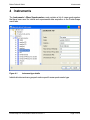
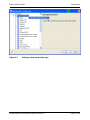
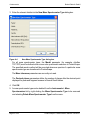
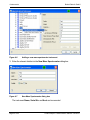
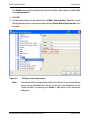
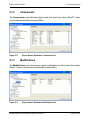
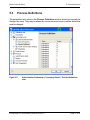
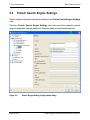
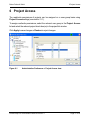
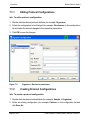
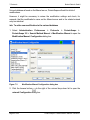
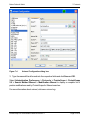
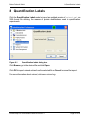
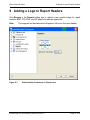
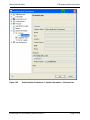
Download proteinscape 3.0 Administration Manual
Transcript
proteinscape 3.0 Administration Manual Bruker Daltonics Revision 1 (November 2011) Legal and Regulatory Notices Bruker Daltonik GmbH Legal and Regulatory Notices Copyright © 2011 Bruker Daltonik GmbH All other trademarks are the sole property of their respective owners. All Rights Reserved Reproduction, adaptation, or translation without prior written permission is prohibited, except as allowed under the copyright laws. Document History ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 (November 2011) Part number: # 276427 First edition: November 2011 Warranty The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. Bruker Daltonik GmbH makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Bruker Daltonik GmbH is not liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance or use of this material. Bruker Daltonik GmbH assumes no responsibility for the use or reliability of its software on equipment that is not furnished by Bruker Daltonik GmbH. Use of Trademarks The names of actual companies and products mentioned herein may be the trademarks of their respective owners. Page 2 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Contact Limitations on Use For Research Use Only (RUO). Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Hyperlink Disclaimer Bruker Daltonik GmbH makes no express warranty, neither written nor oral, and is neither responsible nor liable for data or content from the linked Internet resources presented in this document. Contact Contact your local Bruker Daltonics representative for service and further information. USA Germany Bruker Daltonics Inc Bruker Daltonik GmbH 40 Manning Road Fahrenheitstraße 4 Billerica, MA 01821 28359 Bremen USA Germany Phone: +1 978 6633660 Phone: +49 421 2205-450 Fax: +1 978 6675993 Fax: +49 421 2205-370 Internet: www.bdal.com Internet: www.bdal.de Service Support Service Support Phone: +1 978 6633660-1445 Phone: +49 421 2205- 350 E-mail: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected] ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 3 of 65 Typographic and Application Conventions Bruker Daltonik GmbH Typographic and Application Conventions These conventions list the font styles used for indicating specific graphical user interface (GUI) elements (for example, Menu Items). They also list the meanings of terms used to describe user interactions with the graphical user interface of software (for example, right-click). Typographic Conventions File and Directory Names and Paths File and directory names and paths are written in regular type. Example: "Go to the C:\Bruker\solariXcontrol\test directory and open the file test_ 1.txt." GUI elements GUI (graphic user interface) elements are options that are available in software that enable a user to interact with the software without using the keyboard. Typical GUI elements include windows, menus, menu options, drop-down lists, and buttons. l Names of windows are written in regular, capitalized type. l Names of text entry fields and buttons are written in bold type. Example: "In the New Digest window, type a Name (obligatory) and Note (optional) and click Next." l GUI menus and command names are written in bold type. Example: "Select Window > Show View > LC-MS Survey." Keyboard References to keys on the keyboard are written in UPPER CASE. Example: "Press ALT+F4." Publications References to electronic and printed documents are written in italic type. Example: "See the ProteinScape Administrator Manual for more details." Page 4 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Typographic and Application Conventions URLs Uniform Resource Locators (URLs) are written in italic type. The protocol name (for example, http://) is usually omitted. Example: "Visit www.bdal.com for more details." GUI User Interactions Clear Deactivate a software feature by positioning the mouse pointer over a selected check box and pressing the left mouse button. Example: "Clear the Curve Smoothing option." Click Position the mouse pointer over a GUI element and press the left mouse button to start an action in the software. Example: "Click OK." Click and drag Position the mouse pointer in a window and press the left mouse button. Hold the left mouse button down and move the pointer to select a (usually rectangular) area. Example: "Zoom in on peaks of interest by clicking and dragging in the Spectrum window." Double-click Point to a GUI element and press the left mouse button twice in quick succession to start an action in the software. Example: "Double-click the Sample button." Drag and drop Point to a GUI element and press the left mouse button. Hold the left mouse button down and move the selected element to a new location. Example: "Drag and drop the tab into the desired pane." Select a) Follow the path to a desired menu command. Example: "Select File > Zip > Zip Project" ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 5 of 65 Typographic and Application Conventions Bruker Daltonik GmbH b) Point to a GUI element (for example, a table entry) and press the left mouse button to select it. Example: "Select the desired file in the list and click Export." c) Activate a software feature by positioning the mouse pointer over an empty check box and pressing the left mouse button. Example: "Select the Curve Smoothing option." Right-click Position the mouse pointer over a GUI element and press the right mouse button to open a menu for the selected element. Example: "Right-click in the Spectrum View window". Keyboard Conventions Press Use the indicated key(s) on the keyboard. When modifier keys (for example, SHIFT, ALT, CTRL) are indicated, keep them pressed while pressing the other key. Example: "To toggle between Table and Spectrum view press CTRL+F3." Page 6 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Table of Contents Table of Contents Legal and Regulatory Notices 2 Contact 3 Typographic and Application Conventions 4 Table of Contents 7 1 System Administrator 9 1.1 Logging in for the First Time as System Administrator 1.1.1 Changing the Administrator Password 9 9 2 Administration Preferences 11 3 Managing Calibration Lists 13 3.1 Importing a Calibration List 13 3.2 Exporting a Calibration List 14 3.3 Deleting Calibration Lists 15 3.4 Editing Calibration Lists 15 3.4.1 Adding a Calibrant to a Calibration List 15 3.4.2 Editing a Calibrant in a Calibration List 16 3.4.3 Deleting a Calibrant from a Calibration List 17 4 Instruments 19 4.1 Adding a Mass Spectrometer Type (Non-Bruker Instruments Only) 20 4.2 Adding a Mass Spectrometer Instrument (Non-Bruker Instruments Only) 23 5 Processing Kernel 5.1 Glycan Searches 27 27 5.1.1 Glycan Search Databases 27 5.1.2 Components 29 5.1.3 Modifications 29 5.2 General Properties 30 5.3 Process Definitions 31 5.4 Protein Search Engine Settings 32 5.4.1 Setting up Mascot 33 5.4.2 Setting up Phenyx 33 5.4.3 Setting up SEQUEST 34 5.4.4 Synchronizing Search Engines 34 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 7 of 65 Table of Contents 5.5 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Scheduling 35 6 Project Access 37 7 Protocols 39 7.1 ProteinScape Protocol Configurations 39 7.1.1 Editing Protocol Configurations 40 7.1.2 Creating Protocol Configurations 40 7.1.3 Deleting Protocol Configurations 41 7.1.4 Adding New Modifications 41 7.1.5 Assigning Protocol Configuration User Rights 44 8 Quantification Labels 45 9 Adding a Logo to Report Headers 47 10 Displaying System Information 49 10.1 Managing Licenses 50 10.2 Displaying Logged In Users 52 10.3 Server Logging 53 11 User Management 11.1 55 Managing Groups 55 11.1.1 Creating a New Group 55 11.1.2 Special Groups 56 11.2 11.1.2.1 Assigning Administration Rights to Users 57 Managing Users 58 Index Page 8 of 65 63 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 1 System Administrator 1 System Administrator The system administrator is a special user category that is used to set up and manage ProteinScape administrative tasks. 1.1 Logging in for the First Time as System Administrator The system administrator must log in to ProteinScape using the User Name and Password administrator. After ProteinScape has opened, the system administrator should change the default system administrator password. ►► To set a new administrator password 1. Select File > Change Password to open the Change Password dialog box. 2. Enter the old password (administrator) in the Old Password field. 3. Enter the new password in the New Password field. 4. Reenter the new password in the Confirm New Password field 5. Click OK to save the new password or Cancel to abort. Figure 1-1 1.1.1 Change Password dialog box Changing the Administrator Password Select File > Change Password to open the Change Password dialog box. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 9 of 65 1 System Administrator Bruker Daltonik GmbH ►► To change the administrator password: 1. Enter the old password in the Old Password field. 2. Enter the new password in the New Password field. 3. Reenter the new password in the Confirm New Password field 4. Click OK to save the new password or Cancel to abort. Figure 1-2 Page 10 of 65 Change administrator Password dialog ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 2 Administration Preferences 2 Administration Preferences ProteinScape offers a number of features that are only available to users who have been assigned administrator user rights (see section 11.1.2). These features are accessed by selecting Window > Admin Preferences and include: l Importing, exporting, editing and deleting calibration lists (see section 3) l Defining instrument types (see section 4) l Managing processing kernel processes (see section 5) l Controlling project access (see section 6) l Managing protocols (see section 7) l Structuring reports (see section 9) l Managing system information (see section 10) l Managing users (see section 11) The Window > Admin Preferences options are unavailable to users who have not been assigned administrator user rights. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 11 of 65 2 Administration Preferences Page 12 of 65 Bruker Daltonik GmbH ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 3 Managing Calibration Lists 3 Managing Calibration Lists Calibration lists (= Mass Control Lists, MCL) are required for the ScoreBooster functionality in PMF searches and can be imported from or exported to FlexAnalysis. Refer to the ProteinScape User Manual for details. Figure 3-1 3.1 Calibration list Importing a Calibration List ►► To import a Calibration List 1. Right-click the Calibration Lists node in the Administration Preferences tree structure. 2. Select Import MCL from the shortcut menu. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 13 of 65 3 Managing Calibration Lists Figure 3-2 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Importing a calibration list 3. Find and select the relevant *.mcl file. 4. Click Open. 3.2 Exporting a Calibration List ►► To export a Calibration List 1. Right-click an existing Calibration List. 2. Select Export as MCL from the shortcut menu. Figure 3-3 Page 14 of 65 Exporting a calibration list ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 3 Managing Calibration Lists 3. Find and select the desired location. 4. Click Save. 3.3 Deleting Calibration Lists ►► To delete a Calibration List 1. Right-click an existing Calibration List. 2. Select Delete MCL from the shortcut menu. Figure 3-4 3.4 3.4.1 Deleting a calibration list Editing Calibration Lists Adding a Calibrant to a Calibration List ►► To add a calibrant to a calibration list 1. Select an existing Calibration List. 2. Right-click an empty row in the calibrant table. 3. Select Add calibrant from the shortcut menu. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 15 of 65 3 Managing Calibration Lists Figure 3-5 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Adding a calibrant to a calibration list 4. Type the relevant details directly into the table cells. 5. Click OK and save changes when prompted. 3.4.2 Editing a Calibrant in a Calibration List ►► To edit a calibrant in a calibration list 1. Select an existing calibration List. 2. Select an entry in the calibrant table. Page 16 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Figure 3-6 3 Managing Calibration Lists Editing a calibrant in a calibration list 3. Make the desired change(s). 4. After a change has been made, click Apply to apply the change(s) or Restore to reject the change(s). 5. Click OK and save changes when prompted. 3.4.3 Deleting a Calibrant from a Calibration List ►► To delete a calibrant from a calibration list 1. Select a calibration List. 2. Select and right-click an entry in the calibrant table. 3. Select Remove calibrant from the menu. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 17 of 65 3 Managing Calibration Lists Figure 3-7 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Deleting a calibrant from a calibration list 4. Click OK and save changes when prompted. Page 18 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 4 Instruments 4 Instruments The Instruments > Mass Spectrometers node contains a list of mass spectrometers that have been used for tutorial and experimental data acquisition in the ProteinScape user's labs. Figure 4-1 Instrument type details Individual instruments are grouped under a specific mass spectrometer type. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 19 of 65 4 Instruments Figure 4-2 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Individual instrument details New Bruker mass spectrometers are automatically added to the list the first time that they import data into ProteinScape. The mass spectrometer type and identifier of non-Bruker instruments must be entered manually. 4.1 Adding a Mass Spectrometer Type (Non-Bruker Instruments Only) ►► To add a new mass spectrometer type to the Instruments > Mass Spectrometers list 1. Right-click the Instruments > Mass Spectrometers node in the Administration Preferences tree. 2. Select New Mass Spectrometer Type from the menu. Page 20 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Figure 4-3 4 Instruments Adding a mass spectrometer type ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 21 of 65 4 Instruments Bruker Daltonik GmbH 3. Enter the relevant details into the New Mass Spectrometer Type dialog box. Figure 4-4 New Mass Spectrometer Type dialog box For all mass spectrometer types, the Model parameter (for example, ultraflex TOF/TOF) must be defined when a user sets up automatic searches in ProteinScape. The specified search method will be executed whenever spectra of a particular mass spectrometer type are transferred to ProteinScape. The Mass tolerance parameters are currently not used. The Decimal places parameters define the number of places after the decimal point displayed for peak and fragment masses in Search Result tables. 4. Click OK. 5. A mass spectrometer type can be deleted from the Instruments > Mass Spectrometers list by right-clicking the Mass Spectrometer Type to be removed and selecting Delete Mass Spectrometer Type from the menu. Page 22 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Figure 4-5 4.2 4 Instruments Deleting a mass spectrometer type Adding a Mass Spectrometer Instrument (NonBruker Instruments Only) Any number of individual instruments can be registered under a Mass Spectrometer Type. ►► To add a new mass spectrometer to a Mass Spectrometer Type 1. Right-click the relevant Mass Spectrometer Type node in the Administration Preferences tree. 2. Select New Mass Spectrometer from the menu. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 23 of 65 4 Instruments Figure 4-6 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Adding a new mass spectrometer instrument 3. Enter the relevant details into the New Mass Spectrometer dialog box. Figure 4-7 New Mass Spectrometer dialog box The instrument Name, Serial No. and Host can be recorded. Page 24 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 4 Instruments The Visible option defines whether the instrument will be visible (Yes) or invisible (No) in the Instruments list. 4. Click OK. 5. A mass spectrometer can be deleted from the Mass Spectrometer Type list by rightclicking the instrument to be removed and selecting Delete Mass Spectrometer from the menu. Figure 4-8 Note Deleting a mass spectrometer Instruments that have generated data that is stored on the ProteinScape server cannot be deleted from the list. In this case, the instrument can be "made invisible" by selecting the Visible > No option in the instrument dialog box. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 25 of 65 4 Instruments Bruker Daltonik GmbH Page 26 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 5 Processing Kernel 5 Processing Kernel The ProteinScape Processing Kernel module manages background processes such as protein searches, protein list compilation (ProteinExtractor) and importing spectra. All these processes run on the ProteinScape server. 5.1 Glycan Searches The Glycan Searches node contains three sub-nodes, Glycan Search Databases, Components and Modifications. 5.1.1 Glycan Search Databases The Glycan Search Databases node contains a list of public databases, their most recent synchronization with the ProteinScape server, the number of structures in the database and the number of imported structures. User-defined databases that can contain a selected subset of database entries or novel entries created using the Glycan Structure Editor are also listed. Accessing the GlycomeDB Database ProteinScape performs glycan searches on a local copy of the GlycomeDB (www.glycome-db.org), a meta-database that is frequently updated with structures from a number of individual glycan databases. The GlycomeDB is accessed via the URL in the GlycomeDB URL field of theGlycan Search Databases dialog (see Figure 5-1). Select the User remote access check box to activate remote access to the database. To change the GlycomeDB URL, click Change and type a new URL into the GlycomeDB URL field of the Edit GlycomeDB URL dialog. Synchronizing glycan search databases ProteinScape can be synchronized with GlycomeDB if the ProteinScape server is connected to the Internet. To synchronize the ProteinScape database with one or more glycan search databases, select the desired database(s) and click Resynchronize now. Selecting GlycomeDB (last row in the table) will synchronize all sub-databases. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 27 of 65 5 Processing Kernel Note Bruker Daltonik GmbH The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) may be used for academic purposes only. A license must be obtained for commercial use (www.genome.jp/kegg). The initial ProteinScape installation does not contain the glycan structures from the KEGG database. To access the glycan structures in the KEGG database, select the KEGG or GlycomeDB entry in the Glycan Search Databases list and start the synchronization. Figure 5-1 Glycan Search Databases dialog User-defined databases Protein searches can be performed against user- defined databases that contain a selected subset of database entries or novel entries created using the Glycan Structure Editor. ►► To create a user-defined database 1. Click New DB and type a Name and Abbreviation into the New Database dialog. 2. Click OK to add the new database to the list of user-defined databases. Edit the database name or abbreviation by selecting the database and clicking Edit DB. Delete databases by selecting the database(s) and clicking Delete DBs. Page 28 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 5.1.2 5 Processing Kernel Components The Components node lists basic glycans and their short form name, GlycoCT name, sum formula and molecular ion mass (MH+). Figure 5-2 5.1.3 Glycan Search Databases Components list Modifications The Modifications node lists common glycan modifications and their short form name, GlycoCT name, sum formula and molecular ion mass (MH+). Figure 5-3 Glycan Search Databases Modifications list ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 29 of 65 5 Processing Kernel 5.2 Bruker Daltonik GmbH General Properties Parameters in the General Properties dialog box are settings for background processes. They include the score threshold for peptides in a ProteinExtractor search result below which they will not be imported (proteinextractor.mascot.min_ peptide_ score) and the number of slots for parallel execution of protein list compilations and other steps in the protein search workflows. These parameters are not part of ProteinScape methods. Figure 5-4 Page 30 of 65 Administration Preferences > Processing Kernel > General Properties view ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 5.3 5 Processing Kernel Process Definitions The parameters and values in the Process Definitions window should not normally be changed by users. They may be altered by service personnel when workflow definitions must be changed. Figure 5-5 Administration Preferences > Processing Kernel > Process Definitions view ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 31 of 65 5 Processing Kernel 5.4 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Protein Search Engine Settings Search engine configuration settings are defined in the Protein Search Engine Settings node. Clicking a Protein Search Engine Settings sub-node opens the respective search engine configuration settings dialog box. Obligatory fields are marked with asterisks. Figure 5-6 Page 32 of 65 Search Engine Setting Configuration dialog ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Table 5-1 5 Processing Kernel Protein Search Engine Settings parameters Parameter Description Active Select to activate the search engine Note Free text field for optional comment. cgi-URL and Web- Two URLs are only required for Mascot: the cgi-URL is used for URL starting the search and the Web-URL for receiving results. Engine version Enter the search engine version number here. Weighting for ProteinExtractor Factor used for balancing the different scores when more than one search engine is used. This factor is multiplied by a second weighting factor defined on the ProteinExtractor page of the search method. For example, if the Phenyx Weighting for ProteinExtractor = 4 and the Mascot Weighting for ProteinExtractor = 1, and in the search method the weighting factor for both search engines is = 1, the Phenyx peptide scores are multiplied by 4 before adding them to the Mascot peptide scores to form a protein “meta” score. Slots Number of concurrently running searches. Max. size of subbatch A ProteinExtractor search will be split in chunks of this size (number of spectra). Authentication, Select the relevant check box to activate the desired authentication Engine/Proxy/Http function. 5.4.1 Setting up Mascot The most important step for the administrator is to enter the search engine server name into the cgi-URL field and the version of the search engine into the Engine version field. Click OK to save changes. 5.4.2 Setting up Phenyx Setting up a connection to a Phenyx server is straightforward. The URL settings depend on the setup of the Phenyx server’s web server. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 33 of 65 5 Processing Kernel Bruker Daltonik GmbH cgi-URL http://<phenyxserver>:8080/cgi-bin web-URL OR http://<phenyxserver>:8080/cgi-bin http://<phenyxserver>:8080/pwi The web URL should display the login dialog box of Phenyx. Go to http://<phenyxserver>:8080/cgi-bin/showEnv.pl to display a list of the environment variables on the Phenyx server. To access Phenyx, users must generate a user ID on the Phenyx server. ►► To generate a Phenyx user ID 1. Log in as admin on the Phenyx server using a web browser. 2. In the Management Console select Users > Add, Role: user. 3. Type a user name and a password. This name and password must be entered on ProteinScape’s Search Engine Settings page for Phenyx. 4. Select Administration Preferences > Search Engine Settings and select Phenyx from the search engine list. 5. Click Resynchronize now (see section 5.4.4). 5.4.3 Setting up SEQUEST ProteinScape can communicate with SEQUEST as part of the Proteomics Browser package (versions 3.2 to 3.3SP1). For more information, contact your local Bruker support team. 5.4.4 Synchronizing Search Engines The ProteinScape server can synchronize its lists of available sequence databases, enzymes, and modifications with the lists on the relevant search engine server(s). To synchronize the ProteinScape server with a search engine server, select one or more search engines in the Search Engine Settings window and click Resynchronize now. Page 34 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 5 Processing Kernel The ProteinScape server will automatically try to synchronize with all search engines on startup. Figure 5-7 5.5 Search Engine Settings dialog box Scheduling ProteinScape users can delete Search Results, MS datasets, LC separations, and even whole Projects by right-clicking the corresponding item in the navigation tree and selecting Delete from the menu. However, to prevent the server from slowing down when large amounts of data are deleted, deleted items are first hidden in the ProteinScape GUI and queued for deletion at a later point in time. The time window for deleting the database entries and clearing disk space can be defined using the Scheduling dialog box. Select the Enable check box to activate Cleanup Scheduling between the given Start time and Stop time points. Clear the Enable check box to deactivate Cleanup Scheduling. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 35 of 65 5 Processing Kernel Figure 5-8 Page 36 of 65 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Administration Preferences > Processing Kernel > Scheduling view ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 6 Project Access 6 Project Access The read/write permissions of projects can be assigned on a user-group basis using Project Access settings (see section 11.1). To assign read/write permissions, select the relevant user group in the Project Access list and select the relevant project check box(es) in the project list window. Click Apply to save changes or Restore to reject changes. Figure 6-1 Administration Preferences > Project Access view ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 37 of 65 6 Project Access Page 38 of 65 Bruker Daltonik GmbH ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 7 Protocols 7 Protocols 7.1 ProteinScape Protocol Configurations ProteinScape protocol configurations are listed under Administration Preferences > Protocols > ProteinScape > ProteinScape 2.0. To expand or collapse a node, doubleclick the respective node or use the expand/collapse button. Figure 7-1 Administration Preferences > Protocols view ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 39 of 65 7 Protocols 7.1.1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Editing Protocol Configurations ►► To edit a protocol configuration 1. Double-click the desired protocol attribute (for example, Organism). 2. Select the configuration to be changed (for example, Bos taurus) in the configuration list and make the desired changes to the respective parameters. 3. Click OK to save the changes. Figure 7-2 7.1.2 Organism > Bos taurus parameters Creating Protocol Configurations ►► To create a protocol configuration 1. Double-click the desired node attribute (for example, Sample > Organism). 2. Select an existing configuration (for example, Chicken) in the configuration list and click Save As. Page 40 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 7 Protocols 3. Type the new configuration name in the New method name field of the Save As New Method dialog box. 4. Select the new configuration in the configuration list and make the desired changes to the relevant parameters (click Save to save changes). 5. Click OK to close the dialog box. Note When a new protocol configuration is created, only the user who created the configuration has access rights. Other users require user rights to use the new protocol configuration (see section 7.1.5). Two additional steps must be performed to add and use search- engine specific parameters such as databases. l The parameter must be introduced into the search engine database. For more information, see the respective search engine documentation. l ProteinScape and the search engines must be resynchronized by selecting the respective search engines in the Search Engine Settings dialog box and clicking Resynchronize now (see section 5.4.4). After synchronization, all databases available on the search engine will also be available in the Search Method protocols. Configurations in the Search Method protocols (for example, Sequence Database) should not be edited manually. 7.1.3 Deleting Protocol Configurations ►► To delete a protocol configuration 1. Double-click the desired attribute (for example,Organism). 2. Select an existing configuration (for example, Chicken) in the configuration list and click . 3. Click Yes when prompted to confirm deletion. 7.1.4 Adding New Modifications New protein modifications are generally added to the ProteinScape server during the resynchronization process (see section 5.4.4). If a modification that is not included in the ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 41 of 65 7 Protocols Bruker Daltonik GmbH Unimod database is found on the Mascot server, ProteinScape will add it to its list of modifications. However, it might be necessary to review the modification settings and check, for example, that the modification's name on the Mascot server and in the related unimod entry are identical. ►► To add a new modification to the unimod database 1. Select Administration Preferences > Protocols > ProteinScape > ProteinScape 2.0 > Search Method Mascot > Modification Mascot to open the Modification Mascot Configuration dialog box. Figure 7-3 Modification Mascot Configuration dialog box 2. Click the browse button to the right of the unimod drop-down list to open the unimod Configuration dialog box. Page 42 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Figure 7-4 7 Protocols Unimod Configuration dialog box 3. Type the mass shift and formula into the respective fields and click Save and OK. Select Administration Preferences > Protocols > ProteinScape > ProteinScape 2.0 > Search Method Mascot > Modification Mascot to display a complete list of protein modifications used by ProteinScape for Mascot searches. For more information about unimod, visit www.unimod.org. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 43 of 65 7 Protocols Bruker Daltonik GmbH 7.1.5 Assigning Protocol Configuration User Rights User rights for parameter classes are assigned on the respective configuration Rights tab. Note When a new protocol configuration class is created, only the user who created the class has access rights. Use the following procedure to make the new protocol configuration class available to other users. ►► To assign protocol configuration user rights 1. Click the relevant node to open the protocol configuration dialog box. 2. Click the Rights tab to open the Rights dialog box. 3. Click Configure to display a list of all users and groups currently registered on the ProteinScape server. 4. Select the desired user(s) and/or group(s) and assign read/write permissions by selecting the relevant check box(es). 5. Click OK to save changes. Page 44 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 8 Quantification Labels 8 Quantification Labels Click the Quantification Labels node to import an updated version of unimod.xml, an XML- format file defining the masses of protein modifications used in quantification experiments. Figure 8-1 Quantification labels dialog box Click Browse, go to the desired file and click Open. Click OK to import unimod entries from the selected file or Cancel to cancel the import. For more information about unimod, visit www.unimod.org. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 45 of 65 8 Quantification Labels Page 46 of 65 Bruker Daltonik GmbH ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 9 Adding a Logo to Report Headers 9 Adding a Logo to Report Headers Click Browse in the Reports dialog box to upload a new graphic image for report headers. BMP, JPG, PNG, and GIF graphic formats are supported. Note Figure 9-1 The image will not be scaled and will appear in full size in the report header. Administration Preferences > Reports view ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 47 of 65 9 Adding a Logo to Report Headers Page 48 of 65 Bruker Daltonik GmbH ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 10 Displaying System Information 10 Displaying System Information Clicking the System Information node displays current version information for the most important ProteinScape server modules. Figure 10-1 Administration Preferences > System Information view ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 49 of 65 10 Displaying System Information Bruker Daltonik GmbH 10.1 Managing Licenses ProteinScape licensing is managed by selecting Administration Preferences > System Information > Licenses. New licenses are registered by right-clicking the Licenses node and selecting Register New License Key from the menu. Registering a new license key will overwrite any existing license keys for the same application. The Licenses menu option Show MAC Address can be used when the MAC address/es of the server must be sent to Bruker, for example, to obtain a new license. In this case, the MAC address can be copied using the menu and sent by mail to [email protected]. A new license key will be generated by the ProteinScape support team and mailed to the user. To delete a license, right-click the relevant Licenses sub-node and select Delete License from the menu. Page 50 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Figure 10-2 10 Displaying System Information Administration Preferences > System Information > Licenses view ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 51 of 65 10 Displaying System Information Bruker Daltonik GmbH 10.2 Displaying Logged In Users Clicking the System Information > Logged In Users node displays a table showing users currently logged into the server. This list includes users currently using ProteinScape or external programs that connect to ProteinScape (for example, BioTools and WARP-LC). Right-click a user to open the Logged In Users table menu (see Table 10-1). Table 10-1 Shortcut menu for logged in users. Shortcut Menu Item Explanation/ Comments Refresh Session The session of the respective user is refreshed – effectively this command has no effect. Remove Session The respective user’s session is terminated – effectively a forced logoff. Figure 10-3 Page 52 of 65 Administration Preferences > System Information > Logged In Users view ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 10 Displaying System Information 10.3 Server Logging The ProteinScape server's log files may be required for support issues. Select Administration Preferences > System Information > Server Logging to display a list of currently available log files. If a log file exceeds a certain size, a backup copy will be generated and a fresh log file started. Right-click the Server Logging node to open the Server Logging menu (see Table 102). Table 10-2 Server logging menu Shortcut Menu Item Explanation/ Comments Select All All log files are selected for download Download Recent Log Files The current log file and the existing backup copies are downloaded to the client PC. Download Selected Log Files The selected log files are downloaded to the client PC (select log files using the mouse). Refresh Figure 10-4 The list is refreshed, that is, the data (file names, sizes etc.) are loaded from the server. Administration Preferences > System Information > Server Logging view ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 53 of 65 10 Displaying System Information Page 54 of 65 Bruker Daltonik GmbH ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 11 User Management 11 User Management Individual Users and Groups of Users are configured in the User Management folder. 11.1 Managing Groups Users can be assigned to one or more Groups. Access to a Project or Method can only be assigned to a group, not single users (see section 7.1.5). 11.1.1 Creating a New Group ►► To create a new group 1. Right-click the Administration Preferences > User Management > Groups) node and select Add New Group from the shortcut menu. Figure 11-1 Adding a new group The Define New Group dialog box opens. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 55 of 65 11 User Management Figure 11-2 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Group membership details 2. Type a Name and an optional Description. 3. In the User Membership section, add or remove group members by selecting the respective user(s) and clicking the ◄ or ► button to move them into the Group members or Not group members field. Tip Use the ◄◄and ►►buttons to move all users in the respective direction. 4. Click OK to save changes. Note 11.1.2 Groups cannot be deleted after they are created. Special Groups Two existing ProteinScape groups have special properties: l All Users — Every user is automatically a member of this group. Therefore, if a Project should be accessible to all users, this group must be assigned access in the Page 56 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH 11 User Management Project Rights tab of the relevant project. l User's own group — a group in which each user is the only member is automatically created when a new user is added. This enables projects and methods to be assigned to individual users, that is, on the group rather than the user level. l administrator — In addition to the system administrator (dedicated login “administrator”), any user can become a member of the administrator group. If a member of the administrator Group logs in, they will see the normal user perspective and can work normally. The Administration Preferences window is available for performing administration tasks. 11.1.2.1 Assigning Administration Rights to Users Users can be added to the administrator group by moving the administrator group into the Group Membership > Is a member of: column in Administration Preferences > User Management > Users > [user ID]. Users can be removed from the administrator group by moving the administrator group into the Group Membership > Is not a member of: column in Administration Preferences > User Management > Users > [user ID]. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 57 of 65 11 User Management Figure 11-3 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Group membership details of an individual user 11.2 Managing Users All users must belong to one or more groups. After creation, all users are automatically added to the group All Users and their own group (see section 11.1.2). ►► To create a new user ID 1. Right-click Administration Preferences > User Management > Users) and select Add New User from the menu. Page 58 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Figure 11-4 11 User Management Adding a new user The Define New User dialog box opens. Figure 11-5 Define New User dialog box 2. Type a Last Name, First Name, Login, and Email for the new user ID. 3. Click OK to add the new user to the list of users and open the User configuration dialog box. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 59 of 65 11 User Management Figure 11-6 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Configuring a new user 4. Select or clear the Active check box to activate or deactivate the respective User. Clearing the Active check box means that the user cannot log in to ProteinScape. Page 60 of 65 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Note 11 User Management Because of the number of dependencies to projects, analytes, spectra, methods etc., user IDs cannot be deleted. Users cannot be deleted because there are too many dependencies to Projects, Analytes, Spectra, Methods etc. Deactivated users cannot login to ProteinScape. Optional: An password for the user can be set in the User Password section. Type the administrator password into the Administrators Password field, type the user’s password in the New Password and Confirm New Password fields and click Set Password. 5. In the Group Membership section, add the user to or remove the user from groups by selecting the respective group(s) and clicking the ◄ or ► button to move them into the Is member of or Is not a member of field. A user can be a member of multiple groups, including the administrator group (see section 11.1.2). Tip Use the ◄◄and ►►buttons to move all groups in the respective direction. ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 61 of 65 11 User Management Page 62 of 65 Bruker Daltonik GmbH ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Index Index D Delete MCL A Add calibrant 15 11 Administrator G 9, 61 9 logging in 9 27 Glycan Searches 27 Groups 10 C Calibration list 13-14 adding and removing members 55 Administrator 57 All Users 56 creating 55 managing 55 special groups 56 user's own group 57 adding calibrants 15 deleting 15 deleting calibrants 17 editing 15 I editing calibrants 16 Import MCL exporting 14 Instruments importing 13 Change Password Cleanup Scheduling 9 35 Configurations protocol Confirm New Password 39 10, 61 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 27 synchronizing 57 changing password Administrator password 14 Glycan Search Databases Administration rights assigning E Export as MCL Administration Preferences features 15 mass spectrometer types 13 19 L Licenses managing 50 registering 50 Log files 53 Page 63 of 65 Index Bruker Daltonik GmbH Logged In Users 52 Logo image Protocol configuration class creating 40 deleting 41 M editing 40 Mass spectrometer instruments user rights 44 changing adding Mass Spectrometer Types adding 47 23 19 20 Modifications adding 41 39 39 Q 45 R Read/write permissions 10, 61 O Old Password configurations Quantitation Labels N New Password Protocols 10 P projects 37 Register New License Key 50 Remove calibrant 17 Reports 47 9 S administrator, changing 9 Scheduling 35 Phenyx search engine 33 Search Engine Settings 32 user 61 Mascot 33 27, 36 Phenyx 33 Password Processing Kernel general properties 30 SEQUEST 34 process definitions 31 synchronizing 34 scheduling 35 Server Logging 53 Project Access 37 Synchronizing databases System administrator Projects read/write permissions Page 64 of 65 37 System Information 27, 34 9 49 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Bruker Daltonik GmbH Index U unimod 41, 45 User Management 55, 58 User rights protocol configuration class 44 Users creating 58 display current 52 managing 58 ProteinScape 3.0 Administration Manual Revision 1 Page 65 of 65