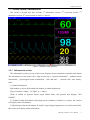
Download About the User`s Manual
Transcript
About the User’s Manual The User’s Manual serves for operating this instrument only. Our company shall not be responsible for any consequences and liabilities caused by using this user’s manual for other purposes. The User’s Manual containing special information is under copyright protection. All rights reserved. Copy, duplication or translation of the whole or any part of the User’s Manual is prohibited in case of no prior written consent from our company. Based on the need of product technical improvement or the file updates, we reserve the right to modify the contents contained in this manual , if the change do not involve safety issues, the contents are subject to amend without notification Due to technical upgrade or special requirements from users and with the precondition that the performance of the instrument will not be lowered, some components may vary from the description of configuration in the User’s Manual. Version:1.0 2011---08 All rights reserved © Shenzhen Biocare Electronics Co., Ltd The CE mark is a protected conformity mark of European Community. The products herewith comply with the requirements of the Medical Device Directive 93/42/EEC Shanghai International Holding Corp. GmbH(Europe) Eiffestraϐe 80 20537 Hamburg GERMANY Shenzhen Biocare Electronics Co.,Ltd. 2nd.Floor, Baili Park, No.636 Baotian 1st Road Tiegang, Baoan, Shenzhen, China Tel: 86-755-27960641 Fax: 86-755-27960643 Website: http://www.biocare.com.cn CONTENTS CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................................................. 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................................................................. 1 SAFETY INFORMATION .............................................................................................................................................. 1 DEVICE LABEL......................................................................................................................................................... 4 INTENDED USAGE .................................................................................................................................................... 4 SCREEN LAYOUTS INTRODUCTION................................................................................................................................ 5 ALARM ................................................................................................................................................................. 7 CONTROL PANEL...................................................................................................................................................... 7 MENU .................................................................................................................................................................. 7 SENSOR SOCKET .................................................................................................................................................... 14 EXTERNAL INTERFACE ............................................................................................................................................. 14 NETWORKS .......................................................................................................................................................... 15 RECHARGEABLE BUILT‐IN BATTERY ............................................................................................................................. 15 INSTALLATION ....................................................................................................................................................... 16 POWER ON THE MONITOR ...................................................................................................................................... 16 CONNECT SENSORS ............................................................................................................................................... 16 CHECK THE RECORDER............................................................................................................................................ 17 CHAPTER 2 ALARMS............................................................................................................................................... 18 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 ALARMS OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................................................... 18 ALARMS PAUSING .................................................................................................................................................. 19 ALARMS SILENCE ................................................................................................................................................ 19 ALARM SETTING ................................................................................................................................................... 19 LIMITS OF THE ALARMS........................................................................................................................................... 20 PHYSIOLOGY ALARM INFORMATION ........................................................................................................................... 23 TECHNICAL ALARM INFORMATION............................................................................................................................. 25 CHAPTER 3 RECORD ............................................................................................................................................... 29 3.1 3.2 3.3 RECORD SETTING................................................................................................................................................... 29 RECORD TYPE ....................................................................................................................................................... 29 RECORD CONTENT ................................................................................................................................................. 30 CHAPTER 4 ADMIT/DISCHARGE ANIMAL ................................................................................................................ 31 4.1 4.2 ADMIT VETERINARY ............................................................................................................................................... 31 DISCHARGE ANIMAL............................................................................................................................................... 31 CHAPTER 5 ECG MONITORING................................................................................................................................ 33 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 CONNECTING ECG ELECTRODES ............................................................................................................................... 33 ECG ELECTRODE PLACEMENT .................................................................................................................................. 33 CONNECTING ECG LEADS RECOMMENDED FOR SURGERY............................................................................................... 34 ECG SETTING ....................................................................................................................................................... 35 CHAPTER 6 RESP MONITORING .............................................................................................................................. 37 6.1 6.2 6.3 PRINCIPLES OF RESPIRATION MEASUREMENT............................................................................................................... 37 PLACING THE ELECTRODES ....................................................................................................................................... 37 RESP SETTINGS ..................................................................................................................................................... 37 CHAPTER 7 SPO₂ MONITORING.............................................................................................................................. 39 7.1 7.2 7.3 MONITORING PROCEDURE ...................................................................................................................................... 39 MEASUREMENT RESTRICTIONS ................................................................................................................................. 40 SPO₂ SETTING ...................................................................................................................................................... 41 CHAPTER 8 NIBP MONITORING .............................................................................................................................. 43 8.1 8.2 NIBP MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE............................................................................................................................ 43 NIBP MEASUREMENT LIMITS ................................................................................................................................... 44 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual I CONTENTS 8.3 8.4 8.5 NIBP SETTINGS .................................................................................................................................................... 45 BLOOD PRESSURE CALIBRATIONS............................................................................................................................... 45 LEAKAGE EXAMINATION .......................................................................................................................................... 46 CHAPTER 9 TEMPERATURE MONITORING............................................................................................................... 48 9.1 9.2 STEPS OF TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT .................................................................................................................... 48 TEMPERATURES SETTINGS MENU .............................................................................................................................. 48 CHAPTER 10 HISTORY REVIEW................................................................................................................................ 49 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 TREND GRAPH ...................................................................................................................................................... 49 TREND TABLE ........................................................................................................................................................ 51 ALARM REVIEW .................................................................................................................................................... 52 NIBP REVIEW ...................................................................................................................................................... 54 WAVE REVIEW ...................................................................................................................................................... 55 CHAPTER 11 DRUG CALCULATION .......................................................................................................................... 57 11.1 11.2 11.3 DRUG CALCULATION .............................................................................................................................................. 57 OPERATING PROCEDURES ........................................................................................................................................ 58 TITRATION TABLE ................................................................................................................................................... 58 CHAPTER 12 MAINTENANCE AND CLEANING .......................................................................................................... 60 12.1 SYSTEM CHECK ..................................................................................................................................................... 60 12.2 GENERAL CLEANING .............................................................................................................................................. 60 CLEANING AGENTS............................................................................................................................................................. 61 STERILIZATION ................................................................................................................................................................... 62 DISINFECTION ................................................................................................................................................................... 62 APPENDIX A PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................................................. 63 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 12.7 12.8 12.9 12.10 12.11 12.12 12.13 12.14 CLASSIFICATION .................................................................................................................................................... 63 POWER SUPPLY ..................................................................................................................................................... 63 BATTERY .............................................................................................................................................................. 63 SIGNAL INTERFACE................................................................................................................................................. 63 STORAGE ............................................................................................................................................................. 63 ENVIRONMENT ..................................................................................................................................................... 64 ECG................................................................................................................................................................... 64 RESPIRATION .................................................................................................................................................... 65 NIBP ............................................................................................................................................................. 66 SPO₂ ............................................................................................................................................................. 66 TEMPERATURE .................................................................................................................................................. 67 RECORDER(OPTIONAL) ....................................................................................................................................... 67 APPENDIX B EMC ‐ GUIDANCE AND MANUFACTURE’S DECLARATION...................................................................... 68 II Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter1 Overview Chapter 1 Overview 1.1 Overview This monitor is suitable for felines, canines and other animals, may monitor the physical parameters, such as electrocardiograph (ECG), noninvasive blood pressure (NIBP), oxygen saturation (SpO₂), respiration rate (Resp), body temperature (Temp) and so on, can display maximum 8 waveforms and all information of the parameters monitored in the same screen. Below shows the monitoring functions of this monitor: 1) electrocardiograph (ECG), including: heart rate, 6 channels ECG waveforms, ST segment analysis, arrhythmia analysis; 2) oxygen saturation (SpO₂), including: oxygen saturation, pulse rate, pulse wave; 3) noninvasive blood pressure (NIBP), including: Systolic pressure, diastolic pressure, mean pressure; 4) body temperature (Temp): 2 channels body temperature data; 5) respiration (Resp): Breath rate, breath waveform; 1.2 Safety information NOTE Points to be noted. CAUTION Points to be noted to avoid damage to the equipment. WARNING Points to be noted to avoid injury to the Veterinary and the operator. Warning z Do not rely only on audible alarm system to monitor animals. When monitoring adjusting the volume to very low or completely muting the sound may result in the disaster to the animals. The most reliable way of monitoring the animals is at the same time of using monitoring equipment correctly, manual monitoring should be carried out. z This multi-parameter Veterinary monitor is intended for use only by medical professionals in health care institutions. z To avoid electrical shock, you shall not open any cover by yourself. Service must be carried out by qualified personnel. z Use of this device may affect ultrasonic imaging system in the presence of the interfering signal on the screen of ultrasonic imaging system. Keep the distance between the monitor and the ultrasonic imaging system as far as possible. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 1 Chapter1 Overview z It is dangerous to expose electrical contact or applicant coupler to normal saline, other liquid or conductive adhesive. Electrical contact and coupler such as cable connector, power supply and parameter module socket-inlet and frame must be kept clean and dry. Once being polluted by liquid, they must be thoroughly dried. If to further remove the pollution, please contact your biomedical department or Factory. Warning Monitor can only monitoring one animal at a time. Warning There could be hazard of electrical shock by opening the monitor casing. All servicing and future upgrading to this equipment must be carried out by personnel trained and authorized by Factory. Warning You must verify if the device and accessories can function safely and normally before use. Warning Possible explosion hazard if used in the presence of flammable anesthetics or other flammable substance in combination with air, oxygen-enriched environments, or nitrous oxide. Warning You must customize the alarm setups according to individual animal situation and make sure that alarm sound can be activated when alarm occurs. Warning Do not touch the animal, table, or the device during defibrillation. Warning Do not use cellular phone in the vicinity of this device. High level electromagnetic radiation emitted from such devices may greatly affect the monitor performance. Warning Devices connected to the monitor shall form an equipotential system (protectively earthed). Connect the grounding wire to the equipotential grounding terminal on the main system. If it is not evident from the instrument specifications whether a particular instrument ombination is hazardous or not, for example due to summation of leakage currents, the user should consult the manufacturers concerned or else an expert in the field, to ensure that the necessary safety of all instruments concerned will not be impaired by the proposed combination. 2 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter1 Overview Warning When used with Electro-surgery equipment, you (doctor or nurse) must give top priority to the animal safety. Warning Do not place the monitor or external power supply in any position that might cause it to fall on the animal. Do not lift the monitor by the power supply cord or cable, use only the handle on the monitor. Warning Consult IEC-601-1-1 for system interconnection guidance. The specific requirements for system interconnection are dependent upon the device connected to the monitor and the relative locations of each device from the animal, and the relative location of the connected device to the medically used room containing the monitor. In all circumstance the monitor must be connected to a grounded AC power supply. The monitor is referred to as an IEC 601/F device in the summary of situations table contained in IEC 601-1-1. Warning Dispose of the packaging material, observing the applicable waste control regulations and keeping it out of children’s reach. Warning Grounding: Connect the monitor only to a three-wire, grounded, hospital-grade receptacle. The three-conductor plug must be inserted into a properly wired three-wire receptacle; if a three-wire receptacle is not available, a qualified electrician must install one in accordance with the governing electrical code. Do not under any circumstances remove the grounding conductor from the power plug. Do not use extension cords or adapters of any type. The power cord and plug must be intact and undamaged. If there is any doubt about the integrity of the protective earth conductor arrangement, operate the monitor on internal battery power until the AC power supply protective conductor is fully functional. Warning For continued safe use of this equipment, it is necessary that the listed instructions be followed. However, instructions listed in this manual in no way supersede established medical practices concerning animal care. Warning It is important for the hospital or organization that employs this equipment to carry out a reasonable maintenance schedule. Neglect of this may result in machine breakdown or injury of human health. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 3 Chapter1 Overview Caution If you have any doubt to the grounding layout and its performance, you must use the built-in battery to power the monitor. 1.3 Device Label This symbol means ”BE CAREFUL“. Refer to the manual. This symbol indicates that the instrument is IEC 60601-1 Type CF applied part. The unit displaying this symbol contains an F-Type isolated (floating) applied part providing a high degree of protection against shock, and is suitable for use during defibrillation. Equipotential grounding system. Protective earth ground. Power On/Off AC power This symbol indicates that the instrument is IEC 60601-1 Type BF applied part. 1.4 Intended Usage The monitor is intended to be used for monitoring, recording, and alarming of multiple physiological parameters of animal in health care facilities. The devices are to be used in health care facilities by trained health care professionals. They are not intended for home use. This device is restricted to be used by or on the order of a physician. Not a therapeutic device. 4 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter1 Overview 1.5 Screen layouts introduction The screen is divided into four sections: 1st information section; 2nd waveform section; 3rd parameters section; 4th menu section (as chart 1-1 shows). Chart 1-1 monitor demo interface 1.5.1 Information section The information section is on top of the screen, displays current conditions of monitor and animal. The information in turn from left to right on the top is “Animal information”, “technical alarm information”, “physiological alarm information”, “date and time” , “network state” and “battery state”. 1) Animal information: Bed number (refers to the hospital bed number of animal monitored); Type of animal (“>20kg”, “10~20kg” or “<10kg”); Name of animal (if operator doesn’t input animal name, this position will displays “NO NAME”); 2) Technical alarm information: Reporting current condition of monitor or sensors, this section will display alarm information; 3) Physiological alarm information: If animal 's physiological parameters exceed the alarm limit, this section will display alarm information; Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 5 Chapter1 Overview 4) Date and time: Updating current date and time every second; 5) Network connection state; 6) Battery state: current battery capacity or its condition. 1.5.2 Parameters section Heart rate: heart rate (unit: beats per minute bpm) ST: ST segment (unit: millivolt mV) PVCs: times of premature ventricular constriction (unit: times/minute) NIBP: From right to left is: systolic pressure, diastolic pressure, mean pressure (unit: millimeter mercury column- mmHg or kilopascal- kPa) SpO₂: oxygen saturation SpO₂ (unit: %), Pulse rate (unit: pulses /minute) Respiration rate: respiration rate (unit: Breaths/Minute BrPM) Temperature: body temperature (unit: centigrade -℃ or Fahrenheit- ℉) The user may change the settings of above monitored parameters which will be introduced in later chapters in detail. 1.5.3 Waveform section The waveform section displays 7 waveforms in standard screen layout, which from top to bottom respectively are: ECG1 waveform, ECG2 waveform, pulse wave, respiration waveform,. Total 8 waveforms can be displayed if in “ECG Full Lead” screen layout. The name appears in upper left side of each waveform. The ECG waveform gain and filter mode will be also displayed besides the ECG wave name. On the right side of the ECG waveform stands a mark with the unit of 1 mV. The gain of breathing waveform is displayed on the right side of the name of breathing wave.. When user push the keys of monitor, a window may pop-up in the waveform section. The waveform section will restore demo after the window is retreated. 1.5.4 Menu section On the bottom of the screen there are 5 menu item: “Animal”, “Review”, “Setting”, “Alarm Limit” and “Service”. When no window displays on the screen, the user may visit these menus by rotating the knobs. When the cursor chooses anyone of the items, sublevel menus will popup. When the user presses down the knob once again, the corresponding dialog will pop-up and the user can change the settings in the dialog. 6 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter1 Overview 1.6 Alarm When the alarm occurs, the warning light will glitter or bright, the color represents certain level of the alarm. The detailed contents please refer to chapter2 “Alarm”. 1.7 Control panel The control panel is on the front panel. The total keys from left to right are listed below: 1) Power key: key to turning on and turning off of the power; 2) Alarm silence key: With this key pressed down, sound of the alarm will shut down, also the “ALARM SILENCE” will be displayed in the information section, and other sounds (key sound, palpitation sound and so on) will not be affected. Pressing down the key again will restore all the alarms. 3) Alarm pausing key: With this key pressed down, the alarm may hang up for 2 minutes (“1 minute”, “2 minutes” and “3 minutes” are optional), and the “ALARM PAUSE” will be displayed in the information section. All the alarm will be restored after this key is pressed again. 4) Freezing key: In the normal mode, all the waveforms on the screen will be frozen with this key pressed down. Pressing down this key once again will release the frozen waveforms; 5) Blood pressure key: Pressing down this key will start to charge the cuff with gas, and to measure the blood pressure. Pressing down the key once again can cancel the measurement; 6) Record/Stop key: If the monitor has a recorder, pressing down this key will start recording the real-time waveforms. Pressing the key again may stop recording; 7) Main menu key: press this key to returning to the main menu; 8) Knob key: With this key, the user may enter the menus and windows and change the monitor settings. 1.8 Menu 1.8.1 animal management By pushing the “Animal” button, the user may choose to enter the window of “Admit new Animal”, “Discharge Current Animal” or “Dose Calculation” the detailed introductions may refer to chapter4 “Admit and Discharge Veterinary”. Chart 1-3 Animal management Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 7 Chapter1 Overview 1.8.2 History review By selecting the “Review” button, the user may choose to enter the window of “Trend Graph”, “Trend Table”, “Alarm Review”,“NIBP review” or “Wave review”. The detailed introductions may refer to chapter12 “History Review”. Chart 1-4 history review 1.8.3 Setting By selecting the “Setting” button, the user may choose to enter the window of “Alarm setting”, “Record setting”, “Screen layout”, “Adjust time”, “Miscellaneous”, “ECG setting”, “ST setting”, “SpO₂ setting”, “NIBP setting”, “Resp setting”, “Temp setting” , or “Load Default “. Chart 1-5 setting 1.8.3.1 Alarm setting Detailed introductions can refer to Chapter2 “Alarm”. 1.8.3.2 Recording setting Detailed introductions can refer to Chapter3 “Recording”. 1.8.3.3 Screens layout After entering the screen layouts window, the user may change the current display interface by selecting the interfaces of 6 types of “Standard”, “ECG Full Lead”, “Big Font”, “OxyCRG”, “NIBP Trend”, “Trend Table”, and choose to turn on or turn off parameter or waveform in the “parameter switch” and “waveform switch”. The user can change trend resolution from “1 min” to “60 min” by setting “Trend Time” if the screen layout is set to “Trend Table”. 8 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter1 Overview The following chart shows the menu of screen layouts: Chart 1-6 screen layouts 1.8.3.4 Screen layout Big font Standard ECG Full Lead OxyCRG Trend table NIBP trrend Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 9 Chapter1 Overview 1.8.3.5 Adjust Time By entering the adjust time window, the user may choose the date format and adjust the current date and time, as the following chart shows: Chart 1-7 adjust time 1.8.3.6 Miscellaneous By entering the miscellaneous windows, the user may change the key volume and the screen brightness. The adjusting scope of key volume is 0~10 (0 means volume closure); The adjusting scope of screen brightness is 1~10 (10 means the highest brightness). If “Wave Smooth” switch is “On”, the wave will be displayed as smooth mode. Chart 1-8 miscellaneous setting 1.8.3.7 ECG setting Detailed introductions of ECG settings can refer to Chapter5 “ECG monitoring”. 1.8.3.8 ST setting Detailed introductions of ST settings can refer to Chapter6 “ST monitoring”. 1.8.3.9 Resp setting Detailed introductions of RESP settings can refer to Chapter8 “RESP monitoring”. 10 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter1 Overview 1.8.3.10 SpO₂ setting Detailed introductions of oxygen saturation settings can refer to Chapter9 “SpO₂ monitoring”. 1.8.3.11 NIBP setting Detailed introductions of noninvasive blood pressure settings can refer to Chapter10 “NIBP monitoring”. 1.8.3.12 Temperature setting Detailed introductions of body temperature settings can refer to chapter11 “temperature monitoring”. 1.8.3.13 Load default setting The following chart shows the window of Apply default settings: Chart 1-9 Load default settings If “Yes” is chosen, then the current settings will be replaced with default settings 1.8.4 Alarm limit By selecting the “limits of alarm” button, the user may choose to enter the windows of “ECG Alarm Limit”, “ SpO₂ Alarm Limit”, “NIBP Alarm Limit”, “Resp Alarm Limit”, “Temp Alarm Limit”, or “Load default Alarm Limit”, the detailed introductions refer to chapter2 “alarms”. Chart 1-10 Alarm Limit Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 11 Chapter1 Overview 1.8.5 Maintenance By selecting the “Service” button, the user may choose to enter the windows of “ECG calibration”, “ Temp Sensor Type”, “NIBP Pneumatic Test”, “NIBP calibration”, “NIBP Reset”, “Demo mode”, “Version info”, “User setting”, “Factory Service” and so on. Chart 1-11 Service 1.8.5.1 ECG calibration Entering the ECG calibration window, the user may turning on or turning off of the ECG calibration signal, as the following chart shows: Chart 1-12 ECG calibration 1.8.5.2 Temp Sensor Type Entering the Temp Sensor Type window, the user may initialize the type of body temperature sensor: 10K or 2.25K, as the following chart shows: Chart 1-13 Temp Sensor Type 1.8.5.3 NIBP Pneumatic test Selecting the “NIBP Pneumatic test”, the user may examine whether the entire air way of blood pressure measurement leaks air or not. 12 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter1 Overview When the blood pressure cuff is connected, the user may start the air leakage test with this key, thus discover whether the airtight condition of gas route is good or not. The examination result is: If air leakage examination is passed, the system will not make any prompt; If isn’t, the corresponding failure prompts will be displayed in the noninvasive blood pressure information section. The detailed introductions refer to 10.5 the air leakage examination. 1.8.5.4 NIBP calibration After selecting the noninvasive blood pressure calibration, the user enters the calibration mode, and at this time the user may calibrate, using a pressure gauge (or mercury sphygmomanometer) with a calibration precision higher than 1 mmHg after calibrated. If the “measure blood pressure” key is presses down during the calibration, the system will stop calibrating. The detailed introductions refer to 10.4 the blood pressure calibrations. 1.8.5.5 NIBP reset After choosing the noninvasive blood pressure reset, the user may restore the blood pressure module to the initial settings. When the blood pressure measurement is abnormal, yet the monitor cannot prompt reasons of the problem, using this key is suggested. Because this causes the blood pressure module to reset, the blood pressure module may commit self-recovery when the abnormity of work is caused by accidental reasons. 1.8.5.6 Demo mode The user input the correct password, the monitor will enter demo mode, and in the centre of the screen a big “DEMO” label will be shown. The demo mode is a particular state just for demonstrating performance of the machine, helping user carry out trainings. In the actual clinical use, this function is forbidden, because it can possibly cause the medical staffs to take demo waveforms as the waveforms and parameters by mistake, to affect animal monitoring. 1.8.5.7 Version information Choosing the “version information”, the user may look over the version information of the software installed in the monitor. 1.8.5.8 User settings The user may carry out user maintenance in the user settings menu, by inputting the password. This item is merely open to the serviceman appointed by the factory. 1.8.5.9 Factory service The user cannot implement functions of maintenance. This item is merely open to the serviceman appointed by the factory. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 13 Chapter1 Overview 1.9 Sensor socket Chart 1-14 sensor socket The following shows sensor socket: T1: temperature channel 1 sensor socket; T2: temperature channel 2 sensor socket; SpO₂: Oxygen saturation sensor socket; NIBP: non-invasive blood pressure cuff socket; ECG: ECG cable socket; 1.10 External interface :This symbol means ”BE CAREFUL“. Refer to the manual. VGA: VGA output, can connect to VGA monitor; NET: RJ45 net socket; : 14 Equipotential grounding system; Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter1 Overview Warning Accessory equipment connected to the analog and digital interfaces must be certified according to the respective IEC standards (e.g. IEC 60950 for data processing equipment and IEC 60601-1 for medical equipment). Furthermore all configurations shall comply with the valid version of the system standard IEC 60601-1-1. Everybody who connects additional equipment to the signal input part or signal output part configures a medical system, and is therefore responsible that the system complies with the requirements of the valid version of the system standard IEC 60601-1-1. If in doubt, consult the technical service department or your local representative. 1.11 Networks The network port of the monitor is the standard RJ45 network interface, may communicate with the central station through the ethernet cable, to achieve the function of remote monitoring. In the top right corner of the screen there is a network icon representing current network status. If the ”; After the network electric cable is disconnected, the network condition icon shows as “ monitor has established connection with the central station, the icon shows as “ ”; If the monitor communicates normally with the central monitoring system, the icon shows as “ ”. 1.12 Rechargeable built-in battery The monitor is equipped with a rechargeable built-in battery. In the top right corner of the screen exists one symbol “ “, indicating the state of the battery capacity, of which the green part denoting electric quantity of the battery. When the battery is charged, the charging condition is expressed with animation. After the battery is full-charged, the symbol will show as “ this monitor has not been installed the built-in battery, the symbol shows as “ ”. When ” indicating no battery. When running with power supply from battery, the monitor detects the volume of the battery, and alarms when the battery is insufficient, and prompts in the information section: “BAT LOW”. At this time, the AC power should be plug in, and immediately charge battery in time. If battery is still used for power supply, the monitor will power off automatically when the battery exhausted. Warning If you have any doubt to the grounding layout and its performance, you must use the built-in battery to power the monitor. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 15 Chapter1 Overview 1.13 Installation 1.13.1 Open the Package and Check Open the package and take out the monitor and accessories carefully. Keep the package for possible future transportation or storage. Check the components according to the packing list. ■ Check for any mechanical damage. ■ Check all the cables, modules and accessories. If there is any problem, contact the distributor immediately. 1.13.2 Connect the Power Cables Connection procedure of the AC power line: Make sure the AC power supply complies with following specification: 100~240 VAC, 50/60 Hz. Apply the power line provided with the monitor. Plug the power line to INPUT interface of the monitor. Connect the other end of the power line to a grounded 3-phase power output. Note Connect the power line to the jack special for hospital usage. Connect to the ground line if necessary. Refer to Chapter Animal Safety for details. 1.14 Power on the Monitor Press power switch to power on the monitor. Then the company logo will show on the screen, After 15 seconds or so, the system will enter monitoring screen after self-test, and you can perform normal monitoring now. During self-test, the Model Code will display. Note If the monitor finds any fatal error during self-test, it will alarm. Note Check all the functions that may be used to monitor and make sure that the monitor is in good status. Note The battery must be recharged to the full electricity after each use to ensure adequate electricity reserve. Warning If any sign of damage is detected, or the monitor displays some error messages, do not use it on any animal. Contact biomedical engineer in the hospital or Biocare Customer Service Center immediately. Note The interval between twice press of POWER should be more than 1 minute. 1.15 Connect Sensors Connect all the necessary sensors between the monitor and the animal. 16 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter1 Overview Note For information on correct connection, refer to related chapter 5-11. 1.16 Check the Recorder If your monitor is equipped with a recorder, open the recorder door to check if paper is properly installed in the output slot. If no paper present, refer to Chapter Recording for details. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 17 Chapter 2 Alarms Chapter 2 Alarms 2.1 Alarms overview 2.1.1 Types of the alarms The alarms can be divided into two types: physiology alarms and technical alarms. Physiology alarms: triggered by some of animal physiological parameters exceed the limits, taking the body temperature exceeding temperature alarm limit as an example. Technical alarms: triggered by the abnormality of certain monitoring function or distortion of monitoring results caused by failure of system or sensors, taking ECG lead off as an example. 2.1.2 Level of alarms The alarms have three levels: high, medium and low. The monitor has set levels for technical alarms and physiology alarms. 2.1.3 Modes of the alarms When alarming, the monitor gives alarm prompts by three ways: sound alarm, light alarm, and alarm message description. The prompts of sound and light come from the speaker, the alarm indicator light and alarm message description. The alarm message description is displayed on the screen. The physiology alarm is displayed in the animal alarm information section, while the technical alarm displayed in the monitor alarm information section. When the physiology alarm occurs, which is caused by the measurement parameters exceeding the alarm limit, the color of high limit and low limit would change from dark to bright, besides the three means of alarm prompting mentioned above. When there is “*” before technical or the physiology information section, it means low level alarm. “**” means medium level alarm and the information bottom color will turn yellow. “***” means high level alarm and information bottom color will turn red. For example: The “** HR TOO HIGH” is the expression of medium alarm. Physical alarm has 2 kind of alarm mode: LATCH or Unlatch. LATCH means that once alarm occurs, the system will give alarm all the time until manual intervention (such as push the “SILENCE” button on the panel). UNLATCH means that the system will stop giving alarm once the alarm condition does not exist. There are three levels of the alarm: high, midium, low, by using the different light and the sound. 18 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 2 Alarms The following table shows in order: Alarm level alarm light High alarm light glitters red, the The flicker frequency is quick sound characteristic of the alarm pattern as “honk - honk - honk------honk - honk, honk - honk honk------honk - honk”, each 8 seconds occur once medium alarm light glitters yellow, the The pattern as “honk - honk - honk”, flicker frequency is slow Low each 25 seconds emit sound once alarm light is bright and The pattern as “honk -”, each 25 seconds always show yellow emit sound once 2.2 Alarms pausing Presses “PAUSE” key on the control panel, all alarm sound and light and the alarm message are closed. Then the system enters alarm suspend state. The suspension countdown time is displayed in the area of the technical alarm. Three options can be set about the alarm suspension time: 1 minute, 2 minute and 3 minutes. The user must enter the window of the alarm setting, chooses correspondingly the suspension time. After presses down of “PAUSE” key again, the system may restore to the normal state. 2.3 Alarms SILENCE Presses “SILENCE” key on the control panel, then may close the sound and the light alarm; when presses down “SILENCE” key again, will quit from alarm silence condition and reactivated correspondingly sound alarm, returns to normal alarm condition. If the alarm still exists under the condition of the silence state, then the information section display this alarm information. If there is no alarm exists under the condition of the silence state, then all the alarm will be eliminated. Attention When the system is under the “SILENCE” condition, any newly triggered alarm will terminate the silence condition, and then makes the system to restore to the normal alarm condition. 2.4 Alarm Setting Enter the alarm setting window, the options below may be set. 1) Alarm Volume: The scope is 1~10 (10 is the highest volume). 2) Suspend Time: 1 minute, 2 minutes, 3 minutes. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 19 Chapter 2 Alarms 3) Flash: if “On” is selected and there is physical alarm, corresponding parameter digit will flash to indicate that the parameter has alarm. 4) Para Alarm: 2 items: LATCH or Unlatch. LATCH means that once alarm occurs, the system will give alarm all the time until manual intervention (such as push the “SILENCE” button on the panel). UNLATCH means that the system will stop giving alarm once the alarm condition does not exist. 5) Alarm Record: If “On” is selected, the recorder will record the alarm event when physical alarm occurs, otherwise it will not record. 6) Voice Alarm: If “On” is selected and alarm event occurs, a human voice alarm will continuously notify the user, otherwise it will not notify by human voice. Chart 2-1 alarm setting 2.5 Limits of the alarms Physiology alarm is triggered according to the settings limits. Various parameters limits are showed by the dark color in the parameter area of the upper corner on the left side. If the parameter exceeds the limits, then triggers the physiology alarm at this parameter by the bright color. For example: the low limit of the heart rate is 80, if at this time the heart rate is 60 pieces, then triggers “HR TOO LOW”, the low limit of the heart rate “80” will be a bright color, the following chart will show: Chart 2-2 Alarm Limit 20 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 2 Alarms 2.5.1 ECG Alarm Limit Choosing “ECG Alarm Limit” may enter “ECG Alarm Limit” window: Chart 2-3 Ecg Alarm Limit Following is the adjustment scope of the heart rate: animal type >20kg 10~20kg <10kg HR high limit 300 350 350 HR low limit 15 15 15 adjustment scope of the ST:- 2.00mV~2.00mV. adjustment scope of the PVCs :0~10. 2.5.2 SpO₂ Alarm Limit Choosing “SpO₂ Alarm limit” may enter “SpO₂ Alarm Limit” window: Chart 2-4 SpO₂ Alarm Limit The SpO₂ limit adjustment scope is 0~100; The Pulse rate alarm limit adjustment scope are 20~300. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 21 Chapter 2 Alarms 2.5.3 NIBP Alarm Limit Choosing “NIBP Alarm Limit” may enter “NIBP Alarm Limit” window: Chart 2-5 NIBP Alarm Limit The NIBP Alarm Limit adjustment scope as follows: animal type >20kg 10~20kg <10kg Systolic pressure high limit 280 220 135 Systolic pressure low limit 40 40 40 Diastolic pressure high limit 220 160 100 Diastolic pressure low limit 10 10 10 mean pressure high limit 240 170 110 mean pressure low limit 20 20 20 2.5.4 Resp Alarm Limit Choosing “Resp Alarm Limit” may enter “Resp Alarm Limit” window: Chart 2-6 Resp Alarm Limit The Resp rate alarm limit adjustment scope is:7~120. 22 animal type >20kg 10~20kg <10kg RR high limit 120 150 150 RR low limit 7 7 7 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 2 Alarms 2.5.5 Temp Alarm Limit Choosing “Temp Alarm Limit” may enter “Temp Alarm Limit” window: chart 2-7 Temp Alarm Limit The Temp alarm limit adjustment scope is:0~50℃ (32~122℉). 2.5.6 Load Default Alarm Limit Choosing “Load Default Alarm Limit” can enter “load default Alarm limit” window: The chart 2-11 Load default Alarm Limit If chooses “Yes”, then the current alarm limit settings will be able to substituted by the default alarm limit settings. 2.6 Physiology alarm information Below is all physiologies alarm tabulates: Alarm Information Trigger Condition ***ASYSTOLE Over 4 seconds non- palpitations signals *** APNEA In a setting time without breath signal *** NO PULSE Over 15 seconds without pulse signals ** HR TOO HIGH The heart rate exceeds the alarm high limit ** HR TOO LOW The heart rate is lower than the alarm low limit ** ST-I TO HIGH the ST value correlate with I surpass the upper alarm limit ** ST-I TOO LOW the ST value correlate with I surpass the lower alarm limit ** ST-II TO HIGH the ST value correlate with II surpass the upper Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 23 Chapter 2 Alarms alarm limit ** ST-II TOO LOW the ST value correlate with II surpass the lower alarm limit ** ST-III TO HIGH the ST value correlate with III surpass the upper alarm limit ** ST-III TOO LOW the ST value correlate with III surpass the lower alarm limit ** ST-AVR TOO HIGH the ST value correlate with AVR surpass the upper alarm limit ** ST-AVR TOO LOW the ST value correlate with AVR surpass the lower alarm limit ** ST-AVL TOO HIGH the ST value correlate with AVL surpass the upper alarm limit ** ST-AVL TOO LOW the ST value correlate with AVL surpass the lower alarm limit ** ST-AVF TOO HIGH the ST value correlate with AVF surpass the upper alarm limit ** ST-AVF TOO LOW the ST value correlate with AVF surpass the lower alarm limit ** ST-V TOO HIGH the ST value correlate with V surpass the upper alarm limit ** ST-V TOO LOW the ST value correlate with V surpass the lower alarm limit ** PVCs TOO HIGH The PVCs value exceeds the alarm high limit ** SPO₂ TOO HIGH The oxygen saturation exceeds the alarm high limit ** SPO₂ TOO LOW The oxygen saturation is lower than the alarm low limit ** Pulse rate TOO HIGH The Pulse rate surpass the alarm high limit ** Pulse rate TOO LOW The Pulse rate are lower than the alarm low limit **NIBP SYS TOO HIGH NIBP systolic pressure exceeds the alarm high limit **NIBP SYS TOO LOW NIBP systolic pressure is lower than the lower alarm limit **NIBP MEAN TOO HIGH NIBP mean pressure exceeds the alarm high limit **NIBP MEAN TOO LOW NIBP mean pressure is lower than the alarm low limit **NIBP DIA TOO HIGH NIBP diastolic pressure exceeds the alarm high limit 24 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 2 Alarms **NIBP DIA TOO HIGH NIBP diastolic pressure is lower than the alarm low limit ** RR TOO HIGH The Breath rate exceeds the alarm high limit ** RR TOO LOW The Breath rate is lower than the alarm low limit ** TEMP1 TOO HIGH The body temperature channel 1 exceeds the alarm high limit ** TEMP1 TOO LOW The body temperature channel 1 is lower than the alarm low limit ** TEMP2 TOO HIGH The body temperature channel 2 exceeds the alarm high limit ** TEMP2 TOO LOW The body temperature channel 2 is lower than the alarm low limit 2.7 Technical alarm information Below is all technical alarm tabulates: Alarm Information Trigger Condition Process Method ** ECG LEAD OFF RL or more than 2 ECG leads check falls off connection RA lead fall off check ** ECG LEAD RA OFF the the ECG lead ECG lead ECG lead ECG lead ECG lead connection ** ECG LEAD LA OFF LA lead fall off check the connection ** ECG LEAD LL OFF LL lead fall off check the connection ** ECG LEAD V OFF V lead fall off check the connection ** MODULE INIT ERR Module self-checking mistake Restart the machine, if error still existed, contact the factory service ***MODULE COMM STOP ** MODULE COMM ERR ** PARA ALARM LMT ERR The module and the main Restart the machine, if error engine communication have still existed, contact the the problem factory service The module and the main Restart the machine, if error engine communication have still existed, contact the the problem factory service The parameter of the alarm contact the factory service limit is modified by the accident ** RANGE EXEED The parameter observed value contact the factory service Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 25 Chapter 2 Alarms has exceed the measurement scope which the system can carry on ** SpO₂ SENSOR OFF ** SpO₂ FINGER OFF SEARCHING PULSE... SpO ₂ sensor does not Check SpO ₂ sensor connected connection The finger fall off from SpO₂ Check SpO₂ sensor connect sensor with the finger SpO₂ sensor connect bad or Check the animal move the arm connection SpO ₂ sensor situation and animal current condition ** Temp1 SENSOR OFF The body temperature channel 1 sensor do not Check temperature sensor connection connect ** Temp2 SENSOR OFF The body temperature channel 2 sensor do not Check temperature sensor connection connect ** WATCHDOG ERR Main engine watch-dog self-checking defeat Restart the machine, if wrong still existed, contact the factory service ** SYSTEM TIME LOST The system clock has not set Change the system time as the current time, if error still existed, related the factory to carry on the service ** 12V HIGH ** 12V LOW ** 3.3V HIGH The 12V voltage examination Restart the machine, if error exceeds the normal voltage still existed, contact the scope factory service The 12V voltage examination Restart the machine, if error is lower than the normal still existed, contact the voltage scope factory service The 3.3V examination voltage exceeds the normal voltage scope ** 3.3V LOW **BAT HIGH The factory service Restart the machine, if error examination is lower than the still existed, contact the normal voltage scope factory service battery examination voltage exceeds the normal voltage scope **BAT LOW 26 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual still existed, contact the voltage The 3.3V Restart the machine, if error The battery capacity Restart the machine, if error still existed, contact the factory service is Meets the alternating current Chapter 2 Alarms insufficient to carry on the charge immediately to the battery * NIBP LOOSE CUFF Reconnects The cuff has not connected the blood pressure cuff * NIBP AIR LEAK check the pipe connection The cuff has not connected situation or replace cuff, if good or the air course leaks the breakdown still existed, air please contact the factory service * NIBP DEFLATE ERR When blood pressure measurement deflates has the problem check the tube connection or replace cuff, if the error still existed, please contact the factory service Examined the animal type * NIBP WEAK SIGNAL When blood pressure set whether correctly, check measurement the pulse signal the too replace cuff, if the error still weak, is unable to calculate the blood pressure tube connection or existed, please contact the factory service * NIBP OUT OF RANGE When blood measurement pressure blood check he tube connection or pressure or the pulse signal replace cuff, if the error still exceeds the normal range, is existed, please contact the unable factory service to the carry on the measurement * NIBP MOVEMENT animal arm move Check the animal situation or replace cuff, if the error still existed, please contact the factory service ** NIBP OVER PRESSURE The pressure value exceeds check the pipe connection the measurement scope situation or replace cuff, if the error still existed, please contact the factory service * NIBP SATURATE When blood pressure Check the animal situation measurement the pulse signal or replace cuff, if the error exceeds the normal range, is still existed, please contact unable the factory service to carry on the measurement * NIBP PNEUMATIC FAIL The cuff has not connected check the pipe connection Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 27 Chapter 2 Alarms good or the air course leaks situation or replace cuff, if air the error still existed, please contact the factory service ** NIBP SYSTEM ERR Blood pressure system self-check defeat Restart the machine, if the error still existed, please contact the factory service ** NIBP TIME OUT Blood pressure measurement Restart the machine, if the overtime error still existed, please contact the factory service ** NIBP MEASURE FAIL ** NIBP RESET ERR This pressure Check the animal situation measurement has not been or replace cuff, if the error able to calculate the blood still existed, please contact pressure the factory service When blood blood measurement reset pressure Restart the machine, if the exceptionally error still existed, please contact the factory service Attention 1. When different level of alarm simultaneously exists, the sound of the alarm is the highest level alarm. 2. In alarm suspend condition, Monitoring will not process any alarm information. 28 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 3 Record Chapter 3 Record 3.1 Record setting Chart 3-1 recording settings 1) record waveform 1, record waveform 2: there are five options of the waveform to be choose: off, ECG1, ECG2, pulse wave, respiratory wave, IBP1 wave, IBP2 wave, CO₂ wave. The user may choose simultaneously two waveforms to record, or choose one waveform to record while close another record wave. 2) record length: there are two options, which are “continuous”, “8 seconds”. “continuous” means that the record can continuously output the wave until presses down the “RECORD” key again. 3) record period: the time interval of two record outputs. There are 10 options which are: off, 10 minutes, 20 minutes, 30 minutes, 40 minutes, 50 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, 3 hour and 4 hours. The recording length is 8 seconds. 4) record speed: There are two options, which are “25.0mm/s” and “50.0mm/s”. 5) record grid: “Off” means non- grid output. “On” means grid output. 3.2 Record type The monitor can carry on several kinds of types record: the continuously real-time records; 8 seconds real-time records; Automatic 8 second records. 3.2.1 Real-time record This means that it starts the real-time recording waveform when presses down the recording key , and stops the record when press down the recording key again in the recording process . 3.2.2 Auto record The monitor can trigger the record output according to the time interval. the recording length is 8 seconds. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 29 Chapter 3 Record 3.3 Record content The record outputs contents: The recording type, the animal information, the parameter table, the record time, the waveform name, the waveform amplitude and waveforms. 30 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 4 Admit/Discharge Aninal Chapter 4 Admit/Discharge Animal 4.1 Admit Veterinary The step of receiving new Veterinary is as follows: enter “Veterinary info” window by choosing the “Admit new Animal” menu, and input the animal information (the following chart to show). Chart 4-1 admit new Veterinary choose the ”OK” button , the animal’s information is accepted. 4.2 Discharge animal Enter the “Discharge animal” window by choosing ”Discharge animal” menu, as the following chart to show. Chart 4-2 Discharge Veterinary Carry on the following operations to relieve the Veterinary: 1) Discharge all animal information; 2) Discharge all historical data (including trend graph, trend table, blood pressure review, waveform review data); Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 31 Chapter 4 Admit/Discharge Aninal Attention If do not relieve the animal firstly before receive new animal, new animal’s measurement data would be save in the preceding animal 's data. The monitor can not distinguish the new animal data from the old one. 32 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 5 ECG Monitoring Chapter 5 ECG Monitoring The ECG monitors the heat electricity activity of the body, and shows the heart electricity waveform and the heart rate on the monitor. 5.1 Connecting ECG electrodes 1) make the animal’s skin preparation at first before place the electrode. A good signal at the electrode provides the monitor with valid information for ECG data processing. Clean the skin with the soap and the water (don’t use aether and pure alcohol, because this can increase skin impedance) or scratches the skin dry to increase the blood stream capillary of the organization, and remove skin filings and fat. If necessary, shave the hairs in which the electrode is placed. 2) place the electrode on the animal’s body. 3) Connect the ECG-lead with the animal cable. 5.2 ECG electrode placement The position of the ECG electrode is as follows: The RA (right arm) electrode — place under the subclavian, approaching the right shoulder. The LA (left arm) electrode — places under the subclavian, approaching the left shoulder. The LL (left leg) electrode — places under the left abdomen. The RL (right leg) electrode — places under the right abdomen. The V (chest) electrode — places on the chest. Chart 5-1 The position of electrode Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 33 Chapter 5 ECG Monitoring Warning When connecting the cables and electrodes, make sure no conductive part is in contact with the ground. Verify that all ECG electrodes, including neutral electrodes, are securely attached to the animal. Warning Verify lead fault detection before start of monitoring. Unplug the ECG cable from the socket, the screen will display the error message “ECG LEAD OFF” and the audible alarm is activated. 5.3 Connecting ECG leads recommended for surgery The position of ECG electrode is decided by the type of the operation. For example, regarding the chest operation, the electrode may be put on the chest side or the back. Sometimes in the operating room, because of using surgical equipment, the artifact possibly can affect the ECG waveform. In order to reduce the artifact, place the electrode on the left or right shoulder, approaching the left or right side of the abdomen, however, the chest leads can be placed on the center of the chest left side. Avoid to place the electrode on the upper arm, otherwise ECG signal can be very weak. A good characteristic of the ECG-waveform: the QRS wave height is great and narrow with no notchs. The R wave height is big and located completely above the baseline or under. The amplitude of the P wave and the T wave is smaller than 0.2mV. Chart 5-2 standard ECG-waveform Warning Do not touch the animal, table nearby, or the equipment during defibrillation. Warning When apply the ECG cable with no resistances to animal monitor or other animal monitors which themselves with no current limit resistance, it can’t be applied to defibrillation. Note Interference from a non-grounded instrument near the animal and ESU interference can cause inaccuracy of the waveform. 34 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 5 ECG Monitoring Warning When using ESU equipment, leads should be placed in a position in equal distance from ESU electrotome and the grounding plate to avoid cautery. ESU equipment wire and ECG cable must not be tangled up. 5.4 ECG setting enter the” ECG setting” window by choosing the “ECG setting” menu, as can be seen from the following chart: Chart 5-3 ECG settings menu 1) Pacemaker: When it is turned on, the pacing signal, which is considered as the pacing symbol, is shown as a vertical line above the ECG waveform l; When it is turned off, the pace maker will not be detected. 2) channel 1 lead, channel 2 lead: There are 7 leads: I, II, III, AVR, AVL, AVF, V. 3) channel 1 gain, channel 2 gain: There are four gains: “×0.25”, “×0.5”, “×1”, “×2”. 1 millivolt ruler mark is displayed on the right of the ECG waveform, the height of which make a direct ratio with the wave amplitude. 4) Notch: work frequency suppression switch, when it is “On” will filter the AC disturbance of ECG signal. 5) filter mode: There are 3 filter modes, diagnostic, monitor and surgery. In “diagnostic” mode, The ECG wave without filtering is displayed; In “monitor” mode, the artifact which causes the false alarm, is filtered out; In “surgery” mode, the artifact and the disturbance caused by the electricity surgical equipment can be reduced. The filter modes can be displayed above the heart electricity waveform. 6) heart volume: the range is from 0 to10, “0” means that the sound of heartbeat is shuted, “10” means it is on the maximum volume. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 35 Chapter 5 ECG Monitoring 7) wave speed: There are three levels of the ECG waveform tracing speed to be chosen, 12.5, 25.0 and 50.0 mm/s. 8) HR source:there are “Auto”, “Ecg”, “SpO₂”. When “Ecg” is selected, HR and heart sound are from ECG; when “SpO₂”is selected, HR and heart sound are from SpO₂;when “Auto” is selected, animal monitor will auto detect the ECG and SpO₂ signal, HR will from ECG when ECG signal exist, otherwise is from SpO₂; 9) ST switch: When it is “On”, the ST analysis is carried on; otherwise, it isn’t. 10) arrhythmia switch: When it is “On”, the arrhythmia analysis is carried on, which shows the PVCs parameter in the parameter area; Otherwise, the arrhythmia analysis isn’t carried on, and the PCVs parameter is not shown. Attention When the Pace analysis is turned on, the arrhythmia which is related to PVC/Premature Ventricular Contractions(including the PVCs computation), will not be detected, simultaneously, the ST section analysis is not carried on. Warning 1) Don’t touch the animal or the monitor in the period of defibrillating. 2) In order to ensure the animal safety, all leads must be connected to the animal 3) When the electricity surgical (ES) equipment is used, lay the ECG-lead in the middle of both the ES ground plate and ES to avoid burning. The cable of the electricity surgical equipment cannot twist with the ECG-cable. 4) When the electricity surgical (ES) equipment is used, don’t place the electrode on the ground plate near the electricity surgical equipment. Otherwise, the ECG-signal will be disturbed. 5) If monitoring a animal with the pacemaker, set “PACE” to On. If monitoring a animal without pacemaker, set “PACE” to Off. 6) Regarding the pacemaker animal, the pacing switch must be “On”, otherwise, it is possibly to consider the pacing pulse as the normal QRS 36 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 6 Resp Monitoring Chapter 6 Resp Monitoring 6.1 Principles of Respiration measurement When the human body breathes, the chest impedance will change along with the breath, the monitor gets the breath signal through the chest impedance value from the RA and the LL electrodes at the chest. After amplify the signal of the impedance between the electrodes (as a result of the thorax activity), the breath wave will be displayed on the screen. 6.2 Placing the electrodes Connect the electrodes like the way that connect the heart electrodes at 5.1. 6.3 Resp settings Choose the “Resp settings” menu and enters “Resp setting” window. Chart 8-1 RESP settings 1) Apnea alarm: Setting the judgment time while the animal is asphyxiating, between 10 seconds and 40 seconds, if switch the settings off, indicate the asphyxiation alarm is closed. 2) Waveform speed: you can choose the waveform speed at 6.25mm/s, 12.5mm/s,25.0 mm/s . 3) Amplitude: The user may setting the amplitude’s enlargement factor, has ×0.25, ×0.5, ×1, ×2, ×4 altogether 5 levels. 4) RR Source: when “Ecg” is selected, RR is from ECG leads; when “CO₂” is selected, RR is from CO₂ module and AwRR is displayed on parameter area. Attention Resp monitoring is not recommended on animal who moves a lot, because this possibly causes wrong alarm. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 37 Chapter 6 Resp Monitoring Attention Place the RA and the LL electrode in the animal opposite angle of the body in order to obtain the best breath wave. Should avoid the liver area and the ventricle at the breath electrode’s lines, this may avoid the false difference to be caused by the heart beat or pulsing blood stream, this is specially important to the animal. 38 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 7 SpO₂ Monitoring Chapter 7 SpO₂ Monitoring The Oxygen Saturation (SpO₂) parameter measurement the artery blood oxygen saturation, it is the percentage of the oxygen gathers hemoglobin .For example, if in the artery blood red blood cell, 97% hemoglobin combine with the oxygen, then this blood has 97% oxygen saturation, the value reading on the monitor should be 97%, this value demonstrated the percent of the carry oxygen hemoglobin molecule which forms the oxygen gathers hemoglobin. 7.1 Monitoring Procedure 1. Switch on the monitor. 2. Attach the sensor to the appropriate site of the animal finger. 3. Plug the connector of the sensor extension cable into the SpO2 socket Note If the sensor cannot be positioned accurately to the part to be measured, it may result in inaccurate SpO2 reading, or even that the SpO2 cannot be measured because no pulse is detected. If this is true, you must position the sensor again. The excessive animal movement may result in inaccurate reading. In this situation, you must keep the animal quiet or change the part for monitoring to reduce the adverse influence of excessive movement. Warning In the process of extended and continuous monitoring, you should check the peripheral circulation and the skin every 2 hours. If any unfavorable changes take place, you should change the measured position in time. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 39 Chapter 7 SpO₂ Monitoring In the process of extended and continuous monitoring, you should periodically check the position of the sensor. In case that the position of the sensor moves during monitoring, the measurement accuracy may be affected. 7.2 Measurement restrictions In the operating process, following factors may affect the accuracy of the oxygen saturation measurement: 1) High-frequency electrical jam, such as the disturbance which is produced by monitor system oneself or comes from such as the electricity surgery instrument disturbance which connected with the system; 2) In magnetic resonance image formation scanning (MRI) period do not use the blood oxymeter and the blood oxygen sensor, the induced current possibly can cause the burn; 3) In vein dye; 4) animal too frequently migration; 5) Outside ray radiation; 6) Sensor installment inappropriate or contact the improper position with the object; 7) Body temperature (best body temperature should in 28℃- 42℃); 8) Lay aside the sensor in the body has the blood pressure cuff, in the ductus 9) arteriosus or the cavity on the pipeline body; 10) The density of the non- function hemoglobin like carbon oxygen hemoglobin (COHb) and blood and iron hemoglobin (MetHb) and so on; 11) Oxygen saturation lowly; To be circular poured is not good at the test part; Shock, anemia, the low temperature and applies the vasoconstriction medicine and so on all possibly cause the artery blood stream to be reduced to the level which was unable to measurement; 12) Measurement is also decided on the oxygen gathers hemoglobin and the absorption situation of the return oxygen gathers hemoglobin to the special wave length light. If other substances which absorb the same wave length light exist, they can cause the measurement to appear pseudo or the low oxygen saturation value. For example: Carbonizes the hemoglobin, the blood and iron hemoglobin, the methylene blue, indigo carmine. 40 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 7 SpO₂ Monitoring 7.3 SpO₂ setting Chooses “SpO₂ settings” menu and enters “SpO₂ setting” window. Chart 9-1 SpO₂ settings 1) Pulse volume: the volume choice scope is the 0~10,0 denotes closure pulse sound, 10 denotes maximum volumes. 2) Sensitivity: the sensitivity for computing oxygen saturation value, has “high”, “medium”, “low” three options. 3) Wave speed: the waveform scanning velocity has 12.5 and 25mm/s ,two levels may choose. 4) Pulse rate: setting as “On”, in parameter area will show Pulse rate; otherwise the Pulse rate will not be displayed. 5) Wave Mode: when “Line” is selected, will use line mode to draw pleth wave; when “Fill” is selected, will use fill mode to draw pleth wave; Warning 1) If it has the carbon oxygen hemoglobin, metahemoglobin or dye dilution chemicals, then the oxygen saturation value can have the deviation; 2) Electricity surgical department equipment electric cable cannot twine with the sensor cable in the same place; 3) Do not place the sensor at the body has the ductus arteriosus or the vein syringe ; 4) Guarantees the nail to block the lights. Sensor should at the back of hand; 5) Do not place SpO₂ or the blood pressure oversleeve blood pressure measurement on the same body, because in the blood pressure measurement process the blood stream unenlightened can affect the oxygen saturation reading. 6) Continually, the excessively long time monitor possibly can increase do not hope danger that the skin characteristic change occurs, for example exceptionally sensitive, changes red, Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 41 Chapter 7 SpO₂ Monitoring bubbles or pressure necrosis, specially in the small animal or has pour barrier as well as the change or juvenility skin kind sickness person; 7) In the long time continuous monitoring process, about every 2 hours inspects the measurement SpO₂ the end circulation situation and the skin situation, if discovered changes not good, should change the measurement SpO₂ promptly, simultaneously should periodical inspection the sensor fastness situation, avoids the sensor fastness situation change caused by the moving and so on the factors affect the accuracy of the measurement; 8) If the test SpO₂ and the sensor cannot locate accurately, possibly causes the oxygen saturation reading inaccurate, even unable to search the pulse wave result in unable to carry on the blood oxygen monitor, this time should relocate; 9) Measurement SpO₂ move excessively possibly creates measurements inaccurate, this time should cause the animal peaceful or the replacement measurement SpO₂, reduces the influence of moves excessively to the measurement 42 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 8 NIBP Monitoring Chapter 8 NIBP monitoring 8.1 NIBP measurement procedure Warning Use accessories specified by Biocare only, otherwise; the device may not function normally. Warning ■ Before starting a measurement, verify that you have selected a setting appropriate for your animal (>20kg, 10~20kg or <10kg.) ■ Do not apply the cuff to a limb that has an intravenous infusion or catheter in place. This could cause tissue damage around the catheter when infusion is slowed or blocked during cuff inflation. Warning Make sure that the air conduit connecting the blood pressure cuff and the monitor is neither blocked nor tangled. Notes The blood pressure of the animal as the basis for establishing therapy may be obtained by using other method such as the cuff/stethoscope auscultation method. Accordingly, the clinical doctor must note that the values obtained by using other method and machine may be different. Notes NIBP monitoring uses the oscillometric method of measurement. Blood pressure determined with this device are equivalent to those obtained by a trained observer using the cuff/stethoscope auscultation method and an intra-arterial blood pressure measurement device, within the limits prescribed by the ANSI/AAMI SP10. Notes This equipment is suitable for use in the presence of electro-surgery. 1) Insert the gas tube into the blood pressure socket of the monitor; 2) Tie the blood pressure cuff on the animal upper arm or the thigh; 3) Use the suitable size cuff for the animal, guaranteed the symbol Ф is located above to the suitable artery. Guarantee the cuff to twine the body is not too tight, otherwise possibly causes the body far-end to change color even lacks the blood; 4) Inspects the edge of the cuff to fall in the range signed <->.If it is not this, exchange a more appropriate cuff; Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 43 Chapter 8 NIBP Monitoring 5) Confirm the cuff deflated completely; 6) Cuff and gaseous tube coupling. The body which will be measured should put in the same horizontal position with the animal heart. If it is unable to achieve, must use the following adjustment method to make the revision to the measurement result If the cuff is higher than the heart horizontal position, each centimeter disparity should add 0.75mmHg(0.10kPa) in the value. If the cuff is lower than the heart horizontal position, each centimeter disparity should reduce 0.75mmHg(0.10kPa) in the value. 7) Confirm the animal type whether correct (animal type shows in the block of information on the monitor, the right side of bed number), if needs to change the animal type, please enter “the animal information” window, change “the animal type”; 8) Press down the blood pressure measurement button on the front panel, start to measures the blood pressure. 8.2 NIBP measurement limits This machine NIBP measuring technique is the vibration mothod, this kind of measuring technique basis has the certain limit according to difference metrical object. The user should realize at following several situations, the observed value changes unreliable, or the time measured press increases or the measurement is unable to carry on. 1) animal movement: If the animal is moving, trembles or the convulsion; 2) Arrhythmia: the irregular heart beat caused by the arrhythmia; 3) Heart-lung machine: such as the animal uses the heart-lung machine connection; 4) Pressure variation: such as while in blood pressure measurement the animal blood pressure rapid change; 5) Serious shock: such as the animal is being in the serious shock or the hypothermia; 6) The heart rate exorbitant or lower: The heart rate is lower than 40bpm (heart beat/minute) and is higher than 240bpm (heart beat/minute), cannot carry on the blood pressure measurement; 7) Obese animal: The excessively thick fat stratum can reduce the accuracy of the measurement, because the fat can cause the artery pulse signal cannot arrive the cuff. 44 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 8 NIBP Monitoring 8.3 NIBP settings Chart 10-1 NIBP settings 1) Pressure unit: mmHg or kPa is optional. 2) measurements mode: have 3 kinds of mode: manual, automatic, STAT. Under the manual measurement way, presses down the blood pressure measurement button on the control panel, then starts the manual measurement once; Under the automatic measurement way, presses down the blood pressure measurement button on the control panel, then starts the automatic measurement once, afterwards the monitor can automatic start blood pressure measurement defer to the period; Under the STAT measurement way, presses down the blood pressure measurement button on the control panel, then starts to continuously measure for 5 minutes. While the blood pressure measuring, the user presses down the blood pressure measurement button on the control panel anytime, can stop the current blood pressure measurement. 3) The automatic sampling interval: If the measurement pattern setting as “automatically”, then the automatic sampling interval button will be available. The automatic sampling interval time can be chosen in 1 minute, 2 minutes, 3 minutes, 4 minutes, 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes, 30 minutes, 60 minutes, 90 minutes, 2 hours, 3 hours, 4 hours, 8 hours. After choose the time interval, presses down the blood pressure measurement button will start the first automatic measurement charge, in order to finish the automatic measurement should choose the “manually” returns to the manual pattern while in sampling interval period. 8.4 Blood pressure calibrations Using the precision of the pressure gauge (or mercury sphygmomanometer) is higher than 1 mmHg after the calibration carries to carry on the calibration, choose “noninvasive blood pressure calibration” in the “the maintenance” menu to start to carry on the calibration, if presses down the blood pressure measurement button while calibrating , then the system will stop calibrating. Connect the pressure gauge, the cuff through a 3-way tube to the blood pressure trachea jack on the monitor, setting the monitor as “the calibration” pattern, then charge the cuff using a air pump, first Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 45 Chapter 8 NIBP Monitoring make the pressure to 250 mmHg, then slowly deflates, when the monitor display 200, 150 and 50 mmHg, the disparity between the standard pressure gauge value and the monitor pressure value should in 3 mmHg. If the value exceeds 3 mmHg, please contact our company’s attendant. Attention: The cuff must entangle in the suitable big and small pillars. Warning You shall calibrate NIBP measurement once every two years (or as required in your hospital’s maintenance regulation). You shall check the performance according to following information. 8.5 leakage examination When the cuff is connected may use this function to start air course charge process, thus to discover whether the air way’s airtight condition is good or not. If the test passes, the system will not make any prompt; If do not passed, then in the noninvasive blood pressure parameter area will have the corresponding wrong prompt. The air leakage examination process: 1) Connect the cuff and the blood pressure socket on the monitor; 2) Wrap the cuff around a suitable cylinder; 3) Choose “NIBP Pneumatic Test” in “Service” menu, the noninvasive blood pressure parameter area diplays “Pneumatic test......”, indicated the system starting to carry out leak air examination; 5) After about 20 seconds, the system will turn on the valve automatically, marking leaks air examination is completed; 6) If in the noninvasive blood pressure parameter area does not prompt the information, indicate the system does not leak air. If “Pneumatic leak!” is displayed, indicate the air course possibly leaks air. The operator should check loose conditions and carry on the leaks air examination again after confirming all connections are ok. Warning 1) Can’t carry on the noninvasive blood pressure on the animal who have the sickle cell anemia or have the skin disrepair or will have damage. 2) To the animal who has the serious hemoglutination machine-made barrier, must according to the clinically appraise decided whether carries on the automatic blood pressure measurement, because the place where the body and the cuff friction will has have the haematoma danger. 3) Before start the measurement, you must confirm the animal type is correct. 4) Do not enwind the cuff to the body have the venous transfusion or inserted the drive pipe, while cuff charging period, when the transfusion reduces speed or stops up, possibly causes damage around the drive pipe. 46 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 8 NIBP Monitoring 5) If the time of the automatic pattern noninvasive blood pressure measurement pull too long, then the body connected with the cuff possibly have the purpura, lack the blood and the neuralgia. When guarding animal, must inspect the luster, the warmth and the sensitivity of the body far-end frequently. Once observes any exception, please immediately stop the blood pressure measurement. 6) The calibration of the noninvasive blood pressure measurement is supposed to be carried on one time every year. (Or according to the maintenance regulation of your hospital). 7) The cuff width should be 40% size of the body perimeter. or the 2/3 of the upper arm length. The length of the cuff charging part should long enough surround 50~80% of the body, the inappropriate size cuff can have the wrong reading. If the cuff size has the question, should use the bigger cuff to reduce the mistake. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 47 Chapter 9 Temperature Monitoring Chapter 9 Temperature Monitoring 9.1 Steps of temperature measurement 1) Insert temperature sensor directly into the socket. 2) Power on animal monitor. 9.2 Temperatures settings menu Chooses “Temperature setting” menu and enters “Temp setting” window: Chart 11-1 Temperature settings Temperature unit: Choose ℃ or ℉. Warning Before start to use the temperature measuring , please examine whether the sensor cable is normal. Unplug the temperature sensor cable from the socket, the screen will display the error message “Temp sensor off” and sends out the sound alarm. 48 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 10 History Review Chapter 10 History Review The monitor can storage 72 hours trend data of the whole monitored parameters and 1000 noninvasive blood pressure measurement data. The monitor collects data of parameter every minute and preserves it in trend data, the operator may choose trend graph or trend table to examine the trend data. Every time the noninvasive blood pressure measurement data is obtained, it will be stored in the noninvasive trend data, the operator may choose the noninvasive blood pressure review to look over the noninvasive blood pressure trend data. 10.1 Trend Graph The trend graph permits operator observing the stored trend data in graph mode. The recent 72 hours trend data is displayed as a trend curve with a resolution of 1 second, 5 second, 1 minute, 2 minutes, 3 minutes, 4 minutes or 5 minutes. Choosing the “Trend Graph” in the “Review” menu will spring out the following window: Chart 12-1 Trend Graph In trend graph window, time shows underneath the X axis, recent time is displayed on the nearest right side, scope value of parameters is displayed on left side of the Y axis. 10.1.1 Select parameters By selecting the “parameter” list box with cursor, the operator may choose the parameter trend that is to be displayed. After the anticipant parameter appears, its trend graph will show in the window by pressing down the revolving button. 10.1.2 Set period By selecting the “period” option, the operator may choose a period of 1 second, 5 seconds, 1 minute, 2 minutes, 3 minutes, 4 minutes or 5 minutes. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 49 Chapter 9 Temperature Monitoring 10.1.3 Adjust observing time With the button “ ” and “ ”, the operator may move the time of trend graph a second length forward or backward (current period). With the button “ ” and “ ”, the operator may move the time of trend graph a page forward or backward. By selecting the button “ ” the operator may move the time of trend graph 72 hours forward, and “ 50 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual ” to current time. Chapter 10 History Review 10.2 Trend table The trend graph permits operator observing the trend data in tabulate mode. The recent 72 hours trend data is displayed as a trend curve with a resolution of 1 minute, 2 minutes, 3 minutes, 4 minutes, 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes, 30 minutes or 60 minutes. Choosing the “Trend Graph” in the “Review” menu will spring out the following window: Chart 12-2 trend table menu In the window of trend table, the time shows underneath the parameter tabulates, the recent time is displayed on the nearest right side, the parameter name and the unit are displayed in the first column. The alarm events may also be observed in the trend table: The alarm time of parameter is saved in the trend data, if the parameter alarm, the trend data in the correspond alarm time period would be displayed with a yellow background color. 10.2.1 Set period By selecting the “period” option with cursor, the operator may choose a period of 1 minute, 2 minutes, 3 minutes, 4 minutes, 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes, 30 minutes or 60 minutes. 10.2.2 Adjust observing time With the buttons “ ” and “ ”, the operator may move the time of trend graph a step length forward or backward (current period). With the buttons “ ” and “ ”, the operator may move the time of trend graph a page forward or backward. By selecting the button “ ”, the operator may move the time of trend graph 72 hours forward, and “ ”the current time. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 51 Chapter 10 History Review 10.3 Alarm Review When physical alarm occurs, the monitor will save all the parameters and 16 seconds waveforms in the alarm event database. the monitor can display 200 alarm event in the alarm review. Choosing the “Alarm Review” in the “Review” menu will display recent alarm event information, just as the following chart shows: z Sequence number: format is I/N which I means the index of alarm event and N means the total alarm event number in the database, as chart 12-4 shown. new alarm has smaller number, eg, No 1 means the closest alarm. z Alarm event’s time; z Alarm event’s type; z Parameters when alarm occurs; z 2 channels of waveform, 16 seconds for both channels; Chart 12-4 NIBP measurement review 10.3.1 Alarm Type There are 6 types of alarm event: “All”, “ECG”, “NIBP”, “SpO2”, “RESP”, “TEMP”, “All” means all parameters. User can select the parameter’s alarm event to view. 52 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 10 History Review 10.3.2 Choose Alarm User may use button “ “ and “ “ to choose alarm event. By selecting “ previous event will be displayed, selecting “ “ button, the “ button, the next event will be displayed, 10.3.3 Select waveform With the buttons “ “ and “ “, the operator may move the alarm waveform a page forward or backward. 10.3.4 Record The recorder will output current alarm event if the user pressed button ”Record”. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 53 Chapter 10History Review 10.4 NIBP Review The monitor may display the recent 1000 pieces of noninvasive blood pressure measurement data in the NIBP review. Choosing the “NIBP Review” in the “Review” menu will display the results and time of the recent 10 pieces of noninvasive blood pressure measurement, just as the following window shows: Chart 12-4 NIBP measurement review The data is arranged in order according to the time, the recent measurement data is displayed on the topside, 10 measurement data can be displayed on the screen each time. The buttons “ ” and “ ”can display the pre or the next measurement data. With the buttons “ ” and “ ”, the operator may move the time of trend graph a page forward or backward. By selecting the button “ ”, the operator may see the earliest measurement data, and “ 54 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual ”the most recent. Chapter 10History Review 10.5 Wave review The monitor can display 1 hour waveform data in the waveform review. Choosing the “wave review” in the “history review” menu will display the recent measurement waveform, just as the following chart shows: Chart 12-5 waveform review Above the waveform shows the interrelated information: waveform scanning velocity, current review time, the currently reviewed parameter measurement tabulate. 10.5.1 Select waveform By selecting “waveform 1” and “waveform 2” with cursor, the operator may choose the waveform that he wants to observe: ECG1, ECG2, pulse wave and resp wave. 10.5.2 Adjust observing time With the buttons “ “ and “ “, the operator may move the waveform a page forward or backward. With the buttons “ “ and “ “, the operator may move the waveform one minute forward or backward. By selecting the button “ “, the operator may move the waveform time one hour backward, and “ “the current time. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 55 Chapter 10History Review Attention The trend data can be preserved for 720 hours after the turning off of the monitor. If the monitor is turned on after 720 hours’ power-off, the trend data would be eliminated. The waveform review data can be preserved for 2 hour after the turning off of the monitor. If the monitor is turned on after 2 hour’s power-off, the waveform review data would be deleted. 56 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 11 Drug Calculation Chapter 11 Drug Calculation This monitor provides the function of computation for 21 kinds of medicines and the titration table. 11.1 Drug Calculation The kinds of medicine that can be computed include: AMINOPHYLLIN, DOBUTAMINE, DOPAMINE, EPINEPHRINE, HEPARIN, ISUPREL, INOCOR, INSULIN, INSUPREL, LIDOCAINE, NIPRIDE, NITROGLYCERIN, NOREPINEPHRINE, PITOCIN, PROCAINAMIDE, VASOPRESIN. DRUG A, DRUG B, DRUG C, DRUG D, DRUG E have been provided in addition to replace any kind of the medicine nimbly. Selecting the “Drug Calculate” in the menu will spring out window as the following chart shows: Chart 13-1 Drug Calculate The drug calculation can apply the following formulas: Concentrate = Amount/volume Inf rate = Dose / Concentrate Durate = Amount / Dose Dose = Inf rate × Concentrate Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 57 Chapter 11 Drug Calculation 11.2 Operating procedures In the Drug Calculate window, first the operator should choose the name of the drug that is to be computed, then confirm the animal’s weight, and input other values that’s already known. Rotate the knob, move the cursor to each calculated item in the formula separately. Press down and rotate the knob, select the calculated values. After the selection, value of the calculated item will be displayed in the corresponding place. Drug name selection: move the cursor to the “drug name”, rotate the knob, may choose among the 21 kinds of medicines, AMINOPHYLLIN, DOBUTAMINE, DOPAMINE, EPINEPHRINE, HEPARIN, ISUPREL, INOCOR, INSULIN, INSUPREL, LIDOCAINE, NIPRIDE, NITROGLYCERIN, NOREPINEPHRINE, PITOCIN, PROCAINAMIDE, VASOPRESIN, DRUG A, DRUG B, DRUG C, DRUG D, DRUG E. Only one type of medicine can be computed each time. 11.3 Titration table Select the “Titration Table” in the “Drug Calculate” menu to turn into the interface of titration table. The following chart shows the interface of the titration table: Chart 13-2 titration table 58 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 11 Drug Calculation 1) Move the cursor to the “DoseType” option, press down the knob to choose dosage unit. 2) Move the cursor to the “Item” option, then press down the knob to choose “Dose”, “Inf Rate”. The selection of “Dose” will calculate the infusion rate taking the dose as the basis of calculation, otherwise the dose taking infusion rate as the basis of calculation. 3) Move the cursor to the “step” option, press down the knob to choose length of step. The optional scope is 1~10. 4) With the buttons “ ” and “ ”, the operator may move the titration table a step backward or forward. With the buttons “ ” and “ ”, the operator may move the table a page forward or backward. By selecting the button “ ”, the operator may display the minimum titration table data, and “ ” the maximum. 5) The recorder will output current titration table if “Record” button is pressed. 6) Move the cursor to the “Return” button, press down the knob to get back to the “Drug Calculate” menu. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 59 Chapter 12 Maintenance and Cleaning Chapter 12 Maintenance and Cleaning 12.1 System Check Before using the monitor, you shall check: ■ Check if there is any mechanical damage; ■ Check if all the outer cables, inserted modules and accessories are in good condition; ■ Check if all the monitoring functions of the monitor can work normally so as to make sure that the monitor is in good condition. If you find any damage on the monitor, stop using the monitor on animal, and contact the biomedical engineer of the hospital or Biocare Customer Service Department immediately. The overall check of the monitor, including the functional safety check, must be performed by qualified personnel once every 6 to 12 month or each time after fix up. All checks that need to open the monitor enclosure must be performed by qualified service personnel. Safety and maintenance check may also be conducted by persons from Biocare. You can obtain the material about the customer service contract from the local Biocare office. Warning If the hospital or agency that is responding to using the monitor does not follow a satisfactory maintenance schedule, the monitor may become invalid, and the human health may be endangered. 12.2 General Cleaning Warning Turn off the power and disconnect the line power before cleaning the monitor or the sensor/probe. The Multi-Parameter animal Monitor must be kept dust-free. It is recommended that you should clean the outside surface of the monitor enclosure and the display screen regularly. Only use non-caustic detergents such as soap and water to clean the monitor enclosure. 60 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Chapter 12 Maintenance and Cleaning Caution Pay special attention to avoid damaging this monitor: 1. Avoid using ammonia-based or acetone-based cleaners such as acetone. 2. Most cleaning agents must be diluted before use. Dilute the cleaning agent as per the manufacturer's direction. 3. Do not use the grinding material, such as steel wool etc. 4. Do not let the cleaning agent enter the monitor. Do not immerse any part of the system into liquid. 5. Do not leave the cleaning agents at any part of the equipment. Cleaning Agents Except the solutions specified in the above Caution, you can use any of the solutions listed below as the cleaning agent. Diluted Ammonia Water Diluted Sodium Hyoichlo (Bleaching agent). Note The diluted sodium hyoichlo from 500ppm (1:100 diluted bleaching agent) to 5000ppm (1:10 bleaching agents) is very effective. The concentration of the diluted sodium hyocihlo depends on how many organisms (blood, mucus) are left on the surface of the enclosure. Diluted Formaldehyde 35% -- 37% Hydrogen Peroxide 3% Alcohol Isopropanol Note You can use hospital-grade ethanol to clean the monitor and its sensor/probe and leave it to dry naturally or use clean cloth to dry it. Note Biocare has no responsibility for the effectiveness of controlling infectious disease using these chemical agents. Please contact infectious disease experts in your hospital for details. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 61 Chapter 12 Maintenance and Cleaning Sterilization To avoid extended damage to the equipment, sterilization is only recommended when stipulated as necessary in the Hospital Maintenance Schedule. Sterilization facilities must be cleaned first. Recommended sterilization materials: Ethylate, and Acetaldehyde. Appropriate sterilization materials for ECG lead and blood pressure cuff are introduced Chapter ECG/RESP Monitoring and Chapter NIBP Monitoring respectively. Caution Follow the manufacturer’s instruction to dilute the solution, or adopt the lowest possible concentration. Do not let liquid enter the monitor. Do not immerse any part of the monitor into liquid. Do not pour liquid onto the monitor during sterilization. Use a moistened cloth to wipe off any agent remained on the monitor. Disinfection To avoid extended damage to the equipment, disinfection is only recommended when stipulated as necessary in the Hospital Maintenance Schedule. Disinfection facilities should be cleaned first. Appropriate disinfection materials for ECG lead, SpO2 sensor, blood pressure cuff and TEMP probe are introduced in relevant chapters. Caution Do not use EtO gas or formaldehyde to disinfect the monitor. 62 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Appendix A Product Specifications Appendix A Product Specifications Warning The animal monitor may not meet its performance specification if stored or used outside the manufacturer’s specified temperature and humidity range. 12.3 Classification Item Specification SFDA classification Class II Anti-electroshock degree Class I equipment with internal power supply Anti-electroshock degree TEMP/SpO2/NIBP: BF ECG/RESP CF Explosion proof level Ordinary equipment,without explosion proof Harmful liquid proof degree Ordinary equipment,without liquid proof Working system Continuous running equipment 12.4 Power Supply 100~240 VAC, 50/60 Hz, Pmax=90VA Fuse T1.5A 12.5 Battery 2.6 Ah 12V rechargeable battery Operating time after full charge is more than 1 hours Operating time after the first alarm of low battery will be about 5 minutes Maximum charging time is less than 6 hours. 12.6 Signal Interface Network interface standard RJ45 Socket 12.7 Storage Trend 720 hours NIBP review 1000 Wave review 2 hours Alarm review 200 alarm events NIBP events All storage data are non volatile. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 63 Appendix A Product Specifications 12.8 Environment Temperature Working 0 ~ 40 °C Storage -20 ~ 50°C Working 15% - 90 % Storage 15% - 90 % (no coagulation) Humidity 12.9 ECG 12.9.1 Lead mode 5 Leads: RA、LA、LL、RL、V; lead mode: I, II, III, AVR, AVL, AVF, V 12.9.2 Gain ×2.5mm/mV, 5.0mm/mV, 10mm/mV, 20mm/mV 12.9.3 Heart rate Measure range: 15 ~ 350 bpm accuracy ± 1% resolution 1 bpm 12.9.4 Sensitivity > 200 μV P-P 12.9.5 Differential Input Impedance > 5 M ohm 12.9.6 Bandwidth Surgery 1 ~ 20 Hz Monitor 0.5 ~ 40 Hz Diagnostic 0.05 ~ 130 Hz 12.9.7 CMRR Diagnostic Mode >90 dB Monitor Mode >110 dB Surgery Mode >110 dB 12.9.8 Electrode offset potential ±300mV 12.9.9 PACE pulse detect 64 range ±4~±700mV width 0.1~2ms Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Appendix A Product Specifications rise time 10~100µs 12.9.10 PACE pulse rejection range ±2~±700mV width 0.1~2ms rise time 10~100µs 12.9.11 Baseline Recovery < 3 s After defibrillation. 12.9.12 Signal Range ± 8 mV p-p 12.9.13 Calibration Signal ± 5% accuracy 1 mV p-p, 12.10Respiration 12.10.1 Method Impedance between RA-LL 12.10.2 Respiration Impedance Range 0.3~3Ω 12.10.3 Base Impedance Range 200Ω-4000Ω 12.10.4 Bandwidth 0.3 ~ 2.5 Hz 12.10.5 Gain ×0.25,×0.500,×1,×2,×4 12.10.6 Respiration Rate Measurement Range 0 ~ 150 BrPM Resolution 1 BrPM Accuracy 0~6 BrPM: unspecified 7~150 BrPM: ±2 BrPM 12.10.7 Apnea Alarm 10 ~ 40 s Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 65 Appendix A Product Specifications 12.11NIBP 12.11.1 Method Oscillometry 12.11.2 Measure mode Manual, Auto, STAT 12.11.3 Measure Interval in AUTO Mode 1,2,3,4,5,10,15,30,60,90,120,180,240,480 min 12.11.4 Measure Period in STAT Mode 5 min 12.11.5 Pulse Rate Range 40 ~ 240 bpm 12.11.6 Measure and Alarm Range SYS 40 ~ 280 mmHg DIA 10 ~ 220 mmHg MEAN 20 ~ 240 mmHg 12.11.7 Static pressure accuracy ±3mmHg 12.11.8 Resolution 1mmHg 12.11.9 Accuracy Maximum Mean error ±5mmHg Maximum Standard deviation 8mmHg 12.11.10 Overpressure Protection 300 mmHg 12.12 SpO₂ 12.12.1 Measurement Range 0 ~ 100 % 12.12.2 Resolution 1% 66 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Appendix A Product Specifications 12.12.3 Accuracy 70% ~ 100% ±2 % <69% unspecified 12.12.4 Pulse Rate Measure and Alarm Range 20~250bpm Resolution 1bpm Accuracy ±3bpm 12.13Temperature Channel 2 Measure and Alarm Range 0 ~ 50 °C Resolution 0.1°C Accuracy(no sensor) ± 0.1℃(0℃ – 50℃) 12.14Recorder(optional) Paper width 48 mm speed 25/50 mm/s wave channel 2 channels Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 67 Appendix B EMC – Guidance and manufacture’s declaration Appendix B EMC - Guidance and manufacture’s declaration Note Using accessories, transducers and cables other than those specified may result in increased electromagnetic emission or decreased electromagnetic immunity of the patient monitoring equipment. The device or its components should not be used adjacent to or stacked with other equipment. If adjacent or stacked use is necessary, the device or its components should be observed to verify normal operation in the configuration in which it will be used. The device needs special precautions regarding EMC and needs to be installed and put into service according to the EMC information provided below. Other devices may affect this monitor even though they meet the requirements of CISPR. When the inputted signal is below the minimum amplitude provided in technical specifications, erroneous measurements could result. B.1 Guidance and manufacture’s declaration-electromagnetic emissions for all EQUIPMENT and SYSTEMS Guidance and Declaration - Electromagnetic Emissions The device is suitable for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or the user of the device should assure that it is used in such an environment. Emission tests Compliance Electromagnetic environment - guidance Radio Group 1 The device uses RF energy only for its internal frequency (RF) emissions CISPR function. Therefore, its RF emissions are very low and 11 are not likely to cause any interference in nearby electronic equipment. RF emissions CISPR 11 Harmonic Class A Class A device establishments is other suitable than for domestic use and in all those indirectly connected to the public low-voltage power supply network that supplies buildings used for emissions IEC61000-3-2 Voltage The Compliance domestic purposes. fluctuations/flicker emissions IEC61000-3-3 B.2 Guidance and manufacture’s declaration-electromagnetic immunity for all EQUIPMENT 68 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Appendix B EMC – Guidance and manufacture’s declaration and SYSTEMS Guidance and Declaration - Electromagnetic Immunity The device is suitable for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or the user of the device should assure that it is used in such an environment. Immunity IEC60601 test Compliance test level level Electrostatic discharge (ESD) IEC 61000-4-2 ±6 kV contact ±8 kV air ±6 kV contact ±8 kV air Electrical fast transient/burst IEC 61000-4-4 ±2 kV for power supply lines ±1 kV I/O for input/output lines (>3 m) ±2 kV for power supply lines ±1 kV I/O for input/output lines (>3 m) Surge 61000-4-5 IEC ±1 kV differential mode ±2 kV common mode ±1 kV differential mode ±2 kV common mode Voltage dips, short interruptions and voltage variations on power supply input lines IEC 61000-4-11 <5 % UT (>95 % dip in UT) for 0.5 cycle <5 % UT (>95 % dip in UT) for 0.5 cycle 40 % UT (60 % dip in UT) for 5 cycles 40 % UT (60 % dip in UT) for 5 cycles 70 % UT (30 % dip in UT) for 25 cycles 70 % UT (30 % dip in UT) for 25 cycles <5 % UT (>95 % dip in UT) for 5 s <5 % UT (>95 % dip in UT) for 5 s Power frequency (50/60 HZ) magnetic field IEC 61000-4-8 3 A/m 3 A/m Electromagnetic environment - guidance Floors should be wood, concrete or ceramic tile. If floors are covered with synthetic material, the relative humidity should be at least 30%. Mains power quality should be that of a typical commercial or hospital environment. Mains power quality should be that of a typical commercial or hospital environment. If the user of our product requires continued operation during power mains interruptions, it is recommended that our product be powered from an uninterruptible power supply or a battery. Power frequency magnetic fields should be at levels characteristic of a typical location in a typical commercial or hospital environment. Note: UT is the AC mains voltage prior to application of the test level. B.3 Guidance and manufacture’s declaration-electromagnetic immunity for EQUIPMENT and SYSTEMS those are not LIFE-SUPPORTING. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 69 Appendix B EMC – Guidance and manufacture’s declaration Guidance and Declaration - Electromagnetic Immunity The device is suitable for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The customer or the user of the device should assure that it is used in such an environment. Immunity test IEC 60601 Test level Conduced IEC61000-4-6 RF Radiated IEC61000-4-3 RF 3 Vrms 150k to 80M Hz 3V/m 80M to 2.5G Hz Compliance level 3 Vrms 1Vrms) (BIS, ICG: 3V/m (Resp: 1V/m) Electromagnetic environment - guidance Portable and mobile RF communications equipment should be used no closer to any part of the device, including cables, than the recommended separation distance calculated from the equation applicable to the frequency of the transmitter. Recommended Separation Distance: Pd1.2 (BIS, ICG: Pd3.5 ) Pd1.2 (Resp: Pd3.5 ) 80 to 800 MHz Pd2.3 800M to 2.5GHz where P is the maximum output power rating of the transmitter in watts (W) according to the transmitter manufacturer and d is the recommended separation distance in meters (m). Field strengths from fixed RF transmitters, as determined by an electromagnetic site survey, a should be less than the compliance level in each frequency range b Interference may occur in the vicinity of equipment marked with the following symbol: . Note 1: From 80 MHz to 800 MHz, the higher frequency range applies. Note 2: These guidelines may not apply in all situations. Electromagnetic propagation is affected by absorption and reflection from structures, objects and people. a Field strengths from fixed transmitters, such as base stations for radio (cellular/cordless) telephones and land mobile radios, amateur radio, AM and FM radio broadcast and TV broadcast cannot be predicted theoretically with accuracy. To assess the electromagnetic environment due to fixed RF transmitters, an electromagnetic site survey should be considered. If the measured field strength in the location in which the device is used exceeds the applicable RF compliance level above, the device should be observed to verify normal operation. If abnormal performance is observed, additional measures may be necessary, such as reorienting or relocating the device. b Over the frequency ranges 150kHz to 80MHz, field strengths should be less than 3V/m. For BIS and ICG monitoring, the field strength should be less than 1V/m B.4 Recommended separation distance between portable and mobile RF communications equipment and the EQUIPMENT or SYSTEM for EQUIPMENT or SYSTEM that are not 70 Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual Appendix B EMC – Guidance and manufacture’s declaration LIFE-SUPPORTING Recommended Separation Distances between Portable and Mobile RF Communications Equipment and The device The device is suitable for use in an electromagnetic environment in which radiated RF disturbance are controlled. The customer or the user of the device can help prevent electromagnetic interference by maintaining a minimum distance between portable and mobile RF communications equipment (transmitters) and the device as recommended below, according to the maximum output power of the communication equipment. Recommended Separation Distances between Portable and Mobile RF Communications Equipment and The device Rated Maximum Output 150k to 80MHz 80M to 800MHz power of Transmitter 800M to 2.5GHz Watts (W) 0.01 0.35 0.35 0.23 0.1 1.11 1.11 0.74 1 3.5 3.5 2.34 10 11.07 11.07 7.38 100 35 35 23.34 The device is suitable for use in an electromagnetic environment in which radiated RF disturbance are controlled. The customer or the user of the device can help prevent electromagnetic interference by maintaining a minimum distance between portable and mobile RF communications equipment (transmitters) and the device as recommended below, according to the maximum output power of the communication equipment. Veterinary Monitor User’s Manual 71