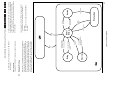
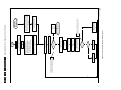
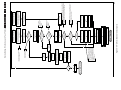
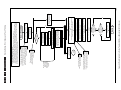
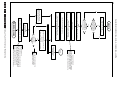
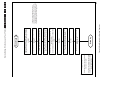
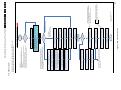
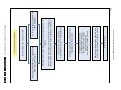
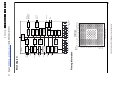
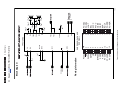
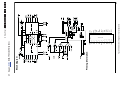
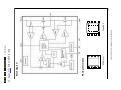
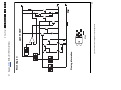
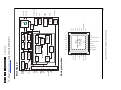
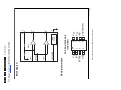
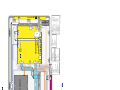
Download Philips PFL6 Series Specifications
Transcript
Page Published by ER/TY 1164 BU TV Consumer Care, the Netherlands © Copyright 2011 Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of Philips. Revision List 2 Technical Specifications, Diversity, and Connections2 Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List 5 Mechanical Instructions 9 Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 14 Alignments 33 Circuit Descriptions 40 IC Data Sheets 45 Block Diagrams Wiring diagram Blockbuster/Emmy 32" 55 Wiring diagram Blockbuster/Emmy 40" - 46" 56 Block Diagram Video 57 Block Diagram Audio 58 Block Diagram Control & Clock Signals 59 Block Diagram I2C 60 Supply Lines Overview 61 10. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts Drawing 62 B01 393912365213 B02 393912365213 73 B03 393912365213 82 B04 393912365213 90 B05 393912365213 95 B06 393912365213 96 B09 393912365213 100 313912365213SSB Layout 101 11. Styling Sheets Blockbuster/Emmy 32" 103 Blockbuster/Emmy 40" - 46" 104 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Contents Color Television Subject to modification 2011-Apr-22 EN 3122 785 19110 19100_000_110214.eps 110214 LA Q552.2L Chassis 65213 2.3 2 4-1 Wire Dressing Dressing 4.3 Mechanics 4 Assembly Removal 3139 123 xxxxx 4.3.7 7 7.4.1 back to div. table 7.2 Descriptions You can download this information from the following websites: http://www.philips.com/support http://www.p4c.philips.com Directions for Use Blockbuster 11-2 40PFL6606D/78 2011-Apr-22 2.2 Styling CTN SSB Connection Overview Table 2-1 Described Model Numbers and Diversity PSU 9-2 9 10-1 10-2 Schematics 10 10-3 10-4 10-5 10-6 - - 10-7 For on-line product support please use the CTN links in Table 2-1. Here is product information available, as well as getting started, user manuals, frequently asked questions and software & drivers. B04 (I/O) B03 (DC/DC / Class D) B02 (PNX85500) Wiring Diagram Notes: • Figures can deviate due to the different set executions. • Specifications are indicative (subject to change). Tuner Technical Specifications B01 (Tuner) 2.1 B05 (DDR) Index of this chapter: 2.1 Technical Specifications 2.2 Directions for Use 2.3 Connections 2.4 Chassis Overview LCD Removal 2. Technical Specifications, Diversity, and Connections Manual xxxx xxx xxxx.0 • First release. 1. Revision List Revision List B06 (non-DVBS-LVDS) Q552.2L LA B07 (DVBS-FE) 1. B08 (DVBS-Supp.) EN 2 B09 (non-DVBS-conn.) 2.3.2 2.3.1 2.3 6 7 7 jq jq jq 4 - AV IN: Cinch: Video CVBS - In, Audio - In Rd - Audio R 0.5 VRMS / 10 kohm Wh - Audio L 0.5 VRMS / 10 kohm Ye - Video CVBS 1 VPP / 75 ohm 12345678 Figure 2-2 Ethernet connector 10000_025_090121.eps 090121 5 - RJ45: Ethernet Rear Connections - Bottom jq jq H k j jq jq jq jq jq 3 - Cinch: Audio - In (VGA/DVI) Rd - Audio R 0.5 VRMS / 10 kohm Wh - Audio L 0.5 VRMS / 10 kohm 2 - Service Connector (UART) 1 - Ground Gnd 2 - UART_TX Transmit 3 - UART_RX Receive 1 - CVI: Cinch: Video YPbPr - In, Audio - In Gn - Video Y 1 VPP / 75 ohm Bu - Video Pb 0.7 VPP / 75 ohm Rd - Video Pr 0.7 VPP / 75 ohm Rd - Audio - R 0.5 VRMS / 10 kohm Wh - Audio - L 0.5 VRMS / 10 kohm Rear Connections 8 back to div. table - TD+ - TD- RD+ - CT - CT - RD- GND - GND 9 2. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Transmit signal Transmit signal Receive signal Centre Tap: DC level fixation Centre Tap: DC level fixation Receive signal Gnd Gnd 1 2 2011-Apr-22 j jk H j j H DDC clock DDC data Gnd Hot Plug Detect Gnd j H j j H j j H j j H j jk kq j H H k k j Data channel Gnd Data channel Data channel Gnd Data channel Data channel Gnd Data channel Data channel Gnd Data channel Control channel Figure 2-3 HDMI (type A) connector 10000_017_090121.eps 090428 - D2+ - Shield - D2- D1+ - Shield - D1- D0+ - Shield - D0- CLK+ - Shield - CLK- Easylink/CEC - n.c. - DDC_SCL - DDC_SDA - Ground - +5V - HPD - Ground 12 11 10 19110_051_110421.eps 110421 7 - HDMI 2: Digital Video, Digital Audio - In 19 18 EN 3 SIDE CONNECTORS Q552.2L LA 6 - Cinch: S/PDIF - Out Bk - Coaxial 0.4 - 0.6VPP / 75 ohm 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Figure 2-1 Connection overview 4 3 2 1 Note: The following connector colour abbreviations are used (acc. to DIN/IEC 757): Bk= Black, Bu= Blue, Gn= Green, Gy= Grey, Rd= Red, Wh= White, Ye= Yellow. 5 BOTTOM REAR CONNECTORS REAR CONNECTORS Connections Technical Specifications, Diversity, and Connections Q552.2L LA - D2+ - Shield - D2- D1+ - Shield - D1- D0+ - Shield - D0- CLK+ - Shield - CLK- Easylink/CEC - ARC - DDC_SCL - DDC_SDA - Ground - +5V - HPD - Ground 10 15 j j j H H H H j H j j j j Gnd Gnd Gnd Gnd +5 V Gnd DDC data 0-5V 0-5V DDC clock D j H j j H j j H j j H j jk k j jk H j j H 0.7 VPP / 75 ohm 0.7 VPP / 75 ohm 0.7 VPP / 75 ohm Refer to chapter Block Diagrams for PWB/CBA locations. Chassis Overview - Video Red - Video Green - Video Blue - n.c. - Ground - Ground Red - Ground Green - Ground Blue - +5VDC - Ground Sync - n.c. - DDC_SDA - H-sync - V-sync - DDC_SCL Figure 2-5 VGA Connector 10000_002_090121.eps 090127 11 1 6 5 Coax, 75 ohm Hot Plug Detect Gnd Data channel Gnd Data channel Data channel Gnd Data channel Data channel Gnd Data channel Data channel Gnd Data channel Control channel Audio Return Channel DDC clock DDC data Gnd 9 - VGA: Video RGB - In 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1 2 10000_017_090121.eps 090428 19 18 back to div. table 2.3.3 VDD GND1 CMD/DI DAT3/CS DAT2/NC 4 3 2 1 9 - +5V - Data (-) - Data (+) - Ground 1 3 4 10000_022_090121.eps 090121 2 Signal Signal Gnd Supply Signal Gnd Signal Signal Signal Signal Gnd Signal Gnd Gnd Gnd 12- HDMI : Digital Video, Digital Audio - In See 7 - HDMI 2: Digital Video, Digital Audio - In 1 2 3 4 CLOCK 5 Figure 2-7 USB (type A) - DAT3/CS - CMD/DI - GND1 - Vdd - CLOCK - GND2 - DAT0/D0 - DAT1/IRQ - DAT2/NC - CD - GND - WP - GND - GND 11 - USB2.0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 GND2 6 10000_049_100210.eps 100210 DAT0/D0 7 10 DAT1/IRQ 11 CD 8 12 WP GND Figure 2-6 SD-Card connector GND 13 14 GND 10 - SD-Card: Secure Digital Card - In/Out (optional) Side Connections Technical Specifications, Diversity, and Connections Figure 2-4 HDMI (type A) connector 8 - Aerial - In - - F-type 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 2011-Apr-22 2.4 2. 7 - HDMI 1: Digital Video - In, Digital Audio with ARC - In/ Out EN 4 k jk jk H jk k H k k H jk jk jk j H j H H • Measure the voltages and waveforms with regard to the chassis (= tuner) ground (H), or hot ground (I), depending on the tested area of circuitry. The voltages and waveforms shown in the diagrams are indicative. Measure them in the Service Default Mode with a colour bar signal and stereo sound (L: 3 kHz, R: 1 kHz unless stated otherwise) and picture carrier at 475.25 MHz for PAL, or 61.25 MHz for NTSC (channel 3). General 3.3.1 All ICs and many other semiconductors are susceptible to electrostatic discharges (ESD w). Careless handling during repair can reduce life drastically. Make sure that, during repair, you are connected with the same potential as the mass of the set by a wristband with resistance. Keep components and tools also at this same potential. Be careful during measurements in the high voltage section. Never replace modules or other components while the unit is switched “on”. When you align the set, use plastic rather than metal tools. This will prevent any short circuits and the danger of a circuit becoming unstable. Notes • • • • Warnings Safety regulations require that after a repair, the set must be returned in its original condition. Pay in particular attention to the following points: • Route the wire trees correctly and fix them with the mounted cable clamps. • Check the insulation of the Mains/AC Power lead for external damage. • Check the strain relief of the Mains/AC Power cord for proper function. • Check the electrical DC resistance between the Mains/AC Power plug and the secondary side (only for sets that have a Mains/AC Power isolated power supply): 1. Unplug the Mains/AC Power cord and connect a wire between the two pins of the Mains/AC Power plug. 2. Set the Mains/AC Power switch to the “on” position (keep the Mains/AC Power cord unplugged!). 3. Measure the resistance value between the pins of the Mains/AC Power plug and the metal shielding of the tuner or the aerial connection on the set. The reading should be between 4.5 MΩ and 12 MΩ. 4. Switch “off” the set, and remove the wire between the two pins of the Mains/AC Power plug. • Check the cabinet for defects, to prevent touching of any inner parts by the customer. Safety regulations require the following during a repair: • Connect the set to the Mains/AC Power via an isolation transformer (> 800 VA). • Replace safety components, indicated by the symbol h, only by components identical to the original ones. Any other component substitution (other than original type) may increase risk of fire or electrical shock hazard. Safety Instructions 3.3 3.2 3.1 Index of this chapter: 3.1 Safety Instructions 3.2 Warnings 3.3 Notes 3.4 Abbreviation List back to div. table 3.3.6 3.3.5 3.3.4 3.3.3 3.3.2 EN 5 All resistor values are in ohms, and the value multiplier is often used to indicate the decimal point location (e.g. 2K2 indicates 2.2 kΩ). Resistor values with no multiplier may be indicated with either an “E” or an “R” (e.g. 220E or 220R indicates 220 Ω). All capacitor values are given in micro-farads (μ = × 10-6), nano-farads (n = × 10-9), or pico-farads (p = × 10-12). Capacitor values may also use the value multiplier as the decimal point indication (e.g. 2p2 indicates 2.2 pF). An “asterisk” (*) indicates component usage varies. Refer to the diversity tables for the correct values. The correct component values are listed on the Philips Spare Parts Web Portal. 2011-Apr-22 It should be noted that on the European Service website, “Alternative BOM” is referred to as “Design variant”. Alternative BOM identification Due to lead-free technology some rules have to be respected by the workshop during a repair: • Use only lead-free soldering tin. If lead-free solder paste is required, please contact the manufacturer of your soldering equipment. In general, use of solder paste within workshops should be avoided because paste is not easy to store and to handle. • Use only adequate solder tools applicable for lead-free soldering tin. The solder tool must be able: – To reach a solder-tip temperature of at least 400°C. – To stabilize the adjusted temperature at the solder-tip. – To exchange solder-tips for different applications. • Adjust your solder tool so that a temperature of around 360°C - 380°C is reached and stabilized at the solder joint. Heating time of the solder-joint should not exceed ~ 4 sec. Avoid temperatures above 400°C, otherwise wear-out of tips will increase drastically and flux-fluid will be destroyed. To avoid wear-out of tips, switch “off” unused equipment or reduce heat. • Mix of lead-free soldering tin/parts with leaded soldering tin/parts is possible but PHILIPS recommends strongly to avoid mixed regimes. If this cannot be avoided, carefully clear the solder-joint from old tin and re-solder with new tin. Lead-free Soldering BGA Temperature Profiles For BGA-ICs, you must use the correct temperature-profile. Where applicable and available, this profile is added to the IC Data Sheet information section in this manual. Introduction For more information on how to handle BGA devices, visit this URL: http://www.atyourservice-magazine.com. Select “Magazine”, then go to “Repair downloads”. Here you will find Information on how to deal with BGA-ICs. BGA (Ball Grid Array) ICs For the latest spare part overview, consult your Philips Spare Part web portal. Spare Parts • • • • • • 3. Where necessary, measure the waveforms and voltages with (D) and without (E) aerial signal. Measure the voltages in the power supply section both in normal operation (G) and in stand-by (F). These values are indicated by means of the appropriate symbols. Q552.2L LA Schematic Notes • 3. Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List Q552.2L LA • • It makes sense to avoid exposure to electrical shock. While some sources are expected to have a possible dangerous impact, others of quite high potential are of limited current and are sometimes held in less regard. Always respect voltages. While some may not be dangerous in themselves, they can cause unexpected reactions that are best avoided. Before reaching into a powered TV set, it is best to test the high voltage insulation. It is easy to do, and is a good service precaution. Practical Service Precautions If a board is defective, consult your repair procedure to decide if the board has to be exchanged or if it should be repaired on component level. If your repair procedure says the board should be exchanged completely, do not solder on the defective board. Otherwise, it cannot be returned to the O.E.M. supplier for back charging! Board Level Repair (BLR) or Component Level Repair (CLR) Figure 3-1 Serial number (example) 10000_053_110228.eps 110228 back to div. table 3.4 DFI DDC D/K DCM DAC DBE CVBS CLR ComPair CP CSM CTI CL B-TXT C CEC BDS BLR BTSC AV AVC AVIP B/G ATV Auto TV ATSC AM AP AR ASF AGC ADC AFC ACI AARA 0/6/12 Abbreviation List Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List Identification: The bottom line of a type plate gives a 14-digit serial number. Digits 1 and 2 refer to the production centre (e.g. SN is Lysomice, RJ is Kobierzyce), digit 3 refers to the B.O.M. code, digit 4 refers to the Service version change code, digits 5 and 6 refer to the production year, and digits 7 and 8 refer to production week (in example below it is 2010 week 10 / 2010 week 17). The 6 last digits contain the serial number. 2011-Apr-22 3.3.8 3.3.7 3. The third digit in the serial number (example: AG2B0335000001) indicates the number of the alternative B.O.M. (Bill Of Materials) that has been used for producing the specific TV set. In general, it is possible that the same TV model on the market is produced with e.g. two different types of displays, coming from two different suppliers. This will then result in sets which have the same CTN (Commercial Type Number; e.g. 28PW9515/12) but which have a different B.O.M. number. By looking at the third digit of the serial number, one can identify which B.O.M. is used for the TV set he is working with. If the third digit of the serial number contains the number “1” (example: AG1B033500001), then the TV set has been manufactured according to B.O.M. number 1. If the third digit is a “2” (example: AG2B0335000001), then the set has been produced according to B.O.M. no. 2. This is important for ordering the correct spare parts! For the third digit, the numbers 1...9 and the characters A...Z can be used, so in total: 9 plus 26= 35 different B.O.M.s can be indicated by the third digit of the serial number. EN 6 SCART switch control signal on A/V board. 0 = loop through (AUX to TV), 6 = play 16 : 9 format, 12 = play 4 : 3 format Automatic Aspect Ratio Adaptation: algorithm that adapts aspect ratio to remove horizontal black bars; keeps the original aspect ratio Automatic Channel Installation: algorithm that installs TV channels directly from a cable network by means of a predefined TXT page Analogue to Digital Converter Automatic Frequency Control: control signal used to tune to the correct frequency Automatic Gain Control: algorithm that controls the video input of the feature box Amplitude Modulation Asia Pacific Aspect Ratio: 4 by 3 or 16 by 9 Auto Screen Fit: algorithm that adapts aspect ratio to remove horizontal black bars without discarding video information Advanced Television Systems Committee, the digital TV standard in the USA See Auto TV A hardware and software control system that measures picture content, and adapts image parameters in a dynamic way External Audio Video Audio Video Controller Audio Video Input Processor Monochrome TV system. Sound carrier distance is 5.5 MHz Business Display Solutions (iTV) Board-Level Repair Broadcast Television Standard Committee. Multiplex FM stereo sound system, originating from the USA and used e.g. in LATAM and AP-NTSC countries Blue TeleteXT Centre channel (audio) Consumer Electronics Control bus: remote control bus on HDMI connections Constant Level: audio output to connect with an external amplifier Component Level Repair Computer aided rePair Connected Planet / Copy Protection Customer Service Mode Color Transient Improvement: manipulates steepness of chroma transients Composite Video Blanking and Synchronization Digital to Analogue Converter Dynamic Bass Enhancement: extra low frequency amplification Data Communication Module. Also referred to as System Card or Smartcard (for iTV). See “E-DDC” Monochrome TV system. Sound carrier distance is 6.5 MHz Dynamic Frame Insertion I 2C I2D I2S IF IR IRQ ITU-656 HDMI HP I FPGA FTV Gb/s G-TXT H HD HDD HDCP FDS FDW FLASH FM EMI EPG EPLD EU EXT EEPROM EDID DVB-C DVB-T DVD DVI(-d) E-DDC DTCP DRAM DRM DSP DST DFU DMR DMSD DNM DNR Directions For Use: owner's manual Digital Media Reader: card reader Digital Multi Standard Decoding Digital Natural Motion Digital Noise Reduction: noise reduction feature of the set Dynamic RAM Digital Rights Management Digital Signal Processing Dealer Service Tool: special remote control designed for service technicians Digital Transmission Content Protection; A protocol for protecting digital audio/video content that is traversing a high speed serial bus, such as IEEE-1394 Digital Video Broadcast - Cable Digital Video Broadcast - Terrestrial Digital Versatile Disc Digital Visual Interface (d= digital only) Enhanced Display Data Channel (VESA standard for communication channel and display). Using E-DDC, the video source can read the EDID information form the display. Extended Display Identification Data (VESA standard) Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory Electro Magnetic Interference Electronic Program Guide Erasable Programmable Logic Device Europe EXTernal (source), entering the set by SCART or by cinches (jacks) Full Dual Screen (same as FDW) Full Dual Window (same as FDS) FLASH memory Field Memory or Frequency Modulation Field-Programmable Gate Array Flat TeleVision Giga bits per second Green TeleteXT H_sync to the module High Definition Hard Disk Drive High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection: A “key” encoded into the HDMI/DVI signal that prevents video data piracy. If a source is HDCP coded and connected via HDMI/DVI without the proper HDCP decoding, the picture is put into a “snow vision” mode or changed to a low resolution. For normal content distribution the source and the display device must be enabled for HDCP “software key” decoding. High Definition Multimedia Interface HeadPhone Monochrome TV system. Sound carrier distance is 6.0 MHz Inter IC bus Inter IC Data bus Inter IC Sound bus Intermediate Frequency Infra Red Interrupt Request The ITU Radio communication Sector (ITU-R) is a standards body subcommittee of the International Telecommunication Union relating to radio communication. ITU-656 (a.k.a. back to div. table PAL P50 OTC O/C OSD OAD NVM NTSC NTC NC NICAM MPEG MPIF MUTE MTV MOP MOSFET MIPS MHEG LPL LS LVDS Mbps M/N LATAM LCD LED L/L' LS iTV Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List 3. EN 7 2011-Apr-22 SDI), is a digitized video format used for broadcast grade video. Uncompressed digital component or digital composite signals can be used. The SDI signal is self-synchronizing, uses 8 bit or 10 bit data words, and has a maximum data rate of 270 Mbit/s, with a minimum bandwidth of 135 MHz. Institutional TeleVision; TV sets for hotels, hospitals etc. Last Status; The settings last chosen by the customer and read and stored in RAM or in the NVM. They are called at start-up of the set to configure it according to the customer's preferences Latin America Liquid Crystal Display Light Emitting Diode Monochrome TV system. Sound carrier distance is 6.5 MHz. L' is Band I, L is all bands except for Band I LG.Philips LCD (supplier) Loudspeaker Low Voltage Differential Signalling Mega bits per second Monochrome TV system. Sound carrier distance is 4.5 MHz Part of a set of international standards related to the presentation of multimedia information, standardised by the Multimedia and Hypermedia Experts Group. It is commonly used as a language to describe interactive television services Microprocessor without Interlocked Pipeline-Stages; A RISC-based microprocessor Matrix Output Processor Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor, switching device Motion Pictures Experts Group Multi Platform InterFace MUTE Line Mainstream TV: TV-mode with Consumer TV features enabled (iTV) Not Connected Near Instantaneous Compounded Audio Multiplexing. This is a digital sound system, mainly used in Europe. Negative Temperature Coefficient, non-linear resistor National Television Standard Committee. Color system mainly used in North America and Japan. Color carrier NTSC M/N= 3.579545 MHz, NTSC 4.43= 4.433619 MHz (this is a VCR norm, it is not transmitted off-air) Non-Volatile Memory: IC containing TV related data such as alignments Open Circuit On Screen Display Over the Air Download. Method of software upgrade via RF transmission. Upgrade software is broadcasted in TS with TV channels. On screen display Teletext and Control; also called Artistic (SAA5800) Project 50: communication protocol between TV and peripherals Phase Alternating Line. Color system mainly used in West Europe (colour carrier = 4.433619 MHz) and South America (colour carrier Q552.2L LA 3. 2011-Apr-22 STB STBY S/PDIF SRAM SRP SSB SSC SIF SMPS SoC SOG SOPS SPI SCL SCL-F SD SDA SDA-F SDI SDRAM SECAM R-TXT SAM S/C SCART RESET ROM RSDS RC RC5 / RC6 PWB PWM QRC QTNR QVCP RAM RGB PTC PSLS PSL POR PSDL POD PIP PLL PCB PCM PDP PFC EN 8 back to div. table YUV YPbPr WXGA XTAL XGA Y Y/C WYSIWYR VSB VGA VL TS TXT TXT-DW UI uP UXGA V VESA SXGA TFT THD TMDS SVGA SVHS SW SWAN Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List PAL M = 3.575612 MHz and PAL N = 3.582056 MHz) Printed Circuit Board (same as “PWB”) Pulse Code Modulation Plasma Display Panel Power Factor Corrector (or Preconditioner) Picture In Picture Phase Locked Loop. Used for e.g. FST tuning systems. The customer can give directly the desired frequency Point Of Deployment: a removable CAM module, implementing the CA system for a host (e.g. a TV-set) Power On Reset, signal to reset the uP Power Supply for Direct view LED backlight with 2D-dimming Power Supply with integrated LED drivers Power Supply with integrated LED drivers with added Scanning functionality Positive Temperature Coefficient, non-linear resistor Printed Wiring Board (same as “PCB”) Pulse Width Modulation Quasi Resonant Converter Quality Temporal Noise Reduction Quality Video Composition Processor Random Access Memory Red, Green, and Blue. The primary color signals for TV. By mixing levels of R, G, and B, all colors (Y/C) are reproduced. Remote Control Signal protocol from the remote control receiver RESET signal Read Only Memory Reduced Swing Differential Signalling data interface Red TeleteXT Service Alignment Mode Short Circuit Syndicat des Constructeurs d'Appareils Radiorécepteurs et Téléviseurs Serial Clock I2C CLock Signal on Fast I2C bus Standard Definition Serial Data I2C DAta Signal on Fast I2C bus Serial Digital Interface, see “ITU-656” Synchronous DRAM SEequence Couleur Avec Mémoire. Colour system mainly used in France and East Europe. Colour carriers = 4.406250 MHz and 4.250000 MHz Sound Intermediate Frequency Switched Mode Power Supply System on Chip Sync On Green Self Oscillating Power Supply Serial Peripheral Interface bus; a 4wire synchronous serial data link standard Sony Philips Digital InterFace Static RAM Service Reference Protocol Small Signal Board Spread Spectrum Clocking, used to reduce the effects of EMI Set Top Box STand-BY Q552.2L LA 800 × 600 (4:3) Super Video Home System Software Spatial temporal Weighted Averaging Noise reduction 1280 × 1024 Thin Film Transistor Total Harmonic Distortion Transmission Minimized Differential Signalling Transport Stream TeleteXT Dual Window with TeleteXT User Interface Microprocessor 1600 × 1200 (4:3) V-sync to the module Video Electronics Standards Association 640 × 480 (4:3) Variable Level out: processed audio output toward external amplifier Vestigial Side Band; modulation method What You See Is What You Record: record selection that follows main picture and sound 1280 × 768 (15:9) Quartz crystal 1024 × 768 (4:3) Luminance signal Luminance (Y) and Chrominance (C) signal Component video. Luminance and scaled color difference signals (B-Y and R-Y) Component video 4.2 4.1 Q552.2L LA For easy servicing of a TV set, the set should be put face down on a soft flat surface, foam buffers or other specific workshop tools. Ensure that a stable situation is created to perform measurements and alignments. When using foam bars take care that these always support the cabinet and never only the display. Caution: Failure to follow these guidelines can seriously damage the display! Ensure that ESD safe measures are taken. Service Positions back to div. table 4.3.1 4.3 EN 9 19100_046_110214.eps 110214 4. 2011-Apr-22 Warning: Disconnect the mains power cord before you remove the rear cover. Note: it is not necessary to remove the stand while removing the rear cover. Rear Cover The instructions apply to the 37PFL6606H/12 (European model). For the 40" and 46" Blockbuster sets, additional instructions (rear cover removal) apply. Refer to subsection Additional instructions for Blockbuster 40-/46PFL6606x/xx. Assy/Panel Removal Blockbuster Styling (xxPFL66xx/xx series) Figure 4-1 Cable dressing 40PFL6606x/xx (Blockbuster) - picture taken from an European set Cable Dressing Blockbuster Styling (xxPFL66xx/xx series) Index of this chapter: 4.1 Cable Dressing Blockbuster Styling (xxPFL66xx/xx series) 4.2 Service Positions 4.3 Assy/Panel Removal Blockbuster Styling (xxPFL66xx/xx series) 4.4 Set Re-assembly Notes: • Figures below can deviate slightly from the actual situation, due to the different set executions. 4. Mechanical Instructions Mechanical Instructions 4. Q552.2L LA 19100_048_110216.eps 110216 1 19100_049_110216.eps 110216 Refer to Figure 4-4 for details. Mains Switch Subwoofer The central subwoofer is located in the centre of the set and is secured by two bosses. When defective, replace the whole unit. Tweeters Each tweeter unit is mounted with two screws. When defective, replace the whole unit. Speakers 2011-Apr-22 4.3.3 4.3.2 It is advised to lay the set with front facing down before executing this operation. 1. Remove all screws from the rear cover. 2. Use a round rod (diameter 2 mm) and insert it in one of the holes [1]. 3. Push the catch located inside the rear cover away by inserting the rod [2] through the hole and lifting the rear cover at the same time. 4. Repeat the same procedure on the other hole. Figure 4-3 Bottom catches 40" and 46" Blockbuster sets -2- 2 Figure 4-2 Bottom catches 40" and 46" Blockbuster sets -1- 1 Additional instructions for Blockbuster 40-/46PFL6606x/xx 40"and 46"Blockbuster (40-/46PFL6606x/xx) sets have a dedicated method to open the bottom catches when removing the rear cover. Refer to Figure 4-2 and Figure 4-3 for details. back to div. table 4.3.5 4.3.4 Mechanical Instructions 1. Remove all screws of the rear cover. 2. Lift the rear cover from the TV. Make sure that wires and flat coils are not damaged while lifting the rear cover from the set. EN 10 19100_047_110216.eps 110216 Figure 4-5 Main Power Supply 1 1 Refer to Figure 4-6 for details. Small Signal Board (SSB) 1. Unplug all connectors [1]. 2. Remove the fixation screws [2]. 3. Take the board out. When defective, replace the whole unit. 2 2 Refer to Figure 4-5 for details. Main Power Supply 19101_008_110407.eps 110407 2 2 The mains switch is mounted on a plastic subframe and can be removed without removing the subframe. 1. Use a screwdriver and push the switch out of its casing [1]. 2. Unplug the connectors. When defective, replace the whole unit. Figure 4-4 Mains switch 1 4.3.6 Figure 4-6 SSB 1 1 2 3 3 2 19101_006_110407.eps 110407 2 2 1. Remove the stand [1]. 2. Remove the stand subframe [2]. Figure 4-8 Keyboard control, IR & LED board [2/2] 2 2 Figure 4-7 Keyboard control, IR & LED board [1/2] 19101_009_110407.eps 110407 1 1 Refer to Figure 4-7 and Figure 4-8 for details. Keyboard Control, IR & LED Board 1. Unplug all connectors [1]. 2. Remove the fixation screws [2]. 3. Take the board out. When remounting, ensure that the side shielding is positioned correctly. 19101_007_110407.eps 110407 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 back to div. table 4.3.7 Q552.2L LA 4. EN 11 2011-Apr-22 1. Remove the SSB as described earlier. 2. Remove the PSU as described earlier. 3. Remove the tweeters with their subframes and subwoofer as described earlier. 4. Remove the stand and -subframe as described earlier. 5. Remove the cables [1]. 6. Remove the mains switch subframe [2]. 7. Remove the keyboard control-, and IR & LED board as described earlier. 8. Remove all remaining cables and subframes. 9. Use a screwdriver to release the catches [3] that secure the panel. 10. Use a screwdriver to release the catches and remove the sidewings [4] that secure the panel. 11. Take the panel out. Remove the clamps from the panel before sending the panel in for Service. Refer to Figure 4-9 to Figure 4-11 for details. LCD Panel 3. Remove the screws [3], unplug the connector and take the board out. When defective, replace the whole unit. Mechanical Instructions 2011-Apr-22 EN 12 4. Figure 4-10 LCD panel [2/3] 3 2 Q552.2L LA 1 19101_004_110407.eps 110407 back to div. table Figure 4-9 LCD panel [1/3] Mechanical Instructions Figure 4-11 LCD panel [3/3] 4 19101_003_110407.eps 110407 19101_005_110407.eps 110407 4.4 Notes: • While re-assembling, make sure that all cables are placed and connected in their original position. • Pay special attention not to damage the EMC foams in the set. Ensure that EMC foams are mounted correctly. To re-assemble the whole set, execute all processes in reverse order. Set Re-assembly back to div. table Mechanical Instructions Q552.2L LA 4. 2011-Apr-22 EN 13 5. Q552.2L LA Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding • • Europe, AP DVB-T All picture settings at 50% (brightness, color, contrast). Sound volume at 25%. PAL B/G 475.25 546.00 PID DVB-T Video: 0B 06 PID PCR: 0B 06 PID Audio: 0B 07 Europe, AP(PAL/Multi) Default system Freq. (MHz) Region Table 5-1 SDM default settings Specifications Purpose • To create a pre-defined setting, to get the same measurement results as given in this manual. • To override SW protections detected by stand-by processor and make the TV start up to the step just before protection (a sort of automatic stepwise start-up). See section “5.3 Stepwise Start-up”. • To start the blinking LED procedure where only LAYER 2 errors are displayed. (see also section “5.5 Error Codes”). Service Default Mode (SDM) Note: For the new model range, a new remote control (RC) is used with some renamed buttons. This has an impact on the activation of the Service modes. For instance the old “MENU” button is now called “HOME” (or is indicated by a “house” icon). This chassis also offers the option of using ComPair, a hardware interface between a computer and the TV chassis. It offers the abilities of structured troubleshooting, error code reading, and software version read-out for all chassis. (see also section “5.4.1 ComPair”). Service Default mode (SDM) and Service Alignment Mode (SAM) offers several features for the service technician, while the Customer Service Mode (CSM) is used for communication between the call centre and the customer. Service Modes Perform measurements under the following conditions: • Service Default Mode. • Video: Color bar signal. • Audio: 3 kHz left, 1 kHz right. As most signals are digital, it will be difficult to measure waveforms with a standard oscilloscope. However, several key ICs are capable of generating test patterns, which can be controlled via ComPair. In this way it is possible to determine which part is defective. Test Points 2011-Apr-22 5.2.1 5.2 5.1 Index of this chapter: 5.1 Test Points 5.2 Service Modes 5.3 Stepwise Start-up 5.4 Service Tools 5.5 Error Codes 5.6 The Blinking LED Procedure 5.7 Protections 5.8 Fault Finding and Repair Tips 5.9 Software Upgrading back to div. table 5.2.2 All service-unfriendly modes (if present) are disabled, like: – (Sleep) timer. – Child/parental lock. – Picture mute (blue mute or black mute). – Automatic volume levelling (AVL). – Skip/blank of non-favorite pre-sets. 19100_057_110217.eps 110217 How to Activate SAM Via a standard RC transmitter: Key in the code “062596” directly followed by the “INFO” or “OK” button. After activating SAM with this method a service warning will appear on the screen, continue by pressing the “OK” button on the RC. Purpose • To perform (software) alignments. • To change option settings. • To easily identify the used software version. • To view operation hours. • To display (or clear) the error code buffer. Service Alignment Mode (SAM) How to Exit SDM Use one of the following methods: • Switch the set to STAND-BY via the RC-transmitter. • Via a standard customer RC-transmitter: key in “00”sequence. How to Navigate When the “MENU” (or “HOME”) button is pressed on the RC transmitter, the TV set will toggle between the SDM and the normal user menu. After activating this mode, “SDM” will appear in the upper right corner of the screen (when a picture is available). Figure 5-1 Service mode pad SDM How to Activate SDM For this chassis there are two kinds of SDM: an analogue SDM and a digital SDM. Tuning will happen according Table 5-1. • Analogue SDM: use the standard RC-transmitter and key in the code “062596”, directly followed by the “MENU” (or “HOME”) button. Note: It is possible that, together with the SDM, the main menu will appear. To switch it “off”, push the “MENU” (or "HOME") button again. Analogue SDM can also be activated by grounding for a moment the solder path on the SSB, with the indication “SDM” (see Service mode pad). • Digital SDM: use the standard RC-transmitter and key in the code “062593”, directly followed by the “MENU” (or "HOME") button. Note: It is possible that, together with the SDM, the main menu will appear. To switch it “off”, push the “MENU” (or "HOME") button again. • 5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding EN 14 Note: When the NVM is corrupted, or replaced, there is a high possibility that no picture appears because the display code is not correct. So, before initializing the NVM via the SAM, a picture is necessary and therefore the correct display option has to be entered. Refer to Chapter 6. Alignments for details. To adapt this option, it’s advised to use ComPair (the correct values for the options can be found in Chapter 6. Alignments) or a method via a standard RC (described below). Changing the display option via a standard RC: Key in the code “062598” directly followed by the “MENU” (or "HOME") button and “XXX” (where XXX is the 3 digit decimal display code as mentioned on the sticker in the set). Make sure to key in all three digits, also the leading zero’s. If the above action is successful, the front LED will go out as an indication that the RC sequence was correct. After the display option is changed in the NVM, the TV will go to the Stand-by mode. If the NVM was corrupted or empty before this action, it will be initialized first (loaded with default values). This initializing can take up to 20 seconds. Contents of SAM • Hardware Info. – A. SW Version. Displays the software version of the main software (example: Q555X-1.2.3.4 = AAAAB_X.Y.W.Z). • AAAA= the chassis name. • B= the SW branch version. This is a sequential number (this is no longer the region indication, as the software is now multi-region). • X.Y.W.Z= the software version, where X is the main version number (different numbers are not compatible with one another) and Y.W.Z is the sub version number (a higher number is always compatible with a lower number). – B. STBY PROC Version. Displays the software version of the stand-by processor. – C. Production Code. Displays the production code of the TV, this is the serial number as printed on the back of the TV set. Note that if an NVM is replaced or is initialized after corruption, this production code has to be re-written to NVM. ComPair will foresee in a possibility to do this. • Operation Hours. Displays the accumulated total of operation hours (not the stand-by hours). Every time the TV is switched “on/off”, 0.5 hours is added to this number. • Errors (followed by maximum 10 errors). The most recent error is displayed at the upper left (for an error explanation see section “5.5 Error Codes”). • Reset Error Buffer. When “cursor right” (or “OK” button) pressed here, followed by the “OK” button, the error buffer is reset. • Alignments. This will activate the “ALIGNMENTS” submenu. See Chapter 6. Alignments. • Dealer Options. Extra features for the dealers. • Options. Extra features for Service. For more info regarding option codes, see chapter 6. Alignments. Note that if the option code numbers are changed, these have to be confirmed with pressing the “OK” button before the options are stored, otherwise changes will be lost. • Initialize NVM. The moment the processor recognizes a corrupted NVM, the “initialize NVM” line will be highlighted. Now, two things can be done (dependent of the service instructions at that moment): – Save the content of the NVM via ComPair for development analysis, before initializing. This will give the Service department an extra possibility for diagnosis (e.g. when Development asks for this). – Initialize the NVM. back to div. table 040 Q552.2L LA EN 15 10000_038_090121.eps 090819 5. • • • • • • • • 2011-Apr-22 Store - go right. All options and alignments are stored when pressing “cursor right” (or the “OK” button) and then the “OK”-button. Operation hours display. Displays the accumulated total of operation hours of the screen itself. In case of a display replacement, reset to “0” or to the consumed operation hours of the spare display. SW Maintenance. – SW Events. In case of specific software problems, the development department can ask for this info. – HW Events. In case of specific software problems, the development department can ask for this info : - Event 26: refers to a power dip, this is logged after the TV set reboots due to a power dip. - Event 17: refers to the power OK status, sensed even before the 3 x retry to generate the error code. Test settings. For development purposes only. Development file versions. Not useful for Service purposes, this information is only used by the development department. Upload to USB. To upload several settings from the TV to an USB stick, which is connected to the SSB. The items are “Channel list”, “Personal settings”, “Option codes”, “Alignments”, “Identification data” (includes the set type and prod code + all 12NC like SSB, display, boards), “History list”. The “All” item supports to upload all several items at once. First a directory “repair\” has to be created in the root of the USB stick. To upload the settings, select each item separately, press “cursor right” (or the “OK” button), confirm with “OK” and wait until the message “Done” appears. In case the download to the USB stick was not successful, “Failure” will be displayed. In this case, check if the USB stick is connected properly and if the directory “repair” is present in the root of the USB stick. Now the settings are stored onto the USB stick and can be used to download into another TV or other SSB. Uploading is of course only possible if the software is running and preferably a picture is available. This method is created to be able to save the customer’s TV settings and to store them into another SSB. Download from USB. To download several settings from the USB stick to the TV, same way of working needs to be followed as described in “Upload to USB”. To make sure that the download of the channel list from USB to the TV is executed properly, it is necessary to restart the TV and tune to a valid preset if necessary. The “All” item supports to download all several items at once. NVM editor. For NET TV the set “type number” must be entered correctly. Also the production code (AG code) can be entered here via the RC-transmitter. Correct data can be found on the side/rear sticker. Figure 5-2 Location of Display Option Code sticker (CTN Sticker) AG 1A0620 000001 PROD.SERIAL NO: MODEL: 32PF9968/10 PHILIPS 39mm Display Option Code Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 27mm Q552.2L LA Key in the code “123654” via the standard RC transmitter. Note: Activation of the CSM is only possible if there is no (user) menu on the screen! How to Activate CSM Also when CSM is activated, the LAYER 1 error is displayed via blinking LED. Only the latest error is displayed (see also section 5.5 Error Codes). To have fast feedback from the field, a flashdump can be requested by development. When in CSM, push the “red” button and key in serial digits ‘2679’ (same keys to form the word ‘COPY’ with a cellphone). A file “Dump_model number_serial number.bin” will be written on the connected USB device. This can take 1/2 minute, depending on the quantity of data that needs to be dumped. When in CSM mode (and a USB stick connected), pressing “OK” will create an extended CSM dump file on the USB stick. This file (Extended_CSM_model number_serial number.txt) contains: • The normal CSM dump information, • All items (from SAM “load to USB”, but in readable format), • Operating hours, • Error codes, • SW/HW event logs. When CSM is activated and there is a USB stick connected to the TV set, the software will dump the CSM content to the USB stick. The file (CSM_model number_serial number.txt) will be saved in the root of the USB stick. This info can be handy if no information is displayed. When in this chassis CSM is activated, a test pattern will be displayed during 5 seconds (1 second Blue, 1 second Green and 1 second Red, then again 1 second Blue and 1 second Green). This test pattern is generated by the PNX51X0 (located on the 200Hz board as part of the display). So if this test pattern is shown, it could be determined that the back end video chain (PNX51X0 and display) is working.For TV sets without the PNX51X0 inside, every menu from CSM will be used as check for the back end chain video. Purpose When a customer is having problems with his TV-set, he can call his dealer or the Customer Helpdesk. The service technician can then ask the customer to activate the CSM, in order to identify the status of the set. Now, the service technician can judge the severity of the complaint. In many cases, he can advise the customer how to solve the problem, or he can decide if it is necessary to visit the customer. The CSM is a read only mode; therefore, modifications in this mode are not possible. Customer Service Mode (CSM) back to div. table Quality items • Signal quality. Bad / average /good (not for DVB-S). • Ethernet MAC address. Displays the MAC address present in the SSB. • Wireless MAC address. Displays the wireless MAC address to support the Wi-Fi functionality. • BDS key. Indicates if the set is in the BDS status. • CI module. Displays status if the common interface module is detected. • CI + protected service. Yes/No. • Event counter : S : 000X 0000(number of software recoveries : SW EVENT-LOG #(reboots) S : 0000 000X (number of software events : SW EVENTLOG #(events) H : 000X 0000(number of hardware errors) Software versions • Current main SW. Displays the build-in main software version. In case of field problems related to software, software can be upgraded. As this software is consumer upgradeable, it will also be published on the Internet. Example: Q55xx1.2.3.4 • Stand-by SW. Displays the build-in stand-by processor software version. Upgrading this software will be possible via ComPair or via USB (see section 5.9 Software Upgrading). Example: STDBY_83.84.0.0. • e-UM version. Displays the electronic user manual SWversion (12NC version number). Most significant number here is the last digit. • AV PIP software. • 3D dongle software version. General • Set Type. This information is very helpful for a helpdesk/ workshop as reference for further diagnosis. In this way, it is not necessary for the customer to look at the rear of the TV-set. Note that if an NVM is replaced or is initialized after corruption, this set type has to be re-written to NVM. ComPair will foresee in a possibility to do this. The update can also be done via the NVM editor available in SAM. • Production Code. Displays the production code (the serial number) of the TV. Note that if an NVM is replaced or is initialized after corruption, this production code has to be re-written to NVM. ComPair will foresee in a possibility to do this. The update can also be done via the NVM editor available in SAM. • Installed date. Indicates the date of the first installation of the TV. This date is acquired via time extraction. • Options 1. Gives the option codes of option group 1 as set in SAM (Service Alignment Mode). • Options 2. Gives the option codes of option group 2 as set in SAM (Service Alignment Mode). • 12NC SSB. Gives an identification of the SSB as stored in NVM. Note that if an NVM is replaced or is initialized after corruption, this identification number has to be re-written to NVM. ComPair will foresee in a possibility to do this. This identification number is the 12nc number of the SSB. • 12NC display. Shows the 12NC of the display. • 12NC supply. Shows the 12NC of the power supply. • 12NC 200Hz board. Shows the 12NC of the 200Hz Panel (when present). • 12NC AV PIP. Shows the 12NC of the AV PIP board (when present). Contents of CSM The contents are reduced to 3 pages: General, Software versions and Quality items. The group names itself are not shown anywhere in the CSM menu. How to Navigate By means of the “CURSOR-DOWN/UP” knob on the RCtransmitter, can be navigated through the menus. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding How to Exit SAM Use one of the following methods: • Switch the TV set to STAND-BY via the RC-transmitter. • Via a standard RC-transmitter, key in “00” sequence, or select the “BACK” key. 2011-Apr-22 5.2.3 5. How to Navigate • In SAM, the menu items can be selected with the “CURSOR UP/DOWN” key on the RC-transmitter. The selected item will be highlighted. When not all menu items fit on the screen, move the “CURSOR UP/DOWN” key to display the next/previous menu items. • With the “CURSOR LEFT/RIGHT” keys, it is possible to: – (De) activate the selected menu item. – (De) activate the selected sub menu. • With the “OK” key, it is possible to activate the selected action. EN 16 5.3 Hibernate St by back to div. table 5. EN 17 GoToProtection 2011-Apr-22 18770_250_100216.eps 100402 GoToProtection Active Protection WakeUp requested (SDM) - St by requested - tact SW pushed WakeUp requested The abbreviations “SP” and “MP” in the figures stand for: • SP: protection or error detected by the Stand-by Processor. • MP: protection or error detected by the MIPS Main Processor. Semi St by Mains on Q552.2L LA in this mode with a faulty FET 7U0X is done, you can destroy all IC’s supplied by the +1V8 and +1v1, due to overvoltage (12V on XVX-line). It is recommended to measure first the FET 7U0X or others FET’s on shortcircuit before activating SDM via the service pads. Figure 5-3 Transition diagram - Tact switch pushed - last status is hibernate after mains ON Tact switch pushed - stby requested and no data Acquisition required - WakeUp requested - Acquisition needed - Tact switch pushed Mains off When the TV is in a protection state due to an error detected by stand-by software (error blinking is displayed) and SDM is activated via shortcutting the SDM solder path on the SSB, the TV starts up until it reaches the situation just before protection. So, this is a kind of automatic stepwise start-up. In combination with the start-up diagrams below, you can see which supplies are present at a certain moment. Caution: in case the start-up Stepwise Start-up How to Exit CSM Press “MENU” (or "HOME") / “Back” key on the RC-transmitter. H : 0000 000X (number of hardware events : SW EVENTLOG #(events). Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 2011-Apr-22 EN 18 No 5. No No back to div. table Stand by or Protection Release AVC system reset Feed initializing boot script disable alive mechanism Yes An EJTAG probe (e.g. WindPower ICE probe) can be connected for Linux Kernel debugging purposes. Enter protection 12V error: Layer1: 3 Layer2: 16 18770_251_100216.eps 100216 - Switch Audio-Reset high. It is low in the standby mode if the standby mode lasted longer than 10s. If the protection state was left by short circuiting the SDM pins, detection of a protection condition during startup will stall the startup. Protection conditions in a playing set will be ignored. The protection mode will not be entered. Figure 5-4 “Off” to “Semi Stand-by” flowchart (part 1) Release AVC system reset Feed cold boot script Yes Cold boot? No EJTAG probe connected ? Detect EJTAG debug probe (pulling pin of the probe interface to ground by inserting EJTAG probe) Set I²C slave address of Standby μP to (A0h) Enable the supply detection algorithm Wait 50ms Enable the DCDC converters (ENABLE-3V3n LOW) Yes Detect2 high received within 2 seconds? +12V, +24Vs, AL and Bolt-on power is switched on, followed by the +1V2 DCDC converter Switch ON Platform and display supply by switching LOW the Standby line. start keyboard scanning, RC detection. Wake up reasons are off. Initialise I/O pins of the st-by μP: - Switch reset-AVC LOW (reset state) - Switch reset-system LOW (reset state) - Switch reset-Ethernet LOW (reset state) - Switch reset-USB LOW (reset state) - Switch reset-DVBs LOW (reset state) - keep Audio-reset and Audio-Mute-Up HIGH st-by μP resets Standby Supply starts running. All standby supply voltages become available. Mains is applied Off Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding Release AVC system reset Feed warm boot script Detect2 is moved to an interrupt. To be checked if the detection on interrupt base is feasible or not or if we should stick to the standard 40ms interval. Q552.2L LA No Initialize video processing IC’s Initialize source selection initialize tuner and channel decoders Initialize audio Startup screen visible 85500 starts up the display. 85500 sends out startup screen No 200Hz set? yes Startup screen cfg file present? yes Wake up reason coldboot & not semistandby? MIPS reads the wake up reason from standby μP. Enable Alive check mechanism Yes SW initialization succeeded within 20s? Semi-Standby Initialize Ambilight with Lights off. back to div. table Startup screen visible 85500 requests Lamp on 200Hz Tcon has started up the display. 2011-Apr-22 18770_252_100216.eps 100216 The first time after the option turn on of the startup screen or when the set is virgin, the cfg file is not present and hence the startup screen will not be shown. 85500 sends out startup screen yes EN 19 Startup screen shall only be visible when there is a coldboot to an active state end situation. The startup screen shall not be visible when waking up for reboot reasons or waking up to semistandby conditions or waking up to enter Hibernate mode.. Wait until AVC starts to communicate Timing needs to be updated if more mature info is available. initialize AutoTV by triggering CHS AutoTV Init interface No No Yes Flash to Ram image transfer succeeded within 30s? RPC start (comm. protocol) Set I²C slave address of Standby μP to (60h) Yes Timing needs to be updated if more mature info is available. Reset-Audio and Audio-Mute-Up are switched by MIPS code later on in the startup process Reset-Audio and Audio-Mute-Up are switched by MIPS code later on in the startup process Bootscript ready in 1250 ms? AVC releases Reset-Ethernet, Reset-USB and Reset-DVBs when the end of the AVC bootscript is detected 5. AVC releases Reset-Ethernet, Reset-USB and Reset-DVBs when the end of the AVC bootscript is detected Reset-system is switched HIGH by the AVC at the end of the bootscript Q552.2L LA Figure 5-5 “Off” to “Semi Stand-by” flowchart (part 2) No Code = Layer1: 2 Layer2: 53 To keep this flowchart readable, the exact display turn on description is not copied here. Please see the Semi-standby to On description for the detailed display startup During the complete display time of the Startup screen, the preheat condition of sequence. 100% PWM is valid. Switch Standby I/O line high and wait 4 seconds switch off the remaining DC/DC converters Wait 5ms Disable all supply related protections and switch off the +3V3 +5V DC/DC converter. Wait 10ms Switch AVC PNX85500 in reset (active low) Code = Layer1: 2 Layer2: 15 No Timing need to be updated if more mature info is available. This cannot be done through the bootscript, the I/O is on the standby μP Enter protection Blink Code as error code Yes 3-th try? No Reset-system is switched HIGH by the AVC at the end of the bootscript Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 2011-Apr-22 EN 20 5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding Yes Yes Active Prepare Start screen Display config file and copy to Flash No Display cfg file present and up to date, according correct display option? Yes Startup screen Option and Installation setting Photoscreen ON? Switch on the Ambilight functionality according the last status settings. Restore dimming backlight feature, PWM and BOOST output and unblank the video. Release audio mute and wait 100ms before any other audio handling is done (e.g. volume change) Switch Audio-Reset low and wait 5ms back to div. table No 18770_253_100216.eps 100216 Initialize audio and video processing IC's and functions according needed use case. Wait until valid and stable audio and video, corresponding to the requested output is delivered by the AVC AND the backlight has been switched on for at least the time which is indicated in the display file as preheat time. Switch on LCD backlight (Lamp-ON) Switch off the dimming backlight feature, set the BOOST control to nominal and make sure PWM output is set to maximum allowed PWM Delay Lamp-on with the sum of the LVDS delay and the Lamp delay indicated in the display file Switch on LVDS output in the 85500 Wait x ms Switch on the display power by switching LCD-PWR-ON low No Display already on? (splash screen) Assert RGB video blanking and audio mute Wait until previous on-state is left more than 2 seconds ago. (to prevent LCD display problems) Semi Standby Figure 5-6 “Semi Stand-by” to “Active” flowchart (EEFL or LED backlight 50/100 Hz only) The higher level requirement is that audio and video should be demuted without transient effects and that the audio should be demuted maximum 1s before or at the same time as the unblanking of the video. return Start POK line detection algorithm A LED set does not normally need a preheat time. The preheat remains present but is set to zero in the display file. The exact timings to switch on the display (LVDS delay, lamp delay) are defined in the display file. CPipe already generates a valid output clock in the semi-standby state: display startup can start immediately when leaving the semi-standby state. The assumption here is that a fast toggle (<2s) can only happen during ON->SEMI ->ON. In these states, the AVC is still active and can provide the 2s delay. A transition ON->SEMI->STBY->SEMI->ON cannot be made in less than 2s, because the standby state will be maintained for at least 4s. - Display may only be started when valid LVDS output clock can be delivered by the AVC. - To have a reliable operation of the EEFL backlight, the backlight should be driven with a maximum PWM duty cycle during the first seconds. Only after this first one or two seconds, the PWM may be set to the required output level (Note that the PWM output should be present before the backlight is switched on). To minimize the artefacts, the picture should only be unblanked after these first seconds. Constraints taken into account: Q552.2L LA No Backlight already on? (splash screen) Release audio mute and wait 100ms before any other audio handling is done (e.g. volume change) Switch Audio-Reset low and wait 5ms Yes Active Prepare Start screen Display config file and copy to Flash No Display cfg file present and up to date, according correct display option? Yes Startup screen Option and Installation setting Photoscreen ON? Switch on the Ambilight functionality according the last status settings. unblank the video. back to div. table 5. No EN 21 2011-Apr-22 18770_254_100216.eps 100216 Initialize audio and video processing IC's and functions according needed use case. Wait until valid and stable audio and video, corresponding to the requested output is delivered by the AVC. Yes Assert RGB video blanking and audio mute Wait until previous on-state is left more than 2 seconds ago. (to prevent LCD display problems) Figure 5-7 “Semi Stand-by” to “Active” flowchart (LED backlight 200 Hz) The higher level requirement is that audio and video should be demuted without transient effects and that the audio should be demuted maximum 1s before or at the same time as the unblanking of the video. return Q552.2L LA Semi Standby Request Tcon to Switch on the backlight in a direct LED or set Lamp-on I/O line in case of a side LED Start POK line detection algorithm There is no need to define the display timings since the timing implementation is part of the Tcon. The assumption here is that a fast toggle (<2s) can only happen during ON->SEMI ->ON. In these states, the AVC is still active and can provide the 2s delay. If the transition ON->SEMI>STBY->SEMI->ON can be made in less than 2s, we have to delay the semi -> stby transition until the requirement is met. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 2011-Apr-22 EN 22 5. Instruct 200Hz Tcon to turn off the display Yes Q552.2L LA back to div. table Figure 5-8 “Active” to “Semi Stand-by” flowchart Semi Standby Switch off the display power by switching LCD-PWR-ON high Wait x ms Switch off LVDS output in 85500 Wait x ms (display file) No 200Hz set? Mute all video outputs switch off LCD backlight (I/O or I²C) Switch off POK line detection algorithm Wait until Ambilight has faded out: Output power Observer should be zero switch off Ambilight Force ext audio outputs to ground (I/O: audio reset) And wait 5ms Set main amplifier mute (I/O: audio-mute) Wait 100ms Mute all sound outputs via softmute Active The exact timings to switch off the display (LVDS delay, lamp delay) are defined in the display file. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 18770_255_100216.eps 100216 Also here, the standby state has to be maintained for at least 4s before starting another state transition. release reset audio 10 sec after entering standby to save power Important remarks: back to div. table Figure 5-9 “Semi Stand-by” to “Stand-by” flowchart Stand by Switch OFF all supplies by switching HIGH the Standby I/O line Wait 5ms Disable all supply related protections and switch off the DC/DC converters (ENABLE-3V3n) Wait 10ms Switch AVC system in reset state (reset-system and reset-AVC lines) Switch reset-USB, Reset-Ethernet and Reset-DVBs LOW Switch Memories to self-refresh (this creates a more stable condition when switching off the power). transfer Wake up reasons to the Stand by μP. Delay transition until ramping down of ambient light is finished. *) If ambientlight functionality was used in semi-standby (lampadaire mode), switch off ambient light (see CHS ambilight) Semi Stand by Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 5. EN 23 2011-Apr-22 18770_256_100216.eps 100216 *) If this is not performed and the set is switched to standby when the switch off of the ambilights is still ongoing, the lights will switch off abruptly when the supply is cut. Q552.2L LA ComPair 5.4.1 Q552.2L LA RC out TO TV PC Multi function RS232 /UART TO UART SERVICE CONNECTOR Optional power 5V DC 10000_036_090121.eps 091118 ComPair II Developed by Philips Brugge I2C TO I2C SERVICE CONNECTOR 2011-Apr-22 Note: When you encounter problems, contact your local support desk. How to Order ComPair II order codes: • ComPair II interface: 3122 785 91020. • Software is available via the Philips Service web portal. • ComPair UART interface cable for Q55x.x. (using 3.5 mm Mini Jack connector): 3138 188 75051. Caution: It is compulsory to connect the TV to the PC as shown in the picture above (with the ComPair interface in between), as the ComPair interface acts as a level shifter. If one connects the TV directly to the PC (via UART), ICs can be blown! Figure 5-10 ComPair II interface connection HDMI I2C only Optional Power Link/ Mode Switch Activity RC in ComPair II TO UART SERVICE CONNECTOR How to Connect This is described in the chassis fault finding database in ComPair. Specifications ComPair consists of a Windows based fault finding program and an interface box between PC and the (defective) product. The ComPair II interface box is connected to the PC via an USB cable. For the TV chassis, the ComPair interface box and the TV communicate via a bi-directional cable via the service connector(s). The ComPair fault finding program is able to determine the problem of the defective television, by a combination of automatic diagnostics and an interactive question/answer procedure. back to div. table 5.5.2 5.5.1 5.5 If no errors are there, the LED should not blink at all in CSM or SDM. No spacer must be displayed as well. There is a simple blinking LED procedure for board level repair (home repair) so called LAYER 1 errors next to the existing errors which are LAYER 2 errors (see Table 5-2). – LAYER 1 errors are one digit errors. – LAYER 2 errors are 2 digit errors. In protection mode. – From consumer mode: LAYER 1. – From SDM mode: LAYER 2. Fatal errors, if I2C bus is blocked and the set reboots, CSM and SAM are not selectable. – From consumer mode: LAYER 1. – From SDM mode: LAYER 2. In CSM mode. – When entering CSM: error LAYER 1 will be displayed by blinking LED. Only the latest error is shown. In SDM mode. – When SDM is entered via Remote Control code or the hardware pins, LAYER 2 is displayed via blinking LED. Error display on screen. – In CSM no error codes are displayed on screen. – In SAM the complete error list is shown. Use one of the following methods: • On screen via the SAM (only when a picture is visible). E.g.: – 00 00 00 00 00: No errors detected – 23 00 00 00 00: Error code 23 is the last and only detected error. – 37 23 00 00 00: Error code 23 was first detected and error code 37 is the last detected error. – Note that no protection errors can be logged in the error buffer. How to Read the Error Buffer Basically there are three kinds of errors: • Errors detected by the Stand-by software which lead to protection. These errors will always lead to protection and an automatic start of the blinking LED LAYER 1 error. (see section “5.6 The Blinking LED Procedure”). • Errors detected by the Stand-by software which not lead to protection. In this case the front LED should blink the involved error. See also section “5.5 Error Codes, 5.5.4 Error Buffer”. Note that it can take up several minutes before the TV starts blinking the error (e.g. LAYER 1 error = 2, LAYER 2 error = 15 or 53). • Errors detected by main software (MIPS). In this case the error will be logged into the error buffer and can be read out via ComPair, via blinking LED method LAYER 1-2 error, or in case picture is visible, via SAM. • • • • • • • New in this chassis is the way errors can be displayed: The error code buffer contains all detected errors since the last time the buffer was erased. The buffer is written from left to right, new errors are logged at the left side, and all other errors shift one position to the right. When an error occurs, it is added to the list of errors, provided the list is not full. When an error occurs and the error buffer is full, then the new error is not added, and the error buffer stays intact (history is maintained). To prevent that an occasional error stays in the list forever, the error is removed from the list after more than 50 hrs. of operation. When multiple errors occur (errors occurred within a short time span), there is a high probability that there is some relation between them. Introduction Error Codes Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding Introduction ComPair (Computer Aided Repair) is a Service tool for Philips Consumer Electronics products. and offers the following: 1. ComPair helps to quickly get an understanding on how to repair the chassis in a short and effective way. 2. ComPair allows very detailed diagnostics and is therefore capable of accurately indicating problem areas. No knowledge on I2C or UART commands is necessary, because ComPair takes care of this. 3. ComPair speeds up the repair time since it can automatically communicate with the chassis (when the μP is working) and all repair information is directly available. 4. ComPair features TV software up possibilities. Service Tools 5. 5.4 EN 24 5.5.4 5.5.3 Via the blinking LED procedure. See section 5.5.3 How to Clear the Error Buffer. Via ComPair. 53 64 PNX doesn’t boot (SW cause) 2 Display MIPS Stby μP MIPS MIPS MIPS MIPS MIPS MIPS MIPS MIPS MIPS MIPS MIPS Stby μP Stby μP MIPS MIPS Extra Info • Rebooting. When a TV is constantly rebooting due to internal problems, most of the time no errors will be logged or blinked. This rebooting can be recognized via a ComPair interface and Hyperterminal (for Hyperterminal settings, see section “5.8 Fault Finding and Repair Tips, 5.8.7 Logging). It’s shown that the loggings which are generated by the main software keep continuing. In this case diagnose has to be done via ComPair. • Error 13 (I2C bus 3, SSB bus blocked). Current situation: when this error occurs, the TV will constantly reboot due to the blocked bus. The best way for further diagnosis here, is to use ComPair. • Error 14 (I2C bus 2, TV set bus blocked). Current situation: when this error occurs, the TV will constantly reboot due to the blocked bus. The best way for further diagnosis here, is to use ComPair. • Error 18 (I2C bus 4, Tuner bus blocked). In case this bus is blocked, short the “SDM” solder paths on the SSB during startup, LAYER error 2 = 18 will be blinked. • Error 15 (PNX8550 doesn’t boot). Indicates that the main processor was not able to read his bootscript. This error will point to a hardware problem around the PNX8550 (supplies not OK, PNX 8550 completely dead, I2C link between PNX and Stand-by Processor broken, etc...). When error 15 occurs it is also possible that I2C1 bus is blocked (NVM). I2C1 can be indicated in the schematics as follows: SCL-UP-MIPS, SDA-UP-MIPS. 5 42 7 T° sensor LED driver/Tcon 42 36 35 34 2 2 Tuner 31 28 T° sensor SSB/set 2 2 2 Channel dec DVB-S Lnb controller 24 23 2 2 Tuner DVB-S 2 HDMI mux I2C switch 21 17 14 Main nvm 3 3 12V 2/9 16 PNX doesn’t boot (HW cause) 2 Inverter or display supply 15 2 PNX51X0 18 2 back to div. table E P E E E E E E E E E E E P P E E • • • • • • BL / EB BL EB EB EB EB EB EB EB EB EB EB EB BL BL BL / EB BL / EB EN 25 Defective Board Display SSB T° sensor T° sensor SSB SSB SSB SSB SSB SSB SSB 200 Hz board Supply Supply SSB SSB SSB SSB 2011-Apr-22 Other root causes for this error can be due to hardware problems regarding the DDR’s and the bootscript reading from the PNX8550. Error 16 (12V). This voltage is made in the power supply and results in protection (LAYER 1 error = 3) in case of absence. When SDM is activated we see blinking LED LAYER 2 error = 16. Error 17 (Invertor or Display Supply). Here the status of the “Power OK” is checked by software, no protection will occur during failure of the invertor or display supply (no picture), only error logging. LED blinking of LAYER 1 error = 3 in CSM, in SDM this gives LAYER 2 error = 17. Error 21 (PNX51X0). When there is no I2C communication towards the PNX51X0 after start-up, LAYER 2 error = 21 will be logged and displayed via the blinking LED procedure if SDM is switched on. This device is located on the 200 Hz panel from the display. Error 23 (HDMI). When there is no I2C communication towards the HDMI mux after start-up, LAYER 2 error = 23 will be logged and displayed via the blinking LED procedure if SDM is switched on. Error 24 (I2C switch). When there is no I2C communication towards the I2C switch, LAYER 2 error = 24 will be logged and displayed via the blinking LED procedure when SDM is switched on. Remark: this only works for TV sets with an I2C controlled screen included. Error 28 (Channel dec DVB-S). When there is no I2C communication towards the DVB-S channel decoder, Altera PNX8550 LM 75 LM 75 STV6110 STM24C64 DTT 71300 LNBH23 STV0903 PCA9540 Sil9x87A PNX51X0 / / PNX8550 SSB SSB SSB I2C4 BL / EB I2C2 E 2 I2C3 MIPS 5. Take notice that some errors need several minutes before they start blinking or before they will be logged. So in case of problems wait 2 minutes from start-up onwards, and then check if the front LED is blinking or if an error is logged. Monitored Error/ Error Buffer/ Layer 1 Layer 2 by Prot Blinking LED Device 13 Q552.2L LA content, as this history can give significant information). This to ensure that old error codes are no longer present. If possible, check the entire contents of the error buffer. In some situations, an error code is only the result of another error code and not the actual cause (e.g. a fault in the protection detection circuitry can also lead to a protection). There are several mechanisms of error detection: • Via error bits in the status registers of ICs. • Via polling on I/O pins going to the stand-by processor. • Via sensing of analog values on the stand-by processor or the PNX8550. • Via a “not acknowledge” of an I2C communication. Description Table 5-2 Error code overview In case of non-intermittent faults, clear the error buffer before starting to repair (before clearing the buffer, write down the Error Buffer Use one of the following methods: • By activation of the “RESET ERROR BUFFER” command in the SAM menu. • If the content of the error buffer has not changed for 50+ hours, it resets automatically. How to Clear the Error Buffer • • Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding Q552.2L LA Introduction 5.6.1 2011-Apr-22 Example: Error 12 8 6 0 0. After activation of the SDM, the front LED will show: 1. One long blink of 750 ms (which is an indication of the decimal digit) followed by a pause of 1.5 s When one of the blinking LED procedures is activated, the front LED will show (blink) the contents of the error buffer. Error codes greater then 10 are shown as follows: 1. “n” long blinks (where “n” = 1 to 9) indicating decimal digit 2. A pause of 1.5 s 3. “n” short blinks (where “n”= 1 to 9) 4. A pause of approximately 3 s, 5. When all the error codes are displayed, the sequence finishes with a LED blink of 3 s (spacer). 6. The sequence starts again. The blinking LED procedure can be split up into two situations: • Blinking LED procedure LAYER 1 error. In this case the error is automatically blinked when the TV is put in CSM. This will be only one digit error, namely the one that is referring to the defective board (see table “5-2 Error code overview”) which causes the failure of the TV. This approach will especially be used for home repair and call centres. The aim here is to have service diagnosis from a distance. • Blinking LED procedure LAYER 2 error. Via this procedure, the contents of the error buffer can be made visible via the front LED. In this case the error contains 2 digits (see table “5-2 Error code overview”) and will be displayed when SDM (hardware pins) is activated. This is especially useful for fault finding and gives more details regarding the failure of the defective board. Important remark: For an empty error buffer, the LED should not blink at all in CSM or SDM. No spacer will be displayed. The Blinking LED Procedure back to div. table 5.7.2 Software Protections 5.7.1 Repair Tip • There still will be a picture available but no sound. While the Class D amplifier tries to start-up again, the cone of the loudspeakers will move slowly in one or the other direction until the initial failure shuts the amplifier down, this cyclus starts over and over again. The headphone amplifier will also behaves similar. The only real hardware protection in this chassis appears in case of an audio problem e.g. DC voltage on the speakers. This protection will only affect the Class D audio amplifier (item 7D10; see diagram B03A) and puts the amplifier in a continuous burst mode (cyclus approximately 2 seconds). Hardware Protections Protections during Start-up During TV start-up, some voltages and IC observers are actively monitored to be able to optimise the start-up speed, and to assure good operation of all components. If these monitors do not respond in a defined way, this indicates a malfunction of the system and leads to a protection. As the observers are only used during start-up, they are described in the start-up flow in detail (see section “5.3 Stepwise Start-up”). Remark on the Supply Errors The detection of a supply dip or supply loss during the normal playing of the set does not lead to a protection, but to a cold reboot of the set. If the supply is still missing after the reboot, the TV will go to protection. Most of the protections and errors use either the stand-by microprocessor or the MIPS controller as detection device. Since in these cases, checking of observers, polling of ADCs, and filtering of input values are all heavily software based, these protections are referred to as software protections. There are several types of software related protections, solving a variety of fault conditions: • Related to supplies: presence of the +5V, +3V3 and 1V2 needs to be measured, no protection triggered here. • Protections related to breakdown of the safety check mechanism. E.g. since the protection detections are done by means of software, failing of the software will have to initiate a protection mode since safety cannot be guaranteed any more. Protections Use one of the following methods: • Activate the CSM. The blinking front LED will show only the latest layer 1 error, this works in “normal operation” mode or automatically when the error/protection is monitored by the Stand-by processor. In case no picture is shown and there is no LED blinking, read the logging to detect whether “error devices” are mentioned. (see section “5.8 Fault Finding and Repair Tips, 5.8.7 Logging”). • Activate the SDM. The blinking front LED will show the entire content of the LAYER 2 error buffer, this works in “normal operation” mode or when SDM (via hardware pins) is activated when the tv set is in protection. How to Activate Two short blinks of 250 ms followed by a pause of 3 s Eight short blinks followed by a pause of 3 s Six short blinks followed by a pause of 3 s One long blink of 3 s to finish the sequence (spacer). The sequence starts again. 5.7 5.6.2 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding LAYER 2 error = 28 will be logged and displayed via the blinking LED procedure if SDM is switched on. Error 31 (Lnb controller). When there is no I2C communication towards this device, LAYER 2 error = 31 will be logged and displayed via the blinking LED procedure if SDM is activated. Error 34 (Tuner). When there is no I2C communication towards the tuner during start-up, LAYER 2 error = 34 will be logged and displayed via the blinking LED procedure when SDM is switched on. Error 35 (main NVM). When there is no I2C communication towards the main NVM during start-up, LAYER 2 error = 35 will be displayed via the blinking LED procedure when SDM is switched “on”. All service modes (CSM, SAM and SDM) are accessible during this failure, observed in the Uart logging as follows: "<< ERRO >>> PFPOW_.C: First Error (id19, Layer_1= 2 Layer_= 35)". Error 36 (Tuner DVB-S). When there is no I2C communication towards the DVB-S tuner during start-up, LAYER 2 error = 36 will be logged and displayed via the blinking LED procedure when SDM is switched “on”. Error 42 (Temp sensor). Only applicable for TV sets equipped with temperature devices. Error 53. This error will indicate that the PNX8550 has read his bootscript (when this would have failed, error 15 would blink) but initialization was never completed because of hardware problems (NAND flash, ...) or software initialization problems. Possible cause could be that there is no valid software loaded (try to upgrade to the latest main software version). Note that it can take a few minutes before the TV starts blinking LAYER 1 error = 2 or in SDM, LAYER 2 error = 53. Error 64. Only applicable for TV sets with an I2C controlled screen. 5. 5.6 • • • • • • • EN 26 5.8.5 5.8.4 5.8.3 5.8.2 5.8.1 5.8 The linear stabilizers are providing: • +1V2 supply voltage (1.2V nominal), stabilized close to PNX855xx device, for various other internal blocks of PNX855xx; SENSE+1V2 signal provides the needed feedback to achieve this. • +2V5 supply voltage (2.5V nominal) for LVDS interface and various other internal blocks of PNX855xx; for 5000 series SSB diversities the stabilizer is 7UD2 while for the other diversities 7UC0 is used. • +3V3 supply voltage (3V3 nominal) for 5000 series SSB diversities, provided by 7UD3; in this case the 12V to 3V3 DC-DC converter is not present. The basic board power supply consists of 4 DC/DC converters and 5 linear stabilizers. All DC/DC converters have +12V input voltage and deliver: • +1V1 supply voltage (1.15V nominal), for the core voltage of PNX855xx, stabilized close to the point of load; SENSE+1V1 signal provides the DC-DC converter the needed feedback to achieve this. • +1V8 supply voltage, for the DDR2 memories and DDR2 interface of PNX855xx. • +3V3 supply voltage (3.30V nominal), overall 3.3 V for onboard IC’s, for non-5000 series SSB diversities only. • +5V (5.15V nominal) for USB, WIFI and Conditional Access Module and +5V5-TUN for +5V-TUN tuner stabilizer. Description basic board DC/DC Converter When CSM is activated and there is a USB stick connected to the TV, the software will dump the complete CSM content to the USB stick. The file (Csm.txt) will be saved in the root of the USB stick. If this mechanism works it can be concluded that a large part of the operating system is already working (MIPS, USB...) CSM To check the AV PIP board (if present) functionality, a dedicated testpattern can be invoked as follows: select the “multiview” icon in the User Interface and press the “OK” button. Apply for the main picture an extended source, e.g. HDMI input. Proceed by entering CSM (push ‘123654’ on the remote control) and press the yellow button. A colored testpattern should appear now, generated by the AV PIP board (this can take a few seconds). AV PIP The Class D-IC 7D10 has a powerpad for cooling. When the IC is replaced it must be ensured that the powerpad is very well pushed to the PWB while the solder is still liquid. This is needed to insure that the cooling is guaranteed, otherwise the Class DIC could break down in short time. Audio Amplifier Due to degeneration process of the LED’s fitted on the ambi module, there can be a difference in the color and/or light output of the spare ambilight modules in comparison with the originals ones contained in the TV set. Via SAM => alignments => ambilight, the spare module can be adjusted. Ambilight Read also section “5.5 Error Codes, 5.5.4 Error Buffer, Extra Info”. Fault Finding and Repair Tips back to div. table 5. EN 27 +5V-TUN supply voltage (5V nominal) for tuner and IF amplifier. Q552.2L LA 2011-Apr-22 Tips • Behavior comparison with a reference TV550 platform can be a fast way to locate failures. • If +12V stays "low", check the integrity of fuse 1U40. • Check the integrity (at least no short circuit between drain and source) of the power MOS-FETs before starting up the platform in SDM, otherwise many components might be damaged. Using a ohmmeter can detect short circuits between any power rail and ground or between +12V and any other power rail. • Short circuit at the output of an integrated linear stabilizer (7UC0, 7UD2 or 7UD3) will heat up this device strongly. • Switching frequencies should be 500 kHz ...600 kHz for 12 V to 1.1 V and 12 V to 1.8 V DC-DC converters, Debugging The best way to find a failure in the DC/DC converters is to check their start-up sequence at power “on” via the mains cord, presuming that the stand-by microprocessor and the external supply are operational. Take STANDBY signal "high"-to-"low" transition as time reference. When +12V becomes available (maximum 1 second after STANDBY signal goes "low") then +1V1 is started immediately. After ENABLE-3V3 goes "low", all the other supply voltages should rise within a few milliseconds. If +24V drops below +15V level then the DVB-S2 supply will stop, even if +3V3 is still present. At start-up, +24V becomes available when STANDBY signal is "low" (together with +12V for the basic board), when +3V3 from the basic board is present the two DC-DC converters channels inside 7T03 are activated. Initially only the 24V to 5V converter (channel 1 of 7T03 generating +5V-DVBS) will effectively work, while +V-LNB is held at a level around 11V7 via diode 6T55. After 7T05 is initialized, the second channel of 7T03 will start and generates a voltage higher then LNB-RF1 with 0V8. +5VDVBS start-up will imply +3V3-DVBS start-up, with a small delay of a few milliseconds => +2V5-DVBS and +1V-DVBS will be enabled. Description DVB-S2: • LNB-RF1 (0V = disabled, 14V or 18V in normal operation) LNB supply generated via the second conversion channel of 7T03 followed by 7T50 LNB supply control IC. It provides supply voltage that feeds the outdoor satellite reception equipment. • +3V3-DVBS (3V3 nominal), +2V5-DVBS (2V5 nominal) and +1V-DVBS (1.03V nominal) power supply for the silicon tuner and channel decoder. +1V-DVBS is generated via a 5V to 1V DC-DC converter and is stabilized at the point of load (channel decoder) by means of feedback signal SENSE+1V0-DVBS. +3V3-DVBS and +2V5-DVBS are generated via linear stabilizers from +5V-DVBS that by itself is generated via the first conversion channel of 7T03. +12V is considered OK (=> DETECT2 signal becomes "high", +12V to +1V8, +12V to +3V3, +12V to +5V DC-DC converter can be started up) if it rises above 10V and doesn’t drop below 9V5. A small delay of a few milliseconds is introduced between the start-up of 12V to +1V8 DC-DC converter and the two other DC-DC converters via 7U48 and associated components. Supply voltage +1V1 is started immediately when +12V voltage becomes available (+12V is enabled by STANDBY signal when "low"). Supply voltages +3V3, +2V5, +1V8, +1V2 and +5V-TUN are switched "on" by signal ENABLE-3V3 when "low", provided that +12V (detected via 7U40 and 7U41) is present. +3V3-STANDY (3V3 nominal) is the permanent voltage, supplying the Stand-by microprocessor inside PNX855xx. • Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding Q552.2L LA No Uart logging at all: • In case there is no Uart logging coming out, check if the startup script can be send over the I2C bus (3 trials to startup) + power supplies are switched on and stable. • No startup will end up in a blinking LED status : error LAYER 1 = “2”, error LAYER 2 = “53” (startup with SDM solder paths short). • Error LAYER 2 = “15” (hardware cause) is more related to a supply issue while error LAYER 2 = “53” (software cause) refers more to boot issues. Uart loggings are displayed: • When Uart loggings are coming out, the first conclusion we can make is that the TV set is starting up and communication with the flash RAM seems to be supported. The PNX855xx is able to read and write in the DRAMs. • We can not yet conclude : Flash RAM and DRAMs are fully operational/reliable.There still can be errors in the data transfers, DRAM errors, read/write speed and timing control. Description possible cases: Guidelines Uart logging When something is wrong with the TV set (f.i. the set is rebooting) you can check for more information via the logging in Hyperterminal. The Hyperterminal is available in every Windows application via Programs, Accessories, Communications, Hyperterminal. Connect a “ComPair UART”cable (3138 188 75051) from the service connector in the TV to the “multi function” jack at the front of ComPair II box. Required settings in ComPair before starting to log: - Start up the ComPair application. - Select the correct database (open file “Q55X.X”, this will set the ComPair interface in the appropriate mode). - Close ComPair After start-up of the Hyperterminal, fill in a name (f.i. “logging”) in the “Connection Description” box, then apply the following settings: 1. COMx 2. Bits per second = 115200 3. Data bits = 8 4. Parity = none 5. Stop bits = 1 6. Flow control = none During the start-up of the TV set, the logging will be displayed. This is also the case during rebooting of the TV set (the same logging appears time after time). Also available in the logging is the “Display Option Code” (useful when there is no picture), look for item “DisplayRawNumber” in the beginning of the logging. Tip: when there is no picture available during rebooting you are able to check for “error devices” in the logging (LAYER 2 error) which can be very helpful to determine the failure cause of the reboot. For protection state, there is no logging. Logging When an “F” is displayed in the screen’s right corner, this means the set is in “Factory” mode, and it normally happens after a new SSB is mounted. To exit this mode, push the “VOLUME minus” button on the TV’s local keyboard for 10 seconds (this disables the continuous mode). Then push the “SOURCE” button for 10 seconds until the “F” disappears from the screen. back to div. table Make sure that the volume is set to minimum during disconnecting the speakers in the ON-state of the TV. The audio amplifier can be damaged by disconnecting the speakers during ON-state of the set! Loudspeakers New in this chassis: While in the download application (start up in TV mode + “OK” button pressed), the display option code can be changed via 062598 HOME XXX special SAM command (XXX=display option in 3 digits). Attention: In case the SSB is replaced, always check the display option code in SAM, even when picture is available. Performance with the incorrect display option code can lead to unwanted side-effects for certain conditions. 5.8.12 Display option code Attention: In case the tuner is replaced, always check the tuner options! 5.8.11 Tuner In case of no picture when CSM (test pattern) is activated and backlight doesn’t light up, it’s recommended first to check the inverter on the PSL + wiring (LAYER 2 error = 17 is displayed in SDM). 5.8.10 PSL 5.8.9 Uart logging changing preset: => COMMAND: calling DFB source = RC6, system=0, key = 4”. Startup in Jett Mode: Check Uart logging in Jet mode mentioned as : “JETT UART READY”. Startup in the SW upgrade application and observe the Uart logging: Starting up the TV set in the Manual Software Upgrade mode will show access to USB, meant to copy software content from USB to the DRAM.Progress is shown in the logging as follows: “cosupgstdcmds_mcmdwritepart: Programming 102400 bytes, 40505344 of 40607744 bytes programmed”. Defective sectors (bad blocks) in the Nand Flash can also be reported in the logging. Uart loggings reporting fault conditions, error messages, error codes, fatal errors: • Failure messages should be checked and investigated.For instance fatal error on the PNX51x0: check startup of the back-end processor, supplies..reset, I2C bus. => error mentioned in the logging as: *51x0 failed to start by itself*. • Some failures are indicated by error codes in the logging, check with error codes table (see Table “5-2 Error code overview”).e.g. => <<<ERROR>>>PLFPOW_MERR.C : First Error (id=10,Layer_1=2,Layer_2=23). • I2C bus error mentioned as e.g.: “ I2C bus 4 blocked”. • Not all failures or error messages should be interpreted as fault.For instance root cause can be due to wrong option codes settings => e.g. “DVBS2Suppoprted : False/True. In the Uart log startup script we can observe and check the enabled loaded option codes. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 900 kHz for 12 V to 3.3 V and 12 V to 5 V DC-DC converters. The DVB-S2 supply 24 V to 5 V and 24 V to +V LNB DC-DC converters operates at 300 kHz while for 5 V to 1.1 V DC-DC converter 900 kHz is used. 5. Exit “Factory Mode” 2011-Apr-22 5.8.8 5.8.7 5.8.6 EN 28 End Final check of all menus in CSM. Special attention for HDMI Keys and Mac address. Check if E - D F U is present. Check and perform alignments in SAM according to the Service Manual. Option codes, colour temperature, etc. If not already done: Check latest software on Service website. Update main and Stand-by software via USB. Go to SAM and reload settings via “Download from USB” function. Yes Saved settings on USB stick? Restart the set After entering the “Display Option” code, the set is going to Standby (= validation of code) Set the correct “Display code” via “062598 -HOME- xxx” where “xxx” is the 3 digit display panel code (see sticker on the side or bottom of the cabinet) 3) Wait until the message “Operation successful !” is displayed and remove all inserted media. Restart the TV set. 2) Now the main software will be loaded automatically, supported by a progress bar. 1) Plug the USB stick into the TV set and select the “autorun .upg” file in the displayed browser. back to div. table Figure 5-11 SSB replacement flowchart Attention point for Net TV: If the set type and serial number are not filled in, the Net TV functionality will not work. It will not be possible to connect to the internet. Program set type number, serial number, and display 12 NC Program E - DFU if needed. Start TV in Jett mode (DVD I + (OSD)) Open ComPair browser Q54x Connect PC via the ComPair interface to Service connector. No 5) Wait until the message “Operation successful !” is logged in the UART log and remove all inserted media. Restart the TV set. 4) Press "Down" cursor and “Ok” to start flashing the main TV software. Printouts like: “L: 1-100%, V: 1-100% and P: 1-100%” should be visible now in the UART logging. 3) Plug the prepared USB stick into the TV set. Follow the instructions in the UART log file, press “Right” cursor key to enter the list. Navigate to the “autorun.upg” file in the UART logging printout via the cursor keys on the remote control. When the correct file is selected, press “Ok”. 2) The TV set will start-up automatically in the download application if main TV software is not loaded. 5. EN 29 Q54x.E SSB Board swap – VDS Updated 22-03-2010 2011-Apr-22 H_16771_007a.eps 100402 - Check if correct “display option” code is programmed. - Verify “option codes” according to sticker inside the set. - Default settings for “white drive” > see Service Manual. In case of settings reloaded from USB, the set type, serial number, display 12 NC, are automatically stored when entering display options. Pictur e displayed Set is starting up without software upgrade menu appearing on screen Pictur e displayed Set is starting up with software upgrade menu appearing on screen Set behaviour? Start-up the set 1. D isconnect the WiF i module fr om the PC I connector (only for Q549.x SSB) 2. Replace the SSB by a Service SSB. 3. Place the WiFi module in the PCI connector. 4. Mount the Service SSB in the set. Due to a possible wrong display option code in the received Service SSB (NVM), it’s possible that no picture is displayed. Due to this the download application will not be shown either. This tree enables you to load the main software step-by-step via the UART logging on the PC (this for visual feedback). No pictur e displayed 1) Start up the TV set, equiped with the Service SSB, and enable the UART logging on the PC. Yes Set is still oper ating? ST AR T C onnect the U SB stick to the set, go to SAM and save the current TV settings via “Upload to USB” Before starting: - prepare a USB memory stick with the latest software - download the latest Main Software (Fus) from www.p4c.philips.com - unzip this file - create a folder ”upgrades” in the root of a USB stick (size > 50 MB) and save the autorun.upg file in this "upgrades" folder. Note: it is possible to rename this file, e.g."Q54x_SW_version.upg"; this in case there are more than one "autorun.upg" files on the USB stick. No Q552.2L LA In st ru ct io n n o t e SSB rep lacem en t Q543.x, Q548.x, Q549.x, and Q55x.x Follow the instructions in the flowchart in case a SSB has to be exchanged. See figure “SSB replacement flowchart”. 5.8.13 SSB Replacement Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 5. Q552.2L LA 2011-Apr-22 back to div. table Figure 5-12 SSB replacement flowchart - Factory mode R estart the set After entering “display option” code, the set is going in stand-by mode (= validation of code) Program display option code via “062598 MENU”, followed by the 3 digits code of the display (this code can be found on a sticker on - or inside - the set). Unplug the mains cord to verify the correct disabling of the Factory mode. The noise on the screen is replaced with the blue mute or the “F” is disappeared! - Press the “SOURCE” button for 10 seconds until the “F” disappears from the screen or the noise on the screen is replaced by “blue mute” - Press the “volume minus” button on the TVs local keyboard for 5 ~10 seconds H_16771_007b.eps 100322 An “F” is displayed (and the HDMI 1 input is displayed). Set is starting up in F actory m ode? Set is st art in g u p in F act o ry m o d e Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding Noisy picture with bands/lines is visible and the RED LED is continuous on. EN 30 5.9.1 5.9 Important: When the NAND-Flash must be replaced, a new SSB must be ordered, due to the presence of the security keys! (CI +, MAC address, ...). Perform the following actions after SSB replacement: 1. Set the correct option codes (see sticker inside the TV). 2. Update the TV software => see the eUM (electronic User Manual) for instructions. 3. Perform the alignments as described in chapter 6 (section 6.5 Reset of Repaired SSB). 4. Check in CSM if the CI + key, MAC address.. are valid. It is possible for the user to upgrade the main software via the USB port. This allows replacement of a software image in a stand alone set, without the need of an E-JTAG debugger. A description on how to upgrade the main software can be found in the electronic User Manual. The set software and security keys are stored in a NANDFlash, which is connected to the PNX855xx. Introduction Always check the latest software version on the servicer website in relation to the correct CTN!!! Attention! Software version numbers for 2011 sets are all defined below number 0.40.x.x. This might confuse servicers who store software versions for more than one set and/or platform on the same storage device (USB stick). Software Upgrading back to div. table 5.9.2 Q552.2L LA EN 31 18753_211_100811.eps 100811 5. The “UpgradeAll.upg” file is only used in the factory. 2011-Apr-22 Manual Software Upgrade In case that the software upgrade application does not start automatically, it can also be started manually. How to start the software upgrade application manually: 1. Disconnect the TV from the Mains/AC Power. 2. Press the “OK” button on a Philips TV remote control or a Philips DVD RC-6 remote control (it is also possible to use Automatic Software Upgrade In “normal” conditions, so when there is no major problem with the TV, the main software and the default software upgrade application can be upgraded with the “AUTORUN.UPG” (FUS part of the one-zip file: e.g. 3104 337 05661 _FUS _Q555X_ x.x.x.x_prod.zip). This can also be done by the consumers themselves, but they will have to get their software from the commercial Philips website or via the Software Update Assistant in the user menu (see eUM). The “autorun.upg” file must be placed in the root of the USB stick. How to upgrade: 1. Copy “AUTORUN.UPG” to the root of the USB stick. 2. Insert USB stick in the set while the set is operational. The set will restart and the upgrading will start automatically. As soon as the programming is finished, a message is shown to remove the USB stick and restart the set. • Main Software Upgrade For the correct order number of a new SSB, always refer to the Spare Parts list! Figure 5-13 SSB start-up Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding Q552.2L LA UART logging 2K10 (see section “5.8 Fault Finding and Repair Tips, 5.8.7 Logging) Below the content of the One-Zip file is explained, and instructions on how and when to use it. • AmbiCpld_Q55XX_x.x.x.x_prod.zip. Contains the program instruction and software content, needed to upgrade the ambilight CPLD on the TV550 platform. • BalanceFPGA_Q555X_x.x.x.x_prod.zip. Contains the BalanceFPGA software in “upg” format. • FUS_Q555X_x.x.x.x_prod.zip. Contains the “autorun.upg” which is needed to upgrade the TV main software and the software download application. • PNX5130UPG_Q555X_x.x.x.x_prod.zip. Contains the PNX5130 software in “upg” format. • StandbySW_Q555X_x.x.x.x_prod.zip. Contains the StandbyFactory software in “upg” format. • ProcessNVM_Q55XX_x.x.x.x_prod.zip. Default NVM content. Must be programmed via ComPair or can be loaded via USB, be aware that all alignments stored in NVM are overwritten here. Content and Usage of the One-Zip Software File In this chassis it is possible to upgrade the Stand-by software via a USB stick. The method is similar to upgrading the main software via USB. Use the following steps: 1. Create a directory “UPGRADES” on the USB stick. 2. Copy the Stand-by software (part of the one-zip file, e.g. StandbyFactory_88.0.0.0.upg) into this directory. 3. Insert the USB stick into the TV. 4. Start the download application manually (see section “ Manual Software Upgrade”. 5. Select the appropriate file and press the “OK” button to upgrade. Stand-by Software Upgrade via USB Back-up Software Upgrade Application If the default software upgrade application does not start (could be due to a corrupted boot sector) via the above described method, try activating the “back-up software upgrade application”. How to start the “back-up software upgrade application” manually: 1. Disconnect the TV from the Mains/AC Power. 2. Press the “CURSOR DOWN”-button on a Philips TV remote control while reconnecting the TV to the Mains/AC Power. 3. The back-up software upgrade application will start. back to div. table Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding Attention! In case the download application has been started manually, the “autorun.upg” will maybe not be recognized. What to do in this case: 1. Create a directory “UPGRADES” on the USB stick. 2. Rename the “autorun.upg” to something else, e.g. to “software.upg”. Do not use long or complicated names, keep it simple. Make sure that “AUTORUN.UPG” is no longer present in the root of the USB stick. 3. Copy the renamed “upg” file into this directory. 4. Insert USB stick into the TV. 5. The renamed “upg” file will be visible and selectable in the upgrade application. 2011-Apr-22 5.9.5 5.9.4 5.9.3 5. a TV remote in “DVD” mode). Keep the “OK” button pressed while reconnecting the TV to the Mains/AC Power. 3. The software upgrade application will start. EN 32 6.3 6.2 6.1.1 6.1 First, set the correct options: – In SAM, select “Option numbers”. – Fill in the option settings for “Group 1” and “Group 2” according to the set sticker (see also paragraph 6.4 Option Settings). – Press OK on the remote control before the cursor is moved to the left. – In submenu “Option numbers” select “Store” and press OK on the RC. OR: – In main menu, select “Store” again and press OK on the RC. – Switch the set to Stand-by. Warming up (>15 minutes). For the next alignments, supply the following test signals via a video generator to the RF input: To store the data: • Press OK on the RC before the cursor is moved to the left • In main menu select “Store” and press OK on the RC • Switch the set to stand-by mode. Put the set in SAM mode (see Chapter 5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding). The SAM menu will now appear on the screen. Select ALIGNMENTS and go to one of the sub menus. The alignments are explained below. The following items can be aligned: • White point • Ambilight. Software Alignments Not applicable. Hardware Alignments • • • Alignment Sequence Perform all electrical adjustments under the following conditions: • Power supply voltage (depends on region): – AP-NTSC: 120 VAC or 230 VAC / 50 Hz (± 10%). – AP-PAL-multi: 120 - 230 VAC / 50 Hz (± 10%). – EU: 230 VAC / 50 Hz (± 10%). – LATAM-NTSC: 120 - 230 VAC / 50 Hz (± 10%). – US: 120 VAC / 60 Hz (± 10%). • Connect the set to the mains via an isolation transformer with low internal resistance. • Allow the set to warm up for approximately 15 minutes. • Measure voltages and waveforms in relation to correct ground (e.g. measure audio signals in relation to AUDIO_GND). Caution: It is not allowed to use heat sinks as ground. • Test probe: Ri > 10 MΩ, Ci < 20 pF. • Use an isolated trimmer/screwdriver to perform alignments. General Alignment Conditions Index of this chapter: 6.1 General Alignment Conditions 6.2 Hardware Alignments 6.3 Software Alignments 6.4 Option Settings 6.5 Reset of Repaired SSB 6.6 Total Overview SAM modes 6. Alignments back to div. table 6.3.1 Off Unscaled Light Sensor Picture format Off 0 Dynamic Backlight Colour Enhancement Gamma 0.282 0.298 x y 0.311 0.292 Normal (8120K) 0.345 0.320 Warm (6080K) 0.282 0.276 x y Cool (11000K) Value 0.296 0.287 Normal (9000K) 0.329 0.313 2011-Apr-22 Warm (6500K) Table 6-2 White D alignment values - LED - Minolta CS-200 Cool (9420K) Value Table 6-1 White D alignment values - LED - Minolta CA-210 In case you have a color analyzer: • Measure, in a dark environment, with a calibrated contactless color analyzer (Minolta CA-210 or Minolta CS200) in the centre of the screen and note the x, y value. • Change the pattern to 90% white screen. If a Quantum Data generator is used, select the “GreyAll” test pattern at level = 230. • Adjust the correct x, y coordinates (while holding one of the White point registers R, G or B on 127) by means of decreasing the value of one or two other white points to the correct x, y coordinates (see Table 6-1 White D alignment values - LED - Minolta CA-210, or 6-2 White D alignment values - LED - Minolta CS-200). Tolerance: dx: ± 0.002, dy: ± 0.002. • Repeat this step for the other color temperatures that need to be aligned. • When finished press OK on the RC and then press STORE (in the SAM root menu) to store the aligned values to the NVM. • Restore the initial picture settings after the alignments. White point alignment LCD screens: • Use a 100% white screen (format: 720p50) to the HDMI input and set the following values: – “Color temperature”: “Cool”. – All “White point” values to: “127”. Go to the SAM and select “Alignments”-> “White point”. Off Off Dynamic Contrast Picture Setting • EN 33 In menu “Picture”, choose “Pixel Plus HD” and set picture settings as follows: 50 0 Colour 100 Brightness Contrast • 6. Choose “TV menu”, “Setup”, “More TV Settings” and then “Picture” and set picture settings as follows: Picture Setting • Q552.2L LA EU/AP-PAL models: a PAL B/G TV-signal with a signal strength of at least 1 mV and a frequency of 475.25 MHz US/AP-NTSC models: an NTSC M/N TV-signal with a signal strength of at least 1 mV and a frequency of 61.25 MHz (channel 3). LATAM models: an NTSC M TV-signal with a signal strength of at least 1 mV and a frequency of 61.25 MHz (channel 3). White Point • • • Alignments 6. Q552.2L LA Warm B t.b.d. t.b.d. t.b.d. 2 8192 4096 2048 1024 512 256 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Tuner Type Perfect Pixel Multi App 16384 Bit 14 Option Name Video Store Streaming Dec. Value Option 1 (prescribed value 327761)) Bit 15 (MSB) 32768 Option & Bit Table 6-4 Option codes at bit level (Option 1 - Option 8) From 2011 onwards, it is not longer possible to change individual option settings in SAM. Options can only be changed all at once by using the option codes as described in section 6.4.4. (Service) Options For dealer options, in SAM select “Dealer options”. See Table 6-5 SAM mode overview. Dealer Options Notes: • After changing the option(s), save them by pressing the OK button on the RC before the cursor is moved to the left, select STORE in the SAM root menu and press OK on the RC. • The new option setting is only active after the TV is switched “off” / “stand-by” and “on” again with the mains switch (the NVM is then read again). 2011-Apr-22 6.4.3 t.b.d. t.b.d. t.b.d. The microprocessor communicates with a large number of I C ICs in the set. To ensure good communication and to make digital diagnosis possible, the microprocessor has to know which ICs to address. The presence / absence of these PNX51XX ICs (back-end advanced video picture improvement IC which offers motion estimation and compensation features (commercially called HDNM) plus integrated Ambilight control) is made known by the option codes. Introduction t.b.d. Cool 6.4.1 t.b.d. Normal Option Settings t.b.d. Colour Temp G e.g. 40PFL6606x R White Tone Table 6-3 White tone default setting 40" (Blockbuster) 6.4 6.4.2 Alignments If you do not have a color analyzer, you can use the default values. This is the next best solution. The default values are average values coming from production. • Select a COLOUR TEMPERATURE (e.g. COOL, NORMAL, or WARM). • Set the RED, GREEN and BLUE default values according to the values in Table 6-3. • When finished press OK on the RC, then press STORE (in the SAM root menu) to store the aligned values to the NVM. • Restore the initial picture settings after the alignments. EN 34 00 = none 01 = multi app (Multiview BASIC) 10 = AVPIP + multi app (Multiview ENHANCED) 11 = future use 00 = Pixel Plus HD 01 = Pixel Precise HD 10 = Perfect Pixel HD 11 = future use 000 = TH2603 (Europe/AP) 001 = FA2307 (Brazil) 010 = VA1E1ED2411 011 = future use 100 = future use 101 = future use 110 = future use 111 = future use 001) 001) 0001) back to div. table 0 = OFF 1 = ON 11) Description Caution When manipulating option codes, know what you’re doing. Wrong option codes could damage the set. Prescribed option codes below are an example, not valid for all sets and are subject to modification. The correct option codes are always present on a sticker inside the set! For test purposes, please find below an overview of the Option Codes on bit level. With a bin/dec converter, you can calculate the Option Code. Option Bit Overview Refer to the sticker in the set for the correct option codes. Important: after having edited the option numbers as described above, you must press OK on the remote control before the cursor is moved to the left! Option Code Overview Diversity Not all sets with the same Commercial Type Number (CTN) necessarily have the same option code! Use of Alternative BOM => an alternative BOM number usually indicates the use of an alternative display or power supply. This results in another display code thus in another Option code. Refer to Chapter 2. Technical Specifications, Diversity, and Connections. Select this sub menu to set all options at once (expressed in two long strings of numbers). An option number (or “option byte”) represents a number of different options. When you change these numbers directly, you can set all options very quickly. All options are controlled via eight option numbers. When the NVM is replaced, all options will require resetting. To be certain that the factory settings are reproduced exactly, you must set both option number lines. You can find the correct option numbers on a sticker inside the TV set. Example: The options sticker gives the following option numbers: • 08192 00133 01387 45160 • 12232 04256 00164 00000 The first line (group 1) indicates hardware options 1 to 4, the second line (group 2) indicate software options 5 to 8. Every 5-digit number represents 16 bits (so the maximum value will be 65536 if all options are set). When all the correct options are set, the sum of the decimal values of each Option Byte (OB) will give the option number. Opt. No. (Option numbers) Prescribed Value1) 6.4.6 6.4.5 6.4.4 Option Name 256 128 64 32 16 8 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 AV3 16384 8192 4096 2048 1024 512 256 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB) HDMI 2 HDMI 3 HDMI Side ViewPort 21_9/PQL Seamless System Headphone Sound in Stand 3D Prepared AV1 AV2 Side IO Light Sensor Light Sensor LUT Super Resolution Smart Bit Enhancement (SBE) 3D Passive AL Select FPGA3Dact/1Ddimm Ambient Light Sunset Option 3 (prescribed value 154211)) Bit 15 (MSB) 32768 1 512 Bit 9 Bit 0 (LSB) 1024 Bit 10 4 2048 Bit 11 2 4096 Bit 12 Bit 1 8192 Bit 13 Bit 2 AL settings storage location 16384 Bit 14 Wall Adaptive AL AL Shop Mode AL Optical Syst MOP AL DNM PQ Profiles Option 2 (prescribed value 000011)) Bit 15 (MSB) 32768 1 Bit 0 (LSB) 8 Bit 3 4 16 Bit 4 2 32 Bit 5 Bit 1 64 Bit 6 Bit 2 128 Dec. Value Bit 7 Option & Bit 0 = Sound in Cabinet 1 = Sound in Stand 0 = OFF 1 = ON 0 = OFF 1 = ON 0 = OFF 1 = ON 0 = OFF 1 = ON 0 = OFF 1 = ON 0 = OFF 1 = ON 01) 11) 11) 11) 11) 01) 11) back to div. table 0 = not prepared 1 = prepared 0 = OFF 1 = ON 11) 01) 00 = Lut 0 01 = Lut 1 10 = Lut 2 11 = Lut 3 001) 00 = Scart/CVBS/RGB/LR 01 = CVBS/YC/YPbPr/HV/LR 10 = CVBS/YC/YPbPr/LR 11 = YPbPr/LR 0 = Super Resolution SD 1 = Super Resolution HD 01) 001) 0 = off 1 = on (200 Hz board present) 01) 00 = Scart/CVBS/RGB/LR 01 = CVBS/LR 10 = YPbPr/LR 11 = none 0 = 2D 1 = 3D passive 01) 111) 0 = AL2k10 1 = AL2k11 01) 000 = none 001 = CVBS 010 = YPbPr 011 = YPbPr/LR 100 = YPbPr/HV/LR 101 = CVBS/LR 110 = CVBS/Yc/LR 111 = future use 0 = OFF 1 = ON 01) 0111) 0000 = none 0001 = 2-sided (3/3) 0010 = 2-sided (4/4) 0011 = 2-sided (5/5) 0100 = 2-sided (6/6) 0101 = 2-sided (7/7) 0110 = 3-sided (5/5/5) 0111 = 3-sided (6/6/6) 1000 = 3-sided (3/6/3) 1001 = 3-sided (6/9/6) 1010 = 2-sided (8/8) 1011 = 3-sided (4/4/4) 1100 = 2-sided (1/1) 1101 = 2-sided (2/2) 1110 = future use 1111 = future use 00001) 0 = not present 1 = present 0 = OFF 1 = ON 01) 01) 0 = OFF 1 = ON 01) 00 = 140 nit 01 = 200 nit 10 = future use 11 = future use 001) 0 = stored in AL modules 1 = stored in SSB CPLD, not used in 2011 01) 01) 00 = Perfect Natural Motion 01 = HD Natural Motion 10 = future use 11 = future use 011) 0 = boost mode in shop is OFF 1 = boost mode in shop is ON 000 = profile 0 001 = profile 1 010 = profile 2 011 = profile 3 100 = profile 4 101 = profile 5 110 = profile 6 111 = profile 7 01) Description 0001) Q552.2L LA Prescribed Value1) Alignments 6. 2011-Apr-22 EN 35 6. Dec. Value 1024 512 256 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB) 2011-Apr-22 2 Bit 1 64 Bit 6 4 128 Bit 7 8 256 Bit 8 Bit 2 512 Bit 9 Bit 3 1024 Bit 10 32 2048 Bit 11 16 4096 Bit 12 Bit 4 8192 Bit 13 Bit 5 Hotel Mode 16384 Bit 14 DVBC light Over the Air Download MHP Ginga PVR Auto Store Mode USB Time Shift Virgin E-sticker Option 6 (prescribed value 366151)) Bit 15 (MSB) 32768 Display Type DVB DVB-C DVB-S DVBT Installation Bit 10 Ethernet 2048 1 Bit 0 (LSB) DLNA 4096 2 Bit 1 WiFi Bit 11 4 Bit 2 Online Service Bit 12 8 Bit 3 Internet SW Upgrade DVBC Installation 16 Bit 4 Video Store SD Card 8192 32 Bit 5 S Video 16384 64 Bit 6 Display MSB Bit 13 128 Bit 7 Bit 14 256 Bit 8 Region 8 Days EPG 512 Bit 9 Cabinet Option 5 (prescribed value 438471)) Bit 15 (MSB) 32768 2048 1024 4096 Bit 12 Bit 10 8192 Bit 13 Bit 11 16384 Bit 14 Alignments Option Name Q552.2L LA Option 4 (prescribed value 022351)) Bit 15 (MSB) 32768 Option & Bit EN 36 0 = ON 1 = OFF 0 = OFF 1 = ON 00 = none 01 = PDC_VPS 10 = TXT page 11 = PDC_VPS_TXT 0 = OFF 1 = ON 00 = OFF 01 = Country dependent 10 = ON 11 = future use 00 = OFF 01 = Country dependent 10 = ON 11 = future use 00 = OFF 01 = Country dependent 10 = ON 11 = future use 0 = OFF 1 = ON (when DVBC Installation is OFF or when ON but selected country is OFF, this option is used) 01) 11) 111) 11) 001) 001) 011) 11) back to div. table 00 = OFF 01 = 1V1 10 = 1V2 11 = future use 001) Display Type (ex.: 327) 010001111) 0 = OFF 1 = ON 0 = analogue only 1 = DVBT (and C/S depending DVBC/S option) 11) 11) 0 = OFF 1 = ON (ATSC/DVB should be ON) 11) 0 = OFF 1 = Ethernet vonnector and HW present 11) 0 = OFF 1 = ON (ATSC/DVB should be ON) 0 = OFF 1 = PC link 11) 01) 0 = OFF 1 = ON (wireless connection to ethernet; no link with “Ethernet option” bit “0”) 01) 00 = OFF 01 = Country dependent 10 = ON 11 = future use 0 = OFF 1 = ON (connection to internet provider Philips) 11) 011) 0 = OFF 1 = ON (automatic software upgradable via internet) 11) 00 = OFF 01 = Country dependent 10 = ON 11 = future use 0 = OFF 1 = ON 11) 011) 0 = OFF 1 = ON 01) 0 = OFF 1 = ON (country dependent) 0 = display option =< 255 1 = display option > 255 11) 11) 000 = Europe (/02, /05 & /12) 001 = AP PAL multi 010 = AP NTSC 011 = Russian (/60) 100 = Latam (/78 & /77) 101 = Australia 110 = China (/93) 111 = future use Cabinet type (no detailed info available) Description 0001) 000011) Prescribed Value1) 6.5 1 Dec. Value 512 256 128 64 32 16 8 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Option Name 4096 2048 1024 512 256 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB) DVB-T2 DVB-T2 Installation HBBTV WM DRM10 not used Test 1 (Monitor out) Test 2 (DBV-T light) Test 3 (XRay) Test 4 (Trick Mode) Test 5 After a repaired SSB has been mounted in the set (set repair on board level), the type number (CTN) and production code of the TV has to be set according to the type plate of the set. For this, you can use the NVM editor in SAM. This action also A very important issue towards a repaired SSB from a Service repair shop (SSB repair on component level) implies the reset of the NVM on the SSB. A repaired SSB in Service should get the service Set type “00PF0000000000” and Production code “00000000000000”. Also the virgin bit is to be set. To set all this, you can use the ComPair tool or use the “NVM editor” and “Dealer options” items in SAM (do not forget to “store”). Reset of Repaired SSB Note 1). Example 8192 Bit 13 Test 6 Test 8 Test 7 16384 Bit 14 FAN Temp Sensor Temp LUT E-box Light Guide Auto Power Down Manet Board Identifier Red LED Config LUT Visual Identity DVBT light Option 8 (prescribed value 000121)) Bit 15 (MSB) 32768 1 1024 Bit 10 Bit 0 (LSB) 2048 Bit 11 4 4096 Bit 12 2 8192 Bit 13 Bit 1 16384 Bit 14 Bit 2 32768 Bit 15 (MSB) Option 7 (prescribed value 330241)) Bit 0 (LSB) Option & Bit back to div. table 2011-Apr-22 In case of a display replacement, reset the “Operation hours display” to “0”, or to the operation hours of the replacement display. After a SSB repair, the original channel map can be restored, provided that the original channel map was stored on a USB stick before repair was commenced and that basic functionality of the TV, needed for this procedure, was not hampered as a result of the defect. The procedure of “channel map cloning” is clearly described in the (electronic) user manual. ensures the correct functioning of the “Net TV” feature and access to the Net TV portals. The loading of the CTN and production code can also be done via ComPair (Model number programming). 0 = OFF 1 = ON 01) - 00001) 0 = OFF 1 = ON 0 = OFF 1 = ON 01) 01) 0 = OFF 1 = ON 01) 0 = OFF 1 = ON 0 = OFF 1 = ON 01) 11) 0 = OFF 1 = ON 0 = OFF 1 = ON 01) 11) 01) 0 = no fan 1 = fan(s) present) 01) - 00 = no temp sensor 01 = temp sensor in display 10 = temp sensor on additional board 11 = temp sensor in AL module 001) 01) 000 = temp lut 0 001 = temp lut 1 010 = temp lut 2 011 = temp lut 3 100 = future use 101 = future use 110 = future use 111 = future use 0001) - 0 = integrated set 1 = e-box/monitor 01) 01) 0 = OFF 1 = ON 01) 01) 0 = OFF 1 = ON 11) not used, should always be “00” 001) 0 = all sets except Manet 1= Manet 000 = LED config LUT 0 001 = LED config LUT 1 010 = LED config LUT 2 011 = LED config LUT 3 100 = LED config LUT 4 101 = LED config LUT 5 110 = LED config LUT 6 111 = LED config LUT 7 0001) 01) 0 = User Interface 2k10 1 = User Interface 2k11 11) 0 = OFF 1 = ON (when DVBT Installation is OFF or Country depend to a country is OFF, this option is used) EN 37 Description 6. 11) Q552.2L LA Prescribed Value1) Alignments 6. Q552.2L LA Alignments A. SW version Hardware Info e.g. “Q5551_0.9.1.0 Sub-menu 2 Off/On None E-sticker Auto store mode Hardware events Display Software maintenance Clear Display Test application crash Test cold reboot Test reboot Display information is for development purposes Display information is for development purposes In case the display must be swapped for repair, you can reset the “”Display operation hours” to “0”. So, this one does keeps up the lifetime of the display itself (mainly to compensate the degeneration behaviour) 0003 Operation hours display Clear Select Store in the SAM root menu after making any changes Software events N.A. Store after changing The second line (group 2) indicates software options 5 to 8 The first line (group 1) indicates hardware options 1 to 4 Select E-sticker On/Off (USP’s on-screen) Select Virgin mode On/Off. TV starts up / does not start up (once) with a language selection menu after the mains switch is turned “on” for the first time (virgin mode) LCD White Point Alignment. For values, see Table 6-3 White tone default setting 40" (Blockbuster) Store back to div. table e.g. “44816.34311.33024.00000” Group 2 Store e.g. “00008.00001.15421.02239” Group 1 PDC/VPS/TXT TXT page PDC/VPS Off/On Virgin mode Select matrix Brightness Select module White point blue Cool Initialise NVM Option numbers Dealer options Ambilight White point green White point red Warn Clears all content in the error buffer 3 different modes of colour temperature can be selected Alignment Normal Reset error buffer Colour temperature Displayed the most recent errors Errors White point Description Display TV & Stand-by SW version and CTN serial number Displays the accumulated total of operation hours.TV switched “on/off” & every 0.5 hours is increase one e.g. “see type plate” Sub-menu 3 Figure 6-1 SSB identification 18310_221_090318.eps 090319 Operation hours C. Production code B. Stand-by processor version e.g. “STDBY_83.84.0.0” Sub-menu 1 Main Menu Table 6-5 SAM mode overview Total Overview SAM modes Whenever ordering a new SSB, it should be noted that the correct ordering number (12nc) of a SSB is located on a sticker on the SSB. The format is <12nc SSB><serial number>. The ordering number of a “Service” SSB is the same as the ordering number of an initial “factory” SSB. SSB identification 2011-Apr-22 6.6 6.5.1 EN 38 NVM editor Download from USB Upload to USB Development file versions see type plate see type plate AG code back to div. table Temp com file version none Flash units software NVM version Q55x1_0.4.5.0 Initial main software 12NC one zip software Ambilight parameters PRFAM 5.0.5.2 PQU - User styles PQF - Fixed settings PQS- Profile set PQ - TV550 1.0.27.22 Acoustics parameters ACSTS 5.0.6.20 Display parameters DISPT5.0.9.29 Digital + Analogue Digital only Type number All (options included) Identification data Alignments Option codes Personal settings Channel list All (options included) History list Identification data Alignments Option codes Personal settings Channel list Development 2 file version Development 1 file version Installation Default install frequency 000 999 Selected 2nd audio PID: 8191 Selected main audio PID: 99 Selected video PID: 35 Hierarchical modulation: 0 Service ID: 3 Transport stream ID: 2 Network ID: 12871 Original network ID: 12871 Symbol rate: QAM modulation: 64-qam Current frequency: 538 Sub-menu 2 Install end frequency Digital info Test setting Install start frequency Sub-menu 1 Main Menu Sub-menu 3 Alignments 6. EN 39 2011-Apr-22 NVM editor; re key-in type number and production code after SSB replacement To download several settings from the USB stick to the TV To upload several settings from the TV to an USB stick Display information is for development purposes Display information is for development purposes Select Digital only or Digital + Analogue before installation Install end frequency as “999” MHz Install start frequency from “0” MHz Display information is for development purposes Description Q552.2L LA 7. Q552.2L LA 7.1.2 7.1.1 removal of TCON from the SSB (comes with the display) changed power architecture new USB hub (where applicable). back to div. table 19110_053_110421.eps 110421 For details about the chassis block diagrams refer to chapter 9. Block Diagrams. An overview of the TV550 2011 architecture can be found in Figure 7-1. TV550 Architecture Overview Key components of this chassis are: • PNX855xx System-On-Chip (SOC) TV Processor • TX26xx Hybrid Tuner (DVB-T/C, analogue) • STV6110AT DVB-S Satellite Tuner • SII9x87 HDMI Switch • TPA312xD2PWP Class D Power Amplifier • LAN8710 Dual Port Gigabit Ethernet media access controller. Implementation The Q552.2L LA chassis comes with the following stylings: • Berlinale (series xxPFL58xx), • Blockbuster (series xxPFL66xx), • Emmy (series xxPFL76xx), • Sundance (series xxPFL86xx). • • • Figure 7-1 Architecture of TV550 platform 2011 The Q552.2L LA is part of the TV550 platform and uses the (same) PNX855xx chipset. The major deltas versus its predecessor Q551 are: • support of DVB-T2 (“second generation” DVBT) • implementation of “passive” 3D Introduction Notes: • Only new circuits (circuits that are not published recently) are described. • Figures can deviate slightly from the actual situation, due to different set executions. • For a good understanding of the following circuit descriptions, please use the wiring-, block- (see chapter 9. Block Diagrams) and circuit diagrams (see chapter 10. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts).Where necessary, you will find a separate drawing for clarification. 2011-Apr-22 7.1 Circuit Descriptions Index of this chapter: 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Power Supply 7.3 DC/DC Converters 7.4 Front-End Analogue and DVB-T, DVB-C; ISDB-T reception 7.5 Front-End DVB-S(2) reception 7.6 HDMI 7.7 Video and Audio Processing - PNX855xx 7. Circuit Descriptions EN 40 7.1.3 SSB Cell Layout back to div. table Figure 7-2 SSB layout cells (top view) Circuit Descriptions Q552.2L LA EN 41 2011-Apr-22 19110_052_110421.eps 110421 7. - 2 3 - 12 13 14 15 GND1 n.c. pin 11 n.c. pin 13 n.c. A1 n.c. OCD n.c. pin 3 n.c. pin 5 n.c. A2 CN2 to display 1316 - 10 11 12 13 14 15 - 5 - - 4 9 - 3 8 L 2 - N 1 - CN1 Pin 7 Mains Descr. 6 1308 no. - Anode_L n.c. L5 Cathode L4 Cathode L3 Cathode L2 Cathode L1 Cathode R1 Cathode R2 Cathode R3 Cathode R4 Cathode R5 Cathode n.c. Anode_R CN2 to display 1316 Connector Table 7-2 Connector overview 37" sets - 9 - - 8 11 - 7 10 - 6 - L 1 - N Pin 5 CN1 Descr. 4 1308 Mains no. Connector Table 7-1 Connector overview 32" sets - GND1 +24V (AL2_DVBS) POK BL-I-CTRL BL-DIM1 (Vsync) BL-ON-OFF GND_SND +Vsnd (+24V) +12V +12V GND1 GND1 Standby +3V3stdby CN4 to SSB 1M95 - GND1 +24V POK BL-I-CTRL BL-DIM1 BL-ON-OFF GND1 +Vsnd +12V3 +12V3 GND1 GND1 Standby +3V3SB CN4 to SSB 1M95 Connector overview Blockbuster (series xxPFL6600/xx) back to div. table Circuit Descriptions In this manual, no detailed information is available because of design protection issues. 2011-Apr-22 7.2.2 Power Supply Unit 7.2.1 Q552.2L LA All power supplies are a black box for Service. When defective, a new board must be ordered and the defective one must be returned, unless the main fuse of the board is broken. Always replace a defective fuse with one with the correct specifications! This part is available in the regular market. Consult the Philips Service web portal for the order codes of the boards. Power Supply 7. 7.2 EN 42 7.3 12 Cathode 4- n.c. Anode 4+ n.c. Cathode 3- n.c. Anode 3+ n.c. Cathode 2- n.c. Anode 2+ n.c. Cathode 1- n.c. Anode 1+ CN2 to display 1316 Connector - GND1 +24V (AL2_DVBS) POK BL-I-CTRL BL-DIM1 (Vsync) BL-ON-OFF GND_SND +Vsnd (+24V) +12V +12V GND1 GND1 Standby +3V3stdby CN4 to SSB 1M95 Diagram B08A contains the DVB-S2-related DC/DC converters and -stabilizers: • a +24V under-voltage detection circuitry is built around item no. 7T04 • the switching frequency of the 24 to 14...20V switched mode converter is 350 kHz (item no. 7T03 and +V-LNB lines) • the output signal on the +V-LNB line goes to the LNBH23Q (item no. 7T50) • the LNBH23Q (item no. 7T50) sends a feedback signal via the V0-CNTRL line Diagram B03D contains the following linear stabilizers: • +2V5 stabilizer, built around item no. 7UCO • +5V-TUN stabilizer, built around items no. 7UA6 and 7UA7 • +1V2 stabilizer, built around items no. 7UA3 and 7UA4. A +12 V under-voltage detector (see diagram B03C) enables the 12V to 3.3V and 12V to 5V DC/DC converters via the ENABLE-3V3-5V line, and the 12V to 1.8V DC/DC converter via the ENABLE-1V8 line. DETECT2 is the signal going to the Stand-by microcontroller and ENABLE-3V3n is the signal coming from the Stand-by microcontroller. The on-board DC/DC converters deliver the following voltages (depending on set execution): • +3V3-STANDBY, permanent voltage for the Stand-by controller, LED/IR receiver and controls; connector 1M95 pin 1 • +12V, input from the power supply for TV550 common (active mode); connector 1M95 pins 6, 7 and 8 • +24V, input from the power supply for DVB-S2 (in active mode); connector 1M09 pins 1 and 2 • +1V1, core voltage supply for PNX855xx; has to be started up first and switched "off" last (diagram B03B) • +1V2, supply voltage for analogue blocks inside PNX855xx • +1V8, supply voltage for DDR2 (diagram B03B) • +2V5, supply voltage for analogue blocks inside PNX855xx (see diagram B03E) • +3V3, general supply voltage (diagram B03E) • +5V, supply voltage for USB and CAM (diagram B03E) • +5V-TUN, supply voltage for tuner (diagram B03E) • +V-LNB, input voltage for LNB supply IC (item no. 7T50) • +5V-DVBS, input intermediate supply voltage for DVB-S2 (diagram B08A) • +3V3-DVBS, clean voltage for silicon tuner and DVB-S2 channel decoder • +2V5-DVBS, clean voltage for DVB-S2 channel decoder • +1V-DVBS, core voltage for DVB-S2 channel decoder. DC/DC Converters - - 11 - - 10 15 - 9 14 - 8 - - 7 13 - - 4 6 - 3 5 N L CN1 Pin 2 Mains Descr. 1 1308 no. Table 7-3 Connector overview 40" sets + 1V 1 + 1V 8 + 3V 3 5100 m A 2450 m A 2371 m A + 1V 8 + 3V 3 + 5V 5-TUN + 1V 2 + 2V 5 + 5V -TUN Hybrid Tuner with integrated SAW filter and amplifier External ISDB-T channel decoder covering the Brazilian digital terrestrial TV standard Bandpass filter Amplifier PNX85500 SoC TV with integrated analogue demodulator. The Front-End for the DVB-S(2) application consist of the following key components: Front-End DVB-S(2) reception Figure 7-4 Front-End block diagram Brazil region 18770_236_100127.eps 100219 Below find a block diagram of the front-end application for this region. • • • • • The Front-End for the Brazil region consist of the following key components: Brazil region 7.5 550 m A 450 m A 18770_226_100127.eps 100426 + 1V 2 s tabiliz er + 2V 5 s tabiliz er + 5V -TUN s tabiliz er 7.4.1 Figure 7-3 DC/DC converters + 1V 1 dc -dc + 1V 8 dc -dc + 3V 3 dc -dc 196 m A 2179 m A Front-End Analogue and DVB-T, DVB-C; ISDB-T reception + 12V + 5V + 5V 5-TUN 7.4 2919 m A + 5V dc -dc Figures gives a graphical representation of the DC/DC converters with its current consumptions: 196 m A the switching frequency of the +5V-DVBS to +1-DVBS switched mode converter is 900 kHz (item no. 7T00) a delay line for the +2V5-DVBS and +1V-DVBS lines is created with item no. 3T03 (R=10k) and 2T06 (C=100n) a 3.3V to 2.5V linear stabilizer is built around item no. 7T01 a 5V to 3.3V linear stabilizer is built around item no. 7T02. Diagram B08B contains the DVB-S2 LNB supply: • the +V-LNB signal comes from item no. 7T03 • the V0-CTRL signal goes to item no. 7T03 • the LNB-RF1 goes to the LNB. • • • • back to div. table 7.6 7. EN 43 Satellite Tuner; I2C address 0xC6 (bridged via channel decoder) Channel decoder; I2C address 0xD0 LNB switching regulator; I2C address 0x14 Amplifier PNX855xx SoC TV processor with integrated DVB-T and DVB-C channel decoder and analogue demodulator. Q552.2L LA The following multiplexers can be used: Figure 7-6 HDMI input configuration 2011-Apr-22 18770_243_100203.eps 100203 In this platform, the Silicon Image Sil9x87 HDMI multiplexer is implemented. Refer to figure 7-6 HDMI input configuration for the application. HDMI This application supports the following protocols: • Polarization selection via supply voltage (18V = horizontal, 13V = vertical) • Band selection via “toneburst” (22 kHz): tone “on” = “high” band, tone “off” = “low” band • Satellite (LNB) selection via DiSEqC 1.0 protocol • Reception of DVB-S (supporting QPSK encoded signals) and DVB-S2 (supporting QPSK, 8PSK, 16APSK and 32APSK encoded signals), introducing LDPC low-density parity check techniques. Figure 7-5 Front-End block diagram DVB-S(2) reception 18770_237_100127.eps 100219 Below find a block diagram of the front-end application for DVB-S(2) reception. • • • • • Circuit Descriptions • • • TS input AUDIO DEMOD AND DECODE AUDIO IN HDMI RECEIVER SSIF, LR SPDIF HDMI I2C IR ADC SPI 560 MHz MIPS32 24KEf CPU MPEG/H.264 VIDEO DECODER 3D COMB MPEG SYSTEM PROCESSOR UART I2C MEMORY CONTROLLER back to div. table AUDIO OUT AUDIO DACS VIDEO ENCODER LVDS GPIO Flash USB 2.0 SD Ethernet Memory MAC x8 Card DMA BLOCK DRAWING ENGINE 450 MHz AV-DSP AUDIO DSP SCALER, DE-INTERLACE AND NOISE REDUCTION Motion-accurate pixel processing SECONDARY VIDEO OUTPUT AV-PIP SUB-PICTURE PRIMARY VIDEO OUTPUT SPDIF I 2S analog audio analog CVBS LVDS for flat panel display (single, dual or quad channel) 18770_241_100201.eps 100219 For a functional diagram of the PNX855xx, refer to Figure 7-7. Figure 7-7 PNX855xx functional diagram PWM GPIO SYSTEM CONTROLLER (8051) DIGITAL IF VIDEO DECODER DVB-T/C channel decoder CI/CA Low-IF CVBS, Y/C, RGB DVB TS out/in for PCMCIA PNX85500x Multi-standard digital video decoder (MPEG-2, H.264, MPEG-4) Integrated DVB-T/DVB-C channel decoder Integrated CI+ The PNX855xx is the main audio and video processor (or System-on-Chip) for this platform. It has the following features: Video and Audio Processing - PNX855xx 2011-Apr-22 7.7 Integrated motion accurate picture processing (MAPP2) High definition ME/MC 2D LED backlight dimming option Embedded HDMI HDCP keys Extended colour gamut and colour booster Integrated USB2.0 host controller Improved MPEG artefact reduction compared with PNX8543 Security for customers own code/settings (secure flash). The TV550 combines front-end video processing functions, such as DVB-T channel decoding, MPEG-2/H.264 decode, analog video decode and HDMI reception, with advanced back-end video picture improvements. It also includes next generation Motion Accurate Picture Processing (MAPP2). The MAPP2 technology provides state-of-the-art motion artifact reduction with movie judder cancellation, motion sharpness and vivid colour management. High flat panel screen resolutions and refresh rates are supported with formats including 1366 × 768 @ 100Hz/120Hz and 1920 × 1080 @ 100Hz/120Hz. The combination of Ethernet, CI+ and H.264 supports new TV experiences with IPTV and VOD. On top of that, optional support is available for 2D dimming in combination with LED backlights for optimum contrast and power savings up to 50%. • Circuit Descriptions The Sil9x87 has the following specifications: • +5V detection mechanism • Stable clock detection mechanism • Integrated EDID • RT control • HPD control • Sync detection • TMDS output control • CEC control • EDID stored in Sil9x87, therefore there are no EDID pins on the SSB. Q552.2L LA • • • • • • • 7. Sil9187A (does not support “Instaport” technology for fast switching between input signals) • Sil9287B (supports “Instaport” technology for fast switching between input signals). The hardware default I2C addresses are: • Sil9187A: 0xB0/0xB2 (random: software workaround) • Sil9287B: 0xB2 (fixed). • EN 44 TT #1 Serial Interface Engine Regulator Port #1 OC Sense Switch Driver/ LED Drivers ... Port Controller OC Sense Switch Driver/ LED Drivers Port #x TT #x Controller Serial Interface SDA SCL To EEPROM or SMBus Master USB Data OC Port Downstream Sense Power Switch/ LED Drivers PHY#x ... PLL 24 MHz Crystal 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 USBDM_UP USBDP_UP XTALOUT XTALIN / CLKIN PLLFILT RBIAS VDD33 Ground Pad (must be connected to VSS) SMSC USB2512/12A/12B USB2512i/12Ai/12Bi (Top View QFN-36) NC OCS_N[2] PRTPWR[2] / BC_EN[2]* VDD33 CRFILT OCS_N[1] PRTPWR[1] / BC_EN[1]* TEST VDD33 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 back to div. table Figure 8-1 Internal block diagram and pin configuration Indicates pins on the bottom of the device. 28 VDD33 1 USBDM_DN[1] SUSP_IND / LOCAL_PWR / NON_REM[0] 2 USBDP_DN[1] Pinning information VBUS_DET The LED port indicators only apply to USB2513i. RESET_N 26 3 USBDM_DN[2] Note : The ‘x’ indicates the number of available downstream ports: 2, 3, 4, or 7. OC USB Data Port Downstream Sense Power Switch/ LED Drivers PHY#1 Routing & Port Re-Ordering Logic CRFILT Regulator 3.3 V HS_IND / CFG_SEL[1] 25 4 3.3 V Upstream PHY BusPower Detect/ Vbus Pulse Repeater Upstream USB Data To Upstream VBUS SCL / SMBCLK / CFG_SEL[0] 24 5 VDD33 USBDP_DN[2] Block diagram Diagram USB Hub B01C, USB2513B (IC 7F25) Q552.2L LA 8. EN 45 2011-Apr-22 18770_301_100217.eps 100217 electrical diagrams (with the exception of “memory” and “logic” ICs). 6 NC 8.1 This chapter shows the internal block diagrams and pin configurations of ICs that are drawn as “black boxes” in the 8. IC Data Sheets IC Data Sheets 7 NC 27 VDD33 23 SDA / SMBDATA / NON_REM[1] 22 NC 21 NC 8 NC 19 NC 20 9 NC 8. Q552.2L LA IC Data Sheets A1 A0 A1 A2 6 5 3 4 OS GND back to div. table Figure 8-2 Pin configuration A0 7 2 SCL OS 18770_300_100217.eps 100217 VCC 8 1 LM75BDP SCL SDA SDA Pinning information A2 POWER-ON RESET GND THYST REGISTER COMPARATOR/ INTERRUPT LOGIC CONTROL AND INTERFACE TOS REGISTER TIMER OSCILLATOR TEMPERATURE REGISTER COUNTER BAND GAP TEMP SENSOR 11-BIT SIGMA-DELTA A-to-D CONVERTER CONFIGURATION REGISTER POINTER REGISTER VCC BIAS REFERENCE LM75B Block diagram Diagram Temp sensor & headphone B01J, LM75BDP (IC 7FD1) 2011-Apr-22 8.2 EN 46 8.3 AUDIO IN HDMI RECEIVER SPDIF HDMI A B C D E F G H J K L M N P R T U V W Y AA AB AC AD AE AF ball A1 index area PWM Px_x ADC SPI I2C AUDIO OUT AUDIO DACS VIDEO ENCODER LVDS GPIO Flash USB 2.0 SD Ethernet Memory MAC x 10 Card PNX8550xE UART Scatter/Gather TS Demux DRAWING ENGINE 450 MHz AV-DSP AUDIO DSP SCALER, DE-INTERLACE AND NOISE REDUCTION Motion-accurate pixel processing SECONDARY VIDEO OUTPUT AV-PIP SUB-PICTURE PRIMARY VIDEO OUTPUT Transparent top view 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 IR 500 MHz MIPS32 24KEf CPU MULTISTANDARD VIDEO DECODER 3D COMB MPEG SYSTEM PROCESSOR MEMORY CONTROLLER back to div. table SPDIF I2S analog audio analog Y/C analog CVBS LVDS for flat panel display (single, dual or quad channel) Q552.2L LA Figure 8-3 Internal block diagram and pin configuration Pinning information I2C SYSTEM CONTROLLER (8051) AUDIO DEMOD AND DECODE DIGITAL IF VIDEO DECODER DVB-T/C channel decoder CI/CA PNX8550x SSIF, LR Direct-IF Low-IF CVBS, Y/C, RGB DVB TS out/in for PCMCIA TS input Block diagram Diagram NANDflash - conditional access B02A, PNX855xx (IC7S00) IC Data Sheets EN 47 2011-Apr-22 18770_308_100217.eps 100217 8. 8. Q552.2L LA 1 F 1 F 1 F GAIN1 GAIN0 VCLAMP PVCCR PVCCL BSL LOUT PGNDL 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 PWP (TSSOP) PACKAGE (TOP VIEW) MUTE SD AVCC AGND BYPASS ROUT RIN PGNDR BSR LIN back to div. table 22 H PGNDL PGNDL LOUT BSL AVCC AVCC GAIN0 GAIN1 BSR ROUT PGNDR PGNDR 1 F 0.22 F 22 H 0.68 F 0.68 F 0.22 F Figure 8-4 Internal block diagram and pin configuration PVCCL SD PVCCL MUTE LIN RIN BYPASS AGND AGND PVCCR VCLAMP PVCCR Pinning information Shutdown Control Block diagram TPA3120D2 IC Data Sheets Diagram Audio B03A, TPA312xD2PWP (IC7D10) 2011-Apr-22 8.4 EN 48 } I_18020_142.eps 100402 Control 470 F 470 F 8.5 DRVL2 LL2 DRVH2 17 16 15 9 10 11 12 13 14 NC VFB2 VO2 EN2 NC VBST2 18 19 20 21 PGND2 TRIP2 TEST2 V5FILT VREG5 8 22 7 GND TEST1 TRIP1 VIN 23 6 24 NC PGND1 25 5 LL1 DRVL1 26 4 3 EN1 DRVH1 27 28 VO1 2 NC VFB1 1 VBST1 Q552.2L LA back to div. table Figure 8-5 Internal block diagram and pin configuration Pinning information Block diagram Diagram DC/DC B03B, TPS53126PW (IC7U03) IC Data Sheets TPS53124 EN 49 2011-Apr-22 18310_300_090319.eps 100416 8. 8. Q552.2L LA IC Data Sheets PowerSO-8 back to div. table Figure 8-6 Internal block diagram and pin configuration DFN8 (4 × 4) Pinning information Block diagram Diagram DC/DC B03E, ST1S10PH (IC 7UD0) 2011-Apr-22 8.6 EN 50 I_18010_083.eps 100402 8.7 DPAK LD1117DT Q552.2L LA back to div. table Figure 8-7 Internal block diagram and pin configuration Pinning information Block diagram Diagram DC/DC B03E, LD1117DT25 (IC 7UD2) IC Data Sheets 8. 2011-Apr-22 F_15710_166.eps 100402 EN 51 Q552.2L LA IC Data Sheets 2011-Apr-22 SMI 10M Rx Logic 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 LED1/REGOFF XTAL2 XTAL1/CLKIN VDDCR RXCLK/PHYAD1 RXD3/PHYAD2 Squelch & Filters 100M PLL Analog-toDigital 100M Transmitter VSS SMSC LAN8710/LAN8710i 32 PIN QFN (Top View) TXD2 TXD1 TXD0 TXEN TXCLK nRST nINT/TXER/TXD4 MDC 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 back to div. table PHYAD[0:2] PHY Address Latches 18770_302_100217.eps 100217 RBIAS Central Bias LED1 LED2 LED Circuitry XTAL2 XTAL1/CLKIN nINT PLL RXP / RXN TXP / TXN Interrupt Generator MDIX Control HP Auto-MDIX 24 Figure 8-8 Internal block diagram and pin configuration 1 VDD2A LED2/nINTSEL 10M PLL 10M Transmitter Transmit Section 100M Tx Logic DSP System: Clock Data Recovery Equalizer Receive Section 100M Rx Logic Management Control Pinning information MDC MDIO CRS COL/CRS_DV RXD[0:3] RXDV RXER RXCLK TXD[0:3] TXEN TXER TXCLK RMIISEL nRST Reset Control 10M Tx Logic 9 RXD2/RMIISEL AutoNegotiation 10 RXD1/MODE1 MODE Control 11 MODE0 MODE1 MODE2 RBIAS 12 VDDIO RXD0/MDE0 Block diagram Diagram Ethernet & Service B04C, LAN8710A-EZKH (IC 7E10) 8. 13 RXER/RXD4/PHYAD0 8.8 EN 52 14 CRS 32 RXP 31 RXN 30 TXP 29 TXN 28 VDD1A 27 RXDV 26 15 COL/CRS_DV/MODE2 TXD3 25 16 MDIO RMII / MII Logic 8.9 Q552.2L LA back to div. table Figure 8-9 Internal block diagram and pin configuration Pinning information Block diagram Diagram HDMI B04D, SII9x87B (IC 7EC1) IC Data Sheets EN 53 2011-Apr-22 18770_303_100217.eps 100217 8. 8. Q552.2L LA IC Data Sheets 2011-Apr-22 BYPASS IN 2− SHUTDOWN 3 6 5 VDD/2 − + − + Bias Control 8 7 6 5 1 2 3 4 VDD VO2 IN2− SHUTDOWN 4 VO2 7 VO1 1 VDD 8 back to div. table Figure 8-10 Internal block diagram and pin configuration VO1 IN1− BYPASS GND D OR DGN PACKAGE (TOP VIEW) IN 1− 2 Pinning information Block diagram 8.10 Diagram Headphone B04E, TPA6111A2DGN (IC 7EE1) EN 54 18770_309_100217.eps 100217 (5216) 18P *AMBILIGHT MODULE 1M86 (1162) AL (1005) 1M95 (PSU) 1. +3V3STDBY 2. STANDBY 3. GND 4. GND 5. +12V 6. +12V 7. +VSND 8. GND_SND 9. BL-ON-OFF 10. BL-DIM1 11. BL-I-CTRL 12. POK 13. +24V 14. GND1 1316 (PSU) 1. ANODE 1 2. NC 3. CATHODE 1 4. GND 5. ANODE 2 6. NC 7. CATHODE 2 8. NC 9. ANODE 3 10. NC 11. CATHODE 3 12. NC 13. ANODE 4 14. NC 15. CATHODE 4 1. N 2. L 1308 (PSU) (8308) MAINS SWITCH 130 8 2P 14P 10P MAIN POWER SUPPLY 32" PLDC-P005A 1M95 1316 *AMBILIGHT ONLY APLICABLE FOR EMMY STYLING LOUDSPEAKER WIRING DIAGRAM 32" BLOCKBUSTER / EMMY 9-1 Wiring diagram Blockbuster/Emmy 32" TO DISPLAY SUPPLY LEADING EDGE 8M95 2011-Feb-18 back to div. table J1 8P C1 41P 1. +3V3-STANDBY 2. STANDBY 3. GND 4. GND 5. +12VIN 6. +12VIN 7. +24V-AUDIO-POWER 8. GND 9. LAMP-ON 10. BACKLIGHT-PWM_BL-VS 11. BACKLIGHT-BOOST 12. POWER-OK 13. +24V GND 1M95 (B03C) 8G50 TO DISPLAY (1108) LCD DISPLAY (1004) 8G51 (5213) IR/LED/CONTROL BOARD C2 51P 8M85 LOUDSPEAKER EN 55 TO DISPLAY 9. B SPDIF 1. +VDISP 2. +VDISP 3. +VDISP 4. +VDISP | | 51. CTRL-DISP 14P 1M95 HDMI HDMI 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. LIGHT-SENSOR GND RC LED-2 +3V3-STANDBY LED-1 KEYBOARD +5V 1M19 (B09A) HDMI 3139 123 6521.x (1150) SSB LEFT-SPEAKER GND-AUDIO GND-AUDIO RIGHT-SPEAKER RIGHT-SPEAKER 1G51 (B06B) 1. 2. 3. 4. 1735 (B03A) 1D38 (B03A) ETHER NET Q552.2L LA 8M59 SD-CARD READER VGA PHONE LOUDSPEAKER 15. GND_AL 16. GND_AL 17. GND_AL 18. GND_AL 19. GND_AL 20. N.C. 21. +24V 22. +24V 23. +24V 24. +24V 25. +24V 26. +24V (5216) 19110_008_110323.eps 110421 1M59 (B09A) 1. AMBI-SPI-CLK-OUT 2. GND 3. AMBI-SPI-SDO-OUT 4. AMBI-SPI-SDI-OUT-GI 5. V-AMBI 6. AMBI-PWM-CLK_B2 7. GND 8. AMBI-SPI-CS-OUTn_R2 9. AMBI-LATCH1_G2 10. V-AMBI 11. AMBI-BLANK_R1 12. AMBI-PROG_B1 13. AMBI-LATCH2_DIS 14. AMBI-TEMP 26P 1M59 TUNER 9. Block Diagrams 8308 41P 1D38 1G51 1G50 3P 51P 8P 1M19 1M85 *AMBILIGHT MODULE Block Diagrams 26P USB HDMI 18P (1161) AL 1M83 SPDIF INLET 1308 (PSU) LEADING EDGE LCD DISPLAY (1004) J1 C1 41P TO DISPLAY 14P 1M95 (B03C) 8G50 1D38 (B03A) ETHER NET 1M99 1308 2P B HDMI HDMI HDMI 3139 123 6521.x (1150) SSB 14P 1M95 VGA 1M95 (PSU) 1. +3V3STDBY 2. STANDBY 3. GND 4. GND 5. +12V 6. +12V 7. +VSND 8. GND_SND 9. BL-ON-OFF 10. BL-DIM1 11. BL-I-CTRL 12. POK 13. +24V 14. GND1 1316 (PSU) 1. ANODE 1 2. NC 3. CATHODE 1 4. GND 5. ANODE 2 6. NC 7. CATHODE 2 8. NC 9. ANODE 3 10. NC 11. CATHODE 3 12. NC 13. ANODE 4 14. NC 15. CATHODE 4 *AMBILIGHT ONLY APLICABLE FOR EMMY STYLING (8308) 1. N 2. L div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to (1108) IR/LED/CONTROL BOARD 8P 1. +3V3-STANDBY 2. STANDBY 3. GND 4. GND 5. +12VIN 6. +12VIN 7. +24V-AUDIO-POWER 8. GND 9. LAMP-ON 10. BACKLIGHT-PWM_BL-VS 11. BACKLIGHT-BOOST 12. POWER-OK 13. +24V GND 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. LIGHT-SENSOR GND RC LED-2 +3V3-STANDBY LED-1 KEYBOARD +5V 1M19 (B09A) 1. LEFT-SPEAKER 2. GND-AUDIO 3. RIGHT-SPEAKER PHONE 26P 1M59 1. AMBI-SPI-CLK-OUT 2. GND 3. AMBI-SPI-SDO-OUT 4. AMBI-SPI-SDI-OUT-GI 5. V-AMBI 6. AMBI-PWM-CLK_B2 7. GND 8. AMBI-SPI-CS-OUTn_R2 9. AMBI-LATCH1_G2 10. V-AMBI 11. AMBI-BLANK_R1 12. AMBI-PROG_B1 13. AMBI-LATCH2_DIS 14. AMBI-TEMP 1. +VDISP 2. +VDISP 3. +VDISP 4. +VDISP | | 51. CTRL-DISP 15. GND_AL 16. GND_AL 17. GND_AL 18. GND_AL 19. GND_AL 20. N.C. 21. +24V 22. +24V 23. +24V 24. +24V 25. +24V 26. +24V 19110_009_110323.eps 110421 1M59 (B09A) 1G51 (B06B) (5216) C2 51P TO DISPLAY 8G51 8M95 SPDIF LOUDSPEAKER MAINS SWITCH (1005) MAIN POWER SUPPLY 40" PLDE-P008A 46" PLDG-P010A TO DISPLY SUPPLT EN 56 8M59 (5216) INLET 8308 10P 1316 9. TUNER LOUDSPEAKER (5213) LOUDSPEAKER WIRING DIAGRAM 40"- 46" BLOCKBUSTER / EMMY 9-2 Wiring diagram Blockbuster/Emmy 40" - 46" 18P *AMBILIGHT MODULE 24 LED 41P 1D38 1G51 1G50 3P 51P 8P 1M19 1M86 (1162) AL SD-CARD READER Q552.2L LA SPDIF 1M85 *AMBILIGHT MODULE 24 LED Block Diagrams 26P USB HDMI 18P (1161) AL 1M83 B01H HDMI 1 2 HDMI SIDE CONNECTOR 19 18 HDMI 3 CONNECTOR 1 2 19 18 HDMI 2 CONNECTOR HDMI 1 CONNECTOR 23 RXD 22 DRX1DRX0+ 20 DRXC- 12 69 RXA 68 ARX2ARX1+ ARX1ARX0+ 3 BRXC- 17 16 15 14 CRX2CRX1+ CRX1CRX0+ +3V3-HDMI 12 CRXC- 12 9,27,64 11 13 CRX0- CRXC+ 9 10 4 6 7 3 18 CRX2+ 1 1P02 2 BRXC+ 12 1 3 BRX0- 9 10 VCC33 RXC 5 RXB 4 BRX1BRX0+ 4 6 7 7 6 BRX2BRX1+ 3 8 BRX2+ 1 1P03 ARXC- OPTIONAL 66 ARXC+ 12 65 67 ARX0- 9 10 4 6 7 71 70 ARX2+ 1 72 19 21 DRX0- DRXC+ 9 10 TX2_N TX2_P TX1_N IF+ IF- BANDPASS FILTER 42 PNX-IF-AGC 30 29 9 YPBPR1-PB YPBPR1-SYNCIN1 YPBPR1-PR B01I VGA VIDEO 3S0W B02E *6000/7000 SERIE MUX SII9187 NON INSTAPORT 8000 SERIE MUX SII9287 INSTAPORT +3V3 HDMIA-RX2- HDMIA-RX1- HDMIA-RX0HDMIA-RX1+ HDMIA-RX0+ HDMIA-RXC+ HDMIA-RXC- V-SYNC-VGA H-SYNC-VGA HDMIA-RX2+ 3 13 14 R-VGA AV2-CVBS AV3-PB AV3-Y AV3-PR G-VGA B-VGA 3E89 3E87 3E90 PNX-IF-N PNX-IF-P RESET-SYSTEMn 57 VGA CONNECTOR TS-FE-DATA 2 2 19 18 60 TS-FE-VALID TS-FE-SOP TS-FE-CLOCK 1 1E05 1E08 B04B ANALOGUE EXTERNALS B YPBPR 1E01 B04A ANALOGUE EXTERNALS A 2F79 2F75 3F81 3F80 IF AGC 58 59 61 59 56 62 TXC_P 63 TXC_N 60 TX0_P 61 TX0_N 58 TX1_P HDMI SWITCH 25 24 DRX2DRX1+ 26 DRX2+ 1P04 TUN-IF-N 11 *7EC1 SII9187BC SII9287BC 3 4 6 7 TUN-IF-P 10 9 B04D HDMI IF-OUT2 IF-OUT1 1 1P05 RF IN 4MHZ_REF MAIN HYBRID TUNER 1T01 FA2327 DEMODULATOR (ISDB-T) 7FE0 TC90517FG 1FE0 B01K TUNER BRASIL 5 1 10 6 1 2 19 18 1 2 19 18 15 11 25M4 B01F TUNER CVBS-_Y2 PB_B1 Y_G1 PR_R_C1 IF_AGC TUNER_N TUNER_P W24 RREF div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to W25 RXC_A_P W26 RXC_A_N V25 RX2_A_P V26 RX2_A_N U25 RX1_A_P U26 RX1_A_N T25 RX0_A_P T26 RX0_A_N B02C HDMI_DV AF16 VGA_R AD16 VGA_G AE16 VGA_B AB18 HSYNC_IN AC18 VSYNC_IN AB14 AD15 AE15 AC15 AD12 AF12 AE12 B02I ANALOG VIDEO R23 TNR_SER1_MIVAL R22 TNR_SER1_SOP T22 TNR_SER1_MICLK T21 TNR_SER1_DATA B02A VIDEO STREAM 7S00 PNX85537EB B02 PNX85500 XIO_D A DQ VREF_1 VREF_2 B02B MEMORY NAND_CE1 NAND_RDY1 NAND_WP_ B02A FLASH LOUT4 LOUT3 LOUT2 LOUT1 USB_DN USB_DP B02E CONROL B02F LVDS XIO-D(00-07) A2 V1 21,37 SDRAM 128Mx8 7B00 H5PS1G83E B05A DDR A1 E2 VCC NAND FLASH DDR2-VREF-CTRL2 DDR2-VREF-CTRL3 9 7 19 1FL5 SDRAM 128Mx8 7B02 H5PS1G83E +3V3 7F20 H27U4G8F2DTR-BC B01B FLASH USB-DM USB-DP E21 NAND-CE1n F21 NAND-RDY1n NAND-WPn A21 R25 R26 B01C USB HUB B06B VIDEO OUT - LVDS D(0-7) 9-3 Block Diagram Video VDDL VREF VIDEO D(8-15) EN 57 A1 E2 VDDL VREF 21 18 17 22 9F26 9 RESET-USBn 14 13 SDRAM 128Mx8 7B03 H5PS1G83E 42 USB HUB 10 9F25 7FL5 CY7C65631 PX4 PX3 PX2 PX1 24M D(16-23) 9. A1 E2 VDDL VREF Q552.2L LA D(24-31) Block Diagrams 4 2 3 TO DISPLAY TO DISPLAY SIDE USB CONNECTOR SIDE USB CONNECTOR ONLY FOR 8000 SERIE 19110_005_110309.eps 110321 DDR2-VREF-DDR +1V8 DDR2-A(0-14) 4 2 3 +5V-USB2 1P07 1 SDRAM 128Mx8 A1 E2 1 3 2 4 40 40 49 50 1G51 51 41 +5V-USB1 1P08 1 I2C N.C. N.C. 3 3 2 1G50 1 DDR2-D(0-31) 7B01 H5PS1G83E B02G USB2-DM USB2-DP USB1-DM USB1-DP +VDISP VDDL VREF 1 3 2 4 1 3 2 4 PNX85537 HDMI SIDE CONNECTOR 23 RXD 22 DRX1DRX0+ 20 DRXC- 12 HDMI 2 CONNECTOR HDMI 1 CONNECTOR 5 RXB 4 BRX1BRX0+ BRXC- 12 15 RXC 14 CRX1CRX0+ CRXC- 12 14 12 11 13 CRX0- CRXC+ 9 10 2F79 2F75 3F81 3F80 IF+ IF- IF AGC 2 4 DIGITAL AUDIO OUT VGA AUDIO AUDIO IN L+R eHDMI+ 1E07 1E10 1E09 1E08 1 2 1 3 4 6 +3V3 1 3 2 TS-FE-DATA TS-FE-VALID TS-FE-SOP TS-FE-CLOCK AUDIO-IN1-R AUDIO-IN1-L PNX-IF-N PNX-IF-P RESET-SYSTEMn B02E 8 +3V3 +3V3 HDMIA-RX2- HDMIA-RX2+ HDMIA-RX1- HDMIA-RX0HDMIA-RX1+ HDMIA-RX0+ 3S0W SEL-HDMI-ARC SPDIF-OUT-PNX HDMIA-RXC+ HDMIA-RXC- 5 4 7S09 74LVC00 2 3 & 1 AUDIO-IN4-R AUDIO-IN4-L AUDIO-IN3-R AUDIO-IN3-L *6000/7000 SERIE MUX SII9187 NON INSTAPORT 8000 SERIE MUX SII9287 INSTAPORT 6000/7000 SERIES SPDIF-OUT 8000 SERIES SPDIF-OPT B04B ANALOGUE EXTERNALS B AUDIO IN L+R 1E02 19 18 60 58 59 61 B02D PNX85500: AUDIO BANDPASS FILTER 42 PNX-IF-AGC 30 29 9 B04A ANALOGUE EXTERNALS A 5EC2 62 TXC_P 63 TXC_N 60 TX0_P 61 TX0_N 58 TX1_P 59 TX1_N 56 TX2_P 57 TX2_N ARC-eHDMI+ 17 16 CRX2CRX1+ 4 6 7 3 18 CRX2+ 9,27,64 1 +3V3-HDMI 1P02 2 1 3 BRX0- BRXC+ 9 10 VCC33 7 6 BRX2BRX1+ 3 4 6 7 BRX2+ 8 65 70 1 1P03 OPTIONAL ARXC- 12 HDMI 3 CONNECTOR 66 ARXC+ ARX0- 9 10 69 68 RXA 67 71 72 ARX1ARX0+ ARX2ARX1+ 3 4 6 7 ARX2+ 1 19 21 DRX0- DRXC+ 9 10 HDMI SWITCH 25 24 26 DRX2DRX1+ 1P04 TUN-IF-N 11 *7EC1 SII9187BCNU SII9287BCNU 3 4 6 7 TUN-IF-P 10 9 B04D HDMI IF-OUT2 IF-OUT1 DRX2+ RF IN 4MHZ_REF MAIN HYBRID TUNER DEMODULATOR (ISDB-T) 7FE0 TC90517FG 1FE0 1T01 FA2327 1 1P05 B01H HDMI 1 2 19 18 1 2 19 18 1 2 19 18 1 2 19 18 25M4 B01K TUNER BRASIL B02D AUDIO IF_AGC TUNER_N TUNER_P B02C HDMI_DV P0_4 B02G STANDBY SPDIF_OUT AIN4_R AIN4_L AIN3_R AIN3_L AIN1_R W24 RREF W25 RXC_A_P W26 RXC_A_N V25 RX2_A_P V26 RX2_A_N U25 RX1_A_P U26 RX1_A_N T25 RX0_A_P T26 RX0_A_N AF18 AF5 AC9 AD9 AF9 AE9 AF10 AE10 AIN1_L AD12 AF12 AE12 B02I ANALOG VIDEO R23 TNR_SER1_MIVAL R22 TNR_SER1_SOP T22 TNR_SER1_MICLK T21 TNR_SER1_DATA B02A VIDEO STREAM 7S00 PNX85537EB B02 PNX85500 div. table PNX85537 2011-Feb-18 back to ADAC_2 ADAC_1 XIO_D A DQ VREF_1 VREF_2 B02B MEMORY NAND_CE1 NAND_RDY1 NAND_WP_ B02A FLASH USB_DN USB_DP B02E CONROL ADAC4 ADAC3 PO_6 PO_7 B02G STANDBY B02D AUDIO A2 V1 DETECT2 XIO-D(00-07) SDRAM 128Mx8 7B00 H5PS1G83EFR B05A DDR 9 7 19 DDR2-VREF-CTRL2 DDR2-VREF-CTRL3 A1 E2 VCC NAND FLASH +3V3 7EE0-1 SDRAM 128Mx8 7B02 H5PS1G83EFR 21,37 7F20 H27U4G8F2DTR-BC B01B FLASH USB-DM USB-DP B01C USB HUB ADAC(4) ADAC(3) RESET-AUDIO B04E HEADPHONE B03C A-PLOP 7D15 7D11 MAINS SWITCH DETECT 8 10 ADAC(2) AUDIO-MUTE-UP 14 12 ADAC(1) 7S05 LM324P A1 E2 7EE0-2 A-STBY A-STBY A-PLOP -AUDIO-R +AUDIO-L B02D PNX85500: AUDIO B03A AUDIO E21 NAND-CE1n F21 NAND-RDY1n NAND-WPn A21 R25 R26 AD6 AF7 AB19 AC19 AE7 AD7 D(0-7) B01F TUNER D(16-23) 9-4 Block Diagram Audio VDDL VREF SDRAM 128Mx8 A1 E2 6 5 IN-R IN-L 21 18 17 2 22 IN-2 IN-1 42 9 A1 E2 DDR2-VREF-DDR +1V8 DDR2-A(0-14) SDRAM 128Mx8 B02G USB2-DM USB2-DP USB1-DM USB1-DP RESET-USBn DDR2-D(0-31) 14 13 10 +3V3 1 3 2 1328 4 2 3 +5V-USB2 1P07 1 4 2 3 +5V-USB1 1P08 1 AMP2 7 8 AMP1 7B01 H5PS1G83EFR USB HUB 7FL5 CY7C65631 9F25 VDD VO_2 VO_1 SHUTDOWN 5D03 3 2 1D38 1 4 3 2 1735 1 SPEAKERS RES 19110_006_110309.eps 110321 ONLY FOR 8000 SERIE USB 2 SIDE CONNECTOR USB 1 SIDE CONNECTOR HEADPHONE OUT 3.5mm B01J TEMP SENSOR + HEADPHONE 1 B04A B03A 7D03 STANDBY & PROTECTION RIGHT-SPEAKER 15 HEADPHONE AMPLIFIER 9F26 6 2 5 OUT-R LEFT-SPEAKER +24V-AUDIO-POWER 22 5D07 10,12 5D08 1,3 7EE1 TPA6111A2DGN A-PLOP SD OUT-L PVCC_R PVCC_L CLASS D POWER AMPLIFIER 7D10 TPA3123D2PWP 4 MUTE B04E 7B03 H5PS1G83EFR 1FL5 AUDIO D(8-15) EN 58 VDDL VREF 9. VDDL VREF 24M Q552.2L LA D(24-31) Block Diagrams VDDL VREF 1 3 2 4 1 3 2 4 SD-CARD ETHERNET + SERVICE B04C B04D 5 6 7 8 6 2 5 8 3 6 29 IF- +5V HDMI 4x HDMI CONNECTOR LED-1 LED-2 ARX-HOTPLUG 1P02-19 BRX-HOTPLUG 1P03-19 CRX-HOTPLUG 1P04-19 DRX-HOTPLUG 1P05-19 TO PIN: 1P02-13 1P03-13 PCEC-HDMI 1P04-13 1P05-13 B03H B03C B02E 45 41 31 35 18 19 7 4 3 5 HDMI SWITCH 7EC1 SII9187BCNU SII9287BCNU 7U43 9 7 19 +3V3 3S0W HDMIA-RX CEC-HDMI W24 AF19 AB22 AC20 AA22 AD23 AD26 AD19 AC25 AE26 LCD-PWR-ONn 7EC0 EF B02A VIDEO STREAM B02A FLASH RREF RX B02C HDMI_DV P1_2 P2_0 P3_2 P3_3 P5_0 PWM_0 PWM_1 P1_0 P5_1 B02G STANDBY XIO_D E21 NAND_CE1 F21 NAND_RDY1 A21 NAND_WP_ DETECT2 RESET-SYSTEMn KEYBOARD LED1 LED2 RC LIGHT-SENSOR +3V3 XIO-D(00-07) NAND-CE1n NAND-RDY1n NAND-WPn TS-FE-DATA TS-FE-VALID TS-FE-SOP TS-FE-CLOCK RXCLK TXCLK R23 TNR_SER1_MIVAL R22 TNR_SER1_SOP T22 TNR_SER1_MICLK T21 TNR_SER1_DATA AA2 B02G AA3 RXD TXD W2 CC_DAT3 W6 CMD W1 CLK W5 DAT_0 W4 DAT_1 W3 DAT_2 U6 SDCD V6 SDWP ETH-TXCLK DC / DC VCC 12,37 9U41 4 5 PNX85500 7S00 PNX85537EB B02E ETHERNET B02A ETH-RXCLK ETH-RXD ETH-TXD SDIO-DAT2 SDIO-CDn SDIO-WP SDIO-DAT1 SDIO-DAT3 SDIO-CMD SDIO-CLK SDIO-DAT0 RESET-ETHERNETn NAND FLASH B03C 7 20 7F20 H27U4G8F2DTR 19 ETHERNET SUNDANCE / INFINITY +3V3-STANDBY 31 30 28 29 7E10 LAN8710A-EZK 7FJ0 CXD2820R RESET-SYSTEMn 30 IF+ ETH-TXP ETH-TXN ETH-RXP ETH-RXN PNX85500: STANDBY CONTROLLER TO IR / LED BOARD AND KEYBOARD CONTROL 2 3 4 4 7 3 CONNECTORS COMP B09A B02E B01F 1M19 1 FLASH B01B 9 10 12 5 7 8 1 2 1N00 1 2 B01F *1M20 1 TUNER BRASIL ETHERNET CONNECTOR RJ45 SD-CARD CONNECTOR Pin9 B1K B02G Pin1 Pin2 Pin3 Pin4 Pin6 Pin5 Pin8 Pin7 1P09 1FE0 B01D 1E70 25M4 CONTROL + CLOCK SIGNALS DEMODULATOR (ISDB-T) 25M N5 N4 Y22 R25 R26 AD5 AC5 V22 D(0-7) 41 40 39 PNX-SPI-CLK PNX-SPI-SDI PNX-SPI-SDO AF20 AB19 AC19 AC21 1E06 B01F B01C 3 2 INP OUTP GND STANDBY RESET-AUDIO AUDIO-MUTE-UP POWER-OK RESET-ETHERNETn LAMP-ON SEL-HDMI-ARC 1 B03A B04E B04C B02D B01C 7S20 NCP303LSN28G TXD-UP 21 18 17 B01E 14 AMBI-TEMP 13 14 10 9 VCC DC / DC 512K SPI-PROG FF29 SDM FF04 8 USB-DM2 USB-DP2 BACKLIGHT-BOOST BACKLIGHT-PWM_BL-VS 4 2 3 B03C DETECT2 ENABLE-1V8 SIDE USB CONNECTOR OPTIONAL TO AMBILIGHT MODULE SIDE USB CONNECTOR ONLY FOR 8000 SERIE B03E 2 19110_007_110318.eps 110321 1M95 9 10 TO 11 POWER SUPPLY 12 B02G B03A B03B B03D RES 1 LEVEL SHIFTED 2 FOR DEBUG USE 4 ONLY 5 1F51 3 4 2 3 +5V-USB2 1P07 1 ENABLE-3V3-5V +3V3-STANDBY BACKLIGHT-BOOST FLASH +12V +3V3-STANDBY B06C 11 12 13 AMBI-BLANK_R1 AMBI-PROG_B1 AMBI-LATCH2_DIS USB-DM1 USB-DP1 9 AMBI-LATCH1_G2 PNX85500-CONTROL 22 USB HUB 7FL5 CY7C65631 7F52 M25P05-AVMN6P B03C 1 5 2 PNX-SPI-CSBn PNX-SPI-SDO PNX-SPI-SDI RXD-UP 6 3 PNX-SPI-CLK 9F25 4 6 8 +5V-USB1 1P08 1 3 AMBI-SPI-SDO-OUT AMBI-SPI-SDI-OUT_G1 AMBI-PWM-CLK_B2 AMBI-SPI-CS-OUTn_R2 ONLY FOR 6000/7000 SERIE 9F26 USB HUB 1M59 1 AMBI-SPI-CLK-OUT NON DVBS CONNECTOR BOARD 9CH0 B01E PNX-SPI-WPn +3V3-STANDBY SDM RESET-STBYn SPI-PROG B03C B09A F8 E8 SDRAM 128Mx8 7B01 H5PS1G83EFR UART SERVICE CONNECTOR RESET-STBYn PNX85500: STANDBY CONTROLLER 1 3 BOOST-PWM DDR2-A(0-13) F8 E8 SDRAM 128Mx8 B01K B02G TXD1-MIPS RESET-USBn AE18 VIO DDR2-D(0-31) 7B03 H5PS1G83EFR BACKLIGHT-PWM_BL-VS 2 26 32 20 19 28 31 30 23 29 22 27 RXD1-MIPS ETHERNET + SERVICE RESET-SYSTEMn SELECT-SAW ENABLE-3V3n AF18 AE20 D(16-23) CPLD VCCIO USB-DM USB-DP PNX85500: MIPS B06C B02G B04C B02E BACKLIGHT-PWM 9GA0 7 43 3 3D-LR PXCLK54 PNX-SPI-CS-BLn B02G 5 B03D B03B PNX-SPI-CSBn SENSE+1V2 7GA0 XC9572XL F8 E8 SDRAM 128Mx8 AMBILIGHT CPLD DDR-CLK_N DDR-CLK_P SENSE+1V1 B06C F8 E8 SDRAM 128Mx8 7B02 H5PS1G83EFR AD21 div. table DDR 7B00 H5PS1G83EFR B05A D(8-15) AD18 AF17 AE17 AF22 AE21 AF21 AB20 AA26 AF25 AE22 AF23 AE23 AF24 V23 Y24 Y23 2011-Feb-18 back to P0_7 P0_6 P2_3 P0_3 P2_6 P0_4 P2_2 P2_7 P1_1 XTAL_OUT XTAL_IN P1_7 RESET_IN P6_4 P3_1 P3_0 SPI_CSB SPI_SDO SPI_SDI SPI_CLK P6_5 GPIO_10 GPI0_3 GPI0_2 AE4 RESET_SYS U23 GPI0_11 USB_DN USB_DP BL_PWM GPI0_7 CLK_54_OUT GPIO_1 B02E CONTROL B02H POWER AF1 VDD_1V1 AA15 VDDA_1V2 CLK_N CLK_P A DQ EN 59 B02B MEMORY 9. D(24-31) Q552.2L LA 1S02 1FL5 PNX85537 Block Diagrams 54M 24M 9-5 Block Diagram Control & Clock Signals 1 2 19 18 CONTROL 1 3 2 4 1 3 2 4 8 FLASH XIO-D(00-07) ETHERNET 7E10 LAN8710A-EZK AA1 AA4 AB1 AB2 AA2 ETH-TXD(2) ETH-TXD(3) ETH-TXCLK 20 AA3 ETH-TXD(0) ETH-TXD(1) 7 22 23 24 25 AC1 Y5 Y6 AB4 ETH-RXD(3) ETH-RXCLK ETH-RXD(2) ETH-RXD(0) ETH-RXD(1) B02G A DQ TXCLK TXD_2 TXD_3 TXD_0 TXD_1 RXD_2 RXD_3 RXCLK RXD_0 RXD_1 ERR 15 GPIO_3 GPIO_2 2_SCL 2_SDA 4_SCL 4_SDA ANALOGUE VIDEO VGA_EDID_SCL VGA_EDID_SDA B02I GPIO_3 GPIO_2 HDMI_DV DDC_A_SCL DDC_A_SDA P3_1 P3_0 MC_SCL MC_SDA 1_SCL 1_SDA B02C ERR 53 STANDBY CONTROL MEMORY B02B XIO_D FLASH B02A 3_SCL 3_SDA PNX85537 B02E ERR 14 ERR 18 W22 W21 A25 B26 A23 B24 AD24 AD25 Y24 Y23 Y26 Y25 AF21 AE21 AC24 3S57 3S56 3S5Z 3S5Y 3S5W 3S58 3S61 3S60 3S2G 3S2F B02G ERR 13 AC23 C26 C25 A24 B25 +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 TXD1-MIPS RXD1-MIPS DDCA-SCL DDCA-SDA TXD-UP RXD-UP TUNER TXD2-MIPS RXD2-MIPS SCL-TUNER 3F76 3F75 ERR 34 MAIN TUNER 1T01 TH2627 7 3F64 3F65 1 +3V3 3E53-1 3E53-3 1 2 3 RES div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to 8 7 5 4 SCL-SET SDA-SET 3E53-2 3E53-4 1E06 3F62 3F63 ETHERNET + SERVICE 7S01 PCA9540B ERR 24 ERR 35 MAIN NVM SW B04C 2 6 EEPROM (NVM) 7F58 M24C64 5 PNX85500-CONTROL 2 CHAN. MULTIPLEX. 6 TUN-P6 TUN-P7 RES 3S5V-3 3S5V-1 PNX85500: ANALOG VIDEO SDA-TUNER B01F B02I +3V3-STANDBY RES +3V3-STANDBY PNX85500: STANDBY CONTROLER SCL-UP-MIPS SDA-UP-MIPS SCL-SSB SDA-SSB B01E 3F60 PNX85500: MIPS 7S00 PNX85537EB AF24 SPI_CLK AE22 P6_5 AF23 SPI_CSB AE23 SPI_SDO AF25 SPI_SDI 8 11 10 9 SDRAM 128Mx8 7B03 H5PS1G83EFR DDR2-D(0-31) DDR2-A(0-13) SDRAM 128Mx8 7B01 H5PS1G83EFR MAIN SW FLASH (4Gx16) PNX-SPI-CSBn PNX-SPI-SDO PNX-SPI-SDI PNX-SPI-WPn 3 1 5 2 PNX-SPI-CLK 6 7F20 H27U4G8F2DTR STANDBY SW 512K VCC ETHERNET + SERVICE SDRAM 128Mx8 7B02 H5PS1G83EFR SDRAM 128Mx8 ETHERNET CONNECTOR RJ45 B04C DDR B05A 7B00 H5PS1G83EFR FLASH B01B +3V3-STANDBY B02E 3S6D 3S69 3S6V 7F52 M25P05-AVMN6P D(0-7) D(16-23) 3S6E 3S6A 3S6W 3F59 PNX85500: CONTROL D(8-15) D(24-31) 2 DEBUG ONLY ERR 42 TEMP SENSOR 7FD1 LM75BDP 1 TEMP SENSOR + HEADPHONE 9S10 9S13 9S11 9S12 UART SERVICE CONNECTOR RES uP LEVEL SHIFTED FOR DEBUG 1 USE ONLY 1F51 3 1 1F52 3 B01J 3FD3 B01E 3S67 3FD4 I²C B04D 54 48 47 44 43 40 39 34 33 30 29 SCL-BL SDA-BL DVBS CONNECTOR BOARD SCL-DISP B09A EDID SW ERR 23 HDMI MUX 7EC1 SII9287B SII9187A 53 HDMI 3EC3 VIDEO OUT - LVDS SDA-DISP B06B +3V3 RES 3ECU-2 9-6 Block Diagram I2C 3EC5 EN 60 3S65 3S1G 3S83 3S6F 3S6B 3S81 3ECU-4 AIN-5V BIN-5V 3EC1-3 CIN-5V 3ECA-2 3EC1-1 15 ARX-DDC-SCL 15 BRX-DDC-SCL 15 CRX-DDC-SCL 1G51 3C83 3C81 1 1M71 3 49 3G2Y ERR 64 50 3G2W 1 1T02 3 TS1 HDMI CONNECTOR 2 1 B01H 9FC1 HDMI CONNECTOR 1 3123 3124 SCL-TEMP1 SDA-TEMP1 TEMP SENSOR LVDS CONNECTOR VGA-SCL-EDID VGA-SDA-EDID VGA-SCL-EDID-HDMI VGA-SDA-EDID-HDMI VGA HDMI CONNECTOR 3 DIN-5V HDMI 9FC4 9FC2 9FC3 TEMP SENSOR 7104 LM75ADP 2 RES 3FE8 45 15 12 HDMI CONNECTOR SIDE OPTIONAL VGA CONNECTOR 1E05 15 16 1P05 DEMODULATOR 7FE0 TC90517FG 46 TUNER BRAZIL +5V-VGA B01I DRX-DDC-SCL DRX-DDC-SDA 16 CRX-DDC-SDA 1P02 16 BRX-DDC-SDA 1P03 16 ARX-DDC-SDA 1P04 B01K +5V-EDID 3ECA-4 1 2 19 18 1 2 19 18 1 2 19 18 3ECA-1 3ECA-3 3ECP-3 3S1H 3S84 3S6G 3S6C 3S80 9. 3FC1 3FE9 Q552.2L LA 3S68 3FBF-2 3ECP-1 3FBF-1 3FC2 1 2 10 6 Block Diagrams 3S66 5 1 19 18 15 11 SW 19110_004_110309.eps 110321 Programmable via USB 8 9 8 9 6 7 8 6 7 8 GND1 +24V B03e B03d B03e B03c B03e B03e B03e B03e B03e B03e B03e +3V3 B01G +5V-TUN B01F +5V T 3.0A 1U40 +T 3FL2 3F32 USB HUB FLASH +T IN OUT COM 7FA3 +1V2-BRA-VDDC +1V2-BRA-DR1 5FA4 +3V3 +5V-TUN-PIN +5V-TUN +5V +3V3-STANDBY +3V3 +3V3-SD +3V3 +5V-USB2 +5V-USB1 +5V +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 +5V +3V3 +24V 5FA3 TOSHIBA SUPPLY TUNER 9F71 PNX85500: CONTROL SD-CARD 3F40 COMMON INTERFACE +T +24V-AUDIO-POWER +12V +12VD +12VIN B02G +3V3-STANDBY ONLY 8000 SERIES +12VIN B02E +12V_AL LAMP-ON B02G BACKLIGHT-PWM_BL-VS B06C BACKLIGHT-BOOST B01E POWER-OK B02G STANDBY 3D-LR GND_AL +3V3-STANDBY +3V3 B01E +3V3 B01D +5V +3V3 B01C +3V3 B01B +3V3 B01A +5V +3V3 14 14 B03e 13 13 11 12 9 10 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 9 BL-ON-OFF 10 BL-DIM1 11 BL-I-CTRL 12 POK +VSND GND1 +12V3 +12V3 STANDBY GND1 GND1 1M95 1 7 5 6 2 3 4 1M99 1 B03C 7 1M95 1 3V3SB PSU GND1 +12V3 N.C. 1M99 1 GND1 2 +12V3 3 GND1 4 +12V3 5 GND1 6 +12V3 DC / DC 9-7 Supply Lines Overview SUPPLY LINES OVERVIEW B09a B02d,B03a B03b,d,e,g, B09a B03h B01e,B02e, g,h,B03a,b,h, B04d,e,B09a B09a B03c B03e B03d B02d B03d B03b B03d B03b B03c B03b B03c B03e B03c B03e B03d B03e B03b B03e B03e B03e B01g B01g B03e B01k B01k VGA 7FE3 IN OUT COM 7S08 +1V8 +1V8 +3V3-STANDBY +3V3-STANDBY +3V3 +2V5-LVDS +2V5-LVDS +3V3 +2V5-AUDIO +2V5-AUDIO +2V5 +1V2 +1V2 +2V5 +1V1 PNX85500: POWER +3V3-STANDBY +1V1 +1V1 B02H +3V3-STANDBY +3V3 +24V-AUDIO-VDD +24V-AUDIO-POWER PNX85500: STANDBY CONTROLLER +3V3-STANDBY +1V1 B02G IN OUT COM PNX85500: MIPS +3V3-STANDBY +3V3 B02E 3S0Z +24V-AUDIO-POWER +2V5-AUDIO +3V3-ARC +2V5 +3V3 +3V3 3S11 PNX85500: AUDIO +3V3 DDR2-VREF-CTRL2 3S06 PNX85500: DIGITAL VIDEO IN DDR2-VREF-CTRL3 +1V8 +3V3 +2V5-BRA +5V +3V3-BRA-FLT +3V3-BRA +3V3 +1V2-BRA-DR1 3S20 PNX85500: SDRAM PNX85500: NANDFLASH CONDITIONAL ACCESS 5FE9 5FE7 9. +1V2-BRA-VDDC +3V3 +5V-VGA DIN-5V +2V5 B02D +3V3 B02C +1V8 B02B +3V3 B02A +5V +3V3 +1V2-BRA-DR1 5FE4 TUNER BRAZIL +1V2-BRA-VDDC B01K +3V3 B01J 1E05 9 TEMP SENSOR + HEADPHONE VGA CONNECTOR B01I 1P05 18 HDMI Q552.2L LA HDMI SIDE CONNECTOR B01H Block Diagrams B02h B04d B04d AUDIO 3U15 3U16 IN OUT COM 7UD0 IN OUT COM 7UD1 6UD0 5UD1 5UD2 T 1.0A 1UM0 VDISP - SWITCH FAN - CONTROL 5UM1 7UU2 LCD-PWR-ONn 7UU0 +12V +VDISP-INT +12VD +3V3-STANDBY +3V3 +12V +3V3 V-AMBI +3V3 +5V +5V5-TUN +3V3 +12V +1V1 +2V5-REF +12V +5V-TUN +5V5-TUN +2V5-LVDS +2V5 +3V3 +5V +1V2 +1V8 +1V1 12V/1V1 COVERSION +1V8 12V/1V8 COVERSION 5U01 CUA0 +AVCC +3V3-STANDBY TEMPSENSOR + AMBILIGHT 5UD0 5UD3 div. table +12VD 7UA0 VOLT. REG. DC / DC 3UA0 +3V3-STANDBY +3V3 B03H +12V +3V3 B03G +3V3 B03F +12V +1V1 B03E +12V 7UA6 IN OUT COM +3V3-STANDBY +24V-AUDIO-POWER 5U00 ENABLE-1V8 7U04 7UC0 +12V 7UA3 DC / DC +5V5-TUN +5V +1V8 B03D 23 1 7U01 12 Dual Synchronous 7U02-2 Step-Down Controller 14 7U03 TPS53126PW +12V 5U02 7U02-1 DC / DC +3V3-STANDBY B03B 3D09 +24V-AUDIO-POWER +3V3-STANDBY B03A 2011-Feb-18 back to B03c B03c B03e B03c B03e B03b B03b B03c B03c B03e B03e B03b B03c B03c B03c B03c EN 61 B03e B03e B06a B03e B03h B03b B03c B03e B01h B03e B01I B03c B03e B03e B03e B03e +3V3 B04D HDMI 5E08 B06a B09a B01,c,e,k, B03c,d,e, B04d,B09a B03d B01,a,b,c,d,e, g,j,k, B02a,c,d,e,h, B03c,f,g,h, B04a,c,d,e, B06b,c,d, B09a B01f B02h B02d,h B02g,h, B03e HEADPHONE 1P02 18 1P03 18 1P04 18 +3V3 B06D +3V3 B06C +VDISP +3V3 B06B 1G03 SPI-BUFFER 5GA1 5GA0 AMBILIGHT CPLD VIDEO OUT - LVDS T 3.0A +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 DDR2-VREF-DDR +1V8 +3V3-STANDBY +3V3 DIN-5V CIN-5V BIN-5V AIN-5V +5V +5V-EDID +5V-VGA +3V3-STANDBY +3V3-HDMI +3V3 +3V3-ET-ANA +3V3 VIO VINT +3V3 +VDISP +3V3 +VDISP +VDISP-INT DISPLAY INTERFACING-VDISP 3B20 DDR +VDISP-INT B06A +1V8 B05A +3V3-STANDBY +3V3 B04E DIN-5V HDMI 1 CONNECTOR HDMI 2 CONNECTOR HDMI 3 CONNECTOR +5V +5V-VGA 5EC0 ETHERNET + SERVICE ANALOGUE EXTERNALS B ANALOGUE EXTERNALS A B02h,g,B03e +3V3-STANDBY B02b,h,B03d, B05a +3V3 B04C +3V3 B04B +3V3 B04A 6EC1 B03f B03c B03c B03e B03c B03e B06b V-AMBI +24V +12V_AL +5V T 2.0A 1C86 T 2.0A 1C87 CONNECTORS COMP +3V3-STANDBY +3V3 B09A 1M71 4 8 5 10 1M59 21 TO AMBILIGHT MODULE TO IR/LED BOARD TEMP SENSOR (OPTIONAL) 19110_003_110309.eps 110321 +24V ONLY 8000 SERIES +12V_AL 8 1M19 1M20 5 6 +5V +3V3-STANDBY +3V3 B01A Common Interface Common Interface 10-1 B01 393912365213 10. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts FF08 FF09 CA-VS1n CA-RDY CA-MDO7 CA-MDO6 CA-MDO5 CA-MDO4 CA-MDO3 CA-MDO2 CA-MDO1 CA-MDO0 CA-MOSTRT CA-MOVAL 3F08-1 3F08-4 1X04 EMC HOLE 10K 2 3F11-2 7 10K 3 3F11-3 6 10K 4 3F11-4 5 10K 8 3F11-1 1 10K 3F12 RES 4 3F10-4 5 10K RES 3 3F10-3 6 10K RES 2 3F10-2 7 10K RES 1 3F10-1 8 10K RES 1 3F09-1 8 10K RES 2 3F09-2 7 10K RES 3 3F09-3 6 10K RES 4 3F09-4 5 10K 4 1 3F07-4 3F07-3 6 10K 5 10K 3F07-1 1 8 10K 3F07-2 2 7 10K 4 3 8 10K 5 FF07 10K 3F08-3 3 6 10K 3F08-2 2 7 10K FF06 FF05 CA-MOCLK CA-CD2n CA-CD1n Q552.2L LA 1X07 REF EMC HOLE Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts IF08 IF04 10. 1X08 REF EMC HOLE div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 EN 62 1X01 REF EMC HOLE SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2 3 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_010_110411.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 B01A B01B Flash Flash NAND-RDY1n XIO-OEn XIO-WEn NAND-WPn NAND-CLE NAND-ALE NAND-CE1n XIO-D00 XIO-D01 XIO-D02 XIO-D03 XIO-D04 XIO-D05 XIO-D06 XIO-D07 +3V3 +3V3 3F22-4 3F23 4 100R 3F20-2 100R 3F20-4 100R 3F21-2 100R 3F21-4 4 2 4 2 2K2 3F24 100R 3F22-3 3 10K 3F22-1 1 5 100R 6 3F21-3 3 7 8 3F21-1 1 2 6 3F20-3 3 3F22-2 8 3F20-1 1 10. 3F19 8 6 5 7 5 7 2F20 IF23 IF21 2011-Feb-18 back to div. table IF22 100R 100R 100R 100R 100R 16 17 9 8 18 19 7 29 30 31 32 41 42 43 44 Φ VCC +3V3 CLE ALE CE RE WE WP R B VSS NC [FLASH] 4G × 16 0 1 2 3 IO 4 5 6 7 100n 2F21 7F20 NAND04GW3B2DN6F 100R EN 63 100n 13 Q552.2L LA 10K 12 36 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts +3V3 37 1 2 3 4 5 6 10 11 14 15 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 33 34 35 38 39 40 45 46 47 48 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_011_110411.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B01B SCENARIO 1x USB 1x USB + WIFI 2x USB 2x USB + WIFI USB-OVR1 USB2-DM USB2-DP RESET-USBn USB1-DM USB1-DP USB-DM USB-DP USB2-DM USB2-DP USB-WIFI-DDn USB-WIFI-DDp 1P07 N N Y Y +3V3 +5V +3V3 1 3 100K 3FLE-2 100K 3FLE-1 7 8 6 1F24 N Y N Y 10K 3FLF 100K 3FLE-3 1P08 Y Y Y Y 3 100K 4 3FLE-4 5 2 1 10K 3FLD 24M 1FL5 12p 3FLG N Y Y N +3V3 +3V3 9FLF 9FLG 3FL2 N N Y Y 3FL4 N N Y Y 3FL7 N Y N Y 10K 3FLH 10K 3FLG 9FLK 9FLL 9FLC 9FLD 9F26 9F25 3F32 Y Y Y Y 9FLH 9FLJ 3F34 N Y Y Y 7FL5 CY7C65621 CY7C65621 CY7C65631 IFL3 IFL1 IFL2 IFLA IFLG IFL4 NC RES DD2DD2+ DD1DD1+ DD+ RESET VBUSPOWER SELFPWR XOUT XIN GND VCC 9FLE 9FLC/D 9F25/6 9FL2 N N Y N N N Y N Y N N Y N N N Y 5 6 42 41 54 1 2 44 43 52 53 51 9 10 13 14 17 18 46 26 45 22 21 7FL5 CY7C65621-56LTXCT +3V3 9FL3 N N N Y 1u0 GND HS VIA SPI_CS SPI_SCK SPI_SD PWR2 OVR2 PWR1 OVR1 GREEN2 AMBER2 GREEN1 AMBER1 IFLC IFLD IFLE IFLB 9FLF/G 9FLH/J 9FLK/L N N N N Y N Y N N N Y Y 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 25 48 49 31 32 29 30 37 38 35 36 100n 10. 100n 2FL4 2FL9 Q552.2L LA 100n USB Hub Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 100n 2FL2 2FL1 B01C 2FL6 EN 64 2FLA 1n0 10K 15K 10K 2FLB 1n0 div. table 2FLC 1n0 2011-Feb-18 back to 3FLA 3FLB 3FLC 9FLE 10n 2FL5 USB Hub 12p 4 2 2FL7 10n 10K 10n 2FL3 2FLD +3V3 3FL7 3 7 11 15 19 23 27 33 39 55 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 34 40 47 50 56 2FL8 57 +3V3 +3V3 100K 6 100K 100K 3F34-2 100K 100K 3F34-3 3F34-4 100K 3FL4-2 7 6 7 100K 1 3F34-1 8 2 3 4 2 1 3FL4-1 8 3 3FL4-3 100K 4 3FL4-4 5 +T 0R3 3F32 +T 0R3 3FL2 FL33 +5V-USB1 +5V +5V-USB2 +5V USB-OVR1 +5V +3V3 USB-WIFI-DDn USB-WIFI-DDp USB2-DM USB2-DP USB1-DM USB1-DP 9FL1-1 9FL1-2 9FL1-3 9FL1-4 9FL2-1 9FL2-2 9FL2-3 9FL2-4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 8 7 6 5 FL32 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD +T 0R3 RES 3FLJ RES RES RES RES +5V-USB2 +5V-USB1 FL42 FL31 9FL3 1 2 3 4 5 1P08 6 IFLF 1P07 6 FL38 FL39 FL30 RES 1F24 7 2 3 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_012_110411.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 502386-0570 1 2 3 4 5 6 (WIFI) USB-16-PBT-B-30-CU1-BRF FL40 FL41 1 2 3 4 5 USB2 USB-16-PBT-B-30-CU1-BRF FL43 FL36 FL37 USB1 B01C B01D SD Card SD-Card +3V3 47K 3F41-4 3 5 2 47K 3 3F42-3 6 47K 6 10K 3F45 RES 47K 3F41-3 IF47 47K 3F42-2 47K 7 1 3F41-1 8 1 3F42-1 8 47K 2 3F41-2 7 4 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 2F40 SDIO-WP SDIO-CDn SDIO-DAT2 SDIO-DAT1 SDIO-DAT0 SDIO-CLK SDIO-CMD SDIO-DAT3 +3V3 0R3 3F40 SDIO-WP SDIO-CDn SDIO-DAT2 SDIO-DAT1 SDIO-DAT0 SDIO-CLK SDIO-CMD SDIO-DAT3 +T Q552.2L LA 22u 16V FF45 10. 100R 3F44-1 100R 3F44-2 8 7 100R 6 div. table 100R 1 3F43-1 8 3 3F43-3 2011-Feb-18 back to 100R 3 3F44-3 6 100R 2 3F43-2 7 1 2 +3V3-SD EN 65 FF50 FF44 FF43 FF42 FF41 FF49 +3V3-SD FF48 FF47 16 14 SCDA7A0200 10 11 12 1P09-2 SCDA7A0200 13 15 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1P09-1 FF46 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_013_110411.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B01D +3V3 2F49 IF59 3F58 PNX-SPI-SDI IF51 1 2 3 0 1 2 7F58 2 W S C D VSS HOLD 512K FLASH Φ VCC IF58 MAIN NVM Q 100n RES 2F52 +3V3-STANDBY ADR SCL WC FF57 SDA Φ (8K × 8) EEPROM 100n 2F58 RES 7 3 1 6 5 IF54 IF53 IF52 IF50 5 6 7 100R 3F59 +3V3-STANDBY 7F52 M25P05-AVMN6 +3V3-STANDBY FF04 FF29 RXD-UP RESET-STBYn SPI-PROG TXD-UP FF63 FF61 100R 3F65 100R 100R div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to 100R FF66 3F63 3F64 3F62 BOOST-PWM FF65 SDA-UP-MIPS SDM SPI-PROG PNX-SPI-WPn PNX-SPI-CSBn PNX-SPI-CLK PNX-SPI-SDO SCL-UP-MIPS IF62 IF61 DEBUG / RS232 INTERFACE 100R 3F60 FF55 FF56 SDA-SSB SCL-SSB DEBUG ONLY 3F52 +3V3-STANDBY 10K PNX85500 Control +3V3 IF55 10K B01E EN 66 3F67 PNX85500 Control 8 4 10. 10K 3F53 +3V3 3F68 RES IF57 5 7F54-2 RES BC847BPN(COL) 7F53 RES PDTA114EU 3F66 +3V3 3F69 Q552.2L LA RES 1u0 10K RES RES 10K 100p 10K 8 4 47K IF56 9CH0 3 4 2 FF58 FF64 FF62 1 7F54-1 RES BC847BPN(COL) 6 +5V 3F54 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 1K0 RES 2F53 7 6 RES 1F51 4 RES 1F52 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 5 UP SDA SCL BACKLIGHT-BOOST SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD USE ONLY DEBUG FOR SHIFTED LEVEL 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_014_110411.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B01E 1T01 2F61 2F62 9F02 9F03 9F04 9F05 9F06 2F73 2F82 2F72 2F80 2F77 5F71 5F74 Item No. * Remarks TUN-P6 TUN-P7 FF74 16 15 TUN FF76 47R 3F75 47R 2F86 15p Component Europe Brazil FA23X7 TH26X3 RES 4u7 5p6 10p Used RES Used RES Used RES Used RES Used RES RES 1p0 RES 1p0 12p 15p 12p 15p 18p 22p 560n 680n 680n 820n 3F76 15p * TUNER 2F84 FF81 FF82 4n7 RES 2F81 TUN-P1 * 4n7 2F59 FF71 RF_IO 1 B+_LNA 2 6p8 RES 2F97 RF_AGC 3 100n 2F60 I2C_ADR 5 FF00 4MHZ_REF FF75 6p8 RES 2F99 4 6p8 RES 2F98 2F61 I2C_SCL 6p8 RES 2F9A 6 I2C_SDA 7 B+_TUN 8 6p8 RES 2F9B +5V-TUN-PIN 6p8 RES 2F9C * IF_OUT1 10 IF88 TUN-P6 SCL-TUNER IF-AGC TUN-IF-N TUN-IF-P 13 14 TUN-P7 SDA-TUNER AF71 AF70 9F04 IF87 100n 9 2F93 IF_OUT2 11 NC 12 6p8 RES 2F9D 1T01 IF-AGC PNX-IF-AGC TUN-IF-P TUN-IF-N 100p Tuner 100p RES 2F96 RES 2F95 4K7 3F77 +5V-TUN FF01 IF82 30R 5F72 RES 9F71 * * 1 2 IF79 ATB2012 5F73 1F75 X7251M 36M17 GND I ISWI O1 O2 IF89 IF86 5 4 IF81 div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to +5V-TUN-PIN 9F00 IF75 * For EU Hybrid Tuner Only 4 3 IF72 3 1 2 IF11 IF10 9F01 10n 10n 2F78 2F74 IF77 IF73 VAGC 4 AGC CONTROL SELECT-SAW 10n 2F91 RES 10n 2F90 INPUT2 INPUT1 3 2 7F75 UPC3221GV-E1 +5V-TUN-PIN VCC 10n 2F71 IF90 7 6 OUTPUT1 OUTPUT2 * * IF74 7F70 PDTC114EU 10n 2F79 10n 2F75 +5V-TUN-PIN IF78 9F03 9F02 B01F 9F05 IF80 IF76 4 1 220R * 5F71 220R 3F81 220R 3F80 3F79-4 220R 3F79-1 10n 2F64 10n 2F63 IF15 IF13 * 5F74 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD IF14 * AF73 5F66 * * For BR NIM Tuner only RES 2F76 IF12 * * * * AF72 2F72 2F80 Tuner 9F06 EN 67 5F70 10. 470n Q552.2L LA 22u 3F71 2F73 2F82 2p2 2F77 1 4K7 GND2 5 2F62 15p 2F70 RES IF16 PNX-IF-P 2010-12-23 19110_015_110415.eps 110415 2 3 IF+ IF- PNX-IF-N 2011-03-09 B01F 3139 123 6521 680n 2F66 2F65 RES 1p0 RES 5F76 15p 330n 3F82 RES Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 2F88 10n 1K0 2F92 3F72 GND1 8 6F72 3F78 RES 2F94 BA591 3K3 820R 10n 47n 2F85 Toshiba supply +3V3 2FA2 B01G 100n Toshiba Supply 3 IN FFA2 COM OUT 7FA3 LD1117DT12 1 2 +1V2-BRA-DR1 div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to FFAF +1V2-BRA-VDDC EN 68 5FA3 2FA3 10. 30R 100n Q552.2L LA 5FA4 2FA4 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 30R 10u SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_016_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B01G B01H HDMI HDMI 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 FFB5 21 23 1P05 20 22 FFB6 FFB3 FFB4 FFB1 FFB2 DIN-5V HDMI CONNECTOR SIDE Q552.2L LA DRX0DRXC+ DRX1DRX0+ DRX2DRX1+ DRX2+ EN 69 div. table DRX-DDC-SCL DRX-DDC-SDA 2011-Feb-18 back to DRX-HOTPLUG DRX-DDC-SCL DRX-DDC-SDA DRXCPCEC-HDMI 10. DIN-5V 1 3FBF-1 8 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 47K 2 3FBF-2 7 47K DIN-5V SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_017_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B01H B01I VGA VGA 17 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1216-02D-15L-2EC VGA CONNECTOR 1E05 FFC6 FFC4 10K RES 3FC2 10K RES 3FC1 Q552.2L LA FFC9 FFC8 FFC7 FFC5 FFC3 FFC2 FFC1 10. EN 70 div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to 2FC5 2FC6 2FC7 2FC8 CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts RES 2FC1 RES 2FC2 47p 47p 47p 47p 2FC4 RES 2FC3 100p 100p 47p 100p 1FC1 1FC2 1FC3 1FC4 1FC5 1FC6 RES 6FC1 RES 6FC2 RES 6FC3 RES 6FC4 RES 6FC5 RES 6FC6 RES 6FC7 RES 6FC8 18R VGA-SDA-EDID 9FC2 VGA-SCL-EDID 9FC4 RES +5V-VGA VGA-SCL-EDID-HDMI 9FC3 RES VGA-SDA-EDID-HDMI V-SYNC-VGA 9FC6 9FC1 H-SYNC-VGA B-VGA G-VGA R-VGA 9FC5 3FC7 18R 3FC6 18R 3FC5 3FC3 3FC4 CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V 4K7 4K7 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_018_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B01I Temp sensor & headphone AMP2 AMP1 SCL-SSB SDA-SSB 100R 3FD4 RES 3FD1 RES 100R 3FD3 6FD1 1K0 IFD4 IFD2 LTST-C190KGKT 2 1 3 SCL SDA OS 7FD1 LM75BDP A2 A1 A0 EN 71 2FD1 5 6 7 IFD1 IFD3 div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to 1K0 B01J 8 +VS GND 4 IFD5 1K0 RES Temp sensor & headphone 3FDG-2 7 2 100n 8 1K0 3FDG-1 1 1K0 9FD1 RES 3FD6 1FD2 3FD2 9FD5 CDS4C12GTA 12V 1FD3 9FD2 RES 1K0 3FD7 6FD2 RES 6FD3 +3V3 RES 10. CDS4C12GTA 12V 2FDC Q552.2L LA FFDB FFDA 22n Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 22n 2FDD FFDC 4 1 2 3 1 3 1328 2MSJ-035-69A-B-RF-PBT-BRF 502382-0370 5 RES 1329 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_019_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B01J SCL-SSB SDA-SSB IF+ IF- 2FG2 AGND 18p 3 25M4 AGND 4 2 1 1FE0 2FG3 18p AGND AGND AGND AGND AGND 3FE8 3FE6 10n 2FG6 100R 3FE9 3FE7 10K 2FH7 100n 2FH6 100n 2FG8 +3V3-BRA-FLT 2FG9 2FG7 2FG4 30R 5FE5 30R AGND 1u0 1u0 1u0 5FE3 BFE3 BFE2 IF49 100R 10K IF29 100n 100n 100n 10n IF17 IF18 45 46 11 7 1 41 8 40 39 26 24 25 28 27 30 29 3 2 18 19 7FE0 TC90517FG X SCL SDA CKI AGCI 0 TSMD 1 S_INFO DTMB DTCLK AGND AD_VREF P AD_VREF N P ADQ_AI N P ADI_AI N 0 XSEL 1 O I IF67 IF65 IF63 IF64 VDDC IF66 Φ VSS VDDS IF68 AGND IF69 TN 0 1 SCL SDA SLADRS SYRSTN STSFLG0 AGCCNTR AGCCNTI STSFLG1 SRDT SRCK SLOCK SBYTE RSEORF RLOCK RERR PBVAL FIL 12 14 6 5 42 51 10 9 38 60 61 52 59 55 54 53 58 21 3 4 2 4K7 33R 33R 30R 5FE8 30R 5FE4 7 2 TS-BR-SOP IF28 9F27-4 33R TS-BR-DATA 9F27-2 9F27-1 +3V3-BRA-FLT 5 7 8 RESET-SYSTEMn IF-AGC TS-FE-DATA TS-FE-CLOCK * * TS-FE-SOP TS-FE-VALID * * * To be drawn near PNX85500 9F28 4 1 TS-BR-VALID +2V5-BRA +1V2-BRA-DR1 +3V3-BRA +1V2-BRA-VDDC TS-BR-CLOCK 33R 6 5 10K 18K 3FE5 +3V3-BRA-FLT div. table 3FG4-1 3FG2-2 IF27 3FG6-2 3FG7 3FG6-3 3FG6-4 2011-Feb-18 back to 4K7 10K AGND 3FG4-2 3FG2-1 DFF2 DFF1 DFE9 DFE8 DFE7 DFE6 1n5 2FH5 +3V3-BRA-FLT 2FE3 2FF2 30R 100n 2FE4 100n 2FF3 5FE0 2FE0 2FE6 2FE8 EN 72 100n 2FE5 100n 2FF4 2FF7 +2V5-BRA 13 35 49 64 100n 2FF0 100n 2FF5 100n 2FF8 2FG0 Tuner Brazil 23 1u0 100n 2FF6 100n 2FF9 B01K 32 AD_DVDD 22 AD_AVDD AD_AVSS 20 PLLVDD AD_DVSS 31 PLLVSS 43 DR2VDD 100n 2FF1 1u0 1u0 1u0 100n 2FG1 Tuner Brazil DR1VDD 16 36 56 63 17 10n 34 48 4 15 33 37 44 47 50 57 62 2FH8 10. +5V +3V3 AGND 30R 5FG2 30R 5FG0 30R 5FE9 30R 5FE7 1u0 BP OUT COM INH IN SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 3 1 7FE3 LD3985M25 2 Q552.2L LA 4 5 FF03 IF48 10n 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_020_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 +2V5-BRA +3V3-BRA B01K 1u0 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 2FH4 2FH3 2FH2 B02A CA-RDY J24 J23 L26 L24 J21 L23 CA-MOVAL N25 N24 L25 N23 K26 K25 J22 P21 P22 P23 P24 P25 P26 N21 N22 7S00-11 PNX85500 CA-MOSTRT IS25 MCLK VPPEN VCCEN RST RDY OOB_EN MOVAL MOSTRT MIVAL MISTRT O I DATA_EN DATA_DIR ADD_EN D25 D26 C24 D23 C23 B23 A22 E22 F24 F25 F26 E23 E24 E25 E26 D24 K21 1 K22 2 K23 1 K24 2 N26 M21 M22 M23 M24 M25 M26 L21 T21 DATA T23 ERR T22 TNR_SER1 MICLK R23 MIVAL R22 SOP CA CD VS 0 1 2 3 MDO 4 5 6 7 E21 CE1_ D21 CE2_ A20 NAND RDY2 F21 RDY1 A21 WP_ B21 B22 OE_ C22 WE_ CLK_BURST XIO VIDEO_STREAM 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 XIO_A 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 0 1 2 3 MDI 4 5 6 7 J25 J26 H21 H22 H23 H24 H25 H26 G21 G22 G23 G24 G25 G26 F22 F23 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 XIO_D 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 FLASH D22 ALE NAND C21 CLE 7S00-5 PNX85500 L22 CA-MOCLK NAND-ALE NAND-CLE PNX85500: NANDflash - conditional access NANDflash - conditional access +3V3 9S08 +3V3 div. table NAND-RDY1n NAND-WPn 2011-Feb-18 back to TS-FE-ERR 9S00 IS00 XIO-OEn XIO-WEn INPACK XIO-D10 XIO-D00 XIO-D01 XIO-D02 XIO-D03 XIO-D04 XIO-D05 XIO-D06 XIO-D07 NAND-CE1n 10K 10-2 B02 393912365213 EN 73 10K 10. 3S1X 3S1W Q552.2L LA +3V3 INPACK 3S1V Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 10K RES IS26 TS-FE-CLOCK TS-FE-VALID TS-FE-SOP TS-FE-DATA CA-CD1n CA-CD2n CA-VS1n CA-MOCLK CA-MDO0 CA-MDO1 CA-MDO2 CA-MDO3 CA-MDO4 CA-MDO5 CA-MDO6 CA-MDO7 10K 3S15 RES 470R 470R 3S29 RES TS-FE-SOP 470R 470R 560R 560R 560R 560R 3S28 3S24 3S23 RES 3S1U RES 3S1T 3S1S 3S1R TS-FE-VALID TS-FE-CLOCK TS-FE-DATA TS-FE-SOP TS-FE-VALID TS-FE-CLOCK TS-FE-DATA +3V3 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2 3 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_021_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 B02A DDR2-VREF-CTRL3 FS02 180R 1% 180R 1% 3S20 3S22 DDR2-VREF-CTRL2 PNX85500: SDRAM FS01 +1V8 3S06 3S07 B02B 180R 1% 180R 1% D1 D5 R3 T5 F3 C2 F2 C3 B4 F1 C1 E1 F4 B2 E5 C5 A4 G5 B3 F5 U3 P2 U2 P3 N1 U1 P1 T1 V4 R5 U5 P5 N3 V3 R4 V5 DDR2-DQM0 DDR2-DQM1 DDR2-DQM2 DDR2-DQM3 DDR2-D0 DDR2-D1 DDR2-D3 DDR2-D2 DDR2-D6 DDR2-D5 DDR2-D4 DDR2-D7 DDR2-D8 DDR2-D9 DDR2-D10 DDR2-D11 DDR2-D12 DDR2-D13 DDR2-D14 DDR2-D15 DDR2-D16 DDR2-D17 DDR2-D19 DDR2-D18 DDR2-D22 DDR2-D23 DDR2-D20 DDR2-D21 DDR2-D24 DDR2-D30 DDR2-D26 DDR2-D25 DDR2-D28 DDR2-D31 DDR2-D27 DDR2-D29 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 DQ 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 0 1 DM 2 3 div. table 1 VREF 2 CASB CKE CSB ODT PCAL RASB WEB N P DQS3 N P DQS1 N P N P DQS0 DQS2 N P CLK M0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 A 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 MEMORY 0 1 BA 2 2011-Feb-18 back to DDR2-BA2 H1 H2 G1 7S00-8 PNX85500 EN 74 DDR2-BA0 DDR2-BA1 10. A2 V1 K3 K4 L5 M4 M1 M5 H3 T3 T4 R1 R2 D3 D4 E2 E3 N5 N4 J1 J3 K1 G4 L3 G3 L2 H5 L1 J5 J2 M3 J4 M2 K5 3S30 100p 2S20 SDRAM Q552.2L LA 3S33 100p 10R 100n 2S25 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts DDR2-VREF-CTRL2 DDR2-VREF-CTRL3 10R IS42 261R 1% 3S0V 100n 2S17 2S24 100u 2.0V 2S12 DDR2-RAS DDR2-WE DDR2-CAS DDR2-CKE DDR2-CS DDR2-ODT DDR2-DQS3_N DDR2-DQS3_P DDR2-DQS2_N DDR2-DQS2_P DDR2-DQS1_N DDR2-DQS1_P DDR2-DQS0_N DDR2-DQS0_P DDR2-CLK_N DDR2-CLK_P DDR2-A0 DDR2-A1 DDR2-A2 DDR2-A3 DDR2-A4 DDR2-A5 DDR2-A6 DDR2-A7 DDR2-A8 DDR2-A9 DDR2-A10 DDR2-A11 DDR2-A12 DDR2-A13 DDR2-A14 10K RES 3S6P 10K 3S6Q SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD DDR2-ODT DDR2-CKE 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_022_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B02B B02C PNX85500: Digital video in Digital video in +3V3 HDMIA-RXC+ HDMIA-RXC- HDMIA-RX0+ HDMIA-RX0- HDMIA-RX1+ HDMIA-RX1- HDMIA-RX2+ HDMIA-RX2- Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 12K 3S0W Q552.2L LA RES 2S2E 10u IS01 10. HDMI_DV P RX0_A N div. table RREF 2011-Feb-18 back to W24 W25 P RXC_A W26 N Y26 SCL Y25 DDC_A SDA V25 P V26 T24 RX2_A N HOT_PLUG_A U25 P U26 RX1_A N T25 T26 7S00-6 PNX85500 EN 75 IS10 DDCA-SCL DDCA-SDA SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_023_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B02C AUDIO-IN4-R AUDIO-IN4-L AUDIO-IN3-R AUDIO-IN3-L AUDIO-IN1-R 1 2 3 4 22K 3S13-2 22K 3S13-1 22K 3S13-3 22K 5 7 7 8 6 3S13-4 22K 2 3S12-2 22K 8 IS1Q IS1P IS0R IS1J IS1H 10K 6 3S17-2 1 2 7 10K 8 10K 3S17-1 6 10K 5 10K 3S17-4 3 3S17-3 4 3S16-4 5 4 10K 3S16-3 3 7 10K 1 3S16-1 8 10K 2 3S16-2 2S3F 3S12-1 10u 2S3E IS19 IS0V IS1B SPDIF-OUT-PNX 56R 3S3F 2S2L 1u0 IS1A 1u0 2S32 1u0 2S33 1u0 2S30 1u0 2S31 1u0 2S2Y 1u0 2S2Z 1u0 2S2V 1u0 2S2W AE5 AF5 AD8 9S06 RES SEL-HDMI-ARC SPDIF-OUT-PNX 1R0 3S11 SPDIF_IN1 SPDIF_OUT +3V3 IS1D IS1E 5 7S09-2 74LVC00APW 4 2 7S09-1 74LVC00APW 1 +3V3 IS1L +3V3-ARC AE1 1 AF2 VREF_AADC 2 AE3 I2S_OUT_SD 3 AC8 AF3 VCOM_AADC 4 AD4 OSCLK AD1 SCK AD2 WS AD7 AE7 AF7 AD6 AE6 AF6 AC6 P AB6 N 1 2 3 ADAC 4 5 6 ADACR I2S_OUT AB9 POS AB8 VR_AADC NEG AF8 L AE8 AIN5 R +3V3 DBS8 3S10 100R AD9 L AC9 AIN4 R AE9 L AF9 AIN3 R AD10 L AC10 AIN2 R AUDIO AC7 AE10 L P AB7 AF10 AIN1 ADACL R N 7S00-2 PNX85500 IS1M & +3V3-ARC & 3S51 6 3 4R7 2S42 1u0 +3V3 +3V3 100n 100R 3S53-4 100R 100R 3S53-3 RES 2S3K 1u0 2S36 100R 3S53-2 100u 4V & +3V3-ARC & 4 5 33R 3S3G-3 6 IS12 33R 3S3U 33R 3S3G-2 2 7 3 4 5 180R 3S6M 100n IN INH COM BP OUT 7S08 LD3985M25 2S3L div. table 11 8 33R 3S3H 33R 3S3G-4 33R 1 3S3G-1 8 FS08 +2V5-AUDIO 2011-Feb-18 back to 13 7S09-4 74LVC00APW 12 10 +3V3-ARC 220R RES 1 3S18-1 8 47R 3S6N IS1N 2S2R 7S09-3 74LVC00APW 9 IS1G IS1S 2S41 1 100n 2S3H 3S53-1 2S3D AUDIO-IN1-L 100n 100n 220R EN 76 1n0 2S3B 10. 3 1 IS13 IS1K 2S34 PNX85500: Audio 3S19 1u0 RES 1n0 2S39 B02D 100n 10u 2S3G Q552.2L LA 4S14 1n0 100n 2S3M IS44 +2V5 +3V3 2S2S Audio 2S3Q 10K 14 7 14 7 220R 2S2T RES 3S18-2 7 2 2 1n0 2S3C 6 RES 3S18-3 3 ADAC(6) ADAC(5) ADAC(4) ADAC(3) ADAC(2) eHDMI+ SPDIF-OUT ADAC(6) ADAC(5) ADAC(2) ADAC(1) +24V-AUDIO-POWER ADAC(1) SPDIF-OPT 10u RES Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 3S25 10u 14 7 14 7 1n0 2S38 68R IS07 IS03 4R7 3S0Z 3 2 11 4 4 7S05-1 LM324 1 22K 2S2J SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 47p 3S32 7S05-2 LM324 7 10K 11 4 +24V-AUDIO-VDD 47p 3S34 6 5 47p 3S36-4 2S2H 10K 7S05-3 LM324 8 22K 2S2K IS06 5 11 4 3S6L 2 3 1 +24V-AUDIO-VDD 10 9 47p 3S36-1 2S2G 10K 7S05-4 LM324 14 +24V-AUDIO-VDD 8 11 4 10K 6 7 13 12 FS03 +24V-AUDIO-VDD 3S37 10K 3S36-3 10K 220n IS02 3S36-2 2S3J 1n0 2S3A 3S38 100R 3S39 100R 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_024_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 AUDIO-OUT-R AUDIO-OUT-L -AUDIO-R +AUDIO-L B02D +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 10K 3S84 10K 3S83 10K 3S64 10K 10K 3S62 RES 3S21 3S80 3S81 10K 10K 3S82 3S40 10K 3S45 10K 10K 3D-LR BOOST-PWM DS52 BOOTMODE GPIO6 FS64 TXD1-MIPS RXD1-MIPS SELECT-SAW PNX-SPI-CS-BLn IS04 FS10 TXD2-MIPS FS11 RXD2-MIPS IS05 USB-DM USB-DP PNX-SPI-CS-BLn BOOST-PWM SELECT-SAW GPIO6 BOOTMODE 3D-LR RXD1-MIPS TXD1-MIPS RXD2-MIPS TXD2-MIPS IS17 9S09 GPIO_0 GPIO_1 GPIO_2 GPIO_3 GPIO_4 GPIO_5 GPIO_6 GPIO_7 GPIO_10 GPIO_11 B25 SDA A24 SCL TRSTN TMS TCK TDO TDI CLK_54_OUT BL_PWM AC5 AD5 AE4 AA25 AA24 AA23 AB26 AB25 B24 SDA A23 4 SCL 3 B26 SDA A25 2 SCL C25 SDA C26 SCL RESET_SYS R26 DN R25 USB IS4Z R24 DP RREF Y21 IS16 Y22 Y23 Y24 W21 W22 W23 V22 V23 U23 1 CONTROL 3S56 2 33R 3S00 1 100R 3S60 2 1 3S5Y 2 100R 3S58 1 2 100R 1 100R RES 10K +3V3 3S5Z 2 2 1 100R 1 100R 47R 3S72 +3V3 3S61 SDA-SSB SCL-SSB 2 3S5W 1 100R +3V3 IS40 1 10K SDA-SET IS09 IS08 2 SCL-SET SCL SDA 1 SCL-SET SDA-SET 7S01 PCA9540B EJTAG-TRSTn-PNX85500 EJTAG-TMS-PNX85500 EJTAG-TCK-PNX85500 EJTAG-TDO-PNX85500 EJTAG-TDI-PNX85500 div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to PXCLK54 BACKLIGHT-PWM RESET-SYSTEMn EJTAG-TRSTn-PNX85500 EJTAG-TMS-PNX85500 EJTAG-TCK-PNX85500 EJTAG-TDO-PNX85500 EJTAG-TDI-PNX85500 SDA-TUNER SCL-TUNER SDA-SSB SCL-SSB SDA-SET SCL-SET SDA-TUNER SCL-TUNER SDA-SET SCL-SET SDA-UP-MIPS SCL-UP-MIPS SDA-UP-MIPS SCL-UP-MIPS EN 77 2 3S57 10. 1 100R 10K 7S00-3 PNX85500 3S26 PNX85500: MIPS 10K B02E 3S27 MIPS 5K6 1% Q552.2L LA 2K2 2K2 4K7 4K7 3S6F 3S6D 3S6B SCL-BL SDA-BL SDA-DISP 9S13 SDA-BL SDA-DISP SD1 FS2Y 4 7 SD0 SCL-BL SCL-DISP 9S12 8 SC1 SCL-DISP 5 SC0 FS2W FS31 VSS I2 C -BUS CTRL VDD 100n 2S89 7 3S6H-2 5 3S6H-4 4 10K +3V3 9S11 9S10 INP FIL +3V3 2K2 2K2 4K7 4K7 3S6K 3S69 8 3S6H-1 10K 3 6 3S6H-3 10K 2 10K 3S6G 3S6E 3S6C 3S6A 3 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 6 3S6J 3S55 SDA-BL SDA-DISP SCL-BL SCL-DISP +3V3-STANDBY EJTAG-DETECTn 3S65 +3V3 2 3S66 1 4K7 1 4K7 3S67 2 1 4K7 3S68 2 1 4K7 2 EJTAG-TRSTn-PNX85500 EJTAG-TMS-PNX85500 EJTAG-TDO-PNX85500 EJTAG-TCK-PNX85500 EJTAG-TDI-PNX85500 SDIO-DAT3 SDIO-CLK SDIO-CMD SDIO-DAT0 SDIO-DAT1 SDIO-DAT2 SDIO-CDn SDIO-WP ETH-RXDV ETH-RXER SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 0 1 AC2 TXD RXDV 2 Y4 RXER 3 ETH TXEN W2 CC_DAT3 TXER W1 CLK COL W6 CMD CRS W5 0 MDC W4 SDIO 1 DAT MDIO W3 2 U6 SDCD V6 SDWP TXCLK ETH-TXD(0) ETH-TXD(1) ETH-TXD(2) ETH-TXD(3) ETH-TXEN ETH-TXER ETH-COL ETH-CRS ETH-MDC ETH-MDIO AA1 AA4 AB1 AB2 AA5 AB3 AC3 Y2 Y3 Y1 2 3 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_025_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 ETH-TXCLK AA2 FOR FACTORY USE ONLY ETHERNET Y5 0 Y6 1 RXD ETH AB4 2 AC1 3 RXCLK AA3 IS50 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 BM08B-SRSS-TBT ETH-RXD(0) ETH-RXD(1) ETH-RXD(2) ETH-RXD(3) 7S00-4 PNX85500 +3V3 10 9 RES 1F10 ETH-RXCLK RES FS57 FS53 FS49 FS50 FS51 FS52 FS44 B02E B02F 9S90 9S91 PX2EPX2E+ PX2DPX2D+ PX2CPX2C+ A16 B16 N C P A18 B18 N D P C19 B19 N E P B A div. table E D C CLK 2011-Feb-18 back to LOUT2 LOUT4 C15 N B15 B P PX2BPX2B+ C17 N B17 CLK P A14 N B14 A P PX2APX2A+ 9S92 9S93 C12 N B12 E P PX1EPX1E+ PX2CLKPX2CLK+ D A11 N B11 D P PX1DPX1D+ E C CLK B A N C P LOUT1 LOUT3 LVDS A9 B9 C10 N B10 CLK P N B P N A P EN 78 PX1CPX1C+ PX1CLKPX1CLK+ C8 B8 PX1BPX1B+ 7S00-7 PNX85500 10. A7 B7 Q552.2L LA PX1APX1A+ PNX85500: Video out - LVDS Video out - LVDS Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts D9 E9 PX4DPX4D+ PX4EPX4E+ D18 N E18 P E19 N D19 P PX4CLKPX4CLK+ PX4CPX4C+ 9S96 9S97 PX4BPX4B+ PX4APX4A+ PX3EPX3E+ PX3DPX3D+ PX3CPX3C+ D16 N E16 P E17 N D17 P E15 N D15 P D14 N E14 P E12 N D12 P D11 N E11 P N P PX3CLKPX3CLK+ PX3BPX3B+ E8 D8 9S94 9S95 PX3APX3A+ D7 E7 E10 N D10 P N P N P SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_026_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B02F +3V3-STANDBY +3V3-STANDBY +3V3-STANDBY 10K RES 3S1K 3S1H 10K 3S3T RES 3S3S 3S3P 3S3M 3S1E 10K 3S1C 10K 10K 10K 10K 3S3L RES 10K RES 3S1F 10K 3S1L 100K RES 3S1J 10K RES 3S2A 3S1G 10K 3S1B 10K RES 10K 3S3N RES 10K 3S3Q RES 10K 3S3R 10K RES 10K 3S1D 27K 100n 2S4E SPI-PROG KEYBOARD RESET-SYSTEMn DETECT2 RXD-UP TXD-UP LCD-PWR-ONn EJTAG-DETECTn LAMP-ON STANDBY FAN-CTRL1 FAN-CTRL2 POWER-OK ENABLE-3V3n RC TACHO CEC-HDMI BACKLIGHT-PWM-ANA-DISP SDM 2S4D 1n0 SPI-PROG PNX-SPI-WPn RESET-SYSTEMn AV2-BLK AV1-BLK KEYBOARD LIGHT-SENSOR AV1-STATUS AV2-STATUS RXD-UP TXD-UP DETECT2 LCD-PWR-ONn EJTAG-DETECTn LAMP-ON STANDBY FAN-CTRL1 FAN-CTRL2 POWER-OK ENABLE-3V3n RC TACHO CEC-HDMI BACKLIGHT-PWM-ANA-DISP SDM 1u0 AF22 4 AE22 P6 5 AD23 0 AE26 1 AE25 P5 2 AE24 3 AE21 0 AF21 1 AA22 2 AB22 P3 3 AC22 4 AD22 5 AC20 0 AD20 1 AE20 2 AF20 3 AA21 P2 4 AB21 5 AC21 6 AD21 7 AD19 0 AE19 1 AF19 2 P1 AA20 3 AB20 7 100n +1V1 IS20 IS3B 3S2K AD26 0 PWM AC25 1 2011-Feb-18 back to div. table AB17 0 AA18 1 AD18 2 AE18 3 AF18 P0 4 AA19 5 AB19 6 AC19 7 AE23 SDO AF25 SDI AF24 SPI CLK AF23 CSB 3S2G IS2Z IS2V 3S2H 100R CTRL-DISP RESET-DVBS RESET-USBn RESET-ETHERNETn SEL-HDMI-ARC RESET-AVPIP RESET-AUDIO AUDIO-MUTE-UP 100R 10K FS45 1 4K7 10K RES 10K RES 10K 3S2L IS2U 5 7S20 NCP303LSN28 2 3S2S RES 3S3W 4K7 RES 10K RES 3S3Y 10K LED2 LED1 SDA-UP-MIPS SCL-UP-MIPS PSEN ALE EA +3V3-STANDBY CTRL-DISP RESET-DVBS RESET-USBn RESET-ETHERNETn SEL-HDMI-ARC RESET-AVPIP RESET-AUDIO AUDIO-MUTE-UP PNX-SPI-SDO PNX-SPI-SDI PNX-SPI-CLK PNX-SPI-CSBn LED1 LED2 SDA-UP-MIPS SCL-UP-MIPS PSEN 100R AC26 10p ALE 3S2F 100R 10p 2S4F AB23 2 4 2S4G EA 1 3 RESET-STBYn 1S02 AB24 1 DS50 54M AA26 AF17 AE17 7S00-9 PNX85500 100n AC23 SDA AC24 SCL MC PSEN ALE EA RESET_IN XTAL_OUT XTAL_IN 2S13 STANDBY RES 5S04 2S11 9S24 VSS_XTAL 2S37 POL 30R AA17 VDDA_1V1_DCS RES AF26 VDDA_ADC2V5 AC17 VDD_XTAL AD17 1u0 2S10 PNX85500: Standby controller RES 9S0E 9S0D B02G 100n Standby controller 2S4K EN 79 CD IS3F RES SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 1 +3V3-STANDBY 10K RESET-STBYn 2 4 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_027_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 FS0Z 10K RES 3S6W +3V3-STANDBY B02G 3S41 4K7 10K 10K 3S42 3S1P 3S43 10K 3S44 3S6V 4K7 +3V3-STANDBY RES IS3D IS3E OUTP NC GND INP 3S2M RES 3S49 3S47 3S46 4 10. 3 Q552.2L LA 1K0 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 1 3S2V 2 A1 A10 A12 A15 A17 A19 A26 A3 A8 B1 B20 C20 C4 D2 D20 E13 E20 E4 F10 F12 F14 F16 F18 F20 F8 G10 G12 7S00-12 PNX85500 VSS +1V1 100n VSS VSS VSSA AA16 AA8 Y11 Y14 Y16 Y9 2S43 SENSE+1V1 PNX85500: Power VSS M7 N2 N20 P10 P12 P14 P16 P18 P4 P6 P7 T10 T12 T14 T16 T18 T2 T6 T7 U4 V10 V12 V14 V16 V18 V2 Y20 100n 100n B02H 2S27 Power 2S28 G14 G16 G18 G2 G20 G8 H4 H6 H7 J20 K10 K12 K14 K16 K18 K2 K6 K7 L20 L4 M10 M12 M14 M16 M18 M6 8 2S5G-1 1 8 2S5K-1 1 7 100n 2S5G-2 2 7 100n 2S5K-2 2 6 100n 2S5G-3 3 6 100n 2S5K-3 +1V1 3 5 100n 2S5G-4 4 5 100n 2S5K-4 4 8 100n 2S5H-1 1 6 100n 2S5J-3 30R 5S94 3 7 100n 2S5H-2 8 100n 2S5J-1 2S4S c001 +1V8 Q552.2L LA 5 100n 2S5H-4 4 5 6 100n 2S5H-3 3 7 100n 2S5J-2 2 2 1 10u RES 100n 100n 100n 100n 2S5J-4 4 2 2S5P 1 100n 2S61 100u 2S60 J7 AF1 AE2 AD3 AC4 AB5 H20 F11 G11 F13 G13 F15 G15 F17 G17 F19 G19 J9 J11 J13 J15 J17 L9 L11 L13 L15 L17 N9 N11 N13 N15 N17 R9 R11 R13 R15 R17 U9 U11 U13 U15 U17 J6 AA6 Y7 W7 F9 G9 7S00-10 PNX85500 10. 100n 2S64 EN 80 100n 2S67 2S62 100n 100n 2S63 VDD_1V1_DDR VDD_1V1 HDMI_VDDA_2V5 B13 Y19 Y18 W20 P20 M20 K20 V7 Y8 C7 C9 C11 C14 C16 C18 2011-Feb-18 back to div. table VDDA_3V3_USB VDDA_2V5_VDAC VDDA_2V5_VADC VDDA_2V5_USB VDDA_2V5_LVDS_BG VDDA_2V5_DCS VDDA_2V5_ADAC VDDA_2V5_AADC VDDA_2V5 R21 Y10 Y13 T20 D13 Y17 AA7 AA9 Y12 AA15 Y15 VDDA_1V2 AA13 VDDA_1V1_LVDS_PLL VDD_3V3_SBY VDD_3V3 VDD_2V5_LVDS VDD_2V5 N6 N7 U22 U20 U21 HDMI_VDDA_1V1 100n V20 V21 100n 2S68 HDMI_VDDA_3V3_TERM VDD_1V8 VDD U24 V24 HDMI_AGND 2S26 100u 220u 2.5V 1u0 2S23 2S29 2S21 100n 2S66 VSSA_USB IS58 30R 5S95 IS3L IS3K IS3S IS3Q +2V5 2 2S6F 1 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 100n 1 2S6G 2 2 100n 2S65 VSSA_1V1_LVDS_PLL A13 VSSA_2V5_LVDS_BG C13 6.3V 10u 2S4V 2S4Y L6 L7 R6 R7 U7 A5 A6 B5 B6 C6 D6 E6 F6 G6 F7 G7 R20 2S4Z 2S46 2S45 2S55 2S5M 2S53 2S6H 2S4T 1 100n 100n 2SHW 2 2S6M 1 2S6D 2 1 2S4N 2 2S6A 1 2 2S6B 1 2S5C 2 100n 2 100n 2S6N 1 100n 100n 100n 100n 2 100n 2S6K 1 10u 2 1 100n 2S6L 100n 100n 100n 100n 2S6E 2 1 2S4P 100n 2S6C 10u 2S4U RES 1u0 2S4W 2S50 2S56 2S5A 100n 2S58 RES 10u RES 10u 30R 5S82 30R 5S81 30R 5S80 30R 5S93 RES 10u 30R 5S92 30R 5S90 30R 5S89 30R 5S88 30R 5S87 30R 5S84 30R 5S83 2S6P 2S5B 2S5D 100n 2 100n 2S59 100n 2S57 10u 100n 100n 100n 10u 1u0 1 10u 10u 1u0 2S4M 10u 220u 6.3V 2S52 2S51 100n 22u 2S4R 22u 2S4Q 30R 5S85 c000 +3V3 +2V5 +2V5 +3V3 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD +2V5-LVDS +2V5 +2V5-AUDIO +2V5-AUDIO POL +1V2 +1V1 +3V3-STANDBY +2V5-LVDS +2V5 +3V3 +2V5 +1V1 2 3 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_028_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 SENSE+1V2 B02H AP: VGA EU: VGA +CVBS SCART2 YPBPR2 EU: YPBPR1 YPBPR1 - AP: AP: EU: AP: EU: SCART1 Connectivity RES 8 VGA-SDA-EDID VGA-SCL-EDID RES 1 3 100R 100R 100R 3S5V-1 3S5V-3 8 6 V-SYNC-VGA 100R 3 3S5T-3 6 3S5T-1 1 H-SYNC-VGA B-VGA G-VGA R-VGA AV4-PB AV4-PR AV4-Y AV2-CVBS AV3-PB AV3-PR AV3-Y YPBPR1-SYNCIN1 AV1-G AV1-B AV1-R 47R 56R 56R 56R * 3S59 22n 2S7K 2S7J 2S7U 2S7R 2S8G 22n 2S86 22n 2S85 22n 2S84 22n 2S7E 22n 22n 22n 22n 2S7P 22n 2S7N 22n 10n 2S7L 2S7M 22n 2S7H 22n 3S4J 3S4L 3S4K 3S4P 3S4R 3S4T 56R 56R 56R 9S18 9S19 9S20 56R 56R 56R 9S21 3S50 3S52 3S54 ANALOG_VIDEO div. table AGND SCL VGA_EDID P TUNER N SDA CVBS_Y1 ATV_CVBS_Y3 R C3 B AV1 CVBS_Y7 G C7 SYNCIN1 Y_G1 CVBS1_OUT PR_R_C1 CVBS2_OUT PB_B1 RESREF CVBS_Y2 CURREF SYNCIN2 Y_G2 1 PR_R_C2 2 PB_B2 3 REF 4 R 5 G VGA 6 B HSYNC_IN IF_AGC IN RF_AGC VSYNC OUT 2011-Feb-18 back to AF16 AD16 AE16 AB18 AC18 AF4 AD24 AD25 AB14 AF14 AE14 AC14 AD14 AF15 AE15 AC15 AD15 AB15 AC13 AD13 AE13 7S00-1 PNX85500 IS5D IS5F IS5G IS5H IS5J IS5E BS13 BS15 IS5C BS10 3S5S 10K IS4W * 319803104790 - RST SM0402 47R PMS Col R at 9S18 for BRZ AE12 AF12 AD12 AB11 AC16 AB16 AB13 AB12 AA12 AA10 AB10 AA11 AF11 AE11 AD11 AC11 AC12 AF13 22n 22n IS4V 2S22 2S8A C-SVHS Y-SVHS 47R 2S87 47p 22n 2S40 AV1-CVBS AA14 3S5B 56R 3S05 560R 3S08 3S5E 560R 8K2 3S09 PNX85500: Analog video 22n 2S75 B02I EN 81 2S19 100R Analog video 10. 10n 2S78 10n 2S77 47K 3S76 10K 3S75 100R Q552.2L LA 3S5T-4 5 4 10n 10n 100R 2S18 22n 100R 2S76 7 3S5T-2 2 22n 3S5V-4 5 4 2S16 22n 7 3S5V-2 2 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts IS11 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2S14 2S15 22n 2 3 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_029_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 PNX-IF-N PNX-IF-P PNX-RF-AGC PNX-IF-AGC CVBS-MON-OUT1 B02I FD03 FD08 FD01 RIGHT-SPEAKER LEFT-SPEAKER A-STBY AUDIO-MUTE-UP +AUDIO-L A-PLOP -AUDIO-R 6 ID14 2 6 4K7 3 GND-AUDIO ID34 3 ID15 3D02-3 4K7 7 3D02-2 2 7D11-2 BC847BS(COL) 4 GND-AUDIO 7D11-1 BC847BS(COL) 1 1u0 2D29 1u0 2D28 +24V-AUDIO-POWER +3V3-STANDBY GND-AUDIO 7D15-2 BC847BS(COL) 4 3 7D15-1 BC847BS(COL) 1 6 47K 3D01-4 5 4 3 100K 3D06-4 100K 5 6 100K 2 10u 2D02 100K 8 3D06-1 1 7 3D06-2 DETECT2 3D06-3 FD07 GND-AUDIO 4 5 47n 2D23 47n 5 10. FD09 ID30 4 GND-AUDIO 11 7 4 2 18 17 5 6 ID12 IN 26 27 28 29 +24V-AUDIO-POWER ID27 GND-AUDIO Φ L CD10 VIA L PGND VIA VIA GND-AUDIO VIA L R BSL OUT BSR GND_HS 37 36 35 34 2D08 ID31 ID32 GND-AUDIO 21 22 15 16 7D10-1 TPA3123D2PWP GND-AUDIO GND-AUDIO VIA div. table R R 220n GND-AUDIO ID28 FD10 PVCC CLASS-D AUDIO AMP AVCC 2011-Feb-18 back to GND-AUDIO FD14 AGND VCLAMP BYPASS MUTE SD 0 GAIN 1 L 2D20 7D10-2 TPA3123D2PWP +3V3-STANDBY 3 7D03-2 BC847BS(COL) 1u0 ID29 ID18 ID19 22K 3D16 R EN 82 7D03-1 BC847BS(COL) GND-AUDIO ID33 ID37 1u0 2D16 ID11 +AVCC 2D24 2D17 MAINS SWITCH DETECT ID35 5 2 4R7 3D09 3D02-4 Audio Q552.2L LA 5 B03A 47K 4 4K7 4K7 3D02-1 8 1 2 2D05 1 10u 35V Audio 6 3D01-3 3 220n 10-3 B03 393912365213 100p 220u 35V Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 2D03 2D06 8 9 10 12 6 3D15 2D07 23 24 40 39 38 30 31 32 33 4K7 220u 35V 19 20 5D07 220n 1 3 220R 5D08 13 14 ID09 ID10 22u 5D01 22u 5D02 RIGHT-SPEAKER GND-AUDIO LEFT-SPEAKER 220n 2D09 220n 2D10 220R 5D03 ID05 ID06 GND-AUDIO 8 220R 2D19 25 5 4 5 4 22K 22K 3D14-4 22K 6 3 6 3 3D10-4 22K 3D14-3 22K 7 2 7 2 1D50 2D01 1D52 3D10-3 22K 3D14-2 22K 3D10-2 22K 220R 5D04 220R 5D05 2D22 220n 2D11 ID07 1 2 3 4 2041145-4 FD02 1735 1 2 3 2041145-3 1D38 LEFT-SPEAKER RIGHT-SPEAKER SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 35V 220u 35V 220u 2D12 ID08 FD05 FD06 GND-AUDIO 2D21 220n 3D14-1 220n 1 8 3D10-1 220n 1 V_NOM 2D14 10n 2D13 V_NOM 10n 10n 2D26 RES 2D27 RES 2 3 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_030_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 B03A +3V3-STANDBY IU03 3U01 10K 3U00 RES ENABLE-1V8 100n 2U06 1 2 3 +1V8 7U00 BC847BW 10u 2U00 2U03 330R 1% 3U08 +1V1 GND-SIG IU24 12K 1K0 1% 3U03 +1V1 +1V8 3U22 GND-SIG 22K GND-SIG 3U02 1n0 RES 10K IU04 IU02 IU01 GND-SIG IU06 20 21 16 5 8 4 9 3 10 2 11 VIN GND-SIG 1 2 1 2 1 2 SW PGND TEST GND 1 2 DRVH V5FILT VREG5 1 2 100n 2U02 DRVL GND-SIG 1 TRIP 2 1 VFB 2 1 VO 2 1 EN 2 1 VBST 2 22K 2U01 3U09 7U03 TPS53126PW 3U10 IU05 GND-SIG 18 19 7 17 22 15 24 13 1 12 23 14 3U05 IU07 3R3 3U04 FU04 IU08 GND-SIG IU25 10u DC/DC 2U04 GND-SIG 10R 3U28 IU16 3R3 IU09 IU11 4 7U02-2 SI4952DY 220p 2U21 2 7 8 GND-SIG FU09 5 6 1 2U24 3U27 3U11 IU10 3 CU01 CU02 CU03 CU04 CU05 CU00 3U14 IU14 4 7U04 SI4778DY 220p 2U22 div. table IU13 4 2011-Feb-18 back to FU08 IU12 7U01 SI4778DY 1 2 3 5 6 78 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 3U23-4 FU06 FU05 IU20 FU02 IU23 IU15 2U16 IU17 IU18 GND-SIG IU21 2u0 5U01 12V/1V1 CONVERSION 3u6 5U00 12V/1V8 CONVERSION 47R 7U02-1 SI4952DY 3R3 6 47R 3U23-3 B03B 1u0 EN 83 6U00 3R3 100n 1K0 1% 1n0 1n0 6 2U07 2U05 3U24-2 2U08 3 47R 3U24-3 3U23-2 1n0 1n0 8 10. STPS2L30A 47u DC/DC RES 100p GND-SIG IU19 GND-SIG 3U21 100R 1% SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD * 30R 0402 Jumper 30R 5U02 5U03 RES FU00 IU22 1u0 100n FU01 FU03 SENSE+1V1 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_031_110415.eps 110415 2 3 +1V1 +1V8 +12V B03B 3139 123 65213 RES 2U29 Q552.2L LA 2U14 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 5K6 5 4 3U24-4 47R 47R 3U19 2U17 2U18 7 2 47R 3U23-1 1 47R 3U24-1 100p RES 47R 2U11 2U09 2U15 2U10 3U17 3U18 1u0 1% 330R 1% 1K0 RES 100u 2.0V 2U20 2U19 10u 22u 2U25 10u 2U13 2U12 47u 10R RES 3U20 22u 10R 2U23 10u 10u +12VIN 1-2041145-4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 1M95 *** 1-2041145-3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 1M99 * FU77 GND_AL GND_AL GND_AL FU76 FU62 FU67 FU58 FU59 FU60 FU61 FU63 FU75 RES 2U57 4U01 4U00 ** ** 2U58 * +12VD GND_AL +24V 10n 1u0 2U47 2U68 +12VIN FU50 FU49 FU48 +12V_AL optionally 1M99 is a 9 pin connector 1n0 100n 2U56 ** 100p 3U64 FU52 FU51 1K0 FU55 FU53 FU66 +3V3-STANDBY GND-AUDIO RES 2U48 1n0 +3V3 LED-1 100R RES 3U84 100R 100R 100R 3U43 IU55 *** 3U42 10K 3U81 IU56 3U71 +12V IU44 POWER-OK BACKLIGHT-BOOST BACKLIGHT-PWM_BL-VS STANDBY BL-SPI-CLK BL-SPI-CSn BL-SPI-SDO 3D-LR IU51 LED1 LED2 IU48 5 10K 3U62-1 IU50 div. table 6 1 7U41-1 BC847BS(COL) 1 8 IU63 IU61 3U60-2 IU62 2 3U62-2 3 4 10K 3U53 10K RES 3U59 7U40-2 BC847BPN(COL) LED1 LED2 IU49 6 7U40-1 BC847BPN(COL) 1 2011-Feb-18 back to 3K3 3U73 2 IU43 3U62-4 10K RES 3U41 9U41 EN 84 7U42 RES BC847BW LAMP-ON +3V3-STANDBY T 3.0A 32V 1U40 100R 10. +3V3-STANDBY IU45 FU07 10K 3U70 3U74 MAINS-OK 100R RES 3U67 100R 100R RES 3U66 RES 3U76 100R RES 3U44 +12VIN 3U45 +3V3 +24V-AUDIO-POWER 2U54 10n FU56 FU57 FU74 FU68 FU54 10K IU47 RES 3U56 7U43 BC847BW 9U42 RES +5V +3V3-STANDBY 3U69 LED-2 RES 10K +3V3 3U75 DC/DC 1n0 2U53 100p RES 2U72 RES 10K B03C 100p *** 2U44 RES 10K 3U72 DC/DC 1n0 2U49 3U65 100p RES 2U52 100p RES 2U51 100n 100K 100p 2U45 1K0 3U68 2U50 6U40 2U55 5 4 3U62-3 10K 3 10K 6 Q552.2L LA 22K ** FU72 22K 3 3U60-3 6 +3V3 3U60-4 4 100K 3U83-3 5 6 5 +3V3-STANDBY IU40 IU52 IU64 7U48-1 BC857BS(COL) 7U41-2 BC847BS(COL) FU73 3 3U82 Sundance / Infinity ( +12V AL) no no yes yes yes 1K0 RES 3U83-4 100K IU41 4 Emmy ( +24V AL) yes yes no yes no Optional table for Ambilight 3 4U00 4U01 1M99 1M95 2U56 Items 2 10K 10n BZX384-C6V2 1u0 RES 2 7 7 2 3U80 10K 4K7 2U71 4 3U61 8 7 22K 3U60-1 100K 3U83-2 1 2 IU57 7U48-2 BC857BS(COL) 100K Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 22K RES 2U43 10n 2U46 5 4 RES 10K 3U63 6 8 3U83-1 1 1 100n 5 RES 10K 3 ** Core Range 100R open 3U43 2 3 14 POLE 13 POLE 1M95 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_032_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 100p 0R 2U44 Optional table for Styling Dream Catcher *** SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD ENABLE-3V3n DETECT2 ENABLE-1V8 ENABLE-3V3-5V BlockBuster (For non-Amblight sets) no no no yes no B03C 3 RES 7U06-2 BC847BS(COL) 4 +2V5-REF 3U25-4 5 470R 3UB6-4 4 5 1K0 3UB7-4 5 4 3U25-3 6 5 100K RES 3 100K RES 4 +12V 3 IU29 6 7UA7-2 4 BC847BS(COL) 5 3UB6-3 6 1K0 IUB2 3UB6-2 6 2 7 1K0 3UB6-1 1 8 1K0 IUB5 3 1 3 2 RES 7U06-1 BC847BS(COL) 1 2UB8 +5V5-TUN 3UA0 K A 2K2 R 22u 7UA0 TS2431 2 IUB6 IUB4 3U25-2 IU30 3U25-1 IU26 +3V3 +3V3 ENABLE-1V8 7UA7-1 BC847BS(COL) 3U13 2 7UA6 BC817-25W 3U12 IUB3 3UB7-2 7 2 470R 3UB7-3 6 3 3UB7-1470R 1 8 330R 1% 330R 1% +2V5-REF 470R 470R 3U29-2 3U29-1 7 8 RES RES 470R 470R 3U29-4 5 RES 4 3 2 470R 470R 3U26-4 3U26-3 470R 470R 3U26-2 5 6 7 RES RES RES 1 3U26-1 8 RES 4 3 3U29-3 6 RES 2 1 +5V-TUN +5V REF NC K div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to 1K0 100K 1 3UB4 NC A 3 3UB5 2 5 7UA4 TS431AILT IUA6 22R 330p RES 2UB4 3UB3 1n0 1K0 3UB1 +12V IUA5 3UB2 2 2UB3 3UB0 IUB0 1 7UA3 PHD38N02LT +1V8 2UB1 1 1 FUA3 SENSE+1V2 RES 1u0 FUA0 2 8 2UB0 2UB2 +12V +5V5-TUN +1V2 +5V * 2UA4 2UB7 +3V3 1u0 1u0 DC/DC 470R 7 100K RES 100K RES 1u0 1u0 100R 100R 3U15-4 100R 3U15-3 3U15-2 100R 3 1 30R BP OUT COM INH IN 7UA5 LDS3985M50 * 5 6 7 8 +3V3 3 +5V CUA0 FUA4 4 3 2 1 4 5 IUB1 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD +5V-TUN 5 6 7 8 +3V3 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_033_110415.eps 110415 2 3 B03D 3139 123 6521 100R 100R 3U16-4 100R 3U16-3 3U16-2 100R * 3U16-1 +2V5-LVDS +2V5 NOT FOR 5000 SERIES OUT COM 3U15-1 * IN RESERVED 5UA0 4 3 2 1 1 * 7UC0 LF25ABDT 2 B03D 4 4K7 4K7 EN 85 2UB5 DC/DC 10. 2 Q552.2L LA 100n 2UB6 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 1u0 * 30R 0402 Jumper 5UD3 IUD1 2UD2 2UE0 * * +12V * 10u 10u 2UD1 2UD9 10u 10u 2UD0 2UD8 IUD0 * ENABLE-3V3-5V +5V ENABLE-3V3-5V 2UD3 30R 0402 Jumper 10u 10u A SYNC INH 11 A SYNC INH S1D 6UD1 10 7UD1-2 ST1S10PH 5 2 7UD1-1 ST1S10PH 10 7UD0-2 ST1S10PH 5 2 7UD0-1 ST1S10PH 4 5UD0 11 13 +12V SW VIA SW VIA IUD5 IUD4 IUD3 COM OUT IN COM 2 2 3u6 5UD2 3u6 5UD1 div. table OUT 7UD3 LD1117DT33 IN 7UD2 LD1117DT25 3 7 3 7 2011-Feb-18 back to 3 3 12 VFB GND P HS VIN 12 VFB GND P HS VIN 8 RES 1n0 1 13 1 8 A 9 9 2UE5 2UE7 4 A 6 SW 15 14 6 SW 15 14 100n 100n DC/DC IUD7 FUD2 IUD2 IUD6 SS36 6UD0 +3V3 2UE2 B03E 2UE8 2UD4 1% 3UD0 2UE1 3UD4 22u 16V 22u 2UD5 68K 3UD1 4n7 3UD3 1M0 3UD5 22u 33K 1% 1% 100K 33K 1% DC/DC 22u 2UE3 EN 86 1 1 22u 2UE6 10. 220u 16V 2UE4 22u 16V Q552.2L LA 6 +1V1 3U06 5 3U07 BC847BS(COL) 2 IU27 IU28 RES 2UE9 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD (*) FOR 5000 SERIES ONLY (**) NOT FOR 5000 SERIES 7U05-2 RES 4 3 +1V1 7U05-1 BC847BS(COL) RES 1 FUD3 +2V5 120K 4n7 3UD2 2UD7 220u 16V RES 2U27 RES RES 2U28 RES 100n 10K 100n 10K Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 22u 2UD6 +3V3 +5V 2 3 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_034_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 +5V5-TUN B03E B03F Temperature sensor & AmbiLight Temperature sensor & AmbiLight Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts +3V3 Q552.2L LA 30R 5UM1 IUM0 10. T 1.0A 63V 1UM0 div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to EN 87 FUM0 V-AMBI SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_035_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 65213 2 3 B03F TACHO TACH02 TACH01 FAN-DRV FAN-CTRL2 3US3 +3V3 10K 10K FAN-CTRL1 1K0 3US7 +12V IUT2 IUT1 RES 3US2 +12V 3US4-2 +3V3 10K 10K +12V 6 7 4 5 IUS5 10 11 8 9 10K Fan control 1 3US4-1 8 B03G +12V 12 3 +12V 12 3 +12V +12V 2011-Feb-18 back to +3V3 10K IUS4 3US5-4 5 4 10K IUS3 3US5-1 8 1 div. table 7US1-4 LM339P 1 7US1-3 LM339P 2 7US1-2 LM339P 13 7US1-1 LM339P 14 FUS0 10K +12V 3US5-2 6 3US5-3 IUS8 3 10K 7 2 10K EN 88 IUS9 BC807-25W 7US3 2US3 IUS7 +12V 7US2 BC807-25W IUS6 3US6 10. 47R Fan control 6 3US4-3 3 7 2 3 12 3 12 5 3US4-4 4 3US9 Q552.2L LA 22R Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 100n 9US0 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_035_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B03G B03H 5 47K RES 3UU0-4 +12VD LCD-PWR-ONn +3V3-STANDBY Vdisp switch 4 2 IUU0 RES 7UU2-1 PUMD12 1 6 5 RES 7UU2-2 PUMD12 3 4 47K 1 1u0 1 9UU0-1 RES 2 9UU0-2 RES 3 9UU0-3 RES 4 9UU0-4 RES 1 9UU1-1 RES 2 9UU1-2 RES 3 9UU1-3 RES 4 9UU1-4 RES 5 6 7 8 5 6 7 8 IUU2 RES 7UU1 SI3441BDV div. table VDISP-SWITCH 2011-Feb-18 back to 47R IUU1 RES 3UU0-1 8 1 RES 3UU1 3UU3-1 47K RES RES 2UU1 8 RES 7UU0 SI4835DDY EN 89 47K Vdisp switch 10. 2 RES 3UU0-2 7 Q552.2L LA 2 7 47K RES 3UU3-2 FUU0 FUU1 2 3 IUU3 22n RES 2UU2 +3V3 47K RES +3V3 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 47K RES IUU4 3UU3-3 IUU5 3UU3-4 6 3 4 5 4K7 RES 3UU2 1 RES 7UU3 BC847BW +VDISP-INT 2UU0 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts RES 100n 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_037_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B03H AV1-R YPBPR1-PR AV1-G YPBPR1-SYNCIN1 AV1-B YPBPR1-PB AUDIO-IN1-L AUDIO-IN1-R IE55 FE86 IE53 1u8 5E76 1u8 5E74 1u8 5E73 BEC3 RES 18R EU 3E78 18R BEC5 3E79 RES 18R 3E77 EU 3E76 18R RES 18R 3E75 EU 3E74 18R Analogue externals A IE22 FE23 2E06 B04A 100p 100p 2E04 Analogue externals A 4 1 8 1K0 5 3E07-4 1K0 3E07-1 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts RES 6E03 10-4 B04 393912365213 2E79 2E83 2E85 150p 150p 150p 2E80 2E84 2E86 150p 150p 150p CDS4C12GTA 12V FE80 CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V 1E31 1E54 1E12 1E18 6E09 2E88 1E19 RES RES 6E23 RES 6E26 RES 6E28 1n0 1n0 100p 2E14 FE81 FE74 FE73 FE71 Q552.2L LA 10. ** ** 4E03 RES RES ** 4E05 4E04 RES RES ** 4E02 RES ** 4E01 ** div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to EN 90 GND_A FE85 2 1E01-1 MSP-8033SH-02-NI-FE-RF-PBT-BRF RED 1 6 1E01-3 MSP-8033SH-02-NI-FE-RF-PBT-BRF GREEN 5 4 1E01-2 MSP-8033SH-02-NI-FE-RF-PBT-BRF BLUE 3 4 1E02-2 MSP-8032SH-01-NI-FE-RF-PBT-BRF WHITE 3 2 1E02-1 MSP-8032SH-01-NI-FE-RF-PBT-BRF RED 1 3 2 1K0 3E07-3 1K0 3E07-2 6 7 CVBS-MON-OUT1 AV2-BLK AV1-BLK AV2-STATUS AV1-STATUS IE51 IE48 IE05 IE18 4K7 +3V3 4K7 +3V3 4K7 3E73 18p 2E91 2E15 100p 100p 2E12 3E32 3E17 3E44 4K7 2E98 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2 3 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_038_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 B04A RES GND_A YELLOW 1 GND_A 1 2 FE42 GND_A 1 1E08-3 4 GND MT 7 6 5 4 VIN 3 1 1E10 3150-831-030-H1 2 VCC FE44 FE01 +3V3 VGA ( OR DVI ) AUDIO GND_A 1E09 MSJ-035-69A-B-RF-PBT-BRF 2 3 1 ** FE43 GND_A RED 5 1E08-2 3 * MSP-8033SH-05-NI-FE-RF-PBT-BRF RES WHITE 4E24 RES ** 4E23 * MSP-8033SH-05-NI-FE-RF-PBT-BRF 6 YPBPR AUDIO RES ** 4E22 MTJ-032-21B-42 NI FE 2 1E04 RES ** 4E21 1E03 MTJ-032-21B-45 NI FE (PBT) ** 4E20 1E08-1 * MSP-8033SH-05-NI-FE-RF-PBT-BRF 2 YPBPR FE51 FE54 Analogue externals B 2E27 2E67 B04B FE49 FE50 FE48 CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V Analogue externals B 100p 100p 100p 1n0 2E68 2E39 1n0 3E9C 2E73 FE03 FE02 1K0 3E96 1K0 3E97 EU EU EU AP 1K0 3E20 1K0 3E21 9E58 9E57 9E04 9E29 IE76 IE74 IE71 IE77 IE75 IE73 FE72 10. EN 91 ** Provision for ESD div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to * SOC Cinch V 3P 1L3 YEWHRDY at 1E08 for Brazil IE10 IE09 IE29 IE31 18R 3E90 18R 3E89 27R 3E88 18R 3E87 Q552.2L LA SPDIF-OPT AUDIO-IN4-R AUDIO-IN4-L AUDIO-IN3-L AUDIO-IN3-R YPBPR1-PR AV3-PR YPBPR1-PB AV3-PB AV2-CVBS YPBPR1-SYNCIN1 AV3-Y 9E28 AUDIO-IN1-L RES 9E22 AV1-R RES RES RES RES RES RES 9E13 9E20 AUDIO-IN3-L AV1-G 9E24 9E25 9E26 RES RES 9E11 9E18 AUDIO-IN3-R AV1-B AV1-STATUS AUDIO-IN1-R AV1-BLK RES RES 9E17 9E14 RES RES 9E19 9E12 AV3-PR RXD1-MIPS AV3-PB TXD1-MIPS RES RES 9E15 9E16 30R RES 5E06 AV3-Y AV1-CVBS SPDIF-OUT IE15 FE59 RES 6E46 +3V3 RES 1E32 31 DF50-30DP 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 32 Provision for Dreamcatcher 10p RES 1E44 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 2E37 RES 2E77 2E40 1E43 1E28 1E39 2E36 RES 6E40 RES 6E51 1n0 1E37 1n0 1E38 100p 1E80 100p RES 6E52 RES 6E06 RES 6E38 V_NOM V_NOM V_NOM 2E72 100p CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V 1E29 1E42 1R0 100n RES 6E19 RES 6E20 RES 6E53 2E35 2E71 CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V CDS4C12GTA 12V 100p 100p 2E38 CDS4C12GTA 12V RES 2E22 2 FE41 RES 1E07 MTJ-032-68B-46-NI-FE 1 SPDIF out SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_039_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B04B FE28 FE29 FE31 ETH-TXN ETH-RXP ETH-RXN ETH-REGOFF ETH-INTSEL FE27 ETH-TXP ETH-MDC ETH-MDIO ETH-TXER ETH-TXD(3) ETH-TXD(0) ETH-TXD(1) ETH-TXD(2) ETH-TXEN ETH-COL 3E51 3E70 RES RES 27n ETH-RXD(0) ETH-RXD(1) ETH-RXD(2) ETH-RXD(3) RESET-ETHERNETn 1K5 3E69 RES 10K IE26 15p +3V3 +3V3-ET-ANA 10K 25M 10p IE32 1 4 1 1E88 3 ACM2012 2 4 34 35 36 CR VIA MDC MDIO 0 1 2 TXD 3 4 INT TXER TXEN COL CRS_DV MODE2 0 MODE 1 RMIISEL PHYAD2 RXD<0:3> RST VSS VIA P N TX RXDV TXCLK P N RX IO VIA RBIAS CRS REGOFF 1 LED 2 INTSEL RXER RXD4 0 PHYAD 1 RXCLK 1A 2A VDD +3V3 IE06 +3V3-ET-ANA +3V3-ET-ANA CLKIN 1 XTAL 2 7E10-2 LAN8710A-EZK 17 16 22 23 24 25 18 21 +3V3 15 11 10 9 8 19 5 4 1E87 3 ACM2012 2 10K 10K IE38 7E10-1 LAN8710A-EZK 100n 2E66 IE33 10u 2E63 1M0 1E70 NX3225GA 3E30 2E62 RES 3E71 RES 3E80 RES 2E70 +3V3 10K 100n 2E52 IE07 100n 2E53 30R 1 5E08 40 41 42 32 14 2 3 7 13 26 20 29 28 31 30 10u IE39 9E42 FE61 FE60 10K 10K FE33 FE32 3E34 3E68 RES 3E35 RES +3V3-ET-ANA 3E72 3E65 IE64 3E64 IE63 10K 10K 10K 10K FE34 FE30 RES RES ETH-CRS ETH-INTSEL ETH-REGOFF ETH-RXCLK ETH-RXER 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 5450-323-183-H3 9 11 10 12 1N00 6 RXD1-MIPS 47R 3E53-3 47R 3E53-2 10 TXD1-MIPS 1 1 1 1 IE49 6E44 +3V3 1 X1 1 X1 1 X1 1 X1 4 1 47R 47R 3E53-4 3E53-1 12 RES 7E11-4 74HC4066PW 11 6 RES 7E11-3 74HC4066PW 8 5 RES 7E11-2 74HC4066PW 4 13 RES 7E11-1 74HC4066PW 1 BZX384-C5V1 5 8 FE57 FE56 10K MODE(1) = 0 MODE(2) = 0 3E70 (RES) 3E71 (RES) div. table 3E72 MODE(0) = 1 MODE(0) = 0 INTERRUPT FUNCTION ENABLED ON nINT/TXER/TXD4 SIGNAL INTERRUPT FUNCTION DISABLED ON nINT/TXER/TXD4 SIGNAL MODE(2) = 1 MODE(1) = 1 Internal 1.2V reg. enabled Internal 1.2V reg. disabled 3E68 (RES) MII mode selected PHYADD(2) = 0 PHYADD(1) = 0 PHYADD(0) = 0 EMPTY RES 3E9D RES 7E12 PDTC144EU 10K 3E69 (RES) RMII mode selected PHYADD(2) = 1 3E66 (RES) PHYADD(0) = 1 POP CONFIGURATION RESISTOR SETTINGS 9 2 TXD-UP PHYADD(1) = 1 3E67 (RES) IE50 3 3 2 RXD1-MIPS RXD-UP 7 TXD1-MIPS 3E65 (RES) 3E64 (RES) Resistor 2011-Feb-18 back to ETHERNET CONNECTOR +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 +3V3 ETH-RXDV ETH-TXCLK ETH-TXP ETH-TXN ETH-RXP ETH-RXN EN 92 100n +3V3 10. RES 2E69 Ethernet & Service 3E25 5E02 3E22 5E01 2E05 3E27 49R9 1% RES 2E56 RES 15p 0 ohm RES RES 27n RES 15p 0 ohm 2E07 3E28 49R9 1% 2E57 RES 2E55 10K 10K 10K 10K 3E66 3E67 3E81 3E82 RES RES RES RES RES 6E43 B04C 15p 4n7 6 RES 3E33 3E95 5E03 2E08 3E29 RES 27n 27 6E47-1 BZX384-C5V1 RES 6E48 12 CDA5C16GTH 16V RES Q552.2L LA 1E85 Ethernet & Service 6E47-2 2E49 CDA5C16GTH 16V RES 10p 49R9 1% 2E58 RES RES 15p 0 ohm RES 12K1 1% CDA5C16GTH 16V RES 10p 15p 3E99 5E04 2E09 15p 3E39 3E26 1E86 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts CDA5C16GTH 16V 2E54 RES 27n RES 15p 0 ohm RES 22n 2E60 33 37 38 39 8 1 22R 100n 7 2 49R9 1% 2E59 RES 22R 3E98 BAS316 14 7 14 7 14 7 14 7 2E48 3E40 6 6E47-3 3 5 6E47-4 4 RES 3E9E RES 7E13 PDTC144EU 1E06 AV2-BLK 4 502382-0370 RES 1E71 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD provision for iTV TXD RXD 1 2 3 5 PROVISION FOR iTV 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_040_110415.eps 110415 2 3 B04C 3139 123 6521 UART SERVICE CONNECTOR MSJ-035-69A-B-RF-PBT-BRF FE58 2 3 1 FECP 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 23 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 FECG 21 23 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 FEC6 21 23 20 22 20 22 20 22 +5V AIN-5V BIN-5V FECM FECN FECK FECL FECJ 100R 3ECD 100K 3ECF IEC4 IE11 +5V-EDID FECZ 3ECG BAT54 6EC1 3ECE IEC7 9EC0 IEC6 1u0 2ECU AIN-5V BIN-5V AIN-5V CIN-5V BIN-5V CIN-5V +5V-VGA CEC-HDMI +3V3-STANDBY CRX-DDC-SCL CRX-DDC-SDA BRX-DDC-SCL BRX-DDC-SDA ARX-DDC-SCL ARX-DDC-SDA +3V3-STANDBY IEC5 22K RES 3E23 CRX-HOTPLUG CRXCPCEC-HDMI ARC-eHDMI+ CRX-DDC-SCL CRX-DDC-SDA CRX0CRXC+ CRX1CRX0+ CRX2CRX1+ CRX2+ BRX-HOTPLUG BRX-DDC-SCL BRX-DDC-SDA BRXCPCEC-HDMI BRX0BRXC+ BRX1BRX0+ BRX2BRX1+ BRX2+ ARX-HOTPLUG 7EC0 BC847BW RES 7E02 BC847BW CIN-5V FECA HDMI CONNECTOR 1 FECE FECF FECC FECD ARXCPCEC-HDMI ARX0ARXC+ ARX1ARX0+ ARX2ARX1+ ARX2+ ARX-DDC-SCL ARX-DDC-SDA HDMI CONNECTOR 2 FEC5 FEC1 FEC2 FEC4 PCEC-HDMI 1P02 1P03 1P04 DDCA-SCL DDCA-SDA ARC-eHDMI+ eHDMI+ DRX-DDC-SDA DRX-DDC-SCL DRX-HOTPLUG CRX-DDC-SDA CRX-DDC-SCL CRX-HOTPLUG BRX-DDC-SDA BRX-DDC-SCL BRX-HOTPLUG ARX-DDC-SDA ARX-DDC-SCL ARX-HOTPLUG IE66 IE65 DIN-5V CIN-5V BIN-5V AIN-5V 10. 10K 3ECU-2 7 8 7 6 5 1u0 30R 5EC0 7 8 BRX2BRX2+ 17 18 CRX2CRX2+ DRX0DRX0+ DRX2DRX2+ 25 26 23 24 21 22 DRX1DRX1+ 19 20 43 44 DRXCDRXC+ 2ECQ IE45 15 16 CRX1CRX1+ 45 46 13 14 CRX0CRX0+ 5 100K 11 12 39 40 CRXCCRXC+ 2ECP 41 42 5 6 BRX1BRX1+ IE44 3 4 BRX0BRX0+ 6 100K 1 2 33 34 BRXCBRXC+ 2ECN IE43 71 72 ARX2ARX2+ 35 36 69 70 ARX1ARX1+ 7 100K 67 68 ARX0ARX0+ 29 30 31 32 100n VCC33 1u0 3ECH FEC3 N P N P N P N P TX2 TX1 TX0 TXC CEC_D DSCL4 DSDA4 R4PWR5V VIA RSVDL CSCL CSDA INT CEC_A TPWR_CI2CA EPAD FECW N R3X2 P N R3X1 P N R3X0 P N R3XC P DSDA3 DSCL3 (CBUS) HPD3 R3PWR5V N R2X2 P N R2X1 P N R2X0 P N R2XC P DSDA2 DSCL2 (CBUS) HPD2 R2PWR5V N R1X2 P N R1X1 P N R1X0 P N R1XC P DSDA1 DSCL1 (CBUS) HPD1 R1PWR5V N R0X2 P N R0X1 P N R0X0 P N R0XC P DSDA0 DSCL0 (CBUS) HPD0 R0PWR5V 2ECV 7EC1 SII9187B 65 66 IE42 2EC6 FEC0 100n ARXCARXC+ 2ECM 8 100K 220u 16V div. table +3V3 1u0 4 3ECN-4 1u0 3 3ECN-3 2 3ECN-2 1u0 1 3ECN-1 RES 2EC1 2011-Feb-18 back to 10K 4 3ECU-4 5 2 30R 10R 3ECM-1 10R 3ECM-2 10R 3ECM-3 10R 3ECM-4 5EC2 1 2 3 4 +3V3-HDMI +3V3 100n 2EC8 EN 93 2EC0 100n 2EC7 HDMI CONNECTOR 3 6 4 10u 9 27 64 HDMI 47K 47K 3EC1-3 3 1 3EC1-1 8 2 3ECA-2 7 8 3ECA-1 1 47K 47K 47K 47K 3ECA-4 5 6 3ECA-3 3 2EC2 RES 2ECW B04D Q552.2L LA 10p 37 MICOM_VCC33 38 SBVCC33 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 10 28 54 53 52 50 55 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 51 48 47 49 MICOM-VCC33 FEC7 FECB 10K 10u Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 2ECC 2EC3 FECY IE12 FECR 30R RES 5EC3 9EC2 RES 9EC3 RES 4K7 3ECJ RES 3ECP-1 HDMI 22K 4R7 73 6 10K 3ECP-3 100n 8 1 3EC3 3EC5 4K7 3ECL RES 100R 100R +3V3 INSTAPORT 4X 100K 4X 100K 9187B 9287B 3ECN 7EC1 SCL-SSB SDA-SSB VGA-SCL-EDID-HDMI VGA-SDA-EDID-HDMI MICOM-VCC33 PCEC-HDMI 4K7 RES 3ECK HDMIA-RXCHDMIA-RXC+ HDMIA-RX0HDMIA-RX0+ HDMIA-RX1HDMIA-RX1+ HDMIA-RX2HDMIA-RX2+ CEC-HDMI +5V-EDID +3V3 SII9187B = 0xB2 I2C Address NON-INSTAPORT RES 2ECX 10K 10p 3 10p RES 2ECY 100K 100K 3ECF SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD SUNDANCE BLOCKBUSTER 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_041_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B04D A-PLOP ADAC(4) ADAC(3) Headphone IEE2 IEE0 1u0 2EE3 1u0 2EE4 IEE1 8 10K 3EE0-1 1 10K 4 10K 3 3EE0-3 6 5 3EE0-4 IEE4 IEE3 1u0 2EE2 RESET-AUDIO 22K B04E IEE6 IEE5 4 1 2 3 5 6 2 VDD IN- 2 1 10 11 7 1 div. table 100n 2011-Feb-18 back to VIA GND GND_HS BYPASS VO AMPLIFIER Φ SHUTDOWN 2 1 5 8 7EE0-1 PUMD12 1 6 EN 94 47p +3V3 22K 2EE5 3EE1-4 22K 47p 3EE1-1 2EE0 10. 7EE1 TPA6111A2DGN FEE0 Q552.2L LA 4 2EE1 Headphone RES 3EE3 8 5 3 4V 100u 2EE7 4V 100u 2EE6 4 PUMD12 7EE0-2 +3V3-STANDBY IEE8 IEE7 1 2 4 3 33R 33R 3EE2-1 3EE2-2 33R 33R 3EE2-4 3EE2-3 8 7 5 6 FE35 FE36 A-STBY A-PLOP AMP2 AMP1 7 2 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 9 6 3 22K 3EE1-3 22K 3EE1-2 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_042_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B04E DDR2-VREF-DDR FB00 +1V8 240R 3B28 240R 3B27 240R 3B22 DDR2-CLK_N DDR2-CLK_P DDR2-CLK_N DDR2-CLK_P DDR2-CLK_N DDR2-CLK_P AT T-POINT DDR2-CLK_P DDR2-CLK_N DDR2-CKE DDR2-CS DDR2-RAS DDR2-CAS DDR2-WE DDR2-DQM2 DDR2-ODT DDR2-BA2 DDR2-BA0 DDR2-BA1 DDR2-A0 DDR2-A1 DDR2-A2 DDR2-A3 DDR2-A4 DDR2-A5 DDR2-A6 DDR2-A7 DDR2-A8 DDR2-A9 DDR2-A10 DDR2-A11 DDR2-A12 DDR2-A13 3B23 3B01 33R RES 240R 1X20 HOOK1 DDR2-CLK_P DDR2-CLK_N DDR2-CKE DDR2-CS DDR2-RAS DDR2-CAS DDR2-WE DDR2-DQM0 DDR2-ODT 1X21 HOOK1 1X22 HOOK1 3B25 3B06 1X23 HOOK1 33R RES 240R 1X24 HOOK1 F9 E8 F8 F2 G8 F7 G7 F3 B3 DDR2-BA0 DDR2-BA1 DDR2-BA2 G2 G3 G1 7B00 EDE1108AGBG-1J-F F9 E8 F8 F2 G8 F7 G7 F3 B3 G2 G3 G1 H8 H3 H7 J2 J8 J3 J7 K2 K8 K3 H2 K7 L2 L8 7B02 EDE1108AGBG-1J-F H8 H3 H7 J2 J8 J3 J7 K2 K8 K3 H2 K7 L2 L8 100n 2B01 100n 2B19 DDR2-A0 DDR2-A1 DDR2-A2 DDR2-A3 DDR2-A4 DDR2-A5 DDR2-A6 DDR2-A7 DDR2-A8 DDR2-A9 DDR2-A10 DDR2-A11 DDR2-A12 DDR2-A13 100n 2B02 100n 2B20 DDR 100n 2B06 100n 2B24 B05A 100n 2B07 100n 2B25 VDD VDD CKE CS RAS CAS WE DM|RDQS VSS CK ODT 0 1 BA 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 A 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 CKE CS RAS CAS WE DM|RDQS VSS CK ODT 0 1 BA 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 A 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 E1 VSSQ VSSDL VSSQ NC NU|RDQS DQS DQ VREF 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 DDR2-VREF-DDR VDDQ SDRAM Φ VDDL +1V8 VSSDL NC NU|RDQS DQS DQ VREF 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 DDR2-VREF-DDR VDDQ SDRAM Φ VDDL +1V8 Q552.2L LA 2B44 RES L3 L7 A2 B7 A8 2B46 33R 3 1 3 2 3B16 33R DDR2-A14 DDR2-DQS0_P DDR2-DQS0_N DDR2-D0 DDR2-D1 DDR2-D3 DDR2-D2 DDR2-D4 DDR2-D5 DDR2-D6 DDR2-D7 div. table 7 33R 6 3B07-3 33R 8 3B08-1 33R 6 3B08-3 33R 3B07-2 DDR2-A14 DDR2-DQS2_P DDR2-DQS2_N DDR2-D16 DDR2-D17 DDR2-D18 DDR2-D19 DDR2-D20 DDR2-D21 DDR2-D22 DDR2-D23 2011-Feb-18 back to 3B17 RES 2p2 5 33R 7 33R 5 33R 8 33R 33R 3B12 33R 7 33R 6 3B00-3 33R 7 33R 5 33R 3B00-2 EN 95 2 6 3B02-3 33R 3 8 3B02-1 33R 2 3B02-2 5 33R 3B02-4 4 8 33R 3B13 2p2 C8 C23B08-4 4 D7 D3 3B08-2 2 D1 D9 3B07-4 4 B1 B9 3B07-1 1 L3 L7 A2 B7 A8 C8 3 C2 D7 D3 1 D1 D93B00-4 4 B1 B9 3B00-11 10. DDR2-CLK_P DDR2-CLK_N DDR2-CKE DDR2-CS DDR2-RAS DDR2-CAS DDR2-WE DDR2-DQM3 DDR2-ODT DDR2-BA2 DDR2-BA0 DDR2-BA1 DDR2-A0 DDR2-A1 DDR2-A2 DDR2-A3 DDR2-A4 DDR2-A5 DDR2-A6 DDR2-A7 DDR2-A8 DDR2-A9 DDR2-A10 DDR2-A11 DDR2-A12 DDR2-A13 DDR2-CLK_P DDR2-CLK_N DDR2-CKE DDR2-CS DDR2-RAS DDR2-CAS DDR2-WE DDR2-DQM1 DDR2-ODT DDR2-BA2 DDR2-BA0 DDR2-BA1 DDR2-A0 DDR2-A1 DDR2-A2 DDR2-A3 DDR2-A4 DDR2-A5 DDR2-A6 DDR2-A7 DDR2-A8 DDR2-A9 DDR2-A10 DDR2-A11 DDR2-A12 DDR2-A13 100n 2B10 100n 2B28 DDR 3B20 3B21 100n 2B11 100n 2B29 10-5 B05 393912365213 180R 1% 180R 1% 2B40 2B42 100n 2B04 100n 2B22 47u 2B00 47u 2B18 100n 2B03 100n 2B21 100n 2B05 100n 2B23 100n 100n A1 E9 L1 H9 A3 E3 J1 K9 A1 E9 L1 H9 A3 E3 J1 K9 A9 C1 C3 C7 C9 A7 B2 B8 D2 D8 A9 C1 C3 C7 C9 E7 E1 E7 2B36 100p 2B08 100n A7 B2 B8 D2 D8 3B24 3B03 33R 3B26 3B09 RES 240R 33R RES 240R 100n 2B15 100n 2B33 F9 E8 F8 F2 G8 F7 G7 F3 B3 G2 G3 G1 H8 H3 H7 J2 J8 J3 J7 K2 K8 K3 H2 K7 L2 L8 F9 E8 F8 F2 G8 F7 G7 F3 B3 G2 G3 G1 VDD CKE CS RAS CAS WE DM|RDQS VSS CK ODT 0 1 BA 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 A 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 7B01 EDE1108AGBG-1J-F H8 H3 H7 J2 J8 J3 J7 K2 K8 K3 H2 K7 L2 L8 VDD CKE CS RAS CAS WE DM|RDQS VSS CK ODT 0 1 BA 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 A 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 7B03 EDE1108AGBG-1J-F 100n 2B16 100n 2B34 E2 2B26 100n 2B38 100p E2 2B41 2B43 100n 2B13 100n 2B31 47u 2B09 47u 2B27 100n 2B12 100n 2B30 100n 2B14 100n 2B32 100n 100n A1 E9 L1 H9 A3 E3 J1 K9 +1V8 VSSDL +1V8 VSSQ VSSDL VSSQ VDDQ SDRAM Φ VDDL NC NU|RDQS DQS DQ VREF 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 DDR2-VREF-DDR NC NU|RDQS DQS DQ VREF 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 DDR2-VREF-DDR VDDQ SDRAM Φ VDDL E1 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts A7 B2 B8 D2 D8 A1 E9 L1 H9 A3 E3 J1 K9 A9 C1 C3 C7 C9 A7 B2 B8 D2 D8 A9 C1 C3 C7 C9 E7 E1 E7 2B17 100n 2B37 100p E2 2B35 100n 2B39 100p E2 2B45 1 4 3 3 L3 L7 A2 B7 A8 2B47 C8 C2 3B11-3 3 3B10-3 33R 3 D7 D3 D1 D93B10-4 4 B1 B9 3B10-1 1 L3 L7 A2 B7 A8 C8 3B05-3 C2 D7 3B04-3 D3 D1 D93B04-4 B1 B93B04-1 33R 33R 3B18 33R 7 3B11-2 8 33R 33R 5 3B11-4 33R SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 3B19 RES 2p2 3B14 33R 2 3B10-2 7 33R 2 1 5 3B11-1 33R 4 8 33R 6 6 33R 3B15 RES 2p2 3B04-2 2 7 6 33R 6 33R 33R 7 3B05-2 33R 2 1 8 3B05-1 33R 5 5 3B05-4 33R 4 8 33R 33R DDR2-A14 DDR2-DQS1_P DDR2-DQS1_N DDR2-D8 DDR2-D14 DDR2-D10 DDR2-D11 DDR2-D12 DDR2-D13 DDR2-D9 DDR2-D15 DDR2-A14 DDR2-DQS3_P DDR2-DQS3_N DDR2-D24 DDR2-D25 DDR2-D26 DDR2-D27 DDR2-D28 DDR2-D29 DDR2-D30 DDR2-D31 2 3 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_043_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 B05A B06A Display interfacing-Vdisp Display interfacing-Vdisp 10-6 B06 393912365213 +VDISP-INT Q552.2L LA 30R RES 2G43 div. table IG11 FG0H 6G00 LTST-C190KGKT RES For Development use only 2K2 RES 3G28 2011-Feb-18 back to T 3.0A 32V RES 30R RES 5G02 T 3.0A 32V 1G03 EN 96 1G00 10. 5G01 22u RES Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 100n 2G44 +VDISP SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2 3 2010-12-10 2010-12-10 19110_044_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 B06A 47p 47p 47p 47p 2G96 2G99 2G97 2G98 FG11 FG1C FG1D FG1E FG1F FG1G FG1H FG19 FG1A FG1B FG1Q FG1P PX4DPX4D+ PX4EPX4E+ FG18 FG15 FG16 FG17 FG12 FG13 FG14 PX4CLKPX4CLK+ PX4APX4A+ PX4BPX4B+ PX4CPX4C+ FG1J 100n 2G95 FG1K FG1L FG1M FG1N 100n 2G94 PX3DPX3D+ PX3EPX3E+ 100n 2G93 PX3CLKPX3CLK+ PX3APX3A+ PX3BPX3B+ PX3CPX3C+ 100n 2G92 1G50 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 FI-RE41S-HF 50 51 48 49 46 47 44 45 42 43 TO DISPLAY FG30 FG31 FG32 FG33 FG2J RES 1X05 REF EMC HOLE FG1R FG1S FG1T FG1U FG1W FG1V PX2CLKPX2CLK+ PX2DPX2D+ PX2EPX2E+ div. table FG28 FG29 FG2A FG2B FG2C FG2D PX2APX2A+ PX2BPX2B+ PX2CPX2C+ 2011-Feb-18 back to FG24 FG25 FG26 FG27 FG1Z FG20 PX1DPX1D+ PX1EPX1E+ FG2E FG2F FG1Y FG2L FG2M FG2K FG35 FG2R FG34 FG2H FG2G FG22 FG23 10K RES 3G33 FG21 10K RES 3G34 PX1CLKPX1CLK+ 100R 100R 100R 100R 100R 100R 100R 100R 100R 10K RES 3G35 PX1APX1A+ PX1BPX1B+ PX1CPX1C+ 3D-LR CTRL-DISP CTRL-DISP 3D-VS-DISP RES 3G2Z FG04 RES 3G30 RES 3G31 RES 3G36 RES 3G38 RES 3G37 CTRL-DISP BACKLIGHT-BOOST RES 3G32 3G2W 3G2Y CTRL-DISP SDA-DISP SCL-DISP 47p 2G75 +VDISP 47p 2G76 47p 2G77 +VDISP 47p +3V3 47p 2G79 2G78 Video out - LVDS EN 97 47p B06B 10. 10p 10p FG2N 1G51 60 61 58 59 56 57 54 55 52 53 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 FI-RE51S-HF TO DISPLAY RES 9G0G FG2P 2G28 2G29 47p 2G24 Video out - LVDS Q552.2L LA 47p 2G25 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 5 6 7 8 9G0K-4 9G0K-3 9G0K-2 9G0K-1 4 3 2 1 47p 2G26 100n 2G7A 2G91 47p 2G27 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_045_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B06B +3V3 7 +3V3 3G15 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 RES 3GA2-1 RES 3GA2-2 RES 3GA2-3 RES 3GA2-4 1 2 3 4 DEBUG ONLY RES 1G35 1u0 8 7 6 5 GTS1 GTS2 GSR AMBI-SPI-CS-OUTn_R2-R AMBI-PWM-CLK_B2 AMBI-SPI-CS-OUTn_R2 AMBI-LATCH1_G2 AMBI-TEMP CPLED3 CPLED2 PNX-SPI-CS-BLn PNX-SPI-SDO PNX-SPI-SDI PNX-SPI-CLK PXCLK54 GCK2 GCK3 30R 5GA1 10p 2G11 RES 1G36 2GA5 1 2 3 4 5 6 SD51022 100R 100R 100R 100R 2GA1 10p 30R 2GA0 2GA3 10K 100n 10p 2G12 5GA0 100n 2GA2 FGA5 FGA3 BACKLIGHT-PWM +3V3 FGA4 33R 3 33R 11 9 24 10 29 30 31 32 37 38 36 34 33 2 3 39 40 41 42 43 44 1 VIO VINT VINT TCK TDI TDO TMS IXO2_29 IXO2_30 IXO2_31 IXO2_32 IXO2_37 IXO2_38 GND IXO2_36|GTS1 IXO2_34|GTS2 IXO2_33|GSR IXO1_2 IXO1_3 IXO1_39 IXO1_40 IXO1_41 IXO1_42 VCCINT Φ IXO1_43|GCK1 IXO1_44|GCK2 IXO1_1|GCK3 9GA0 7GA0 XC9572XL-10VQG44C0100 1 3G14 33R 6 3G11-3 33R FGA6 100n FGA2 8 3G11-1 3GA3 FGA1 FGA0 VIO 19 20 21 22 23 27 28 5 6 7 8 12 13 14 16 18 BACKLIGHT-PWM_BL-VS IXO4_19 IXO4_20 IXO4_21 IXO4_22 IXO4_23 IXO4_27 IXO4_28 IXO3_5 IXO3_6 IXO3_7 IXO3_8 IXO3_12 IXO3_13 IXO3_14 IXO3_16 IXO3_18 VCCIO 3G12 4 3G11-4 4 3G10-4 2 3G10-2 3GA1 5 33R 3 7 3G10-3 33R 3G13 1 10R 5 3G10-1 33R RES 47R 9GA1 RES 10p 2G14 2G13 +3V3 AMBI-SPI-CS-EXTLAMPSn div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to 33R 8 33R 6 33R 10p 2G15 1u0 2G10 3GA4 10p 2G16 26 10K RES 2GA6 10p 2G17 15 35 4 17 25 10p RES 10p 2G18 +3V3 AMBI-SPI-CLK-OUT AMBI-SPI-SDI-OUT_G1 AMBI-SPI-SDO-OUT AMBI-LATCH2_DIS AMBI-PROG_B1 AMBI-BLANK_R1 PNX-SPI-CSBn BACKLIGHT-PWM 3D-LR 3D-VS-DISP BL-SPI-SDO BL-SPI-SDI BL-SPI-CSn BACKLIGHT-PWM_BL-VS BL-SPI-CLK AMBI-SPI-CLK-OUT-R AMBI-SPI-SDI-OUT_G1-R AMBI-SPI-SDO-OUT-R GSR GTS2 GTS1 GCK3 GCK2 CPLED3 CPLED2 GCK3 GTS1 GTS2 GSR IGA3 IGA2 IGA1 2 3GA5-4 3GA5-3 3GA5-2 3GA5-1 4 3 2 1 100R 100R 100R 100R 5 5 6 7 8 SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 5 RES 1G37 RES 7GA1-2 BC847BS(COL) 4 3 +3V3 SD51022 1 2 3 4 5 6 2010-12-23 19110_046_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 2011-03-09 B06C DEBUG ONLY RES 7GA1-1 BC847BS(COL) 1 6 +3V3 RES 7GA2-2 BC847BS(COL) 4 3 2 +3V3 +3V3 RES RES RES RES RES 7GA2-1 BC847BS(COL) 1 6 +3V3 RES 3GA6-2 RES 6GA0 AmbiLight CPLD 7 330R 2 LTST-C190KGKT EN 98 RES 3GA6-1 RES 6GA1 10. 8 330R 1 LTST-C190KGKT Q552.2L LA RES 3GA6-4 RES 6GA2 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 5 330R 4 LTST-C190KGKT B06C 2GA4 RES 3GA6-3 RES 6GA3 AmbiLight CPLD 100n RES 6 330R 3 LTST-C190KGKT 10p 2G19 10p B06D SPI buffer SPI buffer Direct +3V3 47R 3GE0-3 47R 3 RES 47R 3GE3 47R 3 2011-Feb-18 back to div. table 3GE4 RES * ** 4 RES 9GE1 BL-SPI-SDI PNX-SPI-CS-BLn 2 RES 9GE0-2 RES 9GE2 RES 5 9GE0-4 IGE0 3GE1-3 6 7 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 19 PNX-SPI-SDO 2 3EN1 3EN2 G3 RES 7GE0 74LVC245A 1 EN 99 1 1 +3V3 10. RES 9GE0-1 IGE1 100n 8 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 18 RES 2GE0 PNX-SPI-CLK AMBI-SPI-SDI-OUT_G1-R BL-SPI-SDI PNX-SPI-SDO PNX-SPI-CLK Buffer * ** RES Q552.2L LA RES 3GE2 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 20 10 8 RES 47R 4 3GE1-4 47R RES RES 7GE1 PDTC114EU 3GE0-1 RES 5 1 6 RES 10K BL-SPI-CSn PNX-SPI-SDI BL-SPI-SDO BL-SPI-CLK BL-SPI-SDO AMBI-SPI-CLK-OUT-R AMBI-SPI-SDO-OUT-R PNX-SPI-SDI BL-SPI-CLK PNX-SPI-CSBn SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_047_110415.eps 110415 3139 123 6521 2 3 B06D Y N N N 1C86 1C87 FAN-DRV FAN-CTRL2 SDA-BL TACH02 SCL-BL TACH01 FAN-CTRL1 EMMY BLOCKBUSTER 2C70 ITEMS * Option table for Ambilight AMBI-BLANK_R1 AMBI-PROG_B1 AMBI-LATCH2_DIS AMBI-TEMP AMBI-SPI-CS-OUTn_R2 AMBI-LATCH1_G2 AMBI-PWM-CLK_B2 AMBI-SPI-SDO-OUT AMBI-SPI-SDI-OUT_G1 3C70 100n AMBI-SPI-CLK-OUT +12V_AL +24V +3V3 +12V +3V3 10K * RES 3C93 100R RES 3C83 FC86 FC64 RES 3C82 FC63 30R RES 5C54 30R RES 5C53 100R * RES 3C92 100R 100R RES3C81 100R FC85 * RES 3C91 100R T 2.0A 63V * 1C87 T 2.0A 63V 1C86 RES 3C80 * RES 3C90 10K FC84 FC83 * FC62 +3V3 FC61 Y N SUNDANCE / INFINITY 100R IC78 FC97 * 1M59 28 1 2 3 4 2041145-4 FC98 RES 1M71 FC99 div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to RESERVED TEMPERATURE SENSOR iTV 100n RES 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 FH34SRJ-26S-0.5SH(50) FC78 FC77 FC74 FC72 FC70 FC67 FC82 2C96 GND_AL GND_AL FC96 FC81 V-AMBI V-AMBI GND_AL FC79 FC76 FC75 FC73 FC71 30R 5C55 AMBI-POWER 2C94 RES 2C83 Connectors comp 2C95 SDA-SET SCL-SET KEYBOARD LED-1 LED-2 RC LIGHT-SENSOR RES RES 47R 47R +5V +3V3-STANDBY 10R 3C79 100R 3C78 +3V3-STANDBY 100R 3C77 100R 3C76 100R 3C75 2C82 100p 100p 2C80 100p 2C79 100p 2C78 100p 2C77 100p 2C76 9C02-1 9C02-2 9C02-3 9C02-4 0R3 FC66 FC65 Yes No No 1M19 1M20 Sundance / Infinity Yes 8 7 6 5 BlockBuster / Emmy 0R3 3C97 +T 1 2 3 4 +T RES 3C96 BZX384-C5V6 Option table for Leading Edge 3C95 3C94 FC95 IC75 IC74 IC73 FC87 6C03 RES Items ** 9C00 RES 9C01 RES 47n RES 2C93 +3V3 3C74 B09A 100n RES RES 2C85 100K RES EN 100 2C86 RES RES BZX384-C5V6 BZX384-C5V6 Connectors comp RES 1C85 10p 6C02 RES 6C05 10-7 B09 393912365213 T 1.0A 63V 10p 2C87 RES 100n 100p RES 2C84 2C90 10. 100p FC91 FC89 +5V FC93 1u0 Q552.2L LA SPB SSB TV550 2K11 4DDR BR SD FC94 FC92 FC90 1M20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2010-12-23 2011-03-09 19110_048_110415.eps 110415 2 3 B09A 3139 123 6521 FH52-11S-0.5SH 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1M19 TO LED PANEL FC88 2C81 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 1u0 1u0 2C91 ** 100n ** ** ** 3C74 3G38 2C77 3C78 3C77 2C80 2C78 3C79 9U41 3U75 7U42 9U42 3U69 7U43 2C81 3C95 2C86 2C87 2C90 3C94 2C91 6C05 2C82 6C03 2C93 3C76 6C02 3C75 2C76 2G77 2G75 2G76 2G27 2G78 2G26 2G25 2G24 2G79 2G7A 3U68 IC74 IC75 3U59 3U53 3E33 3E51 2E66 9E43 5D05 5D04 2E56 5E02 6E47 3E28 2E07 IE07 2E52 2E53 3E68 5E01 2E63 3E72 3E35 3E34 2E55 2E54 1N00 2E57 3E25 3E22 7E10 9E42 1G50 1D50 1D52 5D08 2D06 2E49 1735 1D38 1G51 1M20 1M19 2G28 3E98 2D24 2D05 2D08 3E71 3E26 2G29 2E62 5E08 2D23 2E48 2D10 2D12 2D11 2E60 3E69 3E40 3E64 1E88 3E67 2D17 2D19 2D20 3E70 2D07 2D09 5D02 5D01 3E65 2E05 3E27 3E30 3E66 1E70 1E87 7D10 1E44 2EE6 3E97 2E39 2E72 9E11 6E46 3EE2 2EE7 2EE3 2EE2 2EE1 3B25 3B17 3B16 3B19 3B13 3B12 3B23 3B14 3B15 3B24 1P04 IEE3 1E42 1E08 7EE1 IEE4 1E29 2B47 3B10 3B18 9E24 3E32 1E19 1E32 1E54 7B03 7B02 7B00 1E02 1E31 6E38 5D07 5E06 4E05 2E40 2G96 IEE6 2G99 4E04 7B01 2EE5 2S2R 2S2T 9E29 3E87 6E40 2E27 3E88 9E17 9E22 3E89 2U58 3S13 BS15 3S12 BS13 9E18 9E20 1E01 1E12 3U43 2S4G DS50 2U49 2S7M 1S02 2S4F 7S00 3U42 3U45 1E18 2U24 2U68 BS10 3S3W 3S43 2S78 2S77 2ECC 1P02 5EC2 div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to 9EC3 2EC1 3EC5 3S81 3S3M 3S50 3S54 3S52 3S80 3ECP 2ECU 2U48 3U76 2S4E 3ECM 2ECM 2ECN 3ECN IE42 6EC1 IE11 3S83 3S84 7EC1 1E03 1E04 3EC3 2U47 5U01 3U24 IU17 2U11 IU18 3E17 2U54 2U72 2U20 3U67 2U50 7U01 7U04 7U02 3U71 3S6H 3S3N 3S3T 3S1J 3U44 IU23 2U18 3U56 3S3L 3S1C 3S1B 3S1K 3S3S 3S21 3S62 1E85 6E19 6E53 2E77 3E9C 2E73 1E38 3E21 IE10 9F27 3US5 IUS6 3US3 3US2 IF62 3UB1 3UB4 2UB1 2UB2 IUT2 2C83 3C92 2C84 2C85 7US1 3C82 5C54 IF61 7UA4 3U07 2U28 3UD3 2UE1 3UD5 3UD4 2UE0 3UD0 3UD1 2UD7 3UD2 2UD3 3C81 3C83 IUS5 3US7 5UM1 2F40 5UD0 2UD2 2UD1 7UD0 5UD3 2UD9 2UD8 7UD1 6F72 3G10 3GA1 9GA0 IF89 2F93 2F9C 9F04 2F9A 2F99 9FC4 9FC3 9FC6 1FC3 1FC4 1FC2 3FC2 2FC7 2F97 2F60 1329 2FL7 1FL5 2FL6 9FLE 3F34 1F52 3F623F63 3GA2 2GA4 9FLC 9FLD 9FLH 9FLJ 3FL4 2FC8 6FC8 6FC6 6FC1 6FC2 6FC4 6FC3 6FC5 6FC7 1P08 1P09 7FL5 1F51 5F73 IF86 5F70 3FLE 7GA1 1G36 3GA5 1G37 6GA2 1G35 3GA6 6UD0 5UD1 2F9D IGA3 5UD2 7F70 IUD4 IGA1 2UE4 2UE2 2UE3 IGA2 7GA0 3G11 1M59 1E05 1FC6 3F78 1F75 2UD0 2U27 3U06 IUD0 IUD2 IUD1 1T01 3UB5 2UB0 7UA3 7F20 3S3Y IUS9 3C80 IUT1 5C55 1F24 1M71 3G13 1M99 3G12 1M95 3U64 2S4M 2S34 IS13 3S3G 1P03 1E43 3S3F 3S53 3S27 2S4P 3S3H 4U01 9S91 2U25 9S00 3B11 3B07 3B08 2B46 2B44 3B00 2B45 3B02 3B05 3B04 9S90 2S33 2S32 DBS8 4U00 2S2W 2S2V 9S06 2U53 2S2Y 3S00 3S26 3S6J 3U65 2S7K 2G97 3U41 3U70 3U74 7EE0 2E22 6E06 1E07 9E13 2EE4 2EE0 4E20 3EE0 3EE1 4E03 4E24 4S14 9S92 2S7H 3S4L 3S3U 7S08 2U44 2S7E 9S21 3S44 3S2M 3B26 1E28 2S7U 2S30 2S31 4E02 2S8G 9S18 9S20 2S2Z 4E22 2S7N 9S93 2S7R 9S19 2U51 3S3Q 2U45 2S7P 3S4T 3U81 2U09 2S87 3S59 3S4R 3F11 3F10 2G98 4E21 3S42 2U46 2S7L 3S4P 2U23 7S00 1F10 3ECF 3F08 3S6K 3G14 Overview top side 2E67 3E96 2E71 3EE3 IEE5 3ECG 3S4K 9E15 2S41 9E04 2S2S 6E51 9E57 4E01 4E23 3S4J 2S7J 1E39 5U02 3S3R 2U43 IU15 2U17 3U84 1E37 6U00 3S6N 2U16 1E86 1E80 2F58 5U03 3S2A 7US2 2U52 2S4D 7US3 3U66 1E09 2US3 2U19 3S1L 1E06 1E71 2E36 3S28 IE09 3S23 2E38 2U56 IUS4 3F59 3F60 3U23 3S29 2E35 2UB3 5C53 3UB3 3C91 3C90 2G16 1UM0 10-8 313912365213SSB Layout 3F58 3UB2 3US6 3US9 7F58 3UB0 IUS3 2UB4 1C85 2UE9 9US0 3C93 2UE6 7U05 2U15 9F28 3E20 9F71 3S24 2E37 6E20 9F05 9F06 2F9B 5F72 2F86 3F75 2F98 2F81 3F09 2ECP 6FD3 6FD2 2F91 3F72 9F00 9F01 2F88 2F92 2F94 2F90 3F71 3US4 3C70 2C70 3F64 5U00 1E10 1FD3 EN 101 3FC7 10. 2FC2 Q552.2L LA 9FC5 1FC1 3FC6 2FC1 2UE8 1FC5 2C94 3FL7 2FC4 2UD4 2C95 3F65 1328 2FC3 6GA1 9FL3 3FL2 2FDD 2FDC 2C96 2FC5 6GA0 7GA2 9FLK Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 3FC5 6GA3 9FLL 1C86 1C87 2UD5 2FC6 3FLC 1FD2 3FC4 3FC3 3FC1 SSB Layout Top 1P05 1P07 9FLF 2UD6 3FDG 9FLG 2 2011-03-07 19110_001_110307.eps 110309 3139 123 6521 FFB6 FFB5 FFB3 FFB1 FL40 FL41 FGA4 FFC6 FFB4 3FBF 9FC2 FGA6 FFC8 FL42 FL39 FFC5 3FLG FFDA FFDC FFC3 FFC9 FFC2 IFL3 3FLH IFLE 2FLB 2FL5 2FL2 2FLC 3U25 IU30 IS40 IUB5 IUB4 IFLG IFL2 2UB5 3FLB FF66 IFLD IFLA IFLC IFLF 2UB6 IFL1 IU29 IGE0 9GE1 2GA2 7UA7 3UB6 3UA0 7UA5 2FLA IFL4 FL36 FUA0 2G13 7GE1 9GE2 9GA1 IGE1 3UB7 9F25 9F26 FL37 2FL3 FL30 FC83 7UA0 IUB1 IUB3 2GA6 9GE0 7U06 FUD3 IS17 FC76 IUD7 FFC7 FF65 FF64 FL43 IFLB 2FL8 2FL1 2FL4 FL32 IUB6 FC77 2G19 2G15 FF82 IU26 IUB2 3GE2 IF79 3GE4 IF90 FF74 FF76 FFDB FF00 AF70 AF71 FF75 3U16 2GA1 3GE0 FF42 FF41 FF46 FF48 FF45 FF49 FF47 FF43 FGA5 FGA0 FGA1 FC73 FUD2 2G17 3F45 3F40 FF50 3U15 2UE7 IFD2 IFD1 2UA4 FC61 FC97 FC63 FC98 FC99 CUA0 2UE5 IUA5 IFD3 IF13 IFD4 IFD5 FF81 IF65 IF48 5FE4 2FF6 IF15 5FE9 2FG7 2FG8 2FH7 2FH6 2FG9 5FE3 5FE0 IF63 IF56 IF10 2F63 2F64 IF11 FF44 IF66 3F66 3F54 2FH5 2FE6 FF03 FFA2 2FH3 2FG6 2FG4 5FE5 IF81 FF61 IF67 IF57 IF27 IF76 IF82 IF52 IF53 FF56 FF04 3FG2 FF62 5FA3 2FF1 IF18 DFF1 2FA3 IF69 IF49 2FF8 IF68 IF51 DFF2 FFAF IF58 FC95 DFE7 DFE8 IF54 2F21 2F49 FF57 FU54 3F12 3F52 FF55 FL31 IF04 FU49 7FE0 3FG4 2F79 2F75 3F77 IF64 3FE5 IF73 IF75 IF50 IUB0 IUA6 IUD5 FUA3 FU50 IUS8 7FA3 FF63 IF17 2FE8 IF28 3F80 3F81 IF12 2FH8 IF14 9F03 9F02 FF01 2F85 2FE0 BFE2 3F67 IF55 7F53 FF58 FF71 3F68 IUD6 IU27 IU28 7UD2 FUA4 IUS7 FU48 FF08 IU50 IU63 2FF0 2FF5 3FG7 2FE4 FU63 2U57 2U55 IU62 3U73 3S1E 3S6A 3S2G IU40 5F74 5F71 3F79 IU48 FU56 2F96 IF80 IS1L IU22 3S41 3S1P 3S2H 2U21 3S69 3S2F IF23 IF08 2U06 IU24 2F20 3F23 3F24 IU09 3F19 IS1K 2S3Q FE44 FE57 3S19 IS1E IS11 3S55 FS50 FECB FE02 2ECQ IE43 3U03 CU05 IU04 FU08 2U05 FU04 2U04 FU58 FU59 IU25 FEC3 IS4Z 2S84 2S86 2S85 IS2V FECZ FE58 FF07 IF88 FS45 IE44 IU45 IU43 FS52 FS53 2U10 3U20 5EC3 FEC7 2EC3 FE01 FS51 3S82 3S5Z 3S6E 3S6G 3S61 IF87 9C00 9C01 FC86 3S6B 3S56 3S57 3S5Y 3S6D 3S6F 3S60 IS00 3S6C FECY FS11 2S89 9S08 2EC8 FE42 FS10 IS05 IU13 FU61 3S5W 3S58 IS09 9S12 3S67 3S65 9S11 FS31 3U14 IU12 IU14 IU08 3U17 FU60 IU20 2U13 2U12 IU21 IS44 IS04 IE45 6E48 IE49 FU09 2U14 FU02 3U22 7U03 FU68 IU16 FS49 6E44 FE03 FE56 3E53 IE50 2F95 FS44 3S18 IS1G 7S09 IS2U IF22 IU10 IU11 2U01 7U00 IU03 FU74 3U04 IU05 FU01 FU57 3S2K 3S6V IF21 FU72 3S6W IU57 IU61 2F73 2F80 2F72 2F82 2F77 2F76 AF73 AF72 FU73 5F76 2F65 3F82 IF16 2U71 IU41 IU49 3U60 IU64 IU52 3U83 3U61 3U82 3U63 FU75 1U40 3U62 6U40 3U72 FU77 IU51 FU07 3U08 9FL2 IC78 3U00 2U03 9FL1 7UC0 IF47 FC62 FUS0 2FD1 IUM0 FUM0 FC72 FC70 IS10 IS3E 3S1H 3S1G IS16 9S09 IS01 DS52 IS58 IS25 IS3F FECR IE05 FECW 3E76 FECK 2S6L FF05 FF06 5S85 3S2S FU66 FECN FECM FECA FE80 FEC0 5EC0 9EC2 FECL 3S2L 5S80 2S27 FU51 6E26 3S5E IS0V IE76 FE48 2S57 IS3L 9S24 IS5C IS5J 3S5S IS5E 2S51 IS5H 9E19 2S75 2S76 IS06 IS4V IE66 IS4W 2S46 2S6G 2S5G 2S4N IS1M FU76 IS1B 2S65 2S36 IS1A 2S6N 2S6E 2S6D FS08 IS19 IS1N 2S61 2S66 IS03 IS1P IS02 IE48 IE65 FE51 9E26 6E23 3ECU FE74 3E74 3S38 3S36 IEC5 FE54 3S06 IS42 FS01 IE71 2E85 IE55 IS50 FS02 3E78 3S33 3S30 IEC4 7EC0 7E02 FECD 9EC0 IE75 3S22 IS12 2S20 3S0V IS07 3S0Z IE73 FECF IEC6 FECC IE74 IE51 IE53 IS1D IS1S 2E79 7S05 5E73 IS0R 2S62 FU62 2S21 div. table 3E90 IE77 2E15 2E98 BEC3 3E75 IS1H IS1Q 2E80 IS1J FU55 5S94 2S5K 5S95 3S76 IS3K 5S83 2S4Y 2S4W 2S5M 2SHW 2S4T FU53 3S16 3S17 IS20 FU52 2S43 IS5G IS3B IS5F 2E84 2S10 IS5D IS2Z 3E77 2S4U 3ECA IE12 2S6B IU55 CXXX FU67 2S5B 3S46 3ECK 2E14 IS3Q 2S6C 5E74 3F07 3S1V 9S97 2011-Feb-18 back to FECP 2U29 3U21 FU00 IU07 IU56 FU06 IS08 IS26 3S1W FF09 2U02 IU06 9S96 FC75 2S6P FC71 3GE1 3GE3 2G11 2GA5 2GE0 2GA0 2G14 3GA3 2G10 FC74 2GA3 5GA1 7U40 FC82 2FLD 3FLF FS2Y FC67 3FD6 3U27 2G12 IUD3 3G15 2G18 3U26 3U29 2U22 FC84 3FLD 9FD2 IU02 3GA4 2UB8 3F32 2FL9 3U12 2UB7 5UA0 7UA6 3FLA FL33 IF72 3FD7 5GA0 3F44 3F43 3FD2 3FD1 7UD3 3F42 3F41 3FD3 9FD1 FC64 7F54 7GE0 2F59 2F53 FGA3 9FC1 3FD4 9FD5 2F66 6FD1 5F66 3S1R 7U48 CU00 CU03 FL38 3F69 FF29 2F78 2F74 FC85 7U41 3S1U 3S1F 2S5H 3U01 FU03 2U08 3S66 FGA2 FFB2 3U13 2F61 FFC4 2FG2 9CH0 5FG0 7FD1 5FE7 2F84 3F76 2FH2 5FG2 2FH4 IF29 3S2V 3F53 2FF7 1FE0 2F71 2FF2 2FG3 7FE3 2FE3 5FE8 BFE3 3FE7 3FE8 IF77 2FA2 7F75 IF78 6UD1 2FF3 IF74 2FE5 2F52 7F52 3FE9 2FF9 2FG0 2FG1 IF59 FS0Z 2S3L FS2W FC79 5FA4 3S11 3U80 3S6M 9S94 FC78 DFE9 9S0E 3S25 6E43 3F20 2FF4 3S1T 2F62 2F70 2S4K 9S10 3U05 3U10 CU04 3U02 CU02 3U28 9S0D 3F21 DFE6 3FE6 2FA4 3S1S 3FG6 2S3M 2E69 FS64 3F22 3U19 IU01 5S82 3S64 3U11 2S3K 7E13 7E12 7E11 3ECH 3S5V 3S5T 7S20 3E9E 3E9D 3U09 CU01 FS57 3S0W IU19 3U18 2U00 IS3D IS3S 9S13 3ECL 3S68 7S01 3S45 2S5D 2S2E 3S15 3S40 3S47 BEC5 3E23 FECE 3ECE FE81 3E79 2E86 6E28 FEC4 5E76 2E12 3B22 IE18 FEC6 2B40 2B13 2B15 2B20 2B24 2B42 2B30 2B32 2B43 2B33 FU05 2EC6 2S5C 3S3P 3S1X 3S49 2S6A C000 2S6F 5S92 2S6H 2S5P 2B41 3B09 3B06 3B28 3B01 2B17 2B37 3B27 2B39 2B35 2U07 9E14 2EC2 2E83 2S67 C001 2B27 2B28 FC96 2EC7 2EC0 9E12 2ECW 3S1D 2S6K 2S5A 2S55 2S6M 2ECY FE86 2S4V 2S28 2S56 2S11 2S4Z 2S58 2S15 2S14 2E68 9S95 2S5J 5S89 2S64 2S60 5S88 2S37 5S87 5S90 2S50 2S53 3S75 5S81 2S16 3S05 5S84 2S22 2S13 9E16 2S59 2ECX 2S19 5S04 6E52 9E58 FE85 FEC1 3EC1 FEC2 FE73 2E04 FEC5 FE41 IE15 IEE2 FEE0 IE31 FE50 6E03 IEE1 IE29 2E06 9E25 FE36 FE71 IE22 FE49 2E88 3E07 FE23 2E91 2B01 9E28 2B00 2B09 2B10 2B22 2B34 2B18 2B31 FECJ 6E09 3B03 FB00 2B36 IEE0 IEE7 IEE8 FE59 FE32 IE33 IE32 FE33 FE60 FE27 IE64 3E29 FE28 FD14 FE31 FE61 5E03 2E58 3E95 FE29 ID08 ID07 ID19 FD10 ID18 FD03 2D29 FD08 2D28 3D09 IE39 FD09 ID09 IE38 3D14 ID06 ID05 3D10 ID31 ID27 ID37 FD01 ID14 ID11 3D15 ID34 2D03 ID12 7D11 ID30 2D02 2E59 5E04 ID33 3E39 FE34 IE26 IUU3 IUU2 IUU4 3UU2 FUU1 2UU0 7UU3 3UU3 IE06 FUU0 5G02 5G01 2G44 2UU2 FE30 ID28 7D15 ID10 ID32 3E99 IE63 ID15 FD07 ID35 2UU1 3UU1 IUU0 7UU0 IUU1 3UU0 IUU5 7UU2 7UU1 FC81 3ECJ 2ECV 3E73 3S5B 2S45 2S3G 5S93 2S4S 3S08 2S52 2S18 2S2K 2S23 3S09 2S2L 2S40 2S8A 3S6L 3S10 3S34 2S3F 2S3B 2S2J 2S3H 2S3D 3S32 2S63 2S68 2S3E 2S17 2S12 2S3A 3S39 2S38 2S3J FS03 2S3C 2S2H 3S6Q 3S6P 2S4R 2S39 3S07 2S24 2S25 2S42 3S37 2S2G 3E44 2S29 3B21 2B26 3B20 2B29 2B25 2B19 2B16 2B23 2B21 2B14 2B38 2B08 2B12 2B04 2B07 2B11 2B02 2B05 3S20 2S4Q 3S51 FE72 2D14 IC73 FC92 2D13 5D03 2D01 1G00 Overview bottom side FE43 FC87 FC91 FC90 FC93 FC66 FG0H 3G33 3G30 3G34 3G2Z IU44 IU47 FC65 FG2K FG2M 3G36 2G91 FG2N 3G35 3G32 FG2L FG2P FG17 FG32 FG31 FG2C FG1P FG11 FG1N FG15 FG19 FG1B FG2R 3G2W FG2H FG1L FC89 SSB Layout Bottom FG2G 3G2Y FG1Z FG2F FG1Y FG2E 3G37 FG20 FG21 FG24 FG29 FG22 FG25 FG26 FG2A FG1R FG1T FG1W FG1D FG16 FG1G FG1F FG1J FG1M FG14 FG18 FG1A FG1Q FG2J FG23 FG28 FG27 FG2B FG1S FG1U FG1V FG1C FG1E FG1H FG1K 2G93 2G92 FG33 6G00 IG11 3G31 FG35 FD02 FD06 FD05 2G43 EN 102 IEC7 2B03 2B06 3D01 3D16 3G28 10. 3S72 3ECD 2D27 3D02 2S26 FECG 2D21 2D22 2D26 7D03 CD10 3D06 ID29 9UU1 9UU0 FG04 2D16 2E09 9G0K FG30 Q552.2L LA FE35 FC88 2C79 2G95 9G0G FG13 FG2D Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts 2E08 1G03 FC94 2G94 FG34 FG12 FFC1 2011-03-07 19110_002_110307.eps 110307 3139 123 6521 2 BLOCKBUSTER / EMMY 32" 11-1 Blockbuster/Emmy 32" 11. Styling Sheets 1108 5216 1150 Styling Sheets Q552.2L LA 0004 11. div. table 2011-Feb-18 back to 1004 EN 103 8308 5213 0029 5216 0004 0011 0029 0260 1004 1005 1085 1108 1150 1161 1162 5213 5216 8191 8308 8G50 8G51 Pos No. 1005 Description Front Cabinet Back Cover Hard Switch bracket Stand Display panel Power Supply Unit Remote Control Keyboard + IR assy Board SSB AmbiLight AmbiLight Loudspeaker box Tweeter Mainscord 1.8m Main (power) switch Cable LVDS FFC Cable LVDS FFC 0011 Not displayed Not displayed Not displayed Not displayed Not displayed Not displayed 19110_049_110420.eps 110420 Remarks 0260 BLOCKBUSTER / EMMY 40"- 46" 11-2 Blockbuster/Emmy 40" - 46" 1108 5216 Styling Sheets 1150 Q552.2L LA 0004 11. div. table 1004 2011-Feb-18 back to 1005 EN 104 8308 0040 POS. NO. 0004 0011 0040 0260 1004 1005 1085 1108 1150 1161 1162 5213 5216 8191 8308 8G50 8G51 5216 5213 DESCRIPTION. Front Cabinet Back Cover Hard Switch bracket Stand Display panel Power Supply Unit Remote Control Keyboard + IR assy Board SSB AmbiLight AmbiLight Loudspeaker box Tweeter Mainscord 1.8m Main (power) switch with cable Cable LVDS FFC Cable LVDS FFC 0011 Not Displayed Not Displayed Not Displayed Not Displayed Not Displayed Not Displayed 19110_050_110420.eps 110420 REMARKS 0260