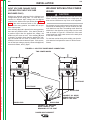
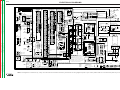
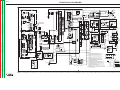
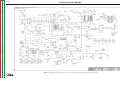
Download Lincoln Electric SVM173-A User's Manual
Transcript
View Safety Info SVM173-A April, 2007 POWER WAVE 455M/STT TM For use with machines having Code Numbers: 10942 10957 11007 11008 11057 11153 11152 View Safety Info Safety Depends on You Lincoln arc welding and cutting equipment is designed and built with safety in mind. However, your overall safety can be increased by proper installation . . . and thoughtful operation on your part. DO NOT INSTALL, OPERATE OR REPAIR THIS EQUIPMENT WITHOUT READING THIS MANUAL AND THE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS CONTAINED THROUGHOUT. And, most importantly, think before you act and be careful. 55 E4 V WA ER W PO PO WE RW AV E4 55 IO N O OF F View Safety Info Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC RETURN TO MAIN MENU View Safety Info Return to Master TOC SERVICE MANUAL Copyright © Lincoln Global Inc. • World's Leader in Welding and Cutting Products • • Sales and Service through Subsidiaries and Distributors Worldwide • Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199 U.S.A. TEL: 1-888-935-3877 WEB SITE: www.lincolnelectric.com Return to Master TOC i i SAFETY WARNING CALIFORNIA PROPOSITION 65 WARNINGS Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents are known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, and other reproductive harm. The Above For Diesel Engines The engine exhaust from this product contains chemicals known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm. The Above For Gasoline Engines ARC WELDING CAN BE HAZARDOUS. PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH. KEEP CHILDREN AWAY. PACEMAKER WEARERS SHOULD CONSULT WITH THEIR DOCTOR BEFORE OPERATING. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Read and understand the following safety highlights. For additional safety information, it is strongly recommended that you purchase a copy of “Safety in Welding & Cutting - ANSI Standard Z49.1” from the American Welding Society, P.O. Box 351040, Miami, Florida 33135 or CSA Standard W117.2-1974. A Free copy of “Arc Welding Safety” booklet E205 is available from the Lincoln Electric Company, 22801 St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199. BE SURE THAT ALL INSTALLATION, OPERATION, MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PROCEDURES ARE PERFORMED ONLY BY QUALIFIED INDIVIDUALS. FOR ENGINE powered equipment. 1.h. To avoid scalding, do not remove the radiator pressure cap when the engine is hot. 1.a. Turn the engine off before troubleshooting and maintenance work unless the maintenance work requires it to be running. ____________________________________________________ 1.b. Operate engines in open, well-ventilated areas or vent the engine exhaust fumes outdoors. ____________________________________________________ 1.c. Do not add the fuel near an open flame welding arc or when the engine is running. Stop the engine and allow it to cool before refueling to prevent spilled fuel from vaporizing on contact with hot engine parts and igniting. Do not spill fuel when filling tank. If fuel is spilled, wipe it up and do not start engine until fumes have been eliminated. ____________________________________________________ 1.d. Keep all equipment safety guards, covers and devices in position and in good repair.Keep hands, hair, clothing and tools away from V-belts, gears, fans and all other moving parts when starting, operating or repairing equipment. ____________________________________________________ 1.e. In some cases it may be necessary to remove safety guards to perform required maintenance. Remove guards only when necessary and replace them when the maintenance requiring their removal is complete. Always use the greatest care when working near moving parts. ___________________________________________________ 1.f. Do not put your hands near the engine fan. Do not attempt to override the governor or idler by pushing on the throttle control rods while the engine is running. ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS may be dangerous 2.a. Electric current flowing through any conductor causes localized Electric and Magnetic Fields (EMF). Welding current creates EMF fields around welding cables and welding machines 2.b. EMF fields may interfere with some pacemakers, and welders having a pacemaker should consult their physician before welding. 2.c. Exposure to EMF fields in welding may have other health effects which are now not known. 2.d. All welders should use the following procedures in order to minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding circuit: 2.d.1. Route the electrode and work cables together - Secure them with tape when possible. 2.d.2. Never coil the electrode lead around your body. 2.d.3. Do not place your body between the electrode and work cables. If the electrode cable is on your right side, the work cable should also be on your right side. 2.d.4. Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as possible to the area being welded. ___________________________________________________ 1.g. To prevent accidentally starting gasoline engines while turning the engine or welding generator during maintenance work, disconnect the spark plug wires, distributor cap or magneto wire as appropriate. 2.d.5. Do not work next to welding power source. Mar ‘95 Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC ii ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. ARC RAYS can burn. 3.a. The electrode and work (or ground) circuits are electrically “hot” when the welder is on. Do not touch these “hot” parts with your bare skin or wet clothing. Wear dry, hole-free gloves to insulate hands. 4.a. Use a shield with the proper filter and cover plates to protect your eyes from sparks and the rays of the arc when welding or observing open arc welding. Headshield and filter lens should conform to ANSI Z87. I standards. 3.b. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation. Make certain the insulation is large enough to cover your full area of physical contact with work and ground. 4.b. Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant material to protect your skin and that of your helpers from the arc rays. In addition to the normal safety precautions, if welding must be performed under electrically hazardous conditions (in damp locations or while wearing wet clothing; on metal structures such as floors, gratings or scaffolds; when in cramped positions such as sitting, kneeling or lying, if there is a high risk of unavoidable or accidental contact with the workpiece or ground) use the following equipment: • Semiautomatic DC Constant Voltage (Wire) Welder. • DC Manual (Stick) Welder. • AC Welder with Reduced Voltage Control. 4.c. Protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable screening and/or warn them not to watch the arc nor expose themselves to the arc rays or to hot spatter or metal. 3.c. In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode, electrode reel, welding head, nozzle or semiautomatic welding gun are also electrically “hot”. 3.d. Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical connection with the metal being welded. The connection should be as close as possible to the area being welded. 3.e. Ground the work or metal to be welded to a good electrical (earth) ground. 3.f. Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and welding machine in good, safe operating condition. Replace damaged insulation. Return to Master TOC ii SAFETY 3.g. Never dip the electrode in water for cooling. 3.h. Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of electrode holders connected to two welders because voltage between the two can be the total of the open circuit voltage of both welders. 3.i. When working above floor level, use a safety belt to protect yourself from a fall should you get a shock. 3.j. Also see Items 6.c. and 8. FUMES AND GASES can be dangerous. 5.a. Welding may produce fumes and gases hazardous to health. Avoid breathing these fumes and gases.When welding, keep your head out of the fume. Use enough ventilation and/or exhaust at the arc to keep fumes and gases away from the breathing zone. When welding with electrodes which require special ventilation such as stainless or hard facing (see instructions on container or MSDS) or on lead or cadmium plated steel and other metals or coatings which produce highly toxic fumes, keep exposure as low as possible and below Threshold Limit Values (TLV) using local exhaust or mechanical ventilation. In confined spaces or in some circumstances, outdoors, a respirator may be required. Additional precautions are also required when welding on galvanized steel. 5. b. The operation of welding fume control equipment is affected by various factors including proper use and positioning of the equipment, maintenance of the equipment and the specific welding procedure and application involved. Worker exposure level should be checked upon installation and periodically thereafter to be certain it is within applicable OSHA PEL and ACGIH TLV limits. 5.c. Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon vapors coming from degreasing, cleaning or spraying operations. The heat and rays of the arc can react with solvent vapors to form phosgene, a highly toxic gas, and other irritating products. 5.d. Shielding gases used for arc welding can displace air and cause injury or death. Always use enough ventilation, especially in confined areas, to insure breathing air is safe. Return to Master TOC 5.e. Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions for this equipment and the consumables to be used, including the material safety data sheet (MSDS) and follow your employer’s safety practices. MSDS forms are available from your welding distributor or from the manufacturer. 5.f. Also see item 1.b. AUG ‘06 Return to Master TOC iii WELDING SPARKS can cause fire or explosion. 6.a. Remove fire hazards from the welding area. If this is not possible, cover them to prevent the welding sparks from starting a fire. Remember that welding sparks and hot materials from welding can easily go through small cracks and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid welding near hydraulic lines. Have a fire extinguisher readily available. 6.b. Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site, special precautions should be used to prevent hazardous situations. Refer to “Safety in Welding and Cutting” (ANSI Standard Z49.1) and the operating information for the equipment being used. Return to Master TOC 6.c. When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode circuit is touching the work or ground. Accidental contact can cause overheating and create a fire hazard. 6.d. Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until the proper steps have been taken to insure that such procedures will not cause flammable or toxic vapors from substances inside. They can cause an explosion even though they have been “cleaned”. For information, purchase “Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of Containers and Piping That Have Held Hazardous Substances”, AWS F4.1 from the American Welding Society (see address above). 6.e. Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or welding. They may explode. 6.f. Sparks and spatter are thrown from the welding arc. Wear oil free protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy shirt, cuffless trousers, high shoes and a cap over your hair. Wear ear plugs when welding out of position or in confined places. Always wear safety glasses with side shields when in a welding area. Return to Master TOC iii SAFETY 6.g. Connect the work cable to the work as close to the welding area as practical. Work cables connected to the building framework or other locations away from the welding area increase the possibility of the welding current passing through lifting chains, crane cables or other alternate circuits. This can create fire hazards or overheat lifting chains or cables until they fail. 6.h. Also see item 1.c. CYLINDER may explode if damaged. 7.a. Use only compressed gas cylinders containing the correct shielding gas for the process used and properly operating regulators designed for the gas and pressure used. All hoses, fittings, etc. should be suitable for the application and maintained in good condition. 7.b. Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely chained to an undercarriage or fixed support. 7.c. Cylinders should be located: • Away from areas where they may be struck or subjected to physical damage. • A safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations and any other source of heat, sparks, or flame. 7.d. Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other electrically “hot” parts to touch a cylinder. 7.e. Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet when opening the cylinder valve. 7.f. Valve protection caps should always be in place and hand tight except when the cylinder is in use or connected for use. 7.g. Read and follow the instructions on compressed gas cylinders, associated equipment, and CGA publication P-l, “Precautions for Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders,” available from the Compressed Gas Association 1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA 22202. FOR ELECTRICALLY powered equipment. 8.a. Turn off input power using the disconnect switch at the fuse box before working on the equipment. 8.b. Install equipment in accordance with the U.S. National Electrical Code, all local codes and the manufacturer’s recommendations. 8.c. Ground the equipment in accordance with the U.S. National Electrical Code and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Return to Master TOC Mar ‘95 Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC iv iv SAFETY PRÉCAUTIONS DE SÛRETÉ Pour votre propre protection lire et observer toutes les instructions et les précautions de sûreté specifiques qui parraissent dans ce manuel aussi bien que les précautions de sûreté générales suivantes: Sûreté Pour Soudage A L’Arc 1. Protegez-vous contre la secousse électrique: a. Les circuits à l’électrode et à la piéce sont sous tension quand la machine à souder est en marche. Eviter toujours tout contact entre les parties sous tension et la peau nue ou les vétements mouillés. Porter des gants secs et sans trous pour isoler les mains. b. Faire trés attention de bien s’isoler de la masse quand on soude dans des endroits humides, ou sur un plancher metallique ou des grilles metalliques, principalement dans les positions assis ou couché pour lesquelles une grande partie du corps peut être en contact avec la masse. c. Maintenir le porte-électrode, la pince de masse, le câble de soudage et la machine à souder en bon et sûr état defonctionnement. d.Ne jamais plonger le porte-électrode dans l’eau pour le refroidir. e. Ne jamais toucher simultanément les parties sous tension des porte-électrodes connectés à deux machines à souder parce que la tension entre les deux pinces peut être le total de la tension à vide des deux machines. f. Si on utilise la machine à souder comme une source de courant pour soudage semi-automatique, ces precautions pour le porte-électrode s’applicuent aussi au pistolet de soudage. 2. Dans le cas de travail au dessus du niveau du sol, se protéger contre les chutes dans le cas ou on recoit un choc. Ne jamais enrouler le câble-électrode autour de n’importe quelle partie du corps. 3. Un coup d’arc peut être plus sévère qu’un coup de soliel, donc: zones où l’on pique le laitier. 6. Eloigner les matériaux inflammables ou les recouvrir afin de prévenir tout risque d’incendie dû aux étincelles. 7. Quand on ne soude pas, poser la pince à une endroit isolé de la masse. Un court-circuit accidental peut provoquer un échauffement et un risque d’incendie. 8. S’assurer que la masse est connectée le plus prés possible de la zone de travail qu’il est pratique de le faire. Si on place la masse sur la charpente de la construction ou d’autres endroits éloignés de la zone de travail, on augmente le risque de voir passer le courant de soudage par les chaines de levage, câbles de grue, ou autres circuits. Cela peut provoquer des risques d’incendie ou d’echauffement des chaines et des câbles jusqu’à ce qu’ils se rompent. 9. Assurer une ventilation suffisante dans la zone de soudage. Ceci est particuliérement important pour le soudage de tôles galvanisées plombées, ou cadmiées ou tout autre métal qui produit des fumeés toxiques. 10. Ne pas souder en présence de vapeurs de chlore provenant d’opérations de dégraissage, nettoyage ou pistolage. La chaleur ou les rayons de l’arc peuvent réagir avec les vapeurs du solvant pour produire du phosgéne (gas fortement toxique) ou autres produits irritants. 11. Pour obtenir de plus amples renseignements sur la sûreté, voir le code “Code for safety in welding and cutting” CSA Standard W 117.2-1974. PRÉCAUTIONS DE SÛRETÉ POUR LES MACHINES À SOUDER À TRANSFORMATEUR ET À REDRESSEUR a. Utiliser un bon masque avec un verre filtrant approprié ainsi qu’un verre blanc afin de se protéger les yeux du rayonnement de l’arc et des projections quand on soude ou quand on regarde l’arc. b. Porter des vêtements convenables afin de protéger la peau de soudeur et des aides contre le rayonnement de l‘arc. c. Protéger l’autre personnel travaillant à proximité au soudage à l’aide d’écrans appropriés et non-inflammables. 1. Relier à la terre le chassis du poste conformement au code de l’électricité et aux recommendations du fabricant. Le dispositif de montage ou la piece à souder doit être branché à une bonne mise à la terre. 4. Des gouttes de laitier en fusion sont émises de l’arc de soudage. Se protéger avec des vêtements de protection libres de l’huile, tels que les gants en cuir, chemise épaisse, pantalons sans revers, et chaussures montantes. 3. Avant de faires des travaux à l’interieur de poste, la debrancher à l’interrupteur à la boite de fusibles. 2. Autant que possible, I’installation et l’entretien du poste seront effectués par un électricien qualifié. 4. Garder tous les couvercles et dispositifs de sûreté à leur place. 5. Toujours porter des lunettes de sécurité dans la zone de soudage. Utiliser des lunettes avec écrans lateraux dans les Mar. ‘93 v - MASTER TABLE OF CONTENTS FOR ALL SECTIONS RETURN TO MAIN MENU Page Safety .................................................................................................................................................i-iv Installation.............................................................................................................................Section A Operation...............................................................................................................................Section B Accessories ..........................................................................................................................Section C Maintenance ..........................................................................................................................Section D Theory of Operation .............................................................................................................Section E Troubleshooting and Repair ................................................................................................Section F Electrical Diagrams ..............................................................................................................Section G Parts Manuals .................................................................................P438 (455M) & P450 (455M/STT) POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT v Return to Master TOC Section A TABLE OF CONTENTS - INSTALLATION SECTION - Installation.............................................................................................................................Section A Technical Specifications.......................................................................................................A-2, A-3 Safety Precautions ......................................................................................................................A-4 Select Suitable Location..............................................................................................................A-4 Lifting ....................................................................................................................................A-4 Stacking ................................................................................................................................A-4 Machine Grounding.....................................................................................................................A-4 High Frequency Protection..........................................................................................................A-4 Input Connection .........................................................................................................................A-5 Return to Master TOC Input Fuse and Supply Wire Considerations ........................................................................A-5 Input Voltage Change Over (For Multiple Input Voltage Machines Only).............................A-6 Welding with Multiple Power Waves ...........................................................................................A-6 Electrode and Work Cable Connections .....................................................................................A-7 Negative Electrode Polarity.........................................................................................................A-7 Voltage Sensing ..........................................................................................................................A-8 Work Voltage Sensing ..........................................................................................................A-9 Electrode Voltage Sensing ...................................................................................................A-9 Power Wave / Power Feed Wire Feeder Interconnections.........................................................A-9 Control Cable Specifications ................................................................................................A-9 External I/O Connector .........................................................................................................A-9 Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Dip Switch Settings and Locations .....................................................................................A-10 Control Board Dip Switch ...................................................................................................A-10 Feed Head Board Dip Switch .............................................................................................A-10 Devicenet/Gateway Board Dip Switch, Bank (S2)..............................................................A-11 POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Section A Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC A-2 A-2 INSTALLATION TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS - POWER WAVE 455M (K2202-1, K2202-3) INPUT AT RATED OUTPUT - THREE PHASE ONLY AMPS / VOLTS / DUTY CYCLE INPUT CURRENT AMPS 208/230/460/575V - 60HZ. [email protected]% 570A@43V. 60% 58/53/25/22 82/78/37/31 200/220/440/575V - 50HZ. [email protected]% 500A@40V. 60% 49/45/23/18 67/61/31/25 OUTPUT CONDITIONS INPUT VOLTSFREQUENCY IDLE POWER POWER FACTOR @ RATED OUTPUT EFFICIENCY @ RATED OUTPUT 400 Watts Max. .95 MIN. 88% Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC OUTPUT OPEN PULSE CURRENT PULSE CIRCUIT RANGE FREQUENCY VOLTAGE AMPS VOLTAGE RANGE 75 VDC 5 - 570A PULSE AND BACKGROUND TIME RANGE 0.15 - 1000 Hz 5 - 55 VDC 100 MICRO SEC. -3.3 SEC. PROCESS CURRENT RANGE (DC) AUXILIARY POWER (CIRCUIT BREAKER PROTECTED) 40 VDC AT 10 AMPS 115VAC AT 10 AMPS CURRENT MIG/MAG FCAW SMAW GTAW Pulse 50-570 Average Amps 40-570 Average Amps 30-570 Average Amps 15-500 Average Amps 5-750 Peak Amps Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC RECOMMENDED INPUT WIRE AND FUSE SIZES FOR MAXIMUM RATED OUTPUT INPUT VOLTAGE / FREQUENCY TYPE 75°C COPPER WIRE IN CONDUIT AWG[IEC] SIZES (MM2) TYPE 75°C GROUND WIRE IN CONDUIT AWG[IEC] SIZES (MM2) TYPE 75°C (SUPER LAG) OR BREAKER SIZE (AMPS) 208/50/60HZ 230/50/60HZ 460/50/60HZ 575/50/60HZ 4(25) 4(25) 8(10) 10(6) 6(16) 6(16) 10(6) 10(6) 110 100 50 40 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS HEIGHT 26.10 in 663 mm WIDTH 19.86 in 505 mm DEPTH 32.88 in 835 mm WEIGHT 286 lbs. 130 kg. TEMPERATURE RANGES OPERATING TEMPERATURE RANGE -20°C to +40°C STORAGE TEMPERATURE RANGE -40°C to +40°C POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC A-3 A-3 INSTALLATION TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS - POWER WAVE 455M/STT (K2203-1) INPUT AT RATED OUTPUT - THREE PHASE ONLY INPUT VOLTS OUTPUT CONDITIONS INPUT CURRENT AMPS 208/230/460/575V - 60HZ. [email protected]% 570A@43V. 60% 58/53/25/22 82/78/37/31 200/220/440/575V - 50HZ. [email protected]% 500A@40V. 60% 49/45/23/18 67/61/31/25 IDLE POWER POWER FACTOR @ RATED OUTPUT EFFICIENCY @ RATED OUTPUT 400 Watts Max. .95 MIN. 88% Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC OUTPUT OPEN PULSE CURRENT PULSE CIRCUIT RANGE/ FREQUENCY VOLTAGE VOLTAGE RANGE STT 75 VDC PULSE AND BACKGROUND TIME RANGE 5-575/5-325 0.15 - 1000 Hz 5 - 55 VDC 100 MICRO SEC. -3.3 SEC. PROCESS CURRENT RANGES (DC) AUXILIARY POWER (CIRCUIT BREAKER PROTECTED) 40 VDC AT 10 AMPS 115VAC AT 10 AMPS CURRENT MIG/MAG FCAW SMAW Pulse STT 50-570 Average Amps 40-570 Average Amps 30-570 Average Amps 5-750 Peak Amps 40-325 Average Amps Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC RECOMMENDED INPUT WIRE AND FUSE SIZES FOR MAXIMUM RATED OUTPUT INPUT VOLTAGE / FREQUENCY TYPE 75°C COPPER WIRE IN CONDUIT AWG SIZES (mm2) TYPE 75°C GROUND WIRE IN CONDUIT AWG SIZES (mm2) TYPE 75°C (SUPER LAG) OR BREAKER SIZE (AMPS) 208/50/60HZ 230/50/60HZ 460/50/60HZ 575/50/60HZ 4(25) 4(25) 8(10) 10(6) 6(16) 6(16) 10(6) 10(6) 110 100 50 40 PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS HEIGHT 26.10 in 663 mm WIDTH 19.86 in 505 mm DEPTH 32.88 in 835 mm WEIGHT 293 lbs. 133 kg. TEMPERATURE RANGES OPERATING TEMPERATURE RANGE -20°C to +40°C STORAGE TEMPERATURE RANGE -40°C to +40°C POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC A-4 A-4 INSTALLATION SAFETY PRECAUTIONS CAUTION Read this entire installation section before you start installation. WARNING ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. DO NOT MOUNT OVER COMBUSTIBLE SURFACES. Where there is a combustible surface directly under stationary or fixed electrical equipment, that surface shall be covered with a steel plate at least .06”(1.6mm) thick, which shall extend not less than 5.90”(150mm) beyond the equipment on all sides. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC • Only qualified personnel should perform this installation. • Turn the input power OFF at the disconnect switch or fuse box before working on this equipment. Turn off the input power to any other equipment connected to the welding system at the disconnect switch or fuse box before working on the equipment. LIFTING • Do not touch electrically hot parts. STACKING • Always connect the Power Wave grounding lug (located inside the reconnect input access door) to a proper safety (Earth) ground. Power Wave machines can be stacked a maximum of three high. CAUTION SELECT SUITABLE LOCATION Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Do not use Power Waves in outdoor environments. The Power Wave power source should not be subjected to falling water, nor should any parts of it be submerged in water. Doing so may cause improper operation as well as pose a safety hazard. The best practice is to keep the machine in a dry, sheltered area. Return to Section TOC Lift the machine by the lift bail only. The lift bail is designed to lift the power source only. Do not attempt to lift the Power Wave with accessories attached to it. Place the welder where clean cooling air can freely circulate in through the rear louvers and out through the case sides and bottom. Dirt, dust, or any foreign material that can be drawn into the welder should be kept at a minimum. Do not use air filters on the air intake, because the air flow will be restricted. Failure to observe these precautions can result in excessive operating temperatures and nuisance shutdowns. Machines above code 10500 are equipped with F.A.N. (fan as needed) circuitry. The fan runs whenever the output is enabled, whether under loaded or open circuit conditions. The fan also runs for a period of time (approximately 5 minutes) after the output is disabled, to ensure all components are properly cooled. If desired, the F.A.N. feature can be disabled (causing the fan to run whenever the power source is on). To disable F.A.N., connect leads 444 and X3A together at the output of the solid state fan control relay, located on the back of the Control PC board enclosure. (See the Wiring Diagram.) The bottom machine must always be placed on a firm, secure, level surface. There is a danger of machines toppling over if this precaution is not taken. MACHINE GROUNDING The frame of the welder must be grounded. A ground terminal marked with the symbol is located inside the reconnect/input access door for this purpose. See your local and national electrical codes for proper grounding methods. HIGH FREQUENCY PROTECTION Locate the Power Wave away from radio controlled machinery. CAUTION The normal operation of the Power Wave may adversely affect the operation of RF controlled equipment, which may result in bodily injury or damage to the equipment. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT A-5 INSTALLATION . Disconnect input power before . inspecting or servicing machine. VOLTAGE=200-208V W / L3 V / L2 200-208V CR1 220-230V U / L1 380-415V Do not operate with covers removed. 'A' 440-460V ELECTRIC . Do not touch electrically live parts. SHOCK Only qualified persons should install, CAN KILL use or service this equipment. . VOLTAGE=220-230V VOLTAGE=380-415V 200-208V 200-208V 200-208V 220-230V 220-230V 220-230V 380-415V 'A' INPUT SUPPLY CONNECTION DIAGRAM WARNING WARNING Disconnect input power before inspecting or servicing machine. Do not operate with covers removed. ELECTRIC ELECTRIC Do not touch electrically live parts. SHOCK SHOCK Only qualified persons should install, CAN KILL CAN KILL use or service this equipment. Return to Master TOC 'A' 440-460V VOLTAGE = 200-208V W / L3 V / L2 200-208V CR1 220-230V U / L1 440-460V VOLTAGE = 440-460V VOLTAGE = 550-575V 200-208V 200-208V 200-208V 220-230V 220-230V 550-575V 'A' 'A' 550-575V 220-230V 440-460V 440-460V 'A' 550-575V 440-460V 'A' 550-575V NOTE: Turn main input power to the machine OFF before performing connection procedure. Failure to do so will result in damage to the machine. INPUT FUSE AND SUPPLY WIRE CONSIDERATIONS INPUT CONNECTION WARNING Only a qualified electrician should connect the input leads to the Power Wave. Connections should be made in accordance with all local and national electrical codes and the connection diagram located on the inside of the reconnect/input access door of the machine. Failure to do so may result in bodily injury or death. Return to Master TOC 380-415V A Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 'A' (K1761-2) CONNECTION DIAGRAM ON CONNECTION/INPUT ACCESS DOOR VOLTAGE = 220-230V Return to Section TOC 380-415V 440-460V 440-460V Return to Section TOC VOLTAGE=440-460V S23847 WARNING THE LINCOLN ELECTRIC CO. INPUT SUPPLY CONNECTION DIAGRAM CLEVELAND, OHIO U.S.A. FIGURE A.1 (K1761-1) CONNECTION DIAGRAM ON CONNECTION/INPUT ACCESS DOOR THE LINCOLN ELECTRIC CO. CLEVELAND, OHIO U.S.A. XA S25198 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC A-5 Use a three-phase supply line. A 1.75 inch (45 mm) diameter access hole for the input supply is located on the upper left case back next to the input access door. Connect L1, L2, L3 and ground according to the Input Supply Connection Diagram decal located on the inside of the input access door, or refer to Figure A.1. Refer to the Technical Specifications at the beginning of this Installation section for recommended fuse and wire sizes. Fuse the input circuit with the recommended super lag fuse or delay type breakers (also called “inverse time” or “thermal/magnetic” circuit breakers). Choose an input and grounding wire size according to local or national electrical codes. Using fuses or circuit breakers smaller than recommended may result in “nuisance” shut-offs from welder inrush currents, even if the machine is not being used at high currents. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC A-6 A-6 INSTALLATION INPUT VOLTAGE CHANGE OVER (FOR MULTIPLE INPUT VOLTAGE MACHINES ONLY) WELDING WITH MULTIPLE POWER WAVES CAUTION Welders are shipped connected for the highest input voltage listed on the rating plate. To move this connection to a different input voltage, see the diagram located on the inside of the input access door. (Figure A.1.) If the main reconnect switch or link position is placed in the wrong position, the welder will not produce output power. Special care must be taken when more than one Power Wave is welding simultaneously on a single part. Arc blow and arc interference may occur or be magnified. If the Auxiliary (A) lead is placed in the wrong position, there are two possible results. If the lead is placed in a position higher than the applied line voltage, the welder may not come on at all. If the auxiliary (A) lead is placed in a position lower than the applied line voltage, the welder will not come on, and the two circuit breakers in the reconnect area will open. If this occurs, turn off the input voltage, properly connect the (A) lead, reset the breakers, and try again. Each power source requires a work lead from the work terminal to the welding fixture. Do not combine all of the work leads into one lead. The welding travel directions should be in the direction moving away from the work lead as shown in Figure A.2. Connect all of the work sense leads from each power source to the work piece at the end of the weld. For the best results when pulse welding, set the wire size and wire feed speed the same for all the Power Waves. FIGURE A.2 – MULTIPLE POWER WAVE CONNECTIONS TWO POWER WAVES I ON I ON Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC POWERWAVE 455/R POWERWAVE 455/R O OFF O OFF SEN SE L EAD ELECTRODE ELECTRODE VEL TRAECTION DIR Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC SENSE LEAD CONNECT ALL WORK SENSE LEADS AT THE END OF THE JOINT WORK LEAD WORK LEAD CONNECT ALL WELDING WORK LEADS AT THE BEGINNING OF THE JOINT POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC A-7 When these parameters are identical, the pulsing frequency will be the same, helping to stabilize the arcs. Every welding gun requires a separate shielding gas regulator for proper flow rate and shielding gas coverage. Do not attempt to supply shielding gas for two or more guns from only one regulator. If an anti-spatter system is in use, each gun must have its own anti-spatter system. See Figure A.2. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC ELECTRODE AND WORK CABLE CONNECTIONS Connect a work lead of sufficient size and length (per Table A.1) between the proper output terminal on the power source and the work. Be sure the connection to the work makes tight metal-to-metal electrical contact. To avoid interference problems with other equipment and to achieve the best possible operation, route all cables directly to the work or wire feeder. Avoid excessive lengths and do not coil excess cable. Do not tightly bundle the electrode and work cables together. Use K1796 coaxial welding cables wherever possible. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Minimum work and electrode cables sizes are as follows: TABLE A.1 (Current (60% Duty Cycle) MINIMUM COPPER WORK CABLE SIZE AWG Up To 100 Ft. Length (30 m) 400 Amps 500 Amps 600 Amps 2/0 (67 mm ) 3/0 (85 mm2) 3/0 (85 mm2) Return to Master TOC Most welding applications run with the electrode being positive (+). For those applications, connect one end of the electrode cable to the positive (+) output terminal on the power source (located beneath the spring loaded output cover near the bottom of the case front). Connect the other end of the electrode cable to the wire drive feed plate using the stud, lockwasher, and nut provided on the wire drive feed plate. The electrode cable lug must be against the feed plate. Be sure the connection to the feed plate makes tight metal-to-metal electrical contact. The electrode cable should be sized according to the specifications given in Table A.1. Connect a work lead from the negative (-) power source output terminal to the work piece. The work piece connection must be firm and secure, especially if pulse welding is planned. CAUTION Excessive voltage drops caused by poor work piece connections often result in unsatisfactory welding performance. When welding with the STT process, use the positive output connection labeled (STT) for STT welding. (If desired, other welding modes can be used on this terminal; however, their average output current will be limited to 325 amps.) For non-STT processes, use the positive output connection labeled (Power Wave), so that the full output range of the machine is available. CAUTION 2 When using an inverter type power source like the Power Wave, use the largest welding (electrode and ground) cables that are practical. At least 2/0 copper wire - even if the average output current would not normally require it. CAUTION Return to Section TOC A-7 INSTALLATION When pulsing, the pulse current can reach very high levels. Voltage drops can become excessive, leading to poor welding characteristics, if undersized welding cables are used. Do not connect the STT and Power Wave terminals together. Paralleling the terminals will bypass STT circuitry and severely deteriorate STT welding performance. NEGATIVE ELECTRODE POLARITY When negative electrode polarity is required, such as in some Innershield applications, reverse the output connections at the power source (electrode cable to the negative (-) terminal, and work cable to the positive (+) terminal). When operating with electrode polarity negative, the Dip switch 7 must be set to ON on the Wire Feed Head PC Board. The default setting of the switch is OFF to represent positive electrode polarity. To set the Negative Polarity switch on Wire Feed Head PC board, refer to the section DIP SWITCH SETTINGS AND LOCATIONS. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC A-8 The sense leads connect to the Power Wave at the four-pin connector located underneath the output terminal cover. Lead 67 senses electrode voltage. Lead 21 senses work voltage. VOLTAGE SENSING The best arc performance occurs when the Power Wave has accurate data about the arc conditions. Depending upon the process, inductance within the electrode and work lead cables can influence the voltage apparent at the terminals of the welder. Voltage sense leads improve the accuracy of the arc conditions and can have a dramatic effect on performance. Enable the voltage sense leads as follows: TABLE A.2 CAUTION Return to Master TOC If the voltage sensing is enabled but the sense leads are missing or improperly connected, extremely high welding outputs may occur. Return to Section TOC A-8 INSTALLATION Do not tightly bundle the work sense lead to the work lead. Process Electrode Voltage Sensing 67 lead * Work Voltage Sensing 21 lead GMAW 67 lead required 21 lead optional GMAW-P 67 lead required 21 lead optional FCAW 67 lead required 21 lead optional STT 67 lead required 21 lead required GTAW Voltage sense at terminals Voltage sense at terminals SAW 67 lead required 21 lead optional * The electrode voltage 67 sense lead is integral to the control cable to the wire feeder. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC FIGURE A.3 – DIP SWITCH LOCATION /R 55 E4 V A RW WE O P REMOVE FRONT COVER IO O N OF F PO WE RW AV E4 55 /R WIRE FEED HEAD BOARD ON RIGHT POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT CONTROL BOARD ON LEFT WORK VOLTAGE SENSING CONTROL CABLE SPECIFICATIONS The Power Wave is shipped from the factory with the work sense lead enabled. It is recommended that genuine Lincoln control cables be used at all times. Lincoln cables are specifically designed for the communication and power needs of the Power Wave / Power Feed system. For processes requiring work voltage sensing, connect the (21) work voltage sense lead from the Power Wave to the work. Attach the sense lead to the work as close to the weld as practical. To enable the work voltage sensing in the Power Wave, refer to the section DIP SWITCH SETTINGS AND LOCATIONS. Enabling or disabling electrode voltage sensing is automatically configured through software. Electrode sense lead 67 must be connected at the wire feeder. CAUTION The use of non-standard cables, especially in lengths greater than 25 feet, can lead to communication problems (system shutdowns), poor motor acceleration (poor arc starting) and low wire driving force (wire feeding problems). Lincoln control cables are copper 22 conductor cable in a SO-type rubber jacket. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Reserved for future use 2 Shutdown2 input 1 Shutdown1 input A work lead must be run from the negative (-) power source output connection to the work piece. The work piece connection must be firm and secure, especially if pulse welding is planned. +15 for shutdown group Output connections on some Power Waves are made via 1/2-13 threaded output terminals located beneath the spring-loaded output cover at the bottom of the case front. On machines which carry the CE mark, output connections are made via Twist-Mate receptacles, also located beneath the spring-loaded output cover at the bottom of the case front. Gas Purge Input The Shutdown Group is always enabled. Shutdown 2 is used for signaling low flow in the water cooler. Unused shutdowns must be jumpered. Machines from the factory come with the shutdowns already jumpered. (See Figure A.4) FIGURE A.4 – INPUT PORT CONNECTIONS Cold Inch Reverse For convenience sake, the electrode and control cables can be routed behind the left or right strain reliefs (under the spring loaded output cover), and along the channels formed into the base of the Power Wave, out the back of the channels, and then to the wire feeder. Cold Inch Forward The Power Wave is equipped with a port for making simple input signal connections. The port is divided into three groups: Trigger group, Cold Inch Group and Shutdown Group. Because the Power Wave is a “slave” on the DeviceNet network, the Trigger and Cold Inch Groups are disabled when the DeviceNet/Gateway is active. +15 VDC for Cold Inch Group Connect the control cable between the power source and wire feeder. The wire feeder connection on the robotic Power Wave is located under the spring loaded output cover, near the bottom of the case front. The control cable is keyed and polarized to prevent improper connection. 4 Step Input EXTERNAL I/O CONNECTOR Dual Procedure Input POWER WAVE / POWER FEED WIRE FEEDER INTERCONNECTIONS Trigger Input Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC ELECTRODE VOLTAGE SENSING Return to Section TOC A-9 INSTALLATION +15 VDC for Trigger Group Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC A-9 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC CAUTION Excessive voltage drops at the work piece connection often result in unsatisfactory pulse welding performance. A D B E C POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT G H F I Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC A-10 A-10 INSTALLATION DIP SWITCH SETTINGS AND LOCATIONS DIP switches on the PC boards allow for custom configuration of the Power Wave. Access the DIP switches as follows: WARNING ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL. CONTROL BOARD DIP SWITCH: switch switch switch switch switch switch switch switch 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 = = = = = = = = reserved for future reserved for future reserved for future reserved for future reserved for future reserved for future reserved for future work sense lead use use use use use use use • Do not touch electrically live parts or electrodes with your skin or wet clothing. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC • Insulate yourself from the work and ground. • Always wear dry insulating gloves. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC • Remove the top four screws securing the front access panel. • Loosen, but do not completely remove, the bottom two screws holding the access panel. • Adjust the DIP switches as necessary. Using a pencil or other small object, slide the switch left for the ON position or to the right for the OFF position, as appropriate. off work sense lead not connected on work sense lead connected switch switch switch switch switch switch switch switch 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 = = = = = = = = reserved for future use reserved for future use reserved for future use reserved for future use reserved for future use reserved for future use negative polarity switch high speed gear switch 7 electrode polarity off positive on negative switch 8 wire drive gear off low speed gear on high speed gear • Replace the panel and screws and restore power. CONTROL BOARD (LOCATED IN CONTROL BOX BEHIND CASE FRONT) DEVICENET/ GATEWAY BOARD (LOCATED BEHIND FRONT COVER) FRONT COVER Return to Master TOC work sense lead FEED HEAD BOARD DIP SWITCH: • Turn off power at the disconnect switch. • Open the access panel, allowing the weight of the panel to be carried by the bottom two screws. Make sure to prevent the weight of the access panel from hanging on the harness. Return to Section TOC switch 8 LEFT BANK S1 FEED HEAD BOARD (LOCATED IN CONTROL BOX BEHIND CASE FRONT) CASE FRONT BANK S2 OPENING IN CASE FRONT TO ACCESS CONTROL BOX RIGHT POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC A-11 INSTALLATION DEVICENET/GATEWAY BOARD DIP SWITCH, BANK (S2): switch 1,2 = configure the baud rate for DeviceNET Prior to S24958-6 software switch 1 switch 2 baud rate off off ------- on off 125K off on 250K on on 500 S24958-6 and later software switch 1 switch 2 baud rate off off 125K off on 250K on off 500K on on 500K Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Programmable value. Consult local Lincoln Technical representative. switch switch switch switch 5 6 7 8 = = = = reserved reserved reserved reserved for for for for future future future future use use use use POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT A-11 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC A-12 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT A-12 Return to Master TOC Section B-1 TABLE OF CONTENTS - OPERATION SECTION - Section B-1 Operation...............................................................................................................................Section B Safety Precautions ......................................................................................................................B-2 Graphic Symbols.........................................................................................................................B-3 General Description ....................................................................................................................B-4 Design Features and Advantages ........................................................................................B-4 Recommended Processes and Equipment.................................................................................B-5 Recommended Processes....................................................................................................B-5 Recommended Equipment ...................................................................................................B-5 Required Equipment .............................................................................................................B-5 Duty Cycle and Time Period.................................................................................................B-5 Case Front Controls ....................................................................................................................B-6 Welding Mode Descriptions ........................................................................................................B-7 Constant Voltage Welding ....................................................................................................B-7 Pulse Welding.......................................................................................................................B-8 STT Welding .........................................................................................................................B-9 Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Limitations.............................................................................................................................B-5 POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC B-2 OPERATION SAFETY PRECAUTIONS Read this entire section of operating instructions before operating the machine. WARNING Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. • Unless using cold feed feature, when feeding with gun trigger, the electrode and drive mechanism are always electrically energized and could remain energized several seconds after the welding ceases. • Do not touch electrically live parts or electrodes with your skin or wet clothing. • Insulate yourself from the work and ground. • Always wear dry insulating gloves. FUMES AND GASES can be dangerous. • Keep your head out of fumes. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC • Use ventilation or exhaust to remove fumes from breathing zone. WELDING SPARKS can cause fire or explosion. • Keep flammable material away. • Do not weld on containers that have held combustibles. ARC RAYS can burn. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC • Wear eye, ear, and body protection. Observe additional guidelines detailed in the beginning of this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT B-2 Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC B-3 B-3 OPERATION GRAPHIC SYMBOLS THAT APPEAR ON THIS MACHINE OR IN THIS MANUAL INPUT POWER SMAW ON GMAW OFF FCAW HIGH TEMPERATURE GTAW MACHINE STATUS U0 OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE CIRCUIT BREAKER U1 INPUT VOLTAGE WIRE FEEDER U2 OUTPUT VOLTAGE POSITIVE OUTPUT I1 INPUT CURRENT NEGATIVE OUTPUT I2 OUTPUT CURRENT 3 PHASE INVERTER PROTECTIVE GROUND INPUT POWER WARNING OR CAUTION Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC THREE PHASE DIRECT CURRENT POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC B-4 OPERATION B-4 GENERAL DESCRIPTION DESIGN FEATURES AND ADVANTAGES The Power Wave power source is designed to be a part of a modular, multi-process welding system. Depending on configuration, it can support constant current, constant voltage, Surface Tension Transfer and pulse welding modes. • Designed to the IEC 974-1 Standard. The Power Wave power source is designed to be used with the family of Power Feed wire feeders, operating as a system. Each component in the system has special circuitry to “talk with” the other system components, so each component (power source, wire feeder, electrical accessories) knows what the other is doing at all times. The components communicate using ArcLink protocol. Robotic systems can communicate with other industrial machines via DeviceNET protocol. The result is a highly intigrated and flexible welding cell. The Power Wave 455/R is a high performance, digitally controlled inverter welding power source capable of complex, high-speed waveform control. Properly equipped, it can support the GMAW, GMAW-P, FCAW, GTAW and STT processes. It carries an output rating of either 450 amps, 38 volts; or 400 amps, 36 volts (both at 100% duty cycle), depending on input voltage and frequency. The Surface Tension transfer process (STT) is supported at currents up to 325 amps, at 100% duty cycle. • Power Wave 455 multiple process output ranges: 5 - 570 amps • Easy access for input connections. Connections are simple strip and clamp (no lugs required). • F.A.N. (Fan As Needed). Cooling fan runs only when necessary (above Code 10500 only, and all STT machines). • Modular construction for easy servicing. • Thermostatically protected. • Electronic over-current protection. • Input over-voltage protection. • Utilizes digital signal processing and microprocessor control. • Simple, reliable input voltage change over. • All system components communicate and transfer information. • Auto device recognition simplifies accessory cable connections. If the duty cycle is exceeded, a thermostat will shut off the output until the machine cools to a reasonable operating temperature. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC B-5 OPERATION RECOMMENDED PROCESSES AND EQUIPMENT B-5 REQUIRED EQUIPMENT • PF-10/R Wire Feeder, K1780-1 • Control Cables (22 pin to 22 pin), K1795-10,-25,-50,100 RECOMMENDED PROCESSES The Power Wave 455/R can be set up in a number of configurations, some requiring optional equipment or welding programs. Each machine is factory preprogrammed with multiple welding procedures, typically including GMAW, GMAW-P, FCAW, GTAW and STT for a variety of materials, including mild steel, stainless steel, cored wires, and aluminum. The STT process supports mild steel and stainless steel welding. • Control Cables (for use on FANUC robot arm, 22 pin to 14 pin, 10 ft), K1804-1 The Power Wave 455/R is recommended only for automatic or mechanized applications such as robotic welding. LIMITATIONS RECOMMENDED EQUIPMENT • Power Waves are not to be used in outdoor environments. Automatic Operation All welding programs and procedures are set through software for the robotic Power Wave. FANUC robots equipped with RJ-3 controllers may communicate directly with the Power Wave. Other pieces of equipment such as PLCs or computers can communicate with the Power Wave using DeviceNET. All wire welding processes require a robotic Power Feed wire feeder. • Control Cables (for use on FANUC robot arm, 22 pin to 14 pin, 18 in), K1805-1 • Control Cables (for use on FANUC robot arm, 22 pin to 14 pin, 18 in), K1804-2 • The Power Wave 455/R is not suitable for SMAW, CAC-A or other processes not listed. • Only ArcLink Power Feed wire feeders and user interfaces may be used. Other Lincoln wire feeders or non-Lincoln wire feeders cannot be used. DUTY CYCLE AND TIME PERIOD The Power Feed wire feeders are capable of welding at a 100% duty cycle (continuous welding). The power source will be the limiting factor in determining system duty cycle capability. Note that the duty cycle is based upon a ten minute period. A 60% duty cycle represents 6 minutes of welding and 4 minutes of idling in a ten minute period. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC B-6 CASE FRONT CONTROLS 3. HIGH TEMPERATURE LIGHT (thermal overload): A yellow light that comes on when an over temperature situation occurs. Output is disabled until the machine cools down. When cool, the light goes out and output is enabled. All operator controls and adjustments are located on the case front of the Power Wave. (See Figure B.1) 1. POWER SWITCH: Controls input power to the Power Wave. 2. STATUS LIGHT: A two color light that indicates system errors. Normal operation is a steady green light. Error conditions are indicated, per Table B.1. 4. 10 AMP WIRE FEEDER CIRCUIT BREAKER: Protects 40 volt DC wire feeder power supply. 5. 10 AMP AUXILIARY POWER CIRCUIT BREAKER: Protects 115 volt AC case front receptacle auxiliary supply. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC NOTE: The robotic Power Waves’ status light will flash green, and sometimes red and green, for up to one minute when the machine is first turned on. This is a normal situation as the machine goes through a self test at power up. Return to Master TOC 6. LEAD CONNECTOR S2 (SENSE LEAD) 7. 5-PIN ARC LINK S1 TABLE B.1 Light Condition 8. 5-PIN DEVICENET CONNECTOR S5 9. I / O CONNECTOR Meaning Steady Green System OK. Power source communicating normally with wire feeder and its components. Blinking Green Normal for first 1-10 seconds after power is turned on. Alternating Green and Red Return to Section TOC B-6 OPERATION Steady Red 10. NEGATIVE OUTPUT TERMINAL 11. INTERFACE CONNECTOR S6 12. STT TERMINAL 13. POSITIVE OUTPUT TERMINAL 14. AUXILIARY OUTPUT Non-recoverable system fault. Must turn power source off, find source of error, and turn power back on to reset. See Troubleshooting Guide. See Troubleshooting Guide. FIGURE B.1 – POWER WAVE CASE FRONT CONTROLS 2 I ON 6 POWERWAVE 455/R 3 1 O OFF 7 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 8 9 11 10 12 13 5 14 4 POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC B-7 OPERATION WELDING MODE DESCRIPTIONS CONSTANT VOLTAGE WELDING For each wire feed speed, a corresponding voltage is preprogrammed into the machine through special software at the factory. The preprogrammed voltage is the best average voltage for a given wire feed speed. With synergic programs, when the wire feed speed changes, the Power Wave will automatically adjust the corresponding voltage. Wave control adjusts the inductance of the wave shape. (This adjustment is often referred to as "pinch". Inductance is inversely proportional to pinch.) Increasing wave control greater than 0 results in a harsher, colder arc, while decreasing the wave control to less than 0 provides a softer, hotter arc. (See Figure B.2.) FIGURE B.2 – CV WAVE CONTROL CHARACTERISTICS Wave Control +10.0 Wave Control 0.00 Wave Control -10.0 Current Return to Master TOC Time Return to Section TOC B-7 POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC B-8 OPERATION PULSE WELDING Pulse welding procedures are set by controlling an overall “arc length” variable. When pulse welding, the arc voltage is highly dependent upon the waveform. The peak current, background current, rise time, fall time and pulse frequency all affect the voltage. The exact voltage for a given wire feed speed can only be predicted when all the pulsing waveform parameters are known. Using a preset voltage becomes impractical, and instead the arc length is set by adjusting “trim.” The Power Wave utilizes “adaptive control” to compensate for changes in electrical stick-out while welding. (Electrical stick-out is the distance from the contact tip to the work piece.) The Power Wave waveforms are optimized for a 0.75" (19mm) stick-out. The adaptive behavior supports a range of stickouts from 0.50" (13mm) to 1.25" (32mm). At very low or high wire feed speeds, the adaptive range may be less due to reaching the physical limitations of the welding process. Trim adjusts the arc length and ranges from 0.50 to 1.50, with a nominal value of 1.00. Trim values greater than 1.00 increase the arc length, while values less than 1.00 decrease the arc length. Wave control in pulse programs usually adjusts the focus or shape of the arc. Wave control values greater than 0 increase the pulse frequency while decreasing the background current, resulting in a tight, stiff arc best for high speed sheet metal welding. Wave control values less than 0 decrease the pulse frequency while increasing the background current for a soft arc good for out-of-position welding. (See Figure B.3.) Most pulse welding programs are synergic. As the wire feed speed is adjusted, the Power Wave will automatically recalculate the waveform parameters to maintain similar arc properties. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC FIGURE B.3 – PULSE WAVE CONTROL CHARACTERISTICS Current Wave Control -10.0 Wave Control 0.00 Wave Control +10.0 Return to Master TOC Time Return to Section TOC B-8 POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC B-9 B-9 OPERATION STT WELDING The pictures illustrate the wave shape of current for the process. They are not drawn to scale, and are intended only for the purpose of showing how the variables affect the waveform. Trim in the STT mode adjusts the tailout and background portion of the waveform. Trim values greater than 1.0 add more energy to the weld and make the weld puddle hotter; trim values less than 1.0 reduce energy to weld. A nominal value of 1.0 will work for most applications. (See Figure B.4.) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC FIGURE B.4 – STT TRIM CONTROL CHARACTERISTICS Trim 1.50 Current Trim 1.00 Time Trim 0.50 For most programs, peak current is adjusted by wave control values. A value of +10.0 maximizes the peak current, while a wave control of -10.0 minimizes peak current. In general, the peak current is proportional to torch arc length. (See Figure B.5.) NOTE: The ranges on Wave Control and Trim are dependent on the weld programs. The values shown are typical ranges. FIGURE B.5 – STT WAVE CONTROL CHARACTERISTICS Wave Control +10.0 Wave Control 0.00 Wave Control -10.0 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Current Time POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC B-10 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT B-10 TABLE OF CONTENTS - ACCESSORIES SECTION - Optional Equipment ....................................................................................................................C-2 Factory Installed ...................................................................................................................C-2 Field Installed .......................................................................................................................C-2 Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Section C-1 Accessories ..........................................................................................................................Section C Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Section C-1 POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC C-2 Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC C-2 OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT FACTORY INSTALLED There are no factory installed options available for the Power Wave 455R. The water cooler is designed to cool only one welding gun and should be not used to cool multiple guns or other devices. FIELD INSTALLED • Return to Section TOC ACCESSORIES Gas Guard Regulator (K659-1) The Gas Guard regulator is available as an optional accessory for the Power Feed Robotic wire drive unit. Install the 5/8-18 male outlet on the regulator to the proper 5/8-18 female gas inlet on the back panel of the wire drive. Secure the fitting with the flow adjuster key at the top. • Voltage Sense Leads (K940-10, -25 or -50) The voltage sense leads connect at the front of the machine. (See Figure A.2.) • Power Wave Water Cooler (K1767-1)* The K1767-1 is the recommended water cooler for the Power Wave. Incorporated into the cooler is an automatic flow sensor to detect low coolant flow. In the event of a low flow condition, a fault signal is sent to the Power Wave, and welding output automatically stops to protect the torch. Water cooler manufacturers often specify additives to the coolant such as fungicides or alkalies. Follow the manufacturers’ recommendations to achieve proper operation and long lifetime without clogging. • Water Flow Sensor (K1536-1) Water cooled guns can be damaged very quickly if they are used even momentarily without water flowing. Recommend practice is to install a water flow sensor such as on the water return line of the torch. When fully integrated into the welding system, the sensor will prevent welding if no water flow is present. • Dual Cylinder Undercarriage, K1570-1* • Coaxial Welding Cable, K1796 *The Dual Cylinder Undercarriage, K1570-1, is not compatible in combination with the Power Wave Water Cooler K1767-1. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT TABLE OF CONTENTS - MAINTENANCE SECTION - Safety Precautions......................................................................................................................D-2 Routine and Periodic Maintenance.............................................................................................D-2 Main Assembly (Exploded View) ...............................................................................................D-3 Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Section D-1 Maintenance ..........................................................................................................................Section D Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Section D-1 POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC D-2 MAINTENANCE PERFORM THE FOLLOWING DAILY: SAFETY PRECAUTIONS 1. Check that no combustible materials are in the welding or cutting area or around the machine. WARNING 2. Remove any debris, dust, dirt, or materials that could block the air flow to the machine for cooling. ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. • Only Qualified personnel should perform this maintenance. • Turn the input power OFF at the disconnect switch or fuse box before working on this equipment. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC • D-2 Do not touch electrically hot parts. 3. Inspect the electrode cables for any slits or punctures in the cable jacket, or any condition that would affect the proper operation of the machine. PERFORM PERIODICALLY: Clean the inside of the machine with a low pressure air stream. Clean the following parts. Refer to Figure D.1. • Transformer and output rectifier assembly. ROUTINE AND PERIODIC MAINTENANCE • Electrode and work cable connections. • PC board connections.. 1. Disconnect input AC power supply lines to the machine before performing periodic maintenance, tightening, cleaning, or replacing parts. See Figure D.1. • Intake and outlet louvers on the machine case. • Any obvious accumulations of dirt within the machine. • Fan Assembly. Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC NOTE: The fan motor has sealed bearings which require no maintenance. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT D-3 MAINTENANCE Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC D-3 FIGURE D.1 – MAIN ASSEMBLY (EXPLODED VIEW) 7 7 1 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 7 3 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 4 2 2 6 5 1. CASE FRONT ASSEMBLY 2. TRANSFORMER AND OUTPUT RECTIFIER ASSEMBLY 3. INPUT ASSEMBLY Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 4. CONTROL BOX AND VERTICAL DIVIDER ASSEMBLY 2 5. BASE, LIFT BAIL AND FAN ASSEMBLY 6. SWITCH BOARD HEATSINK ASSEMBLY 7. CASE PARTS POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC D-4 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT D-4 Return to Master TOC Section E-1 Section E-1 TABLE OF CONTENTS - THEORY OF OPERATION SECTION - Theory of Operation .............................................................................................................Section E Block Logic Diagram ...................................................................................................................E-1 General Description ....................................................................................................................E-2 Input Voltage and Precharge ......................................................................................................E-3 Switch Boards and Main Transformer.........................................................................................E-4 DC Bus Board, Power Board, Feed Head Board, Gateway Board and Voltage Sense Board ...........................................................................................................E-5 Power Wave Communications Diagram .....................................................................................E-6 Control Board ..............................................................................................................................E-7 Return to Master TOC Output Rectifier, Output Choke and STT Chopper Board ..........................................................E-8 Thermal Protection, Protective Circuits, Over Current Protection and Under/Over Voltage Protection ............................................................................................E-9 General Description of STT (Surface Tension Transfer) Process.............................................E-10 Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) Operation .................................................................E-11 Pulse Width Modulation ............................................................................................................E-12 FIGURE E.1 – BLOCK LOGIC DIAGRAM IGBT DRIVE FROM CONTROL BOARD POWER WAVE 455/R INPUT RECTIFIER Return to Master TOC +20 VDC FROM POWER BOARD IGBT DRIVE FROM CONTROL CT CURRENT TO CONTROL BOARD BOARD SW1 CURRENT TRANSDUCER STT CHOPPER BOARD STT ELECTRODE TERMINAL + RIGHT SWITCH BOARD CAP. V/F FEEDBACK ELECTRODE TERMINAL + LEFT SWITCH BOARD RECONNECT SWITCH STT DRIVE CURRENT TRANSDUCER OUTPUT CHOKE WORK TERMINAL 67A INPUT BOARD S1 67B CONTACTOR AND PRECHARGE CONTROL SIGNALS FROM CONTROL BOARD AUX RECONNECT MAIN TRANSFORMER OUTPUT DIODES D1 -D4 CAP. V/F FEEDBACK CR1 CT CURRENT TO CONTROL BOARD S6 VOLT SENSE BOARD VOLTAGE SENSE OUTPUT VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT ARC LINK 2 4 V A C FROM CONTROL BOARD FEED HEAD BOARD 40 VDC 115 VAC FAN RELAY DEVICE NET S5 GATEWAY BOARD CONNECTION TO ROBOT TO LEFT S.B. TO RIGHT S.B. C U R R E N T F B S T T F B 40 VDC TO FAN RELAY IGBT DRIVES CONTACTOR AND PRECHARGE CONTROL SIGNALS ARC LINK 115 VAC Return to Master TOC +5V RS232 65 VDC 52 VAC DC BUS BOARD BUS BOARD RECTIFIER T1 230 VAC WATER COOLER S6 T2 115 VAC POWER BOARD 40 VDC THERMOSTATS CONTROL BOARD +5V SPI S2 WORK SENSE +15V SPI S3 RS232 +5 V +15 V 40 VDC -15 V 40 VDC 115 VAC RECP. CONNECTION TO WIRE DRIVE +5 V ARC LINK S1 ARC LINK WIRE FEEDER RECP. LEFT S.B. CAP. V/F RIGHT S.B. CAP. V/F +20 VDC TO CHOPPER BOARD POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT LEFT CT CURRENT FB RIGHT CT CURRENT FB STATUS LIGHT THERMAL LIGHT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC E-2 FIGURE E.2 – INPUT VOLTAGE AND PRECHARGE IGBT DRIVE FROM CONTROL BOARD POWER WAVE 455/R INPUT RECTIFIER Return to Master TOC +20 VDC FROM POWER BOARD IGBT DRIVE FROM CONTROL CT CURRENT TO CONTROL BOARD BOARD SW1 CURRENT TRANSDUCER STT CHOPPER BOARD STT ELECTRODE TERMINAL + RIGHT SWITCH BOARD CAP. V/F FEEDBACK ELECTRODE TERMINAL + LEFT SWITCH BOARD RECONNECT SWITCH STT DRIVE CURRENT TRANSDUCER OUTPUT CHOKE WORK TERMINAL 67A INPUT BOARD S1 CONTACTOR AND PRECHARGE CONTROL SIGNALS FROM CONTROL BOARD AUX RECONNECT MAIN TRANSFORMER CT CURRENT TO CONTROL BOARD OUTPUT DIODES D1 -D4 CAP. V/F FEEDBACK CR1 Return to Section TOC E-2 THEORY OF OPERATION 67B S6 VOLT SENSE BOARD VOLTAGE SENSE OUTPUT DEVICE NET S5 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT ARC LINK 2 4 V A C FROM CONTROL BOARD FEED HEAD BOARD 40 VDC 115 VAC FAN RELAY GATEWAY BOARD CONNECTION TO ROBOT TO LEFT S.B. TO RIGHT S.B. C U R R E N T F B S T T F B 40 VDC TO FAN RELAY IGBT DRIVES CONTACTOR AND PRECHARGE CONTROL SIGNALS ARC LINK 115 VAC +5V RS232 65 VDC 52 VAC DC BUS BOARD BUS BOARD RECTIFIER T1 230 VAC WATER COOLER S6 CONNECTION TO WIRE DRIVE 40 VDC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC T2 115 VAC +5V SPI S2 WORK SENSE +15V SPI S3 RS232 +5 V +15 V 40 VDC -15 V 40 VDC 115 VAC RECP. POWER BOARD THERMOSTATS CONTROL BOARD +5 V ARC LINK S1 ARC LINK WIRE FEEDER RECP. GENERAL DESCRIPTION The Power Wave 455M/MSTT power source is designed to be a part of a modular, multi-process welding system. It is a high performance, digitally controlled inverter welding power source capable of complex, high-speed waveform control. Depending upon configuration, it can support constant current, constant voltage, surface tension transfer and pulse welding modes. Each machine is factory preprogrammed with multiple welding procedures. Typically these procedures include GMAW, GMAW-P, FCAW, GTAW and LEFT S.B. CAP. V/F RIGHT S.B. CAP. V/F +20 VDC TO CHOPPER BOARD LEFT CT CURRENT FB RIGHT CT CURRENT FB STATUS LIGHT THERMAL LIGHT STT (Surface Tension Transfer) for a variety of materials such as mild steel, stainless steel, cored wires and aluminum. The STT process supports mild steel and stainless steel welding. PW455M/STT only. The Power Wave 455M/STT has an output rating of either 450 amps at 38 volts or 400 amps at 36 volts. The two output ratings are dependent upon input voltage and frequency. Both have a duty cycle of 100%. The STT process is rated at currents up to 325 amps at a 100% duty cycle. NOTE: Unshaded areas of Block Logic Diagram are the subject of discussion. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC E-3 THEORY OF OPERATION E-3 INPUT VOLTAGE AND PRECHARGE The Power Wave 455M can be connected for a variety of three-phase input voltages. Refer to Figure E.2. The initial input power is applied to the Power Wave 455M through a line switch located on the front of the machine. Two phases of the three-phase input power are applied to the Input Board and both auxiliary transformers. The various secondary voltages developed by transformer T1 are applied to the Input Board, the fan motor (via a control relay) and the Bus Board rectifier. The 65VDC produced from the Bus Board rectifier is used by the Bus Board to provide various DC voltages for the Power Board, the Feed Head Board and the wire feeder receptacle. The 115/230VAC developed on the secondary of auxiliary transformer T2 is applied to the 115VAC receptacle and to the water cooler receptacle. the precharge or "soft start" sequence, these two phases are current limited by the Input Board. The AC input voltage is rectified, and the resultant DC voltage is applied through the reconnect switches to the input capacitors located on the right and left switch boards. The Control Board monitors the voltage across the capacitors. When the capacitors have charged to an acceptable level, the Control Board signals the Input Board to energize the main input contactor, making all three phases of input power, without current limiting, available to the input capacitors. At this point the Power Wave 455M is in the "Run Mode" of operation. If the capacitors become undervoltaged, overvoltaged, or unbalanced, the Control Board will signal the Input Board to de-energize the main input contactor, and the Power Wave 455M will be disabled. See Figure E.2. The two phases that are connected to the Input Board, through the input line switch SW1, are connected to the input rectifier through the CR1 precharge relay. During POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC E-4 FIGURE E.3 - SWITCH BOARDS AND MAIN TRANSFORMER IGBT DRIVE FROM CONTROL BOARD POWER WAVE 455/R Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC CONTACTOR AND PRECHARGE CONTROL SIGNALS FROM CONTROL BOARD 67B S6 VOLT SENSE BOARD + STT DRIVE VOLTAGE SENSE OUTPUT DEVICE NET S5 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT ARC LINK 2 4 V A C FROM CONTROL BOARD FEED HEAD BOARD 40 VDC CURRENT TRANSDUCER OUTPUT CHOKE WORK TERMINAL 115 VAC FAN RELAY GATEWAY BOARD CONNECTION TO ROBOT TO LEFT S.B. TO RIGHT S.B. C U R R E N T F B S T T F B 40 VDC TO FAN RELAY IGBT DRIVES CONTACTOR AND PRECHARGE CONTROL SIGNALS ARC LINK 115 VAC +5V RS232 65 VDC 52 VAC DC BUS BOARD BUS BOARD RECTIFIER WATER COOLER S6 CONNECTION TO WIRE DRIVE T2 115 VAC 115 VAC RECP. POWER BOARD THERMOSTATS CONTROL BOARD +5 V ARC LINK 40 VDC +5V SPI S2 WORK SENSE +15V SPI S3 RS232 +5 V +15 V 40 VDC -15 V 40 VDC Return to Master TOC STT ELECTRODE TERMINAL S1 230 VAC Return to Master TOC CURRENT TRANSDUCER STT CHOPPER BOARD 67A INPUT BOARD T1 Return to Section TOC +20 VDC FROM POWER BOARD RIGHT SWITCH BOARD CAP. V/F FEEDBACK ELECTRODE TERMINAL + IGBT DRIVE FROM CONTROL CT CURRENT TO CONTROL BOARD BOARD SW1 AUX RECONNECT MAIN TRANSFORMER LEFT SWITCH BOARD INPUT RECTIFIER CR1 CT CURRENT TO CONTROL BOARD OUTPUT DIODES D1 -D4 CAP. V/F FEEDBACK RECONNECT SWITCH Return to Section TOC E-4 THEORY OF OPERATION ARC LINK WIRE FEEDER RECP. S1 LEFT S.B. CAP. V/F RIGHT S.B. CAP. V/F +20 VDC TO CHOPPER BOARD LEFT CT CURRENT FB RIGHT CT CURRENT FB STATUS LIGHT THERMAL LIGHT SWITCH BOARDS AND MAIN TRANSFORMER There are two switch boards in the Power Wave 455M machine. Each contains an input capacitor and insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) switching circuitry. Refer to Figure E.3. When the machine reconnect switches are configured for a lower input voltage (below 300VAC), the input capacitors are connected in parallel. When the machine is configured for higher input voltages (300VAC and above), the input capacitors are connected in series. When the input capacitors are fully charged, they act as power supplies for the IGBT switching circuits. The insulated gate bipolar transistors switch the DC power from the input capacitors "on and off," thus supplying pulsed DC current to the main transformer primary windings. See IGBT OPERATION DISCUSSION AND DIAGRAMS in this section. Each switch board feeds current to a separate, oppositely wound primary winding in the Main Transformer. The reverse directions of current flow through the main transformer primaries, and the offset timing of the IGBT switch boards induce an AC square wave output signal at the secondary of the main transformer. Current transformers located on the switch boards monitor the primary currents. If the primary currents become abnormally high, the Control Board will shut off the IGBTs, thus disabling the machine’s output. The firing of the two switch boards occurs during halves of a 50microsecond interval, creating a constant 20 KHZ output. NOTE: Unshaded areas of Block Logic Diagram are the subject of discussion. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC E-5 FIGURE E-4 – DC BUS BOARD, POWER BOARD, FEED HEAD BOARD, GATEWAY BOARD AND VOLTAGE SENSE BOARD IGBT DRIVE FROM CONTROL BOARD POWER WAVE 455/R Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 67B CONTACTOR AND PRECHARGE CONTROL SIGNALS FROM CONTROL BOARD STT DRIVE S6 VOLT SENSE BOARD VOLTAGE SENSE OUTPUT DEVICE NET S5 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT ARC LINK 2 4 V A C FROM CONTROL BOARD FEED HEAD BOARD 40 VDC 115 VAC FAN RELAY CURRENT TRANSDUCER OUTPUT CHOKE GATEWAY BOARD CONNECTION TO ROBOT TO LEFT S.B. TO RIGHT S.B. C U R R E N T WORK TERMINAL F B S T T F B 40 VDC TO FAN RELAY IGBT DRIVES CONTACTOR AND PRECHARGE CONTROL SIGNALS ARC LINK 115 VAC +5V RS232 65 VDC DC BUS BOARD BUS BOARD RECTIFIER 230 VAC WATER COOLER S6 CONNECTION TO WIRE DRIVE T2 115 VAC 115 VAC RECP. POWER BOARD THERMOSTATS CONTROL BOARD +5 V ARC LINK 40 VDC +5V SPI S2 WORK SENSE +15V SPI S3 RS232 +5 V +15 V 40 VDC -15 V 40 VDC Return to Master TOC + S1 T1 S1 ARC LINK WIRE FEEDER RECP. DC BUS BOARD, POWER BOARD, AND GATEWAY BOARD The DC Bus Board receives approximately 65VDC from the Bus Board rectifier. The DC Bus Board regulates that 65VDC to a +40VDC supply. This regulated 40VDC is applied to the Feed Head Board, the Power Board, and the wire feeder receptacle. The switching power supplies on the Power Board supply a variety of regulated DC voltages to the Control Board and a +20VDC to the STT Chopper Board. The Control Board uses these regulated voltages to power the many circuits and communication functions incorporated within the Control Board. Return to Master TOC STT ELECTRODE TERMINAL 67A INPUT BOARD 52 VAC Return to Section TOC CURRENT TRANSDUCER STT CHOPPER BOARD RIGHT SWITCH BOARD CAP. V/F FEEDBACK AUX RECONNECT +20 VDC FROM POWER BOARD IGBT DRIVE FROM CONTROL CT CURRENT TO CONTROL BOARD BOARD SW1 ELECTRODE TERMINAL + LEFT SWITCH BOARD INPUT RECTIFIER CR1 MAIN TRANSFORMER CT CURRENT TO CONTROL BOARD OUTPUT DIODES D1 -D4 CAP. V/F FEEDBACK RECONNECT SWITCH Return to Section TOC E-5 THEORY OF OPERATION LEFT S.B. CAP. V/F RIGHT S.B. CAP. V/F +20 VDC TO CHOPPER BOARD LEFT CT CURRENT FB RIGHT CT CURRENT FB STATUS LIGHT THERMAL LIGHT When the Feed Head Board activates the Voltage Sense Board, the actual arc voltage is sensed (lead 67), and this information is delivered through the voltage sense board to the Control Board. The Power Wave 455M uses two digital communication platforms. Internally the PC boards communicate via ArcLink. Externally the Power Wave 455R communicates using the industry standard Device Net protocols. The Gateway Board makes the translation between the two platforms possible. The Power Wave 455R does not have a dedicated interface device or board. The robot (or other input device – PLC, etc.) acts as the user interface, issuing commands through the Device Net protocol that are translated by the Gateway Board to ArcLink compatible messages. The following block diagram (Figure E.5) depicts the flow of communication information. NOTE: Unshaded areas of Block Logic Diagram are the subject of discussion. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT FIGURE E.5 – POWER WAVE 455/R COMMUNICATIONS A rc L ink Arc Link Control Board Gateway Board Translator Feed Head Board Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Weld Controller / Sequencer Return to Section TOC E-6 THEORY OF OPERATION Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC E-6 PF-10R PW-455R D evice N et Device Net Robot Controller POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC E-7 FIGURE E.6 – CONTROL BOARD IGBT DRIVE FROM CONTROL BOARD POWER WAVE 455/R Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 67B CONTACTOR AND PRECHARGE CONTROL SIGNALS FROM CONTROL BOARD S6 VOLT SENSE BOARD STT DRIVE VOLTAGE SENSE OUTPUT DEVICE NET S5 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT ARC LINK 2 4 V A C FROM CONTROL BOARD FEED HEAD BOARD 40 VDC CURRENT TRANSDUCER OUTPUT CHOKE WORK TERMINAL 115 VAC FAN RELAY GATEWAY BOARD CONNECTION TO ROBOT TO LEFT S.B. TO RIGHT S.B. C U R R E N T F B S T T F B 40 VDC TO FAN RELAY IGBT DRIVES CONTACTOR AND PRECHARGE CONTROL SIGNALS ARC LINK 115 VAC +5V RS232 65 VDC 52 VAC DC BUS BOARD BUS BOARD RECTIFIER WATER COOLER S6 CONNECTION TO WIRE DRIVE T2 115 VAC 115 VAC RECP. POWER BOARD THERMOSTATS CONTROL BOARD +5 V ARC LINK 40 VDC +5V SPI S2 WORK SENSE +15V SPI S3 RS232 +5 V +15 V 40 VDC -15 V 40 VDC Return to Master TOC + S1 230 VAC Return to Master TOC STT ELECTRODE TERMINAL 67A INPUT BOARD T1 Return to Section TOC CURRENT TRANSDUCER STT CHOPPER BOARD RIGHT SWITCH BOARD CAP. V/F FEEDBACK AUX RECONNECT +20 VDC FROM POWER BOARD IGBT DRIVE FROM CONTROL CT CURRENT TO CONTROL BOARD BOARD SW1 ELECTRODE TERMINAL + LEFT SWITCH BOARD INPUT RECTIFIER CR1 MAIN TRANSFORMER CT CURRENT TO CONTROL BOARD OUTPUT DIODES D1 -D4 CAP. V/F FEEDBACK RECONNECT SWITCH Return to Section TOC E-7 THEORY OF OPERATION S1 ARC LINK WIRE FEEDER RECP. LEFT S.B. CAP. V/F RIGHT S.B. CAP. V/F +20 VDC TO CHOPPER BOARD LEFT CT CURRENT FB RIGHT CT CURRENT FB STATUS LIGHT THERMAL LIGHT CONTROL BOARD The Control Board performs the primary interfacing functions to establish and maintain output control of the Power Wave 455R machine. The function generator and weld files exist within the Control Board hardware and software. Digital command signals and feedback information is received and processed at the Control Board. Software within the Control Board processes the command and feedback information and sends the appropriate pulse width modulation (PWM) signals (see PULSE WIDTH MODULATION in this section) to the switch board IGBTs. In this manner, the digitally controlled high-speed welding waveform is created. The Control Board also monitors and controls the STT (Surface Tension Transfer) circuitry incorporated in the Power Wave 455R. STT output currents and arc voltages are monitored, and the appropriated gate firing signals are applied (or removed) from the STT Chopper Board and switch boards to create a low spatter, low fume MIG welding process. See GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF STT (SURFACE TENSION TRANSFER PROCESS) in this section. In addition, the Control Board monitors the thermostats, the main transformer primary currents and input filter capacitor voltages. Depending on the fault condition, the Control Board will activate the thermal and/or the status light and will disable or reduce the machine output. In some conditions the input contactor will be de-energized. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC E-8 FIGURE E.7 – OUTPUT RECTIFIER, OUTPUT CHOKE AND STT CHOPPER BOARD IGBT DRIVE FROM CONTROL BOARD POWER WAVE 455/R Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC INPUT BOARD CONTACTOR AND PRECHARGE CONTROL SIGNALS FROM CONTROL BOARD 67B S6 VOLT SENSE BOARD STT DRIVE VOLTAGE SENSE OUTPUT DEVICE NET S5 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT ARC LINK 2 4 V A C FROM CONTROL BOARD FEED HEAD BOARD 40 VDC CURRENT TRANSDUCER OUTPUT CHOKE WORK TERMINAL 115 VAC FAN RELAY GATEWAY BOARD CONNECTION TO ROBOT TO LEFT S.B. TO RIGHT S.B. C U R R E N T F B S T T F B 40 VDC TO FAN RELAY IGBT DRIVES CONTACTOR AND PRECHARGE CONTROL SIGNALS ARC LINK 115 VAC +5V RS232 65 VDC 52 VAC DC BUS BOARD BUS BOARD RECTIFIER WATER COOLER S6 CONNECTION TO WIRE DRIVE T2 115 VAC 115 VAC RECP. POWER BOARD THERMOSTATS CONTROL BOARD +5 V ARC LINK 40 VDC +5V SPI S2 WORK SENSE +15V SPI S3 RS232 +5 V +15 V 40 VDC -15 V 40 VDC Return to Master TOC + S1 230 VAC Return to Master TOC STT ELECTRODE TERMINAL 67A T1 Return to Section TOC CURRENT TRANSDUCER STT CHOPPER BOARD RIGHT SWITCH BOARD CAP. V/F FEEDBACK AUX RECONNECT +20 VDC FROM POWER BOARD IGBT DRIVE FROM CONTROL CT CURRENT TO CONTROL BOARD BOARD SW1 ELECTRODE TERMINAL + LEFT SWITCH BOARD INPUT RECTIFIER CR1 MAIN TRANSFORMER CT CURRENT TO CONTROL BOARD OUTPUT DIODES D1 -D4 CAP. V/F FEEDBACK RECONNECT SWITCH Return to Section TOC E-8 THEORY OF OPERATION S1 ARC LINK WIRE FEEDER RECP. LEFT S.B. CAP. V/F RIGHT S.B. CAP. V/F +20 VDC TO CHOPPER BOARD LEFT CT CURRENT FB RIGHT CT CURRENT FB STATUS LIGHT THERMAL LIGHT OUTPUT RECTIFIER AND CHOKE The output rectifier receives the AC output from the main transformer secondary and rectifies it to a DC voltage level. Since the outuput choke is in series with the negative leg of hte output rectifier and also in series with the welding load, a filtered DC output is applied to the machine output terminals. Refer to Figure E.7. When in the STT mode, the control circuit monitors the voltage conditions at the arc, and turns the STT chopper module on or of as necessary to generate an STT output waveform. The STT current transducer in the STT circuit signals the control board to limit output to 375 amps maximum. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC E-9 THEORY OF OPERATION E-9 THERMAL PROTECTION OVER CURRENT PROTECTION Three normally closed (NC) thermostats protect the machine from excessive operating temperatures. These thermostats are wired in series and are connected to the control board. One of the thermostats is located on the heat sink of the output rectifier, one on the DC bus, and one on the output choke. Excessive temperatures may be caused by a lack of cooling air or by operating the machine beyond its duty cycle or output rating. If excessive operating temperatures should occur, the thermostats will prevent output from the machine. The yellow thermal light, located on the front of the machine, will be illuminated. The thermostats are self-resetting once the machine cools sufficiently. If the thermostat shutdown was caused by excessive output or duty cycle and the fan is operating normally, the power switch may be left on and the reset should occur within a 15-minute period. If the fan is not turning or the intake air louvers are obstructed, the power must be removed from the machine and the fan condition or air obstruction corrected. On later production machines (above code 10500) the cooling fan runs only when necessary. The F.A.N. (fan as needed) system is controlled by the Control Board via a solid state relay. If the average current exceeds 570 amps, the peak current will be limited to 100 amps until the average current decreases to under 50 amps or the system is retriggered. PROTECTIVE CIRCUITS 3. Voltage across a capacitor is under 70 volts. (This would be due to improper input voltage connections.) Protective circuits are designed into the Power Wave 455/R to sense trouble and shut down the machine before damage occurs to the machine’s internal components. UNDER/OVER VOLTAGE PROTECTION A protective circuit is included on the Control Board to monitor the voltage across the input capacitors. In the event that a capacitor voltage is too high, too low, or becomes unbalanced side-to-side, the protection circuit will de-energize the input contactor. Machine output will be disabled, and the "soft start" mode will be repeated. The protection circuit will prevent output if any of the following circumstances occur. 1. Capacitor conditioning is required. (This may be required if the machine has been off for a long period of time and is connected for high input voltage operation.) 2. Voltage across a capacitor exceeds 390 volts. (This could result from high line surges or improper input voltage connections.) 4. Internal component damage. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT E-10 THEORY OF OPERATION Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC E-10 FIGURE E.8 – STT WAVEFORMS Wave Control +10.0 Wave Control 0.00 Wave Control -10.0 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Current Time STT Wave control characteristics Current Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Trim 1.50 Trim 1.00 Time Trim 0.50 STT Trim control characteristics Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE STT (SURFACE TENSION TRANSFER) PROCESS The STT process cannot be classified as either a constant current (CC) or a constant voltage (CV) application. The STT function produces current of a desired waveform to reduce spatter and fumes. The STT process is optimized for short-circuit GMAW welding only. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT FIGURE E.9 – IGBT OPERATION POSITIVE VOLTAGE APPLIED SOURCE Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC n+ Return to Section TOC E-11 THEORY OF OPERATION Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC E-11 GATE SOURCE n+ n+ GATE n+ p BODY REGION p BODY REGION n- DRAIN DRIFT REGION n- DRAIN DRIFT REGION n+ BUFFER LAYER n+ BUFFER LAYER p+ INJECTING LAYER p+ INJECTING LAYER DRAIN DRAIN B. ACTIVE A. PASSIVE INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (IGBT) OPERATION An IGBT is a type of transistor. IGBTs are semiconductors well suited for high frequency switching and high current applications. Drawing A shows an IGBT in a passive mode. There is no gate signal, zero volts relative to the source, and therefore, no current flow. The drain terminal of the IGBT may be connected to a voltage supply; but since there is no conduction, the circuit will not supply current to components connected to the source. The circuit is turned off like a light switch in the OFF position. Drawing B shows the IGBT in an active mode. When the gate signal, a positive DC voltage relative to the source, is applied to the gate terminal of the IGBT, it is capable of conducting current. A voltage supply connected to the drain terminal will allow the IGBT to conduct and supply current to circuit components coupled to the source. Current will flow through the conducting IGBT to downstream components as long as the positive gate signal is present. This is similar to turning ON a light switch. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT THEORY OF OPERATION Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC E-12 E-12 FIGURE E.10 – TYPICAL IGBT OUTPUTS 25 sec sec sec 50 sec sec Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC MINIMUM OUTPUT 24 sec 24 sec 1 sec 1 sec 50 sec MAXIMUM OUTPUT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC PULSE WIDTH MODULATION The term PULSE WIDTH MODULATION (PWM) is used to describe how much time is devoted to conduction in the positive and negative portions of the cycle. Changing the pulse width is known as MODULATION. Pulse Width Modulation is the varying of the pulse width over the allowed range of a cycle to affect the output of the machine. MAXIMUM OUTPUT MINIMUM OUTPUT Return to Master TOC By controlling the duration of the gate signal, the IGBT is turned on and off for different durations during a cycle. The top drawing below shows the minimum output signal possible over a 50-microsecond time period. Return to Section TOC The shaded portion of the signal represents one IGBT group1, conducting for 1 microsecond. The negative portion is the other IGBT group. The dwell time (off time) is 48 microseconds (both IGBT groups off). Since only 2 microseconds of the 50-microsecond time period are devoted to conducting, the output power is minimized. 1 By holding the gate signals on for 24 microseconds each and allowing only 2 microseconds of dwell or off time (one microsecond during each half cycle) during the 50 microsecond cycle, the output is maximized. The darkened area under the minimum output curve can be compared to the area under the maximum output curve. The more darkened area, the more power is present. An IGBT group consists of the sets of IGBT modules grouped onto one switch board. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Section F-1 TABLE OF CONTENTS - TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR SECTION - Troubleshooting & Repair ...................................................................................................Section F How to Use Troubleshooting Guide ...........................................................................................F-2 PC Board Troubleshooting Procedures.......................................................................................F-3 Troubleshooting Guide ................................................................................................................F-4 Test Procedures ..........................................................................................................................F-9 Input Filter Capacitor Discharge Procedure .........................................................................F-9 Switch Board Test ...............................................................................................................F-11 Input Rectifier Test .............................................................................................................F-15 Input Contactor Test............................................................................................................F-19 Return to Master TOC DC Bus Power Supply PC Board Test................................................................................F-23 Power Board Test ..............................................................................................................F-27 Input Board Test .................................................................................................................F-31 STT Chopper Board Test ....................................................................................................F-35 Power Wave Current Transducer Test ...............................................................................F-39 STT Current Transducer Test ............................................................................................F-43 Output Rectifier Test ..........................................................................................................F-47 Auxiliary Transformer No. 1 Test .......................................................................................F-49 Auxiliary Transformer No. 2 Test .......................................................................................F-53 Component Removal and Replacement Procedures................................................................F-55 Input Rectifier Removal and Replacement ........................................................................F-55 Return to Master TOC Input Contactor Removal and Replacement ......................................................................F-57 Auxiliary Transformer No. 1 Removal and Replacement Procedure..................................F-59 Auxiliary Transformer No. 2 Removal and Replacement Procedure..................................F-63 Control, Feed Head, or Voltage Sense PC Board Removal and Replacement .................F-67 Gateway PC Board Removal and Replacement ...............................................................F-71 STT Current Transducer Removal and Replacement ...................................................... F-73 Power Wave Current Transducer Removal and Replacement.......................................... F-77 Output Rectifier, STT Chopper Board and Rectifier Module Removal and Replacement ........................................................................................................F-81 Switch Board and Filter Capacitor Removal and Replacement .........................................F-85 Return to Master TOC Retest after Repair ...................................................................................................................F-88 POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Section F-1 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-2 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR HOW TO USE TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric Factory Trained Personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician and machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid Electrical Shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC This Troubleshooting Guide is provided to help you locate and repair possible machine malfunctions. Simply follow the three-step procedure listed below. Step 1. LOCATE PROBLEM (SYMPTOM). Look under the column labeled “PROBLEM” (SYMPTOMS). This column describes possible symptoms that the machine may exhibit. Find the listing that best describes the symptom that the machine is exhibiting. Symptoms are grouped into two main categories: Output Problems and Function Problems. Step 2. PERFORM EXTERNAL TESTS. The second column, labeled “POSSIBLE AREAS OF MISADJUSTMENT(S)”, lists the obvious external possibilities that may contribute to the machine symptom. Perform these tests/checks in the order listed. In general, these tests can be conducted without removing the case cover. Step 3. PERFORM COMPONENT TESTS. The last column, labeled “Recommended Course of Action” lists the most likely components that may have failed in your machine. It also specifies the appropriate test procedure to verify that the subject component is either good or bad. If there are a number of possible components, check the components in the order listed to eliminate one possibility at a time until you locate the cause of your problem. All of the referenced test procedures referred to in the Troubleshooting Guide are described in detail at the end of this section. Refer to the Troubleshooting and Repair Table of Contents to locate each specific Test Procedure. All of the referred to test points, components, terminal strips, etc., can be found on the referenced electrical wiring diagrams and schematics. Refer to the Electrical Diagrams Section Table of Contents to locate the appropriate diagram. In addition to the troubleshooting information in this manual, Lincoln Electric offers a System Update Utility to reprogram digital power sources. The utility will examine the welding system allowing you to upgrade to the current release of the operating system software and welding programs available for the machine if necessary. This software can be reviewed and downloaded from powerwavesoftware.com or from mylincolnelectric.com. Download and review the entire user manual before attempting to use the software. CAUTION If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-2 Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC F-3 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR PC BOARD TROUBLESHOOTING PROCEDURES WARNING ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. Have an electrician install and service this equipment. Turn the machine OFF before working on equipment. Do not touch electrically hot parts. Sometimes machine failures appear to be due to PC board failures. These problems can sometimes be traced to poor electrical connections. To avoid problems when troubleshooting and replacing PC boards, please use the following procedure: 1. Determine to the best of your technical ability that the PC board is the most likely component causing the failure symptom. 2. Check for loose connections at the PC board to assure that the PC board is properly connected. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 3. If the problem persists, replace the suspect PC board using standard practices to avoid static electrical damage and electrical shock. Read the warning inside the static resistant bag and perform the following procedures: Return to Section TOC F-3 PC Board can be damaged by static electricity. ATTENTION Static-Sensitive Devices Handle only at Static-Safe Workstations • Remove your body’s static charge before opening the static-shielding bag. Wear an anti-static wrist strap. For safety, use a 1 Meg ohm resistive cord connected to a grounded part of the equipment frame. • If you don’t have a wrist strap, touch an unpainted, grounded, part of the equipment frame. Keep touching the frame to prevent static build-up. Be sure not to touch any electrically live parts at the same time. • Remove the PC Board from the static-shielding bag and place it directly into the equipment. Don’t set the PC Board on or near paper, plastic or cloth which could have a static charge. If the PC Board can’t be installed immediately, put it back in the staticshielding bag. • If the PC Board uses protective shorting jumpers, don’t remove them until installation is complete. • If you return a PC Board to The Lincoln Electric Company for credit, it must be in the static-shielding bag. This will prevent further damage and allow proper failure analysis. 4. Test the machine to determine if the failure symptom has been corrected by the replacement PC board. NOTE: Allow the machine to heat up so that all electrical components can reach their operating temperature. 5. Remove the replacement PC board and substitute it with the original PC board to recreate the original problem. a. If the original problem does not reappear by substituting the original board, then the PC board was not the problem. Continue to look for bad connections in the control wiring harness, junction blocks, and terminal strips. b. If the original problem is recreated by substitution of the original board, then PC board was the problem. Reinstall replacement PC board and test machine. the the the the 6. Always indicate that this procedure was followed when warranty reports are to be submitted. NOTE: Following this procedure and writing on the warranty report, “INSTALLED AND SWITCHED PC BOARDS TO VERIFY PROBLEM,” will help avoid denial of legitimate PC board warranty claims. • Tools which come in contact with the PC Board must be either conductive, anti-static or static-dissipative. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC F-4 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE Observe Safety Guidelines detailed in the beginning of this manual. PROBLEMS (SYMPTOMS) F-4 POSSIBLE AREAS OF MISADJUSTMENT(S) RECOMMENDED COURSE OF ACTION OUTPUT PROBLEMS The input fuses repeatedly fail or the input circuit breakers keep tripping. 1. Make certain the fuses or breakers are properly sized. 2. Make certain the reconnect panel is configured properly for the applied voltage. 3. The welding procedure may be drawing too much input current or the duty cycle may be too high. Reduce the welding current and /or reduce the duty cycle. 1. Check the reconnect switches and associated wiring. See the Wiring Diagram. 2. Perform the Input Rectifier Test. 3. Perform the Switch Board Test. 4. Perform the Input Contactor Test. CAUTION If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-5 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE PROBLEMS (SYMPTOMS) Observe Safety Guidelines detailed in the beginning of this manual. POSSIBLE AREAS OF MISADJUSTMENT(S) 1. Make certain the input power switch SW1 is in the ON position. 2. Check the main input fuses (or breakers). If open, replace or reset. Return to Master TOC RECOMMENDED COURSE OF ACTION OUTPUT PROBLEMS The machine is dead—no lights— no output—the machine appears to be off. Return to Section TOC F-5 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR 3. Check the 6 amp CB4 breaker located in the reconnect area. Reset if tripped. 4. Make certain the reconnect panel is configured correctly for the applied input voltage. 1. Check the input power switch SW1 for proper operation. Also check the associated leads for loose or faulty connections. See the Wiring Diagram. 2. Check circuit breaker CB4 for proper operation. 3. Perform the DC Bus Board Test. 4. The power board rectifier may be faulty. Check rectifier and associated wiring. See the Wiring Diagram 5. Perform the Power Board Test. 6. Perform the T1 Transformer Test. Auxiliary Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 7. The Control Board may be faulty. CAUTION If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-6 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE Observe Safety Guidelines detailed in the beginning of this manual. PROBLEMS (SYMPTOMS) POSSIBLE AREAS OF MISADJUSTMENT(S) 1. Turn the input power off and make certain the reconnect panel is configured correctly for the applied input voltage. Return to Master TOC 2. Perform the Input Contactor Test. 3. Perform the Input Board Test. Auxiliary 5. Perform the Input Rectifier Test. 6. Perform the Switch Board Test. 7. Perform the Power Board Test. 8. The Control Board may be faulty. The thermal light is lit. The machine regularly "overheats." Return to Master TOC 1. Check status led on case front evaluate 4. Perform the T1 Transformer Test. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 2. If the Thermal light is lit, See next. Return to Section TOC RECOMMENDED COURSE OF ACTION OUTPUT PROBLEMS The Power Wave 455M does not have welding output. The main input contactor CR1 is not activating. Fan may be running. Return to Section TOC F-6 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR 1. The welding application may be exceeding the recommended duty cycle and/or current limits of the machine. 2. Dirt and dust may have clogged the cooling channels inside the machine. Refer to the Maintenance Section of this manual. 1. One of the thermostats may be faulty. Also check associated wiring for loose or faulty connections. See the Wiring Diagram. 3. Air intake and exhaust louvers may be blocked due to inadequate clearance around the machine. 4. Make sure the fan is functioning correctly. Machines above code 10500 are equipped with F.A.N. (fan as needed) circuitry. The fan runs whenever the output is enabled, whether under load or open circuit conditions. The fan also runs for a period of time (approximately 5 minutes) after the output is disabled. CAUTION If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC F-7 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE PROBLEMS (SYMPTOMS) Observe Safety Guidelines detailed in the beginning of this manual. POSSIBLE AREAS OF MISADJUSTMENT(S) Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC RECOMMENDED COURSE OF ACTION FUNCTION PROBLEMS The machine often "noodle welds" when running a particular process. The output is limited to approximately 100 amps. 1. The machine may be trying to deliver too much power. When the average output current exceeds 570 amps, the machine will "phase back" to protect itself. Adjust the procedure or reduce the load to lower the current draw from the Power Wave 455R machine. The machine often "noodle welds" when running an STT process. STT work/ Electrode sense lead routing 1. Perform the Transducer Test. The Power Wave 455R will not produce full output. 1. The input voltage may be too low, limiting the output capability of the machine. Make certain the input voltage is correct for the machine and the reconnect panel configuration. 3. If using the STT output terminal, be aware that the STT output is limited to 325 amps. Current 2. The Control Board may be faulty. 1. Refer to sense lead route recommendations section 2. Perform the Transducer Test. 2. Make sure all three phases of input power are being applied to the machine. Return to Section TOC F-7 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR Current 1. Perform the Output Rectifier Test. 2. Perform the Current Transducer Test. 3. Perform the Power Board Test. 4. The Control Board may be faulty. 5. If using the STT output terminal, the STT Chopper Board may be faulty. See the Wiring Diagram. CAUTION If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-8 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE Observe Safety Guidelines detailed in the beginning of this manual. PROBLEMS (SYMPTOMS) POSSIBLE AREAS OF MISADJUSTMENT(S) RECOMMENDED COURSE OF ACTION FUNCTION PROBLEMS The Auxiliary Receptacle is "dead." The 120VAC is not present at the receptacle. 1. Check the 3.5 amp circuit breaker (CB3) located in the reconnect area. Reset if necessary. 1. Check the receptacle and associated wiring for loose or faulty connections. See the Wiring Diagram. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC 2. Perform the T2 Transformer Test. Return to Section TOC F-8 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR Auxiliary The Power Wave 455M is "triggered" for output but there is no welding output. 1. Make sure that the triggering method and device is correct and operating properly. Use troubleshooting software to find the problem. When in the STT mode, the spatter is higher than normal and the arc is inconsistent. 1. Make certain the work sense lead (21) is connected properly. 1. Perform the STT Chopper Board Test. 2. Make certain the electrode cable is connected only to the STT output terminal and NOT the Power Wave positive output terminal, or both. 2. Perform the Current Transducer (STT) Test. 3. Make sure the welding parameters are correct for the process. Refer to L.E. setup utility user manual section. 3. Check calibration using L.E. dianolostic software, and confirm correct wire feed speed to display 4. The Control Board may be faulty. CAUTION If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-9 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT FILTER CAPACITOR DISCHARGE PROCEDURE WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. DESCRIPTION This “safety” procedure should be performed before any internal maintenance or repair procedures are attempted on the Power Wave 455M. Capacitance normally discharges within 2 minutes of removing input power. This procedure is used to check that the capacitors have properly discharged. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” Nut driver Volt-ohmmeter 25-1000 ohms @ 25 watts (minimum) resistor Electrically insulated gloves and pliers POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-9 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC F-10 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT FILTER CAPACITOR DISCHARGE PROCEDURE (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.1 – CAPACITOR DISCHARGE PROCEDURE SWITCH BOARD Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC CAPACITOR TERMINALS TEST PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455M. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the left and right case sides. 3. Be careful not to make contact with the capacitor terminals that are located in the bottom center of the left and right side switch boards. See Figure F.1. Return to Master TOC 4. Carefully check for a DC voltage at the capacitor terminals on both boards. Note the polarity is marked on the PC board and also lead #19 is positive. Return to Section TOC F-10 5. If any voltage is present, proceed to Step #6. If no voltage is present, the capacitors are discharged. 6. Using the high wattage resistor (25-1000 ohms @ 25 watts (minimum), electrically insulated gloves and pliers, connect the resistor across the two capacitor terminals. Hold the resistor in place for 10 seconds. DO NOT TOUCH THE CAPACITOR TERMINALS WITH YOUR BARE HANDS. NEVER USE A SOLID CONDUCTOR W/LESS THAN 25 OHM RESISTANCE FOR THIS PROCEDURE. 7. Repeat procedure for the other capacitor. 8. Recheck the voltage across the capacitor terminals. The voltage should be zero. If any voltage remains, repeat the discharge procedure. NOTE: Normally the capacitors discharge in about two minutes after input power is removed. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-11 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR SWITCH BOARD TEST WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. DESCRIPTION This test will help determine if the “power section” of the switch boards are functioning correctly. This test will NOT indicate if the entire PC board is functional. This resistance test is preferable to a voltage test with the machine energized because these boards can be damaged easily. In addition, it is dangerous to work on these boards with the machine energized. Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC MATERIALS NEEDED 3/8” Nut driver 3/8” Wrench Analog/Digital volt-ohmmeter Wiring Diagram POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-11 F-12 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-12 SWITCH BOARD TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.2 – RECONNECT SWITCHES 19C 19D Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC RECONNECT SWITCHES TEST PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455M. 2. Perform the Procedure. Capacitor Discharge Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 3. Locate label and remove leads 19C and 19D from the reconnect switches with the 3/8” wrench. Note lead placement for reassembly. Clear leads. Refer to Figure F.2. 4. Using the Analog ohmmeter, perform the following resistance tests. Refer to Figure F.3 for the test points. Any readings below 100 ohms can be considered a short circuit. However, readings usually are below 30 ohms. Check 11/12 to -20 and 11/12 to +19 Check 13/14 to -20 and +19 to 13/14 5. If any test fails isolate the PC board and retest, if board still fails, replace switch board. See Switch Board Removal and Replacement. 6. If the switch board tests are OK, check the molex pin connections and associated wiring from the switch boards to the control board. See the Wiring Diagram. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC F-13 SWITCH BOARD TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.3 – SWITCH BOARD TEST POINTS 13/14 OR 17/18 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC SWITCH BOARD Return to Section TOC F-13 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR -20 +19 11/12 OR 15/16 8. Reconnect leads 19C and 19D to the reconnect switches. Ensure that the leads are installed in the same location they were removed from. 9. Install the right and left case sides and top using the 3/8” nut driver. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-14 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-14 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-15 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT RECTIFIER TEST WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This test will help determine if the input rectifier has “shorted” or “open” diodes. MATERIALS NEEDED Analog volt-ohmmeter Phillips head screw driver Wiring Diagram 3/8” Nut driver POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-15 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC F-16 INPUT RECTIFIER TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.4 – INPUT RECTIFIER TEST INPUT RECTIFIER B NEG (-) POS (+) TEST PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455M. 3. Perform the Procedure. Return to Master TOC A C 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top. Return to Section TOC F-16 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR Capacitor Discharge 4. Locate the Input Rectifier and lead locations. Refer to Figure F.4. NOTE: Some silicone sealant may have to be removed from the input rectifier terminals. The G.E. silicone or equivalent should be replaced when test is complete. 5. With the phillips head screw driver remove the positive and negative leads from the rectifier. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-17 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR F-17 INPUT RECTIFIER TEST (CONTINUED) 6. Use the analog ohmmeter to perform the tests detailed in Table F.1. 7. If the input rectifier does not meet the acceptable readings outlined in the table, the component may be faulty. Replace. NOTE: Before replacing the input rectifier, perform the Switch Board Test. 9. If the input rectifier is good, be sure to reconnect the positive and negative leads to the correct terminals and torque to 31 in.-lbs. See the Wiring Diagram. 10. Replace any silicone sealant previously removed. 11. Reassemble and test. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 8. When installing a new input rectifier, see Input Rectifier Removal and Replacement procedure. TABLE F.1 – INPUT RECTIFIER TEST POINTS AND ACCEPTABLE READINGS ANALOG METER X100 RANGE Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC TEST POINT TERMINALS + Probe - Probe Acceptable Meter Readings A B C NEG NEG NEG Greater than 1000 ohms Greater than 1000 ohms Greater than 1000 ohms A B C POS POS POS Approx. 500 ohms or less Approx. 500 ohms or less Approx. 500 ohms or less NEG NEG NEG A B C Approx. 500 ohms or less Approx. 500 ohms or less Approx. 500 ohms or less POS POS POS A B C Greater than 1000 ohms Greater than 1000 ohms Greater than 1000 ohms This test can be performed using a digital volt/ohm meter on the “diode test” setting. Acceptable meter readings are: open or O.L., For the “Greater than 1000 ohms” and a decimal value less than one (example 0.045) in the approx 500 ohms position. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-18 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-18 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-19 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT CONTACTOR TEST WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This test will help determine if the input contactor is functional and if the contacts are functioning correctly. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” Nut driver Volt-ohmmeter External 24 VAC supply POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-19 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-20 F-20 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT CONTACTOR TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.5 – INPUT CONTACTOR COIL INPUT CONTACTOR 601 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC X4 TEST PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the input access panel and case top. 4. Using the external 24 VAC supply, apply 24 VAC to the terminals of the input contactor coil. If the contactor does NOT activate, the input contactor is faulty. Replace. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 3. Locate, mark, and remove the two leads (601, X4) that are connected to the input contactor coil. Refer to Figure F.5. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC F-21 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT CONTACTOR TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.6 – INPUT CONTACTOR TEST POINTS L3 T3 L2 T2 L1 T1 5. With the input contactor activated, check the continuity across the three sets of contacts. (Zero ohms or very low resistance is normal.) Refer to Figure F.6. If the resistance is high, the input contactor is faulty. Replace the input contactor. 7. Reconnect the two leads (601, X4) to the input contactor coil. 8. Install the input access door and case top using the 3/8” nut driver. 9. Test. 6. When the contactor is NOT activated, the resistance should be infinite or very high across the contacts. If the resistance is low, the input contactor is faulty. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-21 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-22 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-22 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-23 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR DC BUS POWER SUPPLY PC BOARD TEST WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This test will determine if the DC Bus Power Supply PC Board is receiving and processing the proper voltages. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” Nut driver Volt/ohmmeter Wiring Diagram POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-23 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-24 F-24 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR DC BUS POWER SUPPLY PC BOARD TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.7 – DC BUS POWER SUPPLY POWER SUPPLY PC BOARD LED POWER BOARD Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC DC BUS POWER SUPPLY PC BOARD FAN RELAY J47 J46 CAPACITOR C3 CAUTION! J46 J47 1 2 1 2 3 4 3 4 5 6 7 8 TEST PROCEDURE WARNING 1. Remove input power to the machine. ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top. High voltage is present when input power is applied to the machine. 3. Locate the DC Bus Power Supply PC Board and plugs P46 and P47. See Figure F.7. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 4. Carefully apply input power to the Power Wave 455M. 5. Turn on the Power Wave 455M. The LED on the DC Bus Power Supply PC Board should light. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-25 DC BUS POWER SUPPLY PC BOARD TEST(CONTINUED) 6. Check the DC Bus Power Supply PC Board input and output voltages according to Table F.3. See Figure F.7 and the Wiring Diagram. If plug P46 pin 1-3 voltage is missing, perform T1 Auxiliary Transformer Test. WARNING Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. Return to Section TOC F-25 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR High voltage is present at the terminals of Capacitor C3 near where testing is to be done. 7. If all the voltages are correct, the DC Bus Power Supply PC Board is operating properly. 8. If any of the output voltages are not correct and the input voltage is correct, the DC Bus Power Supply PC Board may be faulty, or the supplied board may be bad. 9. If the input voltage is not correct, check the leads between the DC Bus Power Supply PC Board and the Power PC Board Rectifier. See the Wiring Diagram. 10. When finished testing, replace the case top. TABLE F.2 – DC BUS POWER SUPPLY PC BOARD VOLTAGE TABLE Positive Meter Probe Test Point Negative Meter Probe Test Point Approximate Voltage Reading Conditions/Comments Plug P46 – Pin 1 Plug P46 – Pin 3 65 – 75 VDC Should be same as the Power PC Board Rectifier Plug P47 – Pin 7 Plug P47 – Pin 6 38.0 – 42.0 VDC Supply to Power PC Board Plug P47 – Pin 8 Plug P47 – Pin 6 38.0 – 42.0 VDC Supply to Power PC Board Plug P47 – Pin 4 Plug P47 – Pin 2 38.0 – 42.0 VDC Supply to Feed Head PC Board Plug P47 – Pin 3 Plug P47 – Pin 1 38.0 – 42.0 VDC Supply to S1 Wire Feeder Receptacle POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-26 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-26 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-27 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR POWER BOARD TEST WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This test will help determine if the Power Board is receiving the correct voltages and also if the Power Board is regulating and producing the correct DC voltages. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” Nut driver Volt-ohmmeter Wiring Diagram POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-27 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-28 POWER BOARD TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.8 – POWER BOARD TEST J41 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC J42 1 4 2 3 5 6 J42 1 J43 2 1 2 3 4 3 4 J41 7 8 9 10 11 12 J43 5 6 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC TEST PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455M. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top. 3. Perform the Procedure. Capacitor Discharge 4. Locate the Power Board and plugs J42 and J43. Do not remove plugs or leads from the Power Board. Refer to Figure F.8. 5. Carefully apply input power to the Power Wave 455M. 6. Turn on the Power Wave 455M. Carefully test for the correct voltages at the Power Board according to Table F.3. 7. If either of the 40 VDC voltages is low or not present at plug J41, perform the DC Bus PC Board Test. See the Wiring Diagram. If indicated, perform the T1 Auxiliary Transformer Test. 8. If any of the DC voltages are low or not present at plugs J42 and/or 43, the Power Board may be faulty. 9. If power board is replaced, reassemble and test machine. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC WARNING ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. High voltage is present when input power is applied to the machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-28 Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC F-29 F-29 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR POWER BOARD TEST (CONTINUED) TABLE F.3 – POWER BOARD VOLTAGE CHECKS CHECK POINT LOCATION TEST DESCRIPTION CONNECTOR PLUG PIN NO. LEAD NO. OR IDENTITY POWER BOARD CONNECTOR PLUG J41 CHECK 40 VDC INPUT FROM DC BUS BOARD 2 (+) 1 (-) 477 (+) 475 (-) 38 – 42 VDC POWER BOARD CONNECTOR PLUG J42 CHECK +15 VDC SUPPLY FROM POWER BOARD 225 (+) 222 (-) +15 VDC 221 (+) 222 (-) +5 VDC 222 (+) 223 (-) -15 VDC 274 (+) 273 (-) +5 VDC 475 NORMAL ACCEPTABLE VOLTAGE READING 477 1 (+) 5 (-) 225 222 POWER BOARD CONNECTOR PLUG J42 CHECK +5 VDC SUPPLY FROM POWER BOARD POWER BOARD CONNECTOR PLUG J42 CHECK -15 VDC SUPPLY FROM POWER BOARD 3 (+) 5 (-) 221 222 223 2 (+) 5 (-) 222 POWER BOARD CONNECTOR PLUG J43 CHECK +5 VDC ARCLINK SUPPLY FROM POWER BOARD 5 (+) 10 (-) POWER BOARD CONNECTOR PLUG J43 CHECK +5 VDC “RS-232” SUPPLY FROM POWER BOARD 4 (+) 9 (-) 226 (+) 228 (-) +5 VDC 226 6 (+) 11 (-) 266 (+) 267 (-) +15 VDC 266 478 (+) 476 (-) 38 – 42 VDC 268A (+) 262 (-) +5 VDC 345 (+) 346 (-) +20 VDC 274 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 273 228 POWER BOARD CONNECTOR PLUG J43 CHECK +15 VDC SPI SUPPLY FROM POWER BOARD 267 POWER BOARD CONNECTOR PLUG J41 CHECK +40 VDC INPUT FROM DC BUS BOARD 4 (+) 3 (-) Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 476 POWER BOARD CONNECTOR PLUG J43 CHECK +5 VDC SPI SUPPLY FROM POWER BOARD 268A 478 3 (+) 12 (-) 262 POWER BOARD CONNECTOR PLUG J43 CHECK +20 VDC STT SUPPLY FROM POWER BOARD 346 7 (+) 1 (-) 345 POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-30 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-30 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-31 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT BOARD TEST WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This test will help determine if the Input Board is sending the correct voltages and also if the Input Board is regulating and producing the correct DC voltages. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” Nut driver Volt-ohmmeter Wiring Diagram POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-31 INPUT BOARD TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.9 – INPUT CONTACTOR CR1 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC J60 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC J61 601 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 X4 INPUT CONTACTOR 5 6 7 J60 8 6 7 8 9 10 J61 TEST PROCEDURE WARNING 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455M. ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top, and input access cover. High voltage is present when input power is applied to the machine. Return to Master TOC 3. Remove lead X4 from the coil terminal of main input contactor CR1. Insulate lead X4. Refer to Figure F.9. Return to Section TOC F-32 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-32 4. Carefully apply input power to the Power Wave 455M. 5. Turn on the Power Wave 455M. Carefully test for the correct voltages according to Table F.4. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-33 F-33 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT BOARD FUNCTION TEST(CONTINUED) TABLE F.4 – INPUT BOARD VOLTAGE CHECKS TEST POINTS LEAD NUMBERS EXPECTED VOLTAGE READINGS J61 SAME AS INPUT VOLTAGE PLUG J61 PIN 8 (H1D) TO PLUG J61 PIN 6 (612) #612 COMMENTS Present when Input Switch SW1 is closed. If not, check input lines and line switch and wiring. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC H1D PLUG J60 PIN 3 (238) TO PLUG J60 PIN 4 (604) J60 #238 #604 13 – 15 VDC J61 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC PLUG J61 PIN 10 (T3) TO PLUG J61 PIN 2 (T1) A LITTLE LESS THAN INPUT VOLTAGE T1 T3 J60 PLUG J60 PIN 3 (238) TO PLUG J60 PIN 5 (232) 13 – 15 VDC #238 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC #232 POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT This is the Coil Voltage for the Pre-Charge Relay. Normally this DC Voltage will be present 6 seconds after Input Switch SW1 is activated. This 13 - 15 VDC will remain for approximately 6 seconds and then be removed. The Relay is controlled by the Control Board. See the Wiring Diagram. This is Pre-Charge Voltage and will normally be present 6 seconds after activating Input Switch SW1. The Pre-Charge Voltage should remain for approximately 6 seconds and then be removed. It should start at zero and ramp up to 170 - 200 V.A.C. If zero volts check input board resistors, and check for a shorted main input rectifier. This is the DC Coil Voltage for the Control Relay. Normally this DC Voltage will be present approximately 12 seconds after Input Switch SW1 is activated. The Relay is controlled by the Control PC Board. See the Wiring Diagram. Voltage will not be applied if capacitor precharge is incorrect. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-34 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT BOARD TEST(CONTINUED) 6. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455M. If any of the voltages are low or not present, perform the Input Contactor Test. If that checks out, the Input Board may by faulty. 9. Turn on the Power Wave 455M. Check for the presence of 24 VAC from lead X4 to lead 601. See Figure F. 9. If the voltage is not present, perform the Auxiliary Transformer #1 Test. 7. Reconnect lead X4 to the main input contactor CR1 coil terminal. 9. This 24 VAC is the coil voltage for main input contactor CR1. It will normally be present approximately 12 seconds after input line switch (SW1) is activated. 8. Carefully apply the correct input voltage to the Power Wave 455M. 10. When the test is completed, remove input power from the Power Wave 455M. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC WARNING ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. 11. Install the case top and reconnect cover using the 3/8” nut driver. High voltage is present when input power is applied to the machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-34 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-35 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR STT CHOPPER BOARD TEST WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This test will help determine if the STT Chopper Board is receiving the necessary voltages to function and if the related circuitry is correct. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” Nut driver Volt-ohmmeter Wiring Diagram POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-35 F-36 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-36 STT CHOPPER BOARD TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.10 – STT CHOPPER BOARD TEST DETAILS CONTROL PC BOARD POWER PC BOARD J43 J43 J7 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC J7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 346 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 4W 4R 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 345 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC STT OUTPUT TERMINAL POWER WAVE + OUTPUT TERMINAL TEST PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455M. + probe on the Power Wave + output terminal 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top and the control box cover. See Figure F.10. - probe on the STT output terminal 3. Perform the following resistance tests: + probe on the STT output terminal Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC - probe on the Power Wave + output terminal The reading should be less than 500 ohms If both the polarity resistance tests are low, either the STT Chopper Module is faulty or diode D6 is shorted. See the Wiring Diagram. The reading should be approximately 300,000 ohms POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-37 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR STT CHOPPER BOARD TEST (CONTINUED) 4. Carefully apply input power to the Power Wave 455M. WARNING ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC High voltage is present when input power is applied to the machine. For steps 5 and 6, see Figure F.10. 5. Turn on the Power Wave 455M. Measure the voltage from Power Board plug J43 lead 345 pin 7 (+) to lead 346 pin 1 (-). The voltage should be approximately 20 VDC. If not correct, the Power Board may be faulty. 6. Measure the voltage from Control Board plug J7 lead 4W pin 13 (-) to lead 4R pin 14 (+). The voltage should be 4 – 5 VDC. This is the pulse width modulation signal to the STT Chopper Board. If not correct, the Control Board may be faulty. 7. When the test is completed, remove input power from the Power Wave 455M. 8. Install the case top and control box cover using the 3/8” nut driver. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-37 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-38 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-38 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-39 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR POWER WAVE CURRENT TRANSDUCER TEST WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This test will help determine if the Power Wave current transducer and associated wiring is functioning correctly. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” nut driver Volt-Ohmmeter POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-39 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-40 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR POWER WAVE CURRENT TRANSDUCER TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.11 – POWER WAVE CURRENT TRANSDUCER TEST CONTROL BOARD Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC J8 J8 211 212 213 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 216 CURRENT TRANSDUCER Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 1234 P91 TEST PROCEDURE WARNING 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top and the control box cover. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 3. Locate the Power Wave current transducer leads at Control Board plug J8. See Figure F.11. 4. Carefully apply input power to the Power Wave 455. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. High voltage is present when input power is applied to the machine. F-40 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-41 POWER WAVE CURRENT TRANSDUCER TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.12 – RECEPTACLE S7 TRIGGERED POWER WAVE RECEPTACLE S7 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC STT Return to Section TOC F-41 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR 5. Turn on the Power Wave 455. Check for the correct DC supply voltage to the current transducer at plug J8. See Figure F.11. NOTE: The machine can be triggered by jumpering pin 1 to pin 2 at receptacle S7. See Figure F.12. A. Pin 2 (lead 212+) to pin 6 (lead 216-) should read +15 VDC. 7. With the Power Wave 455 triggered, check the feedback voltage from the current transducer. The current feedback voltage can be read at plug J8 on the Control Board. B. Pin 3 (lead 213-) to pin 6 (lead 216+) should read -15 VDC. If the DC supply voltages are not present, the control board may be faulty. A. Pin 1 (lead 211) to pin 6 (lead 216) should read 2.0 VDC (machine loaded to 250 amps). 6. If both of the supply voltages are low or missing, check the associated leads between plug J8 and current transducer plug P91 and the Control Board. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-42 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR POWER WAVE CURRENT TRANSDUCER TEST (CONTINUED) 8. If for any reason the machine cannot be loaded to 250 amps, Table F.5 shows what feedback voltage is produced at various current loads. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC 9. If the correct supply voltages are applied to the current transducer, and with the machine loaded, the feedback voltage is missing or not correct, the current transducer may be faulty. Also make certain that lead 211 (plug J8 pin 1) has continuity (zero ohms) between the current transducer and the control board. See the Wiring Diagram. 10. Install the right side case cover using the 3/8” nut driver. TABLE F.5 - CURRENT FEEDBACK AT VARIOUS OUTPUT LOADS OUTPUT LOAD CURRENT EXPECTED TRANSDUCER FEEDBACK VOLTAGE 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 4.0 3.6 3.2 2.8 2.4 2.0 1.6 1.2 0.8 0.4 POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-42 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-43 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR STT CURRENT TRANSDUCER TEST WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This test will help determine if the STT current transducer and associated wiring is functioning correctly. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” nut driver Volt-Ohmmeter POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-43 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-44 F-44 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR STT CURRENT TRANSDUCER TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.13 – STT CURRENT TRANSDUCER TEST CONTROL BOARD Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC J8 813 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 811 816 812 J8 1234 P90 CURRENT TRANSDUCER TEST PROCEDURE WARNING 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top and the control box cover. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 3. Locate the STT current transducer leads at Control Board plug J8. See Figure F.13. 4. Carefully apply input power to the Power Wave 455M. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. High voltage is present when input power is applied to the machine. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-45 STT CURRENT TRANSDUCER TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.14 – RECEPTACLE S7 TRIGGERED POWER WAVE RECEPTACLE S7 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC STT Return to Section TOC F-45 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR 5. Turn on the Power Wave 455M. Check for the correct DC supply voltage to the current transducer at plug J8. NOTE: The machine can be triggered by jumpering pin 1 to pin 2 at receptacle S7. See Figure F. 14. A. Pin 8 (lead 812+) to pin 7 (lead 816-) should read +15 VDC. 7. With the Power Wave 455M triggered, check the feedback voltage from the current transducer. The current feedback voltage can be read at plug J8 on the Control Board. B. Pin 4 (lead 813-) to pin 7 (lead 816+) should read -15 VDC. If the DC supply voltages are not present, the control board may be faulty. A. Pin 5 (lead 811) to pin 7 (lead 816) should read 0.4 VDC (machine loaded to 50 amps). 6. If both of the supply voltages are low or missing, check the associated leads between plug J8 and current transducer plug P90 and the Control Board. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-46 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR STT CURRENT TRANSDUCER TEST (CONTINUED) 8. If for any reason the machine cannot be loaded to 50 amps, Table F.6 shows what feedback voltage is produced at various current loads. S.T.T. stud is limited to 325 amps. 10. Install the right side case cover using the 3/8” nut driver. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC 9. If the correct supply voltages are applied to the current transducer, and with the machine loaded, the feedback voltage is missing or not correct, the current transducer may be faulty. Also make certain that lead 811 (plug J8 pin 5) has continuity (zero ohms) between the current transducer and the control board. See the Wiring Diagram. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-46 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-47 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR OUTPUT RECTIFIER TEST WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electrical troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION The test will help determine if any of the output rectifiers are shorted. MATERIALS NEEDED Analog Volt-Ohmmeter 3/8” Nut driver 5/16” Wrench POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-47 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-48 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR OUTPUT RECTIFIER TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.15 – OUTPUT RECTIFIER TEST I ON Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC POWERWAVE 455/R NEGATIVE (-) OUTPUT TERMINAL STT OUTPUT TERMINAL POSITIVE (+) OUTPUT TERMINAL TEST PROCEDURE Return to Master TOC 1. Remove main input supply power to the Power Wave 455M. Return to Section TOC O OFF 2. Remove any output load that may be connected to the Power Wave 455M. 3. With the analog ohmmeter, measure the resistance between the positive and negative output terminals (NOT the STT terminal). Refer to Figure F.15. 4. If the reading is approx. 50 ohms, the output rectifier modules are not shorted. If the reading is less than 10 ohms, one or more of the rectifier modules are shorted. Reverse meter probe and verify low reading. Refer to the Output Rectifier Module Replacement procedure. IMPORTANT: The positive (+) meter probe must be attached to the positive (+) output terminal and the negative (-) meter probe must be attached to the negative (-) output terminal. 6. Using the 5/16” wrench, remove and insulate lead 202A from the negative output terminal. Repeat step 4 to confirm. 7. Reconnect lead 202A to the negative output terminal. 8. Replace the case top and sides. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 5. Remove the case top perform the Input Filter Capacitor Discharge procedure. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-48 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-49 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 1 TEST WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This test will determine if the correct voltage is being applied to the primary of Auxiliary Transformer No. 1 and also if the correct voltages are being induced on the secondary windings of the transformer. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Volt-ohmmeter (Multimeter) 3/8” Nut driver Wiring Diagram POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-49 F-50 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-50 AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 1 TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.16 – AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 1 TEST X3 X5 INPUT CONTACTOR X1 + 601 FAN MOTOR LEADS Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC X4 - X2 POWER BOARD RECTIFIER BRIDGE TEST PROCEDURE 1. Remove the main input power to the Power Wave 455 machine. 5. Locate secondary leads X3 and X5 (fan motor leads). 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top. 6. Locate secondary lead X4 (at main contactor). Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 3. Perform the Capacitor Discharge procedure. 4. Locate secondary leads X1 and X2 (at power board rectifier bridge). Refer to Figure F.16. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC F-51 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 1 TEST (CONTINUED) TABLE F.6 – SECONDARY VOLTAGES LEAD IDENTIFICATION NORMAL EXPECTED VOLTAGE X1 to X2 X3 to X5 X3 to X4 52 VAC 115 VAC 24 VAC 7. Carefully apply the correct input voltage to the Power Wave 455M. 10. If the correct secondary voltages are present, the T1 auxiliary transformer is functioning properly. If any of the secondary voltages are missing or low, check to make certain the primary is configured correctly for the input voltage applied. See the Wiring Diagram. WARNING ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. High voltage is present at primary of the Auxiliary Transformer. 12. Replace any cables ties and insulation removed earlier. 8. Turn on PW455M. Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC 9. Check for the correct secondary voltages according to Table F.6. Return to Section TOC 11. If the correct input voltage is applied to the primary, and the secondary voltage(s) are not correct, the T1 transformer may be faulty. 13. Install the case sides and top using the 3/8” nut driver. NOTE: The secondary voltages will vary if the input line voltage varies. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-51 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-52 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-52 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-53 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 2 TEST WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This test will determine if the correct voltage is being applied to the primary of Auxiliary Transformer No. 2 and also if the correct voltages are being induced on the secondary windings of the transformer. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Volt-ohmmeter (Multimeter) 3/8” Nut driver Wiring Diagram POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-53 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-54 F-54 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 2 TEST (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.17 – AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 2 TEST H1 3 VIEWED FROM TRANSFORMER LEAD SIDE H6 P50 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 5 350 352 1 2 VIEWED FROM TRANSFORMER LEAD END 3 4 33A P52 TEST PROCEDURE Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 1. Remove the main input power to the Power Wave 455M machine. 2. Remove any load that may be connected to the 115 VAC receptacle. 3. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top. 4. Locate plugs P52 and P50 at the Auxiliary Transformer No. 2. Refer to Figure F.17. 5. Carefully apply the correct input power. ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. Return to Master TOC 7. If 115 VAC and 230 VAC are present, Auxiliary Transformer No. 2 is good. 8. If 115 is not present between pins 1 and 4, and 230 VAC is not present between pins 1 and 2, check the associated leads and plugs for loose or faulty connections. 9. Carefully test for the correct AC input voltage applied to the primary windings at plug P50. See the Wiring Diagram. WARNING Return to Section TOC 6. Check for 115 VAC at plug P52 pins 1 and 4 (leads 350 to 33A). Check for 230 VAC at plug P52 pins 1 and 2 (leads 350 to 352). High voltage is present at both plugs. 10. If the correct AC input voltage is applied to the primary of the Auxiliary Transformer No. 2 and the secondary voltage is NOT correct, the transformer may be faulty. Replace. 11. Replace any cables ties and insulation removed earlier. 12. Install the case top using the 3/8” nut driver. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-55 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT RECTIFIER REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. DESCRIPTION This procedure will aid the technician in the removal and replacement of the input rectifier module. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” nut driver 3/16” Allen wrench Phillips head screwdriver POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-55 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-56 F-56 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT RECTIFIER REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.18 – INPUT RECTIFIER REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT INPUT RECTIFIER A B C NEG (-) Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC POS (+) REMOVAL PROCEDURE REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455M. 1. Clean heat sink surfaces. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top, and input access panel. 3. Perform the Capacitor Discharge procedure. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 4. Locate and remove the RTV sealant from the input rectifier connection terminals. See Figure F. 18. 5. Label and, using the phillips head screwdriver, carefully remove the five leads from the input rectifier terminals. Note placement for reassembly. See Figure F.18. 6. Using the 3/16” allen wrench, remove the two mounting screws and washers from the rectifier module. 2. Apply an even coating of joint compound (Penetrox A-13) to both the heat sink and module mounting surfaces. The joint compound should be 0.002 - 0.005 in. thick per surface. 3. Mount the module to the heat sink and evenly torque the mounting screws (with washers) to 44 in/lbs. 4. Assemble the leads to the correct module terminals and torque to 26 in/lbs. See Figure F.18. 5. Apply RTV sealant to the rectifier connection terminals. 6. Install the case top, sides, and input access panel using the 3/8” nut driver. 7. Carefully remove the input rectifier module. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-57 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT CONTACTOR REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This procedure will aid the technician in the removal and replacement of the input contactor. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” nut driver 5/16” nut driver Phillips head screwdriver POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-57 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-58 F-58 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR INPUT CONTACTOR REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.19 – INPUT CONTACTOR REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT INPUT CONTACTOR 601 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC X4 REMOVAL PROCEDURE REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455M. 1. Mount the contactor and tighten the mounting screws. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top, and input access panel. 2. Assemble the leads to the correct terminals. See Figure F.18. 3. Perform the Capacitor Discharge procedure 3. Install the case top, sides, and input access panel using the 3/8” nut driver. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 4. Locate the input contactor. Label and, using the phillips head screwdriver, carefully remove the leads from the input contactor terminals. Note placement for reassembly. See Figure F.19. 5. With the 5/16” nut driver, remove the three mounting screws. See Figure F.19. 6. Carefully remove the input contactor. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-59 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 1 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. DESCRIPTION This procedure will aid the technician in the removal and replacement of auxiliary transformer No. 1. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” Nut driver Wire cutters Wire splicer or soldering equipment POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-59 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-60 AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 1 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.20 – AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 1 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT X3 X5 H1 CB4 RECONNECT TERMINALS H2 H3 H4 H5 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC X1 - INPUT CONTACTOR 601 FAN MOTOR LEADS Return to Section TOC F-60 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR + X4 X2 POWER BOARD RECTIFIER BRIDGE Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC REMOVAL PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455. 4. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case back. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top, and input access panel. 5. Remove lead X4 from the input contactor coil terminal. 3. Perform the Capacitor Discharge procedure. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-61 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 1 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE (CONTINUED) 6. Remove leads X1 and X2 from the power board rectifier bridge. Refer to Figure F.20. 7. Cut X3 and X5 from the fan motor leads. Leave enough lead length to splice in the new transformer leads. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 8. Cut the X3 lead that is connected to the input board. Leave enough lead length to splice in the new transformer lead. 9. Locate, label, and remove primary lead H1 from circuit breaker CB4. 10. Label and remove primary leads H2, H3, H4, and H5 from the reconnect terminals on the reconnect panel. Note lead placement for reassembly. 6. Splice the new transformer fan leads to the fan motor leads X3 and X5. 7. Connect lead X4 to the main contactor coil terminal. 8. Connect leads X1 and X2 to the power board rectifier bridge. 9. Reposition any wire leads and install cable ties as necessary. 10. Install the case back using the 3/8” nut driver. 11. Install the case top, sides, and input access panel using the 3/8” nut driver. 11. Cut any necessary cable ties and clear the leads. 12. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the two mounting screws that hold the transformer to the fan baffle and the machine base. 13. Carefully remove the transformer from the Power Wave 455. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE 1. Carefully place the transformer into the Power Wave 455. 2. Install the two mounting screws that hold the transformer to the fan baffle and the machine base using the 3/8” nut driver. 3. Install the primary leads H2, H3, H4, and H5 to the reconnect terminals on the reconnect panel. 4. Connect primary lead H1 to circuit breaker CB4. 5. Splice the new transformer lead with the X3 lead connected to the input board. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-61 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-62 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-62 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-63 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 2 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This procedure will aid the technician in the removal and replacement of auxiliary transformer No. 2. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” Nut driver Wire cutters POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-63 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-64 F-64 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 2 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.21 – AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 2 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT INPUT CONTACTOR 601 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC X4 P52 P50 CB4 CIRCUIT BREAKER & 115V RECEPTACLE LEADS 33/32 REMOVAL PROCEDURE Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top, and input access panel. 3. Perform the Capacitor Discharge procedure. 5. Disconnect plugs P50 and P52. 6. Disconnect leads 33 and 32 to circuit breaker CB2 and the 115 V receptacle. 7. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the two transformer mounting screws. 4. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case back. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-65 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER NO. 2 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE (CONTINUED) REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE 1. Carefully place the transformer into the Power Wave 455. 2. Install the two mounting screws that hold the transformer to the machine base using the 3/8” nut driver. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC 3. Connect leads 33 and 32 to circuit breaker CB4 and the 115 V receptacle. 4. Connect plugs P50 and P52. 5. Reposition any wire leads and install cable ties as necessary. 6. Install the case back using the 3/8” nut driver. 7. Install the case top, sides, and input access panel using the 3/8” nut driver. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-65 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-66 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-66 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-67 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR CONTROL, FEED HEAD, OR VOLTAGE SENSE PC BOARD REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT WARNING Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. DESCRIPTION This procedure will aid the technician in the removal and replacement of either the Control Board the Feed Head Board, or the Voltage Sense Board. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” Nut driver Anti-static wrist strap POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-67 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-68 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR CONTROL, FEED HEAD, OR VOLTAGE SENSE PC BOARD REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.22 – CONTROL OR FEED HEAD BOARD REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT COMPARTMENT COVER POWER BOARD Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC DC BUS POWER BOARD CONTROL BOARD REMOVAL PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455M. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 3. Perform the Capacitor Discharge procedure. 4. Observe all static electricity precautions. 6. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the two screws holding the rear of the Control Box in place. 7. Clear the leads in the sleeving and the grommets on the sides of the control box. 8. Label and remove the molex plugs from the Control Board and the Feed Head Board. 5. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the PC board compartment cover. Refer to Figure F.22. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-68 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-69 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR CONTROL, FEED HEAD, OR VOLTAGE SENSE PC BOARD REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.23 – VOLTAGE SENSE BOARD REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT COMPARTMENT COVER POWER BOARD Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC CONTROL BOARD VOLTAGE SENSE BOARD 9. Tilt back the rear of the control box to access the PC board mounting nuts. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the self-locking mounting nuts from the Control and Feed Head Boards. Carefully remove the boards. REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE 1. Install either the Control or the Feed Head Board to the back of the control box with the self-locking nuts. Use the 3/8” nut driver. 10. Remove plugs J1 and J2 from the Voltage Sense Board. See Figure F.23. 2. Connect the molex plugs to the Control Board and the Feed Head Board. Be sure the lead harnesses are securely and properly positioned. 11. Using the needle-nose pliers, carefully pinch the three plastic standoffs. Remove the Voltage Sense Board. 3. Secure the rear of the control box in place using two screws and the 3/8” nut driver. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-69 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-70 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR CONTROL, FEED HEAD, OR VOLTAGE SENSE PC BOARD REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) 3. Secure the rear of the control box in place using two screws and the 3/8” nut driver. 4. Press the Voltage Sense Board onto its standoffs. Make sure the board snaps into place on all three standoffs. 5. Connect the two molex plugs to the Voltage Sense Board. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC 6. Install the PC board compartment cover using the 3/8” nut driver. 7. Install the case top and sides using the 3/8” nut driver. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-70 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-71 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR GATEWAY PC BOARD REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT WARNING Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. DESCRIPTION This procedure will aid the technician in the removal and replacement of the Gateway PC Board. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Phillips head screw driver 3/8” Nut driver Anti-static wrist strap POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-71 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-72 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR GATEWAY PC BOARD REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.24 – GATEWAY BOARD REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC DEVICENET/ GATEWAY BOARD (LOCATED BEHIND FRONT COVER) Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC PHILLIPS SCREW REMOVAL PROCEDURE REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455. 1. Install the Gateway Board to the case front cover with the self-locking nuts. Use the 3/8” nut driver. 2. Using the phillips head screw driver, remove the six screws from the case front cover. Tilt open the cover and support it. See Figure F.24. 3. Observe all static electricity precautions. 2. Connect the four molex plugs to the Gateway Board. 3. Using the phillips head screw driver, attach the cover to the case front. Return to Master TOC 4. Label and remove the four molex plugs from the Gateway Board. Return to Section TOC F-72 5. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the selflocking mounting nuts from the Gateway Board. Carefully remove the board. Refer to Figure F.24. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-73 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR STT CURRENT TRANSDUCER REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. DESCRIPTION This procedure will aid the technician in the removal and replacement of the STT Current Transducer. MATERIALS NEEDED 3/8” Nut driver 5/16” Open end wrench 5/16” Socket wrench with extension Universal adapter 3/4” Wrench Phillips head screw driver Wire cutters Wiring Diagram POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-73 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC F-74 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR STT CURRENT TRANSDUCER REMOVAL AND PLACEMENT (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.25 – STT CURRENT TRANSDUCER REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE RESISTOR ASSEMBLY 1234 P90 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC STT OUTPUT TERMINAL (TOP RIGHT) CURRENT TRANSDUCER REMOVAL PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top and right side. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 3. Perform the Capacitor Discharge procedure. 4. Using the wire cutters, cut all cable ties to the transducer lead harness. Unplug the harness and swing it aside. 5. Label and remove the leads to the resistor assembly. See Figure F.25. Using the 5/16” socket wrench, extension and universal adapter, remove the resistor assembly. It may be necessary to remove the plastic high voltage protection shield. (Use the 3/8” nut driver.) It may also be necessary to use a 5/16” open end wrench to remove the inside screws. Carefully swing the resistor assembly aside. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-74 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-75 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR STT CURRENT TRANSDUCER REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) 6. With the 5/16” open end wrench, remove the small screw from the STT output terminal. Label and remove the small leads. See the Wiring Diagram. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 7. Using the 3/4” wrench, remove the bolt, lock washer and flat washer from the STT output terminal. Remove the double heavy output leads. Cut any necessary cable ties. 8. Using the phillips head screw driver, remove the screws and lock washers that hold the transducer to the front panel. 9. Remove the STT current transducer, carefully feeding the output leads through it. 3. Attach the double heavy leads to the STT output terminal with the 3/4” bolt, lock washer and flat washer. 4. Attach the small leads to the STT output terminal with the 5/16” screw. 5. Install the resistor assembly using the 5/16” socket wrench, extension and universal adapter. Install the plastic high voltage protection shield with the 3/8” nut driver. 6. Replace all cable ties cut during removal. 7. Install the case top and right side using the 3/8” nut driver. 10. Remove the standoffs from the transducer and save them for reassembly with the new transducer. REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 1. Attach the standoffs to the transducer. 2. Position the transducer on the back of the front panel and attach it with the two phillips screws and lock washers. Feed the output leads through the transducer. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-75 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-76 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-76 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-77 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR POWER WAVE CURRENT TRANSDUCER REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This procedure will aid the technician in the removal and replacement of the Power Wave Current Transducer. MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” Nut driver 5/16” Open end wrench 9/16” Wrench 3/4” Wrench Phillips head screw driver Wire cutters Wiring Diagram POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-77 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC F-78 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR POWER WAVE CURRENT TRANSDUCER REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.26 – POWER WAVE CURRENT TRANSDUCER REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE CURRENT TRANSDUCER HEAVY LEAD BOLTED CONNECTION (BEHIND CASE FRONT) REMOVAL PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top and sides and the control box cover. Return to Master TOC 3. Perform the Capacitor Discharge procedure. Return to Section TOC F-78 4. Using the 3/8” socket wrench or nut driver, remove the three screws along the bottom case front. See Figure F.26. 6. Label all leads to all output terminals. Using the 5/16” wrench and the 3/4” wrench, remove all leads from the three output terminals. See the Wiring Diagram. 7. Cut any necessary cable ties. Then carefully swing the front panel aside. 8. Remove the insulating tape from the heavy lead bolted connection. See Figure F.26. Using the 9/16” wrenches, remove the bolt, lock washer and nut. 5. Using the 3/8” socket wrench, remove the four screws that hold the case front to the machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-79 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR POWER WAVE CURRENT TRANSDUCER REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) 9. Using the phillips head screw driver, remove the screws and lock washers that hold the transducer to the front panel. 10. Remove the Power Wave current transducer. Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC 11. Remove the standoffs from the transducer and save them for reassembly with the new transducer. 4. Using the 5/16” wrench and the 3/4” wrench, attach all leads to the three output terminals. See the Wiring Diagram. 5. Replace all cable ties cut during removal. 6. Install the case top and sides using the 3/8” nut driver. REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE 1. Attach the standoffs to the transducer. 2. Position the transducer on the back of the front panel and attach it with the two phillips screws and lock washers. Feed the output leads through the transducer. 3. Run the heavy lead through transducer and secure the bolted connection with the 9/16” bolt, lock washer and nut. Replace the insulating tape around the connection. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-79 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-80 NOTES POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-80 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-81 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR OUTPUT RECTIFIER, STT CHOPPER BOARD AND RECTIFIER MODULE REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This procedure will aid the technician in the removal and replacement of the output rectifier assembly and individual rectifier module replacement. This procedure takes approximately 35 minutes to remove and replace the output rectifier, 5 minutes to remove the STT Chopper Board and 5 minutes to remove and replace the rectifier module. Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC F-81 3/8” Nut driver 7/16” Wrench 9/16” Wrench 9/64” Allen wrench 3/16” Allen wrench Needle-nose pliers Slot head screwdriver Penetrox A13 Thermal Joint Compound Wiring Diagram POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC F-82 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR OUTPUT RECTIFIER, STT CHOPPER BOARD AND RECTIFIER MODULE REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.27 – OUTPUT RECTIFIER, STT CHOPPER BOARD AND RECTIFIER MODULE REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT LEAD 287 (SNUBBER DIODE) Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC F-82 PLUG J10 STT LEAD RECTIFIER THERMOSTAT (LEADS 291 & 292) LEAD 289B (STT SNUBBER CAPACITOR) TRANSFORMER LEADS RECTIFIER MODULE POSITIVE OUTPUT LEAD HEATSINK MOUNT BOLTS (4X) Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC HEATSINK RECTIFIER ASSEMBLY REMOVAL PROCEDURE 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top and sides. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 3. Perform the Capacitor Discharge procedure. 4. Using the 9/16” wrench, remove the Power Wave positive output lead from the rectifier heat sink. Note fastener hardware for reassembly. Refer to Figure F.27. 5. Using the 7/16” wrench, remove the STT output lead from the rectifier heat sink. Note fastener hardware for reassembly. Refer to Figure F.27. 6. Using the 7/16” wrench, remove the eight transformer leads from the rectifier modules. Label the leads and take note of lead placement for reassembly. Note that each screw has two flat washers and one lock washer. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-83 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR OUTPUT RECTIFIER, STT CHOPPER BOARD AND RECTIFIER MODULE REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) 7. Using the needle-nose pliers, remove leads #292 and #291 from the rectifier thermostat. 4. Using the 3/16” allen wrench, remove the four screws and lock washers holding the board to the heat sink. 8. Disconnect plug J10 from the STT Chopper Board. 5. Carefully remove the STT Chopper Board. 9. With the 7/16” wrench, remove lead #287 from the STT Snubber Diode D5. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 10. With the 7/16” wrench, remove lead #289B from the STT Snubber Capacitor C10. 11. Using the 7/16” wrench, remove the four nuts and associated washers from the heat sink mounting bolts. The heat-sink assembly can be removed by carefully sliding the assembly forward and removing the mounting bolts. REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE 1. Position the new board on the heat sink, using the standoffs for the slot head nylon screws and the allen head screws. 2. Install the four 3/16” allen head screws and lock washers. 3. Install the two nylon slot head screws. 4. Install the two 7/16” bolts, lock washers and flat washers. STT CHOPPER BOARD REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC 1. Place the output rectifier assembly on a clean bench surface. Return to Section TOC F-83 2. Using a slot head screw driver, remove the two nylon screws holding the board to the heat sink. Save the standoffs for reassembly. 3. Using the 7/16” wrench, remove the two bolts, lock washers and flat washers. Save the standoffs for reassembly. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-84 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR OUTPUT RECTIFIER, STT CHOPPER BOARD AND RECTIFIER MODULE REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) RECTIFIER MODULE REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE RECTIFIER ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE 1. Using the 9/64” allen wrench, remove the cap screw from the center of the rectifier module that is to be replaced. 1. Position the assembly in place with the mounting bolts. 2. Using the 7/16” wrench, remove the two mounting bolts and associated washers from the rectifier module to be replaced. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 3. Remove the faulty module. 4. This module requires special mounting considerations to prevent warping of the base plate. The heat sink surfaces must be clean and flat. Apply a thin, even coating of thermal compound, (Penetrox A13) 0.004 to 0.010 inches thick. Keep the compound away from the area of the mounting holes. 5. Press the new module firmly against the heat sink while aligning the mounting holes. Start all three screws two to three turns by hand. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 6. Tighten each of the outer screws to between 5 and 10 in-lbs. 7. Tighten the center screw to between 12 and 18 in-lbs. 8. Tighten each of the outer screws again, this time to between 30 and 40 in/lbs. 2. Assemble the nuts and associated washers to the mounting bolts. 3. Using the 7/16” wrench, tighten the four nuts on the mounting bolts. 4. Replace leads #292 and #291 to the thermostat. 5. Connect plug J10 to the STT Chopper Board. 6. With the 7/16” wrench, attach lead #287 from the STT Snubber Diode D5. 7. With the 7/16” wrench, attach lead #289B from the STT Snubber Capacitor C10. 8. Connect the eight transformer leads to the correct rectifier modules. Tighten the screws (with two flat washers and one lock washer) to between 30 and 40 in/lbs. Do not stress the terminals when making these connections. 9. Apply a thin coat of Penetrox A13 to the heat sink where the Power Wave positive output lead and the STT output lead attach. 10. Attach the Power Wave positive output lead to the heat sink using the 9/16” wrench. 11. Attach the STT output lead to the heat sink using the 7/16” wrench. Return to Master TOC 12. Install the case top and sides using the 3/8” nut driver. Return to Section TOC F-84 POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-85 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR SWITCH BOARD AND FILTER CAPACITOR REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT WARNING Service and repair should be performed by only Lincoln Electric factory trained personnel. Unauthorized repairs performed on this equipment may result in danger to the technician or machine operator and will invalidate your factory warranty. For your safety and to avoid electrical shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions detailed throughout this manual. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If for any reason you do not understand the test procedures or are unable to perform the test/repairs safely, contact the Lincoln Electric Service Department for electric troubleshooting assistance before you proceed. Call 1-888-935-3877. TEST DESCRIPTION This procedure will aid the technician in the removal and replacement of the switch board(s) and/or filter capacitor(s). MATERIALS NEEDED Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC 3/8” Nut driver 7/16” Wrench 3/16” Allen wrench Slot head screwdriver Penetrox A13 thermal joint compound POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-85 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC F-86 F-86 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR SWITCH BOARD AND FILTER CAPACITOR REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) FIGURE F.28 – SWITCH BOARD AND FILTER CAPACITOR REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT MOLEX PLUG MOUNTING SCREW (4X) 13/14 OR 17/18 SWITCH BOARD 19+ Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 20- 11/12 OR 15/16 REMOVAL PROCEDURE NOTE: Observe all static electricity precautions. Lead and plug references below use a slash (/) to indicate machine right side/left side wire number differences. Return to Master TOC 1. Remove input power to the Power Wave 455. Return to Section TOC NYLON SCREW (2X) 4. Using the 5/16” nut driver, remove the three screws mounting the plastic high voltage protective shield. Remove the shield. 5. Remove molex plug J40/J50 from the top of the switch board. Refer to Figure F.28. 6. Remove the mylar insulating shield covering leads 13/14 or 17/18. Cut the cable tie. 2. Using the 3/8” nut driver, remove the case top. 3. Perform the Capacitor Discharge procedure. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-87 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR SWITCH BOARD AND FILTER CAPACITOR REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT (CONTINUED) 7. Using the 7/16” wrench, remove leads 13/14 or 17/18 from the switch board. 8. Using the 7/16” wrench, remove leads 11/12 or 15/16 from the switch board. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 9. Using the 7/16” wrench, remove leads 19C/D+ and 20C/D- from the switch board capacitor connection bolts. 10. With the slot head screwdriver, remove the two nylon mounting screws at the bottom of the switch board. Note placement of the shake-proof washers and fiber spacers. 11. Using the 3/16” allen wrench, carefully remove the four cap screws that mount the switch board to the heat sink. 12. Carefully remove the switch board from the heat sink. 13. If the filter capacitor is to be removed, carefully slide it out of the mounting bracket. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE 1. If the filter capacitor is to be replaced, carefully slide the new capacitor into the mounting bracket. Position the capacitor so the correct polarity terminal is lined up with the correct hole on the switch board. 2. All heat sink and IGBT mounting surfaces must be clean. 5. Mount the new switch board and tighten the four cap head screws in the following manner. Tighten all until snug. Tighten all from 24 to 28 in-lbs. Tighten all from 40 to 48 in-lbs. 6. Make sure the capacitor is positioned correctly. Connect leads 19C/D+ and 20C/Dto the correct terminals. Tighten to 55 in/lbs. 7. Position and mount the two nylon screws, fiber spacers, and washers. Torque from 4 to 8 in-lbs. 8. Connect leads 11/12 or 15/16 to the correct terminal. 9. Connect leads 13/14 or 17/18 to the correct terminal. 10. Install the mylar insulating shield covering leads 11/12 or 15/16. Replace the cable tie. 11. Connect molex plug J40/J50 to the top of the switch board. 12. Using the 5/16” nut driver, install the plastic high voltage protective shield. 13. Install the case top and sides using the 3/8” nut driver. 3. Apply a thin coat of thermal compound (Penetrox A13) 0.005 to 0.010 inches thick to the mating surfaces. Do not apply around mounting holes. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 4. Apply a thin coat of Penetrox A13 to the capacitor terminals. Be careful not to apply compound to screw threads or threaded area of terminals. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT F-87 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC F-88 F-88 TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR RETEST AFTER REPAIR Retest a machine: If it is rejected under test for any reason that requires you to remove any part which could affect the machine’s electrical characteristics. OR Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC If you repair or replace any electrical components. INPUT IDLE AMPS AND WATTS Input Volts/Hertz Maximum Idle Amps Maximum Idle KW 208/60 230/60 400/60 460/60 575/60 4.0 3.3 2.1 2.0 1.8 0.45 0.45 0.45 0.45 0.45 Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Master TOC MAXIMUM OUTPUT VOLTAGES Input Volts/Hertz 208/60 230/60 400/60 460/60 575/60 Output Terminals - No load 50-70 VDC X1 - X2 Aux. Trans #1 115 Volt Receptacles OCV 10 Amp Load 115 - 123 VAC 111 - 119 VAC 48.5 - 55 VDC POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC Section G-1 TABLE OF CONTENTS - ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS SECTION - Section G-1 Electrical Diagrams ..............................................................................................................Section G Wiring Diagram (Code 10942) (G4212)......................................................................................G-2 Wiring Diagram (Codes 10957 - 11311) (G4420).......................................................................G-3 Schematic - Complete Machine (Code 10942) (G4211) ............................................................G-4 Schematic - Complete Machine (Codes 10957 - 11311) PG 1 of 3 (G4421).............................G-5 Schematic - Complete Machine (Codes 10957 - 11311) PG 2 of 3 (G4421).............................G-6 Schematic - Complete Machine (Codes 10957 - 11311) PG 3 of 3 (G4421).............................G-7 Schematic - Chopper PC Board (STT Models only) (L11340-2) ................................................G-8 PC Board Assembly - Chopper PC Board (STT Models only) (G3339-2)..................................G-9 Return to Master TOC Schematic - DeviceNet/Gateway PC Board (Robotic Model only) Pg 1 of 2 (G3821-2)..........G-10 Schematic - DeviceNet/Gateway PC Board (Robotic Model only) Pg 2 of 2 (G3821-2) ..........G-11 PC Board Assembly - DeviceNet/Gateway PC Board (Robotic Model only) (L11046-2) .........G-12 Schematic - Control PC Board (All Codes) Pg 1 of 4 (G3789-2) .............................................G-13 Schematic - Control PC Board (All Codes) Pg 2 of 4 (G3789-2) .............................................G-14 Schematic - Control PC Board (All Codes) Pg 3 of 4 (G3789-2) .............................................G-15 Schematic - Control PC Board (All Codes) Pg 4 of 4 (G3789-2) .............................................G-16 PC Board Assembly - Control PC Board (All Codes) (L11088-2).............................................G-17 Schematic - Digital Power Supply PC Board (All Codes) (G3631-3) .......................................G-18 PC Board Assembly - Digital Power Supply PC Board (All Codes) (G3632-3)........................G-19 Schematic - FeedHead PC Board #1 (Robotic Model only) Pg 1 of 3 (G3823-3)....................G-20 Return to Master TOC Schematic - FeedHead PC Board #2 (Robotic Model only) Pg 2 of 3 (G3823-3)....................G-21 Schematic - FeedHead PC Board #3 (Robotic Model only) Pg 3 of 3 (G3823-3)....................G-22 PC Board Assembly - FeedHead PC Board (Robotic Model only) (L11087-3) ........................G-23 Schematic - Input PC Board (All Codes) (M19528-2) ..............................................................G-24 PC Board Assembly - Input PC Board (All Codes) (L11396-2) ................................................G-25 Schematic - Switch PC Board (All Codes) (L11385-3) .............................................................G-26 PC Board Assembly - Switch PC Board (All Codes) (G3734-3)...............................................G-27 Schematic - Voltage Sense PC Board (Robotic Model only) (S24779-3) ................................G-28 PC Board Assembly - Voltage Sense PC Board (Robotic Model only) (M19540-3) ................G-29 Schematic - 40 VDC Bus PC Board (All Codes) (M19330-2) ..................................................G-30 Return to Master TOC PC Board Assembly - 40 VDC Bus PC Board (All Codes) (L11078-2) ....................................G-31 NOTE: Many PC Board Assemblies are now totally encapsulated and are therefore considered to be unserviceable. The Assembly drawings are provided for reference only. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT LEFT SIDE OF MACHINE TO TP6 S1 ARCLINK RECEPTACLE DEVICENET CONNECTOR 1 2 +24V CAN_H CAN_L 4 5 L5 53A L2 TO J75 894 893 892 891 +24V GND 3 J70 A B 53 54 C D 67A 67 52 E 51 TO P73 J2VS CB1 J47 L6 54A 52A L7 51A S6 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC J K L M N 53A 54A MODULE INTERFACE CONNECTOR L8 539 541 521 L9 522 BLACK 847 WHITE BLACK A B C D E F G H J71 J16 ROBOTIC/ WIREDRIVE INTERFACE RECEPTACLE 51A 67A 52A 1 3 4 5 6 TO J82 AND J1 OR 73 (IF MODULE IS PRESENT) 153B 154B 51B 67B 52B J72 S2 VOLTAGE SENSE RECEPTACLE 3 CONDUCTOR TWISTED/SHIELDED SHIELD GROUND TO CASE 1 2 3 4 L4 TO J9 21A J74 GND-A RED BLACK GREEN 67C TO J83 J84 J2VS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 S3 RS232 CONNECTOR 253 254 J75 TO J2 251 J76 20 CB1 52 10A CIRCUIT BREAKER TO L2 BUSS BD 50 743 741 800 840 153B 154B 51B 52B 6B 6W 892 893 TO J81 TO S1 J4 TO S5 891 894 J5 830 J6 I/O RECEPTACLE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 S4 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 115V RECEPTACLE TO WORK STT TP6 TO J85 31 32 TO AUX 2 CB2 GND-B GND-A VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT BOARD 202A 50Ω J1 CB2 10A CIRCUIT BREAKER 31 TO S4 AUX 2 33 67C 511 1 2 J2 206A 512 1 2 3 4 5 6 TO WORK ELECTRODE R 1 J7 67B TO S6 TO J16 J8 D6 +40VDC DIODE 1W 2B 5W 6W 1B 2W J9 880 N.D. STATUS LED (R/G) TO J7 AC AC TO J83 886 J10A J10B N.A. THERMAL LED (Y) TO J7 J11 TO J9 206 5B 6B 251 253 254 TO S3 J84 J42 TO J16 J41 1 2 3 4 5 6 539 541 521 522 886 880 TO S6 D6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 WHITE RED BLACK BLACK BLACK GREEN TO S6 J43 847 225 223 221 227 222 228 226 227 221 222 223 225 224 220 TO J42 J43 R5 J85 TO RECT THERM 231 232 J86 504 503 406 405 238 505 TO J20 J40 J50 604 506 403 404 J87 1W 1B 2W 2B 4W 4R 3R 3W 211 212 213 813 811 216 816 812 206 202 67 21A 414 418 514 518 54 53 273 274 + + ELECTRODE 289D R2 TO TP3 TO RECONNECT PANEL A TO J61 H1D (TOP) 288E STT LOAD LINE TO CONTACTOR L3A 2Ω 289E R3 288F 2Ω 289F R4 2Ω SW1 STT SNUBBER RESISTOR BANK POWER TO CB3 612B TO CONTACTOR L1A TO FAN X3A TO AUX #1 224A TO SSR J10CH 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 512 511 5W 5B 291 MAIN CHOKE TO J8 216 211 213 212 P91 4 3 2 1 + DC BUS BOARD TO C3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 J46 TO S7 J47 TO J1VS 220 H5 H4A H3 (220-230) H2 (200-208) H1 220A POS POS NEG NEG H3A H3 51 50 475 476 477 478 THIS AREA VIEWED FROM REAR OF MACHINE 4R 346 4W TO SWITCH BD #2 F4 18 287 TO SWITCH BD #2 POS 13 14 .022 SEC 800V (BOTTOM TO D5 LEFT) TO PRI (BOTTOM SWITCH LEFT) BD #1 20D TO SWITCH BD #2 F3 TO AUX #2 289B TO C10 TO MAIN TRANSFORMER 14 15 16 11 12 F3 TO RECONNECT SWITCH 20 TO ROBOT IFACE 268 268A TO J4 J43 .022 800V AC AC SEC (BOTTOM RIGHT) X2 TO P90 P91 TO C3 AUX. #1 TO J40,J50 TO J6, J10B 2.7 10W SEC (TOP .022 RIGHT) 800V D1 POS POS POS F1 287 - STT CURRENT TRANSDUCER 812 813 811 816 TO J43 S1 P90 1 2 3 4 288B D5 C10 20uF 400V STT SNUBBER CAPACITOR BANK 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 18 J60 13 J50 STT SNUBBER DIODE C5 288A TO C10 TO C8 J61 3500µ F 500V 15 16 20D 19D + 601 X3 238 604 232 TO CR1 J6 AUX #1 POS NEG AC 3 231 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 SWITCH BOARD #2 RIGHT SIDE AC 2 AC 1 T1 T2 612 TO CR1 SW1 CB4 TO J61 TO J60 H1D T3 T2 T1 L3 L2 L1 601 T3 CR1 X4 NOTES: N.A. PIN NEAREST THE FLAT EDGE OF LED LENS (CATHODE) ALIGNS WITH BLACK LEAD OF LED SOCKET. 20uF C8 400V 17 TO SWITCH BD #1 F1 + TO J8 PRI (TOP RIGHT) INPUT RECTIFIER INPUT BOARD 11 TO J46 POWER BD RECT POS 19D F2 NEG NEG NEG 2400µF 100V TO J1 VOLTAGE SENSE WORK ELECTRODE S2 3 4 NEG 17 TP7 C3 33A S8 WATER COOLER RECEPTACLE TO RECONNECT SWITCH HARMONIC FILTER 19 20C F2 NEG TO J73 1 2 TO PRI (BOTTOM SWITCH RIGHT) BD #2 D2 POS TO D6 J47 S1 J11 350 352 15 2.7 10W POWER BD RECTIFIER 200-208V 220-230V 440-460V 550-575V 'A ' TO 20 HARMONIC FILTER 20C 19C D3 EMITTER R5 TO AUX #1 H2 H3 H5 H6 TO SWITCH BD #1 NEG 3500µ F 500V C4 TO SW1 N.C. 19 J40 12 TO C8 289A 262 RECONNECT PANEL TO SWITCH BD #1 TO HARMONIC FILTER SWITCH BOARD #1 2.7 10W COLLECTOR 1 2 3 J10 4 5 6 345 PRI (TOP LEFT) TO RECT THERM 292 N.B. RECONNECT SWITCH D4 X1 289A 289C 288B 288C 288D 288E 289B 289C 289D 289E X5 TO AUX#1 TO J6,J10B F4 220A TO SOLID STATE RELAY 444 19C SEC (TOP LEFT) CIRCUIT BREAKER JUMPER (H1A) H1 TO AUX #1 X3A TO SOLID STATE RELAY 16 291 TO CB1 J41 J82 S1 CB4 6A FAN CURRENT TRANSDUCER 292 TO J61 CB3 612A 612 H2A H2 H1 TO FAN TO CR1 J60 RECT THERM TO CHOKE THERM H1A TO AUX. #2 TO AUX #2 CB4 RECONNECT PANEL H4 MAIN TRANSFORMER LEFT SIDE OUTPUT RECT 224A CHOPPER BOARD TO SSR, J10 CHOPPER BD. 288A 288C H5A TO J5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 CHOKE THERM TO RECT THERM L1 TO J4 J11 R5 228 273 267 262 TO D5 TP5 288D TO R1 206A TP4 TO POWER BD. RECTIFIER X3 W X3 (24V) N X4 (115V) R X5 CIRCUIT BREAKER TO CB4 612A H6A H6 TO RECONNECT SWITCH TO MAIN TRANSFORMER N.C. PLACE "A" LEAD ON APPROPRIATE CONNECTION FOR INPUT VOLTAGE. CONNECTION SHOWN IS FOR 550-575V OPERATION. N.D. PIN NEAREST THE FLAT EDGE OF LED LENS (ANODE) ALIGNS WITH WHITE LEAD OF LED SOCKET. RIGHT SIDE OF MACHINE TO AUX #1 TO SW1 L3A P50 JUMPER N.B. PLACE SWITCH IN APPROPRIATE POSITION FOR INPUT VOLTAGE. CONNECTION SHOWN IS FOR 440-575V OPERATION. C6 .05/600V TP2 444 H6 (550-575) H5 (440-460) H4 (380-415) 1 224 267 266 268 W (51V) U X2 TO J47 TO SW1 612B AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER #1 X1 346 268A 226 274 266 345 - TO J4 2 475 477 476 478 TO TP6 C2 .05/600V Return to Master TOC J83 153B 154B 51B 52B 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 TO J72 CB3 10A 3W 4 REAR OF MACHINE FRONT OF MACHINE S7 Return to Master TOC J3 TO WORK ELECTRODE TP3 Return to Section TOC J73 J2 1 2 3 4 J82 743 741 800 840 SOLID 3R STATE RELAY + 3 414 418 403 404 405 406 TP1 J1 1 2 3 4 J81 DIGITAL POWER SUPPLY BOARD 1 2 3 4 5 6 C1 .05/600V FEED HEAD BOARD 514 518 503 504 505 506 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 WORK 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 1 2 1 2 3 4 TO J7 1 2 3 4 5 6 DEVICE NET GATEWAY BOARD TO CB1 J47 + TO TP3 202A TO R1 - CONTROL BOARD TO J9 202 + Return to Master TOC WIRING DIAGRAM - ENTIRE MACHINE - CODE 10942 (G4212) S5 Return to Section TOC G-2 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS + Return to Section TOC G-2 32 1 33 4 350 33A 352 2 TO S4 CB2 P52 1 4 2 (115V) R (230V) H6 (550-575) H5 (440-460) H4 (380-415) H3 (220-230) H2 (200-208) H1 5 H6A 5 H6A 6 6 H5A 3 3 H4A 2 2 H3A 4 4 H2A 1 H1A 1 H1A W LEAD COLOR CODING B=BLACK COMPONENT VALUES: G=GREEN CAPACITORS=MFD/VOLTS N=BROWN RESISTORS=OHMS/WATTS R=RED LEGEND U=BLUE DASHED " " = STT MACHINE ONLY W=WHITE " = OPTION J10,J2VS J74 1 2 J2,J5,J11, J41,J46,J72 J73,J76,J81 J82 1 2 3 4 J1VS,J9,J10CH, J14,J40J42, J50,J75,J83 1 TO CB3 AUX #1 4 3 6 5 U G TO A SYSTEM GROUND PER NATIONAL ELECTRICAL CODE. J8, J47,J60 J84 1 V TO SUPPLY LINES AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER #2 ELECTRICAL SYMBOLS PER E1537 PHANTOM " W TO SW1 L1A J3, J61,J86 4 1 8 6 J4,J13, J43,J71 5 1 6 1 10 7 12 8 CONNECTOR CAVITY NUMBERING SEQUENCE (VIEWED FROM COMPONENT SIDE OF BOARD) 7 1 14 9 J1,J6,J7 J10,J70,J85 J87 8 16 B G4212 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. The wiring diagram specific to your code is pasted inside one of the enclosure panels of your machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT LEFT SIDE OF MACHINE CONTROL BOARD 253 254 TO TP6 TO J9 202 6B N.D. J72 S5 L2 1 +24V 2 CAN_H CAN_L J73 6B 6W 892 893 894 893 892 891 +24V GND 3 4 5 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 891 894 S9 830 ETHERNET CONNECTOR RJ 45 TYPE 743 741 800 840 153B 154B 51B 52B TO R1 202A WORK N.M. J3 - J74 J4 J76 ETHERNET PORT L10 J5 J710 N.M. N.M. J712 ONLY PRESENT IF FEEDHEAD MODULE IS NOT PRESENT J16 52B J16 J81 GND-A RED BLACK GREEN 67C J82 3 CONDUCTOR TWISTED/SHIELDED SHIELD GROUND TO CASE S7 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 Return to Master TOC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT BOARD J1 J2 539 541 521 522 886 880 1 2 3 4 5 6 WHITE RED BLACK BLACK BLACK GREEN 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 847 I/O RECEPTACLE 1 2 3 4 5 6 512 1 2 67B 1 2 3 4 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 512 511 5W 5B 53A 153B 154B 51B 52B 53 54 C D 67A 67 52 E 51 54A L5 CB1 52 10A CIRCUIT BREAKER 50 228 226 227 221 TO J42 J43 R5 222 223 225 S2 268A 226 274 266 345 TO J47 444 TO RECT THERM 224 220 504 503 406 405 238 505 TP4 TO FAN TO J4 J11 R5 224A MAIN CHOKE TO J8 P91 4 3 2 1 216 211 213 212 220 TO C3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 J46 J47 220A POS POS NEG NEG 2W 2B TO THERMAL LED 50 345 4R 346 4W F4 D3 F3 289B TO C10 F3 2.7 10W TO J4 J43 POWER BD RECTIFIER AC 2B TO J61 H1D 20 POWER HARMONIC FILTER 19 17 1 2 3 4 S8 WATER COOLER RECEPTACLE TO RECONNECT SWITCH N.G. POS INPUT RECTIFIER 19D TO J6, J10B POS NEG SEC (TOP RIGHT) PRI (TOP RIGHT) 17 TO SWITCH BD #1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 18 J60 13 J50 STT CURRENT TRANSDUCER J61 3500µ F 500V C5 15 16 20D 19D + 288A TO C8 D5 601 X3 238 604 232 AC 2 C N.F. TO CR1 J6 AUX #1 AC 1 B A LOAD INPUT LINE FILTER 231 LINE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 SWITCH BOARD #2 RIGHT SIDE + AC 3 INPUT BOARD T1 T2 612 TO CR1 SW1 CB4 TO J61 TO J60 H1D T3 T2 T1 L3 L2 L1 N.K. 601 T3 CR1 X4 STT SNUBBER DIODE TO MAIN TRANSFORMER 288B TO C10 TO RECONNECT SWITCH TO AUX #1 P50 N.E. N.A. THERMAL LED (Y) TO J7 32 P51 1 33 4 352A 6 TO S4 CB2 (TOP) H6 (550-575) 350 P52 1 33A 4 352 2 5 H6A W TO CB3 AUX #1 (115V) R (230V) H1 1 L1B L3B L3A C6 H1A AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER #2 W L3 V U TO SUPPLY LINES .0047 µF 440 LOAD LINE TO CONTACTOR L3A TO SW 1 SW1 TO CB4 612B 350 352 33A NEG F1 287 TO J46 POWER BD RECT N.D. STATUS LED (R/G) TO J7 TO RECONNECT PANEL A TO J2 251 20 PRI TO (BOTTOM SWITCH RIGHT) BD #2 F1 L4 253 254 TO AUX #2 TO RECONNECT SWITCH D1 P90 1 2 3 4 200-208V 220-230V 440-460V 550-575V TO 20 HARMONIC FILTER 11 12 2.7 10W .022 800V 812 813 811 816 TO SW1 'A ' TO MAIN TRANSFORMER 11 21A 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 20D TO SWITCH BD #2 3500µ F 500V C4 TO AUX #1 H2 H3 H5 H6 TO SWITCH BD #1 NEG 20C POS POS POS C3 2400µ F 100V N.C. N.J. 19 F2 NEG NEG NEG J10B RECONNECT PANEL 20C 19C F2 NEG J10A TO SWITCH BD #1 TO HARMONIC FILTER D2 TO C3 AUX. #1 X2 TP7 1B TO PRI (BOTTOM SWITCH LEFT) BD #1 15 POS AC 13 14 SWITCH BOARD #1 14 .022 800V X1 2W N.B., N.G., N.H. TO SWITCH BD #2 POS J40 2.7 10W SEC (BOTTOM RIGHT) TO J8 1W TO SWITCH BD #2 12 TO D5 268 268A R5 TO P90 P91 J11 X5 TO AUX#1 RECONNECT SWITCH F4 TO C8 289A TO AUX #1 THIS AREA VIEWED FROM REAR OF MACHINE 18 SEC .022 (BOTTOM LEFT) 800V FUSE TO SOLID STATE RELAY 444 19C PRI (TOP LEFT) N.L. 10A H1 D4 287 H1 H1B TO INPUT SWITCH TO J61 H2 EMITTER TO SSR 211 212 213 813 811 216 816 812 N.J. H3 TO J6,J10B 16 SEC (TOP LEFT) TO RECT THERM COLLECTOR 1 2 3 J10 4 5 6 612 TO AUX #2 CB3 RECONNECT PANEL X3A TO SOLID STATE RELAY MAIN TRANSFORMER LEFT SIDE 291 TO CB1 J41 J82 S1 475 476 477 478 262 4W 4R 3R 3W H4B FAN CURRENT 292 CHOPPER BOARD TO STATUS LED 612B H4 TO FAN TO CR1 J60 + TRANSDUCER OUTPUT RECT J9 S3 291 H1A CIRCUIT BREAKER TO AUX #2 H6A H6 H5 H3 (220-230) H2 (200-208) H1 RECT THERM TO CHOKE THERM 51 220A J1 & J3 ARE NOT USED RS232 CONNECTOR CHOKE THERM 292 1W 1B TO POWER BD. RECTIFIER X3 W X3 (24V) N X4 (115V) R X5 X3A TO AUX #1 TO RECT THERM 224A 604 506 403 404 H6 (550-575) H5 (440-460) H4 (380-415) TO J5 231 232 TO J20 J40 J50 W (51V) U 1 224 R1 50Ω L1A TO CONTACTOR J N.F. C7 G SWITCH LEAD FILTER TO A SYSTEM GROUND PER NATIONAL ELECTRICAL CODE. S4 115V RECEPTACLE (NEUTRAL BONDED) S4 NOTES: 220V RECEPTACLE N.D. TO J83 351 N.A. PIN NEAREST THE FLAT EDGE OF LED LENS (CATHODE) ALIGNS WITH BLACK LEAD OF LED SOCKET. N.B. PLACE SWITCH IN APPROPRIATE POSITION FOR INPUT VOLTAGE. CONNECTION SHOWN IS FOR 440-575V OPERATION. TO WORK CB2 5A CIRCUIT BREAKER 34 CB2 352A 32 TP6 CE Model N.C. PLACE "A" LEAD ON APPROPRIATE CONNECTION FOR INPUT VOLTAGE. CONNECTION SHOWN IS FOR 550-575V OPERATION. N.D. PIN NEAREST THE FLAT EDGE OF LED LENS (ANODE) ALIGNS WITH WHITE LEAD OF LED SOCKET. 10A CIRCUIT BREAKER CASEFRONT PANEL 33 TO D5 288D 206 TO J9 OR 206A TO R1 STT 288E 2Ω 288F 2Ω C6 .05/600V + ELECTRODE TP5 C2 .05/600V 31 289E R3 TO TP3 32 289D R2 + (EARLIER MODEL) 115V RECEPTACLE (NEUTRAL FLOATING) Return to Master TOC AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER #1 X1 X2 228 273 267 262 206A 1 2 3 4 - TO J4 346 DC BUS BOARD 202A VOLTAGE SENSE RECEPTACLE J85 J43 TO ELECTRODE 32 886 TO J43 21A 414 418 514 518 54 53 273 274 TP3 TO J47 GND-B CASEFRONT TO J40 J50 L7 TO WORK 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 202 67 67 67C 511 880 GND-A L6 J83 J84 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 1 2 1 2 3 4 206 51A C11 .0047/3KV +40VDC DIODE AC A B 52A D6 AC J8 ARCLINK RECEPTACLE 743 741 800 840 1 2 3 4 N.M. 51A 67A 52A S1 FEEDHEAD BOARD 539 541 521 L9 522 BLACK 847 WHITE BLACK 53A 54A 1 3 4 5 6 153B 154B 51B 67B 52B ROBOTIC/WIREDRIVE INTERFACE RECEPTACLE A B C D E F G H J7 MODULE INTERFACE CONNECTOR WIRE DRIVE INTERFACE MODULE L8 1 3 4 5 6 153B 154B 51B OR OR S6 J6 267 266 268 475 477 476 478 CB3 3.5A 3W 4 2 + J77 J K L M N Return to Section TOC ONLY PRESENT IF FEEDHEAD MODULE IS PRESENT 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 THE ETHERNET CONNECTION IS ONLY PRESENT IN THE ETHERNET / DEVICENET MODULE FRONT OF MACHINE Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC J70 & J71 ARE NOT USED J41 225 223 221 227 222 TO J7 REAR OF MACHINE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 C1 .05/600V TP1 J75 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 J42 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 TO TP3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 J2 414 418 403 404 405 406 6W SOLID 3R STATE RELAY + 3 DIGITAL POWER SUPPLY BOARD 1 2 3 4 251 1 2 3 4 5 6 DEVICENET MODULE 514 518 503 504 505 506 OR 1 2 3 4 5 6 ETHERNET / DEVICENET MODULE + Return to Master TOC WIRING DIAGRAM - ENTIRE MACHINE - CODES 10957 - 11311 (G4420) DEVICENET CONNECTOR Return to Section TOC G-3 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS + Return to Section TOC G-3 289F R4 2Ω STT SNUBBER RESISTOR BANK 288A 288C 289A 289C 288B 288C 288D 288E 289B 289C 289D 289E TP2 CB2 RIGHT SIDE OF MACHINE 10A CIRCUIT BREAKER 33 C8 20µF 400V STT SNUBBER CAPACITOR BANK C10 20µF 400V N.E. LEAD 33 IS PRESENT IN MODELS WITH 115V RECEPTACLE ON THE CASE FRONT. LEAD 352A IS PRESENT ONLY IN MODELS WITH 220V RECEPTACLE ON THE CASE FRONT. N.F. ONLY PRESENT ON "CE" MODELS. N.G. ONLY PRESENT ON NON-CE MODELS. N.H. "CE" MODELS DO NOT HAVE A RECONNECT SWITCH. POS LEAD CONNECTS DIRECTLY TO (+) OF C4. LEAD C CONNECTS (-) OF C4 TO (+) C5 AND NEG LEAD CONNECTS TO (-) OF C5. N.J. THE "CE" MODELS DO NOT HAVE A RECONNECT PANEL. INSTEAD LEAD H4B CONNECTS H4 TO SW1. N.K. ON CE MODELS LEADS T1, T2 AND T3 ARE REPLACED BY LEADS A, B AND C. LEADS A, B AND C ARE CONNECTED TO THE INPUT RECTIFIER TERMINALS RATHER THAN CR1. N.L. 10 AMP CIRCUIT BREAKER IS USED IN PLACE OF FUSE ON CODES BELOW 11150. N.M. ON SYNCHRONIZED TANDEM MIG APPLICATIONS J77, J712 OF THE ETHERNET BOARD AND J3, J7 OF THE CONTROL BOARD ARE USED, SEE S26631 FOR DETAILS. REAR FAN FRONT RECONNECT RECONNECT HORIZONTAL HORIZONTAL SHROUD SHELL BRACKET BAFFLE BAFFLE CASE FRONT REAR UPPER BASE FRONT UPPER BASE AUX. 2 N.F. AUX. 1 PROTECTIVE BONDING CIRCUIT LEGEND DASHED " PHANTOM " " = STT MACHINEONLY " = OPTION LEAD COLOR CODING B=BLACK G=GREEN N=BROWN R=RED U=BLUE W=WHITE COMPONENT VALUES: CAPACITORS=MFD/VOLTS RESISTORS=OHMS/WATTS COMPONENT VALUE UNITS: CAPACITOR: MFD/VOLTS RESISTOR: OHMS/WATTS CONNECTOR PIN NUMBERS: EX. 12 PIN CONNECTOR 1 2 6 7 12 LATCH ELECTRICAL SYMBOLS PER E1537 VIEW OF CONNECTOR ONPC BOARD J G4420 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. The wiring diagram specific to your code is pasted inside one of the enclosure panels of your machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT CHANGE DETAIL: Released from "X" MAIN TRANSFORMER T1 SWITCH BOARD #1 (LEFT) N.A. RECONNECT SWITCH 208-230V POS 19D 19 20C 414 NEG L1A 3J40 IGBT DRIVE (+) 404 4J40 V/F (+) 405 5J40 V/F (-) +13V 232 5J60 522 4J83 SOLENOID INPUT 539 1J83 MOTOR "+" 541 2J83 MOTOR "-" WHITE 1J84 6J40 N.A., N.B. GND I OUT -15V D6 886 P91 IGBT DRIVE (-) N.C. C10 SWITCH BOARD #2 (RIGHT) CURRENT TRANSDUCER C8 D5 C H2 200-208V H3 220-230V H5 440-460V H6 550-575V 4J60 T2 4J61 3J60 238 SINGLE PHASE DETECT 8J60 (LOW=1 PHASE) 231 S6 ROBOTIC INTERFACE RECEPTACLE 17 TACH COMMON BLACK 5J84 TACH 2A DIFF. INPUT GREEN 6J84 TACH 2B DIFF. INPUT 847 7J84 SINGLE TACH INPUT 851 1J85 TRIGGER +15VDC 852 2J85 TRIGGER INPUT BLACK 847 WHITE BLACK 3J85 4J85 4 STEP INPUT 855 5J85 COLD INCH +15VDC CT CURRENT (+) 503 3J50 IGBT DRIVE (+) 504 4J50 V/F (+) 505 5J50 V/F (-) 6J50 16 856 6J85 857 7J85 GAS PURGE INPUT 859 9J85 860 10J85 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 861 11J85 SHUTDOWN 2 INPUT 12J85 INPUT B 5B 16J85 +40VDC ARCLINK H 0V STATUS LED (Hi for RED) STATUS LED (Hi for GREEN) + 24V 115V H2 6J10 4W 3J10 4R 886 5J83 2J82 X4 N.A. 1J73 1J82 153B 2J73 3J82 51B 3J73 4J82 52B 741 ARCLINK L 1J81 743 COMMON 3J81 800 +40VDC 4J81 840 2J72 1J72 ARCLINK L ARCLINK H COMMON + 40VDC 3J72 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT (-) 14J85 511 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT (+) 13J85 512 894 893 612B 612A H5A 6 H4A 3 (440-460) POS 65VDC 291 2 H3 CB3 H2A 4 H1A 1 4J72 +40VDC 5J75 OUTPUT RECTIFIER THERMOSTAT 6W 2J74 2 352 230V 352A 33A 2 4 CB2 115V 1J1 512 VOLTAGE SENSE OUTPUT 3J1 67C DC BUS THERMOSTAT 2J75 1J75 CAN_H 891 4J75 CAN_L 262 +15V WORK VOLTAGE SENSE 10A 33 4 S8 WATER COOLER RECEPTACLE 1 3 1 4W 13J7 STT CHOPPER DRIVE (-) 4R 14J7 STT CHOPPER DRIVE (+) 503 6J6 YELLOW THERMAL LED THERMAL LED 10J6 506 14J6 S4 110V RECEPTACLE 2W 7J7 V/F (+) 5J6 505 2B 8J7 THERMAL LED IGBT DRIVE (+) 3J7 1W V/F (-) RED/GREE STATUS LED IGBT DRIVE (-) 514 1J10B CT CURRENT (-) 518 2J10B CT CURRENT (+) 403 15J6 IGBT DRIVE (+) 404 16J6 V/F (+) 405 8J6 V/F (-) 7J6 4J7 1B 1J10A 1J2 345 7J43 346 1J43 POS 1J46 POS 2J46 31 N.A. PC BOARD COMPONENTS SHOWN FOR REFERENCE ONLY. ALL COMPONENTS ARE NOT SHOWN. N.B. WIRING FOR OPTIONAL MODULES MAY NOT BE PRESENT IF MODULE IS NOT INSTALLED. NEG NEG 3J46 224 2J5 THERMOSTAT 220 3J5 THERMOSTAT 3W 16J7 3R 15J7 FAN CONTROL (+) 3J4 +5V SPI 9J6 604 12J6 PRECHARGE CONTROL 231 1J6 SINGLE PHASE DETECT (LOW=1 PHASE) 232 2J6 MAIN CONTACTOR CONTROL +13V 6J43 266 2J4 +15V SPI 11J43 267 1J4 SPI COMMON ARCLINK + 1J11 ARCLINK - 2J11 53 4J9 67 VOLTAGE SENSE 6J16 52B 51A 4J16 51B 67B 54 L7 52A STT COMMON 262 12J43 SPI COMMON 4J42 227 7J4 53A 54A POWER DOWN INTERUPT 67 +15V 1J42 225 12J4 +15V +5V 3J42 221 8J4 +5V SPI +5V CONTROL BOARD COMMON 5J42 222 10J4 CONTROL BOARD COMMON -15V 2J42 223 11J4 -15V 67B 3J43 51A L6 67A 1J41 ARCLINK +5V +40V COMMON 5J43 274 4J11 475 +5V ARCLINK +5V ARCLINK COMMON 2J41 +40V 10J43 273 3J11 477 ARCLINK COMMON L5 S1 ARCLINK RECEPTACLE 53 A ARCLINK - 54 B ARCLINK + 67 C ELECTRODE SENSE 52 D +40VDC 51 E 0VDC S5 DEVICENET CONNECTOR RS232 +5V 4J43 226 6J4 RS232 +5V 894 2 RS232 COMMON 9J43 228 5J4 RS232 COMMON 893 3 +24V GND 892 4 CAN_H 891 5 CAN_L COMMON 6J47 476 3J41 +40V COMMON +40VDC POWER 8J47 478 4J41 +40V COMMON 1J47 L2 51 +24VDC 52 50 CB1 10A ELECTRICAL SYMBOLS PER E1537 N.C. R2, R3 AND R4 ARE 2 W / 300. C8 AND C10 ARE 20 mfd / 400V. N.D. IF FEED HEAD BOARD IS NOT PRESENT, INSERT P82 INTO J73. 52A (NORMALLY CLOSED) 238 7J47 4J46 5J16 J16 } 5J47 3J47 153B 67A FAN CONTROL (-) COMMON +40VDC FEEDER 154B 1J16 CT CURRENT (+) 2J10A STT +20V POWER DOWN INTERUPT 268A 3J16 53A CT CURRENT (-) 418 268 54A IGBT DRIVE (-) +40VDC POWER NOTES : 32 3 POWER BOARD 33 350 32 21A 6J9 4 268A SPI COMMON DC BUS BD N.A. 0V H2 H1 -15V 8J8 511 4J1 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT (+) WIRE FEEDER VOLTAGE SENSE 220A 292 6B 1J74 R5 10Ω 892 N.A. C3 NEG (200-208) 10A 4J8 812 ARCLINK L 24000uF/100V (220-230) EN-170 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC H3A 813 1 2 L4 X2 H4 (380-415) STT FEEDBACK 224A CHOKE THERMOSTAT COMMON +24VDC +24V GND VOLT SENSE BD - X5 H6 (550-575) H5 CONTROL BOARD COMMON 5J8 414 ARCLINK H P80 5 7J8 811 406 TRANSFORMER T2 H6A 816 3J76 COMMON 2J81 830 1J76 154B ARCLINK H RED/GREEN STATUS LED +15V SPI 52V H1 S2 VOLTAGE SENSE RECEPTACLE GND GATEWAY BD 3W X1 (200-208) H1 N.D. 3R FAN H3 (220-230) H2A N.A., N.B. 880 6J83 POWER BD. RECT. X3 H4 H4A 346 ARCLINK L VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT (-) X3 +15 COMMON TP4 (380-415) H3A 1J10 4J10 STATUS LED(Hi for GREEN) 444 H5 (440-460) 2J8 STATUS LED (HI FOR RED) STATUS LED(Hi for RED) SOLID STATE RELAY H6 (550-575) 212 +20V STT 4J73 X3A H5A 345 SHUTDOWN 1 INPUT 862 15J85 -15V STATUS LED (HI FOR GREEN) COLD IN. REVERSE SHUTDOWN +15VDC 5W TP5 320V 160J C6 .05uF 600V IGBT DRIVE (-) COLD IN. FORWARD 8J85 5B CURRENT FEEDBACK 3J8 16 5W RED/GREEN STATUS LED 1J8 213 504 15 C5 (CAP "B") 3500uF 500V 211 7 20 CONTROL BOARD COMMON STT D 18 +40VDC 67C S F + +40VDC AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER T1 612 CT CURRENT (-) 2J50 6J8 251 1J2 DUAL PROC. INPUT 853 854 858 H6A 6A 1J50 518 GND-A RED BLACK GREEN TRIGGER +15VDC 1 TRIGGER INPUT 2 DUAL PROC. INPUT 3 4 STEP INPUT 4 COLD INCH +15VDC 5 COLD IN. FORWARD 6 COLD IN. REVERSE 7 GAS PURGE INPUT 8 SHUTDOWN +15VDC 9 SHUTDOWN 1 INPUT 10 SHUTDOWN 2 INPUT 11 INPUT B 12 CB4 514 506 L9 S7 I/O RECEPTACLE Return to Master TOC 4J84 L8 539 541 521 522 A B C D E F G H J TACH 1A DIFF SIGNAL K TACH 1B DIFF SIGNAL L TACH 2B DIFF SIGNAL M VOLTAGE SENSE N 604 PRECHARGE RELAY +13V MOTOR "+" MOTOR "-" SOLENOID 40VDC SOLENOID INPUT TACH 2A DIFF SIGNAL SINGLE TACH INPUT TACH +15VDC TACH COMMON BLACK T1 +13V AUX. RECONNECT A 2J61 812 6J61 612 P90 F -15V CHOPPER BOARD S A 15 +15V TACH 1B DIFF. INPUT I OUT 3J84 + R4 3J90 BLACK T3 TACH 1A DIFF. INPUT 811 10J61 2J84 216 816 8J61 - ELECTRODE VOLTAGE SENSE + N.C. R2 +15VDC TACH TP1 320V 160J TP6 150V 80J 2J90 A 612B 3J9 RS232 COMMON C1 .05uF 600V 880 1J90 RED 3 A MAIN CHOKE L1 813 MAIN CONTACTOR CONTROL 2 254 4 202 202A R3 H1D 253 4J2 6 C4 (CAP "A") 3500uF 500V SOLENOID +40VDC X3 2J60 OFF 3J83 406 INPUT BOARD 1J60 FEED HD BD 521 N.A. 601 L3A 403 3J2 RS232 TRANSMIT +ELECTRODE VOLTAGE SENSE 5 + 12 RS232 RECEIVE 1J9 LEGEND DASHED = " PHANTOM= " " STT MACHINE ONLY " OPTION THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED PROPRIETARY & CONFIDENTIAL: TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED TOLERANCE MANUFACTURING TOLERANCE PER E2056 DESIGN INFORMATION ON 2 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .02 ON 3 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .002 DRAWN BY: F.Valencic ON ALL ANGLES IS ± .5 OF A DEGREE MATERIAL TOLERANCE (" t ") TO AGREE WITH PUBLISHED STANDARDS. ENGINEER: S.Poole DO NOT SCALE THIS DRAWING APPROVED: J.O'Connor REFERENCE: G3791 SCALE: NONE EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: UF INVERTER WELDERS PW455M MACHINE SCHEMATIC APPROVAL DATE: 3/4/03 PROJECT NUMBER: CRM33689 1 1 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT NUMBER: G4211 DOCUMENT REVISION: A SOLID EDGE N.A., N.B. X4 Return to Master TOC CT CURRENT (+) TP2 320V 160J C2 .05uF 600V TP3 150V 80J CURRENT TRANSDUCER 212 G ON 2J40 20D CR1 SW1 POWER 418 S3 RS232 CONNECTOR ELECTRODE 20 NEG R1 50Ω 2.7Ω 10W CT CURRENT (-) 1J40 + AC1 T3 L3 .022u 800V 11 4J91 NEG T2 206A OUTPUT DIODES D1-D4 B S 216 AC2 L2 HARMONIC FILTER POS CONTROL BOARD ELECTRODE 206 2.7Ω 10W +15V AC3 T1 F 14 19C L1 U .022u 800V 2J91 380-460V + 1J91 CR1 S 13 2.7Ω 10W 3J91 INPUT RECTIFIER W Return to Section TOC N.A. .022u 800V A 2.7Ω 10W .022u 800V F 211 ENGINEERING CONTROLLED MANUFACTURER: No 213 Return to Master TOC SCHEMATIC - ENTIRE MACHINE - CODE 10942 (G4211) V Return to Section TOC G-4 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G4211 Return to Section TOC G-4 STRP NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT ENGINEERING CONTROLLED CHANGE DETAIL: CONTROL BOARD, CHANGED 2J4 TO 3J4 MANUFACTURER: No 15 S 2.7Ω 10W .022u 800V C Located on rear horizontal baffle P91 F Located behind Electrode stud 18 F 514 RED(-) 518 WHITE(+) D5 R3 P90 H3 N.A. 52V H1 H6A 5 H6 230V (550-575) 612A EX. 12 PIN CONNECTOR 33 6 12 LATCH VIEW OF CONNECTOR ON PC BOARD CB3 0V located on reconnect panel 252A 2J52 352 2 33A 4J52 1J52 33A 350 4 350 115V 32 4J51 located on case front H1A 1 H1 3 4J51 CB2 S4 115V RECEPTACLE 32 34 GND -15V SPI COM + 5V SPI 3J4 268A 262 11J43 COM CB2 located on front case 10A 5A 1J51 31 32 3J9 THERMOSTAT Additional input / outputs are illustrated on schematic page 2. LEDS - 10 TOTAL DIP Switch -1, Bank of 8 (See page 3 for detail) 262 DC BUS BD Located on rear of control box (center) 6J43 2J41 NTC + 1J41 477 7J47 +40VDC POWER 478 475 8J47 5J47 +40VDC POWER COMMON 476 6J47 COMMON 3J41 POS 65VDC C3 (earlier version) 115V RECEPTACLE (Neutral Floating) NOTES: N.A. CE MACHINE ONLY. N.B. NON-CE MACHINE ONLY. POS 1J46 POS 2J46 24000uF/100V Located behind DC Bus board Located on center baffle left of lift bale NEG 3J46 NEG 4J46 Located on rear of control box (right) Additional outputs are illustrated on schematic page 2. POWER BD. RECT. LEDS - 2 TOTAL (See page 3 for detail) SPI N.A. 351 6J51 33 1J51 1J9 3J5 6J8 2J5 2J8 1J8 812 8J8 +15V -15V STT FEEDBACK CONTROL BOARD COMMON 3J8 811 813 816 7J8 4J8 4W 13J7 5J8 4R 14J7 STT CHOPPER DRIVE (+) +15V SPI 2J4 1J4 266 RS232 COM POWER DOWN 7J4 6J4 5J4 228 227 ARCLINK COM RS232 +5V 3J11 226 +5V ARCLINK +5V THERMOSTAT POWER BD. RECT. LEDS - 1 TOTAL (See page 3 for detail) V in +72 VDC + V out +40 VDC N.C. ON CE MODELS LEADS T1, T2 AND T3 ARE REPLACED BY LEADS A, B AND C. LEADS A, B AND C ARE CONNECTED TO THE INPUT RECTIFIER TERMINALS RATHER THAN CR1. N.D. FOR SYNCHRONIZED TANDEM MIG APPLICATIONS SEE S26631 FOR DETAILS. THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED Schematic numbers are given for reference only. 1J51 10A 3.5 A N.B. +ELECTRODE VOLTAGE SENSE - ELECTRODE VOLTAGE SENSE -15V NEG CB2 1 33 206 202 CONTROL BOARD COMMON (NORMALLY CLOSED) 6J51 352A CONNECTOR PIN NUMBERS: RS232 S8 WATER COOLER RECEPTACLE AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER T2 COMPONENT VALUE UNITS: CAN CONTROL X2 (right, rear) CAPACITOR: MFD/VOLTS RESISTOR: OHMS/WATTS I OUT 518 2J10B CT CURRENT (+) CT CURRENT (-) H2 H1 10 ohms 224A CHOKE THERM CURRENT FEEDBACK +15V 325A Max STT output 570A Max Output Fold Back = 100A 268 268A 291 292 DC BUS OUTPUT THERM RECTIFIER THERM 220 4J41 X5 (200-208) 10 A 12J43 1J43 +15V X4 346 X1 (220-230) 220A 32 S4 220V RECEPTACLE (Neutral Bonded) located on case front PROPRIETARY & CONFIDENTIAL: TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. THE INFORMATION ON THIS PRINT IS FOR REFERENCE ONLY. COMPONENTS AND CIRCUITRY MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM AN ACTUAL MACHINE. DESIGN INFORMATION DRAWN BY: F.Valencic ENGINEER: S.Poole APPROVED: . REFERENCE: G4050 SCALE: NONE INVERTER WELDERS 455M MACHINE SCHEMATIC EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: UF APPROVAL DATE: 2/1/2007 PROJECT CRM22115-GC NUMBER: 3 1 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT REVISION: DOCUMENT NUMBER: G4421 F SOLID EDGE 115V 7J43 COM 24V H4 (380-415) 612 224A Schematic: M19330 345 9J43 X3 H5 (440-460) Located in Rear of FAN PowerSource POWER BOARD Schematic: G3631 Located on rear of control box (left) 4J42 (550-575) H6A - SOLID STATE RELAY X3 0V 811 418 514 1J10B 414 2J10A 406 1J10A 403 506 15J6 FAN CONTROL (+15 VDC) FAN CONTROL (-) COM H6 EARTH GROUND EN-170 15J7 16J7 POWER DOWN INTERUPT 612B FRAME GROUND 7 3R 3W 273 444 (left, rear) CB4 (Max Output = 325A) 4J43 AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER T1 COMMON 1 2 PRECHARGE CONTROL MAIN CONTACTOR CONTROL 550-575V located on reconnect panel LABELS: 2J6 10J43 LEAD COLOR CODE: B-BLACK G-GREEN O-ORANGE R-RED U-BLUE W-WHITE Y-YELLOW + X3A TP4 232 SINGLE PHASE DETECT (LOW=1 PHASE) +5V " STT MACHINE ONLY " OPTION Located in rear of machine behnid reconnect panel. 1J6 12J6 Schematic: G3789 Located on left side of control box +13V +15V LEGEND DASHED = " PHANTOM= " 220-230V 224 CONTROL BOARD COM H6 200-208V 440-460V 231 604 8 Hertz per Volt 325 Volts = 2600 Hertz 221 H3 H5 9J6 } 222 H2 A Located behind control board (left side) 238 V/F (-) V/F (+) 4J11 N.B. SW1 POWER Located on top right of case front OFF 16J6 274 AUX. RECONNECT 404 V/F (+) V/F (-) 225 H1D 8J6 5J43 X3 ON 5J6 10J6 405 +5V 2J60 504 505 -15V 1J60 4R CONTROL BOARD COMMON 11J4 601 10J4 223 .0047uF 440 232 5J60 +13V 4W 3J10 +15V 2J42 MAIN CONTACTOR CONTROL 12J4 -15V 225A 222A L1A L3A C6 CT CURRENT (-) 604 1J42 N.A. X4 CT CURRENT (+) 6J61 +5V 8J61 612 4J60 601 C7 H1D 8J4 N.B. 6J10 COMMON 0 -15 5J42 3J42 L3 (Located right of Contactor) +13V CR1 COM +5V L3B SWITCH LEAD FILTER Return to Master TOC T3 L3 W 10J61 frequency = 20 kHz +15 IGBT DRIVE (+) T3 PRECHARGE RELAY 7J6 2J61 4J61 4J10 220 T2 V 1J10 346 211 +20V STT 224 IGBT DRIVE (-) T1 T2 231 IGBT DRIVE (+) L2 238 503 L1B 3J60 8J60 6J6 T1 14J6 N.C. L1 U IGBT DRIVE (-) Schematic: M19528 Located in reconnect cavity in rear of machine +13V SINGLE PHASE DETECT (LOW=1 PHASE) 345 212 213 816 812 216 INPUT BOARD CR1 TP5 320V 160J -15 Located on rear horizontal panel Located behind reconnect panel (Located upper left from electrode stud) STT C6 .05uF 600V A.04 0 } IGBT DRIVE (+) 6J50 IGBT DRIVE (-) +15V CHOPPER BOARD +15 3J50 3J90 } + R4 3J43 V/F (-) V/F (+) + R2 +5V 5J50 4J50 Located under Power Switch CURRENT TRANSDUCER 125:1 C8 2J90 1J50 2J50 CT C10 Located above Main Transformer frequency = 20 kHz G Return to Master TOC TP6 150V 80J D 8 Hertz per Volt 325 Volts = 2600 Hertz 503 506 TP1 320V 160J C1 .05uF 600V (Located Behind Work Stud) + N.A. 505 504 MAIN CHOKE L1 1J90 Return to Master TOC 16 S INPUT LINE FILTER 202 WORK (Located bottom left side) - 17 C6 3500uF 500V 202A 813 20D Located behind reconnect panel + 2.7Ω 10W -15 Schematic:L11385 Located on right side of machine N.B. .022u 800V F TP3 150V 80J 267 20 12 0 SWITCH BOARD #2 20C NEG +15 } TP2 320V 160J C2 .05uF 600V STT CHOPPER DRIVE (-) 6J40 IGBT DRIVE (-) I OUT 406 GND 4J40 V/F (+) 5J40 V/F (-) 3J40 IGBT DRIVE (+) R1 CURRENT 50Ω TRANSDUCER 125:1 (Located right of Work stud) 2.7Ω 10W .022u 800V -15V } 404 405 403 S B 4J91 19C NEG 14 216 AC1 19 NEG CT 2J40 frequency = 20 kHz +15V HARMONIC FILTER 206A 2J91 AC2 1J40 8 Hertz per Volt 325 Volts = 2600 Hertz 208-230V POS (Located bottom right side) F 3J91 380-575V 11 414 RED(-) 418 WHITE(+) 1J91 RECONNECT SWITCH OUTPUT DIODES D1-D4 (Located above Main transformer) .022u 2.7Ω 800V 10W A 212 INPUT RECTIFIER + ELECTRODE + S 213 N.B. C6 3500uF 500V 206 T1 13 POS Return to Section TOC ( Located Front Center of Machine) Schematic: L11385 (Located on left side of Machine) 211 Undervoltage = 200V Overvoltage = 467V AC3 Return to Section TOC MAIN TRANSFORMER SWITCH BOARD #1 } Return to Master TOC SCHEMATIC - ENTIRE MACHINE - CODES 10957 - 11311 PG 1 OF 3 (G4421) N.C. Return to Section TOC G-5 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G4421 Return to Section TOC G-5 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT SCHEMATIC - ENTIRE MACHINE - CODES 10957 - 11311 PG 2 OF 3 (G4421) ENGINEERING CONTROLLED CHANGE DETAIL: CONTROL BOARD, CHANGED 2J4 TO 3J4 MANUFACTURER: No ETHERNET/DEVICENET OR DEVICENET BOARD (ETHERNET/DEVICENET BOARD SHOWN) CONTROL BOARD Schematic: G3893 Located on rear, left side of front door see page 3 for details Schematic: G3789 Located on left side of control box 2B 2B 8J7 THERMAL LED YELLOW THERMAL LED 2W 2W 7J7 ETHERNET/DEVICENET DEVICENET LEDS - 12 TOTAL DIP SWITCH - 4 BANKS OF 8 LEDS - 9 TOTAL DIP SWITCH - 2 BANKS OF 8 SEE PAGE 3 FOR DETAILS SEE PAGE 3 FOR DETAILS ETHERNET CONNECTOR (Ethernet Board only) THERMAL LED Located by power switch. See page 3 for details Located under spring loaded cover 1W 1W 3J7 L10 STATUS LED (HI FOR RED) RED/GREEN STATUS LED 1B 1B 4J7 3J76 S3 RS232 CONNECTOR 2 253 253 3J2 RS232 RECEIVE 3 254 254 4J2 RS232 TRANSMIT ETHERNET/DEVICENET BOARD ONLY DEVICENET CONFIGURATION MUST BE IN FOR DEVICENET 1J76 830 DIP SWITCH - 1 BANK OF 8 SEE PAGE 3 FOR DETAILS Return to Master TOC +24VDC 5J75 894 0 VDC 2J75 893 CAN_H 1J75 892 CAN_L 4J75 891 S5 DEVICENET CONNECTOR STATUS LED (HI FOR GREEN) LEDS - 10 TOTAL RED/GREEN STATUS LED 6B 1J74 (HIGH for RED) 6W 2J74 (HIGH for GREEN) L2 4 Located under spring loaded cover see page 3 for details 5 ARCLINK L 3J73 ARCLINK H 4J73 4 CAN_H 891 5 CAN_L Located under spring loaded cover See page 3 for details ARCLINK L 1J73 ARCLINK H 2J73 0 VDC 6 1J2 RS232 COMMON 3J72 251 1J72 251 7 4J72 +40VDC 20 743 ARCLINK + CONTROL BOARD 154B VOLT SENSE BD 741 4J9 VOLTAGE SENSE 67 Schematic:S24779 Located on rear, right side of front door see page 3 for details VOLTAGE SENSE OUTPUT 800 840 153B ELECTRODE SENSE Located behind front door panel. 54A 1J16 53A 67B 5J16 67A 52B 6J16 52A 51B 4J16 51A +40VDC 0 VDC 3J16 N.D. N.E. L7 52A 1 1J11 ARC LINK H Located under spring loaded cover See page 3 for details 2 3 WIRE FEEDER VOLTAGE SENSE L4 21A 21A 6J9 ARC LINK L WORK VOLTAGE SENSE 2J11 1J2 51A J16 54 67B ROBOTIC VOLTAGE SENSE 3J1 Return to Master TOC C422-1 3J6 C422-2 11J6 512 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT (-) 4J1 511 FEED HD BD Schematic: G3823 Located on rear, right side of front door see page 3 for details Additional input / outputs are illustrated on schematic # 1. DC BUS BD 840 4J81 +40VDC 800 3J81 0 VDC 741 2J81 ARCLINK H 743 1J81 ARCLINK L Schematic: M19330 Located on rear of control box (right) Additional input / outputs are illustrated on schematic # 1. 154B 2J82 153B 1J82 ARCLINK H ARCLINK L RED/GREEN STATUS LED 0 VDC 1J47 51 3J47 50 51B 3J82 0 VDC 52B 4J82 +40VDC 5W 15J85 10A located on lower left case front C ELECTRODE SENSE 52 D +40VDC 51 E 0 VDC 14J85 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT (+) 13J85 512 +15VDC TACH 1J84 841 TACH COMMON 4J84 844 841 A TACH +15VDC 844 B TACH COMMON C TACH 1A DIFF SIGNAL TACH 1A DIFF. INPUT 2J84 842 842 TACH 1B DIFF. INPUT 3J84 843 843 D TACH 1B DIFF SIGNAL TACH 2A DIFF. INPUT 5J84 845 845 E TACH 2A DIFF SIGNAL TACH 2B DIFF. INPUT 6J84 846 846 F TACH 2B DIFF SIGNAL SINGLE TACH INPUT 7J84 847 847 G SINGLE TACH INPUT MOTOR "+" 1J83 539 67C 539 I VOLTAGE SENSE J MOTOR "+" MOTOR "-" 2J83 541 541 K MOTOR "-" SOLENOID +40VDC 3J83 521 521 N SOLENOID +40VDC SOLENOID INPUT 4J83 522 522 Located under spring loaded cover See page 3 for details TACH signals are selected by software ( standard or Diff type ) N.D. COMMUNICATION INTERFACE MODULE. TRIGGER +15VDC 1J85 851 851 1 TRIGGER +15VDC TRIGGER INPUT 2J85 852 852 2 TRIGGER INPUT DUAL PROC. INPUT 3J85 853 853 3 DUAL PROC. INPUT 854 4 4 STEP INPUT 855 5 COLD INCH +15VDC (HIGH for GREEN) COLD IN. FORWARD 6J85 856 856 6 COLD IN. FORWARD 857 8J85 858 SHUTDOWN +15VDC 9J85 859 SHUTDOWN 1 INPUT 10J85 860 857 858 859 860 861 862 7 COLD IN. REVERSE 8 GAS PURGE INPUT 9 SHUTDOWN +15VDC 10 SHUTDOWN 1 INPUT 11 SHUTDOWN 2 INPUT 12 INPUT B 886 5J83 +40VDC 880 Located on rear of control box (center) 6J83 +40VDC COLD IN. REVERSE 7J85 GAS PURGE INPUT DIP SWITCHES (see other sheet for use ) NOTES: N.C. IF FEEDHEAD BOARD IS NOT PRESENT, INSERT P82 INTO J73. S7 I/O RECEPTACLE P SOLENOID INPUT T 854 16J85 jumper 9,10,11 for welder to operate Located under spring loaded cover See page 3 for details S6 WIREFEEDER INTERFACE RECEPTACLE 511 855 5B D6 67 4 STEP INPUT 4J85 52 CB1 B ARCLINK + COLD INCH +15VDC 5J85 (HIGH for RED) Blocking Diode for Motor +40VDC FEEDER EN-170 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT (-) GND-A LEDS - 1 TOTAL SEE PAGE 3 FOR DETAILS A ARCLINK - 54 L6 GROUND CURRENT SENSE Located on vertical panel near lift bale N.F. 1J1 L5 GROUND CURRENT SENSE 53 67C VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT (+) CURRENT SENSOR CLOSED IS THE FAULT CONDITION GROUND LEAD CURRENT SENSOR S1 ARCLINK RECEPTACLE 53A 54A 53 4 Return to Master TOC 0 VDC 892 +24VDC ARCLINK L S2 VOLTAGE SENSE RECEPTACLE Return to Section TOC 2 3 N.C. ARCLINK - Return to Section TOC 894 893 ARCLINK H 2J72 Return to Section TOC RJ45 type J710 ETHERNET PORT SHUTDOWN 2 INPUT 11J85 861 INPUT B 12J85 862 Schematic numbers are given for reference only. PROPRIETARY & N.E. ROBOTIC WIRE DRIVE INTERFACE MODULE. N.F. K2202-4 MACHINES ONLY. COMPONENTVALUE UNITS: LEAD COLOR CODE: B-BLACK G-GREEN O-ORANGE R-RED U-BLUE W-WHITE Y-YELLOW Located under spring loaded cover See page 3 for details CAPACITOR: MFD/VOLTS RESISTOR: OHMS/WATTS CONNECTORPIN NUMBERS: EX. 12 PIN CONNECTOR 1 2 6 7 12 LABELS: LEGEND DASHED = " PHANTOM= " COMMON " STT MACHINE ONLY " OPTION FRAME GROUND LATCH EARTH GROUND VIEW OF CONNECTORON PC BOARD THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED CONFIDENTIAL: TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. THE INFORMATION ON THIS PRINT IS FOR REFERENCE ONLY. COMPONENTS AND CIRCUITRY MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM AN ACTUAL MACHINE. DESIGN INFORMATION DRAWN BY: F.Valencic ENGINEER: S.Poole APPROVED: . REFERENCE: G4050 SCALE: NONE INVERTER WELDERS 455M MACHINE SCHEMATIC EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: UF APPROVAL DATE: 2/1/2007 PROJECT CRM22115-GC NUMBER: 3 2 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT REVISION: DOCUMENT NUMBER: G4421 F SOLID EDGE Return to Master TOC G-6 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G4421 Return to Section TOC G-6 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Troubleshooting the PowerWave DEVICENET MODULE Using the Status LED (OPTIONAL K2206) ETHERNET MODULE S1 LED6 LED5 (OPTIONAL K2207) LED4 LED3 MEANING LED8 CONTROL BOARD LED7 S2 J70 J4 J70 LED2 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC J75 COLOR 11 12 Green Green Green Green Green Red Green Red Green Red Green Green Indicates Isolated Module Section Supply is ON Indicates DeviceNet Supply is ON ArcLink Status Indicators (Main System Slave ArcLink Connection) Solid Green only when functional (See software for error codes) Reserved For Future Use DeviceNet Status Indicators (See software group for coding) Indicates Isolated ArcLink Section Supply is ON 10Base-T Link Status ON indicates functional ethernet link has been established Receiver Polarity ON indicates proper ethernet signal polarity Indicates I/O+5V Supply is ON This is used by differential I/O pair 4 circuitry, J712 pins 1 and 2. Description Object Instance LSB (see Table 1) Object Instance MSB (see Table 1) Equipment Group 1 Select Equipment Group 2 Select Equipment Group 3 Select Equipment Group 4 Select Reserved for future use Reserved for future use Bank (S1) Switch 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Description DeviceNet Baud Rate DeviceNet Mac ID Default ID=62 Return to Master TOC Description 1-2 Devicenet Baud Rate 3-4 Devicenet Mac ID LED6 Configuring the DIP switches on the Devicenet Board O N O N 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 'Bank S1 Default' 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 LED 10 'Bank S2 Default' J10A Control Board DIP Switch: Switch 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 off 8 on Description Indication CAN communication bus off. 12 User Interface time out error. 21 Unprogrammed Weld Mode. 22 Empty Weld Table. 23 Weld Table checksum error. 31 Primary overcurrent error. Comments Object Instance LSB Object Instance MSB Equipment Group 1 Select Used for Arclink configuration Equipment Group 2 Select Equipment Group 3 Select Equipment Group 4 Select Reserved for future use work sense lead not connected Used for configuring work sense lead work sense lead connected Low voltage on the main capacitors. May be caused by improper input configuration, or an open/short circuit in the primary side of the machine. Excess voltage on the main capacitors. May be caused by improper input configuration, or an open/short circuit in the primary side of the machine. Indicates over temperature. Usually accompanied by Thermal LED. Check fan operation. Be sure process does not exceed duty cycle limit of the machine. Capacitor precharge failed. Usually accompanied by codes 32-35. The secondary (weld) current limit has been exceeded. When this occurs the machine output will phase back to 100 amps, typically resulting in a condition refered to as “noodle welding” 36 Thermal error 37 Softstart error 41 Secondary overcurrent error 42 Ground lead Current Shutdown (On K2202-4 machines only) 43 Capacitor delta error 49 Single phase error J81 J85 Description of LED functions on the Power Wave 455M For reference only NO P.C. BOARD MOUNTED LED's LED # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Comments J86 S1 COLOR Green Green Green Green Green Green Red Green Green Red L11088 Digital Control PC Board FUNCTION Indicates +15VDC from power supply board is present Indicates –15VDC from power supply board is present Indicates +5VDC for +5SPI from power supply board is present Indicates +15VDC for +15SPI from power supply board is present Indicates +5VDC for +5V from power supply board is present Indicates +5VDC for +5VRS232 from power supply board is present FAULT Signal (See software group for coding) Indicates +5VDC for +5CAN from power supply board is present ArcLink Status Indicators (Main System Master ArcLink Connection) Solid Green only when functional (See software for error codes) Other 6 19 20 17 18 Probably due to excessive number of communication errors. UI is no longer responding to the Power Source. The most likely cause is a fault/bad connection in the communication leads or control cable. Contact the Service Department for instructions on reloading the Welding Software. Contact the Service Department for instructions on reloading the Welding Software. Contact the Service Department for instructions on reloading the Welding Software. Excessive Primary current present. May be related to a switch board or output rectifier failure. 32 Capacitor “A” under voltage (Left side facing machine) 33 Capacitor “B” under voltage (Right side facing machine) 34 Capacitor “A” over voltage (Left side facing machine) 35 Capacitor “B” over voltage (Right side facing machine) LED 8 Indicates Isolated ArcLink Section Supply is ON J82 J10B S1 11 LED7 DeviceNet Status Indicators (See software group for coding) J83 LED 4 J11 L11046 DeviceNet Gateway PC Board FUNCTION Indicates Isolated Module Section Supply is ON Indicates DeviceNet Supply is ON ArcLink Status Indicators (Main System Slave ArcLink Connection) Solid Green only when functional (See software for error codes) Module Status Indicators (See software group) COLOR Green Green Green Red Green Red Green Red Green Error codes for the PowerWave The following is a list of possible error codes that the Power Wave can output via the status light J1 Description of LED functions on Power-Wave type systems LED # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 J84 Used for DeviceNet configuration Error Code interpretation through the Status light is detailed in the Service Manual. Individual code digits are flashed in red with a long pause between digits. If more than one code is present, the codes will be separated by a green light. LED 5 J2 (OPTIONAL K2205) Bank S1 Switch Description Comments 1 Object Instance LSB 2 Object Instance MSB 3 Equipment Group 1 Select Used for Arclink Configuration 4 Equipment Group 2 Select 5 Equipment Group 3 Select 6 Equipment Group 4 Select 7 Reserved for future use 8 Reserved for future use Table 15 Non-recoverable system fault. If the PS Status light is flashing any combination of red and green, errors are present in the Power Wave. Read the error code before the machine is turned off. Error Code # WIRE DRIVE MODULE Ethernet Board DIP Switch : Bank S2 Switch J71 J76 J74 J71 Bank (S1) LED # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Alternating Green and Red To clear the error, turn power source off, and back on to reset. LED 3 J3 J74 J76 Devicenet Board DIP Switch For reference only Occurs during a reset, and indicates the Power Wave is mapping (identifying) each component in the system. Normal for first 1-10 seconds after power is turned on, or if the system configuration is changed during operation J73 LED1 J75 G3894 Ethernet Gateway PC Board FUNCTION LED 9 J9 J8 System OK. Power source communicating normally with wire feeder and its components. LED 2 LED9 Description of LED functions on the Power Wave 455M J7 LED 1 J72 J73 Switch 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 J6 J5 Steady Green Blinking Green The K2202-4 has a special circuit installed that monitors current flowing on the input ground lead. When current is sensed, the machine will turn the welding output off. The machine will need to be turned off for several seconds and then back on to clear this error. The maximum voltage difference between the main capacitors has been exceeded. May be accompanied by errors 32-35. Indicates machine is running on single phase input power. Usually caused by the loss of the middle leg (L2). Error codes that contain three or four digits are defined as fatal errors. These codes generally indicate internal errors on the PS Control Board. If cycling the input power on the machine does not clear the error, try reloading the operating system. If this fails, replace the control board. 3 2 7 J87 1 8 14 POWER BOARDS M19540 J1 Description of LED functions on the Power Wave 455M For reference only J2 99/08/04@11:34:37 Diode Detail R2 TP2 L1 R1 D1 R3 OCI1 C1 Switch 1 2 3 4 5 6 off 7 on off 8 Voltage Sense Board Description Object Instance LSB Object Instance MSB Equipment Group 1 Select Equipment Group 2 Select Equipment Group 3 Select Equipment Group 4 Select Electrode polarity positive (default) Electrode polarity negative Low speed gear (default) COLOR Red Red G3632 Digital Power Supply Board FUNCTION Indicates +5VDC SPI supply is present Indicates +5VDC control supply is present COLOR Red L11078 +40 Volt DC Bus Board FUNCTION Indicates +40 VDC supply is present OCI2 TP1 Feed Head Board DIP Switch: EN-170 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT 99/08/04@11:28:10 LED # 1 2 LED # 1 16 9 12 11 13 4 Comments Used for Arclink Configuration Used for configuring electrode polarity Used for confi guring wirefeeder gear ratio 15 Case Front Detail 10 5 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Power Switch Status Light High Temperature Light 10 Amp Wire Feeder Circuit Breaker Auxiliary Power Circuit Breaker Work Sense Lead Connector Arclink Receptacle DeviceNET Connector (not shown)* I/O Connector* RS232 Connector Work Stud STT Stud Electrode Stud Robotic Interface Connector* Auxiliary Output (110V or 220V) Ethernet Connector* Wire Drive Interface Module (not shown)* Wire Drive Status LED* Communication Interface Module (not shown)* Communication Status LED* * Not Standard in Base Model Power Wave 455M/STT CE (shown with Wire Drive Interface Module & Ethernet communication Module) THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED PROPRIETARY & CONFIDENTIAL: TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. THE INFORMATION ON THIS PRINT IS FOR REFERENCE ONLY. COMPONENTS AND CIRCUITRY MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM AN ACTUAL MACHINE. DESIGN INFORMATION DRAWN BY: F.Valencic ENGINEER: S.Poole APPROVED: . REFERENCE: G4050 SCALE: NONE INVERTER WELDERS 455M MACHINE SCHEMATIC EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: UF APPROVAL DATE: 2/1/2007 PROJECT CRM22115-GC NUMBER: 3 3 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT REVISION: DOCUMENT NUMBER: G4421 F SOLID EDGE ENGINEERING CONTROLLED CHANGE DETAIL: CONTROL BOARD, CHANGED 2J4 TO 3J4 MANUFACTURER: No G4421 Return to Master TOC SCHEMATIC - ENTIRE MACHINE - CODES 10957 - 11311 PG 3 OF 3 (G4421) J72 Return to Section TOC G-7 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS GATEWAY L11046 Return to Section TOC G-7 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-8 SCHEMATIC - CHOPPER PC BD - (STT MODELS ONLY) (L11340-2) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-8 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC PC BOARD ASSEMBLY - CHOPPER PC BD - (STT MODELS ONLY) - (G3339-2) ENGINEERING CONTROLLED MANUFACTURER: No CHANGE DETAIL: REVISED MAKE SPECIFICATION NOTES : N.A. CAUTION: THIS DEVICE IS SUBJECT TO DAMAGE BY STATIC ELECTRICITY. SEE E2454 BEFORE HANDLING. N.B. DO NOT COAT WITH ENCAPSULATION MATERIAL. N.A.,N.J. N.C. THIS AREA TO BE COVERED ON BOTH SIDES OF BOARD WITH SEALANT PRIOR TO ENCAPSULATION. N.D. INJECT SEALANT ITEM 4 THROUGH THE PC BOARD HOLES (6 HOLES) TO SEAL MODULE LEADS. CAVITY BETWEEN BOARD AND MODULE TO BE COMPLETELY FILLED WITH ITEM 4 SEALANT MATERIAL AS PER APPROPRIATE MANUFACTURING WORK INSTRUCTIONS. COVER ALL MODULE LEADS THAT PROTRUDE FROM THE NON-MODULE SIDE OF THE BOARD WITH ITEM 4 SEALANT. N.E. FEMALE EYELET TO BE AGAINST THE OPPOSITE COMPONENT SIDE AS SHOWN. EYELET MUST NOT SPIN AFTER CLINCHING. P.C. BOARD BLANK INFORMATION BUY COMPLETE AS G3339-D (2 LAYER BOARD PER E3281) (SEE ELECTRONIC FILE FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION) N.B. N.F. SOLDER EYELET SO THAT SOLDER COVERS ENTIRE EYELET AND ALL AROUND EYELET ON OPPOSITE COMPONENT SIDE ONLY. NO ICICLES OR SOLDER BLOBS PERMITTED. N.G. ELECTRONIC MODULES TO BE ASSEMBLED AND ENCAPSULATED PER E3875. N.H. THIS DIMENSION APPLIES TO THESE TWO OF THE FOUR EYELETS AS SHOWN. N.J. ELECTRONIC MODULES ON A COMMON P.C. BOARD ASSEMBLY TO HAVE VGE(TH) WITHIN 5 SORT CODES (0.5VSPAN) FOR THE SAME VCE(SAT) CODE AND MANUFACTURING CODE. e.g. M21214-1 X XX XX ........ Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC G-9 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G3339-2 Return to Section TOC G-9 N.A. N.A. N.A. VENDOR CODE ITEM (USED WITH)* QTY PART NUMBER 1 1 G3339-D 2 (X4)* 1 S20590-1 3 (B48,B49,B53,B55)* 4 T9147-11 4 2 oz. E2861 REFERENCES QTY PART NO. A1, A2 2 M21214-1 B48, B49, B53, B55 4 T9147-15 C1 1 T11577-49 C2 1 S13490-8 C3, C7, C9, C10, C21 5 S16668-11 C6, C8, C20 3 S13490-173 C11, C14 2 S16668-10 C12, C17 2 S16668-7 C13, C15, C16 3 S16668-3 C18, C19 2 S20500-2 C22 1 S16668-9 C23 1 S13490-25 D1, D2, D3, D4, D7 5 T12199-1 D5, D6 2 T12705-23 DZ1 1 T12702-29 J10 1 S20351-6 OCI1 1 S15000-10 R1 1 S18380-5 R2 1 S19400-3320 R3, R4, R27 3 S19400-3321 R5 1 S19400-4752 R6 1 S19400-4750 R8, R23 2 S19400-4751 R9, R10, R11, R12, R13, R14, 14 S19400-3010 R15, R16, R17, R18, R19, R20, R21, R22 R25 1 S19400-2213 R26 1 S19400-3323 X1 1 S15018-9 X2 1 S15018-21 X3 1 S15018-15 X4 1 S15128-6 DESCRIPTION PC BOARD BLANK HEAT SINK, TO-220 EYELET, FEMALE SEALANT DESCRIPTION ELECTRONIC MODULE,7 IGBT(T12704-85) EYELET, MALE 500/50 50/25 .1/50 CAPACITOR,MPF,1.0 uF,63VDC 4700pF/50 820pF/50 100pF/100 .47/630 150pF/100 4.7/35 1N4004 1N5818 1N4744A HEADER OPTO ISOLATOR THERMISTOR,PTC,0.5-1.17 OHMS,0.5A 332 1/4W 3.32K 1/4W 47.5K 1/4W 475 1/4W 4.75K 301 1/4W 221K 1/4W 332K 1/4W IC,CMOS,MULTIVIBRATOR,MONOSTABLE,DUAL,4538 (SS) IC,DRIVER,9A LOW-SIDE MOSFET (SS) IC,CMOS,GATE,NAND,2-INPUT,QUAD,SCHM (SS) IC,SMD,VOLT REG,FIXED,3-TERMINAL,POS VOLT,1A,15V VCE(SAT) VGE(TH) N.G. CAPACITORS = MFD/VOLTS RESISTORS = OHMS N.K. BEFORE ENCAPSULATION, APPLY A .19 WIDE BEAD OF ITEM 4 SEALANT IN AREAS SHOWN TO ANCHOR CAPACITORS C18 AND C19 (2 PLACES). .490 ±.005 (RESTRAINED) N.H. N.C. 1 5.50 ±.04 B49 N.D. R15 R23 R8 R16 C10 D6 C6 DZ1 D5 R14 R26 X2 C9 X1 C8 R13 C3 R12 C13 R27 C15 C1 C2 X4 .275 .285 R .045 .116 MAX. CRIMP HEIGHT OPPOSITE COMPONENT SIDE N.K. EYELET DETAIL R11 R19 R3 R4 C12 X3 xx x x x x x x xx x x x x x x x x x x x C18 x x x x x x x x x x xxx x x x x x x xx 3 R21 R10 R25 2 R6 C14 R18 C16 C20 D7 C23 C17 R20 xx x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x C19 x x x x x x x x x x x xxx x x x x x x xx C21 R5 R17 C7 N.E., N.F. STT CHOPPER G3339-2 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC B48 D3 D1 D2 R1 R9 R2 R22 N.H. D4 C22 C11 OCI1 N.H. MAKE PER E1911-ROHS ENCAPSULATE WITH E1844 (1 COAT) J10 B55 B53 .45 TEST PER E3647-CH 0 SCHEMATIC REFERENCE: L11340-2D0 N.B. 1.30 4.00 MANUFACTURED AS: 1.30 7.50 ±.04 ALL COMPONENTS AND MATERIALS USED IN THIS ASSEMBLY ARE TO BE RoHS COMPLIANT PER E4253. G3339-2D0 Return to Master TOC IDENTIFICATION CODE FOR PARTS ORDERS AND SUBSIDIARY ORDERS: INCLUDE (1) S25191PRINT AND (1) T12837-1. THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED PROPRIETARY & CONFIDENTIAL: TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED TOLERANCE MANUFACTURING TOLERANCE PER E2056 DESIGN INFORMATION ON 2 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .02 ON 3 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .002 DRAWN BY: ON ALL ANGLES IS ± .5 OF A DEGREE MATERIAL TOLERANCE (" t ") TO AGREE WITH PUBLISHED STANDARDS. ENGINEER: DO NOT SCALE THIS DRAWING APPROVED: FEI REFERENCE: G3339-1 SCALE: - 1:1 EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: UF INVERTER WELDERS CHOPPER P.C. BOARD ASSEMBLY APPROVAL DATE: 10/2/2006 PROJECT NUMBER: CRM34409 1 1 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT NUMBER: G3339-2 DOCUMENT REVISION: A SOLID EDGE Return to Section TOC 0 STRP NOTE: Lincoln Electric assumes no responsibility for liablilities resulting from board level troubleshooting. PC Board repairs will invalidate your factory warranty. Individual Printed Circuit Board Components are not available from Lincoln Electric. This information is provided for reference only. Lincoln Electric discourages board level troubleshooting and repair since it may compromise the quality of the design and may result in danger to the Machine Operator or Technician. Improper PC board repairs could result in damage to the machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-10 SCHEMATIC - DEVICENET/GATEWAY PC BOARD (ROBOTIC MODEL ONLY) PG 1 OF 2 (G3821-2) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-10 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-11 SCHEMATIC - DEVICENET/GATEWAY PC BOARD (ROBOTIC MODEL ONLY) PG 2 OF 2 (G3821-2) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-11 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT PC BOARD ASSEMBLY - DEVICENET/GATEWAY PC BOARD (ROBOTIC MODEL ONLY) (L11046-2) ENGINEERING CONTROLLED MANUFACTURER: Yes CHANGE DETAIL: NEW ITEM N.E. 3 PART NO. QTY PC BOARD REFERENCE DESCRIPTION DESIGNATORS 1 L11046-F 1 GATEWAY PC BOARD BLANK 2 S24671 1 PLUG, KEYING PLUG 3 M19436-5 1 POTTING TRAY 4 S8025-80 2 SELF TAPPING SCREW 5 E2527 195g. (6.87OZ) EPOXY ENCAPSULATING RESIN 6 E3539 AS REQ. ELECTRICAL INSULATING COMPOUND 7 S24824-3 1 X11 SOFTWARE CPLD N.F. N.G. 8 S24825-1 1 X13 SOFTWARE, FLASH FOR ITEMS LISTED BELOW REFER TO ELECTRONIC COMPONENT DATABASE FOR COMPONENT SPECIFICATIONS 5.84 N.D. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 2 6.34 N.A. N.B. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 4 CAUTION: THIS DEVICE IS SUBJECT TO DAMAGE BY STATIC ELECTRICITY. LINCOLN ELECTRIC TO SEE E2454 BEFORE HANDLING. Return to Master TOC PLACE CONNECTOR KEYING PLUG, OVER HEADER PIN, IN LOCATION SHOWN. PLUG SHOULD BE INSERTED BELOW CONNECTOR TOP SURFACE. N.C. SECURE PC BOARD ASSEMBLY IN PLACE WITH ITEM (4). (2 PLACES, 5.3 +/- .5 IN. LBS) N.D. NO COMPONENTS ON BOTTOM SIDE OF PC BOARD. PLACE BARCODED ASSEMBLY NUMBER IDENTIFICATION AND BARCODED SERIAL NUMBER IDENTIFICATION IN AREA SHOWN. N.E. Return to Section TOC REVISION CONTROL L11046-2F0 NOTES: N.B. N.F. PROGRAM ITEM 60 WITH ITEM 7 . N.G. PROGRAM ITEM 61 WITH ITEM 8 . N.J. MUST BE COVERED BY ITEM 5 . S25020-13SMT S25024-8SMT S13490-179 S25024-5SMT S25024-6SMT S25024-2SMT S25020-3SMT 2 5 1 4 4 4 30 C2,C7 C3,C4,C5,C6,C8 C9 C10,C13,C27,C30 C11,C12,C43,C60 C14,C16,C20,C25 C15,C17,C18,C19,C21,C22 C23,C24,C26,C28,C31,C32 C33,C35,C36,C37,C38,C41 C42,C44,C45,C46,C47,C48 C49,C50,C51,C53,C54,C58 CAPACITOR,SMD,CERAMIC,150pF,100V,5%,C CAPACITOR,SMD,TANTALUM,10MF,16V,10%,S CAPACITOR,ALEL,1000,35V,20% CAPACITOR,SMD,TANTALUM,4.7MF,35V,10%, CAPACITOR,SMD,TANTALUM,22MF,16V,10%,S CAPACITOR,SMD,TANTALUM,1.0MF,35V,10%, CAPACITOR,SMD,CERAMIC,0.1MF,50V,10%,X 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 S25020-15SMT S13490-182 S13490-181 S25040-10SMT S25040-9SMT S25040-2SMT S25040-11SMT S25040-4SMT 3 1 1 2 1 3 3 8 CAPACITOR,SMD,CERAMIC,22PF,50V,5%,COG CAP,ALEL,3300,63V,20% CAP,ALEL,22,63V,20% DIODE,SMD,3A,400V,D0-214AB DIODE,SMD,3A,200V,D0-214AB,ULTRA-FAST DIODE,SMD,1A,400V,DO-214BA/AC DIODE,SMD,1A,600V,S403A,ULTRA-FAST RE DIODE,SMD,DUAL,0.200A,70V,UFR 24 25 26 27 28 29 S25049-3SMT S25049-4SMT S25040-5SMT S25046-1SMT S25046-3SMT S25044-9SMT 1 1 6 1 4 7 30 31 32 33 34 35 S18248-16 S18248-10 S24020-4 S24020-2 S24020-6 S25080-2SMT 1 1 3 1 1 6 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 S25080-1SMT S15000-28SMT S15000-32SMT S25050-2SMT S25051-4SMT S25000-4750SMT S25003-2000SMT S25000-1002SMT 3 4 2 5 6 6 2 25 C29,C39,C40 C56 C59 D1,D5 D2 D3,D6,D21 D4,D16,D20 D7,D8,D9,D10,D12,D13,D14 D15 D17 D19 D22,D23,D24,D25,D26,D27 DZ1 DZ2,DZ3,DZ4,DZ5 DZ6,DZ7,DZ8,DZ10,DZ11,DZ12 DZ13 J70 J71 J72,J73,J76 J74 J75 LED1,LED2,LED3,LED5,LED7 LED9 LED4,LED6,LED8 OCI1,OCI2,OCI3,OCI4 OCI5,OCI6 Q2,Q4,Q5,Q12,Q13 Q6,Q7,Q8,Q9,Q10,Q11 R1,R2,R39,R40,R66,R67 R3,R4 R5,R8,R9,R10,R11,R12,R13 R14,R15,R16,R17,R19,R20 R21,R22,R23,R24,R25,R29 R34,R35,R42,R60,R61,R69 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 S25000-4751SMT S25000-1001SMT S25001-1002SMT S25000-1501SMT S25001-3320SMT S25000-7500SMT S25001-1211SMT S25001-2670SMT 5 6 2 1 6 3 2 7 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 S25000-1000SMT S25001-24R9SMT S25001-2000SMT S18380-5 S19869-8 S20375-8 S20353-1SMT S15128-25SMT S25068-6SMT S15128-5SMT S24841-1 S25068-7SMT S25069-2SMT M15101-14SMT S25070-3SMT S25069-3SMT S17900-11SMT M15104-15 S20353-5SMT S20353-4SMT S25068-4SMT S17900-24SMT S25065-2SMT S25082-1SMT 6 3 3 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 N.C. 2 N.A. 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 PART NO. IDENTIFICATION CODE TEST PER E3856-G POT WITH E2527 SCHEMATIC REFERENCE: G3821-2F0 N.J. N.A. BUY DETAIL MAKE DETAIL BUY PER E3867 MANUFACTURE PER E1911 BUY BLANK COMPLETE (4 BOARDS PER PANEL) N.A. N.A. N.A. N.A.,N.F. N.A.,N.G. N.A. N.A. N.A. N.A. N.A. N.A. N.A. 4 LAYER BOARD BLANK PANEL SEE ELECTRONIC FILE FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED: RESISTANCE = OHMS R6,R38,R43,R45,R101 R18,R37,R41,R65,R68,R100 R27,R28 R30 R31,R32,R33,R46,R47,R72 R36,R44,R76 R48,R49 R50,R51,R52,R53,R57,R58 R59 R54,R55,R56,R80,R81,R82 R73,R74,R75 R77,R78,R79 R83 S1,S2 T1 X2 X3 X4,X24 X5 X6 X7,X9 X8 X10 X11 X13 X14 X15 X16,X18 X17,X22 X20 X23 X31 Y1 DIODE,SMD,3A,40V,SCHOTTKY,CASE 403-3 DIODE,SMD,DUAL,200MA,30V,SCHOTTKY,SOT DIODE,SMD,DUAL,0.200A,70V,UFR ZENER DIODE,SMD,0.5W,5.1V, 5%,SOD123 ZENER DIODE,SMD,0.5W,18V, 5%,SOD123 ZENER DIODE,SMD,3W,6.2V,5%, SMB CONNECTOR,MOLEX,MINI,PCB,16-PIN CONNECTOR,MOLEX,MINI,PCB,10-PIN CONNECTOR,MOLEX,MINI,PCB,4-PIN,TIN CONNECTOR,MOLEX,MINI,PCB,2-PIN,TIN CONNECTOR,MOLEX,MINI,PCB,6-PIN,TIN LED,SMD,GREEN,CLEAR,S1206 LED,SMD,RED,CLEAR,S1206 OPTOCOUPLER,SMD,TTL-OUT,HI-SPD,HI-CMR OPTOCOUPLER,SMD,CMOS,HIGH SPEED,HIGH TRANSISTOR,SMS,PNP,SOT23,0.5A, 40V,MM TRANSISTOR,SMD,NMF,SOT-23,0.115A,60V, RESISTOR,SMD,METAL FILM,1/10W,475OHMS RESISTOR,SMD,1W,200OHMS,1% RESISTOR,SMD,METAL FILM,1/10W,10.0K,1 RESISTOR,SMD,METAL FILM,1/10W,4.75K,1 RESISTOR,SMD,METAL FILM,1/10W,1.00K,1 RESISTOR,SMD,10K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,METAL FILM,1/10W,1.50K,1 RESISTOR,SMD,332OHMS,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,METAL FILM,1/10W,750OHMS RESISTOR,SMD,1.21K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,267OHMS,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,METAL FILM,1/10W,100OHMS RESISTOR,SMD,24.9OHMS,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,200OHMS,1/4W,1206,1%,TR THERMISTOR,PTC,0.5-1.17 OHMS,0.5A SWITCH,DIP,SPST,8-CIRCUITS TRANSFORMER,PCB,PWM,FLYBACK IC,SMD,CMOS,DRIVER,RECEIVER,EIA232,14 IC,SMD,VOLTAGE REGULATOR,FIXED,POSITI IC,SMD,VOLT REG,FIXED,3-T,(+),0.1A,5V IC,VOLT REG,SMD,FIXED,3-T,(+),1A,5V IC,MODULE,CONVERTER,DC-DC,+5V/3A OUT IC,SMD,CMOS,UNDERVOLT-SENSING,RESET,M IC,SMD,CMOS,EEPROM,SERIAL,SPI,64Kx8,S IC,SMD,CMOS,MCU,32-BIT,2K-RAM,TPU,25M CPLD,PROGRAMMABLE,XC9536,44-PIN,VQFP( IC,SMD,CMOS,EEPROM,FLASH,16-BIT,512K IC,SMD,CMOS,TRANCEIVER,BUS,3-STATE,OC RAM,STATIC,16-BIT,64K,44-PIN,TSOP IC,CMOS,CONTROLLER,COMMUNICATION,SERI IC,CMOS,SMD,XCVR,EIA485(SS) IC,SMD,TRANSCEIVER,CAN,UC5350,S0IC-8 IC,SMD,CMOS,GATE,NAND,2-INPUT,QUAD,SC IC,SMD,ACT,LATCH,OCTAL,3-STATE,TSSOPCRYSTAL,SMD,QUARTZ,16MHZ ALL COMPONENTS AND MATERIALS USED IN THIS ASSEMBLY ARE TO BE RoHS COMPLIANT PER E4253 DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED PROPRIETARY & CONFIDENTIAL:THIS TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED TOLERANCE MANUFACTURING TOLERANCE PER E2056 DESIGN INFORMATION REFERENCE: ON 2 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .02 DRAWN BY: JIMJ ON ALL ANGLES IS ± .5 OF A DEGREE MATERIAL TOLERANCE (" t ") TO AGREE WITH PUBLISHED STANDARDS. ENGINEER: ILD L11046-1 SCALE: DO NOT SCALE THIS DRAWING APPROVED: - 1:1 ON 3 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .002 EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: NA COMMON DIGITAL CONTROLS GATEWAY PC BOARD ASSEMBLY APPROVAL DATE: 9-18-2006 PROJECT NUMBER: CRM37943-B 1 1 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT NUMBER: L11046-2 DOCUMENT REVISION: A SOLID EDGE Return to Master TOC G-12 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS L11046-2 Return to Section TOC G-12 STRP NOTE: Lincoln Electric assumes no responsibility for liablilities resulting from board level troubleshooting. PC Board repairs will invalidate your factory warranty. Individual Printed Circuit Board Components are not available from Lincoln Electric. This information is provided for reference only. Lincoln Electric discourages board level troubleshooting and repair since it may compromise the quality of the design and may result in danger to the Machine Operator or Technician. Improper PC board repairs could result in damage to the machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-13 SCHEMATIC - CONTROL PC BOARD (ALL CODES) PG 1 OF 4 (G3789-2) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-13 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-14 SCHEMATIC - CONTROL PC BOARD (ALL CODES) PG 2 OF 4 (G3789-2) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-14 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-15 SCHEMATIC - CONTROL PC BOARD (ALL CODES) PG 3 OF 4 (G3789-2) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-15 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-16 SCHEMATIC - CONTROL PC BOARD (ALL CODES) PG 4 OF 4 (G3789-2) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-16 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT ENGINEERING CONTROLLED MANUFACTURER: Yes CHANGE DETAIL: ADDED MANUFACTURE SPECIFICATION 9 N.J. 9 ITEM 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 N.J. 3 2 N.A. Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC 6.34 9 2 N.M. 8.09 COMPONENT SIDE N.A. N.A. N.A. N.A. N.A. Return to Master TOC N.E. TE AS P N ND D'S I A T R CU BOA 1 1 2 6.01 oz. 0.01 oz. 1 1 3 DESCRIPTION E3868-4 S25020-15SMT S25024-10SMT S25024-5SMT S25020-23SMT S13490-183 S13490-173 2 4 4 9 1 1 2 LAB,THT-53-423-3,BRADY,PLY SCAP,22pF,0805,50V,COG,5%,TR,N SCAP,22uF,TAN,7343,25V,10% SCAP,4.7uF,7343,35V,10%,TR,NP SCAP,1200pF,CER,1206,50V,X7R,10% SCAP,120MF,25V,20%,RADIAL,AE CAP,1uF,RA,63V,10%,NP S25020-3SMT 69 SCAP,0.1uF,0805,50V,X7R,10%,TR S25020-14SMT S25020-12SMT S25020-18SMT S25020-4SMT S25020-10SMT S13490-179 S24833-1 S25020-13SMT S25024-8SMT S25020-2SMT S25024-2SMT S25044-4SMT S25044-10SMT 1 5 1 11 2 1 2 7 4 2 8 2 3 SCAP,330pF,100V SCAP,100pF,0805,COG,100V,5% SCAP,10pF,CER,0805,100V,5% SCAP,820pF,0805,50V,COG,5%,TR, SCAP,4700pF,0805,50V,X7R,10% CAP,1000uF,ALU,35V,20%,NP CAP,0.27uF,MF,50V,5mm,5%,TR,NP SCAP,150pF,0805,100V,COG,5%,TR, SCAP,10uF,TAN,6032,TR,NP SCAP,0.022uF,0805,50V,X7R,10%, SCAP,1uF,TAN,3528,35V,TR,NP SDIO,B5929,15V,1.5W,ZENER,TR,N SDIO,B5930,16V,1.5W,ZENER,TR,N S25046-1SMT 19 SDIO,MMSZ5231BT1,5.1V,NP S25044-5SMT S25049-4SMT S25040-12SMT S25046-3SMT S25044-9SMT 9 8 8 4 7 SDIO,1SMB5931BT3,3W,18V,5% SDIO,BAT54S,DUAL,30V,200mA SDIO,MURS320T3,3A,200V,ULTRAFAST SDIO,MMSZ5248B,18V,ZENER,TR,NP SDIO,1SMB5920BT3,6.2V,NP S25040-5SMT 13 SDIO,BAV99LT1,SOT23,DUAL SWITC S25040-2SMT 13 SDIO,1A,400V,DO-214BA,GLS S25049-2SMT S25040-6SMT T12702-59 T12702-60 S25083-1SMT S18248-16 S24020-2 S18248-10 S24020-12 S24020-4 S24020-16 S24020-8 S24020-6 S25080-1SMT S25080-2SMT S15000-28SMT N/A S25051-7SMT S25050-1SMT S25050-2SMT S25051-4SMT S25051-6SMT S25001-4753SMT S25000-2802SMT S25001-2671SMT S25001-1501SMT S25001-1503SMT S25001-3321SMT S25001-6811SMT S25003-2000SMT 4 6 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 3 2 1 1 2 8 4 1 1 9 5 2 2 1 1 1 7 2 6 2 2 SDIO,MBRA130LT3,1A,30V,SCHOTKY SDIO,BAV70 DIO,1N5333B DIO,1N5358B SIND,FERRITEBEAD,TR,NP CON,16P,MINI,NP CON,2P,TIN,MINI,NP CON,10P,MINI,NP CON,12P,TIN,MINI,NP CON,4P,TIN,MINI,NP CON,16P,TIN,MINI,NP CON,8P,TIN,MINI,NP (or TH600-265) CON,6P,TIN,MINI,NP SLED,RED,1206,TR,NP SLED,GRN,1206,TR,NP SICS,HCPL-0601,OPTOCOUPLER 1E0 ARTWORK SICS,IRF7103,NP STRA,MMBT4401LT,NPN,SOT-23 STRA,2N4403,SO23,TR,(500475),N STRA,2N7002,TR,NP STRA,IRLR120N,10A,100V,MOSFET, SRES,475K,1206,1%,1/8W,TR,NP SRES,28K,0805,1%,1/10W,TR SRES,2.67K,1206,1%,1/8W,TR,NP SRES,1.5K,TKF,1206,1%,1/4W,TR SRES,150K,1206,1%,1/8W,TR SRES,3.32K,1206,1%,1/8W,TR SRES,6.81K,1206,1%,1/4W,TR SRES,200,2512,5%,1W,TR,NP S25006-10ROSMT 10 SRES,10, S25001-1001SMT 33 SRES,1K,1206,1%,1/4W,TR S25001-1002SMT REFERENCE-DESIGNATOR PART NO. DIGITAL CONTROL P.C. BD. BLANK (REF. ONLY) POTTING TRAY SELF TAPPING SCREW EPOXY ENCAPSULATION RESIN ELECTRICAL INSULATING COMPOUND FLASH SOFTWARE CPLD FIRMWARE PLUG, KEYING PLUG 47 SRES,10K,MF,1206,1%,1/8W S25001-7500SMT S25001-2672SMT 1 4 SRES,750,1206,1%,1/4W,TR SRES,26.7K,THK,1206,1%,1/8W,10 S25001-4751SMT 15 SRES,4.75K,1206,1%,1/8W,TR S25001-4750SMT 24 SRES,475,1206,1%,1/8W,TR,NP S25001-1500SMT S25001-1004SMT 2 2 SRES,150,1206,1%,1/8W,TR,NP SRES,1M,1206,1%,1/8W,TR Barcode Labels C118 C116 C128 C130 C119 C110 C49 C54 C12 C102 C1 C9 C10 C39 C40 C16 C61 C126 C13 C136 C135 C7 C138 C134 C133 C125 C55 C96 C98 C100 C28 C82 C14 C11 C83 C103 C121 C101 C117 C115 C111 C113 C85 C90 C48 C93 C109 C120 C127 C106 C95 C105 C73 C68 C8 C114 C108 C99 C77 C76 C75 C84 C79 C67 C88 C80 C50 C78 C23 C21 C91 C51 C92 C58 C57 C52 C60 C59 C131 C123 C122 C124 C30 C129 C139 C140 C137 C141 C142 C42 C143 C15, C18, C22, C25, C27 C32 C43 C4 C74 C3 C71 C19 C70 C5 C72 C6 C17 C44 C69 C45 C56 C34 C64 C89 C26 C35 C36 C38 C37 C66 C62 C65 C63 C86 C87 C94 C97 C104 C107 C47 C81 C2 C46 D10 D11 D18 D15 D43 D25 D45 D44 D17 D9 D6 D2 D5 D7 D8 D35 D36 D38 D37 D42 D41 D40 D39 D69 D27 D32 D26 D30 D31 D29 D24 D14 D16 D34 D54 D28 D47 D80 D81 D82 D83 D51 D55 D56 D57 D98 D99 D100 D101 D53 D52 D58 D59 D62 D61 D60 D13 D12 D1 D46 D66 D50 D33 D49 D19 D78 D79 D102 D103 D104 D105 D106 D107 D68 D67 D4 D3 D75 D63 D64 D65 D70 D72 D71 D73 D74 D76 D77 D114 D115 D84 D85 D86 D89 D90 D91 DZ1 DZ2 DZ3 DZ4 E1 J1 J10A J10B J3 J4 J5 J11 J2 J6 J7 J8 J9 LED7 LED10 LED8 LED1 LED5 LED3 LED2 LED4 LED6 LED9 OCI1 OCI2 OCI3 OCI4 PCB Q11 Q12 Q4 Q7 Q5 Q6 Q1 Q18 Q19 Q20 Q17 Q16 Q15 Q13 Q14 Q3 Q2 Q9 Q10 R100 R107 R109 R113 R118 R122 R74 R76 R80 R78 R117 R125 R123 R128 R129 R179 R246 R251 R127 R130 R132 R133 R151 R154 R157 R160 R148 R161 R158 R155 R152 R149 R171 R178 R177 R193 R231 R167 R61 R34 R89 R82 R163 R135 R136 R169 R131 R112 R60 R56 R126 R71 R54 R69 R68 R143 R144 R58 R206 R213 R214 R90 R168 R255 R256 R173 R191 R181 R164 R170 R172 R189 R186 R180 R91 R92 R93 R94 R95 R96 R97 R98 R22 R174 R201 R185 R104 R87 R33 R99 R260 R261 R139 R140 R121 R200 R199 R103 R221 R229 R204 R242 R241 R216 R217 R218 R252 R253 R254 R257 R258 R259 R183 R187 R114 R120 R72 R190 R192 R182 R184 R137 R146 R209 R210 R222 R42 R43 R46 R47 R51 R67 R195 R194 R41 R11 R83 R86 R166 R165 R21 R15 R20 R88 R81 R17 R19 R18 R141 R138 R119 R116 R85 R84 R40 R36 R196 R198 R212 R211 OPPOSITE COMPONENT SIDE (BACKSIDE) IDENTIFICATION CODE DESCRIPTION REFERENCE-DESIGNATOR 6 9 2 10 6 2 6 SRES,100,0805,1%,1/10W SRES,47.5K,1206,1%,1/8W,TR SRES,511,MF,1206,1%,1/8W,TR SRES,2.21K,1206,1%,1/8W,TR SRES,332,1206,1%,1/4W SRES,47.5,TKF,1206,1%,1/4W,TR SRES,22.1K,1206,1%,1/8W,TR,NP R223, R224, R240, R226, R227, R228 R230 R27 R28 R26 R53 R29 R110 R57 R65 R24 R23 R25 R13 R12 R32 R1 R31 R134 R66 R268 R269 R262 R263 R264 R265 R266 R267 R3 R2 R37 R38 R35 R203 R8 R39 S25001-1003SMT 10 SRES,100K,1206,1%,1/8W,200PPM, R55 R111 R49 R108 R115 R124 R142 R208 R207 R106 S25001-2210SMT 13 SRES,221,1206,1%,1/8W,TR S25001-1000SMT S25001-3322SMT S25001-1213SMT S20620-1003 N.C. S19869-8 N.A. S15128-13SMT N.A. S25065-3SMT N.A. S25069-2SMT N.A. M15105-9SMT N.A. S25067-3SMT N.A. S25067-2SMT N.A. S20353-1SMT N.A.,N.G. S25070-3SMT N.A. S25070-4SMT N.A. S25066-2SMT N.A. S15018-21SMT N.A. S25065-2SMT N.A. S25070-23SMT N.A. S25068-7SMT N.A. M15101-14SMT N.A.,N.F. S25069-24SMT N.A. S25069-7SMT N.A. S20353-5 N.A. S20353-4SMT N.A. S17900-11SMT N.A. S25068-8SMT N.A. S15128-21SMT N.A. S25057-3SMT N.A. S15128-18SMT N.A. S25082-1SMT 4 2 1 4 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 1 SRES,100,1206,1%,1/8W,TR,NP SRES,33.2K,1206,1%,1/8W,TR,NP SRES,121K,1206,MF,1%,1/4W RES,100K,AX,5%,1/2W,HI VOLT,TR SWT,78B08S,DIP,SPST,8P,NP SICS,OP-27G,OPAMP,SO8,TR,NP SICS,74VHC14,NP SICS,25128,SERIAL EEPR,NP SICS,7945 (old package) SICS,ADG417,SPST,CMOS,SWT,SO8 SICS,ADG409BR SICS,MC145407,RECEIVER/DRVR,RS ICS,XC9536-15 VQ44 SICS,XCS20,FPGA SICS,AD7862,DUAL,12BIT,250kSPS ICS,MIC4451BM SICS,74ACT573,OCTAL,TRANS.,LAT SICS,TMS320F240PQA,NP SICS,4.6V,2%,VOLT. DETECTOR,SO SICS,MC68332 SICS,28F800B5-90,FLASH RO,90n SICS,128Kx16,20nS,TSOP SICS,AN82527 SICS,MAX485ESA,NP 74HC245, NEW PACKAGE SICS,MC79L05ABD SICS,LT1016,COMPARATOR SICS,AD8403ARU10 SICS,MC33074,QUAD,OPAMP,SO14,T SXTL,16MHZ,HC40,20PF,NP R59 R48 R102 R197 R45 R9 R10 R14 R16 R101 R50 R64 R105 R62 R44 R52 R30 R63 R233 R70 R73 R79 R75 R77 S1 X1 X10 X30 X11 X12 X13 X31 X15 X16 X17 X18 X19 X2 X3 X21 X22 X23 X24 X25 X27 X28 X29 X33 X4 X5 X7 X6 X32 X8 X14 X20 Y1 NOTES: N.A. CAUTION: THIS DEVICE IS SUBJECT TO DAMAGE BY STATIC ELECTRICITY. LINCOLN ELECTRIC TO SEE E2454 BEFORE HANDLING. N.B. SECURE P.C. BOARD ASSEMBLY IN PLACE WITH (ITEM 3) (2 PLACES, 4.8-5.8 IN. LBS.) N.C. TOP OF THESE COMPONENTS MUST BE FREE OF POTTING MATERIAL. N.D. PLACE BARCODED ASSEMBLY NUMBER IDENTIFICATION AND BARCODED SERIAL NUMBER IDENTIFICATION IN AREA SHOWN. N.E. THERE ARE COMPONENTS ON BOTTOM SIDE OF P.C. BOARD. N.F. PROGRAM X25 WITH ITEM 6. N.G. PROGRAM X17 WITH ITEM 7. N.J. PLACE CONNECTOR KEYING PLUG (ITEM 9) OVER HEADER PIN, IN LOCATION SHOWN. PLUG SHOULD BE INSERTED BELOW CONNECTOR TOP SURFACE. N.K. ALL CONNECTORS MUST BE GREASED WITH (ITEM 5) PRIOR TO ENCAPSULATION. N.L. ENCAPSULATION PER E1911-E TO A MINIMUM DEPTH, SUCH THAT ALL COMPONENT LEADS ARE COVERED. N.M. SOLDER A #30 INSULATED COPPER WIRE FROM PIN 23 OF X27 TO POSITIVE TERMINAL ON C119 AS SHOWN. CAPACITORS = MFD/VOLTS INDUCTANCE = HENRIES RESISTANCE = OHMS MANUFACTURE PER E1911-ROHS SCHEMATIC REF. G3789-2F0 BUY PER E3867 TEST PER E3856-C ALL COMPONENTS AND MATERIALS USED IN THIS ASSEMBLY ARE TO BE RoHS COMPLIANT PER E4253. L11088-2F0 PART NO. REQ'D S25000-1000SMT S25001-4752SMT S25001-5110SMT S25001-2211SMT S25001-3320SMT S25001-47R5SMT S25001-2212SMT BUY AS THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED PROPRIETARY & CONFIDENTIAL: TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED TOLERANCE MANUFACTURING TOLERANCE PER E2056 DESIGN INFORMATION ON 2 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .02 EN-170 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC REQ'D 1 N.D. N.J. PART NO. L11088-F M19436-1 S8025-80 E2527 E3539 S26082-4 S24804-3 S24671 ON 3 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .002 DRAWN BY: ON ALL ANGLES IS ± .5 OF A DEGREE MATERIAL TOLERANCE (" t ") TO AGREE WITH PUBLISHED STANDARDS. ENGINEER: DO NOT SCALE THIS DRAWING APPROVED: FEI REFERENCE: L11088-1 SCALE: . NONE EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: UF INVERTER WELDERS CONTROL P.C. BOARD AS'BLY APPROVAL DATE: PROJECT NUMBER: CRM34409 1 1 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT NUMBER: L11088-2 DOCUMENT REVISION: F.01 SOLID EDGE Return to Master TOC PC BOARD ASSEMBLY - CONTROL PC BOARD (ALL CODES) (L11088-2) N.B. Return to Section TOC G-17 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS L11088-2 Return to Section TOC G-17 STRP NOTE: Lincoln Electric assumes no responsibility for liablilities resulting from board level troubleshooting. PC Board repairs will invalidate your factory warranty. Individual Printed Circuit Board Components are not available from Lincoln Electric. This information is provided for reference only. Lincoln Electric discourages board level troubleshooting and repair since it may compromise the quality of the design and may result in danger to the Machine Operator or Technician. Improper PC board repairs could result in damage to the machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-18 SCHEMATIC - DIGITAL POWER SUPPLY PC BOARD (ALL CODES) (G3631-3) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-18 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT PC BOARD ASSEMBLY - DIGITAL POWER SUPPLY PC BOARD (ALL CODES) (G3632-3) ENGINEERING CONTROLLED MANUFACTURER: Yes CHANGE DETAIL: REVISED IDENTIFICATION CODE, BLANK PART NIMBER, SCHEMATIC REFERFENCE AND UPDATED GRAPHICS N.A. N.A. N.A. 8 7 1 N.G. R50 J42 G3632-3 POWER SUPPLY J41 J43 R24 D7 C11 R17 T1 C26 C13 D8 D24 C18 C20 D6 D25 R40 C38 C19 C17 T2 X8 6 X3 X7 X6 D10 D13 D12 C23 D15 C29 C1 C10 3.64 C40 C47 C12 C33 D18 D22 DZ4 C31 DZ2 X1 C3 OCI1 QTY 1 2 2 AS REQ 2 2 1 2 115g AS REQ PART NUMBER G3632-F CF000003 E106A-13 E1868 S18104-5 S25128-1SMT M19436-3 S8025-80 E2527 E2861 D1 LED1 DZ7 D20 D2 C37 R62 R63 D16 X2 R64 N.A. 6 N.B. N.B. N.B. 6.14 N.A. REFERENCES C1, C3, C6, C10, C17, C18, C19, C20, C24, C33, C38 C2, C5, C7, C9, C14, C21, C22, C25, C34, C39, C44, C53 C4, C8 C11, C43 C12, C31 C13, C26 C16, C42 C23, C29, C30, C40, C47 C28, C32 C36, C37 C45, C46, C52 D1, D2, D3, D6, D7, D8, D9, D15, D25 D10, D12, D13, D17, D24 D16 D18 D19 D20, D21, D22, D23 DZ2, DZ3 DZ4 DZ7, DZ8 J41 J42 J43 LED1, LED2 OCI1, OCI3 Q1, Q2 R1 R2, R4, R13, R22, R27 R3 R5, R10, R29 R6, R7, R57, R58 R8 R9, R60, R61 R11, R30 R12, R28, R45 R14, R20 R15, R16 R17, R24 R18, R49 R19, R23 R21 R25, R44, R62, R63, R64 R31 R32, R43 R33 R35, R36 R37, R46, R48 R38, R39 R40 R41, R53 R42, R51 R50 R52 T1 T2 X1, X2 X3 X4, X5 X6, X7 X8 X9 QTY PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION 11 S13490-197 CAPACITOR,ALEL,82,35V,20%,LOW-ESR 12 S25020-3SMT CAPACITOR,SMD,CERAMIC,0.1MF,50V,10%,X7R,S0805 2 2 2 2 2 5 2 2 3 S25020-4SMT S13490-198 S20500-5 T11577-62 S25020-5SMT S25024-2SMT S25020-18SMT S13490-202 S25020-13SMT CAPACITOR,SMD,CERAMIC,820pF,50V,5%,COG,S0805 CAPACITOR,ALEL,1000,35V,20%,LOW-ESR CAPACITOR,PPMF,.0015,2000V,BOX CAPACITOR,PEMF,1.0,200V,10% CAPACITOR,SMD,CERAMIC,2700pF,50V,5%,X7R,S0805 CAPACITOR,SMD,TANTALUM,1.0MF,35V,10%,S3528 CAPACITOR,SMD,CERAMIC,10pF,100V,5%,COG,S0805 CAPACITOR,ALEL,470MF,10V,20% CAPACITOR,SMD,CERAMIC,150pF,100V,5%,COG,S0805 9 S25040-11SMT DIODE,SMD,1A,600V,S403A,ULTRA-FAST RECOVERY 5 1 1 1 4 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 5 1 3 4 1 3 2 3 2 2 2 2 2 1 5 1 2 1 2 3 2 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 2 1 1 S25040-2SMT S25040-13SMT S25040-3SMT S25040-8SMT S25049-2SMT S25046-5SMT S25044-12SMT S25044-5SMT S24020-4 S24020-6 S24020-12 S25080-1SMT S15000-10 T12704-93 S25001-1502SMT S25001-1002SMT S25001-6191SMT S25001-1003SMT S25002-47R5SMT S25001-4750SMT S25000-10R0SMT S25005-1SMT S25001-5621SMT S25001-1821SMT S25001-33R2SMT S25084-2SMT S25001-4322SMT S25002-2491SMT S25001-4753SMT S25002-1500SMT S25001-7502SMT S25001-15R0SMT S25001-2490SMT S25002-30R1SMT S25002-1211SMT S25001-5622SMT S18380-15 S25001-3320SMT S25001-4422SMT S25084-1SMT S25001-2213SMT S20375-13 S20375-10 S15128-10SMT S25068-9SMT S25071-2SMT S25068-1SMT S15128-6SMT S25068-10SMT DIODE,SMD,1A,400V,DO-214BA/AC DIODE,SMD,DUAL,16A,200V,D2PAK,CC,ULTRA-FAST RECOVERY DIODE,SMD,DUAL,6A,200V,DPAK,CC,ULTRA-FAST RECOVERY DIODE,SMD,3A,600V,D0-214AB,ULTRA-FAST RECOVERY DIODE,SMD,SCHOTTKY,1A,30V,SMA ZENER DIODE,SMD,0.5W,27V,5%,SOD-123 ZENER DIODE,SMD,3W,3.3V,5%, SMB ZENER DIODE,SMD,3W,18V,5%, SMB CONNECTOR,MOLEX,MINI,PCB,4-PIN,TIN CONNECTOR,MOLEX,MINI,PCB,6-PIN,TIN CONNECTOR,MOLEX,MINI,PCB,12-PIN,TIN LED,SMD,RED,CLEAR,S1206 OPTOCOUPLER,PHOTO-Q,70V,CNY17-3 TRANSISTOR,NMF,T220,21A,200V,BUZ30A RESISTOR,SMD,15K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,10K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,6.19K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,100K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,47.5OHMS,1/3W,MF,1%,S1210 RESISTOR,SMD,475OHMS,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,METAL FILM,1/10W,10.0OHMS,1%,S0805 RESISTOR,SMD,METAL STRIP,3W,0.05OHMS,1% RESISTOR,SMD,5.62K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,1.82K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,33.2OHMS,1/4W,1206,1%,TR THERMISTOR,SMD,PTC,0.35./1.4OHMS,2.0A RESISTOR,SMD,43.2K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,2.49K,1/3W,MF,1%,S1210 RESISTOR,SMD,475K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,150OHMS,1/3W,MF,1%,S1210 RESISTOR,SMD,75.0K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,15.0OHMS,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,249OHMS,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,30.1OHMS,1/3W,MF,1%,S1210 RESISTOR,SMD,1.21K,1/3W,MF,1%,S1210 RESISTOR,SMD,56.2K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR THERMISTOR,PTC,0.01/0.03OHMS,4.0A RESISTOR,SMD,332OHMS,1/4W,1206,1%,TR RESISTOR,SMD,44.2K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR THERMISTOR,SMD,PTC,0.06/.25OHMS,1.5A RESISTOR,SMD,221K,1/4W,1206,1%,TR TRANSFORMER,PCB,PWM,FLYBACK TRANSFORMER,PCB,PWM,FLYBACK IC,SMD,VOLTAGE REF,ADJ, PRECISION,431I,SOIC-8 IC,SMD,VOLTAGE REGULATOR,FIXED,3-TERMINAL,0.5A,+15V IC,SMD,PWM-CONTROLLER,SOIC8(SS) IC,SMD,VOLTAGE REGULATOR,FIXED,3-TERMINAL,0.5A,+5V IC,SMD,VOLTAGE REGULATOR,FIXED,3-TERMINAL,1A,+15V IC,SMD,VOLTAGE REGULATOR,FIXED,3-TERMINAL,0.5A,-15V NOTES: N.A. SEE HEAT SINK MOUNTING DETAILS. N.E. N.B. ALL CONNECTORS MUST BE GREASED WITH ITEM 10 PRIOR TO ENCAPSULATION. 5 2 N.H. Q1 OR Q2 N.C. ATTACH ITEM 1 TO ITEM 7 (2 PLACES) WITH ITEM 8 (TORQUE = 5.3 +/- .05 IN-LB). ITEM 1 SHOULD BE ALLIGNED SO THAT THE DISTANCE BETWEEN ITEM 1's CONNECTORS AND ITEM 7 IS AS LARGE AS POSSIBLE. G3632-3F0 N.E . TIGHTEN TO 6-8 in. lbs. WITHOUT APPLYING ANY PRESSURE TO PLASTIC CASE OF Q1 AND Q2. SCHEMATIC REFERENCE: G3631-3F0 N.H. PLACE A HEAVY FILM OF ITEM 4 ON HEAT SINK SURFACE. DO NOT GET ON THREADS. BUY PER E3867 TEST PER E3856-P HEATSINK MOUNTING DETAIL THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED PROPRIETARY & CONFIDENTIAL: TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED TOLERANCE MANUFACTURING TOLERANCE PER E2056 DESIGN INFORMATION ON 2 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .02 EN-170 Return to Master TOC IDENTIFICATION CODE PART NO. N.G. PLACE BARCODED ASSEMBLY NUMBER IDENTIFICATION AND BARCODED SERIAL NUMBER IDENTIFICATION IN AREA SHOWN. 3 CAPACITORS = MFD/VOLTS INDUCTANCE = HENRIES RESISTANCE = OHMS BUY AS N.D. ENCAPSULATION PER E1911-E TO A MINIMUM DEPTH SO ALL OF THE COMPONENTS LEADS ARE COVERED. Return to Section TOC DESCRIPTION PC BOARD BLANK 6-32 X .375 ROUND HEAD MACHINE SCREW # 6 LOCK WASHER THERMO JOINT COMPOUND HEAT SINK,ALUMINUM,EXTRUDED,FOR 1 TO-220,1.0 SMD HEAT SINK FOR D2PAK TO-263 POTTING TRAY SELF TAPPING SCREW EPOXY ENCAPSULTION RESIN ELECTRICAL INSULATION COMPOUND ON 3 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .002 DRAWN BY: ON ALL ANGLES IS ± .5 OF A DEGREE MATERIAL TOLERANCE (" t ") TO AGREE WITH PUBLISHED STANDARDS. ENGINEER: DO NOT SCALE THIS DRAWING APPROVED: REFERENCE: G3632-2 SCALE: . NONE EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: UF INVERTER WELDERS DIGITAL POWER P.C. BOARD AS'BLY APPROVAL DATE: 9/30/2004 PROJECT NUMBER: CRM35510-B 1 1 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT REVISION: DOCUMENT NUMBER: G3632-3 B SOLID EDGE Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC D23 Q1 R11 C30 Q2 LED2 C43 Return to Section TOC DZ8 D9 C36 R30 X4 C2 D17 C7 C24 DZ3 D21 C6 OCI3 X9 D3 X5 Return to Section TOC ITEM (USED WITH) 1 2 (Q1, Q2) 3 (Q1, Q2) 4 (Q1, Q2) 5 (Q1, Q2) 6 (D16, X8) 7 8 9 10 REFER TO ELECTRONIC COMPONENT DATABASE FOR SPECIFICATIONS ON ITEMS LISTED BELOW D19 Return to Master TOC G-19 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G3632-3 Return to Section TOC G-19 STRP NOTE: Lincoln Electric assumes no responsibility for liablilities resulting from board level troubleshooting. PC Board repairs will invalidate your factory warranty. Individual Printed Circuit Board Components are not available from Lincoln Electric. This information is provided for reference only. Lincoln Electric discourages board level troubleshooting and repair since it may compromise the quality of the design and may result in danger to the Machine Operator or Technician. Improper PC board repairs could result in damage to the machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-20 SCHEMATIC - FEEDHEAD PC BOARD #1 (ROBOTIC MODEL ONLY) PG 1 OF 3 (G3823-3) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-20 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-21 SCHEMATIC - FEEDHEAD PC BOARD #2 (ROBOTIC MODEL ONLY) PG 2 OF 3 (G3823-3) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-21 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-22 SCHEMATIC - FEEDHEAD PC BOARD #3 (ROBOTIC MODEL ONLY) PG 3 OF 3 (G3823-3) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-22 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC PC BOARD ASSEMBLY - FEEDHEAD PC BOARD (ROBOTIC MODEL ONLY) (L11087-3) ENGINEERING CONTROLLED MANUFACTURER: Yes CHANGE DETAIL: REVISED MAKE SPECIFICATION 2 ITEM N.B. 3 N.D. Return to Master TOC N.E. Return to Section TOC G-23 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS L11087-3 Return to Section TOC G-23 N.C. 6.34 74 75 76 S25001-3320SMT S25005-1SMT S25001-4751SMT 6 2 4 77 S25000-4751SMT 12 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 S25001-1503SMT S25000-1211SMT S25000-2002SMT S25007-9091SMT S19869-8 S20375-8 S25068-7SMT M15101-14SMT S25069-2SMT S20353-1SMT S25070-6SMT S17900-24SMT S25069-24SMT S25066-2SMT S25057-3SMT M15105-9ASM S15128-21SMT S15128-18SMT S15128-16SMT S15018-20SMT M15104-15 S20353-5 S25065-2SMT S20353-4SMT S25068-8SMT S25068-6SMT S15128-25SMT S17900-11SMT S24841-1 S25082-1SMT S25000-1000SMT 1 1 3 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 3 1 2 1 1 1 1 6 R139,R140,R141,R142,R143,R144 R97,R98 R99,R114,R132,R137 R101,R104,R125,R126,R127, R128,R129,R130,R131,R133, R134,R145 R115 R135 R146,R147,R76 R90,R109 S1 T1 X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X7,X29 X9 X10 X11 X12 X13 X14,X20 X15 X16 X17 X18 X19 X21,X26,X27 X22 X23,X24 X25 X28 X30 Y1 R155,R156,R157,R158,R159,R160 RESISTOR,SMD,332ohms,1/4W,1206,1% SRES,0.05,3W,1% ,TR,NP SRES,4.75K,1206,1% ,1/8W,NP,(SM N.D. N.E. SRES,4.75K,0805,1% ,TR,NP SRES,150K,1206,1% ,1/8W,NP SRES,1.21K,0805,1% ,1/10W,TR,NP SRES,20K,TKF,0805,1% ,01/10W,TR RESISTOR,SMD,9.09K,1/10W,0805,0.1% SWT,78B08S,DIP,SPST,8P,NP TFM,L5936,Noreast,Switching Pwr SICS,4.6V,2% ,VOLT. DETECTOR SICS,MC68332,MICRCONTROLLER,TQ SICS,25128,SERIAL EEPR,NP SICS,MC145407,RECEIVER/DRVR,RS SICS,XC9572-15,CPLD,TQ100,NP SICS,74HC132,NP SICS, FLASH ROM, 16 x 256K, 70 NS SICS,AD7862,DUAL,12BIT,250kSPS SICS,AD8403ARU10,DIGITAL POT,NP SICS,AD7945,12BIT,PARALLEL,DAC SICS,LT1016,COMPARATOR,NP SICS,MC33074,QUAD,OPAMP,S014,T ICS,SMD,OP-AMP,QUAD,HIGH PERFORMANCE 1014 SICS,HIP4082,H-BRIDGE,FET DRIVE IC,SMD,CMOS,RAM,STATIC,16-BIT,64K X 16 SICS,AN82527,CAN CONTROLLER,PL SICS,74ACT573,OCTAL,TRANS. LAT SICS,MAX485,TRANSCEIVER,NP SICS,79L05,V-REG,-5V,SO8 SICS,78L05,V-REG,+5V,SO8 SICS,LM2576HVS-5.0,VREG,60V,SWI SICS,74HC245,SOL20,HCMOS,NP ICS,DC/DC,5V 3A OUT,36-75V IN SXTL,16MHz,HC40,20pF,NP RESISTOR,SMD,100,1/10W,0805,1% UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED: RESISTANCE = OHMS Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC N.F. 5.84 3 ALL COMPONENTS AND MATERIALS USED IN THIS ASSEMBLY ARE TO BE RoHS COMPLIANT PER E4253 REVISION CONTROL N.B. L11087-3E0 NOTES: N.A. CAUTION: THIS DEVICE IS SUBJECT TO DAMAGE BY STATIC ELECTRICITY. LINCOLN ELECTRIC TO SEE E2454 BEFORE HANDLING. N.B. SECURE PC BOARD ASSEMBLY IN PLACE WITH ITEM 4. (2 PLACES) TIGHTEN SCREWS TO A TORQUE OF 5.3±0.5 IN-LBS. N.C. PLACE BARCODED ASSEMBLY NUMBER IDENTIFICATION AND BARCODED SERIAL NUMBER IDENTIFICATION IN AREA SHOWN. PROGRAM ITEM 88 WITH ITEM 6 . PROGRAM ITEM 90 WITH ITEM 7 . PARTS INDICATED MUST BE COMPLETELY COVERED WITH ENCAPSULATION. N.D. N.E. N.F. PART NO. IDENTIFICATION CODE TEST PER E3856-FH POT WITH E2527 SCHEMATIC REFERENCE: G3823-3E0 BUY DETAIL BUY PER E3867 MAKE DETAIL MANUFACTURE PER E1911-ROHS BUY BLANK COMPLETE (4 BOARDS PER PANEL) 4 LAYER BOARD BLANK PANEL SEE ELECTRONIC FILE FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION. PART NO. PC BOARD REFERENCE DESIGNATORS QTY 1 2 3 L11087-E M19436-5 S8025-80 1 1 2 195g 6.88 OZ. AS REQ. 1 1 4 E2527 5 6 7 E3539 Y00552-5 S24823-5 8 S25024-2SMT 4 9 S25020-3SMT 47 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 S25024-8SMT S25020-13SMT S25024-5SMT S25024-10SMT S25020-2SMT S25020-10SMT S25020-9SMT S25020-15SMT S24833-1 S13490-179 S13490-182 S13490-184 S25020-4SMT S25040-12SMT S25040-2SMT 5 2 6 3 1 3 2 3 2 1 1 1 2 2 4 25 S25040-5SMT 10 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 S25049-4SMT S25040-4SMT S25040-11SMT S25040-9SMT S25040-10SMT S25046-3SMT S25046-1SMT S25044-9SMT 4 5 4 1 1 4 3 6 DESCRIPTION FEED HEAD PC BOARD BLANK POTTING TRAY SELF TAPPING SCREW EPOXY ENCAPSULATING RESIN ELECTRICAL INSULATING COMPOUND SOFTWARE,CPLD SOFTWARE,FLASH X5 X9 FOR ITEMS LISTED BELOW REFER TO ELECTRONIC COMPONENT DATABASE FOR COMPONENT SPECIFICATIONS 34 S25044-1SMT 9 35 36 S25046-2SMT S18380-5 4 2 37 S18380-14 12 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 S24020-4 S24020-6 S24020-8 S24020-16 S18248-10 S18248-16 S15000-28SMT S15000-26SMT S25051-4SMT S25050-2SMT 2 1 1 1 1 1 4 1 5 5 48 S25050-1SMT 9 49 50 S25051-16SMT S23060-1SMT 4 1 51 S25000-1002SMT 24 52 53 54 S25001-1002SMT S25011-9092SMT S25003-2000SMT 6 4 2 55 S25001-4750SMT 9 56 S25000-1001SMT 8 57 S25000-4750SMT 2 58 S25004-2430SMT 12 59 S25000-3320SMT 9 60 S25000-2210SMT 9 61 S25001-2000SMT 8 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 S25001-7500SMT S25000-2213SMT S25000-4752SMT S25000-1003SMT S25001-1001SMT S25000-9092SMT S25000-3921SMT S25001-4753SMT S25001-4752SMT S25001-1000SMT S25001-15R0SMT S25001-1500SMT 1 1 2 6 1 2 1 2 2 3 2 4 C1,C2,C7,C50 C3,C4,C5,C6,C8,C9,C12,C14, C15,C19,C20,C22,C25, C26,C27,C28,C29,C30,C31, C32,C34,C35,C38,C39,C41, C43,C45,C46,C47,C48,C49, C51,C54,C56,C57,C59,C60, C64,C65,C69,C72,C75,C76, C77,C78,C81,C82 C10,C11,C17,C18,C80 C13,C16 C23,C63,C66,C67,C68,C71 C24,C36,C73 C37 C40,C42,C44 C52,C79 C55,C58,C83 C61,C62 C70 C74 C84 C85,C86 D1,D12 D2,D17,D20,D27 D3,D4,D5,D6,D9,D18,D21,D28,D29, D31 D7,D8,D10,D19 D11,D13,D14,D15,D16 D22,D23,D24,D25 D26 D30 DZ1,DZ2,DZ3,DZ4 DZ5,DZ28,DZ29 DZ6,DZ7,DZ8,DZ9,DZ26,DZ27 DZ10,DZ11,DZ12,DZ13,DZ14, DZ15,DZ16,DZ17,DZ18 DZ20,DZ21,DZ22,DZ23 F1,F2 F3,F4,F5,F6,F7,F8,F9,F10, F11,F12,F13,F14 J81,J82 J83 J84 J85 J86 J87 OCI1,OCI2,OCI3,OCI4 OCI5 Q1,Q12,Q13,Q15,Q16 Q2,Q3,Q7,Q14,Q17 Q4,Q5,Q6,Q19,Q20,Q21,Q22,Q23,Q 24 Q8,Q9,Q10,Q11 Q18 R2,R3,R4,R5,R6,R7,R9,R16, R17,R18,R19,R20,R21,R22, R23,R53,R54,R77,R80,R106, R116,R138,R148,R149 R8,R10,R13,R83,R100,R118 R84,R85,R86,R152 R11,R12 R14,R15,R62,R68,R78,R102, R103,R107,R112 R24,R25,R55,R105,R113, R136,R153,R154 R26,R27 R28,R29,R30,R31,R32,R33, R34,R35,R36,R37,R38,R39 R41,R42,R48,R49,R50,R51, R52,R121,R123 R43,R44,R45,R46,R47,R65, R108,R122,R124 R56,R57,R58,R61,R64,R66, R110,R111 R1 R63 R67,R72 R69,R71,R73,R75,R82,R117 R70 R74,R81 R79 R87,R120 R88,R119 R89,R93,R96 R91,R92 R94,R95,R150,R151 SCAP,1uF,TAN,3528,35V,TR,NP SCAP,0.1uF,0805,50V,X7R,10% ,TR SCAP,10uF,TAN,6032,16V,10% ,TR,NP SCAP,150pF,CER,0805,100V,COG,5% ,TR,NP SCAP,4.7uF,TAN,7343,35V,10% ,TR,NP SCAP,22uF,TAN,7343,25V,10% ,POLAR,TR SCAP,0.022uF,0805,50V,X7R,10% , SCAP,4700pF,0805,50V,X7R,10% ,T SCAP,47pF,0805,50V,COG,5% ,TR,N SCAP,22pF,0805,50V,COG,5% ,TR,N CAP,0.27uF,PCF,63V,5% ,TR,NP CAP,1000uF,ALU,35V,20% ,NP CAP,3300uF,ALU,63V,20% ,NP CAP,330uF,100V CAPACITOR ,SMD CERAMIC,820PF,50V,5% COG,S0805 SDIO,MURS320T3,3A,200V,ULTRAFA SDIO,400V,0.8A,NP SDIO,BAV99LT1,SOT23,DUAL SWITC SDIO,BAT54S,DUAL/SERIES,30V,20 SDIO,BAW56LT1,SOT23,DUAL SWT,T SDIO,MURS160,1A,600V,FAST RECO SDIO,3A,200V,D0-214AB,UFR DIODE,SMD,3A,400V SDIO,MMSZ5248B,18V,ZENER,TR,NP SDIO,MMSZ5231BT1,5.1V,NP SDIO,1SMB5920BT3,6.2V,NP SDIO,1SMB5918BT3,3W,5.1V,5% ,TR,NP SDIO,MMSZ5240BT1,10V,500mW,ZEN RES,50,VAR,PTC,NP RES,500,PTC,265V CON,MOLEX,15-97-7042,MINI,PCB,4 PIN,TIN CON,MOLEX,15-97-7062,MINI,PCB,6 PIN,TIN CON,MOLEX,15-97-7082,MINI,PCB,8 PIN,TIN CON,MOLEX,15-97-7162,MINI,PCB,16 PIN,TIN CON,10P,MINI,NP CON,MOLEX,39-28-1163,PCB,16 PIN,TIN SICS,Optocoupler, HCPL-0601 (SO-8) SICS,HCPL-0201,OPTOCOUPLE STRA,2N7002,TR,NP, (SM400-020) STRA,2N4403,SO23,TR,(500475),N STRA,2N4401,SOT-23,NPN,TR, STRA,75A,55V,0.007 OHM FET,N-CHAN IC,SMD,SWITCH,LO-SIDE,2.2A60V, SRES,10K,0805,1% ,1/10W,TR,NP SRES,10K,MF,1206,1% ,1/8W,TR RESISTOR,SMD,90.9K,1/4W,1206,0.1% SRES,200,2512,5% ,1W,TR,NP SRES,475,1206,1% ,1/8W,TR,NP SRES,1K,0805,1% ,1/10W,TR,NP SRES,475,0805,1% ,TR,NP SRES,243,WSC-1,1% ,1W,TR,NP SRES,332,0805,1% ,1/10W,TR,NP SRES,221,TKF,0805,1% ,1/10W,TR SRES,200,1206,1% ,1/8W,TR,NP RESISTOR,SMD,750ohms,1/4W,1206,1% SRES,221K,TKF,0805,1% ,01/10W,TR SRES,47.5K,TKF,0805,1% ,01/10W,TR SRES,100K,TKF,0805,1% ,01/10W,TR SRES,1K,1206,1% ,1/8W,TR,NP,(09 SRES,90.9K,TKF,0805,1% ,1/10W SRES,3.92K,TKF,0805,1% ,1/10W,TR SRES,475K,1206,1% ,1/8W,TR,NP SRES,47.5K,1206,1% ,1/8W,TR,NP SRES,100,1206,1% ,1/8W,TR,NP SRES,15,1206,1% ,1/8W,TR,NP SRES,150,1206,1% ,1/8W,TR,NP DO NOT SEND THIS ASSEMBLY. SEND THE APPROPRIATE HARDWARE/SOFTWARE ASSEMBLY ONLY Return to Master TOC DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED PROPRIETARY & CONFIDENTIAL:THIS TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED TOLERANCE MANUFACTURING TOLERANCE PER E2056 DESIGN INFORMATION REFERENCE: ON 2 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .02 L11087-2 SCALE: DRAWN BY: JIMJ ON ALL ANGLES IS ± .5 OF A DEGREE MATERIAL TOLERANCE (" t ") TO AGREE WITH PUBLISHED STANDARDS. ENGINEER: DRS DO NOT SCALE THIS DRAWING APPROVED: ON 3 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .002 - 1:1 EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: UF COMMON DIGITAL CONTROLS FEED HEAD PC BOARD ASSEMBLY APPROVAL 9/18/2006 DATE: PROJECT NUMBER: CRM34409 1 1 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT NUMBER: L11087-3 DOCUMENT REVISION: C.01 SOLID EDGE Return to Section TOC FOR PARTS ORDERS ONLY: STRP NOTE: Lincoln Electric assumes no responsibility for liablilities resulting from board level troubleshooting. PC Board repairs will invalidate your factory warranty. Individual Printed Circuit Board Components are not available from Lincoln Electric. This information is provided for reference only. Lincoln Electric discourages board level troubleshooting and repair since it may compromise the quality of the design and may result in danger to the Machine Operator or Technician. Improper PC board repairs could result in damage to the machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-24 SCHEMATIC - INPUT PC BOARD (ALL CODES) (M19528-2) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-24 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC G-25 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS PC BOARD ASSEMBLY - INPUT PC BOARD (ALL CODES) (L11396-2) L11396-2 Return to Section TOC G-25 CHANGE DETAIL: REVISED MAKE SPECIFICATION ENGINEERING CONTROLLED MANUFACTURER: No REFERENCES C1 CR1, CR2 D1, D3 D2 N.C. J60 N.C. J61 OCI1 R1, R2, R3, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10 R4 R5 R11, R17, R23, TP1, P.C. BOARD BLANK INFORMATION BUY COMPLETE AS L11396-B ( 2 LAYER BOARD PER E3281) Return to Master TOC N.D. 4.50 ±.04 XXXXXXXX INPUT J61 J60 Return to Master TOC TP1 XXX X X X X R9 X X X X XXX X X N.B. S19400-2673 S19400-4750 S19400-3011 267K 1/4W 475 1/4W 3.01K 1/4W T13640-23 MOV,250J,660V REQ'D 1 1.0 OZ. 2 PART NO. IDENTIFICATION SEE BLANK INFO. P.C. BD. BLANK E2861 SEALANT S14020-7 PLASTIC EXPANSION NUT R5 C1 4 DESCRIPTION .022/50 DPST RELAY 1N4004 DIODE,1.0A,1500V HEADER,VERTICAL HEADER,VERTICAL OPTO ISOLATOR 100/1OW D2 TP2 1 R4 TP4 TP3 Return to Section TOC ITEM 1 2 3 XXXXXXX D1 R22 1 1 15 R13, R14, R15, R16, R19, R20, R21, R22, R25 TP3, TP4 PART NO. S16668-5 S14293-18 T12199-1 T12705-58 S24020-8 S24020-10 S15000-22 S24376-3 3 N.D. N.A. D3 Return to Section TOC (MAKES 8 BOARDS PER PANEL, SEE ELECTRONIC FILE FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION) R12, R18, R24, TP2, QTY 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 8 R24 R25 R23 R21 R20 R19 R18 R11 R12 R13 R14 R15 R16 R17 R7 R6 R8 R3 R10 OCI1 CAPACITORS = MFD / VOLTS X X X X X X X X X X RESISTORS = OHMS/WATTS CR1 CR2 X X X X R1 R2 X X X X N.A. THIS AREA TO BE COVERED ON BOTH SIDES OF BOARD WITH ITEM 2 PRIOR TO ENCAPSULATION. MATERIAL MUST BE APPLIED THRU SLOTS FROM BOTTOM SIDE TO COMPLETELY FILL TO UNDERSIDE OF DEVICE ON COMPONENT SIDE. N.B. P.C. BOARD HOLES TO BE FREE OF ENCAPSULATION MATERIAL. N.C. DO NOT COAT WITH ENCAPSULATION MATERIAL. N.D. APPLY ITEM 2 AS SHOWN, ALL EXPOSED LEADS MUST BE COVERED. MATERIAL MUST BE APPLIED PRIOR TO ENCAPSULATION. N.E. APPLY ITEM 2 ON NON-COMPONENT SIDE OF BOARD PRIOR TO ENCAPSULATION. ALL EXPOSED PINS MUST BE COVERED. L11396-2 0 0 N.D. N.D. 6.00 ±.04 MAKE PER E1911-ROHS ENCAPSULATE WITH E1844 TEST PER E3647-I SCHEMATIC REFERENCE: M19528-2B0 MANUFACTURED AS: L11396-2B0 Return to Master TOC ALL COMPONENTS AND MATERIALS USED IN THIS ASSEMBLY ARE TO BE RoHS COMPLIANT PER E4253. DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED PROPRIETARY & CONFIDENTIAL:THIS TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED TOLERANCE MANUFACTURING TOLERANCE PER E2056 DESIGN INFORMATION REFERENCE: ON 2 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .02 L11396-1 SCALE: ON 3 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .002 DRAWN BY: ON ALL ANGLES IS ± .5 OF A DEGREE MATERIAL TOLERANCE (" t ") TO AGREE WITH PUBLISHED STANDARDS. ENGINEER: DO NOT SCALE THIS DRAWING APPROVED: FEI - 1:1 EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: UF INVERTER WELDERS INPUT P.C. BOARD ASSEMBLY APPROVAL DATE: PROJECT NUMBER: CRM34409 1 1 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT NUMBER: L11396-2 DOCUMENT REVISION: B.01 SOLID EDGE Return to Section TOC IDENTIFICATION CODE STRP NOTE: Lincoln Electric assumes no responsibility for liablilities resulting from board level troubleshooting. PC Board repairs will invalidate your factory warranty. Individual Printed Circuit Board Components are not available from Lincoln Electric. This information is provided for reference only. Lincoln Electric discourages board level troubleshooting and repair since it may compromise the quality of the design and may result in danger to the Machine Operator or Technician. Improper PC board repairs could result in damage to the machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-26 SCHEMATIC - SWITCH PC BOARD (ALL CODES) (L11385-3) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-26 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC G-27 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS PC BOARD ASSEMBLY - SWITCH PC BOARD (ALL CODES) (G3734-3) G3734-3 Return to Section TOC G-27 ENGINEERING CONTROLLED MANUFACTURER: No CHANGE DETAIL: REVISED MAKE SPECIFICATION ITEM (USED WITH)* 1 N.D. 2 (B11, B19, B20)* N.X. 3 4 P.C. BOARD BLANK REFERENCE INFORMATION NOTES : BUY COMPLETE AS G3734-E (4 LAYER BOARD PER E3281) N.A. CAUTION: THIS DEVICE IS SUBJECT TO DAMAGE BY STATIC ELECTRICITY. SEE E2454 BEFORE HANDLING. N.D. N.A.,N.J.,N.R. 2 N.E. SOLDER EYELET SO THAT SOLDER COVERS ENTIRE EYELET AND ALL AROUND EYELET ON COPPER SIDE ONLY. NO ICICLES OR SOLDER BLOBS PERMITTED. MUST BE SMOOTH AND EVEN WITHIN .020" OVER SURFACE. N.H. MOLEX CAVITIES AND AREA AROUND LOCKING TAB TO BE FREE OF ENCAPSULATION MATERIAL. MASK PER APPROPRIATE MANUFACTURING WORK INSTRUCTIONS. N.J. ELECTRONIC MODULES TO BE ASSEMBLED, SOLDERED, AND SEALED TO PC BOARD PER E3875. .116 N.Q. N.Q. .275 .285 R .045 MAX. CRIMP HEIGHT N.M. DO NOT COAT THE TOP SURFACES OR THE THREADS WITH ENCAPSULANT MATERIAL (1 TERMINAL). MASK PER APPROPRIATE MANUFACTURING WORK INSTRUCTIONS. COPPER SIDE N.Q. BRACKET MUST HAVE FULL MATING CONTACT WITH POWER TERMINAL AND HAVE HOLES ALIGNED. EYELET DETAIL N.R. ELECTRONIC MODULES ON A COMMON P.C. BOARD ASSEMBLY TO HAVE THE SAME VENDOR CODE. VGE(TH) N.S. AFTER SOLDERING, INSPECT TERMINAL CONNECTIONS PER E1880. N.T. ENCAPSULATE COMPONENT SIDE OF P.C. BOARD TO A THICKNESS OF .30 +.12/-.00 IN AREA SHOWN. N.U. ENCAPSULATE NON COMPONENT SIDE OF P.C. BOARD TO A THICKNESS OF .25 +.12/-.00. N.V. ENCAPSULATION MATERIAL MUST EXTEND BEYOND EDGES OF P.C. BOARD .12 +.12/-.00. N.W. ENCAPSULATE OPPOSITE COMPONENT SIDE OF P.C. BOARD IN AREAS SHOWN TO A MAXIMUM THICKNESS OF .20. N.X. N.W. N.X. N.X. 3 N.X. 6.00 ±.04 SH1 Return to Master TOC VENDOR CODE VCE(SAT) C5 C1 C8 C9 X2 DESCRIPTION PC BOARD BLANK CONNECTOR,EYELET,POWER,FEMALE PC BOARD SHIELD EPOXY ENCAPSULATING RESIN REFERENCES A1, A2 B11, B19, B20 B13 B14 C1 C2 C3 C4, C6, C7 C5 C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, C14, C15, C16, C17 D1, D2 D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12 DZ1 DZ2, DZ3, DZ5, DZ6 DZ4, DZ7 J40 L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, L6, L7, L8, L9, L10 OCI1 R1 R2 R3, R8 R4, R13, R14, R17, R18, R19, R20, R21, R23, R24, R25, R26, R27 R5, R9 R6 R7 R10, R12, R15 R11 R16, R22 R28, R29, R30, R31, R32 SH1 T1 T2 X1 X2 QTY 2 3 1 1 1 1 1 3 1 PART NUMBER M21214-2 T9147-15 S24866 S23006 S20500-14 S16668-11 S16668-5 S16668-6 S13490-93 DESCRIPTION ELECTRONIC MODULE,5-T12704-84 IGBT'S CONNECTOR,EYELET,POWER,MALE BRACKET,POWER-HOLDER CONNECTOR,TERMINAL,POWER CAPACITOR,PPMF,.022,100V,BOX,5% CAPACITOR,CEMO,0.1, 50V,10% CAPACITOR,CEMO,.022,50V,20% CAPACITOR,CEMO,4700pF,50V,10% CAPACITOR,TAEL,27,35V,10% 10 S20500-1 CAPACITOR,PPMF,0.1,1000V,10%,BOX 2 T12705-44 DIODE,AXLDS,1A,1000V,FR, 818 10 T12705-32 DIODE,TO220,15A,600V,FR,MUR1560 1 4 2 1 T12702-4 T12702-29 T12702-40 S24020-6 ZENER DIODE,1W,20V,5%,1N4747A ZENER DIODE,1W,15V,5%,1N4744A ZENER DIODE,1W,6.2V,5%,1N4735A CONNECTOR,MOLEX,MINI,PCB,6-PIN,TIN 10 T12218-15 CHOKE,RF,FERRITE BEAD,180 OHM 1 1 1 2 S15000-22 S16296-5 S19400-6811 S19400-1002 OPTOCOUPLER,PHOTO-Q,70V,CNY17-3/VDE TRIMMER,MT,1/2W,10K, 10%,LINEAR RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,6.81K,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,10.0K,1% 13 S19400-10R0 RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,10.0,1% 2 1 1 3 1 2 5 1 1 1 1 1 S19400-2001 S19400-2213 S19400-1000 S19400-1003 S19400-6191 S19400-1001 T14648-9 S24869-1 T12737-7 M19612 M13552-3 S15128-10 RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,2.00K,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,221K,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,100,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,100K,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,6.19K,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,1.00K,1% RESISTOR,WW,5W,2.5K,5%,SQ PC BOARD SHIELD,0.75 X 1.35 TRANSFORMER,PULSE,3-WINDING CURRENT-TRANSDUCER,125-TURN IC,CONVERTER,V/F,654 VOLTAGE REF,ADJ, PRECISION,431I .30 +.12 -.00 C2 D1 R4 C10 C11 C12 B11 11/12 OR 15/16 Return to Section TOC e.g. M21214-2 X XX XXX...... N.X. BOTH P.C. BOARD SHIELDS SOLDER INTO THE SAME MOUNTING HOLES. ITEM 3 IS MOUNTED ON NON-COMPONENT SIDE OF P.C. BOARD. PART NUMBER G3734-E T9147-11 S24869-2 E2527 REFER TO ELECTRONIC COMPONENT DATABASE FOR SPECIFICATIONS ON ITEMS LISTED BELOW (SEE ELECTRONIC FILE FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION) N.D. FEMALE EYELET TO BE AGAINST THE COPPER SIDE AS SHOWN. EYELET MUST NOT SPIN AFTER CLINCHING. QTY 1 3 1 280 g. X1 R9 R2 R8 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 R10 R1 R3 R11 C3 R12 A1 R5 R15 DZ3 OCI1 DZ2 C6 DZ4 L4 L3 L2 R16 L1 N.H. R13 R17 C4 R18 R6 R19 R7 R20 DZ1 B20 20 L5 R21 DZ5 R 1.62 C7 T1 DZ6 3.00 R30 R29 R28 R14 R26 R25 R24 L10 L9 L8 L7 N.M., N.S.,N.Q. N.E. (3 PLACES) J40 R23 L6 R22 D2 B14 SWITCH G3734-3 1 A2 T2 B13 D8 D9 D10 D11 D12 R32 N.Q. C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 Return to Master TOC R27 2 R31 B19 19 Return to Section TOC DZ7 .30 +.12 -.00 0 N.W. N.W. .00 1.20 1.38 +.12 -.00 N.T.,N.U.,N.V. 2.00 ±.12 11.15 ±.04 MAKE PER E1911-ROHS POT PER E1911-E TEST PER E3901-SW NON COMPONENT SIDE ENCAPSULATION SCHEMATIC REFERENCE: L11385-3E0 MANUFACTURED AS: G3734-3E0 { ALL COMPONENTS AND MATERIALS USED IN THIS ASSEMBLY ARE TO BE RoHS COMPLIANT PER E4253. P.C. BOARD FOR PARTS ORDERS OR SUBSIDIARY ORDERS INCLUDE ONE G3010PRINT, ONE M19661PRINT, ONE S25254PRINT AND ONE T12837-1. N.W. COMPONENT SIDE ENCAPSULATION THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED PROPRIETARY & CONFIDENTIAL: TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED TOLERANCE MANUFACTURING TOLERANCE PER E2056 DESIGN INFORMATION ON 2 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .02 ON 3 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .002 DRAWN BY: ON ALL ANGLES IS ± .5 OF A DEGREE MATERIAL TOLERANCE (" t ") TO AGREE WITH PUBLISHED STANDARDS. ENGINEER: DO NOT SCALE THIS DRAWING APPROVED: FEI REFERENCE: G3734-2 SCALE: - 1:1 INVERTER WELDERS SWITCH P.C. BD ASSEMBLY EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: UF APPROVAL DATE: PROJECT NUMBER: CRM34409 1 1 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT NUMBER: G3734-3 DOCUMENT REVISION: B.01 SOLID EDGE Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC IDENTIFICATION CODE STRP NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-28 SCHEMATIC - VOLTAGE SENSE PC BOARD (ROBOTIC MODEL ONLY) (S24779-3) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-28 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC PC BOARD ASSEMBLY - VOLTAGE SENSE PC BOARD (ROBOTIC MODEL ONLY) (M19540-3) CHANGE DETAIL: REVISED MAKE SPECIFICATION ENGINEERING CONTROLLED MANUFACTURER: No N.A. N.A. P.C. BOARD BLANK INFORMATION BUY COMPLETE AS M19540-C ( 2 LAYER BOARD PER E3281) Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC G-29 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS M19540-3 Return to Section TOC G-29 ITEM REQD C1 D1 1 1 S20500-4 T12199-1 .0047 1000V 1N4004 J1 J2 L1 1 1 1 S24020-6 S24020-2G T12218-7 HEADER HEADER 330uH OCI1,OCI2 R1,R2 R3 TP1,TP2 2 2 1 2 S15000-20 S19400-4750 S18380-1 T13640-18 PHOTO FET 475 1/4W THERMISTOR,PTC 160J PART NO. IDENTIFICATION CAPACITORS = MFD/VOLTS RESISTORS = OHMS INDUCTANCE = HENRYS (MAKES 54 BOARDS PER PANEL, SEE ELECTRONIC FILE FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION) ITEM 1 REQD 1 PART NO. SEE BLANK INFO DESCRIPTION P.C. BOARD BLANK SCHEMATIC REFERENCE: S24779-3CO N.A. DO NOT COAT WITH ENCAPSULATION MATERIAL. .20 N.B. DO NOT COAT WITH ENCAPSULATION MATERIAL .23 MIN. DIA. (3 PLACES) ON NON COMPONENT SIDE. 1.80 N.A. 1.75 1.55 M19540-3 0 J2 TP1 R2 TP2 C1 L1 R1 1.00 MAKE PER E1911-ROHS ENCAPSULATE WITH E1844 (2 DIPS) TEST PER E3689-VS D1 R3 MANUFACTURED AS OCI1 .20 0 VOLTAGE SENSE SELECT J1 OCI2 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC ±.04 N.B. ±.04 2.00 M19540-3CO } IDENTIFICATION CODE ALL COMPONENTS AND MATERIALS USED IN THIS ASSEMBLY ARE TO BE RoHS COMPLIANT PER E4253. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED TOLERANCE MANUFACTURING TOLERANCE PER E2056 DESIGN INFORMATION REFERENCE: ON 2 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .02 FEI M19540-2 SCALE: - 1:1 ON 3 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .002 DRAWN BY: ON ALL ANGLES IS ± .5 OF A DEGREE MATERIAL TOLERANCE (" t ") TO AGREE WITH PUBLISHED STANDARDS. ENGINEER: DO NOT SCALE THIS DRAWING APPROVED: EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: UF COMMON DIGITAL CONTROLS VOLTAGE SENSE PC BRD AS'BLY APPROVAL DATE: PROJECT NUMBER: CRM34409 1 1 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT NUMBER: M19540-3 DOCUMENT REVISION: C.01 SOLID EDGE Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED PROPRIETARY & CONFIDENTIAL:THIS TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. STRP NOTE: Lincoln Electric assumes no responsibility for liablilities resulting from board level troubleshooting. PC Board repairs will invalidate your factory warranty. Individual Printed Circuit Board Components are not available from Lincoln Electric. This information is provided for reference only. Lincoln Electric discourages board level troubleshooting and repair since it may compromise the quality of the design and may result in danger to the Machine Operator or Technician. Improper PC board repairs could result in damage to the machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT Return to Master TOC ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS G-30 SCHEMATIC - 40 VDC BUS PC BOARD (ALL CODES) (M19330-2) Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC Return to Section TOC G-30 NOTE: This diagram is for reference only. It may not be accurate for all machines covered by this manual. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT ENGINEERING CONTROLLED MANUFACTURER: No CHANGE DETAIL: REVISED MAKE SPECIFICATION P.C. BOARD BLANK INFORMATION BUY COMPLETE AS L11078-C (4 LAYER BOARD PER E3281) MAKES 12 BOARDS PER PANEL. PANEL SIZE PER E1911. (SEE ELECTRONIC FILE FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION) Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC .37 MIN. POTTING DIMENSIONS .13 TYP. N.C. N.F. 3.85 ±.04 N.C. DC BUSS 4.30 L11078-2 REFERENCE N.A., N.B., N.D. A1 C1 C2, C3, C5 C6 C7, C8, C9, C10 C11, C17 C13 C14 C15 C16 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 DZ4 DZ5, DZ6 J46 J47 L1 LED1 MOV1 R3, R4, R5, R7, R8 R9, R10, R11 R12, R13 R14, R22 R15, R16 R19 R20, R21 R23 R25 R26, R27 R28 R29 N.A. X1 N.A. X2 3.65 J47 ITEM 1 3 4 C13 L1 C2 R20 C16 DZ5 R16 R15 C7 C8 R29 D4 0 .20 C5 N.E. 4.50 ±.04 1 PART NO. DESCRIPTION SEE BLANK INFO. P.C. BOARD BLANK E2527 EPOXY ENCAPSULATION RESIN E2861 SEALANT MANUFACTURED AS: ALL COMPONENTS AND MATERIALS USED IN THIS ASSEMBLY ARE TO BE RoHS COMPLIANT PER E4253. L11078-2C0 } MAKE PER E1911-ROHS POT PER E1911-E TEST PER E3862 SCHEMATIC REFERENCE - M19330-2C0 DZ4 C6 D2 X2 C10 R12 C9 X1 R14 R13 R25 R10 C11 R21 C14 R9 D3 R23 C17 DZ6 C1 C3 .20 0 REQ'D 1 100 g. .75 oz. N.A. CAUTION: THIS DEVISE IS SUBJECT TO DAMAGE BY STATIC ELECTRICITY. SEE E2454 BEFORE HANDLING. N.B. COVER EXPOSED BOTTOM SURFACE OF ELECTRONIC MODULE TO AVOID POTTING MATERIAL BUILD UP. N.C. MOLEX CAVITIES AND AREA AROUND TAB TO BE FREE OF POTTING MATERIAL. MASK PER APPROPRIATE MANUFATURING WORK INSTRUCTIONS. N.D. ELECTRONIC MODULES TO BE ASSEMBLED AND ENCAPSULTED PER E3875. N.E. COMPLETELY COVER EXPOSED LEADS AND BODY OF R25 RESISTOR WITH ITEM 4 SEALANT. N.F. COVER EXPOSED LEADS OF C15 CAPACITOR WITH ITEM 4 SEALANT. D1 R27 D5 DESCRIPTION ELECTRONIC MODULE,2 MOSFETS(T12704-71)WITH 1DIO CAPACITOR,TAEL,27,35V,10% CAPACITOR,TAEL,4.7,35V 10% CAPACITOR,TAEL,47,35V 10% CAPACITOR,CEMO,0.1, 50V,10% CAPACITOR,CEMO,4700P, 50V,2% CAPACITOR,PPMF,0.47,630V,10%,BOX CAPACITOR,CEMO,100P, 100V,5% CAPACITOR,ALEL,470,100V,+50/-10%, LOW PROFILE CAPACITOR,TAEL,1.0,35V,10% DIODE,AXLDS,1A,1000V DIODE,AXLDS,1A,400V DIODE,AXLDS,3A,600V,UFR DIODE,SCHOTTKY,AXLDS,1A,30V,1N5818 DIODE,AXLDS,1A,400V,FR,1N4936 ZENER DIODE,5W,20V,5% 1N5357B ZENER DIODE, 1W,18V,5% 1N4746A CONNECTOR,MOLEX,MINI,PCB,4-PIN,TIN CONNECTOR,MOLEX,MINI,PCB,8-PIN,TIN CHOKE,HIGH-CURRENT,100UH,10A,10%, LOW PROFILE LED,T-1,3/4,RED,HLMP-3003 MOV,50VRMS,15J,14MM RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,10.0K,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,8.25K,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,100,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,1.82K,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,47.5,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,56.2K,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,26.7K,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,221K,1% RESISTOR,WW,5W,270,5%,SQ RESISTOR,WW,3W,0.05,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,47.5K ,1% RESISTOR,MF,1/4W,332K,1% IC,PWM-CONTROLLER,IMODE,2842A IC,CMOS,DRIVER,MOSFET,2110(SS) 1A R11 R3 R22 R19 Return to Master TOC Return to Section TOC R26 C15 MOV1 R7 R8 R28 PART NO. M21214-6 S13490-93 S13490-25 S13490-66 S16668-11 S16668-10 S20500-2 S16668-3 S13490-174 S13490-42 T12199-2 T12199-1 T12705-59 T12705-23 T12705-34 T12702-25 T12702-45 S24020-4 S24020-8 T12218-16 T13657-2 T13640-15K S19400-1002 S19400-8251 S19400-1000 S19400-1821 S19400-47R5 S19400-5622 S19400-2672 S19400-2213 T14648-17 T12300-86 S19400-4752 S19400-3323 M15458-4 S15018-16 CAPACITOR = MFD/VOLTS RESISTORS = OHMS, 1/4 WATT (UNLESS OTHERSIDE SPECIFIED) J46 LED1 R4 R5 QTY 1 1 3 1 4 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 5 3 2 2 2 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 IDENTIFICATION CODE Return to Master TOC FOR PARTS ORDERS ONLY: INCLUDE (1) S25191PRINT AND (1) T12837-1 DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OWNED BY LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. AND MAY NOT BE DUPLICATED, COMMUNICATED PROPRIETARY & CONFIDENTIAL:THIS TO OTHER PARTIES OR USED FOR ANY PURPOSE WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN PERMISSION OF LINCOLN GLOBAL, INC. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED TOLERANCE MANUFACTURING TOLERANCE PER E2056 DESIGN INFORMATION REFERENCE: ON 2 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .02 L11078-1 SCALE: ON 3 PLACE DECIMALS IS ± .002 DRAWN BY: ON ALL ANGLES IS ± .5 OF A DEGREE MATERIAL TOLERANCE (" t ") TO AGREE WITH PUBLISHED STANDARDS. ENGINEER: DO NOT SCALE THIS DRAWING APPROVED: FEI - NONE EQUIPMENT TYPE: SUBJECT: MATERIAL DISPOSITION: UF MULTI-WELD 350 40V DC BUS P.C. BOARD ASSEMBLY APPROVAL DATE: PROJECT NUMBER: CRM34409 1 1 OF ___ PAGE ___ DOCUMENT NUMBER: L11078-2 DOCUMENT REVISION: B.01 SOLID EDGE Return to Master TOC PC BOARD ASSEMBLY - 40 VDC BUS PC BOARD (ALL CODES) (L11078-2) .50 MAX. Return to Section TOC G-31 ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS L11078-2 Return to Section TOC G-31 STRP NOTE: Lincoln Electric assumes no responsibility for liablilities resulting from board level troubleshooting. PC Board repairs will invalidate your factory warranty. Individual Printed Circuit Board Components are not available from Lincoln Electric. This information is provided for reference only. Lincoln Electric discourages board level troubleshooting and repair since it may compromise the quality of the design and may result in danger to the Machine Operator or Technician. Improper PC board repairs could result in damage to the machine. POWER WAVE 455M/MSTT