x 102 6.59 x 1021 1 7.78 x 102 ft lbf 1.36 1.36 x 107 0.324 8.46 x 1018 1.29 x 10-3 1 kW (kJ/s) erg/s hp ft lbf/s kW (kJ/s) 1 10-10 1.34 7.38 x 102 erg/s 10-10 1 1.34 x 10-10 7.38 x 10-8 hp 7.46 x 10-1 7.46 x 109 1 15.50 x 102 ft lbf/s 1.36 x 10-3 1.36 x 107 1.82 x 10-3 1 MPa dyn/cm2 lb/in2 Conversion of Units - Energy Conversion of Units - Power CES EduPack User Manual and Getting Started Guide 36 Options for Preferred Currency and Units Settings Database Options Preferred Currency Preferred Unit System <Automatic> The Regional Setting from the operating system for currency is used to view data. This will appears as <Automatic - Regional Currency>, e.g. <Automatic - GBP>. The Regional setting from the operating system for unit system is used to view data. This will appear as <Automatic - Regional Units> e.g. <Automatic - Metric>. <None> Data is displayed using the same currency as it is stored with in the database. Attribute data is displayed using the same units as the data is stored with in the database. Named setting Named currency is used to display data. Named unit system is used to display data. 5.1 Legal and Acknowledgments License Agreement The CES EduPack is furnished under a License Agreement and may be used or copied only in accordance with the terms of the License. Trademarks Cambridge Engineering Selector, CES EduPackTM, CES SelectorTM, CES ConstructorTM, and other CES related product names are Trademarks of Granta Design Limited. Reproduction Except as described in the installation instructions, neither the documentation nor the software may be copied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any electronic medium or machine readable form, in whole or part, without prior written consent of Granta Design Limited. Teaching Materials Selection charts, record data, and online teaching resources may be reproduced to be used with students for educational purposes only, as long as Granta Design Limited referenced as the source and copyright owner or licensor. To reproduce these in published works you must: (i) gain prior written permission from Granta Design Limited (contact details to be found at www.grantadesign.com/contact). (ii) acknowledge each instance with the following: bibliographical reference: Charts/data/etc. from “CES EduPack 2014, Granta Design Limited, UK (www.grantadesign.com)”. Images - please see the individual image caption for reproduction information of images.