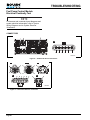
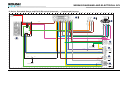
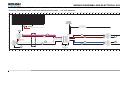
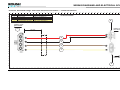
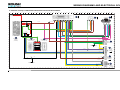
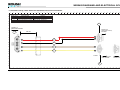
Download Ford E-150/E-250/E-350/E-450 F-250/F-350
Transcript
2011-2013 Ford E-150/E-250/E-350/E-450 F-250/F-350 Liquid Propane Autogas Fuel System (3rd Generation) Includes: E-150/E-250/E-350 Cargo Van/Wagon E-150/E-250/E-350 Extended Range Cargo Van/Wagon E-450 Custom Body F-250/F-350 Revision History -AA Intital Release 2/2013 -AB Revised 5/2013 DIAGNOSTIC MANUAL P-01B101-AB TABLE OF CONTENTS SAFETY INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 Alert Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2 Installation, Garaging and Training . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 Purging and Venting (Tanks and Lines) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 About Diagnostic Trouble Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 System and Diagnostic Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6 Flow Control Solenoid. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Bleed Solenoid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Tank Solenoid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module Supply Solenoid and Wiring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 SRM, CAN Bus Circuit Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10 Fuel System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11 Electronic Fuel Pump Relay (B) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13 Fuel Level Sender . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 DIAGNOSTIC TESTS AND PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16 General Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16 No Fill . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 Slow Fill . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19 Over Fill . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 Engine Does Not Crank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 Engine Cranks, No Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 Engine Stumble, Stall, Rough Idle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25 Excess Flow Valve Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 Maximum Pressure Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 Supply Solenoid Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 Fuel System Fails to Bleed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29 Fuel Pressure Drop. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 Fuel Level Indication Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 Tank Solenoid Electrical Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32 Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module Electrical Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34 Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Electrical Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36 Fuel Pump Electrical Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38 Fuel Pump Control Module Electrical Continuity Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40 Smart Relay Module Electrical Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 Fuel Level Sender Electrical Check. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44 Fuel Level Interface Module Electrical Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46 E-150/150/350 Extended Wiring Harnesses and Connector Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50 E-150/250/350 Extended Range Wiring Harnesses and Connector Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51 E-450 Custom Body Wiring Harnesses and Connector Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52 F-250/350 Pickup, In-Bed Tank Wiring Harnesses and Connector Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53 E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — Underhood Harness . . . . . . . . . . . 54 E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — CAN Bus Harness. . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — Rear Frame Harness . . . . . . . . . . . 56 E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — In-Tank Harness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57 Page iii TABLE OF CONTENTS E-Series Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — Solenoid Harness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58 F-250/350 Pickup, Underhood Harness Electrical Schematic. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59 F-250/350 Pickup, CAN Bus Jumper Harness Electrical Schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60 E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — Rear Frame Harness . . . . . . . . . . . .61 F-250/350 Pickup, Tank Solenoid Harness Electrical Schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62 F-250/350 Pickup, In-Bed Fuel Tank Jumper Harness Electrical Schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63 F-250/350 Pickup, FTPT Jumper Harness Electrical Schematic. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64 Page iv INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Page 1 INTRODUCTION SAFETY INFORMATION The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) publishes a code book of rules that apply to the storage, handling, transportation and use of liquefied petroleum gas (LP-Gas or LPG). The book is known as NFPA 58. It is revised as necessary and published every other year. This code is adopted as law in virtually every political subdivision in the United States. Check with your local authorities for regulations applicable to liquid propane. Alert Messages The following alert messages may appear from time to time in appropriate places in this manual. Ensure that all personnel read and adhere to these alert messages. Although propane is nontoxic, nonpoisonous, has the lowest flammability range of any alternative fuel and dissipates quickly when released into the atmosphere, propane vapor is heavier than air and seeks the lowest point. When the ratio of propane to air is between 2.2% and 9.6%, propane will burn in the presence of an ignition source at 940°F (504°C) or hotter. Keep away from heat, sparks, flames, static electricity or other sources of ignition. Failure to heed this danger may result in severe personal injury or death. The fuel supply lines remain pressurized after engine shutdown. Keep away from heat, sparks, flames, static electricity or other sources of ignition. Do NOT enter storage areas or confined space unless they are adequately ventilated. Failure to heed this danger may result in severe personal injury or death. Page 2 Do NOT carry lighted smoking materials or smoke while working on fuel system components. Failure to heed this danger could result in severe personal injury or death. Disconnect the battery ground at the battery to ensure that the vehicle electrical system has no current. Failure to heed this danger could result in severe personal injury or death. Propane is heavier than air and seeks the lowest available level when released to the atmosphere. Keep heat, sparks, flames, static electricity or other sources of ignition out of the area when venting or purging the fuel lines or tank. Failure to heed this danger can result in severe personal injury or property damage. Technicians working with, or around, fuel systems should be properly trained to utilize extreme care and caution at all times. Failure to exercise extreme caution and care may lead to serious accidents which can result in property damage, personal injury and/or death. Liquid propane is cold. The temperature of propane in its liquid state at atmospheric pressure is −44°F (−42°C). Wear eye and ear protection during venting and repair operations. Keep moisture away from the valves. Failure to heed this warning can result in personal injury. INTRODUCTION Installation, Garaging and Training Chapter 11 of NFPA 58 applies to engine fuel systems using LP-Gas in internal combustion engines, including containers, container appurtenances, carburetion equipment, piping, hose and fittings and their installation. Additionally, this chapter applies to garaging of vehicles and to the training of personnel. Purging and Venting (Tanks and Lines) Venting of LP-Gas to the atmosphere is covered by paragraphs 7.3.1, General, and 7.3.2, Purging of NFPA 58, 2008 edition. Refer to NFPA 58, Local Codes and Proper Training for specific information relating to safe venting of LPG. Paragraph 11.2 specifies that each person engaged in installing, repairing, filling or otherwise servicing an LP-Gas engine fuel system shall be trained. Contact the Propane Education and Research Council to learn more about their CETP E-Learning computer-based training program: [email protected], or [email protected]. Page 3 TROUBLESHOOTING TROUBLESHOOTING Page 4 TROUBLESHOOTING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES About Diagnostic Trouble Codes All diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) known to be affected by the liquid propane autogas (LPA) system are covered in this manual. For all other DTCs, refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual at www.motorcraft.com. System and Diagnostic Terminology Acronym or Abbreviation Description BS Bleed Solenoid CAN Controller Area Network DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code EFPR Electronic Fuel Pump Relay ERFS Electronic Returnless Fuel System EVAP Evaporative FCS Flow Control Solenoid FLIM Fuel Level Interface Module FLS Fuel Level Sender FP Fuel Pump FPCM Fuel Pump Control Module FRP Fuel Rail Pressure FRPCM Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module FTS Fuel Temperature Sensor GRD Ground HEGO Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen IC Instrument Cluster IPTS Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor KOEO Key On Engine Off KOER Key On Engine Running LPA Liquid Propane Autogas MAF Mass Air Flow OEM Original Equipment Manufacturer OPD Overfill Protection Device PCM Powertrain Control Module PID Parameter Identification PWR GND Power Ground SIG RTN Signal Return SRM Smart Relay Module Page 5 TROUBLESHOOTING Acronym or Abbreviation Description SS Supply Solenoid TS Tank Solenoid VMV Vapor Management Valve VPWR Voltage Power VREF Voltage Reference WOT Wide Open Throttle Diagnostic Trouble Code List Code Description Flow Control Solenoid P0090 Fuel Pressure Regulator Circuit Open Bleed Solenoid P009E Fuel Pressure Relief Control Performance Stuck Off P009F Fuel Pressure Relief Control Stuck On P009B Fuel Pressure Relief Control Circuit Open Tank Solenoid P0005 Fuel Shutoff Valve A Control Circuit Open Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module Supply Solenoid and Wiring P26B5 Fuel Shutoff Valve B Function Check P2632 Fuel Pump B Control Circuit Open P2665 Supply Solenoid Circuit Fault SRM, CAN Bus Circuit Wiring U0108 Lost Communication with Alternative Fuel Control Module Fuel System P0148 Fuel Delivery Error P116E Maximum Pressure P0171, P0174 System Too Lean (Bank 1 and Bank 2) P03xx Misfire U0309 Alt Fuel Module-Wrong SRM Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor P2195, P2197 Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor Stuck Electronic Fuel Pump Relay (B) U016C Lost Communication with Fuel Pump Control Module B P027A Fuel Pump Control Module Circuit Range/Performance Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor P0182 Fuel Temperature Sensor (A) Circuit Low P0183 Fuel Temperature Sensor (A) Circuit High P0190 Fuel Pressure Sensor A Circuit P0192 Fuel Pressure Sensor A Circuit Low P0193 Fuel Pressure Sensor A Circuit High Page 6 TROUBLESHOOTING Fuel Level Sender P0460 Fuel Level Sender A Circuit P0461 Fuel Level Sender A Circuit Range/Performance P0462 Fuel Level Sender A Circuit Low Flow Control Solenoid P0090 — Fuel Pressure Regulator Circuit Open Description FCS circuit fault. SRM monitors FCS circuit for open and short circuit faults. Possible Causes 앫 Short to voltage 앫 Water in the harness connector 앫 Open power circuit 앫 GND circuit 앫 Low battery voltage 앫 Corrosion 앫 Incorrect connections 앫 Damaged FCS coil 앫 Blown fuse Symptom Fuel pressure in the rail does not change when commanded. Extended fuel rail flush time. Diagnostic Aid Check the FRPCM and SRM electrical connector for damage, corrosion and water intrusion. Action Refer to the Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module Electrical Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. Bleed Solenoid P009E — Fuel Pressure Relief Control Performance Stuck Off Description Fuel rail failed to bleed. The PCM measures fuel rail pressure on key-up to determine if fuel rail has been properly bled. Possible Causes 앫 BS did not open 앫 FRPCM check valve leaked 앫 FRPCM supply solenoid leaked 앫 Bleed port (bleed rate restrictor in outlet to VMV) clogged 앫 EVAP line kinked 앫 Blown fuse Symptom Fuel pressure present in the fuel rail after bleed event should have occurred; this may result in hard starts. Diagnostic Aid Check that FRPCM bleeds fuel from rail. Leaks to FRPCM can also trigger a fault. Action Refer to the Fuel System Fails to Bleed procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. Page 7 TROUBLESHOOTING P009F — Fuel Pressure Relief Control Stuck On Description Bleed solenoid stuck open. While the engine is running, the PCM seals the EVAP system and checks for a rise in pressure. If pressure in the EVAP system exceeds the threshold, a fault is set. Possible Causes 앫 Short to GRD 앫 Armature stuck in post 앫 Solenoid seal compromised Symptom There is a potential for fuel odor. Diagnostic Aid — Action Refer to the Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module Electrical Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. P009B — Fuel Pressure Relief Control Circuit Open Description Bleed solenoid circuit fault. The SRM monitors bleed solenoid circuit for open and short circuit faults. Possible Causes 앫 Short to voltage 앫 Water in the harness connector 앫 Open power circuit 앫 Open GND circuit 앫 Low battery voltage 앫 Corrosion 앫 Incorrect connections 앫 Damaged BS coil Symptom Fuel rail bleed system does not operate correctly. There is a potential for fuel odor or hard start. Diagnostic Aid Check the FRPCM and SRM electrical for damage, corrosion and water intrusion. Action Refer to the Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module Electrical Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. Tank Solenoid P0005 — Fuel Shutoff Valve A Control Circuit Open Description TS circuit fault. The SRM monitors tank solenoid circuit for open and short circuit faults. Possible Causes 앫 Short to voltage 앫 Water in the harness connector 앫 Open power circuit 앫 Open GND circuit 앫 Low battery voltage 앫 Corrosion 앫 Incorrect connections 앫 Damaged TS coil 앫 Blown fuse Symptom Vehicle does not start. The pumps run but no pressure builds in the fuel rail. Diagnostic Aid Check the FRPCM and SRM electrical connectors for damage, corrosion and water intrusion. Action Refer to the Tank Solenoid Electrical Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. Page 8 TROUBLESHOOTING Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module Supply Solenoid and Wiring P26B5 — Fuel Shutoff Valve B Function Check Description Fuel supply solenoid stuck. The SRM monitors fuel rail pressure before and after the solenoid was commanded open. If the pressure rise is below a threshold, the fault is set. Possible Causes 앫 Electrical fault 앫 Damaged SS coil 앫 Damaged SS armature 앫 Excess flow valve tripped 앫 Tank solenoid stuck closed 앫 Tank manual valve closed 앫 Fuel pumps not powering on 앫 Blown fuse Symptom Vehicle does not start. The pumps run (or may not) but no pressure builds in the fuel rail. Diagnostic Aid Check the FRPCM and SRM electrical connectors for damage, corrosion and water intrusion. Action Refer to the Engine Cranks, No Start procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. P2665 — Supply Solenoid Circuit Fault Description FRPCM supply solenoid circuit fault. SRM monitors supply solenoid circuit for open and short circuit faults. Possible Causes 앫 Short to voltage 앫 Water in the harness connector 앫 Open power circuit 앫 Open GND circuit 앫 Low battery voltage 앫 Corrosion 앫 Incorrect connections 앫 Damaged SS coil 앫 Blown fuse Symptom Vehicle does not start. The pumps run but no pressure builds in the fuel rail. Diagnostic Aid Check the FRPCM and SRM electrical connectors for damage, corrosion and water intrusion. Action Refer to the Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module Electrical Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. Page 9 TROUBLESHOOTING SRM, CAN Bus Circuit Wiring U0108 — Lost Communication with Alternative Fuel Control Module Description Lost communication with SRM. The PCM monitors CAN bus communication for missing messages from the SRM. If the messages are continuously missing, a fault is set. Possible Causes 앫 Wiring between the SRM and PCM 앫 SRM lacks power 앫 Blown fuse Symptom Rough idle. Diagnostic Aid Check the FRPCM and SRM electrical connectors for damage, corrosion and water intrusion. Check for power at the SRM. Action Refer to the Smart Relay Module Electrical Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. Fuel System P0148 — Fuel Delivery Error Description LPA system is operating in vapor space. At least one bank is lean at WOT. Possible Causes 앫 Severely restricted fuel filter 앫 Severely restricted fuel supply line 앫 Damaged or worn fuel pump 앫 Damaged or contaminated MAF sensor 앫 Excess flow valve tripped 앫 TS or SS closed 앫 Tank manual shutoff valve not completely open Symptom Vehicle hesitation or stall condition. Diagnostic Aid — Action Refer to the Engine Cranks, No Start procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. P116E — Maximum Pressure Description Maximum injection pressure reached. The PCM monitors fuel rail pressure and battery voltage. Based on these measurements, the PCM adjusts fuel pump speed to stay below the maximum operating pressure of the injectors. Possible Causes 앫 Operating the vehicle in high ambient conditions Symptom Vehicle hesitation, stall, rough idle, misfire or no start. Diagnostic Aid The P116E code is meant as an indication that the fuel system was operated at the limits of the system. The customer may have experienced drive issues although the system is performing as expected. Action Refer to the Maximum Pressure Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. 앫 Vehicle operated in a low voltage condition Page 10 TROUBLESHOOTING P0171, P0174 — System Too Lean (Bank 1 and Bank 2) Description Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual for more descriptive information. Possible Causes 앫 The LPA system was operated in the vapor region 앫 Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual for a list of other causes. Symptom — Diagnostic Aid Verify that no LPA system faults are present and then follow the Ford service manual procedure. Action Refer to the Fuel Pressure Drop Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. P03xx — Misfire Description Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual for more descriptive information. Possible Causes 앫 The LPA system was operated in the vapor region 앫 Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual for a list of other causes. Symptom — Diagnostic Aid Verify that no LPA system faults are present and then follow the Ford service manual procedure. Action Refer to the Fuel Pressure Drop Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor P2195, P2197 — Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor Stuck Description Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual for more descriptive information. Possible Causes 앫 The LPA system was operated in the vapor region 앫 Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual for a list of other causes. Symptom — Diagnostic Aid Verify that no LPA system faults are present and then follow the Ford service manual procedure. Action Refer to the Fuel Pressure Drop Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. Page 11 TROUBLESHOOTING Electronic Fuel Pump Relay (B) U016C — Lost Communication with Fuel Pump Control Module B Description The SRM repeats the signal from the second EFPR to the PCM over the CAN bus. The PCM monitors this communication. If there is a lack of communication for a long enough period of time, a fault is set. Possible Causes 앫 Wire fault between the EFPR and SRM 앫 Wire fault between SRM and PCM 앫 No power to the EFPR 앫 SRM fault 앫 CAN bus fault 앫 Blown fuse 앫 Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual for a list of other causes. Symptom — Diagnostic Aid — Action Refer to the Fuel Pump Control Module Electrical Continuity Test procedure and also the Smart Relay Module Electrical Test procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. P027A — Fuel Pump Control Module Circuit Range/Performance Description The SRM receives the output of the second fuel pump monitor line and repeats the output over the CAN bus to the PCM. The PCM monitors the commanded output versus the monitor’s feedback. If the monitor is out-of-range, a fault is set. Possible Causes 앫 Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual for a list of other causes. Symptom Poor starts, rough idle, hesitation/surge. Diagnostic Aid — Action Refer to the Fuel Pump Control Module Electrical Continuity Test procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. Page 12 TROUBLESHOOTING Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor P0182 — Fuel Temperature Sensor (A) Circuit Low Description The SRM reads the IPTS and passes the voltage reading over the CAN to the PCM monitors the voltage as if the sensor were plugged into the vehicle. Possible Causes 앫 CAN bus fault between the SRM and PCM 앫 Wiring fault between IPTS and SRM 앫 Short in harness 앫 VREF open or short 앫 Low ambient temperature operation 앫 Incorrect harness connection 앫 Damaged IPTS (or FTS) 앫 IPTS failure 앫 SRM failure Symptom — Diagnostic Aid Verify the fuel rail temperature PID value to determine open or short. Action Refer to the Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Electrical Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. P0183 — Fuel Temperature Sensor (A) Circuit High Description The SRM reads the IPTS and passes the voltage reading over the CAN bus to the PCM. The PCM monitors the voltage as if the sensor were plugged into the vehicle. Possible Causes 앫 CAN bus fault between the SRM and PCM 앫 Wiring fault between IPTS and SRM 앫 Open circuit 앫 Open or short to voltage in harness 앫 Incorrect harness connection 앫 Damaged IPTS (FTS) 앫 IPTS failure 앫 SRM failure Symptom — Diagnostic Aid Verify the fuel rail temperature PID value to determine open or short. Action Refer to the Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Electrical Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. Page 13 TROUBLESHOOTING P0190 — Fuel Pressure Sensor A Circuit Description The SRM reads the IPTS and passes the voltage reading over the CAN bus to the PCM. The PCM monitors the voltage as if the sensor were plugged into the vehicle. Possible Causes 앫 CAN bus fault between the SRM and PCM 앫 Wiring fault between IPTS and SRM 앫 VREF open in harness 앫 VREF open in sensor 앫 Vacuum leaks 앫 IPTS failure 앫 SRM failure Symptom — Diagnostic Aid VREF should be between 4–6 volts. Action Refer to the Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Electrical Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. P0192 — Fuel Pressure Sensor A Circuit Low Description The SRM reads the IPTS and passes the voltage reading over the CAN bus to the PCM. The PCM monitors the voltage as if the sensor were plugged into the vehicle. Possible Causes 앫 CAN bus fault between the SRM and PCM 앫 Wiring fault between IPTS and SRM 앫 IPTS FRP signal short to SIG RTN or PWR GND 앫 Damaged IPTS (or FRP) 앫 IPTS failure 앫 SRM failure Symptom — Diagnostic Aid A FRP PID value during ignition ON, engine OFF, or ignition ON, engine running is less than 0.3 volt. This indicates a concern is present. Action Refer to the Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Electrical Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. P0193 — Fuel Pressure Sensor A Circuit High Description The SRM reads the IPTS and passes the voltage reading over the CAN bus to the PCM. The PCM monitors the voltage as if the sensor were plugged into the vehicle. Possible Causes 앫 CAN bus fault between the SRM and PCM 앫 Wiring fault between IPTS and SRM 앫 IPTS FRP signal short to VREF or VPWR 앫 IPTS (or FRP) open signal 앫 Damaged IPTS (or FRP) 앫 IPTS failure 앫 SRM failure Symptom — Diagnostic Aid Verify the FRP PID value to determine open or short. Action Refer to the Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Electrical Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. Page 14 TROUBLESHOOTING Fuel Level Sender P0460 — Fuel Level Sender A Circuit Description Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual for more descriptive information. Possible Causes Refer to the Ford service manual. Causes are the same except that communication is between the FLS and the SRM and not the IC. Symptom — Diagnostic Aid The SRM reads fuel level sender input and broadcasts it to the IC and PCM. Action Refer to the Fuel Level Indication System Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. P0461 — Fuel Level Sender A Circuit Range/Performance Description Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual for more descriptive information. Possible Causes Refer to the Ford service manual. Causes are the same except that communication is between the sender and the SRM and not the IC. Symptom — Diagnostic Aid The SRM reads fuel level sender input and broadcasts it to the IC and PCM. Action Refer to the Fuel Level Indication System Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. P0462 — Fuel Level Sender A Circuit Low Description Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual for more descriptive information. Possible Causes Refer to the Ford service manual. Causes are the same except that communication is between the sender and the SRM and not the IC. Symptom — Diagnostic Aid The SRM reads fuel level sender input and broadcasts it to the IC and PCM. Action Refer to the Fuel Level Indication System Check procedure in Diagnostic Tests and Procedures. Page 15 TROUBLESHOOTING DIAGNOSTIC TESTS AND PROCEDURES Expected Fuel Tank Pressure — On a tank at ambient temperature conditions, the following pressures can be expected: General Information Pressure (psi) Measuring Fuel Rail and Fuel Tank Pressure Measuring Fuel Tank Pressure — Fuel tank pressure can be measured two ways: Refer to Tools and Equipment, Special Tools in the 2012 Ford E-150/250/350/450 or 2013 F-250/350 Liquid Propane Autogas Fuel System Service Manual Supplement for more information regarding the tools required. Method 1 — Install a 0–500 psi (0–3447 kPa) fuel pressure gauge on the bleeder valve at the tank, or to the remote bleeder valve location. Open the valve to monitor the fuel tank pressure. Record the value. Method 2 — If a 0–500 psi (0–3447 kPa) fuel pressure gauge is not available, fuel rail pressure can be used to infer fuel tank pressure. Refer to Method 1 of Measuring Fuel Rail Pressure. Monitor fuel rail pressure with the engine running. Turn the engine off and continue to monitor fuel rail pressure. When the pressure has stabilized, record the value as fuel tank pressure. Temperature (°F) Min. Nominal Max. 0 15 25 35 5 19 29 39 10 23 33 43 15 28 38 48 20 33 43 53 25 38 48 58 30 43 53 63 35 49 59 69 40 55 65 75 45 62 72 82 50 69 79 89 55 77 87 97 60 84 94 104 65 93 103 113 70 102 112 122 75 111 121 131 80 121 131 141 Measuring Fuel Rail Pressure — Fuel rail pressure can be measured two ways: Refer to Tools and Equipment, Special Tools in the 2012 Ford E-150/250/350/450 or 2013 F-250/350 Liquid Propane Autogas Fuel System Service Manual for more information regarding the tools required. Method 1 — Using the OBD-II scan tool, read the fuel rail pressure PID. If using the Ford IDS tool, it will be necessary to select the tool box tab, then select Powertrain near bottom of selection, OBD Test Modes, Mode 1 Powertrain Data. Then locate and select FRP (pressure) from PID selection table. Method 2 — Empty the fuel rails and fuel lines. Refer to the Fuel Line Purging Procedure in the 2012 Ford E-150/250/350/450 or 2013 F-250/350 Liquid Propane Autogas Fuel System Service Manual Supplement for more information. Using the Jiffy-Tite disconnect tool, disconnect the fuel supply line at the rear of the RH fuel rail. Install the ROUSH service port adapter between the fuel line and the fuel rail. Attach 0–500 psi (0–3447 kPa) fuel pressure gauge to the service port on the adapter. Record the value. 85 131 141 151 90 142 152 162 95 153 163 173 100 165 175 185 105 178 188 198 110 191 201 211 115 205 215 225 120 219 229 239 Page 16 On vehicles that have been operated for extended periods of time, the tank (fuel) can be much warmer and so higher pressures are to be expected. Expected Fuel Rail Pressure — Under normal operating conditions, the fuel pump has two operating speeds. The pump operates in low speed mode at idle and during moderate fuel flow/part throttle driving. Once a fuel demand threshold is met, typically during wide open throttle (WOT) operation, the pump is switched to high speed. The pump is also operated at high speed during the pre-start flush sequence. TROUBLESHOOTING The fuel pressure controls are designed to keep the rails at a certain pressure over tank pressure, therefore, it is important to measure tank pressure prior to collecting fuel rail pressure data. For example, if the fuel tank is at 150 psi (1034 kPa) and pressure in the rail is measured at 200 psi (1379 kPa), the rail is running at 50 psi (345 kPa) over tank. Condition Pump Speed Pressure Over Tank Engine Off Off <10 Idle Low >30 Part Throttle Low <25 Part Throttle High >25 WOT High >25 Under extreme operating conditions, there is a third pump mode. In the event that the fuel system has degraded and the sensor detects vapor, or if the fuel rail pressure is approaching the limit of the fuel system, the pump runs in a variable speed mode, controlling to a target pressure. In this mode there is no predicted rise over tank pressure. The fuel pump will adjust the pressure to maintain a required operating pressure. This condition will likely result in a P116E or P0148 code. No Fill Step Procedure Action 1 Inspect vehicle to check for kinked fill lines. Are fill lines kinked? Yes — Replaced kinked fill lines. No — Go to Step 2. 2 Determine the location of the overflow protection device (OPD). Is the OPD located in the end cap of the fuel tank? Yes — Go to Step 3. No — Go to Step 6. 3 Check the fuel gauge in the instrument cluster. Is the gauge indicating less than 1/4 full? Yes — Go to Step 4. No — Go to Step 6. 4 Check to see if the OPD is being activated. Yes — Go to Step 5. No — Go to Step 6. Fuel splashing off the sides of the empty tank could be activating the OPD float and shutting off the fuel fill line. a. b. Loosen the fuel fill line at the fill valve or at the inlet to the fuel filter to relieve any pressure in the fill line and release the OPD valve. Retighten the fill line. Install a fuel fill pressure tester on the fill valve and close the ball valve. c. Connect the fuel dispensing nozzle to the pressure tester and turn on the pump. Slightly open the ball valve to slowly add approximately 10 gal (38 L) of fuel. d. Did the tank fill? 5 Remove the fuel fill pressure tester and attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank to full 80% capacity. Does the vehicle fuel tank fill to capacity? Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Go to Step 6. 6 Check the fuel gauge in the instrument cluster. Is the gauge indicating more than 1/2 full? Yes — Go to Step 7. No — Go to Step 11. 7 Reverse direction of vehicle at the pump and try to fill the vehicle. Does the vehicle fuel tank fill? Yes — Vehicle not on level ground. Diagnostic is complete. No — Drive vehicle until fuel gauge indicates less than 1/2 full and go to Step 8. Page 17 TROUBLESHOOTING Step Procedure Action 8 Attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank. Does the fuel tank fill? Yes — Go to Step 9. No — Go to Step 11. 9 Open bleeder valve. Does liquid fuel vent? Yes — Go to Step 10. No — Go to Step 12. 10 Check fuel gauge. Does fuel gauge read full? Yes — Diagnostic complete. No — Refer to Fuel Level Indicator Check. 11 Check for sufficient fill station pressure. Yes — Go to Step 12. No — Fill station may not be providing enough pressure to fill. Go to Step 19. a. b. 12 Connect pressure gauge service tool to the fuel tank bleeder valve and record pressure. Using a fuel fill pressure tester installed on the fill valve, attempt to fill the vehicle. c. With the dispensing pump on and dispensing nozzle open, measure and record fill station pump pressure. d. Is fill station pump pressure at least 20 psi (138 kPa) greater than tank pressure? Check body side fuel fill valve; it may be stuck closed. a. b. c. Loosen the fuel fill line connection at the fill valve or at the inlet to the fuel filter to relieve any pressure in the fill line. Attempt to push open the piston in the fill valve to determine if it is stuck closed. Yes — Replace body-side fill valve and go to Step 13. No — Replace filter in the fuel fill line and go to Step 15. Is the fill valve piston stuck closed? 13 Attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank. Does the fuel tank fill? Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Go to Step 14. 14 Replace the filter in the fuel fill line and then attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank. Does the vehicle fuel tank fill? Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Go to Step 16. 15 Attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank. Does the fuel tank fill? Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Go to Step 16. 16 Replace the OPD valve in the vehicle fuel tank. Is the OPD valve located in the end cap of the fuel tank? Yes — Go to Step 17. No — Go to Step 18. 17 Attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank as follows: Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Call ROUSH CleanTech Customer Service at 800-597-6874. When filling a new tank that has the OPD valve mounted in the end cap of the fuel tank, fuel splashing off the sides of the empty tank could be activating the OPD float and shutting off the fuel fill line. a. 18 Page 18 b. Install a fuel fill pressure tester on the fill valve and close the ball valve. Connect the fuel dispensing nozzle to the pressure tester and turn on the pump. Slightly open the ball valve to slowly add approximately 10 gal (38 L) of fuel. c. Remove the fuel fill pressure tester. d. Attempt to fill the remaining tank volume (to 80% full capacity) at full flow from the dispensing nozzle. e. Did the tank fill? Attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank. Does the fuel tank fill? Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Call ROUSH CleanTech Customer Service at 800-597-6874. TROUBLESHOOTING Step 19 Procedure Fill station is not providing enough pressure to fill. a. b. 20 Vehicle fuel tank is at a higher pressure. a. b. 21 Higher pressure is likely caused by heavy vehicle usage heating the fuel. Allow the vehicle (fuel tank) to cool and then recheck pressure in the fuel tank. Measure and compare vehicle fuel tank and fill station pressures. a. b. 22 Using the tables provided at the front of this section, determine expected propane tank pressure based on ambient temperature. Is the vehicle fuel tank pressure greater than 20 psi (138 kPa) over the nominal expected pressure? Connect a pressure gauge service tool to the fuel tank bleeder valve and record fuel tank pressure. Using a fuel fill pressure tester installed on the fill valve, attempt to fill the vehicle. c. With the dispensing pump on and dispensing nozzle open, measure and record fill station pump pressure. d. Is fill station pump pressure at least 20 psi (138 kPa) greater than fuel tank pressure? Attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank. Does the fuel tank fill? Action Yes — Go to Step 20. No — Locate a dispensing facility with pump output capacity in excess of 100 psi (689 kPa) (preferably an Auto Gas-type facility). Then, go to Step 12. When tank pressure is within 10 psi (69 kPa) of expected tank pressure, go to Step 21. Yes — Go to Step 22. No — Fill station is not providing enough pressure to fill vehicle tank. Go to Step 22. Locate a dispensing facility with pump output capacity in excess of 100 psi (689 kPa) (preferably an Auto Gas-type facility). Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Go to Step 12. Slow Fill Step Procedure Action 1 Inspect vehicle to check for kinked fill lines. Are fill lines kinked? Yes — Replaced kinked fill lines. No — Go to Step 2. 2 Determine flow rate at which the vehicle fuel system fills. Yes — System fill rate is OK; diagnostic is complete. No — Fill station is not providing enough pressure to fill vehicle tank. Go to Step 3. a. b. c. 3 b. Connect a pressure gauge service tool to the fuel tank bleeder valve and record fuel tank pressure. Using a fuel fill pressure tester installed on the fill valve, attempt to fill the vehicle. c. With the dispensing pump on and dispensing nozzle open, measure and record fill station pump pressure. d. Is fill station pump pressure at least 50 psi (345 kPa) greater than fuel tank pressure? Check fuel fill valve; it may not be opening completely. a. b. c. 5 Is the fill station pump flow rate at least 6 gal (23 L) per minute? Measure and compare vehicle fuel tank and fill station pressures. a. 4 Time the fill station pump for 10 seconds and record the number of gallons dispensed. Multiply the gallons dispensed by six to determine the flow rate in gallons per minute. Loosen the fuel fill line connection at the fill valve or at the inlet to the fuel filter to relieve any pressure in the fill line. Attempt to push open the piston in the fill valve to determine if it is opening completely. Piston should travel 1/4 inch. Yes — Go to Step 4. No — Fill station is not providing enough pressure to fill vehicle tank. Go to Step 11. Yes — Replace the filter in the fuel fill line and then go to Step 7. No — Replace the fuel fill valve and then go to Step 5. Is the fill valve piston opening completely? Attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank. Does the fuel tank fill at greater than six gal (23 L) per minute? Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Go to Step 6. Page 19 TROUBLESHOOTING Step Procedure Action 6 Replace the filter in the fuel fill line. Does the vehicle fuel tank fill at greater than six gal (23 L) per minute? Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Go to Step 7. 7 Attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank. Does the fuel tank fill at greater than six gal (23 L) per minute? Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Go to Step 8. 8 Replace the overfill protection device (OPD) valve in the vehicle fuel tank. Is the OPD valve located in the end cap of the fuel tank? Yes — Go to Step 9. No — Go to Step 10. 9 Attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank as follows: Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Call ROUSH CleanTech Customer Service at 800-597-6874. When filling a new tank that has the OPD valve mounted in the end cap, fuel splashing off the sides of the empty tank could be activating the OPD float and shutting off the fuel fill line. a. b. Install a fuel fill pressure tester on the fill valve and close the ball valve. Connect the fuel dispensing nozzle to the pressure tester and turn on the pump. Slightly open the ball valve to slowly add approximately 10 gal (38 L) of fuel. c. Remove the fuel fill pressure tester. d. Attempt to fill the remaining tank volume (to 80% full capacity) at full flow from the dispensing nozzle. a. Did the tank fill? 10 Attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank. Does the fuel tank fill at greater than six gal (23 L) per minute? Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Call ROUSH CleanTech Customer Service at 800-597-6874. 11 Fill station is not providing enough pressure to fill. Yes — Go to Step 12. No — Locate a dispensing facility with pump output capacity in excess of 100 psi (689 kPa) (preferably an Auto Gas-type facility). Then, go to Step 2. a. b. 12 Vehicle fuel tank is at a higher pressure. a. b. 13 b. Page 20 Higher pressure is likely caused by heavy vehicle usage heating the fuel. Allow the vehicle (fuel tank) to cool and then recheck pressure in the fuel tank. Measure and compare vehicle fuel tank and fill station pressures. a. 14 Using the tables provided at the front of this section, determine expected propane tank pressure based on ambient temperature. Is the vehicle fuel tank pressure greater than 20 psi (38 kPa) over the nominal expected pressure? Connect a pressure gauge service tool to the fuel tank bleeder valve and record fuel tank pressure. Using a fuel fill pressure tester installed on the fuel fill valve, attempt to fill the vehicle. c. With the dispensing pump on and dispensing nozzle open, measure and record fill station pump pressure. d. Is fill station pump pressure at least 50 psi (345 kPa) greater than fuel tank pressure? Attempt to fill the vehicle fuel tank. Does the fuel tank fill at greater than six gal (23 L) per minute? When tank pressure is within 10 psi (69 kPa) of expected tank pressure, go to Step 13. Yes — Go to Step 14. No — Fill station is not providing enough pressure to fill vehicle tank. Go to Step 14. Locate a dispensing facility with pump output capacity in excess of 100 psi (689 kPa) (preferably an Auto Gas-type facility). Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Go to Step 4. TROUBLESHOOTING Over Fill Step 1 Procedure Suspect overfill because fuel fill volumes achieved during refueling exceed the rated fuel capacity or excessive vehicle range between refueling. a. b. 2 3 b. 4 Check to determine if the vehicle is level using the vehicle frame as reference. Does the vehicle sit level? Locate the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) inspection plate on the fuel tank. a. b. 5 Listen at valve to verify propane vapor is venting. Is propane vapor venting? Park the vehicle at the refueling station. a. Yes — Go to Step 2. No — Drive vehicle until gauge reads below 1/4 tank. Check the fuel gauge. Is the gauge reading below 1/2 tank? Open bleeder valve located on the tank or remotely mounted on the vehicle. a. b. Action Yes — Go to Step 3. No — Bleeder valve is not functioning properly. Replace the valve. Yes — Go to Step 4. No — Using a jack, raise the vehicle to obtain a level condition. Then, go to Step 4. With the value recorded, go to Step 5. Note the tank water capacity listed on the plate. Multiply the listed capacity by 0.05 (5%) and record the value. Refuel the vehicle as follows: Yes — Record the volume of fuel dispensed and then go to Step 6. No — Go to Step 7. If the key is on during refueling, it will take the fuel level gauge in the instrument cluster longer to register full. 6 a. b. Verify that the ignition is in the off position. Install the fuel fill pressure tester on the fill valve and close the ball valve. c. Connect the fuel dispensing nozzle to the pressure tester. Verify that the bleeder valve is open. d. With the bleeder valve open, turn on the pump. Open the ball valve slightly to very slowly refuel the vehicle. e. While refueling, observe the bleeder valve for fuel discharge. f. Stop filling when a solid stream of liquid fuel flows from the bleeder valve or the dispensing pump stops automatically. g. Did a solid stream of liquid flow from the bleeder valve? Resume filling until the dispensing pump stops automatically. a. b. 7 Record the total volume of fuel dispensed and subtract the amount from the volume recorded in Step 5. Is the additional amount of fuel dispensed less than 5% of the tank water capacity determined in Step 4? The dispensing pump stopped automatically and a liquid fuel stream was not observed flowing from bleeder valve. Yes — Tank does not overfill. Diagnostic is complete. No — Tank is overfilling. Replace the OPD fill valve in the fuel tank; then, go to Step 8. Tank does not overfill. Diagnostic is complete. Page 21 TROUBLESHOOTING Step 8 Procedure Refuel the vehicle as follows: Action Yes — Record the volume of fuel dispensed and then go to Step 9. No — Go to Step 7. If the key is on during refueling, it will take the fuel level gauge in the instrument cluster longer to register full. 9 a. b. Verify that the ignition is in the off position. Install the fuel fill pressure tester on the fill valve and close the ball valve. c. Connect the fuel dispensing nozzle to the pressure tester. Verify that the bleeder valve is open. d. With the bleeder valve open, turn on the pump. Open the ball valve slightly to very slowly to refuel the vehicle. e. While refueling, observe the bleeder valve for fuel discharge. f. Stop filling when a solid stream of liquid fuel flows from the bleeder valve or the dispensing pump stops automatically. g. Did a solid stream of liquid flow from the bleeder valve? Resume filling until the dispensing pump stops automatically. a. b. Record the volume of fuel dispensed and subtract the amount from the volume recorded in Step 8. Is the additional amount of fuel dispensed less than 5% of the tank water capacity determined in Step 4? Yes — Tank does not overfill. Diagnostic is complete. No — Tank is overfilling. Replace the fuel tank assembly. Engine Does Not Crank Step Procedure Action 1 Is battery voltage above 10 volts? Yes — Go to Step 2. No — Determine cause of low battery voltage. 2 Verify that the smart relay module (SRM) has communication. Yes — Go to Step 3. No — Go to the Smart Relay Module Electrical Test procedure. Can fuel rail pressure and temperature be read with a scan tool? 3 Page 22 Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emission Diagnosis Service Manual. Is the problem corrected? Yes — Diagnostic is complete. No — Call ROUSH CleanTech Customer Service at 800-597-6874. TROUBLESHOOTING Engine Cranks, No Start For harness and connector layout diagrams and system electrical schematics, refer to System Wiring Diagrams and to System Electrical Schematics. Step 1 Procedure Verify the following: a. b. Is there fuel in the tank of at least 1/8 tank or more? (add fuel if necessary). Is the tank supply manual shutoff valve fully open? c. Is battery voltage above 10 volts? Action Yes — Go to Step 2. No — Correct fault and retry. 2 Check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTC). Are any codes present? Yes — Go to Step 3. No — Go to Step 4. 3 Is the DTC identified on the ROUSH LPA DTC list? Yes— Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes. No — Refer to Ford service manual DTC chart. 4 Check fuel pressure. Yes — Go to Step 11. No — Go to Step 5. a. b. 5 c. Record the highest pressure observed. d. Does fuel pressure rise 25 psi (172 kPa) before engine crank? Check fuel pump operation. a. 6 Measure and record fuel rail and fuel tank pressure, key on, engine off (KOEO). While monitoring fuel pressure, attempt to start engine. b. Using a current clamp, check current draw on both fuel pump power wires at the fuel tank. Refer to In-Tank Harness for correct circuits. Turn ignition switch to start position and release. Vehicle will start the flush cycle and pumps should be running. Check current draw. A minimum of 2 amps should be recorded on both fuel pump circuits. c. Do fuel pumps draw current? Check excess flow valve (XFV). a. b. Turn ignition key to the OFF position. Close the manual shutoff valve on tank. c. Wait 1 minute and then slowly open manual shutoff valve. d. Measure and record fuel pressure, using a scan tool, at integrated pressure temperature sensor (IPTS). e. Is problem resolved? Yes — Go to Step 6. No — If both circuits are showing no current, check the OEM fuel pump (FP) fuse. If only one fuel pump circuit shows current, check the ROUSH CleanTech fuel pump fuse. (See ROUSH CleanTech fuse box for location.) If both fuel pump fuses (OEM and ROUSH CleanTech) are good, go to Step 10. Yes — Go to Step 11. No — Go to Step 7. 7 Check ROUSH fuel pump (FP) fuse. Is fuse intact and OK? Yes — Go to Step 8. No — Determine the cause of the short and repair; replace the fuse. Diagnostic is complete. 8 Check the tank solenoid (TS) and supply solenoid (SS) fuses. Yes — Determine the cause of the short and repair; replace the fuse. No — Go to Step 9. a. b. Locate the TS fuse (E3-E4) and check its condition. Locate the SS fuse (F1-F2) and check its condition. c. Are the fuses blown? Page 23 TROUBLESHOOTING Step 9 Procedure Verify that there is power and proper grounding at the tank solenoid (TS) and supply solenoid (SS) wiring circuits. a. 10 b. Check for +12 volts at the TS and SS connectors. Refer to the Tank Solenoid Electrical Check procedure. Is +12 volts present at the TS connector? c. Is +12 volts present at the SS connector? Verify that there is power and proper grounding in the wiring circuit to the tank. a. b. Check for +12 volts at the fuel pump 1 (FP1) and fuel pump 2 (FP2) connectors. Refer to the Fuel Pump Electrical Check procedure. Is +12 volts present at the FP1 connector? c. Is +12 volts present at the FP2 connector? Action Yes — Voltage present at SS, replace FRPCM. Voltage present at TS, replace fuel supply valve assembly. No — Check for an open(s) in the wiring circuits and repair. Diagnostic is complete. Yes — Go to Step 12. No — Check for an open(s) in the wiring circuits and repair. 11 Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Rationality Does temperature and pressure make sense to verification procedure? Yes — Refer to the Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Electrical Check. No — Verify that wiring in circuit is OK. Refer to the Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Electrical Check procedure. If not, repair wiring. If OK, replace sensor. 12 Check wiring. Yes — Replace harness. No — Go to Step 13. a. b. 13 Drain the propane from the fuel tank. Refer to the Fuel Tank Draining Procedure in the appropriate ROUSH CleanTech Service Manual for more information. Remove tank service cover. c. Check for open or short circuits on tank pass-through harness. d. Is a wiring problem present? Check fuel hoses and quick-connect fittings. 앫 Are in-tank fuel hoses and quick-connect fittings connected and in good condition? Page 24 Yes — Replace fuel pump assembly. No — Replace hose assemblies as needed. TROUBLESHOOTING Engine Stumble, Stall, Rough Idle For harness and connector layout diagrams and system electrical schematics, refer to System Wiring Diagrams and to System Electrical Schematics. Step 1 Procedure Verify the following: a. b. Is there fuel in the tank of at least 1/8 tank or more? (Add fuel if necessary.) Is the tank supply manual shutoff valve fully open? c. Is battery voltage above 11 volts with engine running? Action Yes — Go to Step 2. No — Correct the fault and retry. 2 Check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Are any codes present? Yes — Go to Step 3. No — Go to Step 4. 3 Identify the DTC. Yes — Refer to ROUSH CleanTech Diagnostic Trouble Codes. No — Refer to the appropriate Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual at www.motorcraft.com. a. b. Is the DTC covered in the ROUSH CleanTech DTC listing for LPA-fueled vehicles? Correct all DTCs before continuing. 4 Does the problem occur only after cold start? Yes — Go to Step 6. No — Go to Step 5. 5 Determine fuel pressure. Yes — Go to Step 7. No — Go to Step 6. 6 7 a. b. Measure tank pressure with key on and engine off (KOEO). Measure fuel rail pressure with key on and engine running (KOER). c. Subtract the KOEO pressure from the KOER pressure to obtain the difference. Compare to the chart in Expected Fuel Rail Pressure. d. Is the resulting fuel pressure reading within the expected range? Determine if the excess flow valve (XFV) is tripped. a. b. Turn off the engine. Wait one minute and then restart the engine. c. Is the fault condition resolved? Check fuel pump operation. a. 8 b. Using a current clamp, check current draw on both fuel pump power wires at the fuel tank. Refer to In-Tank Harness for correct circuits. Turn ignition switch to start position and release. Vehicle will start the flush cycle and pumps should be running. Check current draw. A minimum of 2 amps should be recorded on both fuel pump circuits. c. Do fuel pumps draw current? Verify that there is power and proper grounding in the wiring circuit to the tank. a. b. Check for +12 volts at the fuel pump 1 (FP1) and fuel pump 2 (FP2) connectors. Refer to the Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module Electrical Check procedure. Is +12 volts present at the FP1 connector? c. Is +12 volts present at the FP2 connector? Yes — Refer to the Excess Flow Valve Check procedure. No — Go to Step 7. Yes — Go to Step 11. No — If both circuits are showing no current, check the OEM fuel pump (FP) fuse. If only one fuel pump circuit shows current, check the ROUSH CleanTech fuel pump fuse. (See ROUSH CleanTech fuse box for location.) If both fuel pump fuses (OEM and ROUSH CleanTech) are good, go to Step 8. Yes — Go to Step 9. No — Check for an open/short in the wiring circuit and repair. Page 25 TROUBLESHOOTING Step 9 Procedure Check wiring. a. 10 Action b. Drain the propane from the fuel tank. Refer to the Fuel Tank Draining Procedure in the appropriate ROUSH CleanTech Service Manual for more information. Remove tank service cover. c. Check for open or short circuits on tank pass-through harness. d. Is a wiring problem present? Check fuel hoses and quick-connect fittings. 앫 Are in-tank fuel hoses and quick-connect fittings connected and in good condition? Yes — Replace harness. No — Go to Step 10. Yes — Replace fuel pump assembly. No — Replace hose assemblies as needed. 11 Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Rationality Does temperature and pressure make sense to verification? Refer to the Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Electrical Check procedure. Yes — Go to Step 12. No — Verify that wiring in circuit is OK. If not, repair wiring. If OK, replace sensor. 12 Refer to the appropriate Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual at www.motorcraft.com. — Excess Flow Valve Check The excess flow valve (XFV) is designed to restrict fuel exiting the tank if the pump is energized while the fuel lines are not connected to the fuel tank. Under normal circumstances, the XFV should not trip. The XFV will reset itself after the fuel pumps have been off for about one minute. If the fuel lines have not been serviced recently and the problem persists, there may be a leak in the supply side fuel line. If the problem is only present after the vehicle has been sitting for a length of time, but not present during a short soak, or there is a propane odor when the vehicle is running, refer to the Fuel Line Leak Detection procedure. It is common to trip the XFV after the fuel lines have been serviced and contain no pressure. If the XFV trips, turn the vehicle off, wait one minute, and restart. This may take more than one attempt. Step 1 Page 26 Procedure Verify fuel supply line pressure prior to cranking engine. a. b. Read fuel rail pressure and tank pressure. Energize bleed solenoid until rail pressure is at least 50 psi (345 kPa) below tank pressure. If rail is bled, skip to Step D. c. Let pressure stabilize for 1 minute. d. Open the supply solenoid. e. Read fuel rail pressure and tank pressure. f. Does fuel rail pressure jump to tank pressure? Action Yes — Check is OK. No — Repair the leak in the fuel supply line. TROUBLESHOOTING Maximum Pressure Check The LPA system operates over a wide range of pressures depending on ambient temperature, driving mode, etc. When the vehicle is subjected to a severe drive cycle in high ambient temperatures, the fuel rail pressure can rise to the limit of the injectors capabilities. This limit is a function of injector voltage and fuel rail pressure. The PCM protects for this condition by reducing the fuel pump speed when the condition is sensed, however, there still may be drive concerns. When the PCM starts controlling the fuel pump a P116E code is set. While this Step 1 condition can occur in a normally functioning vehicle, it can also be exacerbated by several factors. If the fuel tank was not properly bled during the first fill, trapped air in the vapor space can increase tank pressure. In this condition there is often only a faint smell of propane when the bleeder valve is opened. The tank should be vented until there is a strong propane odor coming from the bleeder valve. The tank pressure should be confirmed against the expected pressure. Allow the fuel tank to cool to ambient temperature before performing the following procedure. Procedure Measure tank pressure and tank surface temperature. Is tank pressure more than 15 psi (103 kPa) over expected tank pressure? Action Yes — Vent the tank until pressure is within the expected range. No — Vehicle is working properly; inform and explain operating characteristics to customer. Supply Solenoid Check For harness and connector layout diagrams and system electrical schematics, refer to System Wiring Diagrams and to System Electrical Schematics. Step 1 Procedure Verify the following: a. b. Is there fuel in the tank of at least 1/8 tank or more? (Add fuel if necessary.) Is the tank supply manual shutoff valve fully open? c. Is battery voltage above 10 volts? Action Yes — Go to Step 2. No — Correct fault and retry. 2 Check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTC). Are any codes present? Yes — Go to Step 3. No — Go to Step 4. 3 Is the DTC identified on the ROUSH liquid propane autogas DTC list? Yes — Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes. No — Refer to the Ford service manual DTC chart. 4 Check fuel pressure. Yes — Go to Step 11. No — Go to Step 5. a. b. Measure and record fuel rail pressure and fuel tank pressure at key on, engine off (KOEO). While monitoring fuel pressure, attempt to start engine. c. Record the highest pressure observed. d. Does fuel pressure rise 20 psi (138 kPa) before engine crank? Page 27 TROUBLESHOOTING Step 5 Procedure Check fuel pump operation. a. 6 b. Using a current clamp, check current draw on both fuel pump power wires at the fuel tank. Refer to In-Tank Harness for correct circuits. Turn ignition switch to start position and release. Vehicle will start the flush cycle and pumps should be running. Check current draw. A minimum of 2 amps should be recorded on both fuel pump circuits. a. Do fuel pumps draw current? Check XFV. a. b. Turn off engine. Wait 1 minute and then restart engine. c. Measure and record fuel rail pressure and fuel tank pressure. d. Is problem resolved? Action Yes — Go to Step 6. No — If both circuits are showing no current, check the OEM fuel pump (FP) fuse. If only one fuel pump circuit shows current, check the ROUSH CleanTech fuel pump fuse. (See ROUSH CleanTech fuse box for location.) If both fuel pump fuses (OEM and ROUSH CleanTech) are good, go to Step 10. Yes — Go to Step 11. No — Go to Step 7. 7 Check ROUSH FP fuse. Is fuse intact and OK? Yes — Go to Step 8. No — Determine the cause of the short and repair; replace the fuse. 8 Check the TS and SS fuses. Yes — Determine the cause of the short and repair; replace the fuse. No — Go to Step 9. 9 a. b. Locate the TS fuse (E3-E4) and check its condition. Locate the SS fuse (F1-F2) and check its condition. c. Are the fuses blown? Verify that there is power and grounding in the TS and SS wiring circuits. a. 10 b. Check for +12 volts at the TS and SS connectors. Refer to the Tank Solenoid Electrical Check procedure. Is +12 volts present at the TS connector? c. Is +12 volts present at the SS connector? Verify that there is power and grounding in the wiring circuit to the tank. a. b. Check for +12 volts at the fuel pump 1 (FP1) and fuel pump 2 (FP2) connectors. Refer to the Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module Electrical Check procedure. Is +12 volts present at the FP1 connector? c. Is +12 volts present at the FP2 connector? Yes — Voltage present at SS, replace FRPCM. Voltage present at TS, replace fuel supply valve assembly. No — Check for an open/short in the wiring circuit and repair. Yes — Refer to Engine Stumble, Stall, Rough Idle Step 12. No — Check for an open/short in the wiring circuit and repair. 11 Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Rationality Does temperature and pressure make sense to verification? Yes — Go to Step 12. No — Verify that wiring in circuit is OK. Refer to the Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Electrical Check procedure. If not, repair wiring. If OK, replace sensor. 12 Refer to the appropriate Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual at www.motorcraft.com. — Page 28 TROUBLESHOOTING Fuel System Fails to Bleed Step 1 2 3 Procedure Determine if fault condition repeats. a. b. Start the engine and allow it to run for a few minutes. Turn off the engine and wait one minute. c. Measure and record the fuel rail pressure, fuel rail temperature and fuel tank pressure with the engine off (KOEO). d. Energize the bleed solenoid. Refer to the Manual Solenoid Activation Procedure. e. With the engine off, monitor fuel rail pressure for 15 minutes. f. Does fuel rail pressure drop more than 20 psi (138 kPa)? Verify solenoid/restrictor function. a. b. Start the engine and allow it to run for a few minutes. Turn off the engine. c. Disconnect the EVAP line from the FRPCM port. d. Energize the bleed solenoid. Refer to the Manual Solenoid Activation Procedure. e. Is there propane flowing from the port? Verify that wiring is in good condition and functioning. a. b. 4 Check for a kinked EVAP line. a. b. 5 Perform wiring checks of the FRPCM harness. Is the wiring OK? Inspect the EVAP line between the FRPCM and EVAP canister. Are there kinks in the line? Check for leaks to the FRPCM. a. b. Start the engine and allow it to run for a few minutes. Turn off the engine and unplug the FRPCM. c. Measure and record fuel rail pressure. d. Bleed pressure from fuel rail until fuel pressure drops more than 50 psi (345 kPa). e. De-energize bleed solenoid. f. Let vehicle sit for 30 minutes. g. Measure fuel rail pressure and fuel tank pressure. h. Does fuel rail pressure rise more than 10 psi (69 kPa)? Action Yes — Go to Step 5. No — Go to Step 2. Yes — Go to Step 4. No — Go to Step 3. Yes — Bleed solenoid stuck closed or port restrictor is plugged. Replace the FRPCM. No — Repair wiring and repeat Step 1. Yes — Replace the kinked EVAP line and then repeat Step 1. No — Go to Step 5. Yes — FRPCM leaks at either supply solenoid or return check valve. Replace FRPCM. No — Potential intermittent fault. Return vehicle to customer and see if problem persists. Page 29 TROUBLESHOOTING Fuel Pressure Drop For harness and connector layout diagrams and system electrical schematics, refer to System Wiring Diagrams and to System Electrical Schematics. Step 1 2 Procedure Verify the following: a. b. Is there fuel in the tank of at least 1/8 tank? Is the tank supply manual shutoff valve fully open? c. Is battery voltage above 10 volts? Determine fuel pressure. a. b. 3 4 c. Subtract the tank measurement from the KOER measurement. d. Is the resulting fuel pressure in the expected range? Determine if the excess flow valve is tripped. a. b. Turn off the engine. Wait one minute and then restart the engine. c. Is the problem resolved? Check fuel pump operation. a. 5 b. Using a current clamp, check current draw on both fuel pump power wires at the fuel tank. Refer to In-Tank Harness for correct circuits. Turn ignition switch to start position and release. Vehicle will start the flush cycle and pumps should be running. Check current draw. A minimum of 2 amps should be recorded on both fuel pump circuits. c. Do fuel pumps draw current? Check tank solenoid (TS) and supply solenoid (SS) fuses. a. b. 6 Measure and record fuel tank pressure. Measure and record fuel rail pressure with key on, engine running (KOER). Locate the TS (E3-E4) and SS (F1-F2) fuses. Are the fuses blown? Verify that there is power and ground in the wiring circuit to the tank. a. b. Check for +12 volts at the fuel pump 1 (FP1) and fuel pump 2 (FP2) connectors. Refer to the Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module Electrical Check procedure. Is +12 volts present at the FP1 connector? c. Is +12 volts present at the FP2 connector? Action Yes — Go to Step 2. No — Correct the fault condition and retry. Yes — Go to Step 4. No — Go to Step 3. Yes — Refer to the Excess Flow Valve Check procedure. No — Go to Step 4. Yes — Go to Step 5. No — If both circuits are showing no current, check the OEM fuel pump (FP) fuse. If only one fuel pump circuit shows current, check the ROUSH CleanTech fuel pump fuse. (See ROUSH CleanTech fuse box for location.) If both fuel pump fuses (OEM and ROUSH CleanTech) are good, go to Step 6. Yes — Find and repair the short; replace the fuse. No — Go to Step 8. Yes — Refer to Engine Stumble, Stall, Rough Idle Step 9. No — Check for an open/short in the wiring circuit and repair. 7 Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Rationality Does temperature and pressure make sense to verification? See the Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Electrical Check procedure. Yes — Go to Step 8. No — Verify that wiring in circuit is OK. If not, repair wiring. If OK, replace sensor. 8 Refer to the appropriate Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual at www.motorcraft.com. — Page 30 TROUBLESHOOTING Fuel Level Indication Check The ROUSH CleanTech fuel level indication system differs from the gasoline system as the fuel level sender is not wired directly to the instrument cluster. Instead, the fuel level sender is wired to the SRM, which reads the fuel level and transmits the signal to the PCM via the CAN bus, and to the FLIM, which in turn simulates the resistance the instrument cluster expects to see for a given fuel level. The gauge on the sending unit must not be used for any diagnostics. The gauge is not accurate. Only resistance or voltage outputs should be used for diagnostic purposes. Symptom Cause/Action to be taken Fuel gauge does not move on a partial fill This behavior is not uncommon. The fuel level sender may not move far enough to trigger movement on the gauge if only a small amount of fuel is added to the tank. Once driven, the gauge may move to reflect the fill. Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) There is a circuit fault that has been identified by the PCM. Initially follow the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual, whenever a circuit check is called for, refer to the Fuel Level Interface Module Electrical Test procedure. Gauge points below E This is an indication of an error state. Initially follow the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual, whenever a circuit check is called for, refer to the Fuel Level Interface Module Electrical Test procedure. Doesn’t read full after a fill This could be the result of either a fuel level sender fault or an OPD valve triggering prematurely. Refer to fill issues and the Fuel Level Sender Electrical Check procedure for more information. Page 31 TROUBLESHOOTING Tank Solenoid Electrical Check For harness and connector layout diagrams and system electrical schematics, refer to System Wiring Diagrams and to System Electrical Schematics. CONNECTORS 5 3 5 1 2 4 3 5 1 B 2 4 6 4 3 2 3 3 E 1 5 A 2 4 1 FUSE BOX 5 2 4 1 F 1 44 1 15 30 31 32 44 18 29 3 15 45 1 2 46 A1 PBT/ASA-GF20 16 17 F E D C B A 100070a Figure 1 — Underhood Harness Connectors 2 21 30 A B C A B D C D E F 100071a Figure 2 — Rear Frame Harness Connectors 3 1 9 D C B A A B 100072a Figure 3 — Solenoid Harness Connectors Page 32 TROUBLESHOOTING PROCEDURE Step Procedure Action 1 Unplug the solenoid harness connector 9 from the tank solenoid. Go to Step 2. 2 Using a multimeter, measure resistance of the solenoid. Is the measured resistance within 6–35 ohms? Yes — Go to Step 3. No — Replace the tank solenoid. 3 Using a multimeter, measure voltage at the tank solenoid as follows: Yes — Supply circuit OK. No — Go to Step 4. a. b. With the ignition key on, check for voltage present at pin-A, connector 9 (solenoid harness). Use the body as the reference ground. Is battery (B+) voltage present? 4 Check fuse (E3-E4, 20A) in auxiliary fuse box. Is fuse blown? Yes — Replace fuse. No — Fuse OK; go to Step 5. 5 Check relay. Is relay functioning properly? Yes — Go to Step 6. No — Replace relay. 6 Check supply circuit continuity from solenoid harness to fuse box. Yes — Go to Step 7. No — Repair supply circuit wiring. a. b. 7 Check continuity between: 앫 Pin-A, connector 9 and pin-A, connector 1 (solenoid harness) 앫 Pin-A, connector 21 and pin-A, connector 30 (rear wiring harness) 앫 Pin-A, connector 15 and cavity A5, fuse box (underhood harness) Is there good continuity in the circuit? Check ground circuit continuity from solenoid harness to smart relay module (SRM) connector. a. b. Check continuity between: 앫 Pin-B, connector 9 and pin-B, connector 1 (solenoid harness) 앫 Pin-B, connector 21 and pin-E, connector 30 (rear wiring harness) 앫 Pin-E, connector 15 and pin-44, connector 1 (underhood harness) Is there good continuity in the circuit? Yes — Refer to the Smart Relay Module Electrical Test procedure. No — Repair ground circuit wiring. Page 33 TROUBLESHOOTING Fuel Rail Pressure Control Module Electrical Check For harness and connector layout diagrams and system electrical schematics, refer to System Wiring Diagrams and to System Electrical Schematics. CONNECTORS 4 30 31 2 32 44 18 29 3 15 6 4 3 5 2 4 1 5 3 3 5 1 46 45 11 46 A1 PBT/ASA-GF20 1 2 4 B 33 1 2 3 3 E 1 5 A 2 4 1 FUSE BOX 5 2 4 1 F F1-F2 16 17 17 F E D C B A 100073a Figure 4 — Underhood Harness Connectors PROCEDURE Step Procedure Action 1 Unplug the fuel rail pressure control module (FRPCM) connector from connector 11 of underhood harness. Go to Step 2. 2 Using a multimeter, check the resistance of each solenoid. Yes — Go to Step 3. No — Replace the FRPCM if resistance for any one of the solenoids is not within the specified range. a. b. 3 Page 34 Check resistance across the terminals of the FRPCM connector in sequence as follows: 앫 Supply Solenoid — Pin-A and pin-F 앫 Flow Control Solenoid — Pin-B and pin-E 앫 Bleed Solenoid — Pin-C and pin-D Is the measured resistance for each solenoid within 6–35 ohms? Check supply voltage to FRPCM solenoids. Using a multimeter, measure voltage between the terminal for each solenoid at the harness side connector 11 and ground as follows: Go to Steps 4–6. TROUBLESHOOTING 4 Supply Solenoid — Pin-A and body ground B+ Voltage — Go to Step 5. No Voltage — Go to Step 5. 5 Flow Control Solenoid — Pin-B and body ground B+ Voltage — Go to Step 6. No Voltage — Go to Step 6 if Step 4 has voltage; if Step 4 has no voltage, go to Step 7. 6 Bleed Solenoid — Pin-C and body ground B+ Voltage — Continue with Step 9. No Voltage — Go to Step 8 if Step 4 has voltage; if Step 4 has no voltage, go to Step 7. 7 Check fuses (F1-F2, 10A) in auxiliary fuse box. Is a fuse blown? Yes — Replace fuse. No — Go to Step 8. 8 Check solenoid supply circuit continuity. Yes — Go to Step 9. No — Repair wiring circuit. a. b. 9 Check continuity between: 앫 Supply Solenoid — Pin-A, connector 11 (underhood harness) and cavity F2 (auxiliary fuse box) 앫 Flow Control Solenoid — Pin-B, connector 11 (underhood harness) and cavity F2 (auxiliary fuse box) 앫 Bleed Solenoid — Pin-C, connector 11 (underhood harness) and cavity F2 (auxiliary fuse box) Is there good continuity in all three circuits? Check solenoid ground circuit continuity. a. b. Check continuity in the underhood harness between: 앫 Supply Solenoid — Pin-F, connector 11 and pin-46, connector 1 at SRM 앫 Flow Control Solenoid — Pin-E, connector 11 and pin-33, connector 1 at SRM 앫 Bleed Solenoid — Pin-D, connector 11 and pin-17, connector 1 at SRM Is there good continuity in all three circuits? Yes — Refer to the Smart Relay Module Electrical Test procedure. No — Repair wiring circuit. Page 35 TROUBLESHOOTING Integrated Pressure Temperature Sensor Electrical Check For harness and connector layout diagrams and system electrical schematics, refer to System Wiring Diagrams and to System Electrical Schematics. CONNECTORS Figure 5 — Underhood Harness Connectors PROCEDURE Step Procedure Action 1 Unplug the connector 8 (underhood harness) to the IPTS. Go to Step 2. 2 Check resistance of the integrated pressure temperature sensor (IPTS). Yes — Go to Step 3. No — Replace the IPTS. a. b. Page 36 With vehicle at ambient room temperature (20–30°C, 68–86°F) and using a multimeter, measure resistance across the IPTS terminals (between pin-1 and pin-3). Is the resistance value between 8K–12K ohms? TROUBLESHOOTING Step 3 Procedure Check circuit continuity between the IPTS and the smart relay module (SRM). a. b. Using a multimeter, check continuity in the underhood harness between: 앫 Pin-1, connector 8 and pin-40, connector 1 앫 Pin-2, connector 8 and pin-7, connector 1 앫 Pin-3, connector 8 and pin-5, connector 1 앫 Pin-4, connector 8 and pin-25, connector 1 Is there good continuity in the circuits? Action Yes — Refer to the Smart Relay Module Electrical Test procedure. No — Repair circuit wiring. Page 37 TROUBLESHOOTING Fuel Pump Electrical Test For harness and connector layout diagrams and system electrical schematics, refer to System Wiring Diagrams and to System Electrical Schematics. CONNECTORS 5 12 13 24 4 1 8 5 27 B A B A 100075a Figure 6 — Rear Frame Harness Connectors 6 1 2 4A 4B A B A B 100076a Figure 7 — In-Tank Harness Connectors PROCEDURE Step 1 Procedure Check fuel pump circuit continuity. a. 2 3 b. Unplug the FPCM connector 12 for fuel pump 1. Check fuel pump circuit continuity. Using a multimeter, measure resistance between pin-5 and pin-8. c. Is resistance between 0.4–1.0 ohm? Check fuel pump circuit continuity. a. b. Unplug the FPCM connector 13 for fuel pump 2. Using a multimeter, measure resistance between pin-5 and pin-8. c. Is resistance between 0.4–1.0 ohm? Check resistance of each fuel pump. a. b. c. Page 38 Unplug the fuel pump connectors (in-tank harness) at the fuel pump assembly. Using a multimeter, measure resistance for fuel pump 1 across the terminals of the fuel pump. Is resistance between 0.4–1.0 ohm? Action Yes — Go to Step 2. No — Go to Step 3. Yes — Refer to the Fuel Pump Control Module Electrical Continuity Test procedure. No — Go to Step 3. Yes — Go to Step 4. No — Replace fuel pump assembly. TROUBLESHOOTING Step 4 Procedure Check resistance continued. a. b. 5 Using a multimeter, measure resistance for fuel pump 2 across the terminals of the fuel pump. Is resistance between 0.4–1.0 ohm? Check harness circuit continuity from fuel pumps to FPCM. a. b. Check continuity for pump 1, wire FPPWR, V+ across: 앫 Pin-A, connector 4A (in-tank harness) to pin-A, connector 1 (in-tank harness) 앫 Pin-A, connector 24 (rear frame harness) and pin-5, connector 12 (rear frame harness) Check continuity for pump 1, wire FPRTN, V– across: c. 앫 Pin-B, connector 4A (in-tank harness) to pin-B, connector 1 (in-tank harness) 앫 Pin-B, connector 24 (rear frame harness) and pin-8, connector 12 (rear frame harness) Check continuity for pump 2, wire FPPWR, V+ across: d. 앫 Pin-A, connector 4B (in-tank harness) to pin-A, connector 2 (in-tank harness) 앫 Pin-A, connector 27 (rear harness) and pin-5, connector 13 (rear harness) Check continuity for pump 2, wire FPRTN, V– across: e. 앫 Pin-B, connector 4B (in-tank harness) to pin-B, connector 2 (in-tank harness) 앫 Pin-B, connector 27 (rear frame harness) and pin-8, connector 13 (rear frame harness) Is there good continuity in all circuits? Action Yes — Go to Step 5. No — Replace fuel pump assembly. Yes — Refer to the Fuel Pump Control Module Electrical Continuity Test procedure. No — Repair circuit wiring. Page 39 TROUBLESHOOTING Fuel Pump Control Module Electrical Continuity Test For harness and connector layout diagrams and system electrical schematics, refer to System Wiring Diagrams and to System Electrical Schematics. CONNECTORS 7 A3 E4 FUSE BOX 6 4 5 3 5 1 2 4 3 5 1 2 4 B A 2 4 1 3 2 3 3 15 E 1 5 5 2 4 1 F A5 F E D C B A 100077a Figure 8 — Underhood Harness Connectors 8 1 12 13 27 1 4 4 1 5 8 8 5 30 A B C D E F A B 41 A B 100078a Figure 9 — Rear Frame Harness Connectors Page 40 TROUBLESHOOTING PROCEDURE Step Procedure Action For fuel pump control module (FPCM) functional testing and diagnostic trouble codes, refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual at www.motorcraft.com. 1 2 Check Ford FPCM circuit continuity to Ford harness. a. b. Disconnect rear frame harness connectors 1 and 12. Check for continuity in the rear frame harness across: c. 앫 Pin-1, connector 1 and pin-1, connector 12 앫 Pin-3, connector 1 and pin-3, connector 12 앫 Pin-4, connector 1 and pin-4, connector 12 앫 Pin-5, connector 1 and pin-5, connector 12 앫 Pin-6, connector 1 and pin-6, connector 12 앫 Pin-7, connector 1 and pin-7, connector 12 Is there good continuity in each circuit? Check FPCM circuit continuity to Ford harness. a. b. Disconnect rear frame harness connector 13. Check wire VPWR (V+) for continuity across: c. 앫 Pin-1, connector 13 (rear frame harness) and pin-A, connector 30 (rear frame harness) 앫 Pin-A, connector 15 (underhood harness) and cavity-A5, fuse box (underhood harness) 앫 Cavity-A3, fuse box (underhood harness) and cavity-E4, fuse box (underhood harness) Is there good continuity in each circuit? Yes — Go to Step 2. No — Repair circuit wiring. Yes — Go to Step 3. No — Repair circuit wiring. 3 Check fuse condition (E3-E4). Is the fuse blown? Yes — Replace the fuse. No — Go to Step 4. 4 Check Roush CleanTech FPCM circuit continuity to Ford harness. Yes — Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service a. Check for continuity in the rear frame harness across: Manual for functional testing of the FPCM. 앫 Pin-A, connector 30 and pin-1, connector 13 No — Repair circuit wiring. 앫 Pin-4, connector 1 and pin-4, connector 13 앫 Pin-A, connector 27 and pin-5, connector 13 앫 Pin-6, connector 1 and pin-6, connector 13 앫 Pin-B, connector 27 and pin-8, connector 13 앫 Pin-A, connector 41 and pin-7, connector 13 b. Is there good continuity in each circuit? Page 41 TROUBLESHOOTING Smart Relay Module Electrical Test For harness and connector layout diagrams and system electrical schematics, refer to System Wiring Diagrams and to System Electrical Schematics. CONNECTORS 9 E1-E2 4 5 3 2 E 1 6 1 3 5 1 2 4 31 F FUSE BOX 1 32 44 18 29 3 15 45 3 5 1 2 46 A1 PBT/ASA-GF20 2 4 3 5 1 31 16 17 B 2 4 3 5 A 2 4 1 30 100079a 2 Figure 10 — Underhood Harness Connectors 10 5 9 7 1 A C D 14 8 F 100080a Figure 11 — CAN Harness Connectors PROCEDURE Step Procedure Action 1 Disconnect the smart relay module (SRM) connector 1 (underhood harness). Go to Step 2. 2 Check for battery voltage (B+) to the SRM. Yes — Go to Step 5. No — Go to Step 3. a. b. 3 Check for battery voltage (B+) to the SRM. a. b. Page 42 Using a multimeter, check for B+ voltage at cavity 2, connector 1. Use a body ground for reference. Is there voltage (B+)? Check circuit continuity between cavity 2, connector 1 and cavity E2, auxiliary fuse box. Is there good continuity in the circuit? Yes — Go to Step 4. No — Repair circuit wiring. TROUBLESHOOTING Step 4 Procedure Check for battery voltage (B+) to the SRM. a. b. 5 Check the SRM ground circuit for continuity. a. b. 6 b. Check condition of fuse (F5-F6, 5A) in auxiliary fuse box. Is fuse blown? E-Series Only: Check CAN harness for SRM circuit continuity. a. b. 9 Using a multimeter, check the underhood harness for continuity in the E-Series system between pin-26, connector 1 and pin-A, connector 23 and in F-Series system between pin-26, connector 1 and pin-1, connector 51/55. Is there good continuity in the circuit? Check fuse. a. b. 8 Using a multimeter, check ground at cavity 31, connector 1 (underhood harness). Use a body ground for reference. Is there good continuity? Check for active signal to SRM. a. 7 Check condition of SRM power fuse (E1-E2, 25A) in the auxiliary fuse box. Is fuse blown? Check continuity between pin-A, connector 9 and pin-12, connector 5. Is there good continuity in the circuit? Check CAN and underhood harness continuity. a. Check CAN-H(+) continuity across: 앫 Pin-28, SRM connector 1 (underhood harness) and pin-C, connector 23 (underhood harness) Action Yes — Replace fuse. No — Go to Step 5. Yes — Go to Step 6. No — Repair circuit wiring. Yes — E-Series: Go to Step 8, F-Series: Go to Step 9. No — Go to Step 7. Yes — Replace fuse. No — Repair circuit wiring Yes — Go to Step 9. No — Repair circuit wiring. Yes — Go to Step 10. No — Repair circuit wiring. 앫 Pin-C, connector 9 (CAN harness) and pin-2, connector 5 (CAN harness) b. 10 Is there good continuity in the circuits? Check CAN and underhood harness continuity. a. Check CAN-H(−) continuity across: 앫 Pin-43, SRM connector 1 (underhood harness) and pin-B, connector 23 (underhood harness) 앫 Pin-B, connector 9 (CAN harness) and pin-3, connector 5 (CAN harness) b. Yes — Refer to the Ford Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Service Manual for functional testing of the CAN bus. No — Repair circuit wiring. Is there good continuity in the circuits? Page 43 TROUBLESHOOTING Fuel Level Sender Electrical Check For harness and connector layout diagrams and system electrical schematics, refer to System Wiring Diagrams and to System Electrical Schematics. CONNECTORS 11 1 15 30 31 32 44 18 29 3 15 45 1 2 46 A1 PBT/ASA-GF20 16 17 3 F E Figure 12 — Underhood Harness Connectors 12 21 30 A A B C B C D D E 100082a Figure 13 — Rear Frame Harness Connectors 13 1 6 A D C B A B 100083a Figure 14 — Solenoid Harness Connectors Page 44 F D C B A 100081a TROUBLESHOOTING PROCEDURE Step Procedure Action For fuel level sender (FLS) functional testing and diagnostic trouble codes, use Diagnostic Tests and Procedures and Diagnostic Trouble Codes. 1 2 3 4 5 Check resistance in FLS circuit wiring. a. b. Disconnect the SRM connector 1 (underhood harness). Using a multimeter, measure the resistance between pin-3 and pin-40 of the harness connector. c. Is resistance between 24–260 ohms? Check resistance of the FLS. a. b. Disconnect the FLS connector 6 (solenoid harness). Using a multimeter, measure the resistance across the FLS connector pins. c. Is resistance between 24–260 ohms? Check circuit wiring continuity between FLS connector and SRM connector. a. b. Disconnect connector 1 of the solenoid harness. Check continuity between pin-B, connector 6 (solenoid harness) and pin-C, connector 1 (solenoid harness). c. Is there good continuity in the circuit? Check circuit wiring continuity between FLS connector and SRM connector. a. b. Disconnect connector 30 of the rear frame harness. Check continuity between pin-C, connector 21 (rear frame harness) and pin-D, connector 30 (rear frame harness). c. Is there good continuity in the circuit? Check circuit wiring continuity between FLS connector and SRM connector. a. b. 6 b. 7 b. 8 b. Yes — Go to Step 5. No — Repair circuit wiring. Yes — Go to Step 6. No — Repair circuit wiring. Yes — Go to 7. No — Repair circuit wiring. Yes — Go to Step 8. No — Repair circuit wiring. Check continuity between pin-D, connector 21 (rear frame harness) and pin-C, connector 30 (rear frame harness). Is there good continuity in the circuit? Check circuit wiring continuity between FLS connector and SRM connector. a. Yes — Go to Step 4. No — Repair circuit wiring. Check continuity between pin-A, connector 6 (solenoid harness) and pin-D, connector 1 (solenoid harness). Is there good continuity in the circuit? Check circuit wiring continuity between FLS connector and SRM connector. a. Yes — Go to Step 3. No — Replace the FLS. With SRM connector 1 and connector 15 of the underhood harness disconnected, check continuity between pin-C, connector 15 and pin-3, SRM connector 1. Is there good continuity in the circuit? Check circuit wiring continuity between FLS connector and SRM connector. a. Yes — Refer to the Smart Relay Module Electrical Test procedure or the Fuel Level Interface Module Electrical Test procedure. No — Go to Step 2. Check continuity between pin-D, connector 15 (rear frame harness) and pin-40, SRM connector (underhood harness). Is there good continuity in the circuit? Yes — Refer to the Smart Relay Module Electrical Test procedure or the Fuel Level Interface Module Electrical Test procedure. No — Repair circuit wiring. Page 45 TROUBLESHOOTING Fuel Level Interface Module Electrical Test For harness and connector layout diagrams and system electrical schematics, refer to System Wiring Diagrams and to System Electrical Schematics. CONNECTORS 14 15 1 35 37 30 31 32 44 18 29 3 15 45 1 2 16 30 A B C D E 17 2 B A C D 100084a Figure 15 — Underhood Harness Connectors 100085a Figure 16 — Rear Frame Harness Connectors PROCEDURE Step Procedure Action For FLIM functional testing and diagnostic trouble codes, use Diagnostic Tests and Procedures and Diagnostic Trouble Codes. 1 2 Check FLIM circuit wiring for continuity to SRM. a. b. Disconnect underhood harness connector 1 to SRM. Check underhood harness continuity between pin-A, connector 35 and pin-2, connector 1. c. Is there good continuity in the circuit? Check FLIM circuit wiring for continuity to SRM. a. b. 3 b. 4 Check underhood harness continuity between pin-C, connector 35 and body ground. Is there good continuity in the circuit? Check FLIM circuit wiring for continuity to SRM. a. b. c. Page 46 Check underhood harness continuity between pin-B, connector 35 and pin-37, connector 1. Is there good continuity in the circuit? Check FLIM circuit wiring for continuity to SRM. a. F 46 A1 PBT/ASA-GF20 9 Disconnect underhood harness connector 15 to rear frame harness. Check underhood harness continuity between pin-D, connector 35 and pin-F, connector 15. Is there good continuity in the circuit? Yes — Go to Step 2. No — Repair circuit wiring. Yes — Go to Step 3. No — Repair circuit wiring. Yes — Go to Step 4. No — Repair circuit wiring. Yes — Go to Step 5. No — Repair circuit wiring. TROUBLESHOOTING Step 5 Procedure Check FLIM circuit wiring for continuity to SRM. a. b. Disconnect rear frame harness connector 9 to Ford harness. Check rear frame harness continuity between pin-F, connector 30 and pin-2, connector 9. c. Is there good continuity in the circuit? Action Yes — Refer to the Smart Relay Module Electrical Test procedure. No — Repair circuit wiring. Page 47 WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS Page 48 WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS E-150/150/350 Extended Wiring Harnesses and Connector Layout E-150/250/350 WIRING HARNESSES AND CONNECTOR LAYOUT APPROXIMATE LOCATION OF LPA SYSTEM HARNESSES AND CONNECTORS 8 5 1 11 27 GND R1 GND R2 23 9 35 1 PASS THRU 15 30 47 41 9 UNDER BODY LPA FUEL TANK 6 4A 7 9 4B GND 4 1 1 27 24 21 13 12 1 UNDERHOOD HARNESS CAN HARNESS REAR FRAME HARNESS IN-TANK HARNESS SOLENOID HARNESS Page 50 100129a WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS E-150/250/350 Extended Range Wiring Harnesses and Connector Layout IN-VEHICLE LPA FUEL TANK 6 4A 7 9 4B 8 5 1 11 27 GND R1 GND R2 23 9 PASS THRU 35 1 15 30 9 GND 4 1 1 13 16 9 E-150/250/350 EXTENDED RANGE WIRING HARNESSES AND CONNECTOR LAYOUT APPROXIMATE LOCATION OF LPA SYSTEM HARNESSES AND CONNECTORS 13 12 1 47 41 1B 1A 4 27 24 21 GND UNDERHOOD HARNESS CAN HARNESS REAR FRAME HARNESS IN-TANK HARNESS SOLENOID HARNESS IN-BED FUEL TANK JUMPER 100152a Page 51 WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS E-450 Custom Body Wiring Harnesses and Connector Layout E-450 WIRING HARNESSES AND CONNECTOR LAYOUT APPROXIMATE LOCATION OF LPA SYSTEM HARNESSES AND CONNECTORS 8 5 1 11 27 GND R1 GND R2 23 9 PASS THRU 35 1 15 30 47 41 1 12 13 GND AFT-AXLE LPA FUEL TANK 6 4A 7 9 4B 4 1 1 27 24 21 UNDERHOOD HARNESS CAN HARNESS REAR FRAME HARNESS IN-TANK HARNESS SOLENOID HARNESS IN-BED FUEL TANK JUMPER Page 52 100153a WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS F-250/350 Pickup, In-Bed Tank Wiring Harnesses and Connector Layout F-250/350 PICKUP, IN-BED TANK WIRING HARNESSES AND CONNECTOR LAYOUT APPROXIMATE LOCATION OF LPA SYSTEM HARNESSES AND CONNECTORS GND R2 1 8 4A 4B 1 13 12 * GND 1B 1A 4 27 24 21 GND 6 15 30 9 4 11 1 4 1 16 13 9 5 1 51 55 35 PASS THRU 9 23 9 7 + – GND R1 6 BATTERY IN-BED LPA FUEL TANK 27 1 47 41 UNDERHOOD HARNESS CAN HARNESS *FTPT Harness depends upon the Ford Fuel Tanks REAR FRAME HARNESS IN-TANK HARNESS SOLENOID HARNESS IN-BED FUEL TANK JUMPER FTPT JUMPER HARNESS 100187a Page 53 WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — Underhood Harness 1 A 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 A UNDERHOOD HARNESS PWR_W PWR 10 Delphi Terminal 02984789 Connector B 1 To Battery Positive TO SRM C 2 D 3 5 31 43 37 40 28 25 44 26 29 1 D C D D F A SUPPLY_SOL FLOW_CNTL_ SOL B BLEED_SOL E A F C S5 B E SUPPLY_SOL_RTN E FLOW_CNTL_SOL_RTN F6 F BLEED_SOL_RTN E6 KEY_PWR_2 H 11 4 IPTS_PWR PWR_W_6 F4 5A 3 IPTS_TEMP_OUT E4 F3 G KEY_PWR_3 20A F5 2 IPTS_PRES_OUT E2 E5 C TO IPTS 46 F2 E3 S4 F 20 36 10A F1 PWR_W_3 17 35 3 SRM_PWR 25A E1 PWR_W_2 15 34 8 Connector IPTS_GND PWR_W_1 E 7 33 1 B TO SOLENOID MODULE Connector 4 2 G H I I CIT RELAY A11CSQ 20A@14VDC J J A2 A5 A3 A4 A1 A1 = 85 A2 = 86 A3 = 30 A4 = 87A A5 = 87 K K Connector L ELECTRICAL CENTER M S1 SOLENOID_PWR 27 L M A KEY_PWR_4 Connector B 35 N D A TO FUEL LEVEL INTERFACE MODULE O D O C C FG_RTN B FG_RTN_SRM N P P FG_SND Q Connector F FRAME GROUND (GND_R2) DELPHI TERMINAL 02984626 S3 FL_RTN_1 R D FL_RTN_2 15 Q TO REAR FRAME HARNESS R E TANK_SOL_RTN C FL_SND B VPWR_RI S S A VPWR_RO T T Connector U B PLUG GND3 FPM_2 A GND1 V E C Y PLUG CAN-H_1(+) CAN-H_1(-) B FRAME GROUND (GND_R1) DELPHI TERMINAL 02984172 PLUG D C X U V F W LAMP_RTN_1 47 TO REAR FRAME HARNESS B A S2 GND2 A KEY_PWR_1 W D X Connector 23 A F TO CAN HARNESS Z 100130b 1 Page 54 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 Y Z WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — CAN Bus Harness E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — CAN Bus Harness 1 A 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 7 CAN BUS HARNESS 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 1 A B B Connector 5 C C CONNECT TO FORD HARNESS CONNECTOR C2142 8 2 8 3 E 10 5 11 7 6 12 13 14 FUSE_33_2 9 4 E D 1 14 D F C F E D C B A KEY_PWR_1 10 CAN-H(-)_2 BRK_PED_POS I 4 CAN-H(+)_2 H 3 PLUG PLUG 9 PLUG CAN-H(-)_1 11 GND J 5 J G 2 CAN-H(+)_1 I F 8 FUSE_18 H 8 1 D G 1 12 FUSE_33_1 6 S1 K 13 K 7 TOW_BRK A 14 F L L Connector 9 7 CONNECT TO ROUSH UNDERHOOD HARNESS M CONNECT TO TRAILER BRAKE MODULE 14 M Connector 1 N N 100131b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 Page 55 WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — Rear Frame Harness E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — Rear Frame Harness 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 REAR FRAME HARNESS 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 A TO ROUSH FPCM MODULE (FUEL PUMP CONTROL MODULE)_2 B Connector Connector 13 12 TO FORD FPCM MODULE (FUEL PUMP CONTROL MODULE)_1 B Connector 1 2 3 4 8 5 7 6 C ENS_2 7 SHILED_3 6 GND_2 5 PLUG 8 FPC_2 4 VPWR_2 3 SHILED_4 VPWR_P2 B PLUG ENS_1 Connector Connector S4 30 PLUG S3 VPWR_RI 2 PLUG B VPWR_1 S1 C VPWR_RI H D H F G 1 A CONNECT TO FORD HARNESS FPCM S2 VPWR_RO S5 G FPC_1 3 F 4 GND_1 E 1 5 TO ROUSH UNDERHOOD HARNESS 7 FPM_1 A E D 8 PLUG FPM_2 6 D 2 ENS_3 1 TO ROUSH UNDERHOOD HARNESS GND_3 C PLUG 41 FPC_3 A 2 S6 SHILED_5 E I D C B FG_SND PLUG 3 2 SHILED_1 A_FPPWR_1 A_FPRTN_1 K A B A Connector 21 PLUG PLUG 4 M J A B L SHILED_2 A_FPRTN_2 SHILED FRAME GROUND (GND) DELPHI TERMINAL 02984626 A_FPPWR_2 K A_SOL_1 J A_SOLRTN_1 A_FLS_1 A_FLSRTN_1 F I TO FUEL TANK_SENDER_SOLONOID 1 Connector Connector 27 24 L M TO FUEL_TANK_1_PWR TO FUEL_TANK_2_PWR Connector N N 9 O O CONNECT TO FORD HARNESS FUEL PUMP MODULE P 100132b 1 Page 56 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 P WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — In-Tank Harness E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — In-Tank Harness 1 A 2 WIRE NO. 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 B C D 3 4 5 6 DESCRIPTION PINK/BLACK 12 AWG BROWN/WHITE 12 AWG DARK BLUE 12 AWG BLACK 12 AWG PINK/BLACK 12 AWG BROWN/WHITE 12 AWG DARK BLUE 12 AWG BLACK 12 AWG 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 IN-TANK HARNESS CIRCUIT INLINE FUEL PUMP-1 (V+) INLINE FUEL PUMP-1 (V-) INLINE FUEL PUMP-2 (V+) INLINE FUEL PUMP-2 (V-) FUEL PUMP-1 (V+) FUEL PUMP-1 (V-) FUEL PUMP-2 (V+) FUEL PUMP-2 (V-) A B C IN-TANK HARNESS PASS THRU E D E 200MM 100MM NO TAPE OR ADHESIVE TAGS ON THIS SIDE OF THE PASS THROUGH GROMMET F DO NOT COVER THIS LENGTH WITH ANY CONVOLUTE F G G 1 H H I 5 A B J K 9 6 A 10 I PUMP-1 J 4A B K 100MM DO NOT COVER THIS LENGTH WITH ANY CONVOLUTE L M L 7 A B 11 8 12 N 4B A B N THIS AREA TO BE FREE OF TAPE. 2 DO NOT APPLY TAPE ONTO THIS SEALING SURFACE O 1 2 3 4 M PUMP-2 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 100133b 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 O 39 Page 57 WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS E-Series Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — E-Series, Extended Range and E-450 Electrical Schematic — Solenoid Harness Solenoid 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 A A WIRE NO. 4 5 6 7 B C D E DESCRIPTION RED 16 AWG BLACK 16 AWG BLACK/ORANGE 18 AWG YELLOW/WHITE 18 AWG SOLENOID HARNESS CIRCUIT SUPPLY SOLENOID V+ SUPPLY SOLENOID VFUEL LEVEL SENDER VFUEL LEVEL SENDER V+ B C 9 D E CONNECT TO THE REAR HARNESS F G F 1 CONNECT TO TANK SOLENOID 100 mm G H H I I A B J K A 4 B 5 J K L L M M 6 C N B N O O D 7 A P P Q Q R R CONNECT TO FUEL LEVEL SENDER S S T T U U 6 V V W 100134b 1 Page 58 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 W WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS Harness F-250/350 Pickup, Underhood Harness Electrical Schematic 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 PWR_W A Connector 1 B TO SRM C 2 D 7 33 17 15 34 35 20 36 40 43 37 28 25 44 26 29 D C C H B E A E F A B F SUPPLY_SOL D FLOW_CNTL_ SOL E SUPPLY_SOL_RTN G F BLEED_SOL KEY_PWR_2 F6 C FLOW_CNTL_SOL_RTN E6 5A F5 IPTS_PRES_OUT E5 PWR_W_6 S4 F4 TO IPTS 4 D F2 F3 3 46 20A E4 2 11 TO FRPCM SRM_PWR_1 10A E3 8 3 1 IPTS_GND F1 PWR_W_3 F E2 E1 PWR_W_2 E SRM_PWR 25A 5 31 S5 PWR_W_1 3 1 B Connector Connector 4 2 BLEED_SOL_RTN PWR Delphi Terminal 02984789 To Battery Positive IPTS_PWR A 2 IPTS_TEMP_OUT 1 G H I I CIT RELAY A11CSQ 20A@14VDC A2 J A3 A4 A5 J A1 A1 = 85 A2 = 86 A3 = 30 A4 = 87A A5 = 87 K K Connector 8 16 R N 9 1 35 TO FLIM 3 10 2 FG_RTN O 11 4 12 P 13 5 FRAME GROUND (GND_R2) DELPHI TERMINAL 02984626 14 Connector F 6 FG_SND FL_RTN_2 S3 FL_RTN_1 FL_SND Q TO REAR FRAME HARNESS R S B VPWR_RI S 15 E 7 TANK_SOL_RTN 15 15 7 Q FG_RTN_SRM 8 10 3 11 4 12 14 6 13 5 P J1A Connector D O J1 J9 J2 J10 J3 J11 J4 J12 J5 J13 J6 J14 J7 J15 J8 J16 M SRM_PWR_2 TO FORD HARNESS 12C508 (C1168) S8 C 2 9 N 55 B 1 TO FORD AUX ENGINE INLINE MODULE L A ELECTRICAL CENTER (FUSE BOX) M S1 SOLENOID_PWR Connector D 51 C Connector 16 27 KEY_PWR_1 L A VPWR_RO T T Connector U GND3 A FPM_2 GND1 V PLUG CAN-H_1(+) Y TO REAR FRAME HARNESS V W F E FRAME GROUND (GND_R1) DELPHI TERMINAL 02984172 PLUG D X LAMP_RTN_1 U X Connector 23 C W 47 B PLUG S2 GND2 TO CAN HARNESS B CAN-H_1(-) Z 100188a 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 Y Z 39 Page 59 WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS F-250/350 Pickup, CAN Bus Jumper Harness Electrical Schematic 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 A A B B Connector 5 C C CONNECT TO FORD HARNESS CONNECTOR C2142 3 2 8 9 4 10 5 11 7 6 12 13 14 E D 1 D E COVERED WITH 3/8" SPLIT CONVOLUTE F F F PLUG E H PLUG D C B I 11 GND J 5 FUSE_33 PLUG 12 A 10 CAN-H(-)_2 BRK_PED_POS 4 J PLUG CAN-H(+)_2 H 3 CAN-H(-)_1 I G 2 CAN-H(+)_1 9 FUSE_18 PASS-THROUGH 8 1 G 6 K 13 GROMMET K 7 NO CONVOLUTE, TAPE ONLY THIS AREA 14 TOW_BRK Connector L L 9 CONNECT TO TRAILER BRAKE MODULE CONNECT TO ROUSH UNDERHOOD HARNESS M M Connector 1 N N 100189a 1 Page 60 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS F-250/350 Pickup, Rear Frame Harness Electrical Schematic 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 A A TO ROUSH FPCM (FUEL PUMP CONTROL MODULE)_2 Connector 30 Connector 13 12 1 4 8 5 6 7 1 2 3 8 4 5 B 7 6 C ENS_2 SHILED_3 GND_2 PLUG FPC_2 VPWR_2 PLUG SHILED_4 C ENS_3 B PLUG VPWR_RI D 3 TO ROUSH FPCM (FUEL PUMP CONTROL MODULE)_1 VPWR_RO VPWR_P2 A C 2 GND_3 B Connector FPC_3 TO UNDERHOOD HARNESS D E 7 6 ENS_1 F E D 8 PLUG FPM_1 4 GND_1 S3 FPC_1 CONNECT TO FORD HARNESS FPCM 3 S5 S2 2 PLUG VPWR_RI VPWR_1 1 G E 1 5 PLUG F r Connector S4 F G S1 Connector 41 H H A SHILED_5 S6 K D C B 3 2 B SHILED_1 A L 21 TO FUEL TANK_SENDER_SOLONOID 1 Connector Connector 27 24 M TO FUEL_TANK_1_PWR TO FUEL_TANK_2_PWR N A_FPPWR_1 A_FPRTN_1 SHILED_2 K A Connector FG_RTN PLUG 4 FG_SND PLUG M J A B L A_FPPWR_2 SHILED FRAME GROUND (GND3) DELPHI TERMINAL 02984626 A_FPRTN_2 A_SOL_1 A_SOLRTN_1 A_FLS_1 J I PLUG TO UNDERHOOD HARNESS A_FLSRTN_1 B I N Connector 9 O O CONNECT TO FORD HARNESS FUEL PUMP MODULE P 100190a 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 P 39 Page 61 WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS F-250/350 Pickup, Tank Solenoid Harness Electrical Schematic 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 A A WIRE NO. 4 5 6 7 B C D DESCRIPTION RED 16 AWG BLACK 16 AWG BLACK/ORANGE 18 AWG YELLOW/WHITE 18 AWG CIRCUIT SUPPLY SOLENOID V+ SUPPLY SOLENOID VFUEL LEVEL SENDER VFUEL LEVEL SENDER V+ B C D 9 E E F F CONNECT TO REAR FRAME HARNESS G H 1 G CONNECT TO TANK (FUEL SUPPLY) SOLENOID 100 mm H I I J J A B K L M A 4 B 5 K L M N N 6 D 7 O P A P C B O Q Q R R 12162000 S CONNECT TO FUEL LEVEL SENDER FUEL LEVEL SENDER CONNECTOR FROM TANK S T T U U 6 V V W 100191a 1 Page 62 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 W WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS F-250/350 Pickup, In-Bed Fuel Tank Jumper Harness Electrical Schematic 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 CONNECT TO TANK SOLENOID HARNESS A A B B Connector 16 CONNECT TO REAR FRAME HARNESS C PUMP_1 C A Connector D D B 1A FUEL_PUMP_1_PWR A E B F F A FUEL_PUMP_2_PWR FUEL_PUMP_2_RTN SHIELD_1 Connector H 1B G S1 B SHIELD_3 SHIELD_2 A B G E FUEL_PUMP_1_RTN H Connector CONNECT TO REAR FRAME HARNESS I 13 SHILED FRAME GROUND (GND) DELPHI TERMINAL 02984626 J I PUMP_2 J CONNECT TO TANK SOLENOID HARNESS C FUEL_LEVEL _SENDER RETURN A TANK (FUEL SUPPLY) SOLENOID_POWER L B N TANK (FUEL SUPPLY) SOLENOID _RETURN A M B L K C FUEL_LEVEL _SENDER POWER D D K M Connector Connector 4 9 N O O CONNECT TO TANK SOLENOID HARNESS CONNECT TO REAR FRAME HARNESS P 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 100192a 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 P 39 Page 63 WIRING DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS F-250/350 Pickup, FTPT Jumper Harness Electrical Schematic 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 3 FTP_REF 2 C SIGRTN FTP FTP 1 D SIGRTN 3 FTP_REF B B 2 A C 1 A D E r Connector F Connector F 1 4 VERSION DEPENDS ON TANK CONFIGURATION G G CONNECT TO FTPT CONNECT TO FORD HARNESS (14405) E H H I I FTP_REF A L SIG_RTN SIG_RTN FTP FTP 3 B K J 2 J K 1 C FTP_REF L M M Connector 1 N N Connector 6 O CONNECT TO FTPT O CONNECT TO FORD HARNESS (14405) P 100193a 1 Page 64 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 P ©2013 by ROUSH CleanTech. All rights reserved. The information in this publication was accurate and effective at the time the publication was approved for publishing and is subject to change without notice or liability. ROUSH CleanTech reserves the right to revise the information herein and to make changes and discontinue production of described parts at any time. LocTite567® and LocTite242® are registered trademarks of Henkel.