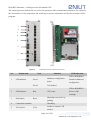
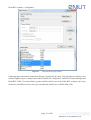
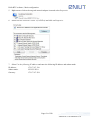
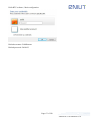
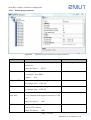
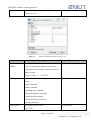
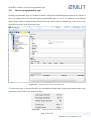
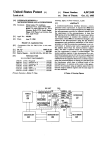
Download Enilit RTU user manual EN
Transcript
Enilit RTU User manual Copyright UAB Enilit. All rights reserved, 2010 – 2015 Content | User manual Content Content .................................................................................................................................................... 2 1. Introduction ...................................................................................................................................... 6 1.1 User manual ................................................................................................................................. 6 1.2 Enilit RTU .................................................................................................................................... 6 2. Safety ............................................................................................................................................... 8 2.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................. 8 2.2 Health and safety .......................................................................................................................... 8 2.2.1 Service and Maintenance ...................................................................................................... 8 2.2.2 Electrical Connections .......................................................................................................... 9 2.2.3 Earthing ................................................................................................................................ 9 2.2.4 Power Supply Connection ..................................................................................................... 9 2.2.5 Terminals............................................................................................................................ 10 2.2.6 Data Transmission Cables ................................................................................................... 10 2.3 Decommissioning and disposal ................................................................................................... 10 2.3.1 Decommissioning ............................................................................................................... 10 2.3.2 Disposal .............................................................................................................................. 10 2.4 Declaration of conformity ........................................................................................................... 10 2.5 Handling of electronic equipment ............................................................................................... 11 2.6 Warnings regarding use of UAB Enilit products ......................................................................... 12 2.7 Guarantees.................................................................................................................................. 12 2.8 Copyright ................................................................................................................................... 13 3. Enilit RTU Hardware ..................................................................................................................... 14 3.1 System Conception ..................................................................................................................... 14 3.2 Rack mounting and Frame .......................................................................................................... 15 3.2.1 Basic frame ......................................................................................................................... 15 3.2.2 Second frame ...................................................................................................................... 16 3.3 Short hardware review ................................................................................................................ 16 3.3.1 Power Supply Module......................................................................................................... 17 3.3.2 Central Processor Modules.................................................................................................. 17 3.3.3 I/O Modules........................................................................................................................ 17 3.4 Additional features ..................................................................................................................... 18 3.5 Central processor unit module CPU ............................................................................................ 19 3.5.1 Serial communication interface (RJ-45) .............................................................................. 22 Page 2 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Content | User manual 3.5.2 Ethernet interface (RJ-45) ................................................................................................... 23 3.5.3 Technical Data .................................................................................................................... 24 3.5.4 WatchDog .......................................................................................................................... 24 3.6 Power Supply Module ................................................................................................................ 25 3.6.1 Wiring diagram ................................................................................................................... 26 3.6.2 Technical Data .................................................................................................................... 27 3.7 Digital Input Module .................................................................................................................. 28 3.7.1 Wiring diagram ................................................................................................................... 29 3.7.2 Technical Data .................................................................................................................... 30 3.8 Digital Output Module ................................................................................................................ 31 3.8.1 Wiring diagram ................................................................................................................... 32 3.8.2 Technical Data .................................................................................................................... 33 3.9 Analogue Input Module AI-31 .................................................................................................... 34 3.9.1 Wiring diagram ................................................................................................................... 36 3.9.2 Technical Data .................................................................................................................... 37 3.10 Fiber optic module ST-61 ........................................................................................................... 38 3.11 Installation of System Housing ................................................................................................... 38 3.12 Order-book ................................................................................................................................. 39 4. 3.12.1 Basic frame ..................................................................................................................... 39 3.12.2 Second frame .................................................................................................................. 42 Enilit RTU software ....................................................................................................................... 43 4.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................ 43 4.2 System capabilities ..................................................................................................................... 43 4.3 Licensing .................................................................................................................................... 43 4.4 User interface ............................................................................................................................. 45 4.5 Configurator ............................................................................................................................... 50 4.5.1 User groups ........................................................................................................................ 51 4.5.2 Create user groups .............................................................................................................. 51 4.5.3 Create user with rights ........................................................................................................ 52 4.6 Users authentication ................................................................................................................... 56 4.7 Project manager .......................................................................................................................... 57 4.7.1 Basic information ............................................................................................................... 57 4.7.2 Import project ..................................................................................................................... 60 4.7.3 Export project ..................................................................................................................... 60 4.8 Main configuration ..................................................................................................................... 61 Page 3 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Content | User manual 4.8.1 IP addresses ........................................................................................................................ 61 4.8.2 Remote management ........................................................................................................... 63 4.9 Hardware configuration .............................................................................................................. 68 4.9.1 Power supply ...................................................................................................................... 69 4.9.2 CPU .................................................................................................................................... 69 4.9.3 Card Slots ........................................................................................................................... 70 4.9.4 Hardware items parameters ................................................................................................. 72 4.9.5 Hardware Tags.................................................................................................................... 75 4.10 Master protocols ......................................................................................................................... 90 4.10.1 IEC 60870-5-103 configuration....................................................................................... 90 4.10.2 IEC 60870-5-101 configuration..................................................................................... 102 4.10.3 IEC 60870-5-104 configuration..................................................................................... 114 4.10.4 IEC 61850 client ........................................................................................................... 123 4.10.5 Modbus RTU/ASCII ..................................................................................................... 131 4.10.6 Modbus TCP client ....................................................................................................... 137 4.10.7 DNP3 serial master configuration.................................................................................. 139 4.10.8 DNP3 UDP/TCP/IP client configuration ....................................................................... 141 4.10.9 Simulator master configuration ..................................................................................... 143 4.10.10 RP-570 configuration .................................................................................................... 146 4.11 Slave protocols ......................................................................................................................... 148 4.11.1 IEC 60870-5-101 protocol configuration ....................................................................... 148 4.11.2 IEC 60870-5-104 protocol configuration ....................................................................... 158 4.11.3 DNP3 serial slave configuration .................................................................................... 167 4.11.4 DNP3 UDP/TCP/IP server configuration ...................................................................... 169 4.12 Tag manager ............................................................................................................................. 172 4.12.1 Tag states ...................................................................................................................... 176 4.13 Internal programmable logic ..................................................................................................... 179 4.14 Programmable logic IsaGRAF .................................................................................................. 182 4.14.1 IsaGraf function blocks ................................................................................................. 184 4.14.2 IsaGraf data types ......................................................................................................... 192 4.15 Time management .................................................................................................................... 194 4.15.1 SNTP client .................................................................................................................. 194 4.16 Self-control and diagnosis ........................................................................................................ 198 4.16.1 Hardware monitoring .................................................................................................... 198 4.16.2 Protocol monitoring ...................................................................................................... 200 Page 4 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Content | User manual 4.16.3 System log .................................................................................................................... 204 4.16.4 Events log ..................................................................................................................... 204 4.17 Redundancy.............................................................................................................................. 207 4.17.1 Redundancy support...................................................................................................... 207 4.17.2 Redundancy types ......................................................................................................... 207 4.17.3 Connection diagram ...................................................................................................... 207 4.17.4 Enilit RTU redundancy principles ................................................................................. 208 4.17.5 Monitored fault locations .............................................................................................. 209 4.17.6 Communication channel configuration .......................................................................... 209 4.17.7 Status signals, commands and measurements ................................................................ 211 4.18 Cyber security capabilities ........................................................................................................ 213 4.18.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................. 213 4.18.2 Electronic access control ............................................................................................... 213 4.18.3 Audit trail ..................................................................................................................... 215 4.18.4 Supervisory monitoring and control .............................................................................. 217 4.18.5 Configuration software.................................................................................................. 217 Abbreviations....................................................................................................................................... 219 Contacts ............................................................................................................................................... 220 Page 5 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Introduction | User manual 1. Introduction 1.1 User manual This document is a helpful resource for utility customers or Enilit partners who are purchasing or evaluating Enilit RTU (remote terminal unit). It is intended for readers who have knowledge of substation automation equipment and applications. This document provides a technical overview of the Enilit RTU. The document is organized as follows: 1. Content: This section provides a content of this document. 2. Introduction: This section provides short overview of this document and main Enilit RTU functions and possible applications. 3. Safety: This section provides safety of working with Enilit RTU system. 4. Hardware: This section provides an overview of the Enilit RTU hardware. 5. Software: This section provides an overview of the Enilit RTU software. Note. User manual for this device gives instructions for its installation, commissioning, and operation. However, the user manual cannot cover all conceivable circumstances or include detailed information on all topics. In the event of questions or specific problems, do not take any action without proper authorization. Contact UAB Enilit office and request the necessary information. 1.2 Enilit RTU The automation technology is rapidly advancing. New communication techniques and devices and standard protocol interfaces combined with the immense computing power of today’s hardware components open the way to new concepts in automation. At the same time, the growing demands of utility owners for more cost-effective control systems must be met. Enilit RTU is our solution for automation applications. The modular and open structure of the Enilit RTU system sets wide range where it could be used: Electric power generation plants; Electricity transmission and distribution networks; Traffic control systems (railways; metro, tramways and etc.) Supply networks of municipal and regional public utilities (gas, electricity, water, sewage, district heating and etc.); Data acquisition and control in buildings systems (escalators, lighting, air conditioning and etc.); Monitoring and control of chemical and petrochemical plants and pipelines; Page 6 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Introduction | Enilit RTU Environmental technology with measured data acquisition and remote evaluation. Main tasks what the Enilit RTU is doing: Control and monitoring of a system from a control center via reliable remote data transmission protocols, Multitude of communication possibilities via various transmission media (LAN, radio relay system and etc.), Fast time-sequential processing of digital and analogue process data with high resolution time marking (1 millisecond), Secure process inputs / outputs with high isolation voltage (2,5 kV), Pre-processing and compressing of acquired process data (e.g. metered value formation, threshold value processing, initiation delay, debouncing, signal damping), Optimized flow of remote data transmission (spontaneous, cyclic or on-demand transmission, differentiated interrogation lists, priority improvement, general interrogation, selective message repeat command), Time-saving, user-optimized parameterization with minimum effort Enilit RTU Configuration and management software (CMS) with Microsoft Windows operating system, Open interfaces which permit connection of peripheral units (e.g. printer or operator panel). Page 7 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Safety | Introduction 2. Safety 2.1 Introduction This documentation includes information for qualified technical personnel. It describes the safety, handling, packing and unpacking procedures applicable to Enilit RTU hardware and software tools. 2.2 Health and safety THIS SAFETY SECTION SHOULD BE READ BEFORE COMMENCING ANY WORK ON THE EQUIPMENT. The information in the Safety Section of the product documentation is intended to ensure that products are properly installed and handled in order to maintain them in a safe condition. It is assumed that everyone who will be associated with the equipment will be familiar with the contents of the Safety Section. To preclude the possibility of personal danger, the following safety requirements must be fulfilled at any time: 1. The operating voltage specified in technical documentation must never be exceeded. 2. Always disconnect the device before changing the system or signaling wiring. 3. The housing does not contain any operation-relevant elements. The device must never be opened. 4. Do not operate the device in inflammable or explosive environments. 5. Do not expose the device to rain or humidity. 6. With regard to the installation location, take care that the ventilation is sufficient to make sure that the permissible operating temperature is not exceeded. 7. For wiring, please make sure that you use only cables that are able to withstand temperatures of at least 85 ºC. 8. Please ensure that not isolated line ends are not exposed in order to minimize the danger of electric shocks or short circuits. 2.2.1 Service and Maintenance The device should be installed in a dry, clean environment. To ensure its proper functioning, it is necessary to make sure that the specified ambient conditions are fulfilled. If there is unlocked access to the rear of the equipment, care should be taken by all personnel to avoid electrical shock or energy hazards. It is not necessary to clean the device after installation. But if it is needed to cleaning, please switch off the device and wipe it off with a soft, clean and dry piece of cloth. Do not use any detergents for cleaning. Page 8 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Safety | Health and safety 2.2.2 Electrical Connections Connections should be made using insulated crimp terminations to ensure that terminal block insulation requirements are maintained for safety. To ensure that wires are correctly terminated the correct crimp terminal and tool for the wire size should be used. 2.2.3 Earthing Before energizing the equipment it must be earthed using the protective earth terminal, or the appropriate termination of the supply plug in the case of plug connected equipment. Omitting or disconnecting the equipment earth may cause a safety hazard. Recommended minimum earth wire size is 2.5mm². 2.2.4 Power Supply Connection This device does not have its own mains switch and starts operation immediately after the application of system voltage. Hence, a switch must be included in the wiring scheme which must be labelled appropriately and which must be installed in the vicinity of the device and within the operator's reach. The switch has to fulfill the requirements acc. to standards IEC 947-1 and IEC 947-3. The recommended maximum rating of the external protective fuse for this equipment is: Supply voltage Fuse, A 110VDC 6 220VDC 4 115VAC 6 230VAC 4 For the supply of the feeder voltage please use cables with the 1.5 mm² cross section. Page 9 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Safety | Decommissioning and disposal 2.2.5 Terminals Terminals exposed during installation, commissioning and maintenance may present a hazardous voltage unless the equipment is electrically isolated. Clamping range: Wire, mm2 Terminals Power supply 0.5 ... 2.5 Process connection 0.2 ...2.5 Data communications 0.2 ...2.5 2.2.6 Data Transmission Cables For data transmission, telecommunications cables with twisted-pair double-core cables with braided shielding (effective core diameter: 0.6/0.8 mm2, optical cover of the screen > 80 %) acc. to VDE0815/ VDE0816 shall be used. The cable shield has to be laid planar on a bonding jumper/earth circuit connector (central earthing point). 2.3 Decommissioning and disposal 2.3.1 Decommissioning The auxiliary supply circuit in the Enilit RTU may include capacitors across the supply or to earth. To avoid electric shock or energy hazards, after completely isolating the supplies to the Enilit RTU (both poles of any dc supply), the capacitors should be safely discharged via the external terminals prior to decommissioning. 2.3.2 Disposal It is recommended that incineration and disposal to watercourses be avoided. The product should be disposed of in a safe manner. Any products containing batteries should have them removed before disposal, in order to avoid short circuits. Particular regulations within the country of operation may apply to the disposal of lithium batteries. 2.4 Declaration of conformity Device being the subject of this instruction was constructed and prepared and it is manufactured for the purpose of use in industrial environment. At device constructing and manufacturing were complied with such norms which fulfilling is being ensure the realization of specific rules and precautions, provided that Page 10 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Safety | Handling of electronic equipment the user obeys the given guidelines of device installing and starting as well as its operation leading. This device is compliance with EU directive resolutions: Name Description 2004/108/EC Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive 2006/95/EC Compliance with the European Commission Low Voltage Directive Conformity to directives was confirmed by tests performed in independent from manufacturer measurement and research laboratories and develops centers. Standard consistent with directive 2004/108/EC Name EN 55022:2010 Description Information technology equipment. Radio disturbance characteristics. Limits and methods of measurement (CISPR 22:2008) EN 55024:2010 Information technology equipment - Immunity characteristics - Limits and methods of measurement (CISPR 24:2010) EN 61000-3-2:2006 + A1:2009 + A2:2009 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) – Part 3-2: Limits - Limits for harmonic current emissions (equipment input current <= 16 A per phase) (IEC 61000-3-2:2005) 2.5 Handling of electronic equipment A person’s normal movements can easily generate electrostatic potentials of several thousand volts. Discharge of these voltages into semiconductor devices when handling circuits can cause serious damage, which often may not be immediately apparent but the reliability of the circuit will have been reduced. The electronic circuits of UAB Enilit products are immune to the relevant levels of electrostatic discharge when housed in their cases. Do not expose them to the risk of damage by withdrawing modules unnecessarily. Each module incorporates the highest practicable protection for its semiconductor devices. However, if it becomes necessary to withdraw a module, the following precautions should be taken in order to preserve the high reliability and long life for which the equipment has been designed and manufactured. 1. Before removing a module, ensure that you are a same electrostatic potential as the equipment by touching the case. 2. Handle the module by its front-plate, frame, or edges of the printed circuit board. Avoid touching the electronic components, printed circuit track or connectors. 3. Do not pass the module to any person without first ensuring that you are both at the same electrostatic potential. Shaking hands achieves equipotential. Page 11 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Safety | Warnings regarding use of UAB Enilit products 4. Place the module on an antistatic surface, or on a conducting surface, which is at the same potential as you. 5. Store or transport the module in a conductive bag. If you are making measurements on the internal electronic circuitry of any equipment in service, it is preferable that you are earthen to the case with a conductive wrist strap. Wrist straps should have a resistance to ground between 500k – 10M Ohms. If a wrist strap is not available you should maintain regular contact with the case to prevent the buildup of static. Instrumentation which may be used for making measurements should be earthen to the case whenever possible. More information on safe working procedures for all electronic equipment can be found in IEC 60147-0F and BS5783. 2.6 Warnings regarding use of UAB Enilit products UAB Enilit products are not designed with components and testing for a level of reliability suitable for use in connection with surgical implants or as critical components in any life support systems whose failure to perform can reasonably be expected to cause significant injuries to a human. In any application, including the above reliability of operation of the software products can be impaired by adverse factors, including - but not limited - to fluctuations in electrical power supply, computer hardware malfunctions, computer operating system, software fitness, fitness of compilers and development software used to develop an application, installation errors, software and hardware compatibility problems, malfunctions or failures of electronic monitoring or control devices, transient failures of electronic systems (hardware and/or software), unanticipated uses or misuses, or errors from the user or applications designer (adverse factors such as these are collectively termed "System failures"). Any application where a system failure would create a risk of harm to property or persons (including the risk of bodily injuries and death) should not be reliant solely upon one form of electronic system due to the risk of system failure to avoid damage, injury or death, the user or application designer must take reasonable steps to protect against system failure, including - but not limited - to back-up or shut-down mechanisms, not because end-user system is customized and differs from UAB Enilit testing platforms but also a user or application designer may use UAB Enilit products in combination with other products. These actions cannot be evaluated or contemplated by UAB Enilit; Thus, the user or application designer is ultimately responsible for verifying and validating the suitability of UAB Enilit products whenever they are incorporated in a system or application, even without limitation of the appropriate design, process and safety levels of such system or application. 2.7 Guarantees Page 12 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Safety | Copyright UAB Enilit guarantees that the information in this document is accurate. The document has been carefully reviewed for technical accuracy. In the event that technical or typographical errors exist, UAB Enilit reserves the right to make changes to subsequent editions of this document without prior notice to holders of this edition. The reader should consult UAB Enilit if errors are suspected. In no event shall UAB Enilit be liable for any damages arising out of or related to this document or the information contained in it. The media on which you received UAB Enilit software are guaranteed not to fail executing programming instructions, due to defects in materials and workmanship, for a period of 90 days from date of shipment, as evidenced by receipts or other documentation. UAB Enilit will, at its option, repair or replace software media that do not execute programming instructions if UAB Enilit receives notice of such defects during the guaranty period. Expect as specified herein, UAB Enilit makes no guaranties, express or implied and specifically disclaims and guaranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Customer's rights to recover damages caused by fault or negligence on the part UAB Enilit shall be limited to the amount therefore paid by the customer. UAB Enilit will not be liable for damages resulting from loss of data, profits, use of products or incidental or consequential damages even if advised of the possibility thereof. This limitation of the liability of UAB Enilit will apply regardless of the form of action, whether in contract or tort, including negligence. Any action against UAB Enilit must be brought within one year after the cause of action accrues. UAB Enilit shall not be liable for any delay in performance due to causes beyond its reasonable control. The warranty provided herein does not cover damages, defects, malfunctions, or service failures caused by owner's failure to follow the UAB Enilit installation, operation, or maintenance instructions. Owner's modification of the product; owner's abuse, misuse, or negligent acts; and power failure or surges, fire, flood, accident, actions of third parties, or other events outside reasonable control. 2.8 Copyright Copyright UAB Enilit all rights reserved. We reserve the right to claim damages in the event of infringements of the above. Page 13 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | System Conception 3. Enilit RTU Hardware 3.1 System Conception Enilit RTU is a modular, freely scalable remote control and automation device. Its field of application is the fully-automatic monitoring and control of decentralized process stations or RTUs (e.g. in medium voltage switches bays). Plug-in I/O modules serve for process connection, and communication modules are available for the additional connection of subsystems (e.g. for serial connection of sensors and actuators). Communication between the different RTUs and between RTUs and the control center can take place via different media, for instance dedicated lines (private or leased lines) based on copper cables or glass FO cables dial-up connections via analogue telephone network, digital ISDN network and GSM networks (900 MHz, e.g. D1 or D2) serial interfaces V.24/V.28 in combination with transmission systems like PCM30, PDH or SDH systems, or with private radio networks LAN/WAN connections via 10/100 MB/s-Ethernet und TCP/IP It supports the following communication protocols: IEC 60870-5-101 IEC 60870-5-103 IEC 60870-5-104 DNP3 serial DNP3 TCP/IP IEC 61850 Modbus RTU/ASCII Modbus TCP RP-570 OPC DA2 Data transmission - in its standard form - takes place via IEC 60870-5-101 protocol (symmetrical and asymmetrical procedure). Protection equipment can be connected via IEC 60870-5-103, Modbus RTU, DNP3, IEC 61850 and RP570 protocols. Network interfaces enable communication via IEC 60870-5-104, DNP3and Modbus TCP protocol. Automation tasks can be integrated by means of the optional PLC functionality according to IEC 61131-3. Page 14 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Rack mounting and Frame Configuration and management can be carried out either locally via the software or via network from remote computer. 3.2 Rack mounting and Frame 3.2.1 Basic frame Enilit RTU frame consists of a metal housing, an internal bus system and plug-in system components. A standard RTU includes at least a power supply module and a central processor module. Maximum number of 12 slots for I/O and communication modules is available. Figure 1. Front view Page 15 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Short hardware review Figure 2. Top view 3.2.2 Second frame More I/O modules can be achieved by connecting two basic frames. Second frame should have Power Supply and can have 16 I/O or communication modules of any type. Frames are connected with external cable for communication between CPU and modules of the second frame. Expanding Enilit RTU with second frame, you can achieve 28 I/O modules. 3.3 Short hardware review The remote terminal unit “Enilit RTU” device comes in one basic 6U frame system. One frame can include: two power supply modules, central processor module (second frame not necessary), 12 slots for I/O and communication modules (at maximum 12 boards inside one rack could be installed. Place of the boards according type in the rack it isn‘t necessary. No difference for RTU what type (DI, DO, AI or ST) board is installed in the slot). Page 16 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Short hardware review 1 2 Figure 3. 3 No. Explanation 1 Power supply module 2 Central processor module 3 I/O modules Front view of Enilit RTU 3.3.1 Power Supply Module There is four type of power supply module available: Application Module Input voltage 115V AC PS-11 Input voltage 230V AC PS-21 Input voltage 110V DC PS-31 Input voltage 220V DC PS-41 3.3.2 Central Processor Modules The central processor module is in charge of communication interface operation, control of I/O modules, acquisition and archiving of process information and execution of PLC programs. The following central Processor Modules are available in the standard versions: Module Communication interfaces CPU-3x 3 Ethernet (RJ45), 12 Serial links (RJ45) CPU-4x 4 Ethernet (RJ45), 12 Serial links (RJ45) 3.3.3 I/O Modules Depending on the scope of process data, it is possible to fit the free slots with the necessary I/O modules, irrespective of the signal type. The following I/O modules are available: Page 17 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Additional features Application 3.4 Module I/O Description Digital input DI-11 24 24VDC Digital input DI-21 24 60VDC Digital input DI-31 24 110VDC Digital input DI-41 24 220VDC Digital output DO-31 24 DC13, 250 VDC, 0.2A Analogue input AI-31 12 Fiber optic module ST-61 6 -20 mA to +20 mA or -10V to 10 V. 6 x FO (ST type) Additional features External VGA compatible monitor, keyboard and mouse for RTU monitoring, management and configuration. External Touch Screen monitor for one or several feeders visualization and control (HMI). Computer with SCADA for local substation management. Protocol converter (gateway). Page 18 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Central processor unit module CPU 3.5 Central processor unit module CPU There are seven types of central processor unit modules available: Module CPU-31 Communication interfaces 3 x Ethernet (RJ45), 12 x RS485 Serial links(RJ45) 3 x Ethernet (RJ45), CPU-32 4 x RS232 Serial links(RJ45), 8 x RS485 Serial links(RJ45) 3 x Ethernet (RJ45), CPU-33 8 x RS232 Serial links(RJ45), 4 x RS485 Serial links(RJ45) CPU-34 CPU-41 3 x Ethernet (RJ45), 12 x RS232 Serial links(RJ45) 4 x Ethernet (RJ45), 12 x RS485 Serial links(RJ45) 4x Ethernet (RJ45), CPU-42 4 x RS232 Serial links (RJ45), 8 x RS485 Serial links (RJ45) 4x Ethernet (RJ45), CPU-43 8 x RS232 Serial links (RJ45), 4 x RS485 Serial links (RJ45) CPU-44 4x Ethernet (RJ45), 12 x RS232 Serial links (RJ45) Page 19 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Central processor unit module CPU The central processor module CPU serves for the operation of the communication interfaces, for control of the I/O modules, for the acquisition and archiving of process information and for the execution of PLC programs. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Central processor unit front and side view Figure 4. No 1 Explanation LED indicator Note Error1 Error2 Function Hardware configuration status LED indication LED is BLINKING– mistake in hardware configuration User defined LED is BLINKING - 2 LED indicator Run CPU status device is OK (running) 3 Push button 4 Connection terminals 5 VGA socket Reset Manually reset device by pushing Watchdog VGA Socket to connect LCD monitor Page 20 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Central processor unit module CPU Socket to connect 6 USB socket USB1-USB4 keyboard, mouse, USB stick and etc. Serial 7 communication interface socket RJ- COM1-COM12 Connect others RTUs or protection devices 45 Ethernet 8 communication interface socket RJ- ETH1-ETH3 Connect control centers or protection devices 45 Note. If Error1 and Error2 LEDs lights up and RUN LED is OFF, that means CPU error or system is starting. Page 21 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Central processor unit module CPU 3.5.1 Serial communication interface (RJ-45) The CPU-3x has 12 serial communication ports. The CPU-7x has 8 serial communication ports. The serial communication interfaces (RS232 or RS422/485) is designed as 8-pole RJ45 connector with integrated LEDs. CPU module RJ-45 (COM) connector pin assignment for RS422/485: Designation Pin RS-232 RS-422 RS-485 (4 wire) RS-485 (2 wire) 1 Not used Not used Not used Not used 2 RX RX + RB + DB + 2 - 3 pins should be 3 TX TX + TB + DB + linked together 4 Not used GND GND 5 GND RX - RA - DA - 5 - 6 pins should be 6 Not used TX - TA - DA - linked together 7 Not used Not used Not used Not used 8 Not used Not used Not used Not used a) RTU side Figure 5. GND b) Cableside RJ45 connector The status of each communication interface is shown via the two software-controlled LEDs that are installed in the connectors. The yellow LED lights up if there is a physical connection to a device, i.e. if the connection layer is in operation. The green LED is activated during transmission of data in the transmission or the receive direction. Page 22 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Central processor unit module CPU 3.5.2 Ethernet interface (RJ-45) The Ethernet communication interfaces are designed as 8-pole RJ45 connector with integrated LEDs. Pin assignment: Pin Designation 1 -TX 2 +TX 3 +RX 4 Not used 5 Not used 6 -RX 7 Not used 8 Not used Figure 6. RJ45 connector The status of each communication interface is shown via the two software-controlled LEDs that are installed in the connectors: The yellow LED lights up if there is a physical connection to a device, i.e. if the connection layer is in operation. The green LED is activated during transmission of data in the transmission or the receive direction. Page 23 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Central processor unit module CPU 3.5.3 Technical Data Feature Value Processor 64-bit microprocessor – 1.6 - 1.8 GHz; Intel Atom internal watchdog; 1024...2048 MB Dynamic memory DRAM; 16 GB Solid State Drive (for software, databases, events, waveforms, parameters); Communication interfaces RS485 / RJ45 socket (8-pin socket); DTE / max. speed: 115,2 Kb; Ethernet interface Ethernet (10/100/1000 Base-TX) / RJ45 socket (8-pin socket) Twisted-pair cable CAT5 / speed: 10/100/1000 Mbps Working temperature 0 ~ +60°C, on request range can be extended Working humidity 5 ~ 95%, non-condensing 3.5.4 WatchDog WatchDog State Description Normal Device is turned on, Enilit CMS is working, RTU hardware configuration state has no abnormal card states Normal Device is starting, Watchdog relay time out timer didn’t end. Error Device is turned off Error Enilit CMS is closed and Watchdog relay time out timer ended Error RTU hardware configuration state has abnormal card states Error RTU has detected a hardware error. Terminal Function 1 NO 2 COM 3 NC Page 24 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Power Supply Module 3.6 Power Supply Module There is four type of power supply module available: Application Module Input voltage 115V AC PS-11 Input voltage 230V AC PS-21 Input voltage 110V DC PS-31 Input voltage 220V DC PS-41 Each type off power supplies has 12V DC output which can be used to connect power supply for external monitor or some other device. Max power for this output is 3 Amps. In one Enilit RTU can be installed two power supply units whose one can work from different voltages: one from AC and another from DC supply voltage at the same time. 1 2 3 5 4 Figure 7. No Explanation Note Power supply front and side view Function LED indication 1 LED indicator 5V PS output voltage status LED is ON - voltage is OK 2 LED indicator 12V PS output voltage status LED is ON - voltage is OK Page 25 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Power Supply Module 110V AC, 3 230V AC, LED indicator 110V DC, PS input voltage status LED is ON - voltage is OK 220V DC Input voltage 4 connection terminals 12V DC output 5 connection terminals 3.6.1 Wiring diagram Function Terminal AC DC Voltage Voltage L(+) L1 + N(-) N - PE Ground Ground Figure 8. Power supply wiring diagram Page 26 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Power Supply Module 3.6.2 Technical Data Feature Value Output voltage: 5V 12V Rated current 7.7A 7.7A Current range 2 ~ 15A 0.5 ~ 10A Rated power 130.9W Setup rise time 500ms, 20ms/230V 1200ms, 30ms/115V at full load Hold up time (Typ.) 25ms/230V 30ms/115V at full load Input voltage range - Input voltage range PS 11 88 ~ 132VAC - Input voltage range PS 21 176 ~ 264VAC - Input voltage range PS 31 88 ~ 132VDC - Input voltage range PS 41 176 ~ 264VDC Frequency range 47 ~ 63Hz Current (Typ.) 3A/115V 2A/230V Inrush current (Typ.) COLD START 40A/230V Leakage current <2mA / 240VAC Working temperature -25 ~ +70°C (Refer to output load derating curve) Working humidity 20 ~ 90% RH non-condensing Page 27 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Digital Input Module 3.7 Digital Input Module The digital input module serves for the processing of up to 24 digital input signals. 1 2 Digital input board front and side view Figure 9. No Explanation Function LED indication LED is ON – input is active; 1 LED indicators for each digital input Digital input status LED is OFF – input is inactive; ALL LEDS are blinking together – no connection with CPU or digital input board error. 2 Connection terminals - - Page 28 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Digital Input Module 3.7.1 Wiring diagram Terminal Function 1 DI 1 2 DI 2 3 DI 3 4 DI 4 5 DI 5 6 DI 6 7 DI 7 8 DI 8 G1 COM 9 DI9 10 DI10 11 DI11 12 DI12 13 DI13 14 DI14 15 DI15 16 DI16 G2 COM 17 DI17 18 DI18 19 DI19 20 DI20 21 DI21 22 DI22 23 DI23 24 DI24 G3 COM Figure 10. Digital input board wiring diagram Page 29 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Digital Input Module 3.7.2 Technical Data Feature Value No. of inputs 24 Time tag 1 ms Galvanic isolation - from system electronics Yes (optocoupler) - of the channels from one another No (groups of 8 channels share a common ground) Signaling-circuit voltage - Input voltage range DI 11 24...30 V DC - Input voltage range DI 21 39...72 V DC - Input voltage range DI 31 88...150 V DC - Input voltage range DI 41 175...264 V DC Increased insulation resistance acc. to IEC 602555 2.5 kV ; 50 Hz, 1 min - Power-frequency withstand voltage 4.4 kV; 1.2/50 μs; 0.5 J - Surge voltage Page 30 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Digital Output Module 3.8 Digital Output Module The digital output module serves for the processing of up to 24 digital outputs. 1 2 Figure 11. No Explanation Digital output board front and side view Function LED indication LED is ON – output is active; 1 LED indicators for Digital each digital output status output LED is OFF – output is inactive; ALL LEDS are blinking together – no connection with CPU or digital output board error. 2 Connection terminals Page 31 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Digital Output Module 3.8.1 Wiring diagram Function Function 1 DO1 2 DO2 3 DO3 4 DO4 5 DO5 6 DO6 7 DO7 8 DO8 G1 COM 9 DO9 10 DO10 11 DO11 12 DO12 13 DO13 14 DO14 15 DO15 16 DO16 G2 COM 17 DO17 18 DO18 19 DO19 20 DO20 21 DO21 22 DO22 23 DO23 24 DO24 G3 COM Figure 12. Digital output board wiring diagram Page 32 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Digital Output Module 3.8.2 Technical Data Feature Value No. of outputs 24 Galvanic isolation - from system electronics Yes (optocoupler) - of the channels from one another Yes Switching capacity: AC1 16 A / 250 V AC AC15 3 A / 120 V 1,5 A / 240 V (B300) AC3 750 W (single-phase motor) DC1 16 A / 24 V DC (see Fig. 3) DC13 0,22 A / 120 V 0,1 A / 250 V (R300) Voltage (control circuit of the relay) - rated value 12 V DC - operating range 3 ... 110 V Increased insulation resistance acc. to IEC 60255-5 - Power-frequency withstand voltage 2.5 kV ; 50 Hz, 1 min - Surge voltage 4.4 kV; 1.2/50 μs; 0.5 J Page 33 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Analogue Input Module AI-31 3.9 Analogue Input Module AI-31 The AI-31 analogue input module serves for the processing of up to twelve analogues, current or voltage input signals. Note. Measuring current or voltage could be selected for each input separately by the internal jumper position. 1 Figure 14 2 Figure 13. Analogue input board front and side view Page 34 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Analogue Input Module AI-31 Current -20 mA to +20 mA measuring Voltage -10 V to +10 V measuring Analogue input switch position Figure 14. No Explanation Function LED indication LED is OFF – normal measured value; 1 LED indicators for Analogue each analogue input status input LED is blinking – measured value is under or over range, ALL LEDS are blinking together – no connection with CPU or analog input board error. 2 Connection terminals Page 35 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Analogue Input Module AI-31 3.9.1 Wiring diagram Terminal Function +1 Analogue input 1+ -1 Analogue input 1- +2 Analogue input 2+ -2 Analogue input 2- +3 Analogue input 3+ -3 Analogue input 3- +4 Analogue input 4+ -4 Analogue input 4- +5 Analogue input 5+ -5 Analogue input 5- +6 Analogue input 6+ -6 Analogue input 6- +7 Analogue input 7+ -7 Analogue input 7- +8 Analogue input 8+ -8 Analogue input 8- +9 Analogue input 9+ -9 Analogue input 9- +10 Analogue input 10+ -10 Analogue input 10- +11 Analogue input 11+ -11 Analogue input 11- +12 Analogue input 12+ -12 Analogue input 12- G1 Ground G2 Ground Figure 15. Analogue input board wiring diagram Page 36 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Analogue Input Module AI-31 3.9.2 Technical Data Feature Value No. of inputs 12 Galvanic isolation - from system electronics Yes (optocoupler) - of the channels from one another Yes Measuring ranges (standard fitting) Configurable via switch Resolution in all ranges 16 bit Acquisition cycle max. 100 ms Increased insulation resistance acc. to IEC 602555 2.5 kV ; 50 Hz, 1 min - Power-frequency withstand voltage 4.4 kV; 1.2/50 μs; 0.5 J - Surge voltage Page 37 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Fiber optic module ST-61 3.10 Fiber optic module ST-61 The ST-61 is designed to provide communication from six fiber optic ports to one RS-422/RS-485 serial port. The ST-61 uses a separate LED emitter and photo-detector operating at an 820 nm wavelength. Connections to the emitter and detector are done with ST type connectors. Almost any multimode glass fiber size can be used including 50/125 µm, 62.5/125 µm, 100/140 µm, and 200 µm. Two fibers are required between the two devices, one each direction of data. Figure 16. 3.11 Fiber optic board Installation of System Housing Multi-frame systems/RTUs are usually installed in a cabinet (horizontal installation). A station's height is 6 height units (U), i.e. 266 mm. It is important to leave one U free between two stations in order to allow for sufficient ventilation. Another possibility is to install the RTUs in a swing frame or on a mounting plate. Note. The RTUs should be installed in a dry, clean environment with an ambient temperature range of 0 °C ... + 60 °C (standard) and an air humidity of 0 … 95 % (non-condensation). Page 38 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Order-book 3.12 Order-book 3.12.1 Basic frame Enilit RTU order number: Slot Nr. Enilit RTU 232-123456900003-111111-0 10 11 12 Choice row 2 3 2 - 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 0 0 0 0 3 - 1 1 1 1 1 1 - 0 Functions Power supply PS-11, auxiliary voltage 115V AC PS-21, auxiliary voltage 230V AC PS-31, auxiliary voltage 110V DC PS-41, auxiliary voltage 220V DC Without redundant power supply CPU module CPU 31, with 3 Ethernet RJ45, 12 RS485 Serial links CPU 32, with 3 Ethernet RJ45, 4 RS232 Serial links, 8 RS485 Serial links CPU 33, with 3 Ethernet RJ45, 8 RS232 Serial links, 4 RS485 Serial links CPU 34, with 3 Ethernet RJ45, 12 RS232 Serial links CPU 41, with 3 Ethernet RJ45, 12 RS485 Serial links CPU 42, with 3 Ethernet RJ45, 4 RS232 Serial links, 8 RS485 Serial links CPU 43, with 3 Ethernet RJ45, 8 RS232 Serial links, 4 RS485 Serial links 1 3 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 0 0 6 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Page 39 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Order-book CPU 44, with 3 Ethernet RJ45, 12 RS232 Serial links Inputs / outputs boards DI 11, 24 x DI, operating voltage 24 VDC DI 21, 24 x DI, operating voltage 48 VDC DI 31, 24 x DI, operating voltage 110 VDC DI 41, 24 x DI, operating voltage 220 VDC DO 31, 24 x DO AI 31, 12 x AI ST 61, 6 x FO, fiber optic connector type ST Without board Communications IEC 60870-5-101 (serial communication protocol to upper or lower levels) IEC 60870-5-104 (ethernet-based communication protocol to upper or lower levels) IEC 61850 (ethernet-based communication protocol to upper or lower levels) IEC 60870-5-103 (legacy IED communication protocol to lower levels) DNP3, Modbus Without communication protocol PLC Automation Enabled ISaGRAF runtime for Programmable Logic, Automation, etc. Disabled 8 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 Frame Page 40 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Order-book With second frame Without second frame Accessories Equipments: Wall mounted adapter Ethernet cable for any connection Cache for empty slots Connectors (3 points) Connectors (9 points) Connectors (12 points) Softwares: Enilit RTU configuration tool always included in order ISaGRAF software PLC Editor Manuals: Technical and Operation guides in English Technical and Operation guides in German Technical and Operation guides in Russian Technical and Operation guides in Lithuanian 1 0 Page 41 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU Hardware | Order-book 3.12.2 Second frame Enilit RTU ordernumber: Enilit RTU 30-1234569090909090 Slot Nr. Choicerow 1 3 3 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4 0 - 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 0 9 0 9 0 9 0 9 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 5 6 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Functions Power supply PS-11, auxiliaryvoltage 115V AC PS-21, auxiliaryvoltage 230V AC PS-31, auxiliaryvoltage 110V DC PS-41, auxiliaryvoltage 220V DC Withoutredundantpowersupply Inputs / outputsboards DI 11, 24 x DI, operatingvoltage 24 VDC DI 21, 24 x DI, operatingvoltage 48 VDC DI 31, 24 x DI, operatingvoltage 110 VDC DI 41, 24 x DI, operatingvoltage 220 VDC DO 31, 24 x DO AI 31, 12 x AI ST 61, 6 x FO, fiberopticconnectortype ST Withoutboard Accessories Equipments: Wallmountedadapter Ethernetcableforanyconnection Cacheforemptyslots Connectors (3 points) Connectors (9 points) Connectors (12 points) Page 42 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Introduction 4. Enilit RTU software 4.1 Introduction The Enilit RTU Configuration and Management Software (CMS) is the tool for simple and straightforward configuration, maintenance, management and PLC programming of Enilit RTU with IsaGRAF software. In the course of RTU configuration, the user can specify communications protocols and define relationships between master and slave protocols. Also you can define relationships between hardware connections and slave protocols. Supported protocols are: control direction: o IEC 60870-5-101 o IEC 60870-5-103 o IEC 60870-5-104 o DNP3 serial o DNP3 IP o IEC 61850 o Modbus RTU/ASCII o Modbus TCP o RP-570 monitor direction: o IEC 60870-5-101 o IEC 60870-5-104 o DNP3 serial o DNP3 IP Enilit RTU can be used as gateway between the IEC61850 substation bus and SCADA protocols IEC 60870-5-101 and -104. 4.2 System capabilities Enilit RTU CMS capabilities: 4.3 Not less than 50.000 information objects database; Not less than 1000 events/second. Up to 96 serial slave devices Licensing Page 43 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Licensing Enilit RTU CMS software is included by default. Windows 7 Embedded operating system license is included in the Enilit RTU price. IsaGRAF license can be added by the request. Figure 17. Enilit RTU Substation and SCADA system concept Page 44 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | User interface 4.4 User interface Following figure shows Main window of Enilit RTU CMS. You can choose one of the buttons to configure Master protocols, Slave protocols, Hardware, PLC Isagraf or enter Tag manager. The main architectural concept is that you create some points in Master protocols from IED devices then you create tags with Tag manager and connect it to the Master protocols points. Then you create points in Slave protocols and connect it to the tags, which you have created before. And now you will have some points from controlled device to the SCADA or some other controlling device. In the Main window you can save Enilit RTU configuration to the hard disk. Figure 18. Menu item Main window Description Click to log on as a user. Click to open Hardware manager. Page 45 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | User interface Click to open Master protocols. Click to open Slave protocols. Click to open PLC programming interface. Click to open TAG manager. Click to open TAG states window. Click to open Redundancy management window (button is visible only if Redundancy is used) Click to open Time management window. Click to open Console window. Click to save configuration. Click to close Enilit RTU software. The following figure shows the standard perspective of the program window of Enilit RTU CMS. The display and work area is subdivided into several views. As is usual with all Windows applications, all windows can be resized, moved or closed. Page 46 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | User interface Figure 19. Standard application window The program window is subdivided in the following areas: Side Left side Description Communications tree. RTU of a project and their respective communications are shown in the form of a structured tree diagram. In this view you can use the “+” and the “-” characters, respectively, to open and close the different branches of the tree. By clicking left mouse button on the tree item, the user opens settings window in the right application side. When clicking on tree item with the right mouse button, a corresponding popup menu enables access to further functions available for this tree item. Right side Settings table. When clicking on tree item in left side of window, the corresponding Settings table is opened, enabling the user to view and edit the settings. Help section Help section is located in the bottom of the right side. The help section contains some information about the parameter on which the cursor is currently positioned. The following figure shows popup menu of first tree item (CPU).Menu items: Menu item Description Expand All Expand all tree branches Collapse All Collapse all tree branches Page 47 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | User interface Create New Shows window in which you can choose protocol. Keyboard shortcut Ctrl+N. Communication Port Figure 20. CPU popup menu If you use menu item Create New Communication Port, you will see following figure. Then you can select protocol. The new tree item will appear in the communications tree. Popup menu is fast and simple way for creating RTU communications. Figure 21. Select Master protocol window The following window shows Select Slave protocol window. Figure 22. Select Slave protocol window Page 48 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | User interface Figure 23. Tag Manager window Page 49 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Configurator 4.5 Configurator With the help of Enilit RTU Configurator you can change some initial system parameters regarding with CPU, Serial ports, Ethernet ports, OPC, Isagraf, Graphics, Logs, Debug and other. Figure 24. Configurator window Figure 25. File menu Menu item Description Log On Log on as a user. Log Off Log off currently logged user. Save (Ctrl+S) Save configuration Exit Exit Configurator Page 50 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Configurator Figure 26. File menu Menu item Description Check configuration Checks RTU description file Create Enilit user groups Creates Enilit user groups in Windows user groups list Remove Enilit user groups Removes Enilit user groups from Windows user groups list 4.5.1 User groups Figure 27. Created user groups in Windows user groups list There are three groups of users: Menu item Description Enilit Users Users must belong to this group if they want to work with Enilit CMS. Enilit Allow Control Allows users to simulate controls in Enilit CMS. Enilit Allow Edit. Allows users to edit Enilit CMS configuration. 4.5.2 Create user groups First step to start working with Enilit RTU software is to Create Enilit user groups from Enilit RTU Configurator. To create Enilit user groups in Windows user group list you can use Enilit Configurator. Run Enilit Configurator program and select from the menu Edit, then Create Enilit user groups. Successful creation shows the following figure. You can use this function without log in. Page 51 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Configurator Figure 28. User groups successfully created. 4.5.3 Create user with rights Second step, open Computer Management tool from Control Panel, Administrative Tools. Go to Local Users and Groups. Create new user in Users folder, like shown in following figure. Figure 29. Computer management window In the General tab of Enilit User properties uncheck User must change password at next logon checkbox, and check Password never expires checkbox. Page 52 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Configurator Figure 30. Enilit user password options After that open created user properties window and click Member Of tab, then Add new Groups. Page 53 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Configurator User properties window Figure 31. Click Advanced. Figure 32. Select group window Select all Enilit user groups and click OK. Page 54 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Configurator Figure 33. Advanced Select group window Following figure shows how should look Member Of tab in the last step. Click OK and you will have user with the rights to log in, configure and control Enilit RTU Configurator, Enilit RTU Project Manager and Enilit RTU CMS. User with all three groups will have full access to the Enilit RTU software, but if you need users with different access level you can add only Enilit Users or Enilit Allow Edit. Page 55 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Users authentication Figure 34. 4.6 User Member of tab Users authentication After run of Configurator, Project Manager or CMS user must authenticate himself with own user name and password. Figure 35. Log on window Without user registration you can only review configuration, but not able to do anything else. Even without user log on, you can’t manually start/stop RTU with current configuration. After user log on you will see in the Main window user name which have logged on. The following figure shows that logged on user: Enilit. Figure 36. Logged on user Page 56 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Project manager 4.7 Project manager 4.7.1 Basic information With the help of Project Manager you can manage Enilit RTU configurations. It allows import/export project of Enilit RTU configuration. You can have here many projects and start Enilit RTU CMS with specific RTU configuration. Figure 37. Project Manager project parameters window Menu item Description Name Project name Description Additional project description Startup If enabled, then project is startup project Directory Projects directory (read-only). Change possible only in Projects.xml file in Enilit CMS directory. Configuration Version of project configuration version Created on RTU of computer name on which project is created Created user User who created the project Creation date Date when the project was created Page 57 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Project manager Modified on Computer name on which was made last modification Modified user User who made last modification Modification date Date when was last modification Figure 38. Menu item Project Manager RTU parameters window Description Default value Name Name of RTU EnilitRTU Description Additional description Additional description IP IP address to connect to RTU 127.0.0.1 Enabled Enables Redundancy No Redundant RTU Redundant RTU name Empty Name Redundant RTU IP address of redundant RTU Empty IP Figure 39. File menu Page 58 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Project manager Menu item Description Log On Log on as a user. Log Off Log off currently logged user. Save (Ctrl+S) Save Project Manager configuration Exit Exit Project Manager Figure 40. Edit menu Menu item Description Create branch (Ctrl+N) Create branch in the tree Create project… Create Project in the selected branch Add RTU… Add RTU to the selected project Delete Delete branch, project or RTU Figure 41. Menu item Project menu Description Start project Start Enilit RTU CMS with the selected project Edit RTU configuration Edit Enilit RTU configuration with CMS Show Project directory Opens project directory Go to startup project Selects startup RTU in the projects tree Check projects Validates projects Import project Import project from ezip file (Enilit ZIP) Page 59 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Project manager Export project Export project to ezip file (Enilit ZIP) 4.7.2 Import project With the Import project feature you can import project from external, network or other storage. Figure 42. Import project window Menu item Description Destination directory Directory where to save imported project Project file Ezip file of importing project New project name New imported project name 4.7.3 Export project With the Export project feature you can export project to external, network or other storage for RTU configuration backup. Figure 43. Export project window Menu item Description Destination directory Where to save exported project Project name File name of exported project (in our case Test.ezip) Page 60 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Main configuration 4.8 Main configuration Enilit RTU has Windows Embedded Operating System. Parameters regarding network configuration you can configure with default Windows applications without need of any third party applications. 4.8.1 IP addresses Enilit RTU has by default three Network adapters. Network adapters are independent and each has own MAC address. In that case all Network adapters can have different IP address with a different gateway. You can choose also Static IP address or obtain it by DHCP. To configure a Static IP address for one of three Enilit RTU network adapters, work through the following steps: 1. Launch Control Panel 2. Click on Network and Internet 3. Click on Network and Sharing Center 4. On the left pane, click on Change adapter settings Page 61 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Main configuration 5. Right mouse click on the targeted network adapter icon and select Properties 6. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click on Properties. 7. Select Use the following IP address and enter the following IP address and subnet mask: IP address: 172.17.217.130 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 Gateway: 172.17.217.254 Page 62 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Main configuration 4.8.2 Remote management Enilit RTU can be configured and managed not only locally, but also remotely. If you have TCP/IP connection to Enilit RTU, you can connect to it with Remote Desktop Connection application from Windows Operating System. Remotely you can do everything what you can do locally: Enilit RTU Selfcontrol and Diagnosis, change configuration, import/export project, configure Windows OS. Remote Desktop is not enabled by default. You must specifically enable it to allow remote access to the Enilit RTU. When it is enabled, configured member of the Administrators group can connect to the Enilit RTU. 4.8.2.1 To configure Enilit RTU To configure remote access, follow these steps: 1. In Control Panel, click System and Security. 2. Then click System. Page 63 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Main configuration 3. On the System page, click Remote Settings in the left pane. This opens the System Properties dialog box to the Remote tab. 4. To enable Remote Desktop, you have two options. You can: Select Allow Connections from Computers Running Any Version of Remote Desktop to allow connections from any version of Windows. Select Allow Connections Only from Computers Running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication to allow connections only from Windows 7 or later computers (and computers with secure network authentication). 5. Click Select Users. This displays the Remote Desktop Users dialog box. 6. To grant Remote Desktop access to a user, click Add. This opens the Select Users dialog box. In the Select Users dialog box, click Locations to select the computer or domain in which the users you want to work with are located. Type the name of a user you want to work within the Enter the Object Names to Select field, and then click Check Names. If matches are found, select the account you want to use and then click OK. If no matches are found, update the name you entered and try searching again. Repeat this step as necessary, and then click OK. Page 64 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Main configuration 7. Click OK twice when you have finished. 4.8.2.2 To connect to Enilit RTU 1. Go to Start>All Programs>Accessories>Remote Desktop Connection 2. Enter the Computer Name or IP address of the Enilit RTU you wish to connect to. Page 65 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Main configuration 3. For more connection options, click on Show Options. Here you can save the connection profile, adjust display properties, run specified programs upon connection, adjust connection bandwidth, etc. For more information on specific tabs, click on Help. 4. Click on Connect. 5. Enter your log in credentials of a user account on the Enilit RTU that is allowed to do a remote desktop connection. Page 66 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Main configuration Default username: EnilitRemote Default password: Enilit123 Page 67 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration 4.9 Hardware configuration The main Hardware configuration window looks like following figure. Left side you will see RTU Card Slots and Hardware Tags trees. In the Card Slots you can configure which module is mounted on the particular slot. Hardware Tags enables you to configure signals, measurements, commands and counters items and connect it to the RTU hardware. In the right pane you will see selected branch items parameters. Hardware configuration window Figure 44. Field name ID Description RTU unique identification number. Default value 1 Range of Values: 1 … 65535 Name Name of RTU. RTU For example: “Substation 1” Extended Does RTU contain extension rack. No Event count Number of event to keep in one file. 1000 Range of Values: 100 … 100000 History days Number of days to keep files in history. 100 Range of Values: 1 … 1000 Max files size Maximum log files size. 10 Range of Values: 1 … 100 Mb UTC time stamp Allows to choose the time stamp used in log files. No Page 68 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration Values: No, Yes 4.9.1 Power supply Power supply parameters Figure 45. Field name Description Default value Installed Power supply is installed in slot Description Free user description or comment No 4.9.2 CPU Figure 46. Field name CPU parameters Description CPU enabled CPU enabled on system startup. Description Free user description or comments Version Hardware and software version of card Barcode Barcode of installed card. Led Error1 Blink Led Error1 blink rate in 100 ms rate Default value Yes 5 Range of Values: 1 … 254 Page 69 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration Led Error1 Blink Led Error1 blink rate in 100 ms, when there is no 255 rate (no CPU) communication with CPU Range of Values: 0 … 255 0 – means always OFF Led Error2 Blink Led Error2 blink rate in 100 ms rate 5 Range of Values: 1 … 254 Led Error2 Blink Led Error2 blink rate in 100 ms, when there is no 255 rate (no CPU) communication with CPU Range of Values: 0 … 255 0 – means always OFF Led Run Blink Led Run blink rate in 100 ms, when there is no 0 rate (no CPU) communication with CPU Range of Values: 0 … 255 0 – means always OFF Time out with Communication time out with CPU in 100 ms. 10 CPU Time when no activity got from Main CPU. Range of Values: 10 … 255 Watchdog relay Watchdog relay time out in seconds. Time when 20 time out no activity got from Main CPU (Operating system or Main program not running or loading). Range of Values: 1 … 255 Watchdog COM COM communication ports will be disabled after 3000 ports set time of milliseconds. Range of Values: 0 … 65535 0 – communication ports will never be disabled. 4.9.3 Card Slots Following figure shows Card Slots tree. Here you can assign hardware modules to the particular slot. The type of the module is written on the top of the module front panel. Page 70 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration RTU Slots tree Figure 47. Figure 48. Field name Slot number Slot parameters pane Description Number of RTU slot. Only for internal use. Default value Depends on slot number. For example: 10 … 21 Card enabled Card is enabled Yes Card Type Choose type of module. Empty Values: DI-31 Digital Input, DO-31 Digital Output, AI-31 Analog Input, ST-61 Fiber optics Description Description of card Version Hardware and software version of card Barcode Barcode of installed card. Page 71 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration LED brightness Enables to configure LED brightness on 100 particular module. Range of Values: 0 … 100 % 4.9.4 Hardware items parameters 4.9.4.1 Digital input Digital Input parameters Figure 49. Field name Description Default value Digital input Number of digital input. Only for internal use. Depends on digital input number For example: 1 … 24 Debouncing Debouncing checking time in milliseconds. If check time the value is 0, then debouncing filter is not used. 5 Range of Values: 0 … 255 ms Filtering time Filter checking time in milliseconds. If value is 0, 1 then filtering is not used. Range of Values: 0 … 255 ms Toggling end Time delay after which no changes are detecting. 1 time Range of Values: 0 … 60 s Toggling time Toggling checking time. If value is 0, then 1 toggling is not used. Range of Values: 0 … 60 s Transition Transition count in toggling time to set quality of 8 number binary input to Not Topical. Range of Values: 2 … 60 Page 72 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration 4.9.4.2 Digital output Figure 50. Field name Digital outputs parameters Description Digital output Number of digital output. Only for internal use. number For example: 1 … 24 Default value Depends on digital output 4.9.4.3 Analog input Figure 51. Field name Analog input parameters Description Default value Analog input Number of analog input. Only for internal use. Depends on analog input number For example: 1 … 12 Analog input Configuration allows you to set the analog input type type to the measuring range. Current 4 … 20 mA Range of Values: Current 0 … 1 mA Current -1 … 1 mA Current 0 … 5 mA Current -5 … 5 mA Page 73 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration Current 0 … 10 mA Current -10 … 10 mA Current 4 … 20 mA Current 0 … 20 mA Current -20 … 20 mA Voltage -10 … 10 V Voltage -5 … 5 V Voltage -2,5 … 2,5 V Voltage -1,25 … 1,25 V Maximum value Here the maximum raw value of analog input for 100 the conversation to normalized measured value. Range of Values: -32767 … 32767 Minimum value Here the minimum raw value of analog input for 0 the conversation to normalized measured value. Range of Values: -32767 … 32767 4.9.4.4 Fiber optics Figure 52. Field name Enabled Fiber optics parameters Description Turn on or off fiber optic port. Default value Yes Values: No, Yes Light ON Light on or off fiber optic port. No Values: No, Yes Port Nr Physical port number from the top. Depends on IO Port number Range of Values: 1 … 6 Page 74 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration 4.9.5 Hardware Tags Here you create Hardware tags, which you connect to hardware digital inputs, analog inputs, and command outputs. The following figure shows popup menu of hardware tags. With it you can create Hardware Tags tree. After that you can create tags like single point status, double point status, multi point status, single commands, double commands, multi point commands, measurements, and counter single, counter doubles. Figure 53. Popup menu of hardware tags. 4.9.5.1 Single point parameters Figure 54. Hardware Tags tree and single point signal parameters Page 75 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration Field name ID Description Default value Identification number of hardware tag. Only for Depends on tag internal use. Range of Values: 1 … 65535 Name Hardware tag name. Item SPS1 For example: “IED fault” Length: 1 … 255 DI input Allows connecting hardware tag to binary input. Not set For example: Slot : 13 DI : 01 OFF delay Delay on stable state after which the hardware tag 0 is set to OFF. (100 ms) Range of Values: 0 … 1000 ON delay Delay on stable state after which the hardware tag 0 is set to ON. (100 ms) Range of Values: 0 … 1000 Time tagging Type of tag timestamp. Event can be with start or Yes start end of filtering timestamp. Values: Yes, No Auto reset Auto reset hardware tag from ON to OFF. No Values: No, Yes Inverse Invert of hardware tag. No Values: No, Yes Tag Name Hardware tag connection to Tag manager. Tag manager tag name. Page 76 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration 4.9.5.2 Double point parameters Figure 55. Hardware Tags tree and double point signal parameters Field name ID Description Default value Identification number of hardware tag. Only for Depends on tag internal use. Range of Values: 1 … 65535 Name Hardware tag name. Item DPS1 For example: “Item DPS1” Length: 1 … 255 DI input OFF Allows connecting hardware tag to binary input. Not set For example: Slot : 13 DI : 04 DI input ON Allows connecting hardware tag to binary input. Not set For example: Slot : 13 DI : 05 Intermediate Delay on stable state after which the hardware tag 0 (00) delay is set to Jammed (both inputs are not active). (100 ms) Range of Values: 0 … 1000 OFF delay Delay on stable state after which the hardware tag 0 is set to OFF. (100 ms) Range of Values: 0 … 1000 Page 77 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration ON delay Delay on stable state after which the hardware tag 0 is set to ON. (100 ms) Range of Values: 0 … 1000 Indeterminate Delay on stable state after which the hardware tag 0 (11) delay is set to Undefined (both inputs are active). (100 ms) Range of Values: 0 … 1000 Time tagging Type of tag timestamp. Event can be with start or Yes start end of filtering timestamp. Range of Values: Yes, No Inverse Invert of hardware tag. No Range of Values: Yes, No Tag Name Hardware tag connection to Tag manager. Tag manager tag name. Page 78 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration 4.9.5.3 Multipoint status Figure 56. Hardware Tags tree and double multipoint status parameters Field name ID Description Default value Identification number of hardware tag. Only for Depends on tag internal use. Range of Values: 1 … 65535 Name Hardware tag name. Item MPS1 For example: “Item MPS1” Length: 1 … 255 Type Select type of multipoint status. Binary Page 79 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration Range of Values: Binary, BCD, 1 from N bits, Gray DI Input bit01 Allows connecting one of multipoint status item Not set … to binary input. DI Input bit16 For example: Slot : 13 DI : 04 DI Sign Allows connecting binary input used for Not set multipoint status sign. For example: Slot : 13 DI : 04 Stable delay Delay on stable state before changing tags value 0 in 100 ms. Range of Values: 0 … 1000 Time tagging Type of tag timestamp. Event can be with start or Yes start end of filtering timestamp. Range of Values: Yes, No Offset Offset value for conversion. 0 Range of Values: 0 … 100 Scale Scale value for conversion. 1 Range of Values: 0 … 100 Tag Name Hardware tag connection to Tag manager. Tag manager tag name. Page 80 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration 4.9.5.4 Single command parameters Figure 57. Hardware Tags tree and single command parameters Field name Long pulse Description Long pulse length in seconds. Default value 1 Range of Values: 1 … 600 Short pulse Short pulse length in 10 milliseconds. 10 Range of Values: 10 … 6000 Type If command got with unknown or undefined type Pulse short it will be overridden with this type of pulse. Range of Values: Pulse short, Pulse long, Persistent ID Identification number of hardware tag. Only for Depends on tag internal use. Range of Values: 1 … 65535 Name Hardware tag name. Item SPC1 For example: “Item SPC1” Length: 1 … 255 DO output Allows connecting hardware tag to digital output. Not set For example: Slot : 11 DO : 01 Page 81 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration Inverse Invert of hardware tag. No Range of Values: Yes, No Tag Name Hardware tag connection to Tag manager. Tag manager tag name. 4.9.5.5 Double command parameters Figure 58. Hardware Tags tree and double command parameters Field name Long pulse Description Long pulse length in seconds. Default value 1 Range of Values: 1 … 600 Short pulse Short pulse length in 10 milliseconds. 10 Range of Values: 10 … 6000 Type If command got with unknown or undefined type Pulse short it will be overridden with this type of pulse. Range of Values: Pulse short, Pulse long, Persistent ID Identification number of hardware tag. Only for Depends on tag internal use. Range of Values: 1 … 65535 Page 82 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration Name Hardware tag name. Item DPC1 For example: “Item DPC1” Length: 1 … 255 DO output OFF Allows connecting hardware tag to digital output. Not set For example: Slot : 11 DO : 04 DO output ON Allows connecting hardware tag to digital output. Not set For example: Slot : 11 DO : 05 Inverse Invert of hardware tag. No Range of Values: Yes, No Tag Name Hardware tag connection to Tag manager. Tag manager tag name. Page 83 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration 4.9.5.6 Multipoint command Figure 59. Hardware Tags tree and multipoint command parameters Field name Long pulse Description Long pulse length in seconds. Default value 1 Range of Values: 1 … 600 Short pulse Short pulse length in 10 milliseconds. 10 Range of Values: 10 … 6000 Type If command got with unknown or undefined type Pulse short it will be overridden with this type of pulse. Range of Values: Pulse short, Page 84 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration Pulse long, Persistent ID Identification number of hardware tag. Only for Depends on tag internal use. Range of Values: 1 … 65535 Name Hardware tag name. Item MPC1 For example: “Item MPC1” Length: 1 … 255 Type Select type of multipoint command. Binary Range of Values: Binary, BCD, 1 from N bits, Gray DO Output bit01 Allows connecting one of multipoint command Not set … item to binary output. DO Output bit16 For example: Slot : 13 DO : 04 Offset1 Offset value for conversion. 0 Range of Values: 0 … 100 Offset2 Offset value for conversion. 0 Range of Values: 0 … 100 Scale Scale value for conversion. 1 Range of Values: 0 … 100 Tag Name Hardware tag connection to Tag manager. Tag manager tag name. Page 85 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration 4.9.5.7 Measurement parameters Figure 60. Field name ID Hardware Tags tree and measurement parameters Description Default value Identification number of hardware tag. Only for Depends on tag internal use. Range of Values: 1 … 65535 Name Hardware tag name. Item MV1 For example: “Voltage U1” Length: 1 … 255 AI input Allows connecting hardware tag to analog input. Not set For example: Slot : 15 AI : 01 Dead band type Type of measurement dead band. Simple Range of Values: Simple, Integrated Dead band value Change of measurement is sent if the change is 0 more than this dead band value. If the value is 0, then all changes are sent. Range of Values: 0 … 32767 Zero suppression Set value to zero if it reaches below this value. 0 Page 86 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration Range of Values: 0 … 32767 Offset Offset value for conversion. 0 Range of Values: 0 … 100 Scale Scale value for conversion. 1 Range of Values: 0 … 100 Scale offset type Type of conversion. Linear Range of Values: Linear, Quadratic Tag Name Hardware tag connection to Tag manager. Tag manager tag name. 4.9.5.8 Single counter parameters Figure 61. Field name Auto reset Hardware Tags tree and single counter parameters Description Automatically reset counter value after Default value Yes accumulation period. Values: Yes, No Period Period for which accumulation should be 1 hour proceeded. Range of values: 1 minute … 12 hours Send type Yes – counter value is sent only on period end. Yes Page 87 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration No – counter value is sent on period end and every second. Values: Yes, No Valid delay Stable ON delay before increasing tags value. 10 Range of Values: 0 … 1000 ms ID Identification number of hardware tag. Only for Depends on tag internal use. Range of Values: 1 … 65535 Name Hardware tag name. Item SCT1 For example: “Counter C1” Length: 1 … 255 DI input Allows connecting hardware tag to digital input. Not set For example: Slot : 12DI : 01 Tag Name Hardware tag connection to Tag manager. Tag manager tag name. 4.9.5.9 Double counter parameters Figure 62. Field name Auto reset Hardware Tags tree and double counter parameters Description Automatically reset counter value after Default value Yes accumulation period. Page 88 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Hardware configuration Values: Yes, No Invalid delay Delay after which binary inputs not went to 5 normal state. Tags value is not increased. Range of Values: 0 … 1000 ms Period Period for which accumulation should be 1 hour proceeded. Range of values: 1 minute … 12 hours Send type Yes – counter value is sent only on period end. Yes No – counter value is sent on period end and every second. Values: Yes, No Valid delay Stable ON delay before increasing tags value. 10 Range of Values: 0 … 1000 ms ID Identification number of hardware tag. Only for Depends on tag internal use. Range of Values: 1 … 65535 Name Hardware tag name. Item DCT1 For example: “Counter C1” Length: 1 … 255 DI input OFF Allows connecting hardware tag to digital input. Not set DI input used for OFF counting. For example: Slot : 12DI : 01 DI input ON Allows connecting hardware tag to digital input. Not set DI input used for ON counting. For example: Slot : 12DI : 01 Tag Name Hardware tag connection to Tag manager. Tag manager tag name. Page 89 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols 4.10 Master protocols 4.10.1 IEC 60870-5-103 configuration 4.10.1.1 Communication port parameters Field name Description ID For internal use. Port name Name of the port and protocol. Default value New IEC-103 master protocol For example: “COM1 IEC103 master protocol” Enabled on start Port enabled on system startup. No Values: No, Yes Com port Communication port number. Not assigned Range of values: 1 … 255 Baud rate Serial port baud rate. 19200 Range of values: 110 … 921600 Data bits Serial port data bits. 8 Values: 7,8 bits Stop bits Serial port stop bits. 1 Values: 1, 1.5, 2 bits Parity Serial port parity. None Values: None, Odd, Even, Mark, Space Page 90 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols RS-485 Mode If used two wires mirrored data check should be Four wire used. If serial port is RS-232, parameter is not important. Range of values: Four wires, Two wires Reconnect How often try to reconnect to communication 10 port if there was error. Range of values: 1 … 600 seconds Next request Wait time before sending next request 50 Range of values: 0 … 1000 ms Port Monitor Show port monitor on system startup. No Values: No, Yes Log raw data Log raw communication data. Yes Values: No, Yes 4.10.1.2 Data link layer parameters Field name Description Default value Page 91 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols ID For internal use. Data link name Data link layer name. New Data Link layer For example: “Feeder 1”. Enabled on start Enables or disables data link on start. Yes Values: No, Yes Data link Data link address 1 address Range of values: 1 … 254 Frame size Maximum frame length 255 Range of values: 50 … 255 bytes Broken link Number of retries to determine if the connection 5 is broken. Range of values: 1 … 10 Priority Request data every cycle. 1 Range of values: 1 … 255 Class1 Count How many times request the same data link 1 layer, if there is Class1 events. 0 – request until no Class1 events or Class1 timer expires. Range of values: 0 … 255 Class1 Time How long request the same data link layer, if 0 there is Class1 events. 0 – time is not checked. Range of values: 0 … 255000 ms Reconnect How often try to reconnect to communication 10 port if there was error. Range of values: 1 … 600 seconds Answer timeout Wait timeout of response from controlled 500 device. Range of values: 50 … 30000 milliseconds Allow E5 Enables or disables E5 response from controlled Yes device. Values: No, Yes Use Status link Enables or disables use Status of link frame Yes before Reset Link is sent. Values: No, Yes Page 92 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols User Data with Sends User Data with confirmation request. confirm Values: No, Yes Use CU Enables to use Reset Communication Unit. Yes No Values: No, Yes Use CU timeout Use Reset CU command if no link more than 0 – use always this timeout. This parameter has no effect if “Use CU” is disabled. Range of values: 0 … 43200 minutes Ignore DFC bit Enables to ignore DFC bit. Yes Values: No, Yes Log header Log data link header. Yes Values: No, Yes Log Answer Log data link answer timeouts to system log. Timeout Values: Never, First time, Always. First Time 4.10.1.3 Application layer parameters Field name ID Description Default value For internal use. Page 93 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Application layer Application layer name. New Application layer name name For example: “Feeder 1”. Enabled on start Enables or disables application layer on start. No Values: No, Yes Common address Common address of data unit. 1 Range of values: 1 … 254 General Cycle time of general interrogation to the Interrogation controlled device. 600 Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds Auto add Automatically adds all data points received after Yes General Interrogation responses from controlled device. Values: No, Yes Reconnect How often try to connect to remote application. 600 Application is considered connected, on received any application data from remote device. Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Time Cycle time of clock synchronization to the synchronization controlled device. 600 Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds Day of Week In request with timestamp use Day of Week bit. No Values: No, Yes Summer time In request with timestamp use Summer time bit. No Values: No, Yes Allow Enables or disables clock synchronization. synchronization Values: No, Yes UTC time In requests and responses use UTC time. Yes Yes Values: No, Yes Generic Generic data request refresh rate. command Range of values: 500 … 600000 ms Log header Log headers of frames in protocol log. 2000 Yes Values: No, Yes Page 94 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols LogIO Log configured information objects to protocol Yes log. Values: No, Yes Log IO not Log not configured points to protocol log. configured Values: No, Yes No 4.10.1.4 Points Application layer has Points branch. You can manage here signals, measurements from controlled device and commands to controlled device. You can add points manually or use the function Auto add in the application layer, which will add all data points to the list. You must add commands manually anyway, hence commands doesn’t include in General Interrogation. Following figure shows points popup menu, which you can run with right mouse button. You can Add status point, Edit status point, Delete status point, Select All status points or commands. Also you can Connect or Remove connection to the Tag. You can Remove connection to source also from Tag Manager. All menu items have keyboard shortcuts. They will simplify and quicken the work with the software. Figure 63. Points popup menu Following figure shows Add new data points dialog window. The parameters which you can specify on IEC 60870-5-103 protocol are proposed in the next table. Page 95 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Figure 64. Field name IEC Type Add new data points Description Default value IEC 60870-5-103 data type. Time Tagged Message (Type 1 Values: and Type 2) Time Tagged Message (Type 1 and Type 2), Measurement (Type 3 and Type 9), Measurement (Type 4), Time Tagged Message (Type 1 and Type 2) Double (composed from two Time Tagged Messages, both Time Tagged Messages should be addressed in a row). Function Here, the function type of the employed 1 protection equipment can be defined: The following paragraph lists the meaning of some of the function types: 128: Distance protection 160: Overcurrent time protection Page 96 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols 176: Transformer - differential protection 192: Line differential protection 254: Generic function type 255: Global function type For a complete list of all function types, please refer to the IEC 60870-5-103 norm. Range of values: 0...255 Function Used only for configuration. After adding new Increment status point function will be automatically 0 incremented by set value. Information Here, the information number can be specified. 1 Ranges for information numbers in monitoring direction: 0...15 System functions 16...31 Status 32...47 Monitoring 48...63 Earth faults 64...127 Short circuits 128...143 Automatic reclosing 144...159 Measured values 240...255 Generic functions Ranges for information numbers in control direction: 0...15 System functions 16....31 General commands 240...255 Generic functions For a complete list of all information numbers, please refer to the IEC 60870-5-103 norm. Range of values: 0 … 255 Information Used only for configuration. After adding new Increment status point function will be automatically 1 incremented by set value. Index Parameter is relevant only with IEC Type 1 Measurement (Type 3 and Type 9). Page 97 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Range of values: 0 … 255 Timer 00 This parameter is relevant only if IEC Type is 0 Time Tagged Message (Type 1 and Type 2) Double. If received value is intermediate and timer is set to not zero, it will be delayed for set time and if some data change occurs it will be ignored. Range of values: 0 … 3600 seconds, 0 – not used Timer OFF This parameter is relevant only if IEC Type is 0 Time Tagged Message (Type 1 and Type 2) Double. If received value is OFF and timer is set to not zero, it will be delayed for set time and if some data change occurs it will be ignored. Range of values: 0 … 3600 seconds, 0 – not used Timer ON This parameter is relevant only if IEC Type is 0 Time Tagged Message (Type 1 and Type 2) Double. If received value is ON and timer is set to not zero, it will be delayed for set time and if some data change occurs it will be ignored. Range of values: 0 … 3600 seconds, 0 – not used Timer 11 This parameter is relevant only if IEC Type is 0 Time Tagged Message (Type 1 and Type 2) Double. If received value is indeterminate and timer is set to not zero, it will be delayed for set time and if some data change occurs it will be ignored. Range of values: 0 … 3600 seconds, 0 – not used Change to SP IEC-60870-5-103 protocol all status signals are Unchecked double points. If you want to use single point signal in upper direction (IEC 60870-5-101 or Page 98 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols IEC 60870-5-103 slave protocols), you must check this checkbox. Values: Checked, Unchecked Auto reset IEC 60870-5-103 data Type 2 are transient Unchecked signals, which means that slave device transmits only start of signal, but never transmits the end of it. In this case you must check this checkbox. Values: Checked, Unchecked Invert Inversion of signals Type 1 and Type 2. Unchecked Values: Checked, Unchecked Offset 1 New value = (Old value + Offset1) * Scale + 0 Scale Offset2 1 Offset 2 0 Following three figures shows the list of data points and commands. You can use double click to edit data or command point. You can also select many points and then edit it with keyboard shortcut Ctrl+E. Figure 65. List of status points Columns between Function type and Offset 2 are status point configuration parameters. Value, Time, Quality, Cause will show real-time data from controlled device. Page 99 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Figure 66. Field name IEC Type Create new command point window Description IEC 60870-5-103 data type. Default value General Command Values: General Command General Command Double (composed from to General Commands which is addressed in a row) Function Here, the function type of the employed 1 protection equipment can be defined: The following paragraph lists the meaning of some of the function types: For a complete list of all function types, please refer to the IEC 60870-5-103 norm. Range of values: 0...255 Function Used only for configuration. After adding new Increment command, function will be automatically 0 incremented by set value. Information Here, the information number can be specified. 1 Ranges for information numbers in monitoring direction: Page 100 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Range of values: 0 … 255 Information Used only for configuration. After adding new Increment command, function will be automatically 1 incremented by set value. Offset 1 New value = (Old value + Offset1) * Scale + 0 Scale Offset2 1 Offset 2 Invert 0 Inversion of signals Type 1 and Type 2. Unchecked Values: Checked, Unchecked Figure 67. List of commands In the Command points window Value, Time will show last transmitted command data. Result will show response from controlled device. 4.10.1.5 Measured information coefficient calculation Sometimes it is hard to understand how Scale parameter is calculated to get real value of measurement. Most of relays for measurement transmission use coefficients – 1.2 or 2.4 (It is according to IEC-60870103 standard). We will name it COF. According IEC-60870-103 standard measurements are transmitted in range from -4096 to 4096. ScaleI=Inom* COF/4096; ScaleU=Unom* COF/4096; ScaleUL=Unom* COF*√3/4096; ScaleP= Inom*Unom* COF*√3/4096; ScaleQ= Inom*Unom* COF*√3/4096; Remember if you use kilovolts in equations, so for power you will get kilowatts and so on. Page 101 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols 4.10.2 IEC 60870-5-101 configuration 4.10.2.1 Communication port parameters Field name Description ID For internal use. Port name Name of the port and protocol. Default value New IEC-101 master protocol For example: “COM2 IEC-101 master protocol” Enabled on start Port enabled on system startup. No Values: No, Yes Com port Communication port number. Not assigned Range of values: 1 … 255 Baud rate Serial port baud rate. 38400 Range of values: 110 … 921600 Data bits Serial port data bits. Values: 7, 8 Stop bits Serial port stop bits. 1 Values: 1, 1.5, 2 Parity Serial port parity. None Values: None, Odd, Even, Mark, Space Page 102 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols RS-485 Mode If used two wires mirrored data check should be Four wire used. If serial port is RS-232, parameter is not important. Range of values: Four wires, Two wires Reconnect How often try to connect to communication port 10 if there was error. Range of values: 1 … 600 seconds Next request Wait time before sending next request 50 Range of values: 0 … 1000 ms Data link Data link layer address size in bytes. address size Range of values: 0 … 2 bytes Port monitor Show port monitor on system startup. 1 No Values: No, Yes Log raw data Log raw communication data. Yes Values: No, Yes 4.10.2.2 Data link layer parameters Page 103 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Field name Description ID For internal use. Data link name Data link layer name. Default value New Data Link layer For example: “Measurements data controller”. Enabled on start Enables or disables data link on start. No Values: No, Yes Data link Data link address address Range of values: 1 1 … 65534 (if Data link addr. length is set to 2), 1 … 254 (if Data link address length is set to 1), If Data link address length is set to 0, this parameter is not used. COT size Cause of transmission size 1 Range of values: 1 … 2 bytes CAA size Common address size 2 Range of values: 1 … 2 bytes Frame size Maximum frame length 255 Range of values: 50 … 255 bytes Broken link Number of retries to determine if the connection 5 is broken. Range of values: 1 … 10 Priority Request data every cycle. 1 Range of values: 1 … 255 Class1 Count How many times request the same data link 1 layer, if there is Class1 events. 0 – request until no Class1 events or Class1 timer expires. Range of values: 0 … 255 Class1 Time How long request the same data link layer, if 0 there is Class1 events. 0 – time is not checked. Range of values: 0 … 255000 ms Reconnect How often try to reconnect to communication 10 port if there was error. Range of values: 1 … 600 seconds Page 104 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Answer timeout Wait timeout of response from controlled 500 device. Range of values: 50 … 30000 milliseconds Allow E5 Enables or disables E5 response from controlled Yes device. Values: No, Yes Use Status link Enables or disables use Status of link frame Yes before Reset Link is sent. Values: No, Yes User Data with Sends User Data with confirmation request. confirm Values: No, Yes Log header Log data link header. Yes Yes Values: No, Yes Log Answer Log data link answer timeouts to system log. Timeout Values: Never, First time, Always. First Time Page 105 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols 4.10.2.3 Application layer parameters Field name Description ID For internal use. Application name Application link layer name. Default value New Application Link layer For example: “Measurements data controller”. Enabled on start Enables or disables application on start. No Page 106 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Values: No, Yes Common address Common address of data unit. 1 Range of values: 1 … 254 Originator Originator 0 Range of values: 0 … 255 Object address size Size of information object address 3 Range of values: 1 … 3 Object address Object address structure shows in what format structure information object address is entered in Unstructured configuration. Range of values: Unstructured, Structured 8.8.8, Structured 8.16, Structured 16.8, Structured 8.8 Auto add Automatically adds all data points received after Yes General Interrogation to the controlled device. Values: No, Yes Allow same IOA Allow to have same information object address No for status and command points. Values: No, Yes Cyclic start Yes – next cyclic operation time is calculated at Yes the end of operation. No – next cyclic operation time is calculated at the start of operation. Values: No, Yes BO IOA Class1 Information object address of buffer overflow for 0 – not used Class1. Range of values: 0 - 16777215 BO IOA Class2 Information object address of buffer overflow for 0 – not used Class2. Range of values: 0 - 16777215 Page 107 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Wait COT Wait response of activation termination for set termination points. Yes Values: No, Yes Use C_TA Enables to use commands with timestamp. No Values: No, Yes Timeout IC Timeout for interrogation commands. 60 Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Reconnect If application layer is not connected how often to 10 send station interrogation command. Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Interrogation Cycle time of General Interrogation to the 3600 general controlled device. Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds Interrogation group Cycle time of Group Interrogation to the controlled 0 – disabled Group 1 … 16 device. Interrogation Range of values: 0 … 86400 seconds Page 108 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Field name Timeout CI Description Default value Timeout for Counter Interrogation requests. 60 Range of values: 0 … 3600 seconds Counter Cycle time of Counter Interrogation to the 0 – disabled Counter Interrogation controlled device. Interrogation general Range of values: 0 … 86400 seconds Counter Cycle time of Counter Interrogation group to the 0 – disabled Counter Interrogation group controlled device. Interrogation 1…4 Range of values: 0 … 86400 seconds Timeout CS Timeout for clock synchronization. 10 Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Page 109 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Allow Enables or disables clock synchronization. synchronization Values: No, Yes Clock Cycle time of clock synchronization to the synchronization controlled device. Yes 600 Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds UTC time Enables to use UTC time in requests and Yes responses. Values: No, Yes Day of Week In request with timestamp use Day of Week bit. No Values: No, Yes Summer time In request with timestamp use Summer time bit. No Values: No, Yes Acquisition delay Use acquisition delay before sending clock No synchronization (C_CD_NA_1). Values: No, Yes Timeout CD Timeout for delay acquisition. 10 Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Use for test Use test frame format C_TS_TA_1. Yes C_TS_TA_1 Values: No, Yes Test Cycle time of test frame. This parameter is not 0 - disabled used, when Is test frame used are set to No. Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds FBP Fixed test bit pattern 21930 Range of values: 0 … 32768 Timeout TC Timeout for test command. 10 Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Timeout RP Timeout for reset process. 10 Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Enabled Enables file transfer function. No Values: No, Yes Dir on connect Request directory after connection starts. Yes Values: No, Yes Receive files After receive list of files, download all files from No controlled device. Page 110 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Values: No, Yes Segment size Segment size to use in file transfer. 0 – segment 0 size is calculated from max frame length. If segment size plus headers is more than max frame length, segment size will be calculated from max frame length. Range of values: 0 … 255 bytes Log header Log application layer header. Yes Values: No, Yes Log IO Log information objects. Yes Values: No, Yes Log IO not Log not configured information objects. configured Values: No, Yes Yes 4.10.2.4 Points Following figure shows data points of IEC 60870-5-101 protocol. Figure 68. Figure 69. IEC 60870-5-101 status points table IEC 60870-5-101 command points table Following figure shows Add new data points IEC 60870-5-101 protocol. You can use very useful function Auto increment by 1. For example, you need to configure some points with information addresses in interval 1001 and 1010. You can configure first point with 1001 address and then check the checkbox Auto Page 111 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols increment by 1. Then you can click Add button and in this case it will not close the dialog, but automatically configure information address with 1002. So you will get 10 points with only 10 mouse clicks. Add new data point IEC 60870-5-101 Figure 70. Field name Description Information Here, the information address can be specified. address Range of information address depends from Default value 1 Application layer parameter Information object address length. Range of values: 0 … 16777215 IEC Type IEC 60870-5-101 data type. Single Point Values: Single point Double point Step position Bit string of 32 bits Measured value, normalized value Measured value, scaled value Measured value, short floating point value Calculations Calculation of status item. No conversion New Value = (Old value + Offset1) * Scale + Offset2 Page 112 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Invert Inversion of signals Type 1 and Type 2. No Values: No, Yes Add new command points IEC 60870-5-101 Figure 71. Field name Description Information Here, the information address can be specified. address Range of information address depends from Default value 1 Application layer parameter Information object address length. Range of values: 0 … 16777215 IEC Type IEC 60870-5-101 command type. Single Command Values: Single command Double command Regulating step command Setpoint normalized command Setpoint scaled command Setpoint short float command Bitstring command Calculations Calculation of status item. No conversion New Value = Page 113 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols (Old value + Offset1) * Scale + Offset2 Invert Inversion of command. No Values: No, Yes 4.10.3 IEC 60870-5-104 configuration 4.10.3.1 Communication port parameters Field name Description Default value ID Port name Port name. New IEC-104 master protocol For example: “IEC-104 master 172.29.37.113”. Enabled on start Enables or disables communication port on start. No Values: No, Yes Ethernet port Which Ethernet port to use for connection to All ETH server. Values: All ETH, ETH 1, ETH 2, ETH 3. Server name or Name or IPv4 address of the host. 127.0.0.1 TCP port. 2404 IP TCP port Range of values: 1 … 65535 Page 114 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Redundancy Enables or disables redundant communication. No enabled Values: No, Yes Ethernet port Redundant Ethernet port to use for connection to All ETH server. Values: All ETH, ETH 1, ETH 2, ETH 3. Server name or Name or IPv4 address of the redundant host. IP TCP port Redundant TCP port. Range of values: 1 … 65535 TCP Keep Alive TCP Keep Alive. Do not set low values, because 0 - disabled it will add overhead to communication. Range of values: 0 … 2147483647 milliseconds TCP No delay TCP No delay disables the Nagle Algorithm. Yes Values: No, Yes Connect Timeout Reconnect If the connection is broken, cycle time of 10 reconnection. Range of values: 1...600 seconds Next request Wait time before sending next request 50 Range of values: 0 … 1000 ms Port monitor Show port monitor on system startup. No Values: No, Yes Log raw data Log raw communication data. Yes Values: No, Yes Page 115 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols 4.10.3.2 Data layer parameters Field name Description Default value Data link name. New Data link ID Data link name For example: “Data link”. Enabled on start Enables or disables communication port on start. No Values: No, Yes T1 Acknowledgement time-out 1 15 Range of values: 1...600 seconds T2 Acknowledgement time-out 2 10 Range of values: 1...600 seconds T3 Connection test timeout 20 Range of values: 1...600 seconds k Maximum number of unacknowledgments 12 ADPUs Range of values: 1...32,767 w Maximum number of received ADPUs for 8 acknowledgments Range of values: 1...32,767 No frame I Change behavior of I frame. Not used Values: Not used, Send STOP DT, Disconnect. Page 116 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols No frame I Timeout of I frame 60 timeout Range of values: 1...600 seconds Common Common address size address size Range of values: 1 … 2 bytes Cause of Cause of transmission size 2 2 transmission size Range of values: 1 … 2 bytes Frame size Maximum frame size. All start, stop, checksum 255 and other bytes are included. Range of values: 50 … 255 bytes Log APCI Log Application Protocol Control Information. Yes Values: No, Yes Page 117 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols 4.10.3.3 Application layer parameters Field name Description ID For internal use. Application name Application layer name. Default value New Application link layer For example: “Other RTU”. Enabled on start Enables or disables application on start. No Values: No, Yes Common address Common address of data unit. 1 Page 118 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Range of values: 1 … 254 Originator Originator 0 Range of values: 0 … 255 Object address size Size of information object address 3 Range of values: 1 … 3 Object address Object address structure shows in what format structure information object address is entered in Unstructured configuration. Range of values: Unstructured, Structured 8.8.8, Structured 8.16, Structured 16.8, Structured 8.8 Auto add Automatically adds all data points received after Yes General Interrogation to the controlled device. Values: No, Yes Allow same IOA Allow to have same information object address No for status and command points. Values: No, Yes Cyclic start Yes – next cyclic operation time is calculated at Yes the end of operation. No – next cyclic operation time is calculated at the start of operation. Values: No, Yes BO IOA Information object address of buffer overflow. 0 – not used Range of values: 0 - 16777215 Wait COT Wait response of activation termination for set termination points. Yes Values: No, Yes Use C_TA Enables to use commands with timestamp. No Values: No, Yes Timeout IC Timeout for interrogation commands. 60 Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Page 119 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Reconnect If application layer is not connected how often to 10 send station interrogation command. Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Interrogation Cycle time of General Interrogation to the 3600 general controlled device. Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds Interrogation group Cycle time of Group Interrogation to the controlled 0 – disabled Group 1 … 16 device. Interrogation Range of values: 0 … 86400 seconds Field name Timeout CI Description Timeout for Counter Interrogation requests. Default value 60 Page 120 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Range of values: 0 … 3600 seconds Counter Cycle time of Counter Interrogation to the 0 – disabled Counter Interrogation controlled device. Interrogation general Range of values: 0 … 86400 seconds Counter Cycle time of Counter Interrogation group to the 0 – disabled Counter Interrogation group controlled device. Interrogation 1…4 Range of values: 0 … 86400 seconds Timeout CS Timeout for clock synchronization. 10 Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Allow Enables or disables clock synchronization. synchronization Values: No, Yes Clock Cycle time of clock synchronization to the synchronization controlled device. Yes 600 Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds UTC time Enables to use UTC time in requests and Yes responses. Values: No, Yes Day of Week In request with timestamp use Day of Week bit. No Values: No, Yes Summer time In request with timestamp use Summer time bit. No Values: No, Yes Acquisition delay Use acquisition delay before sending clock No synchronization (C_CD_NA_1). Values: No, Yes Timeout CD Timeout for delay acquisition. 10 Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Use for test Use test frame format C_TS_TA_1. Yes C_TS_TA_1 Values: No, Yes Test Cycle time of test frame. This parameter is not 0 - disabled used, when Is test frame used are set to No. Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds FBP Fixed test bit pattern 21930 Range of values: 0 … 32768 Timeout TC Timeout for test command. 10 Page 121 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Timeout RP Timeout for reset process. 10 Range of values: 1 … 3600 seconds Enabled Enables file transfer function. No Values: No, Yes Dir on connect Request directory after connection starts. Yes Values: No, Yes Receive files After receive list of files, download all files from No controlled device. Values: No, Yes Segment size Segment size to use in file transfer. 0 – segment 0 size is calculated from max frame length. If segment size plus headers is more than max frame length, segment size will be calculated from max frame length. Range of values: 0 … 255 bytes Log header Log application layer header. Yes Values: No, Yes Log IO Log information objects. Yes Values: No, Yes Log IO not Log not configured information objects. configured Values: No, Yes Yes 4.10.3.4 Points Figure 72. Status points Page 122 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Figure 73. Command points Configuration of IEC 60870-5-104 protocol data and command points are the same like of IEC 60870-5101 protocol. Refer to the paragraph above. 4.10.4 IEC 61850 client Enilit RTU supports also IEC 61850 client protocol. You can connect IED devices via 61850 protocol standard. The main requirement is that you will need SCD (Substation Configuration Description) file extracted from IED device configuration software. SCD file is part of Substation Configuration Language (SCL). 4.10.4.1 Communication port Field name Description ID For internal use. Port name IEC 61850 port name. Default value New IEC 61850 client protocol For example: “IEC-61850 client protocol”. Enabled on start Enables or disables port on start. No Values: No, Yes Ethernet port Which Ethernet port to use for connection to All ETH server. Values: All ETH, ETH 1, ETH 2, ETH 3. Page 123 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols SCD file SCD file of substation. You can browse the file with Open file dialog button . Values: File name and path. SCD Enilit CMS saves the file in Projects SCD folder. When you select SCD file, the main parameters like IP address, Gateway, Subnet mask are taken from SCD file automatically. You should see following figure with your IEDs. Figure 74. Imported IED devices from SCD file Page 124 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols IEC 61850 IED device parameters window Figure 75. Field name Description Default value ID For internal use. Read only Name Name of IED. After import from SCD file name will be concatenated from IED Name and AP Name Enabled on start IED is enabled on system startup. No Values: No, Yes IED Name IED name in SCD file. AP Name Access point name in SCD file. IP IP address of IED in SCD file. TCP Keep Alive TCP Keep Alive. Do not set low values, because 0 - disabled Read only it will add overhead to communication. Range of values: 0 … 2147483647 milliseconds TCP No delay TCP No delay disables the Nagle Algorithm. Yes Values: No, Yes Log SCSM Log SCSM communication. Yes Values: No, Yes Log SCSM TX Log SCSM requests. Yes Values: No, Yes Log SCSM RX Log SCSM responses. Yes Values: No, Yes GetDataValues Enables log GetDataValues requests and Yes responses. Values: No, Yes Only needed data Start only buffered and unbuffered reports which No contains needed data. Values: No, Yes BRCB No Data Print error in system log, if for buffered report Yes Set control block dataset is not set. Values: No, Yes URCB No Data Print error in system log, if for unbuffered report Yes Set control block dataset is not set. Values: No, Yes Page 125 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Synchrocheck Set synchrocheck bit in command to YES. No Values: No, Yes Interlock Set interlock bit in command to YES. No Values: No, Yes Operate Term Wait for command termination, in case of Yes negative operate response. Values: No, Yes Cancel Term Wait for command termination, in case of No negative cancel response. Values: No, Yes 4.10.4.2 Points Figure 76. Points window IEC 61850 Following figure shows add data point popup menu. With it you can Browse ICD, Add data point, Edit data point, Delete data point, Select All data points and Remove connection to Tag, Import and Export points. Figure 77. Data points popup menu IEC 61850 Page 126 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols If you select from the above menu Browse ICD file, following ICD file window will open. There you can choose which data point to add to the data points list. This is an automated way to create data points IEC 61850. Browse data point you needed and double click to add it to the points list. Figure 78. Add new data points from IEC 61850 ICD file If you choose to Add new data points manually, you will see following dialog box. You must enter information like Logical device, Logical node, Data object, Functional constraint, Data attribute, Time attribute, Quality attribute, Invert and Value variables. Page 127 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Add new data points manually IEC 61850 Figure 79. Field name LDevice Description Default value Logical device name of IEC 61850 structure. For example: “System” LNode Logical device node of IEC 61850 structure. Each logical device contains one or more logical nodes. A logical node is a named grouping of data and associated services that is logically related to some power system function. For example: “LLN0” DATA Data object name of IEC 61850 structure. Each logical node contains one or more elements of Data. Each element of data has a unique name. These Data Names are determined by the standard and are functionally related to the power system purpose. For example: “DPC” FC Functional constraints for status (ST) attributes, ST substituted value (SV) attributes, description Page 128 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols (DC) attributes, measurement attributes (MX), and extended definition (EX) attributes Values: MX, ST DA Value Data attribute for Value. For example: “stVal” DA Time Data attribute for Time. DA Quality Data attribute for Quality. Calculations Calculation of status item. No conversion New Value = (Old value + Offset1) * Scale + Offset2 Invert Inversion of command. No Values: No, Yes Following figure shows manual creation of new command points for IEC 61850 protocol. Figure 80. Field name LDevice Add new command points manually IEC 61850 Description Default value Logical device name of IEC 61850 structure. For example: “System” LNode Logical device node of IEC 61850 structure. Page 129 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Each logical device contains one or more logical nodes. A logical node is a named grouping of data and associated services that is logically related to some power system function. For example: “LLN0” DATA Data object name of IEC 61850 structure. Each logical node contains one or more elements of Data. Each element of data has a unique name. These Data Names are determined by the standard and are functionally related to the power system purpose. For example: “DPC” FC Functional constraints for status (ST) attributes, ST substituted value (SV) attributes, description (DC) attributes, measurement attributes (MX), and extended definition (EX) attributes Values: MX, ST DA Value Data attribute for Value. For example: “stVal” Calculations Calculation of status item. No conversion New Value = (Old value + Offset1) * Scale + Offset2 Invert Inversion of command. No Values: No, Yes Page 130 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols 4.10.5 Modbus RTU/ASCII 4.10.5.1 Communication port parameters Field name Port name Enabled on start Description Default value Name of the port and protocol. New Modbus RTU/ASCII For example: “COM1 Modbus master” master protocol Port enabled on system startup. No Values: No, Yes Protocol type Enables to select protocol version. RTU Values: RTU/ASCII Polling type “One by one” means first polling all data from Cyclic first device, then second and so on. “Cyclic” means sending first request to first device, second request to second device and so on. Values: Cyclic, One by one Com port Communication port number. Not assigned Range of values: COM 1 … 255 Baud rate Serial port baud rate. 19200 Range of values: 110 … 921600 Data bits Serial port data bits. 8 Values: 7,8 Stop bits Serial port stop bits. 1 Values: 1, 1.5, 2 Page 131 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Parity Serial port parity. Even Values: None, Odd, Even, Mark, Space RS-485 mode If used two wires mirrored data check should be Four wires used. If serial port is RS-232, parameter is not important. Values: Two wires, Four wires. Next request Wait time before sending next request. 10 Range of values: 0 … 1000 ms Log raw data Log raw communication data. Yes Values: No, Yes 4.10.5.2 Application layer parameters Field name Description Default value Application layer Application layer name. New Application layer name name For example: “Application layer”. Enabled on start Enables or disables application layer on start. No Values: No, Yes Device address Device link address. 1 Range of values: 1 … 255 Max PDU Size Maximum PDU size in bytes. 252 Range of values: 10 … 252 Pooling time The time to pool the data. 5000 Range of values: 50 … 65535 ms Response timeout Time to wait response after request. 1000 Page 132 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Range of values: 10 … 65535 ms Broken link Determine the connection as broken after so 3 many retries. Range of values: 1 … 100 No link time Request data every this time when connection 10000 is broken. Range of values: 100 … 65535 ms Log header Enables to log headers in Port Monitor. Yes Values: No, Yes Log values Enables to log values in Port Monitor. Yes Values: No, Yes 4.10.5.3 Points To add new data or command point to the points list you must call popup menu in the Points window. With the following menu items you can Add, Edit or Delete data points, Select all or Remove connection to the Tag manager. Import and Export functionality included also. Figure 81. Points window popup menu Page 133 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Add new data point window Figure 82. Field name Address Description Default value Here, the information address can be specified. 1 Range of values: 0 … 65535 Modbus type Modbus data type. Read coil Values: 1. Read coil 2. Read discrete input 3. Read holding register 4. Read input register Data subtype Available only if Modbus type is Read holding register or Read input register. Available data subtypes: 16 bits unsigned (B1B2), 16 bits unsigned (B2B1), 16 bits signed (B1B2), 16 bits signed (B2B1), 32 bits unsigned in one register (B1B2B3B4), 32 bits unsigned in one register (B4B3B2B1), 32 bits signed in one register (B1B2B3B4), 32 bits signed in one register (B4B3B2B1), Page 134 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols 32 bits unsigned in two register (B1B2B3B4), 32 bits unsigned in two register (B4B3B2B1), 32 bits signed in two register (B1B2B3B4), 32 bits signed in two register (B4B3B2B1), 32 bits float in one register (B1B2B3B4), 32 bits float in one register (B4B3B2B1), 32 bits float in two register (B1B2B3B4), 32 bits float in two register (B4B3B2B1) Invert Inversion of command. No Values: No, Yes Calculations Calculation of status item. No conversion New Value = (Old value + Offset1) * Scale + Offset2 Figure 83. Data points window Columns between Function and Offset 2 are data point configuration parameters. Value, Time, Quality will show real-time data from controlled device. Page 135 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Add new command points window Figure 84. Field name Address Description Default value Here, the information address can be specified. 1 Range of values: 0 … 65535 Modbus type Modbus data type. Write single coil Values: 1. Write single coil 2. Write single register Data subtype Available only if Modbus type is Write single register. Available data subtypes: 16 bits unsigned (B1B2), 16 bits unsigned (B2B1), 16 bits signed (B1B2), 16 bits signed (B2B1) Calculations Calculation of status item. No conversion New Value = (Old value + Offset1) * Scale + Offset2 Invert Inversion of command. No Values: No, Yes Figure 85. Commands window In the Command points window Value, Time will show last transmitted command data. Result will show response from controlled device. Page 136 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols 4.10.6 Modbus TCP client 4.10.6.1 Communication port parameters Field name Port name Enabled on start Description Default value Name of the port and protocol. New Modbus For example: “TCP Modbus client” protocol Port enabled on system startup. No TCP master Values: No, Yes Allow multiple Allow multiple ADU in one TCP frame. ADU Values: No, Yes Max ADU size Maximum ADU size. Yes 260 Range of values: 20 … 260 bytes Max TCP RX Maximum servers receive buffer size. buffer Range of values: 300 … 10000 Max TCP TX Maximum clients transmit buffer size. buffer Range of values: 300 … 10000 Max transaction Maximum transaction on the same time 1024 10224 16 Range of values: 1 … 16 Page 137 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Ethernet port Which Ethernet port to use for connection to All ETH server. Values: All ETH, ETH 1, ETH 2, ETH 3. Modbus Server Server IP address. 127.0.0.1 Values: xxx.zzz.yyy.nnn TCP/IP Port TCP port for TCP/IP connection. Must be 502 the same port on the server side. Values: 1 … 65535 Connect Timeout TCP connect timeout. 3 Range of values: 1 … 60 seconds Response timeout Time to wait response after request. 1 Range of values: 0 … 65535 ms TCP Keep Alive Force TCP activity when idle to long. Do 1000 not set low values, because it will add overhead to communication. Range of values: 0 … 2147483647 TCP No delay Enables or disables the Nagle algorithm. Yes Values: No, Yes Next request Time to wait before new request is 10 transmitted. Range of values: 1 … 65535 ms Log raw data Enables to log raw data in Port Monitor. Yes Values: No, Yes Log MBAP header Enables to log Modbus application headers Yes in Port Monitor. Values: No, Yes Page 138 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols 4.10.6.2 Application layer parameters Field name Appl Name Description Default value Application layer name. New Application layer For example: “Application layer”. Enabled on start Enables or disables application layer on start. No Values: No, Yes Unit identifier Slave Address (255 if not used) 1 Range of values: 0 … 255 Pooling time The time to pool the data. 5000 Range of values: 50 … 65535 ms Log header Enables to log headers in Port Monitor. Yes Values: No, Yes Log values Enables to log values in Port Monitor. Yes Values: No, Yes 4.10.6.3 Points Refer to the Modbus RTU/ASCII paragraph “Points”. 4.10.7 DNP3 serial master configuration 4.10.7.1 Communication port parameters Field name Baud rate Description Default value Serial port baud rate. 38400 Range of values: 110 … 921600 Com port Communication port number. For example with 1 default value will be used COM1. Page 139 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Range of values: 1 … 255 Data bits Serial port data bits. 8 Values: 7,8 Parity Serial port parity. None Values: None, Odd, Even, Mark, Space Stop bits Serial port stop bits. 1 Values: 1, 1.5, 2 Port enabled Port enabled on system startup. No Values: No, Yes Port name Name of the port and protocol. “New Communication Port” For example: “COM1 DNP3 master” 4.10.7.2 Data link layer parameters Field name Master address Description RTU’s master address Default value 1 Range of values: 0 … 65535 bytes Slave address IED slave address 2 Range of values: 0 … 65535 bytes Answer timeout Wait timeout of response from controlled 500 device. Range of values: 50 … 30000 milliseconds Broken link Number of retries to determine if the connection 5 is broken. Range of values: 1 … 10 No link cycle This parameter is important if there is no link to 10 the controlled device. With default value it sends requests every tenth cycle. Range of values: 1 … 10 Ask data every This parameter is important if you have more 1 than one controlled device on one communication port. You can use it for raring data requests to the desirable device. Range of values: 1 … 10 Data link name Data link layer name. New Data Link layer Page 140 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols For example: “Measurements data controller”. Enabled on start Enables or disables data link on start. Yes Values: No, Yes 4.10.7.3 Application layer parameters Field name Time UTC Description Use UTC time in communication. Default value Yes Values: No, Yes Time Cycle time of clock synchronization to the synchronization controlled device. 600 Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds Use time Enables or disables clock synchronization. synchronization Values: No, Yes Application DNP3 application layer answer timeout timeout Range of values: 0..255 seconds Class 0 pooling Period of class 0 data pooling Yes 10 seconds 1800 seconds 0 – no pooling Range of values: 0..3600 seconds Application layer Application layer name. New Application layer name name For example: “Application layer”. Enabled on start Enables or disables application layer on start. Yes Values: No, Yes 4.10.7.4 Points Refer to the IEC-101 paragraph “Points”. (The configuration is very similar) 4.10.8 DNP3 UDP/TCP/IP client configuration 4.10.8.1 Communication port parameters Field name Port Description TCP port Default value 2404 Range of values: 1 … 65535 Server IPv4 address of the host. 127.0.0.1 Master address RTU’s master address 1 Range of values: 0 … 65535 bytes Page 141 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Slave address IED slave address 2 Range of values: 0 … 65535 bytes Reconnect If the connection is broken, cycle time of 10 reconnection. Range of values: 1...600 seconds T0 Connection timeout 30 Range of values: 1...600 seconds UDP Use UDP or TCP type No No – TCP Yes - UDP Port enabled Enables or disables communication port on start. Yes Values: No, Yes Port name Port name. New communication port name For example: “IEC-104 master 172.29.37.113”. 4.10.8.2 Application layer parameters Field name Time UTC Description Use UTC time in communication. Default value Yes Values: No, Yes Time Cycle time of clock synchronization to the synchronization controlled device. 600 Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds Use time Enables or disables clock synchronization. synchronization Values: No, Yes Application DNP3 application layer answer timeout timeout Range of values: 0..255 seconds Class 0 pooling Period of class 0 data pooling Yes 10 seconds 1800 seconds 0 – no pooling Range of values: 0..3600 seconds Application layer Application layer name. name For example: “Application layer”. Enabled on start Enables or disables application layer on start. New Application layer name Yes Values: No, Yes Page 142 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols 4.10.8.3 Points Refer to the IEC-101 paragraph “Points”. (The configuration is very similar) 4.10.9 Simulator master configuration With simulator interface you can simulate data points to upper level protocols. It is very useful in testing environment. You can use it to test SCADA system without IED devices. 4.10.9.1 Port parameters Field name Description ID For internal use only. Port name Simulator port name. Default value New Simulator master For example: “Simulator”. Enabled on start Enables or disables port on start. No Values: No, Yes Port monitor Show port monitor on system startup. No Values: No, Yes 4.10.9.2 Points Following figure shows Add new simulation point dialog window. You can specify some parameters like Name, Value type, Change type, Min value, Max value, Step, Change every. Page 143 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Add new simulation point Figure 86. Field name Name Description Name of status point. Default value Name For example: “Data Point 1”. Type Type of data point. Integer Range of values: Integer, Float Min value Minimum value of simulation data point. 0 Range of values: 0 … 16777215 Max value Maximum value of simulation data point. 1000 Range of values: 0 … 16777215 Step Step size to change simulation data point between 1 Min and Max values Range of values: 0 … 16777215 Change type Data point simulation type. Increment Range of values: Increment, Decrement, Random, Manual. Change every Cycle time of data point change. 100 Range of values: 0 … 60000 milliseconds Page 144 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols If you have configured manual data point change type, you can change data point manually by entering Manual set value dialog from data point popup menu. Following figure shows this menu. Figure 87. Figure 88. Simulator data point popup menu Manual change type dialog With manual change type you can simulate also Cause of transmission and Quality of data point. Cause of transmission can be: Not defined, Initialize, Periodic, Background, Spontaneous, General Interrogation, Requested, Control local, Control remote, Disconnected source, Disabled source, Deleted source, Test mode, Calculated. Quality values can be in the range: Not Init, Blocked, Not Topical, Invalid, Substituted, Overflow, Invalid Time, Substituted time, Clock failure. Page 145 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols 4.10.10 RP-570 configuration 4.10.10.1 Communication port parameters Field name Baud rate Description Serial port baud rate. Default value 19200 Range of values: 110 … 921600 Com port Communication port number. For example with 1 default value will be used COM1. Range of values: 1 … 255 Data bits Serial port data bits. 8 Values: 7, 8 bits Parity Serial port parity. None Values: None, Odd, Even, Mark, Space Stop bits Serial port stop bits. 1 Values: 1, 1.5, 2 bits Port enabled Port enabled on system startup. No Values: No, Yes Port name Name of the port and protocol. “New Communication Port” For example: “COM1 RP-570 master” 4.10.10.2 Data link layer parameters Field name RTU Number Description RTU Number or address Default value 1 Range of values: 1 … 254 Max frame size Maximum frame length 255 Range of values: 50 … 255 bytes Answer timeout Wait timeout of response from controlled 500 device. Range of values: 50 … 30000 milliseconds Ask data every This parameter is important if you have more 1 than one controlled device on one communication port. You can use it for raring data requests to the desirable device. Range of values: 1 … 10 Page 146 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Master protocols Broken link Number of retries to determine if the connection 5 is broken. Range of values: 1 … 10 No link cycle This parameter is important if there is no link to 10 the controlled device. With default value it sends requests every tenth cycle. Range of values: 1 … 10 Data link name Data link layer name. New Data Link layer For example: “Feeder 1”. Enabled on start Enables or disables data link on start. Yes Values: No, Yes Page 147 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols 4.11 Slave protocols 4.11.1 IEC 60870-5-101 protocol configuration 4.11.1.1 Communication port parameters Field name Port Name Enabled on start Description Default value Name of the port and protocol. “New For example: “COM3 IEC-101 slave” protocol” Port enabled on system startup. No IEC_101 slave Values: No, Yes Init time Protocol initialization time on startup. During this 0 time no events will be generated. Range of values: 0 … 600 seconds Com port Communication port number. Not assigned Range of values: COM 1 … COM 255 Baud rate Serial port baud rate. 19200 Range of values: 110 … 921600 Data bits Serial port data bits. 8 Values: 7, 8 Stop bits Serial port stop bits. 1 Values: 1, 1.5, 2 Parity Serial port parity. None Values: None, Odd, Even, Mark, Space Page 148 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols RS-485 Mode If used two wires mirrored data check should be Four wires used. If serial port is RS-232, parameter is not important. Values: Two wires, Four wires. Link Address Data link address size. 1 size Range of values: 0 … 2 bytes Max frame size Maximum frame length 250 Range of values: 40 … 255 bytes Log raw data Log raw communication data. Yes Values: No, Yes 4.11.1.2 Data link layer parameters Field name Data Link Name Description Data link layer name. Default value New Data Link For example: “Measurements data controller”. Enabled on start Enables or disables data link on start. No Values: No, Yes Data link Data link address address Range of values: 1 1 … 65534 (if Data link addr. length is set to 2), 1 … 254 (if Data link address length is set to 1), If Data link address length is set to 0, this parameter is not used. COT size Cause of transmission size. 1 Range of values: 1 … 2 bytes Page 149 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Common Common address size. 2 address size Range of values: 1 … 2 bytes Ack E5 Enables or disables E5 response to controlling Yes device. Values: No, Yes Class1 answers Enables or disables Class1 data response to to Class2 Class2 requests. Yes Values: No, Yes Disconnect time If data link layer doesn’t get requests for more 10 than particular time, it will be considered as disconnected. Values: 0 … 60 seconds Log Log data link layers. Yes Values: No, Yes Page 150 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols 4.11.1.3 Application layer parameters Field name Appl Name Description Default value Application layer name. New application layer For example: “SCADA 1”. Enabled on start Enables or disables data link on start. No Values: No, Yes Common address Common address of data unit. 1 Range of values: 1 … 254 Object address size Size of information object address field. 3 Range of values: 1 … 3 Object address Object address structure shows in what format structure information object address is entered in Unstructured configuration. Page 151 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Range of values: Unstructured, Structured 8.8.8,Structured 8.16, Structured 16.8,Structured 8.8 Max Frame size Maximum frame size. 250 Range of values: 40 … 255 End of init Enables or disables station initialization frame Yes transmission to controlled station. Values: No, Yes Interrogation How to behave if received general interrogation command response command request, but general interrogation No already is going. No – general interrogation is restarted. Values: No, Yes Commands Time Time difference to discard command execution. difference Range of values: 10 … 10000 milliseconds Allow Allows clock synchronization from controlled synchronization station. 10000 No Values: No, Yes UTC Time synchronization with UTC timestamp. Yes Values: No, Yes Time difference Time difference to synchronize internal RTU 1000 clock. Range of values: 20 … 10000 milliseconds Day of Week In responses with timestamp use Day of Week Yes bit. Values: No, Yes Summer time In responses with timestamp use Summer time Yes bit. Values: No, Yes Hour change Transmit spontaneous clock synchronization No command on hour change. It is only used for events with CP24Time2a timestamp. Values: No, Yes Page 152 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Periodic Cycle time of data marked with Cyclic/Periodic 10 COT. Range of values: 10 … 10000 seconds Background Cycle time of data marked with Background 60 COT. Range of values: 10 … 10000 seconds Event buffer Class1 Spontaneous Events buffer of Class 1 size. size 1000 Change has only take effect after system restart. Range of values: 10 … 10000 events Event buffer class1 If the buffer of class 1 events overflows, with overflow this parameter you can select which event to Remove first remove from queue. Range of values: Remove first, Remove last, Remove all. Overflow IOA Overflow information object address for Class1. Class1 On buffer overflow this IOA will be set to 1 and 0 – not used when there is free places in buffer it will be set to 0. When it changes to 0, controlling device should initiate general interrogation. Event buffer Class2 Spontaneous Events buffer of Class 2 size. size 1000 Change has only take effect after system restart. Range of values: 10 … 10000 events Event buffer class2 If the buffer of class 2 events overflows, with overflow this parameter you can select which event to Remove first remove from queue. Range of values: Remove first, Remove last, Remove all. Overflow IOA Overflow information object address for Class2. Class2 On buffer overflow this IOA will be set to 1 and 0 – not used when there is free places in buffer it will be set to Page 153 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols 0. When it changes to 0, controlling device should initiate general interrogation. SQ Use SQ bit. Recommended to use only if most Yes part of information object addresses are incremented by one. Values: No, Yes Log DUI Log data unit identifiers. Yes Values: No, Yes Log IO Log information objects. Yes Values: No, Yes 4.11.1.4 Points Data points and command points in monitoring direction are freely configurable. All the configured data and command points you will connect to the tag, which you have already connected to the data sources. Figure 89. Data points for IEC 60870-5-101 slave Page 154 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Figure 90. Add new data points dialog for IEC 60870-5-101 slave Field name Address Description Default value Here, the information address can be specified. 1 Range of information address depends from Application layer parameter Information object address length. Range of values: 0 … 16777215 Address After adding new data point address will be 1 Increment automatically incremented by set value. It is used only for configuration. IEC Type IEC 60870-5-101 data type. Single Point Values: Single point Double point Step position Bit string of 32 bits Measured value, normalized value Measured value, scaled value Measured value, short floating point value Time type Timestamp of data point. No time Range of values: No time, Page 155 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Short time (3 bytes) Long time (7 bytes) Interrogation Assign data point to the specific interrogation General group. Range of values: General, Group1, Group2, Group3, Group4, Group5, Group6, Group7, Group8, Group9, Group10, Group11, Group12, Group13, Group14, Group15, Group16. On change You can specify data point class or cause of Class1 Event transmission. If you choose to be Class1 Event or Class2 Event, data point will be marked with Spontaneous cause of transmission. Range of values: Class1 Event, Class1 Event, not buffered when no link, Class2 Event, Class2 Event, not buffered when no link, Send only on general interrogation request, Periodic. Value Conversion of measurements. No conversion Value = ( X + a) * b + c X – Value from slave device. a, b, c – free configurable variables. Invert Inversion of signals Type 1 and Type 2. No Values: No, Yes Figure 91. Command points for IEC 60870-5-101 slave Page 156 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Figure 92. Add new command points dialog for IEC 60870-5-101 slave Field name Description Information Here, the information address can be specified. address Range of information address depends from Default value 1 Application layer parameter Information object address length. Range of values: 0 … 16777215 IEC Type IEC 60870-5-101 command type. Single Command Values: Single command Double command Regulating step command Setpoint normalized command Setpoint scaled command Setpoint short float command Bitstring command Value Conversion of commands. No conversion Value = ( X + a) * b + c X – Value from slave device. a, b, c – free configurable variables. Invert Inversion of commands. No Values: No, Yes Page 157 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols You can select some data points and then press Ctrl+Shift+N to connect all selected data points to the tags in a row. If tag icon is grayed out, it is not possible to connect to slave status point or command point. It means if you have to choose Status point in slave protocol, it is possible to connect only to status tag. And if you have to choose Command point in slave protocol, it is possible to connect only to command tag. Figure 93. Status point or command point connection to tag dialog box 4.11.2 IEC 60870-5-104 protocol configuration 4.11.2.1 Communication port parameters Field name Port Name Description Default value Port name. New IEC-104 slave protocol For example: “IEC-104 slave” Enabled on start Enables or disables communication port on start. Yes Values: No, Yes Page 158 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Init time Protocol initialization time on startup. During this 0 time no events will be generated Range of values: 1 … 60 Ethernet port Which Ethernet port to use to create server. All ETH Values: All ETH, ETH 1, ETH 2, ETH 3. IP Port TCP port 2404 Range of values: 1 … 65535 TCP Keep Alive Checks the connected socket and determines 10000 whether the connection is still up and running or if it has broken. Range of values: 1 … 2147483647 milliseconds 0 – disabled. TCP No delay Controls TCP packet batching. No Values: No, Yes Log RAW Enables to log RAW. Yes Values: No, Yes Log IP Enables to log IP. Yes Values: No, Yes Page 159 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols 4.11.2.2 Client parameters Field name Client Name Description Client name. Default value New IEC104 client For example: “IEC-104 client” Enabled on start Enables or disables client on start. Yes Values: No, Yes T1 Acknowledgement time-out 1. 15 Range of values: 1...600 seconds T2 Acknowledgement time-out 2. 10 Range of values: 1...600 seconds T3 Connection test timeout. 30 Range of values: 1...600 seconds k Maximum number of unacknowledged I format 12 ADPU’s. Range of values: 1...32,767 w After how many I frame APDU’s 8 acknowledgment is needed. Range of values: 1...32,767 Common Common address size. address size Values: 1, 2 2 Page 160 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Cause of Cause of transmission size. 2 transmission size Values: 1, 2 IP 1 … IP 9 Access list of clients IPs. 127.0.0.1 Range of values: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx Log ACPI Enables to log ACPI header values. Yes Values: No, Yes 4.11.2.3 Application layer parameters Field name Appl Name Description Application layer name. Default value New application layer For example: “SCADA 1”. Enabled on start Enables or disables data link on start. No Values: No, Yes Common address Common address of data unit. 1 Range of values: 1 … 254 Page 161 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Object address size Size of information object address field 3 Range of values: 1 … 3 Object address Object address structure shows in what format structure information object address is entered in Unstructured configuration. Range of values: Unstructured, Structured 8.8.8,Structured 8.16, Structured 16.8,Structured 8.8 Max Frame size Maximum frame size. 250 Range of values: 40 … 255 End of init Enables or disables station initialization frame Yes transmission to controlled station. Values: No, Yes Interrogation How to behave if received general interrogation command response command request, but general interrogation No already is going. No – general interrogation is restarted. Values: No, Yes Commands Time Time difference to discard command execution. difference Range of values: 10 … 10000 milliseconds Allow Allows clock synchronization from controlled synchronization station. 10000 No Values: No, Yes UTC Time synchronization with UTC timestamp. Yes Values: No, Yes Time difference Time difference to synchronize internal RTU 1000 clock. Range of values: 20 … 10000 milliseconds Day of Week In responses with timestamp use Day of Week Yes bit. Values: No, Yes Summer time In responses with timestamp use Summer time Yes bit. Values: No, Yes Page 162 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Hour change Transmit spontaneous clock synchronization No command on hour change. It is only used for events with CP24Time2a timestamp. Values: No, Yes Periodic Cycle time of data marked with Cyclic/Periodic 10 COT. Range of values: 10 … 10000 seconds Background Cycle time of data marked with Background 60 COT. Range of values: 10 … 10000 seconds Event buffer size Spontaneous Events buffer size. Change has only 1000 take effect after system restart. Range of values: 10 … 10000 events Event buffer If the buffer of events overflows, with this Remove first overflow parameter you can select which event to remove from queue. Range of values: Remove first, Remove last, Remove all. Overflow IOA Overflow information object address. On buffer 0 – not used overflow this IOA will be set to 1 and when there is free places in buffer it will be set to 0. When it changes to 0, controlling device should initiate general interrogation. SQ Use SQ bit. Recommended to use only if most Yes part of information object addresses are incremented by one. Values: No, Yes Log DUI Log data unit identifiers. Yes Values: No, Yes Log IO Log information objects. Yes Values: No, Yes Page 163 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols 4.11.2.4 Points Figure 94. Figure 95. Field name Address IEC-60870-5-104 status points window Add new data points dialog for IEC 60870-5-104 slave Description Here, the information address can be specified. Default value 1 Range of information address depends from Application layer parameter Information object address length. Page 164 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Range of values: 0 … 16777215 IEC Type IEC 60870-5-104 data type. Single Point Values: Single point Double point Step position Bit string of 32 bits Measured value, normalized value Measured value, scaled value Measured value, short floating point value Time type Timestamp of data point. No time Range of values: No time, Short time (3 bytes) Long time (7 bytes) Interrogation Assign data point to the specific interrogation General group. Range of values: General, Group1, Group2, Group3, Group4, Group5, Group6, Group7, Group8, Group9, Group10, Group11, Group12, Group13, Group14, Group15, Group16. On change You can specify data point class or cause of Class1 Event transmission. If you choose to be Class1 Event or Class2 Event, data point will be marked with Spontaneous cause of transmission. Range of values: Class1 Event, Class2 Event, Interrogation only, Periodic cycle, Background cycle. Calculations Calculation of status item. No conversion New Value = Page 165 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols (Old value + Offset1) * Scale + Offset2 Invert Inversion of signals Type 1 and Type 2. No Values: No, Yes Command points for IEC 60870-5-104 slave Figure 96. Figure 97. Add new command points dialog for IEC 60870-5-104 slave Field name Description Information Here, the information address can be specified. address Range of information address depends from Default value 1 Application layer parameter Information object address length. Range of values: 0 … 16777215 IEC Type IEC 60870-5-104 command type. Single Command Values: Single command, Double command, Regulating step command, Setpoint normalized command, Setpoint scaled command, Page 166 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Setpoint short float command, Bitstring command. Calculations Calculation of status item. No conversion New Value = (Old value + Offset1) * Scale + Offset2 Invert Inversion of signals Type 1 and Type 2. No Values: No, Yes 4.11.3 DNP3 serial slave configuration 4.11.3.1 Communication port parameters Field name Baud rate Description Serial port baud rate. Default value 38400 Range of values: 110 … 921600 Com port Communication port number. For example with 1 default value will be used COM1. Range of values: 1 … 255 Data bits Serial port data bits. 8 Values: 7, 8 Parity Serial port parity. None Values: None, Odd, Even, Mark, Space Stop bits Serial port stop bits. 1 Values: 1, 1.5, 2 Port enabled Port enabled on system startup. No Values: No, Yes Port name Name of the port and protocol. “New Communication Port” For example: “COM3 DNP3 slave” 4.11.3.2 Data link layer parameters Field name Master address Description RTU’s master address. Default value 1 Range of values: 0 … 65535 bytes Slave address IED slave address. 2 Range of values: 0 … 65535 bytes Page 167 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Data link name Data link layer name. New Data Link layer For example: “Measurements data controller”. Enabled on start Enables or disables data link on start. Yes Values: No, Yes 4.11.3.3 Application layer parameters Field name Description Default value On buffer class1 If the buffer of class 1 events overflows, with this overflow parameter you can select which event to remove Remove first from queue. Range of values: Remove first, Remove last, Remove all. On buffer class2 If the buffer of class 2 events overflows, with this overflow parameter you can select which event to remove Remove first from queue. Range of values: Remove first, Remove last, Remove all. On buffer class3 If the buffer of class 2 events overflows, with this overflow parameter you can select which event to remove Remove first from queue. Range of values: Remove first, Remove last, Remove all. Allow one Allow one command at the time. No command Values: No, Yes Allowed Allows clock synchronization from controlled synchronization station. Yes Values: No, Yes Page 168 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Time difference in Time difference to synchronize internal RTU milliseconds clock. 1000 Range of values: 20 … 10000 milliseconds UTC Time synchronization with UTC timestamp. No Values: No, Yes Spontaneous Spontaneous messages enabled. No Values: No, Yes Spontaneous Class Spontaneous Class messages class. Class 1 Range of values: None Class 1 Class 2 Class 1&2 Class 3 Class 1 & 3 Class 2 & 3 Class 1 & 2 & 3 4.11.3.4 Points Refer to the IEC-101 paragraph “Points”. (The configuration is very similar) 4.11.4 DNP3 UDP/TCP/IP server configuration 4.11.4.1 Communication port parameters Field name Ethernet port Description Default value Which Ethernet port to useto create server. All ETH Values: All ETH, ETH 1, ETH 2, ETH 3. IP Port TCP port. 2404 Range of values: 1 … 65535 TCP Keep Alive Checks the connected socket and determines 10000 whether the connection is still up and running or if it has broken. Range of values: 1 … 2147483647 milliseconds 0 – disabled. Page 169 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols TCP No delay Controls TCP packet batching. No Values: No, Yes Log IP Enables to log IP. Yes Values: No, Yes Log RAW Enables to log RAW. Yes Values: No, Yes Init time Protocol initialization time on startup. During this 0 time no events will be generated Range of values: 1 … 60 Port enabled Enables or disables communication port on start. Yes Values: No, Yes Port name Port name. New DNP3 server protocol For example: “DNP3 slave” 4.11.4.2 Application layer parameters Field name Description Default value On buffer class1 If the buffer of class 1 events overflows, with this overflow parameter you can select which event to remove Remove first from queue. Range of values: Remove first, Remove last, Remove all. On buffer class2 If the buffer of class 2 events overflows, with this overflow parameter you can select which event to remove Remove first from queue. Range of values: Remove first, Remove last, Remove all. On buffer class3 If the buffer of class 2 events overflows, with this overflow parameter you can select which event to remove Remove first from queue. Range of values: Page 170 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Slave protocols Remove first, Remove last, Remove all. Allow one Allow one command at the time. No command Values: No, Yes Allowed Allows clock synchronization from controlled synchronization station. Yes Values: No, Yes Time difference in Time difference to synchronize internal RTU milliseconds clock. 1000 Range of values: 20 … 10000 milliseconds UTC Time synchronization with UTC timestamp. No Values: No, Yes Spontaneous Spontaneous messages enabled. No Values: No, Yes Spontaneous Class Spontaneous Class messages class. Class 1 Range of values: None Class 1 Class 2 Class 1&2 Class 3 Class 1 & 3 Class 2 & 3 Class 1 & 2 & 3 4.11.4.3 Points Refer to the IEC-101 paragraph “Points”. (The configuration is very similar) Page 171 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Tag manager 4.12 Tag manager Tag manager is intermediate software part which connects status and command points from master to slave protocols or connects hardware tags to slave protocols. Either you can create here tags for internal logic or IsaGRAF programming. There you can create structure of substation for easier work with tags. Figure 98. Main windows of Tag manager Page 172 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Tag manager Figure 99. Name Active popup menu when tree branch is selected Description Keyboard shortcut New Branch Creates new branch in the tree structure. Ctrl+N New Tag Creates new tag in selected branch. You need to select from following types of Tags. Delete Deletes selected branch Del Goto Data source If Tag is selected, you can reach the data source G of Tag. Remove Data source Disconnect Data source from Tag. Show Change Monitor Opens Change monitor window Test event Test event with forced value and quality Test command Test command with forced value and quality Import Tags Import Tags from CSV file. Export Tags Export Tags to CSV file. Export OPC Tags for Export Tags to CSV file for Wonderware Wonderware InTouch InTouch FSGateway software. Page 173 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Tag manager Figure 100. Field name Tag edit window Description Default value ID ID number. Only for internal use. Automatically increment value Type Tag data type. You can’t edit this value. You must delete the tag and then create one new with the type you want. Values: Status Integer 64 bits, Status Float 64 bits, Command Integer 64 bits, Command Float 64 bits, Manual Status Integer 64 bits, Manual Status Float 64 bits, Manual Command Integer 64 bits, Manual Command Float 64 bits, Mapped Command. Name Name of the tag. Status 1 State ID Tag states configuration ID. Not connected State Name Tag states configuration Name. Not connected State Real time state of Tag. Value Real time value of Tag. Time Time of last change. Quality Quality of last change. 0 0x00000000 Not init Page 174 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Tag manager Cause Cause of transmission of last change. Not defined Port ID Data source Port ID. Not connected Port Name Data source Port Name. Not connected Point ID Data source Point ID. Not connected Point Name Data source Point Name. Not connected Offset 1 With those parameters you have possibility to 0 Offset 2 change value, which you will take from the data 0 Scale 1 source. 1 Scale 2 NewValue=(OldValue+Offset1)*Scale+Offset2 1 Following picture shows Connect Tag to data source window. In the left side you will see structure which you have created in Master protocols. You can expand tree and find particular data point from master protocols points. To the tag you can connect only one data or command point. Figure 101. Connect tag to data source window In the above picture right top corner you can choose primary data source. You can connect tags to Communication ports, RTU hardware points or PLC. If you have connected Tag to the Data source and connected it also to Slave protocol, all the information regarding linkage you can see in the tag configuration of window. Also you can see here real-time value, state, timestamp, quality and cause of transmission of selected tag. Page 175 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Tag manager Signal monitoring Figure 102. 4.12.1 Tag states Tag states configuration tool allows you to configure description to Tag Values. If it is configured, then Change Monitor you can see state of the signal or command, not only value. For example it is possible to configure description SET if Value=1 and RESET if Value=0. Tag States have two types of states: Status State and Command State. Figure 103. New Tag State window Following picture shows initial Tag States window. Page 176 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Tag manager Figure 104. Initial Tag states window When you start to configure state for status signal, it’s needed to add with the priority 0, type irrelevant and quality Not topical with the value Yes. Then you add normal states, like Reset = 0 and Set = 1. Following picture show this configuration. Page 177 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Tag manager Figure 105. Configured status state If the state is configured properly, then is possible to assign state to the signal or command in the Tag Manager window, like in the following picture. Figure 106. Configured Tag with assigned state Page 178 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Internal programmable logic 4.13 Internal programmable logic Internal programmable logic are included in Enilit Configuration and Management Software by default. It gives you opportunity to use fast and simple programmable logic. To use it, it’s needed to create Manual Status Integer 64 bits or Manual Status Float 64 bits tags. After creation of Manual tag, you will see Logic calculation area like in the following figure. Figure 107. Manual Tag with Logic calculations area. To create some logic, it is needed to add Logic calculations with the help of right mouse button on the Logic calculation window like in the following figure. Figure 108. Logic calculation context menu. Page 179 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Internal programmable logic If you click Add Logic element you will get following window: Figure 109. Add new Logic calculation. It is needed to assign Tag from Tag Manager and Operation, then if Result is TRUE it will give value 1 to the next calculation, else if Result is FALSE it will output value 0 to the next calculation. With the parameters Result TRUE and Result FALSE it is possible to change result values to the next logic calculation. Operation can be one of: = (assign), == (equal), <> (not equal), < (less), <= (less or equal), > (more), >= (more or equal), OR, OR bits, AND, AND bits, XOR, XOR bits, + (addition), - (subtraction), *(multiplication), / (division). Figure 110. Integer type Logic operations. Page 180 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Internal programmable logic Float type Logic operations. Figure 111. Figure 112. Field name Integer type Manual tag parameters. Description Default value ID For internal use. Type Type of Manual tag. Name Name of Manual tag. Status 1 Description Description of Manual tag. Empty Comments Additional user comments. Empty State ID Tag state ID. State Name Assigned Tag State name. Not assigned Page 181 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Programmable logic IsaGRAF State Actual state. Value Actual value. Time Date/Time of last change. Quality Actual quality. 0x00000000 Not init Cause Actual cause. Not defined Offset 1 With those parameters you have possibility to 0 Offset 2 change value, which you will take from the data 0 Scale 1 source. 1 Scale 2 NewValue=(OldValue+Offset1)*Scale+Offset2 1 Start Value Initial Value of logic calculation with the first 0 0 operation. 4.14 Programmable logic IsaGRAF Enilit RTU CMS provides an interface to the IsaGRAF programming tool for the programming of additional function of RTU. The following figure shows interface which enables to create inputs and outputs for the Programmable logic IsaGRAF. Figure 113. Field name PLC Programming window Description Default value Name Branch name. CPU Download Download IsaGRAF solution to IsaGRAF on system No configuration start, in case Port enabled is Yes. on start Values: No, Yes Page 182 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Programmable logic IsaGRAF ETCP Start TCP communication with remote PC for No debugging and diagnosis. Values: No, Yes Hidden Start Isagraf modules hidden. Yes Values: No, Yes Minimized Start Isagraf modules minimized. Yes Values: No, Yes Port enabled Enables programmable logic IsaGRAF port. No Values: No, Yes Figure 114. Field name Popupmenu window Description Active New Branch Creates new branch. Branches New Resource Creates new resource. Branches New input Creates new input to the Isagraf. Resources New output Creates new output from the Isagraf. Resources Delete Enables to delete branch, resource, input or Everywhere output. Open Isagraf Open the integrated programmable logic Everywhere workbench environment IsaGRAF by selecting this menu item. Build Isagraf Build IsaGRAF program. Everywhere Starts IsaGRAF runtime. Everywhere solution Start ISAGRAF Page 183 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Programmable logic IsaGRAF Add connection Enables to connect input or output to the Tag Inputs, outputs to Tag from the Tag manager. Remove Enables to remove Tag connection. Inputs, outputs Goes to the connected Tag in the Tag manager. Inputs, outputs connection to Tag Go to connected Tag IsaGRAF is an IEC 61131 open control software for automation. For more information on all operating functions of IsaGRAF, please refer to the Isagraf User Manual which can be called up via IsaGRAF software. 4.14.1 IsaGraf function blocks Functional blocks designed specifically for Enilit RTU. With these functional blocks, you can manipulate events and commands. E_Create_Command_Ack_LINT Figure 115. Creates integer command acknowledgement. Field name Variable Description Input of command. Data type: ENILIT_OUT_COACK_LINT ID Commands identification number. Data type: UDINT Result Command acknowledgement type: positive, negative, termination. Data type: BYTE Create Enable or disable acknowledgement. Data type: BOOL Page 184 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Programmable logic IsaGRAF Figure 116. E_Create_Command_Ack_LREAL Creates float command acknowledgement. Field name Variable Description Input of command. Data type: ENILIT_OUT_COACK_LREAL ID Commands identification number. Data type: UDINT Result Command acknowledgement type: positive, negative, termination. Data type: BYTE Create Enable or disable acknowledgement. Data type: BOOL Figure 117. E_Create_Command_LINT Creates integer command. Field name Description Page 185 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Programmable logic IsaGRAF Variable Output of command to RTU. Data type: ENILIT_IN_COACK_LINT ID Commands identification number. Data type: UDINT Value Value of command. Data type: LINT TimeOut Wait for command acknowledgement. Data type: TIME Type Type of command: single, double. Data type: BYTE SubType Type of command: activation, deactivation. Data type: BYTE Test Command with test flag. Data type: BOOL Create Enable or disable acknowledgement. Data type: BOOL Ret_ID Identification number of command acknowledgement. Data type: UDINT Ret_Result Result of command acknowledgement. Data type: BYTE Ret_TimeStamp Timestamp of command acknowledgement. Data type: LINT Ret_Ack Acknowledgement positive or negative. Data type: BOOL Page 186 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Programmable logic IsaGRAF Figure 118. E_Create_Command_LREAL Creates float command. Field name Variable Description Output of command to RTU. Data type: ENILIT_IN_COACK_LREAL ID Commands identification number. Data type: UDINT Value Value of command. Data type: LREAL TimeOut Wait for command acknowledgement. Data type: TIME Type Type of command. Data type: BYTE SubType Type of command: activation, deactivation. Data type: BYTE Test Command with test flag. Data type: BOOL Create Enable or disable acknowledgement. Data type: BOOL Ret_ID Identification number of command acknowledgement. Data type: UDINT Ret_Result Result of command acknowledgement. Data type: BYTE Page 187 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Programmable logic IsaGRAF Ret_TimeStamp Timestamp of command acknowledgement. Data type: LINT Ret_Ack Acknowledgement positive or negative. Data type: BOOL E_Create_Event_LINT Figure 119. Creates integer event. Field name Variable Description Output of Event to RTU. Data type: ENILIT_OUT_EV_LINT Value Value of event. Data type: LINT Quality Quality of event. Data type: UINT Create Enable or disable event creation. Data type: BOOL Figure 120. E_Create_Event_LREAL Creates float event. Field name Description Page 188 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Programmable logic IsaGRAF Variable Output of Event to RTU. Data type: ENILIT_OUT_EV_LREAL Value Value of event. Data type: LREAL Quality Quality of event. Data type: UINT Create Enable or disable event creation. Data type: BOOL E_Get_TimeStamp Figure 121. Gets timestamp of RTU. Field name TimeStamp Description TimeStamp of RTU. Data type: LINT Figure 122. E_Wait_Command_LINT Waits integer command. Field name Variable Description Input of command from RTU. Data type: ENILIT_OUT_COACK_LINT Page 189 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Programmable logic IsaGRAF ID Commands identification number. Data type: UDINT Value Value of command. Data type: LINT TimeStamp TimeStamp of command. Data type: LINT Type Type of command. Data type: BYTE SubType Type of command: activation, deactivation. Data type: BYTE Test Command with test flag. Data type: BOOL IsCommand If Yes, then Command is active. Data type: BOOL Figure 123. E_Wait_Command_LREAL Waits integer command. Field name Variable Description Input of command from RTU. Data type: ENILIT_OUT_COACK_LREAL ID Commands identification number. Data type: UDINT Value Value of command. Data type: LREAL Page 190 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Programmable logic IsaGRAF TimeStamp TimeStamp of command. Data type: LINT Type Type of command. Data type: BYTE SubType Type of command: activation, deactivation. Data type: BYTE Test Command with test flag. Data type: BOOL IsCommand If Yes, then Command is active. Data type: BOOL Figure 124. E_Wait_Event_LINT Waits integer event. Field name Variable Description Input of event from RTU. Data type: ENILIT_IN_EV_LINT Value Value of event. Data type: LINT TimeStamp TimeStamp of event. Data type: LINT Quality Quality of event. Data type: UDINT IsEvent If Yes, then Event is active. Data type: BOOL Page 191 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Programmable logic IsaGRAF Figure 125. E_Wait_Event_LREAL Waits float event. Field name Description Variable Input of event from RTU. Data type: ENILIT_IN_EV_LREAL Value Value of event. Data type: LREAL TimeStamp TimeStamp of event. Data type: LINT Quality Quality of event. Data type: UDINT IsEvent If Yes, then Event is active. Data type: BOOL 4.14.2 IsaGraf data types Field name Description Command type E_CO_CANCEL Deactivation E_CO_EXECUTE Execute E_CO_SELECT Select E_CO_SELECT_EXECUTE Select before Operate (SBO) Commandacknowledgement E_COACK_BAD_COMMAND_TYPE Bad command type E_COACK_BAD_CONFIGURATION Bad configuration E_COACK_BAD_VALUE Bad value E_COACK_CANCEL_DONE Deactivation confirmation E_COACK_CANCEL_REJECTED Deactivation rejected Page 192 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Programmable logic IsaGRAF E_COACK_COMMAND_ALREADY_IN_PROGRESS Command already in progress E_COACK_COMMAND_IN_PROGRESS Command in progress E_COACK_COMMAND_QUEUE_FULL Command queue full E_COACK_EXECUTE_DONE Activation confirmation E_COACK_EXECUTE_REJECTED Activation rejected E_COACK_INTELOCKED Interlocked E_COACK_LINK_DISABLED Link disabled E_COACK_LINKLAYER_ACK Link layer acknowledgement E_COACK_LINKLAYER_NACK Link layer no acknowledgement E_COACK_LINKLAYER_UNKNOWN Link layer unknown acknowledgement E_COACK_NO_COMMAND No command E_COACK_NO_LINK No link E_COACK_SELECT_DONE Select confirmation E_COACK_SELECT_REJECTED Select rejected E_COACK_TIME_OUT Command time out E_COACK_UNDEFINED_RESULT Command execution undefined result Command quality E_COSUB_LONG_PULSE Long pulse E_COSUB_NOT_DEFINED Not defined E_COSUB_PERSISTENT Persistent E_COSUB_SHORT_PULSE Short pulse Quality of event E_QUAL_BLOCKED Blocked E_QUAL_GOOD Good E_QUAL_INVALID Invalid E_QUAL_INVALIDTIME Invalid time E_QUAL_NOTINIT Not initialized E_QUAL_NOTTOPICAL Not topical E_QUAL_OVERFLOW Overflow E_QUAL_SUBSTITUTED Substituted Page 193 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Time management 4.15 Time management 4.15.1 SNTP client In the time management window you can create new SNTP client to synchronize RTU date and time with external SNTP server. SNTP client window Figure 126. Field name Log Description Default value Log clock synchronizations from slaves. Yes Values: No, Yes Startup state Clock is synchronized on startup. Yes Values: No, Yes Clock not synchronized If there was no clock synchronization for 86400 particular time, it will be considered that clock is not synchronized. Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds Synchronization from After what time allow synchronization from 60 slaves slave communication protocols. 0 – means allow always synchronize, 1 – 86400 seconds – when there was no time synchronization from SNTP clients. Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds Time precision Requested time precision in milliseconds. 10 Clock will be synchronized only if time offset is larger than requested precision. Range of values: 1 … 60000 ms Page 194 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Time management Create new SNTP client Figure 127. If you have created new SNTP client, you will see following window with default parameters. Other opportunity is to run Show monitor window. Monitoring window will show log data which you have enabled in the SNTP client configuration with the parameters Log Data, Log IP, Log Raw. SNTP client window Figure 128. Field name Ethernet port Description Here, the information address can be Default value All ETH specified. Range of values: ETH1 … ETH3 Server SNTP server IP address. 127.0.0.1 Values: xxx.zzz.yyy.nnn UDP Port UDP port to connect with server. 123 Range of values: 1 … 65535 Log Data Enables to view data log. Yes Values: No, Yes Log IP Enables to view IP log. Yes Values: No, Yes Log Raw Enables to view raw log. Yes Page 195 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Time management Values: No, Yes Enabled Enable or disable SNTP client. No Values: No, Yes ID ID of SNTP client. Internal use. 1 Range of values: 1 … 255 Name Name of SNTP client. SNTP client For example: “SNTP1” Priority If you will configure more than one SNTP 1 server, you can rank servers in your order. Range of values: 1 … 255 Connect timeout Connect timeout to SNTP server. 5 Range of values: 1 … 60 seconds Reconnect timeout Reconnect timeout if connection before 60 was failed. Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds Synchronization period The time period to make synchronization. 15 Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds SNTP server response Response timeout after request has been timeout sent. 5 Range of values: 1 … 86400 seconds Figure 129. SNTP client popup window With the Show monitor, you can open diagnostic tool for communication with SNTP server. The following window shows Time management monitor window. Page 196 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Time management Figure 130. Time management monitor window Page 197 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Self-control and diagnosis 4.16 Self-control and diagnosis Enilit RTU CMS also provides diagnostic facilities which enable the user to view hardware status of RTU with its configuration, to analyze and view serials and TCP protocols data, to monitor current status of information objects, to test its and commands with test values, to view and keep saved system and events log. 4.16.1 Hardware monitoring With the popup menu in Enilit RTU Hardware configuration window you can run Enilit RTU Hardware state monitoring. Figure 131. Hardware popup menu When you click Show Hardware state, you will see following figure. With this window you can check if the hardware is well configured and working. In this hardware monitoring window you can see current states of all modules, output voltage of power supply, CPU temperature, Watchdog status, binary inputs and command outputs states, measurements current (mA) or voltage (V). Figure 132. Hardware state window Page 198 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Self-control and diagnosis - Configured and working, or not configured and empty. - Not configured, but found. - Configured, but found another type of module. - Configured and not working. 4.16.1.1 Status signals, commands and measurements Hardware status can be monitored via communication protocols. You can connect hardware status signals to tags with Tag Manager, you can control also hardware with commands from SCADA. Following figure shows Hardware status signals, commands and measurements window. Figure 133. Hardware status signals, commands and measurements Field name Connected Description Card types Central processor communicates with card. The All card works without error. Type: Status item 0 – Normal Page 199 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Self-control and diagnosis 1 – Fault Voltage Power supply voltage measurement. PS31 Type: Status item Enabled Enabled or disabled card. All Type: Status item 0 – Enabled 1 – Disabled Enable Enables or disables central processor All communication with card. Type: Command item 0 – Disable command 1 – Enable command Wrong Card Central processor detects wrongs card type. Type Type: Status item AI31, DI31, DO31, CPU 0 – Ok 1 – Fault Temperature Central processor voltage measurement. CPU Type: Status item Led2 State Central processor Led2 state. CPU Type: Status item 0 – Led2 off 1 – Led2 on Led2 Control Control of central processor Led2 state. CPU Type: Command item 0 – Off 1 – On 4.16.2 Protocol monitoring The following figure show communication port popup menu. With this popup menu you can run Protocol monitoring tool “Port monitor”. Page 200 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Self-control and diagnosis Figure 134. Communication port popup menu Next figure shows this window in which you can view receiving and transmitting data through communication port. This window is for IEC 60870-5-103 protocol, but you can use it for all serial or TCP protocols even for SNTP. Figure 135. Field name Enabled Standard master protocol monitor window Description Enables to view communication data. Default value Unchecked Values: Checked, Unchecked Follow Enables to follow last communication data. Unchecked Values: Checked, Unchecked Log to file Enables to log all data to log file. Unchecked Values: Checked, Unchecked Next figure shows that you can view communication data in monitoring direction either serial or TCP/IP between RTU and SCADA. Page 201 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Self-control and diagnosis Figure 136. Field name Enabled Standard slave protocol window Description Enables to view communication data. Default value Unchecked Values: Checked, Unchecked Follow Enables to follow last communication data. Unchecked Values: Checked, Unchecked Log to file Enables to log all data to log file. Unchecked Values: Checked, Unchecked This communication port monitoring tool is very useful at substation commissioning stage. Commissioning engineer doesn’t need any additional testing software, even worse hardware for port monitoring and so on. Page 202 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Self-control and diagnosis 4.16.2.1 Status signals, commands and measurements Figure 137. Standard system status items for master protocols Field name Connected Description Connected to the slave device. Protocols All Type: Status item 0 – Normal 1 – Communication error Enabled Enabled or disabled communication protocol. All Type: Status item 0 – Enabled 1 – Disabled TX Bytes Count of protocol transmitted bytes. All Type: Float TX Packets Count of protocol transmitted packets. All Type: Float RX Bytes Count of protocol received bytes. All Type: Float RX Packets Count of protocol received packets. All Type: Float RX Err Answer Type: Float IEC-101, 103 Type: Float IEC-101, 103 Timeout RX Err First Char Page 203 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Self-control and diagnosis RX Err Last Char Type: Float IEC-101, 103 RX Err Check Type: Float IEC-101, 103 RX Err Length Type: Float IEC-101, 103 RX Err Mirrored Type: Float IEC-101, 103 Sum 4.16.3 System log When you start Enilit RTU CMS the first window is System log window. This window is also written to the file. The location of logs is described in the RTU description file. Figure 138. System log window 4.16.4 Events log In the Tag Manager tool you can configure Events log. This window is also written to the file. By default Events log files are stored in the RTU configuration directory Logs. The location of logs is described in the RTU description file. Page 204 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Self-control and diagnosis Figure 139. Field name Log RTU Time Main Tag manager window Description Default value Additional column will be added to history files, No which shows event received time in TAG Manager. Values: No, Yes Days for history How many days to keep events in Events list. 365 Range of values: 10 … 1000 days Max file size Maximum size of all Events list files 100 Range of values: 10 … 1000 Mb Record count Record count in one Events list file 10000 Range of values: 1000 … 100000 UTC time stamp Time stamp of events to be saved in Events list. No Values: No, Yes Log status tags Log status changes to Events list files. Yes Values: No, Yes Page 205 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Self-control and diagnosis Log measurements Log measurements changes to Events list files. tags Values: No, Yes Log command tags Log commands changes to Events list files. Yes Yes Values: No, Yes Log incoming Log incoming changes to Events list files. changes Values: No, Yes Log outgoing Log outgoing changes to Events list files. changes Values: No, Yes Yes Yes Page 206 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Redundancy 4.17 Redundancy 4.17.1 Redundancy support Safety, reliability, high availability, and functionality are vital components of every control system in today’s world. Enilit system utilize dual RTU and power supplies redundancy. The system provide for automatic monitoring of primary and hot standby RTU. Failures are detected automatically and trigger a switchover from the primary RTU to hot standby RTU. All communication channels are automatically switched to primary RTU. The switchover and data transfer is fast and bumbles, thereby ensuring that there is no interruption in process control. 4.17.2 Redundancy types 4.17.2.1 Cold-Standby A method of redundancy in which the secondary RTU system is only called upon when the primary system fails. The system on cold standby receives scheduled data backups, but less frequently than a warm standby. Cold standby systems are used for non-critical applications or in cases where data is changed infrequently. 4.17.2.2 Warm-Standby A method of redundancy in which the secondary RTU system runs in the background of the primary system. Data is mirrored to the secondary RTU at regular intervals, which means that there are times when both servers do not contain the exact same data. 4.17.2.3 Hot-Standby A method of redundancy in which the primary RTU and secondary RTU systems run simultaneously. The data is mirrored to the secondary RTU in real time so that both systems contain identical information. This method lets fast switchover from active to standby RTU, because both of RTUs have the same data. Hotstandby redundancy is default used in Enilit RTU, but on customer request it can be change to Cold-Standby or Warm-Standby. Further description is mostly about this type of redundancy. 4.17.3 Connection diagram To support redundancy, RTU’s must be connected one with other using LAN or RS-485 or RS-232 interfaces. These communication paths are used to exchange real time data between active and standby RTU. It is possible to use maximum of 4 redundant connections between RTU’s. - RS-485 or RS-232 (COM1-COM12) - RS-485 or RS-232 (COM1-COM12) Page 207 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Redundancy - LAN (ETH1-ETH7) - LAN (ETH1-ETH7) Figure 140. Example of connections between redundant RTU’s Only one of these connections is used for data exchange. Others are used for health monitoring of active RTU. In case of broken data communication path, other active connection will be selected. Ethernet connections are much faster, so first one of these connections will be used for data exchange. In case when there are no Ethernet connections, serial will be selected. Even if serial selected, by default 115,200 kbs speed it is possible to transfer about 500 events per second between RTU’s. On request, speed can be increased for serial connections. 4.17.4 Enilit RTU redundancy principles Enilit redundancy system consists of two RTU’s. One of it is called Active and another Standby. At any time there can be only one Active RTU. The Active RTU is responsible: data acquisition from slave and server devices command transmission to slave and server devices PLC calculation process information transmission to upper communication levels process information transmission to Standby RTU The Standby RTU is responsible: data acquisition from Active RTU process information transmission to upper communication levels monitoring of connections to Active RTU If Standby RTU is healthy and running, it receives all process information from Active RTU so it can transmit all necessary data to upper communication levels. No matter how many redundant connections are configured between Active and Standby RTU’s, if there at least one connection healthy, Standby RTU knows that Active RTU is running correctly. If there are no connections between Standby and Active RTU, Standby RTU changes its state to Active. The switchover can be also executed manually. In this case the Page 208 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Redundancy Standby RTU will change to Active RTU, and Active RTU will change to Standby RTU. Because Standby RTU always acquires process information from Active RTU, the switchover is fast and bumbles. 4.17.5 Monitored fault locations This section describes what can be monitored and used for automatic switchover form standby to active RTU. Most of those monitored information is user selectable from system self-control and diagnosis Tags (See description about 4.13Self-control and diagnosis). Monitored information: - Communication paths between Active and Standby RTU‘s (this is done by default and is not user selectable). - RS-485, RS-232 port hardware errors and state. - Ethernet port hardware errors and state. - Cards hardware errors and state. - Inner voltages and temperatures. - Main CPU state. - Power supply state. - Main Watchdog relay on CPU card (Digital Input type card will be needed on both of RTU‘s to check relay state). - Other specifics can be added on customer request. All this monitored information can be used for configuration of automatic switchovers, according to user needs. 4.17.6 Communication channel configuration 4.17.6.1 Redundancy Connection LAN1 parameters Field name Ethernet port Description Default value Choose RTU Ethernet port. Empty Values: ETH1, ETH2...ETHn IP Address IP Address of redundant RTU 127.0.0.1 For example: 10.2.2.1 IP Port TCP/IP connection port. 5404 Timeout Communication timeout. In case if this is last 1000 milliseconds connection between RTU’s and it is timed out, then switchover from Standby RTU to Active happens. Page 209 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Redundancy 4.17.6.2 Redundancy Connection LAN2 parameters Field name Ethernet port Description Default value Choose RTU Ethernet port. Empty Values: ETH1, ETH2...ETHn IP Address IP Address of redundant RTU 127.0.0.1 For example: 10.2.2.1 IP Port TCP/IP connection port. 5404 Timeout Communication timeout. In case if this is last 1000 milliseconds connection between RTU’s and it is timed out, then switchover from Standby RTU to Active happens. 4.17.6.3 Redundancy Connection RS-485 1 parameters Field name Com port Description Default value Choose RTU COM port. Empty Values: COM1 COM2 ... COMn Timeout Communication timeout. In case if this is last 1000 milliseconds connection between RTU’s and it is timed out, then switchover from Standby RTU to Active happens. 4.17.6.4 Redundancy Connection RS-485 2 parameters Field name Com port Description Choose RTU COM port. Default value Empty Values: COM1 COM2 ... COMn Page 210 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Redundancy Timeout Communication timeout. In case if this is last 1000 milliseconds connection between RTU’s and it is timed out, then switchover from Standby RTU to Active happens. 4.17.7 Status signals, commands and measurements 4.17.7.1 Standard system status items for redundant connections Field name Connected Description Connected to the redundant RTU. Redundant connections All Type: Status item 1 – Normal 0 – Communication error Enabled Enabled or disabled redundant connection. All Type: Status item 1 – Enabled 0 – Disabled Transmitted Protocol transmitted bytes. Bytes Type: Measurement Transmitted Protocol transmitted packets. Packets Type: Measurement Received Bytes Protocol received bytes. All All All Type: Measurement Received Protocol received packets. Packets Type: Measurement All 4.17.7.2 Standard system status items for redundancy Field name State Description RTU redundancy state. Type: Status item 0 – Standby 1 – Active Switchover Switchovers current RTU to new state. Type: Command item Page 211 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Redundancy 0 – To Standby 1 – To Active Connections Current active redundancy connections Type: Measurement Page 212 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Cyber security capabilities 4.18 Cyber security capabilities 4.18.1 Introduction Cyber data security is a vital element of system’s reliability. It decreases cyber-crimes and increases the security and availability of the system communication network. System where RTU‘s are used (power, water, oil supply systems) usually are critical infrastructure. Security threats generally consist of attacks against assets. These assets may not only be physical facilities, but also cyber information, databases and software applications. Targets such as IEDs, SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, EMS (Energy Management Systems), databases, applications and web services can be attacked. Even if the network is completely isolated and no remote equipment is connected, attacks may even be initiated by operational personnel who lack special training and awareness. Cyber data security is a vital element of system’s reliability. It decreases cyber-crimes and increases the security and availability of the system communication network. In order to prevent from such attacks in Enilit RTU is made data cyber security capabilities according standard IEEE 1686-2007, IEEE Standard for Substation Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) Cyber Security Capabilities, February 2008. IEEE 1686-2007 is a security standard for IEDs. It establishes requirements for IED security in accordance with NERC CIP. This standard defines the functions and features to be provided in substation IEDs to accommodate critical infrastructure protection programs. The main Enilit RTU Cyber security Capabilities are given in the chapters below, if some extra security functions is required they could be added on client request. 4.18.2 Electronic access control All electronic access to the Enilit RTU locally through a communication/diagnostic port with a test set or personal computer, or remotely through a communications media is password protected. It is not possible to gain access to the device without a proper password that has been generated by the user. 4.18.2.1 Password defeat mechanisms The Enilit RTU has no means whereby the user-created password control can be defeated or circumvented. This includes such mechanisms and techniques such as: Vendor-embedded master password; Chip-embedded diagnostic routines made accessible by hardware or software failures; Hardware bypass capabilities such as jumpers and switch settings. The UAB Enilit guaranties that no such mechanisms exist which would allow circumvention of the usercreated password control. Page 213 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Cyber security capabilities 4.18.2.2 Number of individual password supported The thousands of unique user-access passwords could be created. 4.18.2.3 Password construction User-created passwords follow a set of rules which must be adhered to in the creation of each password. A minimum of 8 characters is used. The password characters should contain the following: At least one uppercase and one lower case letter At least one number At least one non-alphanumeric character (e.g., @%&*) Any attempt to create a password which violates these rules is captured at the time of attempted creation and the user will be notified and prompted to choose another password which conforms to the rules. For more information about users passwords see paragraph 4.5.3 of this document. 4.18.2.4 Authorization levels by password The Enilit RTU supports the ability to assign authorization to utilize Enilit RTU functions and features based on individual user-created passwords. At a minimum, the following functions and features shall have this assignability available: View Data – the ability to view operational data (voltage, current, power, energy, status, alarms, et. al); View Configuration Settings – the ability to view configuration settings of the Enilit RTU such as scaling, communications addressing, programmable logic routines; Force Values – the ability to manually override real data with manually inputted data and/or the ability to cause a control output operation to occur; Configuration Change – the ability to download and upload configuration files to the unit and/or effect changes to the existing configuration; Password Management – The ability to create, delete or modify passwords and/or password authorization levels; Audit Log – The ability to view and download the audit log. For more information about User groups (Roles of Users) see paragraph 4.5.2 of this document. 4.18.2.5 Password display It is not possible to cause Enilit RTU access passwords displayed through any means, including configuration software connection and terminal access. Page 214 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Cyber security capabilities 4.18.2.6 Access timeout The Enilit RTU has a timeout feature which revokes all access levels granted through password entry after a period from user inactivity. Inactivity shall be defined as the absence of input keystroke activity on a computer connected to the Enilit RTU port. The period of time before the timeout feature activates is settable between 1 and 60 minutes by the user in the configuration of the Enilit RTU. 4.18.3 Audit trail The Enilit RTU records in events in the order in which they occur. This audit trail is in the form of a file which can be viewed on a computer attached to the Enilit RTU diagnostic/maintenance port. 4.18.3.1 Storage capability The audit trail facility has the capability to store more than 10 000 events before the circular buffer begins to overwrite the oldest event with the newest event. There is no capability to erase or modify the audit trail. It is not possible to remove the storage media of the audit trail without permanently damaging the Enilit RTU beyond the capability of field repair. 4.18.3.2 Storage record For each audit trail event, the following information is recorded: Event Record Number; Time & Date – Time and date of the event will be recorded in a yy/mm/dd/hh/mm format; User Identification – The user ID logged into to the Enilit RTU at the time of the event; Event Type. 4.18.3.3 Audit trail event Types The following events shall cause an entry into the Audit Trail record Log In – Successful log in; Manual Log Out – User Initiated; Timed Log Out – Log out of User after defined period of inactivity elapses; Value forcing – Operator action that overrides real data with manual entry and/or causes a control operation; Configuration Access – Download of the configuration file; Configuration Change – Upload to the Enilit RTU of a new configuration file or keystroke entry of new configuration parameter; Password Creation – Creation of new password or modification of password level of authorization; Page 215 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Cyber security capabilities Password Revocation – Revocation of a password; Audit Log Access – User access of audit log for viewing or file download; Time/Date Change – User request to change time and date; Figure 141. Figure 142. Audit Trial log Settings of Audit Trial. Enilit RTU CMS independently from Windows Operation System stores some of those events in System Log file. This is important if it’s needed to send Security events through IEC or DNP communication protocols to SCADA. Page 216 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Cyber security capabilities 4.18.4 Supervisory monitoring and control In addition to the Audit Trail capability, the Enilit RTU monitors security-related activity and make the information available through a real-time communication protocol for transmission to a supervisory system. If serial communications are used for the configuration of the Enilit RTU and the supervisory communications port, separate serial communications ports is provided for configuration and supervisory monitoring. Configuration port activity not interfere nor disable the supervisory monitoring port with the exception of a configuration. Information to be monitored and transmitted falls into two groups: Event and Alarm. 4.18.4.1 Events Events are defined as authorized activities which can be expected to occur in the routine use and maintenance of the Enilit RTU. All events can be monitored and transmitted to the supervisory system. Event points have momentary change detect capability so that the occurrence of an event will be reported on the next scan of the Enilit RTU by the supervisory system. The Enilit RTU reports each occurrence as an individual event. 4.18.4.2 Alarms Alarms are defined as activities which may indicate unauthorized activity. The following will cause an Alarm occurrence: Unsuccessful login attempt – defined as configured incorrect password entries insuccession; Reboot; Attempted use of unauthorized configuration software; 4.18.5 Configuration software The Enilit RTU has an authentic configuration software. It could be configured with any software except supported by UAB Enilit. ENILIT RTU configuration software has the ability to assign features to specific users. At a minimum, the following functions and features could be assignable on an individual user basis: View Configuration Data – in this mode, a user can only view configuration data. No changes to the configuration can be made. Change Configuration Data – in this mode, the user can change and save configuration data to be uploaded to the Enilit RTU at a later point in time. Full Access – in this mode, all functions, including password changes and user assignment levels can be made. Page 217 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Enilit RTU software | Cyber security capabilities The configuration software is password controlled so that the software cannot be accessed without the proper password. All communications ports other on the Enilit RTU have the capability to be enabled or disabled through configuration of the Enilit RTU. When disabled through configuration, no communications will be possible through that port. Page 218 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Abbreviations | Cyber security capabilities Abbreviations ADU Application Data Unit APDU Application Protocol Data Unit CMS Configuration and Management Software CPU Central processing unit CS Clock synchronization DPC Double point command DPS Double point signal GI General interrogation ICD IED Capability Description IED Intelligent Electronic Device MV Measurement value PLC Programmable logic controller RTU Remote terminal unit SCADA Supervisory control and data acquisition SCL Substation Configuration Language SNTP Simple Network Time Protocol SPC Single point command SPS Single point signal TCP Transmission Control Protocol UTC Coordinated Universal Time Page 219 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03 Contacts | Cyber security capabilities Contacts UAB "Enilit" Veiverių str. 134-221 LT-46352 Kaunas, Lithuania Support e-mail: Tel.: +370 655 53155 Tel. / Fax.: +370 37 291708 E-mail: [email protected] www.enilit.lt [email protected] Page 220 of 220 Enilit RTU User Manual 15.03