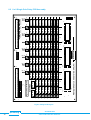
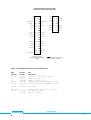
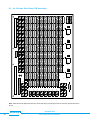
Download USER MANUAL pickering
Transcript
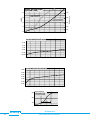
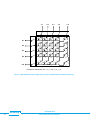
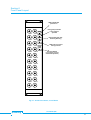
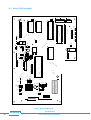
USER MANUAL pickering Model No. 20-520/20-525 R.F. Matrix Module with Self-Test Designed & Manufactured by:Pickering Interfaces Limited. Stephenson Road Clacton-on-Sea Essex CO15 4NL England Tel: Fax: 01255-428141 01255-475058 +44 1255-428141 (International) +44 1255-475058 (International) Internet: www.pickering.co.uk E Mail: [email protected] Issue 2.00 June. 1996 © Copyright (1996) Pickering Interfaces Ltd. All Rights Reserved pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 1 HELP!!! If you need assistance with your Pickering Interfaces Switching System: Switching problems, Programming or Integration within your Test System. – Please ring Pickering Interfaces and ask for “Technical Support”. Alternatively you may fax, email or connect to our Internet Web Site. A full set of operating manuals, application notes and software drivers is available on CD ROM. pickering 2 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Contents Section 1 High Density Matrix Modules ..................................................................................... 5 Section 2 Constructing Large Matrix Systems .......................................................................... 11 Section 3 Self Test ................................................................................................................... 15 Section 4 Programming ........................................................................................................... 17 Section 5 Connector Pin-Out Diagrams................................................................................... 19 Section 6 Front Panel Layout .................................................................................................. 21 Section 7 Reconfiguring Driver Card to Your Application ......................................................... 23 Section 8 Circuit Diagrams ...................................................................................................... 25 Section 9 Adapting Matrix for Analogue Bus Connection ........................................................ 41 Section 10 Electrical, Environmental, Mechanical & Firmware Specifications .......................... 43 pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 3 pickering 4 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Section 1 High Density Matrix Modules 1.1 Features • High Isolation RF Switching Matrix, Available in 16 x 4 and 8 x 8 Configurations. • • Single Pole Version Available in 50Ω or 75Ω Version with 100MHz Bandwidth Double Pole Version Available with 50Ω Triaxial Connectors. • • • Full Matrix Self-Test for Total Switch Contact Confidence. On-Board Isolation Switches Remove Unused Crosspoint Rows/Columns. Large Low Frequency Matrices Easily Built Up Using Internal 24 Pole Analogue Bus. • • • Up to 31 Matrix Modules May Be Cascaded to Form Matrices with Sizes to Over 2000 Crosspoints. Very Large Partially Filled Matrices May Be Constructed When Used In Conjunction with 20-700 Series RF Multiplexer Modules. Front Panel Mounted BNC Co-Axial Connectors. • • Two Reed Switch Types: Standard Dry or Ruthenium. Switch up to 100Vd.c., 10W, 0.5A (1.2A carry). 1.1.1 Matrix Description This manual covers all models in the 20-520 range of Very High Isolation Matrix Modules switching frequencies to beyond 100MHz, available in both 50Ω & 75Ω versions. Also suitable for high accuracy, low frequency instrumentation requiring good isolation/noise performance. Built-In Self-Test gives complete switch confidence. System 20 High Isolation RF Matrix Modules are intended for easy construction of high performance matrix switching systems; modules may be simply cascaded to form matrices of almost any size. Connections are made via industry standard BNC connectors. Larger low frequency matrices are easily constructed using the internal 24 pole guarded analogue bus. Isolation Switches on each module remove all unselected columns and rows from the system, maximising both isolation and RF performance. Full Self-Test is performed both at power up and at any other time either manually or under program control. Self-Test is of particular importance in large systems where relay contact integrity is a very major consideration. In the unlikely event of relay failure (either high on-state or low off-state resistance) the front panel will indicate a fault. The diagnosis - including the position of the suspect relay - will be indicated using the DIAGNOSTIC? command. For a summary of switching capabilities please refer to tables 1.1 & 1.2. This is a double height module and must be mounted into a double height (6U) case: Available case types: 10-934, 10-936 20-930 and 20-935. 1.1.2 Applications Main applications will be for very high quality switching where standard matrix units have inadequate RF and isolation performance, these include: high quality data acquisition (usually 2 pole with frequencies < 1MHz), RF matrices (1 pole to beyond 100MHz), telecommunications and video applications (75Ω impedance) and high quality signal routing in functional ATE systems. 1.1.3 Front Panel The module front panels are illustrated in Section 6, they comprise of three elements: Status Display, 4 LED Indicators:Power LED. Active LED. Connected to power system supply. On whenever one or more matrix switches are closed. For a list of all active switches use the VIEW? command. Self-Test LED. Active when self-test in progress. Error LED. Indicates that error found during self-test. Self-Test Button. Press to initiate a self-test, this will first disconnect the matrix, then perform a full functional self-test, finally reconnecting the matrix when complete. While in progress the “Self-Test” LED will be on, if a failure is detected then the “Error” LED will be set on permanently. Use the DIAGNOSTIC? command to find the exact cause of any failure, refer to section 3 for further details. NB: Self-Test button will only respond when matrix is inactive (i.e. no crosspoints set). Matrix Connectors. Provides connection to and from matrix, BNC Co-Axial and BNC Tri-Axial connectors, please refer to Section 6. pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 5 Isolation Switch Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Y6 Y7 Y8 X1 X2 X3 X4 Matrix Crosspoint X5 X6 X7 X8 Fig 1.1 Matrix Schematic (8 x 8, 2 Pole) Characteristic Impedance 50 or 75Ω RF Specification For 1 Pole Version Only: Maximum Frequency 200MHz Rise Time < 1nS † Insertion Loss (< 100MHz) < 3dB † V.S.W.R. (< 70MHz) < 1:1.8 † Isolation (< 100MHz) > 75dB Crosstalk (< 100MHz) > 60dB Maximum Voltage Maximum Power Maximum Switch Current Maximum Carry Current 100V d.c. 10W 0.5A 1.2A On Path Resistance < 500 mΩ Off Path Resistance > 109 Ω Noise < -75dBm Differential Thermal Offset < 20µV Capacitance: Open Channel to Ground < 40pF Capacitance: Selected Channel to Ground < 70pF Capacitance: Open Input to Output < 4pF Expected Life (Low Power) Expected Life (Max Power) > 1x108 ops > 5x106 ops Switching Time < 10mS Table 1.1 Switching Specification † RF Performance is entirely dependant upon the combination of crosspoints currently selected, these figures are for one selected crosspoint only, please refer to graphs in Sec 1.4. pickering 6 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 1.2 Matrix Module Model Numbers The following table lists the standard options available with the matrix module:Configuration Connect Type Imdepance No. of Poles Dry Reed Switch Low Level Switch 16 x 4 BNC Coax 50Ω 1 20-520-501 20-520-521 16 x 4 BNC Triax 50Ω 2 20-520-502 20-520-522 16 x 4 BNC Coax 75Ω 1 20-520-701 20-520-721 8x4 BNC Coax 50Ω 1 20-522-501 20-522-521 8x4 BNC Triax 50Ω 2 20-522-502 20-522-522 8x4 BNC Coax 75Ω 1 20-522-701 20-522-721 8x8 BNC Coax 50Ω 1 20-525-501 20-525-521 8x8 BNC Triax 50Ω 2 20-525-502 20-525-522 8x8 BNC Coax 75Ω 1 20-525-701 20-525-721 Configuration Options † : –Y Y Coordinates connected to analogue bus. –X X Coordinates connected to analogue bus † Default configuration is no connections to internal analogue bus. Further options (see notes below): –R Limiting Resistor (e.g. 20-525-701-R). –L Loop Through Option: All of the above modules are available with a loop through option, see diagram, frequently used in the construction of large self terminating RF matrices. Please order option -L (e.g. 20-525-501-L) Further options are available for interconnecting matrix modules to form very large matrices, please contact factory to discuss your application in more detail. All reed relay switching modules have the facility for a built in limiting resistor on each switch. This can be very useful in preventing high current in-rushes which may result in damage to the reed switch. These links are normally shorted, however when ordering you may specify limiting resistors if you wish, option -R. pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 7 Y1 Y2 Y4 To Self Test Circuit X1 X2 X 16 To Self Test Circuit Fig 1.2 Full Schematic of 16 x 4 Single Pole Matrix Module (104 Relays with 64 used in main Cross-Point Matrix) pickering 8 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 1.3 Reed Switch & Connector Options A summary of these modules capability is in tables 1.1 and 1.2. Additional data is included below:1.3.1 Dry Reed Switch Reed Relay Type Expected Life 50Ω 1/2 Pole: 102M-1-A-12/1D 75Ω 1 Pole: 101-1-A-12/949D > 108 operations at low current/voltage load. > 5x106 at 260mA, 28V. 1.3.2 Low Level Ruthenium Reed Switch - for low level signal use only Reed Relay Type 50Ω 1/2 Pole: 102M-1-A-12/2D 75Ω 1 Pole: 101-1-A-12/949D SW 2 Expected Life > 108 operations at low current/voltage load. NB This switch is not suitable for switching high current loads. 1.3.3 Front Panel and Connectors Two connector types are currently available, both are front panel mounted:1 Pole Version 16 x 4 Matrix: 20 x BNC Coaxial Connector Sockets, see Fig 6.1. 8 x 8 Matrix: 16 x BNC Coaxial Connector Sockets, see Fig 6.2. 2 Pole Version 16 x 4 Matrix: 20 x BNC Triax Connector Sockets, see Fig 6.1. 8 x 8 Matrix: 16 x BNC Triax Connector Sockets, see Fig 6.2. Module width is 12 HP (2.4 inches, 60.8mm). Front Panel layouts are illustrated in Section 6. 1.4 Typical RF Performance Plots (Single Pole Versions) Typical RF Performance Plots for 20-525-501 (8 x 8, Single Pole) Curves are shown for matrix rows/columns with: 1 or 2 interconnected crosspoints set. For optimum insertion loss and VSWR (reflection) performance ensure only one crosspoint is set in any one row/column. Performance curves for all versions of the single pole matrix modules have similar characteristics, any differences are shown. For further information please contact factory. 0 dB 20-525 MATRIX INSERTION LOSS -0.4 dB 1 Crosspoint Set -0.8 dB -1.2 dB -1.6 dB -2.0 dB -2.4 dB -2.8 dB 2 Crosspoints Set -3.2 dB 50MHz pickering 100MHz 150MHz 200MHz 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 9 20-525 MATRIX VSWR (RETURN LOSS) VSWR 1.6 1 Crosspoint Set (75Ohm Version) 13dB 1 Crosspoint Set (50Ohm Version) 1.4 16dB 1.2 21dB 26dB 1.0 50MHz 100MHz 20-525 MATRIX ISOLATION -50 dB -60 dB -70 dB -80 dB -90 dB -100 dB 50MHz 100MHz 150MHz 200MHz 20-525 MATRIX CROSSTALK -40 dB -50 dB -60 dB -70 dB -80 dB -90 dB -100 dB 50MHz 100MHz 150MHz 20-525 TYPICAL 90% STEP RESPONSE (1 Crosspoint Set) 50% 0.7nS 10% 0.4nS pickering 10 0.8nS 1.2nS 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 200MHz Return Loss 11dB 1.8 Section 2 Constructing Large Matrix Systems 2.1 Creating Large Matrices Each System 20 interface can directly support cascaded matrices up to 128x16 or 32x64 using 16x4 matrix modules or up to 64x32 using 8x8 matrix modules, i.e. up to 31 modules per matrix, larger sizes can be supported using multiple System 20 interface modules mounted in separate cases. Forming larger matrices is usually only a question of plugging in additional matrix modules, a 24 pole guarded analogue bus is provided on the System 20 Analogue Backplane. So constructing large matrices is very straight forward, no time consuming daisy-chained wiring harnesses. Further expansion is simply a matter of adding additional matrix modules, please refer to notes in Section 2.4. All matrix modules in a cascaded matrix must have the same primary address, their position within the matrix is determined by their bank address (see sec 4.2, figs 2.1 & 2.2), this is set on an additional 5 way dip switch. The cascaded matrix is then programmed as a whole, the programmer does not need to address each matrix module individually, only a pair of coordinates for the required crosspoint need be sent. 2.2 Isolation Switches Both the X and Y axes have on-board automatic isolation switches. In large matrix systems the parasitic capacitance associated with each cross-point switch can result in a large capacitance if several matrix modules are interconnected. The isolation switches only switch in those columns and rows on a module that contain an active switch. Thereby keeping matrix capacitance to a minimum., this may be important for applications requiring high isolation and crosstalk as well as good insulation resistance. NB. These isolation switches are also used to remove the matrix from the external circuit when performing self-test. 2.3 “Partially Filled” Matrices For users requiring very large matrix systems the cost of a fully populated matrix may prove prohibitive, in many instances a combination of multiplexer input/output and small “core” matrix may prove quite acceptable. This approach may prove to be more effective in terms of both cost and performance, the main draw backs being additional programming complexity and restricted matrix versatility (particularly for future unforeseen requirements). Please contact Pickering if you wish to discuss your matrix application in greater detail. Pickering can build large Matrix systems constructed and tested to your exact requirements, (especially if your application involves switching RF or very high isolation signals), please contact sales office for further details. 2.4 Expanding an RF Matrix Using the Analogue Bus If the signals being switches are not RF, typically < 1MHz bandwidth then using the analogue bus will be very straightforward. However, if RF frequencies (>1MHz) are being switches then particular attention must be paid to matrix interconnection. If the analogue backplane bus is used to interconnect two or more matrices switching RF signals then return loss (VSWR) will be very severely affected (e.g. around 10dB at around 10MHz), insertion loss will also be degraded This is due to the effect of the long bus lines (typically 45cm in length). Performance can be maximised by interconnecting the matrix modules using the front panel mounted Coaxial connectors or by ordering a system with a reduced length analogue backplane bus (e.g. quarter length). However if very low VSWR performance is required when switching RF signals, particularly in a large system, it may be worth looking at the Pickering Interface’s range of RF multiplexers, these can be used to construct very high performance matrix systems. Please contact factory for further information or advice. pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 11 Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y8 X1 X2 X3 X4 X8 Crosspoints Closed are at x = 2, y = 2 & x = 2, y = 4. Fig 2.1 Typical Matrix (8 x 8 Single Pole) in Use with Automatic Isolation Switching pickering 12 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 8 6 3 4 5 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 4 5 8 8 4 5 4 5 8 8 8 x 8 Matrix 8 x 8 Matrix R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Fig 2.2 32 x 8 Matrix Switch 32 Inputs 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 5 8 8 8 x 8 Matrix 1 2 1 2 8 Outputs 3 4 5 3 4 5 8 Poles of the internal guarded Analogue Bus are used to interconnect the 4 matrix modules. Additional matrix modules may be simply plugged in to give further expansion. 1 2 8 6 3 4 5 1 2 8 6 3 4 5 1 2 8 6 3 4 5 pickering 1 2 INTERNAL 24 POLE ANALOGUE BUS 8 8 8 x 8 Matrix 20-520/20-525 13 pickering 14 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Section 3 Self Test 3.1 Self-Test Function Self-Test is invoked at power on (taking up to 60 seconds) and may also be operated under software (*TST?) or via a recessed push button. Self-Test pass is indicated on a front panel LED with a full pass/fail description available using the DIAGNOSTIC? command. Self-Test comprises 3 levels, see Fig 3.1:1. Logic Test: Checks all logic including on-board microprocessor, relay drivers etc. 2. 3. (i) Relay Coil Test: All reed relay coils are checked for continuity. Full Contact Test: Tests all the relay contacts in the matrix block. Two test are undertaken: On-state resistance failure test. Fails if switch has on-state > 2Ω. (iii) Off-state resistance test. A switch fails if it’s isolation resistance is < 106Ω. The threshold for contact resistance is preset to approximately 2Ω at the factory. However this threshold may set to customers precise requirements (from 200mΩ to 10Ω). If a very low threshold is selected, the self test could be used to detect switches which are not failing to operate but which have reached an end of life condition, where the contact resistance is starting to rise, indicating that the relay is due for replacement. NB. The contact self test will only check the relay contacts in the core matrix block, isolation switches and self test switches are not tested, please refer to section 3.4 for further details. Note: Fault diagnosis on 2 pole matrix modules will identify down to a pair of relays. Both these relays must be replaced, only the position of the first relay in the pair is given by the REPORT? command, please refer to Section 8.3. 3.2 Self-Test Operation Self Test is always run at power on, taking approximately 60 seconds. If self test is run under software control it will firstly clear the whole matrix (Manual Test will only function when the module is in a clear state). So it is very important to prepare your external instruments and U.U.T. for this! During self-test all isolation switches are opened so your external circuitry will see only very high resistance inputs. When the self-test has finished the matrix will be returned to an all clear state (i.e. the previous state will not be remembered!). Please note that because of the long self-test time that your computer may time out waiting for the test result (many PC's have default timeouts set to 10 seconds). 3.3 Detailed Self Test Reporting using DIAGNOSTIC? Query The DIAGNOSTIC? query will give an ASCII string detailing any self test failures. These will include:Logic: µP, RAM, EPROM, Relay Drivers, Invalid Link Settings etc. Relay Coils: Open Circuit Coil. Switch Contacts: High On Resistance, Low Off Resistance. This string is not intended to be processed by the user’s software, it is suitable for copying directly onto the screen of your control computer. This information will then indicate maintenance required (please contact Pickering for further help). 3.4 Self Test Limitations Self Test covers all aspects of the Matrix Module which are liable to fail in normal use. The only exception to this are the following:“Isolation Relays”: These switches are used to isolate the matrix from the users external circuitry, for this reason they cannot be included in the contact self test routine, refer to fig 2.1. These relays always “cold switch” (i.e. they are always operated without any load, as opposed to the matrix switches which always “hot switch”), therefore they should have an expected life in excess of 108 operations. These switches will only fail if a very heavy current is passed through the contacts (greater than around 3-4A for 10's of milliseconds, see section 5.1.1), this may result in switch weld to either an isolation or matrix switch. Please note that all relays including isolation and self test relays are included in the coil test, so an open circuit coil or faulty driver IC will be picked up and reported. “Self Test Relays”: There are self test relays on every x and y axis on the matrix board, if one of these contacts welds (very, unlikely) then all relays on that axis will appear to fail self test. pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 15 SELF TEST INITIATED BY: • POWER ON • *TST? QUERY • MANUAL BUTTON LOGIC TEST: • µP BOARD • RELAY BOARD LOGIC TEST FAIL YES NO RELAY COIL TEST COIL TEST FAIL YES NO CONTACT TEST: • SWITCH ON STATE RESISTANCE < 2Ω • SWITCH OFF STATE RESISTANCE > 1MΩ CONTACT TEST FAIL YES NO SELF TEST PASS SELF TEST FAIL: • ERROR LED ON • USE DIAGNOSTIC? COMMAND TO GET ERROR MESSAGE Fig 3.1 Self-Test: Basic Flow Diagram pickering 16 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Section 4 Programming 4.1 Select Module Address Choose module address (from 0 - 30) using the address select switch (SW1) on the top of the driver card (the top screen of the module may need to be removed to reveal the address switch). The module address selected in the illustration is 22 (i.e. 16 + 4 + 2 = 22). 4.2 Select Module Bank Address When more than one module is used to make up a large matrix (see Fig 1.2), where four 20 x 12 modules are used to make up a 40x24 matrix), then all matrix units must have the same module address, the location of each module within the matrix is given by its bank address. The matrix bank address is composed of two x and y components, see Fig 1.3 , these determine the individual matrix modules position within the larger matrix. The bank address is constructed using 5 bits, see diagram, 3 bits for x and 2 bits for y. For example bit settings 0 0 1 0 0 represent bank address x = 1, y = 0. 16 bank address 8 4 2 SW1 module address 16 8 4 2 1 1 ON 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 PCB Side View Top View There must always be a module present at the base address x = 0, y = 0, otherwise the matrix will not be recognised by the intelligent interface. If there is a problem with any of the modules used to make up a large matrix then an error will be detected (use the DIAGNOSTIC? query to discover the cause). 4.3 Using the Intelligent GPIB Interface X2 X1 X0 Y1 Y0 Switching matrices are controlled using the MCLOSE and MOPEN commands:To close switch at position X = 17, Y = 9 on matrix with address 11. MCLOSE 11,17,9 Now to look at status of matrix 11. VIEW? 11 will return “17,9” To open last switch and close switches at positions X = 1, Y = 1 and X = 2, Y = 1 on matrix 11. MOPEN 11,17,9;MCLOSE 11,1,1;MCLOSE 11,2,1 Now to look at status of matrix 11. VIEW? 11 will return “1,1;2,1” To reset all switches on matrix 11. ARESET 11 Now to look at status of matrix 11. VIEW? 11 will return “0,0" - 0,0 indicates no coordinates set. Note: The 10-920 Interface imposes a maximum limit allowing up to 100 crosspoints to be on at any one time (this is to prevent the power supply becoming overloaded). pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 17 4.4 Instruction Set The Matrix module is very easy to program using the Model 10-920 IEEE-488.2 Interface:ARESET a Open all switches on device a MCLOSE a,x,y Close switch at coordinates x,y on matrix a MOPEN a,x,y Open switch at coordinates x,y on matrix a RESET VIEW? a Open all switches on all modules View status of device a. Self Test Functions:DIAGNOSTIC? Return diagnostic string (self test fail details, if any). Refer to Sec 3.3 for further details *TST? Execute Full Self Test (IEEE-488.2 query) 4.5 Operating Speed Maximum switching frequency is approximately 25mS to open or close any one crosspoint when using the 10-920 IEEE488.2 Interface Module, the higher speed 10-921 interface reduces this time to 10mS. pickering 18 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Section 5 Connector Pin-Out Diagrams ROW A C 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 Analogue 2.1 Analogue 2.2 Analogue 2.3 Ground Analogue 2.4 Analogue 2.5 Analogue 2.6 Ground Analogue 2.7 Analogue 2.8 Analogue 2.9 Ground Analogue 2.10 Analogue 2.11 Analogue 2.12 Ground Analogue 2.13 Analogue 2.14 Analogue 2.15 Ground Analogue 2.16 Analogue 2.17 Analogue 2.18 Ground Analogue 2.19 Analogue 2.20 Analogue 2.21 Ground Analogue 2.22 Analogue 2.23 Analogue 2.24 Ground A & C contacts are commoned. All analogue bus lines are surrounded by a grounded guard track to minimise inter–channel crosstalk. Analogue Bus Approximate RF Characteristic Impedance = 65Ω. Fig 5.1 24 Pole Internal Analogue Bus Connector (Type: 64 Pin DIN 41612) pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 19 AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA ROW A C GND 5V(relay) 5V(logic) DIO1 DIO3 EOI NRFD IFC ATN DIO5 DIO7 REN Settled Reserved (SCK) Analogue 1.1 Analogue 1.2 Analogue 1.3 Analogue 1.4 Analogue 1.5 Analogue 1.6 Analogue 1.7 Analogue 1.8 Analogue 1.9 Analogue 1.10 Slot Address Bit 0 Slot Address Bit 2 Slot Address Bit 4 Backplane Address Bit 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 GND 12V(relay) POWER SUPPLIES 5V(logic) DIO2 DIO4 DAV NDAC SRQ SYSTEM DIGITAL BUS Reserved (Parallel and Serial Bus) DIO6 DIO8 Reserved (-SS) Reserved (MOSI) Reserved (MISO) Analogue 1.1 Analogue 1.2 Analogue 1.3 Analogue 1.4 Analogue 1.5 ANALOGUE BUS Analogue 1.6 Analogue 1.7 Analogue 1.8 Analogue 1.9 Analogue 1.10 Slot Address Bit 1 Slot Address Bit 3 POSITION Backplane Address Bit 0 LOCATOR Backplane Address Bit 2 AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA 12V(relay) 5V(logic) GND 12V(relay) 5V(logic) GND POWER SUPPLIES 10/92 Note: The Analogue bus on this connector is not used by any matrix module (only multiplexers). All analogue bus lines are surrounded by a grounded guard track to minimise inter–channel crosstalk. Analogue Bus Approximate RF Characteristic Impedance = 65Ω. Fig 5.2 Power/Control/Analogue Bus Connector (Type: 64 Pin DIN 41612) pickering 20 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Section 6 Front Panel Layout LED (red) Module powered on X1 X2 POW X3 X4 LED (green) Indicates if any switch is operated ACT TEST X5 X6 X7 X 8 MAN TEST X9 X 10 X 11 X 12 X 13 X 14 X 15 X 16 Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 LED (yellow) Self-Test Currently Running ERR LED (red) error found during self-test Self-Test Switch (recessed to prevent accidental operation) Fig 6.1 20-520 Front Panel, 16 x 4 Matrix pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 21 X1 X2 POW X3 X4 ACT TEST ERR X5 X6 MAN TEST X7 X8 Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Y6 Y7 Y8 Fig 6.2 20-525 Front Panel, 8 x 8 Matrix pickering 22 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Section 7 Reconfiguring Driver Card to Your Application Your multiplexer driver card will leave the factory preconfigured, so take great care if you wish to change any of the settings. If in doubt contact Pickering for further details. 7.1 Universal Driver Card: Configuration Links Configuration switches are provided on the driver board at position SW2, on the top edge of the PCB, adjacent to the 10 way address selection lever switch. The five switches, see Fig 7.1, are used as follows:Relay Settling Time There are four choices of relay settling time, this is to allow for different applications and relay types. 1 2 Relay Settling Time † 0 0 4.0ms 0 1 1 0 1.0ms - default setting 0.5ms 1 1 0.0ms † The “Settled” line is triggered after this delay Matrix Intelligent Isolation Switching This will allow intelligent isolation switching, i.e. only those matrix rows and columns that have an active crosspoint switch will be connected in circuit. Note intelligent isolation switching may operate a little slower (up to around 5ms per operation because all isolation switches always cold switch). 3 0 4 – 5 – Function 1 Pole Switching (used for self test only) 1 – – – 0 1 – – – 2 Pole Switching (used for self test only) Enable Full Self Test (60 Seconds) - default setting Enable Logic Only Self Test (5 Seconds) – – – – 0 1 Enable Automatic Isolation Switching - default setting Disable Automatic Isolation Switching 7.2 Repeating Self Test with Burn In - Factory Use Only A burn-in test facility is built into the module, this is initiated by pressing the selftest button until the Active LED goes on (around 5 seconds). Here the module will run the usual full selftest together with some additional isolation tests followed by 15 minutes of “switch rattling”, the test procedure will then be repeated. This process may only be stopped by powering off or holding the manual test button in for several seconds. This feature is for factory use where matrix modules are burned-in prior to undergoing final test. 5 4 3 2 1 O N SW2 Fig 7.1 Driver Card Configuration Links on SW2 pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 23 pickering 24 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Section 8 Circuit Diagrams Two sets of circuit diagrams and documentation are contained:- • 8.1 Driver PCB Assembly PCB Layout Circuit Diagram (6 pages) Inter PCB Connectors Parts List • 8.2 8 x 8 Single Pole Relay PCB Assembly PCB Layout Inter PCB Connectors Parts List • 8.3 8 x 8 Double Pole Relay PCB Assembly PCB Layout Parts List pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 25 D.1 Driver PCB Assembly C6 C8 C7 1 2 4 8 16 1 2 4 8 16 5 4 3 2 1 5 4 3 2 1 J1 BANK SW1 ADDR SW2 LD1 R4 R8 U8 k LD2 U7 k LD3 k LD4 C9 Q3 U6 k R9 C13 U9 Q4 X1 R23 R22 SW3 C2 J3 C1 + J4 C3 U1 C4 Q1 U3 R7 R3 R2 R1 R5 U4 J2 C12 U5 R6 R16 R15 U2 R17 R11 C5 R18 U10 R21 Q2 R14 R10 R19 RL1 RL2 RL3 RL4 C10 R20 C11 pickering Fig 8.1 Driver PCB Layout pickering 26 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 27 C2 C1 GND +5V 4 3 2 1 C6 GND +5V U1 GND CT C7 Vcc -RESET RESET SENSE 7705 -RESIN Vref System 20 Driver Card - GPIB 80 Rev 0 C8 5 6 7 8 C9 R1 C10 C11 -RES C12 C13 -LD4 -LD3 -LD2 14.11.90 Sheet 1 of 6 GND R4 STAT LD1 R2 LD2 Miscellaneous: Reset control, LEDs, Power Supply decoupling, 'Settled' line driver LD3 R3 GND +5V Q1 LD4 +5V STLD pickering 28 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE -IRQ1 MODDATA -LEAK1 -CTEST2 -DROP -CTEST1 -LEAK2 Serial Debug 5 4 3 2 1 J3 SERCLK IGIDATA -LD4 -LD3 -LD2 GND +5V R23 +5V Q4 GND U5 R22 74HCT244 GND 2Y1 1A4 2Y2 1A3 2Y3 1A2 2Y4 1A1 -1G GND 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 GND 2A1 1Y4 2A2 1Y3 2A3 1Y2 2A4 1Y1 -2G Vcc 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 R5 +5V +5V +5V SW3 INH RDATA5 RDATA4 RDATA3 RDATA2 GND R6 C3 -RES GND X1 STAT C4 R7 +5V STRB5 STRB4 STRB3 STRB2 STRB1 LDATA LCLK -STFAIL 14.11.90 Sheet 2 of 6 +5V GND +5V CPU, address decoding, ROM and buffers 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -WR EXTAL A15 Vcc P67 A14 A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 Vss A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 P66 P65 P64 P63 P62 P61 P60 P57 P56 P55 P54 P53 P52 P51 P50 P27 P26 P25 P24 P23 P22 P21 D2 D1 P20 D0 BA -NMI -RES -STBY -LIR MP1 R/-W -RD XTAL MP0 E 6303X U2 Vss GND System 20 Driver Card - GPIB 80 Rev 0 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 -GPIACS -PIACS2 +5V A15 A14 A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 A14 A13 GND D2 D1 D0 A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1Y1 1Y0 1B 1A 1G Vss D2 D1 D0 A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 U3 2Y3 2Y2 74HCT139 Vss 1Y3 2Y1 2Y0 2B 2A 2G Vcc 27256 16 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 -CS A10 -OE A11 A9 A8 A13 Vcc A14 U4 Vpp A12 1Y2 GND GND A12 -WR E GND +5V 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 +5V A15 A10 A11 A9 A8 A13 A14 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 29 -RES E -WR -GPIACS 6 10 D3 13 14 D6 D7 20 19 18 17 16 15 12 D5 11 9 D4 8 D2 7 D1 D0 5 4 3 2 1 +5V -IFC RFD Vcc -SRQ DAC -REN TRIG -DAV -RES -EOI DMA Req T/-R2 -ATN T/-R1 DB6 -IB7 -IB6 -IB5 -IB4 -IB3 -IB2 -IB1 DB7 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 E -IB0 RS0 R/-W RS1 -CS -ASE -IRQ RS2 Vss U6 DMA Gra GND 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 A0 38 A1 39 A2 40 -IRQ1 GPIA, bus transceivers 14.11.90 Sheet 3 of 6 System 20 Driver Card - GPIB 80 Rev 0 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Bus 0 Bus 5 Data 5 GND Bus GND Logic GND 3447 S/-R (7) Bus 7 Data 7 S/-R (6) Bus 6 Data 6 S/-R (1-4) Bus 4 Data 4 S/-R (5) Bus 3 Bus 2 Bus 1 Bus 0 Vcc Data 3 Data 2 Data 1 Data 0 S/-R (0) S/-R (7) Bus 7 Bus 6 Bus GND GND U8 Bus 5 Bus 4 Bus 3 Bus 2 S/-R (1-4) 3447 Logic GND S/-R (6) Data 7 Data 6 S/-R (5) Data 5 Data 4 Data 3 Data 2 Bus 1 Data 0 Data 1 Vcc U7 S/-R (0) 24 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 +5V +5V REN ATN NRFD DIO8 DIO6 DIO4 DIO2 SRQ IFC EOI NDAC DIO7 DIO5 DIO3 DIO1 DAV pickering 30 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Secondary Address Primary Address LSB MSB LSB MSB GND 5 4 3 2 1 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 SW2 SW1 RDATA1 +5V R8 -CTEST1 R9 PIA, selector switches 14.11.90 Sheet 4 of 6 GND +5V 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -CS2 CS0 R/-W CB2 Vcc CS1 EN D7 CB1 PB7 PB6 PB5 D6 D5 PB3 PB4 D4 PB2 D2 D1 D0 -RES RS1 RS0 -IRQB -IRQA CA2 CA1 D3 6321 U9 PB1 PB0 PA7 PA6 PA5 PA4 PA3 PA2 PA1 PA0 Vss GND -LEAK1 System 20 Driver Card - GPIB 80 Rev 0 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 A12 A1 A0 GND -WR -PIACS2 E -RES pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 31 -CTEST1 R10 VSEL R11 R12 GND Q2 Q3 TSTGND TST2 TST1 R13 -LEAK2 -DROP -CTEST2 R14 R15 VREL RL4 RL3 RL2 RL1 Self-test analog circuits 14.11.90 Sheet 5 of 6 R16 R17 System 20 Driver Card - GPIB 80 Rev 0 C5 R19 R18 4 3 2 1 V- IN+ IN- OUT NULL V+ NULL STRB U10 R20 5 6 7 8 GND -STFAIL R21 +5V pickering 32 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 21 16 33 STRB2 15 32 SERCLK LCLK RDATA1 STRB1 LDATA INH MODDATA 17 Primary Serial Loop Internal Bus and RDATA2 RDATA3 RDATA4 RDATA5 TST2 STRB5 TSTGND TST1 STRB4 STRB3 7 14 14 31 34 5 6 13 13 30 IGIDATA 4 11 12 12 29 3 and Self-Test Secondary Serial Loops 10 2 11 1 28 9 STLD 10 27 J2 DIO8 8 8 26 DIO6 9 7 25 (for display) 24 6 5 4 GND Serial Loop No 5 6 5 4 3 2 1 ATN 22 3 2 19 20 1 18 J4 IFC VSEL J1 +5V 23 GND +5V VREL Sheet 6 of 6 14.11.90 Inter-PCB Connectors System 20 Driver Card - GPIB 80 Rev 0 NRFD EOI DIO3 DIO1 DIO2 DIO4 DAV NDAC SRQ DIO5 DIO7 REN The pin rows of connectors J1, J2 are interchanged relative to their physical positions. Note :- GPIB80 System 20 Driver Card inter-PCB connectors (from component side) LCLK 1 8 LDATA +5v RDATA2 2 9 STRB2 3 20 DIO1 RDATA3 3 10 STRB3 DIO4 4 21 DIO3 RDATA4 4 11 STRB4 DAV 5 22 EOI RDATA5 5 12 STRB5 NDAC 6 23 NRFD TSTGND 6 13 INH SRQ 7 24 IFC 7 14 TST1 DIO5 8 25 ATN DIO7 9 26 DIO6 REN 10 27 DIO8 GND 11 28 STLD LCLK 12 29 LDATA RDATA1 13 30 STRB1 INH 14 31 GND MODDATA 15 32 IGIDATA SERCLK 16 33 NC NC 17 34 NC VREL 1 18 VSEL (+12v) GND 2 19 DIO2 TST2 Primary connector pickering Secondary connector Note : Pin numbering is PIL convention only (not industry standard) 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 33 Parts List for GPIB80 Rev0 PCB Assembly PCB Location PIL Part Number Part Description R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 R8 R9 R10 R11 R12 R13 R14 R15 R16 R17 R18 R19 R20 R21 R22 R23 C/RS/012 C/RS/012 C/RS/012 C/RS/016 C/RS/012 C/RS/013 C/RS/012 C/RS/013 C/RS/013 C/RS/025 C/RS/012 C/RS/024 C/RS/025 C/RS/026 C/RS/027 C/RS/025 C/RS/024 C/RS/012 C/RS/005 C/RS/024 ———— C/RS/012 C/RS/012 Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Res Omit Res Res Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 C/SC/001 C/SC/001 C/SC/018 C/SC/001 Transistor Transistor Transistor Transistor BC182L BC182L RFP 12P08 BC182L RL1 RL2 RL3 RL4 C/RL/000 C/RL/000 C/RL/000 C/RL/000 Reed Reed Reed Reed 109-1-A-5/2D 109-1-A-5/2D 109-1-A-5/2D 109-1-A-5/2D U1 U2 U3 U4 U5 U6 U7 U8 U9 U10 C/IC/019 C/IC/018 C/IC/028 C/IC/024 C/IC/033 C/IC/020 C/IC/021 C/IC/021 C/IC/016 C/IC/037 IC IC IC IC IC IC IC IC IC IC C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C/CP/009 C/CP/005 C/CP/010 C/CP/010 C/CP/005 C/CP/003 C/CP/001 C/CP/001 C/CP/001 C/CP/001 C/CP/001 C/CP/001 C/CP/001 Cap Cap Cap Cap Cap Cap Cap Cap Cap Cap Cap Cap Cap SW1 C/SW/005 DIP Switch pickering 34 6k8Ω 6k8Ω 6k8Ω 8-pin 6k8Ω 9-pin 6k8Ω 9-pin 9-pin 22kΩ 6k8Ω 180kΩ 22kΩ 470kΩ 470RΩ 22kΩ 180kΩ 6k8Ω 180RΩ 180kΩ 5% 1/4W 5% 1/4W 5% 1/4W SIP, 4 x 330R separate 5% 1/4W SIP, 8 x 10k commoned 5% 1/4W SIP, 8 x 10k commoned SIP, 8 x 10k commoned 5% 1/4W 5% 1/4W 5% 1/4W 5% 1/4W 5% 1/4W 5% 1/4W 5% 1/4W 5% 1/4W 5% 1/4W 5% 1/4W 5% 1/4W 6k8Ω 6k8Ω 5% 5% Relay Relay Relay Relay 1/4W 1/4W DIG 7705 DIG 63B03X DIG 74HCT139 DIG 27256 EPROM DIG 74HCT244 DIG 68488P DIG 3447 DIG 3447 DIG 63B21 LIN CA3140E 10uF elect 100nF 22pF 22pF 100nF 22uF tant 10nF 10nF 10nF 10nF 10nF 10nF 10nF 10-pole dip piano key 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE SW2 C/SW/001 DIP Switch SW3 C/SW/004 Switch LD1 LD2 LD3 LD4 C/SC/004 C/SC/007 C/SC/004 C/SC/008 LED LED LED LED X1 C/MS/000 Xtal 4.00 MHz J1 J2 J3 J4 C/CN/097 C/CN/077 ———— C/CN/110 34-way pin header (2 row, gold pl.) 14-way pin header (2 row, gold pl.) C/PC/086 PCB pickering 5-pole dip slide 1pst p/button (red) (green) (red) (yellow) 6-way pin header (1 row) 6U PTH 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 35 8.2 8 x 8 Single Pole Relay PCB Assembly B J 4 BB8 B8 8 BB2 4 BB2 3 BB2 2 BB2 1 BB2 0 BB1 9 BB7 B7 BB1 8 BB1 7 BB1 6 BB1 5 BB1 4 BB1 3 BB6 B6 BB1 2 BB1 1 BB1 0 BB 9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0 U 3 K B 7 J B 6 H S Out B BB5 B5 5 C 5 G U 2 B BB4 B4 4 J 3 C 6 F B BB3 B3 3 E B BB2 B2 2 J 1 D C 3 B C 4 U 1 BB1 B1 1 C J 2 RL 97 B S In RL 98 A F 1 F 2 F 3 F 4 F 5 F 6 F 7 F 8 Fig 8.8 Relay PCB Layout pickering 36 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 5 V C 1 12 V C 2 System 20 Relay Card inter-PCB connectors (from component side) NC NC 34 17 33 16 NC SERCLK (14a) TST1 14 7 TST2 INH 13 6 TSTGND STRB5 12 5 RDATA5 IGIDATA (13c) 32 15 MODDATA (14c) GND (1a, c) 31 14 INH STRB4 11 4 RDATA4 STRB1 30 13 RDATA1 STRB3 10 3 RDATA3 LDATA 29 12 LCLK STRB2 9 2 RDATA2 STLD (13a) 28 11 GND (1a, c) LDATA 8 1 LCLK DIO8 (11c) 27 10 REN (12a) DIO6 (10c) 26 9 DIO7 (11a) ATN (9a) 25 8 DIO5 (10a) IFC (8a) 24 7 SRQ (8c) NRFD (7a) 23 6 NDAC (7c) EOI (6a) 22 5 DAV (6c) DIO3 (5a) 21 4 DIO4 (5c) DIO1 (4a) 20 3 DIO2 (4c) 19 2 GND (1a, c) 18 1 VREL +5v (3a, c) VSEL (+12v) (4c) Primary connector backplane bus pin connects in brackets Secondary connector Note : Pin numbering is PIL convention only (not industry standard) Parts List for GPIB86 Rev0 Relay (1 Pole) PCB Assembly PCB Location PIL Part Number Part Description J1, J4 J3 J2 B1..B8 F1..F8 C/CN/001 C/CN/077 C/CN/000 C/CN/118 C/CN/118 Connector DIN 41612 64 Way A/C Header 14 pin 2 row Header 34 pin 2 row PC Mount Dielectric FeedThru 2, 6/50 PC Mount Dielectric FeedThru 2, 6/50 C1..C6 C/CP/001 Cap RL1..RL98 U1..U3 C/IC/026 C/PC/086 pickering 10nF RF Reed Relay See Sec 1.3 for type IC DIG UCN 5818A PCB 6U 4 Layer 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 37 8.3 8 x 8 Double Pole Relay PCB Assembly 24 B8.2 23 B8.1 K d c 22 L-T 21 20 1A 19 18 B7.2 17 16 B7.1 1C J d c 1 L-T 15 14 13 12 11 10 1A C9 C10 B6.2 B6.1 H d c U4 L-T 9 8 7 C7 C8 B5.2 B5.1 G d c 6 5 4 L-T 1 3 2 1 J4 B4.2 B4.1 F d c U3 L-T B3.2 J3 B3.1 E d c L-T B2.2 1 B2.1 D d c L-T B1.2 C5 C6 U2 B1.1 C d c C3 C4 L-T 19 20 1 B C1 C2 1 U1 2 RL193 RL194 b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a A L-T L-T 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 L-T L-T F1. 1 F2. 1 F3. 1 F4. 1 F5. 1 F6. 1 F7. 1 F8. 1 L-T L-T J2 J1 L-T F1. 2 F2. 2 F3. 2 F4. 2 F5. 2 F6. 2 F7. 2 F8. 2 L-T Note: Self Test Fails are diagnosed down to a pair of reed relays (so both relays must be removed), the pairs are shown above. pickering 38 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Parts List for GPIB110 Rev0 Relay (2 Pole) PCB Assembly PCB Location PIL Part Number Part Description J1, J4 J2 J3 C/CN/001 C/CN/124 C/CN/128 Connector DIN 41612 64 Way A/C 34 Way Mini-DIP Transition Connector 14 Way Mini-DIP Transition Connector B1..B8 F1..F8 C/CN/118 C/CN/118 PC Mount Dielectric FeedThru 2, 6/50 PC Mount Dielectric FeedThru 2, 6/50 C1, C2 C3..C10 C/CP/003 C/CP/001 Cap Tant 22uF 16V Cap Cer 10nF 50V RL(A3-K20),195,196 RL193,194,197 C/RL/057 RF Reed Relay, See Sec 1.3 for type 107-1-C-12/3D U1..U4 C/IC/035 IC DIG C/PC/110 PCB 6U pickering UCN 5818EPF 4 Layer 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 39 pickering 40 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Section 9 Adapting Matrix for Analogue Bus Connection 9.1 Configuring Matrix for Analogue Bus Connection All RF matrix modules are shipped from the factory configured for front panel interconnection (please refer to Sec 2.5), therefore if the analogue bus is to be used then the module should be ordered in that configuration or the module must be modified by the user. To reconfigure the matrix module for analogue bus connection for a single pole 8 x 8 matrix:• Remove all Coaxial Launchers, locations B1, B2,...... B8 on relay PCB. • Connect links BB8 to B8, BB7 to B7 .........BB1 to B1. The operation is similar for 16 x 4 and all double pole versions. Please contact factory if you require further information or assistance, module can also be returned to Pickering for modification. pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 41 pickering 42 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE Section 10 Electrical, Environmental, Mechanical & Firmware Specifications Environmental Operating Temperature 0°C to 50°C. Storage Temperature -20°C to 75°C. Humidity 95% non condensing. Weight Dimensions and Power Requirements Approx. Weight/g 1000 Dimensions/mm † Front Panel Width 60.5 Height 268 Overall Length 189 Power /Current Consumption Maximum 5V /mA 12V 250 1000 Minimum 150 0 5V 12V † Approx. dimensions. Standard 160mm, 6U, Eurocard, as specified in DIN 41494. Voltage Supplies Logic Supply 5Vdc ±5%. Relay Supply 12Vdc ±10% Current Firmware Revision: 2.00 pickering 20-520/20-525 R.F. SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE 43 pickering 44 20-520/20-525 SWITCHING MATRIX MODULE