Download CP485x4 User Manual
Transcript
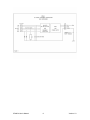
CP485x4 User’s Manual Version 1.0 © 2005 ZYPEX, Inc. CP485-4 User’s Manual Table of Contents Table of Contents Product Description 1 CP485x4 Configuration & Setup Power Baud Rate Control Mode Duplex Mode Termination Key-Down Delay 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 Control Mode Description RTS Mode Data Mode 4 4 4 Duplex Mode Description Full Duplex Mode Half Duplex Mode 5 5 5 Termination Description 5 LEDs 5 DIP Switch Settings 6 Transient Protection and Grounding Transient Protection Shield Connection Static Control 7 7 7 7 Connectors Power RS-232 9 9 9 Power Consumption 9 Product Specifications 10 Contact Information 11 CP485-4 User’s Manual Table of Contents Product Description The CP485x4 line driver is a quad RS-232 to RS-485 interface converter. It allows an RS-232 device to reliably transmit data over long distances (up to 4000 feet). The CP485x4 has many features not normally found in typical line drivers, and is intended for operation in harsh industrial environments. The CP485x4 may be used in point-to-point applications as well as multi-drop applications using either 4-wire or 2-wire configurations. Up to 128 devices may be connected together on one communication line in half-duplex mode, or 64 devices in full-duplex mode. A variety of timing and control options are available on the CP485x4. Each channel is individually isolated, and may be operated in either RTS mode or Data mode. In RTS mode, the RS-232 RTS signal controls the RS-485 driver. In Data mode, the CP485 controls the RS-485 driver. When incoming data is detected on the RS-232 RX line, the CP485 enables the RS-485 driver, and starts buffering the incoming data. After a 2-character time delay (keyup delay), the data is transmitted on the RS-485 line. When all of the characters have been sent, the CP485 leaves the RS-485 driver enabled for a fixed time of either 50 or 500 microseconds (DIP Switch selectable) to allow the transmitted bytes to propagate out, and then disables the RS-485 driver (keydown delay). Electronic switches are used to control all configuration options. The user need only set the baud rate, duplex mode (full or half), control mode (RTS or Data) and whether the line is to be terminated. A unique capability of the CP485x4 is the ability to sense the presence of a received RS-485 carrier (remote RS-485 driver enabled). This is very useful for controlling devices that require a turn-on delay before data can be transmitted (e.g., devices such as radio modems). All timing functions are crystal controlled and provide very accurate and stable delays. Temperature and voltage fluctuations will not affect the CP485x4’s operation. The CP485x4 has 1500-volt optical isolation between the RS-232 side and the RS-485 side. The RS-485 lines are protected with 2 stages of surge protection. CP485-4 User’s Manual 1 Version 1.0 CP485x4 Configuration and Setup Power Connect a DC power supply to J5 pins 1 & 2. Connect the positive side to J5 pin 1, and the common or return to J5 pin 2. Voltage can be 5 VDC to 30 VDC. CAUTION! The CP485 will be damaged if these connections are reversed! Connect J5 pin 3 to an earth ground. This connection enables the first stage of transient protection for each RS-485 channel, and keeps any static charge from building up on the RS-485 lines. The earth ground must be a short wire, directly to a suitable building ground, using 14-gauge wire (minimum size wire)!!! Baud Rate Set DIP Switches 1 – 3 to configure the channel for the desired baud rate (see DIP Switch Settings). The data format is automatically set to 8 data bits, no parity and 1 stop bit. Control Mode Set DIP Switch 4 to the desired Control Mode setting (RTS control or Data control). “DATA” mode is with DIP Switch 4 in the ON position. See the “Control Mode Description” in the next section for a full explanation of these two modes of operation. If you set DIP Switch 4 to ON, then you must set DIP Switch 7 to be either 8-bit mode or 9-bit mode (OFF or ON, respectively). Use 8-bit mode (in “DATA” mode only) if your data packets have either: • 7 data bits, plus parity (odd or even) • 8 data bits, no parity Use 9-bit mode (in “DATA” mode only) if your data packets are 8 data bits, with parity. Duplex Mode Set DIP Switch 5 to the desired Duplex Mode setting (full or half duplex). Full duplex is 4-wire mode, and half duplex is 2-wire mode. In half duplex mode, electronic switches connect the TX pair to the RX pair. The RS-485 lines may be connected to either the TX+ / TX- pair or the RX+ / RX- pair. CP485-4 User’s Manual 2 Version 1.0 Termination Set DIP Switch 6 to enable or disable termination of the RS-485 trunk. The “TERM” LED will illuminate if termination is enabled. Key-Down Delay DIP Switch 8 is only used in “DATA Mode”, and allows you to set a very short or very long key-down delay. This is the amount of time that the RTS line is held ON, following the transmission of the last bit of the last byte of a data packet. The OFF position is a key-down time of 10 microseconds. The ON position of this switch makes the key-down time 50 microseconds. For short, hard copper lines, we recommend that this switch be in the OFF position. For “slow” devices like modems, we suggest that you position DIP Switch 8 in the ON position. Factory Test Options If any DIP Switch is moved (from OFF to ON, or ON to OFF) during the one- to two-seconds of power-up self-test (when the lights flash in the pretty power-up sequence, it is in self-test mode), then the CS485x4 enters a “factory test mode”. At this point, the various DIP Switches are used to enable various factory test options. The only way to get the CS485x4 out of this “factory test mode” is to unpower the device, wait a few seconds, then re-apply power. CP485-4 User’s Manual 3 Version 1.0 Control Mode Description RTS Mode When RTS Mode is selected (DIP Switch 4 ON), the baud rate setting has no effect, and any type of data format may be used (7 data bits, even parity, 2 stop bits, or 8 data bits, odd parity, 1 stop bit, for example). The RS-232 RTS signal is used to control the RS-485 driver. Data Mode When Data Mode is selected (DIP Switch 4 OFF), DIP Switches 1 – 3 are used to set the baud rate. Data on the RX-232 RX line is used to control the RS-485 driver. The RS-232 RTS signal is not used. The data format handles both 1 and 2 stop bits. However, the CP485 does need to know how many TOTAL data bits (data plus parity) will be in each byte. The options are: 8-bit mode (7 data bits, plus a parity bit, or 8 data bits with no parity), or 9-bit mode (8 data bits, with a parity bit). DIP Switch 4 set to OFF selects 8-bit mode, while setting DIP Switch 4 to ON selects 9-bit mode. When incoming data is first detected on the RS-232 RX line, the RS-485 driver is enabled and the incoming data is stored in a buffer. After a 2-character time delay (for the selected baud rate), the buffered data is then transmitted out the RS-485 trunk. This allows the CP485 to provide a turn-on delay, which allows any transients on the RS-485 lines to settle before data is sent. After the transmission of the last character, the CP485 keeps the RS-485 driver enabled for some small time period (50 or 500 microseconds; DIP Switch selected) to allow the data to propagate down the RS-485 lines. This is called a “key-down delay”, and makes sure the data is completely received at the other end, before the RS-485 transmitted is disabled. This insures that the receiver on the end-devices does not have “splatter” or “squelch noise” at the end of the data packet, and yet is expected to be a short enough time period that no response from the other device is lost. This time is somewhat arbitrary, and you may have to try different settings of DIP Switch 8 to see what works best with your wiring and device configurations. Generally speaking, hard-copper lines don’t require much key-down delay, and DIP Switch 8 should be OFF; whereas modems (especially RF modems) need much longer “quiet times”, and we suggest that these applications DIP Switch 8 should be ON. If you have problems with very slow (antique) devices, especially older, low-frequency RF modems, these timings can be changed at the factory—Contact Zypex or Centaurus Prime if any longer time period is required for your particular application. CP485-4 User’s Manual 4 Version 1.0 Duplex Mode Description Full Duplex Mode In Full Duplex Mode, data is transmitted on the TX+ / TX- pair, and data is received on the RX+ / RX- pair. The RX+ / RX- pair is always active. Half Duplex Mode In Half Duplex Mode, the TX+ / TX- pair is internally connected to the RX+ / RXpair. TX+ is connected to RX+, and TX- is connected to RX-. Either pair may be used (but not both). Termination Description If termination is enabled in full duplex mode, the TX+ / TX- pair is terminated and the RX+ / RX- pair if terminated. If termination is enabled in half duplex mode, the TX / RX combination is terminated. Termination consists of a 120-ohm resistor across the two RS-485 lines, plus a 1.2K pull-up resistor and a 1.2K pull-down resistor. LEDs RTS LED The RTS LED is illuminated when the RS-485 driver is enabled. TX LED The TX LED is illuminated when data is being transmitted on the RS-485 lines. RX LED The RX LED is illuminated when data is being received on the RS-485 lines. DCD LED The DCD LED is illuminated when the voltage on the RX+ / RX- pair is greater than 800mV. If the RX pair is terminated (either end), the DCD LED will illuminate when the remote RS-485 driver is enabled. If the RX pair is not terminated, the LED will be ON continuously. TERM LED The TERM LED is illuminated when the RS-485 channel is terminated. CABLE LED The CABLE LED is illuminated when an active RS-232 cable is plugged into the DB-9 connector. The LED will not illuminate if the RS-232 cable is crossed or improperly wired. CP485-4 User’s Manual 5 Version 1.0 DIP Switch Settings Switch Switch 1 Switch 2 Switch 3 OFF OFF OFF ON OFF OFF OFF ON OFF ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON ON OFF ON OFF ON ON ON ON ON Description Baud Rate Select 1200 Baud 2400 Baud 4800 Baud 9600 Baud 19.2K Baud 38.4K Baud 57.6K Baud 115.2K Baud Switch 4 Data / RTS Mode OFF – Data Mode ON – RTS Mode Switch 5 Duplex Select OFF – Half Duplex ON – Full Duplex Switch 6 RS-485 Termination OFF – No Termination ON – Termination Enabled Switch 7 Data-Mode ONLY: total number of bits OFF – 8-bit mode (e.g. 8-bit, no parity) ON – 9-bit mode (e.g. 8-bit w/parity) Switch 8 Key-Down Delay OFF – Normal (50 microseconds) ON – Slow (500 microseconds) CP485-4 User’s Manual 6 Version 1.0 Transient Protection and Grounding Transient Protection The CP485x4 has 2-stages of transient protection for each channel. The first stage connects each RS-485 data line to a SiDACtor. The common side of the SiDACtors are connected to the “EARTH” terminal of J5 (Figure 1). SiDACtor’s provide ultra-fast transient response and provide a path to earth ground for highvoltage transients. The second stage of transient protection uses Transorbs that are connected to the isolated common of the RS-485 section. The Transorbs make sure all transient signals are clamped to within the normal operating voltage of the RS-485 electronics. Under certain conditions, some devices introduce a large ac or dc voltage on the RS-485 communication lines (referred to as common-mode voltage). This does not present a problem unless the common-mode voltage exceeds the SiDACtor’s clamping voltage. If common-mode voltages in excess of 60V are expected, leave the connection from J5-3 (Earth) to ground open so that the SiDACtor’s will not try to clamp the common-mode voltage to earth ground. The SiDACtor’s and Transorbs will still provide transient protection, but not as effectively for very large transients (lightning for example). Leaving the Earth connection open allows the CP485x4 to operate reliably with common-mode voltages in excess of 100V. Shield Connection The isolated ground or common of the CP485x4 is connected to center pin of the RS-485 connector (SHLD). The connection is made through a 100-ohm resistor. The shield wires of the communication cables are normally connected to this point. Care must be taken to avoid ground loops. Only one end of the shield should be connected to earth ground. Under some conditions other devices may induce a large common-mode voltage on the shield wire. Under these circumstances, leave the CP485x4’s connection to earth ground (J5-3) open (see “485x4 Transient Protection and Grounding”, and Figure 1). Static Control When pin J5-3 is connected to earth ground, the CP485x4 provides a “bleed resistor” which prevents static voltage buildup on the isolated section. The bleed resistor ensures that the isolated section is always at a safe voltage potential. The same connection provides a filter capacitor that deflects any high-frequency noise that may be induced on the RS-485 communication lines to earth ground. CP485-4 User’s Manual 7 Version 1.0 CP485-4 User’s Manual 8 Version 1.0 Connectors Power (J5) Pin J5-1 J5-2 J5-3 Description +5 Vdc to +30Vdc Common for J5-1 Earth Ground RS-485 (J7 – J10) Pin Jx-1 Jx-2 Jx-3 Jx-4 Jx-5 Description TX+ TXIsolated Common (Shield) RX+ RX- RS-232 (J1 – J4) Pin Jx-1 Jx-2 Jx-3 Jx-5 Jx-7 Jx-8 Description DCD RX Data TX Data Common RTS CTS Signal Output Output Input Ground Input Output Power Consumption Voltage 5 Vdc 12 Vdc 16 Vdc 24 Vdc 30 Vdc CP485-4 User’s Manual Current (Typical) 1.0 Amp (inrush); 400 mA operational 9 Version 1.0 CP485x4 Specifications RS-485 Channels 4 Individually Isolated RS-485 Channels Max Data Rate 250kbps (RTS control) 1200 to 115.2K Baud (Data Mode) Line Loading ¼ Load, 128 nodes / trunk Isolation 1500V RMS Operation 2-wire Half-Duplex, 4-wire Full-Duplex Data Format 7 Data bits with parity, or 8 data bits (both with or without parity); 1 or 2 Stop Bits Input Voltage +5Vdc to +30Vdc Removable 3-pin connector Transmit Control RTS Control or DATA Control 2 character keyup delay (Data Mode ONLY) 50 or 500 microsecond key-down delay (Data Mode ONLY) DCD Operation True Carrier Detect or synthesized Data Detect Status Indication LED Indicators for TX, RX, RTS, DCD Termination, RS232 Cable and Power Transient Protection Power Input Peak Pulse Power – 600 watts (10/100us waveform) Peak Surge Current – 100 amps (8.3ms single half sine-wave) RS-232 Port ESD Protected ±15kV Human Body Model ±8kV Contact Discharge ±15kV Air-gap Discharge RS-485 Port 2-Stage Surge Protection 1st Stage: 150A Peak Pulse (2x10us waveform) 2nd Stage: 600 watts (10x100us waveform) Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C 10% to 90% RH (non-condensing) Size 4.0 in. × 8.0 in. Mounting Standoffs with #4 machine screws CP485-4 User’s Manual 10 Version 1.0 Contact Information ZYPEX, Inc. 2795 E Bidwell Street #100-405 Folsom, CA 95630 (916) 983-9450 (916) 983-9448 fax www.zypex.com [email protected] Contact Information Centaurus Prime 4425 Cass Street, Suites A-B San Diego, CA 92109 (858) 270-4552 (858) 273-7769 fax www.centaurusprime.com [email protected] CP485-4 User’s Manual 11 Version 1.0