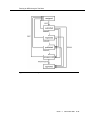
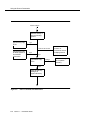
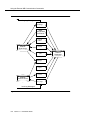
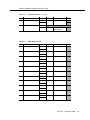
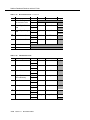
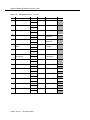
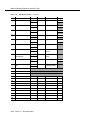
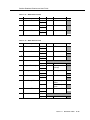
Download Contents - Sablime
Transcript
Sablime v5.2 User’s Guide Issue 1.1 November 2000 Copyright© 2000 Lucent Technologies All Rights Reserved Printed in U.S.A. Notice Every effort was made to ensure that the information in this document was complete and accurate at the time of printing. However, information is subject to change. Trademarks UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the U.S. and other countries. Sablime is a registered trademark of Lucent Technologies. Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. X-Windows is a trademark of Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Contents 1 2 3 4 Introduction 1-1 n Purpose 1-1 n Scope 1-1 n Intended Audience 1-1 n Organization 1-1 n Conventions 1-3 n Icons 1-4 Getting Started 2-1 n The Sablime User Interfaces 2-2 n Using the Command Line Interface 2-5 n Using the Curses Forms Interface 2-8 n Using the Graphical User Interface on the X Window System2-16 n Using the Web Sablime Interface 2-27 Using the Administrative Commands 3-1 n Changing or Viewing A Sablime Profile 3-1 n Creating, Changing, and Deleting Sablime Groups 3-5 n Creating a User’s Working Environment 3-9 n Troubleshooting 3-12 Using the MR Commands 4-1 n MRs and MRGs 4-1 n The MR and MRG Life Cycles 4-1 n The MR Commands 4-3 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 i Contents 5 n MRG Dependencies 4-6 n Creating an MR 4-15 n Killing an MR 4-18 n Deferring an MR or MRG 4-20 n Activating an MR or MRG 4-23 n Studying an MR or MRG 4-27 n Accepting an MR 4-29 n Unaccepting an MR 4-33 n Nochanging an MRG 4-35 n Spawning an MRG 4-38 n Assigning an MRG 4-42 n Submitting an MRG 4-45 n Assigning an MRG to a Tester 4-47 n Passing an MRG through a Test State 4-49 n Rejecting an MRG 4-52 n Approving an MRG 4-54 n Closing an MR 4-56 Using the Source Commands n Source File Control 5-1 n The Source Commands 5-3 n Adding a New Source File 5-6 n Adding a Source File 5-9 n Getting a Source File to Edit 5-13 n Unlocking a Retrieved Source File 5-16 n Putting Back a Changed Source File 5-18 n Backing Out Changes to Source Files 5-20 n Getting Copies of Source Files 5-22 n Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific MRs5-28 n Printing a Source File Listing 5-48 n Making Source Files Common 5-50 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page ii Issue 1.1 5-1 November 2000 Contents n 6 7 Making Source Files Not Common 5-52 Using the Report Commands 6-1 n Using the query Command 6-3 n Using the report Command 6-9 n Using the ssql Command 6-124 n Using the ptsaudit Command 6-137 Using the External MR Communication Commands7-1 n Overview 7-1 n The External MR Commands 7-7 n Displaying the Contents of Messages 7-11 n Putting a Message on the Queue 7-15 n Reviewing Messages on the Queue 7-17 n Sending Messages to an External Project 7-28 n Creating an MR 7-29 n Requesting MR Reports 7-29 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 iii Contents A Sablime Database Relations and their Fields A-1 B Error Messages Generated by Sablime for Users B-1 C External MR Error Messages C-1 n D External MR Message Formats n GL Error Messages Message Formats Glossary November 2000 D-1 D-1 GL-1 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page iv Issue 1.1 C-1 Figures 1 Introduction 2 Getting Started 3 2-1 Sablime Application Window (X Window System) 2-20 2-2 Sablime Error Box (X Window System) 2-23 2-3 Sablime Template Text 2-24 2-4 Sablime Load File Box 2-26 Using the Administrative Commands 3-1 4 5 Sample Project Directory Structure 3-10 Using the MR Commands 4-1 MR and MRG Life Cycles 4-2 4-2 Dependency on Unapproved MRs 4-8 4-3 Dependency on a New MR 4-9 4-4 Mutual Dependency 4-9 4-5 Hardware Sample Test States 4-50 4-6 Document Sample Test States 4-51 Using the Source Commands 5-1 SCCS/SBCS Version Identifiers 5-2 5-2 Source Commands and Their Effects 5-4 AT&T — PROPRIETARY Use pursuant to Company Instructions Issue 1.1 November 2000 v Figures 6 7 Using the Report Commands 6-1 query First Screen 6-3 6-2 query Second Screen 6-4 6-3 report First Screen 6-10 6-4 report Second Screen 6-11 6-5 pie report Screen 6-17 6-6 bar report Screen 6-18 6-7 stat report Screen 6-18 6-8 pie Chart 6-37 6-9 bar Chart 6-40 6-10 stat Chart 6-43 6-11 ssql -help Screen 6-126 6-12 ssql -help from MR Screen 6-126 Using the External MR Communication Commands 7-1 Scenario for Establishing MR Linkage 7-2 External MR Communication Command Overview 7-8 7-3 Type 12 Screen 7-22 7-4 Type 11 Screen 7-23 7-5 review Command UDF Screen 7-24 AT&T — PROPRIETARY Use pursuant to Company Instructions vi Issue 1.1 November 2000 7-4 Figures A Sablime Database Relations and their Fields B Error Messages Generated by Sablime for Users C External MR Error Messages D External MR Message Formats AT&T — PROPRIETARY Use pursuant to Company Instructions Issue 1.1 November 2000 vii Figures AT&T — PROPRIETARY Use pursuant to Company Instructions viii Issue 1.1 November 2000 Tables 1 Introduction 2 Getting Started 2-1 Default Settings of prompt Keyword 2-2 Relationship between Command Line Entry and Interface2-5 2-3 Default Values in Command Line Interface 3 Using the Administrative Commands 4 Using the MR Commands 4-1 5 2-7 4-3 Using the Source Commands 5-1 6 MR and MRG Life Cycle Commands 2-4 Source Commands 5-5 Using the Report Commands 6-1 Default Sort Fields for Sortable Reports 6-13 6-2 Predetermined Sort Fields 6-13 6-3 MR report Formats 6-15 6-4 mrVSfile extract_file Sections 6-104 6-5 Parallel MRG States 6-125 AT&T — PROPRIETARY Use pursuant to Company Instructions Issue 1.1 November 2000 ix Tables 7 A Using the External MR Communication Commands 7-1 External MR Commands 7-9 7-2 review Command Actions and Results 7-18 7-3 Results of enter and move Responses 7-19 7-4 Results of enter, link, and remove Responses to Message Type 11 7-21 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields 1-1 Database Relations A-2 1-2 Ranges Allowed in query A-3 A-3 ADM Relation Fields A-5 A-4 CAS Relation Fields A-6 A-5 COM Relation Fields A-6 A-6 CP Relation Fields A-6 A-7 CRIT Relation Fields A-7 A-8 DEP Relation Fields A-8 A-9 EMG Relation Fields A-8 A-10 EMR Relation Fields A-9 A-11 ES Relation Fields A-11 A-12 FTD Relation Fields A-11 A-13 FZ Relation Fields A-12 A-14 G Relation Fields A-13 A-15 GRP Relation Fields A-14 A-16 GRPM Relation Fields A-14 A-17 GS Relation Fields A-15 A-18 GT Relation Fields A-16 A-19 HC Relation Fields A-17 A-20 MD Relation Fields A-18 A-21 MG Relation Fields A-19 A-22 MR Relation Fields A-23 AT&T — PROPRIETARY Use pursuant to Company Instructions x Issue 1.1 November 2000 Tables B A-23 MRS Relation Fields A-25 A-24 MRX Relation Fields A-25 A-25 MS Relation Fields A-26 A-26 ORG Relation Fields A-26 A-27 PDEP Relation Fields A-27 A-28 PDI Relation Fields A-28 A-29 PR Relation Fields A-30 A-30 PRX Relation Fields A-31 A-31 PTS Relation Fields A-32 A-32 SNAP Relation Fields A-33 A-33 TR Relation Fields A-35 A-34 UMS Relation Fields A-35 Error Messages Generated by Sablime for Users B-1 C B-1 External MR Error Messages C-1 D Error Messages External MR Communications Error Messages C-1 External MR Message Formats AT&T — PROPRIETARY Use pursuant to Company Instructions Issue 1.1 November 2000 xi Tables AT&T — PROPRIETARY Use pursuant to Company Instructions xii Issue 1.1 November 2000 Contents 1 Introduction 1 n Purpose 1 n Scope 1 n Intended Audience 1 n Organization 1 n Conventions 3 n Icons 4 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 i Contents AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page ii Issue 1.1 November 2000 Introduction 1 Purpose This guide provides all the general and procedural information the user needs to make effective use of Sablime. It is intended to be used in conjunction with the User’s Reference Manual, which contains manual pages that provide detailed information about each of the Sablime user-level commands. Scope This issue of the User’s Guide applies to version 5.2 of Sablime. Intended Audience This guide is intended for all users of the Sablime system. Organization This guide comprises an introduction (Chapter 1), information about the Sablime environment and interfaces (Chapter 2), and information about using the administrative commands (Chapter 3), the MR commands (Chapter 4), the source commands (Chapter 5), the report commands (Chapter 6), and the external communication commands (Chapter 7), as well as four Appendices (Appendix A D), a Glossary, and an Index. A summary of the contents of the chapters and appendices follows. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 1-1 Introduction n Chapter 1, Introduction, describes the purpose, scope, intended audience, and organization of the guide. It also lists the typographical conventions and the product safety labels used in the guide. n Chapter 2, Getting Started, describes the four interfaces to Sablime - the Command Line interface, the Curses Forms interface, the Graphical User interface on X Windows, and the Graphical User interface on a PC - and tells how to use them. n Chapter 3, Using the Administrative Commands, describes how to use the administrative commands available to the general user, and gives examples of their use. n Chapter 4, Using the MR Commands, distinguishes between a modification request (MR) and a modification request in a generic (MRG), describes the life cycles of each, and shows how to use the commands that affect MRs and MRGs. n Chapter 5, Using the Source Commands, discusses source file control, provides an overview of the commands used for source control, shows how to use them, and gives examples of their use. n Chapter 6, Using the Report Commands, describes the three report commands (query, report, and ssql), shows how to use them, and gives examples of their use. n Chapter 7, Using the External MR Commands, describes how to exchange MR information with another system, shows how to use the commands that make such exchange possible, and gives examples of their use. n Appendix A, Sablime Database Relations and their Fields , lists all the database fields that can be retrieved by the three report commands, provides the name, keyword, and screen label for each, and indicates the range of the field and whether it can be used as a sort or print field. n Appendix B, Error Messages Generated by Sablime , lists by field the error messages Sablime produces and the appropriate response if incorrect data is entered into a field, and also contains the error messages that may appear when Sablime processes mail from a command. n Appendix C, External MR Error Messages, lists by field the error messages Sablime produces and the appropriate response if incorrect data is entered into a field when the external MR facility is being used. n Appendix D, External MR Message Formats, describes the fourteen messages used by the external MR facility and provides the format of each. n The Glossary contains definitions of terms used in this guide. n The Index is a comprehensive index that provides a quick and easy way of locating information. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 1-2 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Conventions Conventions The following conventions are used throughout this guide: n Command Syntax — Words or symbols in this type are to be entered literally, exactly as shown. — Words in italics stand for variables for which you should make the appropriate substitution (usually a file name). — Square brackets ([ ]) indicate that the enclosed word (which can be a variable or the actual word to enter) is optional. If you use an option, do not enter the brackets. — A pipe symbol (|) indicates a choice of options, i.e., y | n indicates a choice between entering y or n. — Output generated in response to a command example is shown immediately following the command and is shown in this type. n File names and directory names are shown in this type. This type is also used when referencing executable programs, such as sget. In diagrams, directories may be indicated by a slash (/); executables may be indicated by an asterisk (*). n Computer output and file listings are shown in this type. n If a command extends over multiple lines, each line ends with a backslash (\). (One or more whitespace characters should either precede the backslash or start the next line.) n Input and output lines that wrap to the following line due to the margin constraints of this guide contain a backslash (\) at the end of each line. n n UNIX* system commands are referenced as name(n), where name is the name of the UNIX system command and n identifies the section of the UNIX system manual in which the manual page for the command is found. When you are instructed to enter a series of characters, type the characters and then press the RETURN key. That key may be labeled RETURN or ENTER, or may show an arrow (↵). NOTE: All menus and defaults listed in this guide are standard in the software as delivered; however, many of them may be customized. Ask your Sablime Administrator if your menus and defaults have been customized. If they * UNIX is a registered trademark of X/Open Corporation. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 1-3 Introduction have, note the changes in this guide so that your documentation will accurately reflect your customized system. Icons This document uses two icons, Caution and Note. ! CAUTION: The Caution icon is used to mark activities that could affect the proper functioning of the Sablime system. NOTE: The Note icon is used to call particular attention to something in the text. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 1-4 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Contents 2 Getting Started 1 n The Sablime User Interfaces 2 n Using the Command Line Interface 5 Help n n 8 Using the Curses Forms Interface 8 Screen Design 10 Field Entry 11 Pop-Up Menu Displays 12 Changing or Deleting Existing Data 12 Date Fields 13 Copy To Field 13 Confirm Menu 13 System Messages 13 Help 14 Screen Navigation 14 Terminal Types 15 Using the Graphical User Interface on the X Window System 16 Preliminary Setup 16 Customizing the X Window System GUI 16 Setting Up for a Product and Generic 19 Sablime Window Elements 21 Menu Bar 21 Status Bar 22 Message Boxes 22 Operation of Boxes and Windows 23 Box Types 26 Help n 27 Using the Web Sablime Interface 27 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 i Contents AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page ii Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Started 2 Sablime works by creating and manipulating objects called MRs and MRGs, together with other objects such as MR groups and product configurations. These objects reside in Sablime’s database and can evolve over time. Most Sablime commands collect data from the user and either create a new object or update an existing object. An "object" may correspond to a single record in a single relation, or it may be implemented as several records in one or more relations. (For information about relations, see Appendix A, Sablime Database Relations and their Fields.) Almost all Sablime commands organize their input in "fields". A field can be a short string such as a due date or a problem identifier or a release name or a yes/no flag; a field can also be a longer string such as a problem abstract. These fields usually correspond to fields in the database records that implement Sablime’s objects. Sablime has report commands that tell you about the state of particular objects, and query commands that let you examine the underlying database tables and records. The major Sablime commands support several different interfaces, each of which is useful in different ways. These interfaces differ in how they gather and present information, but each interface works in the same general way from one command to another. This chapter describes the interfaces, so that you can work in each one comfortably. Later chapters describe the commands themselves, and the objects they manipulate. See also the User’s Reference Manual and the Administrator's Guide for further information. Sablime also includes many commands that do not support the interfaces described in this chapter. These are mainly utility commands such as database audit scripts, or shortcut commands that toggle individual flags in particular records. You can use Sablime effectively without becoming acquainted with all AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-1 Getting Started the minor commands. The most important material to master is the MR/MRG lifecycles and their associated commands, and the commands for changing source files and constructing build configurations. These items are discussed at the beginning of Chapters 4 and 5. The Sablime User Interfaces 2 The user interfaces you will read about are the Curses Forms interface, the Command Line interface, and the Graphical User interface (or GUI). The interfaces are also called "modes"; this document uses the terms interchangeably. The Curses Forms interface is a full-screen interface for character terminals. It takes its name from the venerable Unix "curses" screen-manipulation library. In the Curses Forms interface you supply information by filling out on-screen forms, one field at a time. You can also prepopulate some fields by specifying information on the command line. The Sablime command you are executing gives you information in return by arranging the fields and labelling them, by populating some fields for you (read-only fields, fields with default values, or fields whose values are determined by the values of earlier fields), by displaying pop-up menus, by displaying help text for fields on request, by skipping you over any fields you are not allowed to enter, and by updating the display when something you do makes a field change its value. Some fields will scroll horizontally to accommodate input wider than the displayed field size. You can jump back to the beginning of a screen, or back up one field at a time, but forward motion is always one field at a time. Sablime validates each field as you move forward out of it, and forward motion will be blocked if the validation checks do not pass. Sablime lets your administrator customize the field labels and field positions, but Sablime traverses the fields in their original order, however they are arranged on the screen. Error messages, while you are filling out a screen form, are limited to a single line at the bottom of the screen; this sometimes limits Sablime’s ability to tell you how to correct your input. The Command Line interface takes all its input from the command line, and uses keywords to identify which input goes with which field. The keywords may be customized for your project by your administrator; the User’s Reference Manual shows the keywords for each command as shipped. If you type a keyword the command does not recognize, the command will list the keywords it accepts, together with explanatory labels, any default values that apply, and asterisks next to keywords whose fields are mandatory. Commands will also display this help information on request, if you supply a "-help" or "-?" argument. The Command Line interface is useful in situations where you only need to specify a few fields, or in non-interactive environments such as shell scripts and cron jobs. You can specify keywords in any order, but Sablime interprets the fields in the same fixed order as in Curses Forms mode, and your choices for "earlier" fields can cause Sablime to blank out your choices for "later" fields in some cases. This is not an AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-2 Issue 1.1 November 2000 The Sablime User Interfaces error, but it can seem mysterious; it will seem less mysterious the more accustomed you are to Curses Forms mode. The GUI interface uses forms with widgets, properties dialogues, and dialog boxes to gather field information from you, and it computes menus of choices dynamically in many places where the Curses Forms interface makes you figure out what input to enter. For the most part, you can fill out the fields in any order. Sablime validates each field as you leave it, or, for some groups of interrelated fields, waits until you activate the dialog (by typing RETURN or clicking the OK button). For fields that require file or directory names, you can browse the local file system, or your product’s Sablime directory structure, to find the item you are looking for. In general, the GUI gives more information to you the user than the other interfaces, at a corresponding cost in reduced performance. The GUI interface is not implemented for as many commands as the Curses Forms or Command Line interfaces. Most of the major MR and source commands are available in the GUI, but some important ones such as getversion, unedput, and addgsrc are missing. In summary, the Curses Forms interface offers: n Full screen of fields n Fixed-order field entry, with optional back ups and restarts n n Validation field by field Visual feedback when fields are updated n Left/right scrolling n Display of default entry (when selected) n Menus of acceptable entries n n Explanations for each field, on request Ability to move back and forth among fields to correct errors or change data The Command Line interface offers: n Ability to supply all input to a command up front, without filling out screen forms n Quick entry of commands for which the default value for fields is to be used n No need to move through fields in which no entry is necessary n Ability to execute commands in non-interactive environments, such as shell scripts and cron jobs n Customizable keywords to identify which data goes with which field. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-3 Getting Started n On-line help for each command, showing the available keywords and showing which fields are mandatory The Graphical User Interface offers: n An X Window System interface n Customizable master menu of available commands n Field entry in (mostly) arbitrary order n n n Drop-down menu boxes Visual file and directory navigation Limited command set The Web Sablime interface offers: n a completely platform-independent interface n a report facility that allows developers to view the MRs assigned to them, n access to the most frequently-used Sablime commands, and n access to the Sablime documentation. If you use the Command Line interface or the Curses Forms interface, it is important to know that your Database Administrator had to choose one of these interfaces as your default interface when setting up your PTS ID. You can change your default interface by using the pts command and changing the value in the HMI Command Mode field. (See Changing or Viewing a Sablime Profile in Chapter 3, Using the Administrative Commands.) Table 2-1 lists the default setting of the prompt keyword for the two possible values of the HMI Command Mode field. (HMI stands for Human-Machine Interface, fs stands for full-screen, and np stands for no-prompt.) Table 2-1. HMI Command Mode Default Settings of prompt Keyword Prompt Default fs prompt=y np prompt=n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-4 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Command Line Interface Table 2-2 shows the results of entering the prompt keyword on the command line. Table 2-2. Relationship between Command Line Entry and Interface Command Line Entry Interface prompt=y Curses Forms Interface prompt=n Command Line Interface Even when you have specified fs as your default HMI command mode, you can enter data values on the command line when you issue a command. You can also enter prompt=n on the command line to use the Command Line interface. If you have specified np as your default HMI command mode, you do not have to enter prompt=n on the command line. If you enter keywords and values on the command line without specifying prompt=n and your default HMI command mode is the Curses Forms interface, the corresponding fields are populated with those values when the screen is displayed. As you press RETURN to move through the fields, the entries are validated. In the Command Line interface, Sablime processes the keywords given and includes default values where available for all unspecified fields. If any mandatory keywords or corresponding values are missing and have no default or are unacceptable, the command terminates and produces an error message. Using the Command Line Interface 2 NOTE: Do not use the Command Line interface to delete data from the database. Entry of a keyword followed by a null entry, either blanks (i.e., key= ) or blanks in quotation marks (i.e., key=" "), causes an error. (See Changing or Deleting Existing Data in Using the Curses Forms Interface, below.) Before you can use the command-line interface, the Database Administrator must add you to the Personnel Tracking System (PTS) relation. Once you have a PTS ID, you must issue the dot sablime command (. sablime generic) every time you log in to your machine and want to use the Sablime system. The dot (.) must be followed by a space. This command provides access to the Sablime databases established for your product and creates the necessary environment and directory paths. The path to the dot sablime program should be included in the PATH in your .profile file or on the command line. To execute the dot sablime command, enter: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-5 Getting Started . sablime generic where generic is the name of the generic/release of your product in which you want to work. For example, if the generic is named abc5.2, enter: . sablime abc5.2 When you enter this command, a screen like the following is displayed: ****** Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 ****** The Sablime Configuration Management System is proprietary property of Lucent Technologies and is not to be disclosed or used except in accordance with applicable agreements. Copyright (c) 1999 Lucent Technologies Unpublished & Not for Publication All Rights Reserved When you run any Sablime command, it is executed under the effective user ID (effid) of sablime. The effid allows you to access source files, update the databases, and carry out other processing as though you had the permissions allowed to the sablime login. You actually retain your real user ID (login) while running the commands. (When you use the Curses Forms interface, login and effid names are displayed in the upper left corner of each screen.) All user directories that are used when running Sablime must have permissions of at least 444 so that Sablime can read and write the files in them. Files that are to be stored in the Sablime system must have permissions of at least 444. (See the chmod command in the UNIX System User’s Reference Manual for information about file permissions.) ! CAUTION: To avoid problems with terminal hang-up and unusual command reactions, do not execute any Sablime command with a here document reference (e.g., pts <<!). The following considerations apply when using the Command Line interface: n You do not have to enter keywords in any special order on the command line. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-6 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Command Line Interface n If a field has a Pop-Up Selection Window (PSW) in the Curses Forms interface, the values entered on the command line must be chosen from the entries for that PSW. n In fields that use a left/right scrolling buffer for screen or line entry, the number of characters that can be entered as the value on the command line is equal to the length of the left/right scrolling buffer. In this type of field, you can generally enter 256 characters for MRs or file names, 128 for generics, 140 for directories. See the description of the field on the manual page for the appropriate command for more information. NOTE: ksh has a limit of 255 characters for command-line entry. If your commandline entry exceeds this length, you can put your entry in a file and execute the file. n Whenever spaces appear in a value entered on a command line, the value must be enclosed in double quotes (e.g., abst="Problem with mail message for sget"). n Whenever you use the Command Line interface, the Sablime system processes the keywords given and includes default values where available for unspecified fields. The general processing of default values in the Command Line interface is shown in Table 2-3. Table 2-3. Default Values in Command Line Interface keyword=value Specified onCommand Line Value is validated and accepted keyword=value Omitted onCommand Line Field is Mandatory Field is Optional Error message is produced. No change is made to the current value of field. If any mandatory keywords and/or values are missing or unacceptable and have no default, the command terminates and produces an error message. For example, suppose you enter: assign mr=sab970034 g=g2 dev=gar prompt=n Processing begins when you press RETURN, and the appropriate processing messages are displayed. MR sab970034 in generic g2 is assigned to developer gar with a severity of 3 (default). No due date is specified. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-7 Getting Started Fields that have a default value in the delivered version of the Sablime system are not shown as required in the Command Line interface because the Sablime system automatically supplies the default value if no other data is available when RETURN is pressed. Help 2 Typing -help or -? after a command name will give the user a listing of the keywords available for the command along with the names of the fields they represent. Mandatory keywords will be preceded by an asterisk, and defaults will be enclosed in parentheses and will appear after the field names. Using the Curses Forms Interface 2 Before you can use the Curses Forms interface, the Database Administrator must add you to the Personnel Tracking System (PTS) relation. Once you have a PTS ID, you must issue the dot sablime command (. sablime) every time you log in to your machine and want to use the Sablime system. The dot (.) must be followed by a space. This command provides access to the Sablime databases established for your product and creates the necessary environment and directory paths. The path to the dot sablime program should be included in the PATH in your .profile file or on the command line. To execute the dot sablime command, enter: . sablime generic where generic is the name of the generic/release of your product in which you want to work. For example, if the generic is named abc5.2, enter: . sablime abc5.2 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-8 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Curses Forms Interface When you enter this command, a screen like the following is displayed: ****** Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 ****** The Sablime Configuration Management System is proprietary property of Lucent Technologies and is not to be disclosed or used except in accordance with applicable agreements. Copyright (c) 1999 Lucent Technologies Unpublished & Not for Publication All Rights Reserved When you run any Sablime command, it is executed under the effective user ID (effid) of sablime. The effid allows you to access source files, update the databases, and carry out other processing as though you had the permissions allowed to the sablime login. You actually retain your real user ID (login) while running the commands. The login and effid names are displayed in the upper-left corner of each screen. All directories that you use when running Sablime must have permissions of at least 755 so that Sablime can read the files in them. Files that are to be stored in the Sablime system must have permissions of at least 444. (See the chmod command in the UNIX System User’s Reference Manual for information about file permissions.) ! CAUTION: When you use the Curses Forms interface on a windowing terminal or computer, the window in which Sablime commands will be displayed must be at least 24 rows by 80 columns. Any smaller window causes the screen or terminal to hang up and prevent further work until reset. The following sections describe various aspects of the Curses Forms interface. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-9 Getting Started Screen Design 2 Each screen used in the Curses Forms interface is similar to the one below. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 effid:sablime Heading 12:03:00 03/02/00 Title Field: ___________________________________________________________________ Field: _________________________ Field: _________________________ Field: _________________________ Field: _________________________ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ When the screen is first displayed, the cursor is located at the first character position of the first field in which data can be entered. When you enter data in a field, you cannot type beyond the end of the displayed line unless left/right scrolling is allowed for that field. The lines shown in this guide are approximations of those you see on your display and may not reflect the actual number of characters allowed. When the number of characters in an entry is important, that information is available in this guide or in the on-screen help message or error message. The number of characters available when left/right scrolling is in effect is stated in each field description when appropriate. In a field where entry of data lists is allowed (e.g., the MR Number field may allow entry of more than one MR), you can enter as many comma-separated items as completely fit in the displayed space or the left/right scrolling buffer. If you run out of space, repeat the command until all data has been entered or create groups of items for easy entry. ! CAUTION: In a comma-separated list, do not insert spaces after the commas. Spaces can cause the entry to be rejected as invalid or cause the command to behave unpredictably. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-10 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Curses Forms Interface Field Entry 2 Enter data into a field by typing the information and pressing RETURN. If a field is mandatory and a default entry is available, the default is displayed when you press RETURN without typing data in that field and the cursor is placed at the end of the field value. The default value is also displayed and highlighted in the PopUp Selection Window if one exists for the field. Even when the Curses Forms interface is the default interface, you can include data for some or all of the fields in the command on the command line. When you press RETURN, the requested screen is displayed with the data you have entered shown in the appropriate fields. For example, if you enter: accept mr=sab990034 g=g1,g2 class=software \ type=modification The Sablime system displays the following screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 03/02/00 12:28:35 Accept MR for Specified Generic MR Number: sab990034__________________________________________________________ Generic: g1,g2______________________________________________________________ MRG Class: software________________ MRG Type: modification____________ MRG Subclass: ________________________ MRG Subtype: ________________________ Auto Assign: _ MRG Severity: _ Due Date: ________ Estimated Effort: _____ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ The cursor is located after the data in the first field. Data is verified as you press RETURN to move the cursor from field to field. The Sablime system verifies that you have entered data in all mandatory fields. The system also validates your input to be sure it is valid and, if a menu is provided, verifies that the response is one of the menu items. In fields for which menus are provided, you need enter only one or two characters of the selected entry. The greater-than symbol (>) will appear in front of the first AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-11 Getting Started menu item containing those characters. (The item is also displayed in reverse video on terminals that support that feature.) When the > symbol points to the selection you want, press RETURN. The system will fill in the correct entry. NOTE: Your Database Administrator can change the mandatory or optional status of fields in your system so that it differs from that shown in this guide. Also, fields that appear in this guide may not be used in your customized version, and some of the menus or defaults shown may differ in your Sablime instance because of customization. See your Database Administrator to learn if Sablime has been customized for your project. Pop-Up Menu Displays 2 Certain fields display Pop-Up Selection Windows (PSWs) that give you a list of valid selections for the field. If the number of selections exceeds the size of the PSW, the words END and MORE appear in the upper and lower borders of the PSW. MORE indicates that there are more selections available by scrolling in that direction. You can scroll down one line by entering ^D (Control and D at the same time); you can scroll up one line by entering ^U (Control and U at the same time). END indicates that there are no more selections in that direction. If you have trouble scrolling, check your terminal settings with the UNIX system command stty -a. Some pop-up menus also include explanatory comments. These comments are usually separated from the actual entry by two spaces and are not displayed in the field when you select a menu item. NOTE: See your Database Administrator to learn whether the Sablime menus have been customized for your project. The menu for a particular field is displayed in a PSW if a valid entry is not made within the delay time specified in the Pop-up Delay field of your PTS record. (The default is zero seconds.) You cannot change the size or placement of a PSW. Changing or Deleting Existing Data 2 When you want to change data that already exists in the database, it is generally easiest to enter the command, the keyword, and the modified value on the command line using the Command Line interface. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-12 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Curses Forms Interface However, if you want to delete existing data (i.e., make a field entry blank), you must use the Curses Forms interface; you cannot use the Command Line interface. Date Fields 2 The acceptable date formats for all date fields are mmddyy or mm/dd/yy. Leading zeros are not required if slashes are used. The Sablime system verifies that the date is valid and is between 1/1/80 and 12/31/50. (If yy is 80 to 99, the system sets the date to 19yy; if yy is 00 to 50, the system sets the date to 20yy.) If a problem is found, an error message is generated. With report or query, a range of dates can be entered in the format mmddyymmddyy or mm/dd/yy-mm/dd/yy. See the manual pages for report and query in the User’s Reference Manual for more information. Copy To Field 2 Entering a PTS ID in this field ensures that the user you have entered will receive any mail generated by the command. This mail cannot be blocked. Confirm Menu 2 The CONFIRM (continue) menu appears on every screen after you enter all required information and press RETURN to move out of the last field. Type y and press RETURN to send the screen data to the system for processing and to initiate any required database updates. Type n (default) and press RETURN to move the cursor to the prior field if you want to change entries before processing. Use ^P to move to previous fields. Type q and press RETURN to abort the command. If you decide not to process the data, press the DELETE (^X) key to cancel input and return to the system prompt. (If this does not work, use the output of stty -a to determine which key to use. Ususally the interrupt key will work.) The following message will be displayed: ***** User Termination Requested ***** System Messages 2 Sablime provides error information and processing messages to help you enter acceptable and accurate data. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-13 Getting Started n Error information is displayed at the bottom of the screen when an error is detected by the system. Two types of errors are detected: — User errors (e.g., ***USER_ERR) usually result from errors that are detected when the system attempts to validate data the user has entered. See Appendix B, Error Messages Generated by Sablime, for more information about user errors. — System errors (e.g., ***SYS_ERR) indicate that something is wrong with the system itself, the Sablime environment, or the Sablime databases. If this type of error occurs, make a note of the error and what you were doing on the system when it occurred, and notify your Database Administrator. You should examine the product_dbawarn file (where product is the name of your product) in the $sabGDB/tmp directory, where $sabGDB is the location of the Sablime Global Database. If you cannot resolve the problem, your Database Administrator should call the Sablime hotline. n Processing messages are displayed while a request is being processed after input data has been confirmed. The messages shown in this guide are examples of what is displayed if you specify y in the Verbose Info field of the pts command. NOTE: If you specify y in the Verbose Info field, you see all messages about database updates and mail. If you specify n, processing time remains the same but such messages are not displayed. In the processing messages displayed when you are using the Sablime system, information shown in brackets in this guide (e.g., [MR #]) is replaced in the actual display with information specific to your Sablime instance (e.g., sab970032). Help 2 You can request information about any field by placing the cursor in the field and pressing the question mark (?) key; Sablime will then provide information about that field. The amount of information you will receive depends on the setting of the Verbose Help field in your PTS record. (See Changing or Viewing a Sablime Profile in Chapter 3, Using the Administrative Commands.) Screen Navigation 2 Keystrokes allow you to move around the screen, enter data, get help, and perform other functions. Since most people cannot remember all the characters for screen navigation, the user always has access to this information. A help line AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-14 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Curses Forms Interface will appear on the last line of all Sablime Curses Forms Screens when the user types any meaningless character, such as <control>Z. If the user is inside a help window and types a meaningless character, help about navigating through a help window will appear on the last line of the Curses Forms Screen. It will look like this: ^N/^P: Page Up/Down ^U/^D: Scroll Up/Down ^T/^B: Top/Bottom q: End Help If the user has no help window up and types a meaningless character, the last line on the Curses Forms Screen will tell what to type to get field navigation help: Press ^A for field navigation help. If the message that Sablime is about to display in the message line is already in the message line, an alternate message appears, so the user always knows that Sablime received the input. When the user types <control> A and a help screen is up, the bottom line of the Curses Forms Screen shows the navigational help, since <control>A is a meaningless character when the help window is up. When the user types <control> A and no help screen is up, the navigation pop-up window shown below appears. Terminal Types 2 The screen-handling package used by the Sablime system supports any terminal type supported by terminfo (4). NOTE: Make sure that your terminal type matches the terminal you are using. A mismatch is a common source of screen management problems. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-15 Getting Started Using the Graphical User Interface on the X Window System 2 Preliminary Setup 2 Before you can use the X Window System GUI interface, the Database Administrator must add you to the Personnel Tracking System (PTS) relation. Once you have a PTS ID, you must issue the dot sablime command (. sablime) every time you log in to your machine and want to use the Sablime system. The dot (.) must be followed by a space. This command provides access to the Sablime databases established for your product and creates the necessary environment and directory paths. Customizing the X Window System GUI 2 Before using the X Window System GUI, set the following variable: export DISPLAY=machine_name:0.0 where machine_name is the name of your local machine. If you are running the X Window System commands on a machine other than your local machine, you may execute the following command in a local window: xhost +host where host is the name of the machine where the X Window System commands are run. For a complete list of security options available with this command, see xhost (1). You can customize the look and behavior of your GUI interface in a resource file called XSab; XSab is the application class name of all the X Window System Sablime commands. The default location for the XSab file is your home directory; if you prefer to locate the XSab file elsewhere, consult X Window System documentation concerning the location of app-defaults files. NOTE: If you want an individualized XSab file, copy the one in $sabLCB/xbin and modify it. ($sabLCB is the location of the Sablime Local Control Bin.) Otherwise, you may lose important functionality. You can customize your interface in the following ways: n The Run, Cancel, and Reset buttons in the Sablime command window can be relabeled. To relabel these buttons, use strings like the ones below in your XSab file. (Note that either spaces or a tab must separate variables AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-16 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Graphical User Interface on the X Window from their assignments.) *Run.labelString: *Cancel.labelString: *Reset.labelString: n Do it! Dismiss Restart The position of the labels within these buttons can be modified by the following string in your XSab file: *buttons.entryAlignment: alignment_beginning which would make the labels left aligned. The other choices are alignment_center and alignment_end. n Similarly, the position of field names can be modified by: *alignment: n alignment_end If you want your Sablime window to use colors other than your default colors, you can include in your XSab file, for example: *background: *foreground: n DarkGreen tan The following string in the XSab file can be modified to adjust the font: *fontList: -adobe-courier-bold-r-normal--12-*-iso8859-1 The following strings in the XSab file can be altered to change the appearance of tables: *xrtTblForegroundSeries:(allcells allcells black) *xrtTblBackgroundSeries:(allcells allcells grey) (label all wheat) *xrtTblFrameShadowThickness: 2 *xrtTblShadowThickness:1 1 *xrtTblFontListSeries: \ (all all -adobe-courier-bold-r-normal--12-120-*-iso8859-1) \ (label all -adobe-courier-bold-r-normal--12-120-*-iso8859-1) *xrtTblAllowResize: RESIZE_VERTICAL or RESIZE_NONE or RESIZE_ALL or RESIZE_HORIZONTAL n The following section of the XSab file shows you how to customize the menus in the Sablime command window by disabling, removing, modifying, and adding commands. ! Customizing the xsab Menus ! ! menu ------- menu choices ------------------ used by default: ----------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-17 Getting Started ! fil_menu button_0 - button_9 button_0 ! mr_menu button_0 - button_19 button_0 - button_14 ! src_menu button_0 - button_9 button_0 - button_4 ! rpt_menu button_0 - button_9 button_0 - button_1 ! opt_menu button_0 - button_9 button_0 - button_1 ! cus_menu button_0 - button_9 none (for use by customer) ! hlp_menu button_0 - button_9 button_0 - button_3 ! ! Resource use ! --------------! mnemonic keyboard shortcut ! labelString text to appear on button or menu selection ! sensitive True if selectable, False otherwise ! mappedWhenManagedTrue if visible, False if not ! userData UNIX command and help clue, separated by ";" ! ! UNIX commands must be in LCB/xbin, and are executed under real user id. ! ! special-purpose command fields for xsab menu: ! ! ! ! Keyword Use ! --------------! EXIT Usual exit sequence from xsab (including confirmation) ! ABOUT Display the "About Sablime" window ! PRODGEN Display the "Product/Generic..." selection window ! ! xsab*fil_menu*mnemonic: F ! xsab*fil_menu.labelString: File ! xsab*fil_menu.sensitive: True ! xsab*fil_menu.mappedWhenManaged: True ! ! xsab*cus_menu.mappedWhenManaged: False ! ! xsab*fil_menu*button_0.mnemonic: x ! xsab*fil_menu*button_0.labelString: Exit ! xsab*fil_menu*button_0.sensitive: True ! xsab*fil_menu*button_0.mappedWhenManaged: True ! xsab*fil_menu*button_0.userData: EXIT;Exit program ! ! xsab*rpt_menu*button_0.mnemonic: S", ! xsab*rpt_menu*button_0.labelString: Standard...", ! xsab*rpt_menu*button_0.mappedWhenManaged: True", ! xsab*rpt_menu*button_0.userData: xreport;Generate a standard report", You can also set a global variable to customize the behavior of your interface: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-18 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Graphical User Interface on the X Window n n The sabCONFIRM variable can be used to suppress some of the confirmation pop-ups you get by default. In particular: sabCONFIRM=n suppresses the exit confirmation for the Sablime application window if no command windows are open and the Cancel/Close confirmation for Sablime command windows sabCONFIRM=N suppresses the exit confirmation for the Sablime application window even if command windows are open. The sabNO_BOTHER variable is an optional variable that disables the MR list regeneration function of the X GUI accept and closemr commands. This is useful because it takes a long time to regenerate the MR list after the Run button is pressed. Setting Up for a Product and Generic 2 Your Sablime Administrator has established one or more products in the Sablime databases. Work is done on a product generic—a formal release or version of the product. You must tell Sablime the product and generic on which you intend to work when you first sign in to Sablime and at any time you want to change to work with a different product or generic. Before you bring up your Sablime application window with the xsab command, you can set up for the product and generic in which you want to do work with the dot sablime command. After you have started xsab, you can use Options›Product/ Generic to reach a series of pull-down menus to change the setup product and generic. NOTE: Changing the product and generic in the Sablime application window does not cause a similar change to Sablime command windows that are already open; it affects only subsequently opened windows. The path to the dot sablime program should be included in the PATH in your .profile file or on the command line. To execute the dot sablime command, enter: . sablime generic where generic is the name of the generic/release of your product in which you want to work. For example, if the generic is named sab5.2, enter: . sablime sab5.2 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-19 Getting Started When you enter this command, a screen like the following is displayed: ****** Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 ****** The Sablime Configuration Management System is proprietary property of Lucent Technologies and is not to be disclosed or used except in accordance with applicable agreements. Copyright (c) 1999 Lucent Technologies Unpublished & Not for Publication All Rights Reserved Then, from a window where you are set up for a Sablime generic, issue the following commands: export sabDOT=full_path_of_dot_sablime xsab & The sabDOT variable enables the Options›Product/Generic window. After the logo is displayed, the Sablime application window appears, as shown in Figure 2-1. Figure 2-1. Sablime Application Window (X Window System) AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-20 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Graphical User Interface on the X Window The following sections describe the various elements of the GUI window and explain how to use them. NOTE: The Sablime application window shown above and the elements described below are based on the Sablime software as delivered. Many of the features they show are customizable. If your system does not appear as shown, and you have not made changes to it yourself, consult your Sablime System Administrator for information about the changes that have been made. Sablime Window Elements 2 Menu Bar 2 The menu bar contains the Sablime menus: — File menu The File menu has only one option, Exit. This option cancels the Sablime application window. — MR menu n create n accept n assign n fcreate n submit n testassign n testpass n reject n approve n unaccept n closemr n killmr n spawnmr n study n propose AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-21 Getting Started n depend n mrnote These commands are described in Chapter 4. — Source menu n addisrc n edget n edput n unedget n sget These commands are described in Chapter 5. — Reports menu The Reports menu has a single option, Standard. Reports are described in Chapter 6. — Options menu The Options menu has a single option, Product/Generic. For information on changing the setup product and generic, see Setting Up for a Product or Generic, above. — Help menu n User’s Reference Manual n User’s Guide n Administrator’s Guide n About Sablime The Help menu is described in the section Help, which appears at the end of the section on the X Window System GUI. Status Bar 2 The status bar contains two fields. The first field contains information about the command selected from the menu. The second field contains the setup product/ generic. Message Boxes 2 Sablime windows adhere to Motif conventions. (For details on window functions, see the documentation that accompanies your machine.) AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-22 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Graphical User Interface on the X Window Operation of Boxes and Windows 2 Boxes and windows are operated as follows. n Click Run to update the Sablime database according to the changes you have made in the command window. NOTE: After the command processes, the command window remains on the screen with current values in many of the fields. n Click Cancel (Close) to close the window, ignoring any changes you have made in the command window since starting the window (Cancel) or since the last Run (Close). n Command pop-up windows Secondary windows with multiline text fields are confirmed by File›Quit or Ctrl-C. The Cancel or No button closes the pop-up window without registering any information. n Reset The Reset button reloads the list selection from the Sablime database. n If you fail to make an entry in a mandatory field, a Sablime error box like the one in Figure 2-2 appears. Figure 2-2. Sablime Error Box (X Window System) Click OK. Fill in the missing information and click Run on the command window again. n Data Validation AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-23 Getting Started Where possible, each data field is validated when you move on to the next field. If allowable values for one field depend on the values of other fields, validation is deferred until Run is clicked. n Date fields in all text boxes must be in one of the following formats: — mm/dd/yy — mmddyy — mm/d/yy — m/dd/yy — m/d/yy where m and mm represent the month expressed as digits, d and dd represent the day of the month expressed as digits, and yy represents the last two digits of the year. All legal forms are converted automatically to the first form shown. n Multiline Text Fields All text fields that have both vertical and horizontal scroll bars, such as the Solution... field for the propose command shown below, are entered into separate pop-up windows, containing a standard Motif text widget with both horizontal and vertical scroll bars, as well as additional buttons and menus that extend the editing capabilities. The figures in this guide, such as Figure 2-3, show standard template text in these fields; the templates may be different on your system. Figure 2-3. Sablime Template Text AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-24 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Graphical User Interface on the X Window Such windows have a File›Load menu item, which opens a Load File dialog box like the one shown in Figure 2-4. You can use this box to find a file and load it to use as a template. NOTE: If you enter full_path/*.c in the Filter field and press the Filter button, the Files list will only show files with a .c extension. The default is full_path/* which shows all files. Loaded files overwrite any existing text in the widget. Changes made to the Sablime version of the file do not affect the original file. Use the File›Quit option to save your information and return to the main window. Use the File›Save option to save your information and keep the text window current. Use the File›Save As option to save your information to a file. The Edit and Search menus are standard Motif menus. The Edit›Clear Selection option does not affect the current text; it deselects the currently selected (highlighted) text. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-25 Getting Started Figure 2-4. Sablime Load File Box Box Types 2 Some fields allow only one selection from the pop-up; others allow multiple selections. If only one selection is allowed, the pop-up disappears when a selection is made. If more than one selection is allowed, the pop-up remains on the screen until it is dismissed by clicking the OK button at the bottom of the pop- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-26 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Web Sablime Interface up. Some fields also allow entries to be typed into the text portion of the box; the typed entry does not need to match an item in the list, but if it does match one, that item becomes highlighted when the focus is changed. Help 2 The Help menu has four items. Select User’s Reference Manual to display the User’s Reference Manual. Select User’s Guide to display the User’s Guide. Select Administrator’s Guide to display the Administrator’s Guide. Select About Sablime to display the About Sablime dialog box. Help is available from the Help menu on each command window, as well as from the Sablime application window. Pressing F1 causes information about the field that has the focus to appear in a help window. If selecting Contents or pressing F1 fails to bring up a help window, proceed as follows: 1. Exit xsab. 2. export HHHOME=$sabLCB or $sabMCB 3. Restart xsab. Using the Web Sablime Interface 2 The web interface to Sablime offers: n a report facility that allows developers to view the MRs assigned to them, n access to the most frequently-used Sablime commands, and n access to the Sablime documentation. Access to the interface, which requires a login and password obtainable from your System Administrator, is through the URL //http://hawk.stc.lucent.com:8080/wsab2.html. A typical command interface screen, which would appear if the user wanted to create a new MR, is shown on the following page: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-27 Getting Started The contents of the main help screen, which appears when the user clicks on the question mark below Config View, is as follows: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-28 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Web Sablime Interface Web Sablime v5.2 Help - Main User’s Manual Admin’s Manual User’s Reference Web Sablime provides an interface to allow users to run Sablime from anywhere. In this release, Web Sablime offers a developer’s view through "My MRs" along with 27 frequently used Sablime commands. Product Select the product you want Web Sablime to run on from the selection box. The product selected will be used when you click on any button or link in that frame. Note: Changing the product will not automatically refresh the current page you are on. In order to propagate your change, you must click on the button or link again. My MRs The My MRs page presents the developer with a comprehensive view of relevant MRs through three tables: MRs Assigned To You For Study, MRs Assigned To You For Development, and MRs Assigned To You For Testing. You may configure the My MRs view by going to the Config View page first. If no configuration is done for a product, the default configuration will be used. The defuault configuration consists of retrieving MRs from all generics available in the selected product and displaying the four tables above in the order. Config View Click on Config View to configure the My MRs page for the product selected. You may choose which generic(s) to retrieve MRs from as well as the tables to be displayed as wellas the order displayed. If the product is not configured, the default configuration will be applied. Generic Select the generic you want to use as the default for the Sablime Commands. The generic selection is only used by the Sablime Commands as a default generic. Changing this value will not affect the My MRs or Config View pages. Sablime Commands The Sablime Commands folder contains 27 frequently used commands. They are categorized into 4 sub-folders: MRs, Source, Reports, and Administration. The table below provides a quick lookup for where commands reside. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-29 Getting Started Running a command To run a command, go to the appropriate folder and click on the desired command. In each command, field labels are links to their corresonding vhelp files. Fields with * are mandatory fields that you must provide input for. Other mandatory fields that already have a default value will not have an * next to it. Output window When you move from field to field in each command, checks will be run to verify the data you’ve entered is valid. This will cause a new window to pop up which will contain the outputs of those verifications. If the input is valid, the output window will be blank. Otherwise, the error will be displayed. For your convenience, please don’t kill that window. simply minimize it. If an error does occur, an alert box will be displayed telling you to check the output window for details on the error. Command output Once you executed the command, the outpu twill be displayed in the output window. This is regardless of successful completion or not. However, if the command failed, you will see an alert box telling you the command did not run successfully and to check the output window for details. Browse vs. Compose For fields that require file input (description, resolution), there are two choices. You may either use the Browse button and select a file already created or you may select the Compose button to create the file. Compose will bring up a textarea with the default template. Once you are done editing the textarea, click on done and the file will be saved. Index to commands MRs Source accept activate approve assign closemr create defer depend fcreate killmr mrnote nochange propose reject spawnmr study submit testassign testpass unaccept addisrc edget edput sget AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-30 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Web Sablime Interface unedget Reports report Administration qmr unedput ReportWizard setgroup dismiss AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 2-31 Getting Started AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 2-32 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Contents 3 Using the Administrative Commands n n n 1 Changing or Viewing A Sablime Profile 1 Changing a Profile 3 Looking at a Profile 4 Creating, Changing, and Deleting Sablime Groups Sablime Groups 5 Guidelines for Creating Groups 5 Creating a Group 6 Changing a Group 7 Deleting a Group 8 Creating a User’s Working Environment 9 Source Database n 5 11 Troubleshooting 12 Using sabhelp: Example 1 15 Using sabhelp: Example 1 (continued) 16 Using sabhelp: Example 2 17 Using sabhelp: Example 3 19 Using sabhelp: Example 4 21 Using the shrec, shabs, and sherr Commands 22 Using shrec: Example 1 23 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 i Contents AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page ii Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Administrative Commands 3 This chapter provides information about the administrative commands that may be run by any user of Sablime and examples of how they may be used. The topics covered are; changing or viewing a Sablime profile, creating, changing and deleting groups, creating or updating a node, and troubleshooting. NOTE: The GUI does not provide access to any of the administrative commands. NOTE: Sablime has a command permissions function that allows the Sablime Administrator to change command permissions for each individual command. Therefore, it is sometimes possible for users to run a command even though they are not in the group normally permitted to do so. The documentation decribes the system as delivered. Changing or Viewing A Sablime Profile 3 NOTE: For detailed information about the pts command, see the pts manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The Personnel Tracking System (PTS) tracks all personnel and allows them access to the Sablime commands and databases. The information provided through the pts command can be used to identify creators of MRs, to generate reports about MRs, and to provide contact information. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 3-1 Using the Administrative Commands Sablime users must be entered in the PTS relation before any commands are available to them. Before the DBA attempts to create personnel groups, intended group members must be included in the PTS relation. Only the DBA can create or delete a record with the pts command. All users can modify their own records or view any PTS record in the database. When you select modify or view, current data is displayed. You can specify: n Curses Forms or Command Line interface n the number of seconds to delay before a menu is displayed in the Curses Forms interface n the use of verbose or terse messages n whether you want mail sent if you are the MR originator n whether you want mail sent if you are the MR assignee (developer) n whether the MR description is to be included in mail messages received n the editor to be used when editing a file (favorite editor) n where you want mail sent, or whether you want to block all automatically generated MR messages. These changes will affect all commands. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3-2 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Changing or Viewing A Sablime Profile Changing a Profile 3 Suppose you want to change your favorite editor from vi to emacs in your PTS record. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would enter pts, modify, and your PTS ID. The screen below would appear, containing your current PTS record, and you could then change the Favorite Editor field to emacs, as shown below. logid:ral effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 Administrative System Command 06/25/00 08:50:39 Personnel Tracking System Maintenance Function: modify___ Sablime PTS ID: _________________ Licensed: _ Auth Prod: sab5.2___________________________________________________________ Full Name: Robert Lippman___________________________________________________ Dept Code: 12345____________________ Manager: dave_____________________ HMI Command Mode: fs Popup Delay: 0 Verbose Prompts: n Loc Code: MH_______________________ Room: 2D-355___________________ Phone: 908 582-9999_____________ Verbose Info: n Verbose Help: n Auto Orig Mail: y Auto Asgn Mail: y Verbose Email: n Last Usage: 06/25/00__ Favorite Editor: emacs___________________ Receive Mail Flag: y Email Address: [email protected]_____________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: pts fcn=modify ed=emacs prompt=n Note that when using the Command Line interface you need only enter values for the fields to be changed; Sablime uses the current values for the remaining fields. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 3-3 Using the Administrative Commands Looking at a Profile 3 If you simply want to look at your profile (or the profile of another user), you would enter pts, followed by view and the PTS ID of the user whose profile you want to see, as shown below. logid:ral effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 Administrative System Command 06/25/00 08:50:30 Personnel Tracking System Maintenance Function: view_____ Sablime PTS ID: ral______________ Licensed: y Auth Prod: sab5.2___________________________________________________________ Full Name: Robert Lippman___________________________________________________ Dept Code: 12345____________________ Manager: dave_____________________ HMI Command Mode: fs Popup Delay: 0 Verbose Prompts: n Loc Code: MH_______________________ Room: 2D-355___________________ Phone: 908 582-9999_____________ Verbose Info: n Verbose Help: n Auto Orig Mail: y Auto Asgn Mail: y Verbose Email: n Last Usage: 0/25/00_ Favorite Editor: vi______________________ Receive Mail Flag: y Email Address:[email protected]______________________________________________ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3-4 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Creating, Changing, and Deleting Sablime Groups Creating, Changing, and Deleting Sablime Groups 3 NOTE: For detailed information about the setgroup command, see the setgroup manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. Sablime Groups 3 A Sablime Group is a way of linking together like or common items. Groups and their members are stored in the Sablime databases. They may be used to: n make it unnecessary to type a long list of items over and over again n extract an exact version of a release, by using a list of MRs n display selections shown in a Pop-Up Selection Window (PSW) during screen execution n send email to a number of recipients n determine command permissions based on the product, release, and other criteria Guidelines for Creating Groups 3 The PTS ID that creates the group is considered the group owner; only the group owner and the Database Administrator can modify or delete the contents of the group Each group has a type; ptsid, mr, or other. When a group is created type MR or PTSid, all members are checked to make sure they fit the group member criteria. Groups cannot contain any duplicate items or any of the following special characters, as they might cause corruption in the Sablime databases: n backslash (\) n blank/space n asterisk (*) n semicolon (;) n ampersand (&) n comma (,) n slash (/) AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 3-5 Using the Administrative Commands Each group must have a unique identifier or name associated with it. The group name can be almost anything, but its length cannot exceed 14 characters. In addition, the group name cannot begin with either an exclamation point (!) or a caret(^). Creating a Group 3 Suppose you want to create a group of PTS IDs. You would first create a file containing the members of the group you wanted to create and give it a name (perhaps gpmems1). Then, using the Curses Forms interface, you would enter setgroup, enter the group name (perhaps newstt) and type, and finally provide the name of the file you created earlier containing the group members. The screen would then appear as shown below. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 06/01/97 effid:sablime Administrative System Command 15:16:17 Add/Delete Members to/from Groups Group Name: newstt________ Group Owner: sablime__________ Group Type: ptsid_____ Member File: gpmems1__________________________________________________________ Copy To: _________________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would simply enter: setgroup grp=newstt type=ptsid mfile=gpmems1 prompt=n The default: owner=sablime (user’s PTS ID) is entered automatically and need not be typed. NOTE: A group may own itself. For example, the owner of the group above could be newstt. This can be useful in situations in which the Assigned Developer for an MRG is a group. Normally, this would mean that only the owner of the AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3-6 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Creating, Changing, and Deleting Sablime Groups group could submit the MRG. However, if the group owns itself, any member of the group can submit the MRG. Using the Curses Forms interface, if you do not specify a member file, a temporary file is opened in your editor for the entry of group members. After you enter your list and exit the editor, the setgroup screen is redisplayed. A message is displayed if any members are invalid, and you are required to correct them. When you confirm the command, a group named newstt is created and the items in your file become the members of the group. Changing a Group 3 To modify the members of the group newstt using the Curses Forms interface, you would use setgroup, enter the group name, and then press RETURN at the Member File field. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 06/01/97 effid:sablime Administrative System Command 15:17:32 Add/Delete Members to/from Groups Group Name: newstt________ Group Owner: sablime__________ Group Type: ptsid_____ Member File: _________________________________________________________________ Copy To: _________________________________________________________________ A temporary file is opened in your editor for modification of the list of members. After you modify the list and exit the editor, the setgroup screen is redisplayed. A message is displayed if any members are invalid, and you are required to correct them. When you confirm the command, the entries in your file become the members of the group, newstt. Using the Command Line interface, you would first create a file (perhaps gpmems2) containing the modified list of the members of the group, and then enter: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 3-7 Using the Administrative Commands setgroup grp=newstt mfile=gpmems2 type=ptsid prompt=n The default: owner=sablime (user’s PTS ID) is entered automatically and need not be typed. When the Command Line interface is being used, a copy of the file gpmems2 is used as the new list-of-members file. Deleting a Group 3 To delete a group, enter setgroup and the name of the group as shown below. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 06/01/97 effid:sablime Administrative System Command 15:18:16 Add/Delete Members to/from Groups Group Name: newstt______________ Group Owner: sablime__________ Group Type: ptsid_____ Member File: _________________________________________________________________ Copy To: _________________________________________________________________ A temporary file is opened in your editor for modification of the list of members. Delete all the members from the list. After you exit the editor, the setgroup screen is redisplayed. When you confirm the command, the group newstt and its members are deleted. Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: setgroup grp=newstt mfile=emptyfile type=ptsid \ prompt=n where emptyfile must be an empty file. The default: owner=sablime (user’s PTS ID) is entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3-8 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Creating a User’s Working Environment NOTE: To delete a group using the Command Line interface, you must supply a zero-length file to the mfile keyword. Creating a User’s Working Environment 3 NOTE: For detailed information about the setnode command, see the setnode manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. NOTE: The behavior described in this section represents the default behavior of the Sablime system. Your System Administrator may have customized this behavior for your product. For a software development project, files are usually stored in directories that group them logically by function. For example, suppose that your product’s name is ancl (Another Network Communication Link) and that the first generic for ancl is a1.0. The files for a1.0 are organized as in Figure 3-1 (directories are indicated by a /). This structure must be represented for the Sablime system in a file named for the generic and placed in the $sabGDB/DIR directory. The sabDIRF variable points to this file. The contents of a1.0 would look like the following: ! CAUTION: Be careful not to allow any spaces at the ends of the lines of this file. src doc doc/manuals doc/manuals/user src/cmd src/lib src/lib/syslib src/lib/xwinlib AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 3-9 Using the Administrative Commands src/ lib/ xwinlib/ x1.c Figure 3-1. x2.c doc/ cmd/ syslib/ a1.c c1.c manuals/ c2.c a2.c user/ sec.01 sec.02 Sample Project Directory Structure This file specifies the relative directory structure for generic a1.0 of the ancl product. When you issue the dot sablime command for the first time, the default behavior of the Sablime system is to create the directory structure represented in the $sabDIRF file in your home node. Thereafter, when you issue the dot sablime command, any new directories that have been added to that file since your last session in this generic are added to your relative directory structure. A product directory structure is thus created for all users who issue the dot sablime command for a generic. Your home node is defined in the following way: if your home directory is /usr1/ home/li and the generic for which you have issued the dot sablime command is called a1.0, your home node for this session is /usr1/home/li/a1.0. The sablime node is defined as $sabBASE/generic. The default value of the sabBASE variable (as defined in the xsablime.sh script) is the home directory for the sablime login. If the home directory for the sablime login is /sabhome/sablime and the generic for which you have issued the dot sablime command is a1.0, the sablime node for this session is defined as /sabhome/sablime/a1.0. The user’s node and the sablime node are used to define the default value of a variable called VPATH; it is defined as user’s_node:sablime_node. For our example above, the result of echo $VPATH is: /user1/home/li/a1.0:/sabhome/sablime/a1.0 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3-10 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Creating a User’s Working Environment The Sablime system uses the VPATH variable to calculate the default relative directory for the Directory and Current Directory fields in the following commands: addgsrc, addisrc, edget, edput, unedget, unedput, sget, source, and srcpr. The default relative directory is calculated by matching the first node in the VPATH variable to the full path of the current working directory; if there is an exact match, the default relative directory is the path that remains from stripping the first node from the current working directory. If the default relative directory is not valid for the generic (i.e., does not match a directory listed in the $sabDIRF file), an error message is generated. If you reset the first node of the VPATH variable (e.g., for load building with nmake) so that there is no match between the current working directory and the first node, the Sablime system does not calculate the default relative directory for these commands; you must type in the relative directory. As the sablime login and different users execute dot sablime, the Sablime system creates the generic directory structure under their home nodes. The same generic directory structures can be created in other nodes with the setnode command. Parallel directory structures are useful for populating your node with the getversion command, performing product builds (for example with nmake), and understanding the storage structure in the SDB. As an example of the value of parallel directory structures, let us assume that the last official build for your generic a1.0 resides under the sablime node, and that you want to make a change to the a1.c file, which resides in the relative directory src/lib/syslib. The relative directory structures appear in Figure 3-2. You would get a1.c out to edit with edget, make your changes, and recompile. Then when you do a build with nmake, the VPATH variable is set to the correct value, picking up the a1.c executable from your node and the makefile and the other files from the official sablime node. When the module is fully tested, you put back the file with edput. If you are positioned in the src/lib/syslib relative directory in your node, these commands calculate the relative directory for you. Source Database 3 Figure 3-2 also shows part of the directory structure in the SDB. The directory structure in the SDB represents the union of all the directory structures for all the generics in that product. Directories under ancl in the SDB would include all directories specified for all generics for the ancl product, e.g., in generics a1.0, a1.1, etc. The SDB stores the SCCS or SBCS files; these files are not directly editable by the user. The only valid directories for your generic are the ones established in the $sabDIRF file; in all Sablime commands, the Directory field and dir keyword refer AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 3-11 Using the Administrative Commands to these directories. To verify the directory structure for your generic, check the $sabDIRF file. NOTE: When files are added with the addgsrc command, they can be added to different directories. See addgsrc for details. Troubleshooting 3 NOTE: For detailed information about the sabhelp command, see the sabhelp manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The basic troubleshooting tool provided by Sablime is the sabhelp command. It searches and retrieves information to help you resolve a Sablime problem or answer a question about Sablime. NOTE: Additional troubleshooting tools provided by Sablime that your Sablime Administrator may use include the database audits, and the hotline.ck, setperm, and spacecheck programs. The database that has been provided by the Sablime team contains information that has been found to be useful in resolving calls to the Sablime hotline. If you use the sabhelp command, you may not need to make a call to the hotline. sabhelp is advantageous for two reasons: First, the time it takes to get your answer is shortened. Second, by reducing the quantity of hotline calls, it increases the chances that you will get a quicker response to your problems when you do need to call. The sabhelp command is supported by four other commands: shcat, shrec, shabs, and sherr. shcat is used to print out the entire contents of a record when a match is found. shrec, shabs, and sherr are convenience programs that allow you to search the database directly from the command line (without having to go through the sabhelp menu). Each of these is described below in more detail. At the UNIX system prompt, type: sabhelp AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3-12 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Troubleshooting to display the following menu: Welcome to the Sablime Help Utility Remember: Run the database audits regularly. If your Sablime Administrator hasn’t run audits recently, you may solve the problem by running audits now (if the problem is database related). Run the hotline.ck program. The hotline.ck (hotline check) program can find problems with Sablime executables, directory permissions, environment variables, and other common sources of errors. You may find the solution to your problem by having your Sablime Administrator run hotline.ck now. Also, if you suspect your problem is related to a lack of disk space, have your Sablime Administrator run the spacecheck program. Specify the section of the help database records to search (or select 4 to quit): 1) all_sections 2) abstract 3) error_message 4) quit #? At the #? prompt, specify which section of the database records you wish to search. Each sabhelp database record contains the following sections: SUBJECT A few key terms that serve as an index to the record ABSTRACT A summary of the problem addressed by the record ERRMSG The error message that appears when the problem occurs RES The resolution to the problem: that is, what you should do to fix the problem. The sabhelp command initially displays some messages and presents a menu of choices. If you specify choice 1, all_sections, then all the sections of each record are searched. This is the most inclusive search method. Any records matched by the other two options are also matched by this one. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 3-13 Using the Administrative Commands If you specify choice 2, abstract, only the ABSTRACT section of each record is searched. Use this option when you want to narrow down the number of records matched by your search term(s). If you specify choice 3, error_message, only the ERRMSG section of each record is searched. Use this option when you have seen a specific error message associated with your problem. After you select the section of the records to search, you are prompted to enter up to three terms to search for in the sabhelp database. Terms are separated by spaces. If you specify more than one term, all the terms that you specify must be found in the sections of the records to be searched. (Using sabhelp: Example 4 shows a case in which two search terms are specified.) After you enter one or more search terms and press the RETURN key, a search is done in the database. The abstract of each record that was matched is then printed. Preceding each abstract is a message that gives a code number to be used to view the entire record. To view the record, give the code number as an argument to the shcat command (Sablime help cat), as in shcat 203. Press the DELETE key to exit at the #? prompt. If the DELETE key fails to operate as described, execute stty -a at your shell prompt to verify control-character mapping for your login. (See your UNIX system administrator for details.) In the following examples, the reminders to run the database audits and the hotline.ck program are not shown, even though they appear when you run the sabhelp command. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3-14 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Troubleshooting Using sabhelp: Example 1 3 $ sabhelp Specify the section of the help database records to search (or select 4 to quit): 1) all_sections 2) abstract 3) error_message 4) quit #? 1 You may enter up to 3 terms to search for (or press the <DELETE> key to quit). Terms: addisrc FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 1’ command fails with call_sccs error message in the dba_warn file FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 329’ primsdb and/or addisrc fail, error message says writeable file exists FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 364’ when doing addisrc, getting error message the directory doesn’t exist FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 1222’ The addisrc command fails for a specific files. Other files are OK. FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 1703’ Attempt to put a file under SCCS fails with the "child returns" error message. FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 1817’ Customer attemnpts to use addisrc to add a file to a generic. Get error message: call_sccs file message: "<file name>: line too long" AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 3-15 Using the Administrative Commands Using sabhelp: Example 1 (continued) 3 $ shcat 329 SUBJECT primsdb addisrc VERSION all ERRMSG call_sccs: writeable file exists ABSTRACT primsdb and/or addisrc fail, error message says writeable file exists RES Check if there is a file in /usr/tmp with the same name as the file being retrieved (without the s. prefix). If it is there, remove it and run the command again. You may also want to run the audits to make sure the active and source databases are in sync. In Using sabhelp: Example 1, the user typed sabhelp at the shell prompt to start the command. In response to the sections prompt (#?), the user entered 1 to specify that all sections of each database record should be searched. Only one search term (addisrc) was given in response to the search prompt. The sabhelp command then searched all the sections of each record in the database and found six records that matched the search term. The abstract section of each matching record was printed, along with a code number for every match. The sabhelp command terminated at this point. The user decided to view a complete record. Viewing was accomplished by typing shcat 329 at the shell prompt. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3-16 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Troubleshooting Using sabhelp: Example 2 3 $ sabhelp Specify the section of the help database records to search (or select 4 to quit): 1) all_sections 2) abstract 3) error_message 4) quit #? 2 You may enter up to 3 terms to search for (or press the <DELETE> key to quit). Terms: addisrc FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 329’ primsdb and/or addisrc fail, error message says writeable file exists FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 364’ when doing addisrc, getting error message the directory doesn’t exist FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 1222’ The addisrc command fails for a specific files. Other files are OK. FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 1817’ Customer attempts to use addisrc to add a file to a generic. Get error message: call_sccs file message: "<file name>: line too long" $ shcat 329 SUBJECT primsdb addisrc VERSION all ERRMSG call_sccs: writeable file exists ABSTRACT primsdb and/or addisrc fail, error message says writeable file exists RES Check if there is a file in /usr/tmp with the same name as the file being retrieved (without the s. prefix). If it is there, remove it and run the command again. You may also want to run the audits to make sure the active and source databases are in sync AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 3-17 Using the Administrative Commands In Using sabhelp: Example 2, the search was restricted to the ABSTRACT section only (2 was entered as the response to the first prompt). Only four records were matched this time. In Example 1, there were six matches. However, two of those matched records had the word addisrc in a section other than the ABSTRACT. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3-18 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Troubleshooting Using sabhelp: Example 3 3 $ sabhelp Specify the section of the help database records to search (or select 4 to quit): 1) all_sections 2) abstract 3) error_message 4) quit #? 3 You may enter up to 3 terms to search for (or press the <DELETE> key to quit). Terms: 6952 FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 77’ 6952 openfil.c: can’t open file in mode [a] 9001 - command does not run; gives 9001 error message (getuid failed message in warn file) $ shcat 77 SUBJECT multi-machine create ERRMSG 6952 openfil.c: can’t open file in mode [a] 9001 - command does not run; gives 9001 error message (getuid failed message in warn file) VERSION all ABSTRACT setting up multi-machine mode of NFS, getting error message from create command 6952 from openfil.c: can’t open file in mode [a] RES NOTE: Running hotline.ck will often show what’s wrong! - Make sure that the files in the $sabLCB directory are owned by the same login as the login that owns the database on the host. - Make sure that the group for the login above is the same on the host and the satellite. - Make sure the mode of the executables in the satellite bin is 4755. - Make sure that the $sabMCB value is set to correct directory on host. - Make sure the $sabNET values on the satellite and the host are correct (should be 5 on satellite and 0 on host) - Make sure the PR relation field #3 is correct (should be 1) - The sablime login should have the same password on the host and satellite - Verify that the file system was mounted for the satellite machine with read and write permissions. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 3-19 Using the Administrative Commands In Using sabhelp: Example 3, a search was done to find a specific error number (6952) in the ERRMSG section of the database records. One match was found. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3-20 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Troubleshooting Using sabhelp: Example 4 3 $ sabhelp Specify the section of the help database records to search (or select 4 to quit): 1) all_sections 2) abstract 3) error_message 4) quit #? 2 You may enter up to 3 terms to search for (or press the <DELETE> key to quit). Terms: addisrc directory FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 364’ when doing addisrc, getting error message the directory doesn’t exist $ shcat 364 SUBJECT addisrc ERRMSG directory doesn’t exist VERSION all ABST when doing addisrc, getting error message the directory doesn’t exist RES Chances are that the directory structure in the sdb was not set up properly. Check that the following format is in place: ..../sdb/<prod_name>/<source_code_dirs> The generic name should not appear in this path, either in place of the <prod_name> or after it. As an example, suppose the customer has a directory with the generic name in between the directory with the product name and the directories with the source. The following steps should be taken: - $ cd <prod_name> - $ rm -rf <generic_name> - $ cd .. # to sdb - $ . sablime <generic_name> # make sure set up for correct generic - $ setnode <prod_name> AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 3-21 Using the Administrative Commands In Using sabhelp: Example 4, two search terms were supplied. Therefore, only records that contain both addisrc and directory in the ABSTRACT section were matched. Only one matching record was found. Using the shrec, shabs, and sherr Commands 3 The shrec, shabs, and sherr commands allow you to search the sabhelp database without having to interact with the sabhelp menu. Each of these commands searches a different part of the sabhelp database records, and each takes up to three search term arguments. The syntax of each of the commands is: shrec pattern1 [pattern2] [pattern3] shabs pattern1 [pattern2] [pattern3] sherr pattern1 [pattern2] [pattern3] At least one argument is required. The second and third arguments are optional. If more than one argument is present, all of the arguments given must appear in the section being searched. The shrec command searches all sections of the sabhelp database records for the search pattern(s) specified. The shabs command searches only the ABSTRACT section of the records. The sherr command searches only the ERRMSG section of the records. Once the records are found and their abstracts printed, use the shcat command to view the entire contents of the record. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3-22 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Troubleshooting Using shrec: Example 1 3 $ shrec addisrc FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 1’ command fails with call_sccs error message in the dba_warn file FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 329’ primsdb and/or addisrc fail, error message says writeable file exists FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 364’ when doing addisrc, getting error message the directory doesn’t exist FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 1222’ The addisrc command fails for a specific files. Other files are OK. FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 1703’ Attempt to put a file under SCCS fails with the "child returns" error message. FOR MORE INFO ON THE FOLLOWING ITEM, TYPE ’shcat 1817’ Customer attempts to use addisrc to add a file to a generic. Get error message: call_sccs file message: "<file name>: line too long" $ shcat 329 SUBJECT primsdb addisrc VERSION all ERRMSG call_sccs: writeable file exists ABSTRACT primsdb and/or addisrc fail, error message says writeable file exists RES Check if there is a file in /usr/tmp with the same name as the file being retrieved (without the s. prefix). If it is there, remove it and run the command again. You may also want to run the audits to make sure the active and source databases are in sync This example produces the same output as Using sabhelp: Example 1. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 3-23 Using the Administrative Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3-24 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Contents 4 Using the MR Commands 1 n MRs and MRGs 1 n The MR and MRG Life Cycles 1 n The MR Commands 3 n MRG Dependencies 6 MRG Dependency: An Example 10 n Creating an MR 15 n Killing an MR 18 n Deferring an MR or MRG 20 n Activating an MR or MRG 23 n Studying an MR or MRG 27 n Accepting an MR 29 n Unaccepting an MR 33 n Nochanging an MRG 35 n Spawning an MRG 38 n Assigning an MRG 42 n Submitting an MRG 45 n Assigning an MRG to a Tester 47 n Passing an MRG through a Test Phase 49 n Rejecting an MRG 52 n Approving an MRG 54 n Closing an MR 56 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 i Contents AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page ii Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the MR Commands 4 MRs and MRGs 4 When a product is developed under the Sablime system, all work must be associated with a Modification Request (MR). MRs are created to indicate a problem with or suggest an enhancement to a product. If it is decided that the problem must be resolved or that the enhancement should be introduced, the MR describing the problem or enhancement is accepted into one or more generics (releases) of the product and gives rise to a Modification Request in a Generic (MRG) in each generic into which it is accepted. Subsequent work is done in response to the MRGs that have been generated. But the MR itself remains active (open) until all the work associated with the MRGs has been completed; it is only closed when all the MRGs associated with it have been approved or nochanged. MRs are the responsibility of MR Administrators (MRAs), while MRGs are the responsibility of Generic Administrators (GAs). The MR and MRG Life Cycles 4 Figure 4-1 shows the various states associated with MRs and MRGs. The state of the MR or MRG is shown in italics within a box, while the command that puts the MR or MRG in that state is shown in this type next to the directional arrow. The large dashed box encloses the MRG states. As can be seen, many of the socalled MR commands actually work on MRGs rather than MRs. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-1 Using the MR Commands Figure 4-1. MR and MRG Life Cycles AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-2 Issue 1.1 November 2000 The MR Commands The MR Commands 4 The commands in Figure 4-1 are described in Table 4-1. The table follows the flow indicated in the figure NOTE: Sablime has a command permissions function that allows the Sablime Administrator to change command permissions for each individual user. Therefore, it is sometimes possible for users to run a command even though they are not in the group normally permitted to do so. The documentation decribes the system as delivered.. Table 4-1. MR and MRG Life Cycle Commands Command Description create Any user can create an MR using the create command. When the command is processed, an MR is created, assigned a number, and moved to the created state. Your Database Administrator establishes an MR numbering convention for your product that is used each time the Sablime system creates an MR for your product. killmr If an MR has been created and the MRA decides that no changes should be made with this MR in any of the active generics, the killmr command can be issued to set the MR to the killed (a terminal) state. The MR data is moved from the Active Database to the Inactive Database. defer/ activate The MRA may decide that work on the MR should not be performed now. The defer command can be used to postpone a decision and set the state of the MR to mra_deferred until an activate command is entered to return the MR to the created state. study/ propose If the MRA needs more information before deciding in which generic an MR should be accepted or whether it should be accepted at all, the study command can be used to name an Assigned Developer to examine the request. The study command sets the MR to the mra_study state. It can be used when the MR is in the created state. The study command can be reissued for the MR to change the Assigned Developer, severity, or due date. When the study is complete, the Assigned Developer reports the results with the propose command. This command sets the MR to the created state. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-3 Using the MR Commands Table 4-1. MR and MRG Life Cycle Commands—Continued Command Description accept/ unaccept The MRA, having been notified that an MR was created, decides whether work should be performed as suggested. If the recommended work is to be done, the MRA selects the generics in which the MR is to be resolved. The change procedure begins when the MRA issues the accept command. The accept command changes the MR state to active and generates an MRG (Modification Request in a Generic) for each generic for which the MRG is accepted. After an MR has been created and accepted into a generic, the GA would use the unaccept command to take the MR out of the generic if it is in the accepted state and no files were touched by this MR. nochange/ activate The GA may decide that no change should be made to the generic in response to an MRG. The nochange command sets the state of the MRG to nochange. Under normal circumstances, the nochange state is terminal for an MRG. However, the MRG can be returned to the accepted state with the activate command if the nochange decision needs to be reversed. spawnmr The GA may want to divide the work for the MRG into several MRG classes or to assign it to more than one Assigned Developer for separate work efforts. The spawnmr command is used to produce one or more spawned MRGs from an accepted original MRG. Once an MRG has been spawned, no work can be performed using the original MRG; all work must be done in response to the MRG spawns. Once the original MRG has been spawned, the only action that can be taken on it is to close it. All MRGs spawned from an original MRG must be in the approved or nochange state before the original MRG can be closed. defer/ activate The GA may decide that work on the MRG should not be performed now. The defer command is used to postpone a decision and set the state of the MRG to deferred until an activate command is entered to return the MRG to the accepted state. study/ propose If the GA needs more information about the impact or feasibility of the change requested, the study command is used to name an Assigned Developer to investigate the request. The study command sets the MRG to the understudy state. It can be used when the MRG is in the accepted state. The study command can be reissued for the MRG to change the Assigned Developer, severity, or due date. When the study is complete, the Assigned Developer reports the results with the propose command. This command sets the MRG to the accepted state. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-4 Issue 1.1 November 2000 The MR Commands Table 4-1. MR and MRG Life Cycle Commands—Continued Command Description assign When the GA decides that the product should be changed in response to an MRG, the assign command authorizes the Assigned Developer to make the necessary changes. The assign command can be reissued for the MRG by the GA to change the Assigned Developer, severity, or due date. If your project allows reassignment of MRGs, the Assigned Developer can issue the assign command to reassign the MRGs to another developer. When the MRG is in the assigned state, the Assigned Developer can use several commands to make changes in response to the MRG. Once the MRG has been assigned, it is possible for the Assigned Developer to set the state of the MRG to nochange if no file changes have been made with the MRG. It is also possible to unassign the MRG and return it to the accepted state by leaving the Developer field empty. fcreate The fcreate (fast create) command is issued by the GA or Assigned Developer to create, accept, and assign an MR with one command. submit After the requested changes have been made and unit tested in response to the MRG, the Assigned Developer uses the submit command to set the state of the MRG to submitted. The appropriate test team or (if no test teams exist for the generic) the Approval Team is notified. testassign The testassign command is used by the GA to assign an MRG to a tester, reassign an MRG from one tester to another, or undo the assignment of an MRG to a tester. Only the Assigned Tester can testpass or reject the MRGs. testpass The testpass command is used by a member of a Test Team to indicate that an MRG has passed a particular phase or phases of testing. It moves an MRG from one test state to a succeeding one or to approved. approve/ reject When the MRG has passed required testing, the AT approves the changes and moves them into the official branch with the approve command or returns the MRG to an earlier state with the reject command. An MRG can be rejected at any point in the testing cycle. The approve command sets the state of the MRG to approved and links any associated changes made to source files in the mr branch to the ofc branch in the Source Database. No further action can be taken on the MR other than closure. If the MRG is rejected, notification is sent that additional changes are necessary. If it is approved, the MRA is notified that the changes in response to the MRG have been made, tested, and approved. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-5 Using the MR Commands Table 4-1. MR and MRG Life Cycle Commands—Continued Command Description closemr After all activity has taken place for an MR, the MRA issues the closemr command to move all references to the MR across all generics from the Active Database to the Inactive Database. An MR can be closed only if its MRGs are in an appropriate state (i.e., nochange or approved) in each of the generics into which the MR has been accepted. If the MRG is in the spawned state, all child MRGs must be in the approved or nochange state as well. The MR is then in the closed state in the MG relation and in the completed state in the MR relation. Before you work with the Sablime MR commands, it is important to have some understanding of the concept of MR dependency. The following section describes this concept and offers an example demonstrating the importance of setting up dependencies properly. NOTE: The name by which an MR is identified (e.g., sab970013) does not change when the MR is accepted into a generic; the MRG is still referred to as sab970013. It is important to bear this in mind to avoid being confused by some of the examples that follow. NOTE: The GUI provides access to the following MR and MRG commands: accept, approve, assign, closemr, create, depend, fcreate, mrnote, propose, reject, spawnmr, study, submit, and testpass. A note in the text indicates those commands which cannot be accessed using the GUI. MRG Dependencies 4 An MRG dependency is a condition between at least two MRGs in which the changes of one MRG (e.g., sab970001) do not make sense without the changes made by another MRG (e.g., sab970000). If the changes for sab970000 must be retrieved along with the changes for sab970001, we say that sab970001 is dependent upon sab970000, and we call sab970000 the depended-upon MRG. MRG dependencies are important because the load-building process relies on a good list of MRGs to incorporate all the changes into a product for a release. When you include sab970001 in a list of MRGs for building a load, you must have a way of knowing that sab970000 must be included as well. MRG dependencies provide the mechanism for knowing which other MRGs must be included. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-6 Issue 1.1 November 2000 MRG Dependencies The depend command allows you to create dependencies between MRGs. The Sablime commands that require information about MRG dependencies are addgsrc, approve, getversion, report (mrVSfile report), and sget. A dependency issue may arise in a case where MRGs touch different files. For example, sab970015 has changed the header file h1.c and sab970016 has changed the file create.c. If the changes made by sab970016 to create.c relate to changes made by sab970015 to h1.c, you must use the depend command to make sab970016 dependent upon sab970015. This type of dependency must be created manually by the developer(s) working on sab970015 and sab970016. In cases where more than one MRG touches the same file, the Sablime system can generate some dependencies automatically during execution of the edput command. n If a file is stored under SBCS, the current MRG is made dependent upon the last MRG that touched the file, regardless of the current state of the last MRG. n For a file stored under SCCS, the Sablime system provides two types of automatic MRG dependencies: file level and line level. The default type of dependency is selected when the Sablime product is first set up; it can be changed with the ADM subcommand of the setrel command. — If file-level dependency is selected, the MRG used to edput a file is made dependent on all the unapproved MRGs that have touched this file. — If line-level dependency is selected, the MRG used to edput a file is made dependent upon all unapproved MRGs that have touched the same lines in this file that the current MRG touched. File-level dependency is conservative; line-level dependency may miss logical dependencies. The DBA must select the appropriate default type of dependency for your product development. n If the initialization MRG for a given file is still unapproved, edput makes the current MRG dependent upon the MRG used to initialize a file (addgsrc, addisrc, or primsdb). This check avoids problems encountered by retrieving versions from the ofc branch when the initialization MRG has not been approved. For files stored under SBCS, the Sablime system creates a chain of dependencies; each MRG is dependent upon the MRG that created the previous version. When using SBCS, the dependency issue is relatively straightforward. For files stored under SCCS, however, the dependency issue is more complicated: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-7 Using the MR Commands When the edget command is used to retrieve a file for editing in response to a specified MRG, a list of unapproved MRGs is given in the processing message after the command is executed and confirmed. This list shows the MRG numbers of all unapproved MRGs used to make changes to the requested files, including the specified MRG. You should consider whether the current MRG may need to be made dependent upon each MRG in the list. (Depending upon the default dependency type chosen for your product, this dependency may be created for you automatically.) Creation of such a dependency has the following advantages: n Changes associated with earlier MRGs are always included when the current MRG is retrieved with sget or getversion. n The MRG for which the files are currently being modified must be approved either at the same time or after the approval of the MRGs that previously touched the file(s). The arrows in Figure 4-2, Figure 4-3, and Figure 4-4 show such a dependency. For example, in Figure 4-2, sab970003 depends on sab970002; sab970002 must be approved before or at the same time as sab970003. Developer retrieves file via edget with sab970003 List of Unapproved MRs sab970001 sab970002 When a developer retrieves a file with edget, all changes are included. The edget command informs the developer of any other unapproved MRs that touched the file. Depending upon the default dependency type chosen for your product, the new MR may need to be made dependent upon each MR shown in the edget list. Figure 4-2. Dependency on Unapproved MRs A test of the changes to a source file made in response to an MRG may cause a new MRG to be issued. When this occurs, you should consider whether the MRG used to make the original changes must be made AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-8 Issue 1.1 November 2000 MRG Dependencies Developer sab970001 sab970002 sab970003 sab970004 Integration Test Team System Test Team sab970001 sab970002 sab970001 The System Test Team finds a problem and creates a new MR, sab970004, to fix it. Because sab970001 may now need the changes for sab970004, sab970001 may need to be made dependent upon sab970004. Figure 4-3. Dependency on a New MR Developer Integration Test Team System Test Team sab970001 sab970002 sab970001 sab970001 sab970002 sab970001 sab970002 has been made dependent upon sab970001 because they both touch the same file. The System Test Team finds a problem and rejects sab970001 back to the developer. The developer may need to make sab970001 dependent upon sab970002 because new changes made for sab970001 may be dependent upon the earlier changes made with sab970002. Figure 4-4. Mutual Dependency AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-9 Using the MR Commands dependent upon the new MRG created to allow additional changes to be made. With such a dependency, the original MRG must be approved with the new MRG. A test of the changes made to a source file made in response to an MRG may cause the MRG to be rejected. If that MRG is already dependent upon any other MRGs, the MRGs may need to be made mutually dependent because changes may now be interdependent, and so all would have to be approved at the same time. Mutual dependency ensures that changes for both the MRGs are retrieved together. Making MRGs dependent in this manner also ensures that all MRGs that have touched the file are approved together. MRG Dependency: An Example 4 This example shows how the use of depend can prevent the user from retrieving incorrect versions of files. NOTE: For brevity, all the examples employ the Command Line interface. The file print.c prints a heading followed by 56 lines of information. Assuming that MRG sab970021 authorizes you to change the 56 to 55 lines of information, you edget the file with sab970021 to edit it. 1. The file print.c is to be changed in response to MRG sab970021. a. A copy of print.c is gotten for edit. edget prompt=n mr=sab970021 g=sab1.0 srf=print.c\ dir=src/admin AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-10 Issue 1.1 November 2000 MRG Dependencies print.c main (argc, argv) int argc; char *argv[]; { . . . for (i=0; i<56; i++) { . . . if (!i) print_heading(); . . . } } AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-11 Using the MR Commands b. Changes are made to print.c: the for statement is changed to begin at 1 rather than 0. print.c main (argc, argv) int argc; char *argv[]; { . . . for (i=1; i<56; i++) { . . . if (!i) Change made in response to sab970021 print_heading(); . . . } } All changes should, of course, be unit tested before a file is returned to the Source Database. For the purpose of this example, however, assume that this activity is performed under pressure. c. The edited copy of print.c is returned to the Source Database. edput prompt=n mr=sab970021 g=sab1.0 srf=print.c\ dir=src/admin d. MRG sab970021 is submitted. submit prompt=n mr=sab970021 g=sab1.0\ rfile=resolution 2. When the program is run, you realize that the heading does not print. A new MRG, sab970022, is created to fix this problem. The file print.c is retrieved with edget under MRG sab970022. a. A copy of print.c is gotten for edit. edget always retrieves the latest version of the file from its mr branch. edget prompt=n mr=sab970022 g=sab1.0 srf=print.c\ dir=src/admin The retrieved file looks like the version above. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-12 Issue 1.1 November 2000 MRG Dependencies b. Changes are made to the if statement. print.c main (argc, argv) int argc; char *argv[]; { . . . for (i=1; i<56; i++) { . . . if (i==1) Change made in response to sab970022 print_heading(); . . . } } This time the change is unit tested. It performs correctly, and the file is returned to the Source Database. c. The edited copy of print.c is returned to the Source Database. Your project uses the conservative file-level dependency, so sab970022 is made dependent on sab970021 automatically. edput prompt=n mr=sab970022 g=sab1.0 srf=print.c\ dir=src/admin d. MRG sab970022 is submitted. submit prompt=n mr=sab970022 g=sab1.0\ rfile=resolution 3. In the meantime, the system test organization has been notified to test sab970021, so they use getversion, adding sab970021 on top of the official version. The version of the source file associated with MRG sab970021 is retrieved. getversion prompt=n br=ofc g=sab1.0 mrs=sab970021\ node=/u6/sab/it AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-13 Using the MR Commands print.c main (argc, argv) int argc; char *argv[]; { . . . for (i=1; i<56; i++) { . . . if (!i) print_heading(); . . . } } This file shows the changes made to print.c in response to MRG sab970021 applied to the latest version of the official branch of the file. The test team sees only the changes of sab970021, which have already been seen to be incorrect by the developer and corrected by sab970022. print.c does not have the final change made by sab970022 because sab970021 has not been made dependent on sab970022. 4. Meanwhile, the system test organization has been notified to test sab970022, so they use getversion, adding sab970022 on top of the official version. This time getversion requires that the dependent MRG sab970021 be included. getversion prompt=n br=ofc g=sab1.0 \ mrs=sab970021,sab970022 \ node=/u6/sab/it This is the correct version of the file, because it contains both MRGs sab970021 and sab970022. The previous version of the file was not correct because sab970021 was not declared dependent on sab970022. This is a clear case of logical dependency because the changes in the for statement and the if statement are mutually dependent; consequently, the MRGs should be made mutually dependent. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-14 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Creating an MR If MRG sab970022 had been made dependent upon MRG sab970021, the file could not have been retrieved without both MRGs being specified to getversion. In that case, getversion would have prompted the user to enter the number of the dependent MRG before executing the command and the correct version of the file would have been retrieved. Creating an MR 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the create command, see the create manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. Any user can use the create command to create an MR. You might create an MR when something in your product does not work or when someone has thought of a way to improve your product. Or, an MR might just be associated with some task to be handled as part of developing your product. But note that creating an MR is simply the first step in producing the changes you think desirable. No work can be done in response to an MR until it has been accepted and assigned to a developer. Issuing the create command simply creates an MR, assigns it a number, puts it into the created state, and sends mail to the MRA indicating that there is a request that work be done on the product. Once the MR has been created, it may be accepted (if the work is to be done), killed (if the work is not considered necessary or there is no time to do it), studied (if more information is needed about the changes it proposes), or deferred (if there is no time to consider it further at the moment). As an example of creating an MR, suppose that you know that there is a bug in your software product and you want to make changes to the code to correct the problem. In the Curses Forms interface, you might enter data as shown in the screen below: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-15 Using the MR Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/04/97 12:54:09 Create a New Modification Request Originator PTS ID: ktf______________ Origination Date: 05/04/97 Request Severity: 2 Required Date: ________ Product: Sablime_________________ Site: MH______________________ System: lib_____________________ Subsystem: libCOM__________________ Module: ________________________ Rel. Detected: 5.0_____________________ Phase Detected: system_test_____________ Category: dev_found_______________ Abstract of Request: Will not accept group name in MR field__________________ Request Desc File: _________________________________________________________ Copy To: _________________________________________________________ After you enter a description of the request and confirm, the MR is created. The name of the temporary file is shown in the Request Description File field when the create screen is redisplayed. NOTE: If the desc keyword is not included on the command line and you are Using the Curses Forms interface, Sablime uses the default temporary file name and displays the usual template in your editor. Or, using the Command Line interface, you might enter: create sev=2 abst="Will not accept group name in MR \ field" desc=desc_file prompt=n In this case, the defaults: org=ktf (login) odate=05/04/97 (current date) prod=Sablime sys=lib sub=libCOM rel=5.0 site=MH cat=dev_found are entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-16 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Creating an MR Suppose next that your project has its own template for entering MR descriptions and that it has created two User-Definable fields, called Number and Load. In this case your entries using the Curses Forms interface might appear as shown below: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/04/97 12:57:30 Create a New Modification Request Originator PTS ID: ktf______________ Origination Date: 05/04/97 Request Severity: 2 Required Date: ________ Product: Sablime_________________ Site: MH______________________ System: lib_____________________ Number: 9_______________________ Subsystem: libCOM__________________ Load: 970713.v40______________ Module: ________________________ Rel. Detected: 4.0_____________________ Phase Detected: system_test_____________ Category: test_found______________ Abstract of Request: Will not accept group name in MR field___________________ Request Desc File: /proj/desc_file__________________________________________ Copy To: _________________________________________________________ Or, if you were using the Command Line interface, you might enter: create sev=2 cat=test_found abst="Will not accept\ group name in MR field" desc=/proj/desc_file num=9\ load="970713.v40" pd=system_test prompt=n In this case, the defaults: org=ktf (login) odate=05/04/97 (current date) prod=Sablime sys=lib sub=libCOM rel=5.0 site=MH are entered automatically and need not be typed. The MR is created. The temporary file /proj/desc_file is displayed for possible changes. The file used as a template remains unchanged. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-17 Using the MR Commands As processing takes place, information like that shown below appears on the screen: + You have successfully created a new MR called [MR #]. – The Problem Description File has been entered in the active database. – The MR Relation tuple has been created in the active database. – The ORG Relation tuple has been created in the active database. – Mail will be sent to MR Administrator at [login]. + A Master Trace Record has been generated for the Database Administrator. The messages marked + will always appear. Those preceded by - will only appear if the Verbose Information flag in your PTS record is turned on. NOTE: It is a good practice to note the MR number generated by Sablime for use when issuing other commands that affect the MR. Killing an MR 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the killmr command, see the killmr manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. NOTE: The GUI does not provide access to this command. The killmr command may only be used by the MRA and then only to kill an MR in the created state. This command is used when the MRA decides that the changes proposed by the MR will not be made in any active generic. This command puts the MR in the killed state, and moves it to the Inactive Database. No work may be done on any generic using this MR. As an example, suppose that a user has entered an MR (sab970053) describing a problem that had already been described by another MR (sab970032) entered by a different user. Using the Curses Forms interface, the MRA could then kill this new MR as follows: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-18 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Killing an MR logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/31/97 10:27:14 Kill the Specified MR MR Number: sab970053__________________________________________________________ Reason Code: duplicate___________ Duplicate MR Number: sab970032_____ Reason for Killing: __________________________________________________________ Copy To: __________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface: killmr mr=sab970053 code=duplicate dupmr=sab970032\ prompt=n In either case, all data concerning MR sab970053 would be moved to the Inactive Database, and no work could be done using this MR. Suppose now that two similar MRs (sab970172 and sab970175) have been entered by different users, but the problem they describe has already been fixed. Using the Curses Forms interface, the MRA could kill the two MRs at the same time as follows: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/31/97 10:26:31 Kill the Specified MR MR Number: sab970172,sab970175________________________________________________ Reason Code: other_______________ Duplicate MR Number: ______________ Reason for Killing: already fixed_____________________________________________ Copy To: __________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface: killmr mr=sab970172,sab970175 rsn="already fixed"\ prompt=n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-19 Using the MR Commands The default: code=other is entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, all data concerning MRs sab970172 and sab970175 would be moved to the Inactive Database, and no work could be done using these MRs. Finally, suppose that the same two MRs (sab970172 and sab970175) have been entered, but this time the problem they describe is being worked on using another MR (sab970151). Using the Curses Forms interface, the MRA could then kill the two MRs at the same time as follows: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/31/97 10:28:00 Kill the Specified MR MR Number: sab970172,sab970175________________________________________________ Reason Code: duplicate___________ Duplicate MR Number: sab970151_____ Reason for Killing: another mr being used to fix the problem__________________ Copy To: __________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface: killmr mr=sab970172,sab970175 dupmr=sab970151\ code=duplicate \ rsn="another mr being used to fix the problem"\ prompt=n In either case, all data concerning MRs sab970172 and sab970175 would be moved to the Inactive Database, and work on the problem would continue using MR sab970151. Deferring an MR or MRG 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the defer command, see the defer manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-20 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Deferring an MR or MRG NOTE: The GUI does not provide access to this command. The defer command may be used by the MRA to defer action on a created MR or by the GA to defer action on an accepted MRG. The defer command changes the state of a created MR to mra_deferred and the state of an accepted MRG to deferred. Neither an mra_deferred MR nor a deferred MRG is reactivated automatically; the MRA or GA must specifically reactivate them using the activate command. Suppose an MR (sab970072) requests an enhancement that cannot be worked on in the current release, which is due out in the fall of 1997. And suppose planning for the next release is to begin in the spring of 1998. Using the Curses Forms interface, the MRA might then decide to defer consideration of the enhancement until that time as follows: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/26/97 15:50:19 Defer MR or MRG MR Number: sab970072__________________________________________________________ Generic: ___________________________________________________________________ Activate Date: 04/10/98 Reason Code: enhancement_________ Reason to Defer: ____________________________________________________________ Copy To: ____________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface: defer mr=sab970072 date=04/10/98 code=enhancement\ prompt=n In either case, consideration of the enhancement has been deferred until 4/10/98, when the new release is being planned. The MR will remain in the mra_deferred state until the MRA uses the activate command to reactivate it. Suppose now that the same MR (sab970072) has already been accepted into two generics, g1 and g2, but the GA for g1 and g2 decides that, due to time AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-21 Using the MR Commands constraints, no work should be done on the MRG in either generic. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA would then enter the following: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/26/97 15:51:54 Defer MR or MRG MR Number: sab970072__________________________________________________________ Generic: g1,g2______________________________________________________________ Activate Date: 06/01/97 Reason Code: enhancement_________ Reason to Defer: ____________________________________________________________ Copy To: ____________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface: defer mr=sab970072 g=g1,g2 date=06/01/97\ code=enhancement prompt=n In either case, the MR sab970072, which had already been accepted in generics g1 and g2, has now been deferred in both generics until 6/1/97. However, nothing will happen automatically on that date. The MRGs will remain in the deferred state in both generics until the GA uses the activate command to reactivate them. The date merely serves as a reminder. Finally, suppose two modification MRs (sab970073 and sab970077) have been accepted into a generic g1, but extensive investigation is needed to determine their effects on other parts of the product. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA might then defer a decision on the two MRGs as follows: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-22 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Activating an MR or MRG logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/26/97 15:52:48 Defer MR or MRG MR Number: sab970073,sab970097________________________________________________ Generic: g1_________________________________________________________________ Activate Date: 07/15/97 Reason Code: other_______________ Reason to Defer: Results of the modifications need clarification.____________ Copy To: ____________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface: defer mr=sab970073,sab970097 date=07/15/97\ rsn="Results of the modifications need\ clarification." prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) code=other are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, MRGs generated by MRs sab970073 and sab970077 will be deferred until 7/15/97 and the reason for the deferral will be entered into the Sablime database. But even though the GA has entered a date, the MRGs will remain in the deferred state until the GA uses the activate command to reactivate them. Activating an MR or MRG 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the activate command, see the activate manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. NOTE: The GUI does not provide access to this command. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-23 Using the MR Commands NOTE: The GUI does not provide access to this command. The activate command can be used by the MRA to return an MR to the created state from the mra_deferred state or by the GA to return an MRG to the accepted state from the nochange state or the deferred state. Further processing is not affected by the fact that the MR or MRG was previously deferred. As an example, suppose an MRA wants to activate a deferred MR (sab970043). Using the Curses Forms interface, the MRA would enter: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/26/97 07:07:14 Activate MR or MRG MR Number: sab970043__________________________________________________________ Generic: ___________________________________________________________________ Copy To: ___________________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface: activate mr=sab970043 prompt=n In either case MR sab970043 is brought back to the created state from the mra_deferred state and may be accepted, studied, or killed. Now suppose that a GA wants to activate a deferred MRG (sab970043). Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA would enter: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-24 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Activating an MR or MRG logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/26/97 07:08:57 Activate MR or MRG MR Number: sab970043__________________________________________________________ Generic: g2_________________________________________________________________ Copy To: ___________________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface: activate mr=sab970043 prompt=n The default: g=g2 (setup generic) is entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, MRG sab970043 in generic g2 is brought back to the accepted state from the deferred state and may now be assigned, nochanged, or studied. Next suppose that a GA wants to activate three MRGs (sabl970013, sab970017, and sab970012) that are in the nochange state in two different generics (g1 and g2). Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA would enter: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/26/97 07:09:22 Activate MR or MRG MR Number: sab970013,sab970017,sab970012______________________________________ Generic: g1,g2______________________________________________________________ Copy To: ___________________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface: activate mr=sab970013,sab970017,sab970012 g=g1,g2\ prompt=n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-25 Using the MR Commands MRGs sab970013, sab970017, and sab970012 are all returned to the accepted state in generics g1 and g2. Even though neither the current state of the MRGs nor the generics they belong to is entered in the command, Sablime is able to figure out that all the MRGs are in the nochange state and that sab970013 and sab970017 are in g1 and sab970012 is in g2 and to return all three MRGs to the accepted state. Note that activating MRGs from multiple generics will only work if all the MRGs are in the same state when the command is run. Finally, suppose the GA wants to activate two MRGs (sab970047 and sab970049) that are in the same generic, g1, but in different states. Suppose that sab970047 is in the deferred state and that sab970049 is in the nochange state. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA can make the following entries on the activate screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/26/97 07:11:04 Activate MR or MRG MR Number: sab970047,sab970049________________________________________________ Generic: g1_________________________________________________________________ Copy To: ___________________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface: activate mr=sab970047,sab970049 prompt=n The default: g=g1 (setup generic) is entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, both MRGs, sab970047 (which was in the deferred state) and sab970049 (which was in the nochange state), are returned to the accepted state in generic g1. Even though the states are not entered in the command, Sablime knows which state each MRG is in and returns each MRG to the accepted state. Note that activating MRGs from different states will only work if all the MRGs are in the same generic. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-26 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Studying an MR or MRG Studying an MR or MRG 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the study command, see the study manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The study command can be used by an MRA to put an MR in the created state into the mra_study state or by a GA to put an MRG in the accepted state into the understudy state so that a developer can investigate it and propose a solution. It can also be used to reassign an MR or MRG that is being studied to another developer for further study. Neither an MR in the mra_study state nor an MRG in the understudy state is reactivated automatically. The MRA or the GA must enter the activate command to reactivate them. Suppose the MRA wants to assign two MRs (sab970043 and sab970024) to a developer for study. Using the Curses Forms interface, the MRA would make the following entries on the study screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 06/02/97 14:42:12 Assign MR to Developer for Study MR Number: sab970043,sab970024_________________________________________________ Generic: ___________________________________________________________________ Developer: skc______________ Severity: 3 Due Date: ________ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, the MRA would enter: study mr=sab970043,sab970024 dev=skc prompt=n The default: sev=3 is entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-27 Using the MR Commands In either case, MRs sab970043 and sab970024 would be assigned to developer skc for study, and the severity level for each would be set to 3. Similarly, suppose a GA wants to assign two MRGs (sab970087 and sab970049) to a developer for study. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA would make the following entries on the study screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 06/02/97 14:44:19 Assign MR to Developer for Study MR Number: sab970087,sab970049________________________________________________ Generic: g1_________________________________________________________________ Developer: skc______________ Severity: 3 Due Date: ________ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, the GA would enter: study mr=sab970087,sab970049 dev=skc prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) sev=3 are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, MRGs sab970087 and sab970049 in generic g1 would be assigned to the developer skc for study, and the severity level for each would be set to 3. Finally, suppose the GA has previously assigned an MRG for study, but the developer to whom it was assigned is too busy to do the study. The GA decides to reassign the MRG and to indicate that the study must be complete by October 15,1997. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA would make the following entries on the study screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-28 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Accepting an MR logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 06/02/97 14:46:53 Assign MR to Developer for Study MR Number: sab970043__________________________________________________________ Generic: g1_________________________________________________________________ Developer: lsp______________ Severity: 3 Due Date: 10/15/97 Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, the GA would enter: study mr=sab970043 due=10/15/97 dev=lsp prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) sev=3 are entered automatically and need not be typed. The MRG sab970043 would now be reassigned to developer lsp for study; study should be completed and a solution proposed by October 15, 1997. Accepting an MR 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the accept command, see the accept manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. After an MR has been created, the MRA may use the accept command to accept the MR into a generic. When an MR is accepted into a generic, it enters the active MR state and gives rise to an MRG (Modification Request in a Generic). The MR remains in the active state until it is closed. The MRG is now in the accepted state. At that point, the GA for the generic is notified that the MR has been accepted. It is up to the GA to decide what to do with the MRG. The GA can: n create one or more spawned MRGs (spawnmr); n defer activity on the MRG (defer); AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-29 Using the MR Commands n assign a developer or group of developers to study the feasibility and the method of making the suggested changes (study); n decide that the changes are not to be made (nochange); n assign a developer or group of developers to make the suggested changes (assign). (If the project is using the Automatic Assignment feature, the MRG is assigned accordingly.) Suppose the MRA wants to accept an MR into a generic. Using the Curses Forms interface, the MRA would make the following entries on the accept screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/25/97 14:02:50 Accept MR for Specified Generic MR Number: sab970023__________________________________________________________ Generic: g1_________________________________________________________________ MRG Class: software________________ MRG Type: modification____________ MRG Subclass: ________________________ MRG Subtype: ________________________ Auto Assign: n MRG Severity: _ Due Date: ________ Estimated Effort: _____ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, the MRA would enter: accept mr=sab970023 class=software prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) autoasgn=(per Auto Assign flag in ADM) type=modification are entered automatically and need not be typed. This command causes Sablime to set MR sab970023 to the active state and generate MRG sab970023 in the accepted state in generic g1 with class specified as software and type specified as modification. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-30 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Accepting an MR Or suppose that the MRA wants to accept an MR (sab970045) in two generics, g1 and g2. In generic g1 the class will be software and the type modification, while in generic g2 the class will be document and the class will be enhancement. Because the MR is to be accepted with a different class and type in each generic, the MRA must execute the command twice. Using the Curses Forms interface, the MRA would make the following entries in the two accept screens: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/25/97 14:11:19 Accept MR for Specified Generic MR Number: sab970045__________________________________________________________ Generic: g1_________________________________________________________________ MRG Class: software________________ MRG Type: modification____________ MRG Subclass: ________________________ MRG Subtype: ________________________ Auto Assign: n MRG Severity: _ Due Date: ________ Estimated Effort: _____ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-31 Using the MR Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/25/97 14:12:28 Accept MR for Specified Generic MR Number: sab970045__________________________________________________________ Generic: g2_________________________________________________________________ MRG Class: document________________ MRG Type: enhancement_____________ MRG Subclass: ________________________ MRG Subtype: ________________________ Auto Assign: n MRG Severity: _ Due Date: ________ Estimated Effort: _____ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, the MRA would enter: accept mr=sab970045 class=software prompt=n accept mr=sab970045 g=g2 class=document\ type=enhancement prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) autoasgn=(per Auto Assign flag in ADM) type=modification sev=3 are entered automatically and need not be typed. These commands cause Sablime to set MR sab970045 to the active state and generate two MRGs in the accepted state, one in each of the generics, g1 and g2. Sablime records the class for the MRG in g1 as software and the type as modification and the class for the MRG in g2 as document and the type as enhancement. Finally, suppose the MRA wants to accept an MR (sab970084) in multiple generics with a class of mixed so that the MRG can be spawned in different AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-32 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Unaccepting an MR classes. Using the Curses Forms interface, the MRA would make the following entries on the accept screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/25/97 14:21:23 Accept MR for Specified Generic MR Number: sab970084__________________________________________________________ Generic: g1,g2______________________________________________________________ MRG Class: mixed___________________ MRG Type: modification____________ MRG Subclass: ________________________ MRG Subtype: ________________________ Auto Assign: n MRG Severity: 3 Due Date: ________ Estimated Effort: _____ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ In the Command Line interface, the MRA would enter: accept mr=sab970084 g=g1,g2 class=mixed prompt=n The defaults: type=modification sev=3 are entered automatically and need not be typed. This command will cause Sablime to set MR sab970084 to the active state and to generate an MRG in the accepted state in each of the generics, g1 and g2, with the class specified as mixed. Unaccepting an MR 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the unaccept command, see the unaccept manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. After an MR has been created and accepted into a generic, the GA can use this command to take the MR out of the generic if the MR is in the accepted state and no files have been touched by it. If the MR was accepted into more than one AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-33 Using the MR Commands generic, it must be unaccepted out of each of those generics before it reverts to the created state. Suppose a GA wants to unaccept an MR out of a generic. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA would make the following entries on the unaccept screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 06/25/00 11:18:08 Unaccept MRs for Specified Generics MR Number:cv5000000_______________________________________________________ Generic: mka5.0_________________________________________________________ Copy To: ________________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, the GA would enter: unaccept mr=cv5000000 prompt=n The default: g=mka5.0 (setup generic) is entered automatically and need not be typed. This command causes Sablime to set MR cv5000000 back to the created state, if all of the following apply: n it is not currently accepted into any generics other than the setup generic n it had not been spawned n it had not touched any files n it has no physical dependencies n if it is logically dependent on another MR, that MR must be unaccepted. In any case, if the MR is unaccepted the following changes will be made: n any history, resolution, testnotes, rejection and/or solution file for that MRG will be deleted n if it had a commitment ID, the MR number will be removed from the commitment file AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-34 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Nochanging an MRG n if there was an associated EMR, and the unaccept flag was set to send this type of information, a message will be sent to the external project telling it to delete the associated EMG record. If the GA wants to unaccept several MRs from several generics, a single unaccept command suffices, as long as all the MRs in the list were accepted to all the generics in the generic list. Nochanging an MRG 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the nochange command, see the nochange manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. NOTE: The GUI does not provide access to this command. The GA can use the nochange command to specify that no changes are to be made in the generic as a result of an MRG. The MRG can be in the accepted state or in the assigned state if it has not yet been used to make any changes. The command places the MRG in the nochange state. This is a terminal state for an MRG; it can remain in this state until the originating MR is closed. However, if at any time before the MR is closed, it is decided that the work the MRG proposes should be done in the generic, the GA can reactivate the MRG by using the activate command. Suppose the GA decides that the work proposed by MRG sab970129 should not be done in either of two generics. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA could make the following entries on the nochange screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-35 Using the MR Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/31/97 14:48:55 Make No Change to MRs for Given Generics MR Number: sab970129__________________________________________________________ Generic: g1,g2______________________________________________________________ Actual Effort: _____ Reason Code: unnecessary_________ Duplicate MR Number: ______________ Reason for Nochange: _________________________________________________________ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, the GA could enter nochange mr=sab970129 g=g1,g2 code=unnecessary\ prompt=n In either case, MRG sab970129 would be put in the nochange state in generics g1 and g2. Next suppose that the GA has decided that the work proposed by two MRGs (sab970012 and sab970014) should not be done until a later release. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA would make the following entries on the nochange screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-36 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Nochanging an MRG logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/31/97 14:49:12 Make No Change to MRs for Given Generics MR Number: sab970012,sab970014________________________________________________ Generic: g1___________________________________________________________________ Actual Effort: _____ Reason Code: other_______________ Duplicate MR Number: ______________ Reason for Nochange: Planned for later generic________________________________ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, the GA would enter: nochange mr=sab970012,sab970014\ rsn="Planned for later generic" prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 code=other are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, MRGs sab970012 and sab970014 are put in the nochange state in generic g1, and the reason for the decision is saved in the database. Finally, suppose the GA decides that two earlier MRGs (sab970012 and sab970014) have been superseded by MRG sab970178. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA would make the following entries on the nochange screen to indicate the reason for the action and to record the time already spent on the problem: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-37 Using the MR Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/31/97 14:51:17 Make No Change to MRs for Given Generics MR Number: sab970012,sab970014________________________________________________ Generic: g1_________________________________________________________________ Actual Effort: 2.5__ Reason Code: duplicate___________ Duplicate MR Number: sab970178_____ Reason for Nochange: fixed by another MR______________________________________ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, the GA would enter: nochange mr=sab970012,sab970014 ne=2.5\ code=duplicate dupmr=sab970178 rsn="fixed by another\ mr" prompt=n The default: g=g1 is entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, MRGs sab970012 and sab970014 would be put in the nochange state for generic g1, and MRG sab970178 would be used to resolve the problem. Spawning an MRG 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the spawnmr command, see the spawnmr manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The spawnmr command allows the GA to spawn multiple MRGs from one original MRG for use when several developers are responsible for different aspects of the resolution of an MRG or when different MRG classes are required to cover different aspects (e.g., software and documentation) of the MRG. When an MR is accepted with a class of mixed, the MRG must be spawned to name a specific class before any work can be done in response to the MRG. The state of the original MR remains active, and the state of the original MRG is set to spawned. Each accepted MRG spawn can then move independently through various states AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-38 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Spawning an MRG as it progresses through the system. (Once an original MRG has spawned additional MRGs, all activity takes place in response to the spawned MRGs.) The original MRG remains in the spawned state until all its spawns have been approved (or set to the nochange state). Then the original MR can be closed with the closemr command and the spawned MRGs are then closed automatically. Suppose that an MRG (sab970043) has been accepted into generic g1 with a class of mixed, and suppose that the MRG has implications for both hardware and documentation. The GA would then spawn two MRGS, one with a class of hardware, the other with a class of document to track the work to be done. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA would use the spawnmr command twice, making the entries shown below: logid:ral effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 MR Management System Command 15:55:32 02/28/97 Spawn New MR from Original MR Original MR: sab970043_____ Generic: g1____________ Number of Spawns: 1__ System: lib_____________________ MRG Class: hardware________________ Subsystem: none____________________ MRG Subclass: ________________________ Module: ________________________ MRG Type: modification____________ Rel. Detected: 4.0_____________________ MRG Subtype: ________________________ Auto Assign: n MRG Severity: _ MRG Due Date: ________ Est. Effort: _____ Abstract: replace drive unit #1_______________________________________ Spawn Notes File: spnt1.file__________________________________________________ Copy To: ____________________________________________________________ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-39 Using the MR Commands logid:sablime effid:Sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 02/28/97 MR Management System Command 15:58:19 Spawn New MR from Original MR Original MR: sab970043_____ Generic: g1____________ Number of Spawns: 1__ System: lib_____________________ MRG Class: document________________ Subsystem: none____________________ MRG Subclass: ________________________ Module: ________________________ MRG Type: modification____________ Rel. Detected: 4.0_____________________ MRG Subtype: ________________________ Auto Assign: n MRG Severity: _ MRG Due Date: ________ Est. Effort: _____ Abstract: figure 3-1 needs to reflect redesign________________________ Spawn Notes File: spnt2.file__________________________________________________ Copy To: ____________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, the GA would enter: spawnmr mr=sab970043 spawns=1 class=hardware sys=lib\ sub=none abst="replace drive unit #1" \ snotes=spnt1.file prompt=n spawnmr mr=sab970043 spawns=1 class=document sys=lib\ sub=none\ abst="figure 3-1 needs to reflect redesign" \ snotes=spnt2.file prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) type=modification rel=5.0 (product-defined default) autoasgn=(per Auto Assign flag in ADM) are entered automatically and need not be typed. These commands cause Sablime to create two new MRG spawns numbered sab970043.00 (class=hardware) and sab970043.01 (class=document) in generic g1. A spawnotes file is created for each spawned MR. The new spawns have an MRG status of accepted. Because the Automatic Assignment feature is not being used, the GA must assign each spawned MRG before work can be performed in response to the original MRG. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-40 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Spawning an MRG Now suppose that an MR (sab970034) has been accepted into generic g1 and that it involves three different aspects of the product that are the responsibility of three different developers. In order to track the work, the GA spawns three MRGs, one for each of the developers. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA would make the following entries on the spawnmr screen: logid:ral effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 02/28/97 MR Management System Command 15:55:32 Spawn New MR from Original MR Original MR: sab970034______ Generic: g1____________ Number of Spawns: 3__ System: lib_____________________ MRG Class: software________________ Subsystem: none____________________ MRG Subclass: ________________________ Module: ________________________ MRG Type: modification____________ Rel. Detected: 4.0_____________________ MRG Subtype: ________________________ Auto Assign: y MRG Severity: 3 MRG Due Date: ________ Est. Effort: _____ Abstract: ____________________________________________________________ Spawn Notes File: fix97-14____________________________________________________ Copy To: ____________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface: spawnmr mr=sab970034 spawns=3 class=software sys=lib\ sub=none rel=4.0 snotes=fix97-14 prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) type=modification sev=3 autoasgn=(per Auto Assign flag in ADM) are entered automatically and need not be typed. This command causes Sablime to create three new MRG spawns numbered sab970034.00, sab970034.01, and sab970034.02 in generic g1 with class specified as software. Each of these MRGs can be tracked separately from the others. Because the auto assignment flag is on, the spawned MRGs are assigned automatically if there is a match with any of the auto-assignment criteria entries. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-41 Using the MR Commands Assigning an MRG 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the assign command, see the assign manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The GA can use the assign command to assign an MRG to a developer or group or to reassign or unassign an MRG. Assigning the MRG puts it into the assigned state. No work can be done on the MRG until it has been assigned to a developer. Once it has been assigned, the developer to whom it is assigned can make the changes it proposes. When the changes have been made and unit-tested, the developer should use the submit command to indicate that the changes have been made and to submit the changes for further testing. To assign an MRG to a developer, the GA, using the Curses Forms interface, would make the following entries on the assign screen: logid:ral effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 MR Management System Command 08:01:25 02/28/97 Assign MR to a Developer MR Number: sab970065__________________________________________________________ Generic: g1_________________________________________________________________ Developer: ksl___________ MRG Severity: 2 MRG Due Date: 06/08/97 Estimated Effort: _____ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, the GA would enter: assign mr=sab970065 sev=2 due=06/08/97 dev=ksl\ prompt=n The default: g=g1 (setup generic) is entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-42 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Assigning an MRG In either case, developer ksl may now make changes to the product in response to MRG sab970065 in generic g1. The severity has been set to 2 (high), and the changes are supposed to be completed by 06/08/97. Suppose that two MRs (sab970047 and sab970039) have been accepted into generic g2 and that the changes they propose all fall within the area of responsibility of the group of developers grp3. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA can assign both these MRGs to grp3 by making the following entries on the assign screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 02/28/97 08:01:25 Assign MR to a Developer MR Number: sab970047,sab970039________________________________________________ Generic: g2_________________________________________________________________ Developer: grp3__________ MRG Severity: 3 MRG Due Date: 04/03/97 Estimated Effort: _____ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, the GA would enter: assign mr=sab970047,sab970039 dev=grp3 sev=3\ due=04/03/97 prompt=n The default: g=g2 (setup generic) is entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, any member of group grp3 is now allowed to make changes in response to MRGs sab970047 and sab970039 in generic g2; The changes are supposed to be completed by 04/03/97. Now suppose that the GA realizes that grp3 is overworked and will not have time to complete the changes requested by MRG sab970047. Using the Curses Forms interface, the GA can reassign sab970047 to grp2 by making the following entries on the assign screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-43 Using the MR Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 02/28/97 08:01:25 Assign MR to a Developer MR Number: sab970047__________________________________________________________ Generic: g2_________________________________________________________________ Developer: grp2__________ MRG Severity: 3 MRG Due Date: 04/03/97 Estimated Effort: _____ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, the GA would enter: assign mr=sab970047 dev=grp2 sev=3 due=04/03/97\ prompt=n The default: g=g2 (setup generic) is entered automatically and need not be typed. After this command has been processed, any member of group grp2 (but no member of grp3) is allowed to make changes in response to MRG sab970047 in generic g2. The severity and due date remain unchanged. Finally, suppose the GA now realizes that grp3 is so overworked that it will not be able to make the changes proposed by sab970039 either, but it is not clear who if anyone will be able to do the work. While waiting to decide who should do the work, the GA, using the Curses Forms interface, can unassign MRG sab970039 by making the following entries on the assign screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-44 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Submitting an MRG logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 02/28/97 08:01:25 Assign MR to a Developer MR Number: sab970039__________________________________________________________ Generic: g2_________________________________________________________________ Developer: ______________ MRG Severity: _ MRG Due Date: ________ Estimated Effort: _____ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, the GA would enter: assign mr=sab970039 g=g2 prompt=n The default: g=g2 (setup generic) is entered automatically and need not be typed. By omitting the developer on the assign screen (or by not entering the dev=AD keyword on the command line) the GA unassigns the MRG and returns it to the accepted state. Submitting an MRG 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the submit command, see the submit manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. Only the developer to whom an MRG has been assigned can submit it. Once submitted, the MRG is in the submitted state. When a developer has finished making the changes required to complete the work on an MRG and has unittested the changes, the developer can submit the MRG for further testing using the submit command. The developer should not submit the MRG until all the AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-45 Using the MR Commands changes it requests have been made and successfully unit-tested. Depending on the levels of testing established for the generic, the MRG may go on to further testing after it is submitted. Suppose that a developer has finished all the work on two MRGs and wants to submit them for testing. (In this example, the in-process metrics and all five MRGUDFs are used along with their default keywords and screen labels.) Using the Curses Forms interface, the developer would make the following entries on the submit screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/05/97 15:51:03 Submit MR for a Specified Generic MR Number: sab970149,sab970073________________________________________________ Generic: g1____________ Resolution Code: as_proposed___ Rel Introduced: 4.0__________________ Phase Introduced: design_______________ Root Cause: project_methodology__ Optimal Det Phase: design_insp__________ RC Subcat: _____________________ MRG UDF1: test_________________ Non-Det Cause: _____________________ MRG UDF2: 100__________________ NDC Subcat: _____________________ MRG UDF3: 10.03________________ Fault Type: _____________________ MRG UDF4: _____________________ Actual Effort: 8.4__ MRG UDF5: _____________________ Hcode Number: ___________________________________ PDI Number: ______________ Resolution File: solv1________________________________________________________ Copy To: _____________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, the developer would enter: submit mr=sab970149,sab970073 code=as_proposed\ ri=4.0 pi=design odp=design_insp\ rc=project_methodology ae=8.4 mrgudf1=test\ mrgudf2=100 mrgudf3=10.03 rfile=solv1 prompt=n The default: g=g1 (setup generic) is entered automatically and need not be typed. NOTE: solv1 is a file that exists in the current working directory. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-46 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Assigning an MRG to a Tester In either case, MRGs sab970149 and sab970073 would be submitted in generic g1, their states set to submitted; and the appropriate test teams notified that the two MRGs are ready for further testing. Assigning an MRG to a Tester 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the testassign command, see the testassign manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. NOTE: The GUI does not provide access to this command. The testassign command gives the Generic Administrator more control over who can test what MRG. While Sablime allows a project to define testing teams who are responsible for testing MRGs in certain states, the testassign command allows the Generic Administrator to assign an MRG to a specific tester or group (AD). The Generic Administrator can also use this command to reassign an MRG, or unassign an MRG. The Generic Administrator who issues the testassign command must be responsible for all generics specified in the command. When using the testassign command, it is important to remember the following: n The testassign command only checks that the PTS ID that has been entered is a valid one. The user may enter one or more MRGs and one or more test levels. n A software MRG and a document MRG can be assigned to the same tester. n The testassign command can operate on MRGs that are in states from accepted to stpassed. n As long as an MRG is within the range of valid states, the testassign command will allow the user to assign a tester to it. However, the assigned tester may never use this privilege if, for example, the project decides not to use any of the test phases. Similarly, if an MRG is already in the itpassed state (a level 2 state), and is then assigned to a user1 for test level 1, user1 will never use this privilege unless the MRG is rejected. (See the testpass manual page for detailed information about testing levels and phases.) n The testpass and reject commands will validate the assigned tester, if there is one. (The assigned tester must belong to the Test Team, which is defined in the GT relation.) Only the assigned tester will be allowed to perform the testpass and reject commands. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-47 Using the MR Commands The test levels applicable to an MRG are determined by the class of the MRG to be tested. For information about the classes, see the testassign manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. For example, using the Curses Forms interface, the Generic Administrator would assign MRG sab970073 to tester gjs by making the following entries on the testassign screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime 06/16/97 MR Management System Command 14:37:19 Assign MR to Tester for Testing Function: modify MR Number: sab970073______________________________________________ Generic: v5.0____________________ Test Level: 4____________________ Tester: gjs____________________ Copy To: _________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, the Generic Administrator would enter: testassign mr=sab970073 level=4 tester=gjs prompt=n The default: g=v5.0 (setup generic) is entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-48 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Passing an MRG through a Test State Passing an MRG through a Test State 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the testpass command, see the testpass manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. Because there is wide diversity in the procedures used by different organizations when testing their products, four sets of parallel test states are available between the submitted state and the approved state to track MRGs through the testing process. (For details, see the testpass manual page.) None of the test states are mandatory. When adding a generic, the Database Administrator selects the appropriate classes for the generic and then decides how many levels of testing are needed. Based on this decision, test teams are assigned. The selection of test states is performed automatically based on the team assignments made when the generic is established. If no test teams were selected when the generic was established, an MRG proceeds directly from the submitted state to the approved state. Only testers who are in the proper test team can pass an MRG. The test notes field is an optional field. As an example of how an MRG passes through test states, suppose that MR sab940003 with a class of hardware has been accepted, assigned, and submitted in generic g1. For the hardware class in that generic, groups have been assigned for Hardware Integration Test Team and Pre-Approval Team only. Figure 4-5, below, shows the paths the MRG might follow as it proceeds from the submitted to the approved state. NOTE: If the MRG is rejected at any time during the testing process, it may be returned to any previous state. In the interest of clarity, this part of the figure is simplified. NOTE: By default, the testpass command sets the target state to the next state for which a test team is established. The user can promote through multiple states by setting the target state to some state higher than the default. The user must be a member of all the intermediate test teams as well as the test team for the target state. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-49 Using the MR Commands Figure 4-5. Hardware Sample Test States As another example of the flow of an MRG through testing states, suppose that MR sab940003 in the document class has been accepted, assigned, and submitted in generic g1. For the document class in that generic, groups have been assigned for Inspection Team, Publish Team and Pre-Approval Team only. Figure 4-6, below, shows the paths the MRG might follow as it proceeds from the submitted to the approved state. NOTE: If the MRG is rejected at any time during the testing process, it may be returned to any previous state. In the interest of clarity, this part of the figure is simplified. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-50 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Passing an MRG through a Test State . Figure 4-6. Document Sample Test States AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-51 Using the MR Commands Finally, suppose a tester wanted to indicate that software MR sab990406 had passed system testing. Using the Curses Forms interface, the tester would make the following entries on the testpass screen: logid:ral effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 MR Management System Command 06/04/00 12:03:03 Promote an MRG to a higher MRG state MR Number:sab990406_________________________________________________________ Generic: v5.2______________________________________________________________ Target State: stpassed________________ Copy To:___________________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, the tester would enter: testpass mr=sab990406 \ tstate=stpassed prompt=n In either case, MR sab990406 in generic v5.2 would move from prestpassed to stpassed. Rejecting an MRG 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the reject command, see the reject manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. After an MRG has been submitted by a developer, there is normally further testing of the changes by a test team. If the changes fail to pass these tests, any member of the test team may use the reject command to set the state of the MRG back to a AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-52 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Rejecting an MRG previous state. Further changes must then be made to correct the errors found by the test team and the MRG must then be resubmitted or testpassed on to a subsequent state. Using the Curses Forms interface, the test team might reject the changes made in response to MRG sab990138 by making the following entries on the reject screen: logid:ral effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 MR Management System Command 06/04/00 12:13:34 Reject MR for a Specified Generic MR Number: sab990138_______________________________________________________ Generic: ______________ Target State: __________________________ Reject Code: no_documentation____ Reject File: /usrs1/rej1____________________________________________________ Copy To: _________________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, the test team would enter: reject mr=sab990138 code=no_documentation\ rfile=/usrs1/rej1 prompt=n The default: g=g1 (setup generic) is entered automatically and need not be typed. Using the Curses Forms interface, a copy of the file /usrs1/rej1 is read into the user’s favorite editor; the original file remains unchanged. The name of the temporary file is shown in the Rejection File field when the reject screen is redisplayed. Using the Command Line interface, a copy of the file is used as the rejection file. In either case, MRG sab990138 is rejected in generic g1 and the state is set to assigned. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-53 Using the MR Commands Using the Curses Forms interface, a temporary file is opened in the user’s editor for entry of the reason for rejecting the MRG. This file must be written before Sablime processes the reject command. The name of the temporary file is shown in the Reject File field when the reject screen is redisplayed. You must enter an explanation for your rejection in the file provided regardless of the entry in the Reject Code field. Approving an MRG 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the approve command, see the approve manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The approve command is used by the approval team to approve MRGs and associated changes for the official branch of the product. After it has been run, the file changes made to the unofficial branch (mr) in response to the specified MRGs in the specified generic are reflected in the official (ofc) branch and the state of the MRG is set to approved. The MRAs, GAs, and ATs are notified that the MRG has been approved. Because versions created from the official branch are built on top of the latest official version of files, it is essential that any MR used to add files to a generic be moved through the Sablime system to the approved state before any additional changes are made to those files. This creates a baseline official branch that contains the files as they were when added to the generic. If the MR is not approved, the files in the official branch are empty. It is also important to remember to approve MRGs in the order in which they were worked on or as a group. In this way, changes made to the file are added to the official version of the file without danger of losing the latest changes. If MRGs are approved as a group, the Sablime system determines the correct order in which to apply the deltas. See the suggestions in the section MRG Dependencies for making MRGs dependent to ensure the correct sequence of approval. For example, the approval team would approve an MRG (sab970046) in generic g1 by making the following entries on the approve screen Using the Curses Forms interface: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-54 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Approving an MRG logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/26/97 07:46:00 Approve MRs for Specified Generics Generic: g1_________________________________________________________________ MR Number: sab970046__________________________________________________________ Copy To: ___________________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, the approval team would enter: approve mr=sab970046 prompt=n The default: g=g1 (setup generic) is entered automatically and need not be typed. After this command has processed, all the changes made in response to MRG sab970046 in generic g1 will appear in the official branch of the project. The MRG state will be set to approved for generic g1. The approval team could approve multiple MRGs in multiple generics by making the following entries on the approve screen Using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/26/97 07:48:31 Approve MRs for Specified Generics Generic: g1,g2______________________________________________________________ MR Number: sab970038,sab970039________________________________________________ Copy To: ___________________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, the approval team would enter: approve g=g1,g2 mr=sab970038,sab970039 prompt=n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 4-55 Using the MR Commands 4 After this command has processed, all the changes made in response to MRGs sab970038 and sab970039 in both generics g1 and g2 will appear in the official branch of the project. The MRG state will be set to approved for generics g1 and g2. Closing an MR 4 NOTE: For detailed information about the closemr command, see the closemr manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. When all the MRGs generated by a given MR have reached a terminal state (approved or nochange) in all the generics into which the MR was accepted, the MR administrator may close the MR with the closemr command. This command moves all information relating to the MR and its MRGs to the Inactive Database. No further work may be done on the MR. For example, the MR administrator could close an MR across all generics by making the following entries on the closemr screen Using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime MR Management System Command 05/26/97 08:18:49 Close MR for All Affected Generics MR Number: sab970023__________________________________________________________ Copy To: ___________________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, the MR administrator would enter: closemr mr=sab970023 prompt=n 4 In either case, most of the information relating to MR sab970023 in all the generics in which it was accepted will be moved to the Inactive Database. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 4-56 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Contents 5 Using the Source Commands 1 Source File Control 1 File Locking 1 Branches 1 SCCS and SBCS 2 n The Source Commands 3 n Adding a New Source File 6 n Adding a Source File 9 n Getting a Source File to Edit 13 n Unlocking a Retrieved Source File 16 n Putting Back a Changed Source File 18 n Backing Out Changes to Source Files 20 n Getting Copies of Source Files 22 n Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific MRs 28 n Printing a Source File Listing 48 n Making Source Files Common 50 n Making Source Files Not Common 52 n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 i Contents AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page ii Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the Source Commands 5 Source File Control 5 Sablime controls changes to source files by allowing them to be made only in response to an MR and by locking files to prevent simultaneous changes being made to a file in a generic. (See the section, File Locking, below for more information about file locking.) File versions for all the generics in which a file occurs are stored in a single master file in the Source Database. For each generic, the file changes are tracked in two separate branches; one contains changes made in response to all MRs (approved and unapproved), the other only those changes made in response to approved MRs. (See the section, Branches, below for more information about the two branches.) The existence of the two separate branches is transparent to Assigned Developers during development work. File Locking 5 The Sablime system controls changes by maintaining a master copy of each file in a designated directory and allowing that file to be copied to the Assigned Developers work node for changes. Once the edget command has copied the file from the system directory to an Assigned Developer’s directory, no one else is allowed to edit the file for the same generic until that developer releases it with the unedget or edput command. Branches 5 Internally, the Sablime system stores master copies of files in two branches for each file; an MR or unofficial branch (mr) and an official branch (ofc). AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-1 Using the Source Commands For each generic, the mr branch of a file contains the initial version of the file added to a generic with the addisrc, addgsrc, or primsdb command. Then, as changes are made and edput to the Source Database, these changes are stored in the mr branch of the file. Each MR for which changes have been made is associated with those changes in the database. For each generic, the official branch of a file contains all the changes made in the mr branch for MRs that have been approved for that generic. SCCS and SBCS 5 The Sablime system controls changes to files through the UNIX system Source Code Control System (SCCS) or Source and Binary Control System (SBCS). With SCCS, the Sablime system keeps track of versions of files by assigning numeric codes to changes (deltas) made to each of the branches of each file, the mr branch and the official branch. With SBCS, the Sablime system still keeps track of the mr branch and the official branch although they are both represented internally in SBCS as a single branch. When files are added to a Sablime generic, an SCCS/SBCS code is assigned to the initial version of the file as added to the generic. The code is made up of the three parts shown in Figure 5-1. Figure 5-1. Generic ID Number Branch Number 1=ofc, 2=mr Delta Identifier (SCCS/SBCS Sequence Number) 4.1 .1 .2 SCCS/SBCS Version Identifiers The first box shows the generic ID created by SCCS/SBCS for the Sablime generic. This number is incremented by one for each new generic in a product and usually bears no resemblance to the internal generic specification. For example, a first generic sab1.0 might be given the generic ID 1.1. Then, if a second generic, sab1.1, is created, SCCS/SBCS will give it the generic ID 2.1, and so on. The generic ID number is never reused within a product even after a generic has been closed. The digit after the dot (.) in the generic ID is always 1. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-2 Issue 1.1 November 2000 The Source Commands The second box shows the Branch Identifier. The official branch is indicated by the number 1. The mr branch is indicated by the number 2. The third box shows the Sablime Delta Identifier. This number changes whenever a change is made to a file in the specified branch as follows: n For the mr branch: The Delta Identifier is incremented by one whenever an edget/edput sequence is performed on a file. The edget command reserves the identifier for the file, but the identifier does not become permanent until the edput command is issued for that file. The first delta in the mr branch of a file in a generic contains the version that was added to the generic with primsdb, addisrc, or addgsrc. Changes are made on top of the first delta in the mr branch. n For the official branch: In SCCS, the Delta Identifier is incremented by one whenever the approve command is issued for one or more MRs. The changes to the files made for the approved MRs are stored as part of the official version of the files for the product. In SBCS, an initial dummy delta is created for the official branch. The rest of the deltas are made in the mr branch. Each time an MR is approved, the GS relation keeps track of the last approved version. Initially, the official branch of a file in a generic is empty because the MR used to add the file to the generic has not been approved. The Source Commands 5 The source commands are shown in Figure 5-2. The boxes indicate the effect of each command. Mandatory actions are shown in the vertical flow, while optional actions are displayed to the left or right of the main flow. The table following the figure describes each of the commands in greater detail. NOTE: The GUI provides access to the following source commands: addisrc, edget, edput, unedget, and sget. NOTE: Sablime has a command permissions function that allows the Sablime Administrator to change command permissions for each individual user. Therefore, it is sometimes possible for users to run a command even though they are not in the group normally permitted to do so. The documentation decribes the system as delivered. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-3 Using the Source Commands addisrc/addgsrc add files initially or from an existing generic get read-only copy of file sget getversion common/uncommon get read-only copy of latest version of file with MR information srcpr edget get editable copy of file unedget edput copy file with any changes to system directory Figure 5-2. Source Commands and Their Effects AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-4 Issue 1.1 mark/declare files common or uncommon across multiple generics November 2000 unlock unchanged file in system directory The Source Commands . Table 5-1. Source Commands Command Description addisrc/ addgsrc/ primsdb The addisrc (add source initially) command allows the Source Administrator or the Assigned Developer to add a file to the Source Database in a generic for the first time. The addgsrc command (add source from another generic) allows the Source Administrator or the Assigned Developer to add a file to the Source Database from one generic to another generic for the same product. If you want to add a large number of files at one time, see your Database Administrator about using the primsdb command (described in the Administrator’s Guide). This command is a script that successively calls addisrc or addgsrc. edget The edget command is used by the Assigned Developer to retrieve the latest copy of a file for a generic from the MR branch of the Source Database. The file is retrieved to allow work on the MRG specified in the command. Once the file is retrieved, no other Assigned Developer can retrieve this file in its generic for edit until it is returned to the Source Database with an edput command or released for use with an unedget command. unedget The unedget command is used by the Assigned Developer to unlock a file and allow a subsequent edget with another MRG or by another Assigned Developer. This command can be used if the file is currently checked out with edget. When a file is released with unedget, the edit lock on the file is removed and the relationship between the file and the MRG established by the edget is removed, unless the file had previously been edgotten and edput in response to that MRG. edput The edput command is used by the Assigned Developer to return an edgotten file to the Source Database and create a permanent record of the changes. This command can be issued only after a corresponding edget has been issued. This command must be issued from the same PTS ID that issued the corresponding edget command. unedput The unedput command is used by the Assigned Developer to undo the effects of an edput command. This command will undo the last delta (i.e., the last edput changes) made to a file and will put a copy of the file as it was before the unedput changed it in the user’s working directory. sget The sget command is used to retrieve a read-only copy of files from a specified branch of the Source Database for unit testing or browsing purposes only. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-5 Using the Source Commands Table 5-1. Source Commands—Continued Command Description getversion The getversion command is issued to retrieve a specified version of the files and place them in a user-specified node, usually for testing or building purposes. srcpr The srcpr (source print) command allows the user to produce a source file listing of the latest version of a non-binary file stored under SCCS that indicates, for each line of the source file, the MRG that last touched that line. common The common command is issued by the Source Administrator to maintain consistency of files across generics. To be common, files must be exactly the same in the common generics. Any changes made to a file in one generic are also made to that file in all other generics for which the file is common. uncommon The uncommon command is issued by the Source Administrator to remove the common connection of files across generics. The following sections describe and provide examples of the use of these commands. Except where noted, you must use either the Command Line or the Curses Forms interface to run the commands. Adding a New Source File 5 NOTE: For detailed information about the addisrc command, see the addisrc manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. NOTE: The GUI provides access to this command. The addisrc (add initial file) command is used to add a new file to a generic in the Source Database. It is only used if the file for a specific relative directory is not currently in any generic in the database. (If the file is already in a generic, you should use addgsrc to add it to the current generic. See Adding a Source File, below.) You can use addisrc if the MRG requiring the new file is assigned to you or to a group of which you are a member. In addition, the Source Administrator can use addisrc regardless of the PTS ID to which the MRG is assigned. When this command is issued, the file is copied into the appropriate directory in the Source Database, and Sablime begins tracking changes made to the file in response to the controlling MRG(s). AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-6 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Adding a New Source File Only the MR branch of the added file is now available for viewing or editing in the generic; the official branch contains only a null file. When the MRG that authorized the addisrc for the file is approved, the initial version of the file, with any changes made using the authorizing MRG, is copied to the official branch of the file. ! CAUTION: The authorizing MRG should always submitted immediately after adding a file so that the official branch of the file contains the official version of the file as a base. Until the initial MR is approved, a zero-length file will exist in the official branch. Also, making further modifications with the initial MRG makes it difficult to get back to the version of the file containing those modifications. You can store binary files as well as non-binary files using addisrc. The criteria that define a binary file for Sablime purposes are: n line length greater than 509 characters on any line or n octal 1 (^A [Control-A]) in the first column of any line or n a character greater than octal 177 on any line. addisrc allows you to specify whether you have a binary file, whether to use SBCS or SCCS to store the file, and whether to count the file for Quality Assurance (QA) purposes. Binary files must be stored under SBCS, but non-binary files can be stored under SBCS or SCCS. Binary files are automatically excluded from QA counts, but non-binary files can be included regardless of the version control tool. With addisrc, files must be added one at a time; if you have many new files to add, see your Sablime Administrator about using the primsdb script. After the file has been added, if any of the file attributes set using the addisrc command need to be changed, the Source Administrator can change them with the source command. (See the manual page for the source command in the Administrator’s Gude.) As an example of the use of the addisrc command, suppose you have been assigned an MRG (sab990404) that requires that a new file be added to the Source Database. Using the Curses Forms interface, assuming that you were in the src/mrmgmt directory and that this directory contained the file create.c, you might make the following entries on the addisrc screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-7 Using the Source Commands logid:ral effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 Source Management System Command 06/04/00 11:44:10 Initially Adding a Source File to a Generic Generic: g1____________ MR Number: sab990404_____ Source File: create.c____ File Owner: _________________ Use Extension for Type: n File Type: c++_____ SDB Directory Location: src/mrmgmt________________________________________ Current File Location: /usr/src/sablime/mrmgmt/create.c__________________ Store As Binary: yes________ Control Tool: SBCS Count File for QA: y Or, using the Command Line interface, you might enter: addisrc mr=sab990404 srf=create.c \ initsrc=/usr/src/sablime/mrmgmt/create.c\ bfile=yes prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) exttype=n fltype=c++ dir=src/mrmgmt (current directory) vct=SBCS sqflag=y are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, this command would add the file /usr/src/sablime/mrmgmt/create.c to generic g1 using MRG sab990404. The file name is create.c, the relative directory is src/mrmgmt, and SBCS is used as the version control tool for the file. When the command finishes processing, the file create.c is available in the MR branch of generic g1 and can be modified after retrieval by edget or tested or reviewed after retrieval by sget or getversion. At this point, only a zero-length version of the file is available in the official branch of g1. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-8 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Adding a Source File ! CAUTION: MRG sab990404 should be taken to the approved state as soon as all files have been added to establish a base in the official branch before other MRs are issued that touch the file. Adding a Source File 5 NOTE: For detailed information about the addgsrc command, see the addgsrc manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The addgsrc (add a source file to a generic) command is used to retrieve any version of source files in the Source Database from an existing generic and copy them to another generic. You can use addgsrc if an MRG is assigned to you or to a group of which you are a member. In addition, the Source Administrator can use addgsrc regardless of the PTS ID to which the MRG is assigned. You can use addgsrc to select the: n latest official (ofc) branch version, n latest official branch version plus changes associated with a list of unapproved MRGs from the MR branch, n latest MR branch version, or n earliest MR (mr) branch version plus changes associated with a list of approved and/or unapproved MRGs from the MR branch of the files to retrieve from the existing generic and copy to another generic. You can copy files from one relative directory in the existing generic to the same or a different relative directory in another generic. These files can be declared common between the two generics even if they are in different relative directories, provided that addgsrc is retrieving the latest mr branch version of the file. You can copy files from a newer generic to an older generic, provided that the files were added to the newer generic with Sablime version 3.0.2 or later of addisrc or primsdb. Once the files have been copied, they are available for viewing or editing only in the MR branch of the generic to which they were just added. Zero-length files are entered into the official branch. When the MR that authorized the addgsrc for the files is approved, the version of the files that were copied with addgsrc, with any changes made to the files using that MR, are copied to the official branch. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-9 Using the Source Commands ! CAUTION: The authorizing MRG should always submitted immediately after adding a file so that the official branch of the file contains the official version of the file as a base. Until the initial MR is approved, a zero-length file will exist in the official branch. Also, making further modifications with the initial MRG makes it difficult to get back to the version of the file containing those modifications. NOTE: If a large number of source files are to be added, see your Administrator about using the primsdb script. After the file has been added, if any of the values set using the addgsrc command need to be changed, the Source Administrator can change them with the source command. As an example of the use of the addgsrc command, suppose you want to copy a source file in the Source Database from the official branch of an existing generic to a later generic. Using the Curses Forms interface, assuming you are in the src/ mrmgmt directory, you would make the following entries on the addgsrc screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 06/20/00 effid:sabdev Source Management System Command 14:06:10 Adding Source Files From an Existing Generic Generic: g2____________ MR Number: sab99032______ Old Generic: g1____________ Common: n Branch: ofc Count Files for QA: n File Owner: _______________ Directory: src/mrmgmt__________________________________________________ Old Directory: src/mrmgmt__________________________________________________ Source Files: accept.c_____________________________________________________ Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: _ MRs for Specifying Version: _________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, you would enter: addgsrc mr=sab99032 sqflag=n oldg=g1 srf=accept.c\ prompt=n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-10 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Adding a Source File The defaults: g=g2 (setup generic) br=ofc common=n dir=src/mrmgmt (current directory) olddir=src/mrmgmt (same as dir) are entered automatically and need not be typed. The file accept.c in the src/mrmgmt directory is copied from the official branch of generic g1 to the MR branch of generic g2. The file is not declared common between the generics. The file is now available in the MR branch of generic g2 and can be modified after retrieval by edget or tested or reviewed after retrieval by sget or getversion. Suppose next that you want to copy a source file in the Source Database from the MR branch of an older generic to a newer generic. And suppose further that you want to make the file common between generics, so that changes to the file in one generic appear in the other generic as well, and that you want the lines of code to be counted for Quality Assurance. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the addgsrc screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 03/31/97 15:43:14 Adding Source Files From an Existing Generic Generic: g3____________ Common: y MR Number: sab970017_____ Branch: mr_ Old Generic: g2____________ Count Files for QA: y File Owner: same_____________ Directory: src/mrmgmt_____________________________________________________ Old Directory: src/mrmgmt_____________________________________________________ Source Files: depend.c_______________________________________________________ MRs for Specifying Version: __________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter the following: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-11 Using the Source Commands addgsrc g=g3 mr=sab970017 br=mr oldg=g2 common=y\ srf=depend.c prompt=n The defaults: sqflag=y owner=same dir=src/mrmgmt (current directory) olddir=src/mrmgmt (same as dir) are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, the source file depend.c in the src/srcmgmt directory will be copied from the MR branch of generic g2 to the MR branch of generic g3, and the file will be declared common between the generics and registered to be counted for Quality Assurance. The file is now available in the MR branch of generic g3 and can be modified after retrieval by edget or tested or reviewed after retrieval by sget or getversion. Also, changes made to either generic will appear in the other generic too. Finally, suppose you want to copy a source file from the earliest MR branch version of an existing generic to a different relative directory in the current generic. And suppose also that you want to Include changes from additional approved and/or unapproved MRGs (e.g., sab970001 and 970007). Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the addgsrc screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 03/31/97 15:43:14 Adding Source Files From an Existing Generic Generic: g3____________ Common: n MR Number: sab970017_____ Branch: mr_ Old Generic: g2____________ Count Files for QA: y File Owner: _________________ Directory: src/newsys/admin_______________________________________________ Old Directory: src/admin______________________________________________________ Source Files: depend.c_______________________________________________________ MRs for Specifying Version: sab970001,sab970007_______________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, you would enter: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-12 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting a Source File to Edit addgsrc g=g3 mr=sab970017 br=mr oldg=g2\ dir=src/newsys/admin \ olddir=src/admin srf=depend.c\ mrs=sab970001,sab970007 prompt=n The defaults: common=n sqflag=y are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, the file depend.c in the src/admin directory in generic g2, with the changes resulting from MRGs sab970001 and sab970007, is copied to the src/newsys/admin directory in generic g3. The file is not declared common between the generics. The file is now available in the MR branch of generic g3 and can be modified after retrieval by edget or tested or reviewed after retrieval by sget or getversion. ! CAUTION: MRG sab970017 should be submitted immediately to establish a base in the official branch before other MRs are issued that touch the file. Getting a Source File to Edit 5 NOTE: For detailed information about the edget command, see the edget manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. NOTE: The GUI provides access to this command. After an MRG has been assigned to you or a group of which you are a member, you can use it to retrieve the latest copy of any file it requires you to change from the MR branch of the Source Database with the edget command. The retrieved file is copied to your current working directory. NOTE: If an owner has been named for the file, only the named owner is permitted to edget the file and make changes. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-13 Using the Source Commands Once edget has been issued for a file in a generic, a lock is placed on the file and no one else can edget that file for the same generic until an edput or an unedget command has been issued for that file. If the file is a common file, the MR must be in the assigned state for all of the generics for which the file is common and assigned to the same PTS ID. The file is then locked in all of the generics for which the file is common. The processing message includes a list of those generics. When you confirm the edget command, a list of unapproved MRGs associated with the files, assignees, and the MR Abstracts are displayed for the edgotten files. Your project may use the Automatic Dependency feature for SCCS files. n If your project declares file-level dependencies, the MRG used for the edget command automatically becomes dependent upon any unapproved MRs that have touched the same file. n If your project declares line-level dependencies, the MRG used for the edget command automatically becomes dependent upon any unapproved MRGs that have touched the same lines in the file. See the Administrator’s Guide or your Sablime Administrator for more information. NOTE: Before you use the edget command, it is best to be positioned in the relative directory of your node into which you want to copy the files. This directory must correspond to the Sablime relative directory from which the files are copied. This position allows you to use the default entry in the Directory field and to avoid path confusions. As an example of the use of the edget command, suppose that you want to retrieve the latest version of a file create.c in the src/mrmgmt directory of generic g1 so you can make the changes authorized by an MRG that has been assigned to you. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the edget screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-14 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting a Source File to Edit logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 05/05/97 07:21:20 Getting Source Files to Edit Generic: g1____________ MR Number: sab970032_____ Remove Files: n Directory: src/mrmgmt______________________________________________________ Source Files: create.c________________________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, you would enter: edget mr=sab970032 srf=create.c prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) dir=src/mrmgmt (current relative directory) rm=n are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, this command will retrieve an editable version of the file create.c from the relative directory src/mrmgmt in the MR branch of generic g1. Any changes to the file will be recorded against MRG sab970032. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-15 Using the Source Commands As processing takes place, information like that shown below will appear on the screen: + Processing the inputted data; please stand by! + Processing the file [filename] – The file has been extracted from the source DB. – The tuple in GS relation has been updated. – A tuple in MD relation has been created. + The unapproved MRs on file [filename] in generic [generic] are: MR Number Assignee MR number xxxxxx Abstract abstract text + You have successfully done ’edget’ for the file [filename] + A Master Trace Record has been generated for the Database Administrator. Unlocking a Retrieved Source File 5 NOTE: For detailed information about the unedget command, see the unedget manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. NOTE: The GUI provides access to this command. The unedget command is used by the Assigned Developer to unlock a file retrieved by edget. unedget removes only the lock created by the last edget for the file in the specified generic; once a file has been edput after the last edget, you cannot unedget the file. This command is useful if the wrong files have been retrieved or if someone else needs the files and cannot wait for your changes. It can also be used if the files retrieved by edget have been corrupted and you need to edget a new copy. You can unedget a file even if you have made changes to the file in your directory. When you execute unedget, the file retrieved by edget is not removed from your AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-16 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Unlocking a Retrieved Source File directory and changes are not written to the Source Database, but the lock on the file is removed. The file is left in 644 mode. You can also use unedget to release the lock on a file made by a member of a group to which the MRG is assigned, provided you and the user who retrieved the file with edget are both members of the group to which the MRG is assigned. If the file is a common file, all record of the edget is removed for all generics to which the file is common, and an informative message listing those generics is generated. Before you use the unedget command, it is best to be positioned in the relative directory of your node from which you want to unedget the files. This position allows you to use the default entry in the Directory field and avoid path confusions. As an example, suppose you are in the src/mrmgmt directory and you want to unlock two files, create.c and accept.c in generic g1that you have previously retrieved with edget, using MRG sab970130. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the unedget screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 03/21/97 13:29:24 Returning Unedited Source Files Generic: g1____________ MR Number: sab970130_____ Directory: src/mrmgmt______________________________________________________ Source Files: create.c,accept.c_______________________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, you would enter: unedget mr=sab970130 srf=create.c,accept.c prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) dir=src/mrmgmt (current directory) are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, this command unlocks the files create.c and accept.c in relative directory src/mrmgmt for generic g1. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-17 Using the Source Commands Putting Back a Changed Source File 5 NOTE: For detailed information about the edput command, see the edput manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. NOTE: The GUI provides access to this command. After changes have been made to files retrieved with edget, the Assigned Developer who issued the edget command can return the modified files to the MR branch of the Source Database using the edput command. This unlocks the files, allowing another developer to edget it. Your project may use Sablime’s Automatic Dependency feature. For files stored under SCCS: n If your project declares file-level dependencies, the MRG used for the edput command automatically becomes dependent upon any unapproved MRGs that have touched the same file. n If your project declares line-level dependencies, the MRG used for the edput command automatically becomes dependent upon any unapproved MRGs that have touched the same lines in the file. NOTE: For files stored under SBCS, automatic MR dependency is file level; filelevel is the protected default. See the Administrator’s Guide or your Sablime Administrator for more information. For files stored under SBCS, file-level dependency is created for the last MR that touched the file regardless of the state of the last MR (approved or unapproved). For files stored under both SBCS and SCCS, if the initialization MR has not been approved, the MR used to edput the file is made dependent on the initialization MR. For files stored under SCCS, edput verifies that the file still meets the criteria for successful non-binary storage under SCCS (see Adding a New File, above). If the file fails the criteria check, an error message is generated. The edput command has an option that allows the user to see what dependencies would be created if the edput command were to complete successfully. Then, if undesirable dependencies would be created, the user can abort the command; if not, the user can allow the command to proceed with the changes. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-18 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Putting Back a Changed Source File The Assigned Developer can enter comments describing specific changes made to the edput files in response to the specified MRG. These comments are included in the Resolution File for the specified MRG; they are particularly useful when the MRG is assigned to a group or when changes are made over an extended period of time. If the file is a common file, these differences are marked for all the generics to which the file is common. An informative message that contains a list of those generics is produced. As an example, suppose you have finished making changes to a file that you have retrieved by edget, using MRG sab970032. Assuming you are in the src/mrmgmt directory that contains the file create.c, you would make the following entries on the edput screen using the Curses Forms interface: NOTE: If you do not have a comments file prepared, you can enter y in the Comments field and Sablime will open a temporary file in which you can write your comments. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime 04/17/97 Source Management System Command 14:30:52 Returning Edited Source Files Generic: g1____________ MR Number: sab970032_____ Directory: src/mrmgmt_____________________________________ Source Files: create.c_______________________________________ Comments File: cmts.fl________________________________________ Auto Dependency: file-level Remove Files: y Show Dependencies First: y Or, using the Command Line interface, you would enter: edput mr=sab970032 srf=create.c com=cmts.fl prompt=n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-19 Using the Source Commands The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) dir=src/mrmgmt (current relative directory) adep=file-level (file is stored under SBCS) rm=y are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, this command will return the file create.c to the src/mrmgmt directory to the Sablime Source Database using MRG sab970032 and will remove the file from the developer’s current directory. The file will be returned to the MR branch of generic g1. File-level dependency will be created for the MRG, and the text of the file cmts.fl will be added to the existing Resolution File for MRG sab970032. Backing Out Changes to Source Files 5 NOTE: For detailed information about the unedput command, see the unedput manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The unedput command is used by the Assigned Developer to undo the changes made by an edput command. unedput removes any changes made to the file(s) in the specified generic and in any other generics in which the file(s) are common. Since the last delta (i.e., the last edget/edput pair) is removed from the file(s), unedput saves the original file(s) for the user so that the user can recover from the removal of the last delta if desired. This command may be invoked multiple times to remove multiple deltas made to file(s). You can also use unedput to remove changes made to file(s) by a member of a group to which the MR is assigned, provided you are a member of the group. NOTE: Before you use the unedput command, it is best to be positioned in the relative directory of your node from which you want to unedput the files. This position allows you to use the default entry in the Directory field and avoid path confusions. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-20 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Backing Out Changes to Source Files As an example, suppose you want to back out changes you had made to the source file sa.c in the src directory. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the unedput screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime 06/17/97 Source Management System Command 21:46:48 Undoing Last Changes in Source Files Generic: g1__________ Directory: src_____________________________________________________ Source Files: sa.c____________________________________________________ Remove Files?: _ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter unedput srf=sa.c prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) dir=src (current relative directory) rm=n are entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-21 Using the Source Commands Getting Copies of Source Files 5 NOTE: For detailed information about the sget command, see the sget manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The sget (simple get) command retrieves read-only copies of specified files from the specified branch of the Source Database. If you request the official branch of a file, the current official version is used as a base; if you request the mr branch of a file, the original version of the file from the mr branch is used as a base. If MRGs are specified, changes made in response to those MRGs are included. The MRGs can be in either the active or completed state. The active MRGs are retrieved from the Active Database; completed MRGs are retrieved from the Inactive Database. This command is used to retrieve files for testing or browsing purposes only. No lock is placed on the files in the Source Database. The user may tell sget whether or not to include depended-upon MRGs, that is, MRGs that are depended upon by the MRGs the user has listed. If the user wants the dependent MRGs included, sget will determine all the dependent MRGs, display them for the user, and use them in the retrieval of files. If the user does not want dependent MRGs included, sget will still determine all the dependent MRGs and display them for the user, but it will not use them to retrieve files. If a file is a common file, an informative message provides a list of the generics for which the file is common. If a file has been retrieved by edget, a message indicates that the file has been taken out for edit. NOTE: Before you use the sget command, it is best to be positioned in the relative directory of your node that corresponds to the system directory from which the files will be copied. This position allows you to use the default entry in the Directory field and to avoid path confusions. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-22 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Copies of Source Files As an example, suppose you want to look at the latest version of the files create.c and accept.c in the MR branch of generic g1. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the sget screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/17/97 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 13:31:37 Getting a Specified Version of Source Files Generic: g1____________ Branch: mr_ Directory: src/mrmgt____________________________ Source Files: create.c,accept.c____________________ Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: n MR Numbers: _____________________________________ Cutoff Date: _________________ Remove Files?: n Expand ID Keywords?: n Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: sget br=mr srf=create.c,accept.c kx=n prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) dir=src/mrmgmt (current relative directory) rm=n are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, the latest versions of files create.c and accept.c are copied to your current relative directory src/mrmgmt from the MR branch of generic g1. SBCS/ SCCS ID keywords are not expanded. Now suppose you want to look at the same files, but this time you want the original version in the MR branch modified only by the changes made in response AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-23 Using the Source Commands to MRGs sab970184 and 970054. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the sget screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/17/97 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 13:31:37 Getting a Specified Version of Source Files Generic: g1____________ Branch: mr_ Directory: src/mrmgt____________________________ Source Files: create.c,accept.c____________________ Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: y MR Numbers: sab970184,sab970054__________________ Cutoff Date: _________________ Remove Files?: n Expand ID Keywords?: n Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: sget br=mr mrs=sab970184,sab970054 \ srf=create.c,accept.c kx=n prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) dir=src/mrmgmt (current relative directory) rm=n are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, this command will retrieve the files create.c and accept.c from the src/ mrmgmt directory as they were when they were first added to generic g1, except that all the changes made to the files in response to MRGs sab970184 and sab970054 will also be included. ID keywords will not be expanded. Next suppose you want to look at the same files, but this time you want the original version in the MR branch modified only by those changes made in response to MRGs sab970184 and 970054 by a specified date. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the sget screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-24 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Copies of Source Files logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/17/97 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 13:31:37 Getting a Specified Version of Source Files Generic: g1____________ Branch: mr_ Directory: src/mrmgt____________________________ Source Files: create.c,accept.c____________________ Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: y MR Numbers: sab970184,sab970054__________________ Cutoff Date: 06/08/97 13:08:00 Remove Files?: n Expand ID Keywords?: n Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: sget br=mr mrs=sab970184,sab970054 brdt="02/03/97 \ 13:08:00" srf=create.c,accept.c kx=n\ prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) dir=src/mrmgmt (current relative directory) rm=n are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, this command retrieves the files create.c and accept.c from the src/ mrmgmt directory as they were when they were first added to generic g1, except that all changes made to these files in response to MRGs sab970184 and sab970054 before February 3, 1997 at 1:08 p.m. are included. SBCS/SCCS ID keywords are not expanded. Now suppose you want to retrieve the latest version of a file (create.c) from the official branch. This version includes all changes made in response to approved MRGs. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the sget screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-25 Using the Source Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/17/97 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 13:31:37 Getting a Specified Version of Source Files Generic: g1____________ Branch: ofc Directory: src/mrmgt____________________________ Source Files: create.c,____________________________ Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: y MR Numbers: _____________________________________ Cutoff Date: _________________ Remove Files?: n Expand ID Keywords?: y Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: sget srf=create.c prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) br=ofc dir=src/mrmgmt (current relative directory) kx=y rm=n are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, the version of the file create.c from directory src/mrmgmt that will be copied to the user’s directory will contain all the changes made in response to approved MRGs in generic g1. SBCS/SCCS ID keywords will be expanded. Finally, suppose you want to retrieve the latest version of the same file (create.c) from the official branch, but this time you want to include changes made in response to unapproved MRGs (sab970072 and sab970043) from the MR AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-26 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Copies of Source Files branch. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the sget screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/17/97 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 13:31:37 Getting a Specified Version of Source Files Generic: g1____________ Branch: ofc Directory: src/mrmgt____________________________ Source Files: create.c,____________________________ Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: y MR Numbers: sab970072,sab970043__________________ Cutoff Date: _________________ Remove Files?: n Expand ID Keywords?: y Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: sget mrs=sab970072,sab970043 srf=create.c prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) br=ofc dir=src/mrmgmt (current relative directory) kx=y rm=n are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, this command will retrieve the file create.c from the src/mrmgmt directory of the Source Database for generic g1 and will copy it to your current directory. The retrieved version will contain the latest version of the file from the official branch as well as the changes made in response to the unapproved MRGs sab970072 and sab970043. ID keywords will be expanded. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-27 Using the Source Commands Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific MRs 5 NOTE: For detailed information about the getversion command, see the getversion manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. Any user can use the getversion command to retrieve copies of all the files that have been changed in response to specific MRs. getversion extracts files from either the official or the unofficial branch and places them in the appropriate directories in the node specified by the user. NOTE: If you populate a node with a large number of files, you can cause the file system to run out of space. Check how much space a populated node (for example, the official node of your generic) uses with the UNIX system command du full_path_to_base_of_populated_node, and check how much space is available in your file system with the UNIX system command df. If you do not have enough space, see your System Administrator. The following example will give an idea of the different output produced by using getversion with various parameters. For brevity, all commands in the example are shown using the Command Line interface, but they can be executed using any interface. 1. Suppose that MRG sab97001 adds three files, file1, file2, and file3, to Sablime for generic g1, and that the MRG has been taken to the approved state. At this point, the versions of the files in both the official and the unofficial branches look like this: file1 f1() { file2 f2() { f3() { line a line l line x line b line m line y line c line n line z } } AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-28 Issue 1.1 file3 November 2000 } Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific 2. Now suppose that, in response to MRG sab970002, the following changes are made to file1 and file2. file1 file2 f1() { f2() { line a LINE 1 line b line l LINE 1 line m line c line n } 3. Changes made in response to sab970002 } Next, the following changes are made to file2 and file3 in response to MRG sab970003. (Assume that no dependency has been established between MRGs sab970003 and sab970002). file2 file3 f2() { Changes made in response to sab970003 f3() { line l line x line m LINE 2 line n line y LINE 2 line z } 4. } If we now issue the getversion command as follows: getversion g=g1 br=ofc prompt=n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-29 Using the Source Commands the following versions of the files are retrieved: file1 file2 f1() { f2() { file3 f3() { line a line l line x line b line m line y line c line n line z } } } because when the mrs parameter is not used, the getversion command retrieves the latest version of all the files in the generic from the specified branch. 5. Now issuing either of the following getversion commands: getversion g=g1 mrs=sab970002 br=ofc prompt=n getversion g=g1 mrs=sab970002 br=mr prompt=n retrieves the following versions of the files: file1 file2 f1() { f2() { line a LINE 1 line b line l LINE 1 line m line c line n } } because when MRGs are specified with the mrs parameter, the getversion command: n retrieves only those files that were changed in response to the MRGs specified n retrieves the changes made in response to the MRGs specified and applies them to the — initial version of the files for br=mr — latest version of the files for br=ofc. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-30 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific 6. Similarly, issuing either of the following getversion commands: getversion g=g1 mrs=sab970002 umrs=sab970003 br=ofc\ prompt=n getversion g=g1 mrs=sab970002 umrs=sab970003 br=mr\ prompt=n retrieves the following versions of the files: file1 file2 f1() { f2() { line a LINE 1 line b line l LINE 1 line m LINE 2 line n line c } } because when MRGs are specified with the mrs and umrs parameters, the getversion command: n retrieves only those files that were changed in response to the MRGs specified in the mrs parameter n retrieves the changes made in response to the MRGs specified in both the parameters and applies them to the — initial version of the files for br=mr — latest version of the files for br=ofc. 7. Therefore, issuing either of the following getversion commands: getversion g=g1 mrs=sab970003 umrs=sab970002 br=ofc\ prompt=n getversion g=g1 mrs=sab970003 umrs=sab970002 br=mr\ prompt=n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-31 Using the Source Commands retrieves the following versions of the files: file2 f2() { file3 f3() { line l LINE 1 line m LINE 2 line n } 8. line x line y LINE 2 line z } while the following getversion commands: getversion g=g1 mrs=sab970002,sab970003 br=ofc\ prompt=n getversion g=g1 mrs=sab970002,sab970003 br=mr\ prompt=n retrieve the following versions of the files: file1 file2 f1() { f2() { line a LINE 1 line b f3() { line l LINE 1 line m LINE 2 line n line c } 9. file3 } line x line y LINE 2 line z } If we now issue the getversion command: getversion g=g1 umrs=sab970002 br=ofc prompt=n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-32 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific the following versions of the files are retrieved: file1 file2 f1() { file3 f2() { f3() { line a LINE 1 line b line l LINE 1 line m line x line c line n line z } line y } } because if br=ofc and MRGs are specified only in the umrs parameter, the getversion command: 10. n retrieves the latest version of all the files from the official branch n applies the changes made in response to the MRGs specified in the umrs parameter. But if we issue the getversion command: getversion g=g1 umrs=sab970002 br=mr prompt=n it produces an error, because if br=mr and no MRGs are specified in the mrs parameter, getversion retrieves the latest version of all the files from the MR branch. (Entering the umrs parameter in this case has no effect and is an error). Now that we have seen how different parameters affect the versions of the files getversion retrieves, we are ready to look at some specific examples. Suppose that you want to retrieve from the MR branch all the files changed by two MRGs (sab970054 and sab970084) and copy them to the node /usr/tpc/sablime5.0. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the getversion screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-33 Using the Source Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime 05/19/97 Source Management System Command 12:06:45 Getting Source Files Associated with Specified MRs Generic: g1____________ Information File: stdout_____________________________ Use Snapshot ID: ______________ MRG Test State: ___________________________________ Branch: mr_ Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: no____ MRs for File Selection: sab970054, sab970084_______________ MRs for Additional Changes: ___________________________________ List of Files Only: n Target Node: /usr/tpc/sablime5.0________________ Get Files Under Directories: ___________________________________ Cutoff Date: _________________ Remove Files?: n Expand ID Keywords?: y New Snapshot ID: ______________ Snapshot Comments: ___________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: getversion br=mr mrs=sab970054,sab970084 \ node=/usr/tpc/sablime5.0 prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) ifile=stdout incldep=no list=n rm=n kx=y are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, any files in generic g1 that have been changed by either MRGs sab970054 or sab970084 will be retrieved and placed in the specified target node in the appropriate relative directory. For example, if the retrieved files are associated with relative path src/include, they are written under the src/include directory of the specified node. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-34 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific The version retrieved will use as a base the file originally added to the generic by addisrc, addgsrc, or primsdb and will add to that all changes (additions, modifications, or deletions) made in response to MRGs sab970054 and sab970084. ID keywords will be expanded in the retrieved files. The information file (in this case, stdout) will look like this: ***** Specified MRs For File Selection ***** sab970054 approved sab970084 approved ***** Specified MRs For Additional Changes ***** ***** Source File(s) And The Corresponding Directories ***** h1 | src/include h2 | src/include h7 | src/include h8 | src/include f1 | src/sys1 f2 | src/sys1 f5 | src/sys2/sub1 f6 | src/sys2/sub1 f7 | src/sys2/sub2 f8 | src/sys2/sub2 f3 | src/sys2 f4 | src/sys2 f10 | src/sys3 f9 | src/sys3 + You have successfully done getversion and populated the node with 14 source file(s). The file-count line is always printed to stderr; it does not appear in the information file if a file other than stdout is specified. Now suppose you want to retrieve from the MR branch all the files changed by MRGs sab970152 and sab970135, include in those files any changes made by MR sab970124, and copy the files to the node /usr/tpc/sablime5.0. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the getversion screen. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-35 Using the Source Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime 05/19/97 Source Management System Command 12:06:45 Getting Source Files Associated with Specified MRs Generic: g2____________ Information File: stdout_____________________________ Use Snapshot ID: ______________ MRG Test State: ___________________________________ Branch: mr_ Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: no____ MRs for File Selection: sab970152, sab970135_______________ MRs for Additional Changes: sab970124__________________________ List of Files Only: n Target Node: /usr/tpc/sablime5.0________________ Get Files Under Directories: ___________________________________ Cutoff Date: _________________ Remove Files?: n Expand ID Keywords?: y New Snapshot ID: ______________ Snapshot Comments: ___________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: getversion g=g2 br=mr mrs=sab970152,sab970135 \ umrs=sab970124 node=/usr/tpc/sablime5.0\ prompt=n The defaults: ifile=stdout incldep=no list=n rm=n kx=y are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, any files in generic g1 that have been changed in response to either MRG sab970152 or sab970135 will be retrieved and placed in the specified target node in the appropriate relative directory. For example, if the retrieved files are associated with relative path src/include in generic g2, they are written under the src/include directory of the specified node. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-36 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific The version retrieved will use as a base the file originally added to the generic by addisrc, addgsrc, or primsdb and will add to that all changes (additions, modifications, or deletions) made in response to MRGs sab970152, sab970135, and sab970124. ID keywords will be expanded in the retrieved files. The information file (in this case, stdout) will look like this: ***** Specified MRs For File Selection ***** sab970152 approved sab970135 approved ***** Specified MRs For Additional Changes ***** sab970124 submitted ***** Source File(s) And The Corresponding Directories ***** h3 | src/include h4 | src/include h7 | src/include h8 | src/include f7 | src/sys2/sub2 f8 | src/sys2/sub2 f13 | src/sys2 f14 | src/sys2 f10 | src/sys3 f9 | src/sys3 + You have successfully done getversion and populated the node with 10 source file(s). The file-count line is always printed to stderr; it does not appear in the information file if a file other than stdout is specified. Now suppose that you do not want to retrieve files, but want to know which files from the MR branch would be retrieved if you asked for the files changed by MRG sab970074. You could do this using the Curses Forms interface by making the following entries on the getversion screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-37 Using the Source Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime 05/19/97 Source Management System Command 12:06:45 Getting Source Files Associated with Specified MRs Generic: g1____________ Information File: stdout_____________________________ Use Snapshot ID: ______________ MRG Test State: ___________________________________ Branch: mr_ Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: no____ MRs for File Selection: sab970074__________________________ MRs for Additional Changes: ___________________________________ List of Files Only: y Target Node: ___________________________________ Get Files Under Directories: ___________________________________ Cutoff Date: _________________ Remove Files?: _ Expand ID Keywords?: _ New Snapshot ID: ______________ Snapshot Comments: ___________________________________ Or, using the Command Line interface, you could enter: getversion br=mr mrs=sab970074 list=y prompt=n The defaults: ifile=stdout incldep=no g=g1 (setup generic) are entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-38 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific In either case, the names of any files that have been changed in response to MRG sab970074 will be listed with their corresponding directories in the information file, as shown below: ***** Specified MRs For File Selection ***** sab970074 approved ***** Specified MRs For Additional Changes ***** ***** Source File(s) And The Corresponding Directories ***** accept.c | src/mrmgmt create.c | src/mrmgmt spawnmr.c | src/mrmgmt + You have successfully done getversion with list option listing 3 file(s). The file-count line is always printed to stderr; it does not appear in the information file if a file other than stdout is specified. Next suppose you want to retrieve all the files from the MR branch that have been changed in response to MRGs sab970102 and sab970103, to include in the files all changes made in response to these two MRGs and MRG sab970131 before January 23, 1997 at 6:45 p.m., and to copy the files retrieved to the node /usr/tpc/ sablime5.0. Moreover, you want to overwrite any existing read-only files. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would do this by making the following entries on the getversion screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-39 Using the Source Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime 05/19/97 Source Management System Command 12:06:45 Getting Source Files Associated with Specified MRs Generic: g2____________ Information File: stdout_____________________________ Use Snapshot ID: ______________ MRG Test State: ___________________________________ Branch: mr_ Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: no____ MRs for File Selection: sab970102, sab970103_______________ MRs for Additional Changes: sab970131__________________________ List of Files Only: n Target Node: /usr/tpc/sablime5.0________________ Get Files Under Directories: ___________________________________ Cutoff Date: 01/23/97 18:45:00 Remove Files?: y Expand ID Keywords?: y New Snapshot ID: ______________ Snapshot Comments: ___________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: getversion g=g2 br=mr mrs=sab970102,sab970103\ umrs=sab970131 brdt=1/23/97 18:45\ node=/usr/tpc/sablime5.0 rm=y prompt=n The defaults: ifile=stdout incldep=no list=n kx=y are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, any files in generic g2 that have been changed in response to either MRG sab970102 or MRG sab970103 will be retrieved and placed in the specified target node in the appropriate relative directory. (Any existing read-only files that match files extracted by this call to getversion will be overwritten.) ID keywords will be expanded. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-40 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific The versions retrieved will use as a base the files as they were when originally added to the generic using addgsrc, addisrc, or primsdb, and will add to that all changes (additions, modifications, or deletions) made before 6:45 p.m., January 23, 1997 in response to MRGs sab970102, sab970103, and sab970131. Now suppose you want to retrieve from the latest official branch version all files from generic g1 that have been changed in response to MRGs sab970054 and sab970084 and you want to include in these files all the changes made in response to these two MRGs and the MRG sab970161. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the getversion screen:. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime 05/19/97 Source Management System Command 12:06:45 Getting Source Files Associated with Specified MRs Generic: g1____________ Information File: stdout_____________________________ Use Snapshot ID: ______________ MRG Test State: ___________________________________ Branch: ofc Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: no____ MRs for File Selection: sab970054,sab970084________________ MRs for Additional Changes: sab970161__________________________ List of Files Only: n Target Node: /usr/tpc/sablime5.0________________ Get Files Under Directories: ___________________________________ Cutoff Date: _________________ Remove Files?: n Expand ID Keywords?: y New Snapshot ID: ______________ Snapshot Comments: ___________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: getversion mrs=sab970054,sab970084 umrs=sab970161 \ node=/usr/tpc/sablime5.0 prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) br=ofc ifile=stdout incldep=no AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-41 Using the Source Commands list=n rm=n kx=y are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, any files that have been changed in response to either sab970054 or sab970084 in generic g1 are retrieved and placed in the specified target node in the appropriate relative path. Files containing all the changes made in response to approved MRGs are used as the basis. All changes (additions, modifications, or deletions) made in response to MRGs sab970054, sab970084, and sab970161 are added. ID keywords are expanded. Now suppose you want to list all the files in the official branch of generic g1 that have been changed in response to MRGs in the test state stpassed. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the getversion screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime 05/19/97 Source Management System Command 12:06:45 Getting Source Files Associated with Specified MRs Generic: g1____________ Information File: stdout_____________________________ Use Snapshot ID: ______________ MRG Test State: stpassed___________________________ Branch: ofc Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: inumrs MRs for File Selection: ___________________________________ MRs for Additional Changes: ___________________________________ List of Files Only: y Target Node: ___________________________________ Get Files Under Directories: ___________________________________ Cutoff Date: _________________ Remove Files?: n Expand ID Keywords?: y New Snapshot ID: ______________ Snapshot Comments: ___________________________________ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-42 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: getversion mrgstate=stpassed\ node=/usr/tpc/sablime5.0 prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) br=ofc ifile=stdout incldep=inumrs list=n rm=n kx=y are entered automatically and need not be typed. All files in generic g1 that have been changed in response to MRGs in the stpassed state are listed in the information file. Depended-upon MRGs not in the stpassed state are automatically included as MRs for Additional Changes : ***** MRs In Given Test State(s) For File Selection ***** sab970243 stpassed ***** Missing Depended-Upon MRs Included In MRs For Additional Changes ***** ***** Source File(s) And The Corresponding Directories ***** nf1433 | src/admin nf1627 | src/admin nf1629 | src/admin nf1648 | src/inforet bf07340.exe | src bf07350.exe | src nf1648 | src + You have successfully done getversion with list option listing 7 file(s). The file-count line is always printed to stderr; it does not appear in the information file if a file other than stdout is specified. Next suppose you want to retrieve the latest version of all the files for generic g1 from the official branch and copy them to the node /usr/tpc/sablime5.0. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the getversion screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-43 Using the Source Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime 05/19/97 Source Management System Command 12:06:45 Getting Source Files Associated with Specified MRs Generic: g1____________ Information File: stdout_____________________________ Use Snapshot ID: ______________ MRG Test State: ___________________________________ Branch: ofc Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: no____ MRs for File Selection: ___________________________________ MRs for Additional Changes: ___________________________________ List of Files Only: n Target Node: /usr/tpc/sablime5.0________________ Get Files Under Directories: ___________________________________ Cutoff Date: _________________ Remove Files?: n Expand ID Keywords?: y New Snapshot ID: ______________ Snapshot Comments: ___________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: getversion node=/usr/tpc/sablime5.0 prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) br=ofc ifile=stdout incldep=no list=n rm=n kx=y are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, the latest version of all files in the official branch for generic g1 will be copied to the specified target node. ID keywords will be expanded. Finally, suppose you want to retrieve all the files in generic g3 changed in response to MRG sab970107. Assume that g3 is the setup generic and that sab970107 is in the submitted state and dependent on MRG sab970106. Using AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-44 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific the Curses Forms interface, you might make the following entries on the getversion screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime 05/19/97 Source Management System Command 12:06:45 Getting Source Files Associated with Specified MRs Generic: g3____________ Information File: /tmp/myfile________________________ Use Snapshot ID: ______________ MRG Test State: ___________________________________ Branch: ofc Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs: no____ MRs for File Selection: sab970107__________________________ MRs for Additional Changes: ___________________________________ List of Files Only: n Target Node: /u1/user/g1________________________ Get Files Under Directories: ___________________________________ Cutoff Date: _________________ Remove Files?: y Expand ID Keywords?: y New Snapshot ID: ______________ Snapshot Comments: ___________________________________ Sablime will detect the dependency of sab970107 on sab970106. Because you specified no in the Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs field, Sablime has no AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-45 Using the Source Commands default action to take on this required MR. Consequently, you are placed in a temporary file in your favorite editor with a message like the following: YOU ARE IN YOUR FAVORITE EDITOR The following missing depended-upon MRs (shown with their current MRG status) are required. You must include each of these MRs either in the MRs for Additional Changes field (initial ’A’) or in the MRs for File Selection field (initial ’F’). In the following lines, ONLY change the first character from ’A’ to ’F’, if you so desire. IT IS NOT NECESSARY TO DELETE THE ABOVE LINES BEFORE YOU EXIT THE EDITOR. A sab970106 stpassed At this point, you must choose to include sab970106 in the MRs for Additional Changes field (the default; indicated by an A in the first column), or in the MRs for File Selection field (indicated by an F in the first column). If your choice is the default, write and quit the editor without making any changes. If you prefer to include the MRG in MRs for File Selection, change the A to an F; then write and quit the editor. Any other change will cause an error. After you write and quit, you are returned to the List of Files Only field. When processing is complete, the information file (/tmp/myfile) contains the following: ***** Specified MRs For File Selection ***** sab970107 submitted ***** Specified MRs For Additional Changes ***** ***** Missing Depended-Upon MRs Included In MRs For Additional Changes ***** sab970106 stpassed ***** Source File(s) And The Corresponding Directories ***** h1 | src/include f5 | src/sys2/sub1 f7 | src/sys2/sub2 f3 | src/sys2 f4 | src/sys2 Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-46 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Getting Copies of Source Files Associated with Specific getversion ifile=/tmp/myfile mrs=sab970107 rm=y\ prompt=n The defaults: g=g1 (setup generic) br=ofc incldep=no list=n kx=y are entered automatically and need not be typed. Because there is a missing depended-upon MR, processing terminates and an error message is produced: Err[ 999]: 1 missing depended-upon MRs, see [/tmp/myfile] file. Err[9605]: MR List is missing needed MR for an SBCS file: MR [sab970106]. Err[9999]: Argument errors detected; [getversion] execution terminated. The information file contains the following message: ***** Additional Required Depended-Upon MRs ***** sab970106 stpassed NOTE: Missing depended-upon MRs always produce an error in the Command Line interface unless incldep is set to inmrs or inumrs. As processing takes place, information like that shown below appears on the screen: + Processing the inputted data; please stand by. – All the MS tuples have been retrieved. + List of source files and the corresponding directories: : [filename] | [relative directory] If list=y: + You have successfully done getversion with list option. If list=n: + You have successfully done getversion and populated the node with all the above mentioned source files. + A Master Trace Record has been generated for the Database Administrator. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-47 Using the Source Commands If files are selected by MRG status, information like that shown below appears on the screen: + Processing the inputted data; please stand by. – All the MS and GS tuples have been retrieved. + You have successfully done getversion and populated the node with [number] files. + A Master Trace Record has been generated for the Database Administrator. Printing a Source File Listing 5 NOTE: For detailed information about the srcpr command, see the srcpr manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The srcpr command prints a file listing for non-binary files stored under SCCS. The file, as printed, represents the latest version from the mr branch and includes all changes on the mr branch. When the file is printed, the MRG that last affected a line is prepended to the line. Each line contains only one MRG name; that MRG corresponds to the last MRG that affected the line. If more than one MRG affected a line (i.e., deleted the current line and replaced it with a new line), only the latest MRG used is prepended to the text line. A letter is also shown next to the MRG name. The letter, A, C, or U is used to indicate the current status of the MRG. A is for approved MRG, C is for closed MRG, and U is for unapproved MRG. If the file is a common file, a message that includes a list of the generics for which the file is common is produced. NOTE: srcpr does not work for binary files and non-binary files stored under SBCS. An attempt to run srcpr on a file stored under SBCS yields a message like the following: Cannot run srcpr for file [filename] stored under SBCS. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-48 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Printing a Source File Listing As an example, suppose you want to print a listing of the source file IProgram.c on the screen with the MR numbers of the last MRs to affect each line. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the srcpr screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 06/02/97 11:02:37 Printing Source Files With MR Numbers Generic: v5.0__________ Directory: /src/lib/libCOM_________________________________________________ Source Files: IProgram.c______________________________________________________ Output File: stdout__________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: srcpr srf=IProgram.c prompt=n The defaults: g=v5.0 (setup generic) dir=src/lib/libCOM (current directory) ofile=stdout are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a listing is displayed showing the number of the last MR to have affected each line of the file IProgram.c. The following listing is partial output from the srcpr command on IProgram.c. sab900163 C// SYNOPSIS sab900163 C// ======== sab900163 C// sab920059 A// void IProgram(argv, argc, nopts) sab920059 A// void IProgram(argv, argc, nopts, call_isgen) sab900163 C// sab920059 A// char **argv The arguments passed to\ the command sab920059 A// int argc The argument count sab920059 A// int nopts No. of Positional\ Parameters sab920059 A// int call_isgen An OPTIONAL argument\ (default = TRUE). sab920193 A// This argument is used to determine\ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-49 Using the Source Commands whether sab920193 A// generic validation is to be done or not. sab920059 A// If this argument is not given or FALSE sab920193 A// then generic validation will NOT be\ sab900163 C// sab900163 C// RETURNS Making Source Files Common done. 5 NOTE: For detailed information about the common command, see the common manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The common command is used by the Source Administrator to declare a file common across two or more generics. When a file is common, any file manipulation (edget, unedget, edput, or unedput) to that file in one generic affects the other generics as well. Any MR used to touch a common file must be accepted and assigned to the same developer or group of developers in all the generics for which the file is common before the common file can be touched. To be declared common, the file must exist in all the specified generics. The latest MR branch of the file, the language type, and the owner must be the same for all the generics. Files in different relative directories in different generics can be declared common only if the files were added with version 3.0.2 or later of addisrc. Files that have already been declared common in one set of generics can also be declared common in another set of generics. If you plan to declare files common, you can do so while running the addgsrc or primsdb command. NOTE: You must have used addgsrc or primsdb (with the addgsrc option) to add a file to another generic if you want to make the file common across generics. Another file added with addisrc, even if the name and contents are identical, cannot be made common. This is because common files are stored in the same physical directory in the Source Database. addisrc establishes a unique file in a unique physical directory in the Source Database. Subsequently, when that file is added into other generics using addgsrc, the information for these other generics is appended to the same physical file in the Source Database. Therefore, this file can be made common among the generics for which it was added by addgsrc, but it cannot be made common with any other file added using another addisrc. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-50 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Making Source Files Common A message is created listing the generics for which the file has been declared common. For example, suppose you want to make a file common across two generics, g1 and g2. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the common screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 03/04/97 14:43:15 Declaring Files as Common Generics: g1,g2___________________________________________________________ Directory: src/mrmgmt______________________________________________________ Source Files: create.c________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: common g=g1,g2 dir=src/mrmgmt srf=create.c prompt=n In either case, the file create.c in the directory src/mrmgmt will be made common in generics g1 and g2. Any edget, unedget, edput or unedput command issued in either generic g1 or g2 for the file create.c affects the version of the file used by both the generics. Now suppose you want to make a file common across three generics (g1, g2, and g3), and the file exists in a different relative directory in one of the generics (g1). Using the Curses Forms interface, you might make the following entries on the common screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 03/04/97 16:15:06 Declaring Files as Common Generics: g1,g2,g3________________________________________________________ Directory: src/mrmgmt,src/newsys/mgmnt_____________________________________ Source Files: create.c________________________________________________________ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-51 Using the Source Commands Or, using the Command Line interface, you might enter: common g=g1,g2,g3 dir=src/mrmgmt,src/newsys/mgmnt \ srf=create.c prompt=n In either case, the file create.c, which is in directory src/mrmgmt in generic g1 and directory src/newsys/mgmnt in generics g2 and g3, is declared common for all three generics. Any edget, unedget, edput or unedput to create.c affects the file in all three generics. Note that only two directories were specified. This is because common assumes that the last directory named applies to any remaining generics. Making Source Files Not Common 5 NOTE: For detailed information about the uncommon command, see the uncommon manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The uncommon command is used by the Source Administrator to change common files to independent, non-common files. Thereafter, all edget, edput, unedget and unedput commands that refer to the file for one of the specified generics are applied only to the specified generic. To be declared uncommon, the source file must exist and be free (no current edget) in all specified generics. For each generic affected by this command, an informative message is produced listing the generics to which the file remains common. For example, suppose that the file create.c has been designated common in generics g1 and g2, and you want to remove the common designation from the source files so that changes made to the file in one generic will not be reflected in the other. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the uncommon screen: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-52 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Making Source Files Not Common logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Source Management System Command 06/03/97 07:46:27 Declaring Files as No Longer Common Generics: g1,g2___________________________________________________________ Directory: src/mrmgmt______________________________________________________ Source Files: create.c________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: uncommon g=g1,g2 srf=create.c prompt=n The default: dir=src/mrmgmt (current directory) is entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, the file create.c in relative directory src/mrmgmt in generics g1 and g2 is no longer common in those generics. It is now possible to make changes to the file in g2 while leaving the file unchanged in g1. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 5-53 Using the Source Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 5-54 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Contents 6 Using the Report Commands 1 n Using the query Command 3 n Using the report Command 9 Report Classes 11 Selection Fields 12 Sort Fields 13 Output File 14 Producing MR Reports 14 Standard Reports 15 Custom Report 16 Extract File 16 Management Reports 16 Producing a SHORT Report 19 Producing a LONG Report 22 Producing an ALL Report 25 Producing a bydeveloper Report 30 Producing a CUSTOM Report 33 Producing a pie Report 35 Producing a bar Report 38 Producing a stat Report 41 Producing a bycategory Report 44 Producing a byclass Report 49 Producing a byseverity Report 53 Producing a bysite Report 60 Producing a bystatus Report 64 Producing a bysystem Report 69 Producing a bytype Report 73 Producing External MR Reports 78 Standard Reports 78 Extract File 78 Producing a complete Report 79 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 i Contents Producing an emr80 Report 81 Producing an emr_html Report 83 Producing an External MR Extract File 84 Producing Group Reports 85 Standard Reports 85 Extract File 85 Producing a Group Summary Report 86 Producing a Group Aggregate Report 88 Producing a Group Extract File 91 Producing Source Reports 92 Standard Report 92 Extract File 92 Producing a Source edgotten Report: Example 1 93 Producing a Source edgotten Report: Example 2 95 Producing a Source Extract File 101 Producing Cross-Reference Reports 102 Internal Processing 102 Standard Report 103 Extract File 103 Producing a Cross-Reference Report: Example 1 105 Producing a Cross-Reference Report: Example 2 114 Producing a Cross-Reference Extract File n n Using the ssql Command 124 Compound ssql Statements 127 Nested ssql Statements 128 ssql Examples 130 Using the ptsaudit Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page ii Issue 1.1 121 November 2000 137 Using the Report Commands 6 To get the information you need from the Sablime databases effectively, you must understand the structure of the databases. Each Sablime relation is a directory. In each relation, there are tuples (files), each of which has a two-character name. Each tuple contains records (lines) that are made up of fields and, in some cases, subfields. Fields are separated by semicolons; subfields are separated by commas. Fields with subfields are not available for query. Appendix A provides a complete listing of all the database relations, showing the name of each field in the relation, its position within the relation, the keyword and screen label that appear in the command menus, and whether the field can be used as a sort field, can be printed on certain reports, or allows you to specify a range of values. The Sablime system offers four commands that you can use to extract information from the Sablime databases: query, report, and ssql, and ptsaudit. Each of these commands approaches the organization of information in a different way to give you maximum flexibility. In choosing the right command for the information you need, take into consideration the capabilities of each command. query: n retrieves information from a single relation n uses selection criteria from that relation only n prints unformatted output only n prints an entire record n can be run using the Command Line interface or the Curses Forms interface AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-1 Using the Report Commands report: n retrieves information from multiple relations n uses selection criteria from any relation n prints formatted and unformatted output n prints an entire record (for unformatted output) n can be run using the Command Line interface, the Curses Forms interface, or the GUI NOTE: The GUI only provides access to the MR Reports (see the section Producing MR Reports later in this chapter.) ssql: n retrieves information from a single relation n uses selection criteria from any relation (nested queries) n prints unformatted output only n prints selected fields in a record n based on standard Structured Query Language (SQL) n can only be run from the UNIX system shell prompt NOTE: The descriptions of the query and report commands in this chapter assume you are using the Curses Forms interface, but the examples employ both the Command Line interface and the Curses Forms interface. ptsaudit: n retrieves information from multiple relations n uses selection criteria from many relations n prints formatted output only n prints selected fields in a record n can only be run from the UNIX system shell prompt AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-2 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the query Command Using the query Command 6 NOTE: For detailed information about the query command, see the query manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The query command selects records from a single relation that meet the given specifications and prints them on the screen or writes them to a file. The query command works even if the databases are stopped, although it may produce inaccurate results if changes are being made in the databases. The query command can be used in either the Curses Forms interface or the Command Line interface. The first query screen, shown in Figure 6-1, allows you to specify the relation from which you would like to retrieve data and the specific fields on which to select. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 07/08/97 09:42:50 Query Database for Records that meet given Specifications Relation: ____ Database: ________ Hash: _ Sort Records: _ Print all Records: _ Selection Fields: _________________________________________________________ Output File: _________________________________________________________ Figure 6-1. query First Screen If you specify Selection Fields fields, one or more Selection Fields screens are generated. The first 16 fields specified appear on the first selection screen, the next 16 appear on the second, etc. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-3 Using the Report Commands The outline of the second screen is shown in Figure 6-2. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 07/08/97 09:42:50 screen label 1: ___________________________________________________________ screen label 2: ___________________________________________________________ . . . screen label 15: ___________________________________________________________ screen label 16: ___________________________________________________________ Figure 6-2. query Second Screen If no selection criteria are specified on the Selection Fields screens, all the tuples are printed. Selection criteria specified for a single field (i.e., on the same line) are treated as logical or criteria, i.e., records matching any one of the criteria are selected. Selection criteria specified for multiple fields (i.e., on separate lines) are treated as logical and criteria, i.e., records matching all the criteria are selected. For efficiency reasons, FTD (Field Tracking Data) relation records of the query command itself are designated in the database by the fictitious command name Qrelation_name (where relation_name is the relation name in lower-case letters), i.e., Qpts. In the Command Line interface, query output is sent to stdout unless ofile is specified on the command line. Processing messages are sent to stderr. You can separate the two by specifying an ofile and redirecting stderr as follows: query relation=GRPM hash=y all=y ofile=myfile prompt=n \ 2> /tmp/query.processing The three examples below are intended to give some idea of the range of queries that can be made using the query command. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-4 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the query Command Example 1 6 Suppose that you want to sort and print all the records from the GRPM relation in the Active Database and that you want to include the hashed tuple name as the first field of each record. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the query screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 07/08/97 09:42:50 Query Database for Records that meet given Specifications Relation: GRPM Database: active__ Hash: y Sort Records: y Print all Records: y Selection Fields: _________________________________________________________ Output File: stdout___________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: query relation=GRPM hash=y all=y prompt=n The defaults: db=active sort=y ofile=stdout are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, all tuples in the GRPM relation in the Active Database will be displayed on the screen sorted by group name. The relation name and the twocharacter tuple name will be shown at the beginning of each record. The display will look similar to the one below. GRPM/ap:wina+scott;scott GRPM/ap:wina+scott;wina GRPM/ac:xteam;dbk GRPM/ac:xteam;tai GRPM/ac:xteam;twh AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-5 Using the Report Commands Example 2 6 Now suppose you want to sort and print the tuples from the MR relation in the Active Database, selecting MRs of severities 2 or 3 for creators dgf or lrp and sending the results to a file. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the query screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 07/08/97 09:42:50 Query Database for Records that meet given Specifications Relation: MR__ Database: active__ Hash: n Sort Records: y Print all Records: n Selection Fields: sev,cid__________________________________________________ Output File: query.MR_________________________________________________ Because you specified Selection Fields fields, the following selection screen will be displayed for you to make your selections: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 07/08/97 09:42:59 Specify MR Relation Field Values Severity: 2,3______________________________________________________ MR Creator: dgf,lrp__________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: query relation=MR sev=2,3 cid=dgf,lrp ofile=query.MR prompt=n The defaults: db=active hash=n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-6 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the query Command sort=y all=n select=sev,cid are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, all MR records for MRs created by dgf or by lrp in the Active Database with a severity of either 2 or 3 will be sent to a file named query.MR in the user’s current directory. The file will contain data like the following: sab970000;dgf;killed;;neednewname;;3;;;duplicate;02/25/97 \ 15:43:39;03/05/97 14:32:17;dgf;;;;;;; sab970001;dgf;completed;;programcausesloop;;2;;;02/25/97 \ 16:07:59;;;;;;;;; sab970002;lrp;active;;screenfieldsdonotalign;;2;;;;02/25/97 \ 16:10:34;;;;;;;;; Example 3 6 Finally, suppose that you want to print all the records from the MG relation in the Active Database that have the developer field as wjb and a submit date between February 1 and March 16, 1997 and that you want to send the results to a file named query.febmar. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the query screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 03/16/97 15:17:49 Query Database for Records that meet given Specifications Relation: MG__ Database: active__ Hash: n Sort Records: y Print all Records: n Selection Fields: dev,submtdt______________________________________________ Output File: query.febmar_____________________________________________ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-7 Using the Report Commands Because you specified Selection Fields fields, the following selection screen will be displayed for you to make your selections: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 03/16/97 15:21:23 Specify MG Relation Field Values Developer(Group): wjb_____________________________________________ Submit Date: 02/01/97-03/16/97_______________________________ As processing takes place, information like that shown below will appear on the screen: + Processing the inputted data; please stand by! – A temporary file of selected records is created. – The temporary file is sorted. (Any records selected will be listed here if printed to the screen.) + A query output of [#] selected records is generated. + The output of your query has been generated + A Master Trace record has been generated for the Database Administrator Assume that, using the Command Line interface, you want to send the processing messages to /dev/null. Then you would enter: query relation=MG dev=wjb submtdt=02/01/97-03/16/97 \ ofile=query.febmar prompt=n 2> /dev/null The defaults: db=active hash=n sort=y all=n are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, all records in the MR relation in the Active Database with a creation date between February 1 and March 16 will be displayed on the screen sorted by MR Number. The display will look similar to the one below. sab970347;v5.0;submitted;02/24/97 14:55:37;wjb;3;;\ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-8 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command as_proposed;;30;document;modification;0;;n;;;;;3.1;;\ development;enhancement;enhancement;0.12;;0;0;0;0;0;\ none;;;;;0;;;;;;;08/04/97 11:22:50;08/04/97 \ 11:22:50;02/24/97 14:55:37;;;;;;;oversight;\ project_documentation;;;;;; sab970363;v5.0;submitted;03/07/97 11:14:11;wjb;3;;\ as_proposed;;30;document;modification;0;;n;;;figure;\ correctness(sw);3.1;;;oversight;;0.12;;0;0;0;0;0;\ none;;;;;0;;;;;;;08/24/97 15:16:49;08/24/97 \ 15:16:49;03/07/97 11:14:11;;;;;;;oversight;\ oversight;;;;;; sab970377;v5.0;submitted;02/28/97 15:31:28;wjb;3;;\ as_proposed;;30;document;enhancement;0;;n;;;figure;\ correctness(sw);3.1;;;enhancement;enhancement;0.25;;\ 0;0;0;0;0;none;;;;;0;;;;;;;09/02/97 16:59:28;\ 09/02/97 16:59:53;02/28/97 15:31:28;;;;;;;\ enhancement;enhancement;;;;;; sab970525;v4.2;submitted;03/04/97 10:09:37;wjb;3;;\ as_proposed;;30;document;modification;0;;n;;;text;;\ 3.1;;;enhancement;enhancement;0.25;;0;0;0;0;0;none;\ ;;;;0;;;;;;;11/10/97 19:56:21;11/10/97 19:56:21;\ 03/04/97 10:09:37;;;;;;;enhancement;enhancement;;;;;; sab970597;v5.0;submitted;02/28/97 15:46:39;wjb;3;;\ other;;30;document;modification;0;;n;;;text;\ readability(sw);3.1;;;enhancement;enhancement;0.00;\ ;0;0;0;0;0;none;;;;;0;;;;;;;12/07/97 15:38:30;\ 12/07/97 15:38:30;02/28/97 15:46:39;;;;;;;\ enhancement;enhancement;;;;;; Using the report Command 6 NOTE: For detailed information about the report command, see the report manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The report command allows you to retrieve information from multiple relations using selection criteria from any relation. You may use either the Curses Forms interface or the Command Line interface. The report command works even if the databases are stopped, although it may produce inaccurate results if the databases are being changed. The report command allows you to produce reports based on a wide variety of data and in a variety of formats for MRs, external MRs, groups, or source files entered for your product. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-9 Using the Report Commands The first report screen, shown in Figure 6-3, allows you to specify the report that you want to produce. Further, the screen allows you to specify fields for which selection and sorting should occur. If you specify Selection Fields or Sort Fields, one or more additional screens are generated after you confirm the first screen. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/09/97 07:42:51 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: ______________ Name of Report: ______________ Database: _____________ Selection Fields: ________________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: ________________________________________________________ Figure 6-3. report First Screen AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-10 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command The outline of the second screen is shown in Figure 6-4. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/09/97 07:48:22 Selection Fields for report screen label 1: _____________________________________________________________ screen label 2: _____________________________________________________________ . . . screen label 15: _____________________________________________________________ screen label 16: _____________________________________________________________ Figure 6-4. report Second Screen Report Classes 6 Sablime allows you to produce five classes of reports: n MR reports provide information about MRs created for your product. You can produce fifteen types of reports with MR information, including custom reports, summary reports, and management reports. You can also produce an extract_file that can be used with your own report generator. n External_MR reports provide information about MRs that have a link with an external project. (See chapter 7, Using the External MR Communication Commands, for more information about communication with an external project.) You can produce four types of reports with information about external MRs. You can also produce an extract_file that can be used with your own report generator. n group reports provide information about the groups that are defined for your product. You can produce two types of reports on groups and group members. You can also produce an extract_file that can be used with your own report generator. n source reports provide information on files under Sablime control. You can produce one standard report with file information. You can also produce an extract_file that can be used with your own report generator. n mrVSfile Cross-Reference reports provide information jointly on MRs and files under Sablime control. The reports highlight the association of userspecified MRs and their dependencies with files. You can produce one standard report with MR/file relationships. You can also produce an extract_file that can be used with your own report generator. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-11 Using the Report Commands For each report class, the unformatted extract_file is a series of semicolonseparated fields. The extract_file contains all the information from which the other report types are derived. Selection Fields 6 For any report, you can specify selection criteria by which records are chosen. The Selection Fields menu provides a list of all selection criteria applicable to the Class of Report chosen. If you select Selection Fields fields, Selection Fields input screens containing a maximum of sixteen input fields are generated. The first 16 fields specified appear on the first selection screen, the next 16 appear on the second, etc. These values represent the values provided by Sablime. They are subject to project customization. If these keywords and/or labels are not present at execution time, speak to your Sablime Database Administrator. Leaving the Selection Fields field blank produces a report that includes all existing records for the specified report class. If the Display flag field of the FTD (Field Tracking Data) relation is n for a particular keyword, the keyword is excluded from the Selection Fields menu and thus does not show up as a field on the Selection Fields screen. (For detailed information about the FTD relation, see Appendix A, Sablime Database Relations and their Fields.) You can specify any number of fields on which MRs, groups, or files are selected (e.g., Generic: g1; Originator:diane). MRs, groups, or files having data that match all the selections are included in the report (i.e., MRs in generic g1 originated by diane). You can specify more than one item on a field line (e.g., Release Det.: 4.0, 4.2, 4.3). All MRs, groups, or files matching any one of these items are included in the report (i.e., all MRs in release 4.0, in 4.2, or in 4.3). NOTE: Menus are not displayed for Selection Criteria fields unless your Sablime Administrator has customized your version of Sablime to display them. Be sure that selections are entered exactly as they were used when the data was originally created. If menus are displayed, you cannot enter names of groups in Selection Criteria fields. NOTE: Your Sablime Administrator must ensure that the items that appear in popup menus for selected criteria are complete (i.e., include formerly used fields). AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-12 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Sort Fields 6 For the following reports in the MR class, you can specify the fields by which the records are sorted: ALL, LONG, SHORT, CUSTOM, group, and source, and the mrVSfile extract_file. Once you have specified the sort data in the Sort Fields field, Sablime sorts the information, invoking /bin/sort. The default sort fields for sortable reports are shown in Table 6-1. Table 6-1. Default Sort Fields for Sortable Reports Report Class/Type Default Sort Fields MR ALL LONG SHORT CUSTOM extract_file MR Number group extract_file Group Name source extract_file Generic, Directory, File mrVSfile extract_file MR, Directory, File NOTE: The Sun sort (1) utility imposes a limit of nine sort keys; no such limitation has been found on other platforms. All other reports are not sortable, i.e., sort fields are predetermined. Table 6-2 contains the predetermined sort field information. Table 6-2. Predetermined Sort Fields Report Type Predetermined Sort Fields MR bycategory Product, Generic, Category, MRG Severity, MR # MR byclass Product, Generic, Class, MRG Severity, MR # MR bydeveloper Product, Generic, Developer, MRG Severity, MR # MR byseverity Product, Generic, MRG Severity, MR # MR bysite Product, Generic, Site, MRG Severity, MR # MR bystatus Product, Generic, MRG Status, MRG Severity, MR # AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-13 Using the Report Commands Table 6-2. Predetermined Sort Fields—Continued Report Type Predetermined Sort Fields MR bysystem Product, Generic, System, MRG Severity, MR # MR bytype Product, Generic, Type, MRG Severity, MR # External_MR emr80 emr132 complete External Project, External Product, Severity, MR # External_MR extract_file MR Number group summary Group Name group aggregate Group Name, Member source edgotten Generic, Directory, Source File mrVSfile xref MR, Directory, Source File Output File 6 The default for the Output File field for all but management reports is stdout; the default for management reports is name.process_ID, where name is pie, bar, or stat and process_ID is the UNIX system process ID number. If you do wish to send the management report output to stdout, you can specify “stdout” as the output file name. Otherwise, you can specify a file in the local directory or give the full path to a file in another directory. If the specified file already exists: n In the Curses Forms interface, a warning appears at the bottom of the screen n Using the Command Line interface, the file is overwritten with no warning. Producing MR Reports 6 NOTE: The MR reports may be run using the GUI. To produce reports for MRs, select the MR report class from the Class of Report field on the first report screen. You can produce a number of standard reports, a CUSTOM report, or an extract_file. If you specify Selection Fields fields, additional screens are generated to allow you to produce a report with records selected by specified criteria. If you do not specify Selection Fields fields, an MR report including all MR records is produced when the first screen is confirmed or, in special cases, after the screens for Management Format data are confirmed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-14 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Standard Reports 6 Fourteen standard MR reports are available. The formats for each of the reports are predesigned and standard. The reports produced in a management format (pie, bar, and stat) are created differently from those in text formats. Special screens are displayed for these reports. See Management Reports below for information and the related screens. Table 6-3 lists the the name and format of each of the standard reports. Table 6-3. MR report Formats Report Format ALL block LONG block SHORT block bycategory 132 column byclass 132 column bydeveloper 80 column byseverity 132 column bysite 132 column bystatus 80 column bysystem 80 column bytype 132 column pie (Management) graphic bar (Management) graphic stat (Management) graphic NOTE: You can produce management reports only if the UNIX system grap (1) command is on your machine. grap (1) is part of the Documenter’s Workbench* (DWB) Release 3.0 and above. See your System or Sablime Administrator for more information. NOTE: Be sure to use landscape mode when running wide reports. * Documenter’s Workbench is a registered trademark of Novell, Inc. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-15 Using the Report Commands Custom Report 6 When you select CUSTOM from the MR report Name of Report menu, you can specify the fields to be printed on the report. A menu is displayed showing the fields that can be specified for the report. Sablime writes those fields specified in the Print Fields menu and sends the results to the file named in the Output File field from the first screen. See Producing a CUSTOM Report for more information about creating a CUSTOM report. Extract File 6 When you select extract_file from the MR report Name of Report menu, instead of producing a formatted, formal report, a file consisting of 97 semicolonseparated fields selected from the MG, MRX, MR, and ORG relations of the Sablime database is produced. Management Reports 6 NOTE: The environment variable sabMFR must be set to /usr/bin/grap for you to run the management reports. See your Sablime Administrator if you are unable to run the reports. When you select pie, bar, or stat from the MR report Name of Report menu, you produce a management report that can be printed in graphic format using the UNIX system pic or tbl program with troff processing. Use the -mm option for all three reports. For the pie and bar reports, be sure that your local print command includes the -p/-pic option for the pic preprocessor; for the stat chart, be sure that your local print command includes the -t/-tbl option for the tbl preprocessor. See your Sablime or System Administrator for the appropriate print command to use with your machine. A special Print Fields menu is displayed for management reports. You can select one print field for pie or bar charts and one or two print fields for stat reports. No sort fields are available for management reports. When you select one of the management reports, an additional screen is displayed after all allowed selections have been made. This screen is different for each of the three management report formats and allows you to specify a title, labels, and footnotes appropriate to the report you are producing. See Figure 6-5 through Figure 6-7 for samples of these screens. Output from management reports is in troff format. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-16 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Management Report Screens 6 If you have selected a management report (pie, bar, or stat), the appropriate additional screen is displayed after the first screen is confirmed. The three screens are shown in this section. If you select the pie report, the screen shown in Figure 6-5 is displayed. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/09/97 11:15:12 Management Format Report Information Pie Chart Title: ________________________________________________________ Footnote: ________________________________________________________ Would you like field labels in the chart instead of a legend: _ Figure 6-5. pie report Screen AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-17 Using the Report Commands If you select the bar report, the screen shown in Figure 6-6 is displayed. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/09/97 11:18:04 Management Format Report Information Bar Graph Title: ________________________________________________________ X-Axis Title: ________________________________________________________ Footnote: ________________________________________________________ Would you like field labels in the chart instead of a legend: _ Figure 6-6. bar report Screen If you select the stat report, the screen shown in Figure 6-7 is displayed. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/09/97 11:27:12 Management Format Report Information Stat Chart Title: ________________________________________________________ Footnote: ________________________________________________________ Would you like field labels in the chart instead of a legend: _ Figure 6-7. stat report Screen AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-18 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Producing a SHORT Report 6 To produce a SHORT report for all MRs in the Active Database sorted on MR Number and display the report on the screen, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/19/97 11:43:56 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: SHORT_________ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: ________________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: stdout__________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR rname=SHORT db=active ofile=stdout are entered automatically and need not be typed. A standard SHORT report is produced for all MRs in the Active Database. A sample report appears below. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-19 Using the Report Commands logid: ral effid: nmake Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command 05/19/97 15:29:09 ------------------------- REPORT FOR MR nmake970000 ------------------------MR Status: active MR Severity: 3 Product: nmake Release Det.: not_applicable System: all Phase Det.: general_availability Subsystem: not_applicable Module: Org. Date: 01/17/97 Create Date: 01/17/97 09:44:46 Study Dev: Due Date: Abstract: to populate the nmake databases with source ----------- GENERIC INFORMATION FOR MR nmake970000 ----------- Generic: nmake3.0 Type: initialization SubType: new_source MRG Severity: 3 Due Date: Class: software SubClass: MRG Status: approved Developer: arg_mar Chg. Date: 01/19/97 11:56:18 ------------------------- REPORT FOR MR nmake970001 ------------------------MR Status: active MR Severity: 3 Product: nmake Release Det.: not_applicable System: none Phase Det.: unit_test Subsystem: not_applicable Module: Org. Date: 01/21/97 Create Date: 01/21/97 13:42:43 Study Dev: Due Date: Abstract: to add more files under product nmake generic nmake3.0 ----------- GENERIC INFORMATION FOR MR nmake970001 ----------- Generic: nmake3.0 Type: initialization SubType: MRG Severity: 3 Due Date: Class: software SubClass: MRG Status: approved Developer: Sablime Chg. Date: 01/21/97 17:26:14 ------------------------- REPORT FOR MR nmake970002 ------------------------MR Status: active MR Severity: 3 Product: nmake Release Det.: not_applicable System: none Phase Det.: system_test Subsystem: not_applicable Module: Org. Date: 01/31/97 Create Date: 01/31/97 13:23:04 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-20 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Study Dev: Due Date: Abstract: customer requests to have error message list and explanation ----------- GENERIC INFORMATION FOR MR nmake970002 ----------- Generic: nmake3.0 Class: document Type: enhancement SubClass: text SubType: readability(sw) MRG Status: assigned MRG Severity: 3 Developer: ocg Due Date: Chg. Date: 01/31/97 13:23:05 ------------------------- REPORT FOR MR nmake970003 ------------------------MR Status: active MR Severity: 3 Product: nmake Release Det.: not_applicable System: none Phase Det.: system_test Subsystem: not_applicable Module: Org. Date: 01/31/97 Create Date: 01/31/97 13:25:53 Study Dev: Due Date: Abstract: customers request to include more complicated examples ----------- GENERIC INFORMATION FOR MR nmake970003 ----------- Generic: nmake3.0 Class: document Type: enhancement SubClass: text SubType: readability(sw) MRG Status: assigned MRG Severity: 3 Developer: ocg Due Date: Chg. Date: 01/31/97 13:25:53 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-21 Using the Report Commands Producing a LONG Report 6 To produce a LONG report for specified MRs in specified generics and save the report to a file named report, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:nmake Information Retrieval System Command 05/19/97 15:35:51 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: LONG__________ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: mr,g____________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: report__________________________________________________ Because you specified Selection Fields fields, the following screen is displayed. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:nmake Information Retrieval System Command 05/19/97 15:37:22 Selection Fields for Report MR Number: nmake970007_____________________________________________ Generic: nmake3.0________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=LONG ofile=report mr=nmake970007 g=nmake3.0 prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR db=active AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-22 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command are entered automatically and need not be typed. A LONG report will be produced in a file named report for MR number nmake970007 in generic nmake3.0. A sample report appears below. logid: ral effid: nmake Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command 05/19/97 15:40:11 ------------------------- REPORT FOR MR nmake970007 ------------------------MR Status: active Duplicate MR: MR Severity: 3 Product: nmake Release Det.: not_applicable System: none Phase Det.: development Subsystem: not_applicable Category: Module: Spawns: 0 Org. Date: 02/02/97 Create Date: 02/02/97 16:12:03 Site: not_applicable Reason Code: Reqd. Date: Compl. Date: Originator: ftd Creator: nmake Closer: Est. Effort: Study Dev: Due Date: Study Effort: Abstract: delta new man pages to 3.0 Description: This mr will be used to delta man page fixes to makerules, nmake, and cpp. Reason Deferred: None. MR Proposed Solution: None. ----------- GENERIC INFORMATION FOR MR nmake970007 ----------- Generic: nmake3.0 Class: document Type: modification SubClass: text SubType: readability(sw) MRG Status: submitted Duplicate MR: MRG Severity: 3 MRG Spawns: 0 Developer: pha Due Date: Chg. Date: 03/31/97 13:55:48 MG Reason CD: as_proposed Com Id: Ext. MR Flag: n In-Process Metrics Information Rel. Intro.: not_applicable Root Cause: project_documentation Phase Intro.: RC Subcat: Op Det Phase: inspection Fault Type: Nondet Cause: NC Subcat: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-23 Using the Report Commands Actual Effort Staff Days ---------------------Study: 0.00 Assignee: 0.00 Test Team 1: 0.00 Test Team 2: 0.00 Test Team 3: 0.00 Test Team 4: 0.00 Test Team 5: 0.00 ---------------------Total: 0.00 Est. Effort: 1.00 Generic Proposed Solution: None. Resolution: The updated man pages have been placed for cpp.1 in cmd/cpp dir, nmake.1, and makerules.1 in cmd/nmake dir. Rejection: None. Associated Files: cmd/cpp/cpp.1 cmd/nmake/makerules.1 cmd/nmake/nmake.1 logid: ral effid: nmake Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command 05/19/97 15:40:12 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-24 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Producing an ALL Report 6 To produce an ALL report on all MRs in the Active Database sorted by MRG Status, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: . logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 07:27:24 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: ALL___________ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: ________________________________________________________ Sort Fields: mrgstat_________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: stdout__________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=ALL sort=mrgstat prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR db=active ofile=stdout are entered automatically and need not be typed. A standard ALL report will be produced sorted by MRG Status. A sample report appears below. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-25 Using the Report Commands logid: Sablime effid: Sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 05/20/97 Information Retrieval System Command 07:38:58 -------------------------- REPORT FOR MR sab970227 -------------------------MR Status: active Duplicate MR: MR Severity: 3 Product: sab++ Release Det.: 4.1 System: lib Phase Det.: new_development Subsystem: libPC Category: internal Module: Spawns: 0 Org. Date: 04/08/97 Create Date: 04/08/97 14:14:33 Site: MurrayHill Reason Code: Reqd. Date: Compl. Date: Originator: rga Creator: rga Closer: Est. Effort: Study Dev: Due Date: Study Effort: ORIGINATOR/CREATOR INFORMATION: Name: Guido Rijo Phone: 8069 Email: **NOMAIL Department: abcde Location: LC Room No: 4N-C07 Abstract: Change "/" to "\" in directory structure menu on PC Description: Currently if the UNIX FTD data for the "Directory:" field in the edget command has the following information. Field Type: 2 Group/File: dirgroup Where "dirgroup" has the following members, src src/lib src/mrmgmt The "/" do not get converted to "\" before the group is delivered to the PC. Document Changes: n Problem Found On: sun4 Reason Deferred: None. MR Proposed Solution: None. ------------ GENERIC INFORMATION FOR MR sab970227 ------------ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-26 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Generic: v5.0 Class: software Type: enhancement SubClass: algorithm SubType: correctness(sw) MRG Status: assigned Duplicate MR: MRG Severity: 3 MRG Spawns: 0 Developer: rga Due Date: Chg. Date: 04/08/97 14:14:35 MG Reason CD: Com Id: Ext. MR Flag: n In-Process Metrics Information Rel. Intro.: Phase Intro.: Op Det Phase: Nondet Cause: Root Cause: RC Subcat: Fault Type: NC Subcat: Actual Effort Staff Days ---------------------Study: 0.00 Assignee: 0.00 Test Team 1: 0.00 Test Team 2: 0.00 Test Team 3: 0.00 Test Team 4: 0.00 Test Team 5: 0.00 ---------------------Total: 0.00 Est. Effort: 0.00 Unit Tested On: None. Generic Proposed Solution: None. Resolution: *----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----* * * THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS PUT BY THE [edput] COMMAND EXECUTED BY * [gar] ON [04/21/97 16:28:06] FOR THE FOLLOWING: * * DIRECTORY: [src/lib/libPC] * SOURCE FILE(S): [ChckScrInfo.c] * *----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----* Function:libPC/ChckScrInfo.c Changes: 1) Adjusted arrays to handle the number of commands that will be implemented. From: char *CmmndName[10]; AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-27 Using the Report Commands To: char *CmmndName[9]; From: To: int *Nopts[10]; int *Nopts[9]; 2) Removed commented code left from the initial implementation. 3) Removed debugging code from the initial implementation 4) Changed for loop From: To: for (i = 0; i < CmmndNmbr; i++) for (i = 0; i <= CmmndNmbr; i++) 5) Added appropriate code to handle the conversion of "/" to "\" in the relative directory menus for the commands that have the "Directory:" fields set to Popup Menu type, that is, 2. 6) Found and Fixed the following bug: The ChckScrInfo.c function was loading all the popup menu groups in the MENUS.TXT file. It was loading the groups for commands that are not currently being implemented on the PC environment. The result was a very large file that was difficult to read on the PC. ChckScrInfo.c now only loads the groups for the commands that are being implemented on the PC. *----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----* * * THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS APPENDED BY THE [edput] COMMAND EXECUTED BY * [gar] ON [04/22/97 12:52:02] FOR THE FOLLOWING: * * DIRECTORY: [src/lib/libPC] * SOURCE FILE(S): [ChngString.c] * *----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----*----* Function:libPC/ChngString.c Changes: the function is now overloaded. a) One version of the function replaces a string with a new string in a file. b) The other version of the function replaces a string with a new string in a menu, that is, group. Rejection: None. Associated Files: src/lib/libPC/ChckScrInfo.c AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-28 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command src/lib/libPC/ChngString.c History: 04/08/97 14:14:35 [gar] fcreate 04/21/97 16:28:05 [gar] edput depend sab970216 auto:INITfile-level 04/21/97 16:28:06 [gar] edput depend sab970216 auto:INITfile-level,auto:line-level logid: Sablime effid: Sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 05/20/97 Information Retrieval System Command 07:38:59 -------------------------- REPORT FOR MR sab970261 -------------------------MR Status: active Duplicate MR: MR Severity: 3 Product: sab++ Release Det.: 4.1 System: pcsab Phase Det.: development Subsystem: Category: internal Module: Spawns: 0 Org. Date: 05/02/97 Create Date: 05/02/97 15:49:17 Site: MurrayHill Reason Code: Reqd. Date: Compl. Date: Originator: rga Creator: rga Closer: Est. Effort: Study Dev: Due Date: Study Effort: ORIGINATOR/CREATOR INFORMATION: Name: Guido Rijo Phone: 8069 Email: **NOMAIL Department: abcde Location: LC Room No: 4N-C07 Abstract: Remove "^ " from last line of sub and mod menus Description: Jim requested that in the MENUS.TXT the menus information for the subsystem and module fields do not have the "^ " to identify the last line in the file. Document Changes: n Problem Found On: none Reason Deferred: None. MR Proposed Solution: None. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-29 Using the Report Commands Producing a bydeveloper Report 6 To produce a bydeveloper report for all MRs in the Active Database created in the range of dates between 2/22/97 and 3/5/97 by anil, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 07:58:24 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: bydeveloper___ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: cdate,crid______________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: report__________________________________________________ Because you specified Selection Fields fields, the following Selection Fields screen is displayed. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 08:10:12 Selection Fields for Report Creation Date: 02/22/97-03/05/97_______________________________________ Creator: anil____________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=bydeveloper crid=anil cdate=02/22/97-03/05/97 \ ofile=report prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR db=active AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-30 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command are entered automatically and need not be typed. A bydeveloper report will be produced showing the MRs created by anil between February 22, 1997 and March 5, 1997, inclusive. A sample report appears below. PTSid: Sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 05/20/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 08:20:50 BY-DEVELOPER SUMMARY REPORT --------------------------- Page: 1 Developer: anil --------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date Status System Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- --------- -------- ----------------------------sab970101 3 86 approved other To put Sablime v4.2 & v5.0 u\ pgrade memos under Sablime -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for developer [ anil ] = 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v5.0 ] = 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-31 Using the Report Commands PTSid: Sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 05/20/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 08:20:50 BY-DEVELOPER SUMMARY REPORT --------------------------- Page: 2 Developer: anil --------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date Status System Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- --------- -------- ----------------------------sab970101 3 86 approved other To put Sablime v4.2 & v5.0 u\ pgrade memos under Sablime sab970102 3 86 stpassed srcmgmt For SBCS files, edput should create new kind of MR dep. sab970106 3 84 stpassed srcmgmt Need automatic dependency for initalization unapproved MR sab970113 3 80 itpassed srcmgmt srcmgmt commands give error if filetype default set with -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for developer [ anil ] = 4 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v5.0 ] = 4 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for product [ sab++ ] = 5 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-32 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Producing a CUSTOM Report 6 To produce a CUSTOM report for all MRs in the Active Database sorted on Originator ID, and to print only the MR Number, Origination Date, Severity, and Originator ID, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 08:30:45 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: CUSTOM________ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: ________________________________________________________ Sort Fields: org_____________________________________________________ Print Fields: org,odate,sev___________________________________________ Heading: Report on MRs by Originator_____________________________ Output file: stdout__________________________________________________ Because you selected a CUSTOM report, the Print Fields and Heading fields are unprotected. Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=CUSTOM sort=org heading="Report on MRs by \ Originator" print=org,odate,sev prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR db=active ofile=stdout are entered automatically and need not be typed. A CUSTOM report will be produced showing all MRs in the Active Database sorted on Originator ID. Only the specified fields will be printed. A sample report appears below. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-33 Using the Report Commands Report on MRs by Originator -------------------------- REPORT FOR MR sab960429 -------------------------MR Severity: 3 Org. Date: 10/01/96 Originator: anil -------------------------- REPORT FOR MR sab960462 -------------------------MR Severity: 3 Org. Date: 10/10/96 Originator: anil -------------------------- REPORT FOR MR sab960004 -------------------------MR Severity: 3 Org. Date: 01/08/96 Originator: anil -------------------------- REPORT FOR MR sab960590 -------------------------MR Severity: 3 Org. Date: 09/10/96 Originator: anil -------------------------- REPORT FOR MR sab960596 -------------------------MR Severity: 3 Org. Date: 09/10/96 Originator: anil -------------------------- REPORT FOR MR sab960602 -------------------------MR Severity: 3 Org. Date: 09/18/96 Originator: anil -------------------------- REPORT FOR MR sab960661 -------------------------MR Severity: 3 Org. Date: 10/05/96 Originator: anil -------------------------- REPORT FOR MR sab970121 -------------------------MR Severity: 3 Org. Date: 01/28/97 Originator: anil -------------------------- REPORT FOR MR sab970175 -------------------------MR Severity: 3 Originator: anil Org. Date: 03/22/97 . . . NOTE: The MR number is always included in a CUSTOM report. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-34 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Producing a pie Report 6 To produce pie reports for all MRGs in the Active Database assigned to rga and printed by MRG Severity, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 08:45:54 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: pie___________ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: dev_____________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: mrgsev__________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: pie.6630________________________________________________ Because you specified the pie report, the Print Fields fields are unprotected. The Sort Fields and the Heading fields are protected. You can specify only one print field for the pie report. Because you specified a Selection Fields field, the following screen is displayed: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 08:48:33 Selection Fields for Report Developer: rga_____________________________________________________ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-35 Using the Report Commands Because you specified the pie report, the following screen is displayed: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 08:51:11 Management Format Report Information Pie Chart Title: MRs Assigned to rga by Severity_________________________ Footnote: ________________________________________________________ Would you like field labels in the chart instead of a legend: y Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=pie dev=rga print=mrgsev title="MRs Assigned to \ rga by Severity" fldlbl=n prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR db=active outfile=pie.6630 (default + process ID) are entered automatically and need not be typed. A pic program will be written to produce a pie chart showing all MRGs assigned to rga. The MRGs will be apportioned by severity. A printout of a sample pie chart is shown in Figure 6-8. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-36 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Sablime Management Report v5.0 Sablime 05/20/97 08:57:16 MRs Assigned to rga by Severity 3[3.8%] 1[2.6%] 2[97.6%] This report represents MRs by Severity Selection Criteria: db=active prod=sab++ dev=rga Legend: 1="2" 2="3" 3="4" The total number of MRs represented in this graph is 235, 6 of which are child MRs. Figure 6-8. pie Chart AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-37 Using the Report Commands Producing a bar Report 6 To produce a bar report for all MRGs in the Active Database assigned to scott, by MRG state, and to print a legend instead of labeling the fields directly on the report, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 10:24:11 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: bar___________ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: dev_____________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: mrgstat_________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: bar.12814_______________________________________________ Because you specified the bar report, the Print Fields field is unprotected. The Sort Fields and the Heading fields are protected. Only one print field can be specified for the bar report. Because you specified a selection field in the Selection Fields field, the following screen is displayed: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 10:25:08 Selection Fields for Report Developer: scott___________________________________________________ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-38 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Because you specified the bar report, the following screen is displayed: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 10:25:24 Management Format Report Information Bar Graph Title: MRs Assigned to Scott by State__________________________ X-Axis Title: Status__________________________________________________ Footnote: ________________________________________________________ Would you like field labels in the chart instead of a legend: y Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=bar dev=scott print=mrgstat title="MRs Assigned to \ Scott by State" xcol=Status fldlbl=y prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR db=active select=dev outfile=bar.12814 (default + process ID) are entered automatically, and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-39 Using the Report Commands In either case, a pic program will be written to produce a bar chart showing all MRGs assigned to scott. The MRGs will be displayed by state. A printout of a sample bar chart is shown in Figure 6-9. Sablime Management Report v5.0 Sablime 05/20/97 10:26:34 MRs Assigned to Scott by State 100 MRs 50 0 approved assigned itpassed nochange preitpassed published stpassed submitted understudy Status This report represents MRs (row) by Status (column) Selection Criteria: db=active prod=sab++ dev=scott The total number of MRs represented in this graph is 383, 17 of which are child MRs. Figure 6-9. bar Chart AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-40 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Producing a stat Report 6 To produce a stat report for all MRGs in the Active Database assigned to scott printed by MRG Severity and MRG Status, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 11:33:00 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: stat__________ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: dev_____________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: mrgsev,mrgstat__________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: stat.17236______________________________________________ Because you specified the stat report, the Print Fields fields are unprotected. The Sort Fields and the Heading fields are protected. You can specify only one or two print fields for the stat report. Because you specified a Selection Fields field, the following screen is displayed: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 11:33:29 Selection Fields for Report Developer: scott___________________________________________________ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-41 Using the Report Commands Because you specified the stat report, the following screen is displayed. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/20/97 11:33:49 Management Format Report Information Stat Chart Title: MRs Assigned to Scott by Severity and State_____________ Footnote: ________________________________________________________ Would you like field labels in the chart instead of a legend: n Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=stat dev=scott print=mrgsev,mrgstat title="MRs \ Assigned to Scott by Severity and State" fldlbl=n prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR db=active outfile=stat.17236 (default + process ID) are entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-42 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command In either case, a tbl program will be written to produce a stat chart showing all MRGs assigned to scott. The MRGs will be displayed by state and severity. A printout of a sample stat chart appears in Figure 6-10. Sablime Management Report v5.0 Sablime 05/20/97 11:35:17 MRs Assigned to Scott by Severity and State mrgstat mrgsev 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 2 2 0 0 0 1 0 3 64 142 45 28 9 1 6 42 1 4 18 4 5 4 0 0 0 6 0 This report represents MRG Severity (row) by MRG Status (column) Selection Criteria: db=active prod=sab++ dev=scott Row Legend: 1="1" 2="2" 3="3" 4="4" Column Legend: 1="approved" 2="assigned" 3="itpassed" 4= "nochange" 5="preitpassed" 6="published" 7="stpassed" 8="submitted" 9="understudy" The total number of MRs represented in this graph is 383, 17 of which are child MRs. Figure 6-10. stat Chart AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-43 Using the Report Commands Producing a bycategory Report 6 To produce a bycategory report for developer ljh and generic v5.0, you would make the folllowing entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/14/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 07:53:04 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: bycategory____ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: dev,g___________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: ________________________________________________________ Because you specified Selection Fields fields, the following screen appears: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/14/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 07:53:10 Selection Fields for Report Developer: ________________________________________________________ Generic: ________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=bycategory dev=ljh g=v5.0 prompt=n The following defaults are entered automatically: rclass=MR db=active In either case, a formatted bycategory report will be produced. A sample report appears on the following pages. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-44 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Category: field_enh ------------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 07:53:36 BY-CATEGORY SUMMARY REPORT -------------------------- Page: 1 3 09/15/97 other assigned ljh software enhancement for multiple hosts Enhance license key to allow -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for category [ field_enh ] = 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v5.0 ] = 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for product [ sab ] = 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970514 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- --------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample bycategory Report Using the report Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-45 6-46 Issue 1.0 Category: field_enh ------------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 07:53:36 BY-CATEGORY SUMMARY REPORT -------------------------- Page: 2 November 2000 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 3 04/19/97 3 06/04/97 3 05/04/97 sab970160 sab970248 sab970267 admin mrmgmt admin mrmgmt assigned assigned assigned assigned ljh ljh ljh ljh software enhancement submitted MR is rejected software enhancement easy to use software enhancement PTSid files software enhancement generic id when not needed cannot edit IPM info when a mrnote is not user friendly and extend UDF feature for the The mrnote command requires a -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for category [ field_enh ] = 4 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 3 03/17/97 sab970103 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- --------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab++ Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample bycategory Report (cont.) Using the Report Commands Category: field_mod ------------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 07:53:36 BY-CATEGORY SUMMARY REPORT -------------------------- 3 07/25/97 sab970447 mrmgmt inforet ljh ljh assigned assigned software enhancement software enhancement should go to stderr Page: 3 Information Retrieval Msg about expiring .usrid file -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for category [ field_mod ] = 2 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 3 06/17/97 sab970357 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- --------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab++ Gen: v5.0 LPTSid: ray Sample bycategory Report (cont.) Using the report Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-47 6-48 Issue 1.0 Category: internal ------------------ Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 07:53:36 BY-CATEGORY SUMMARY REPORT -------------------------- Page: 4 November 2000 3 11/11/97 sab970535 mrmgmt admin assigned assigned ljh ljh software enhancement when changing MRG status mrgedit should give a warning software enhancement improve warning messages and protect Duplicate MR field -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for category [ internal ] = 2 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v5.0 ] = 8 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for product [ sab++ ] = 8 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------^LTotal number of MRs for 2 products = 9 3 06/14/97 sab970266 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- --------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab++ Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample bycategory Report (cont.) Using the Report Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Using the report Command Producing a byclass Report 6 To produce a byclass report for MRs created on June 3, 1997, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/14/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 08:41:10 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: byclass_______ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: cdate___________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: ________________________________________________________ Because you specified a Selection Fields field, the following screen appears: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/14/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 08:41:51 Selection Fields for Report Creation Date: 06/03/97________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=byclass cdate=06/03/97 prompt=n The following defaults are entered automatically: rclass=MR db=active In either case, a byclass report for MRs created on 06/03/97 will be generated. A sample report appears on the following pages. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-49 6-50 Issue 1.0 Class: document --------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 08:41:08 BY-CLASS SUMMARY REPORT ----------------------- Page: 1 November 2000 3 06/03/97 user_man assigned heimer internal enhancement remove MG date stamp Unassigning an MR should not -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for class [ document ] = 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970245.02 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Category Type Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- -------- --------- --------- ---------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab++ Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample byclass Report Using the Report Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Class: mixed ------------ Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 08:41:08 BY-CLASS SUMMARY REPORT ----------------------- Page: 2 06/03/97 mrmgmt spawned internal enhancement remove MG date stamp Unassigning an MR should not -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for class [ mixed ] = 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970245 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Category Type Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- -------- --------- --------- ---------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab++ Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample byclass Report (cont.) Using the report Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-51 6-52 Issue 1.0 Class: software --------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 08:41:08 BY-CLASS SUMMARY REPORT ----------------------- Page: 3 November 2000 3 06/03/97 sab970245.01 admin mrmgmt assigned prasad internal enhancement remove MG date stamp assigned gar internal enhancement remove MG date stamp Unassigning an MR should not Unassigning an MR should not -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for class [ software ] = 2 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v5.0 ] = 4 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for product [ sab++ ] = 4 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 3 06/03/97 sab970245.00 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Category Type Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- -------- --------- --------- ---------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab++ Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample byclass Report (cont.) Using the Report Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Using the report Command Producing a byseverity Report 6 To produce a byseverity report for MRGs due on April 15.1997, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/14/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 09:01:24 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: byseverity____ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: due_____________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: ________________________________________________________ Because you specified a Selection Fields field, the following screen appears: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/14/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 09:01:09 Selection Fields for Report MRG Due Date: 04/15/97________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=byseverity due=04/15/97 prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR db=active are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a byseverity report for MRGs due on 04/15/97 will be generated. A sample report appears on the following pages. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-53 6-54 Issue 1.0 Sev: 1 ------ Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 09:01:56 BY-SEVERITY SUMMARY REPORT -------------------------- November 2000 02/14/97 04/15/97 admin assigned scott software modification solaris primsdb doesn’t work. Page: 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for sev [ 1 ] = 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970027 MR Number Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v4.2 PTSid: ray Sample byseverity Report Using the Report Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Sev: 2 ------ Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 09:01:56 BY-SEVERITY SUMMARY REPORT -------------------------- 12/09/97 04/15/97 inforet submitted twh software modification ssql is calling dummy1 %19 of PTS in place of mgr (manager) Page: 2 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for sev [ 2 ] = 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v4.2 ] = 2 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970640 MR Number Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v4.2 PTSid: ray Sample byseverity Report (cont.) Using the report Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-55 6-56 Issue 1.0 Sev: 2 ------ Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 09:01:57 BY-SEVERITY SUMMARY REPORT -------------------------- November 2000 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 03/31/97 04/15/97 pc_windo assigned vjg software enhancement information about MRs 03/31/97 04/15/97 pc_windo assigned wina software enhancement information about MRs 03/31/97 04/15/97 pc_windo assigned heimer document modification drop-down list box 03/31/97 04/15/97 pc_windo assigned vjg software modification drop-down list box sab970335.01 sab970335.02 sab970044.00 sab970044.01 Include "assigned" MRs in the MR list needs to display extra MR list needs to display extra MR list needs to display extra Page: 3 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for sev [ 2 ] = 5 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Include "assigned" MRs in the 03/31/97 04/15/97 pc_windo assigned heimer document enhancement information about MRs sab970335.00 MR Number Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v4.3 PTSid: ray Sample byseverity Report (cont.) Using the Report Commands Sev: 3 ------ Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 09:01:57 BY-SEVERITY SUMMARY REPORT -------------------------- 03/31/97 04/15/97 pc_windo assigned vjg software modification re-download product info. When generic is changed, do not Page: 4 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for sev [ 3 ] = 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v4.3 ] = 6 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970326.01 MR Number Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v4.3 PTSid: ray Sample byseverity Report (cont.) Using the report Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-57 6-58 Issue 1.0 Sev: 1 ------ Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 09:01:57 BY-SEVERITY SUMMARY REPORT -------------------------- November 2000 02/14/97 04/15/97 admin assigned scott software modification solaris primsdb doesn’t work. Page: 5 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for sev [ 1 ] = 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970027 MR Number Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample byseverity Report (cont.) Using the Report Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Sev: 2 ------ Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 09:01:57 BY-SEVERITY SUMMARY REPORT -------------------------- 12/09/97 04/15/97 inforet submitte twh software modification ssql is calling dummy1 %19 of PTS in place of mgr (manager) Page: 6 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for sev [ 2 ] = 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v5.0 ] = 2 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for product [ sab ] = 10 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970640 MR Number Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample byseverity Report (cont.) Using the report Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-59 Using the Report Commands Producing a bysite Report 6 To produce a bysite report for MRs created at sites Virginia, Middletown, and Red Hill, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/14/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 09:15:34 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: bysite________ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: site____________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: ________________________________________________________ Because you specified a Selection Fields field, the following screen appears: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/14/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 09:15:59 Selection Fields for Report Origination Site: Virginia,Middletown,Red_Hill____________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=bysite site=Virginia,Middletown,Red_Hill prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR db=active are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a bysite report for MRs created at Virginia, Middletown, and Red_Hill will be generated. Excerpts of a sample report appear on the following pages. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-60 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Site: Red_Hill -------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 09:16:20 BY-SITE SUMMARY REPORT ---------------------- 3 10/06/97 admin stpassed ljh software modification file is copied to host create failed after description Page: 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for site [ Red_Hill ] = 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v5.0 ] = 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970537 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- --------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample bysite Report Using the report Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-61 6-62 Issue 1.0 Site: Virginia -------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 09:16:20 BY-SITE SUMMARY REPORT ---------------------- November 2000 3 06/24/97 admin created restartable. make closegen command Page: 4 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for site [ Virginia ] = 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ ] = 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970278 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- --------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab++ Gen: PTSid: ray Sample bysite Report (cont.) Using the Report Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Site: Middletown ---------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/14/97 Time: 09:16:21 BY-SITE SUMMARY REPORT ---------------------- 3 07/25/97 admin assigned anil software enhancement and SBCS licence Check for permissions of .usrid Page: 7 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for site [ Middletown ] = 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970448 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Type Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- --------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab++ Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample bysite Report (cont.) Using the report Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-63 Using the Report Commands Producing a bystatus Report 6 To produce a bystatus report on MRGs where addgen is the specified subsystem, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/14/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 09:44:31 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: bystatus______ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: sub_____________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: ________________________________________________________ Because you specified a Selection Fields field, the following screen appears: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/14/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 09:44:27 Selection Fields for Report Sub-System: addgen__________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=bystatus sub=addgen prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR db=active are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a bystatus report will be generated on MRGs where addgen is the specified subsystem. A sample report appears below. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-64 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v4.2 Time: 09:44:57 BY-STATUS SUMMARY REPORT ------------------------ Page: 1 Status: nochange ---------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date System Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960368 *** admin Record Generic/Database Sizes -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for status [ nochange ] = 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v4.2 Time: 09:44:57 BY-STATUS SUMMARY REPORT ------------------------ Page: 2 Status: submitted ----------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date System Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960337 3 *** admin scott accepting spawned MRs into new generic gives SYS_ERR -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for status [ submitted ] = 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v4.2 ] = 2 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-65 Using the Report Commands PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v4.3 Time: 09:44:57 BY-STATUS SUMMARY REPORT ------------------------ Page: 3 Status: accepted ---------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date System Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960552 976 admin allow to specifying a previo\ us generic for MRs to be acce -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for status [ accepted ] = 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v4.3 Time: 09:44:57 BY-STATUS SUMMARY REPORT ------------------------ Page: 4 Status: approved ---------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date System Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960175.00 3 *** admin scott addgen does not remove temporary error file sab960185 3 *** admin scott addgen allows empty flags for the different teams sab960337 3 *** admin scott accepting spawned MRs into new generic gives SYS_ERR -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for status [ approved ] = 3 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-66 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v4.3 Time: 09:44:57 BY-STATUS SUMMARY REPORT ------------------------ Page: 5 Status: assigned ---------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date System Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960368 3 *** admin scott Record Generic/Database Sizes sab960702 3 967 admin scott Current values not set in the addgen command -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for status [ assigned ] = 2 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v4.3 Time: 09:44:57 BY-STATUS SUMMARY REPORT ------------------------ Page: 6 Status: nochange ---------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date System Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960132 *** admin addgen accept field should a\ llow specification of generic -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for status [ nochange ] = 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v4.3 ] = 7 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-67 Using the Report Commands PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 09:44:57 BY-STATUS SUMMARY REPORT ------------------------ Page: 7 Status: accepted ---------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date System Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960132 *** admin addgen accept field should a\ llow specification of generic sab960596 976 admin There should be a way to blo\ ck work in a particular gener -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for status [ accepted ] = 2 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 09:44:57 BY-STATUS SUMMARY REPORT ------------------------ Page: 8 Status: assigned ---------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date System Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960754 3 906 admin scott A capability to generate a n\ ew generic as copy of an old sab960869 3 850 admin scott make addgen, newgen, initsab MR class field consistent -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for status [ assigned ] = 2 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v5.0 ] = 4 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for product [ sab++ ] = 13 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-68 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Producing a bysystem Report 6 To produce a bysystem report for MRGs in generic v5.0 assigned to developer ljh, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:heimer effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/14/97 Information Retrieval System Command 09:29:56 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: bysystem______ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: g,dev,mrgstat___________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: ________________________________________________________ Because you specified Selection Fields fields, the following screen appears: logid:heimer effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/14/97 Information Retrieval System Command 09:30:03 Selection Fields for Report Generic: v5.0____________________________________________________ Developer: ljh_____________________________________________________ MRG Status: assigned________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=bystatus g=v5.0 dev=ljh mrgstat=assigned prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR db=active are entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-69 Using the Report Commands In either case, a bysystem report will be generated for MRGs in v5.0 in the assigned state for developer ljh. A sample report appears below. PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 09:30:09 BY-SYSTEM SUMMARY REPORT ------------------------ Page: 1 System: admin ------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date Status Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab970542 3 185 assigned ljh mrgedit forces reason with r\ code=other even for reject -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for system [ admin ] = 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v5.0 ] = 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for product [ sab ] = 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 09:30:09 BY-SYSTEM SUMMARY REPORT ------------------------ Page: 2 System: admin ------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date Status Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960340 3 *** assigned ljh An idea to further improve s\ ecurity in TCP/IP multi-machi sab960385 3 *** assigned ljh provide a way to change UDF’s for related commands sab960497 3 980 assigned ljh What changed not indicated by mrgedit mail -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for system [ admin ] = 3 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-70 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Page: 3 Using the report Command Gen: v5.0 Time: 09:30:09 BY-SYSTEM SUMMARY REPORT -----------------------System: all ----------- MR Number Sev Age Due Date Status Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960514.23 3 *** assigned ljh Fix DBA Warning messages sab960147.03 3 *** assigned ljh Improve and correct the Sablime SYS_ERR Messages -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for system [ all ] = 2 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 09:30:09 BY-SYSTEM SUMMARY REPORT ------------------------ Page: 4 System: inforet --------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date Status Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960503 3 976 assigned ljh ByCustomer Selection sab970134 3 742 assigned ljh sreport not received, but uucp confirmation is -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for system [ inforet ] = 2 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-71 Using the Report Commands PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 09:30:09 BY-SYSTEM SUMMARY REPORT ------------------------ Page: 5 System: mrmgmt -------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date Status Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960176 3 *** assigned ljh No Description Sent sab960833 3 876 assigned ljh mrnote does not generate msg queue entry for MRs -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for system [ mrmgmt ] = 2 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 04/14/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 09:30:09 BY-SYSTEM SUMMARY REPORT -----------------------System: xmrmgmt --------------MR Number Sev Age Due Date Status Developer Abstract -------------- --- --- -------- -------- --------- ----------------------------sab960405 3 *** assigned ljh suucpdm should use cron instead of at -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for system [ xmrmgmt ] = 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v5.0 ] = 10 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for product [ sab++ ] = 10 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for 2 products = 11 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-72 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Page: 6 Using the report Command Producing a bytype Report 6 To produce a bytype report for all approved MRGs in generic v5.0, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface:. logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/17/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 12:20:57 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: MR____________ Name of Report: bytype________ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: g,mrgstat_______________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: ________________________________________________________ Because you specified Selection Fields fields, the following screen appears: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/17/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 12:20:15 Selection Fields for Report Generic: v5.0____________________________________________________ MRG Status: approved________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rname=bytype g=v5.0 mrgstat=approved prompt=n The defaults: rclass=MR db=active are entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-73 Using the Report Commands In either case, a bytype report will be generated for all MRGs in the approved state in generic v5.0. A sample report appears on the following pages. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-74 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Type: enhancement ----------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/17/97 Time: 12:21:24 BY-TYPE SUMMARY REPORT ---------------------- Page: 1 3 01/12/97 user_manual approved heimer document internal_enh install initial version of v5.0 User’s Manual -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for type [ enhancement ] = 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970677 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Category Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- ----------- ---------- --------- -------- ------------ ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample bytype Report Using the report Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-75 6-76 Issue 1.0 Type: modification ------------------ Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/17/97 Time: 12:21:24 BY-TYPE SUMMARY REPORT ---------------------- Page: 2 November 2000 3 01/13/97 user_manual approved heimer document internal_mod add three more files to original setup -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for type [ modification ] = 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v5.0 ] = 2 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for product [ sab ] = 2 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sab970684 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Category Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- ----------- ---------- --------- -------- ------------ ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample bytype Report (cont.) Using the Report Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Type: initialization -------------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/17/97 Time: 12:21:24 BY-TYPE SUMMARY REPORT ---------------------- Page: 3 3 02/23/97 3 03/23/97 sab970101 sab970182 admin other lib scott Need to bring hotline.ck into document internal To put Sablime v4.2 & v5.0 upgrade memos under Sablime software internal If the vhelp number starts from 0, commands are aborted approved ray software internal v5.0 approved anil approved -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for type [ initialization ] = 3 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for generic [ v5.0 ] = 3 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for product [ sab++ ] = 3 3 05/13/97 sab970202 MR Number Sev Cr. Date Due Date System Status Developer Class Category Abstract -------------- --- -------- -------- ----------- ---------- --------- -------- ------------ ------------------------------- Prod: sab++ Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample bytype Report (cont.) Using the report Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-77 Using the Report Commands After processing takes place, information like that shown below appears on the screen: + Processing the inputted data; please stand by! – Selection of records from MR relation is complete. – Selection of records from MRX relation is complete. – Selection of records from ORG relation is complete. – Selection of records from MG relation is complete. – A temporary file of information is created. – The intermediate extract file is sorted. + A Master Trace Record has been generated for the Database Administrator. Producing External MR Reports 6 Some Sablime projects communicate MR information about their products to other projects. If you select the External_MR report class, you can produce reports for MRs shared with external projects. You can produce a standard report or an extract_file. If you specify Selection Fields, a second screen is generated to allow you to produce a report with records selected by specified criteria. If you do not specify Selection Fields, an External_MR report including all external MR records is produced when the first report screen is confirmed. Standard Reports 6 There are four External_MR reports: emr80, and emr132, emr_html, and complete. Extract File 6 When you select extract_file, instead of producing a formatted, formal report, you produce a file consisting of 47 semicolon-separated fields selected from the EMR, MG, MR, and ORG relations of the Sablime database. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-78 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Producing a complete Report 6 To produce a complete report for all external MRs in the Active Database and display the report on the screen, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/10/97 07:22:01 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: External_MR___ Name of Report: complete______ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: ________________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: stdout__________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rclass=External_MR prompt=n The defaults: db=active rname=complete ofile=stdout are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a standard complete report will be produced for all external MRs. A sample report appears below. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-79 Using the Report Commands PTSid: ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Proj: Sablime Date: 05/10/97 Prod: sab++ Time: 09:17:09 ------REPORT FOR MR sab970078-----Internal Information -------------------Product: sab++ System: admin Subsystem: dbcross Module: Release Det.: 4.2 Category: testing Site: LbrtyCrnr MR Severity: 4 MR Status: active Phase Det.: system_test Originator: gar Org Date: 03/22/97 Create Date: 03/22/97 13:52:48 Reqd. Date: Document Changes: None. Problem Found On: None. Abstract: change the word "by" for "with" Description: command: dbcross problems: 1) there is a warning message in the dbcross command that has the following sentence: In addition, do not approve any other MRs that have touched the file added by the MRs listed above. the word "by" should be a "with" External Information --------------------- # 1 -Ext Project: sable Ext Product: sable Route: Ext Id: in sable970012 Ext System: admin Ext Severity: 4 Ext Subsytem: not_applicable Ext MR Status: open Ext Module: Ext Phase Det: Ext Rel. Det.: 4.2 Ext Org: mozart!gar Ext Category: system_test Ext Org Date: 03/22/97 Ext Site: LbrtyCrnr Trans Date: 03/22/97 13:51:23 Ext Reqd Date: ------------------ END OF REPORT FOR MR sab970078 ------------------ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-80 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Page: 1 Using the report Command Producing an emr80 Report 6 To produce an emr80 report selected by all external MRs from a specified External Project and send the output to a file, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/10/97 09:46:58 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: External_MR___ Name of Report: emr80_________ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: eproj___________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: report__________________________________________________ Because you specified Selection Fields fields, the following screen is displayed: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/10/97 09:49:14 Selection Fields for Report Ext Project: sable___________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rclass=External_MR rname=emr80 eproj=sable \ ofile=report prompt=n The defaults: db=active select=eproj are entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-81 Using the Report Commands A standard emr80 report for all external MRs originated by the external project sable will be produced in a file named report. A sample report appears below. PTSid: ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Proj: Sablime Date: 05/10/97 Prod: sab++ Time: 10:02:23 Page: 1 External MR Report for Project-Product: sable-sable --------------------------------------------------External Trans MR Number Sev Identifier Rte Date Abstract -------------- --- -------------- --- -------- ------------------------------sab970078 4 sable970012 in 03/22/97 change the word "by" for "with" -----------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for Ext project-product [ sable-sable ] = 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of MRs for project-product [ Sablime-sab++ ] = 1 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-82 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Producing an emr_html Report 6 To produce an emr_html report of all external MRs from a specified external project, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 Information Retrieval System Command 06/25/00 09:29:38 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: External_MR___ Name of Report: emr_html______ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: eproj___________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: ________________________________________________________ Because you specified Selection Fields, the following screen is displayed: logid:ral effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.2 Information Retrieval System Command 06/25/00 09:38:58 Selection Fields for Report Ext Project: ________________________________________________________ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-83 Using the Report Commands Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rclass=External_MR, rname=emr_html eproj=JPTST ofile=report prompt=n The defaults: db=active select=eproj are entered automatically and need not be typed. Producing an External MR Extract File 6 To produce an extract_file for all external MRs in the Active Database and send the data to a file named extract, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:heimer effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 05/10/97 Information Retrieval System Command 10:12:40 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: External_MR___ Name of Report: extract_file__ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: ________________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: extract_________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rclass=External_MR rname=extract_file ofile=extract prompt=n The default: db=active AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-84 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command is entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, an extract file will be produced and stored as extract in the current directory. A sample extract file appears below. testing;03/22/97 13:52:48;system_test;;;;sable970012;;open;03/22/97;\ mozart!gar;sable;sable;;4.2;4;LbrtyCrnr;not_applicable;admin;sab970078;\ 03/22/97;gar;sab++;;4.2;in;4;active;dbcross;admin;03/22/97 13:51:23;\ change the word "by" for "with";LbrtyCrnr;;system_test;;;;;;;;;;;; Producing Group Reports 6 If you select the group report class, you can produce a summary report about group names, group owners, and group types, or an aggregate report about group members. In addition to the two standard reports, you can produce an extract_file. If you do not specify Selection Fields, a group report including all group records is produced when the first screen is confirmed. If you do specify Selection Fields, a second screen is displayed to allow you to produce a report with records selected by specified criteria. Standard Reports 6 There are two standard group reports available. The summary report lists highlevel information about groups selected without listing the members. The aggregate report lists the same high-level information about groups selected but also provides the list of members. Both reports indicate whether the group is under Sablime-level, product-level, or user-level control. Extract File 6 Instead of producing a formatted, formal report, you can produce a file consisting of five semicolon-separated fields selected from the GRP and GRPM relations of the Sablime database. The extract_file contains the information about groups that support the standard reports. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-85 Using the Report Commands Producing a Group Summary Report 6 To produce a group summary report for all groups in the Active Database and display the report on the screen, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/10/97 12:19:11 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: group_________ Name of Report: summary_______ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: ________________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: stdout__________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rclass=group prompt=n The defaults: db=active rname=summary ofile=stdout are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a standard group summary report will be produced for all existing groups. Excerpts of a sample report appear below. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-86 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command PTSid: ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: 4tst Date: 05/10/97 Time: 12:20:12 GROUP SUMMARY REPORT -------------------Group Name Group Owner Group Type Controlled At -------------- ---------------- ---------- ------------- ----------- Page: 1 No. Members _ATYPE Sablime other PRODUCT-level 3 _CMRCS Sablime other PRODUCT-level 3 _DEFCODE Sablime other PRODUCT-level 2 _DOCUCLASS Sablime other PRODUCT-level 6 _DOC_FLTYPE Sablime other PRODUCT-level 4 _ECAT Sablime other PRODUCT-level 1 _ENHTYPE Sablime other PRODUCT-level . . . PTSid: ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: 4tst Date: 05/10/97 Time: 12:20:12 GROUP SUMMARY REPORT -------------------_PIGRP Sablime other PRODUCT-level 10 Page: 2 4 _PMRCS Sablime other PRODUCT-level 4 _RCGRP Sablime other PRODUCT-level 6 _REJCODE _RELS Sablime Sablime other other PRODUCT-level PRODUCT-level _RESCODE Sablime other PRODUCT-level . . . -------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of groups = 147 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 7 1 2 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-87 Using the Report Commands PTSid: Sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: 4tst Date: 05/10/97 Time: 12:20:12 GROUP SUMMARY REPORT -------------------- Page: 7 SELECTION CRITERIA SPECIFIED ---------------------------No Selection Criteria were specified. Producing a Group Aggregate Report 6 To produce a group aggregate report for all PTS ID groups in the Active Database and write the report to a file, specifying a group name, gname, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/10/97 12:44:27 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: group_________ Name of Report: aggregate_____ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: gname___________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: pts.grps________________________________________________ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-88 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Because you have specified a Selection Fields field, the following screen is displayed: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/10/97 12:47:42 Selection Fields for Report Group Name: OurSites________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rclass=group rname=aggregate gtype=ptsid \ ofile=pts.grps gname=OurSites prompt=n The default: db=active is entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a group aggregate report will be produced showing the members of a group called OurSites owned by ral. A sample report appears below. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-89 Using the Report Commands PTSid: ral Prod: 4tst Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 05/10/97 Time: 13:00:27 GROUP AGGREGATE REPORT ---------------------Group Name: OurSites -------------------- Owner: heimer Type: other Page: 1 Controlled At: USER-level No. of Members: 8 GROUP MEMBERS: -------------Bangalore Beiping Brussels Derry Saint_Petersburg San_Juan Santo_Domingo Taipei PTSid: ral Prod: 4tst Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 05/10/97 Time: 13:00:27 GROUP AGGREGATE REPORT ---------------------- Page: 2 SELECTION CRITERIA SPECIFIED ---------------------------gname=OurSites gowner=heimer AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-90 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Producing a Group Extract File 6 To produce a group extract_file sorted by Group Owner and Group Type and save the output to a file, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 05/10/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 13:08:59 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: group_________ Name of Report: extract_file__ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: ________________________________________________________ Sort Fields: gowner,gtype____________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: grp.extr________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rclass=group rname=extract_file sort=gowner,gtype \ ofile=grp.extr prompt=n The default: db=active is entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a standard group extract_file will be produced sorted by Group Owner and Group Type. A sample report appears below. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-91 Using the Report Commands Bangalore;OurSites;8;heimer;other Beiping;OurSites;8;heimer;other Brussels;OurSites;8;heimer;other Derry;OurSites;8;heimer;other Saint_Petersburg;OurSites;8;heimer;other San_Juan;OurSites;8;heimer;other Santo_Domingo;OurSites;8;heimer;other Taipei;OurSites;8;heimer;other heimer;mark1.0_team;3;heimer;ptsid Sablime;mark1.0_team;3;heimer;ptsid wina;mark1.0_team;3;heimer;ptsid 1;__CSEV;4;Sablime;other 1;__DELAY;10;Sablime;other 1;__DEVSEV;4;Sablime;other 1;__MM;2;Sablime;other 1;__SABSEV;4;Sablime;other 1;__STSEV;4;Sablime;other 1;ftd_test1;5;Sablime;other 2;__CSEV;4;Sablime;other 2;__DELAY;10;Sablime;other . . . Producing Source Reports 6 If you select the source report class, you can produce a summary report on files under Sablime control that are out for edit. You can produce a standard report or an extract_file. Standard Report 6 The edgotten report provides information on files that are out for edit by generics and directories. Extract File 6 Instead of producing a formatted, formal report, you can produce an extract_file consisting of ten semicolon-separated fields selected from the GS, MD, and MR relations. NOTE: Be sure to use landscape mode when running wide reports. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-92 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Producing a Source edgotten Report: Example 1 6 To produce a source edgotten report for all edgotten files in the database and display the report on the screen, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 03/07/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 09:05:48 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: source________ Name of Report: edgotten______ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: ________________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: stdout__________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rclass=source prompt=n The defaults: rname=edgotten db=active ofile=stdout are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a standard source edgotten report will be produced for all existing source files out for edit. A sample report appears on the following page. 6 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-93 6-94 Issue 1.0 DIRECTORY: src/pcsab/libWINPC ----------------------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 03/07/97 Time: 09:05:50 EDGOTTEN REPORT --------------- November 2000 VB SCCS nmw 12/02/97 sab970626 function add lclose to is_binary ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of Files for directory [ src/pcsab/libWINPC ] = 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of Files for generic [ v5.0 ] = 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of Files for product [ sab ] = 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- isbinary.c File Name File Type Ver Ctrl File Owner Developer Date MR Number Abstract -------------------- --------- -------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v5.0 PTSid: Sablime Page: 1 Sample source edgotten Report Using the Report Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Using the report Command Producing a Source edgotten Report: Example 2 6 To produce a source edgotten report for all source files for generic v5.0 edgotten by anil and write the output to a file, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/18/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 08:39:48 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: source________ Name of Report: edgotten______ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: g,srcdev________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: edg.report______________________________________________ Because you specified Selection Fields fields, the following screen is displayed: logid:ray Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/18/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 08:39:58 Selection Fields for Report Generic: v5.0____________________________________________________ Developer: anil____________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rclass=source g=v5.0 srcdev=anil ofile=edg.report prompt=n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-95 Using the Report Commands The defaults: rname=edgotten db=active are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a standard source edgotten report will be produced showing information on all the v5.0 files out for edit by anil. A sample report appears on the following pages. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-96 Issue 1.0 November 2000 DIRECTORY: src/lib/libPOST -------------------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/18/97 Time: 08:41:17 EDGOTTEN REPORT --------------- c++ SCCS anil 03/20/97 sab970102 While reviewing screated MRs, MRUDFs cannot be specified Page: 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of Files for directory [ src/lib/libPOST ] = 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- rvw_action.c File Name File Type Ver Ctrl File Owner Developer Date MR Number Abstract -------------------- --------- -------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample source edgotten Report Using the report Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-97 6-98 Issue 1.0 DIRECTORY: src/lib/libPRE ------------------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/18/97 Time: 08:41:17 EDGOTTEN REPORT --------------- November 2000 c++ SCCS anil 03/20/97 sab970102 While reviewing screated MRs, MRUDFs cannot be specified Page: 2 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of Files for directory [ src/lib/libPRE ] = 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- p_rvw_msgn.c File Name File Type Ver Ctrl File Owner Developer Date MR Number Abstract -------------------- --------- -------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample source edgotten Report (cont.) Using the Report Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page DIRECTORY: src/mrmgmt --------------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/18/97 Time: 08:41:17 EDGOTTEN REPORT --------------- c++ SCCS anil 03/20/97 sab970102 While reviewing screated MRs, MRUDFs cannot be specified Page: 3 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of Files for directory [ src/mrmgmt ] = 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of Files for generic [ v5.0 ] = 3 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total number of Files for product [ sab ] = 3 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- create.c File Name File Type Ver Ctrl File Owner Developer Date MR Number Abstract -------------------- --------- -------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------- ------------------------------- Prod: sab Gen: v5.0 PTSid: ray Sample source edgotten Report (cont.) Using the report Command AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-99 6-100 Issue 1.0 srcdev=anil g=v5.0 Prod: sab PTSid: ray SELECTION CRITERIA SPECIFIED ---------------------------- Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Date: 04/18/97 Time: 08:41:17 EDGOTTEN REPORT --------------- Page: 4 Sample source edgotten Report (cont.) Using the Report Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page November 2000 Using the report Command Producing a Source Extract File 6 To produce a source extract_file for all edgotten files touched by MR sab970102 and write the report to a file, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/18/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 08:36:18 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: source________ Name of Report: extract_file__ Database: active_______ Selection Fields: mr______________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: ext.rpt_________________________________________________ Because you specified a Selection Fields field, the following screen is displayed: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 04/18/97 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 08:37:42 Selection Fields for Report MR Number: sab970102_______________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rclass=source rname=extract_file mr=sab970205,sab970250 \ sort=srcdate,dir,srf ofile=ext.report prompt=n The default: db=active is entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-101 Using the Report Commands In either case, a standard source extract_file will be produced of all files out for edit by MR sab970102. A sample extract_file follows. src/lib/libPOST;c++;sab;v5.0;sab970102;;97/03/20 15:06:02;anil;\ While reviewing screated MRs, MRUDFs cannot be specified;\ rvw_action.c;SCCS src/lib/libPRE;c++;sab;v5.0;sab970102;;97/03/20 14:44:27;anil;\ While reviewing screated MRs, MRUDFs cannot be specified;\ p_rvw_msgn.c;SCCS src/mrmgmt;c++;sab;v5.0;sab970102;;97/03/20 13:58:12;anil;While \ reviewing screated MRs, MRUDFs cannot be specified;create.c;SCCS Producing Cross-Reference Reports 6 The mrVSfile xref report produces a block report that provides information jointly about MRs and files under Sablime control. The report allows you to specify MRs or MRG selection criteria (developer, severity, state, or type) to retrieve information about files that have been touched by the set of specified MRs and related depended-upon MRs. The information is particularly useful for retrieving or monitoring different versions of the deliverable. It can also be used to document the set of MRs and files that make up the deliverable. This report is an excellent adjunct to the getversion command and the build process. Internal Processing 6 The xref report requires you to specify MRs or MRG selection criteria. The internal processing is as follows: 1. Get the list of specified MRs. This list is composed of MRs specified directly by the user or generated from the specified MRG selection criteria. 2. Find the list of MRs on which all specified MRs depend. MRs in this list are called depended-upon MRs. These MRs would have to be included in a build. 3. Find the files touched by all specified and depended-upon MRs. The list of files can be restricted by specifying selection criteria for specific files or directories of interest. 4. Generate the output: information about all specified MRs, depended-upon MRs, and files touched by any of these MRs. NOTE: Specified MRs that touched no files are not included. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-102 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Standard Report 6 The xref report consists of four sections: MR SECTION, FILE SECTION, MR LEGEND, and MRG STATUS SUMMARY. All data retrieved is for user-specified generics. The MR SECTION is organized by MR. It lists associated files for each specified and depended-upon MR and the user who last edgot them. The FILE SECTION is organized by directory and file. It lists separately specified and depended-upon MRs that touched each file. It also provides edgotten status (busy or free), file ownership, the date the status last changed, file type, the user who last edgot the file, and Quality Assurance information. The MR LEGEND is an optional section that provides information about each specified and depended-upon MR in the report. For each specified MR, a list of depended-upon MRs is generated in the DEPENDED UPON MRS field. Any specified MR that appears in the DEPENDED UPON MRS field is marked with an asterisk (*); its dependency tree appears under its listing as a specified MR. For each depended-upon MR, a list of specified MRs dependent on it appears in the DEPENDENT SPECIFIED MRS field. The MRG STATUS SUMMARY is an optional section that displays summary groupings of all the MRs and their approval state ( approved or unapproved). The summary groupings are listed by specified MRs and depended-upon MRs. If no specified or related depended-upon MRs touched any files, and if you requested the LEGEND or MRG STATUS SUMMARY information, these two sections appear in the report; the MR SECTION and FILE SECTION do not appear. Extract File 6 Instead of producing a formatted, formal report, you can produce an extract_file. An extract file consists of a set of five types of records for each specified generic. Each set of records comprises a header and four sections. The first field of each AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-103 Using the Report Commands record is the sec field; it is used to determine the type of record (i.e., the record that supplies information for each report section), as shown in Table 6-4. Table 6-4. sec Number (modulo 5) mrVSfile extract_file Sections Section 0 Header 1 MR SECTION 2 FILE SECTION 3 MR LEGEND 4 MRG STATUS SUMMARY In the sec field, the label base equates to (ith generic listed– 1) * 5. In other words, the first set of files is numbered 0000–0004, the second set is numbered 0005– 0009, etc. Given input about generics gen1, gen2, and gen3: gen1's sec numbers span 0000–0004, gen2's sec numbers span 0005–0009, and gen3's sec numbers span 0010–0014. When modulo 5, these numbers all become 0–4, representing the record types of the report, e.g., sec 5 is a Header record for the second generic specified (or according to the sort) and sec 8 is a MR LEGEND record for the same generic. Each record contains 26 semicolon-separated fields containing information selected from the MD, MR, MG, DEP, and GS relations in the Active and the Inactive Databases. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-104 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command Producing a Cross-Reference Report: Example 1 6 To produce an xref report for all files touched by MRs 4sol970105, 4sol970109, and 4sol970116 without printing out the MR Legend section, and to save the report to a file, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:heimer effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 05/17/97 Information Retrieval System Command 12:18:09 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: mrVSfile______ Name of Report: xref__________ Database: both_________ Selection Fields: mr______________________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: mymVr___________________________________________________ Because you specified a Selection Fields field, the following screen appears: logid:heimer effid:sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 05/17/97 Information Retrieval System Command 12:22:48 Selection Fields for Report MR Number: 4sol970105,4sol970109,4sol970116________________________ Generic: mark1.0_________________________________________________ Do you want the MR Legend: n Do you want the MRG Status Summary: n Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-105 Using the Report Commands report rclass=mrVSfile ofile=mymVf \ mr=4sol970105,4sol970109,4sol970116 prompt=n The defaults: name=xref db=both g=mark1.0 legend=n summary=n are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a standard xref report will be produced showing information on all the files touched by MRs 4sol970105, 4sol970109, and 4sol970116 and any MRs upon which the set of specified MRs depend. The MRs are grouped by files in the FILE SECTION. The MRG STATUS SUMMARY section groups the total set of MRs by their inclusion reason (specified or depended upon). The report, however, does not contain an MR LEGEND section. Only the files touched by MRs in generic mark1.0, the current generic, have information retrieved for them. The report is sorted by MR Number, Directory, and Source File and written to the output file mymVf. A sample report follows. PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: 4sol Date: 05/17/97 Time: 12:18:51 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT --------------------------------- Page: 1 SELECTION CRITERIA SPECIFIED ---------------------------g=mark1.0 mr=4sol970105,4sol970109,4sol970116 PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: 4sol Date: 05/17/97 Gen: mark1.0 Time: 12:18:51 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-106 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Page: 2 Using the report Command MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT ------------------------------------------------------------------ MR SECTION ---------------------------------MR Number: 4sol970105 MR Inclusion: Specified DIRECTORY: src/include ---------------------Associated Files ---------------h1 h2 Last Touched By ---------------chanda chanda DIRECTORY: src/sys1 ------------------- f1 f2 chanda chanda DIRECTORY: src/sys2 ------------------- f3 f4 chanda chanda DIRECTORY: src/sys2/sub1 ------------------------ f5 f6 chanda chanda DIRECTORY: src/sys2/sub2 ------------------------ f7 f8 chanda chanda DIRECTORY: src/sys3 ------------------- f10 f9 chanda chanda -------------------------------------------------- MR Number: 4sol970109 MR Inclusion: Specified DIRECTORY: src/include ---------------------hi Sablime AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-107 Using the Report Commands ------------------------------------------------------------------End of Section PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: 4sol Date: 05/17/97 Gen: mark1.0 Time: 12:18:51 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT ----------------------------------------------------------------- FILE SECTION --------------------------------DIRECTORY: src/include ---------------------FILE NAME: h1 Current Status: busy for Unspecified MR File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/18 09:23:27 File Type: ascii Edgotten By: Counted for QA: n Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970105 Depended Upon MRs: None. -------------------------------------------------FILE NAME: h2 Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/18 09:23:55 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: n Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n ascii ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970105 Depended Upon MRs: None. -------------------------------------------------FILE NAME: hi Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/25 09:16:23 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: y Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n document ASSOCIATED MRS AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-108 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Page: 3 Using the report Command -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970109 Depended Upon MRs: None. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: 4sol Date: 05/17/97 Gen: mark1.0 Time: 12:18:51 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT --------------------------------- Page: 4 --------------------------------- FILE SECTION --------------------------------DIRECTORY: src/sys1 ------------------FILE NAME: f1 Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/18 09:24:32 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: n Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n ascii ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970105 Depended Upon MRs: None. -------------------------------------------------FILE NAME: f2 Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/18 09:24:59 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: n Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n ascii ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970105 Depended Upon MRs: None. -------------------------------------------------DIRECTORY: src/sys2 ------------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-109 Using the Report Commands FILE NAME: f3 Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/18 09:25:48 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: n Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n ascii ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970105 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: 4sol Date: 05/17/97 Gen: mark1.0 Time: 12:18:51 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT ----------------------------------------------------------------- FILE SECTION --------------------------------Depended Upon MRs: None. -------------------------------------------------FILE NAME: f4 Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/18 09:38:18 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: n Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n ascii ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970105 Depended Upon MRs: None. -------------------------------------------------DIRECTORY: src/sys2/sub1 -----------------------FILE NAME: f5 Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/18 09:40:15 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: n Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n ascii ASSOCIATED MRS AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-110 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Page: 5 Using the report Command -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970105 Depended Upon MRs: None. -------------------------------------------------FILE NAME: f6 Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/18 09:40:39 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: n Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n ascii -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: 4sol Date: 05/17/97 Gen: mark1.0 Time: 12:18:51 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT --------------------------------- Page: 6 --------------------------------- FILE SECTION --------------------------------ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970105 Depended Upon MRs: None. -------------------------------------------------DIRECTORY: src/sys2/sub2 -----------------------FILE NAME: f7 Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/18 09:45:09 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: n Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n ascii ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970105 Depended Upon MRs: None. -------------------------------------------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-111 Using the Report Commands FILE NAME: f8 Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/18 09:46:00 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: n Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n ascii ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970105 Depended Upon MRs: None. -------------------------------------------------DIRECTORY: src/sys3 ------------------FILE NAME: f10 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: 4sol Date: 05/17/97 Gen: mark1.0 Time: 12:18:51 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT ----------------------------------------------------------------- FILE SECTION --------------------------------DIRECTORY: src/sys3 ------------------Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/18 09:46:57 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: n Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n ascii ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970105 Depended Upon MRs: None. -------------------------------------------------FILE NAME: f9 Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/02/18 09:46:31 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: n ascii AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-112 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Page: 7 Using the report Command Version Ctrl Tool: SBCS Binary File: n ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: 4sol970105 Depended Upon MRs: None. ------------------------------------------------------------------End of Generic AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-113 Using the Report Commands Producing a Cross-Reference Report: Example 2 6 To produce an xref report for all files in the directory src/pcsab touched by MRGs assigned to developer rga in generic v5.0, to display both the MR LEGEND and the MRG STATUS SUMMARY sections, and to write the output to stdout, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/18/97 09:19:08 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: mrVSfile______ Name of Report: xref__________ Database: both_________ Selection Fields: mrgstat,dev,dir_________________________________________ Sort Fields: ________________________________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: stdout__________________________________________________ Because you specified Selection Fields fields, the following screen appears: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/18/97 09:53:52 Selection Fields for Report MRG Status: assigned________________________________________________ Developer: rga_____________________________________________________ Directory: src/pcsab_______________________________________________ Generic: v5.0____________________________________________________ Do you want the MR Legend: y Do you want the MRG Status Summary: y Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rclass=mrVSfile mrgstat=assigned dev=rga \ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-114 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command dir=src/pcsab g=v5.0 legend=y summary=y prompt=n The defaults: rname=xref db=both select=dev,dir,mrgstat ofile=stdout are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a standard xref report will be produced showing information on all the files in the directory src/pcsab touched by MRGs in the assigned state and assigned to developer rga. Additionally, any depended-upon MRs touching files in these directories will be output, along with the files these MRs touch. The MRs are grouped by files in the FILE SECTION. The MRG STATUS SUMMARY section groups the total set of MRs by their inclusion reason (specified or depended upon). Only the files touched by MRs in generic v5.0 are included. The report will be sorted by MR Number, Directory, and Source File and written to stdout. A sample report follows. PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 05/18/97 Time: 10:05:14 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT --------------------------------- Page: 1 SELECTION CRITERIA SPECIFIED ---------------------------dev=rga dir=src/pcsab g=v5.0 mrgstat=assigned PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 05/18/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 10:05:14 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT --------------------------------- Page: 2 ---------------------------------- MR SECTION ---------------------------------MR Number: sab970216 MR Inclusion: Depended Upon DIRECTORY: src/pcsab AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-115 Using the Report Commands -------------------Associated Files ---------------- Last Touched By ---------------- addisrcfile.c createmr.c edgetfile.c edputfile.c fcreatemr.c proposemr.c sgetfile.c submitmr.c unedgetfile.c rga rga rga rga rga rga rga rga rga ------------------------------------------------------------------End of Section PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 05/18/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 10:05:14 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT ----------------------------------------------------------------- FILE SECTION --------------------------------DIRECTORY: src/pcsab -------------------FILE NAME: addisrcfile.c Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/05/16 13:14:23 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: y Version Ctrl Tool: SCCS Binary File: n c++ ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: None. Depended Upon MRs: sab970216 -------------------------------------------------FILE NAME: createmr.c Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/04/06 13:59:58 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: y Version Ctrl Tool: SCCS Binary File: n c++ ASSOCIATED MRS -------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-116 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Page: 3 Using the report Command User Specified MRs: None. Depended Upon MRs: sab970216 -------------------------------------------------FILE NAME: edgetfile.c Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/04/06 13:58:51 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: y Version Ctrl Tool: SCCS Binary File: n c++ ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: None. Depended Upon MRs: sab970216 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 05/18/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 10:05:14 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT --------------------------------- Page: 4 --------------------------------- FILE SECTION --------------------------------DIRECTORY: src/pcsab -------------------FILE NAME: edputfile.c Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/05/16 13:18:58 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: y Version Ctrl Tool: SCCS Binary File: n c++ ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: None. Depended Upon MRs: sab970216 -------------------------------------------------FILE NAME: fcreatemr.c Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/05/16 13:19:12 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: y c++ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-117 Using the Report Commands Version Ctrl Tool: SCCS Binary File: n ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: None. Depended Upon MRs: sab970216 -------------------------------------------------FILE NAME: proposemr.c Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/05/16 13:17:33 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: y Version Ctrl Tool: SCCS Binary File: n c++ ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: None. Depended Upon MRs: sab970216 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 05/18/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 10:05:14 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT ----------------------------------------------------------------- FILE SECTION --------------------------------DIRECTORY: src/pcsab -------------------FILE NAME: sgetfile.c Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/05/16 13:18:10 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: y Version Ctrl Tool: SCCS Binary File: n c++ ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: None. Depended Upon MRs: sab970216 -------------------------------------------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-118 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Page: 5 Using the report Command FILE NAME: submitmr.c Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/05/16 13:18:21 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: y Version Ctrl Tool: SCCS Binary File: n c++ ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: None. Depended Upon MRs: sab970216 -------------------------------------------------FILE NAME: unedgetfile.c Current Status: free File Owner: Status Last Changed: 97/05/16 13:18:37 File Type: Edgotten By: Counted for QA: y Version Ctrl Tool: SCCS Binary File: n c++ ASSOCIATED MRS -------------User Specified MRs: None. Depended Upon MRs: sab970216 ------------------------------------------------------------------End of Section PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 05/18/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 10:05:14 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT --------------------------------- Page: 6 ------------------------------- LEGEND SECTION -------------------------------MR Number: sab970216 MR Inclusion: Depended Upon MRG Status: submitted MRG Severity: 3 MRG Status Date: 97/05/16 13:31:59 Developer: rga Abstract: to add new PC-Sablime code to Sablime DEPENDENT SPECIFIED MRS ----------------------- sab970227 sab970261 -------------------------------------------------MR Number: sab970227 MR Inclusion: Specified AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-119 Using the Report Commands MRG Status: assigned MRG Severity: 3 MRG Status Date: 97/04/08 14:14:35 Developer: Abstract: rga Change "/" to "\" in directory structure menu on PC ****NOTE**** This MR does not touch selected source file(s) in this generic. DEPENDED UPON MRS ----------------sab970216 -------------------------------------------------MR Number: sab970261 MR Inclusion: Specified MRG Status: assigned MRG Severity: 3 MRG Status Date: 97/05/02 15:49:18 Developer: rga Abstract: Remove "^ " from last line of sub and mod menus ****NOTE**** This MR does not touch selected source file(s) in this generic. DEPENDED UPON MRS ----------------sab970216 -------------------------------------------------MR Number: MRG Status: sab970297 assigned MR Inclusion: Specified MRG Severity: 3 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 05/18/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 10:05:14 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT --------------------------------- Page: 7 ------------------------------- LEGEND SECTION -------------------------------MRG Status Date: 97/05/16 13:03:20 Developer: rga Abstract: Add new functionalities to the PC-Sablime package ****NOTE**** This MR does not touch selected source file(s) in this generic. DEPENDED UPON MRS ----------------None. ------------------------------------------------------------------End of Section AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-120 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command PTSid: chanda Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 Information Retrieval System Command Prod: sab++ Date: 05/18/97 Gen: v5.0 Time: 10:05:14 MR vs FILE CROSS-REFERENCE REPORT --------------------------------- Page: 8 ----------------------------- MRG STATUS SUMMARY -----------------------------ALL SPECIFIED MRS ----------------Approved MRs: None. Unapproved MRs: sab970227 sab970261 sab970297 ALL DEPENDED UPON MRS --------------------Approved MRs: Unapproved MRs: None. sab970216 ------------------------------------------------------------------End of Generic Producing a Cross-Reference Extract File 6 To produce an extract_file for all files touched by severity 3 MRGs in generic v5.0, display both the MR LEGEND and the MRG STATUS SUMMARY sections, sort the output by the MR inclusion reason field (i.e., is MR in the report because it was specified or depended upon by at least one specified MR), and the MR Number, Directory, and Source File fields, and write the output to a file, you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-121 Using the Report Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/18/97 10:46:35 Specifying a Sablime report Class of Report: mrVSfile______ Name of Report: extract_file__ Database: both_________ Selection Fields: mrgsev__________________________________________________ Sort Fields: mrincrsn,mr,dir,srf_____________________________________ Print Fields: ________________________________________________________ Heading: ________________________________________________________ Output file: /tmp/ex1________________________________________________ Because you specified Selection Fields fields, the following screen appears: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime Information Retrieval System Command 05/18/97 10:47:08 Selection Fields for Report MRG Severity: 3_______________________________________________________ Generic: v5.0____________________________________________________ Do you want the MR Legend: y Do you want the MRG Status Summary: y Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: report rclass=mrVSfile rname=extract_file mrgsev=3 g=v5.0 \ sort=mrincrsn,mr,dir,srf legend=y summary=y ofile=/tmp/ex1 prompt=n The default: db=both is entered automatically and need not be typed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-122 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the report Command In either case, an extract_file will be generated for all source files touched by MRGs of severity 3 in generic v5.0. An example of such an extract_file follows. The sec field numbers 0000–0004 correspond to the header and sections 1 through 4 (i.e., MR SECTION, FILE SECTION, MR LEGEND, and MRG STATUS SUMMARY) of the report for generic v5.0. The report is sorted within sections by mrincrsn, mr, dir, and srf where appropriate and written to the output file /tmp/ex1. Sample Extract File Output 0000;sab++;v5.0;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/lib/libPC;Authnticate.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/lib/libPC;BuildFile.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/lib/libPC;ChckScrInfo.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/lib/libPC;ChngString.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/lib/libPC;GetTmpFile.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/lib/libPC;SetEnvrnmnt.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/lib/libPC;SetupCAS.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/pcsab;addisrcfile.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/pcsab;createmr.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/pcsab;edgetfile.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/pcsab;edputfile.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/pcsab;fcreatemr.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/pcsab;proposemr.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/pcsab;sgetfile.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/pcsab;submitmr.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970216;;;;;s;;src/pcsab;unedgetfile.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970227;;;;;s;;src/lib/libPC;ChckScrInfo.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970227;;;;;s;;src/lib/libPC;ChngString.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0001;;;sab970261;;;;;s;;src/lib/libPC;BuildFile.c;;;;;;;rga;;;;;;;;; 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/lib/libPC;Authnticate.c;;y;c++;free;97/04/06 15:19:09;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/lib/libPC;BuildFile.c;;y;c++;free;97/05/02 16:03:02;;;\ sab970216,sab970261;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/lib/libPC;ChckScrInfo.c;;y;c++;free;97/04/21 16:28:01;;;\ sab970216,sab970227;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/lib/libPC;ChngString.c;;y;c++;free;97/04/22 12:51:58;;;\ sab970216,sab970227;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/lib/libPC;GetTmpFile.c;;y;c++;free;97/04/06 14:03:04;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/lib/libPC;SetEnvrnmnt.c;;y;c++;free;97/04/06 17:22:53;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/lib/libPC;SetupCAS.c;;y;c++;free;97/04/06 17:23:28;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/pcsab;addisrcfile.c;;y;c++;free;97/05/16 13:14:23;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/pcsab;createmr.c;;y;c++;free;97/04/06 13:59:58;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/pcsab;edgetfile.c;;y;c++;free;97/04/06 13:58:51;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/pcsab;edputfile.c;;y;c++;free;97/05/16 13:18:58;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-123 Using the Report Commands 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/pcsab;fcreatemr.c;;y;c++;free;97/05/16 13:19:12;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/pcsab;proposemr.c;;y;c++;free;97/05/16 13:17:33;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/pcsab;sgetfile.c;;y;c++;free;97/05/16 13:18:10;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/pcsab;submitmr.c;;y;c++;free;97/05/16 13:18:21;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0002;;;;;;;;;;src/pcsab;unedgetfile.c;;y;c++;free;97/05/16 13:18:37;;;\ sab970216;;;;;;;SCCS;n 0003;;;sab970216;submitted;97/05/16 13:31:59;3;rga;s;to add new PC-Sablime code \ to Sablime;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;y;; 0003;;;sab970227;assigned;97/04/08 14:14:35;3;rga;s;Change "/" to "\" in \ directory structure menu on PC;;;;;;;;;;;*sab970216;;;;;y;; 0003;;;sab970261;assigned;97/05/02 15:49:18;3;rga;s;Remove "^ " from last line \ of sub and mod menus;;;;;;;;;;;*sab970216;;;;;y;; 0003;;;sab970269;nochange;97/05/18 09:22:09;3;joa;s;Should not check for \ sab3.1clean/sab3.1conv/sab3.1rollbk.;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;n;; 0003;;;sab970273;nochange;97/05/18 09:22:07;3;pf1;s;Update header for \ .BuildInfo file in admin/makefile;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;n;; 0003;;;sab970278;nochange;97/05/18 09:22:10;3;rga;s;fix processing message\ ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;n;; 0003;;;sab970297;assigned;97/05/16 13:03:20;3;rga;s;Add new functionalities to \ the PC-Sablime package;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;n;; 0004;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;sab970216,sab970227,sab970261,sab970269,sab970273,\ sab970278,sab970297;;;;; Using the ssql Command 6 NOTE: For detailed information about the ssql command, see the ssql manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The ssql (Sablime Structured Query Language) command is used to query the Sablime databases across relations, allowing you to: n specify the relations to query, n use UNIX system egrep(1) regular expressions (REs) to specify the contents of a field, n select operators to be used on the specified attributes (less than, greater than, etc.), n specify the fields of interest by position or name, and n make nested queries across relations or within a relation. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-124 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the ssql Command With ssql, you can query based on any field in any relation in any of the Sablime databases. In most cases, ssql positional parameters and keywords correspond to the respective field in the database relation being queried. For the MRG, MR, MRX, and SNAP relations, however, some of the ssql positional parameters and keywords refer to information stored elsewhere in the Sablime database. For example, the ssql hist keyword for the MG relation accesses information in the product_name/FILES directory, but ssql treats it as if it were part of the MG relation. Most ssql keywords reflect the internal keyword of a command that updates the database. For example, the ssql g keyword in the MRG relation refers to the same information as the g keyword in the create command. In other cases, however, there is no direct relationship between the ssql keyword and a command internal keyword. For example, the ssql hist keyword in the FTD relation refers to the seventh field in the FTD relation, but this information was gathered by a number of keywords or fields in the ftd command. NOTE: Accessing information from a text file (e.g., a description or resolution file) can take some time. ssql can be used by any user on the host machine or a satellite machine in an NFS/RFS or TCP/IP network. Help screens are available to assist the user. Two such help screens are illustrated on the following page (figures 6-11 and 6-12). Only 20 characters of the description are displayed on the help screen. Some unused fields are marked dummy on the help screens. Table 6-5. Parallel MRG States State MR Type Document Firmware Hardware Software preinspected prefitpassed prehitpassed preitpassed inspected fitpassed hitpassed itpassed prepublished prefstpassed prehstpassed prestpapssed published fstpassed hstpassed stpassed AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-125 Using the Report Commands Sablime SQL Query Tool Retrieve all or specific fields from tuple records in a Relation based upon search criteria. Fields can be specified using positional parameters or keywords. By default the Active Database is queried. The inActive Database can be searched by specifying INACTIVE as illustrated in the syntax below. SYNTAX : ssql -dbhelp | ssql -help | all | [positional parameter|keyword] ... from [Sablime_relation | INACTIVE.Sablime_relation] where [keyword | %position].[lt|eq|gt|ne|le|ge|lk].[value | { ssql ... }] [and]... [or]... For keyword and positional parameter help on any Sablime Relation: ssql -help from relation_name Example: Retrieve MR number, developer, and generic from the MG relation where generic is greater than v4.2 and developer name begins with sab ssql %1 dev g from MG where g.gt.v4.2 and dev.lk."^sab" Figure 6-11. ssql -help Screen Sablime Relation MR Only the following fields can be retrieved from this relation. You can give positional parameters or keywords. (%) Keyword Description (%) Keyword Description 1 mr MR Number 12 cldate Completion Date 2 cid MR Creator 13 clid MR Closer 3 stat MR Status 14 dummy 4 cat MR Category 15 pd Phase Detected 5 abst Abstract 16 mrudf1 Document Changes 6 rdate Required Date 17 mrudf2 Problem Found On 7 sev Severity 18 mrudf3 MRA Reviewed 8 spawns Spawns 19 mrudf4 MR UDF4 9 reason Reason 20 mrudf5 MR UDF5 10 rcode Reason Code 21 dupmr Duplicate Killed MR 11 crdate Create Date 22 desc MR Description Figure 6-12. ssql -help from MR Screen AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-126 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the ssql Command Compound ssql Statements 6 Compound ssql statements are introduced with one of the logical operators, and or or. A compound statement allows you to specify multiple fields or alternate values for fields from a single relation. Keywords are processed from left to right without grouping unless keywords are repeated. A typical use for a compound ssql statement would be the need to retrieve some information from the PTS relation: ssql name phone from PTS where loc.eq.MH and name.lk."^S" Your output would look like the following: Processing main query now ... Sablime;582-7118 Scott Crawford;908-577-8139 Suhasini Sabnis;577-8134 3 records selected. NOTE: Repeated keywords are grouped before processing, regardless of their position in the statement. or has a higher precedence than and. For example, in the following ssql statement, ssql mr dev g from MG where mrgstat.eq.submitted and \ mr.lk."^sab97" or mrgstat.eq.assigned the query results in ssql searching all tuples in the MG relation in the Active Database. It first groups mrgstat.eq.submitted or mrgstat.eq.assigned together and selects those records in which the MRG state is submitted or assigned. From this set of records, it selects the records that contain MRs whose string begins with sab97. From the MG tuples satisfying these conditions, the MR number, developer, and generic are printed. NOTE: ssql syntax does not support parenthetical grouping. In the above example, you cannot force ssql to select all records in which the MRG state is submitted for MRs whose prefix begins with sab97 and all records in which the MRG state is assigned for MRs with any prefix. This set must be retrieved in two separate ssql queries. You must be careful when you construct your statement. For example, the following statement: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-127 Using the Report Commands ssql mr mrxast from MRX where rcode.eq.other and mrxsev.lt.3 and \ rcode.eq.enhancement and mrxdue.gt.3/6/97 results in the null set, because the two values given for rcode are grouped together first; because of the logical contradiction (no Reason Code can be both enhancement and other), no MRs satisfy that condition. If you change the statement to an or case, e.g.: ssql mr mrxast from MRX where rcode.eq.other and \ mrxsev.lt.3 or rcode.eq.enhancement and mrxdue.gt.3/6/97 you may get output, because there is no logical contradiction in the statement: ssql searches for all MRs whose Reason Code is other or enhancement and whose Severity is less than 3 and whose Due Date is later than March 6, 1997. To find all MRs whose Reason Code is other and whose Severity is less than 3 and all MRs whose Reason Code is enhancement and whose Due Date is later than March 6, 1997, you must run two separate ssql queries. Some complex queries can be handled via nested ssql statements. Nested ssql Statements 6 Nested statements are needed when the information you need is not available from a single relation or when complex queries are needed from a single relation. For example, if you need the MR number and description for all MRGs assigned to a developer, the mr keyword is common to both the MR and the MG ssql relations, but the desc keyword appears only on the MR relation, and dev and mrgstat appear only on the MG relation. The MR number is the link between the two relations for ssql. The statement would be: ssql mr desc from MR where mr.eq. { ssql mr from MG \ where dev.eq.svs and mrgstat.eq.assigned } The output will be of the format mr;desc for all MRGs for which the developer is svs and the MRG state is assigned. NOTE: Fields can be printed only from the first relation named in the statement. The curly braces({ }) must be surrounded by spaces. You can specify only one keyword in the nested statement. Suppose you want information on all MRGs in generic v5.0 for which the developer is svs and the MRG state is submitted and on all MRGs in generic 3.1 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-128 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the ssql Command for which the developer is gar and the MRG state is assigned. To create this type of statement, you can use a nested ssql statement, even though all the information you want is in the same relation: ssql mr dev g mrgstat from MG where g.eq.v5.0 and \ dev.eq.svs and mrgstat.eq.submitted or \ mr.eq. { ssql mr from MG where g.eq.v4.2 and \ dev.eq.gar and mrgstat.eq.assigned } This statement works as follows: 1. Records are selected in which the generic is v4.2, the developer is gar, and the MRG state is assigned. 2. Records are selected in which the generic is v5.0, the developer is svs, and the MRG state is submitted. 3. The MR number is passed from the nested statement to the primary statement. 4. ssql prints out the developer, generic, and MRG state for all MRs matching the specifications in the primary statement. 5. ssql prints out the MR number, developer, generic, and MRG state for all MR numbers passed by the nested statement. Output from this statement looks like: sab970561;svs;v5.0;submitted sab970704.21;gar;v4.2;assigned sab970704.21;;v4.2;nochange sab970704.21;;v5.0;accepted NOTE: The potential problem in this case is that only the MR number is passed to the primary statement. The output will include all the correct information specified in the nested statement; however, if the MR from the nested statement is accepted in other generics as in the above example, it may also include additional information about those MRs in other generics because the MG relation contains multiple records on MRs that are accepted in more than one generic. The last two lines of the above output show information about MR sab970704.21 in generics v4.2 and v5.0. If you had not specified the generic in the output, you would not know which of the MRs matched the specification in the nested statement and which are additional hits. For this reason, you may find it easier to run two separate statements. ! CAUTION: You must have a very clear understanding of the information stored in each relation from which you print information. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-129 Using the Report Commands ssql Examples 6 Example 1 6 Display the help screen for the GRPM relation. ssql -help from GRPM The following screen is displayed: Sablime Relation GRPM Only the following fields can be retrieved from this relation. You can give positional parameters or keywords. (%) Keyword Description (%) Keyword Description 1 grpname Group Name 2 item Member Name Example 2 6 Retrieve all fields from the GRPM relation of which anil is a group member. ssql all from GRPM where %2.eq.anil dat_a1.0;anil dat_a4.2;anil ga_a1.0;anil mra_ancl;anil sa_ancl;anil sat_a1.0;anil sst_a1.0;anil sst_a4.2;anil Example 3 6 Retrieve the first, third, fifth, and tenth fields from the MG relation for all MRs assigned to anil that have reached at least the stpassed state. ssql %1 %3 %5 %10 from MG where dev.eq.anil and \ mrgstat.ge.stpassed AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-130 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the ssql Command sab970028;approved;anil;80 sab970236;published;anil;60 sab970386;approved;anil;80 sab970261;approved;anil;80 sab970282;stpassed;anil;60 sab970283;stpassed;anil;60 sab970284;stpassed;anil;60 sab970306;stpassed;anil;60 NOTE: The comparison operators process the MRG states according to the MR life cycle rather than alphabetically. If you want to restrict retrieved information to the same MR type, you must specify type in addition to mrgstat. Example 4 6 Retrieve the MR number and generic for all MRs from the DEP relation that depend on ancl970027. ssql mr g from DEP where dep.eq.ancl970027 ancl970025;a1.0 ancl970028;a4.2 ancl970030;a1.0 Example 5 6 Retrieve the internal key and HMI attributes from the FTD relation for commands whose internal key is reason and whose screen label contains the word Dependency. ssql intkey hmi from FTD where intkey.eq.reason and \ hmi.lk."Dependency" reason;1,1,_,0,left,Reason for Dependency: ,0,0 Example 6 6 Retrieve group members for all groups owned by anil that begin with d or s. ssql all from GRPM where grpname.eq. { ssql grpname \ AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-131 Using the Report Commands from GRP where owner.eq.anil } and grpname.lk."^d" \ or grpname.lk."^s" dat_a1.0;anil dat_a1.0;Sablime dat_a4.2;anil dat_a4.2;Sablime dba_ancl;Sablime sa_ancl;anil sa_ancl;Sablime sat_a1.0;anil sat_a1.0;Sablime sat_a1.0;svs sst_a1.0;anil sst_a1.0;Sablime sst_a4.2;anil sst_a4.2;Sablime sst_a4.2;svs To select fields from different relations, you must use a common field between the two relations to link the main ssql statement and the nested ssql statement. In this example, grpname is the only keyword common to both the GRP and GRPM relations. The nested ssql statement retrieves from the GRP relation all group names of groups owned by anil and passes this information to the grpname keyword in the principal ssql statement. For records in the GRPM relation that contain the group names found in the second ssql statement, all fields are printed when the group name begins with d or s. Example 7 6 Get all file names in generic v5.0 that are out for edit by anil; %3 represents the filename, and %7 represents the file status in the MD relation. (Positional parameters and keywords can be mixed in a single statement.) ssql %3 mdstat from MD where dev.eq.anil and \ %7.eq.nodelta and g.eq.v5.0 GetvList.c;nodelta GetvMRs.c;nodelta GetvStat.c;nodelta GetvUMRs.c;nodelta AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-132 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the ssql Command getv_brdt.c;nodelta getv_node.c;nodelta getversion.c;nodelta Example 8 6 Get all MRs in generic v5.0 for which the developer is svs, that are currently in the submitted state, and that were put in that state after October 27, 1997. ssql mr from MG where mrgstat.eq.submitted and \ dev.eq.svs and submtdt.gt.10/27/97 and g.eq.v5.0 This compound statement yields the following MR numbers: sab970510 sab970511 Get all these MRs along with their descriptions. The description files for these MRs can be obtained with a nested statement: ssql mr desc from MR where mr.eq. { ssql mr from MG \ where mrgstat.eq.submitted and dev.eq.svs and \ submtdt.gt.10/27/97 and g.eq.v5.0 } sab970510; Description for MR sab970510: Fields such as value in FTD relation are comma separated and when ssql tries to query value.eq.NULL, the result is incorrect because the sub token parsing in process.c does not return a null sub-token sab970511; Description for MR sab970511: If an ssql query finds that the queried field in any relation is comma separatd then it parses it into sub-tokens and compares the sub-tokens instead of treating the entire field as a single value. For instance, a query of the type ssql value from FTD where value.eq.21 will parse the value string into 3 sub-tokens and compares 21 with each of them. This should be changed to treat the entire field with commas as one string. 2 records selected. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-133 Using the Report Commands Example 9 6 Get all MRs in generic v5.0 in the Active Database whose state is greater than or equal to preitpassed and less than or equal to preapproved. ssql mr mrgstat from MG where g.eq.v5.0 and \ mrgstat.ge.prestpassed and mrgstat.le.preapproved sab970041;stpassed sab970131;stpassed sab970145;stpassed . . . NOTE: The comparison operators process the MRG states according to the MR life cycle rather than alphabetically. Example 10 6 Get the PTS records in which the phone number has the string 815. ssql all from PTS where phone.lk."815" anil;anil midha;xxxxx;ZH;1q-420;555-8150;\ fs,n,y,n,4;vi;anil;internal;;sab++;;n;n;n;;;; twh;Tulan W. Hu;xxxxx;ZH;1q-482;555-8156;\ fs,n,n,n,0;vi;**NOMAIL;internal;;sab++;;n;n;y;;;; Example 11 6 Get the PTS record where name is Suhasini Sabnis. ssql all from PTS where name.eq.”Suhasini Sabnis” svs;Suhasini Sabnis;xxxxx;ZH;1Q-442;555-8123;\ fs,n,y,y,0;vi;svs;internal;;sab++;;y;y;y;;;steve; AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-134 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the ssql Command Example 12 6 Get the MR number and description for all MRs whose number is greater than sab970400 and whose description contains the string conversion program. ssql mr desc from MR where mr.gt.sab970400 and \ desc.lk."conversion program" Processing main query now ... sab970417; Description for MR sab970417: Please answer the following questions: 1) Project Name: Red Cosmics 2) Project Contact:a Anne Singh She pointed out that conversion program doesn’t fill in 8th. field of GS relation. It should be ’y’ for binary files and ’n’ for non-binary files. Example 13 6 The value field in FTD consists of three comma-separated subfields. Retrieve all the value records in which the third subfield is nonempty. ssql value from FTD where value.lk.".*,.*,." 1,1,_ 1,1,y 1,14,__GENERIC . . . 2,6,view 2,61,vi 2,9,files 49 records selected. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-135 Using the Report Commands Example 14 6 Get the PTS records in which the PTS ID is twh or svs. ssql all from PTS where ptsid.lk."twh|svs" svs;Suhasini Sabnis;xxxxx;QH;3D-612;555 - 8123;\ fs,n,y,y,0;vi;svs;internal;;sab++;;y;y;y;;;steve; twh;Tulan W. Hu;xxxxx;QH;3D-652;8156;\ fs,n,n,n,0;vi;**NOMAIL;internal;;sab++;;n;n;y;;;; Example 15 6 Get all .c files in generic v5.0 with their relative directory names. ssql sfile dir g from GS where g.eq.v5.0 and \ sfile.lk..*\.c In the regular expression, .* represents any string; \. represents a literal dot. Processing main query now ... AdgMRs.c;src/lib/libPOST;v5.0 BldDList.c;src/lib/libCOM;v5.0 CheckInPath.c;src/lib/libCOM;v5.0 Chgmod.c;src/lib/libCOM;v5.0 . . . srl_dbadm.c;src/lib/libPOST;v5.0 ssql.c;src/inforet;v5.0 ueg_file.c;src/lib/libCOM;v5.0 ueg_srf.c;src/lib/libPOST;v5.0 uncommon.c;src/srcmgmt;v5.0 86 records selected. Example 16 6 Get the history information for MR prod970001 in generic v5.0. ssql mr g hist from MG where g.eq.v5.0 and \ mr.eq.prod970001 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-136 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the ptsaudit Command NOTE: The mr and g keywords are required for sorting purposes to retrieve the right history file. Failure to specify these keywords causes an error. If you do not specify the where clause, all MRGs from all generics are retrieved. prod970001;v5.0; MR History for MR sab970004: 01/06/97 13:52:23 [gsm] fcreate 01/31/97 18:12:03 [jsingh] assign anil+jjr 3 02/02/97 17:48:56 [jsingh] edput depend sab970122 auto:line-level 02/02/97 18:42:36 [jsingh] edput depend sab960610 auto:line-level 02/07/97 11:37:23 [vin] edput depend sab970122 auto:line-level, auto:file-level 02/07/97 11:37:25 [vin] edput depend sab970158 auto:file-level 02/16/97 12:13:12 [jsingh] submit 03/07/97 12:52:26 [jsingh] reject incomplete 03/07/97 13:59:26 [jsingh] edput depend sab970285 auto:file-level,auto:line-level 03/07/97 17:51:00 [jsingh] submit 03/07/97 19:10:30 [jsingh] depend sab970296 n Interdependent changes in source.c 03/22/97 14:37:09 [fredk] mrnote resolution 03/22/97 14:37:22 [fredk] preitpass 03/22/97 14:37:26 [fredk] itpass 03/22/97 14:37:30 [fredk] stpass 1 record selected. Using the ptsaudit Command 6 NOTE: For detailed information about the ptsaudit command, see the ptsaudit manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The ptsaudit command allows you to retrieve specific or complete information about a particular Sablime user. It works interactively through the Command Line interface. The ptsaudit command works even if the databases are stopped, although it may produce inaccurate results if the databases are being changed. The ptsaudit command allows you to produce a report about any single user or group of users. This report may contain all available information on the user(s), or only selected information. The ptsaudit report interacts with the user to find out what sort of report the user wants to see. After the user has entered the ptsaudit command, the following information appears to guide the user in selecting an appropriate report. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-137 Using the Report Commands +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ PTS Audit This script is used to get information about specific PTS IDs. The following is a list of available PTS audits and a brief description: ALL Returns an exhaustive compilation of all areas that are associated with particular PTS ID(s). CUSTOM You may select what information you would like to be displayed for particular PTS ID(s). DEV Given a PTS ID, will return a list of assigned MRs with the PTS ID as the developer, the files touched by those MRs, and their respective generics. LONG Given a PTS ID, will return a list of all MRs created by the PTS ID; all MRs studied by the PTS ID, all MRs assigned to the PTS ID, their current states and all files touched by those MRs; all files touched by the PTS ID, all MRs testassigned to the PTS ID; and all administrator and test groups the PTS ID belongs to. +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Following is an example of an “ALL” ptsaudit: ******************************************************************************* PTS ID = mka -------------------- PTS RECORD ----------------------------------------------Name: Organization Code: Manager: Location Code: Room Number: Telephone Number: Email: Email Flag: License Flag: Date of Last Usage: Automatic Originator Flag: Automatic Assignee Flag: Mail with description Flag: Merryll Kim Abrahams BL1234567 MH 3D-417 (908)582-5012 [email protected] y y 06/12/00 n n y AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-138 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the ptsaudit Command -------------------- MRS CREATED ---------------------------------------------MR: cv5000001 MR: cv5000002 MR: cv5000003 MR: cv5000003.00 MR: cv5000003.01 MR: cv5000003.02 -------------------- MRS STUDIED ---------------------------------------------MR: cv5000002 Generic: Current Status: mra_deferred -------------------- ASSIGNED DEVELOPMENT MRS --------------------------------MR: cv5000001 Generic: mka5.0 Files Out For Edit: Files Touched: Current Status: submitted MR: cv5000003.00 Generic: mka5.0 Files Out For Edit: Files Touched: src/admin/file.1 Current Status: assigned MR: cv5000003.01 Generic: mka5.0 Files Out For Edit: Files Touched: src/admin/file.1 src/admin/file.2 Current Status: submitted -------------------- ASSIGNED TEST MRS ----------------------------------------------------------- MRS KILLED ----------------------------------------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-139 Using the Report Commands -------------------- FILES OUT FOR EDIT ---------------------------------------------------------- FILES TOUCHED -------------------------------------------Source File: src/admin/file.1 MR: cv5000003.00 Generic: mka5.0 Current State: assigned Source File: src/admin/file.1 MR: cv5000003.01 Generic: mka5.0 Current State: submitted Source File: src/admin/file.2 MR: cv5000003.01 Generic: mka5.0 Current State: submitted -------------------- FILES OWNED ----------------------------------------------------------------- GROUPS OWNED ---------------------------------------------------------------- GROUPS MEMBERS OF ---------------------------------------Group Name: dba_cv5 Group Name: mra_cv5 Group Name: pint_mka5.0 Group Name: sa_cv5 Group Name: sat_mka5.0 Group Name: sint_mka5.0 -------------------- SNAPIDS CREATED -----------------------------------------Here is an example of a run of a “CUSTOM” ptsaudit. Notice that it will ask the user to select the items to be reported. Please select the details of your audit. The input should be comma separated. ( Type ? for help ) ownedFiles dvpMRs ownedGrp memGrp tstMRs stdyMRs AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-140 Issue 1.0 November 2000 crtMRs killMRs Using the ptsaudit Command edgFiles orgCode email orgFlag snapid locCode lic asgFlag tchFiles rmNum lstUsage descFlag name telNum mng emailFlag Enter Field : dvpMRs,tstMRs,stdyMRs,killMRs,edgFiles,descFlag,emailFlag Processing your request... ******************************************************************************* PTS ID = mka -------------------- PTS RECORD ----------------------------------------------Email Flag: y Mail with description Flag: y -------------------- ASSIGNED DEVELOPMENT MRS --------------------------------MR: cv5000001 Generic: mka5.0 Files Out For Edit: Files Touched: Current Status: submitted MR: cv5000003.00 Generic: mka5.0 Files Out For Edit: Files Touched: src/admin/file.1 Current Status: assigned MR: cv5000003.01 Generic: mka5.0 Files Out For Edit: Files Touched: src/admin/file.1 src/admin/file.2 Current Status: submitted -------------------- ASSIGNED TEST MRS ----------------------------------------------------------- MRS STUDIED ---------------------------------------------- AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-141 Using the Report Commands MR: cv5000002 Generic: Current Status: mra_deferred -------------------- MRS KILLED ------------------------------------------------------------------ FILES OUT FOR EDIT --------------------------------------Here is an example of a run of a “DEV” ptsaudit. It simply reports on the development MRs fo the PTS IDs requested. Processing your request... ******************************************************************************* PTS ID = mka -------------------- PTS RECORD ----------------------------------------------Name: Merryll Kim Abrahams -------------------- ASSIGNED DEVELOPMENT MRS --------------------------------MR: cv5000001 Generic: mka5.0 Files Out For Edit: Files Touched: Current Status: submitted MR: cv5000003.00 Generic: mka5.0 Files Out For Edit: Files Touched: src/admin/file.1 Current Status: assigned MR: cv5000003.01 Generic: mka5.0 Files Out For Edit: Files Touched: src/admin/file.1 src/admin/file.2 Current Status: submitted Here is an example of a run of a “LONG” ptsaudit. It reports the same information as a CUSTOM report with the following details selected: name,crtMRs,stdyMRs,dvpMRs,tstMRs,tchFiles,memGrp. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-142 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Using the ptsaudit Command Processing your request... ******************************************************************************* PTS ID = mka -------------------- PTS RECORD ----------------------------------------------Name: Merryll Kim Abrahams -------------------- MRS CREATED ---------------------------------------------MR: cv5000001 MR: cv5000002 MR: cv5000003 MR: cv5000003.00 MR: cv5000003.01 MR: cv5000003.02 -------------------- MRS STUDIED ---------------------------------------------MR: cv5000002 Generic: Current Status: mra_deferred -------------------- ASSIGNED DEVELOPMENT MRS --------------------------------MR: cv5000001 Generic: mka5.0 Files Out For Edit: Files Touched: Current Status: submitted MR: cv5000003.00 Generic: mka5.0 Files Out For Edit: Files Touched: src/admin/file.1 Current Status: assigned MR: cv5000003.01 Generic: mka5.0 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 6-143 Using the Report Commands Files Out For Edit: Files Touched: src/admin/file.1 src/admin/file.2 Current Status: submitted -------------------- ASSIGNED TEST MRS ---------------------------------------- -------------------- FILES TOUCHED -------------------------------------------Source File: src/admin/file.1 MR: cv5000003.00 Generic: mka5.0 Current State: assigned Source File: src/admin/file.1 MR: cv5000003.01 Generic: mka5.0 Current State: submitted Source File: src/admin/file.2 MR: cv5000003.01 Generic: mka5.0 Current State: submitted -------------------- GROUPS MEMBERS OF ---------------------------------------Group Name: dba_cv5 Group Name: mra_cv5 Group Name: pint_mka5.0 Group Name: sa_cv5 Group Name: sat_mka5.0 Group Name: sint_mka5.0 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 6-144 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Contents 7 Using the External MR Communication Commands n Overview 1 1 External MR Messages 2 Linking MRs 3 Linking Spawned MRs 6 n The External MR Commands 7 n Displaying the Contents of Messages 11 n Putting a Message on the Queue 15 n Reviewing Messages on the Queue 17 n Sending Messages to an External Project 28 n Creating an MR 29 n Requesting MR Reports 29 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 i Contents AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page ii Issue 1.1 November 2000 Using the External MR Communication Commands 7 Overview 7 The External MR Communications feature allows a Sablime project (i.e., a project that is using the Sablime system to develop a product) to communicate MRs and their states to another Sablime or non-Sablime project. The other Sablime project could be in the same Sablime instance or in another Sablime instance on the same or different machine. If the two communicating Sablime products are not on the same machine, this feature can be used, provided the two Sablime development machines can communicate with each other via TCP/IP, IPC, or UUCP. A Sablime project can communicate MRs and their states to and receive them from a non-Sablime project, provided the non-Sablime project can transmit and receive data in the same format as a Sablime project does. If the two Sablime projects are installed to use the External MR Communications feature, they can “share” their MRs with each other. The sharing of MRs in this context has a special meaning. For the shared MRs, both the projects have knowledge of each other's MR number, the MR attributes that are available on the Sablime create screen, and the MR description file. These MRs are considered externally linked MRs. Both the Sablime projects work on the linked MRs in the same way as they would work on regular unlinked MRs. As part of the External MR Communication installation procedure, each project can also establish whether it will send the MR state changes to the other side and if so, which state changes will be sent. As the linked MRs progress through their life cycles, the respective state-change commands automatically generate state change information messages to be sent to the other side. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-1 Using the External MR Communication Commands External MR Messages 7 Sablime projects communicate MR information to external projects in the form of messages. There are 15 different message types, numbered 1 through 13, 15, and 16. Each message is a single line of semicolon-separated fields in a file. The file name is the message number itself. The message numbers are generated by Sablime commands; they vary from 000 through 999. These numbers are cyclically used as they become available when a message is deleted from the queue. ! CAUTION: If you plan to generate more than several hundred messages in a short time, you should warn the project that receives them so that the receive queue can be cleaned out. The fields of a message are grouped in two parts: message header fields and message text fields. The first nine fields of message types 1 through 12 constitute the message header. They are shown below. (For a description of the header fields in message types 15 and 16, see Appendix D.) 1. Message Number 2. Message Type 3. Sender’s Project Name 4. Sender’s Product Name 5. Receiver’s Project Name 6. Receiver’s Product Name 7. External MR Number 8. Message Originator 9. Message Time Stamp Sender’s Project Name and Receiver’s Project Name refer to the name of the system being used for sharing information. For example, if two Sablime projects are communicating with each other, the Sender’s Project Name and Receiver’s Project Name are both sablime. The Sender’s Product Name and Receiver’s Product Name refer to the respective product names of the communicating projects as defined in the PR relation of the Sablime instances. Message text fields, which vary with message type, follow the message header fields. Each message type has a specific set of fields that depend upon the purpose of the message; these fields constitute the message text portion of a message. The formats of the message text fields of all the message types are described in Appendix D, External MR Message Formats. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-2 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Overview Linking MRs 7 Figure 7-1 illustrates the process by which an MR against a product in one Sablime project is linked with an MR against another product in another Sablime project, when the MR is not a spawned MR. (We assume that the appropriate installation steps for external MR communications links have been taken by both Sablime projects.) The following steps are illustrated: 1. An MRA for Sablime Product A executes the qmr command specifying the destination as the Sablime project’s Product B, for an internal MR that is to be linked to an external MR. The qmr command gathers the MR information (the MR attributes available on the create screen and the MR description) from the Active Database of Product A and creates from this information a message type 11 in the send queue of the Sablime instance of Product A. The qmr command also creates partial MR linkage information in the EMR relation of the Active Database of Product A. 2. The MRA of Product A executes the sendmsgs command to send the created message in the send queue to its destination product—Sablime Product B. The sendmsgs command transfers the message to its destination with the help of the rcv_msgs program or the uucp daemon on the receiving side and puts it in the receive queue of Product B. Once the message is successfully transferred to its destination, the sendmsgs command deletes it from the send queue of Product A. 3. The MRA of Product B executes the review command to take action on the received message. If the MRA wants to associate the external MR with an internal MR, the MRA can choose an action of enter or link. If enter is chosen and the Sablime environment variable sab1MR is not set to y, the review command creates a new MR in Product B, links it to the external MR, and enters the linkage information in the EMR relation, and generates a response message type 12 in the send queue. If enter is chosen and sab1MR is set to y, the operation is the same except the new MR created in Product B will have the same name (or MR number) as the external MR. The advantage of using sab1MR is that now both communicating Sablime products can use the same MR name to refer to related MRs in both products. If link is chosen, an MR number must be supplied. This MR number must be an existing internal MR in the Active Database of Product B. The review command then enters all the linkage information in the EMR relation and generates a response message type 12 in the send queue. In this case, message type 12 contains the information about the action taken while reviewing the received message and the MR attributes of the Product B MR that became linked with the Product A MR. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-3 Using the External MR Communication Commands Product A Product B 1 qmr message type 11 (in send queue) 2 sendmsgs message type 11 (in receive queue) 3 review (enter, link, remove) message type 12 4 (enter, link) (in send queue) sendmsgs MR in ADB message type 12 (in receive queue) 5 review (enter) ADB 1 accept message type 3 (in send queue) 2 sendmsgs message type 3 3 Figure 7-1. review (enter) Scenario for Establishing MR Linkage AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-4 Issue 1.0 November 2000 (in receive queue) ADB Overview If the MRA does not want to associate the external MR with the internal MR, the MRA can choose the remove action of the review command and specify a reason for not wanting to create the link. The review command will then create a response message type 12 in the send queue containing information about the removal action and the reason for the removal. Once an action has been taken, the review command will delete the message type 11 that generated the action from the receive queue. 4. The MRA of Sablime product Product B executes the sendmsgs command to send the response message type 12 from the send queue to the Sablime product Product A. The sendmsgs command transfers the message to its destination with the help of the rcv_msgs program or the uucp daemon on the receiving side and puts it in the receive queue of Product A. Once the message is successfully transferred to its destination, the sendmsgs command deletes it from the send queue of Product B. 5. The MRA of Product A executes the review command to take an action on the received message type 12. The MRA must choose the enter action while reviewing a message type 12. The effect of the enter action is as follows: n If the MRA of Product B honored the MR linkage request sent from Product A (i. e., chose the enter or link action instead of remove), the enter action of the review command for a message type 12 will complete the linkage information in the EMR relation of the Active Database of Product A. n If the MRA of Product B did not honor the MR linkage request sent from Product A (i.e., chose the remove action instead of enter or link), the enter action of the review command will break the partial linkage established in the EMR relation of the Active Database of Product A. Once linkage has been established between the MRs of two Sablime products (as outlined in the five steps above), MRG state-change messages will automatically be generated in the send queue by the Sablime MRG state-change commands when these commands are executed for the linked MRs. (State changes will only be communicated if the DBA has set up the External MR Communication feature to exchange state change information between projects.) These messages will be sent by the sendmsgs command. On the receiving side, the MRA will review these messages and use the enter action of the review command to record the external MRG state in the EMG relation. When an External_MR report is run for the linked MRs, it will show the internal as well as external MR attributes and states. (See Using the Report Commands for details about External_MR reports.) AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-5 Using the External MR Communication Commands Linking Spawned MRs 7 If an MR against Product A in one project that is already linked to an MR against Product B in another project is spawned, and the spawn flag in the ES relation is on, a spawn message (i.e., a type 3 message showing the status being changed to spawned) will be created for the parent, and a type 13 message will be sent to Product B for each spawned child. Then the MRA of Product A will execute the sendmsgs command to send the type 3 message to Product B. At some point, the MRA of Product B will execute the review command to take action on received messages. (The review command will display the type 13 message on the screen using a type 11 format.) When the MRA of Product B reviews the type 13 messages, the MRA may enter or remove the links. If the MRA decides to enter the message that links mr-a.00 to mr-b, an EMR tuple will be created in the EMR relation of Product B, and no response will be sent back to Product A. Now that both Product A and Product B have a record of the link, state changes on either side will be sent to the other side. If the MRA for Product B decides to remove the message that links mr-a.01 to mrb, a type 13 message with disposition field (i.e., field number 11) "removed" will be sent back to Product A. In this case, the external MR field (i.e., field number 7) will be mr-a.01 and the MR number field (i.e., field number 10) will be mr-b. When the MRA for Product A reviews this message, the link between mr-a.01 and mr-b in the EMR relation will be removed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-6 Issue 1.0 November 2000 The External MR Commands The External MR Commands 7 Figure 7-2 shows the External MR commands and their interaction with the Sablime databases and queues. Table 7-1, following the figure, describes each of the commands in greater detail. NOTE: The GUI does not provide access to any of the external MR commands. NOTE: For all commands in the External MR Communications feature, the following screen labels and keywords require entries that are all lower case, e.g., sablime. External Project(s) proj Destination Project proj External Product prod Destination Product(s) prod AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-7 Using the External MR Communication Commands Outgoing Messages sendmsgs MRG Change-State Commands closemr killmr Sablime Send Queue mrnote qmr listmsgs report review Sablime Receive Queue rcv_msgs Incoming Messages Figure 7-2. External MR Communication Command Overview AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-8 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Sablime Databases The External MR Commands Table 7-1. External MR Commands Command Function qmr Allows an MRA to place a message carrying MR information in the send queue. It captures all the relevant MR information (MR attributes entered on the create screen) including the MR description file, forms an appropriate message, and puts it in the send queue for transmission to its destination. The qmr command also initiates the MR linkage process in the EMR relation of the sending product’s Active Database. sendmsgs Allows an MRA to send the queued messages to their respective destinations and delete them from the send queue after they have been successfully sent. listmsgs Allows a user to display the contents of the messages in the send queue or the receive queue. review Allows an MRA to scan and take an action on the messages in the receive queue. It allows an MRA to: report n enter the received information into the database n link a received MR with an existing MR n remove the received information without entering it into the database n hold the message in the queue for later attention and redisplay the initial review screen n quit the review command and hold the message in the queue for later attention. Allows a user to produce special reports (External_MR reports) that show both the internal MR information and the externally linked MR information. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-9 Using the External MR Communication Commands Table 7-1. External MR Commands Command Function mrnote Automatically produces a description file notation message in the send queue if the notes are added to the description file of an MR that is linked with an external MR. closemr, killmr Automatically produces an MR completion message in the send queue for the MRs that have an external link. MRG StateChange Commands The Sablime commands that change the MRG state (accept, approve, assign, commit, defer, nochange, reject, submit, study, testpass) automatically produce a state-change notification message in the send queue if: n The MR is linked with an external MR, and n For the external products with which it is linked, the DBA had set the flag in the ES relation to send that particular state-change notification. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-10 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Displaying the Contents of Messages Displaying the Contents of Messages 7 NOTE: For detailed information about the listmsgs command, see the listmsgs manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The listmsgs command displays the contents of messages in the send queue or the receive queue. The contents are displayed in either header format or complete format. The header format shows only the message header information; the complete format shows all the information in the message(s). You can also choose the message(s) to be displayed based on external project, product, and message type. If the send queue is selected, the choices made in the External Project(s) and External Product(s) fields specify to whom the messages will be sent. If the receive queue is selected, the choices made in those fields specify from whom the messages have been received. For example, to produce a list of headers for all messages in the receive queue, you would enter the following using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 07/19/97 07:06:19 List/Display Messages Queue: receive_queue Format: header__ External Projects: ___________________________________________________________ External Products: ___________________________________________________________ Message Types: ___________________________________________________________ Output File: stdout_____________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: listmsgs prompt=n The defaults: q=receive_queue fmt=header ofile=stdout AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-11 Using the External MR Communication Commands are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, headers for all the messages in the receive queue will be displayed. A sample report follows. PTSid: sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 External MR Management System Command Project: sablime Date: 07/19/97 Product: sol Time: 07:06:19 Header Report on Message(s) in Receive_Queue -------------------------------------------- Page: 1 Msg Msg Sending Sending External Message # Typ Project Product Identification Originator Time-Stamp --- --- --------- --------- -------------- ---------------- ----------------016 3 sablime fuzz sol970758 015 11 sablime fuzz sablime sablime 06/02/97 14:47:20 06/02/97 14:40:22 7 Suppose now that you want to see the complete messages in the send queue for an external project; you would enter the following using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 07/19/97 07:08:51 List/Display Messages Queue: send_queue___ Format: complete External Projects: sablime____________________________________________________ External Products: prodb______________________________________________________ Message Types: ___________________________________________________________ Output File: stdout_____________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: listmsgs q=send_queue fmt=complete proj=sablime prod=fuzz \ prompt=n The default: ofile = stdout AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-12 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Displaying the Contents of Messages is entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, the complete messages for project sablime and product prodb in the send queue will be displayed. A sample report follows. PTSid: sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 External MR Management System Command Project: sablime Date: 07/19/97 Product: sol Time: 07:08:47 Complete Report on Message(s) in Send-Queue ------------------------------------------- Page: 1 Message Number: 015 ------------------Message Header: Message Type: 3 Receiving Project: sablime Receiving Product: fuzz External Id: fuzz970320 Message Originator: wina Message Time Stamp: 06/07/97 16:31:23 Message Content: MR Number: sol970770 Status: accepted Generic: s1 Reason: PTSid: sablime Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 External MR Management System Command Project: sablime Date: 07/19/97 Product: sol Time: 07:08:47 Complete Report on Message(s) in Send-Queue ------------------------------------------- Page: 2 Message Number: 016 ------------------Message Header: Message Type: 11 Receiving Project: sablime Receiving Product: fuzz External Id: Message Originator: sablime Message Time Stamp: 07/03/97 10:18:40 Message Content: MR Number: sol970074 Severity: 3 Release: not_applicable Origination Date: 03/10/97 System: none Required Date: Subsystem: not_applicable MR Originator: sablime Module: Phase Detected: unit_test Site: not_applicable MR Category: testing AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-13 Using the External MR Communication Commands Abstract: Regression test 1-changes for foo.c Description: This is a modification MR (1) for src/mrmgmt/foo.c AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-14 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Putting a Message on the Queue Putting a Message on the Queue 7 NOTE: For detailed information about the qmr command, see the qmr manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The qmr command queues an MR to an external product. The command gathers all the MR data as entered on the create screen, including the MR description file, and generates a message type 11 for a Sablime external project or a message type 9 for a non-Sablime external project. These messages are transmitted to the external product with the sendmsgs command. (See Appendix D, External MR Message Formats, for a description of each of these messages.) When the message is successfully generated, mail is sent to the MRAs of the product and updates the Active Database to indicate that an external link has been initiated for the specified MR(s). ! CAUTION: Do not queue the same MR more than once to an external product. Wait until the cycle is complete (after the review command) before queueing the same MR to the same external product (see Figure 7-1). If you queue the same MR more than once to the same product before the first cycle is complete, you may corrupt the EMR relation of the database. As an example, suppose you want to send two MRs for an external project to the send queue. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the qmr screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 04/12/97 13:40:36 Queue MRs for Sending to an External Project Destination Project: sablime_______ Destination Product: prodb_________ Generic: ______________ MR Number: proda970010,proda970015___________________________________________ External MR Number (to be Linked with): ______________ Copy To: ____________________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-15 Using the External MR Communication Commands qmr proj=sablime prod=prodb mr=proda970010,proda970015 \ prompt=n In either case, messages in the message type 11 format will be created for MRs proda970010 and proda970015 and stored in the Sablime send queue, and a link will be initiated in the EMR relation of the Active Database. The messages can now be transmitted via the sendmsgs command to the Sablime project for the product prodb. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-16 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Reviewing Messages on the Queue Reviewing Messages on the Queue 7 NOTE: For detailed information about the review command, see the review manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The review command is used by the MRA to scan the messages in the receive queue and to take appropriate action for each message. This command reads the receive queue and populates the Message Number menu with the message numbers for messages that have been received from external products for the product for which you are currently set up via the dot sablime command. You should review the messages in the order in which they have been received, as determined by the time stamp. To see the time stamp, run the listmsgs command; the time stamp appears in both the header list and the complete list. ! CAUTION: Review messages in the order in which they arrived; if you review them out of order, you may get unpredictable results. ! CAUTION: Two MRAs should not review the same message at the same time; this action could corrupt the database. When you select a message to review, the review command displays the message header and contents. You can then select one of the actions listed in Table 7-2. For important information about the result of entering or removing messages by message type, see Table 7-3. NOTE: You may want to execute the listmsgs command to get more information on the receive message queue before taking action on the messages. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-17 Using the External MR Communication Commands Table 7-2. review Command Actions and Results Action Result enter Allows the user to enter the received information into the user’s Sablime database. If the message is type 1 or type 11, an MR is created in the user’s Sablime database. If you want to use the same MR number across products, you must set the environment variable sab1MR=y. After an MR is created and the external MR linkage is established, the review command automatically creates message type 2 in response to type 1 or message type 12 in response to type 11 and puts the message into the send queue for transmission to the sender of the original message. The new message can be transmitted with the sendmsgs command. The message in the receive queue is deleted and the first screen is redisplayed for selection of another message. link For message type 11, the link action allows the received MR to be linked with an existing MR (rather than creating a new MR as in the enter action). Once the MR is linked, the review command creates a response message type 12 in the send queue for transmission to the sender of the original message. The new message can be transmitted with the sendmsgs command. The message in the receive queue is deleted and the first screen is redisplayed for selection of another message. remove Deletes the message from the receive queue without entering any information into the user’s Sablime database and redisplays the first screen for selection of another message. Also puts a response message in the send queue. hold Holds the message for later attention (i.e., no action is taken) and redisplays the first screen for selection of another message. quit Holds the message for later action and terminates the review command without redisplaying the first screen. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-18 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Reviewing Messages on the Queue In Table 7-3, external project refers to either a Sablime or non-Sablime external project, unless otherwise noted. Table 7-3. Results of enter and move Responses Response Result Type 1 Message Description enter remove MR/TR from a nonSablime external project to a Sablime project 1. An MR is created with information given on the right of the screen and linked to the external MR/ TR. 1. A response message is generated for sending to the non-Sablime external project that sent the original message. 2. A response message is generated for sending to the non-Sablime external project that sent the original message. 2. Remove the corresponding type 3 (state-change) messages for this MR. Not Applicable 2 MR/TR disposition information from a Sablime project to a non-Sablime external project (response to type 1) Not Applicable 3 MR state-change information from Sablime to any external project External MRG state change External MRG state change is not updated in is updated in the EMG relation. the EMG relation. 4 MR/TR closure information from any external project to Sablime External MR/TR state change is updated in the EMR relation. External MR/TR state change is not updated in the EMR relation. 5 MR closure from Sablime to a nonSablime external project Not Applicable Not Applicable 6 MR description notes from Sablime to any external project New description/notes are appended to the associated internal MR description. No change is made to internal MR description. 7 MR commitment information from Sablime to an external project External MRG commitment information is updated with the commitment information in the EMG relation. No change is made in the EMG relation. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-19 Using the External MR Communication Commands Table 7-3. Results of enter and move Responses—Continued Response Result Type Message Description enter remove 8 High-severity MR information from Sablime to a nonSablime external project Not Applicable Not Applicable 9 Customer-affecting MR Not Applicable information from Sablime to a nonSablime external project Not Applicable 10 MR disposition from a non-Sablime external project to Sablime (response to type 8 or 9) 1. If the disposition is entered, the external MR information in the EMR relation is updated with the TR number. Not Allowed 2. If the disposition is removed, the external MR information is deleted from the EMR relation and the link with the internal MR is removed. 11 See Table 7-4. 12 MR disposition information from Sablime to Sablime (response to type 11) Not Allowed. 1. If the disposition is entered or linked, the external MR information is updated with the received information. 2. If the disposition is removed, the external MR information is deleted from the EMR relation and the link with the internal MR is removed. 13 Spawned MR information for an external MR. If the disposition is entered, a corresponding EMR record is created in the EMR relation. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-20 Issue 1.0 November 2000 If the disposition is remove, remove the EMR record that links the spawned MR to the external MR. Reviewing Messages on the Queue Table 7-4. Type 11 Results of enter, link, and remove Responses to Message Type 11 Message Description Response enter link MR from Sablime to Sablime 1. An MR is created with information given on the right of the screen and linked to the external MR. 1. The external MR/ 1. No link is established with TR is linked with any internal MRs. an internal MR number. The Abstract and Description File information are appended to the existing internal MR Description File. 2. A response message is generated for sending to the project that sent the original message. 2. A response message is generated for sending to the project that sent the original message. remove 2. A response message is generated for sending to the project that sent the original message. Information from the Reason field is included. 3. Remove the corresponding type 3 (statechange) messages for this MR. When you are using the Curses Forms interface, the first screen simply allows you to enter the number of the message you want to review. A pop-up list displays the numbers of the messages available for review. Then, once you have chosen the message you want to review, and regardless of the message type, a second screen is displayed showing the information for the message specified. For all message types other than type 11, the information received is displayed on the top portion of the screen and the corresponding internal MR information (from the user’s database) is displayed for reference. For example, if the message type is 12, a screen like that in Figure 7-3 is displayed. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-21 Using the External MR Communication Commands logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 04/12/97 14:58:00 Review Response of an External Project for the Sent MR Message Number: ____ Ext Project: ______________ Ext Id: ______________ Message Type: __ Ext Product: ______________ Ext TS: ________________ External Action: _______ EXTERNAL Severity: _ Site: ________________________ Originator: ________________ Category: ________________________ Org Date: ________ Phase Det: ________________________ Reqd Date: ________ EMR UDF1: ________________________ System: ________________________ Subsystem: ________________________ Module: ________________________ Release Det: ________________________ INTERNAL MR Number: ______________ Abstract: ____________________________________________________________ Action: _______ Figure 7-3. Type 12 Screen However, if the message type is 11, the internal and external information are displayed side by side, as shown in Figure 7-4. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-22 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Reviewing Messages on the Queue logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 04/12/97 14:48:17 Review an MR/TR Sent from an External Project Msg No: ____ Msg Type: __ Ext Proj: ______________ Ext Prod: ______________ EXTERNAL INTERNAL Id/MR Number: ______________ ______________ Severity: _ _ Originator: ________________ ________________ Org Date: ________ ________ Reqd Date: ________ ________ System: ________________________ ________________________ Subsystem: ________________________ ________________________ Module: ________________________ ________________________ Release Det: ________________________ ________________________ Site: ________________________ ________________________ Category: ________________________ ________________________ Phase Det: ________________________ ________________________ Abstract: ____________________________________________________________ Desc File: ____________________________________________________________ Action: _______ Reason: ______________________ Copy To: ______________________ Figure 7-4. Type 11 Screen If the second screen is for message type 11, the cursor will move directly to the Abstract field. If you want to enter an MR in the Sablime database for the external MR, press RETURN to use the abstract used by the external project. (You can also change the Abstract line.) When the cursor moves to the Desc File field, the description from the external project will be displayed. You can then edit the file for entry in the Sablime database or accept it as it is. The cursor moves to the Action field. If the selected action is enter, the cursor moves through all the fields in the column on the right to allow entry of data for a new MR in the user’s Sablime database. If the decision to enter an MR was not made before passing through the Abstract or Desc File fields, you can return to these fields by entering n in the CONFIRM pop-up window and then moving back them. If User-Definable Fields (UDFs) are used by either the external or internal product, a third screen appears after the second screen has been confirmed. (See Figure 7-5.) For the data in the UDF fields to be visible, your Database Administrator must have set the Display flag to y for the appropriate MR and EMR AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-23 Using the External MR Communication Commands UDFs. If blank UDFs appear on the screen, break out of the command and inform your DBA. logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 04/12/97 14:48:17 Review an MR/TR Sent from an External Project Msg No: ____ Msg Type: __ Ext Proj: ______________ Ext Prod: ______________ EXTERNAL INTERNAL Id/MR Number: ____________ EMR UDF1: _____________________ MR UDF1: __________________________ EMR UDF2: _____________________ MR UDF2: __________________________ EMR UDF3: _____________________ MR UDF3: __________________________ EMR UDF4: _____________________ MR UDF4: __________________________ EMR UDF5: _____________________ MR UDF5: __________________________ Figure 7-5. review Command UDF Screen If the action you selected on the second screen was link, the cursor will move directly to the Id/MR Number field of the UDF screen. If the external MR specified one of your product’s MRs as the MR to which it should be linked, the number of that internal MR will appear in this field. If this MR number is appropriate, you should simply press RETURN; the rest of the internal fields will be filled in automatically. If it is not, you can erase the suggested MR number and enter the internal MR number to which you want to link the external MR. Then, after the system has validated the internal MR number, it will fill in the other internal fields. If you do not want to link the external MR to any internal MR, you can return to the Action field and select enter. If the action you selected on the second screen was remove, the cursor will move to the Reason field to allow you to enter a reason for not entering the MR into the Sablime database. After you have entered the reason, a message will be created and sent to the external project. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-24 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Reviewing Messages on the Queue As an example of the use of the review command, suppose you want to review a message and enter an MR in the Sablime database; you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 04/12/97 13:56:20 Review Incoming Messages Message Number: 067_ logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 04/12/97 14:48:17 Review an MR/TR Sent from an External Project Msg No: 067_ Msg Type: 11 Ext Proj: sablime_______ Ext Prod: ancl__________ EXTERNAL INTERNAL Id/MR Number: ancl970124____ ______________ Severity: 3 3 Originator: mgt_____________ xuserid_________ Org Date: 03/05/97 03/05/97 Reqd Date: ________ 05/01/97 System: library_________________ library_________________ Subsystem: functions_______________ functions_______________ Module: ________________________ ________________________ Release Det: 1.1_____________________ 2.2_____________________ Site: Dayton__________________ Versailles______________ Category: ________________________ ________________________ Phase Det: sys_test________________ maintenance_____________ Abstract: put_val returns bad value if cur_fcn=read____________________ Desc File: /tmp/edfile123456___________________________________________ Action: enter__ Reason: ______________________ Copy To: ______________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: review msgno=067 action=enter rdate=050197 rel=2.2 \ site=Versailles phase=maintenance prompt=n The defaults: sev=3 org=xuserid (must be a valid PTS ID for the internal product) odate=03/05/97 (message origination date) sys=library (system of external MR) sub=functions (subsystem of external MR) abst="putval returns bad value if cur_fcn=read" (abstract of external MR) desc=/tmp/edfile123456 (description file of external MR) AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-25 Using the External MR Communication Commands are entered automatically and need not be typed. In either case, a new MR will be created with the specified MR attributes and will be linked with external MR ancl970124. A response message will be created in the send queue, and message 067 will be removed from the receive queue. Suppose now that you want to review a message and link it to an existing internal MR; you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 04/12/97 13:56:20 Review Incoming Messages Message Number: 068_ logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 04/12/97 14:48:17 Review an MR/TR Sent from an External Project Msg No: 068_ Msg Type: 11 Ext Proj: sablime_______ Ext Prod: ancl__________ EXTERNAL INTERNAL Id/MR Number: ancl970125____ sab970097_____ Severity: 3 3 Originator: mgt_____________ mjf_____________ Org Date: 03/05/97 04/12/97 Reqd Date: ________ 05/01/97 System: library_________________ library_________________ Subsystem: functions_______________ fcns____________________ Module: ________________________ ________________________ Release Det: 1.1_____________________ 2.2_____________________ Site: Dayton__________________ Versailles______________ Category: ________________________ ________________________ Phase Det: sys_test________________ maintenance_____________ Abstract: sendval returns bad value if cur_fcn=read____________________ Desc File: /tmp/edfile123459___________________________________________ Action: link___ Reason: ______________________ Copy To: ______________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: review msgno=068 action=link mr=sab970097 prompt=n Only the internal MR number need be specified; current values for the internal MR are retrieved from the Sablime database. In either case, external MR ancl970125 will be linked with existing internal MR sab970097. A response message will be created in the send queue and message 068 will be removed from the receive queue. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-26 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Reviewing Messages on the Queue 7 Finally, suppose you want to remove an MR from the receive queue without linking it to any internal MRs; you would make the following entries using the Curses Forms interface: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 04/12/97 13:56:20 Review Incoming Messages Message Number: 069_ logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 04/12/97 14:48:17 Review an MR/TR Sent from an External Project Msg No: 069_ Msg Type: 11 Ext Proj: sablime_______ Ext Prod: ancl__________ EXTERNAL INTERNAL Id/MR Number: ancl970126____ ______________ Severity: 3 _ Originator: mgt_____________ ________________ Org Date: 03/05/97 ________ Reqd Date: ________ ________ System: library_________________ ________________________ Subsystem: functions_______________ ________________________ Module: ________________________ ________________________ Release Det: 1.1_____________________ ________________________ Site: Dayton__________________ ________________________ Category: ________________________ ________________________ Phase Det: sys_test________________ ________________________ Abstract: sendval returns bad value if cur_fcn=read____________________ Desc File: /tmp/edfile123466___________________________________________ Action: remove_ Reason: duplicate for 125_____ Copy To: ______________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: review msgno=069 action=remove rsn="duplicate for 125" prompt=n In either case, external MR ancl970126 will not be linked with any internal MRs. A response message including the reason given in the Reason field will be created in the send queue, and message 067 will be removed from the receive queue. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-27 Using the External MR Communication Commands Sending Messages to an External Project 7 NOTE: For detailed information about the sendmsgs command, see the sendmsgs manual page in the User’s Reference Manual. The sendmsgs command is used to transfer messages from the send queue to an external project. You can send all messages in the queue, groups of messages by project/product/type, or individual messages by message number. NOTE: The MRA may decide to set up a UNIX system cron process to execute sendmsgs at a specified frequency. As an example, suppose you want to send all type 11 messages to an external Sablime project. Using the Curses Forms interface, you would make the following entries on the sendmsgs screen: logid:ral Sablime Configuration Management System v5.0 effid:sablime External MR Management System Command 04/12/97 14:14:07 Send Messages to External Project-Product Message Selection: group_____ Destination Projects: sablime_________________________________________________ Destination Products: prodb___________________________________________________ Message Types: 11______________________________________________________ Message Numbers: ________________________________________________________ Using the Command Line interface, you would enter: sendmsgs fcn=group proj=sablime prod=prodb type=11 prompt=n In either case, all type 11 messages in the send queue for external product prodb will be sent to their destination. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-28 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Creating an MR Creating an MR 7 The web_create HTML page can be used to create an MR against the Sablime product from any machine that can send email to the Sablime machine mozart at the Lucent Technologies facility in Murray Hill, New Jersey. It can also be used to create an MR against another product (if set up by the SDA), and similar requirements apply. The URL for creating an MR against the Sablime product is http://www.stc.lucent.com/sablime/web_create.html. Contact the Database Administrator for the URLs for other products. When Sablime is installed for a project, communications are established that allow the web_create command to be used to transmit MRs to the Sablime team or another Product Team and the web-report command to be used to produce reports about customer-affecting MRs. Five of the fields ( Name, Phone,Email, Fax, and Site) in web_create contain data about you. This information is used by the Sablime or another Product Team when they respond to your MR. When Sablime receives an MR from a customer, a Sablime MR Administrator decides what action should be taken, and a message is sent to the customer explaining the action taken. The MR can be accepted for work or it can be rejected. A similar set of actions occurs for MRs delivered to a Product Team’s MR Administrator. Requesting MR Reports 7 You can use the web_report HTML page to request reports from a Sablime release or from another product release that your Database Administrator has set up for your team. The URL for getting a report from theSablime database is http://www.stc.lucent.com/sablime/web_report.html. Contact the Database Administrator for the URL for your product. NOTE: You must supply a valid email address to obtain an MR report; the report output is mailed to this address. A summary report and a long report are available. For information about these reports, see Chapter 6, Using the Report Commands. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 7-29 Using the External MR Communication Commands AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page 7-30 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields A To get the information you need from the Sablime databases effectively, you must understand something of the structure of the databases. Briefly, each Sablime relation is a directory. In each relation, there are tuples (files), each of which has a two-character name. Each tuple contains records (lines) that are made up of fields and, in some cases, subfields. Fields are separated by semicolons; subfields are separated by commas. Fields with subfields are not available for query. There are three commands that you can use to extract information from the Sablime databases: query, report, and ssql. For a comparison of these commands and examples of their use, see Chapter 6, Using the Report Commands. The relations and their respective databases are shown in Table A-1, below. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-1 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table 1-1. Database Relations Database Relation Active ADM DS GS ORG CAS EMG GT PDEP COM EMR HC PDI CP FILES MD SNAP CRIT FTD MG UMS DBLOCK FZ MR recover DEP G MRS tmp DOC GRP MRX DOL GRPM MS Global Inactive DBLOCK PRX rd tmp DIR PTS rq ES TR sd PR cron sq CAS DS HC ORG COM EMG MD PDEP CRIT EMR MG PDI DBLOCK FILES MR SNAP DEP G MRS tmp DOC GS MRX DOL GT MS NOTE: Some relations exist in both the Active Database and Inactive Database. Make sure that you select the right database for the information you need. Tables A-3 to A-34 show, by relation, the position of the information in the tuple records (the Pos column) and the keyword and screen label that appear in the query command menus, along with the description. (The keywords also appear in the ssql help screen.) The Cmd column uses query to indicate the query command and ssql to indicate the ssql command. Because these commands were developed at different times, there is, in some cases, a variation between keywords and screen labels; thus far, AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-2 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields customers have preferred to keep the keywords as they are because of shell script dependency. NOTE: Your Sablime Administrator can customize the keywords if your project prefers to make them consistent across commands. You can specify ranges for some fields. Four types of ranges are available. For each range, Table 1-2 shows the type of range, the relation containing fields in which the range is allowed, and a sample entry. Do not leave spaces before or after the dash separating the ranges. Table 1-2. Ranges Allowed in query Range Type Relation Entry Format Date COM EMG EMR G GS GT Decimal G MG MRX n.nn–n.nn Example: 0.5–10.5 Number COM MG MR MRX n–n Example: 1–3 State MG MRG state–MRG state Example: assigned–preapproved MD MG MR ORG PTS mm/dd/yy–mm/dd/yy Example: 06/01/91–05/31/97 The acceptable states for this field in range sequeryuence are shown below. Range hierarchy is left to right, top to bottom. nochangedeferredunderstudyacceptedspawned assignedsubmitted[preinspected*prefitpassedprehitpassed preitpassed][inspectedfitpassedhitpasseditpassed] [prepublishedprefstpassedprehstpassedprestpassed][published fstpassedhstpassedstpassed]preapprovedapproved closed * States in square brackets are parallel MRG states. When you select records based on information in the Developer field, query normally expands a group name to its members. To change this behavior, AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-3 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields precede the group name with an exclamation point (!) to cause query to select records containing the literal group name instead of expanding the group to its members, e.g., !srcteam gives records that have srcteam as the developer. Also when you select records based on information in the Developer field, if a PTS ID is given, query does not find the PTS ID within groups. To change this behavior, precede the developer’s PTS ID with a caret (^login) to cause query to include the groups the PTS ID is in when selecting records, e.g., ^jhn gives records that have jhn as the value of the developer field and have jhn as the member of the developer field.. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-4 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields The ADM relation is available to the query command only. Since a single tuple is the output of the query, no keywords, sorting, or printing are relevant. Table A-3. Pos ADM Relation Fields Field Description Cmd 1 DBA Group Name query 2 MRA Group Name 3 Next MR Number 4 MR Prefix 5 Trace Flag 6 History Flag 7 Mail Flag 8 Field Value Separator 9 In-Process Metrics Flag 10 Not Used 11 Automatic Routing Flag 12 Automatic Assignment Flag 13 Reassignment Flag 14 Automatic Dependency Specifier 15 Dependency Override Flag 16 Source Administrator Group Name 17 Mail Dispatch Interval 18 Hardware Administrator Group 19 Default Version Control Tool for NonBinary Files 20 Not Used Keyword Screen Label Range AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-5 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-4. CAS Relation Fields Pos Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label 1 Cascading Type query type Cascade Type key Upper Level Key group Lower Level Group Name Range ssql 2 Upper-Level Key query ssql 3 Lower-Level Group query ssql Table A-5. Pos 1 COM Relation Fields Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range Generic query g Generic comid Commitment Id comdate Commitment Date Date nusers Number of Users Affected Num ssql tstamp Date and Time Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Command query cmd Command g Generic fcntype CommandFunction ssql 2 Commitment ID query ssql 3 Commitment Date query ssql 4 Number of Users query ssql 5 Time Stamp Table A-6. Pos 1 query CP Relation Fields ssql 2 Generic query ssql 3 Function query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-6 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Range Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-6. Pos 4 CP Relation Fields—Continued Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Executor(s) query exec Executor(s) email Email Recipient(s) Range ssql 5 Email Recipient(s) query ssql Table A-7. Pos 1 CRIT Relation Fields Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Criteria Type query crtype Criteria Type crowner Criteria Owner g Generic class MR Class subclass MR Subclass type MR Type subtype MR Subtype sys System subsys Subsystem mod Module site Site Range ssql 2 Criteria Owner query ssql 3 Generic query ssql 4 MR Class query sql 5 MR Subclass query ssql 6 MR Type query ssql 7 MR Subtype query ssql 8 System query ssql 9 Subsystem query ssql 10 Module query ssql 11 Site query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-7 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-7. Pos 12 CRIT Relation Fields—Continued Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Release query rel Release Detected ssql 13 Not Used 14 Not Used Table A-8. Pos 1 2 Range DEP Relation Fields Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Dependent MR Number query mr ssql Dependent MR Number Generic query g Generic dep Depended-Upon MR reason Reason for Dependency Range ssql 3 4 Depended-Upon MR Number Reason for Dependency Table A-9. Pos 1 query ssql query ssql EMG Relation Fields Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label External ID. query emgid External Id. esg Ext Generic esprod External Product emgstat External Status emgcomi d Commitment Id Range ssql 2 External Generic query ssql 3 External Product query ssql 4 External Status query ssql 5 Commitment ID query ssql 6 Commitment Date query ssql emgrdate Commitment Date AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-8 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Date Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-9. Pos 7 EMG Relation Fields—Continued Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Message Type query mtype Message Type reason Reason tstamp Time Stamp Range ssql 8 Reason query ssql 9 Time Stamp query ssql Table A-10. EMR Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range MR Number query mr MR Number eproj Ext Project esprod Ext Product esid Ext Id. rte Route esnorg Dialog Originator estat Ext Status reason Reason ssql tstamp Time Stamp query extorg Ext MR Org extodate Ext Org Date ssql 2 External Project query ssql 3 External Product query ssql 4 External ID query ssql 5 Route query ssql 6 Dialogue Originator query ssql 7 Status query ssql 8 Reason query ssql 9 10 11 Time Stamp External Project MR Originator External Project Origination Date query ssql query Date ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-9 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-10. EMR Relation Fields—Continued Pos 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range External Project Requeryuired Date query extrdate Ext Requeryd Date Date External Project Severity query extsev Ext MR Severity extsys Ext System extsub Ext Subsystem extrel External Release extsite Ext Site extcat Ext Category extmod Ext Module extpd Ext Phase Det emrudf1 EMR UDF1 emrudf2 EMR UDF2 emrudf3 EMR UDF3 emrudf4 EMR UDF4 emrudf5 EMR UDF5 External Project System External Project Subsystem External Project Release External Project MR Origination Site ssql ssql query ssql query ssql query ssql query ssql External Project MR Category ssql External MR Module query query ssql 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 External Phase Detected External MR UserDefinable Field 1 External MR UserDefinable Field 2 External MR UserDefinable Field 3 External MR UserDefinable Field 4 External MR UserDefinable Field 5 query ssql query ssql query ssql query ssql query ssql query ssql Not Used AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-10 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-11. ES Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range External Project query proj External Project prod External Product host Remote Machine net Network Type prog Remote Program ssql parm Parameters query sflag Status Flag stats Status ssql 2 External Product query ssql 3 Host Machine query ssql 4 Network Type query ssql 5 Program Name query ssql 6 7 Program Parameters Status Exchange Flag query ssql 8 Status Flags query ssql Table A-12. FTD Relation Fields Pos Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label 1 Command Name query prog Sablime Program intkey Internal Key flag Flags ssql 2 Internal Key Name query Range ssql 3 3 subfields: Mandatory Flag Hideable Flag Show Flag query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-11 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-12. FTD Relation Fields—Continued Pos 4 5 6 7 8 Field Description Cmd 4 subfields: Prompt Name Pad Spaces Not Used Help Msg. Number query 3 subfields: Type of Field Code Maximum Length Default Value Group Name of Value Choices Keyword Screen Label text Text Fields ssql value Values query fvalue Group/File hmi HMI Attributes extkey External Key ssql query ssql query 8 subfields: Row Number for HMI ssql Column Number for HMI Background Character Left/right scrolling buffer length Prompt Position Complete Field Name Attribute Number of Menu Choices Allowed External Key Name Range query ssql Table A-13. FZ Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Source File query sfile Source File dir Directory g Generic ssql 2 Directory query ssql 3 Generic query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-12 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Range Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-13. FZ Relation Fields—Continued Pos 4 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Snapshot ID query snapid Snapshot ID sid Delta ID Range ssql 5 Delta ID query ssql Table A-14. G Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range Generic query g Generic ssql gstat Status Generic Source ID String (SID) query gsid Generic SID Generic Administrator query ga GA Group gdoc Document Flag gfirm Firmware Flag ghard Hardware Flag gsoft Software Flag gsrdate Creation Date gcrid Generic Creator gcldate Close Date ssql 2 3 4 Generic Status query Dec ssql ssql 5 Documentation Flag query ssql 6 Firmware Flag query ssql 7 Hardware Flag query ssql 8 Software Flag query ssql 9 Creation Date query Date ssql 10 Generic Creator query ssql 11 Close Date query Date ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-13 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-14. G Relation Fields—Continued Pos 12 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Generic Closer query gclid Generic Closer rflag Released Flag srccnt For Future Use relgen For Future Use Range ssql 13 Generic Release Flag query ssql 14 Not Used query ssql 15 Not Used query ssql 16 Not Used Table A-15. GRP Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Group Name query grpname Group Name owner Group Owner grptype Group Type Range ssql 2 Group Owner query ssql 3 Group Type query ssql Table A-16. GRPM Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Group Name query grpname Group Name item Member Name ssql 2 Member Name query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-14 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Range Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-17. GS Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range Source Files query sfile Source File dir Directory g Generic sdir SDB Directory gschg Change Date gsstat GS Status common Common Generic bfile Binary File fltype File Type sqflag Count File for QA owner File Owner ssql 2 3 Logical Relative Source Directory ssql Generic query query ssql 4 5 Source Data Base Relative Source Directory ssql Change Date query query Date ssql 6 GS Status query ssql 7 Common Generics query ssql 8 Binary File Flag query ssql 9 Source Type query ssql 10 QA Count Flag query ssql 11 Source File Owner query Source File Owner ssql 12 Version Control Tool query verctl ssql 13 14 Latest mr Branch Version Number in the SBCS File that is declared official ssql Not Used query query ssql Version Control Tool lastofcsid Last Official SID srcid For Future Use AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-15 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-17. GS Relation Fields—Continued Pos 15 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Not Used query srcudf1 For Future Use ssql srcudf2 For Future Use Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Generic query g Generic class Class tt1 Test Team1 tt2 Test Team2 tt3 Test Team3 tt4 Test Team4 tt5 Test Team5 at Approval Team mt Manufacturing Team qat QA Team ssql 16 Not Used Range query Table A-18. GT Relation Fields Pos 1 ssql 2 Class query ssql 3 Test Team 1 query ssql 4 Test Team 2 query ssql 5 Test Team 3 query ssql 6 Test Team 4 query ssql 7 Test Team 5 query ssql 8 Approval Team query ssql 9 Manufacturing Team query ssql 10 11 Quality Assurance Team ssql Not Used query query qadate ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-16 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Range Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-19. HC Relation Fields Pos 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Hardware Code Identifier query code Code Id rel Product Release ver Version stat Status fenum Number in Fully Equeryuip Sys newcode New Code cfact Complexity Factor usecode Use Code in Fault Density usemr Use MR in Fault Density stdt Initial System Test Date Date reldt Initial Release Date Date Generic/Product Release Number Version Number of Hardware Code Hardware Code Tuple Status ssql query ssql query ssql query ssql Quantity of this Hardware Code in a Fully Equeryuipped System query A Flag to Indicate Whether this Code is New or Reused for this Release query ssql Num ssql A Number that Reflects an Hcode’s Complexity query A Flag to Indicate Whether this Hcode is to be used To Calculate the Hardware Fault Density query A Flag to Indicate Whether Mrs Against this Hcode are to be used to Calculate the Hardware Fault Density Range ssql ssql query ssql The Date When this Hcode First Went to System Test query The Date When this Hcode was First Released query ssql ssql Dec AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-17 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-19. HC Relation Fields—Continued Pos 12 13 14 15 Field Description Cmd A Short Description of the Hardware Code query Hcode Tuple Creation Date Hcode Tuple Change Date Keyword Screen Label Range ssql abst Code Abstract query crdate Creation Date Date chgdate Change Date Date hcudf1 HC UDF1 hcudf2 HC UDF2 ssql query ssql User-Definable Field 1 query ssql 16 User-Definable Field 2 query ssql 17 Not Used 18 Not Used Table A-20. MD Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label MR Number query mr MR Number g Generic sfile Source File dir Directory sid Delta Id dev Developer mdstat MD Status mdchg Change Date Range ssql 2 Generic query ssql 3 Source File query ssql 4 5 Logical Relative Source Directory ssql Delta ID query query ssql 6 Developer query ssql 7 Delta Status query ssql 8 Delta Date query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-18 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Date Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-21. MG Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range MR Number query mr MR Number g Generic mrgstat MG Status Status chgdate Change Date Date dev Developer (Group) sev Severity Num due Due Date Date rcode Reason Code ssql reason Reason query mgstcd MG Status Code Number class MG Class type MG Type spawns Spawns mgcomid Commitment Id. mrgeflag External MR Flag hcode Code Number ssql 2 Generic query ssql 3 MG Status query ssql 4 Change Date query ssql 5 Developer (Group) query ssql 6 Severity query ssql 7 Due Date query ssql 8 Reason Code query ssql 9 10 11 Reason if Code is Other query System Code for Status ssql MRG Class query ssql 12 MRG Type query ssql 13 Number of Spawns query ssql 14 Commitment ID query ssql 15 External Link Flag query ssql 16 Hardware Code Number query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-19 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-21. MG Relation Fields—Continued Pos 17 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range Hardware PDI query pdi PDI Number subclass MG Subclass subtype MG Subtype rel Release Introduced pi Phase Introduced odp Optimal Detection rootc Root Cause rootsubc Root Cause Subcategory acteff Actual Effort esteff Estimated Effort Dec tte1 Test Team Effort 1 Dec tte2 Test Team Effort 2 Dec tte3 Test Team Effort 3 Dec tte4 Test Team Effort 4 Dec tte5 Test Team Effort 5 Dec ssql 18 MR Subclass query ssql 19 MR Subtype query ssql 20 Release Introduced query ssql 21 Phase Introduced query ssql 22 23 Optimal Detection Phase ssql Root Cause query query ssql 24 25 Root Cause Subcategory ssql Actual Effort query query ssql 26 Estimated Effort query ssql 27 Test Team 1 Effort query ssql 28 Test Team 2 Effort query ssql 29 Test Team 3 Effort query ssql 30 Test Team 4 Effort query ssql 31 Test Team 5 Effort query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-20 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-21. MG Relation Fields—Continued Pos 32 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range User-Definable Field1 query mrgudf1 MRG UDF1 mrgudf2 MRG UDF2 mrgudf3 MRG UDF3 mrgudf4 MRG UDF4 mrgudf5 MRG UDF5 studyeff Study Effort Dec ncdt Nochange Date Date ancdt Activate from Nochange Date Date defdt Defer Date Date adefdt Activate from Defer Date Date stdydt Under Study Date Date propdt Propose from Date Understudy Date accptdt Accept Date Date assgndt Assign Date Date submtdt Submit Date Date tstdt1 Test 1 Date Date ssql 33 User-Definable Field2 query ssql 34 User-Definable Field3 query ssql 35 User-Definable Field4 query ssql 36 User-Definable Field5 query ssql 37 Actual Study Time query ssql 38 Nochange Date query ssql 39 40 Activate from Nochange Date query Defer Date query ssql ssql 41 42 Activate from Defer Date query Under Study Date query ssql ssql 43 44 Propose from Under Study Date query Accept Date query ssql ssql 45 Assign Date query ssql 46 Submit Date query ssql 47 Test 1 Date query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-21 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-21. MG Relation Fields—Continued Pos 48 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range Test 2 Date query tstdt2 Test 2 Date Date tstdt3 Test 3 Date Date tstdt4 Test 4 Date Date tstdt5 Test 5 Date Date apprdt Approve Date Date fltype Fault Type ndc Non-detection Cause ndcs Non-detection Cause cost Cost of Problem dupmr Duplicate Nochanged MR ssql 49 Test 3 Date query ssql 50 Test 4 Date query ssql 51 Test 5 Date query ssql 52 Approve Date query ssql 53 Fault Type query ssql 54 Non-detection Cause query ssql 55 56 Non-detection Cause Subcategory ssql Cost of Problem query query ssql 57 Duplicate Nochanged MR 58 Not Used 59 Not Used 60 Not Used query ssql 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-22 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Num Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-21. MG Relation Fields—Continued Pos Field Description Cmd 71 MRG Resolution query ssql 72 MRG History MRG Rejection MRG Solution 76 Spawn Notes Test Notes reso MRG Resolution hist MRG History reject MRG Rejection solu MRG Solution query ssql 75 Range query ssql 74 Screen Label query ssql 73 Keyword query ssql spawnote Spawn Notes s query testnotes MRG Test Notes ssql Table A-22. MR Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range MR Number query mr MR Number cid MR Creator stat MR Status cat MR Category abst Abstract rdate Requeryuired Date Date sev Severity Num ssql 2 MR Creator query ssql 3 MR Status query ssql 4 MR Category query ssql 5 Abstract query ssql 6 Requeryuired Date query ssql 7 Severity query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-23 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-22. MR Relation Fields—Continued Pos 8 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Spawns query spawns Spawns Range ssql 9 10 Reason if Code is Other ssql reason Reason Reason Code query rcode Reason Code crdate Create Date Date cldate Completion Date Date clid MR Closer query ssql 11 Create Date query ssql 12 Completion Date query ssql 13 MR Closer query ssql 14 15 Not Used query Phase Detected ssql dummy query pd Phase Detected mrudf1 MR UDF1 mrudf2 MR UDF2 mrudf3 MR UDF3 mrudf4 MR UDF4 mrudf5 MR UDF5 dupmr Duplicate Killed MR desc Description ssql 16 User-Definable Field1 query ssql 17 User-Definable Field2 query ssql 18 User-Definable Field3 query ssql 19 User-Definable Field4 query ssql 20 User-Definable Field5 query ssql 21 Duplicate Killed MR query ssql 22 Description query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-24 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-23. MRS Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label MR Number query mr MR Number g Generic mrs Spawned MR Range ssql 2 Generic query ssql 3 Spawned MR query ssql Table A-24. MRX Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range MR Number query mr MR Number adate Activation Date rcode Reason Code ssql reason Reason query mrxdev Developer (Group) mrxsev Severity Num mrxdue Due Date Date mrxast Actual Study Effort Dec ssql 2 Activation Date query Date ssql 3 Reason Code query ssql 4 5 Reason Assigned Developer query ssql 6 Severity query ssql 7 Due Date query ssql 8 Actual Study Effort query Actual Study Time ssql 9 Estimated Effort query mrxee Estimated Effort globsolu Global Solution Dec ssql 10 Global Solution query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-25 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-25. MS Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label MR Number query mr MR Number g Generic sfile Source File dir Directory msstat MS Status Range ssql 2 Generic query ssql 3 Source File query ssql 4 5 Logical Relative Source Directory ssql Status query query ssql Table A-26. ORG Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label MR Number query mr MR Number org MR Originator odate Origination Date prod Product Range ssql 2 MR Originator query ssql 3 Origination Date query ssql 4 Product query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-26 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Date Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-26. ORG Relation Fields—Continued Pos 5 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label System query sys System sub Subsystem rel Release Detected site Site mod Module Range ssql 6 Subsystem query ssql 7 Release Number query ssql 8 Site query ssql 9 Module query ssql Table A-27. PDEP Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range Source File query sfile Source File dir Directory sid Version Control ID mr Dependent MR Number g Generic dep Depended-Upon MR reason Reason for Dependency ssql 2 3 Relative Directory Name ssql Delta Identifier query query ssql 4 MR Number query ssql 5 Generic Name query ssql 6 7 Depended-Upon MR Number query Reason for Dependency query ssql ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-27 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-28. PDI Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range PDI Number query pdi PDI Number rel Product Release stat Status class Change Class isdate Issue Date aff Affected Drawings/Do reason Reason for Change c1 Cost1 Num c2 Cost2 Num c3 Cost3 Num ssql 2 3 The Release to Which the PDI Applies ssql PDI Tuple Status query query ssql 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Hardware Change Classification Date when Hardware Change was Issued Other Drawings or Documents Affected by this PDI query ssql query ssql query ssql Reason for Making query this Hardware Change ssql Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate query ssql query ssql query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-28 Issue 1.0 Date November 2000 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-28. PDI Relation Fields—Continued Pos 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate query c4 Cost4 Num Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate query c5 Cost5 Num Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate query c6 Cost6 Num Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate query c7 Cost7 Num Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate query c8 Cost8 Num Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate query c9 Cost9 Num Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate query c10 Cost10 Num ssql ssql ssql ssql ssql ssql ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-29 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-28. PDI Relation Fields—Continued Pos 18 19 20 21 22 23 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate query c11 Cost11 Num c12 Cost12 Num tcost Total Cost of Change Num crdate Creation Date Date chgdate Change Date Date pdiudf1 PDI UDF1 pdiudf2 PDI UDF2 Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate ssql query ssql Total Cost of Change as Determined by the Appropriate Product Management Organization or Their Delegate query PDI Tuple Creation Date query PDI Tuple Change Date ssql ssql query ssql User-Definable Field 1 query ssql 24 User-Definable Field 2 query ssql 25 Not Used 26 Not Used Table A-29. PR Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Product query pr Product prtype Product Type ssql 2 Product Type query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-30 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Range Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-29. PR Relation Fields—Continued Pos 3 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Multi-Machine Flag query mm Multi-Machine host Host mcbdir Master Bin adbdir Active DB idbdir Inactive DB sdbdir Src Control DB sadb For Future Use sys For Future Use rel For Future Use loc For Future Use Range ssql 4 Host query ssql 5 6 7 8 9 Master Control Bin Directory Path Active Database Directory Path Inactive Database Directory Path query ssql query ssql query ssql Source Database Directory Path ssql Not Used query query ssql 10 Not Used query ssql 11 Not Used query ssql 12 Not Used query ssql Table A-30. PRX Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Range Product query pr Product ssql prname Product Name query prlan Prog. Language prcust Billing Customer ssql 2 3 4 Product Name Major Prog. Language for Product query ssql First Billable Customer query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-31 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-30. PRX Relation Fields Pos 5 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Organization Number query prorg Organization prid Sablime Product ID dummy1 For future use Range ssql 6 Sablime Product ID query ssql 7 Not Used query ssql Table A-31. PTS Relation Fields Pos Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label 1 Sablime PTS ID query ptsid Sablime PTS ID name Full Name dept Department loc Location Code room Room phone Phone ssql vflags Verbose Flags query ed Favorite Editor ssql 2 Full Name query ssql 3 Department query ssql 4 Location Code query ssql 5 Room Assignment query ssql 6 Phone Number query ssql 7 8 5 subfields: HMI Flag Verbose Prompt Flag Verbose Info Flag Verbose Help Flag Pop-up Delay Favorite Editor query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-32 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Range Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-31. PTS Relation Fields—Continued Pos 9 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Email Address query email Email Address Range ssql 10 Not Used query access ssql 11 Email Flag mflag Email Flag auth Auth.Products lu Last Usage aom Auto Orig Mode aam Auto Asgn Mail mwd Verbose Email main For Future Use ssql count For Future Use query mgr Manager query ssql 12 Authorized Products query ssql 13 Last Usage query Date ssql 14 15 16 Automatic Originator Flag query ssql Automatic Assignee Flag ssql Verbose Email query query ssql 17 Main PTS ID query ssql 18 19 Number of PTS IDs Manager’s PTS ID query ssql 20 Not Used Table A-32. SNAP Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Snapshot ID query snapid Snapshot ID g Generic Range ssql 2 Generic query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-33 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-32. SNAP Relation Fields—Continued Pos 3 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Creator query cid Creator crdate Creation Date comments Comments mrgstat Mrgstate br Branch incldep Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs mrs MRs for File Selection umrs MRs for Additional Changes dir Directory brdt Cutoff Date kx Expand ID Keywords? Range ssql 4 Creation Date query Date ssql 5 Comments query ssql 6 Mrgstate query ssql 7 Branch query ssql 8 9 Include Missing Depended-Upon MRs ssql MRs for File Selection query query ssql 10 11 MRs for Additional Changes ssql Directory query query ssql 12 Cutoff Date query ssql 13 Expand ID Keywords? query ssql 14 Files extracted ssql files Files Extracted 15 Output of getversion call ssql gout Output of getversion call 16 Extraction script ssql vcmds Command script AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-34 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Date Sablime Database Relations and their Fields Table A-33. TR Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Generic query g Generic pr Product Range ssql 2 Product query ssql 3 Not Used Table A-34. UMS Relation Fields Pos 1 Field Description Cmd Keyword Screen Label Source File query sfile Source File dir Directory g Generic mr MR Number Range ssql 2 3 Logical Relative Source Directory ssql Generic query query ssql 4 MR Number query ssql AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 A-35 Sablime Database Relations and their Fields AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page A-36 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Error Messages Generated by Sablime for Users B User error messages provide information about a problem in data entry that you can correct by entering acceptable data. Table B-1 lists each field alphabetically with the error. A suggested response to the message is included to help you enter acceptable data. System errors are not listed here. If a system error occurs, write down the situation in which it occurred and have your Sablime Administrator report it to the Sablime hotline. Table B-1. Error Messages Field Error Message Response Any field The current __ Buffer of size __ is full. There is not enough room for the data you are trying to enter. The help message tells you how many characters you can use. Keyword __ entry doesn’t match any Popup selection. The information you entered does not match allowed responses. The menu lists acceptable entries. Your entry doesn’t match any Popup selection. The information you entered does not match allowed responses. The menu lists acceptable entries. You many not use the ';' character (Sablime Database Delimiter) You cannot use a semicolon in your input data. No other status(es) can be given when [all, none] is entered. If you enter all or none in this field, you cannot specify statuses. Accept MRs With Statuses AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 B-1 Error Messages Generated by Sablime for Users Table B-1. Error Messages—Continued Field Error Message Response Active DB Active DB [adb] must be the system’s adb for the product Enter the full path name for the ADB directory. Actual Effort Number [#] is an invalid number. The number you have entered is not in the right format. Format is n, n.n, nn.n, or nn.nn, where n is an integer. Criteria Owner The PTS ID you have entered is not legitimate. Your entry is not valid. Check spelling and group type or make a different entry. The Criteria Owner [name] does not exist in the CRIT relation. You are trying to modify, view, or delete a record that does not exist. Check the spelling and correct or add the record. The Criteria Owner [name] already exists in the CRIT relation. You are trying to add a record that already exists. Enter a different name or change the function. Group/PTSid [name] is not in the Active DB. The name you have specified does not exist. Check the spelling. You do not have the privilege to delete. Only a DBA or MRA can delete routing criteria. Only a DBA or GA can delete assignment criteria. You do not have the privilege to modify. Only a DBA or MRA can modify routing criteria. Only a DBA or GA can modify assignment criteria. The entered value [string] is not a valid MRA in this product. The specified PTS ID or a member of the specified group is not an MRA. Criteria Type This program requires MRA or DBA privileges. You must be the MRA or the DBA to use this command. Current File Name Only 1 filename may be specified. Enter only one file name. If you want to work DBA Group with more files, reissue the source command for each file. Cannot access GS record for [file] in generic[g]. The GS record in the data base is not accessible. See your Sablime Administrator. No GS record for file [file]. The GS record for the file does not exist. See your Sablime Administrator. You cannot modify a DBA’s group name [name] that is not in the ADM relation. You are trying to modify a DBA group that is not in the ADM relation. Check it and reenter. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page B-2 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Error Messages Generated by Sablime for Users Table B-1. Error Messages—Continued Field Error Message Response Delete Please enter ‘y' again to confirm, or just <CR> if you didn't really mean it! If you want the file you specified removed from the data base, enter y and press RETURN. The file is not deleted until you confirm the command. To keep the file, press RETURN without an entry. Developer You must not unassign an MR by mrgedit command. Use the assign command with a blank entry in the Developer field to unassign the MR. You must not assign an MR by mrgedit command. Use the assign command to assign or reassign the MR. The group member [name] is not a valid ptsid in this product. The group you have specified contains a member that is not a valid PTS ID. Use the setgroup command to change or delete that member. MR [#] is not a valid MR. Verify the number of the MR you cite as the duplicate MR. Duplicate MR Number Estimated Effort Number [#] is an invalid number. The number you have entered is not in the right format. Format is n, n.n, nn.n, or nn.nn, where n is an integer. External Product You cannot add an ES record that is already in the database. The external project/product you have entered already exists. Change the function, the external project or the external product. You cannot [delete | modify | view] an ES Record that is not in the database. The external product you have entered does not exist. Change the function, the external project or the external product. Previous Generic must be given, mandatory field. You must enter a generic in this field. The given generic [g] is not valid for this product. The generic specified is not correct for the product specified. Change the product name or the generic. You are not the GA for generic [g]. Can only assign to yourself. You must have GA privileges for the specified generic to perform the function chosen. Some of the MRs associated with this Generic are still open. Check the MG relation to locate the MRs that are not yet in a terminal state or ask the GA for the information. Generic AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 B-3 Error Messages Generated by Sablime for Users Table B-1. Error Messages—Continued Field Error Message Response Key for Edit The tuple to edit does not exist, to continue hit <CR>. No tuple record has been found with the specified key. Press RETURN to continue. You are allowed to enter a different key. Record [#], expected to find [#] fields, found [#]. The number of fields in the specified record is incorrect. Notify your Sablime Administrator. Hit a <CR> in the ’Tuple to Edit’ field to continue. The cursor moves to the Tuple to Edit field. Press RETURN to enter your editor and edit the tuple. Entry must be a number between [n] and [n]. Your entry is too large or too small. Enter a number between the parameters given. The mail interval in seconds must be a positive integer. Your entry contains illegal characters. Enter only positive integer numbers. The mail interval in seconds must be between [2] and [99]. Your entry is too large or too small. Enter a number between the parameters given. Master Bin Master Bin [MCB] must be the Master Bin for the product Enter the full path for the MCB directory. Maximum Popup Choices The number entered must be a positive integer. Your entry contains illegal characters. Enter only positive integer numbers. Entry must be a number between [n] and [n]. Your entry is too large or too small. Enter a number between the parameters given. No cascade is set for sysCASsub [name]. Because no cascade is set, no entry is allowed in this field. No cascade is set for sysCASsub OR subCASmod. Because no cascade is set, no entry is allowed in this field. Invalid [module] Module for this product. The module you have given is not valid. Enter a valid module for the product. Invalid [g] generic for this product. The generic given is not valid. Enter a different generic. The given Generic is not for any particular MR class. The generic you have specified does not have a class associated with it. See your Sablime Administrator. No Class is set for this product in the G relation. The generic specified has no class. See your Sablime Administrator. Invalid [class] class for the given generic(s). The specified class is not valid. Enter a different class. L/R Scroll Size Mail Interval Module MRG Class AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page B-4 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Error Messages Generated by Sablime for Users Table B-1. Error Messages—Continued Field Error Message Response MR Suffix ORG Relation tuple for the given MR does not exist. Verify the MR number and the ORG relation in the ADB. ORG relation tuple for MR [ ] does not exist. Verify the MR number and the ORG relation in the ADB. No cascade is set for clsCASscls. Because no cascade is set, no entry is allowed in this field. Invalid [subclass] Subclass for this product. The subclass you have given is not valid. Enter a valid subclass for the product. MRG Subtype Invalid [subtype] Subtype for this product. The subtype you have given is not valid. Enter a valid subtype for the product. MR Type There is no MR Type set for this product. Because no type is set, no entry is allowed in this field. No FTD data is found for MR Type in this product. Because no system information exists in the FTD relation, no entry is allowed in this field. Invalid [type] MR Type for this product. The type you have given is not valid. Enter a valid type for the product. MRA Group You cannot modify a MR’s group name [name] that is not in the GRP relation. The group name you have entered does not exist. Check it and re-enter. New Directory Directory must be specified as a relative pathname. Enter the correct relative path. Do not precede or follow the name with a slash (/). Be sure that you begin the name from the base of your node. See Product Directory Structure in Chapter 1 of the Sablime User’s Manual for information about specifying nodes. Directory pathname must not end with /. Remove the final slash in the relative pathname. Directory pathname should not have two consecutive slashes. You have entered two slashes in a row (//). Delete one of the slashes. MRG Subclass New File Type See VHELP for why you can't convert this file yet./Unable to find directory structure file. Origination Date The Origination Date must be <= today’s date. Press ? from the field to see VHELP. Enter a date in a valid format which is today or later. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 B-5 Error Messages Generated by Sablime for Users Table B-1. Error Messages—Continued Field Error Message Response Product Product ID for the [product] Prod- The product for the generic for which you uct is missing from the Global DB have set up is not in the GDB. See your [group] [program]. Sablime Administrator. Product ID for the [product] Prod- The product for the generic for which you uct is missing from the PTS rela- have set up is not in the PTS relation. See tion. your Sablime Administrator. Invalid product name or option specified - try again. Enter an item from the system-supplied menu. You cannot [add] a [PR | PRX] PRODUCT that is already in the database. The product you have entered already exists. Change the function or the product. You cannot [delete | modify | view] a [PR | PRX] PRODUCT that does not exist. The product you have entered does not exist. Change the function or the product. Reason for ... When Reason Code is ’other’, a Reason is mandatory. You must enter a reason if you have specified other in the Reason Code field. Release Detected Product Release [rel] does not exist in Active DB. Enter a valid release number. You must select at least one criterion from the above. If you have specified route as the Criteria Type, you must enter data in one of the fields on the left side of the screen. No FTD data for Release field of the create command. Because no release information exists in the FTD relation, no entry is allowed in this field. Invalid [release] Release detected for this product. The release you have given is not valid. Enter a valid release for the product. Request Desc File Request Desc Rile [desc] can be a text file (w/size 0) or hit [return] Press RETURN or enter the name of a file for access to a temporary file in your editor. Required Date The Required Date must be >= to the Origination Date. Enter a date in a valid format, i.e., 113096, 5/10/96, 11/9/96, 12/02/96. Site No FTD data for site in create command. Because no site information exists in the FTD relation, no entry is allowed in this field. Invalid [site] Site for this product. The site you have given is not valid. Enter a valid site for the product. No cascade is set for sysCASsub. Because no subsystem information exists in the FTD relation, no entry is allowed in this field. Invalid [subsystem] Subsystem for this product. The subsystem you have given is not valid. Enter a valid subsystem for the product. Subsystem AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page B-6 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Error Messages Generated by Sablime for Users Table B-1. Error Messages—Continued Field Error Message Response System No FTD data is set for sys field of the create command. Because no system information exists in the FTD relation, no entry is allowed in this field. Upper Level Key A group already exists for key [key]. You are trying to add a group where one already exists. Select another function. No group exists for key [key]. You are trying to modify, view, or delete a group that doesn’t exist. Add it or change the key. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 B-7 Error Messages Generated by Sablime for Users AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page B-8 Issue 1.1 November 2000 External MR Error Messages C Error Messages C User error messages provide information about a problem in data entry that you can correct by entering acceptable data. Table C-1 lists each field alphabetically with the error message. If the message relates to a particular command, the command name is shown in italics in the Field column in line with the message. A suggested response to the message is included. Table C-1. External MR Communications Error Messages Field Error Message Response Any field The current f Buffer of size [n] is full! There is not enough room for the data you entered. The help message will tell you how many characters you may use. You are trying to enter an illegal character [octal #] The key you pressed (usually a non-character key) is not acceptable to Sablime. The help message will give you information about acceptable keys. You can’t move back further; You are in the HOME field already. The key(s) you pressed are to be used to take you to the HOME field but the cursor is already there. An [field name] field is mandatory; no You cannot advance to the next default available. step without entering data in this field. CONFIRM MR [xx] has already been accepted for Generic [g]. Check the MR number and the generic name to be sure they are correct. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 C-1 External MR Error Messages Table C-1. External MR Communications Error Messages—Continued Field Error Message Response External Product Unknown product [prod] for external project [proj]. The product entered is not valid for the project entered. Check your data and enter correct information. Message Type Unknown message type [type]. The entry must be a number from 1 to 12. Enter the correct number. External Project Unknown external project name [proj]. The project entered is not valid. Check your data and enter correct information. Generic For [proj], generic is a required parameter. You must enter a valid generic. For [proj], it should be a ‘released’ generic. You must enter a valid generic that has been released to the field. MR Number MR [mr] is not in the `active' state. Be sure the MR number you entered is correct. If so, exit this program and be sure the MR is in the correct state. Message Number Unknown message number [mr]. Use listmsgs to verify that the message number is in the queue. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page C-2 Issue 1.1 November 2000 External MR Message Formats D Message Formats D External MR messages are generated in 14 types, numbered 1 through 12, 15, and 16. Message types1 through 12 contain a common nine-field header, called the message header. (For a description of this header, see External MR Messages in Chapter 7, Using the External MR Commands.) Message types 15 and 16 contain an eight-field header that is described in this appendix. The remaining fields, which contain the text of the message, are different in each message. They are listed and described in this appendix. Message Type 1 4 MR/TR from a non-Sablime External Project to Sablime Message Type 1 contains information about a trouble report (TR). This message is created by a non-Sablime project to send to a Sablime project. This message is created by a non-Sablime project to send to a TR to Sablime. The message text fields in message type 1 are: 10 Severity The severity of the MR or TR. 11 Release The release identification of the MR or TR. 12 System The name of the system to which the MR or TR refers. 13 Subsystem The name of the subsystem to which the MR or TR refers. 14 Site The name of the site where the MR or TR originated. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 D-1 External MR Message Formats 15 Origination Date The date (mm/dd/yy) when the MR or TR originated. 16 Abstract The description in abstract form (up to 60 characters) of the MR or TR. 17 Required Date The date (mm/dd/yy) when the MR or TR is to be resolved. The description file containing a full description of the problem or the modification request appears in the description directory (rd) with the same message number. Message Type 2 4 MR/TR Disposition from Sablime to non-Sablime External Project Message type 2 contains information about action taken on an MR or TR in reply to message type 1. It informs the original sender whether the MR was created for the received message type 1 after being reviewed in the Sablime project. This message is created by a Sablime project to send to a non-Sablime external project. Sablime creates this message to send to the non-Sablime external project. The message text fields in message type 2 are: 10 Disposition The disposition of the MR or TR (entered or removed). 11 MR Number The number of the Sablime MR created as a result of entering the external MR or TR. This field is blank if the disposition is removed. 12 Reason One line of text explaining why the MR or TR was not honored. This field is blank if the disposition is entered. Message Type 3 4 MR State from Sablime to Any External Project Message type 3 contains information about MR state changes. These state changes are sent only: n If the MR is associated with an external MR or TR as indicated in the EMR relation and AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page D-2 Issue 1.1 November 2000 External MR Message Formats n If it has been determined that state changes will be communicated to the external project for this state (as indicated in the ES relation). (See the setrel command in the Sablime Administrator’s Manual for more information about establishing the ES relation.) This message is created by a Sablime project to send to another Sablime project or non-Sablime project when a state-change command (e.g., the accept command) is performed on an externally linked MR. The message text fields in message type 3 are: 10 MR Number The number of the Sablime MR for which the state is being sent. 11 Generic The generic for which the MR state is being sent. 12 MR Status The state of the MR in a generic. Any valid Sablime state may be communicated. For a non-Sablime project, only the accepted, deferred, understudy, nochange, submitted, or approved states may be communicated. 13 Reason One line of text explaining the reason for the state change. This field is blank for normal, forward-moving state changes in the MR life cycle. Message Type 4 4 MR/TR Closure from Any External Project to Sablime Message type 4 contains information about closure of an external MR or TR so that any corresponding MR(s) in Sablime can be closed. This message is created by a Sablime project or a non-Sablime project to send to a Sablime project when it closes an MR or TR linked to a Sablime MR. The message text fields in message type 4 are: 10 MR Number The number of the Sablime MR or external TR that is being closed. 11 Reason A short explanation of why the MR or TR is being killed (for Sablime MRs) or closed (for external TRs). AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 D-3 External MR Message Formats Message Type 5 4 MR Closure from Sablime to non-Sablime External Project Message type 5 contains information about closing or killing a Sablime MR that is associated with an external TR. This message is created when the Sablime closemr and killmr commands are performed on MRs linked to TRs in an non-Sablime external project. The fields in message type 5 are: 10 MR Number The number of the MR that has been closed/ killed. 11 MR Status The terminal state of the MR as defined by the project. 12 Generic The generic for which the MR closure is being reported. 13 Reason A short explanation of why the MR is being closed/killed. Message Type 6 4 New MR/TR Description from non-Sablime External Project to Sablime or MR Description notes (generated by the Sablime mrnote command) from Sablime to Sablime The mrnote command generates this message type only if the notes are being added to an MR description that was sent out to an external project. Message type 6 contains information about a changed description for an internal MR that is linked to an external MR or TR. The message text field in message type 6 is: 10 MR Number The number of the Sablime MR for which the new description is being sent. The new description (added by the mrnote command) appears in the description directory (rd or sd) with the same message number. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page D-4 Issue 1.1 November 2000 External MR Message Formats Message Type 7 4 MR Commitment from Sablime to External Project Message type 7 contains information about commitment of MRs associated with external projects. This message is created when the Sablime commit command is performed on an MR linked to an external Sablime or non-Sablime project. The message text fields in message type 7 are: 10 MR Number The number of the Sablime MR for which commitment information is being sent. 11 Generic The generic for which the MR has been committed. 12 Commitment ID The commitment identification of the committed MR. 13 Commitment Date The date (mm/dd/yy) when the MR is committed to be released. Message Type 8 4 High-Severity MR from Sablime to non-Sablime External Project This message is relevant in a Sablime-non-Sablime project communication. Message type 8 contains information about MR(s) that were not originated from the non-Sablime project or have not been shared with the non-Sablime project and are being accepted with a developer-assigned severity of 1 or 2 in a released generic. The accept or fcreate command automatically generates this message if: n The MR is not already linked with the non-Sablime project n The MR severity is 1 or 2 and n The MR is being accepted for a generic that has already been released. The message text fields in message type 8 are: 10 MR Number The number of the Sablime MR. 11 Generic The name of the generic in which the MR is accepted. 12 Severity The MR severity. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 D-5 External MR Message Formats 13 Release The name of the release. 14 System The system to which the MR belongs. 15 Subsystem The subsystem to which the MR belongs. 16 Site The site that originated the MR. 17 Origination Date The date when the MR originated. 18 Abstract The description in abstract form (up to 60 characters) of the MR. 19 Required Date The date when the MR or TR is to be resolved. 20 Originator Login of the originator of the MR. 21 Phone The phone number of the originator of the MR. 22 Location The location of the originator of the MR. The description file containing a full description of the modification request appears in the description directory (sd) with the same message number. Message Type 9 4 MR from Sablime to non-Sablime External Project Message type 9 is relevant in a Sablime-to-non-Sablime project communication. This message contains information about developer-generated MRs in released generics that are not fixed and may affect customers. The qmr command generates this message for Sablime-to-non-Sablime project communication. The message text fields in message type 9 are: 10 MR Number The number of the Sablime MR. 11 Generic The name of the generic in which the MR is accepted. 12 Severity The MR severity. 13 Release The name of the release. 14 System The system to which the MR belongs. 15 Subsystem The subsystem to which the MR belongs. 16 Site The site that originated the MR. 17 Origination Date The date when the MR originated. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page D-6 Issue 1.1 November 2000 External MR Message Formats 18 Abstract The description in abstract form (up to 60 characters) of the MR. 19 Required Date The date when the MR or TR is to be resolved. 20 Originator Login of the originator of the MR. 21 Phone The phone number of the originator of the MR. 22 Location The location of the originator of the MR. The description file containing a full description of the modification request appears in the description directory (sd) with the same message number. Message Type 10 4 MR Disposition from non-Sablime External Project to Sablime The non-Sablime project sends message type 10 to Sablime in response to a review of message type 8 or 9. This message contains information about action taken for MRs sent from Sablime. (See Message Type 8 and Message Type 9.) The message text fields in message type 10 are: 10 MR Number The number of the Sablime MR for which the message is being sent. 11 Generic The generic for which the MR was accepted. 12 External Disposition The disposition of the non-Sablime project for the MR (entered or removed). 13 Reason One line of text explaining the reason for the MR disposition. Message Type 11 4 MR from Sablime to Sablime Message type 11 is relevant in Sablime-to-Sablime communication. This message is generated by the qmr command to send an MR to another Sablime project. For example, if product P1 of a Sablime project sends an MR to product P2 of another Sablime project, the fields refer to the MR information for product P1. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 D-7 External MR Message Formats The message text fields in message type 11 are: 10 MR Number The number of the Sablime MR. 11 Severity The MR severity. 12 Release The name of the release. 13 System The system to which the MR belongs. 14 Subsystem The subsystem to which the MR belongs. 15 Site The site that originated the MR. 16 Origination Date The date when the MR originated. 17 Abstract The description in abstract form (up to 60 characters) of the MR. 18 Required Date The date when the MR or TR is to be resolved. 19 Originator Machine name and login of the originator of the MR. 20 Category The way in which the MR was found. 21 Module The module that is associated with the MR. 22 Phase Detected The phase in which the MR was detected. 23 MR UDF1 24 MR UDF2 25 MR UDF3 User-definable fields associated with the MR. 26 MR UDF4 27 MR UDF5 The description file containing a full description of the modification request appears in the description directory (rd or sd) with the same message number. Message Type 12 4 MR Disposition from Sablime to Sablime Message type 12 is relevant in Sablime-to-Sablime communication. This message is generated by the review command in response to message type 11. If the Disposition field contains entered, the Reason field is blank and the MR Number field and all other fields contain information about the new MR created or linked with the external product. If the Disposition field contains remove, all other fields are blank. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page D-8 Issue 1.1 November 2000 External MR Message Formats For example, when the Sablime project with the product P2 reviews the MR sent by Sablime project with the product P1 and enters a corresponding MR in its own system, message type 12 is generated and the data refers to MR information for product P2. The message text fields in message type 12 are: 10 MR Number The number of the Sablime MR. 11 Disposition entered, removed, or linked. 12 Reason The reason for removing the MR. This line is blank if the disposition is entered. 13 Severity The MR severity. 14 Release The name of the release. 15 System The system to which the MR belongs. 16 Subsystem The subsystem to which the MR belongs. 17 Site The site that originated the MR. 18 Origination Date The date when the MR originated. 19 Required Date The date when the MR or TR is to be resolved. 20 Originator Machine name and login of the MR originator. 21 Category The way in which the MR was found. 22 Module The module that is associated with the MR. 23 Phase Detected The phase in which the MR was detected. 24 MR UDF1 25 MR UDF2 26 MR UDF3 User-definable fields associated with the MR. 27 MR UDF4 28 MR UDF5 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 D-9 External MR Message Formats Message Type 13 4 Spawned MR from Sablime to Sablime This message is generated in response to either of two actions: n an MR that is linked to an external project is spawned n a review and “enter” command is issued in response to such a spawn The review command should show the spawned state when the spawn message is received. The review command should display the type 13 message on the screen using the type 11 format. The spawn message and type 13 message will be reviewed when the linked MR is spawned on the other side. The type13 message will be sent back if the external project does not want to create a link for the child MR. The message text fields in message type 12 are: 11 Disposition entered or removed. 12 Reason The reason for removing the MR. This line is blank if the disposition is entered. 13 Severity The MR severity. 14 Release The name of the release. 15 System The system to which the MR belongs. 16 Subsystem The subsystem to which the MR belongs. 17 Site The site that originated the MR. 18 Origination Date The date when the MR was spawned. 19 Abstract The description in abstract form of the spawned MR.. 20 Required Date The date when the MR is to be resolved. 21 Originator Machine name and login of the originator of the MR. 22 Category The way in which the MR was found. 23 Module The module that is associated with the MR. 24 Phase Detected The phase in which the MR was detected. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page D-10 Issue 1.1 November 2000 External MR Message Formats 25 MR UDF1 26 MR UDF2 27 MR UDF3 User-definable fields associated with the MR. 28 MR UDF4 29 MR UDF5 NOTE: Message type14 is not used. Message Header for Message Types 15 and 16 D The headers for message types 15 and 16 contain the eight fields listed in the following table. 1 Message Type Either 15 or 16. 2 sablime 3 customer 4 sablime 5 Product Name For example, sab or tst. 6 Product ID The sixth field of the PRX relation. 7 cust Indicates that it is a customer’s MR. 8 Current date and time stamp. The format is mm/dd/yy hh:mm:ss. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 D-11 External MR Message Formats Message Type 15 4 MR from Customer to Sablime The message text fields in message type 15 are: 9 Severity The MR severity. Choices are 1,2,3, and 4. 10 Origination Date The date when the MR originated in mm/dd/yy format. Default: today’s date 11 Required Date The date by which the MR is to be resolved in mm/dd/yy format.. 12 System Name The system name. It must be the same as one of the names in the System field on the create screen. 13 Command Name The command name. It must be the same as one of the names in the Subsystem field on the create screen. 14 MR Type Must be field_enh or field_mod. 15 Release Detected The name for the Release Detected field on the review window. 16 Site The customer’s site. 17 MR Abstract An abstract of the MR. 18 Email Address The customer’s email address. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page D-12 Issue 1.1 November 2000 External MR Message Formats Message Type 16 4 MR Report Request from Customer to Sablime The message text fields in message type 16 are: 9 MR Type Enhancement, modification, or all. 10 Email Address The customer’s email address. 11 MR Number The MR number. 12 XYZ Used as the name of the report. 13 Product Name The product name. 14 Release Detected A generic name for the Release Detected field. 15 Report Name Long or summary. 16 Severity The MR severity. Choices are 1,2,3,4, or all. 17 Command Name The command name. It must be the same as one of the names in the Subsystem field on the create screen. 18 System Name The system name. It must be the same as one of the names in the System field on the create screen. 19 Site The customer’s site. 20 MR Status Either created or killed. 21 MG Status Contains accepted, deferred, understudy, nochange, assigned, submitted, itpassed, stpassed, approved, or closed. 22 Not Used AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 D-13 External MR Message Formats AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page D-14 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Glossary A Active Database (ADB) Contains all the active information about a Sablime product. It includes MR descriptions and information relating MRs to generics, developers, and file changes. Approval Team The staff responsible for approving resultant changes for an MR. Assigned Developer (AD) The user or group responsible for work related to an MR. B Bin The directory where Sablime commands are installed on a machine. The recommended bin is the home directory of the sablime login. Branch Every file for each generic has two branches representing an approval level associated with it: the modification request (mr) branch and the official (ofc) branch. The mr branch contains all unapproved changes; the ofc branch contains all approved changes. An official source file corresponds to the version of the file that contains all deltas on the official branch that were made to the current date. C Command An executable program that usually handles a user transaction. D Database Administrator (DBA) Owner of the sablime login, the Sablime databases and the Sablime commands. Certain commands are restricted to use by the DBA. Delta The set of changes made to a Sablime file by each sequence of edget/edit/edput. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 GL-1 Each delta consists of administrative data added to the beginning of the file and the changes, if any, to the body or text of the file. Deltas are also made to a file when MRs are approved or new generics defined; however, these deltas generally add administrative data to the file without changing the body or text portion of the file. dot sablime Command A shell script that sets up the Sablime environment on a UNIX server. See the Sablime Administrator’s Manual for details. E External Communications Network The network used by the Sablime system to communicate with outside projects or other machines. F File Binary and non-binary files, test scripts, and document input files are all considered files. Changes to files are generated outside of the Sablime system and are documented and controlled by Sablime in the Source Database. G Generic A version of the product that has been or may be released and must be maintained. Each generic is maintained separately. The setup generic is the generic specified when the dot sablime command was issued. Generic Administrator (GA) Administrator with the authority to accept an MR for a generic and to assign a developer to study the MR or make changes in response to it. Certain commands are restricted to the GA. Global Database (GDB) Contains data that is used across the entire Sablime instance (personnel information, product information, etc.). Group Name The name assigned to a group in Sablime using the setgroup command. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page GL-2 Issue 1.1 November 2000 H Hideable Field A field that can be removed from Sablime windows. If the field is not displayed, no data will be gathered in the field and the field in the database will always be blank. Host Machine A machine linked to zero or more satellite machines through a network that allows users of other machines to execute Sablime commands sharing common Sablime databases located on the host. I Inactive Database (IDB) Contains all the information that is no longer required for the current work being done on a product. When an MR is killed or completed for all generics or all work on a generic is completed, all the information about it in the ADB can be moved to the product’s IDB for historic purposes. Instance A set of Sablime commands and programs and its databases that supports development and maintenance of various products and that is owned by a single sablime login. M Modification Request Administrator (MRA) The person or persons responsible for administering newly created MRs and completed MRs. The MRA has responsibility for the total MR including the determination of the generics to which it applies but not for the activity of the MR within a generic. Certain commands are restricted to use by the MRA. MR Modification Request—The description of an enhancement or of a problem in the existing product. In the Sablime system, an MR is required to request or make changes to the controlled product. MR History File A file created and maintained by Sablime if the History File flag in the ADM relation is set to y. Every time a Sablime command that affects an MR is executed, a record is written to this file. N Node A set of files arranged in a UNIX system directory structure. The base of the node is the topmost directory in the structure. Any file that can be reached as a descendant from the base is contained in the node. A file in a node is identified by a relative directory path describing the path from the base of the node to the file. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 GL-3 P Product Any combination of software, firmware, hardware, or documentation that is eventually generated for use by customers. A Sablime instance supports the development and maintenance of one or more products. Product Directory Structure The organization of the directories and the files associated with a generic in a Sablime product. The highest-level directory associated with the structure is referred to as the base or the product node. The remaining directories must be at a lower level and reachable from the base. References to any directory within the product directory is considered to be the relative directory path from the base of the node. Project The MR trouble-reporting system with which a Sablime product communicates through the External MR Communications feature; it can be another Sablime project or a different type of trouble-reporting system. PTS ID Personnel Tracking System ID—the Sablime system identifier that allows a user access to a product. R Relation A directory in the GDB, ADB, or IDB used to store tuple files containing lines of data ( records) to be accessed by Sablime commands for information about MRs, generics, and source files. Record A line of data in a tuple file in a directory (relation) in the GDB, ADB, or IDB to be accessed by Sablime for information about MRs, generics, and files. Request Severity The impact of a fault on product operation as judged by the MR creator. Severity ratings are defined below. n Severity 1—The basic service provided by the product is interrupted. n Severity 2—The basic service provided by the product is degraded; some functions may not be available or may be inadequate. n Severity 3—Functional problems cause inconvenience to users, administrators, or maintenance personnel; work-arounds exist or the software recovers on its own but the problem will be fixed. n Severity 4—A minor deficiency exists that is of little consequence. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page GL-4 Issue 1.1 November 2000 S Satellite Machine A machine linked to a host machine through a network that allows users of the machine to access Sablime commands sharing common Sablime databases located on the host. Source Administrator (SA) The person or persons responsible for maintenance of the Product Directory Structure and for the administration of the files associated with a product. Source Database (SDB) The collection of version-controlled files placed under Sablime for your product. SBCS Source and Binary Control System, used by Sablime to control versions of binary and non-binary files in response to MRs. SCCS Source Code Control System, used by Sablime to control versions of non-binary files in response to MRs. T Template An ASCII text file describing a format or guide designed to promote project consistency in documentation and programming structures. Trace File A file created and maintained by Sablime if the Trace Flag in the ADM relation is set to y. Every time a user executes a Sablime command, a trace record is written in the trace file with the same name as that user’s PTS ID. A second trace file exists on the Windows client; it tracks the command execution from the Windows interface (see Options›Environment). Tuple File A file in a directory (relation) in the GDB, ADB, or IDB used to containing lines of data (records) to be accessed by Sablime for information about MRs, generics, and files. V Value Data entered in a field. AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.1 November 2000 GL-5 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page GL-6 Issue 1.1 November 2000 Index A accept Command, 4-4, 7-10, D-3, D-5 description, 4-29 accepted MRG State, 4-4, 4-24, 4-29, 4-35 activate Command, 4-3, 4-4 description, 4-24 Active Data Base, 4-3, 5-22, 7-3 relations, A-1 active MR State, 4-4, 4-29, 4-38 addgen Command, 3-12 addgsrc Command, 4-7, 5-2, 5-3, 5-5 common files, 5-50 description, 5-9 addisrc Command, 4-7, 5-2, 5-3, 5-5, 5-9 common files, 5-50 description, 5-6 approve Command, 4-5, 4-7, 5-3, 7-10 description, 4-54 approved MRG State, 4-4, 4-5, 4-6, 4-49, 4-50, 4-54, 4-56 assign Command, 4-5, 4-30, 7-10 description, 4-42 assigned MRG State, 4-5, 4-35 Automatic Dependency, 5-14, 5-18 B bar Chart see Management Reports Branches definition, 5-1 mr, 5-1, 5-2, 5-9 ofc, 4-7, 4-54, 5-1, 5-2, 5-7, 5-9 Buttons Cancel, 2-23 Close, 2-23 Run, 2-23 C Cancel Button, 2-23 Canceling a Command, 2-23 Close Button, 2-23 closed MRG State, 4-6 closemr Command, 4-6, 4-39, D-4 Command Name query fictitious, 6-4 Command Permissions, 3-1 Command Window Operation, 2-23 Commands accept, 7-10, D-3, D-5 approve, 7-10 assign, 7-10 closemr, D-4 commit, 7-10 create, 7-1, 7-3, 7-9, 7-15 defer, 7-10 fcreate, D-5 killmr, D-4 listmsgs, 7-11, 7-17 mrnote, D-4 nochange, 7-10 qmr, 7-3, 7-15, D-6 reject, 7-10 report, 7-5 review, 7-3, 7-5, 7-17 sendmsgs, 7-3, 7-5, 7-16, 7-18, 7-28 setrel, D-3 study, 7-10 submit, 7-10 commit Command, 7-10 common Command, 5-6 description, 5-50 Common Files, 5-6, 5-9, 5-14, 5-19, 5-50 addisrc, 5-50 Confirming a Command, 2-23 Confirming a Dialog Box, 2-23 create Command, 4-3, 7-1, 7-3, 7-9, 7-15 description, 4-15 created MR State, 4-3, 4-24 D Data Bases stopped, 6-3 Date Formats, 2-13, 2-24 defer Command, 4-3, 4-4, 4-29, 7-10 deferred MRG State, 4-4, 4-24 Dependencies definition, 4-6 file level, 5-18 file-level, 5-14 line level, 5-18 line-level, 5-14 logical, 4-14 MR, 4-6 Directory Structure parallel, 3-11 Display Flag, 6-12 dot sablime Command, 3-10, 3-11 definition, 2-5, 2-8, 2-16 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 IN-1 Index E G edget Command, 3-11, 4-8, 5-1, 5-3, 5-5, 5-16, 5-18, 5-50, 5-52 description, 5-13 Editor setting favorite, 3-2 edput Command, 3-11, 5-1, 5-3, 5-5, 5-14, 5-16, 5-50, 5-52 dependencies, 4-7 description, 5-18 effid, 2-6, 2-9 egrep Regular Expressions, 6-124 Error Messages, B-1 ES Relation, 7-10, D-3 External MR Communications description, 7-1 External MR Messages, 7-2 header, 7-2 External_MR Reports, 6-78–?? extract_file description, 6-12 External_MR, 6-78 group, 6-85 MR, 6-16 mrVSfile, 6-103 source, 6-92 Generic, 2-19 getversion Command, 4-7, 4-8, 4-15, 5-6 description, 5-28 Global Data Base relations, A-1 grap, 6-15 Group Members matching behavior, A-3, A-4 group Reports, 6-85–?? H Help, 2-8, 2-14, 2-27 I Inactive Data Base, 4-3, 4-6, 5-22 relations, A-1 K F Favorite Editor setting, 3-2 fcreate Command, 4-5, D-5 Fields, 6-1, A-1 File Permissions, 2-6, 2-9 File-Level Dependency, 5-14, 5-18 Files binary, 5-7 common, 5-14 locked, 5-1, 5-14 non-binary definition, 5-7 FTD display flag, 6-12 FTD Records query, 6-4 Full Screen Mode, 2-6 Keywords ssql, 6-125 order, 6-127 killed MR State, 4-3 killmr Command, 4-3, D-4 L Line-Level Dependency, 5-14, 5-18 Linked MRs, 7-1 listmsgs Command, 7-17 description, 7-11 Locked Files, 5-14 M Mail setting, 3-2 AT&T -- PROPRIETARY See notice on first page IN-2 Issue 1.0 November 2000 Index Management Reports, 6-15, 6-16, 6-17 printing, 6-16 Matching group behavior, 6-12 group members, A-3, A-4 Menu Bar, 2-21 Menu Display setting, 3-2 Messages external MR, 7-2 external MR header, 7-2 setting verbose or terse, 3-2 Mode specifying, 3-2 MR definition, 4-1 mr Branch, 5-1, 5-2, 5-9 MR Dependencies, 4-6 MR Reports, 6-14–?? MR States active, 4-4, 4-29, 4-38 created, 4-3, 4-24 killed, 4-3 mra_deferred, 4-3, 4-21, 4-24 mra_study, 4-3 mra_deferred MR State, 4-3, 4-21, 4-24 mra_study MR State, 4-3 MRG definition, 4-1 MRG State approved, 4-54 MRG States accepted, 4-4, 4-24, 4-29, 4-35 approved, 4-4, 4-5, 4-6, 4-49, 4-50, 4-56 assigned, 4-5, 4-35 closed, 4-6 deferred, 4-4, 4-24 nochange, 4-4, 4-5, 4-6, 4-24, 4-39, 4-56 spawned, 4-39 submitted, 4-5, 4-49, 4-50 understudy, 4-4 mrnote Command, D-4 MRs depended-upon, 6-102, 6-103 linked, 7-1 shared, 7-1 mrVSfile Reports, 6-102–?? Node, 3-10, 5-6, 5-17, 5-20, 5-28 SABLIME, 3-10 O ofc Branch, 4-7, 4-54, 5-1, 5-2, 5-7, 5-9 Output File, 6-14 P Permissions, 2-6, 2-9 pic, 6-16 pie Chart see Management Report Popup Selection Windows, 2-12 Positional Parameters, 6-125 primsdb Script, 4-7, 5-2, 5-5, 5-7, 5-9, 5-10, 5-50 Product, 2-19 propose Command, 4-3, 4-4 pts Command description, 3-1 PTS Relation, 2-5, 2-8, 2-16, 3-2 Q qmr Command, 7-3, D-6 description, 7-15 query Command, 2-13, 6-3–?? R N nmake, 3-11 nochange Command, 4-4, 4-30, 7-10 description, 4-35 nochange MRG State, 4-4, 4-5, 4-6, 4-24, 4-39, 4-56 Ranges, A-3 date, A-3 decimal, A-3 number, A-3 query and report, A-3 state, A-3 rcv_msgs Program, 7-3, 7-5 Receive Queue, 7-17 Records, 6-1, A-1 reject Command, 4-5, 7-10 description, 4-52 Relations, 6-1, A-1 by data base, A-1 PTS, 2-5, 2-8, 2-16, 3-2 report Command, 2-13, 6-9–??, 7-5 AT&T — PROPRIETARY See notice on first page Issue 1.0 November 2000 IN-3 Index Reports management, 6-15, 6-16, 6-17 Resolution File, 5-19 review Command, 7-3, 7-5 description, 7-17 Run Button, 2-23 see Management Reports Status Bar, 2-22 study Command, 4-3, 4-4, 4-30, 7-10 description, 4-27 Subfields, 6-1, A-1 submit Command, 4-5, 7-10 description, 4-45 submitted MRG State, 4-5, 4-49, 4-50 S sabhelp Command description, 3-12 SABLIME Generic, 2-19 SABLIME Product, 2-19 SBCS, 3-11, 4-7, 5-2, 5-7, 5-18 SCCS, 3-11, 5-2, 5-6, 5-7, 5-18 dependencies, 4-7 Screens use of fields in, 2-10 Selection Criteria query, 6-4 mechanics of, 6-4 report, 6-12 Selection Fields, 6-12 sendmsgs Command, 7-3, 7-5, 7-16, 7-18 description, 7-28 setnode Command, 3-11 setrel Command, D-3 sget Command, 3-11, 4-7, 4-8, 5-5 description, 5-22 shabs Command description, 3-12 Shared MRs, 7-1 shcat Command description, 3-12 sherr Command, 3-12 shrec Command description, 3-12 Sort Fields report, 6-13 predetermined, 6-13 source Command, 3-11, 5-7, 5-10 Source Data Base, 3-11, 5-1, 5-5, 5-22 source Reports, 6-92–?? spawned MRG State, 4-39 spawnmr Command, 4-4, 4-29 description, 4-38 srcpr Command, 3-11, 5-6 description, 5-48 ssql, 6-124–?? ssql Statements compound, 6-127 construction, 6-127 nested, 6-128 stat Chart T tbl, 6-16 TCP/IP, 7-1 Test Commands description, 4-49 troff, 6-16 Tuples, 6-1, A-1 U uncommon Command, 5-6 description, 5-52 understudy MRG State, 4-4 unedget Command, 3-11, 5-1, 5-5, 5-14, 5-50, 5-52 description, 5-16 User-Definable Fields, 7-23 uucp, 7-3, 7-5 V Variables VPATH, 3-11 VPATH Variable, 3-11 W Window Elements, 2-21 X XSab file, 2-16 AT&T -- PROPRIETARY See notice on first page IN-4 Issue 1.0 November 2000