Download ST7 FLASH STICK User Manual
Transcript
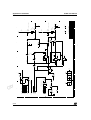
ST7 FLASH STICK User Manual c u d e t le o s b O - ) Release 1.2 s ( t c u d o r P e t e l o s b O Ref: DOC-STICK-PP October 2004 o r P ) s t( c u d e t le ) s t( o r P o s b O - INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE—WARNING This product is conform to the 89/336/EEC Directive. It complies with the ITE EN55022 standard for EMC emissions and generic 50082-1 (1992 edition) immunity standards. This product is an FCC Class-A apparatus. In a residential environment, it may cause radioelectrical disturbances. ) s ( ct In addition, this programming board is not contained in an outer casing; consequently, it cannot be immune against electrostatic discharges (ESD). It should therefore be handled only in static safe working areas. Please refer to Appendix A Safety Requirements on page 15 for relevant safety information u d o r P e t e l o USE IN LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS MUST BE EXPRESSLY AUTHORIZED. STMicroelectronics PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF STMicroelectronics. As used herein: s b O 1. Life support devices or systems are those which (a) are intended for surgical implant into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and whose failure to perform, when properly used in accordance with instructions for use provided with the product, can be reasonably expected to result in significant injury to the user. 2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can reasonably be expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. Table of Contents Chapter 1: 1.1 1.2 1.3 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 About this manual... ...................................................................................... 5 Host PC system requirements ...................................................................... 6 Getting assistance ........................................................................................ 6 Chapter 2: 2.1 2.2 2.3 Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Delivery checklist .......................................................................................... 7 Setting up the hardware ................................................................................ 7 In-circuit programming considerations .......................................................... 9 Chapter 3: 3.1 3.2 Programming with STVD7 or STVP7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 ) s t( Start programming with STVD7 .................................................................. 12 Start programming with STVP7 .................................................................. 13 c u d Appendix A Safety Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 o r P Appendix B: Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 e t le B.1 B.2 B.3 B.4 Test pins ..................................................................................................... 16 Error messages .......................................................................................... 17 “Problem on supply voltages” ..................................................................... 17 “Cannot communicate with the device” ....................................................... 18 o s b O - Appendix C: Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 ) s ( ct Appendix D: Schematics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 u d o Product Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 r P e Software updates ...................................................................................................... 23 Hardware spare parts ............................................................................................... 23 Contact List ............................................................................................................... 24 t e l o s b O Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 3/26 1 - Introduction 1 STICK User Manual INTRODUCTION Thanks for choosing ST7! This manual will help you get started programming your ST7 microcontrollers with your ST7 FLASH STICK. The ST In-circuit Communication Kit (STICK) is a powerful, flexible programming tool that is ideal when you are getting started developing applications in the world of ST7 Flash microcontrollers. The STICK provides the programming hardware interface between your ST7 and your host PC, running either ST7 Visual Programmer (STVP7) or ST7 Visual Develop (STVD7) software. c u d ) s t( The STICK takes advantage of the In-Circuit Communication (ICC) protocol for ST7 to provide both in-circuit programming (ICP) of the ST7 soldered on your application board, or socket programming of your microcontroller using an ST7SBxx socket board. e t le ) s ( ct u d o r P e t e l o s b O o s b O - o r P Socket Programming Configuration STVP7 or STVD7, ST7 FLASH STICK, ST7SBxx Socket Board In-Circuit Programming Configuration STVP7 or STVD7, ST7 FLASH STICK ST7 on your application board Figure 1: Programming configurations 4/26 STICK User Manual 1 - Introduction The STICK is delivered ”ready-to-use” for in-circuit programming of an MCU that has been installed on a properly configured application board. However, socket programming of ST7 MCUs requires an additional ST7SBxx socket board. For more information about socket programming with the STICK, you can refer to the ST7SBxx Socket Board User Guide. 1.1 About this manual... This manual will help you set up your STICK programming tool and connect it to your PC. Here you will find: • Setup instructions • Detailed hardware information • A trouble shooting guide for your programming tool c u d ) s t( For more information about the hardware and software intended for use with your STICK, refer to the following documents: o r P ST7 Visual Programmer online help– information about the STVP7 programming interface e t le ST7 Visual Develop User Manual– information about the STVD7 programming interface o s b O - ST7SBxx Socket Board User Guide– setup information for socket programming ST7xxxx Datasheet– includes information about ICC connection and microcontroller programming that is specific to your MCU 1.1.1 u d o Date r P e Nov 2000 t e l o s b O ) s ( ct Revision history Jun 2001 Revision Description 1.1 • Updated Section 1.2 – includes support of windows XP 1.2 • Added Table 1 – Revision history table • Added Section 2.3 – setting up ICP connection • Added Section 3.1 – programming from STVD7 Table 1: STICK User Manual Revision History 5/26 1 - Introduction 1.2 STICK User Manual Host PC system requirements Both hardware and software components of the STICK have been designed to work with PCs meeting the following requirements: One of the following operating systems: Microsoft® Windows® 98, 2000, • Millennium, NT® or XP®. • Intel® Pentium (or compatible) processor with minimum speed of 133 MHz. • Minimum RAM of 32 MB (64 MB recommended). • 50 MB of free hard disk space to install all of the ST7 tools. • Parallel port ) s t( Note: Windows® 2000, NT® and XP users must have administrator privileges to install the required software. 1.3 Getting assistance c u d o r P For more information, application notes, FAQs and software updates on all the ST microcontroller families, check the CD-ROM or our website: e t le www.st.com/mcu For assistance on all ST microcontroller subjects, for help using your programming tools, refer to the contact list provided in Product Support on page 23. We’ll be glad to help you! ) s ( ct u d o r P e t e l o s b O 6/26 o s b O - STICK User Manual 2 - Getting Started 2 GETTING STARTED 2.1 Delivery checklist Check that your ST7 FLASH STICK contains the following: 2.2 • One STICK interface board (marked “ST7 FLASH STICK-LPT”). • One AC/DC power supply adaptor. • One PC parallel port cable. • One 10-pin HE10 type ribbon cable for ICC connectors. • The “Microcontroller Development Tools” CD-ROM containing ST7 Visual Programmer (STVP7) software, ST7 Visual Develop (STVD7) and other ST7 software development tools. c u d Setting up the hardware 1 Set the W1 jumper on your STICK to correspond to the application power supply (VDD). e t le ) s ( ct o r P o s b O - r P e O bs Power supply connector (J2) W1 Jumper ICC connector (JP1) u d o t e l o ) s t( Test Points (TP1) Figure 2: STICK component layout The W1 jumper must be set to one of the three following positions: - VDD: The power supply voltage of the STICK’s ICC buffer follows the VDD used by your ST7. This position allows you to work with any power supply voltage supported by your MCU (refer to your ST7xxxx Datasheet for supported VDD). When the jumper is in this position, you must connect the application power supply to pin 7 of the ICC connector. 7/26 2 - Getting Started - STICK User Manual 5 V: The power supply voltage of the STICK’s ICC buffer is 5 V. You don’t need to connect the application VDD to pin 7 of the ICC connector, but your application must be powered by 5 V +/- 5%. - 3.3 V: The power supply voltage of the STICK’s ICC buffer is 3.3 V. You don’t need to connect the application VDD to pin 7 of the ICC connector, but your application must be powered by 3.3 V +/- 5%. 2 Note: Connect the STICK to the parallel port of your host PC with the supplied parallel cable. Be sure to use the provided PC parallel port cable—using a longer cable may cause malfunctions. Connect the cable directly between the host PC and the STICK—using additional cables or switch boxes between the host PC and the STICK may cause malfunctions. If a dongle is already connected to the PC’s parallel port, it should not interfere with the STICK. However, if your STICK malfunctions, remove the dongle and restart the setup. c u d ) s t( 3 Power on the STICK using the provided AC/DC power supply, which you plug into the J2 connector. Ensure that the power supply is adapted to the mains voltage and outlet type used in your country. 4 Connect the ICC cable to the ICC connectors on your STICK (JP1) and your application board (for more information about installing an ICC connector on your application board, refer to Section 2.3). 5 e t le o s b O - o r P Power up your application board. You are now ready to program your ST7. For more information about the programming sequence, refer to Chapter 3: Programming with STVD7 or STVP7 on page 12, or refer to your software’s on-line help file. ) s ( ct u d o r P e t e l o s b O 8/26 STICK User Manual 2.3 2 - Getting Started In-circuit programming considerations The In-Circuit Communication (ICC) protocol for ST7 makes it possible to in-circuit program your application to an ST7 FLASH microcontroller while the device is mounted on your application board. However, when you start developing your application, you must integrate an ICC connector into your application hardware. To help you implement in-circuit programming (ICP) in the development of your application, this section provides a summary of points you should consider when installing an ICC connector. 2.3.1 ICC Connection Requirements To connect to your application board for ICP, you must install a 10-pin, HE-10 type connector, which receives the STICK’s ICC cable and relays the required signals to the ST7 on your application board. Using the In-Circuit Communication (ICC) protocol for ICP requires that a minimum of 4 and as many as 6 pins of your ST7 be connected to the STICK (see Figure 3, below and Table 1 on page 10). e t le ) s ( ct ) s t( HE-10 type connector c u d o r P o s b O - u d o r P e ST7 FLASH STICK t e l o s b O Figure 3: ICC interface 9/26 2 - Getting Started STICK User Manual ST7 pin Connects to ICCDATA ICC input serial data pin ICCDATA ICCCLK ICC output serial clock pin ICCCLK RESET Device reset ICCRESET ICCSEL/VPP Programming voltage ICCSEL/VPP OSC1 or OSCIN * Main clock input for external ICCOSC VDD * Device power supply VDD_APPLI VSS Device power supply (ground) GND * Optional connection for the STICK, see text. c u d Table 1: ICC connection requirements Isolation of ICCDATA and ICCCLK pins e t le ) s t( o r P As soon as your STICK is plugged into the application board the ICCDATA and ICCCLK pins must not be used by other application devices, even if you are not programming your MCU. If the application uses these pins as inputs, isolation such as a serial resistor must be implemented to prevent other application devices from forcing a signal on either of these pins. The application board must not drive current in excess of 1mA. ) s ( ct o s b O - If the ICCDATA and ICCCLK pins are only used as outputs by the application, no signal isolation is necessary. u d o For ST7 MCUs with no ICCSEL pin, during normal operation the ICCCLK pin must be pulled-up internally or externally (10KΩ pull-up required in noisy environments). This is to avoid entering ICC mode unintentionally during a reset. For more information, refer to the ST7 ICC Protocol Reference Manual. r P e t e l o s b O 10/26 Isolation of the RESET pin During a programming session, you must ensure that the programming tool controls the ST7’s RESET pin so that no external reset is generated by the application. This can lead to a conflict if the application reset circuitry signal exceeds 5mA (push-pull output or pull-up resistor <1k). To avoid such conflicts, a Shottky diode can be used to isolate the application reset circuit. STICK User Manual 2 - Getting Started ICCSEL/VPP pin The application pull-down resistor must not be lower than 10kΩ. ICCOSC pin * The ICCOSC pin of the ICC connector must be connected to the ST7’s OSC1 or OSCIN pin if the clock is not provided by the application, or if the application clock source is not programmed in the option byte. This connection allows you to start your ICP session using the ICP OPT Disable programming mode. In this mode, the STICK provides a clock source to initiate communication with the ST7 at a frequency of 8MHz. For ST7 devices with multi-oscillator capability, when the ICCOSC pin is connected, the OSC2 pin should be grounded. ) s t( If your application provides a clock signal and you are certain that it is programmed in the ST7’s option byte, you can start your ICP session using the ICP OPT Enable programming mode. In this mode, your application clock source provides the clock signal for initiating communication with your ST7 and ICCOSC is not connected to your ST7. c u d e t le VDD_APPLI pin * o r P o s b O - This pin is used by the programming tool’s power supply follower, which adapts the voltage of the tool’s signals to your application’s VDD. If the application board VDD is equal to 5v or 3.3v, VDD_APPLI is not connected. However, the W1 jumper must be set to the appropriate position (5v or 3.3v). For all other VDD values supported by your ST7 (refer to your ST7xxxx Datasheet), this pin must be connected and the W1 jumper set to the VDD position. ) s ( ct u d o r P e t e l o s b O 11/26 3 - Programming with STVD7 or STVP7 3 STICK User Manual PROGRAMMING WITH STVD7 OR STVP7 You can configure and control the programming of your ST7 with ST7 Visual Programmer (STVP7) or ST7 Visual Develop (STVD7) software running on your host PC. This chapter provides a brief procedure to help you get started programming with each software. For more details refer to their respective on-line help files. 3.1 Start programming with STVD7 1 Launch STVD7. 2 Open the workspace and project that you used when developing your application. You will have selected your MCU during the early stages of application development. 3 Select Tools>Programmer. 4 Configure the options in the Settings tab: c u d ) s t( o r P - Board: STICK - Port: LPT1 or LPT2 - Check Erase Before Programming if you are reprogramming an MCU with HDFlash memory. - Programming Mode: e t le o s b O - If your ST7’s option byte does not include OSCTYPE, then ICP is the only in-circuit programming mode available to you. Note: ) s ( ct For some of the most recent circuits that include OSCTYPE, ICP programming mode is available instead of ICP OPT Disable or Enable. u d o If your ST7’s option byte includes OSCTYPE, then you can choose: r P e t e l o s b O provided either by the STICK via the ICC connector pin 9 (ICCOSC safe clock), or your application. ICP OPT Enable– used only if your application clock circuitry matches the OSCTYPE option byte selection. In this case, the ICC connector pin 9 is not connected and the ICCOSC safe clock is not used. 5 12/26 ICP OPT Disable– a safe mode that must be used if your application clock circuitry doesn’t match the OSCTYPE option byte selection. In this mode, an external source with a square wave signal from 0 V to VDD must be Power on your application board and connect the ICC cable between your STICK and the application. STICK User Manual 3.2 3 - Programming with STVD7 or STVP7 6 Select the Memory Area tab then select a memory area. Click on Add, then use the browse window to identify the file (.s19, .hex) to program the selected memory area with. Repeat this step as necessary for each memory area. 7 Select the Option Byte tab to configure any option byte settings. 8 Select the Program tab and click on Start to program your ST7. Start programming with STVP7 The following describes a basic procedure for programming your application to your MCU without creating a project in STVP7. Note: Setting up a project is a way of configuring STVP7 so that you can use the same configuration each time you run STVP7. For more information about projects, refer to STVP7’s on-line help. 1 Launch STVP7 2 In the Configuration window specify: - Hardware: STICK - Port: LPT1 or LPT2 - Programming mode: c u d e t le ) s t( o r P o s b O - Select ICP mode if your ST7’s option byte does not include OSCTYPE. The Device field will change to show the list of devices that only use this mode. Note: For some of the most recent circuits that include OSCTYPE, ICP programming mode is available instead of ICP OPT Disable or Enable. ) s ( ct If your ST7’s option byte does include OSCTYPE, you can choose one of the following options: u d o ICP OPT Disable– a safe mode that must be used if your application clock circuitry doesn’t match the OSCTYPE option byte selection. In this mode, an external source with a square wave signal from 0 V to VDD must be r P e t e l o O bs provided either by the STICK via the ICC connector pin 9 (ICCOSC safe clock), or your application. ICP OPT Enable– used only if your application clock circuitry matches the OSCTYPE option byte selection. In this case, the ICC connector pin 9 is not connected and the ICCOSC safe clock is not used. When you choose one of the modes, the Device field will display the list of devices that support these modes. 13/26 3 - Programming with STVD7 or STVP7 - STICK User Manual Device: Select the name of your MCU from the list in the Device field. Keep in mind that the list displayed for ICP mode is different from that displayed for the other two in-circuit programming modes. 3 Erase memory before reprogramming (HDFlash only) by selecting Erase>Active sector(s). If you want the memory to be erased systematically before programming, you can activate the Erase Device Memory Before Programming feature (Edit>Preferences). 4 Select files (.s19, .sx, .hex) for programming to memory areas. Select the tab for the memory area (for example, PROGRAM MEMORY or DATA MEMORY), then select File>Open. Locate the file using the resulting browse window and click on Open. 5 c u d Select the Option Byte tab. Option bytes can be configured using the list boxes in this tab or by loading a HEX or S19 file with the previously used option byte settings. To program option bytes from a file, select the Option Byte tab, then click on File>Open to load the file containing the option byte settings. e t le Program your ST7 by selecting Program>All Tabs (on active sectors, if any). 7 Check the content by selecting Verify>All Tabs (on active sectors, if any). If you want to check the programmed content systematically after programming, ensure that the Verify After Programming feature is activated (Edit>Preferences) u d o r P e t e l o 14/26 o r P 6 ) s ( ct s b O ) s t( o s b O - STICK User Manual Appendix A Safety Requirements APPENDIX A SAFETY REQUIREMENTS • Any tester, equipment, or tool used at any production step, or for any manipulation of semiconductor devices, have its shield connected to ground. • The product must be placed on a conductive table top, made of steel or clean aluminum, or covered by an antistatic surface (superficial resistivity equal to or higher than 0.5 MΩ/cm2), grounded through a ground cable (conductive cable from protected equipment to ground isolated with a 1 MΩ resistor placed in series). All manipulation of finished goods must be done at such a grounded worktable. • The worktable free of all non-antistatic plastic objects. • An antistatic floor covering grounded through a conductive ground cable (with serial resistor between 0.9 and 1.5 MΩ) should be used. • It is recommended that you wear an antistatic wrist or ankle strap, connected to the antistatic floor covering or to the grounded equipment. • If no antistatic wrist or ankle strap is worn, before each manipulation of the powered-on tool, you touch the surface of the grounded worktable. • It is recommended that antistatic gloves or finger coats be worn. • It is recommended that nylon clothing be avoided while performing any manipulation of parts. c u d e t le ) s ( ct ) s t( o r P o s b O - u d o r P e t e l o s b O 15/26 Appendix B: Troubleshooting STICK User Manual APPENDIX B: TROUBLESHOOTING This appendix covers some of the problems that may occur, and how to solve them. B.1 Test pins The STICK is equipped with test pins located at TP1 (see board layout in Figure 2 on page 7). If you have problems with programming, these pins can help you pinpoint anomalies in the ICC communication by testing or checking the ICC signals. Pin Signal 1 GND 2 Power 3 VCC 4 VCC_a Description This pin is marked with a white dot. The external power supply value can be checked here. It is an unregulated 12 V DC power supply. Its value should be in the range 13.5 V to 23 V depending on the current load. e t le r P e u d o t e l o s b O 16/26 ICCSEL_VPP o r P The VCC is regulated at 5 V +/- 5%. o s b O - This is the operational amplifier output that follows the voltage value selected by the W1 jumper. It should be equal to: • your application VDD voltage value if W1 is in the VDD position, • 5 V if W1 is in the 5 V position, • 3.3 V if W1 is in the 3.3 V position. ) s ( ct 5 c u d ) s t( This signal may be at 0 V, 5 V or 12 V. This test point is used during factory test. You do not have to check it. Table 1 Test pins STICK User Manual B.2 Appendix B: Troubleshooting Error messages The following sections explain the cause of some common error messages. B.2.1 “PC parallel port cable not connected” Most communication failures between the host PC and the STICK stem from problems in the parallel port connection. To prevent communication problems, when setting up your parallel port connection: • Use the parallel cable provided with your STICK—using a longer parallel cable may cause malfunctions. • Connect the cable directly between the host PC and STICK interface board— the insertion of additional cables or switch boxes between the host PC and the interface board may cause malfunctions. c u d ) s t( • Remove any parallel port dongles. • Ensure that the parallel port address is in the range 03BC-03BF or 0378-037F or 0278-027F. • Ensure that the parallel port is not disabled in your PC. For example, in the e t le o r P IBM® ThinkPad™, you can select “infrared printing (LPT) port on”. B.3 o s b O - “Problem on supply voltages” When you have supply voltage problems the green LED will not come on. To find the cause of the problem: ) s ( ct • Check that the AC/DC power supply adaptor is firmly connected to both the main power supply and to the STICK interface board. To check that the main power supply is on, disconnect the ICC cable and measure the voltage on test pin 2 of TP1 (see Test pins on page 16). This pin should have an unregulated DC value in the range 18 V to 21 V. u d o Note: r P e Ground is on TP1 pin 1 (white dot mark). t e l o • s b O • Check that the W1 jumper is set to one of the three positions, see Section 2.2 on page 7. If it is set on the “VDD” position, check that the ICC cable is connected properly and that your application’s VDD is connected to ICC connector pin 7. Your application VDD must be in the range 2.4 V to 5 V. The voltage measured on test pin 4 of TP1 (see Test pins on page 16), must be the same voltage value that you selected with the W1 jumper. Check that there is 5 V on test pin 3 of TP1 (see Test pins on page 16). 17/26 Appendix B: Troubleshooting STICK User Manual If you have made all of these checks and you still get the “Problem on supply voltages” message, contact your ST distributor or sales office (see Product Support on page 23) in order to have your STICK repaired. B.4 “Cannot communicate with the device” Check that: • The ICC cable is correctly connected. • You have selected the right ST7 device. • The ICC signals are clear and within the following ranges: - ICCDATA: This application signal must not drive more than 1 mA. - ICCCLK: This application signal must not drive more than 1 mA. - ICCRESET: This application signal must not drive more than 5 mA. - ICCSEL_VPP: The pull-down resistor must not be lower than 10 kOhm. c u d - - e t le If you use ICP OPT Enable mode, check that your application clock circuitry does match the CLOCK SOURCE and OSCTYPE options already programmed in the ST7 Flash microcontroller option byte. For devices out of factory you have to check these values in datasheet. If you don’t know these values you have to select ICP OPT Disable. ) s ( ct r P e t e l o o s b O - ICP OPT Disable mode, ensure that external source clock is a square wave signal from 0 V to VDD. If not, you have to connect ICCOSC safe clock (ICC connector pin 9) to the OSC1 pin of the ST7Flash microcontroller in your application u d o 18/26 o r P You have selected the right programming mode (see Chapter 3 on page 12). Remember that: • s b O ) s t( STICK User Manual Appendix C: Glossary APPENDIX C: GLOSSARY This appendix gives a brief definition of acronyms and names used in this manual. HDFlash High density FLASH memory is based on FLASH technology. HDFlash is used for microcontrollers with 4K up to 60Kbytes of FLASH memory. It is programmed byte by byte but erased by sector. ICC protocol In-Circuit Communication protocol is a way of exchanging data between an ST7 Flash microcontroller and an external system (i.e. PC) using minimum hardware and ST7 I/Os in the user application. In the ST7 Flash microcontrollers, this protocol is handled by the ICC monitor. c u d ICC monitor ) s t( Software that handles the ICC protocol, embedded in a reserved memory area of the ST7 Flash microcontroller. At RESET, using specific signal sequence, the ST7 jumps to this ICC monitor which allows it to download programs in RAM and to execute them. This feature is used to implement the ICP functionality. In-Circuit Programming (ICP) e t le o r P o s b O - This is programming the ST7 FLASH memory while ST7 Flash microcontroller is plugged into the application board. ) s ( ct In-Circuit Testing (ICT) This is testing ST7 Flash micro and/or your application through the ST7 Flash microcontroller while it is plugged into the application board. u d o In-Circuit Debugging (ICD) r P e This is debugging your application while the ST7 Flash microcontroller is plugged into the application board. t e l o ST7 Flash microcontroller s b O An ST7 microcontroller with electrically erasable memory that can be either XFlash or HDFlash memory. STICK ST In-circuit Communication Kit. 19/26 Appendix C: Glossary STICK User Manual XFlash Extended FLASH memory is based on EEPROM technology. XFlash provides extended features such as byte re-programming (by means of byte erasing) and data EEPROM capability. XFlash microcontrollers are available between 1K to 16 Kbytes. c u d e t le ) s ( ct u d o r P e t e l o s b O 20/26 o s b O - o r P ) s t( 1 2 3 + (5V) VCC GND VDD_APPLI 1 2 3 JACK_2.5mm J2 SUBD25C_F_COUDE GND BUSY GND PEND GND SLCT ACK GND Z1 GND GND 10K 7 5 3 1 8 6 4 2 100 C12 4.7nF 1 RS3 R7 GND C14 1 C13 5V 3.3V 3 1 MW2X3C 1 3 5 W1 C23 CG CG CG CB 100nF 2 4 6 BNX002 B PSG U2 2 5 6 4 B C10 C6 C15 C16 C18 C24 180pF 180pF 180pF 180pF 180pF 180pF C5 4.7nF 2 A DATA7 DATA2 NSELIN DATA3 GND DATA4 GND DATA5 GND DATA6 GND INIT NSTROBE NAUTF DATA0 NERROR DATA1 2 1 1 2 1 14 2 15 3 16 4 17 5 18 6 19 7 20 8 21 9 22 10 23 11 24 12 25 13 P6KE24A 1 2 2 J1 1 2 2 1 2 1 3 5 7 2 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 4 6 8 2. 2nF 1 2 2 1 4 14 13 C3 GND - GND 3 8 6 4 2 7 RS4 5 3 1 RS1 7 5 3 1 33 8 6 4 2 RS6 7 5 3 1 33 2 10K 1 R9 GND + C1 8 33 GND U1 I GND 180-1W R4 2 40mA max 1 C29 100pF MW1X5C 1 2 3 4 5 C 8 6 4 2 O 1 VCC D5 D6 Rbusy D2 EN_OSC GND D3 D4 pcPULSES Rnautf D0 Rnerror D1 VCC L78L05-SO8 RS2 100K Power 1.2W L272D U7B Power + C2 GND 1 1 2 4 6 8 2.2nF 2 10K 100nF 1 C36 C38 C28 C27 C25 C26 C31 180pF 180pF 180pF 180pF 180pF 180pF 180pF 22 0MF RS5 2 3 6 7 1 3 5 7 1 100nF 2 TP1 4.7MF 16V C4 + VEE + C8 1 19 GND C 4.7MF 16V C22 22K R8 100nF C21 1 GND 2 enVPP enSEL VCC VCC_a 2 4 6 8 11 13 15 17 U9A R_VCC_a 74VHC126_a 2 GND 3 6 11 10 9 13 14 15 12 1 5 2 4 R13 c u d Date: Size A4 Title 1 RS8 7 5 3 1 D 2 8 6 4 2 3 GND 12 Power D3 D4 D1 pcDOUT pcACK pcRESET pcCLKen pcRW pcPULSES 5 + R16 1 1MF 35V C34 12K VDD_APPLI EN_OSC ICCSEL_VPP L272D U7A R1 1.5K Tuesday, June 04, 2002 Sheet PC Parallel Port Link 1 E C33 2 1.2K R15 of 2 Rev C 10K R11 MMBT2907 T3 47 R14 Power VDD_APPLI EN_OSC pcSTATUS pcDATAIN ICCSEL_VPP0 pcDOUT pcACK pcRESET pcCLKen pcRW pcPULSES GND 2 MB372C: ST7-FLASH STICK-LPT MCDT - Development Tools - GRENOBLE Document Number 33K 10K X V1 E ST7ICC - Parallel Port www.st.com/mcu 11 PEND enSEL enVPP Rbusy Rnerror 1 pcSTATUS pcDATAIN 18 16 14 12 9 7 5 3 LED_Green 74HC4051 INH A B C X0 X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 D LD1 1Y1 1Y2 1Y3 1Y4 2Y1 2Y2 2Y3 2Y4 2 U10 74VHCT244 1G 2G 1A1 1A2 1A3 1A4 2A1 2A2 2A3 2A4 U6 GND D0 Rnautf D2 R_VCC_a D5 D6 pcDATAIN pcSTATUS Power VCC VCC_a ICCSEL_VPP VCC_a 2 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 1 2 1 2 4 6 1 1 2 B 1 2 1 00nF 6 4 1 2 A 1 2 1 1 2 1 2 1 2 + VCC 100nF 1 3 1 2 - s b O t e l o r P e u d o ) s ( ct o s b O e t le o r P 2 1 2 3 4 STICK User Manual Appendix D: Schematics APPENDIX D: SCHEMATICS ) s t( 21/26 1 2 3 4 GND 2 pcRW pcCLKen 10 A 9 ICCSEL_VPP 8 74VHC125_a U3C 1 3 5 7 9 100nF C19 VCC 1 HEADER 5x2/SM 2 4 6 8 10 JP1 100 R6 5 9 U9C 1 100nF 2 GND 8 6 U9B 74VHC126_a 10K R10 100nF C9 pcACK 13 100nF C20 74VHC126_a VDD_APPLI ICCOSC GND C39 ICC connector GND VDD_APPLI pcSTATUS pcDATAIN pcRESET pcPULSES 74VHC14_a U4E 3.3K EN_OSC 33pF C11 11 1 R2 ICCDATA ICCCLK ICCRESET ICCSEL_VPP VDD_APPLI pcSTATUS pcDATAIN ICCSEL_VPP0 pcRESET pcPULSES pcRW pcCLKen pcDOUT pcACK 10 4 2 ICCRESET B 100nF C30 11 12 100nF C7 VCC_a 12 74VHC14_a U4F GND 6 CLK D Q 100nF C32 74VHC74_a 8 9 VCC_a Q U8B V4 74VHC14_a U4C 5 CLKINicc 4 pcCLKen 74VHC14_a U4B pcRW pcDOUT C VCC_a VCC_a Q 3 2 3 U5A CLK D 2 Q V5 Q 11 U9D CLK D CLK D VCC_a 11 12 VCC_a 3 2 Q C Q Q 74VHC74_a 8 U8A 74VHC74_a 6 5 V2 V3 GND c u d o r P U5B 9 12 74VHC126_a V6 74VHC74_a 6 5 1 VCC_a 74VHC14_a U4A D 5 U4D U3D 12 U3B pcPULSES 3 1 4.7K R3 6 74VHC14_a 9 2 74VHC125_a 11 74VHC125_a 74VHC125_a pcDATAIN 8 tie_CLK_low U3A 2 GND C17 22pF D Date: Size A3 Title 1 R12 5.6K 180pF C35 6 GND ICCCLK 33 RS7-1 2 7 33 RS7-4 3 Schottky BAR42 D2 GND 33 RS7-2 8 Tuesday, June 04, 2002 ICC Link E Sheet 2 MB372C: ST7-FLASH STICK-LPT 4 of C37 180pF ICCDATA 2 MBT2907 or SO2907 SOT23 33 RS7-3 MMBT2907 T2 Power 5 Schottky BAR42 D1 MBT2907 or SO2907 SOT23 MMBT2907 E MCDT - Development Tools - GRENOBLE 2 2 Document Number VCC_a VCC_a R5 5.6K T1 Power 1 2 B 13 1 2 pcDOUT 1 2 1 pcACK 10 10 PR CL 13 4 PR CL 1 1 VCC 3 A 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 4 PR CL 1 10 PR CL 4 13 3 1 3 2 1 2 3 2 1 1 2 1 1 22/26 2 s b O t e l o r P e u d o ) s ( ct o s b O e t le 13 Rev C 1 2 3 4 Appendix D: Schematics STICK User Manual ) s t( STICK User Manual Product Support PRODUCT SUPPORT If you experience any problems with this product, contact the distributor or the STMicroelectronics sales office where you purchased the product. Phone numbers for major sales regions are provided in the Contact List, below. In addition, at our Internet site www.st.com/mcu, you will find a complete listing of ST sales offices and distributors, as well as documentation, software downloads and user discussion groups to help you answer questions and stay up to date with our latest product developments. Software updates ) s t( All our latest software and related documentation are available for download from the ST Internet site, www.st.com/mcu. c u d Hardware spare parts o r P Your development tool comes with the hardware you need to set it up, connect it to your PC and connect to your application. However, some components can be bought separately if you need additional ones. You can order extra components, such as sockets and adapters, from STMicroelectronics, from the component manufacturer or from a distributor. e t le o s b O - To help you find what you need, a listing of accessories for ST development tools is available on the ST internet site, www.st.com/mcu. ) s ( ct u d o r P e t e l o s b O 23/26 Product Support STICK User Manual Contact List North America Canada and East Coast Mid West STMicroelectronics Lexington Corporate Center 10 Maguire Road, Building 1, 3rd floor Lexington, MA 02421 Phone: (781) 402-2650 STMicroelectronics 1300 East Woodfield Road, Suite 410 Schaumburg, IL 60173 Phone: (847) 585-3000 West coast STMicroelectronics, Inc. 1060 E. Brokaw Road San Jose, CA 95131 Phone: (408) 452-8585 Note: c u d For American and Canadian customers seeking technical support the US/ Canada is split in 3 territories. According to your area, contact the appropriate sales office from the list above and ask to be transferred to an 8-bit microcontroller Field Applications Engineer. e t le o s b O Europe France +33 (0)1 47 40 75 75 Germany +49 89 46 00 60 U.K. +44 162 889 0800 ) s ( ct u d o Japan +81 3 3280 4120 Hong-Kong +85 2 2861 5700 Sydney +61 2 9580 3811 Taipei +88 6 2 2378 8088 r P e t e l o s b O 24/26 o r P ) s t( Asia/Pacific Region Index A I application ICP connection........................................ 9 voltage selection ..................................... 7 ICC connector pinout ......................................9 definition of protocol ..............................19 ICP B application requirements .........................9 configuration ............................................4 board schematics .......................................... 21 P C circuitry.......................................................... 21 configurations programming hardware........................... 4 D parallel connection restrictions/requirements .........................8 programming board setting up .................................................7 programming software STVD7 ...................................................12 STVP7 ...................................................12 definitions...................................................... 19 delivery checklist............................................. 7 E error messages ............................................. 17 F ) s ( ct finished goods manipulation of...................................... 15 safety requirements .............................. 15 u d o G r P e glossary......................................................... 19 t e l o H hardware ICP .......................................................... 4 setting up ................................................ 7 socket programming ............................... 4 supplied................................................... 7 s b O o r P S e t le c u d ) s t( schemas ........................................................21 setting up the STICK .......................................7 socket programming accessories..............................................4 configuration ............................................4 software updates ...........................................23 STVD7 start programming .................................12 STVP7 start programming .................................13 support for programming board ..........................23 o s b O - T terminology ....................................................19 test pins .........................................................16 V voltage setting with W1 jumper ............................7 25/26 c u d e t le ) s ( ct ) s t( o r P o s b O - u d o Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. 2 STMicroelectronics products are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without the express written approval of STMicroelectronics. r P e 6 t e l o The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics ©2004 STMicroelectronics - All Rights Reserved. Purchase of I2C Components by STMicroelectronics conveys a license under the Philips I2C Patent. Rights to use these components in an I2C system is granted provided that the system conforms to the I2C Standard Specification as defined by Philips. s b O STMicroelectronics Group of Companies Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America 26 www.st.com