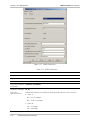
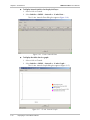
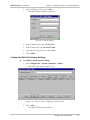
Download RAD Data comm FCD-IP User`s manual
Transcript
RADview-TDM Element Management System for TDM Applications FCD-IP © 1994–2004 RAD Data Communications Publication 12/04 Contents Chapter 1. Introduction 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Overview..................................................................................................................... 1-1 Introducing RADview FCD-IP ...................................................................................... 1-1 The FCD-IP Workplace................................................................................................ 1-2 Edit and Agent Views ................................................................................................... 1-3 LEDs............................................................................................................................ 1-3 Chapter 2. System Management 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Selecting the System Level ........................................................................................... 2-1 Viewing and Modifying System Configuration .............................................................. 2-2 Setting Bridging Parameters.......................................................................................... 2-3 Routing the IP.............................................................................................................. 2-5 Forwarding Table.................................................................................................................. 2-5 Address Resolution Protocol Table ........................................................................................ 2-7 IP Address Table ................................................................................................................... 2-8 2.5 OSPF ......................................................................................................................... 2-10 Configuring OSPF ............................................................................................................... 2-10 OSPF Information ............................................................................................................... 2-14 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 2.10 2.11 Viewing the Connection Status .................................................................................. 2-18 Configuring the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) .................................. 2-19 Resetting the Device .................................................................................................. 2-21 Polling the Agent ....................................................................................................... 2-22 Configuring SNMP ..................................................................................................... 2-22 Switching Between Edit and Agent View .................................................................... 2-23 Chapter 3. Port Management 3.1 Edit and Agent Views ................................................................................................... 3-1 3.2 Configuring Interface Information ................................................................................ 3-1 Configuring E1/T1, CHANNEL, ISDN, and Voice Interface Information .................................. 3-1 Configuring SHDSL Interface Information.............................................................................. 3-4 Configuring E1/T1 over SHDSL Interface Information ............................................................ 3-6 Configuring LAN Interface Information .................................................................................. 3-9 3.3 Configuring Physical Parameters ................................................................................ 3-10 Configuring Async Link (V.24) Physical Parameters .............................................................. 3-10 Configuring ISDN Physical Parameters................................................................................. 3-13 Configuring E1/T1 Link Mode.............................................................................................. 3-16 Configuring General E1/T1 Physical Parameters ................................................................... 3-17 Configuring E1/T1 Time Slot (TS) Assignments ..................................................................... 3-19 Reading the E1/T1 Configuration from the Agent ................................................................. 3-22 Updating the E1/T1 Configuration in the Agent ................................................................... 3-22 Configuring SHDSL Physical Parameters .............................................................................. 3-23 Configuring SHDSL Status Parameters ................................................................................. 3-25 Configuring Voice Interface Physical Parameters.................................................................. 3-26 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual i Table of Contents 3.4 Configuring Protocol Parameters................................................................................ 3-29 Configuring Frame Relay Protocol Parameters ..................................................................... 3-29 Configuring the DLCI Table................................................................................................. 3-30 Configuring PPP Parameters ................................................................................................ 3-32 3.5 Configuring Network Parameters ............................................................................... 3-34 Configuring IP Addresses..................................................................................................... 3-34 Configuring the IP Routing Protocol .................................................................................... 3-35 Configuring the IP RIP Mode............................................................................................... 3-36 Configuring DHCP Relay..................................................................................................... 3-37 3.6 Resetting the Link ...................................................................................................... 3-37 3.7 Performing Diagnostic Tests ....................................................................................... 3-38 Chapter 4. Fault Management 4.1 Edit and Agent Views ................................................................................................... 4-1 4.2 Displaying Sanity Check Errors (E1/T1 Link) ................................................................. 4-1 4.3 Displaying SHDSL Alarms ............................................................................................ 4-2 Chapter 5. Performance 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Edit and Agent Views ................................................................................................... 5-1 Setting the Polling Interval............................................................................................ 5-2 Performing Diagnostic Tests ......................................................................................... 5-2 Displaying E1/T1 Statistics............................................................................................ 5-3 Packets Data Statistics ........................................................................................................... 5-3 Packets Graph Statistics......................................................................................................... 5-4 Physical Layer Statistics ......................................................................................................... 5-6 Protocol Layer Statistics......................................................................................................... 5-9 5.5 Displaying E1 Over SHDSL Statistics .......................................................................... 5-12 Physical Layer Statistics ....................................................................................................... 5-12 5.6 Displaying Ethernet LAN Statistics .............................................................................. 5-15 Chapter 6. Configuring FCD-IP for a Typical Application 6.1 Overview..................................................................................................................... 6-1 Application ........................................................................................................................... 6-1 6.2 Configuring WAN Parameters ...................................................................................... 6-2 Configuring the WAN Interface ............................................................................................. 6-2 Configuring the WAN IP Address .......................................................................................... 6-3 6.3 Configuring the E1 Interface......................................................................................... 6-4 Configuring E1 Parameters .................................................................................................... 6-4 Mapping E1Timeslots ............................................................................................................ 6-5 6.4 Configuring the LAN Interface...................................................................................... 6-5 Enabling the LAN.................................................................................................................. 6-5 Configuring the LAN IP Address ............................................................................................6-6 Configuring Default Gateway Settings.................................................................................... 6-7 ii RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Table of Contents List of Figures 1-1. FCD-IP Main Window........................................................................................................... 1-2 1-2. Password Dialog .................................................................................................................... 1-3 2-1. FCD-IP Main Window........................................................................................................... 2-1 2-2. System Information ............................................................................................................... 2-2 2-3. Static Forwarding Table ......................................................................................................... 2-3 2-4. Add Static Entry..................................................................................................................... 2-4 2-5. IP Forwarding Table .............................................................................................................. 2-5 2-6. ARP Stations Table ................................................................................................................ 2-7 2-7. IP Addresses Table................................................................................................................. 2-8 2-8. Add IP Address...................................................................................................................... 2-9 2-9. Change IP Address ................................................................................................................ 2-9 2-10. OSPF Parameters (Enable) ................................................................................................. 2-10 2-11. OSPF Parameters (Disable) ................................................................................................ 2-11 2-12. OSPF Area Table ............................................................................................................... 2-12 2-13. OSPF Area Aggregation Table ............................................................................................ 2-13 2-14. Add Area Aggregation........................................................................................................ 2-14 2-15. Interfaces Table ................................................................................................................. 2-15 2-16. Neighbors Table ................................................................................................................ 2-16 2-17. Database Table ................................................................................................................. 2-17 2-18. All Links Connections List .................................................................................................. 2-18 2-19. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Table ...................................................................... 2-19 2-20. Add DHCP Entry ............................................................................................................... 2-20 2-21. Change DHCP Entry.......................................................................................................... 2-21 2-22. Reset Brouter .................................................................................................................... 2-21 2-23. Manager List...................................................................................................................... 2-22 2-24. Password Dialog Box ......................................................................................................... 2-23 3-1. Interface Information Info Tab ............................................................................................... 3-2 3-2. Interface Information Link Data Tab ...................................................................................... 3-3 3-3. Interface Information Info Tab for E1/T1 over SHDSL ............................................................ 3-6 3-4. Interface Information Link Data Tab for E1/T1 over SHDSL ................................................... 3-7 3-5. Interface Information – Ethernet LAN .................................................................................... 3-9 3-6. Async Link Parameters Dialog Box....................................................................................... 3-11 3-7. Add New Modem Dialog Box.............................................................................................. 3-12 3-8. ISDN Parameters – Interface Tab......................................................................................... 3-13 3-9. ISDN Parameters –Terminal End Point Tab.......................................................................... 3-14 3-10. ISDN Parameters -Channel Tab ......................................................................................... 3-15 3-11. E1/T1 Link Mode............................................................................................................... 3-16 3-12. General Link Parameters (E1/T1 Ports) ............................................................................... 3-17 3-13. TS Assignment ................................................................................................................... 3-19 3-14. TS Assignment (New HW) ................................................................................................. 3-20 3-15. Read Configuration ........................................................................................................... 3-22 3-16. Update Configuration........................................................................................................ 3-23 3-17. SHDSL Parameters ............................................................................................................ 3-24 3-18. SHDSL Status .................................................................................................................... 3-25 3-19. Voice Parameters Dialog Box............................................................................................. 3-26 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual iii Table of Contents 3-20. FR Parameters ................................................................................................................... 3-29 3-21. DLCI Table........................................................................................................................ 3-31 3-22. Add DLCI .......................................................................................................................... 3-32 3-23. PPP Protocol ..................................................................................................................... 3-32 3-24. IP Address ......................................................................................................................... 3-34 3-25. IP Routing Protocol Dialog Box........................................................................................... 3-35 3-26. IP RIP Mode Dialog Box .................................................................................................... 3-36 3-27. DHCP Relay Parameters.................................................................................................... 3-37 3-28. Testing .............................................................................................................................. 3-38 4-1. Sanity Check Errors List ......................................................................................................... 4-2 4-2. SHDSL Alarms....................................................................................................................... 4-2 5-1. Polling Interval....................................................................................................................... 5-2 5-2. Testing .................................................................................................................................. 5-2 5-3. Link Statistics ......................................................................................................................... 5-3 5-4. Link Packets .......................................................................................................................... 5-4 5-5. Link Octets............................................................................................................................ 5-5 5-6. Link Error Frames .................................................................................................................. 5-5 5-7. E1 Link Statistics .................................................................................................................... 5-6 5-8. Current Graph Statistics ......................................................................................................... 5-7 5-9. Errors Statistics Intervals ......................................................................................................... 5-7 5-10. Intervals Graph.................................................................................................................... 5-8 5-11. FR Error Statistics ................................................................................................................. 5-9 5-12. DLCI Statistics ................................................................................................................... 5-10 5-13. 15 min. Current Data ........................................................................................................ 5-12 5-14. 15 min. Current Graph...................................................................................................... 5-13 5-15. 1-Day Current Data........................................................................................................... 5-13 5-16. 15 min. Intervals Data ....................................................................................................... 5-14 5-17. 15 min. Intervals Graph..................................................................................................... 5-14 5-18. LAN General ..................................................................................................................... 5-15 5-19. LAN Errors Statistics........................................................................................................... 5-16 5-20. LAN Packets ...................................................................................................................... 5-18 5-21. LAN Octets ....................................................................................................................... 5-18 5-22. ETH Error Frames .............................................................................................................. 5-19 5-23. ETH Tx & Rx Errors............................................................................................................ 5-19 5-24. ETH FCS & Test Errors ....................................................................................................... 5-20 5-25. LAN Collisions ................................................................................................................... 5-20 6-1. FCD-IP Providing Access to the Internet and to the PSTN ...................................................... 6-1 6-2. WAN Interface Information Link Data Tab............................................................................. 6-2 6-3. IP Addresses Table................................................................................................................. 6-3 6-4. Add IP Address...................................................................................................................... 6-3 6-5. The E1 Link Parameters ......................................................................................................... 6-4 6-6. TS Assignment ....................................................................................................................... 6-5 6-7. Interface Information - Ethernet LAN ..................................................................................... 6-6 6-8. IP Addresses Table................................................................................................................. 6-6 6-9. Add IP Address...................................................................................................................... 6-7 6-10. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Table ........................................................................ 6-7 6-11. Add DHCP Entry Table........................................................................................................ 6-8 iv RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Table of Contents List of Tables 1-1. FCD-IP LEDs ......................................................................................................................... 1-3 2-1. System Information Parameters ............................................................................................. 2-2 2-2. Static Forwarding Table Parameters ....................................................................................... 2-4 2-3. IP Forwarding Parameters...................................................................................................... 2-6 2-4. ARP Stations Parameters........................................................................................................ 2-7 2-5. IP Address Parameters ........................................................................................................... 2-8 2-6. OSPF Parameters................................................................................................................. 2-11 2-7 OSPF Area Table Parameters ................................................................................................. 2-12 2-8 OSPF Area Aggregation Parameters ....................................................................................... 2-13 2-9. Interfaces Parameters .......................................................................................................... 2-15 2-10. Neighbors Parameters ....................................................................................................... 2-16 2-11. Database Parameters ......................................................................................................... 2-17 2-12. All Links Connections Parameters ...................................................................................... 2-18 2-13. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Parameters ............................................................. 2-19 2-14. Manager List Parameters.................................................................................................... 2-23 3-1. Info Tab Parameters for E1/T1, CHANNEL, ISDN, and Voice................................................. 3-2 3-2. Interface Information Link Data Tab Parameters .................................................................... 3-3 3-3. Info Tab Parameters for SHDSL ............................................................................................. 3-5 3-4. Interface Information Link Data Tab Parameters for SHDSL ................................................... 3-5 3-5. Info Tab Parameters for E1/T1 over SHDSL............................................................................ 3-7 3-6. Interface Information Link Data Tab Parameters for E1/T1 over SHDSL ................................. 3-8 3-7. Interface Information – Ethernet LAN Parameters .................................................................. 3-9 3-8. Async Link Parameters......................................................................................................... 3-11 3-9. Add New Modem Parameters ............................................................................................. 3-12 3-10. ISDN Parameters – Interface Tab....................................................................................... 3-13 3-11. ISDN Parameters – Terminal End Point Tab....................................................................... 3-14 3-12. ISDN Parameters -Channel Tab ......................................................................................... 3-15 3-13. E1/T1 Link Mode............................................................................................................... 3-16 3-14. General Link Parameters (E1/T1 Ports) ............................................................................... 3-17 3-15. SHDSL Parameters ............................................................................................................ 3-24 3-16. SHDSL Status Parameters .................................................................................................. 3-26 3-17. Voice Parameters .............................................................................................................. 3-26 3-18. Protocol Options per Interface and Link Types .................................................................. 3-29 3-19. FR Parameters ................................................................................................................... 3-30 3-20. DLCI Table Parameters...................................................................................................... 3-31 3-21. PPP Protocol Parameters ................................................................................................... 3-33 3-22. IP Address Parameters ....................................................................................................... 3-34 3-23. IP Routing Protocol Parameters ......................................................................................... 3-35 3-24. IP RIP Mode Parameters.................................................................................................... 3-36 3-25. DHCP Relay Parameters.................................................................................................... 3-37 3-26. Testing Parameters ............................................................................................................ 3-38 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual v Table of Contents 5-1. 5-2. 5-3. 5-4. 5-5. 5-6. 5-7. 5-8. Testing Parameters – E1/T1.................................................................................................... 5-3 Link Statistic Parameters ........................................................................................................ 5-4 Link Statistic Parameters ........................................................................................................ 5-6 FR Error Statistics Parameters ............................................................................................... 5-10 DLCI Statistics Parameters ................................................................................................... 5-11 15 min, Current Data Parameters ........................................................................................ 5-12 LAN General ....................................................................................................................... 5-15 LAN Errors Statistics Parameters........................................................................................... 5-16 6-1. Configuration Summary......................................................................................................... 6-2 vi RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview This chapter describes the RADview management application for FCD-IP, and includes the following sections: • Introducing RADview FCD-IP • The FCD-IP Workplace. 1.2 Introducing RADview FCD-IP RADview FCD-IP enables you to monitor and manage FCD-IP. FCD-IP is an E1/T1 or E1/T1 over SHDSL, fractional integrated access device (IAD), which enables service providers to bundle data, voice and IP access services over a single E1 or T1 access line. Additionally, FCD-IP can be used for management applications in cellular or SDH environments. An integrated router supports IP/IPX routing and transparent bridging. The FCD-IP supports an optional internal 4-port Ethernet/Fast Ethernet switch, which can be installed in place of the LAN ports. Introducing RADview FCD-IP 1-1 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 1 Introduction 1.3 The FCD-IP Workplace The RADview FCD-IP main window displays FCD-IP front and back panels, including all LEDs and interfaces. You can select most of the displayed interfaces in each section, or select the entire device for system configuration. A blue border marks the selected item. Note To select the device itself, click on any area outside of the ports. Figure 1-1. FCD-IP Main Window When an interface is selected, two views are available: • Edit View (Edit mode) is used for configuring the interface. When configuring the interface, the configuration is stored in the management station until you update the device. When you update the device, the configuration is saved on the device itself. • Agent View (Agent mode) displays the current state of the interface. The current mode is indicated by “E.#” or “A.#” at the top-left of the dialog box. The menus and the available menu options vary, depending on the item selected in the main window (the device or one of its ports), and the current mode (Edit or Agent). Certain actions can only be performed in one of the modes. For example, the link mode can be configured only in the Edit mode and switching traffic between links can only be performed in Agent mode. 1-2 The FCD-IP Workplace RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Edit and Agent Views Note Certain TDM ports can be displayed in both Edit and Agent Views. Configuration is performed in the Edit mode. In Agent View, the parameters are Read-Only. To switch between Edit and Agent views: 1. Select the appropriate Link. 2. Switch the view by doing one of the following: Click the Edit/Agent View button on the toolbar or From the Window menu, select Edit View/Agent View to switch to Edit/Agent View. 3. When entering Edit View, you must enter the password. Type the password in the field provided and click <Set>. Figure 1-2. Password Dialog 1.5 LEDs Table 1-1 describes the device LEDs. Table 1-1. FCD-IP LEDs Object Description Function PWR Green LED ON when the device is powered on. READY Green LED ON when the packets can be transferred. LAN1 DATA LAN2 DATA Yellow LED ON when a packet is received or transmitted on the LAN side. LAN1 ERR LAN2 ERR Red LED ON when a LAN interface indicates an error. LINK 1 DATA LINK 2 DATA Yellow LED Turns ON briefly when a packet is received or transmitted on the LINK side. Blinks constantly to show ISDN link integrity. LEDs 1-3 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 1 Introduction Table 1-1. FCD-IP LEDs (Cont.) Object Description Function LINK1 ERR LINK2 ERR Red LED OFF when there is a physical connection and no LINK interface error. Turns ON briefly when the LINK interface indicates an error. Continuously ON when there is no physical connection. LAN 1 LAN 2 (Back Panel, UTP only) Green LED ON when synchronized with the network. FX0 & FXS: VOICE 1 LOCAL VOICE 2 LOCAL VOICE 3 LOCAL VOICE 4 LOCAL Green LED On when the device is OFF hook. FX0 & FXS: VOICE 1 REMOTE VOICE 2 REMOTE VOICE 3 REMOTE VOICE 4 REMOTE Green LED On when the remote side is calling. E&M VOICE 1M LOCAL VOICE 2M LOCAL VOICE 3M LOCAL VOICE 4M LOCAL Yellow LED Mouth E&M VOICE 1M REMOTE VOICE 2M REMOTE VOICE 3M REMOTE VOICE 4M REMOTE Green LED Ear Fast ETH - LINK (1 UTP LAN) Top Green LED ON when synchronized with the network. Fast ETH - 100M (1 UTP LAN) Bottom Green LED ON when synchronized with the network. Fast ETH - LINK (4 UTP LANS) Left Green LED ON when synchronized with the network. Fast ETH - 100M (4 UTP LANS) Right Green LED ON when synchronized with the network. ALARM LINK1 RED SUB RED Red LED ON when T1 link is in Red alarm. ALARM LINK1 YEL SUB YEL Yellow LED ON when T1 link is in YELLOW alarm. 1-4 LEDs RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 1 Introduction Table 1-1. FCD-IP LEDs (Cont.) Object Description Function SYNCH LOSS LINK1 LOC SUB1/LINK2 LOC SUB2 LOC SUB3 LOC Red LED ON when E1 link is in local sync loss alarm. SYNCH LOSS LINK1 REM SUB1/LINK2 REM SUB2 REM SUB3 REM Red LED ON when E1 link is in remote sync loss alarm LEDs 1-5 Chapter 1 Introduction 1-6 LEDs RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management This chapter discusses how to monitor and configure the FCD-IP system. Managing the FCD-IP system includes the following tasks: • Selecting the System Level • Viewing and Modifying FCD-IP System Configuration • Setting Bridging Parameters • Routing the IP • Viewing the Connection Status • Configuring the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) • Resetting the Device • Polling the Agent • Configuring SNMP • Switching Between Edit and Agent View. 2.1 Selecting the System Level To select the system level: • Click on the outside frame of the device window. A blue border outlines the entire device. Figure 2-1. FCD-IP Main Window Selecting the System Level 2-1 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management 2.2 Viewing and Modifying System Configuration RADview enables you to view and modify the configuration of the FCD-IP. To view or modify FCD-IP system information: 1. Select Configuration > System Info... or click the shortcut key on the toolbar . The System Information dialog box appears (See figure below). Figure 2-2. System Information 2. Enter the required settings. You can change the following fields: Name, Contact, Location, Aging (minutes allowed for station to be inactive without being removed from the network) and Enable Broadcast Control. 3. Click<Set>to implement the changes. Table 2-1. System Information Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Description Description of hardware and software. Object ID Device type. Name Meaningful name assigned to this device. Contact Name of contact person responsible for device. Location Location of this device. 2-2 Viewing and Modifying System Configuration RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management Table 2-1. System Information Parameters (Cont.) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks System Up Time Length of time since last power-up of device. Aging (Min) IP aging time for the station. Enable Broadcast Control Enables blocking or forwarding broadcast frames. Block: blocks broadcast frames. Forward: forwards broadcast frames. Block Link Propagation: blocks broadcast frames to the links, transmitting to the LAN. Number of Interfaces Number of interfaces this device contains. 2.3 Setting Bridging Parameters RADview enables you to add and remove addresses from the static portion of the LAN table. To add/remove addresses to the Static Table: • Select Configuration > Bridging > Static Forwarding…. The Static Forwarding Table appears (Figure 2-3). Figure 2-3. Static Forwarding Table Setting Bridging Parameters 2-3 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management Table 2-2. Static Forwarding Table Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks MAC Address The physical address of the device. Interface The selected interface. DLCI# Data Link Control Identifier Only for links with FR protocol type. [Add…] Click <Add…> to open the Add IP Net Entry dialog box (Figure 2-4). Enter the desired parameters and click <Set>. [Remove] Remove an address from the Static Forwarding Table by selecting an address and clicking <Remove>. To add a static entry: 1. In the Static Forwarding table (Figure 2-3), click <Add…>. The Add Static Entry dialog box appears (Figure 2-4). Figure 2-4. Add Static Entry 2. Configure desired parameters (see Table 2-2). 3. Click <Set>. 2-4 Setting Bridging Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management 2.4 Routing the IP Forwarding Table To display the IP Forwarding Table: • Select Configuration > IP Routing > Forwarding.... The IP Forwarding Table appears (Figure 2-5). Figure 2-5. IP Forwarding Table Routing the IP 2-5 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management Table 2-3. IP Forwarding Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks IP Address The IP address of forwarding device. IP Mask A unique 32 bit value allowing the recipient of IP packets to distinguish between different host IDs. Next Hop IP Address The IP address of the next hop. Interface The selected interface. DLCI# Data Link Control Identifier Only for links with FR protocol type. Interface Cost (Metric) The number of routers through which a packet must pass to arrive at its destination. 1..15 Type Other, Invalid, Direct, Indirect Protocol The protocol of the interface. Local indicates a local IP address NetMgnt indicates a static IP address RIP2 indicates a dynamic IP address OSPF indicates IP address is determined using OSPF protocol. Age The number of seconds since this route was last updated. [Add…] Click <Add…> to open the Add IP Net dialog box. Enter the desired parameters and click <Set>. [Remove] Remove an address from the IP Forwarding Table by selecting an address and clicking <Remove>. Only static addresses can be changed. 2-6 Routing the IP RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management Address Resolution Protocol Table To display the ARP table: • Select Configuration > IP Routing > ARP.... The ARP Stations Table appears (Figure 2-6). Figure 2-6. ARP Stations Table Table 2-4. ARP Stations Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. MAC Address The physical address of the device. Net Address The IP address of the MAC Address. Net to Media Type Other, Invalid, Dynamic, Static Routing the IP 2-7 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management IP Address Table To display the IP address table: • Select Configuration > IP Routing > IP Address.... The IP Addresses Table appears (Figure 2-7). Figure 2-7. IP Addresses Table Table 2-5. IP Address Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks IP Address The IP address of forwarding device. 1.0.0.0..255.255.255.255 IP Mask A unique 32 bit value allowing the recipient of IP packets to distinguish between different host IDs. 0.0.0.0..255.255.255.255 Interface The selected interface. DLCI# Data Link Control Identifier Only for links with FR protocol type. [Add…] Click <Add…> to open the Add IP Address dialog box (Figure 2-8). Enter the desired parameters and click <Set>. [Change…] Change an address from the IP Address Table by selecting an address and clicking <Change…>. The Change IP Address dialog box appears. Change parameters and click <Set>. [Remove] Remove an address from the IP Address Table by selecting an address and clicking <Remove>. 2-8 Routing the IP RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management To add an IP address: 1. In the IP Address Table (Figure 2-7), click <Add…>. The Add IP Address dialog box appears (Figure 2-8). Figure 2-8. Add IP Address Note When working in OSPF mode, each LAN can have only one IP address. 2. Configure desired parameters (see Table 2-3). 3. Click <Set>. To change an IP address: 1. In the IP Address Table (Figure 2-7), click <Change…>. The Change IP Address dialog box appears (Figure 2-9). Figure 2-9. Change IP Address 2. Configure desired parameters (see Table 2-3). 3. Click <Set>. Routing the IP 2-9 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management 2.5 OSPF RADview allows you to configure OSPF and view OSPF information. Configuring OSPF To enable OSPF: 1. Select Configuration > OSPF > Parameters…. The OSPF Parameters dialog box appears. Figure 2-10. OSPF Parameters (Enable) 2. In the Admin Status field, select Enable. 3. Enter the Router ID. 4. Enable or disable Redistribute Routes. 5. Click <Set> to implement the changes. The following confirmation message appears: This operation will cause Restart of the device /n Connection with Agent will be lost.” 6. Click <OK>. 2-10 OSPF RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management To disable OSPF: 1. Select Configuration > OSPF > Parameters…. The OSPF Parameters dialog box appears. Figure 2-11. OSPF Parameters (Disable) 2. In the Admin Status field, select Disable. 3. Click <Set> to implement the changes. The following confirmation message appears: “This operation will cause Restart of the device /n Connection with Agent will be lost.” 4. Click <OK>. Table 2-6. OSPF Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Admin Status Enable/Disable Router ID The IP address format. Required if OSPF is enabled. Not available is OSPF is disabled. Redistribute Routers Enable/Disable Not available is OSPF is disabled. OSPF 2-11 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management OSPF Areas To display the OSPF Area Table: • Select Configuration > OSPF > Area Table.... The OSPF Area Table appears. Figure 2-12. OSPF Area Table Table 2-7 OSPF Area Table Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks ID The IP address of the area. 1.0.0.0..255.255.255.255 Behavior Type Transit, Stub, NSSA [Change…] Change an OSFP Area behavior by selecting an ID and clicking <Change…>. The Change Area Parameters dialog box appears. Change parameters and click <Set>. To change parameters of an area: 1. In the OSPF Area Table, click <Change…>. The Change Area Parameters dialog box appears. 2. Configure desired parameters (see Table 2-7). 3. Click <Set>. OSPF Area Aggregation To display the OSPF Area Aggregation Table: • Select Configuration > OSPF > Area Aggregation.... The OSPF Area Aggregation Table appears. 2-12 OSPF RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management Figure 2-13. OSPF Area Aggregation Table Table 2-8 OSPF Area Aggregation Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Area The ID of the area. 1.0.0.0..255.255.255.255 IP The IP address of the network. 1.0.0.0..255.255.255.255 Mask A unique 32 bit value allowing the recipient of IP packets to distinguish between different host IDs. 0.0.0.0..255.255.255.255 Advertised Advertising matching is enabled/disabled. [Add…] Click <Add…> to open the Add Area Aggregation dialog box (Figure 2-8). Enter the desired parameters and click <Set>. [Change…] Change an address from the Area Aggregation Table by selecting an address and clicking <Change…>. The Change Area Aggregation dialog box appears. Change parameters and click <Set>. [Remove] Remove an address from the Area Aggregation Table by selecting an address and clicking <Remove>. OSPF 2-13 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management To add an Area Aggregation entry: 1. In the Area Aggregation Table, click <Add…>. The Add Area Aggregation dialog box appears. Figure 2-14. Add Area Aggregation 2. Configure desired parameters (see Table 2-8). 3. Click <Apply>. (Clicking <Apply> performs Set operation without closing dialog box.) 4. When all entries have been added, click <Close>. The Add Area Aggregation dialog box closes and all added entries appear at the end of the list. To enable/disable Advertising for an area aggregation: 1. In the Area Aggregation Table, click <Change…>. The Change Area Aggregation dialog box appears. This dialog is the same as the Add Area Aggregation dialog box, except that the only parameter that can be changed is Advertised. 2. Select Yes or No for the Advertised parameter and click <Set>. OSPF Information RADview enables you to view information regarding the following categories: 2-14 OSPF • Interfaces • Neighbors • Database. RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management OSPF Interfaces Information To display the OSPF Interfaces table: • Select Configuration > OSPF > Information > Interfaces.... The Interfaces Table appears. Figure 2-15. Interfaces Table Table 2-9. Interfaces Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks IP Address/Interface The IP address or the link number of the interface. Area ID The IP address associated with the area. Interface Type Broadcast, NBMA, Point To Point, Point To Multipoint Priority The interface priority. Designated Router The IP address of the router. OSPF Neighbors Information To display the OSPF Neighbors table: • Select Configuration > OSPF > Information >Neighbors.... The Neighbors Table appears. OSPF 2-15 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management Figure 2-16. Neighbors Table Table 2-10. Neighbors Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks IP Address/Interface The IP address or the link number of the interface. Router ID The IP address of the relevant router. Priority The interface priority. State Down, Attempt, Init, Two Way, Exchange Start, Exchange, Loading, Full 2-16 OSPF RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management OSPF Database Information To display the OSPF Database table: • Select Configuration > OSPF > Information > Database.... The Database Table appears. Figure 2-17. Database Table Table 2-11. Database Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Area ID The IP address associated with the area. DB Type Link Router, Network, Summary, AS Summary, AS External, Multicast, NSSA External Link State ID The IP address format. Originating Router The IP address of the originating router. Seq No The sequence number. Age Age in seconds Check Sum Check sum validation value OSPF 2-17 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management 2.6 Viewing the Connection Status RADview enables you to view the list of all the logical links related to the physical links of the device. To display the connection status of the device: • Select Configuration > Connection Status... The All Links Connections list appears (Figure 2-18). Figure 2-18. All Links Connections List Table 2-12. All Links Connections Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. DLCI# Data Link Control Identifier Only for links with FR protocol type. Routing Type The routing type of the selected interface. Protocol The protocol being used. Connection Status The present connection status of the device. Link Status The link status of the device. 2-18 Viewing the Connection Status RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management 2.7 Configuring the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) RADView enables you to configure the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). To display the DHCP: • Select Configuration > System Commands > DHCP… The DHCP table appears (Figure 2-19). Figure 2-19. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Table Table 2-13. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks IP Address Allocation Enable, Disable Low IP Address Specifies the lower boundary for the IP address range. High IP Address Specifies the upper boundary for the IP address range. IP Mask Specifies the IP Mask for the IP address range. Default Gateway Specifies the default Gateway IP address for workstations that receive IP addresses in the range defined by Low and High IP Address. Primary DNS The IP address of the DNS server that can be used by the workstation. Secondary DNS The IP Address of an additional DNS server used as an alternative to the Primary DNS. Configuring the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 2-19 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management Table 2-13. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Parameters (Cont.) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The interface through which the remote interface of the IP address is received. All, LAN1, LAN2, Any LAN, WAN [Apply] To save changes in table, click <Apply>. [Add…] To add an entry to the table, click <Add…>. Configure the parameters in the Add DHCP Entry table and click <Set>. A maximimum of 10 entries is allowed in the table. [Change…] To change an entry, select it and click <Change…>. Make desired changes in Change DHCP Entry table and click <Set>. [Remove] To delete an entry, select it and click <Remove>. To add an DHCP entry: 1. In the DHCP Table, click <Add…>. The Add DHCP Entry dialog box appears. Figure 2-20. Add DHCP Entry 2. Configure desired parameters (see Table 2-13). 3. Click <Set>. The Add DHCP Entry dialog box closes. To change a DHCP entry: 1. In the DHCP Table, click <Change…>. The Change DHCP dialog box appears. 2-20 Configuring the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management Figure 2-21. Change DHCP Entry 2. Configure desired parameters (see Table 2-13). 3. Click <Set>. The Add DHCP Entry dialog box closes. 2.8 Resetting the Device RADview enables you to reset the device. To reset the device: 1. Select Configuration > System Commands > Reset… or click the shortcut key on the toolbar . The following message appears: “RESETTING BROUTER. Operation may disrupt network data.” Figure 2-22. Reset Brouter 2. Click <OK> to confirm reset. The system is reset. Resetting the Device 2-21 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management 2.9 Polling the Agent RADview allows you to poll the FCD-IP device. To poll the agent: • Select Configuration > Poll Agent or click the shortcut key on the toolbar . The system polls the agent immediately. 2.10 Configuring SNMP RADview enables you to view and modify SNMP settings; enabling you to specify management stations that can receive FCD-IP traps. In the FCD-IP Manager List, you can enter up to ten IP addresses of the relevant management stations. To view/specify management station IP addresses to which to send traps: 1. Select Options > Manager List…. The Manager List dialog box appears (Figure 2-23). Figure 2-23. Manager List 2-22 Configuring SNMP RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 2 System Management 2. Configure the IP Address for the different managers. 3. Click <Set>. Table 2-14. Manager List Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Manager ID The ID number of the manager. IP Address The IP address of the manager. 2.11 Switching Between Edit and Agent View The device is managed with two different community views: one for the TDM scope, and one for the rest of the parameters. A password provides protection for the TDM scope preventing you from unintentionally changing the parameters of the E1/T1, SHDSL and Voice parameters. The Password is configured via the terminal. Note Once the password has been entered, you will not need to re-enter it again when switching between Edit and Agent Views in other levels. To enter the password: 1. Select Options > Password… The password dialog box appears (Figure 2-24). Figure 2-24. Password Dialog Box 2. Enter a password (up to twenty characters). Switching Between Edit and Agent View 2-23 Chapter 2 System Management 2-24 Switching Between Edit and Agent View RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management This chapter describes RADview’s configuration and operation procedures for the FCD-IP LINK and LAN. The LINK or LAN Level is available when a LINK or LAN is selected. Some LINKS have both edit and agent levels. This chapter details the different management options for each LINK and LAN separately. 3.1 Edit and Agent Views Note Certain TDM ports can be displayed in both Edit and Agent Views. Configuration is performed in the Edit mode. In Agent View, the parameters are Read-Only. To switch between Edit and Agent views: 1. Select the appropriate interface. The Agent view is displayed for the selected link. 2. Switch to Edit View by doing one of the following: Click the Edit/Agent View button on the toolbar or Select Window > Edit View/Agent View to switch to Edit/Agent View. 3.2 Configuring Interface Information This section describes how to view and configure interface information. Note For information on configuring physical port parameters, see Configuring Physical Parameters. Configuring E1/T1, CHANNEL, ISDN, and Voice Interface Information This section describes how to view and configure E1/T1, CHANNEL (V.24, V.35), ISDN and Voice (FXS, FXO and E&M) interface information. The parameters of the Interface Information dialog boxes differ depending on the selected interface. Notes • For information on E1/T1 over SHDSL, see Configuring E1/T1 over SHDSL Interface Information. • Voice interface configuration can be performed in both Agent and Edit Views. Configuring Interface Information 3-1 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management To configure interface information: 1. Select a Link or Channel. The Agent view is displayed for the selected object. 2. Select Configuration > Interface Info… The Interface Information dialog box appears. There are two tabs: Info and Link Data. Figure 3-1. Interface Information Info Tab 3. Click on the required tab. 4. Configure the desired parameters. 5. Click <Set>. Table 3-1. Info Tab Parameters for E1/T1, CHANNEL, ISDN, and Voice Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. Description Description of the selected interface. Type The type of interface. DS0 Bundle, DS1. Modem, E&M, FXO, FXS Oper Status The operational status of link. Up, Down MTU (not available for Voice, Channel, or Sub Link interfaces) The maximum Transmit Unit for IP fragmentation. Frames lager than MTU are fragmented into smaller units when sent through the specified interface 3-2 Configuring Interface Information RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Figure 3-2. Interface Information Link Data Tab Notes • Link Data tab is disabled for Sub and Voice links. • Changing the protocol type from Frame Relay (RFC 1490) to any other protocol will cause the device to reset. The following message appears “This operation will cause HW reset of the Device. Continue?” Click <OK> to confirm reset. Table 3-2. Interface Information Link Data Tab Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. State Enable, Disable, Backup (only if there is more than one link) Backup of Link The combo box listing links in current configuration. Note: This field is disabled for SUB links Link Type Synchronous, Asynchronous (only for V.24 connector) Protocol Type (not available for the SUB LINK or CHANNEL) Slip, Cslip, PPP, HDLC Framing, RFC 1490 Configuring Interface Information 3-3 Chapter 3 Port Management RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Table 3-2 Interface Information Link Data Tab Parameters (Cont.) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Routing / Bridging (not available for the SUB LINK or CHANNEL) Bridge, IP Router, IPX Router, IP and IPX Router, IP Brouter, IPX Brouter, IP and IPX Brouter IP Transparent Mode Enables/disables IP transparent mode. When this mode is enabled, all frames (including broadcast and multicast frames) are forwarded from E1/T1 to LAN and from LAN to E1/T1. Disable, Enable All Note: This field is not available in the following cases: • If any of the following interfaces exists on the device: LINK 3; LAN 2; ISDN; or a non-Channel X.21(4), V.24(11), RS-530(3), or DB-25(17) • When the value in the Routing/Bridging field is one of the following: Bridge, IPX Router, IPX Brouter When the selected interface is a Channel IP Transparent Default Gateway Specifies the default Gateway IP address used for transparent IP. Configuring SHDSL Interface Information This section describes how to view and configure SHDSL interface information. To configure interface information: 1. Select an SHDSL Link. The Agent view is displayed for the selected link. 2. Select Configuration > Interface Info… The Interface Information dialog box appears. There are two tabs: Info and Link Data. Note Link Data tab is disabled for Sub and Voice links. 3. Click on the required tab. 4. Configure the desired parameters. 5. 3-4 Click <Set>. Configuring Interface Information RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Table 3-3. Info Tab Parameters for SHDSL Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. Type The type of interface. SHDSL Description Description of the selected interface. Oper Status The operational status of link. Up, Down MTU The maximum Transmit Unit for IP fragmentation. Frames lager than MTUare fragmented into smaller units when sent through the specified interface Note Changing the protocol type from Frame Relay (RFC 1490) to any other protocol will cause the device to reset. The following message appears “This operation will cause HW reset of the Device. Continue?” Click <OK> to confirm reset. Table 3-4. Interface Information Link Data Tab Parameters for SHDSL Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. State Enable, Disable, Backup (only if there is more than one link) Backup of Link The combo box listing links in current configuration. Note: If Link 3 is a SUB link, it is not avalable as a backup link. Link Type Synchronous Protocol Type PPP, RFC1490, HDLC Framing Routing / Bridging Bridge, IP Router, IPX Router, IP and IPX Router, IP Brouter, IPX Brouter, IP and IPX Brouter IP Transparent Mode Disable, Enable All Note: This field is not available in the following cases: • If any of the following interfaces exists on the device: LINK 3; LAN 2; ISDN; or a non-Channel X.21(4), V.24(11), RS-530(3), or DB-25(17) • When the value in the Routing/Bridging field is one of the following: Bridge, IPX Router, IPX Brouter When the selected interface is a Channel IP Transparent Default Gateway Specifies the default gateway IP address used for transparent IP. Configuring Interface Information 3-5 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Configuring E1/T1 over SHDSL Interface Information This section describes how to view and configure E1/T1 over SHDSL interface information. Note For information on E1/T1 interfaces that are not over SHDSL, see Configuring E1/T1, CHANNEL, ISDN, and Voice Interface Information. To configure interface information: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Configuration > Interface Info… The Interface Information dialog box appears. There are two tabs: Info and Link Data. This dialog box is divided into two sections: the upper section displays SHDSL parameters and the lower section displays E1/T1 parameters. Note Link Data tab is disabled for Sub links. Figure 3-3. Interface Information Info Tab for E1/T1 over SHDSL 3-6 Configuring Interface Information RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Figure 3-4. Interface Information Link Data Tab for E1/T1 over SHDSL 3. Click on the required tab. 4. Configure the desired parameters. 5. Click <Set>. Table 3-5. Info Tab Parameters for E1/T1 over SHDSL Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. Description Description of the selected interface. Oper Status The operational status of link. Up, Down MTU The maximum Transmit Unit for IP fragmentation. Frames lager than MTUare fragmented into smaller units when sent through the specified interface Note t Changing the protocol type from Frame Relay (RFC 1490) to any other protocol will cause the device to reset. The following message appears “This operation will cause HW reset of the Device. Continue?” Click <OK> to confirm reset. Configuring Interface Information 3-7 Chapter 3 Port Management RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Table 3-6. Interface Information Link Data Tab Parameters for E1/T1 over SHDSL Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. State Enable, Disable, Backup (only if there is more than one link) Backup of Link The combo box listing links in current configuration. Note: This field is disabled for SUB links Link Type Synchronous Protocol Type PPP, RFC1490, HDLC Framing Routing/Bridging Bridge, IP Router, IPX Router, IP and IPX Router, IP Brouter, IPX Brouter, IP and IPX Brouter IP Transparent Mode Disable, Enable All Note: This field is not available in the following cases: • If any of the following interfaces exists on the device: LINK 3; LAN 2; ISDN; or a non-Channel X.21(4), V.24(11), RS-530(3), or DB-25(17) • When the value in the Routing/Bridging field is one of the following: Bridge, IPX Router, IPX Brouter • When the selected interface is a Channel IP Transparent Default Gateway 3-8 Specifies the default gateway IP address used for transparent IP. Configuring Interface Information RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Configuring LAN Interface Information To configure interface information for an Ethernet LAN: 1. Select the desired Ethernet LAN. 2. Select Configuration > Interface Info… The Interface Information dialog box appears. Figure 3-5. Interface Information – Ethernet LAN Note Changing the values for Burn In MAC or Locally Administered will cause disconnection with the agent. Table 3-7. Interface Information – Ethernet LAN Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. Description Description of the interface. Type The type of interface that appears in the MIB IF Table. Oper Status The operational status of link. MTU The maximum Transmit Unit for IP fragmentation. Frames lager than MTUare fragmented into smaller units when sent through the specified interface. Rate (Mbps) The transmission speed in Mbps. Configuring Interface Information 3-9 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Table 3-7. Interface Information – Ethernet LAN Parameters (Cont.) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Active Address Burn In MAC Changing this parameter will cause disconnection with the agent. Locally Administered Changing this parameter will cause disconnection with the agent. LAN State Enable, Disable Selecting Disable for this parameter will cause disconnection with the agent. Routing/Bridging Bridge, IP Router, IPX Router, IP and IPX Router, IP Brouter, IPX Brouter, IP and IPX Brouter Note: Only for two LANS. 3.3 Configuring Physical Parameters This section describes how to view and configure physical layer parameters of Async, ISDN, E1/T1, and SHDSL ports. Notes • For information on configuring interface information, see Configuring Interface Information. • When configuring TDM parameters a password is required. Configuring Async Link (V.24) Physical Parameters Note Async links can only be V.24. To configure Async physical parameters: 1. Select the Async Link. 2. Select Configuration > Physical Parameters… The Async Link Parameters dialog box appears. 3. Configure the desired parameters. 4. Click <Set>. 3-10 Configuring Physical Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Figure 3-6. Async Link Parameters Dialog Box Table 3-8. Async Link Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface LINK1, LINK2 Rate (Kbps) 2.4, 4.8, 9.6, 19.2, 38.4, 57.6, 115.2 Data Bits 8 Parity None, Odd, Even Stop Bits One, Two Connection Type Originate, Answer, Originate and Answer Modem Name Maximum 50 characters Unlisted Setting String Maximum 80 characters in two rows AT&C1&D2 Autobauding Disable, Enable Analyze Answers Disable, Enable Speaker Off, On Reset Config Select the checkbox to reset the configuration Checked, Unchecked Dialing Number Maximum 40 characters. Valid characters are: 0..9, P, T, W , ', @ Configuring Physical Parameters 3-11 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Table 3-8. Async Link Parameters (Cont.) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Local Number Maximum 40 characters. Valid characters are: 0..9, P, T, W , ', @ Number of rings before answer 1..2..255 [Add Modem…] Click <Add Modem…> to open the Add Modem dialog box (Figure 3-7). Enter the desired parameters and click <Set>. [Remove Modem] Remove a modem by selecting a modem from the Modem Name drop-down list and clicking <Remove Modem>. To add a new modem to the modems list: 1. In the Async Link Parameters dialog box, click <Add Modem...>. The Add New Modem dialog box appears. 2. Configure the desired parameters. 3. Click <Set>. Figure 3-7. Add New Modem Dialog Box Table 3-9. Add New Modem Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Name Maximum 50 characters Setting String Maximum 80 characters in two rows To remove a modem from the modems list: 1. In the Async Link Parameters dialog box, select a modem from the Modem Name drop-down list. 2. Click <Remove Modem>. 3. The system confirms the removal of the modem: “Removing the selected modem.” 3-12 Configuring Physical Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Configuring ISDN Physical Parameters To configure ISDN physical parameters: 1. Select the ISDN Link. 2. Select Configuration >Physical Parameters… The ISDN dialog box appears. 3. Click on the desired tab and configure desired parameters. 4. Click <Set>. Figure 3-8. ISDN Parameters – Interface Tab Table 3-10. ISDN Parameters – Interface Tab Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface LINK1, LINK2 ISDN Line Type Dialup, Leased ISDN Standard V1, ETSI, 5ESS, DMS100, National-1, NTT Enabled when ISDN Line Type=Dialup Connection Mode Point to Point, Multi Point Clock Rate (Kbps) 56, 64 Configuring Physical Parameters 3-13 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Figure 3-9. ISDN Parameters – Terminal End Point Tab Table 3-11. ISDN Parameters – Terminal End Point Tab Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface LINK1, LINK2 ETSI Abstract Terminal 1 Terminal Index The Terminal Index. Service Provider ID (SPID) The Service Provider ID . Up to 20 digits Directory Number The Directory Number. Up to 18 digits TEI Management Dynamic, Static TEI Value 0..63 Abstract Terminal 2 Terminal Index The Terminal Index. Service Provider ID (SPID) The Service Provider ID. Up to 20 digits Directory Number The Directory Number. Up to 18 digits 3-14 Configuring Physical Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Figure 3-10. ISDN Parameters - Channel Tab Table 3-12. ISDN Parameters - Channel Tab Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. Calling Number The Calling Number. Up to 18 digits Calling Sub-Number The Calling Sub-Numbe.r Up to 6 digits Called Phone Number The Called Phone Number. Up to 18 digits Called Sub-Number The Called Sub-Number. Up to 6 digits Permission Originate, Answer, Originate and Answer Dial Back Phone Number The Dial Back Phone Number. Up to 18 digits Dial Back Sub Number The Dial Back Sub-Number. Up to 6 digits Configuring Physical Parameters 3-15 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Configuring E1/T1 Link Mode Notes • Link mode configuration is available for Main E1/T1 link for devices having two E1/T1 ports. • Note that, while the link mode can be configured only in the Edit View, switching traffic between links can only be performed in Agent mode, which detects the actual current mode of the link. To configure E1/T1 link mode: 1. Select Link1. 2. Select Configuration >Physical Parameters > Mode…. The E1/T1 Link Mode dialog box appears. Figure 3-11. E1/T1 Link Mode Table 3-13. E1/T1 Link Mode Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Mode Normal,Chain,Ring SUB,Ring Main, Redundancy Wait to Restore Wait to restore interval in minutes. 1-99 Note: This field is available only if Mode =Ring Redundancy Online Primary, Secondary Note: This field is available only if Mode = Redundancy [Flip Cmd] Toggles the Redundancy Online parameter. To change a redundant link from Primary to Secondary or vice versa, click <Flip Cmd> and then confirm the command by clicking OK when the confirmation message appears: “This operation will change the online link” Note that this button is Password protected. 3-16 Configuring Physical Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Configuring General E1/T1 Physical Parameters To configure E1/T1 general physical parameters: 1. Select an E1/T1 Link or Channel. 2. Select Configuration > Physical Parameters > General…. The E1/T1 Link Parameters dialog box appears. Figure 3-12. General Link Parameters (E1/T1 Ports) Table 3-14. General Link Parameters (E1/T1 Ports) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. Admin Status Enable, Disable Clock Source The clock source that synchronizes the network. Internal - system source clock is generated from an internal clock oscillator. Link1 – Sublink1/Link 2 Sublink 1 Sublink 2 Sublink 3. Configuring Physical Parameters 3-17 Chapter 3 Port Management RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Table 3-14. General Link Parameters (E1/T1 Ports) (Cont.) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Multiplier (Kbps) The data rate of each DATA time slot. 56, 64 Note: This parameter is only enabled for the main link only. T1: ESF (24 frames per multiframe), D4 (12 frames per multiframe). Line Type E1: E1 (G732N-2 frames per multiframe), - CCITT Rec. G.704 - Table 4a E1-CRC (G732NCRC), - CCITT Rec. G.704 - Table 4b E1-MF - CCITT Rec. G.704 - Table 4a, with TS16 multiframing enabled. E1-CRC-MF (G732SCRC-16 frames per multiframe),- CCITT Rec. G.704 - Table 4b, with TS16 multiframing enabled. Line Code The line coding method used for zero suppression. Note: This parameter is only applicable for T1. B7ZS coding, Jammed Bit zero suppression. A pulse is forced in bit 8 of each 8-bit period of each channel. Therefore, only 7 bits per channel (1.344 Mbps) is available for data. B8ZS coding, a specified pattern of normal bits and bipolar variations replaces a sequence of 8 zero bits. This option provides clear channel capability. Trans - Transparent (AMI) coding, no zero suppression is present. Sync Defines time required for the link to return to normal operation after a red alarm event (local loss of synchronization) has terminated FAST (after one second), AT&T 62411 (after ten seconds), CCITT (after 100 msec) Tx Gain Mask (db) The selected attenuation value brings your signal level closer to the expected repeater signal level on the cable. Note: This parameter is only applicable for T1. NA, 7.5, 15, 22.5 Line Length (feet) Note: This parameter is only applicable for T1. NA, 0-133, 134-266, 267-399, 400-533, 534-655 Idle code (Hex) Hexadecimal code transmitted to fill idle (unused) time slots in frames transmitted through the selected port. 00 - 7C - FF Rx Gain The maximum receive sensitivity in dB for the interface. E1: 12dB, 30dB T1: 30dB, 36dB 3-18 Configuring Physical Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Table 3-14. General Link Parameters (E1/T1 Ports) (Cont.) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks RAI The Remote Alarm Indication (for main links with sub links). Off, On For main links: On transmits a yellow alarm indication on the E1 sub link when Link 1 is in yellow alarm state . For Sub links: On transmits a yellow alarm indication on Link 1 when sub link E1 is in either yellow or red alarm state. Note: This field exists only when the E1/T1 has a sub link. Inband Management The identifier of inband management over the link. Off, Dedicated TS TS Number TS being used as Dedicated TS Only applicable when Inband Management=Dedicated TS. Configuring E1/T1 Time Slot (TS) Assignments RADview enables you to program the routing of time slots. A complete description of the TS assignment function is discussed below. To configure TS parameters: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Configuration >Physical Parameters > TS Assign… or click the shortcut key on the toolbar The TS Assignment dialog box appears. Figure 3-13. TS Assignment Configuring Physical Parameters 3-19 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management MAIN E1 1 2 3 4 5 21 DATA 1 +2 23 24 D D 30 31 D D D SUB1/ LINK 2 VOICE 1 22 D D V VOICE 2 V VOICE 3 VOICE 4 Figure 3-14. TS Assignment (New HW) A rectangular grid displays the time slot assignments. Each row and each column represents the possible connections of a specific port. Since all ports are connected to MAIN E1/T1 port, the top row shows the TS assignments of the MAIN E1/T1. For the MAIN E1, there are 31 Time Slots. For the MAIN T1, there are 24 Time Slots. Colors, letters and guides indicate information about the time slots and ports represented in the grid. Their meanings are described below. In addition a ToolTip appears when the mouse cursor passes over a row, indicating the TS Color Codes Since each TS has only one type and can be connected to only one port, each TS column can have only one cell with a letter inside. Both connection cells and port indicator cells use color codes to relay connection information. Green + number TS in this port is connected and is not being used for Management. Gray + number TS in this port is available for connection, but currently has no TS connection. Blue + number TS in this port has no connections and cannot be TS connected. Inside Cells Color Codes Gray empty 3-20 Cell's port has no current TS connections but can be TS connected. Blue empty Cell's port has no TS connections and cannot be TS connected. Yellow + letter Cell's port has at valid TS connection of type indicated by letter. Configuring Physical Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management TS Letter Codes The connection cells use letter codes to describe the type of the connected time slots. D Data V Voice Port Name Color Codes Green All of the port's connectable TS connections are connected. Gray None of the port's connectable TSs are being used. Yellow Some of the ports have TS connections. This is valid for the MAIN or SUB ports only. Selecting a Port Cell To select a cell: • Click on the desired cell. A selected cell is outlined with a blue border . Creating a TS Connection New TS connections are created only on gray cells (cells with connectable TSs). To create a new TS connection: 1. Click an empty gray cell. 2. Click <Voice/Data>. Disconnecting TS Connections You can disconnect individual TS connections or all TS connections in the selected port. To disconnect an individual TS connection: 1. Click on a cell representing a TS connection (yellow). 2. Click <Disconnect>. The gray color indicates that the cell's ports have no TS connection but their TSs are connectable. If the cell becomes blue, TS connection is impossible between the two corresponding ports. Resetting All TS Connections To reset all TS connections: • In the TS Assignment dialog box, click <Reset All>. Configuring Physical Parameters 3-21 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Exiting the TS Assignment Window To exit the TS Assignment window: • Double-click the control box in the upper left corner of the window or click on the X in the upper right-hand side of the window. Reading the E1/T1 Configuration from the Agent Note Read is only available for TDM ports in Edit View. RADview enables you to upload the current Agent configuration to the Edit Configuration mode. The Read command is only available when there is communication with the agent. To read the current configuration from the agent: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Configuration > Physical Parameters > Read... The following message appears: Figure 3-15. Read Configuration 3. Click <OK> to confirm the operation. Updating the E1/T1 Configuration in the Agent Note Update is only available for TDM ports in Edit View. RADview enables you to download the Edit Configuration to the agent. To upload the Edit Configuration to the agent: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Click the Edit View button on the toolbar . 3. Select Configuration >Physical Parameters > Update… The following message appears: 3-22 Configuring Physical Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Figure 3-16. Update Configuration 4. Click <OK> to update the configuration. To abort the Update operation: • Click <Abort>. Configuring SHDSL Physical Parameters To configure SHDSL physical parameters: 1. Select a SHDSL Link. 2. Select Configuration > Physical Parameters > SHDSL > Parameters… The SHDSL Link Parameters dialog box appears. 3. Configure the desired parameters. 4. Click <Set>. Configuring Physical Parameters 3-23 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Figure 3-17. SHDSL Parameters Table 3-15. SHDSL Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface LINK 1 Type SHDSL Transmission Mode Annex A, Annex B Power Specral Density Symmetric, Asymmetric (PSD) Mask Asymmetric PSD Rate R1, R2 (only when PSD=Asymmetric) Selected rate depends on transmission mode specified in Annex A or B of G.991.2: • Annex A R1 = 776 or 784 kbps R2 = 1544 or 1552 kbps • Annex B: R1 = 2312 kbps R2 = 2056 kbps 3-24 Configuring Physical Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Table 3-15. SHDSL Parameters (Cont.) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Wire Interface 2 Wire, 4 Wire Rate Mode Fixed, Adaptive SNR Startup Margin Specifies the downstream current condition target SNR margin for a SHDSL line. The SNR margin is the difference between the desired SNR and the actual SNR. Target SNR margin is the desired SNR margin for a unit. -10..10 (Signal to noise ratio) Line Probe Enabled Enables/Disables support for Line Probe of the units in a SHDSL line . Enabled: the system performs Line Probing to find the best possible rate. Disabled: rate adaptation phase is skipped, to shorten set up time. Line Mode STU-C, STU-R Loop Attenuation Threshold (dB) Configures the loop attenuation alarm threshold. Off, 1…127 Note: Off setting indicates that threshold crossings are not reported SNR Margin Threshold Configures the SNR margin alarm threshold. Off, 1…15 (dB) Note: Off setting indicates that threshold crossings are not reported TS Compaction Mode Configures how timeslots will be compacted over the SHDSL line. No Compaction, No Mapping, With Mapping, Low TSs Mapping Configuring SHDSL Status Parameters To configure status parameters: 1. Select a SHDSL Link. 2. Select Configuration > Physical Parameters > SHDSL > Status… The SHDSL Status dialog box appears. Figure 3-18. SHDSL Status Configuring Physical Parameters 3-25 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Table 3-16. SHDSL Status Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Actual Rate (Kbps) Contains the actual line rate in this HDSL2/SHDSL span. 192…4608 Loop Attenuation (dB) Current loop attenuation for this endpoint as reported in a Network or Customer Side Performance Status message. -127…128 SNR Margin (dB) Current SNR margin for this endpoint as reported in a Status Response/SNR message. -127…128 Configuring Voice Interface Physical Parameters This section describes how to view and configure voice interface (FXS, FXO and E&M) parameters. Note Voice interface configuration can be performed in both Agent and Edit Views. To configure voice parameters: 1. Select a voice port. 2. Select Configuration > Physical Parameters… The Voice Parameters dialog box appears. Figure 3-19. Voice Parameters Dialog Box Table 3-17. Voice Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Port VOICE 1, VOICE 2, VOICE 3, VOICE 4 Interface Type FXS, FXO, E&M 4 W, E&M 2 W 3-26 Configuring Physical Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Table 3-17. Voice Parameters (Cont.) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Tx Gain (dBm) The transmit gain in dBm. -10, -8, -6, -4, -2, 0, 2, 4, 5 Rx Gain (dBm) The receive gain in dBm. -10, -8, -6, -4, -2, 0, 2, 4, 5 Coding Law Indicates the Method/Law for decoding/encoding the voice information. A Law, U Law Signaling Tx On/Off Hook This object represents 2 Octets, 4 nibbles: A bit, A bit Inverted, B bit, B bit inverted, NA (FXO and E&M) where: 0001=Tx A bit 0010=Tx A bit inverse 0011=Tx B bit 0100=Tx B bit inverse 0000=NA Rx On/Off Hook This object represents 1 Octets, 2 nibbles: A bit, A bit Inverted, B bit, B bit inverted, NA(E&M) where: 0001=Rx A bit 0010=Rx A bit inverse 0011=Rx B bit 0100=Rx B bit inverse 0000=NA Tx M Signal This object represents 2 Octets, 4 nibbles: A bit, A bit Inverted, B bit, B bit inverted, NA (FXS and FXO) where: 0001=Tx A bit 0010=Tx A bit inverse 0011=Tx B bit 0100=Tx B bit inverse 0000=NA Rx E Signal This object represents 1 Octets, 2 nibbles: A bit, A bit Inverted, B bit, B bit inverted, NA (FXS and FXO) where: 0001=Rx A bit 0010=Rx A bit inverse 0011=Rx B bit 0100=Rx B bit inverse 0000=NA Configuring Physical Parameters 3-27 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Table 3-17. Voice Parameters (Cont.) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Tx Ring Detection This object represents 2 Octets, 4 nibbles: A bit, A bit Inverted, B bit, B bit inverted, NA (FXS and E&M) where: 0001=Tx A bit 0010=Tx A bit inverse 0011=Tx B bit 0100=Tx B bit inverse 0000=NA Default ABCD Bits For all interfaces: When A bit or A bit inverted: For E1 Link: 0001, 0010, 0011, 0100, 0101, 0110, 0111 For T1 Link: 0000, 0101 Else, For E1 Link: 0001, 0010, 0011, 1000, 1001, 1010, 1011 For T1 Link: 0000, 1010 Reversed Polarity Indicates the Signaling Profile of the port. Enabled, Disabled Seize Ack Indicates whether the device will acknowledge a seize signal (On/Off Hook). When the value is Yes and device receives an on/off hook signal, it will transmit back an on/off hook signal. When the value is set to No and device receives an on/off hook signal, it will NOT transmit back an on/off hook signal. Yes, No, NA (FXS and E&M) Out of Service Forced Idle, Forced Busy, NA (FXS) Remote E&M Wires Remote device’s wiring. 2 Wires, 4 Wires, NA (FXS and FXO) E&M Type Indicates signaling type on the E&M analog side. Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, Type 5 (SSDC5), NA (FXS and FXO) 3-28 Configuring Physical Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management 3.4 Configuring Protocol Parameters RADview enables you to configure parameters for the different protocols. Table 3-18. Protocol Options per Interface and Link Types Note Interface Link Type Protocol V24 Async SLIP, CSLIP, PPP V24 Sync HDLC, RFC1490, PPP V35, V11 Sync HDLC, RFC1490, PPP ISDN Sync PPP 4W, E1/T1, SHDSL Sync HDLC, RFC1490, PPP CHANNEL (N × 64) Sync No protocols over CHANNEL For IP Routing protocol, see Protocol Type. Configuring Frame Relay Protocol Parameters To configure Frame Relay parameters: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select a port where the Protocol Type (see Protocol Type) has been defined as FR. 3. Select Configuration > Protocol Parameters… The FR Parameters dialog box appears. Figure 3-20. FR Parameters Configuring Protocol Parameters 3-29 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Table 3-19. FR Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Port Interface The selected interface. DLCI / Maintenance Self Learning Specifies whether device self learns maintenance protocol on FR link and the existing DLCIs and staus of the existing DLCIs (Up or Down). On, Off When Off, maintenance protocol and DLCI must be configured manually. Maintenance Protocol Specifies maintenance protocol of the FR link. This parameter is available for configuration only when DLCI / Maintenance Self Learning is Off. T1.617/Annex D, Q.933/Annex A, LMI, None CLLM Status (on/off) Specifies whether or not CLLM frames used for congestion are supported. Disable, Enable Polling Interval (Sec) Specifies number of seconds between transmission of two successive status enquiry frames. 5 - 30 Full Enquiry Interval Specifies number of polling intervals after which a full status request frame is transmittted. 1 - 255 Error Threshold Specifies number of umacknowledged monitored events allowed in a sliding monitored event window before link is declared DOWN. 1 - 10 Monitored Events Specifies number of monitored events (status enquiry frames and full status enquiry frames). 1 - 10 Configuring the DLCI Table To configure DLCI parameters: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Configuration > Protocol Parameters > DLCI… or from the FR Parameters dialog box (Figure 3-20) click <DLCI Table…>. The DLCI Table dialog box appears. 3-30 Configuring Protocol Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Figure 3-21. DLCI Table Table 3-20. DLCI Table Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. DLCI # Specifies DLCI number. State Specifies state of DLCI. Active, Inactive (for receive/transmit) CIR Value Specifies maximum number of data bits that the network guarantees to transfer during the measurement interval. Excess Value Specifies maximum number of uncommitted data bits the network attempts to deliver during measurement interval. Throughput Value Specifies the average number of data bits pre second transferred by the network. When CIR is defined as one second, Throughput Value should also be one second. To add an entry to the DLCI Table: 1. In the DLCI Table, click <Add...>. The Add DLCI dialog box appears. 2. Configure the desired parameters (see Table 3-20). 3. Click <Set>. Configuring Protocol Parameters 3-31 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Figure 3-22. Add DLCI To remove an entry from the DLCI Table: 1. In the DLCI Table, select an entry. 2. Click < Remove>. Configuring PPP Parameters To configure PPP parameters: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select a port where the Protocol Type (see Protocol Type) has been defined as PPP. 3. Select Configuration > Protocols > PPP… The PPP Protocol Parameters dialog box appears. Figure 3-23. PPP Protocol 3-32 Configuring Protocol Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Table 3-21. PPP Protocol Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. For ISDN the parameters will appear on two tabs: Channel 1 and Channel 2. Bad Controls The number of packets received on this link with an incorrect control field. Bad FCSs The number of received packets that have been discarded due to having an incorrect FCS. Local MRU 1 - 2147483648 Remote MRU 1 - 2147483648 Local to Remote ACC Map 4 octets Remote to Local ACC Map 4 octets Local to Remote Compression Protocol Enabled, Disabled Remote to Local Compression Protocol Enabled, Disabled Local to Remote ACC Compression Protocol Enabled, Disabled Remote to Local ACC Compression Protocol Enabled, Disabled Tx FCS Size 0 - 128 Rx FCS Size 0 - 128 Header and Control Compression Used for troubleshooting only. Change the setting only if there is a problem with PPP negotiation. Yes, No Protocol Field Compression Used for troubleshooting only. Change the setting only if there is a problem with PPP negotiation. Yes, No IP Compression Activates Van Jacobson TCP Header Compression on a specified link. Yes, No Note: Since PPP is used for point to point transmissions, both the local and remote devices must have Van Jacobson TCP Header Compression enabled for compression to be performed. Configuring Protocol Parameters 3-33 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management 3.5 Configuring Network Parameters RADview enables you to set IP addresses, IP routing protocol and DHCP Relay parameters for the selected interface or DLCI. Configuring IP Addresses To set an IP Address: 1. Select the required interface. 2. Select Configuration >Network Parameters > IP Addresses… The IP Address Table dialog box appears. The IP Address Table dialog box varies depending on the selected link or DLCI. The parameters of the different dialog boxes are provided below. Figure 3-24. IP Address Table 3-22. IP Address Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. For ISDN there are two tabs: Channel 1 and Channel 2. IP Address The WAN/LAN IP Address. IP Mask The IP Address mask. Interface The selected interface. DLCI# Specifies DLCI number. 3-34 Configuring Network Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Configuring the IP Routing Protocol Configuring the IP routing protocol varies slightly, depending on the software version you are running. The appropriate one of the following two options will appear in the Network Parameters menu: • IP Routing Protocol • IP RIP Mode To set IP Routing Protocol: 1. Select a link in which protocol type is not FR. 2. Select Configuration >Network Parameters > IP Routing Protocol… The IP Routing Protocol dialog box appears. Figure 3-25. IP Routing Protocol Dialog Box Table 3-23. IP Routing Protocol Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. For ISDN the parameters below will appear on two tabs: Channel 1 and Channel 2. Routing Mode RIP 1: Send and receive routing information about IP nets only RIP 2: Send and receive full routing information including subnets RIP 1 & RIP 2: Send and receive both RIP 1 (routing information about IP nets only) and RIP 2 (full routing information including subnets) OSPF: Routing is determined by the OSPF protocol No Routing Protocol Configuring Network Parameters 3-35 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Table 3-23. IP Routing Protocol Parameters (Cont.) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks OSPF Area ID The IP address that identifies the OSPF area. […] Opens the Select Area dialog box listing the existing OSPF areas and the behavior type of each area. To select an OSPF area, click<…>. Select the desired area from the listing and click <OK>. Priority Hello Interval The interval (in seconds) at which a hello message is transmitted in the area. Dead Interval The interval (in seconds) after which, if no hello message is transmitted from a unit, it will be considered “dead”. Metric Configuring the IP RIP Mode To set IP RIP Mode: 1. Select a link in which protocol type is not FR. 2. Select Configuration >Network Parameters > IP RIP… The IP RIP Mode dialog box appears. Figure 3-26. IP RIP Mode Dialog Box Table 3-24. IP RIP Mode Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. For ISDN the parameters below will appear on two tabs: Channel 1 and Channel 2. Mode RIP 1: Send and receive routing information about IP nets only RIP 2: Send and receive full routing information including subnets RIP 1 & RIP 2: Send and receive both RIP 1 (routing information about IP nets only) and RIP 2 (full routing information including subnets) No RIP 3-36 Configuring Network Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management Configuring DHCP Relay To set DHCP Relay: 1. Select the desired link. 2. Select Configuration >Network Parameters > DHCP Relay… The DHCP Relay Parameters dialog box appears. Figure 3-27. DHCP Relay Parameters Table 3-25. DHCP Relay Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface Link 1, Link 2, Link 3 Description String containing information about the interface. Type DS1, MODEM, Frame Relay, PPP, SHDSL Enable Relay Enabled, Disabled Relay IP Address 0.0.0.0, 1.0.0.0…223.255.255.255 3.6 Resetting the Link To reset the link: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Configuration > Reset… or click the Reset icon on the toolbar . The following message appears: “RESETTING LINK. Operation may disrupt network data.” 3. Click <OK> to confirm Reset. Resetting the Link 3-37 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 3 Port Management 3.7 Performing Diagnostic Tests RADview enables you to run diagnostic tests for: E1/T1 Link, E1/T1 Sublink, SHDSL, SUB1/ LINK2, SUB 2, SUB 3, Voice Port. Note When configuring TDM (Voice) parameters a password is required. To run diagnostics tests: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Diagnostics > Test… The Testing dialog box appears. Figure 3-28. Testing Table 3-26. Testing Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Port The selected port. Voice 1, Voice 2, Voice 3, Voice 4 Interface Type The interface type of selected port. FXS, FX0, E&M 4 W, E&M 2W Current Test The currently running test. New Test Remote Digital Loopback (T1 only), Remote Analog Loopback, Local Analog Loopback [Stop Test] Click <Stop Test> to stop a currently running test. [Set] To run a different test, ensure that no test is currently running (click Stop Test). Select the test to be run from the New Test list box and click <Set>. To run a different test: 1. Click <Stop Test> to stop any currently running test. 2. Select a new diagnostic test. 3. Click <Set>. 3-38 Performing Diagnostic Tests Chapter 4 Fault Management This chapter discusses how to manage faults for the FCD-IP system. Managing faults includes the following tasks: • Displaying Sanity Check Errors (E1/T1 Link) • Displaying SHDSL Alarms. 4.1 Edit and Agent Views Note Certain TDM ports can be displayed in both Edit and Agent Views. Configuration is performed in the Edit mode. In Agent View, the parameters are Read-Only. To switch between Edit and Agent views: 1. Select the appropriate Link. 2. Switch to Edit View by doing one of the following: Click the Edit/Agent View button on the toolbar . or Select Window > Edit View/Agent View to switch to Edit/Agent View. 4.2 Displaying Sanity Check Errors (E1/T1 Link) RADview enables you to display the Sanity Check Errors List. Note Sanity Check Errors is available only for E1/T1 interfaces (Edit View). To display the sanity check errors list: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Click the Edit View button on the toolbar . 3. Select Fault >Sanity Check Errors… The system performs a sanity check. If there are no errors, the following message appears “NO SANITY ERRORS”. If there are errors or warnings, the Sanity Check Errors List appears (Figure 4-1). Displaying Sanity Check Errors (E1/T1 Link) 4-1 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 4 Fault Management Figure 4-1. Sanity Check Errors List 4.3 Displaying SHDSL Alarms To view SHDSL alarms: 1. Select an SHDSL Link. 2. Select Fault >SHDSL > Alarms… The SHDSL alarms dialog box appears (Figure 4-2). Figure 4-2. SHDSL Alarms 4-2 Displaying SHDSL Alarms Chapter 5 Performance This chapter discusses how to monitor the performance of the FCD-IP system. Performance monitoring includes the following tasks: • Setting the Polling Interval • Performing Diagnostic Tests • Displaying E1/T1 Statistics • Displaying E1 Over SHDSL Statistics • Displaying Ethernet LAN Statistics. 5.1 Edit and Agent Views Note Certain TDM ports can be displayed in both Edit and Agent Views. Configuration is performed in the Edit mode. In Agent View, the parameters are Read-Only. To switch between Edit and Agent views: 1. Select the appropriate Link. 2. Switch to Edit View by doing one of the following: Click the Edit/Agent View button on the toolbar . or Select Window > Edit View/Agent View to switch to Edit/Agent View. Edit and Agent Views 5-1 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance 5.2 Setting the Polling Interval RADview enables you to set the current statistics polling interval to automate FCD-IP statistics updates, per assigned elapsed time intervals. To set the polling interval: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >Physical Layer > Polling Interval… or Select Statistics >Physical Layer > SHDSL > Polling Interval… The Polling Interval dialog box appears (Figure 5-1). 3. Enter the polling interval in seconds and check the Polling Enable checkbox. 4. Click <Set>. Figure 5-1. Polling Interval 5.3 Performing Diagnostic Tests RADview enables you to run diagnostic tests. Note When configuring TDM (E1/T1) parameters a password is required. To run diagnostics tests: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Diagnostics >Test… The Testing dialog box appears. Figure 5-2. Testing 5-2 Performing Diagnostic Tests RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance Table 5-1. Testing Parameters – E1/T1 Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected port. Link1, Link2, Link3, SUB1/Link2, SUB 2, SUB 3, Interface Type The interface type of the selected port. E1/T1 Current Test The currently running test. New Test Remote Digital Loopback (T1 only), Remote Analog Loopback, Local Analog Loopback [Stop Test] Click <Stop Test> to stop a currently running test. [Set] To run a different test, ensure that no test is currently running (click Stop Test). Select the test to be run from the New Test list box and click <Set>. 5.4 Displaying E1/T1 Statistics The following types of statistics are available for E1/T1 links: • Packets Data Statistics • Packets Graph • Physical Layer Statistics Packets Data Statistics To display link statistics: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >Packets Data Table… The Link Statistics dialog box appears (Figure 5-3). Figure 5-3. Link Statistics Displaying E1/T1 Statistics 5-3 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance Table 5-2. Link Statistic Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. Packets Rx Unicast Frames The number of subnetwork Unicast packets received froma higher layer protocol. Rx Multicast Frames The number of subnetwork Multicast packets received from a higher layer protocol. Tx Unicast Frames The number of subnetwork Unicast packets transmitted to a higher layer protocol. Tx Multicast Frames The number of subnetwork Multicast packets transmitted to a higher layer protocol. Masked frames The number of masked frames received on this physical link. Octets Rx Bytes (k) The number of octets received on this interface including framing characters. Tx Bytes (k) The number of octets transmitted on this interface including framing characters. Error Frames RxError Frames Number of errored packets received on this physical link. TxError Frames Number of errored packets transmitted by this physical link. Packets Graph Statistics To display link packet statistics in a graph: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >Packets Graph > Packets… The Link Packets graph appears (Figure 5-4). Figure 5-4. Link Packets 5-4 Displaying E1/T1 Statistics RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance To display link octet statistics in a graph: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >Packets Graph > Octets... The Link Octets graph appears (Figure 5-5). Figure 5-5. Link Octets To display link error frame statistics in a graph: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >Packets Graph > Error Frames... The Link Error Frames graph appears (Figure 5-6). Figure 5-6. Link Error Frames Displaying E1/T1 Statistics 5-5 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance Physical Layer Statistics RADview enables you to display link statistics about the physical layer of the selected interface. To display physical layer statistics: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >Physical Layer > Current Interval > Table… The E1 Link Statistics dialog box appears (Figure 5-7). Figure 5-7. E1 Link Statistics Table 5-3. Link Statistic Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. Type E1, T1 Current Data Each parameter displays the number of seconds for the particular type of error encountered by the interface during the current 15-minute interval. Time Elapsed (sec) Amount of time that has passed since the beginning of the current 15-minute interval. LCV The number of Line Code Violations seconds. ES The number of Errored Seconds (containing one or more CRC error events, one or more OOF events, or one or more controlled slip events). SES The number of Severely Errored Seconds (with 832 or more CRC error events, or one or more OOF events). UAS The number of Unavailable seconds (in which a failed signal state exists). CSS The current Slip Second Counter (second with one or more controlled slip events). BES The number of Bursty Error Seconds (with 2 to 831 CRC error events). 5-6 Displaying E1/T1 Statistics RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance To display the physical layer statistics in graph form: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >Physical Layer > Current Interval > Graph… The Current Graph dialog box appears (Figure 5-8). Figure 5-8. Current Graph Statistics To display interval statistics for the physical layer: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >Physical Layer > Intervals Data > Table… The Errors Statistics Intervals dialog box appears (Figure 5-9). Figure 5-9. Errors Statistics Intervals Displaying E1/T1 Statistics 5-7 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance To display the next 20 entries in the table: • Click <Next>. To display statistics starting at a specific interval: 1. Select the desired interval from the Starting from Interval list box (upper right hand corner of Error Statistics Intervals dialog box). 2. Click <Start From…>. To display the table data in a graph: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >Physical Layer > Intervals Data > Graph… The Intervals Graph dialog box appears (Figure 5-10). Figure 5-10. Intervals Graph 5-8 Displaying E1/T1 Statistics RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance Protocol Layer Statistics RADview enables you to display statistics about the protocol layer of the selected interface. Note Protocol Layer statistics are available only for FR ports. To display FR Error statistics: 1. Select a FR port. 2. Select Statistics >Protocol Layer… The FR Error Statistics dialog box appears (Figure 5-11). Figure 5-11. FR Error Statistics Displaying E1/T1 Statistics 5-9 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance Table 5-4. FR Error Statistics Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. Type Displays the type of error. Time The system up time when error was detected. Faults The number of faults that have occurred. Fault Time The time when the error was detected. Data Provides information about the different faults. [DLCI…] Click <DLCI> to view DLCI Statistics dialog box (Figure 5-12). To display DLCI statistics: • From the FR Error Statistics dialog box (Figure 5-11), click <DLCI…>. The DLCI Statistics dialog box appears. Figure 5-12. DLCI Statistics 5-10 Displaying E1/T1 Statistics RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance Table 5-5. DLCI Statistics Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. DLCI The DLCI value. FECN The number of frames received from the network indicating forward congestion since the virtual circuit was created. BECN The number of frames received from the network indicating backward congestion since the virtual circuit was created. Sent Frames The number of frames sent from this virtual circuit since it was created. Sent Octets The number of octets sent from this virtual circuit since it was created. Received Frames The number of frames received over this virtual circuit since it was created. Received Octets The number of octets received over this virtual circuit since it was created. Committed Burst The maximum amount of data, in bits, that the network agrees to transfer under normal conditions, during the measurement interval. Excess Burst The maximum amount of uncommitted data bits that the network will attempt to deliver over the measurement interval. Throught Put The average number of 'Frame Relay Information Field' bits transferred per second across a user network interface in one direction, measured over the measurement interval. Circuit Discards The number of inbound frames dropped because of format errors, or because the VC is inactive. Received DE The number of frames received from the network indicating that they were eligible for discard since the virtual circuit was created. Sent DE The number of frames sent to the network indicating that they were eligible for discard since the virtual circuit was created. Displaying E1/T1 Statistics 5-11 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance 5.5 Displaying E1 Over SHDSL Statistics Physical Layer Statistics To display physical layer statistics: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >SHDSL > Current > 15 min Data… The 15 min, Current Data box appears (Figure 5-13). Figure 5-13. 15 min. Current Data Table 5-6. 15 min, Current Data Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Index Link 1 Type SHDSL Time Elapsed (sec) The amount of time that has passed since the beginning of the current 15-minute interval. 0..900 ES The number of Errored Seconds (containing one or more CRC error events, one or more OOF events, or one or more controlled slip events). 0..900 SES The number of Severely Errored Seconds (with 832 or more CRC error events, or one or more OOF events). 0..900 CRC Anomolies Integer LOSW 0..900 UAS The number of Unavailable seconds (in which a failed signal state exists). 0..900 5-12 Displaying E1 Over SHDSL Statistics RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance To display the physical layer statistics in graph form: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >SHDSL > Current > 15 min Graph… The 15 min, Current Graph box appears (Figure 5-13). Figure 5-14. 15 min. Current Graph To display interval statistics for one day: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >SHDSL > Current > One Day Data… The 1 Day Current Data dialog box appears (Figure 5-15). Figure 5-15. 1-Day Current Data Displaying E1 Over SHDSL Statistics 5-13 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance To display interval statistics for the physical layer: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >SHDSL > Intervals > 15 min. Data… The 15 min. Intervals Data dialog box appears (Figure 5-16). Figure 5-16. 15 min. Intervals Data To display the table data in a graph: 1. Select a Link or Channel. 2. Select Statistics >SHDSL > Intervals > 15 min. Graph… The 15 min. Intervals Graph dialog box appears (Figure 5-17). Figure 5-17. 15 min. Intervals Graph 5-14 Displaying E1 Over SHDSL Statistics RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance 5.6 Displaying Ethernet LAN Statistics RADview enables you to display general statistics as well as error statistics for the Ethernet LAN interface. To display general statistics for the LAN: 1. Select the Ethernet LAN. 2. Select Statistics >Table > LAN General… The LAN General dialog box appears (Figure 5-18). Figure 5-18. LAN General Table 5-7. LAN General Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. Packets RX Unicast Packets The number of subnetwork Unicast packets received froma higher layer protocol. RX Multicast Packets The number of subnetwork Multicast packets received from a higher layer protocol. TX Unicast Packets The number of subnetwork Unicast packets transmitted to a higher layer protocol. Octets RX Bytes (k) The number of octets received on this interface including framing characters. TX Bytes (k) The number of octets transmitted on this interface including framing characters. Displaying Ethernet LAN Statistics 5-15 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance To display error statistics for the LAN: 1. Select the Ethernet LAN. 2. Select Statistics >Table > Errors… The LAN Errors Statistics dialog box appears (Figure 5-19). Figure 5-19. LAN Errors Statistics Table 5-8. LAN Errors Statistics Parameters Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Interface The selected interface. Error Frames Received Error Frames The number of error frames received. Transmitted Error Frames The number of error frames transmitted. Frame Too Long The number of frames that were too long. FCS & Test Errors FCS Errors The number of frames received with CRC errors. Alignment Errors The number of frames received with alignment errors. SQE Test Errors The number of times the SQE test error is generated by the PLS sublayer for the selected interface. 5-16 Displaying Ethernet LAN Statistics RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance Table 5-8. LAN Errors Statistics Parameters (Cont.) Parameter Possible Values / Remarks Tx & Rx Errors Internal Mac Transmit Errors The number of frames for which transmission to selected interface fails due to internat MAC sublayer transmitt error. Internal Mac Receive Errors The number of frames for which transmission to selected interface fails due to internat MAC sublayer receive error. Deferred Transmissions The number of frames for which first transmission attemp on selected interface delayed due to the media bing busy. Carrier Sense Errors The number of time that carrier sense condition was lost or never asserted when attempting to trasmit frames on selected interface. Collisions Single Collision Frames The number of successfully transmitted frames for which transmission is inhibited by exactly one collision. Multiple Collision Frames The number of successfully transmitted frames for which transmission is inhibited by more than one collision. Late Collisions The number of times that a collision is detected on selected interface later than 512 bit-times into the transmission of a packet. Excessive Collisions The number of frames detected on selected interface that failed due to excessive collisions. The following group statistics can also be displayed in a graph: • Packets • Octets • Error Frames • Tx & Rx Errors • FCS & Test Errors • Collisions. To display the statistics for the Packets group in a graph: • Select Statistics >Graph > Packets… The LAN Packets dialog box appears (Figure 5-20). Displaying Ethernet LAN Statistics 5-17 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance Figure 5-20. LAN Packets To display the statistics for the Octets group in a graph: • Select Statistics >Graph > Octets… The LAN Octets dialog box appears (Figure 5-21). Figure 5-21. LAN Octets 5-18 Displaying Ethernet LAN Statistics RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance To display the statistics for the Frame Errors group in a graph: • Select Statistics >Graph > Frames Errors… The ETH Error Frames dialog box appears (Figure 5-22). Figure 5-22. ETH Error Frames To display the statistics for the Tx & Rx Errors group in a graph: • Select Statistics >Graph > Tx & Rx Errors… The ETH Tx & Rx Errors dialog box appears (Figure 5-23). Figure 5-23. ETH Tx & Rx Errors Displaying Ethernet LAN Statistics 5-19 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 5 Performance To display the statistics for the FCS & Test Errors group in a graph: • Select Statistics >Graph > FCS & Test Errors… The ETH FCS & Test Errors dialog box appears (Figure 5-24). Figure 5-24. ETH FCS & Test Errors To display the statistics for the Collisions group in a graph: • Select Statistics >Graph > Collisions… The LAN Collisions dialog box appears (Figure 5-25). Figure 5-25. LAN Collisions 5-20 Displaying Ethernet LAN Statistics Chapter 6 Configuring FCD-IP for a Typical Application This chapter provides detailed instructions for configuring a typical FCD-IP application. This application involves configuring: • WAN Interface • E1 Interface • LAN Interface. Each section shows the appropriate interface connections for those applications on the FCD-IP rear panel. 6.1 Overview Application The section provides detailed instructions for configuring FCD-IP unit with a sub-E1 and 10/100BaseT LAN interface, operating in the IP router mode (see Figure 6-1). Figure 6-1. FCD-IP Providing Access to the Internet and to the PSTN Overview 6-1 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 6 Configuring FCD-IP for a Typical Application Table 6-1. Configuration Summary WAN Parameters E1 Parameters LAN Host Parameters • Link mode: Synchronous • Master clock: Link 1 • LAN Status: Enable • Routing: IP router • Multiplier: 64 kbps • Host IP address: 192.168.10.2 • Protocol: PPP • Timeslots 1–4: FIX SUB Voice • Host IP mask: 255.255.255.000 • WAN IP address: 192.168.10.1 • Timeslots 5–8: DATA LINK1 • WAN IP mask: 255.255.255.252 • Default gateway setting by: Interface • Default gateway interface: LINK 1 6.2 Configuring WAN Parameters Configuring WAN parameters includes the following: • Configuring the WAN Interface • Configuring the WAN IP Address. Configuring the WAN Interface To configure the WAN interface: 1. Select Link1. 2. Switch to Edit View: Click the Edit View button on the toolbar . 3. Select Configuration > Interface Info… The Interface Information dialog box appears. There are two tabs: Info and Link Data. 4. Click the Link Data tab. Figure 6-2. WAN Interface Information Link Data Tab 6-2 Configuring WAN Parameters RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 6 Configuring FCD-IP for a Typical Application 5. From the State drop-down list, select Enable. 6. In the Link Type field, type Synchronous. 7. From the Protocol drop-down list, select PPP. 8. From the Routing/Bridging drop-down list, select IP Router. 9. Click <Set>. Configuring the WAN IP Address To configure the WAN IP address: 1. Switch to Agent View: Click the Agent View button on the toolbar . 2. Select Configuration > Network Parameters > IP Address.... The IP Address Table appears (Figure 6-3). Figure 6-3. IP Addresses Table 3. In the IP Address Table (Figure 6-3), click <Add…>. The Add IP Address dialog box appears (Figure 6-4). Figure 6-4. Add IP Address Configuring WAN Parameters 6-3 Chapter 6 Configuring FCD-IP for a Typical Application RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual 4. In the IP Address field, type 192.168.10.1. 5. In the IP Mask field, type 255.255.255.252. 6. In the Interface drop-down list, select LINK1. 7. Click <Set>. 6.3 Configuring the E1 Interface Configuring the E1 interface includes the following: • Configuring E1 Parameters • Mapping E1 Timeslots. Configuring E1 Parameters To configure E1 parameters: 1. Select LINK1. 2. Switch to Edit View: Click the Edit View button on the toolbar 3. Select Configuration > Physical Parameters > General…. The E1 Link Parameters dialog box appears. Figure 6-5. The E1 Link Parameters 4. From the Clock Source drop-down list, select Link 1. 5. From the Multiplier drop-down list, select 64 kbps. 6. Click <Set>. 6-4 Configuring the E1 Interface . RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 6 Configuring FCD-IP for a Typical Application Mapping E1Timeslots To configure TS parameters: 1. Select LINK1. 2. Switch to Edit View: Click the Edit View button on the toolbar . 3. Select Configuration >Physical Parameters > TS Assign… or click the shortcut key on the toolbar . The TS Assignment dialog box appears (Figure 6-6). Figure 6-6. TS Assignment 4. Configure the first eight timeslots as follows: TS1, TS2, TS3 and TS4 – FIX SUB Voice TS5, TS6, TS7 and TS8 – DATA LINK 1. 5. Click <Set>. 6.4 Configuring the LAN Interface Configuring the LAN interface includes the following: • Enabling the LAN • Configuring the LAN IP Address • Configuring Default Gateway Settings Enabling the LAN To configure LAN Host Parameters: 1. Select the Ethernet LAN. 2. Switch to Edit View: Click the Edit View button on the toolbar . 3. Select Configuration > Interface Info… The Interface Information dialog box appears. Configuring the LAN Interface 6-5 Chapter 6 Configuring FCD-IP for a Typical Application RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Figure 6-7. Interface Information - Ethernet LAN 4. From the LAN State drop-down list, select Enable. 5. Click <Set>. Configuring the LAN IP Address To configure the LAN IP Address: 1. Switch to Agent View: Click the Agent View button on the toolbar 2. Select Configuration > Network Parameters > IP Address.... The IP Addresses Table appears (Figure 6-3). Figure 6-8. IP Addresses Table 6-6 Configuring the LAN Interface . RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Chapter 6 Configuring FCD-IP for a Typical Application 3. In the IP Addresses Table, click <Add…>. The Add IP Address dialog box appears. Figure 6-9. Add IP Address 4. In the IP Address field, type 192.168.10.2. 5. In the IP Mask field, type 255.255.255.000. 6. In the Interface drop-down list, select LAN1. 7. Click <Add>. Configuring Default Gateway Settings To configure default gateway settings: 1. Select Configuration > System Commands > DHCP… The DHCP table appears (Figure 6-10). Figure 6-10. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Table 2. Click <Add…>. The Add DHCP Entry table appears. Configuring the LAN Interface 6-7 Chapter 6 Configuring FCD-IP for a Typical Application RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Figure 6-11. Add DHCP Entry Table 3. In the Default Gateway drop-down list, select Interface. 4. In the Interface drop-down list, select Link1. 5. Click <Set>. 6-8 Configuring the LAN Interface Index —A— A.#, 1-2 Address resolution protocol, 2-7 Agent polling, 2-22 Agent View, 1-2 Alarms SHDSL, 4-2 Async physical parameters, 3-10 —B— Bridging parameters, 2-3 —C— Channel interface configuration, 3-1 interface information, 3-1 Configuration manager list, 2-22 network parameters, 3-34 protocol parameters, 3-29 reading E1/T1 from Agent, 3-22 SNMP, 2-22 typical application, 6-1 updating E1/T1, 3-22 Connection status, 2-18 Current statistics polling interval, 5-2 —D— DHCP, 2-19 default gateway, 6-7 network parameters, 3-37 Diagnostics, 3-38, 5-2 DLCI parameters, 3-30 statistics, 5-10 —E— E.#, 1-2 E1 over SHDSL physical layer statistics, 5-12 E1/T1 interface configuration, 3-1 interface information, 3-1 link mode, 3-16 physical layerstatistics, 5-6 physical parameters, 3-17, 6-4 reading configuration from Agent, 3-22 sanity errors, 4-1 statistics, 5-3 time slots, 3-19, 6-5 updating current configuration, 3-22 E1/T1 over SHDSL interface configuration, 3-6 interface information, 3-6 Edit View, 1-2 password, 1-3 Ethernet collisions statistics, 5-20 error statistics, 5-16 FCS & test errors statistics, 5-20 frame error statistics, 5-19 general statistics, 5-15 interface configuration, 3-9, 6-5 interface information, 3-9, 6-5 octet statistics, 5-18 packet statistics, 5-17 statistics groups, 5-17 Tx and Rx errors statistics, 5-19 —F— Fault management, 4-1 FCD-IP description, 1-1 workplace, 1-2 Forwarding IP, 2-5 static, 2-3 Frame relay protocol layer statistics, 5-9 protocol parameters, 3-29 reset, 3-3 —I— Info tab, 3-2 Information interfaces, 3-1 Interface configuration Channel, 3-1 E1/T1, 3-1 E1/T1 over SHDSL, 3-6 Ethernet, 3-9, 6-5 ISDN, 3-1 I-1 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Index SHDSL, 3-4 Voice, 3-1 Interfaces configuration, 3-1 information, 3-1 selecting, 1-2 IP address table, 2-8 addresses forwarding, 2-5 RIP mode routing, 2-5 ISDN interface configuration, 3-1 interface information, 3-1 physical parameters, 3-13 —L— LAN configuration, 6-5 IP addresses, 6-6 LEDs, 1-3 Link connection, 2-18 reset, 3-37 statistics, 5-3 database, 2-17 disable, 2-11 enable, 2-10 information, 2-14 interfaces, 2-15 neighbors, 2-15 —P— Password, 1-3 setting, 2-23 Performance, 5-1 Physical layer statistics interval, 5-7 Physical parameters async, 3-10 configuration, 3-10 E1/T1, 3-17, 6-4 ISDN, 3-13 SHDSL, 3-23 SHDSL status, 3-25 V.24, 3-10 voice, 3-26 Polling Agent, 2-22 interval, 5-2 graph, 5-4 octet, 5-5 link mode PPP Link tab, 3-3, 6-2 Protocol parameters, 3-29 E1/T1, 3-16 —M— Main window, 1-2 LEDs, 1-3 selecting interfaces, 1-2 selecting system level, 2-1 Management station, 1-2 Manager list, 2-22 Mode agent, 1-2 edit, 1-2 indicator, 1-2 switching between, 1-3, 2-23, 3-1, 4-1, 5-1 Modem adding, 3-12 removing, 3-12 —N— Network parameters, 3-34 DHCP relay, 3-37 IP addresses, 3-34, 6-3, 6-6 IP RIP mode, 3-36 IP routing, 3-35 —O— OSPF, 2-10 areas, 2-12 I-2 protocol parameters, 3-32 Protocol layer statistics, 5-9 DLCI, 3-30 Frame Relay, 3-29 PPP, 3-32 —R— Reset, 2-21 frame relay, 3-3 link, 3-37 —S— Sanity errors, 4-1 SHDSL alarms, 4-2 interface configuration, 3-4 interface information, 3-4 physical parameters, 3-23 SNMP, 2-22 configuration, 2-22 Static forwarding, 2-3 Statistics DLCI, 5-10 E1 over SHDSL physical layer, 5-12 E1/T1, 5-3 E1/T1 physical layer, 5-6 error frames, 5-5 Ethernet collisions, 5-20 Ethernet error, 5-16 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual Ethernet FCS & test errors, 5-20 Ethernet frame errors, 5-19 Ethernet general, 5-15 Ethernet groups, 5-17 Ethernet octets, 5-18 Ethernet packets, 5-17 Ethernet Tx and Rx errors, 5-19 link, 5-3 packets data, 5-3 physical layer protocol layer, 5-9 System configuration, 2-2 information, 2-2 level, 2-1 —T— Tests, 3-38, 5-2 Time slots assignment, 3-19, 6-5 color codes, 3-20 color codes inside cells, 3-20 Index creating a connection, 3-21 disconnecting, 3-21 letter codes, 3-21 port name color codes, 3-21 resetting all connections, 3-21 selecting a port cell, 3-21 Typical application configuration, 6-1 —V— V.24 physical parameters, 3-10 View agent, 1-2 edit, 1-2 indicator, 1-2 switching between, 1-3, 2-23, 3-1, 4-1, 5-1 Voice interface configuration, 3-1 interface information, 3-1 physical parameters, 3-26 I-3 Index I-4 RADview FCD-IP User’s Manual