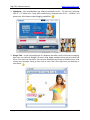
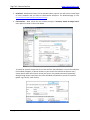
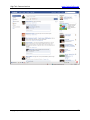
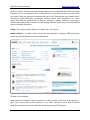
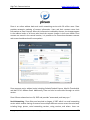
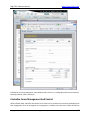
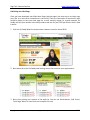
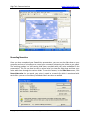
Download High-Tech Communications
Transcript
A S A R e s e a r c h HighTech Communications Master the New Technologies that are Changing the Way We Communicate J. Carlton Collins ASA Research ‐ Atlanta, Georgia 770.734.0950 [email protected] High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com High Tech Communications for CPAs Table of Contents Course Information ................................................................................................ 3 1. Introduction ............................................................................................................ 6 2. Old versus New ..................................................................................................... 11 3. How We Learn ....................................................................................................... 15 4. Non Verbal Communications ................................................................................ 23 5. Low Tech Communication Methods ..................................................................... 34 6. Voice Over IP & Video Conferencing .................................................................... 37 7. Remote Desktop Control ...................................................................................... 52 8. Social Networking ................................................................................................. 62 a. Facebook ................................................................................................... 63 b. Linked‐In .................................................................................................... 75 c. Plaxo .......................................................................................................... 79 d. Twitter ....................................................................................................... 81 9. High Tech Kiosk ..................................................................................................... 83 10. Survey Solutions .................................................................................................... 90 11. Microsoft InfoPath ................................................................................................ 96 12. Instant Messaging ............................................................................................... 101 13. Communications Equipment .............................................................................. 107 14. Building A Successful Web Site ........................................................................... 114 15. Selling Online ...................................................................................................... 140 16. The Problems with Phone Communications ....................................................... 145 17. Mobile Phones .................................................................................................... 150 18. Synchronization .................................................................................................. 165 19. Web Conferencing .............................................................................................. 170 20. Microsoft Office Live Meeting ............................................................................ 175 21. Microsoft Office SharePoint Designer 2007 ....................................................... 180 22. Microsoft Visio .................................................................................................... 183 23. Microsoft PowerPoint ......................................................................................... 190 24. Amazon Kindle .................................................................................................... 198 25. Wireless Networking & Internet Hotspots ......................................................... 200 26. Speech Recognition ............................................................................................. 216 Appendix A ‐ Instructor’s Biography ................................................................... 219 CPE Course Evaluation Form .............................................................................. 221 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 2 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com High Tech Communications for CPAs Course Information Learning Objectives Course Level Pre‐Requisites Advanced Preparation Presentation Method To help CPAs learn about the very best communication techniques available today Intermediate None None Live lecture using full color projection systems and live Internet access with follow up course materials Recommended CPE Credit Handouts Instructors 8 hours Templates, checklists, web examples, manual J. Carlton Collins, CPA AdvisorCPE is registered with the National Association of State Boards of Accountancy (NASBA) as a sponsor of continuing professional education on the National Registry of CPE Sponsors. State boards of accountancy have final authority on the acceptance of individual courses for CPE credit. Complaints regarding registered sponsors may be addressed to the national Registry of CPE Sponsors, 150 Fourth Avenue, Nashville, TN, 37219‐ 2417. Telephone: 615‐880‐4200. Copyright © May 2010, ASA Research, AdvisorCPE, & Accounting Software Advisor, LLC 4480 Missendell Lane, Norcross, Georgia 30092 770.734.0450 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form without the express written consent of AdvisorCPE. Request may be e‐mailed to [email protected] or further information can be obtained by calling 770.842.5904 or by accessing the AdvisorCPE home page at: http://www.advisorcpe.com/ ASA Research and AdvisorCPE are subsidiaries of Accounting Software Advisor, LLC. All trade names and trademarks used in these materials are the property of their respective manufacturers and/or owners. The use of trade names and trademarks used in these materials are not intended to convey endorsement of any other affiliations with these materials. Any abbreviations used herein are solely for the reader’s convenience and are not intended to compromise any trademarks. Some of the features discussed within this manual apply only to certain versions of Office, and from time to time, Microsoft might remove some functionality. Microsoft Office is known to contain software bugs which may prevent the successful use of some features in some cases. AdvisorCPE makes no representations or warranty with respect to the contents of these materials and disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability of fitness for any particular use. The contents of these materials are subject to change without notice. Instructor Contact Information J. Carlton Collins [email protected] Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 3 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Web Sites Maintained by ASA Research: Main Web Site Accounting Software Web Site Technology Advice Web Site Mirrored Web Site Accounting Software Feature Reports Accounting Software Advice Web Site Top Accounting Software Consultants Accounting Software News Web Site QuickBooks Web Site CPE Information Web Site Miscellaneous and Example Web Site Microsoft Excel Web Site Microsoft Accounting Systems Web Site Microsoft SBA Web Site Microsoft Office Web Site www.Carltoncollins.com www.ASAResearch.com www.CPAAdvisor.us www.AccountingSoftwareAdvisor.com www.AccountingSoftwareReports.com www.AccountingSoftwareAnswers.com www.AccountingSoftwareConsulting.com www.AccountingSoftwareNews.com www.QuickbooksAdvisor.info www.AdvisorCPE.com www.CarltonCollins.com www.ExcelAdvisor.net www.MBSAdvisor.com www.SBAAdvisor.com www.OfficeAdvisor.us We publish selected materials, power point slide shows and downloadable example files on the web as a service to the CPA community. Please feel free to learn about our other topics at these great web sites. Thank you. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 4 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Preface While this course it titled “High Tech Communications for CPAs”, it is certainly not my intention to throw older traditional communication methods out the door – just the opposite. I believe that older proven communication techniques must be obeyed even when employing newer communication techniques. For example, just because you are speaking over a video web camera does not mean that you need not sit up straight, make good eye contact, or convey positive body language – these old communication methods are just as important today as ever, perhaps even more so because today’s newer high tech methods sometimes make it harder to communicate clearly and convey the best impressions. My goal for this course is simply – “Communications”. Any communication topic, old or new, is fair game. At the completion of this course, I hope that you will have compiled a list of communication techniques that you will consider adopting to help you: 1. Communicate more effectively. 2. Communicate more efficiently. 3. Save money. Therefore please do not be surprised as we meander through new high tech methods mixed in with older communication methods. Thank you. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 5 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Introduction Chapter 1 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 6 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Introduction Technology is changing the way business communicates. New technologies, devices, and software applications have evolved and as a result, people and businesses are communicating far differently, often with greater efficiency and better results. Are you keeping up? Do your communication efforts promote you as a leader or laggard? Is there more that you could do to better communicate with your customers, prospects, employees, executive team, and board of directors? Every leader in the world will tell you that the ability to communicate is the foundation of success. This course is dedicated to reviewing and demonstrating the vast new wave of communication tools and solutions that technology has brought forth. Specific discussion points will include some of the following points (as time permits): Carlton’s List of Today’s Newer Communication Methods 1. Internet Phone and Video Conferencing: a. Skype b. ooVoo c. GoToMeeting d. SightSpeed e. GoogleTalk f. Gizmo project g. iChat h. VoIP Buster i. Jajah j. Amicima k. ComBOTS l. OpenWengo m. Vbuzzer n. Majic Jack o. Vonage 2. Remote Desktop Connections a. GoToMyPC b. LogMeIn c. WebEx d. pcAnywhere e. Remote Desktop Connection f. RemotePC g. Citrix h. Terminal Services i. Array Networks Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 7 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 3. Electronic Forms: a. Example ‐ GSCPA CPE Course Evaluation Forms b. QuickBooks c. InfoPath 4. Social Networking a. Linked In b. Plaxo c. FaceBook d. Twitter e. MySpace 5. Web Conferencing or Teleconferencing Tools: a. WebEx b. GoToMeeting c. Yugma d. Acrobat 6. Collaborative Environments: a. Wikis b. WetPaint c. PBWiki d. MediaWiki e. Wrike f. Basecamp g. GoogleDOCs 7. Meeting Facilitation Solutions: a. Participants may gather in a single room, but sit at separate terminals b. Participants may be located miles apart c. Advantages 8. Using Computers in Presentations: a. PowerPoint b. Projectors c. Presentation Tips 9. Pictures: a. Digital Photography b. Photoshop 10. Videos: a. YouTube b. GoogleVideos Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 8 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com c. FlickR 11. Microsoft Outlook: a. Setup Tips b. Managing Groups c. Meeting Requests d. Sharing Calendars e. E‐Mail mail Merging – Word & Outlook f. E‐Mail Marketing g. E‐Mail List Management 12. Secure e‐Mail Solutions: a. Hush Mail b. Pretty Good privacy c. Secure Hive d. Vormetric e. ShyFile 13. Electronic Forms: a. InfoPath b. Web Based From Controls 14. Electronic Surveys: a. Zoomerang b. Web Monkey 15. Synchronization: a. Cell Phone Data to computers b. Synchronizing Excel Files to Your Web Site c. Web pages to computers 16. Hand‐held communication tools a. iPhone b. Cell phones c. PIMs d. Ear Pieces 17. Contact Management Tools a. Personal Information Management (PIM) Tools b. Sales Force Automation (SFA) Tools c. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools 18. Web Site Development & Web Site Management Tools: a. Microsoft FrontPage Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 9 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com b. Microsoft Expression Web c. Dreamweaver d. Blogging 19. Supply Chain Automation Solutions a. Communications between Accounting Systems b. Microsoft BizTalk 20. RFID Technology: a. Asset Tracking b. Inventory Management c. Measurement 21. Desktop Publishing: a. Microsoft Publisher b. Electronic Newsletters c. Electronic Marketing & Communications 22. Digital Dashboards – Windows into your accounting system and financials 23. Push Technology a. RSS Feeds b. Scheduled Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 10 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Old versus New Chapter 2 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 11 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com What’s Wrong with the Old Style Communications? Letters, Telephones & Face‐to‐Face Meetings are the top three traditional approaches to communicating – and all three still have their rightful place today. Personalized letters are often appreciated, a telephone call can be a great way to engage someone, and in many cases there is no substitute for a face‐to‐face meeting. However, each of these methods has disadvantages as well: 1. Disadvantages of Letters: a. They take time to be delivered – sometimes days. b. It cost money to mail or FedEx a letter. c. There is physical labor involved stuffing envelopes, applying postage, calling for pick‐up or delivering to a mailbox. d. The recipient cannot easily copy and paste information from the letter. e. The recipient must start from scratch when replying (ie: there is no reply button). f. The recipient must then shred, scan or file your letter away – all of which involves labor. g. Computers cannot later search for text within that letter for easy identification, unless OCR scans are applied. 2. Disadvantages of Telephone Calls: a. Telephone calls do not result in a hard copy of notes that can be refereed to later. b. Both parties must be available at the same time. c. There is a cost to phone calls, particularly long distance phone calls. 3. Disadvantages of Face‐to‐Face Meetings: a. Studies show that most people consider face‐to‐face meetings to be a huge waste of time. b. The cost of meeting space c. Documenting the information conveyed in a meeting is often labor intensive and time consuming. d. Finding time slots where all parties are available can be tough to accomplish. e. Physically bringing people together can be costly, especially where airfare is involved. f. Dynamics of Face‐to‐face meetings can be anti‐productive – one person may dominate the meeting while others are afraid to speak up. g. Exchanging information at a meeting often does not give recipients adequate time to read, digest and prepare to discuss the information. The focus of this session is to suggest that technology now offers us many new ways to communicate, and these new communications can often save money, save time and produce better results. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 12 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Why Focus on Communications? I believe that everybody fully understands the importance of focusing on communications – no explanation is really needed. Nonetheless, just to ensure that these materials are complete, here are a few reasons why it is important to study, adopt, learn and utilize the best communication avenues possible: 1. Organizational expert Kelly Krauskopf answers as follows: “[Communicating is important] because you can’t do anything without it. Communication is necessary in order to avoid confusion. It’s vital to any successful organization to be clear. When you communicate, you eliminate mistakes. Everybody understands his responsibilities within the system, so that he can carry them out.” 2. Communication student Uttara Manohar says: “Communication is a very important aspect of the human life, since it is the communication that helps human beings to connect with each other as individuals and as independent groups. Communication is the very basis, which drives the process of development in all the fields. Here are some of the reasons, which explain why communication is important…” 3. Carlton Collins says: “We are always communicating, whether we intend to or not. If you have no web site, you may be inadvertently communicating that you have not fully embraced technology. If you do have a web site, but it is a poorly designed web site with feeble or old content, you may be communicating an even worse message. However, a nice, well designed web site with good current information can help you make a good impression. This same concept is conveyed through all of your outward appearances, be them your letter writing, your company logo and colors, your marketing brochures, e‐mails, social networking, voice mail greeting, phone conversations, face‐to‐face meetings, etc. Wouldn’t you always want to make the best impression possible via all of your communications? Goals of Communicating: The following bullets were helpful to me for establishing a foundation for discussing the new communication methods listed below. We communicate for different reasons. For example: 1. Information Dissemination: We communicate to deliver or exchange information. 2. Creativity – We communicate to spark and identify new ideas, creativity, brain storming, 3. Test Our Reasoning – We communicate to articulate our points of view, to articulate our reasoning, to state our positions out loud to see how they sound to others, to gain feedback, and to refine our positions. 4. Education – We also communicate to educate one another. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 13 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 5. Marketing – It is said that marketing is really a simple matter of educating potential customers about your products and services via various communication channels. 6. Relationship Building – We communication to facilitate dialogue, the exchange of ideas, and the expression of human emotions which help build and maintain relationships – both personally and professionally. 7. Decision‐Making ‐ Communication facilitates the process of decision making, be it an individual decision or group decision. 8. Expressing Emotions/Ideas ‐ Communication helps people express their ideas and emotions, to share thoughts with one another. 9. Entertainment ‐ Movies, music, television shows, theater, or even anecdotes narrated by people are types of communication, which are a source of entertainment for us. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 14 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com How We Learn Chapter 3 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 15 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com How We Learn 7% Verbal (words only) 38% Verbal (voice tone, inflection, sounds) 55% Non Verbal Source: Albert Mehrabian 1% Through Taste 1.5% Through Touch 3.5% Through Smell 11% Through Hearing 83% Through Sight Source: Bob Pike How We Remember 10% From what we read 20% From what we hear 30% From what we see 30% From what we see and hear 80% From what we say 90% From what we say as we act Source: Bob Pike Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 16 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Effectiveness of Teaching Activities Firsthand Experience Guided Practice Structured Role Playing Microteaching Analyzing/Calculating Testing Video Taping Spontaneous Role Playing Interviewing Problem Solving Buzz Session Reading Brainstorming Observing Social Interaction Demonstrating Mediating Writing or Drawing Discussion Viewing Film/Video Panel presentation Audio Listening Lecturing 21 19 18 18 16 16 16 16 15 15 14 14 13 13 13 12 12 12 11 10 8 8 7 Source: B. M. Harris Keys to Success 15% believe the key to success is Aptitude 85% believe the key to success is Attitude Source: Harvard Business School Study Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 17 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The Four Quadrants of the Brain Different people favor a different quadrant of the brain. This effects the way they think, they way they learn, and the way they communicate. One of the many tools that are available to us to help better understand not only our preferences for communicating for how other individuals prefer to communicate is the Herrmann Brain Dominance Instrument (HBDI). Ned Herrmann developed the HBDI more than 25 years ago while he was working as a head of management education at General Electric. The HBDI measures a person's preference for right‐ or left‐brained thinking and for intellectual, more visceral or gut‐oriented thinking. The model combines these two dimensions to create four quadrants (A through D). Quadrant A is the Rational Self (Analyze) Quadrant B is the Safekeeping Self (Organize) Quadrant C is the Feeling Self (Personalize) Quadrant D is the Experimental Self (Strategize) Each quadrant representing a different thinking‐style preference. (You can determine your style by completing this 120 question survey and sending it to Alpha training for evaluation: http://hrda.co.uk/Resources/HBDI_Survey_E.pdf ) Based on this information, individuals and/or teams can better predict, understand and improve their problem‐solving, idea generation and communication patterns. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 18 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com With this information, you can better prepare yourself for communicating. If you know in advance the preference of the individual with whom you will be communicating, you will be more effective in delivering your message because you are now delivering it in a manner that person understands. Accordingly, he or she will be more willing to invest their time to listen to you. Herrmann's research has shown that although we clearly prefer some quadrants over others, we all have access to each of these quadrants. If you prefer communicating from the Experimental Quadrant, your preference will tend to be to challenge established policies, to think outside the box for solutions and look at the big picture. On the other hand, if you prefer to communicate from the Rational Quadrant, you will tend to want to gather facts, and look at ways to solve problems logically, and you will want to make your point clearly and concisely. The Feeling Quadrant will be more likely to be more intuitive, expressive and sensitive, in contrast to the Organized Quadrant, which focuses on plans, details, how things will get done and timing. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 19 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Based on Hermann’s theory, the following teaching methods appeal best to the following quadrants of the brain: A Problem Solving Lectures Research Findings Handouts Bibliographies Panels Use of Experts Quiz Applied logic/Analysis Theories Games/Crossword Puzzles Laboratory Symposium & Forums Case Studies Debates Textbooks, Readings News Articles D Picture Studies Brainstorm/Buzz Group Visuals/Illustrations/Art Metaphors Skits/Commercials/Games Shows Videos, Films Big Picture/Hypothetical Develop Goals Concepts Cartoon/Poems Experimentation Creativity/Pull Together Discussions/Possibility Thinking Exercises Self‐Assessment B Demonstrations Case Studies Modeling Objective learning Checklists/Worksheets Review Programmed learning Build Skills Policies and procedures Projects Field Trips Questions – Who, What, When, Where Summaries Lectures Reports C Testimonies Interaction Role Plays Videos People Oriented Cases Listening & Sharing Ideas Sharing Personal Experiences Kinesthetic Activities Discussion Feelings Interviews Stories Music Breakout Rooms Team Projects Group Discussions Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 20 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 21 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Carlton’s Tips for Delivering an Effective Presentation 1. Room Set up – Angle chairs so participants face the center and can see one another a little. 2. Tables – Allow participants to lean forward, write, deal with snacks and drinks, rest arms, change body position. I prefer 2 people per 6 foot table if possible. 3. Screen – As large as possible. Avoid bleed through screens. Project image as large as possible. 4. Projector – As bright as possible. I use 4300 lumens. 1500 lumens is not enough, 2000 to 2500 will work OK with good screen and dimmed lights. I avoid running the projector in econo mode. 5. Timing – Start on time, end early. 6. The First three Minutes – The first 3 to 5 minutes are crucial, the audience will determine their opinion of you within 5 minutes. I like to teach the audience something in the first three minutes. Often I time instructors only to find that they are still introducing the topic 20 to 25 minutes later, and have said virtually nothing of value. 7. Set Expectations – tell them when you will start, stop and break. Tell them what your objectives are. 8. Don’t say “UMMM” – Nothing makes you looks less confident or more like an amateur than repeatedly saying “UMMM”, “You Know”, or “Like”. 9. Embrace Dead Air – Dead air is your friend. Unfortunately your natural inclination is to believe that dead air makes you look like you don’t know what you are talking about, that’s why your brain subconsciously fills in the dead air with “UMMM”, “You Know”, or “Like”. Instead, stop mid sentence...let the dead air fill the room...stare down the audience...then continue. 10. Change Voice Inflection – Try speaking softly or boldly for a change of pace. 11. Set Up Your Topics – Tell the audience that the next topic they are about to hear will be the most important topic they hear all day. After that, tell them you were just kidding about the last topic, but this next topic really is the most important... 12. Quadrant Techniques ‐ Use some of the various teaching techniques from each quadrant to appeal to the entire room. 13. Names – ask participants their names when the ask you a question, then remember that name and refer back to that name throughout the day when appropriate to do so. 14. Read Your Audience – If they start to dwain, tell a story or a joke – change the subject, ask a question – bring them back from the dead – that is YOUR job. 15. Repeat Questions – so everybody can hear the question. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 22 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Non Verbal Communications Chapter 4 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 23 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Why Discuss Non Verbal Communications? OK, I realize this book course is based on high tech communications; however, because 94% of all communications is non verbal (and 50% based on body language alone), we ought to address this topic. Additionally, some high tech methods of communication, such as video conferencing, will convey your body language, therefore a brief study of non verbal ques and signals is entirely appropriate to help you communicate most effectively. Specifically, I have several key points that I would like to make in this chapter as follows: 1. Most high tech communications don’t convey the non verbal signs and signals that are often very important to some people in evaluating sincerity and gaining their trust. You should be aware of this flaw and perhaps take steps to compensate for this. 2. Some people don’t make that good of an impression initially for a variety of reasons, be it nervousness, a weak voice, insecurities, physical appearance, etc. For these people, high tech communications could be a good equalizer that allows them to establish important business relationships. 3. The high tech communication methods discussed in this manual are not intended to completely eliminate personal interaction, eventually you will probably meet the people you communicate with face‐to‐face. Personal Appearance According to experts, your personal appearance communicates plenty. The wrong image can shut people down before you even begin your communications. Since you want to communicate effectively, often you must start with your personal image. Exactly how does one convey a professional image? Sure, an attractive face or healthy physique helps, but they not absolutely necessary to convey a professional image. According to experts, the simple tricks that seem to matter most are as follows: 1. 2. 3. 4. Clean. Nice haircut for guys or hair style for women. Nice clothes that fit well. Clothes that have been ironed. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 24 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Hand Gestures Hand gestures are a great tool for enhancing your communication, and for reading between the lines to evaluate the communication of others. Experts say that those people who use more hand gestures can often command greater attention from their audiences. At least one expert says that we respond to hand gestures with an extreme alertness because dedicated nerve cells in our primate brain's lower temporal lobe respond exclusively to hand outlines, positions, and shapes (Kandel et al. 1991:458‐59). (Wow, that’s deep!) Presented below is a summary of some of the hand gestures commonly used. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 25 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Presented below are a few tips for using hand gestures when communicating: 1. You might want to add hand gesture notations to your speech notes. 2. You should avoid using the same hand gesture over and over. 3. You shouldn’t animate or mime your entire speech. 4. You should refrain from copying others, the best gestures are unique to you. 5. New gestures feel strange to your body. Practice them until they are comfortable. 6. One‐handed gestures are often more effective than two‐handed gestures. 7. Avoid finger and fist gestures that may be insulting to other cultures. 8. Gestures are a physical activity, you cannot learn to do them by reading. 9. Use a mirror to verify that your gestures reinforce your message. Mudras ‐ The earliest bronze statues in India were cast in the Indus Valley about 2300 BC, reaching an artistic peak during south India's Chola Dynasty (c. 9th to 13th centuries AD). Known as mudras, the hand positions of each statute has a different meaning as follows: Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 26 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Body Language There are four parts to tactical body language: facial expression, gestures, stance and personal space. Unfortunately, it is a two‐way street — while you are watching a person’s body language, he or she is simultaneously watching yours. Study your body language in a mirror. What messages do you send? You might be surprised. Understanding body language can be critical. There is more to body language than movement. Behavioral studies indicate that individuals establish a personal space circumference, which may change depending on the type of message they are sending and their goal. We establish a comfortable distance for personal interaction and nonverbal (unconsciously) define this as our perimeter. Personal distance is just as much a part of non‐verbal communication as a smile or a snarl. By the way, notice if a smile uses all of the face muscles or just a few around the mouth. More muscles equal a more natural, unforced smile. If one is distrustful (e.g., paranoia), his or her space will probably be larger. If you find yourself moving back from a person, you have probably picked up a warning signal at a subconscious level. Pay attention! If a person moves into your personal space it may well be a sign of aggression or implied intimidation. Facial Indicators Here are a few obvious facial signals: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Nostril flare (arousal, anger). Grin (happiness, affiliation, contentment); Grimace (fear); Lip compression (anger, high emotion, frustration); Canine snarl (disgust); Lip pout (sadness, submission, uncertainty, seduction). Sneer (contempt, intimidation. Frown (anger, sadness, concentration); Brow raise (intensity, curious, slight surprise). Big pupils (arousal, fight‐or‐flight, drugs). Small pupils (rest‐and‐digest,); Direct gaze (affiliate, threaten, deception); Gaze‐down (submission, deception, distraction). (Adapted from Givens, 1998‐202, Center for Nonverbal Studies.) Remember, you are not the only person who studies body language. Misleading body language can be used to do just that — mislead. Look at the individual’s entire presentation when in doubt. Incongruity may be an attempt to conceal or mislead. The truth is consistent. When the spoken word is at cross Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 27 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com purposes with body language, normally it is safer to believe the body because body language is more likely to be unconscious. Learning to Read Body Language Whether you know it or not, your body language tells more about you than you think. Although many of the pictures presented below display exaggerated body language, most people can pick up on even subtle tell‐tale signals. Most of us are already aware of body language, but we don’t think about it enough when it comes to our own body language, or reading other’s body language. To help you understand body language a little better, presented below are some typical signals that you send off with your body language, along with pictures and a brief description. It is to your advantage to understand how to read and deliver body language. Aggressive Body Language: Showing Physical Threat Not smiling. Shoulders squared off. Pointing. Furrowed brow. Leaning forward while not smiling. Deep breaths. Attentive Body Language: Showing Real Interest Good eye contact. Eyes wide open. Leaning forward. Smiling or slight smile. Good posture. Eyebrows lifted. Nodding in agreement. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 28 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Bored Body Language: Just Not Being Interested Leaning back. Arms folded. Sleepy eyes. Propping up head. Yawning. Not smiling. Slouching. Doodling. Sitting back too comfortable. Frozen stiff. Closed Body Language: Many Reasons Are Closed Arms folded. No smile. Defensive hand gestures. Non accommodating eyes. Legs crossed at the knees. Deceptive Body Language: Seeking To Cover Up Lying Or Other Deception Avoiding eye contact. Hiding one’s face. Speaking through one’s hand. Looking up or looking away. Wringing hands. Biting or sucking on lips. Defensive Body Language: Protecting Self From Attack Covering Up. Frowning. Pursing lips. Looking away. Withdrawing. Furrowed brow. Distant stare. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 29 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Dominant Body Language: Dominating Others Fist Pounding. Finger shaking. Blocking. Finger pointing. Leaning in. Yelling. Being louder than necessary. Interupting. Emotional Body Language: Identifying Feelings Evaluating Body Language: Judging And Deciding About Something Greeting Body Language: Meeting Rituals Open Body Language: Many Reasons For Being Open Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 30 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Power Body Language: Demonstrating One's Power Serious expression. Looking down nose. Looking over glasses. Steepling fingers. Crossed arms. Fist pumping. Leaning in without smiling. Ready Body Language: Displeased With What They Are Hearing Grimacing. Eyes shut. Scratching. Looking away. Lips pursing. Teeth gritting. Silence. Relaxed Body Language: Comfortable And Unstressed Big smile. Comfortable posture. Legs crossed. Fingers interlocked. Aror arms up. Romantic Body Language: Showing Attraction To Others Slight smile, not showing teeth. Whispering. Giggling. Winking. Touching hair or face. Getting close. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 31 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The Most Important Non Verbal Signal When it is all said and done, there is one key piece of body language that stands out from all the other signals – and that key is a smile. If you want to come across to others in a positive manner, make sure you smile. If you study the pictures above, the smile is the single most important factor that dictates whether a person is projecting a negative, devious, bored, cautious, uncaring, depressed, evasive image versus a positive, cheerful, trustworthy, likable, believable, interested image. So the next time you are communicating with someone, be them your employees, colleagues, kids, parents, spouse, neighbor – whomever, put on a smile. And if the situation calls for it, extend a hand of friendship, not negative body language that turns people off before you open your mouth. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 32 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Body Language on the Dating Scene To illustrate the power of body language, consider this advice. when meeting people in a bar or social setting, the web site eHOW suggests that sending out the following five non verbal signals is often more effective than throwing out a pick up line. 1. Posture is Important ‐ Be sure to stand tall. Posture is the first thing that sets you apart in a room full of slouching or uptight individuals. 2. Use Your Eyes ‐ If you have down a good, flirty wink, you may wink; however, if it looks unnatural, stick to the "smiling eyes" tactic. 3. Show Some Teeth – Give them a teeth‐flashing smile! 4. Show Some Tongue ‐ Whether taking a sip of a drink or licking your lips, allowing your tongue to wet your lips garners attention. 5. Move Closer – Move in closer to let him/her know that you're interested. Once you get closer, you'll be able to tell if the body language is reciprocal. From there, you'll have to come up with your own pick up line! While I am not sure about pints 4 & 5, points 1 through 3 could easily apply to any business situation. See if you can tell what message or impression these people are sending. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 33 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Low Tech Communication Methods Chapter 5 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 34 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Low Tech Communication Methods By no means do I suggest that you should ignore low tech communication methods, they work too. Presented below are some of the low tech communication methods you should also employ. 1. Yellow Page Ad ‐ In an effort to get noticed, Yellow Pages ads are getting more and more graphically outrageous. A picture can help, but remember that eyeballs are the single most effective graphic image for drawing and holding attention. Make sure that your Yellow Pages ad accurately conveys the image you want. 2. Display Ads ‐ Similar to yellow page ads, prospects can draw a number of conclusions from your display ads in newspapers and magazines. Does your ad convey a dignified, professional image or does it make you look low‐end? Does your ad speak softly and clearly to your prospect or does it scream? 3. Brochure – A brochure offers a good leave behind or mailer that provides prospect with the information you want them to have make sure that it does not leave out important facts that would help your prospect decide to hire you. Make sure that your brochure looks crisp, clean, neat, attractive, informative, complete, and professional. Plenty of white space, high quality graphics and color, printed with a readable size Calibri font, shadowing and transparency will convey a 2010 impression. Avoid making fonts larger to fill edge to edge – that will make your brochure look amateurish. 4. Business Cards – Your business cards should be crisp, clean and professional, and the type size and font should be easy to read. Keep in mind that background colors and patterns can interfere with high tech card scanning devices. 5. Stationery, Envelopes & Stamps – Bite the bullet and order a box of fine linen stationary and envelopes, then use them. Of course you won’t use this for mailing invoices or bills – but when you want to say thank you or invite someone to join you, the traditional letterhead and envelope will make a good impression – whether you handwrite the note or not. Don’t forget to purchase some attractive stamps as well. Include your business card in your letter too. 6. Web Site and E‐Mail Address –Yes, a web site is more of a high tech communication tool, but don’t forget to reference your web site and e‐mail address in your stationary and business cards. Tips for designing a professional web site will be covered later in this manual. 7. Telephone Reception ‐The person who answers your phone is critical to your marketing success. You can create powerful, effective marketing in every area, but if you have a weak person answering your phone, you've got problems. You want the person who answers to be friendly, informed and efficient. The person calling your office can notice a weakness on the telephone in the first three seconds. It's a negative impression you don't want to make. Experts say that the person answering the phone should be the highest paid person in the office, other than you. When prospects call your office, are they greeted promptly by someone who makes sure their calls get to the proper person without delay? Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 35 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 8. Voice Mail Message – Some people hate reaching voice mail, but I actually like voice mail because it sometimes allows me to leave the information you requested without having to string out a longer conversation. However, what I do hate are those long instructions. Believe me – by now we’ve all learned what to do at the beep. The best advice is to make sure that you telephone is answered during reasonable business hours within a few seconds. Thereafter, keep your voice mail instructions as short as possible. When you're fortunate enough to have prospects calling your office, make sure the message they receive ‐‐ even a voice mail message ‐‐ is professional, upbeat, friendly and inviting. 9. Leave Detailed Voice Mails – In the event that you do reach voice mail, go ahead and leave a detailed message so as not to waste your time or your parties time. One of my pet peeves are people who leave messages that just say “call me”. After playing phone tag for numerous missed calls on both sides, you finally reach them only to find out that they had a simple question that you could have easily answered if they had left a detailed message in the first place. 10. Scheduling Phone Calls – I’ve had people spend more time and effort calling me to schedule a call than the call actually took. 11. Tchotchkes – Tchotchkes are inexpensive promotional products that typically have your company name and contact information stamped on. These types of promotional products typically show that a company is generous and big enough to absorb the cost of a few trinkets. It makes the recipient feel a little more comfortable that they are dealing with an established company. Everything a prospects sees, hears, and reads about your firm creates an image in their mind. Make sure the impressions you create are consistent with the images you want to convey. In addition to attracting new clients, your marketing program should be designed to convey, refine and polish your firm's image so you always ‐‐ always! ‐‐ make a positive first impression. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 36 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Voice Over IP & Video Conferencing Chapter 6 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 37 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Internet‐based Phone Calls & Video Conferencing Technology continues to change the way we communicate. Many new technologies, devices, and software applications have emerged to improve the way we communicate. Two such technologies are Internet‐based phone calls and video conferencing. Using these technologies, many businesses are communicating with greater efficiency and better results. Are you keeping up? Is there more that you could do to better communicate with your customers, prospects, employees, business partners, executive team, and board of directors? This article focuses on this new age of communicating, and offers suggestions for embracing these new technologies and avoiding the pitfalls they offer. lectronic mail hit the scenes in the early nineties and dramatically changed the way we communicate. Today new technologies continue to emerge ushering in a new era of dramatic changes in the way we communicate. Consider internet‐based phone calls (also known as voice over IP) and video conferencing. The first video conferencing solution was deployed in 1936 by the Germans, but this concept became well known in 1962 via the futuristic cartoon “The Jetsons”. In this cartoon people used television screens to communicate, and both parties could see and hear one another. E Today, video conferencing has become a reality with dozens of proven solutions available such as GoogleTalk, GoToMeeting, iChat, Jajah, ooVoo, Vonage, and Gizmo. Each of these solutions has their own advantages; however, this article focuses on the most popular internet‐based phone call and video conferencing solution today – Skype. Today more than 100 million people use Skype to place internet‐based phone calls and video conference throughout the world, with between 10 to 20 million active users at any time. The basic Skype service is free and takes only 2 to 5 minutes to set up – simply visit Skype.com to download and install the application. Next, search for the Skype users you want to call (this is Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 38 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com similar to searching for their name in a phone book) and add them to your contact list. Double click the user name to initiate the Internet phone call, and the recipients computer will ring just like a telephone. Once the person you are calling answers you can speak to one another using your computer’s speakers and microphone. If you both have web cameras, you can see one another as well. Skype allows you to speak to other Skype users around the world and each day tens of millions of people use this service. Because the service is free and video support is included, the experience is different compared to traditional telephone calls. It is common for Skype users to keep video‐based phone calls active for hours as they work together on a common project. This arrangement encourages teamwork and enables managers to more easily supervise remote users, even when team members are physically located thousands of miles apart. However, the basic service is just the beginning. For a small fee, Internet‐based Skype offers many additional features as follows. For example, users can also use Skype to call land lines and cellular phones throughout the world directly from their computer. I used this feature personally in 2009 while traveling in Morocco. I simply logged into the internet locally, and used Skype to call telephone numbers back in the United States. The many people I spoke to had no idea that I was initiating the phone call from a computer. In total my phone calls from the African continent to the United States cost me about $1.36, these same calls would have cost more than $300 had a I made the calls with my cell phone. Skype also supports call forwarding and Voicemail, and can be used to video conference with up to 15 parties simultaneously. I also use the Skype service as a security device. With auto answering enabled, I am able to use Skype to log into my office or home computers and view live video of the premise. I even have a Skype computer setup in my dog room, so I can log in to check on my dogs, say hello, and make their Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 39 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com tails wag. This same type of inexpensive solution might be used by companies to keep watch on their warehouses or workers from long distance, or from just across the street. Other Skype features allow conversations to be recorded and the chat translation tools allow users to text one another, even if both parties speak different languages. The Skype Mobile feature allows users to make nation‐wide or international calls from cellular phone, with only Skype charges applied of about 1.8 cents per minute. Skype extras offer even more functionality such as the following: a. The mcePhone extra allows your incoming Skype calls to pop up on your TV screen. b. The KishKish extra monitors the level stress level of the person you are talking with over Skype to detect when a person is lying c. The Yugma Skype extra provides a conference room metaphor on users’ desktops, and includes IM, voice, video, a whiteboard, and file sharing capabilities. d. The Skylook Extra integrates Outlook with Skype to send you alerts to your cell phone and to read important emails to you on your phone when you are away from your desk. Today’s Tech Savvy CPA would certainly embrace the opportunity to try out these exciting technologies to save money and improve the quality of their communications. If you prefer a different service other than Skype or maybe you think Skype is a bit too expensive, consider these Skype alternatives. 1. ooVoo – Free 2 way video chat. Share documents while on a video conference. Built in video effects. Record video conferences (1,000 minutes of online storage). Desktop sharing. Try all premium features free for 30‐days. Full product pricing: $40/month. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 40 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 2. SightSpeed – Mac and Windows app offering unlimited free PC – PC VoIP calls, unlimited free PC – PC video calls. 9 way video conferencing. Reduced rates for PC – landline / cell phone calls. Also features video blogging capabilities. 3. Google Talk – A soft VoIP application for Windows that offers VoIP and instant messaging. Mac users can talk with Google Talk users using Jabber‐enabled clients such as Adium and iChat. Linux users can use Gaim. See real‐time availability and status of friends online. Send instant text messages. Easily go from text to voice chat. Chat right from your desktop or from Gmail. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 41 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 4. Gizmo5 – Make calls anywhere without downloading. Add Gizmo5 to your Desktop. Add Gizmo5 to your mobile phone. Claims best per minute rates available to landlines and mobile. No monthly fee. No set up fee. PC‐to‐PC calls are always free! SIP based P2P client in the same ilk as Skype with integrated call recording. 5. iChat – Mac OS X application that offers PC – PC calls between iChat and AIM users. Put on a photo slideshow, click through a Keynote presentation, or play a movie — in full screen, accompanied by a video feed of you hosting — while your buddy looks on. 6. Amicima – Publishers of a soft VoIP application called amiciPhone that offers a combination of user presence, file transfers, photo sharing and instant messaging. However, in 2009 this solution was acquired by Adobe and is being overhauled – look for it to come out even stronger than before. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 42 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 7. VoIP Buster – Windows app offering free PC – PC calls and 120 days of free calls to landlines. 8. Jajah – It connects you using your existing phone. Web‐based VoIP interface where you enter your phone number and the number of who you want to dial. Jajah calls the caller and the person you are calling. You both answer, the calls begins and you can talk. Does not require any new software or hardware. 9. OpenWengo – A European solution. Open Source app based on the SIP protocol for free VoIP calls between 2 PCs with SIP‐compliant software. You can hook into any other VoIP provider that uses SIP. Also offers SMS, video chat and instant messaging. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 43 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 10. Vbuzzer – Soft VoIP Windows app offer free calls between Vbuzzer users and reduced call rates to landlines. Also offers instant messaging. Phone to PC calls are just $2 per month. Make calls from internet browser of your cell phones. Supports PBX systems. Schedule and manage conference calls for $10/month. Supports callbacks. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 44 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Review of Skype By J. Carlton Collins, CPA Skype is a software application that allows users to make voice calls over the Internet, in addition to instant messaging, file transfer and video conferencing. Presented below are Skype highlights. 1. Using Skype, you can call any computer in the world free of charge (SkypeIn). 2. You can also call any telephone in the world for a small charge, currently 1.8 cents a minute (SkypeOut). 3. If you have a camera, your party can see you. If they have a camera, you can see them. 4. You can also use Skype to make conference calls to up to 16 Skype users. 5. You can also use Skype to transfer files back and forth. 6. You can also use Skype to send instant messages back and forth. 7. As of September 2009, there were 521 million Skype accounts throughout the world. In the 3rd quarter of 2009, Skype users made 27.7 billion minutes of free phone calls from one computer to another. During that same period Skype users made 3.1 billion phone calls to telephones generating revenue of $185 million. 1. Skype is adding about 40 million subscribers a quarter. 8. The Idea for Skype ‐ You may recall that Napster was the first peer‐to‐peer file sharing system, and Kazaa was the European version modeled after Napster, and was ten times bigger than Napster. Both Napster and Kazaa were attacked legally because it’s users could easily use those platforms to illegally share music and even movies. Eventually Kazaa’s developers figured out that they could use the same technology to share voice files rather than music files, and “Voila”, the idea for Skype was born. 9. Founders ‐ Skype was developed by Estonian developers Ahti Heinla, Priit Kasesalu and Jaan Tallinn in Sweden, with headquarters in Luxembourg. One of the initial names for the project was "Sky peer‐to‐peer", which was then abbreviated to "Skyper". However, some of the domain names associated with "Skyper" were already taken. Dropping the final "r" left the current title "Skype", for which domain names were available. 10. SOLD! – Skype was acquired by eBay in September 2005 for $2.6 billion. eBay has since written Skype down to $1.7 billion on its books and announced a public stock offering for 2010 to spin Skype off as a separate company. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 45 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 11. Lawyers Screwed Up ‐ It was discovered that Skype’s holding company had always owned the underlying peer‐to‐peer technology. On September 1, 2009, a group of investors led by Silver Lake bought 65% of Skype for $1.91 billion and the lawsuit was eventually settled with ownership being divided with the new investors owning 56%, the original founders owning 14% and eBay retaining 30%. 12. Phone to Computer ‐ SkypeIn now allows Skype users to receive calls on their computers dialed by regular phone subscribers to a local Skype phone number; local numbers are available for Australia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Denmark, the Dominican Republic, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Hong Kong, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Mexico, New Zealand, Poland, Romania, South Africa, South Korea, Sweden, Switzerland, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and the United States. A Skype user can have local numbers in any of these countries, with calls to the number charged at the same rate as calls to fixed lines in the country. (Some jurisdictions, including France, Germany and South Africa, forbid the registration of their telephone numbers to anyone without a physical presence or residency in the country.) 13. Video conferencing between two users was introduced in January 2006 for the Windows and Mac OS X platform clients. Skype 2.0 for Linux, released on March 13, 2008, also features support for video conferencing. 14. In 2008 Skype added support for "High Quality Video", full‐screen and screen‐in‐screen modes. 15. Skype audio conferences currently support up to 25 people at a time, including the host. 16. Skype does not provide the ability to call emergency numbers such as 911 in the United States and Canada. The FCC has ruled that, for the purposes of section 255 of the Telecommunications Act, Skype is not an "interconnected VoIP provider". 17. On April 24, 2008, Skype announced Skype on around 50 mobile phones. 18. On October 29, 2007, Skype launched its own mobile phone under the brand name 3 Skypephone, which runs a BREW OS. 19. Skype is available for the Nokia N800 and Nokia N810 Internet Tablets, and the Nokia N900. 20. An official free Skype application for the iPhone OS was released in the iTunes store on March 31, 2009. An improved version, v1.3, was released on January 19, 2010. 21. Skype and Verizon Wireless are set to launch a new service, Skype mobile™ that enables customers to use Skype on a variety of best‐selling Verizon Wireless BlackBerry® and Android™ 3G Smartphones. This plan provides free Skype‐to‐Skype global calling and low rates to international landlines and cell phones, Skype will be ‘always on’, meaning customers can receive Skype calls, instant messages and see friends’ presence anytime. Skype usage won’t be charged against customers’ monthly Verizon Wireless data plans or minute allowances. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 46 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 22. As of January 2009, Skype is available for Android and over 100 Java enabled mobile phones. 23. Skype has become the largest international voice carrier. International computer‐to‐computer traffic between Skype users in 2005 was 2.9%, 4.4% in 2006, and about 8% in 2009. 24. Skype is a secure communication; encryption cannot be disabled, and is invisible to the user. Skype reportedly uses non‐proprietary, widely trusted encryption techniques: RSA for key negotiation and the Advanced Encryption Standard to encrypt conversations. 25. In October 2008 it was revealed that Skype sends content of text messages and encryption keys to monitoring servers. So governments are listening in! Skype Milestones: - - - April 2003 — Skype.com and Skype.net domain names registered. August 2003 — First public beta version released. September 2005 — SkypeOut banned in South China. October 2005 — eBay purchased Skype (Oct 14). December 2005 — Video telephony introduced. April 2006 ‐ Number of registered users reaches 100 million. January 18, 2007 ‐ Skype changes pricing structure, charges for all SkypeOut calls. March 2007 — Skype adds a new feature called Send Money which allows users to send money via PayPal from one Skype user to another. August 17, 2007 — Skype users were unable to connect to full Skype network in many countries. Skype reports the system‐wide crash was the result of exceptional number of logins after a Windows patch reboot (this day is referred to as "Patch Tuesday"). July 9, 2008 — Skype changes system into a full‐screen application. September 2008 — Skype discontinues its SkypeCast service, without explanation. September 2008 — Skype adds 'Compact mode', after user criticism of the new default full‐ screen mode. October 2008 — Analysis reveals TOM‐skype sends content of text messages and encryption keys to monitoring servers. November 2008 — Skype adds internal monthly and daily usage caps on their SkypeOut subscriptions advertised as "Unlimited". March 2009 — Skype launched Skype for SIP, a service aimed at business users. At the time of launch around 35% of Skype's users were business users. April 2009 — eBay announced plans to spin off of Skype through an initial public offering in 2010. August 2009 — Joltid files a motion with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, seeking to terminate a licensing agreement with eBay which allows eBay (and therefore Skype) to use the peer to peer communications technology on which Skype is based. If successful, this may cause a shutdown of Skype in its current form. September 1, 2009 — eBay announces sale of 65% of Skype to a consortium comprised of Index Ventures and Silver Lake Partners. Using Skype Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 47 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 1. Download ‐ Download and setup is free and takes about a minute. You will want to install Skype on every computer that you want to communicate with/from. The download page is here: http://www.skype.com/download/skype/windows/downloading/ 2. Find Contacts – Next, search for your contacts using the “Contacts; Search for Skype Users” menu option as shown in the screen below. To search for a person simply enter their name and click the FIND button. You can also add users from Outlook, MySpace, or phone numbers in your contact list. Notice that there are many search options which allow you to narrow your search. For people interested in potentially dating through Skype, simply leave the name field blank and search for persons of a specific gender, age, country, state and city. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 48 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com There is also a tool called “Directory” that allows you to search for businesses. Show below I have searched for restaurants in my area. Remember, you can contacts up using either their Skype address or their telephone number. 3. Configure Your Skype Settings – There are numerous setting adjustments you can make, a few of the more important ones are listed below: a. Setup your profile information so people can find you. b. Tune your microphone using the audio settings. c. Set up your video and screen sharing to receive and send automatically when connected to people in your contact list. (I would not recommend that you set your video to automatically send or receive from anyone) d. If needed, adjust your webcam settings brightness, contrast, flicker, etc. e. Check the box labeled “Start Skype when I start Windows”. f. Adjust your privacy settings to only receive phone calls from people on your approved contact list. g. Add anyone your wish to your blocked contacts list under privacy to prevent them from contacting you. h. I have my system set to answer incoming calls automatically. That way I can connect and view my house when traveling. You may not want to do this. i. For a fee, Skype can receive your calls, and automatically forward them to your telephone or cell phone. j. For a fee, Skype also offers voice mail. 4. Make your First Video Call ‐ Access the Contacts Page and double click a contact to make a computer to computer phone call. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 49 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 5. Make your First Phone Call – Access the Call Phones Page and dial the number you want. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 50 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Remote Desktop Control Chapter 7 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 51 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Remote Desktop Control Introduction to Remote Access emote access becomes important when you travel away from your computer, or when two or more separated people need to share the same data. For more than 15 years, Citrix MetaFrame was the defacto standard for establishing high performance remote access while pcAnywhere was the defacto low cost solution. In recent years new solutions have risen to challenge both of these solutions. In particular, Microsoft Terminal Services is arguably as good as Citrix, and priced far lower (30% to 40% lower). In addition, web based solutions such as “GotoMyPC” and LogMeIn have become the preferred low cost and easy solutions. In addition, Microsoft Windows includes a remote solution as well. There are more than 425 downloadable solutions located here: http://www.download.com/Remote‐Access/3150‐ 7240_4‐0.html; however the main solutions are as follows: Some Low Cost Remote Access Solutions Some High End Remote Access Solutions R Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 52 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Benefits of Using Remote Access There are numerous situations that call for a remote access solution. Traveling employees often need access to their e‐mail, calendar or contact list. Traveling sales representatives need access or to the accounting system for entering orders of looking up inventory levels and customer history information. Work‐at‐home employees need access to their office computer. Multiple location companies need to connect remote locations to a centralized accounting system. Troubleshooting/support professionals need to log into the customer’s remote system for maintenance purposes. Presented below are specific examples of how you might use a remote access solution in your organization: Customer 1. See or conduct live product demonstrations on any machine that has an internet connection 2. CPAs can have remote access to their client’s accounting data to assist them in closing entries 3. Data could be obtained from the client's machine and then the accountant could perform necessary accounting tasks remotely Employees 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Conduct work from any remote venue using remote access Ideas can be documented and initiated immediately without going into the office Employees unable to physically go into the office can perform tasks from home Traveling employee can use a notebook without compromising secure office data Remote access allows employees to travel with less costly computers than their primary PCs Ensures data integrity since the data can remain on one machine without the need to update Support 1. Technical or product support is often simplified as accessing the PC in question becomes easier 2. Support agents physically see the issue rather than relying on user descriptions 3. Web based tools can detect and evaluate hubs, routers and other devices from a central location. GoToMyPC is a web‐based remote access solution that requires only a browser. This product technology can be installed and set up in about 2 to 5 minutes, and thereafter, you can connect any two PCs in the world in about 35 seconds. What makes GoToMyPC better than pcAnywhere is that no static IP address is needed to make the connection. What makes GoToMyPC better than Citrix or Terminal Server is the product is very inexpensive and much easier to configure and use. Other comments about GoToMyPC are as follows: 1. Features 128‐bit encryption. 2. Does not require a static IP. 3. Prints to printers at both host or remote site. 4. Supports File Transfer Protocol. 5. Can adjust time out from 1 minute to 9,999 minutes. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 53 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 6. Can blank out host screen while logged in. 7. Can invite remote users to take over. 8. Accessible from wireless devices such as PDA's without synchronization or data conversion. 9. Works from any PC with Internet connectivity anywhere in the world. 10. Can link Windows computers to Apple computers. 11. One‐time use passwords available to foil key‐logging scripts. 12. Web interface requires far less set‐up and maintenance compared to VPNs. Problem Areas: 13. Multiple users cannot access the same host PC using GoToMyPC at the same time. The first remote user must be logged out before another remote user can log in. Pricing for Personal GoToMyPC Accounts The following pricing as of October 2009 includes unlimited remote access, the ability to swap host PC's at will, software and service upgrades, and technical support and maintenance during operating hours: Key Demonstration points for GoToMyPC 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Show logging in – takes about 45 seconds or less. Show remote control. Show dual screens. Show security – Lock out screen and keyboard. Show security – Set automatic logoff greater than 15 minutes. Demonstrate voice over IP. Discuss printing locally or remotely. Demonstrate File Transfer. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 54 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The screen above shows the GoToMyPC web page where you can log into any computer on the interest around the world. The screen below shows some of the preferences that can be set to make GoToMyPC behave to your particular tastes. pcAnywhere pcAnywhere has been a long time favorite remote access solution that allows you to connect through a phone line or internet connection. Based on The NPD Group’s retail Top Selling Business Software list, Symantec’s pcAnywhere was the top‐selling remote access software product from August 1999 through April 2003. pcAnywhere’s underlying technology was made obsolete by newer solutions, and eventually Symantec changed the underlying programming to reflect the newer technologies. For a while it appeared that Symantec waited too late as pcAnywhere was no longer a front runner in this area. However, it appears that many users like the $199.99 per computer cost more than a monthly fee approach, and today Symantec claims on their web site that pcAnywhere is the number one best‐selling remote control software. Citrix Citrix has been the defacto standard for remote control solutions for many years, especially for larger companies and companies who want the best possible remote access performance. However Citrix is not cheap. A minimal installation of Citrix will typically cost about $15,000 to $18,000 by the time you purchase the software and implement a high powered Citrix server. Here are comments about Citrix: 1. Allows users to securely access corporate data through a customizable interface. 2. Centralizes data management and provides a Single Point of Access for users. 3. Consolidation of data provides a controlled environment for data manipulation and distribution. 4. Resources are available through an interface on a web browser. 5. Data can be accessed through any machine with an internet connection. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 55 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 6. Any user who has been granted permission may access data, including partners, customers, and employees. 7. Citrix can transfer all types of data, including internet sites, file shares, documents, and streaming media. 8. The user interfaces can be tailored to the needs of specific user types. 9. Available for sale from resellers since it was designed for the data management for large corporations. Microsoft Windows Terminal Server Microsoft Terminal Server functions similarly to Citrix, but typically costs about 30% to 70% less to implement. While many Citrix installers argue that Citrix performs better that Terminal Server, many users who have used both report that there is either no difference in performance or that Terminal Server performs faster. Presented below are comments about Windows Terminal Server: 1. Included in Windows NT, Windows 2003 Server, Windows XP Server, Windows Vista Server, and Window System 7 Server operating systems. 2. User has remote desktop control capabilities. 3. The host computer sends screen images to the client or remote access user. 4. Because recently used files on the host are spooled to RAM, Windows Terminal Server results in a very fast solution. 5. This well‐proven solution is widely used by larger corporations. Microsoft Remote Desktop Connection Microsoft Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows System 7 provides a built‐in thin client utility called Remote Desktop Connection which can be used to connect remotely to other Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 56 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com computer running any Windows operating system based on the use of an IP address. The connection wizard is shown above. Additional comments follow: 1. Host users invite remote clients to connect via email or .NET passport. 2. Host computers can specify time of invitation and duration of assistance. WsFTP There are many other remote connection options as well, for example WSFTP can be used to connect two computers together for transferring files back and forth. FTP, or File Transfer Protocol, establishes a direct connection between computers for the purposes of file sharing and communication. Be advised that FTP requires intermediate Internet and connectivity knowledge to configure an FTP server which may be accessed by client computers. Remote Control Software Vs Virtual Private Networks Which approach is better? These two solutions are dramatically different as follows: 1. With remote control solutions, the remote keyboard and monitor take control of the host computer located many miles away. It is as if the keyboard cable and monitor cable are no longer 6 feet long, but many miles long. The host computer sends screen images to the remote computer, and these screen images are relatively small files. When the remote user opens a 50 MB Word document, the word document opens instantly on the host computer, and only the screen images are transmitted. Likewise, when the remote user saves the word document, it is saved instantly on the host computer from the host computer’s RAM. 2. With “virtual private networking”, the host computer is seen as a node on the network just like a traditional node on a network. When a remote user opens a 50 megabyte Word Document from the host computer, the entire 50 megabyte document must travel through the Internet connection to the remote computer and is loaded into the computer’s RAM. This means that opening a large Word document across a VPN connection many take many minutes. Likewise, when the remote user saves the 50 megabyte word document, the entire 50 megabyte Word document must travel back through the internet connection to the host computer, once again taking many minutes. There are still instances where VPN connections offer advantages, but for most users the remote control solutions offer faster performance which also allow the users to utilize a cheaper less powerful computer for remote access purposes. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 57 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com “Electronic Forms” There is a great deal of attention paid to the process of scanning working papers, documents, and contracts into electronic format in pursuit of a paperless work environment, and rightfully so as there are many advantages to this approach. However, there is far less attention paid to converting your paper‐based forms to a paperless environment. This article focuses on the many benefits of adopting paperless solutions for the purposes of automating the data collection function in your organization. aper‐based time sheets, expense reports, and other forms are old‐school – there is a better approach to collecting, tabulating and reporting data. Today’s tech‐savvy CPAs prefer to use electronic forms which can be e‐mailed to recipients accessed from the web. As users complete and submit these electronic forms, the information is automatically delivered and tabulated. The results can be compiled in a variety of data formats including Excel, CSV (comma separated value), text, or database formats. Many organizations that have adopted paperless forms have reaped many benefits. For example, in 2008, the Georgia Society of CPAs (GSCPA) replaced their old paper‐based CPE course evaluation forms with electronic evaluations. Instead of completing paper‐based evaluation forms at the end of each course, attendees receive an e‐mail containing an electronic evaluation form. As attendees complete the forms and click the submit button, the evaluation results are instantly compiled in a database which automatically tabulates the results. This new process eliminates the labor‐intensive tasks of producing, distributing, completing, collecting, reentering, reporting and storing data using paper forms. The Society simply logs into the database to view the evaluation summary reports as needed. According to Paige Brooks of the GSCPA, the transition to electronic forms “... has definitely been worth the money”. She further explains that in addition to reducing the amount of processing time, full reports are available instantly whereas the older method sometimes did not produce results until months after the event. Many software application shave added paperless data collection capabilities as well. For example, in 2007 Intuit launched new web‐based electronic timesheet functionality called QuickBooks Time Tracker. For a monthly fee, this solution enables QuickBooks users to enter their timesheet data via a web‐based form, and the resulting data flows directly into QuickBooks. This data is used to calculate payroll checks and create customer invoices. P Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 58 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The QuickBooks Time Tracker Web‐Based Data Entry Screen The built‐in drop down list boxes and automatic tabulation makes the forms quicker and easier to fill out. The resulting data is submitted electronically, avoiding the need to hand deliver, fax, mail, or send paper‐based timesheets. Electronic documents are less prone to errors and are more easily shared, sent for approval, or backed up off site. (The QuickBooks Time Tracker add‐ in is priced at $7.00 per user per month.) There are many solutions available to help you create your own electronic forms. For example, Microsoft InfoPath is designed to help you create and deliver electronic forms. Default templates (such as expense reports) are provided and the built‐in user tools can be used to edit those templates or if you prefer, you can create your own forms from scratch. Some of these basic tools include text boxes, drop down list boxes, check boxes, and drop down calendars. InfoPath allows validation rules to be assigned to data fields to ensure that all fields are properly completed and meets specified criteria. An advantage to InfoPath is that all submitted data is automatically stored in XML form in an awaiting database, which makes it easy to retrieve the data in other XML‐based applications. InfoPath forms can also be integrated into Word or Excel files so that data entered into these documents are delivered electronically using the InfoPath delivery engine. Presented below is an example of a health insurance claim Microsoft InfoPath’s form prepared in InfoPath. Standard Tools Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 59 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Example InfoPath screen used to create Health Insurance Claim Form Web site authoring tools such as Dream Weaver, Front Page and Expression Web also provide form tools for creating electronic documents such as vacation request forms, and surveys, loan applications, order forms, and rules‐base product configurators. Because time is always saved when data is only entered once and the resulting data is automatically delivered, collected, tabulated and reported electronically; tech savvy CPAs are always on the lookout for situations where electronic forms can be implemented to save time, reduce expenses, and promote accuracy. If you would like to expand your practices by providing electronic document management services to your clients, consider becoming certified as a CDIA (Certified Document Imaging Architect) by passing the required online exams. For those CPAs who possess an extraordinary amount of knowledge in this area, you may also consider obtaining the EDP (Electronic Document Professional) designation from Xplor International – a group of experts in the electronic document industry who set standards and judge the qualifications of applicants. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 60 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Social Networking Chapter 8 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 61 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Social Networking Who you know does matter – right? Social networks help you maintain your relationships be them business, personal, or casual. Linked‐In is geared more for business relationships whereas FaceBook is geared more as a social tool that helps you maintain more personal relationships – but they both work well helping you keep track of all the people you know that might enrich your life professionally or personally. ocial Networking Solutions such as FaceBook are having a dramatic impact on you both personally and professionally. What started out as a social playground for kids has evolved into an environment that adults are finding useful and rewarding. S Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 62 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com FaceBook Discussion Points: 1. FaceBook Statistics: General Growth - More than 300 million active users - 50% of our active users log on to Facebook in any given day - The fastest growing demographic is those 35 years old and older User Engagement - Average user has 130 friends on the site - More than 6 billion minutes are spent on Facebook each day (worldwide) - More than 40 million status updates each day - More than 10 million users become fans of Pages each day Applications - More than 2 billion photos uploaded to the site each month - More than 14 million videos uploaded each month - More than 2 billion pieces of content (web links, news stories, blog posts, notes, photos, etc.) shared each week - More than 3 million events created each month - More than 45 million active user groups exist on the site International Growth - More than 70 translations available on the site - About 70% of Facebook users are outside the United States Platform - More than one million developers and entrepreneurs from more than 180 countries - Every month, more than 70% of Facebook users engage with Platform applications - More than 350,000 active applications currently on Facebook Platform - More than 250 applications have more than one million monthly active users - More than 15,000 websites, devices and applications have implemented Facebook Connect since its general availability in December 2008 Mobile - There are more than 65 million active users currently accessing Facebook through their mobile devices. - People that use Facebook on their mobile devices are almost 50% more active on Facebook than non‐mobile users. - There are more than 180 mobile operators in 60 countries working to deploy and promote Facebook mobile products 2. Free of Charge, Takes About 4 minutes to Set Up 3. Finding Friends: Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 63 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. a. Use “Friend Finder” tool to Search by high school, college, business, or groups to find old friends b. Refer to your friend’s “friend list” to find old friends you have in common; your friends might have already done a lot of the friend finding work for you c. Search for new friends based on profile data (more like a dating site), you find potential new friend who share your same interests, religion, location, etc. It’s all about the Pictures and Videos a. A picture is worth a thousand words – right? b. Like sharing your photo album, complete with all the comments your other friends have made about your photos and videos. c. Provides starting points for opening dialogs. d. This is why Facebook beats Linked in. Facebook Mobile: a. Allows you to stay up to date on Facebook activity via your cell phone – free of charge. b. Allows you to post and reply to your Facebook postings and requests via your cell phone, free of charge. Privacy Settings: a. Controlling the content you post b. Controlling who can see your information Avoiding the Games: a. Games can be time wasters b. Games can be Data Miners that harvest your data To get the most out of Facebook: a. Invest time to find your old friends. b. Take time to post pictures, especially older pictures of your friends c. Take time to post interesting status quotes frequently. d. Take time to read the status posts of your friends, view their pictures, and comment or indicate that you like the post. e. Use the forum to communicate with your friends, ask questions, share articles, links and videos that might be of common interest to one another. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 64 High Tech Communications Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) www.CarltonCollins.com 65 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Fortify your Facebook Privacy By J. Carlton Collins Thousands of CPAs and many state CPA societies are now using Facebook to help establish and maintain relationships; even the AICPA now hosts a highly active forum on Facebook. As more CPAs continue to embrace this new venue, privacy concerns are on the rise. In particular, Facebook’s new default privacy settings introduced in December 2009 makes most of your FaceBook content viewable by everyone. In the wake of these dramatic changes, CPAs need to adjust their Facebook privacy settings in order to protect their information. This can be a rather difficult task for two reasons, as follows. 1. The FaceBook privacy settings are scattered throughout Facebook; CPAs must visit multiple areas in order to change those settings, and this can be a confusing process. 2. In some cases, Facebook offers conflicting privacy settings in two different areas and when this occurs, Facebook obeys the less restrictive setting (unlike Microsoft Windows which obeys the more restrictive setting). For example, if you restrict the visibility of a photo, but fail to also make the photo album private, then the picture may still be visible. To help you protect your FaceBook privacy, this article provides a list of twelve privacy setting adjustments you should consider. 1. Friends Only CPAs should consider changing all of their settings throughout FaceBook to "Friends Only". This measure will help ensure that the only people that can see your Facebook content are those people you actually accept as friends. (From a CPAs’ standpoint, your Facebook friends may be your fellow employees, professional colleagues, clients, prospects, or other contacts.) The problem is there are many places you need to visit to make these changes. The four main areas you will need to visit are listed below, and you will need to toggle to dozens of items within each category to change all settings to “Friends Only”. 1. Account – Account Settings – Edit the networks privacy settings 2. Settings ‐ Privacy Settings – Edit the privacy settings for each of the following: a. Profile Information (12 different privacy settings) b. Contact Information (9 different privacy settings) c. Applications and Websites (1 privacy setting) d. Search (2 privacy settings) 3. Settings ‐ Application Settings ‐ Edit the privacy settings for each application you have running such as Groups, Photos, Video, Notes, Events, Gifts, Etc. 4. Each individual Photo Album (1 privacy setting) Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 66 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Exceptions to “Friends Only” ‐ The only exception might be under "Settings, Privacy Settings, Search". Here you might want to keep this setting set to "Everyone" so you can be found via a search. (I also allow my pictures to be viewed by "Friends of Friends".) 2. Use Lists to Help Organize your Privacy Settings The Facebook “List” feature allows you to organize your friends by groups. These groups can then have individual privacy policies applied to each of them to extend or suppress your Facebook information by “List”. For example, the screen below shows that I have set up several lists including "Neighbors", "Relatives" and “Professional Relationships”. These three groups can then be used to apply different privacy policies. For example, I may want your "Relatives " to see the photos from my vacation, but I don’t want my "Neighbors" or "Professional Relationship" friends to view them. Please note that a single friend can belong to more than one group. You can create new “Lists” by selecting “Create a List” on the Facebook’s “Friends” page. 3. Hide Your Friend List from Non‐Friends By default, your Facebook friends list is viewable by everyone. Imagine for a moment how an unscrupulous person might use this information to steal your identity or discredit you in some way, or how a competitor might use this information to target your client list. To hide your list of friends from the public, click the pencil icon in the Friends box on your profile page and uncheck the "Show Friend List to Everyone" box. Thereafter, non‐friends who view your profile will not be able to see your list of friends. Please remember that your “Friends List” is always visible to you and your friends. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 67 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 4. Block Third Party Facebook Applications Most third party applications are geared towards personal use, but some applications such as Greeting cards might be used for business reasons. CPAs should know that by default, third party applications such as Gifts, Mafia Wars, Birthday Greeting Cards, etc. can access any of your Facebook information. This means that your name, phone number, e‐mail address, street address, photos, videos, your comments, and any of your responses to third party questionnaires can be harvested for information and then used to build a profile of you and your likes and dislikes, and other preferences. Who knows how this information might be used in the future? Even if you do not use a particular third party application, it can still mine your data through your friends. For example, if your friend sends you a birthday card, the birthday application can harvest your birthday information from your Facebook account, even if you don’t use that application yourself. To protect your Facebook data from third party applications, follow these four rules: a. Start by not including any personal information in your profile page that you don’t want outsiders to see. b. Refrain from using any third party applications, most applications are games or quizzes that can waste time. c. Block all third party applications. d. Block your content which friends can share through their use of applications. This is accomplished from the “Account”; “Privacy Settings”; “Applications and Websites” menu. 5. Remove Yourself From Facebook Search Results There are many reasons why you might not want your information to show up in search results on Facebook and if so, it’s easy to turn off your public visibility. For example, if you are in the process of applying for a job, it might be best to temporarily remove yourself from Facebook search results if you feel that your Facebook page conveys a less than professional image. To do this select “Account”; “Privacy Settings”; “Search”; Facebook Search Results; and select “Only Friends”. (Remember, by choosing this action, you will no longer be findable.) Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 68 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 6. Protect Yourself from Networks Most CPAs join networks, or groups, without giving the matter a second thought. However, there might be valid reasons to avoid networks completely. For starters, the networks you belong to are treated by Facebook as public information; therefore anyone can see which networks you belong to. Belonging to a controversial network might convey the wrong message to your clients or colleagues, so be careful as to which networks you join. By default network members have the same access to your information (such as your birthday or political and religious views) as your approved Facebook friends. Belonging to a network makes your Facebook information searchable by all members of that network as if they were your approved Facebook friends, even if you have disabled public searches. To protect yourself from networks, CPAs should refrain from joining any network or group in which they have concerns about everybody in that group having access to their Facebook information. If a CPA does join a network, they should consider limiting the access to their Facebook information by selecting “Privacy Settings”; “Profile Information”; and for every option that displays “Friends and Networks” change that setting by selecting “Customize” then select “Only Me” and click OK. Then Select “Customize” again, and change it to “Only Friends”. (This will ensure that the setting is set to “Only Friends” and not to “Friends and Networks”.) (Be advised that it can be a tedious process to make these types of setting adjustments on such a granular level.) 7. Protect Yourself from FaceBook Advertisers Many of the advertisers who display ads on Facebook deposit tracking cookies on your computer to collect information about you and your computer habits. To protect yourself somewhat, CPAs should consider opting out of the placement of cookies by many of these advertisers at this web site: http://www.networkadvertising.org/managing/opt_out.asp. CPAs may also adjust the cookie settings in their browsers to limit or prevent tracking cookies by Facebook advertisers and others. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 69 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 8. Remove Your Facebook Content From Google By default, all Facebook user profiles are indexed by Google and other search engines. This means that some of your profile information is accessible through Google including your profile picture, friends list, and fan pages to which you belong. Some CPAs may use their Facebook presence for generating new contacts and may therefore like being included in Google search results while other CPAs may not want their information to be that public. If you prefer privacy, you can remove your Facebook content from all search engines by selecting “Account”, “Privacy Settings”, “Search” and unchecking the “Allow” check box next to the “Public Search Results” option as pictured in the screen below. 9. Prevent Photo/Video Tag Mistakes Reportedly, this is a frequent Facebook problem ‐ you let loose for a few hours one night at the company party and photos or videos of the moment are suddenly posted for all to view, not just your close friends who shared the moment with you, but potentially the entire world can see them. In some cases, the results can be devastating. It has been well documented that some Facebook users have been fired from work after incriminating photos/videos were posted Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 70 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com for the boss to see. For others, randomly tagged photos/videos have ended relationships. At the least, a tagged photo/video can result in personal embarrassment. To avoid this potential problem, you can prevent tagged photos or videos from showing up in all of your friends news feeds by selecting “Account”, “Privacy Settings”, “Profile Information”, “Photos and Videos of Me” and select “Customize” to limit your photos to specific “Friends” or specific “Lists of Friends”. (Early in 2010, Facebook provided the option to select “Only Me and None of My Networks”, but this privacy option has since been removed which is an indication as to how public Facebook allows your information to be.) 10. Protect Your Albums One of the facets that makes Facebook an interesting social tool is the unique and easy ability to share tagged photos and videos of one another. Although this concept is probably difficult for non Facebook users to understand, the sharing of photos and videos truly helps you and your Friends get to know one another on a deeper level. For this reason Facebook photos and videos should be embraced, not shunned. However, if you do decide to publish photos and videos to your Facebook, you should take a moment to ensure that you are not also sharing them with the entire world. Just because you’ve enabled the privacy settings to hide your photos from public searches does not mean that your photos are fully protected. It is possible that the photo may still be viewable by others who are tagged in the photo, and all of their Facebook “Friends” and “Friends of Friends”. To fully protect the privacy of your photos you must visit each photo album’s privacy settings and make the appropriate adjustments. To do this select “Photos”, “Album Privacy” from your “Profile Page” and make the appropriate adjustments as shown in the screen below. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 71 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com This way you can store your photos indefinitely on Facebook yet ensure that the only people that can view your photos are the ones who you really want to see them. 11. Avoid Your Friend’s Embarrassing Wall Posts Just because you use Facebook as a business tool doesn’t mean that your friends always do. That’s why once in a while a friend of yours might post something embarrassing or not necessarily “work friendly” on their Facebook page, which is automatically displayed on your Facebook “Wall” page. To protect against this possibility, Facebook provides the ability to customize the visibility of your wall postings. To access these settings select “Options”; “Settings” from your “Wall” page. Make the appropriate setting adjustments as shown in the screen below. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 72 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com In addition to controlling who can view wall postings, you can also control who can post to your wall as follows: Select “Account”, Privacy Settings”; “Profile Information” and make the appropriate adjustments under the “Posts by Friends” option. Notice too that this page provides a checkbox allowing you to completely suppress all wall postings by friends from being displayed. Conclusion As a CPA, I use Facebook both professionally and personally, and I admit that sometimes there is an uncomfortable blur between the two. However, “who you know matters” – right? That’s exactly why I use Facebook. I have reconnected with past colleagues and old friends as well as established new relationships through Facebook. I believe that Facebook has enhanced my life in many ways, both personally and professionally. That said, I am amazed at how vulnerable my Facebook information is by default, and I strongly recommend that all CPAs who also use Facebook take time to lock down their information using the steps described above. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 73 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Linked‐In LinkedIn is a business‐oriented social networking site. Launched in May 2003, it is mainly used for professional networking. As of February 11, 2010, LinkedIn had more than 60 million registered users, spanning more than 200 countries and territories worldwide, of which approximately half are in the United States. 11 million are from Europe. With 3 million users, India is the fastest‐growing country as of 2009. The Netherlands has the highest adoption rate per capita at 30%. Corporate Info ‐ LinkedIn is headquartered in Mountain View, California, with offices in Omaha, Chicago, New York and London. LinkedIn's CEO is Jeff Weiner, previously a Yahoo! Inc. executive. LinkedIn reached profitability in March 2006. Goal ‐ The purpose of the site is to allow registered users to maintain a list of contact details of people they know and trust in business. The people in the list are called Connections. Users can invite anyone (whether a site user or not) to become a connection. This list of connections can then be used in a number of ways, as follows: 1. A contact network is built up consisting of their direct connections, the connections of each of their connections (termed second‐degree connections) and also the connections of second‐degree connections (termed third‐degree connections). This can be used to gain an introduction to someone a person wishes to know through a mutual, trusted contact. 2. It can then be used to find jobs, people and business opportunities recommended by someone in one's contact network. 3. Employers can list jobs and search for potential candidates. 4. Job seekers can review the profile of hiring managers and discover which of their existing contacts can introduce them. The "gated‐access approach" (where contact with any professional requires either a preexisting relationship, or the intervention of a contact of theirs) is intended to build trust among the service's users. Groups ‐ The searchable LinkedIn Groups, feature allows users to establish new business relationships by joining alumni, industry, or professional and other relevant groups. LinkedIn groups can be created in any subjects and by any member of LinkedIn. Some groups are specialized groups dealing with a narrow domain or industry whereas others are very broad and Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 74 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com generic in nature. These groups add a unique element to the networking site in that it provides connections on a more personal basis. Professionals are more likely to want to connect with you online if they are somehow connected with you in life. These groups may include: alumni associations, greek affiliations, professional societies, sports team connections, etc. These groups also allow for professionals to post job openings or answer questions concerning a professional hardship. The connections made through LinkedIn Groups may be more beneficial than an unknown connection. Polling ‐ The newest LinkedIn feature is LinkedIn Polls, still in alpha. Mobile Linked In ‐ A mobile version of the site was launched in February 2008 which gives access to a reduced feature set over a mobile phone. 10 Ways to Use LinkedIn Most people use LinkedIn to 'get to someone' in order to make a sale, form a partnership, or get a job. It works well for this because it is an online network of more than 60 million experienced professionals from around the world representing 170 industries. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 75 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 1. Increase Your Visibility ‐ By adding connections, you increase the likelihood that people will see your profile first when they're searching for someone to hire or do business with. 2. Improve Your Connectability ‐ Most new users put only their current company in their profile. By doing so, they severely limit their ability to connect with people. You should fill out your profile like it's an executive bio, so include past companies, education, affiliations, and activities. You can also include a link to your profile as part of an email signature. The added benefit is that the link enables people to see all your credentials, which would be awkward if not downright strange, as an attachment. 3. Improve Your Google Page Rank ‐ LinkedIn allows you to make your profile information available for search engines to index. Since LinkedIn profiles receive a fairly high PageRank in Google, this is a good way to influence what people see when they search for you. To do this, create a public profile and select 'Full View.' Also, instead of using the default URL, customize your public profile's URL to be your actual name. To strengthen the visibility of this page in search engines, use this link in various places on the web. For example, when you comment in a blog, include a link to your profile in your signature. 4. Enhance Your Search Engine Results ‐ In addition to your name, you can also promote your blog or website to search engines like Google and Yahoo! Your LinkedIn profile allows you to publicize websites. There are a few pre‐selected categories like 'My Website', 'My Company,' etc. If you select 'Other', you can modify the name of the link. If you're linking to your personal blog, include your name or descriptive terms in the link, and voila! instant search‐engine optimization for your site. To make this work, be sure your public profile setting is set to 'Full View.' 5. Perform Blind, 'Reverse,' And Company Reference Checks ‐ LinkedIn's reference check tool to input a company name and the years the person worked at the company to search for references. Your search will find the people who worked at the company during the same time period. Since references provided by a candidate will generally be glowing, this is a good way to get more balanced data. Companies will typically check your references before hiring you, but have you ever thought of checking your prospective manager's references? 6. Increase The Relevancy Of Your Job Search ‐ Use LinkedIn's advanced search to find people with educational and work experience like yours to see where they work. For example, a programmer would use search keywords such as 'Ruby on Rails,' 'C++,' 'Python,' 'Java,' and 'evangelist' to find out where other programmers with these skills work. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 76 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 7. Make Your Interview Go Smoother ‐ You can use LinkedIn to find the people that you're meeting. Knowing that you went to the same school, plays hockey, or shares acquaintances is a lot better than an awkward silence after, 'I'm doing fine, thank you.' 8. Gauge The Health Of A Company ‐ Perform an advanced search for company name and uncheck the 'Current Companies Only' box. This will enable you to scrutinize the rate of turnover and whether key people are abandoning ship. Former employees usually give more candid opinions about a company's prospects than someone who's still on board. 9. Gauge The Health Of An Industry ‐ If you're thinking of investing or working in a sector, use LinkedIn to find people who worked for competitors‐or even better, companies who failed. For example, suppose you wanted to build a next generation online pet store, you'd probably learn a lot from speaking with former Pets.com or WebVan employees. 10. Track Startups ‐ You can see people in your network who are initiating new startups by doing an advanced search for a range of keywords such as 'stealth' or 'new startup.' Apply the 'Sort By' filter to 'Relationship' in order to see the people closest to you first. 11. Ask For Advice ‐ LinkedIn's product, LinkedIn Answers, aims to enable this online. The product allows you to broadcast your business‐related questions to both your network and the greater LinkedIn network. The premise is that you will get more high‐value responses from the people in your network than more open forums. For example, here are some questions an entrepreneur might ask when the associates of a venture capital firm come up blank: 'Who's a good, fast, and cheap patent lawyer?' 'What should we pay a Vice president of business Development?' 'Is going to a Demo worth it?' 'How much traffic does a Google Ad generate?' Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 77 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Plaxo is an online address book and social networking service with 20 million users. Plaxo provides automatic updating of contact information. Users and their contacts store their information on Plaxo's servers. When this information is edited by the user, the changes appear in the address books of all those who listed the account changer in their own books. Once contacts are stored in the central location, it is possible to list connections between contacts and access the address book from anywhere. Plaxo supports major address books including Outlook/Outlook Express, Mozilla Thunderbird, and Mac OS X's Address Book. Additionally, Plaxo can also be maintained through an online version. Plaxo 3.0 was released on June 24, 2007 and provides "automated, multi‐way sync." Social Networking ‐ Plaxo Pulse was launched on August 4, 2007 which is a social networking service which enables sharing of content from multiple different sources across the social web, including blogs, photos, social networking services, rating services, and others. Users can Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 78 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com selectively share and view content according to either pre‐determined categories (e.g. friends, family, business network) or customized groups. Charges ‐ On July 30, 2009 Plaxo began charging for Outlook synchronization service. Founders ‐ Plaxo was founded by Napster co‐founder Sean Parker, Minh Nguyen and two Stanford engineering students, Todd Masonis and Cameron Ring. The company was named by David Weekly. Plaxo, based in Mountain View, California, is currently privately held and supported by venture capital including funds from Sequoia Capital. On May 14, 2008, Plaxo reported it had signed an agreement to be acquired by Comcast. Criticism ‐ Plaxo received criticism from technology journalist David Coursey, who was upset about receiving a number of requests from Plaxo users to update their contact information (similar to spam email), and who wondered how the company was planning to make money from a free service that collects personal contact and network information. However after "changes at Plaxo and discussions with the company's remaining co‐founders", Coursey reversed his stance. Plaxo also responded to these issues in a section of their website. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 79 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Twitter is a social networking and microblogging service that enables its users to send and read messages known as tweets. Tweets ‐ Tweets are text‐based posts of up to 140 characters displayed on the author's profile page and delivered to the author's subscribers who are known as followers. Free ‐ While twitter is free, your phone service provider may charge your texting fees. Popularity ‐ Since its creation in 2006 by Jack Dorsey, Twitter has gained notability and popularity worldwide. It is sometimes described as "SMS of the Internet." By the end of 2007, about 500,000 tweets per quarter were posted. By the end of 2008, 100 million tweets per quarter were posted. By the end of 2009, 2 billion tweets per quarter were posted. In the first quarter of 2010, 4 billion tweets per quarter were posted. Lists ‐ Since late 2009, users can follow lists of authors instead of following individual authors. History ‐ Twitter began in a "daylong brainstorming session" that was held by board members of the podcasting company Odeo in an attempt to break a creative slump. During that meeting, Jack Dorsey introduced the idea of an individual using an SMS service to communicate with a small group, a concept partially inspired by the SMS group messaging service TXTMob. The tipping point for Twitter's popularity was the 2007 South by Southwest (SXSW) festival. During the event usage went from 20,000 tweets per day to 60,000. "The Twitter people cleverly placed two 60‐inch plasma screens in the conference hallways, exclusively streaming Twitter messages," remarked Newsweek's Steven Levy. "Hundreds of conference‐goers kept tabs on each other via constant twitters. Panelists and speakers mentioned the service, and the bloggers in attendance touted it. Soon everyone was buzzing and posting about this new thing that was sort of instant messaging and sort of blogging and maybe even a bit of sending a stream of telegrams." Reaction at the festival was overwhelmingly positive. Social software researcher Danah Boyd said Twitter "own[ed]" the festival. Twitter staff accepted their prize for the festival's Web Award with the remark "we'd like to thank you in 140 characters or less. And we just did!" On March 2010, Twitter has recorded a 1,500 per cent growth in the number of registered users, the number of its employees has grown 500 percent, while over 70,000 registered apps have been created for the microblogging platform, according to the first email newsletter on the company's progress by the website's co‐founder Biz Stone. Character Limit ‐ The 140‐character limit on message length was initially set for compatibility with SMS messaging, and has brought to the web the kind of shorthand notation and slang commonly used in SMS messages. The 140 character limit has also spurred the usage of URL Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 80 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com shortening services such as bit.ly, goo.gl, and tr.im, and content hosting services, such as Twitpic, memozu.com and NotePub to accommodate text longer than 140 characters. Bit.Ly ‐ Twitter uses bit.ly for automatically shortening all URLs posted on its website. Content Of Tweets ‐ According to Pear Analytics.San Antonio‐based market research firm tweets fall into the following six categories: 1. Pointless babble ‐ 41% 2. Conversational ‐ 38% 3. Pass‐along value ‐ 9% 4. Self‐promotion ‐ 6% 5. Spam ‐ 4% 6. News ‐ 4% Rankings ‐ Twitter is ranked as one of the 50 most popular websites worldwide by Alexa's web traffic analysis. With an estimated 6 million unique monthly users visitors, only 40 percent of Twitter's users are retained. Demographics ‐ Just 11 percent of Twitter's users are aged 12 to 17, according to comScore. Privacy And Security ‐ Twitter collects personally identifiable information about its users and shares it with third parties. The service considers that information an asset, and reserves the right to sell it if the company changes hands. While Twitter displays no advertising, advertisers can target users based on their history of tweets and sometimes may quote tweets in ads. Hacked ‐ On January 5, 2009, 33 high‐profile Twitter accounts were compromised after a Twitter administrator's password was guessed by a dictionary attack. Falsified tweets— including sexually explicit and drug‐related messages—were then sent from the accounts. Celebrity ‐ Twitter launched the beta version of its Verified Accounts service on June 11, 2009, allowing famous or notable people to make it clear which Twitter accounts belong to them. The home pages of these verified accounts display a badge to indicate this special status. Change Of Focus ‐ In November 2009 Twitter changed the question it asks users for status updates from "What are you doing?" to "What's happening?". Criticism ‐ The Wall Street Journal wrote that social‐networking services such as Twitter "elicit mixed feelings in the technology‐savvy people who have been their early adopters. Fans say they are a good way to keep in touch with busy friends. But some users are starting to feel 'too' connected, as they grapple with check‐in messages at odd hours, higher cellphone bills and the need to tell acquaintances to stop announcing what they're having for dinner." Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 81 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com High Tech KIOSK Chapter 9 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 82 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Introduction to Kiosks There are a large number of companies producing high tech KIOSKs – which are unattended computer stations that provide customers and passer‐bys with the information they need via electronic methods. Most kiosks provide unattended access to web site applications, and the device is restricted to displaying that one web site. Interactive kiosks are typically placed in high foot traffic settings such as hotel lobbies or airports. Presented below are a few discussion points concerning KIOSKs. 1. History ‐ The first self‐service, interactive kiosk was developed in 1977 at the University of Illinois at Urbana‐Champaign by a pre‐med student, Murray Lappe and allowed students and visitors to find movies, maps, directories, bus schedules, extracurricular activities and courses. When it first debuted in the U of Illinois Student Union in April 1977, more than 30,000 students, teachers and visitors stood in line during its first 6 weeks, to try their hand at a "personal computer" for the first time. 2. First Commercial KIOSK ‐ In 1991 the first commercial kiosk with internet connection was displayed at Comdex. The application was for locating missing children. 3. Marriage of the KIOSK, Robotics & Vending Machine – Many of today's kiosks brings together the classic vending machine with high‐tech communications and complex robotic and mechanical internals. Such interactive kiosks can include self‐checkout lanes, e‐ticketing, information and way‐finding, and vending. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 83 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 4. Components ‐ Typical KIOSK components include Touch‐screen, P.C., pointing device, keyboard, bill acceptor, mag‐stripe and/ or bar‐code scanner, surge protector, UPS etc. 5. Government Kiosks ‐ Several countries have implemented kiosks nation‐wide for various purposes. In the United Kingdom, thousands of special‐purpose kiosks are now available to aid job‐seekers in finding employment. The United States Department of Homeland Security has created immigration kiosks where visitors register when they enter the United States. There are also Exit kiosks where visitors register when they leave the U.S. 6. It is estimated that over 131,000 kiosk terminals exist in the U.S. 7. Businesses Use ‐ Businesses who provide kiosks to their customers include: Delta, Northwest Airlines, JetBlue Airways, GTAA, Future Shop, The Home Depot, Target Corporation, and Wal‐ Mart. 8. AT&T ‐ By the end of 2010, AT&T expects to install the largest bill pay kiosk network system in the world for the phone customers which allows customers to pay their phone bill and learn about services. Verizon and Sprint have similar units for their customers. 9. Kodak Photo Kiosk – Kodak provides an interactive kiosk which allows users to print pictures from their digital images. Kodak has over 100,000 units up and running in the U.S. Two major classes of photo kiosks exist: a. Digital Order Stations – In retail locations, this kiosk allows users to place orders for prints and photographic products. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 84 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com b. Instant Print Stations ‐ This kiosk uses internal printers to instantly create photographic prints for a self serve paying customer. Some systems will only print 4x6 inch prints while other systems allow for 4x6, 5x7, 8x10, 8x12. 10. Internet Kiosk ‐ An Internet kiosk is a terminal that provides public Internet access. Internet kiosks are typically placed in settings such as hotel lobbies, long‐term care facilities, medical waiting rooms, apartment complex offices, or airports for fast access to e‐mail or web pages. Some Internet kiosks are based on a payment model similar to vending machines or Internet cafés, while others are free. A common arrangement with pay‐for‐use kiosks has the owner of the Internet kiosk enter into a partnership with the owner of its location, paying either a flat rate for rental of the floor space or a percentage of the monthly revenue generated by the machine. 11. Many Diverse Uses ‐ Many business and organization use Kiosks to provide information, or to communicate with customers. Here are a few examples: a. Disney ‐ Disney has unattended outdoor ticketing kiosks. b. Amtrak ‐ Amtrak has automated self‐service ticketing kiosks. c. Busch Gardens ‐ Busch Gardens uses kiosks for amusement parks. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 85 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com d. Cruise Ships ‐ Cruise ships use ticketing kiosks for passengers. e. Hertz – Hertz provides Kiosks for auto rentals as do Alamo and National. f. Churches ‐ Non‐profit organizations, Church facilities, and other corporations use a giving kiosk to accept funds, donations, tithes, offerings at the self serve kiosk. g. Movie Ticket Kiosk ‐ Many movie theater chains have specialized ticket machines that allow their customers to purchase tickets and/or pick up tickets that were purchased online. 12. Visitor Management And Security Kiosk ‐ Visitor management and security kiosks are used to facilitate the visitor check in process at businesses, schools, and other controlled access environments. These systems can check against blacklists, run criminal background checks, and print access badges for visitors. School security concerns in the United States have led to an increase in these types of kiosks to screen and track visitors. 13. Building directory and way‐finding kiosk ‐ Many hospitals today utilize interactive kiosks to allow visitors to find doctor's offices, departments and patient rooms. This use of the kiosk alleviates some of the mundane tasks of the hospital staff and allows them to focus on the more important ones. Harris County Hospital District, Baptist Hospital of Miami, the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia and the Cayuga Medical Center are but a few medical centers utilizing interactive touch screen kiosks with a building directory and wayfinding solutions. Interactive Kiosks Solutions There are numerous different providers and the price varies greatly based on many different factors, but generally start near $4,000 per Kiosk. 1. SeePoint Interactive ‐ http://www.seepoint.com/default.asp ‐ Used by Polaris, Pfizer and Neutrogena. 2. InTouch Interactive Kiosks ‐ http://www.intouchkiosk.com/index.php Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 86 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Microsoft Surface Microsoft’s high‐tech coffee table shaped computer called 'Surface'! Surface is a Windows Vista powered computer placed inside a shiny black table base. These machines are user‐friendly and have a 30‐inch touch screen in a clear acrylic frame. The Surface can interact with cell phones, digital cameras and other physical objects wirelessly. Users can interact with the machine by touching or dragging their fingers across the screen, or by setting real‐world items tagged with special bar‐code labels or identification tags. $5,000. A restaurant might use this technology to communicate with guests, take orders, and even collect the bill. A radio Shack might use this to educate customers about the products placed on the table. A hotel might use this as a concierge to provide guests with restaurant suggestions, driving directions and even to make reservations. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 87 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 1. 2. 3. 4. Codename Milan Allows a user, or users, to manipulate digital content by the use of gesture recognition. It was announced on May 29, 2007 at D5 conference. Targeted towards the hospitality businesses, such as restaurants, hotels, retail, public entertainment venues and the military for tactical overviews. 5. The preliminary launch was on April 17, 2008, when Surface became available for customer use in AT&T stores. 6. Surface was used by MSNBC during its coverage of the 2008 US presidential election 7. Surface is used by Disneyland’s future home exhibits 8. As of March 2009, Microsoft had 120 partners in 11 countries that are developing applications for Surface's interface. 9. Microsoft Surface has a 30‐inch reflective surface with a XGA DLP projector underneath the surface which projects an image onto its underside, while five cameras in the machine's housing record reflections of infrared light from objects and human fingertips on the surface. 10. Surface has been optimized to respond to 52 touches at a time. 11. Mark Bolger is the Surface Computing group's marketing director. 12. A commercial Microsoft Surface unit is priced at $12,500 (for the unit only), whereas a developer Microsoft Surface unit costs $15,000. Microsoft said it expects prices to drop enough to make consumer versions feasible in 2010. 13. A similar concept was used in the 2002 science fiction movie Minority Report . As noted in the DVD commentary, the director Steven Spielberg stated the concept of the device came from consultation with Microsoft during the making of the movie. 14. A unique feature that comes preinstalled with Surface is the pond effect "Attract" application ‐ a "picture" of water with leaves and rocks within it and by touching the screen, you can create ripples in the water just like you were putting your hand into a real stream. Additionally, the pressure of touch alters the size of the ripple created, and objects placed into the water create a barrier that ripples bounce off, just as they would in real life. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 88 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Survey Solutions Chapter 10 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 89 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Survey Software Solutions When was the last time you asked your customers, business partners or employees to rate your products, services, professionalism? It has been shown that the sheer act of asking for feedback has a positive impact, even if the customers, business partners of or employees don’t respond. The emergence of e‐mail and web based survey tools now makes it fast and easy to create and conduct your own surveys. Today, survey Tools like Zoomerang, Survey Monkey and Survey Gizmo make it quick and easy to conduct surveys and the results are tabulate and updated automatically as results pour in. Some of the features offered by these survey applications are summarized below. 1. Question Types ‐ Wizards help you create your survey questions which may consist of Yes‐No, Multiple Choice, radio buttons, drop down selection, check boxes, fill in the blanks, Polling, Ratings, table responses, page piping, question skipping, response redirects, question suppression, linking, question reordering, Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 90 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 2. Survey Delivery – Surveys can be published to web sites, e‐mailed, or embedded in electronic documents via JavaScript, iFrame or HTML code. Data can be securely encrypted before transmission. 3. Automated Tabulation of Result – Results are automatically tabulated as received, simply log into to view the latest reports. 4. Highly Stratified Reports‐ Zoomerang has the ability to provide detailed reports that are highly stratified. 5. Pricing – Zoomerang offers free pricing for up to 30 questions and 100 responses; $200 a year for unlimited questions and $600 a year for Zoomerang’s entire bundle of survey features. Surveys are one of the most powerful communication tools available to the business community, but until now they have been terribly expensive and time consuming to use. Other survey solutions are list below: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Survey Monkey CheckBox Constant Contact NoviSystems Feedback server SurveySolution Vovici Zarca QuestionPro SurveySaid SurveyGizmo 4QSurvey Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 91 High Tech Communications SurveyMonkey www.CarltonCollins.com Survey Monkey claims to be the world's leading provider of web‐based survey solutions, used by millions of companies, organizations and individuals alike to gather the insights they need to make more informed decisions. Highlights regarding Survey Monkey are presented below: 1. High Satisfaction ‐ SurveyMonkey claims to have a satisfaction rating of 99.5%. 2. Easy – SurveyMonkey claims to be simple and cost‐effective. 3. Privacy & Security ‐ SurveyMonkey uses SSL encryption and multi‐machine backup. 4. Very Popular ‐ SurveyMonkey claims that 100% of the Fortune 100, as well as other businesses, academic institutions, and organizations of all shapes and sizes use their product. 5. Many Uses ‐ SurveyMonkey is used for everything from customer satisfaction and employee performance reviews, to course evaluations and research of all types. 6. Free ‐ The Basic subscription is completely free! 7. Never Expires ‐ Your surveys never expire, even if you choose to never upgrade from the free program. Additionally you responses never expire, even if you choose to stay as Basic. 8. Unlimited – You can create and administer as many surveys as you want for as long as you want! They are stored indefinitely. 9. Basic Features ‐ Following are the features provided by a free SurveyMonkey account as they range from survey design to data collection to analysis features: a. Create unlimited number of surveys. b. Allows up to 10 questions per survey . c. Choose from 15 available question types . d. Supports any language, including Unicode. e. Survey completion progress bar. f. Automatic numbering for pages/questions. g. 15 pre‐built survey themes. h. Validate/require survey responses. i. Randomize/sort answer choices. j. Accessible and 508 compliant and certified surveys. k. *100 responses per survey (Upgrade to Pro/Unlimited (annual) in order to view additional responses.). l. Collect responses via weblink. m. Collect responses via email. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 92 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com n. Create Up to 3 Collectors per survey. o. View live results as they are recorded . p. Browse through individual responses. q. View open‐ended comments from the Response Summary page 10. Upgrade to Pro or Unlimited ‐ Upgrade your basic account to Pro at any time and all surveys created during the Basic status will be upgraded. The following professional features can then be applied to those surveys. a. No Limits ‐ Surveys can have an unlimited number of questions. You are not charged extra for long surveys. Create as many surveys as you want. b. Create Surveys in Any Language ‐ You can create your survey in any language, even multi‐byte languages such as Chinese and Arabic. All text and buttons in the survey can be customized for the respondent's native language. c. Create Surveys from Templates ‐ Over 50 survey templates are provided to jumpstart your survey design. d. Select from 15 Question Types ‐ We support everything from multiple choice to rating scales to open‐ended text. e. Validate/Require Survey Responses ‐ Validation options allow you to require a f. g. h. i. j. k. l. particular number of answers, or validate the text that is entered. You can also make survey questions mandatory for your respondents to answer. Randomize or Sort Your Question Choices ‐ To help minimize "ordering bias", you can automatically randomize the choices in your questions. If you have a long list of items, you can sort them automatically. Create Skip Logic (Conditional Logic) ‐ You can customize the path a respondent takes through your survey by adding skip logic. This eliminates unnecessary confusion by skipping non‐applicable questions. It is a proven way to reduce "drop‐outs" and overall frustration. Add a Logo ‐ Branding your survey can give your survey a professional feel. You can use any logo up to 50K in size at the top of every page in your survey. Create Custom Themes ‐ Every element of your survey can be customized such as fonts, sizes, and colors. After creating your own custom theme, you can apply it to all your future surveys. Create PDF ‐ You have the ability create a printable PDF version of your survey. Fully Accessible and 508 Compliant ‐ All standard survey designs are accessible and 508 certified and compliant for respondents with disabilities. Unlimited Number of Collectors ‐ You can collect responses from multiple sources simultaneously, and open and close each collection method individually, without having to close the entire survey. m. Set Collection Restrictions ‐ You can set a max response count, or a cut off date for your survey. You can require a password, or even restrict responses by IP address. n. Create a Simple WebLink ‐ Send out a link to your survey via email or post it on a website. Respondents simply click the link to go directly to your survey. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 93 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com o. Manage Your Participants ‐ If you have a list of emails, and you would like to track who responds, SurveyMonkey provides tools to manage your list and create custom email invitations. You can also send follow up reminder emails to those who haven't responded. With a Pro or Unlimited subscription, the email list size restriction is increased compared to a Basic account limit. p. Generate Popup Invitations ‐ To increase response rates, you can create a custom invitation popup for your own website. Simply cut and paste the code into any webpage to start generating invitations. To minimize annoyance to your visitors, invitations will only pop up once. q. Custom Redirect ‐ Once your survey is complete, respondents will be redirected to the page of your choice. r. Thank You Page Feature ‐ Create a custom thank you page to appear at the end of your survey. s. View Results in Real Time ‐ You can view your results as soon as they are collected. t. Browse Individual Responses – Drill down to the individual response level to see u. v. w. x. y. the details of particular respondents, or to read the comments of open‐ended questions. Filter Results ‐ Ask questions such as: "Show me only those respondents who answered choice x in question y." Any question in your survey (even open‐ ended) can be filtered. The entire results section will reflect your filter choices. Cross Tab Results ‐ Cross tabulated data is useful for showing a side by side comparison of how respondents answered two or more survey questions. This is a comparison of two items within one survey, such as product usage and demographics, to determine how they are interrelated. Share Results ‐ Let others view your results without giving them access to your account. You can control which results are visible and how the results may be used. Download Results ‐ All data can be downloaded to your local computer for further analysis. Take your summary results into Excel to create graphs. Save the detail results to your hard drive for safekeeping. Create PDF ‐ You can export a PDF version of the results. Download individual questions with comments for easier printing. 11. Pricing: a. Pro Monthly: $19.95 (month to month) x 1000 free responses every monthly billing cycle. Responses over the 1000 are charged $.05 every cycle. b. Pro Quarterly: $59.85 (covers 3 months) x 1000 free responses every monthly billing cycle. Responses over the 1000 are charged $.05 every cycle. c. Unlimited Annual: $200 (covers 12 months) x unlimited survey responses at no additional charge. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 94 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Microsoft Office InfoPath 2007 Chapter 11 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 95 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Microsoft Office InfoPath 2010 is an information‐gathering program. Using Office InfoPath 2010, you can create and deploy electronic forms solutions to gather information efficiently and reliably. You can also use the InfoPath Forms Services capabilities in Microsoft Office SharePoint Server 2010 to extend your business processes beyond your corporate firewall, delivering forms as Microsoft Office Outlook e‐ mail messages, Web browser forms, or forms for mobile devices. Gather Information Efficiently And Reliably Office InfoPath 2010 makes information gathering more efficient by delivering electronic forms that reach the necessary participants, reduces redundant data entry, and improves the quality of the data collected. InfoPath forms help you reach more users by providing an easy form fill‐in experience across Web browsers, e‐mail messages, or mobile devices. Office InfoPath 2010 provides real‐time validation, pre‐populated fields, and connections to important sources of information. Office InfoPath 2010 solutions are integrated with the Microsoft Office system to deliver powerful electronic forms capabilities in a familiar package. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 96 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com InfoPath forms can be deployed to many Web browsers for fill‐in, including Microsoft Internet Explorer, Netscape, Mozilla, Safari, and others. Centralize Forms Management And Control Office InfoPath 2010 and Office SharePoint Server 2010 can be combined to centralize the deployment and management of forms throughout your organization. InfoPath Forms Services of Office SharePoint Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 97 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Server 2010 help you get control over your forms solutions by providing centralized management of electronic forms for the entire organization. Office SharePoint Server 2010 provides a unified portal and a forms and content management solution for your enterprise to help you manage electronic forms in the same context as other critical business functions. InfoPath Forms Services is fully integrated with Office SharePoint Server 2010 to help ensure organizations can centrally manage and deploy electronic forms. View a larger image. Streamline Forms‐Driven Business Processes Office InfoPath 2010 integrates with your current business applications and systems using industry standards so you can automate existing business processes without having to reinvent them. InfoPath form solutions provide an way for your organization to gather and present information from your existing line‐of‐business systems using the familiar Office interface. Office InfoPath 2010, Office SharePoint Server 2010, and Microsoft BizTalk Server 2006 combine to deliver a comprehensive solution for optimizing business processes. Advanced form design and development tools enable Office InfoPath 2010 to streamline complex processes using dynamic, interactive forms that connect users to the right data. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 98 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The integration capabilities of Office InfoPath 2010 and the Microsoft Office system enable InfoPath to extend into other programs to improve information gathering for databases, documents, and more. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 99 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Instant Messaging Chapter 12 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 100 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Introduction to Instant Messaging D epending on how you use the Internet, the technology can improve your efficiency and productivity or drain your company’s resources and waste valuable time. Instant messaging represents one instance of new Internet technology that can be both a burden and a blessing. In keeping with the rapid pace of the modern world where email has all but replaced the conventional letter or phone call, Instant Messaging may do away with the need for ordinary conversation. While it may not replace casual water cooler type chat Instant Messaging can provide a platform for everything from tech support to communicating with relatives without huge long distance bills or an inefficient use of time. Following increased consumer involvement with the Internet and proprietary communication services offered by AOL, CompuServe, Prodigy, and others a new program called ICQ heralded the first free Instant Messaging client. By installing the communication client and signing on with a userID and password, users received real time information on friends and contacts also signed onto the system. Message transaction took place through a proprietary protocol which directed messages to a server which then routed them to the appropriate IP address and port number of the intended receiver. Users then establish a veritable direct link to their contacts by clicking on any given contact and conversing in text messages back and forth. Later ISP giant AOL designed its own Instant Messaging program using the same basic format for communication as ICQ and every other IM client. Due to its built‐in client base of AOL subscribers, the new program quickly outpaced pioneer ICQ to become the most popular tool for sending Instant Messages. All the current IM programs perform basically the same functions with a few special features enabled for each system. MSN Messenger comes preinstalled with Windows XP and actually requires some effort to remove, however this program offers the best support for real time voice conversations when both parties involved use a microphone and Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 101 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com speakers/headphones. AOL IM, or AIM, offers a java‐based program which does not require the downloading or installation of software thereby offering infinite access points for mobile users. AIM also became the first Instant Messaging program licensed to cell phone companies for inclusion in their digital products. In response to the incredibly large Instant Messaging community, programs like OMNI and Trillian offer users a method to consolidate and manage user accounts from all the various providers in one simple interface. While Instant Messaging (IM) is likely to be viewed more as a time‐waster for teenagers and lonely geeks, a lot can get done via IM. IM allows you and your partners to maintain a long‐term virtual “presence” as you work, posting questions, updates, and ideas as they strike you or as you come across problems in your work. Since IM programs maintain a full record of the chat session, there’s no danger of missing anything or losing it – just scroll up. There are a couple of rules to follow for productive IM’ing. 1. Cut the chatter. To keep things focused, each person should speak only a) when they have something important to add, or b) in response to a question. 2. No frills. Today’s IM software comes with voice and video capabilities, avatars, face‐ morphing functions, multi‐colored fonts, and more. Leave those for your twelve‐year old daughter – you’re working, not playing IM. Alternatives to AOL’s IM include private chat rooms like Campfire or even Twitter if you can resist the siren call of your friends’ tweets. AOL Instant Messenger – http://www.aim.com Service PSYC User Count 53 million active, '>100 million total 35 million total [1], mobile and PC Over 6 million active (majority in Poland) 40 million total (licensed, entitled users in enterprises) unknown 50 million active 1 million total 40‐50 million total 1 million active (daily) 1 million total 11 million total (9 million in South Africa) 3.3 million unique visitors per month 1 million active (daily) (majority in Brazil) Skype 19 million peak online, 309 million total AIM eBuddy Gizmo5 Gadu‐Gadu IBM Lotus Sametime iChat ICQ IMVU XMPP Mail.ru Agent Meebo MXit Paltalk Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 102 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Tencent QQ VZOchat Windows Live Messenger Xfire Yahoo! Messenger 990 million total registered accounts. (majority in China) >550,000 330 million active 11.5 million total 248 million active registered Yahoo global users (refers to ALL Yahoo users not Instant Messaging users) Google Talk unknown users. Chat within Gmail, iGoogle, and orkut, All on the web, PC and Mac Facebook Claimed 400 million users: Facebook statistics Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 103 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Teleconferencing I f more personal contact and real‐time sharing is needed, try a teleconferencing system like Adobe’s Acrobat.com or GoToMeeting. Most services allow screen sharing, collaborative white boarding, and other substitutes for same‐room presence – without the commute to the meeting (even if it’s just down three floors), the incessant interruptions for coffee and bathroom breaks, the face‐to‐face socializing, or the forced absence from your desktop while you wait for that crucial email. Since most also create a transcript, you don’t need someone taking minutes, either. Wikis W ikis provide a collaborative environment that is ideal for the development of working documents and statements, as well as material that will need to be referred to again and again. For one‐off projects, an online wiki like WetPaint or PBWiki are ideal: free, easy to set up, and easy to use. For more mission‐critical material, especially when you plan to use it repeatedly, and where security is a major concern, your organization can fairly easily set up an internal wiki on your intranet, using advanced software like MediaWiki, the software that runs Wikipedia. Wikis are self‐organizing and easy to create and edit, and they keep track of changes made along with a record of who is responsible for each edit (no more dickering over credit!). Where real‐time interaction isn’t a necessity, building a wiki over a long period of time can be far more productive than a chain of meetings – but make sure to assign responsibilities and allow time for wiki work. Email Lists/Groups A nother solution where real‐time interaction is not a factor is the old‐fashioned email list. Somewhat out of fashion these days, email lists can still be quite productive ways to get things done as a group – and both Yahoo and Google offer services that are free and easy to set up. An effective email list should probably have a moderator – not to approve messages, but to remind people when they’re going off track. Good etiquette is essential in this environment; something about the medium encourages flame wars. But with a few precautions, email lists can still be quite effective tools, allowing for thoughtful, considered exchanges and automatically maintaining a searchable archive of past discussions. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 104 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Collaboration Apps F inally, effective use of a project management application can forestall the need for most meetings. Systems like Wrike and Basecamp allow notes to be exchanged, tasks to be assigned, and files to be shared. They also offer a number of ways for users to interact: SMS, email, online, RSS, or using a third‐party application through Basecamp’s API. If full‐fledged project management is too much, consider using online services like Google Docs (which can be installed to your own domain via Google Apps) alongside Google Talk or another IM – you can share documents, add to and edit each others work, and create a repository of materials at the same time. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 105 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Communications Equipment Chapter 13 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 106 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Projection Systems A Pricegrabber search for video projectors with a contrast ratio of 1,000:1 or better yields over 30 results from several well known manufacturers of computers and consumer electronics: BenQ HP PLUS Sharp Philips Sony Viewsonic NEC InFocus Toshiba Mitshibishi Pocket Projector ‐ $699 Prices range from just under $500 to well over $6,000, a stark contrast for two devices that simply take a video signal and use light to shine it on a wall right? Well, yes and no. There can be a tremendous difference in price from unit to unit; however, no current model operates so simply as to just shine light on a wall, and you pay for every extra built‐in feature and convenience. Video Projection Vs Film Projection The video projector is similar to a film or slide projector in that they both accept a source, and project the image from that source onto a screen. After that the two become vastly different. Inside a video projector is a processor that converts an analog or digital video input signal into something that can be projected onto a screen and viewed not just by the family gathering to see home movies or pictures, but typically by large groups in meeting rooms and auditoriums. LCD vs. DLP Digital Light Processing There are currently two competing technologies used in video projectors today; LCD or Liquid Crystal Display common to many computer monitors and televisions, and DLP which stands for Digital Light Processing. An LCD projector basically works by passing a powerful light source Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 107 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com through a transparent LCD chip made up of single pixels to project an image through a lens to a large screen. These types of projectors are highly portable, well‐suited for multimedia use, and feature high contrast and brightness capability, as well as low power consumption. LCD Projector Limitations 1) An LCD projector can often times exhibit what is called "the screen door” or “window” effect. Since the screen is made up of individual pixels, the pixels project in a pronounced manner when viewed on a very large screen, thus giving the appearance of looking through a "screen door". 2) Just like their LCD monitor counterparts, LCD projectors can contain dead pixels due to manufacturing defects. Coupled with an enlarged view of this black or discolored pixel, an LCD projector can become frustrating to watch. 3) Also like similar monitors, LCD projectors typically have a native resolution which enables their best viewing characteristics. Using a higher or lower resolution source than the projector’s native resolution can lead to distortion, illegible fonts, and eye strain. NEC MT1075 4200 Lumens $6,995 New $4,995 in 2006 $2,995 in 2007 $3,890 in 2008 $3,298 in 2009 $2,328 in 2010 In terms of sales, the fastest growing type of video projector used today is the DLP projector. As with LCDs, the actual image is displayed on a chip, however, the chip used in a DLP projector is different. The chip in a DLP projector is referred to as a DMD (Digital Micromirror Device). In essence, every pixel on a DMD chip is a reflective mirror. The advantages of this system make the DLP projector suitable not only for business and home theater application, but DLP technology is also in use in some movie theaters for feature film projection. The micromirrors on a DLP projector’s chip tilt very rapidly as the image changes. This process produces the grayscale base for the image. Then, color is added as light passes through a high‐ speed color wheel and is reflected off of the micromirrors on the DLP chip as they rapidly tilt towards or away from the light source. Advantages of the DLP projector include excellent color Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 108 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com accuracy, no "screen door" effect (as with an LCD), due to its micro‐mirror construction, compactness, and higher contrast ( they are sometimes not as bright as LCDs but images often look smoother). DLP Projector Limitations 1) Just as with LCD, each DLP chip has a finite number of pixels. It is always best to conform to this native resolution. 2) A DLP projector can exhibit what is referred to as "the rainbow effect". This aberration is exhibited by a brief flash of colors (like a small rainbow) when the viewer rapidly looks from side to side on the screen or looks rapidly from the screen to side of the room. Fortunately, this does not occur frequently and many people do not have sensitivity to this effect at all. Although DLP isn't perfect, the DLP projector has become an instant hit amongst home theater enthusiasts. InFocus IN24 DLP Projector ( $ BenQ MP511+ DLP Projector (800x600, 2100 Lumens, 2,100:1 $442.99 Sharp PG‐MB66X DLP Projector (1024x768, 3000 Lumens, 2000:1 $995 BenQ SP820 DLP Projector 1024x768, 4000 Lumens, 2000:1 $1,439 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 109 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com NEC NP4000 DLP Projector 1204x768, 5200 Lumens, 2100:1, 35 pounds $3,019 Panasonic PT‐D5700U DLP Projector 1024x768, 6000 Lumens, 2000:135 30 pounds $5,129 Sanyo PLC‐XF45 LCD Projector 1024x768, 10,000 Lumens, 100:1, 81.6 pounds, $5,129 Specifications Whether you intend to use a projector for small business meetings, large auditorium presentations, or even as a high end display for your home theater system several factors are universally important. 1. Resolution – Like LCD monitors, projectors have a native resolution, outside of which their projected image becomes blurry and fuzzy. The standard resolution is also 1024 x 768 with higher resolution models bringing a premium price, though some lower resolution models which can project an 800 x 600 image are coming down in price and would serve as an adequate backup projector. 2. Brightness – Measured in Lumens, 1500 is a fine specification for small groups or moderate home theaters, 3000+ works for large meeting halls and home theater enthusiasts. I generally look for at least 2500 lumens in a fairly portable presentation unit. 3. Contrast Ratio – This value has a substantial impact on image definition. The greater the ratio, the greater the disparity between light and dark areas‐higher numbers allow for virtually true blacks and whites. 1000:1 = good 2000:1 or higher = excellent. 4. Bulb life – Because the actual light source comes from a physical bulb‐projectors have a limited life span before the bulb must be changed. Never let the bulb come into contact with skin or the oil residue will contaminate the bulb creating display artifacts, hotspots, or worse. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 110 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 5. Bulb cost – The benefit of changing the bulb lies in the fact that brightness and contrast levels are returned to a vibrant “like new” state. However an expense of $350 for one bulb every 1,000 to 3,000 hours is a bargain and high‐end units will cost far more to renew. 6. Weight – While this may seem like a feature of interest only to the road warrior, lighter projectors make for easier home and office installations. Some units weigh as little lbs. though brightness is generally sacrificed to reach this compact size. 7. Noise – Not necessarily a specification listed on the box, but this is the first thing you notice when you turn the unit on, and loud whirring in the background can distract from any presentation. While breaking out the decibel meter for every model on display may be problematic, you can always check reviews at PC Magazine (pcmag.com) or Laptop Magazine (techworthy.com) to find out if your prospective projector wails or whispers. 8. Connectivity/Input – Some projectors feature digital media slots or an attachment module which allows you to run a presentation from a Compact Flash, Secure Digital card or a Pocket PC. This added functionality is a bonus and can save weight and time if you eliminate the need to carry a laptop. 9. Cable/Source Input – Not all sources are created equal. Almost every projector will feature a standard D‐sub 15‐pin input. Many will also have an S‐video connector or legacy RCA inputs. The higher end projectors will also have a DVI connection for use with outputting HDTV signals in their appropriate expanded resolution. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 111 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Web Cameras W ebcams range from the silly to the serious. From videoconferencing with a client to following the movements of animals at your favorite zoo, webcams have great communicative potential. Until a few years ago I often demonstrated one webcam conferencing product that was particularly user friendly. With Microsoft’s NetMeeting users could converse and send video feeds in real time. You could even join a random video conference and meet someone from across the globe. Unfortunately that program became overrun with users’ “inappropriate” personal webcams. However there are still lots of productive uses for webcams. For example: Linksys Wireless‐G Internet Video 1. You will be out of town for a week and you want to keep an eye on your home/office 2. You'd like to be able to check on the babysitter and make sure everything is okay while you’re out 3. You'd like to know what your dog does in the backyard all day long 4. You want to monitor activity in your warehouse/loading dock/showroom Some webcams can even operate wirelessly, like the Linksys Wireless‐G Internet Video Camera, allowing wireless video transmission and monitoring. Once in place, the camera does not need to be tethered to a PC for wireless audio and video broadcast via the Internet. If there is something that you would like to monitor or display remotely, a webcam makes it easy. Webcams were never terribly expensive but some devices have dropped well below $15 and they are easy to connect through a USB port. A piece of software initializes the camera and grabs a frame from it periodically. For example, the software might grab a still image from the camera once every 30 seconds. The program then turns that image into a normal JPG file and uploads it to your Web server. The JPG image can be placed on any Web page. If you don't have a Web server, several companies such as now offer you a free place to upload your images, or host video conferences saving you the trouble of having to set up and maintain a Web server or a hosted Web site. Many companies like CUWorld actually allow you to use their service for free video conferencing. In order to send and receive audio you will also need a microphone and speakers. We recommend a headset with a boom mic for clarity and convenience. While webcams may seem like novelties they can serve valuable uses as teaching/consulting tools or simply by allowing you to stay in close contact with distant friends or relatives. Logitech Quickcam Orbit $112.99 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 112 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Building A Successful Web Site Chapter 14 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 113 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Why are so many CPAs Are Missing the Internet Boat? Take a deep breath. Do you smell that? That smell my friend, is the smell of opportunity. Today the Internet offers more opportunity than any other time in our history, including the Industrial Revolution. Unfortunately I think most CPAs are completely missing the boat. There are many, many ways to take advantage of the Internet – to find out if you are doing all that you can on the web, answer these questions: Your Web Site 1. Do you have a deep rich web site with lots of valuable content (i.e.: not a simple 4 panel brochure regurgitated to the web)? 2. Does your web site have a submit page where readers can submit their information to you and perhaps request follow up information? 3. Does your web site provide checklist, articles, case studies, or advice to your readers? 4. Does your web site provide a bio and contact for each key employee? 5. Does your web site provide driving directions, including a map to your offices? 6. Does your web site provide a calendar of events, including classes you hold to help educate your clients on various topics such as taxes, financial reporting, selecting accounting software or using a computer? 7. Is your web site attractive, look professional, and make a positive impression? 8. Do you have a separate web site and domain name for each major service or product that you sell? 9. Does your web site provide electronic versions of all documents such as product manuals, installation instructions, exploded diagrams, etc? 10. Does your web site contain key words so that you can be found easier? 11. Has your web site URLs been submitted to the various search engines for indexing? 12. Do you have a concerted effort to establish cross links back to your web sites so they will rank higher in a search. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 114 High Tech Communications 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. www.CarltonCollins.com Reading the Web Do you read the web frequently to stay abreast of news and stories related to your interests, business, and clients? Do you use Google alerts to automatically deliver to you relevant stories? Do you maintain a clickable list of dozens of web sites that your frequent to save time –perhaps through your favorites list or some other list of hyperlinks? Do you save relevant articles to your computer for future reference? Buying On Line Do you shop all major purchases online before buying? Do you use price harvesting web sites such as Pricegrabber.com or Pricescan.com to help you search for the best prices? Do you use customer feedback and ratings to help you select the right product or company to do business with? Do you shop online to educate yourself about the features, options and competing products before making a purchase – even when making a non Internet purchase? Do you shop airfares, hotels and rental cars online at multiple Internet sites in order to find the best pricing? Communicating Do you use e‐mail? Do you have your own domain named e‐mail account to convey the right image? (i. e. don’t use and AOL, Hotmail, Gmail, or Yahoo e‐mail address). Do you leave your computer up and running 24/7 so that e‐mail is always retrieved and waiting on you when you are ready to read it? Does your e‐mail have an automatic signature block containing all of your contact information so recipients don’t have to hunt down your information to communicate with you or refer you via phone or snail mail? 26. Do you use Skype or some other Voice over IP to make computer to computer or computer to phone calls? 27. Do you have a camera installed on your computer so that you can also make video calls? Background Checks Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 115 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 28. Do you use the internet to perform background checks on potential employees, customers or vendors before doing business with them? 29. Do you also check police mug shots or sex offender pages as a precaution before doing business with someone? 30. Do you check out traffic cameras on the web before heading out of your home or office to find out if the streets are open? 31. Do you print out turn‐by‐turn driving directions and maps from the Internet to help you find your way to a new location? Social & Business Networking 32. Do you use social networking sites such as linked in, Plaxo, MySpace, FaceBook, Twitter, etc to help build and maintain your professional and personal relationships? Accounting System 33. Do you have remote access set up so remote employees working from home, from satellite locations, or from the road can log in and access the system? 34. Does your accounting system provide web portals so company executives and employees can keep track of the accounting data easily via web based dashboards and summary reports? 35. Do your traveling sales representatives log in during the evening and enter sales orders from the road so they can begin being processed the very next morning? 36. Do you have an automated e‐commerce solution which automatically orders and replenishes inventory as needed without (or with little) human intervention? 37. Do you have a web store online which describes your products and pricing, and allows readers to order those products and services on a real time basis? 38. Does your accounting system automatically link to and update the pricing, description, pictures and inventory quantities on hand of your web site on a real time basis? 39. Does your accounting system provide your employees access to human resource functions so they can adjust their withholdings, request vacations, or move money around in their retirement funds online? 40. Does you accounting system send your customers periodic e‐mails advising them as to deliveries in progress? 41. Do your asset and resources report back to your accounting system critical information, such as a coke machine reporting how many drinks have been sold or a truck reporting how the average speed or how many hard brakes have been applied. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 116 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Developing an Effective Web Site Overview ‐ Today, building a web page is as easy as choosing “File Save As” from the main menu. Most of today’s applications will save your document automatically to a web page format (HTML format). By far, the most difficult parts of creating an effective web site are organization, layout, and content. The approach will depend on your objective. For example, if your web site is intended for use on the Internet to attract new customers, you may have a different strategy than the Information Systems person who is posting a corporate web site internally on the Intranet. As a starter, let us assume you want to attract new customers and sell products or services over the Internet. et us start by considering the old “company brochure”. This document was used to describe the company and summarize the products or services sold. Now imagine that your brochure is one of two thousand similar brochures on display at the airport available to arriving passengers. How is your brochure going to catch their attention over the other 1,999 brochures? What if your brochure is difficult to read because the font is too small, too large or busy? Where is your brochure located on the display? – at eye level, or on the bottom row? This image paints a similar image of the problems associated with creating an effective web site. This session features a discussion of some strategies you can employ to make your web site as effective as possible. L Get Found! ‐ The first problem to overcome is being found on the Internet. To play this game properly, you need to understand exactly how search engines index your web pages and rate them. The specific algorithms used to rank the web pages found in a search vary from one search engine to another, and even vary within the same search engine over time. However in general, if all of your search words are contained in the title of the found web site, that site is generally ranked extremely high. If only a portion of your search words are contained in the title, then the resulting rank is a little lower. If your search words are contained only in the keyword list, then the resulting ranking is still a little lower. If the search words are contained only in the body of the home page, then the resulting ranking is still lower. If the search words are contained in sub pages (this applies to some, but not all search engines), then the resulting rank is lower still. In the event that search words are contained in the title, keyword list, home page and sub pages, an algorithm is used to calculate the resulting rank based on some allocation method. In the example below, a user has used the Google engine to search for “International Tax Consulting” which resulted in over 1,380,000 hits. The 3rd from the top hit was to the KPMG. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 117 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Notice that only a few of the web pages listed use the title “International Tax Consulting”. The result is that if you were to create a web page with this title, chances are good that your web page would be returned to the top of the hit list every time someone searched the Google for a company that offers international tax consulting services. What we can learn from this observation is two things. First, you need create a web page with precisely the right title and keywords in order to have your best chances of being sorted among the top web sites. Unless your company is one‐dimensional, there is no way that you can do this with just one web site. Therefore, to be effective, you may need to create a web site for every service you offer. This concept is discussed further below. The second thing we learn is that it may be beneficial to first test your title against the various Internet search engines before you finalize it. You can usually tell by the resulting rankings of the top hits whether your intended title will sort higher on the list. Conclusion: Choose an appropriate title for your web page. Choose appropriate keywords. Make sure all of the relevant buzz words are included in the body of your home page. Test your title before finalizing. These steps will help you get found on the Internet. Get Chosen ‐ Just because you made it to the top of a hit list from a search engine does not mean the user is going to click on your site. You need to make sure your web page summary is well written and to the point. The screen below shows the summaries for just a few of the international Tax Consulting links we hit in the example above. The reader will most likely continue to scroll down the hit list until they find a hit that is most relevant to the search, based on the brief description. Some search engines require the user to provide a summary at the time the URL is submitted to the search engine while others simply use the first few lines of text in the home page as the summary. Either way, you want your summary read as if it is right on point with the users needs. As mentioned above, it is impossible to accomplish this with just one web page. To be effective, you must create a specific web page for every service or product Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 118 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com (group) your company offers. The good news is that it costs very little extra in terms of hard dollars to create 50 web pages compared to just one web page. Only time and effort is involved. Conclusion: Your summary should be well written and to the point to attract prospects to your site. Don’t Chase the Prospect Away ‐ Let us assume that your web page has ranked high in a search list and the user has clicked on your link. You can inadvertently chase them away if you make them wait too long for the web page. Common mistakes are locating your web page on a slow web server (such as those provided by America On‐Line); adding large graphic images that take too long to load, adding background music that slows down the loading process, and making the web page difficult to read. Your web page should get right to the point without a lot of hype. Often a short introductory summary followed by a well designed menu of links is the best way to pull someone into your page. The information should not be buried too deep in the web site – if a user feels that they are on a tiger hunt for the information they are seeking, they may leave your web site altogether. Other mistakes include fonts that are too small, fonts that are too large, backgrounds that make it tough to read the text, and formatting that does not work well with a wide variety of browsers. Conclusion: A clean, fast web site will help keep the prospect interested in exploring your web pages. Don’t get too fancy on the home page – for example link to impressive slower movies and voice in sub pages and warn the user by advising them how big the files are so they can judge whether they want to wait for this information. Don’t Hide Your Company Info ‐ Some web pages make it virtually impossible to find the company name, address, telephone and e‐mail information. Our advice is to add this information to the bottom of every web page you create. With this approach, the moment the user decides that they would like to contact you, your information will be close at hand. Content, Content, Content ‐ Sometimes it pays to give away the farm in order for the cows to come running. If your web site provides only sales information and no answers to common questions, no insights, no examples, and no hints, tips or war stories, then it will not be very effective. A person searching for an international tax consultant would spend a great deal of time on your page if it contained links to the following: o Click here for the “Top Ten International Tax Planning Mistakes” corporations make. o Click here for four cases studies featuring tax planning strategies for a small, medium, large and Fortune 500 companies. o Click here to read about several fraudulent tax strategies that some consultants employ that could land you in jail. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 119 High Tech Communications o www.CarltonCollins.com Click here to read about current bills in congress which could affect your International tax planning strategy o Click here for more good links to International Tax Planning Information on the Web Certainly an interested party would spend time reading and printing this material – another good reason to have your name and address on every page. The idea is to provide such a good site for relevant information that the user bookmarks your site so they can easily come back to it. After all, how many times has a person found a good site, and then later was unable to find that site again. Keep your Web Site Current ‐ People can tell when a web site is out of date. For the best results, add information weekly (or even daily) to your web site. Deep Information ‐ Your web site can contain almost an infinite amount of information for almost no additional cost. For this reason, you should supply the user with as much “well organized” information as possible. For example, consider posting a 5‐page biography for each officer or Partner in your organization. Consider adding pictures of all employees to your web site in an effort to help the user associate a face with your company. Add a complete history of the company, information on every product, and information on all of your services. Reference letters can be a great addition as users can view those letters without necessarily bothering the person who wrote you the reference. Include Prices ‐ While some people may disagree, we think it is a good idea to clearly state your fees and prices for products and services. People on the web are often shopping around for the best price available. With no price to go on, they may not give your site further consideration. Some companies report to have even received e‐mails complaining that because no pricing is included, the sender has elected not to do business with that company. Because web users use the web 24 hours a day, it may be unreasonable to expect them to be able to call easily to obtain prices. On the other hand, it may be dangerous to allow your competitors to see your prices. Multiple Web Pages ‐ Perhaps the most important step you should take is to develop multiple web sites to represent each product or service you sell. For example, a given CPA firm might have a web site devoted exclusively to individual tax preparation, another for Pension and Profit Sharing, another for corporate tax, write‐up services, systems work, etc. This will allow you to design a web site that will come across as right on point for the user searching for your particular service or product. Designing Your Web Site ‐ The design and layout of an effective web site can become quite confusing – especially over time as the web site is improved and new personnel are brought in to manage the site. For this reason, you should approach the design in an organized manner. Your first step might be to use a large grease board or poster board to sketch out your general desired layout – complete with arrows to indicate links. For example, you initial rough draft may look like the following: Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 120 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Home Page Company History Products Order Form Once you have sketched out the basic design of your web site, the next step is assign persons to develop the content for each site. This content can be developed in any standard word processor, spreadsheet or database application. However, once you begin to actually develop your web site, it is highly recommended that you use a common web page development tool such as Dreamweaver or Microsoft Front Page. These web page development tools not only provide tools for developing web pages, but also contain tools that make it far easier to develop and manage a web site on an ongoing basis. Microsoft Front Page is discussed later in these session materials. Web Site Mistakes O ver the past seven years, many companies have erected web sites and web stores only to fail miserably. Unfortunately, a large percentage of the companies behind these failed efforts have concluded that there must be little or no market for e‐commerce web stores. I believe that they are wrong ‐ dead wrong. I believe that their failures can be chalked up to a multitude of mistakes, missteps, and misconceptions regarding web stores. This article discusses some of the most common site blunders. Poor Web Design • Too Much Clicking ‐ I am amazed by how poorly some web sites are designed. In many cases users must click five, six, or even eight clicks deep into the web site to find what they are looking for. My rule is to build web sites in which the entire contents of the web site are only one click away from the home page ‐ unless you have hundreds of pages on a given topic and then I will allow two clicks deep, but no more. • Hidden Contact Info ‐ Contact information should be displayed on every page in the web site. You never know when that reader will want to print the page, forward the page via e‐mail or pick up the phone and call. • No Pictures ‐ All items offered for sale should include a picture, if not multiple pictures. People like to touch and feel stuff before they buy, but a web store does not offer this capability. Pictures and movies offer the next best thing. For example, we've all seen the Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 121 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com boom box stereo system promoted on television for just $9.95. It looks great on television but when it arrives at your door you discover that it is only 3.5 inches high. Hey, I got one ‐ check it out. Most people just want to know what they are ordering. A picture helps tremendously. Multiple pictures, diagrams, schematics, blueprints, dimensions, and VRML's all help the shopper understand the item before they purchase. • Weak Descriptions ‐ Web stores should provide detailed descriptions of each product. You would think that this would be obvious, but evidently it is not. Some web sites do not even attempt to describe their products or provide a picture. You have to wonder what they are thinking? For an example, check out this web page which compares the descriptions provided by two separate web stores for the same exact product. Hey, when there is no printing or publishing cost, why not offer a longer description? • No Prices ‐ Most importantly, web stores should always provide pricing information. When I encounter a web store without prices ‐ I leave immediately ‐ so do you. Often we leave because we usually shop during non‐business hours and; therefore, the web store's instructions to "call for a price quote" at 11:00pm doesn't cut it. In most cases we conclude that because there are no prices listed, they must be high prices ‐ or else why wouldn't they list them ‐ right? In any event, I for one am not willing to go through the extra effort to determine the price – it is far easier to just move on to the next click. • No Competitive Information ‐ Most web sites do not include detailed lists of competitive products. What a mistake. You have an interested shopper reading your web site, but because you don't inform that shopper about all of their alternatives, and the pros and cons of those alternatives ‐ you force them to go elsewhere on the web to find the answers they seek. To do this, they must leave your web site and visit your competitor's web site. Now they have them ‐ and you don't. People want to be informed shoppers. If all you sell on your web store is a toaster, that's fine. But you should consider providing the shopper with a list of every toaster available ‐ along with their prices, descriptions, and pros and cons. By doing this, you've squelched the need for the shopper to visit any further web sites. They now have all of the information they need to make their decision, and they are now on your web site (a web site in which you control the content) ‐ doesn't this sound like a good thing? Savvy shoppers will shop around if necessary, but if you provide all of the information they need, you will attract more shoppers, and generate more sales. Yeah, I know ‐ creating deep content is tough. But it's easier for you to dig up this information than your customers. Do them the favor of providing them with the information they truly need to make the decision and close the deal – you won’t be sorry. • Can't Get Found ‐ Another common mistake web stores make is they can't get found. You may have a good web site, but nobody can find you. For example, search for tennis racquets and you will find more than 166,000 results. What good is it to be number 457 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 122 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com on this list, not to mention being number 45,757? It's useless. To yield top results, your customers must be able to find you. In my opinion, here are the common mistakes web stores make which prevent them from being found. • Lack of Understanding How Search Engines Work ‐ Search tools like Google and Wisenut visit billions of web pages and index every word on each web page, including the file name, title, and embedded keywords. When readers use these search engines to search for say "toasters", the search engines quickly find every web page that remotely mentions the word "toasters", and then scores each web page on its relevance to the word "toasters". A web page that contained the word "toasters" in its key word list, its title, and in the body of the web page, would score higher, and therefore would be ranked higher than another web page that simply mentioned the words "toasters" in the body of the page. Based on what I've seen, it appears that many web stores don't understand this simple concept. Further, both Google and Wisenut use algorithms that will rate your web page more highly when other web sites link to you using the search phrase. The only real way to get other web sites to link to your web site is to offer a truly stellar web site. If for example you published the definitive toaster web site, other toaster enthusiasts would link to your site, and you would fair far better in Google and Wisenut searches. • Lack of Keywords ‐ To rank high, you must add keywords to your web store. Doing so is very easy, here is an example of the line of html code you add to your web page: <meta name="keywords" content="tennis, tennis elbow, racket, racquet> Adding this line of code will not ensure that you rank high, but omitting it will almost always assure that you don't. If you are an astute individual, you may have noticed a slight problem here. If a web store sells hundreds of items, wouldn't they need hundreds or even thousands of key words in their web page? The answer is yes, they would. Unfortunately, many top search engines actually penalize web pages with a lower score for excessive key word use. (To learn how to mitigate this problem, please refer to my article entitled Web Impressions.) • Improper Page Title ‐ Most search engines award "brownie points" to your web page when the search term is part of the page title. For example, if the person is searching for "toasters", then Billy Bob's Toaster Museum page will receive more "brownie points" than the Wal‐Mart web site. Herein lies a fundamental problem with large web sites that offer thousands of products ‐ they can't include all of the product names in their keywords and page titles. In this case, the advantage goes to the little guy. Like keywords, the title of a page is embedded into the page's programming code via a command line as follows: <TITLE>Accounting Software: []</TITLE> Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 123 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com • Failure to Submit ‐ Once you've built your web site and included all of the key parameters, the next step is to visit each search engine and submit your web pages. The process is fairly easy, but submitting to multiple search engines takes time. There are services out there that will submit your web pages for you for a fee. Personally, I find that that you can simply submit your web page on your own to the top ten or twelve search engines and obtain good results. Here is a link to my list of search engine submission pages. • Failure to Submit All Pages ‐ Some companies simply submit their home page to the popular search engines, and fail to submit all of their relevant sub pages. • Lack of Good, Deep Content ‐ A lack of good, deep content can hurt you plenty. The top search engines usually award brownie points to those web sites that are frequently linked to by other web sites. If your web site has little or no content, then others will not link to you. If others do not link to you, you won't score as high on a typical search. The only real way to get others to link to your web site, is to provide good content that others will find useful. Few people will link to a "cyber sales pitch". Conclusion As a general rule, I buy everything I purchase over the Internet – unless I plan to eat it right away. Why do I do this? Because I like to be a more informed shopper and I like to save 20 to 25% on everything I purchase. (After all, CPA stands for Cheapest Price Available). Therefore if you want my business, you’d better have a good web presence – else you will never sell a single product or service to me (except for maybe an occasional ice cream cone). I am not alone. Millions of others also take to the web to find products, services, and rock bottom prices. Call us savvy or call us tight wads. Either way our group is growing and there will be more web shoppers in the future, not fewer. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 124 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com How to Build A Web Page Building Your Web Page ‐ The next several pages explain the basic procedures for building and posting a standard web page. In the nineties, building a web page involved the use of complicated HTML (Hyper‐Text Markup Language) tools such as HTML Editor or HotMetal Editor. As far as basic tools go, these products were complicated to learn, and contained many limitations such as the inability to edit in WYSIWYG mode and a serious limitation on the size of the web page itself. Today, the process of developing a web page has been made much easier with the introduction of numerous new web development tools and the addition of HTML file format support in the popular word processing packages such as Microsoft Word. Many of today’s desktop publishing, spreadsheet, and database packages also support HTML file formats. This makes the creation of a web page as simple as saving the file to the HTML format. As an example, this chapter on posting a Web Page could be transferred into a web page simply by selecting File Save As Web Page from the Microsoft Word menu as follows: Word saves files to an HTML file format This action saves the file to the proper HTML format ready for uploading to a web server. Even the pictures, screen captures, and graphic images included in this file would be converted to GIF images. Of course, the creative side of web development remains to be a difficult obstacle for many business people. In the past, your company probably called in a graphic artist or other specialist to help prepare your company brochure. These creative people typically have a flair for creating vivid products which catch the eye and convey professionalism. These specialists also have access to better desktop publishing equipment such as scanners, color printers, and photographic equipment. This puts them in a better position to develop brochures and print media. The development of web pages generally calls for the same skill set. Therefore, while generating your own home page is relatively easy, producing an attractive web page that conveys the right look may require the use of a professional. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 125 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Publishing Your Web Page Once you have developed your Web Home Page (and sub pages), the next step is to simply copy your files to a web server somewhere in the world. There are thousands of web servers who would be happy to host your web page for a small monthly charge. As a good example, Go Daddy will host your domain name and provide a web site for just $4.95 per month. Here is how it works: 1. Visit the Go Daddy Web Site and purchase a domain name for about $9.00. 2. Next subscribe to the Go Daddy web hosting service that matches your requirements. 3. Next, start posting your content to the web site. You can use Dreamweaver, Cold Fusion, Front Page, Word, or even Excel to accomplish this task. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 126 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Submitting Your Home Page to Web Search Engines Once your web page is up and running, you want the world to be able to find it. You perform this step by “submitting” your URL to the various popular search engines. As an example, to update the Google search engine, go to the Google Web Page and click the “Submit” button as shown in the screen capture below: This button will take you to a form which will allow you to list up to ten URLs. Within a few hours, Google will “crawl” over to your web page and index the key words off of your web page. Thereafter, users of the Internet may (or may not) find your web page by keying in search criteria that match your key words. The reason that they may not find you is simply because of volume. Assume for example that one of your key words is “medicine”. On March 25, 2004, a search for the key word “medicine” resulted in 39,500,000 web pages which contained that word. Whether or not your web page appears at the top of the list depends on luck. Of course, most users would refine their search. For example, let us assume that a user were to search for the words medicine and aspirin. This search resulted in only 500,000 web pages which contains both of those words. Therefore, if these two words were part of your web page, you would have a higher probability that someone will find your web page. Advanced Web Page Design Techniques ‐ Aside from developing a great looking web page with text and graphic pictures, there are other measures you can take to spice up your page. One of the most popular advanced techniques is to add RealAudio to your web page. With real audio, wave files can be embedded directly on your web page. As the user accesses the real audio file, the real audio player buffers the first ten seconds of the file, and then begins playing the wave stream. The result is that sound starts fairly quickly and continues playing uninterrupted. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 127 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Characteristics of a Successful Web Page 1. No Invisible Webs ‐ It is difficult sometimes to find web pages in the haystack of the Internet. To keep the site from being invisible, it must be registered with all of the online search engines like Google, Bing, Lycos, WebCrawler, Alta Vista, InfoSeek, etc. and with the catalog listings such as EINet Galaxy, Yahoo, the Commercial Sites Index, etc. In addition, the registrations should be kept up to date with new categories and new sites. 2. No Dead Webs ‐ Some Web pages have a "ghost‐town" feel about them because it seems as if no one has been tending them in a while. On good sites, the content is always fresh. 3. information‐Rich ‐ Successful pages are information‐rich, so the site offers good content, content, content. 4. Good Clear Navigation – Easy to use menus that guide readers around and through the site is a must. The navigational elements (icons, arrows, etc.) should be consistent. Moving around on the page and among the pages should feel intuitive. You should be able to see where you are going, and return easily. 5. The Site Has True Value Added ‐ Services, content, products, resources. It is not just a place to market and sell. Users should be able to get real information and perhaps some services for free. 6. The Site Maintainers Are Responsive ‐ They answer queries and trouble shoot problem links. You don't get the dreaded: "404, URL not found" messages that mean that the document you are hunting for is not there. 7. Organizational Support ‐ The site should have organizational support. This means that the site is not set up and maintained by a couple of guys and no one else in the organization knows anything about the site. The site should have both budget and personnel support. 8. Feedback Forms ‐ The web site should be capable of gathering information about users through feedback forms, questions, surveys, contests, newsletters, surveys, etc. so that the maintainers know who has been visiting the site. 9. Cross Reference Other Media ‐ The Web site is a marketing channel integrated with other channels such as print‐media, TV, radio, for example. 10. Looks Professional ‐ The site has a structurally sound and aesthetically pleasing design. 11. Supports Multiple Browsers – Often a web site that looks perfect in one browser will be completely unacceptable in another browser. The site should be tested and viewable with a variety of browsers. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 128 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 12. Convey the Correct Image ‐ The web site should include graphics, design and colors are in synch with the corporate image. For example, a church’s web site should not have scantily dressed models or pictures of people behaving irresponsibly. 13. Consistency ‐ The site has consistent imagery and content from page to page. Web Development Tips: 1. Test Your Web Site on Multiple Browsers ‐ Test your pages on multiple platforms before you release them to the world. What may look wonderful on the Internet Explorer or Netscape browser, may look horrible on an Safari, Google Chrome, AOL, Macintosh, or UNIX NCSA Xmosaic browser. 2. Your server logs are a gold mine of information. For example, you can see the percentage of users that are loading the pages but not the images in the pages. You can also see which pages have never or rarely been accessed. 3. Check Your Own Page Regularly ‐ Don't wait for people to tell you that there are problems. Most people who find a problem with your web site go away without saying a thing. 4. Don't Use Long Titles ‐ Remember that the title goes into the hotlist, where display space is limited. 5. Link Your Images ‐ Always use at least some text, and make sure that images have links. It can be frustrating to encounter a home page that is a series of images without a single word on the entire page. 6. One Topic Per Page ‐ Don't go overboard and put everything on one page; your reader still has to download your document over the Internet. It is better to have several smaller pages. Try to present one topic per page. However, if you have a large number of topics, maintaining and linking them can be a daunting task. Consider combining smaller, related topics onto a single page instead. 7. Avoid Extremely Large Images – make sure you compress extremely large images so they will display fast. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 129 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Selling on the Web T ake a deep breadth. Do you smell that? That smell my friend, is the smell of opportunity. Today the Internet offers more opportunity than any other time in our history, including the Industrial Revolution. Why do I think so? Consider: The Internet now enables virtually anybody to start a new business with virtually no overhead costs. For example, suppose you and I had wanted to launch a new magazine business back in 1990 ‐ "The Trout Fisherman". We would have developed and written our first issue and printed 50,000 copies for a cost of $90,000. Then we needed to somehow distribute that magazine. Our options are to use the U. S. Mail, or set up a fleet of couriers to deliver our magazines. Or maybe we needed to develop a distribution channel into stores across America. Whatever method we used to distribute our magazine, it would have been costly ‐ probably 50 cents per magazine at best. But wait, we're not making any money. We need subscribers. We invest $100,000 to launch a marketing campaign aimed at attracting paying readers. Unfortunately, there is little demand for our efforts, and our business never takes off. We lose a quarter of a million dollars in just a few months time, not to mention a lot of lost work. Now fast forward to today. You and I could develop and write our first issue of "The Trout Fisherman" and post it to a web site in a matter of days. Our web site cost would probably be just $10 per month. We submit our web site to the some of the popular search engines and people around the world start finding our web site. They find that it is well written, and full of good content. They bookmark our web site and keep coming back. Within a few months, we have an impressive list of readers. OK, ok. We haven't made any money off our web site ‐ but we haven't lost any either. This is the key point. Now we shift gears and start selling fishing gear on line. Our web orders are automatically forwarded to another company who handles fulfillment, and we pocket a small profit on each sale. We start selling maps to well stocked fishing holes on line ‐ the reader submits their credit card and the map is e‐mailed to them. T‐ shirt and cap sales bearing our logo start moving as well. Fulfillment is carried out by another company. Fishing companies start paying us to advertise on our web site. Based on our recognition, fishing companies pay us to speak at their conferences for a fee. We receive endorsement contracts and our empire continues to grow. In this case we can see several clear differences between the process of launching a new magazine in 1990 and launching one today. To recap: 1. Today, launching a web magazine has virtually no financial risk. 2. With a web magazine, there are no printing costs, and no distribution costs. 3. A web magazine is instantly accessible to millions of people around the world. 4. Today the web makes automatic order receipt and forwarding to fulfillment companies a real possibility. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 130 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com This, my friends is what I call opportunity...unprecedented opportunity! Seize the opportunity Still not convinced? Maybe you think that a magazine might have a good chance, but that other companies who do business via the web are doomed. After all, print media is ideally suited for the web. Well, you are a skeptic and I appreciate that. Let me attempt to sway you further over to my point of view. Let's take you to the complete opposite end of the spectrum. Let's assume for example that you are launching a new grocery store. Consider these two examples: • The process of launching a typical retail grocery store is rather expensive. It typically starts with the purchase or lease of prime commercial real estate property. Here in the suburbs of Atlanta, the typical grocery store sits on roughly 12 acres of land costing $300,000 per acre or $3.6 million. Leasing that same real estate runs approximately $8.00 to $12.00 per square foot for stores which typically run from 60,000 to 85,000 square feet which translates to $480,000 to $1,020,000 per year in lease fees. These rates reflect favorable pricing afforded to grocery stores which are considered to be an anchor for most shopping centers. From here, the grocery store expends fees for a paved parking lot, cash registers, customer shopping carts, attractive flooring, fancy lighting, decorations, etc. The costs are staggering and the overhead associated with the typical grocery store today must be recaptured through higher product prices. The grocery store then serves the immediate community which is usually a couple of miles or so. • By comparison, today a company could erect a cinder block building in an industrial park setting located 15 miles outside of town. We will call it “Billy Bob's Grocery Store". The building may have a dirt road and unpaved parking. The building provides concrete floors and ordinary lighting. There are no decorations and cash registers are basic. The cost of such a facility here in Atlanta presently runs about $90,000 to $120,000 a year. A web site could then be established listing all of the products. Users need only log on, and click a check mark next to the items they wish to purchase. In a matter of minutes, the order is entered, and within a time period specified by the customer ‐ a pizza hut type delivery person shows up to deliver the groceries. In this case, there is an extra $10 delivery fee; however, because Billy Bob's Grocery store has dramatically lower overhead costs, their prices are dramatically lower as well, and you save $24 compared to the retail store down the road. In comparing these two models, there are some important differences to note as follows: 1. Billy Bob's overhead is much smaller; other things being equal, Billy Bob's prices can be much lower. 2. Billy Bob's can serve a larger market covering a 15 to 20 mile radius, instead of the 2 mile radius covered by many traditional retail grocery stores. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 131 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 3. Billy Bob's customers save time. Five minutes on the web versus 1 hour in the store is a major time savings. The customer also saves gasoline, does not risk having a head on collision, does not risk being mugged in the parking lot, and does not succumb to impulse buying when they walk down the candy aisle. (Grocery stores have all kinds of tricks designed to make you buy more products, or more expensive products. For example, the more expensive, higher profit items are at eye level. Workers pass out free samples of food for you to taste. These techniques obviously work, because they keep doing them.) 4. Maybe you wouldn't purchase 100% of your groceries from a web store, but maybe you would have dog food, canned drinks, soups and canned foods, and common staple goods delivered by Billy Bob. You might still visit you local grocery store for broccoli and meat so that you can pick it out yourself. In this case, Billy Bob's allows you to save money on the items you purchase there, and it reduces your shopping time in the retail store. At this point, you are probably thinking "Carlton, if this is such a great idea, then why have other online grocery stores such as WebVan and Peapod lost money and gone out of business?" Do not worry, I have the answer for you. Peapod embraced the web model only to the extent that customers could place orders over the web. However, they did not embrace the most important part of the model, which is to avoid the high cost of overhead. Here in Atlanta, Peapod contracted with Brunos ‐ the most expensive grocery store chain in Atlanta to fulfill their web orders. As a result, their prices were actually higher than the local grocery store and the added delivery fee inflated those prices higher still. Instead of saving money and time, Peapod only allowed you to save time. I am sorry, but web shoppers like myself have come to expect lower prices via the Internet. Webvan's troubles were related to growing too fast, technical problems, and a botched merger with Homer Grocer. Webvan's CEO Robert Swan claimed that the Webvan model could have worked, however the company simply ran out of start up capital. (They started with $1.2 billion). Conclusion I believe that the Internet offers the greatest opportunity our world has ever seen for both big companies and common people to launch new businesses. The cost of establishing a web store is extremely small and due to the power of the web, goods and services are instantly available to millions of prospective consumers. These factors are the foundation which will fuel wide spread web commerce for years to come. As high speed internet access becomes more prevalent, web businesses will experience greater successes. I highly recommend that you read my related article ‐ I believe in e‐commerce which is located here: http://www.accountingsoftwareadvisor.com/ec/ecommerce.htm Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 132 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Carlton’s Multiple Web Site Strategy I t is my belief that if your company offers 15 different services, then you need to have 15 different web sites in order to make the right web impression and promote those services. I have never read this idea anywhere before, or heard this idea presented by anyone before. I arrived at this conclusion by myself. Further, I have been arguing this idea for the past three years to thousands of businesses who attend my lectures. So far, no one has even attempted to challenge my premise. Please allow me to make my case with the following lines of thinking: Suppose that Good Growth, Inc. is in need of a good international tax advisor. Good Growth's management turns to the Internet in search of a list of international tax advisors and relevant information pertaining to international tax strategy and law. Presented below is a discussion about two hypothetical consulting firms that both offer international tax consulting ‐ ABC Consultants and XYZ Consultants. ABC Consultant's web site is a basic web site that contains the same information in the firm's 4‐ panel fold‐out printed brochure. The information clearly states that the firm offers the following 15 services: 1040 tax preparation; 1120 tax preparation; state tax preparation; fiduciary tax preparation; 1065 tax preparation; client write‐up services; compilation services; financial review services; audits; international tax consulting; SBA loan applications, etc. In this example, because international tax consulting is a mere bullet on the web page, ABC's web site does not rank very high as a result of a web search on the term "international tax consultants". In fact, Google returns 298,000 web site hits, and ABC Company's web site is number 49,300 on that hit list. Only those web sites which are solely dedicated to the topic "international tax consultant" rank among the top 20 to 30 hits. As a result, ABC Consultants are not found by Good Growth, Inc. However, let us assume that Good Growth does find the ABC web site ‐ what then. In this case, the folks at Good Growth are not impressed. The fact that international tax consulting is listed as a mere bullet does not compel Good Growth to follow up ‐ instead, they simply move on to the next web site. By contrast, XYZ Consultants have created a separate web site to promote each of their specific services. Their international tax consulting web site exudes international tax information. The title contains the words "international tax consultants". The keyword list contains the words "international tax consultants". The content spouts off a multitude of relevant international tax information including: 1. A checklist of the ten most important international tax issues to consider; 2. A list of laws currently pending in Congress which could affect international tax law; 3. Case studies where the firm assisted other companies with international tax issues; 4. Lists of conferences and seminars on international tax law; 5. Biographies of firm consultants as they relate to international tax issues; 6. The top ten questions you should ask of your international tax advisor; 7. Published articles designed to educate you about international tax issues; 8. References to news stories about companies with international tax problems; 9. A list of links to other relevant international tax information. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 133 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com As a result, XYZ's web site ranks high in Good Growth's search and is found. When Good Growth's management accesses XYZ's web site ‐ they shout "halleluiah ‐ we've hit the "mother load". The company proceeds to immerse themselves in the XYZ web site, printing pages for their own use and forwarding other pages to their colleagues. Having found many of the answers they were searching for, the folks at Good Growth stop their web search and concentrate on the XYZ material. They find the materials very informative and useful. They conclude that XYZ is a firm that has the expertise they were looking for. They end up calling XYZ and engaging their services. In this case, having multiple web sites enabled XYZ to make the right impression and land the customer. The web can be a cold environment and you usually have only a few seconds to make a good web impression. Companies wishing to promote their goods and services via the web need to provide separate web sites for each service and product in order to accomplish this most important objective. It is important to note that once a company has created one web site, the second, third and forth web sites are really quite easy. The infrastructure is already in place and additional web impressions are only a matter of a little sweat. Read on as I a develop my point further with another example. Tower Records We all know about Tower Records, but when I visit this web site, I wonder why they only have one web site. Why don't they have fifty web sites. For example, the company could maintain web sites specifically dedicated to country music, rock and roll, classical music, big band, punk rock, and Christian music. The Christian music web site for example might be adorned with pictures on angels, harps, and the pearly white gates of heaven along with a quick reference to the top 50 Christian music songs. Thereafter Tower Records could market this particular web site to the church community. Similarly, the country music web site might display cowboy boots and guitars and be marketed towards the country music crowd. In each case, the massive database and engine that has already been developed and published by Tower Records is the same database and engine that drives these additional web pages. In this manner, Tower Records need not re‐create the wheel from scratch, they need only create new home pages that link to the database and engine that is already in place. A key point is that the effort needed to create a second third and forth web impression requires only a small fraction of the effort involved in creating the original web site. The Cost of Creating Multiple Web Sites The cost of this additional effort is a lot less than you might think. Web hosting companies like Go Daddy offer web hosting services which will allow you to maintain dozens of domain names for less than $1,000 per year. Domain names cost about $10 per year. As you can see, the hard costs involved are trivial compared to the potential benefits of the additional exposure and multiple images that can be achieved. Of course there is a cost associated with developing the additional home pages and administrating those pages. However this effort does not need to Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 134 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com be extensive. I am frequently asked to explain how much effort is involved in creating a web site. Here's what I do when I get this question: I simply ask them to give me the name of their current web site. I then visit that web site and from my browser menu I choose File, Save As and I download their web site onto my computer ‐ this whole process takes only a few seconds. Next I open that web page up in Microsoft Front Page and edit the page. I quickly change the background color and font. I quickly insert a few pictures of fish which I have previously saved to my computer. I then copy the revised web page out to my web server and browser to that new page. Proudly I explain ‐ there you go ‐ there is your new web page, complete with a fishy theme. It already contains your content and links and it is ready to go. The whole process takes me about 5 minutes. People are always impressed by this quick example using their own web page. Content ‐ It is important to note that any web site needs extraordinarily good content, or else all other efforts are for naught. This whole idea does not work unless each and every web site you create is dedicated to delivery a bevy of relevant, well‐written content which is useful to the prospective customer you are trying to attract. Please keep this in mind. Conclusion I think that the idea that a company should have one, and only one web site is very short sighted. Many companies target different markets via other more expensive efforts such as print ads, television commercials, trade journals, etc. Why not do the same on the Internet where the incremental cost of doing so is minimal? Mark my words ‐ this concept will become standard operating procedure with five years ‐ but always remember that you read it here first. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 135 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Buying on the Web Remember our focus today is communicating your products and services t your customers. So at first glance, the topic “Buying on the Web” might not seem to fit. However, I think it does I think that it is useful to view your efforts to communicate from the customer’s perspective. I Do Most of My Shopping on the Web To start with, for the past 15 years I have purchased almost everything over the internet. I wouldn't buy furniture, a bike, a car, a camera, a boat, a house, office supplies, airline tickets, toys, clothes, computers, books, without first shopping it over the internet. Unless I plan to eat it right then, I turn to the web for most of my purchases. The web saves me time, it makes me a more informed consumer, and it almost always saves me 20% to 25% of my purchase price. Here are some of my personal examples, just to share a few: Item Best Retail Web Price I Price Paid Savings Savings % Hooker Bedroom Furniture Electric Dog Fence Hotel Rooms in Paris, France Bass Fishing Boat Sony Camcorder Kodak Digital Camera Delta Airline Ticket to Seattle Trumpet Fireplace Screen Bicycle Third Wheel Lego Mindstorm Tennis Racquet Childs Tennis Racquet Baseball Bat Compaq 24 inch Monitor $ 6,000 $ 250 $ 1,495 $ 6,200 $ 1,600 $ 869 $ 1,800 $ 600 $ 369 $ 229 $ 199 $ 210 $ 100 $ 229 $ 1,800 $ 4,200 $ 180 $ 995 $ 4,500 $ 1,200 $ 600 $ 429 $ 360 $ 140 $ 129 $ 150 $ 140 $ 70 $ 169 $ 950 $ 1,800 $ 70 $ 500 $ 1,700 $ 400 $ 269 $ 1,371 $ 240 $ 229 $ 100 $ 49 $ 70 $ 30 $ 60 $ 850 30% 28% 33% 27% 25% 31% 76% 40% 62% 44% 25% 33% 30% 26% 47% Totals $ 21,950 $ 14,212 $ 7,738 35% As you can see by the above few examples, the cost savings can be impressive. These prices do not reflect savings for sales taxes, which usually more than covers shipping costs. In 1999, I calculated that I saved more than $18,000 by shopping on the web ‐ most of these savings were related to travel. My wife and I also purchase numerous books, gifts, supplies, and other items Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 136 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com over the web. Not only do I save money, but this also saves me time. A trip to the store can eat 1 to 3 hours of your time here in Atlanta, but a similar trip to the web takes only 10 to 15 minutes. Other benefits of web shopping include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Not risking a head on collision traveling to the store Not polluting the atmosphere with my automobile's combustible engine No wear and tear on my automobile, no rubber worn off my tires Not being mugged in the parking lot once there Not succumbing to impulse purchasing once I am in the store I told this story in December 2001 during a conference in a Salt Lake City, Utah and made my usual boastful claim that I save 20% to 25% on almost everything I purchase over the Internet. Before I could go much further, a participant from the audience called me on it. He pretty much insinuated that I was lying, or at least exaggerating. He challenged me in front of the entire audience by stating that he had just purchased a German Martindale bridle for $99 and that he had searched many retail outlets before finding this great price. He challenged me to do better. The gauntlet had been thrown down. I knew that I had to respond or my credibility would have been shot. I started using the search tools to locate the item in question. It took me about 4 minutes, but I was able to find the exact German Martindale bridle for just $59.00. Needless to say, my skeptical friend was amazed and he hung around after the presentation to tell me. Why Some People Avoid Shopping on the Web In my opinion, there are several reasons why so many people don't shop on‐line as follows: 1. Slow Internet – In years past, many people had slow dial up access to the internet and as a result, shopping on line takes hours, not minutes. Heck, if my microwave oven took 8 hours to bake a potato, I wouldn't use it either. 2. Wrong Search Tools ‐ Many people use the wrong search tools to search the internet. Try this for yourself. Go to Yahoo! and search for the word magazine, then do the same in Google. On march 1, 2002, Yahoo! found 14,861 hits while Google found 23,700,000 hits. Yes, that's right ‐ 15 thousand compared to 24 million. Most people who use Yahoo to search the Internet are in fact using one of the worst search tools possible. No wonder they can't find what they are looking for. 3. Searching Ignorance ‐ Many people don't know how to use the search tools. Instead of looking for "baseball" and "equipment", try looking for "baseball" and "equipment" and "$" and "order" and "credit card". In this manner you are far more likely to find web sites that actually sell the gear you are looking for. 4. Fear of the Internet ‐ Many people have a fear of using their credit card over the internet. This is ridiculous. Using your credit card over the internet is one of the safest things you can do. If you want to take a risk, try pulling out your credit card at a Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 137 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com restaurant or convenience store ‐ that's where your number gets ripped off most. Besides, there is a federal law that limits your liability to just $50. 5. Physical Inspection ‐ Many people want to examine and inspect the items before purchasing. I'll give you that. The Internet does not allow you to touch and feel items before purchasing. However, you can always find the items at the store, and then shop them on‐line later. Many web stores offer a 30 day money back return guarantee that helps a little. In 2001, my wife and I took our kids to see Santa Claus at the mall, and afterwards we shopped for a couple of hours. It wasn't until we walked out of the mall that I noticed that we had not purchased a single item in the mall, but we had compiled a list of items to shop online. It was not intentional mind you, it is just a habit that comes natural to us now. I certainly don't want those stores to go out of business, but saving 20% to 25% is fairly important to me. How about you? 6. Fear Viruses ‐ Many people avoid Internet shopping because they fear fraud, viruses and pornography. It is true that the Internet is a quick source for viruses and pornography. However, it is possible to prevent viruses and block pornography. I recommend that you purchase and install Norton Antivirus protection (or some other virus protection product) for about $16. I also recommend that you purchase a SonicWall firewall device (or some other firewall device) for about $242. The SonicWall device will protect against Internet viruses, and for an additional monthly fee, will block all pornography. It is also wise to upgrade your Windows operating system and Office applications with the latest security patches and adjust your security levels to high. 7. Fear Fraud – Fraud is definitely a problem, or so I hear. After 15 years of purchasing the bulk of our purchases, I’ve never encountered fraud, and have only encountered a problem a couple of time. But because it is harder to hide when conducting fraud from a retail location, retail is a little safer bet. You can hedge your bets by purchasing only from well established internet companies – Pricegrabber.com has thousands of them. I am wary when purchasing on eBay because anybody can get online and sell through eBay immediately – but I do use eBay anyway. Often my neighbors, family and friends ask me to find good prices for them. They know that I have the high speed internet connection and a stellar command of the Internet search tools needed to locate their item at the best prices possible. At least they know where the bargains are, even if they don't take the initiative to install high‐speed web access or learn the search tools for themselves. Conclusion ‐ In conclusion, I am a believer in the future of web‐commerce because I have personally made the transition to web shopping. I know in my heart that most of you out there would make this transition too, if only you had high speed access and a good working knowledge of searching the web. This being the case, it is only a matter of time before we all do a sizable chunk of our purchasing online. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 138 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Selling Online Chapter 15 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 139 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Selling Online Are you selling your products and services on line? Are you selling them online effectively? Are you selling them through your own web site, through someone’s else’s web site, or both? Perhaps you would be well advised to sell online through multiple avenues, including PriceGrabber, Amazon, Overstock and eBay. Working the Web Are you using the web to communicate with your customers? For example: Dominos Pizza allows yo8u to track your order as it is processed. The web site uses cookies so it knows what you have purchased before which makes it easy to reorder the same thing again without creating the wheel. Arby’s sends out coupons and special deals to help keep their brand on your mind and to bring you into the store. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 140 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Fat Wallet allows you to register an item and set a price point, and when the price falls to your price point, you are notified immediately so you can purchase that product for the price you want. Facts & Comments About Online Shopping: 1. According to the Journal of Electronic Commerce, research shows that the higher the level of education, income, and occupation of the head of the household, the more favorable the perception of non‐store shopping. 2. At first, the main users of online shopping were young men with a high level of income and a university education. This profile is changing. For example, in USA in the early years of Internet there were very few women users, but by 2001 women were 52.8% of the online population. 3. One third of people that shop online use a search engine to find what they are looking for and about one fourth find websites by word of mouth. 4. When an online shopper has a good first experience with a certain website, sixty percent of the time they will return to that website to buy more. 5. I Am Shocked By This ‐ About one fourth of travelers buy their plane tickets online. Only 1/4th? You’ve got to be kidding me? What do the other 3/4ths do? Stand in line at ticket counters? Purchas tickets over the phone? I can’t think of poorer use of my time or a poorer way to price shop for the best value. 6. Shopping Cart Software ‐ Most online retailers use shopping cart software to allow the consumer to accumulate multiple items and to adjust quantities, prior to completing the purchase. 7. Market Share ‐ E‐commerce product sales totaled $146.4 billion in the United States in 2006, representing about 6% of retail product sales in the country. The $18.3 billion worth of clothes sold online represented about 10% of the domestic market. 8. 24/7 Shopping ‐ Visits to a conventional retail store requires travel and must take place during business hours. Internet shoppers can shop 24 hours a day, whenever they feel the need to shop. 9. Benefits of Online Shopping ‐ Searching or browsing an online catalog can be faster than browsing the aisles of a physical store. One can avoid crowded malls resulting in long lines, and no parking. 10. Returns ‐ Some online companies have more generous return policies to compensate for the traditional advantage of physical stores. For example, the online shoe retailer Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 141 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Zappos.com includes labels for free return shipping, and does not charge a restocking fee, even for returns which are not the result of merchant error. 11. Additional Information – Most Online stores describe products with text, photos, and multimedia files. Some provide or link to supplemental product information, such as instructions, safety procedures, demonstrations, or manufacturer specifications. Some provide background information, advice, or how‐to guides designed to help consumers decide which product to buy. Some stores even allow customers to comment or rate their items. 12. Price And Selection ‐ One advantage of shopping online is being able to quickly seek out deals for items or services with many different vendors. 13. Fraud And Security Concerns ‐ Given the lack of ability to inspect merchandise before purchase, consumers are at higher risk of fraud on the part of the merchant than in a physical store. Merchants also risk fraudulent purchases using stolen credit cards or fraudulent repudiation of the online purchase. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption has generally solved the problem of credit card numbers being intercepted in transit between the consumer and the merchant. Identity theft is still a concern for consumers when hackers break into a merchant's web site and steal names, addresses and credit card numbers. A number of high‐profile break‐ins in the 2000s has prompted some U.S. states to require disclosure to consumers when this happens. Computer security has thus become a major concern for merchants and e‐commerce service providers, who deploy countermeasures such as firewalls and anti‐virus software to protect their networks. Phishing is another danger, where consumers are fooled into thinking they are dealing with a reputable retailer, when they have actually been manipulated into feeding private information to a system operated by a malicious party. 14. Assurances ‐ Quality seals can be placed on the Shop web page if it has undergone an independent assessment and meets all requirements of the company issuing the seal. The purpose of these seals is to increase the confidence of the online shoppers; the existence of many different seals, or seals unfamiliar to consumers, may foil this effort to a certain extent. 15. Downside ‐ Although the benefits of online shopping are considerable, when the process goes poorly it can create a thorny situation. A few problems that shoppers potentially face include identity theft, faulty products, and the accumulation of spy ware. Whenever you purchase a product, you are going to be required to put in your credit card information and billing/shipping address. If the website is not secure a customer’s information can be accessible to anyone who knows how to obtain it. One of the hardest areas to deal with in online shopping is the delivery of the products. Most companies offer shipping insurance in case the product is lost or damaged; however, if the buyer opts not to purchase insurance on their products, they are generally out of luck. Some shipping companies will offer refunds or compensation for the damage, but Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 142 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com it is up to their discretion if this will happen. It is important to realize that once the product leaves the hands of the seller, they have no responsibility (provided the product is what the buyer ordered and is in the specified condition). 16. Tracking Habits ‐ Many websites keep track of consumers shopping habits in order to suggest items and other websites to view. Brick‐and‐mortar stores also collect consumer information. Some ask for address and phone number at checkout, though consumers may refuse to provide it. Many larger stores use the address information encoded on consumers' credit cards (often without their knowledge) to add them to a catalog mailing list. This information is obviously not accessible to the merchant when paying in cash. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 143 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The Problems with Phone Communications Chapter 16 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 144 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The telephone is a great way to communicate in some situations, but in many situations it can be a very poor method of communicating, particularly in professional situations. Consider the following problems with a telephone call: 1. Written Record ‐ After the call there is no record of what was said. If you had sent me an e‐ mail, I could refer to that same e‐mail days or even years later to find that name, data, or information which you conveyed to me – but with a phone call, I will have no record of that data. Taking time to write up your notes is a redundant use of time. 2. Forwarding – Often, you want to convey things that were said in a phone conversation to others. This requires you to call that other person or persons and repeat everything that you want to convey. Had it been an e‐mail, you could forward the information to others in just a few seconds. 3. Interrupting – I don’t like to interrupt people, but with a phone call, you never really know whether your party will want to or have time to talk when you call them. 4. Being Interrupted – I don’t like being interrupted when I am deep in thought or entrenched in a task. Often, interruptions such as a phone call undermine my train of thought and my productivity. I do watch e‐mails displayed as received and can easily make a decision whether to respond instantly or wait until later. 5. Thoughtful Responses – Many reporters insist on interviewing me through a phone call rather than through e‐mail. Sometimes they ask complex questions and want an answer off the top of my head. Had they instead asked me those questions via e‐mail, I would have time to contemplate my response, research some facts and figures to support my response, and craft my response in the best possible light. If the reporter’s intentions are to catch me off guard to gain a poor response, then a phone call will help them achieve that goal. But if they truly want quality responses, e‐mail works better. This same concept applies to other callers as well as reporters. 6. Scheduling Calls – I’ve worked with many people who sometimes put more effort into scheduling a phone call than the actual phone call itself. In some cases it took weeks for the conversation to finally happen. With e‐mail, the parties do not have to both be available at the same time. You send me an e‐mail when you have time – I will respond when I have time. No time is wasted scheduling a phone call. 7. Accompanying Data – Often, phone conversations are weaker because one party has a report or data that is relevant to the conversation. Unfortunately there is no good way to share that report or data via a phone call. Therefore the phone call conversation relies on the one party reading, reciting or interpreting the report or data accurately for the other party. Had it been an e‐mail conversation instead, all relevant reports and data could have been attached. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 145 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 8. Ability to Hear – I sometimes have trouble hearing phone conversations. Sometimes the problem is background noise, poor cell phone reception. Other times I am a little hard of hearing or I have trouble understanding someone’s foreign accent, especially when I cannot see their lips moving. All of these problems evaporate when e‐mail instead of phone calls are the method of communication. 9. Long Winded People – Another problem I have with telephone calls is talking to long winded people who take forever to get to the point, or have no point. If they had to send me an e‐mail instead, they would not be so long winded and if they were, they would be wasting their own time, and not as much as mine. Sometimes just getting the people to hang up is a problem. Don’t get me wrong, I do believe that the telephone is a great way to communicate. I enjoy talking to my friends and family and hearing the sound of their voice and laughing at their jokes. However, when it comes to business, the telephone conversation often falls short. I am not the only one who questions the efficiency of the telephone; you might enjoy the following cartoon provide by the Oatmeal.com. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 146 High Tech Communications Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) www.CarltonCollins.com 148 Mobile Phones Chapter 17 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 1G ‐ Analog Cellular Telephony ‐ The first commercially automated cellular network (the 1G generation) was launched in Japan by NTT in 1979. The initial launch network covered the full metropolitan area of Tokyo's over 20 million inhabitants. The second launch of 1G networks was the simultaneous launch of the Nordic Mobile Telephone (NMT) system in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden in 1981. NMT was the first mobile phone network featuring international roaming. The Swedish electrical engineer Östen Mäkitalo started to work on this vision in 1966, and is considered as the father of the NMT system and some consider him also the father of the cellular phone. The first 1G network launched in the USA was Chicago based Ameritech in 1983 using the famous first hand‐held mobile phone Motorola DynaTAC. Cellular systems required several leaps of technology, including handover, which allowed a conversation to continue as a mobile phone traveled from cell to cell. 2G ‐ Digital Mobile Communication ‐ The first "modern" network technology on digital 2G (second generation) cellular technology was launched by Radiolinja (now part of Elisa Group) in 1991 in Finland on the GSM standard. The first data services appeared on mobile phones starting with person‐to‐person SMS text messaging in Finland in 1993. First trial payments using a mobile phone to pay for a Coca Cola vending machine were set in Finland in 1998. 3G ‐ Wideband Mobile Communication ‐ In 2001 the first commercial launch of 3G (Third Generation) was again in Japan by NTT DoCoMo on the WCDMA standard. These changes increased the maximum burst rate from 2.45 Mbit/s to 3.1 Mbit/s. Also included were protocols that would decrease connection establishment time (called enhanced access channel MAC), the ability for more than one mobile to share the same time slot (multi‐user packets) and the introduction of QoS flags. Further performance increases provide speeds of up to 42 Mbit/s downlink and 84 Mbit/s with Release 9 of the 3GPP standards. 4G ‐ Broadband Fourth Generation ‐ The recently released 4th generation provides broadband wireless access with nominal data rates of 100 Mbit/s to fast moving devices, and 1 Gbit/s to stationary devices. 4G systems may be based on the 3GPP LTE (Long Term Evolution) cellular standard, offering peak bit rates of 326.4 Mbit/s. It may perhaps also be based on WiMax or Flash‐OFDM wireless metropolitan area network technologies that promise broadband wireless access with speeds that reaches 233 Mbit/s for mobile users. In 2011 it is expected that more wireless companies will launch 4G Broadband networks. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 150 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Mobile phone subscribers per 100 inhabitants 1997–2007 Text Messaging ‐ The most commonly used data application on mobile phones is SMS text messaging ‐ 74% of all mobile phone users. Other Non‐SMS Data Services ‐ Led by mobile music, downloadable logos and pictures, gaming, gambling, adult entertainment and advertising (source: Informa 2007). Standardization Of Micro‐Usb Connector For Charging ‐ Starting in 2010, many mobile phone manufacturers have agreed to use the Micro‐USB connector for charging their phones. The mobile phone manufacturers who have agreed to this standard include: 1. Apple 2. LG 3. Motorola 4. Nokia 5. Research In Motion 6. Samsung 7. Sony Ericsson The new chargers are up to three times more energy‐efficient Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 151 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com than unrated chargers. Having a standard charger for all phones, means that manufacturers will no longer have to supply a charger with every new phone. (The majority of energy lost in a mobile phone charger is in its no load condition, when the mobile phone is not connected but the charger has been left plugged in and using power.) Newer Lithium‐Polymer Batteries ‐ Formerly, the most common form of mobile phone batteries were nickel metal‐hydride, as they have a low size and weight. Lithium ion batteries are sometimes used, as they are lighter and do not have the voltage depression that nickel metal‐hydride batteries do. Many mobile phone manufacturers have now switched to using lithium‐polymer batteries as opposed to the older Lithium‐Ion, the main advantages of this being even lower weight and the possibility to make the battery a shape other than strict cuboid. The Cellular Phone Market – The world's largest individual mobile operator is China Mobile with over 500 million mobile phone subscribers. The world's largest mobile operator group by subscribers is UK based Vodafone. There are over 600 mobile operators and carriers in commercial production worldwide. Over 50 mobile operators have over 10 million subscribers each, and over 150 mobile operators have at least one million subscribers by the end of 2008 (source wireless intelligence). In mobile phone handsets, in Q3/2008, Nokia was the world's largest manufacturer of mobile phones, with a global device market share of 39.4%, followed by Samsung (17.3%), Sony Ericsson (8.6%), Motorola (8.5%) and LG Electronics (7.7%). These manufacturers accounted for over 80% of all mobile phones sold at that time. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 152 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com How Secure are your Cellular Phone Calls? In December 2009, the encryption method used by most cellular phone companies was decoded and the instructions for intercepting wireless cell phone calls were published to the Internet for all to see. Many claim that your cellular phone calls were vulnerable even before this crack occurred. Exactly how secure is your cell phone? Can your cellular phone calls be intercepted by others? Do land lines offer a more secure form of communication? Should you avoid discussing sensitive information over a cellular line? This article addresses these questions and provides advice for ensuring that your cellular phone calls remain protected. How Secure Are Your Cell Phone Calls? Historically, your cell phone calls have been secure (encrypted) between your cell phone and your cellular network. However, a vulnerability typically occurs when you call another party on a different cellular network. In this situation, your cell phone call is usually encrypted and decrypted as it is passed from one network to another; therefore your calls may be vulnerable as they are transmitted between networks as illustrated below. When you place a cell phone call, your cell phone automatically encrypts the call and transmits it to your network. Your encrypted call is received by your network where it is decrypted and sent to the next network. Your decrypted call is received by the next network, encrypted and transmitted to your party. Your encrypted call is received and decrypted by your party’s cell phone. Because your cell phone call is typically un‐encrypted as it is passed from one network to another, it is potentially vulnerable as a corrupt network employee could conceivably intercept your call. (Reportedly, the cellular networks have controls in place to monitor and prevent such abuse.) Further complicating matters is the possibility that your cellular phone calls may pass through multiple network points, which is often the case when cell phone calls are made in Europe. In this situation cell phone calls are routed from one country’s network to another as they makes their way across Europe, providing multiple opportunities for a breach of privacy. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 153 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Encryption Codes Cracked Until recently, your cell phone calls have been encrypted between your cell phone and your network and your calls were considered to be safe from most of the world. This is not the case any longer. In December 2009 28‐year‐old German computer engineer Karsten Nohl announced and proved that he had cracked the encryption code used by approximately 80% of all US cell phones called the A5/1 cipher. The cracked code was published to the internet allowing virtually anyone with significant technology skills to intercept most cell phone calls. To fully understand the issue, most major networks operate under and follow the rules produced by the GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications, or originally Groupe Special Mobile). The GSM uses two cryptographic algorithms for security ‐ A5/1 and A5/2 stream ciphers. A5/1 was developed first and is a stronger algorithm used within Europe and the United States; A5/2 is weaker and used in other countries. It was widely reported that the weaker A5/2 cipher was broken in theory about ten years ago; however until December 2009, the A5/1 encryption had proven to be unbreakable. As a result, until the GSM implements new cryptographic algorithms, your cellular phone calls are considered to be potentially vulnerable throughout the entire transmission. While it is unlikely that your particular cell phone calls are being monitored by hackers due to sheer volume of world‐wide calls, it is important to understand that it is at least technically possible at this point in time. Is the Government Listening to Your Cell Phone Calls? While most people assume that the networks operate a clean ship and protect you against inside employee abuse, many people wonder if any governments might be listening in on your cellular phone calls. It is true that the government can tap your cell phone – this is accomplished at the network and is similar to the wiretap of land line telephone calls ‐ a warrant must first be issued for a cellular phone tap before the government can breach your privacy. Even more alarming to some is the notion that the US Government is listening to all of your cellular phone calls using a program called Echelon. This program was implemented several decades ago and is still in operation today. Under this program the United States government works jointly with Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom to operated the Echelon intelligence program which intercepts and inspects telephone calls, faxes, e‐mails, satellite communications, and other digital data across the globe. The program primarily resides at the fiber optic backbone switches where all electronic communications are downloaded and disseminated; which means that a software program looks for and flags communications that contain potentially threatening or illegal language. The program is intended to search for terrorist plots, drug dealers, and political intelligence. While governments have not publically admitted to listening in on cell phone calls, it is widely suspected that they are. For more information, please see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Echelon_(signals_intelligence) Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 154 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Cell Phone Hacking Tools In addition to the problems mentioned above, the hacker community is also armed with an arsenal of hacking tools designed to intercept your cell phone calls and voice email messages. Cell phone hacking became front page news in 2008 when Paris Hilton's cell phone was hacked and all her celebrity friends and their phone numbers were placed on the Internet. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qP1BOZqrp5g. Some examples of the cell phone hacking tools are listed below. 1. Roving Bug ‐ The FBI uses a hacking tool called a "roving bug," (originally approved by top U.S. Department of Justice officials for use against members of a New York organized crime family) in which the FBI can activate your cell phone’s microphone and use it to eavesdrop on nearby conversations. Here is a video clip: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjEA9gEEfpU&feature=related 2. Bluesnarfing ‐ Bluesnarfing hack tools allows a hacker to contact your cell phone without your knowledge and download your phone’s information, including pictures or video. 3. Brickhouse Sim Card Spy – There are many tools which can read deleted text messages off of a cell phone. This is because most cell phone storage cards are formatted with FAT, which means that data is not really deleted when erased, it can be retrieved. For $99 Brickhouse provides a device that will quickly display all deleted messages. For example, this could be used by a parent to determine if a child is making drug deals or having inappropriate conversations about sex. See a video clip here: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nmBzBJYkmnU&feature=player_embedded# Solutions For Protecting Your Cell Phone And Cell Phone Calls Given the current state of security surrounding the use of cellular phones, there is plenty to worry about. However, there are some measures you can take to protect your cell phone’s data and your cell phone conversations and text messages. The number one measure you can take is to use third party products to secure all of your cell phone calls. For example, British‐based CellCrypt offers software for the Nokia, BlackBerry and Windows Mobile smartphone. You will have to make a few extra clicks each time you initiate a call, but this will enable you to make secure calls over the 3G/2G or Wi‐Fi data network. This solution completely bypasses the cellular networks by using its’ own central switch. As a result, your cellular conversations are encrypted using strong Encrypted Mobile Content Protocol (EMCP). (www.CellCrypt.com) Another popular cellular phone encryption solution is Gold‐Lock 3G. This is an encryption product which the company claims is used use by government leaders, international business executives, intelligence officers, and law enforcement agencies around the world. The product works with popular cell phones (iPhone, Nokia, BB, windows Mobile, and PCs) and utilizes Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 155 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com military grade encryption algorithms which change randomly to enhance security. The encryption keys are generated automatically by your cell phone, making it easy to use. The price starts at $79 per cell phone. (www.gold‐lock.com) Other Cell Phone Security Measures In addition to encrypting your cell phone with third party products, you might also consider these additional measures: 1. Don’t assume that your cell phone calls are secure – Do not discuss confidential or sensitive issues over your cellular phone. 2. Do not leave confidential voice or text messages. 3. Use a PIN to protect your cell phone and your voicemail. 4. Be wary of texts, system messages or events on your phone that you did not initiate or expect. 5. Turn off Bluetooth feature if you don’t use it. 6. Do not leave your cell phone laying around unattended. Conclusion In conclusion, cell phone conversations and text messages have never been 100% secure, and with the recent breach of standard encryption methods, there is more cause for alarm than before. To be absolutely secure, you should consider purchasing a third party encryption program and implement additional measures to protect your cell phone from viruses, theft and breach. However perhaps the most important measure we all can take is to be careful not to share sensitive information when using your cell phone. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 156 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The Apple iPhone The iPhone is a line of Internet‐ and multimedia‐enabled smartphones designed and marketed by Apple Inc. and released in 2007. An iPhone functions as: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Mobil Phone Camera phone Text messaging Visual voicemail Portable media player (equivalent to a video iPod) Internet client (with e‐mail, web browsing, and Wi‐Fi connectivity) The user interface is built around the device's multi‐touch screen, including a virtual keyboard rather than a physical one. Third‐party applications are available from the App Store, which launched in mid‐2008 and now has well over 100,000 "apps" approved by Apple. These apps have diverse functionalities, including games, reference, GPS navigation, social networking, and advertising for television shows, films, and celebrities. Screen And Input ‐ The touchscreen is a 9 cm (3.5 in) liquid crystal display (320×480 px at 6.3 px/mm, 160 ppi, HVGA) with scratch‐resistant glass,[40] and 18‐bit color (rendering 262,144 colors). Gestures ‐ The touch and gesture features of the iPhone are based on technology originally developed by FingerWorks. The iPhone 3GS also features a fingerprint‐resistant oleophobic coating. The display responds to three sensors, as follows:\ Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 157 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 1. A proximity sensor deactivates the display and touchscreen when the device is brought near the face during a call. This is done to save battery power and to prevent inadvertent inputs from the user's face and ears. 2. An ambient light sensor adjusts the display brightness which in turn saves battery power. 3. A 3‐axis accelerometer senses the orientation of the phone and changes the screen accordingly, allowing the user to easily switch between portrait and landscape mode. Photo browsing, web browsing, and music playing support both upright and left or right widescreen orientations. GPS Tracking ‐ A software update in January 2008 allowed the first generation iPhone to use cell tower and Wi‐Fi network locations trilateration, despite lacking GPS hardware. The iPhone also has a digital compass. Switches ‐ The iPhone has three physical switches on the sides: wake/sleep, volume up and down, and ringer on and off. These are made of plastic on the original iPhone and metal on all later models. A single "Home" hardware button below the display brings up the main menu. The touchscreen furnishes the remainder of the user interface. Audio And Output ‐ One of two speakers (left) and the microphone (right) surround the dock connector on the base of the iPhone. If a headset is plugged in, sound is played through it instead. One loudspeaker is located above the screen as an earpiece, and another is located on the left side of the bottom of the unit, opposite a microphone on the bottom‐right. Volume controls are located on the left side of the unit and as a slider in the iPod application. Both speakers are used for handsfree operations and media playback. The 3.5 mm TRRS connector for the headphones is located on the top left corner of the device. The headphone socket on the original iPhone is recessed into the casing, making it incompatible with most headsets without the use of an adapter. While the iPhone is compatible with normal headphones, Apple provides a headset with additional functionality. A multipurpose button near the microphone can be used to play or pause music, skip tracks, and answer or end phone calls without touching the iPhone. The iPhone Battery ‐ The iPhone features an internal rechargeable battery. Like an iPod but unlike most other cell phones, the battery is not user‐replaceable. The iPhone can be charged when connected to a computer for syncing across the included USB to dock connector cable, similar to charging an iPod. Alternatively, a USB to AC adapter (or "wall charger," also included) can be connected to the cable to charge directly from an AC outlet. Battery Life ‐ Apple's website says that the battery life "is designed to retain up to 80% of its original capacity after 400 full charge and discharge cycles", which is comparable to iPod batteries. Apple claims that the 3GS iPhone battery can last for up to ten hours of video, nine hours of web browsing on Wi‐Fi or five on 3G, twelve hours of 2G talk time, or five on 3G, 30 hours of music, or 300 hours of standby. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 158 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Battery Criticism ‐ The battery life of the iPhone has been criticized by several technology journalists as insufficient and less than Apple's claims. This is also reflected by a J. D. Power and Associates customer satisfaction survey, which gave the "battery aspects" of the iPhone 3G its lowest rating of 2 out of 5 stars. Battery Warranty ‐ If the battery malfunctions or dies prematurely, the phone can be returned to Apple and replaced for free while still under warranty. The warranty lasts one year from purchase and can be extended to two years with AppleCare. Battery Replacement Kit ‐ Since July 2007 third party battery replacement kits have been available at a much lower price than Apple's own battery replacement program. These kits often include a small screwdriver and an instruction leaflet, but as with many newer iPod models the battery in the original iPhone has been soldered in. Therefore a soldering iron is required to install the new battery. The iPhone 3G uses a different battery fitted with a connector that is easier to replace, although replacement by any besides Apple still voids the warranty. Camera ‐ The iPhone 3GS has a 3.2 megapixel camera, manufactured by OmniVision, featuring autofocus, auto white balance, and auto macro (up to 10 cm). It is also capable of capturing 640x480 (VGA resolution) video at 30 frames per second, although compared to higher‐end CCD based video cameras it does exhibit the rolling shutter effect. The video can then be cropped on the device itself and directly uploaded to YouTube, MobileMe, or other services. The older iPhone and iPhone 3G featured a built‐in Fixed focus 2.0 megapixel camera located on the back for still digital photos. It has no optical zoom, flash or autofocus, and does not support video recording, however jailbreaking allows users to do so. Moisture Sensors ‐ Like many modern electronics devices, the iPhone has moisture sensors to indicate whether water damage has affected a device. The sensors on an iPhone include a small disc located in the headphone jack and an area near the dock connector. The sensors are often used by Apple employees to determine whether the device qualifies for a warranty repair or replacement, and if the sensors show that the device has absorbed moisture they may determine that the device is not covered. However, the moisture sensors might be "tripped" through routine use, and if a device is worn while exercising the sweat from an owner may dampen the sensors enough to indicate water damage. On many other mobile phones from different manufacturers, the moisture sensors are located in a protected location, such as beneath the battery behind a battery cover, but the sensors on an iPhone are directly exposed to the environment. This has led to criticism of the placement of the sensors, which may also be affected by steam in a bathroom or other light environmental moisture. Operating System ‐ The iPhone (and iPod Touch) run an operating system known as iPhone OS. It is based on a variant of the same Darwin operating system core that is found in Mac OS X. Also included is the "Core Animation" software component from Mac OS X v10.5 Leopard. Together with the PowerVR hardware (and on the iPhone 3GS, OpenGL ES 2.0),[4] it is Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 159 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com responsible for the interface's motion graphics. The operating system takes up less than half a GB of the device's total storage (4 to 32 GB). Like the iPod, the iPhone is managed with iTunes. Included Applications ‐ By default, the Home screen contains the following icons: Messages (SMS and MMS messaging), Calendar, Photos, Camera, YouTube, Stocks, Maps (Google Maps), Weather, Voice Memos, Notes, Clock, Calculator, Settings, iTunes (store), App Store, and (on the iPhone 3GS only) Compass. Docked at the base of the screen, four icons for Phone, Mail, Safari (Internet), and iPod (multimedia) delineate the iPhone's main purposes. Internet Connectivity ‐ By default, the iPhone will ask to join newly discovered Wi‐Fi networks and prompt for the password when required. Alternatively, it can join closed Wi‐Fi networks manually. The iPhone will automatically choose the strongest network, connecting to Wi‐Fi instead of EDGE when it is available. The iPhone 3G has a maximum download rate of 1.4 Mbps in the United States. Furthermore, files downloaded over cellular networks must be smaller than 10 MB. Safari is the iPhone's native web browser, and it displays pages similar to its Mac and Windows counterparts. Web pages may be viewed in portrait or landscape mode and supports automatic zooming by pinching together or spreading apart fingertips on the screen, or by double‐tapping text or images. The iPhone supports neither Flash nor Java. Consequently, the UK's Advertising Standards Authority adjudicated that an advertisement claiming the iPhone could access "all parts of the internet" should be withdrawn in its current form, on grounds of false advertising. MAPs ‐ The maps application can access Google Maps in map, satellite, or hybrid form. It can also generate directions between two locations, while providing optional real‐time traffic information. During the iPhone's announcement, Jobs demonstrated this feature by searching for nearby Starbucks locations and then placing a prank call to one with a single tap. Directions ‐ Support for walking directions, public transit, and street view was added in the version 2.2 software update, but no voice‐guided navigation. The iPhone 3GS can orient the map with its digital compass. YouTube ‐ Apple has also developed a separate application to view YouTube videos on the iPhone, which streams videos after encoding them using the H.264 codec. Simple weather and stock quotes applications also tap in to the Internet. Google Searches ‐ iPhone users can and do access the Internet frequently, and in a variety of places. According to Google, the iPhone generates 50 times more search requests than any other mobile handset. Nielsen found that 98% of iPhone users use data services, and 88% use the internet. Text Input ‐ The iPhone has automatic spell checking and correction, predictive word capabilities, and a dynamic dictionary that learns new words. The keyboard can predict what word the user is typing and complete it, and correct for the accidental pressing of keys near the Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 160 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com presumed desired key. The keys are somewhat larger and spaced farther apart when in landscape mode, which is supported by only a limited number of applications. E‐Mail And Text Messages ‐ The iPhone features an e‐mail program that supports HTML e‐mail, which enables the user to embed photos in an e‐mail message. PDF, Word, Excel, and Powerpoint attachments to mail messages can be viewed on the phone.Apple's MobileMe platform offers push email, which emulates the functionality of the popular BlackBerry email solution, for an annual subscription. Yahoo! offers a free push‐email service for the iPhone. IMAP (although not Push‐IMAP) and POP3 mail standards are also supported, including Microsoft Exchange and Kerio Connect. E‐Mail Syncing ‐ The iPhone will sync e‐mail account settings over from Apple's own Mail application, Microsoft Outlook, and Microsoft Entourage, or it can be manually configured on the device itself. With the correct settings, the e‐mail program can access almost any IMAP or POP3 account. Jailbreaking ‐ The iPhone's operating system is designed to only run software that has an Apple‐approved cryptographic signature. This restriction can be overcome by "jailbreaking" the phone, which involves replacing the iPhone's firmware with a slightly modified version that does not enforce the signature check. Apple, in a statement to the United States Copyright Office in response to EFF lobbying for a DMCA exception for this kind of hacking, claimed that jailbreaking the iPhone would be copyright infringement due to the necessary modification of system software. Some jailbroken phones are at risk of an iPhone worm, created by Ashley Towns, a 21‐year‐old Australian technical college student. He told an Australian media outlet that he created the virus to raise the issue of security. The virus exploits a default password in SSH of jailbroken units to rickroll users of infected devices. iPhone on Verizon – As of early 2010, the iPhone only runs on AT&T networks. However, expected in the summer of 2010, Apple iPhone’s will be available for Verizon customers. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 161 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com iPhone vs. BlackBerry vs. Droid As mobile phones continue to improve, three of the top monster cell phone’s out there are the older Blackberry, the newer iPhone, and the brand new Google Droid. Here is a brief look at these three smart phone options. Will the latest Android 2.0‐based "iPhone killer" kill the iPhone? Is the cheaper HTC Droid Eris smartphone what Apple should be concerned about? There are now six smartphones on the market that will appeal to business and professional users, each with different strengths and weaknesses, as follows: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Apple iPhone HTC Droid Eris Motorola Droid Palm Pre Research in Motion BlackBerry Bold RIM BlackBerry Storm 2 PC World’s buying advice is simple as follows: 1. f you want a mobile device that takes full advantage of Web connectivity, applications, and personal media that you can also use for business connectivity such as e‐mail and calendaring, get the iPhone, even with the inferiority of AT&T's 3G network. 2. If you're subject to high security requirements, such as for regulatory compliance, need to manage lots of devices, or just can't handle using a touch‐based screen keyboard, you want the BlackBerry Bold, which is available from several U.S. carriers. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 162 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 3. If you can't stand the thought of using the AT&T 3G network and don't need to access corporate e‐mail (outside of POP and IMAP mail servers), you want the HTC Droid Eris, which, like the Motorola Droid, is available only from Verizon Wireless. Here are problem with evaluating smartphones: 1. The WebOS‐based Palm Pre is dying as its’ sole U.S. carrier, Sprint, appears to have moved on from the Pre, now focusing on Android devices. 2. The Motorola Droid's keyboard is lacking multitouch support in its included apps. 3. The BlackBerry Storm 2’s Tapping is very slow on the screen. It's not surprising that within weeks of its release, carriers are selling it as part of two‐for‐one specials. 4. Windows Mobile devices have been out of the picture. Microsoft's long‐delayed Windows 7 Mobile remained vaporware until February 2010, but not much buzz or market share has been created since then. 5. Nokia's Symbian OS isn't in the same league as modern mobile OSes; Nokia plans to move to a new OS called Maemo someday. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 163 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Synchronization Chapter 18 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 164 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Synchronization Introduction Implementing a synchronization solution can be one of the best measures you can take to make you more productive. In effect, you can carry the equivalent of your Rolodex, calendar, and notebook with you wherever you go and eliminate the need to rerecord on your PC the information you enter on your PDA and vice versa. You generally will sync data to achieve two goals as follows: 1. You can sync data among the various computers and devices you use, or 2. You can sync data between computers and devices used by other people Syncing Examples: 1. 2. 3. 4. Sync your contacts, emails, calendar, and to do list with your hand held device. Sync your contacts, emails, calendar, and to do list with your laptop computer. Sync your contacts, emails, calendar, and to do list with your cellular phone. Sync your contacts with a master contact file maintained by your company. Hand Held Devices ‐ Let’s face it, inputting large volumes of data into a hand held device such as a Palm Pilot or iPAQ is a tedious activity; it is much easier to input this information into a desktop computer using a full keyboard and large screen. Thereafter you can use a cradle to simply sync your desktop data with your hand held device. Once configured, it is as easy as plugging in your hand held device, and today’s syncing technologies update your information automatically. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 165 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com SYNCing Products There are many syncing tools designed to keep your data in sync, a few of which are listed below: Microsoft ActiveSync Palm's HotSync Pumatech's Intellisync ActiveSync ‐ Microsoft's approach to synchronization started with H/PC Explorer, which was basically a Windows Explorer add‐on that gave desktop users access to files and data on Windows CE 1.0‐based handheld PCs (H/PCs). H/PC Explorer evolved into Windows CE Services for Windows CE 2.0 and Windows CE 2.1, then into ActiveSync for Windows CE 2.2, 3.x, and now PocketPC devices. Like HotSync, ActiveSync synchronizes data between desktop applications and Pocket PCs or other Windows CE‐based PDAs. However, ActiveSync synchronizes only with Outlook (and the older Schedule+). The screen shot below shows a successful Calendar, Contacts, and Tasks synchronization with ActiveSync 3.1. Required hardware depends on the device in question. You can use serial ports, the default for older devices; USB ports for newer devices; infrared ports; modems for dial‐up access; or Ethernet PC‐cards and CompactFlash cards for access over the corporate LAN. Microsoft doesn't provide a server‐ side synchronization product comparable to HotSync Server. The company relies on third‐party developers and solution providers to extend the enterprise features of its Pocket PCs and other mobile devices. In my experience, ActiveSync is almost as reliable as HotSync. Occasionally, however, a user's PDA will refuse to synchronize with its host PC. You can usually solve this problem by rebooting the PDA and, if necessary, restarting Windows on the host PC. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 166 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Along with the release of the new OS for PocketPCs, Windows Mobile 7.0, Microsoft is also unveiling a new and improved version of ActiveSync. According to synthetic tests the synchronization speed has increased slightly by 10‐15%. Data access speed has also skyrocketed. Even if the connection drops out, the next connection will resume the process from that point. Windows Mobile 5.0 offers users new features such as the ability to sync pictures in contacts and wirelessly sync over Bluetooth®. Users can easily sync media files, playlists and song ratings right from Windows Media Player 10 Mobile on their desktop PC, and listen to them on their mobile device. The new OS adds support for integrated hard drives, allowing users to carry several gigabytes of music or information right on their phone or PDA, and provides added support for USB 2.0, which will greatly increase file transfer speeds and synchronization of information between PCs and Windows Mobile‐based devices. End users now can take a picture from their phone and easily assign it to a contact for display not only in the Contacts application, but also in the caller ID window and e‐mail message header when that contact calls or sends e‐mail. Pictures also can be assigned on a PC in Outlook and synchronized to a user’s device. Basic synchronization settings also increased in the new version. The user can now choose contact groups for synchronization and exclude separate contacts from the process. The same is true for Calendar and Tasks. To synchronize e‐mail you can choose folders and subfolders. Fear not however, because ActiveSync 5.0 supports devices that are not running Windows Mobile 5, but new features to ActiveSync (like the media sync feature) will not be available. The era of ActiveSync 3.x is OVER. Windows Mobile 5 introduces ActiveSync 5.0 which boasts a new style and new features, but also legacy support. ActiveSync 4.0 still supports old devices, but not to the same extent of Windows Mobile 5 devices. In ActiveSync 5.0, device setup is easier, USB 2.0 is supported, music and video transfer is supported, and improved error handling is integrated into the software. If you are thinking of upgrading your handheld or are purchasing for the first time, look for models running Windows Mobile 5 and ActiveSync 5.0. Of course ActiveSync can still be synced over a Wireless connection but first the connection settings and synchronization must be achieved through a wired or serial connection for the initial setup. After partnership is established using a serial, Bluetooth, or USB connection, open the Connection Settings dialog box and check the box marked "allow network and Remote Access Service connection with this desktop computer. After closing the box, start ActiveSync on your device and tap the sync icon. If you connected to the same Wi‐fi network as your host PC, synchronization should commence. The PocketPC will disconnect after synchronization to Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 167 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com conserve battery power, but you can also alter this setting by opening the Options dialog in the Tools menu. HotSync ‐ Palm initially designed HotSync to work with Palm Desktop, Palm's personal information manager (PIM). However, Palm quickly realized that supporting third‐party desktop PIMs was crucial to convincing enterprises to accept the Pilot and its successor devices. To that end, Palm came up with conduits, a standard technology for translating data between Palm OS‐ based PDAs and various PIMs. Today, Palm's connected organizers work well out‐of‐the‐box with most desktop PIMs, including Microsoft Outlook. For enterprise users and network administrators, Palm offers Network HotSync, an application that lets users synchronize their organizers across a network connection. The application still synchronizes only between users' Palm devices and users' desktop PCs but allows this synchronization across a LAN. Palm also offers HotSync Server, a server‐based application that includes a conduit for Microsoft Exchange Server, which lets you synchronize multiple PDAs from one server. (Conduits for Lotus Notes and Actual Software's MultiMail Professional are on the way.) HotSync Server supports synchronization with a serial cradle, a wired or wireless modem, and standard RJ‐45 cabling and Palm's Ethernet Cradle to connect through the corporate LAN. In day‐to‐day use, I've found HotSync to be almost bulletproof. The only problems I've encountered with the product result from HotSync's methods for mapping fields from the PDA's built‐in databases to fields on the desktop PIM. These problems are usually minor and inconsequential. For example, the mapping process might change delimiters (e.g., quotation marks) in names. In some cases, a PDA's space limitations might cause HotSync to truncate long notes. Intellisync ‐ If your company uses Pocket PCs and a different PIM or groupware application than Outlook, your users will need a third‐party add‐on to provide synchronization. Of such products, Intellisync is the most popular. Intellisync runs on both Palm and PocketPC platforms and synchronizes with a range of PIMs and enterprise email and groupware products, including various versions of Outlook, Schedule+, and Exchange Server; Symantec's ACT!; Lotus Organizer and Lotus Notes; Novell's GroupWise; Interact Commerce's SalesLogix; and Palm Desktop Software. Intellisync's power lies in its flexibility. The product lets the user select different desktop software with which to synchronize each of the PDAs' built‐in databases. For example, you can synchronize contacts with ACT!, the calendar with Outlook, and email with Lotus Notes. Intellisync also lets the user modify how desktop application fields map to the PDA, a feature that both HotSync and ActiveSync lack. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 168 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Web Conferencing Chapter 19 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 169 How Web Conferencing Differs from Video Conferencing We have already discussed video conferencing earlier in this manual, and web conferencing is a little different in that you are constantly communicating with large groups of people, and often different people such as prospective customers. Therefore there is a class of products that cater specifically to this market. A few facts about web conferencing are presented below. 1. Types ‐ Web conferencing is typically used in three ways as follows: a. Live meetings b. Training c. Presentations via the Internet (called webinars) 2. Client Software Needed ‐ In a web conference, each participant sits at his or her own computer and is connected to other participants via the internet via a downloaded application on each of the attendees' computers or a web‐based application where the attendees access the meeting by clicking on a link distributed by e‐mail (meeting invitation) to enter the conference. 3. Webinar ‐ A webinar is a specific type of web conference. It is typically one‐way, from the speaker to the audience with limited audience interaction. 4. Webcast ‐ A recorded webinar which is later played back is often referred to as a webcast. Unlike a webinar, there is no interaction. 5. Interactive ‐ A webinar can be collaborative and include polling and question & answer sessions to allow full participation between the audience and the presenter. In some cases, the presenter may speak over a standard telephone line, while pointing out information being presented onscreen, and the audience can respond over their own telephones, speaker phones allowing the greatest comfort and convenience. There are web conferencing technologies on the market that have incorporated the use of VoIP audio technology, to allow for a completely web‐based communication. Depending upon the provider, webinars may provide hidden or anonymous participant functionality, making participants unaware of other participants in the same meeting. 6. Slide Show Presentations – Often PowerPoint or Keynote slides are presented to the audience via web conferencing while markup tools and a remote mouse pointer are used to engage the audience while the presenter discusses slide content. For example: : http://www.asaresearch.com/expo_files/frame.htm 7. Live or Streaming Video – This type of web conferencing is preferred but often difficult to achieve to high levels of satisfaction due to bandwidth issues on the part of the presenter, or the audience members. Using this technology, full motion webcam, digital video camera or multi‐media files are pushed to the audience. 8. VoIP ‐ VoIP is where real time audio communication through the computer via use of headphones and speakers; also vulnerable to bandwidth issues when engaging large groups. High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 9. Web Tours ‐ Where URLs, data from forms, cookies, scripts and session data can be pushed to other participants enabling them to be pushed though web based logons, clicks, etc. This type of feature works well when demonstrating websites where users themselves can also participate.As an example, try QuickBooks Online ‐ https://qbo.intuit.com/redir/trialperiod 10. Meeting Recording ‐ Where presentation activity is recorded on the client side or server side for later viewing and/or distribution. 11. Whiteboard with Annotation ‐ Allowing the presenter and/or attendees to highlight or mark items on the slide presentation. Or, simply draw or make notes on a blank whiteboard. 12. Text Chat ‐ For live question and answer sessions, limited to the people connected to the meeting. Text chat may be public (echo'ed to all participants) or private (between 2 participants). 13. Polls and Surveys ‐ Allows the presenter to conduct questions with multiple choice answers directed to the audience. 14. Screen sharing/desktop sharing/application sharing ‐ Where participants can view anything the presenter currently has shown on their screen. Some screen sharing applications allow for remote desktop control, allowing participants to manipulate the presenters screen, although this is not widely used. GoToMeeting is a remote meeting and desktop sharing software that enables the user to meet with other computer users, customers, clients or colleagues via the Internet in real‐time. Highlights of the GoToMeeting product are presented below: 1. Avoiding Firewall Problems ‐ With software installed on the host and client computers, transmissions are passed through highly restrictive firewalls. 2. History ‐ GoToMeeting was developed in July 2004 by Citrix Online of Santa Barbara, CA. 3. Two Editions ‐ GoToMeeting is sold in two editions ‐ Personal and Corporate. 4. GoToMeeting features ‐ In all editions include: - End‐to‐end 128‐bit Encryption - Application sharing - 24‐bit color - Multi‐monitor support for a client PC - Meeting recording and playback - Audio supports both toll based phone or conferencing via VoIP - GoToMeeting hosts up to 15 users and one organizer Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 171 High Tech Communications - www.CarltonCollins.com GoToMeeting Corporate offers up to 25 users with multiple organizer option. GoToMeeting Features are summarized below: Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 172 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The four screens below show how you use GoToMeeting, start your meeting, Invite others to attend, demonstrate and collaborate while your attendees see your screen or document. As the meeting organizer you can share either your whole screen or choose to just show a specific application. You can record your meeting sessions – including all phone and microphone audio – for future review and reuse. You can interact on the screen using the pen, highlighter, arrow and spotlight tools. Specific tools you have include the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Audio conferencing via phone and computer Full desktop sharing Specific application sharing* Recording* Invite others on the fly Instantly change presenters Transfer keyboard and mouse control Drawing tools* Multiple monitor support* Mac and PC support Chat Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 173 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Microsoft Office Live Meeting Chapter 20 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 174 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Microsoft Live Meeting Surveys show that most business professionals consider some meetings to be important, most meetings are simply a large waste of time, particularly when extensive travel is involved. In today’s world technology has changed the face of meetings from long and expensive ordeals that eat cash and rob companies of productivity, into quick and inexpensive tasks that make meetings almost as simple as a phone call. Using the internet and your computer, you can now meet with one to one thousand people from the comfort of your own desk. The software that makes this work is Microsoft Live Meeting, and it promises to be the next great technology break through that will change the way business does business. The live meeting screen is shown below. Not only does Live Meeting allow you to hold meetings without incurring heavy travel and travel expenses, but it is changing the core structure of the businesses operate. For example, not too long ago, it was common for companies to hire employees that lived locally and provide them with office space in a centralized building. This meant that either the pool for hiring talent was limited to the immediate area or that large costs would be incurred to relocate employees and their families. Today, things are different. It is now practical for companies to hire Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 175 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com employees who live thousands of miles away, and work closely with those employees using technologies such as e‐mail, remote access, and Live Meeting to make them an integral part of the organization. This means that companies can now hire from around the world in order to find the best talent at the lowest salaries. Outsourcing is one example of an industry that has risen in recent years based largely on these new technologies. While the media tends to discuss outsourcing in the context of losing American jobs, it is true that many foreign countries have outsourced jobs to the United States. The continued march of technology advancement has left millions of companies and many industries in the dust. For example, Wal‐Mart used superior supply chain technology to bury the competition and force K‐Mart, JC Penny’s and federated Department stores into bankruptcy. Internet based meetings are having a similar impact as those companies that conduct numerous small and inexpensive meetings daily are leaner and meaner than those older traditional companies that rely on expensive travel intensive, long lasting meetings that occur only periodically. Some of the highlights of Live Meeting are as follows: 1. Meet with colleagues, customers, and suppliers, no matter where you are. 2. Meet with just one person, or as many as two thousand people at the same time. 3. You can edit files together such as a Word document or excel worksheet. 4. You can collaborate on a whiteboard, drawing a diagram or laying out a critical path chart – and the whiteboard image can be captured, saved, and shared with others. 5. The entire Live Meeting event can be recorded and archived or shred with others. Record your presentation as easily as clicking the mouse, without any special equipment required. It is easy for people who missed the meeting (or class) to view recordings on‐ demand using Microsoft Windows Media Player or by downloading the recording for viewing at their convenience. You can leverage your presentation many times with full‐ quality recordings. 6. Secure Sockets Layer encryption means that your meetings are absolutely secure from prying eyes. 7. Live meeting is integrated with Outlook to make scheduling as simple as sending an e‐ mail. 8. Live Meeting leverage the full capabilities of Microsoft Office PowerPoint presentations with high‐resolution support for all types of animations and slide transitions, and enable participants to better engage by switching in or out of full‐screen view as they choose. 9. Live Meeting allows participants to share any printable document on‐the‐fly for online review or editing. With the high‐resolution viewer, participants can zoom in or zoom out without losing the quality of text and graphics. 10. Live Meeting allows participants to share control of software on your desktop without losing sight of participant feedback or text questions. 11. Meeting participants can request control, and presenters can quickly grant control to any participant. This is useful for demonstrating a complex system such as Great Plains Software to a potential purchaser. 12. Live Meeting a Question Manager that enables any of the presenters to view and respond to questions by replying to individuals or to all participants. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 176 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 13. Live Meetings interactive tools include: Real‐Time Polls, Mood Indicator, Chat, Annotations, Whiteboard, Text Slide, and Web Slide. 14. Internet Audio Broadcast enables presenters to stream audio over the Internet so participants only need the speakers on their PC to participate. 15. Live Meeting incorporates the Microsoft Office look and feel which means that this tool is very intuitive for Microsoft Office users. The presenter can even run a camera so that participants can see the presenter, including facial expressions, hand gestures, or even visual aides as shown below. Top 10 Benefits of Live Meeting According to Microsoft, Live Meeting can help you participate in meetings around the world, at a moment's notice, and at a fraction of the cost. On the Live Meeting web site, Microsoft lists the following top 10 benefits of Live Meeting. 1. Travel Less - Save time and money by meeting online and avoid all the hassles of business travel. Spend your time wisely and avoid downtime associated with getting to and from your meetings. You can meet more frequently with customers, colleagues, and business partners, thereby increasing your business output in the same amount of time. 2. Increase Productivity - Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 177 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com By conducting online meetings, online training, and online events, Live Meeting helps you save money compared to the cost of conducting business face‐to‐face. 3. Reduce Costs - 4. Easily Collaborate - All you need is a computer with an Internet connection to conduct your online meetings. Live Meeting works directly with your other business productivity applications, such as Microsoft Office and Windows Messenger. Live Meeting supports all types of online meetings, from small collaborative team meetings, to training, and even events with thousands of participants. 5. Use One Service For All Your Online Meetings – With Live Meeting, you can deliver remote presentations with the same effectiveness as being in person. With full support of Microsoft Office PowerPoint animations and transitions, and the ability to receive real‐time feedback from your audience, you can successfully get your point across without having to be in the same room. 6. Deliver Effective Online Presentations - 7. Extend Your Customer Base—Without Geographical Limits - Widen your potential client and customer base. Easily access people—no matter where they are. Reach more people, in less time. 8. Collaborate In Real Time - Share, collaborate, and discuss your projects in real time. Windows of opportunity are short, and you can’t afford to wait for everyone to be in the same place, at the same time. Make critical decisions quickly, with all the stakeholders, regardless of geography. Whether you are a company with 5 employees or 50,000 you can easily enable everyone in your organization to conduct effective online meetings. With a variety of administration tools, you can comply with corporate policies and easily manage users of the Live Meeting service. 10. Instant Meetings ‐ Live Meeting enables you to conduct your online meetings, training, and events at a moment's notice, anytime, anywhere. 9. Get Easy Administration And Deployment - Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 178 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Microsoft Office SharePoint Designer 2007 Chapter 21 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 179 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com SharePoint Designer 2010 When groups of people need to share files or information, the Internet provides the best platform of all for achieving this goal. This is often true even when only tow people are involved and when they are seat close together in the same building, but it is especially true when large numbers of people are involved and they are located in different locations. To accomplish this task, you could secure a domain name and create a web site from scratch, but this is not the best approach because you will need to build the web site pages, hyperlinks and implement security to prevent others from accessing your information. There is a better way. SharePoint provides a ready to use, Internet based project management platform. Simply add the participants who are authorized to access the site, list the tasks, and you are off and running. SharePoint then allows all participants to post their shared files to the SharePoint site, and others can check out those files like checking out a book from the library. This enables you to share files, but prevents users from working on the same file at the same time. The SharePoint system also enables users to keep track of their progress, indicate tasks that have been completed, post notes, and in general maintain all relevant information about a job or project in a centralized location for all authorized person to see. An example of this system is shown below. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 180 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com In this SharePoint web site shown above, the tasks have been set up to prepare 24 chapters on an accounting software system. You can see all the chapters listed as separate tasks, along with an indicator as to percentage complete. Below you see the home screen in which the participants are listed, the shared documents are available, the tasks to be completed are accessible, and links to relevant information is provided. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 181 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Microsoft Office Visio 2010 Chapter 22 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 182 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Visio 2010 is a diagramming program for creating business and technical diagrams that document and organize complex ideas, processes, and systems. Diagrams created in Visio 2010 enable you to visualize and communicate information clearly, concisely, and effectively in ways that text and numbers cannot. Visio 2010 also automates data visualization by synchronizing directly with data sources to provide up‐to‐date diagrams, and it can be customized to meet the needs of your organization. The Visio product is used to create business and technical diagrams to think through, organize, and better understand complex ideas, processes, and systems. Product features include: 1. The ability to assemble diagrams by dragging predefined Microsoft SmartShapes® symbols. 2. Tools designed for specific professional disciplines. 3. Generate diagrams from existing data. 4. Task‐specific templates are updated regularly from the Web. 5. Track reviewers' comments and changes to shapes and digital ink using the new review mode. 6. Publish diagrams with Save as Web Page functionality. 7. Import and export diagrams in Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) format, a new Extensible Markup Language (XML) standard for Web graphics. 8. Integrate business processes and systems by extracting data from your Visio diagrams and importing it to Access, Excel, Word 2003, SQL Server™, XML, and other formats. 9. Convert a Microsoft Outlook® calendar to a Visio calendar that can be formatted and shared with others. Following are some documents that were created using Visio. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 183 High Tech Communications Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) www.CarltonCollins.com 184 High Tech Communications Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) www.CarltonCollins.com 185 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com New in Visio 2010 – PivotDiagrams are similar to PivotTables in Excel. They allow you to work with data where you want to see groups and subtotals. An example of PivotDiagram is shown below: PivotDiagrams are great when you need to communicate the key pieces of information in your data to other people in a very visual way. It's also easy to drill into your data with PivotDiagrams and find exactly the right parts of data that you want to present. PivotDiagrams can take advantage of all of the power of Data Graphics that I've been showing you in previous posts, so you can create some graphically rich ways to show your data. To create a PivotDiagram select the PivotDiagram template in the startup screen. This triggers the Data Selector wizard that lets you choose which data source you want to connect to (PivotDiagrams are always connected to external data). PivotDiagrams can connect to Excel, Access, SQL Server, SQL Server Analysis Services, SharePoint lists, and other OLE/DB or ODBC data sources. When you select your data source, you end up with a single shape in your PivotDiagram that shows you the sum total of all of the rows in your data. Choose the totals that you want to display, and then choose how you want to break out your data into groups and subtotals. To do this you use the "Add Category" control in the task pane. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 186 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Click on one of the categories to break out the currently selected shape. In this example, I'm breaking out the totals by the different types of calls: Hardware, Software, etc: You can continue to break out subtotals; for example in the screen shot below we have selected the "Software" shape, and broken these totals out: We can also add some Data Graphics to show the data in richer, more visual ways. In the example below, the Customer Satisfaction with the different call centers can be visualized as a speedometer data bar, and we can also show a trend arrow indicating if customer sat is going up or down: We could leave the PivotDiagram like this ‐‐ it's already showing us some important information in a visual, easy‐to‐understand way. But since this information is geographically related, it Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 187 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com might be even easier to understand if we placed it on a map. This brings us to another important point about PivotDiagrams: you can easily customize the layout to better communicate the data. While they start out looking like a tree diagram, similar to an organizational chart, this is just a starting point for you to customize to suit your needs. In this case, you can simply select and delete the connectors between the shapes, drag out a U.S. map shape to the page, and place the different PivotDiagram shapes in their appropriate locations around the map: Once you end up with a graphic that you are happy with, you can save it and refresh it on a regular basis as data changes. This is an easy way to create a graphical report that can be distributed to keep people updated on current status. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 188 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 Creating Professional Presentations Chapter 23 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 189 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Introduction Communication is frequently identified as the primary key to the success of any business. All businesses must continually communicate with employees, customers, shareholders, prospects, vendors, etc. Given this premise, one should naturally ask “what tools exist to help our organization communicate better?” The answer is Microsoft PowerPoint. PowerPoint is designed to help you convey information, and it does so in a surprisingly wide variety of ways. This article will broaden your perception of PowerPoint and inform you about some of the simple but powerful features that can help you use this product more efficiently. The “Projection System Required” Myth Many people are under the wrong impression that you must use a computer and projection system to deliver a PowerPoint presentation‐ this is not the case. While PowerPoint is ideally suited for a computer projection system, there are many ways in which you can deliver a PowerPoint slide show without the use of a projection system, as follows: Printed Pages – PowerPoint slide shows can be printed to paper with your choice of 1, 2, 4, 6 or 9 slides per page. If desired, you can suppress the slide show background to make the slides more readable, especially when printed on a black and white printer. Assuming duplex printing (2‐sided page printing), you could print a 36‐page PowerPoint slide show on just 2 pieces of paper (using 9 slides per page). This would allow you to provide handouts to all meeting participants, hence they will not have to frantically take notes to capture the content of your slide show. Printing 9 slides per page Transparencies ‐ PowerPoint slide shows can be printed to transparencies, which can then be used on an overhead projector. Of course transparencies can be printed in black and white or color. This approach allows you to use a simple overhead projector to deliver your presentation, a low tech approach that may offer less risk compared to using a laptop and computer projection system. Such a solution might be preferable for Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 190 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com travelers who prefer to leave their laptop computers at the home or for use as a backup delivery method. Publish As a Web Page – PowerPoint slide shows can be published to the web instantly using the built‐in web publishing wizard. This option allows you to make your PowerPoint slide show instantly available to your meeting group, as well as the rest of the world. A key benefit of this approach is that your complete slide show, including animations and sound will automatically work on the published web site. Packaged for CD ‐ The Packaged for CD wizard will package your PowerPoint presentation to run on another computer, including linked files, animations, TrueType fonts, etc. You can also choose to include the Microsoft PowerPoint Viewer which will allow the Packaged for CD file to run on a computer that doesn't have Microsoft PowerPoint installed. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 191 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com E‐Mail – Of course we should not overlook the fact that PowerPoint slide shows can be e‐mailed directly to a recipient, or group of recipients. PowerPoint provides this capability from the File menu as shown below. Advancing Slides Tip When delivering a PowerPoint presentation, you already know the left mouse button will advance the slide show with each left mouse click. However, as a default, the right mouse button pops up a menu, rather than displaying the previous slide. This can result in an awkward moment in the presentation when the presenter truly wants to slip back to the previous slide. Instead of fumbling with this dialog box, I find it is better to set the presentation to display the previous screen on right mouse click. To do this, in the Tools menu, select Options, select the View tab, and clear the Popup menu on right mouse click box as shown below. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 192 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Controlling the Master Slide PowerPoint provides a slide master page which allows you to set up the background, fonts, and formats to be used for every page throughout your slide show. Setting up the slide master page first makes it easier to then position your text and objects in an attractive manner as you create your presentation. The slide master page is accessed under the View menu. In the sample screen below, you can see I have inserted a washed‐out image of myself as part of the background—this image will now appear on all slides. Custom Animations By selecting the Slide Show menu and clicking on Custom Animation, you can create motion paths that cause text and pictures to move across the screen. However, a rather professional effect can be achieved by using a motion path on an object larger than your slide, such as a photograph. In the example presented in Figure 1.3, I have inserted a picture of clouds which is larger than the slide, and applied an animation in which this image crawls slowly across the screen. When displayed, the text remains stationary as the background image seems to slowly float by. This illusion makes this slide play more like a movie and results in an interesting affect. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 193 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Recording Narration Once you have completed your PowerPoint presentation, you can run the slide show on your computer and use a microphone to record your comments, advancing the slides as you speak. The resulting product is a self‐running slide show, complete with your voice embedded in the presentation. This file can then be sent to others who can view the slide show and hear your voice walk them through the various slides. To use this feature, in the Slide Show menu, click Record Narration. As you speak, your voice is saved as a sound clip which is associated with each slide—you can re‐record any individual slide's narration as needed. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 194 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Custom Shows You can create different versions of your PowerPoint presentation, and save them as "custom shows." For example, the screen below shows how I pared down my primary PowerPoint presentation, which runs 90 minutes in length, to create a custom 10‐minute version of this presentation using only five slides. With this approach, I can maintain multiple versions of my presentation, but I need only update a given slide once to have those updates automatically reflected in all of my custom shows. In the Slide Show menu, click Custom Shows to take advantage of this option. Conclusion PowerPoint can help you develop, organize and present information. I find that developing materials in PowerPoint can be five times faster than developing materials in my word processor. Why? Because PowerPoint invites you to develop your material using bullets, lists, charts, and pictures whereas your word processor begs for complete paragraphs including introductory and conclusion sentences. With a word processor you end up writing more, reviewing more, and then summarizing more in order to deliver your presentation. PowerPoint also helps you organize your presentation. Once the data is assembled, you can reorganize slides by simply clicking and dragging them to a new position. You can even lasso multiple slides and move them with one drag of the mouse. This type of organization is much more difficult to accomplish in a word processing environment. PowerPoint also helps you deliver a presentation because the slides act as your lecture notes. These notes keep you on course. Audience participants whose minds naturally drift away can use the slides to catch up to you in your presentation. Presenters who have a natural fear of speaking in public are comforted somewhat because PowerPoint draws the audience’s eyes more toward the screen, and away from the presenter. In this manner, the reluctant presenter Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 195 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com does not feel quite as nervous. PowerPoint is also a great platform for presenting pictures and charts which plays into the old adage that a picture is worth a thousand words. Of course, death by PowerPoint is an all‐too‐frequent occurrence at many conferences, and presenters should be mindful to avoid boring their audience to tears with dozens of slides. Presenters should also avoid building slides which contain complete sentences because this often results in the presenter simply “reading” the slides to the audience – a situation which always comes across negatively. As a general rule, use one PowerPoint slide for every five minutes of lecture. In conclusion, PowerPoint is a great tool which helps you deliver information. As we have learned, PowerPoint is not only good for live presentations, but it also is useful for developing and delivering presentations through e‐mail, the web and even the printed page. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 196 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The Amazon Kindle Chapter 24 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 197 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The Amazon Kindle is a convenient, portable reading device with the ability to wirelessly download books, blogs, magazines, and newspapers. Just over 1/3 of an inch, as thin as most magazines, and weighing in at 10.2 ounces, you can wirelessly download books in under 60 seconds ‐ no PC required. There are no annual contracts, no monthly fees, and no hunting for Wi‐Fi hotspots because the Kindle has built in cell phone that does tall the work. The Kindle reads like real paper without glare, even in bright sunlight and holds up to 1,500 books. The battery life between charging is about 4 days. The Kindle can also display PDF documents natively. And has a Text‐to‐Speech feature so the Kindle can read newspapers, magazines, blogs, and books out loud to you, unless the book's rights holder made the feature unavailable. Over 450,000 books are available including 101 of 112 New York Times® Best Sellers, plus U.S. and international newspapers, magazines, and blogs. Additionally, over 1.8 million free, out‐of‐ copyright, pre‐1923 books are available to read on Kindle, including titles such as The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes, Pride and Prejudice, and Treasure Island. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 198 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Wireless Networking & Internet Hotspots Chapter 25 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 199 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The Electromagnetic Spectrum Generally, Electromagnetic radiation is classified by wavelength into radio wave, microwave, infrared, the visible region we perceive as light, ultraviolet, X‐rays and gamma rays. The behavior of EM radiation depends on its wavelength. When EM radiation interacts with single atoms and molecules, its behavior also depends on the amount of energy per quantum (photon) it carries. Fancy Talk & Impressive Formula ‐ EM waves are typically described by any of the following three physical properties: the frequency f, wavelength λ, or photon energy E. Wavelength is inversely proportional to the wave frequency, so gamma rays have very short wavelengths that are fractions of the size of atoms, whereas wavelengths can be as long as the universe. Photon energy is directly proportional to the wave frequency, so gamma rays have the highest energy (around a billion electron volts) and radio waves have very low energy (around femto electron volts). These relations are illustrated by the following equations: where: c = 299,792,458 m/s is the speed of light in vacuum and h = 6.62606896(33)×10−34 J s = 4.13566733(10)×10−15 eV s is Planck's constant. Electromagnetic radiation interacts with matter in different ways in different parts of the spectrum. The types of interaction can be so different that it seems to be justified to refer to Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 200 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com different types of radiation. At the same time, there is a continuum containing all these "different kinds" of electromagnetic radiation. Thus we refer to a spectrum, but divide it up based on the different interactions with matter. Region Of The Spectrum Main Interactions With Matter Radio Collective oscillation of charge carriers in bulk material (plasma oscillation). Microwave ‐ far infrared Plasma oscillation, molecular rotation Near infrared Molecular vibration, plasma oscillation (in metals only) Visible Ultraviolet X‐rays Gamma rays High energy gamma rays Molecular electron excitation (including pigment molecules found in the human retina), plasma oscillations (in metals only) Excitation of molecular and atomic valence electrons, including ejection of the electrons (photoelectric effect) Excitation and ejection of core atomic electrons, Compton scattering (for low atomic numbers) Energetic ejection of core electrons in heavy elements, Compton scattering (for all atomic numbers), excitation of atomic nuclei, including dissociation of nuclei Creation of particle‐antiparticle pairs. At very high energies a single photon can create a shower of high energy particles and antiparticles upon interaction with matter. While not technically accurate, it helps to visualize communications this way: Electrons vibrate more slowly at one end of the EM spectrum, and faster at the other end of the EM spectrum. When you speak through a cell phone to a person in New Zealand, your voice is converted into digital signal which is then carried to New Zealand by atoms vibrating at the same speed. Each vibrating electron affects the adjacent electron with the same digital signal, and so on, and so on all the way around the world. This happens eloquently like the silver balls in the Newton’s Cradle pictured below. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 201 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The Electromagnetic Spectrum http://www.ntia.doc.gov/osmhome/allochrt.pdf Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 202 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Wi‐Fi ‐ MIMO and N Wireless technology has become the de facto networking standard, from hotspots to homes, even small businesses are beginning to reap the benefits of low installation costs and convenient fast throughput. While any Wi‐Fi connection, even a weak one, is adequate to surf the Internet and transfer data, if distance and obstacles sap too much bandwidth from a network, high volume or streaming content such as video can begin to break up or degrade. With the growing popularity of home theatre personal computers (HTPCs), Personal Video Recorders (PVRs) such as Tivo, and voice over internet protocol (VOIP), and other bandwidth intensive applications, the need for a long range stable wireless standard is more apparent than ever. One technology that has delivered greater range and faster more reliable throughput is an innovation called MIMO, short for multiple input, multiple output. This new technology was originally referred to initially as Pre‐N, and later as DRAFT‐N and now as “N” or “MIMO”. It uses a number of antennas to overlay the signals of two or more Wireless‐G compatible radios, MIMO effectively increases the wireless data rate from 54 Mbit/s to 600 Mbit/s with the use of four spatial streams at a channel width of 40 MHz. MIMO overcomes the weaknesses of other wireless networking technologies that are confused by signal reflections, instead using reflections to increase the range and reduce "dead spots" in the coverage area. The stronger signal allows for wireless connections up to 3 times farther than standard than those possible with regular G networks. Additionally, by utilizing the reflected signal, MIMO can also hypothetically increase throughput about 8x more than regular G. MIMO routers avoid interference by dynamically switching to the clearest channel available. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 203 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com MIMO technology uses multiple antennas to resolve more information than possible using a single antenna. One way it provides this is through Spatial Division Multiplexing (SDM). SDM spatially multiplexes multiple independent data streams, transferred simultaneously within one spectral channel of bandwidth. MIMO SDM can significantly increase data throughput as the number of resolved spatial data streams is increased. Each spatial stream requires a discrete antenna at both the transmitter and the receiver. In addition, MIMO technology Diagram of proposed speed increase using a Netgear requires a separate radio frequency chain and analog‐ WIMAX WPN824 router with Smart MIMO technology to‐digital converter for each MIMO antenna which translates to higher implementation costs compared to non‐MIMO systems. 40 MHz channels is another feature incorporated into 802.11n which doubles the channel width from 20 MHz in previous 802.11 PHYs to transmit data. It can be enabled in the 5 GHz mode, or within the 2.4 GHz if there is knowledge that it will not interfere with any other 802.11 or non‐802.11 (such as Bluetooth) system using those same frequencies. WiMAX Linksys WRT300N WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) is a telecommunications technology that provides fixed and fully mobile internet access. The technology provides up to 30 Mbps in real world end‐user throughput. WiMAX is based on the IEEE 802.16 standard (also called Broadband Wireless Access). WiMAX offers an acceptable alternative to cable and DSL. Because of it’s ability to span long distances up to 34 miles and deliver data at 1 gigabit per second, WiMAX is dramatically superior to the previous wireless standards such as “a”, “b”, “g”, and even “n”. On May 7, 2008, Sprint, Nextel, Google, Intel, Comcast, Bright House, and Time Warner announced a pooling of an average of 120 MHz of spectrum and merged with Clearwire to form a company called “Clear”. The new company hopes to leverage this technology along with their combined services offerings to springboard past their competitors. The cable companies will provide media services to other partners while gaining access to the wireless network as a Mobile virtual network operator to provide triple‐play services. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 204 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com The Basics ‐ What is Wi‐Fi? Wireless Fidelity hardware uses radio technology in the 2.4GHz or 5GHz range. Wi‐Fi technology currently supports three main standards called 802.11a, b, and g, each with varying degrees of compatibility and connectivity. Wireless Frequency Standard 802.11a 802.11b 802.11g Super G G standard using dual channels 802.11n 5GHz 2.4GHz 2.4GHz 2.4GHz 802.16e 802.16m Bluetooth‐ Typically used to connect cellular phones and wireless headsets Range/ Interference short range, easily obstructed long range, high signal integrity long range, high signal integrity long range, greater vulnerability to interference due to using greater amount of available spectrum 2.4GHz or Long range 5.0 GHz 10 GHz to long range, covering 18 to 34 66 GHz miles and 2GHz to 11GHz 2.45GHz No native support for IP, so it does not support TCP/IP and wireless LAN applications well. Not originally created to support wireless LANs. Best suited for connecting PDAs, cell phones and PCs in short intervals. Maximum Possible Throughput 54Mbps 11Mbps 54Mbps 108Mbps Only possible with other Super G devices 300 Mbps 1,000 Mbps 2 Mbps Backward compatibility ‐ When 802.11g was released to share the band with existing 802.11b devices, it provided ways of ensuring coexistence between the legacy and the new devices. 802.11n extends the coexistence management to protect its transmissions from legacy devices, which include 802.11g, 802.11b and 802.11a. Access Points ‐ A Wi‐Fi hotspot is created by installing an access point to an internet connection. The access point transmits a wireless signal over a short distance — typically covering around 300 feet. When a Wi‐Fi –enabled device, such as a Pocket PC, encounters a hotspot, the device can then connect to that network wirelessly. Most hotspots are located in places that are readily accessible to the public, like airports, coffee shops, hotels, book stores and campus environments. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 205 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Where can I find a Wi‐Fi hotspot? Other than ISP and hotspot provider websites, users can locate hotspots using the internet prior to traveling. www.WiFreespot.com and www.Wifinder.com both feature databases of active hotspots. Wi‐Fi internet access costs vary depending on the Wi‐Fi service provider and the access plan type, typically daily, monthly, or hourly. Like a public hotspot, homes and businesses can support a Wi‐Fi network by adding a wireless access point and equipping the PCs and networked devices with wireless network adapters or WLAN cards. Equipment needed for Home or Office Wi‐Fi network 1) Access Points – Many companies offer wireless routers that perform all the functions of an access point and with the additional security of an integrated firewall. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 206 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 2) Wlan Cards And Adapters – For desktop computers, notebooks and PDAs without integrated Wi‐Fi, the addition of a wireless adapter is a simple and convenient way to enable wireless connectivity on your device. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 207 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Wireless Security The use of a wireless device provides an invisible access point into your computer network in a range up to 300 feet radius from your wireless device. Hackers use empty tennis ball cans to build devices designed to detect and boost your signal, like the device shown below. Many users setting up wireless home and small office networks rush through the job to get their Internet connectivity working as quickly as possible, but the fail to take the additional measures needed to properly lock down this new access point. The recommendations below summarize the steps you should take to improve the security of your home wireless network. 1. Change Default Administrator Passwords (and Usernames) – The first order of business is to log into your wireless device settings and change the default username and password. The default login name and password is usually “admin” and “password” – and all of the hackers out there know this. Therefore you should change these settings immediately. Here’s how: a. First, you must be connected to the wireless device with a physical wire (such as an Ethernet cable), you sometimes cannot do this wirelessly. b. Log In to the Network Router by typing the following into your browser: HTTP://192.168.0.1 or whatever IP address is printed on the bottom of the wireless device, if different. c. Navigate the menu to the Router's Change Password Page. d. Choose and Enter a New Password. e. Save the New Password. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 208 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 2. Turn on WPA2 or WPA Encryption ‐ All Wi‐Fi equipment supports some form of encryption scheme as follows: a. WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) – Found to have serious shortcomings in 2001. b. WEP 2 – Also, found deficient, WEP2 mutated into TKIP. c. WEPplus – Lucent’s attempt to correct WEP shortcomings, but this fell short. d. Dynamic WEP – 3COM’s attempt to correct WEP shortcomings which fell short. e. WPA (Wi‐Fi Protected Access) ‐ the answer to WEP. f. WPA2.0 – Better than WPA, but does not always work with older devices. g. WPAPSK‐TKIP – Software driven h. WPA2PSK‐AES – Hardware driven i. WPA2PSK‐TKIP – Software driven Encryption technology scrambles messages sent over wireless networks so that they cannot be easily read. Several encryption technologies exist for Wi‐Fi today. Naturally you will want to pick the strongest form of encryption that works with your wireless network. However, the way these technologies work, all Wi‐Fi devices on your network must share the identical encryption settings. Therefore you may need to find a "lowest common denominator" setting. Here’s how you set up WPA: j. First, verify that each computer is running Windows XP Service Pack 1 (SP1) or later. k. On each computer, verify that the client's network adapter is compatible with the Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) service. (To do this, consult the adapter's product documentation, manufacturer's Web site, or appropriate customer Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 209 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com service line for details. Upgrade the network adapter driver and configuration software to support WZC on clients where needed). l. For each computer, download and install the Windows XP Support Patch for Wi‐Fi Protected Access, walk through the installation dialog boxes and following the instructions. m. Continue following the instructions and configure all Wireless Access Points (your wireless devices). n. Continue following the instructions and configure all Wireless Network Adapters (your LAN cards). 3. Change the Default SSID ‐ Access points and routers all use a network name called the SSID. Manufacturers normally ship their products with the same SSID set. For example, the SSID for Linksys devices is normally "linksys." True, knowing the SSID does not by itself allow your neighbors to break into your network, but it is a start. More importantly, when someone finds a default SSID, they see it is a poorly configured network and are much more likely to attack it. Change the default SSID immediately when configuring wireless security on your network. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 210 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com a. b. c. d. Log In to the Network Router Navigate to the Router's Basic Wireless Settings Page Choose and Enter a New SSID Save the New SSID 4. Enable MAC Address Filtering ‐ Each piece of Wi‐Fi gear possesses a unique identifier called the physical address or MAC address. Routers keep track of the MAC addresses of all devices that connect to them. Many routers offer the owner an option to key in the MAC addresses of their home or small business equipment which restricts network connections to those devices only. Here’s how: a. To set up MAC address filtering, first prepare a list of computers and devices that will be allowed to join the network. b. Next, obtain the MAC addresses of each computer or device from its operating system or configuration utility. c. Next enter those addresses into a configuration screen of the wireless router. An example screen is shown below. d. Finally, switch on the filtering option. e. Once enabled, whenever the wireless router receives a request to join with the WLAN, it compares the MAC address of that client against the administrator's Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 211 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com list. Clients on the list authenticate as normal; clients not on the list are denied any access to the WLAN. (While this feature represents yet another obstacle/deterrent to hackers, there are many software programs available that enable hackers to defeat this measure by easily faking a MAC addresses.) 5. Disable SSID Broadcast ‐ In Wi‐Fi networking, the wireless router typically broadcasts the network name (SSID) over the air at regular intervals. This feature was designed for businesses and mobile hotspots where Wi‐Fi clients may roam in and out of range. In the home or small business, this roaming feature is probably unnecessary, and it increases the likelihood someone will try to log in to your home network. Fortunately, most Wi‐Fi access points allow the SSID broadcast feature to be disabled by the network administrator. To do this simply log into your wireless router device, navigate to the SSID menu, and click the disable button as shown below. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 212 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 6. Do Not Auto‐Connect to Open Wi‐Fi Networks ‐ Connecting to an open Wi‐Fi network such as a free wireless hotspot or your neighbor's router exposes your computer to security risks. Although not normally enabled, most computers have a setting available allowing these connections to happen automatically without notifying you (the user). This setting should not be enabled except in temporary situations. Here’s how: a. To verify whether automatic Wi‐Fi connections are allowed, open Control Panel. b. Click the "Network Connections" option if it exists (otherwise first click "Network and Internet Connections" and then click "Network Connections.") c. Right‐click "Wireless Network Connection" and choose "Properties." d. Click the "Wireless Networks" tab on the Properties page. e. Click the "Advanced" button. f. Find the "Automatically connect to non‐preferred networks" setting. If checked, this setting is enabled, otherwise it is disabled. 7. Assign Static IP Addresses to Devices ‐ Most home and small business networks use dynamic IP addresses because DHCP technology is easy to set up and use. Unfortunately, this convenience works to the advantage of network attackers, who can then obtain valid IP addresses from your network's DHCP pool. To be more secure, you may want to turn off DHCP on the router, set a fixed IP address range instead, then configure each connected device to match. Use a private IP address range (like 12.12.12.x) to prevent computers from being directly reached from the Internet. The specific procedures to follow will vary on the devices you are using, therefore you should refer to the user manual or web for detailed instructions for each device you have on your network. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 213 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com 8. Enable Firewalls On Each Computer and the Router – Wireless routers contain built‐in firewall capability, but the option also exists to disable them. Ensure that your router's firewall is turned on. For extra protection, consider installing and running personal firewall software on each computer connected to the router. To do this simply log into your wireless router device, navigate to the Firewall menu, and click the Enable button as shown below. 9. Position the Router or Access Point Safely ‐ Wi‐Fi signals normally reach beyond the walls of a home or small office. A small amount of signal leakage outdoors is not a problem, but the further this signal reaches, the easier it is for others to detect and exploit. Wi‐Fi signals often reach through neighboring homes and into streets, for example. When installing a wireless home network, the position of the access point or router determines its reach. Try to position these devices near the center of the home rather than near windows to minimize leakage. 10. Turn Off the Network During Extended Periods of Non‐Use ‐ The ultimate in wireless security measures, shutting down your network will most certainly prevent outside hackers from breaking in! While impractical to turn off and on the devices frequently, at least consider doing so during travel or extended periods offline. Computer disk drives have been known to suffer from power cycle wear‐and‐tear, but this is a secondary concern for broadband modems and routers. If you own a wireless router but are only using it wired (Ethernet) connections, you can also sometimes turn off Wi‐Fi on a broadband router without powering down the entire network. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 214 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Speech Recognition Chapter 26 Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 215 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Speech Recognition Speech recognition converts spoken words to text. Speech recognition applications include: 1. 2. 3. 4. Voice dialing (e.g., "Call home"), Call routing (e.g., "I would like to make a collect call"), Simple data entry (e.g., entering a credit card number), Speech‐to‐text processing (e.g., word processors or emails) The first speech recognizer appeared in 1952 and consisted of a device for the recognition of single spoken digits [1] Another early device was the IBM Shoebox, exhibited at the 1964 New York World's Fair. Windows Speech Recognition Windows Speech Recognition is a speech recognition application included in Windows Vista and more recently, Windows 7. Windows Speech Recognition allows the user to control the computer by giving specific voice commands. The program can also be used for the dictation of text so that the user can control their Vista or Windows 7 computer. Windows Speech Recognition relies on Microsoft SAPI version 5.3 (included in Windows Vista) to function. The application also utilizes Microsoft Speech Recognizer 8.0 for Windows as its speech profile engine. To use Speech Recognition, the first thing you need to do is set it up on your computer. To learn how to do that, see Set up Speech Recognition. When you're ready to use Speech Recognition, you need to speak in simple, short commands. The tables below include some of the more commonly used commands. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 216 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Microsoft Narrator Windows 7 Narrator is a light‐duty screen reader utility included in Microsoft Windows. Narrator reads dialog boxes and window controls in a number of the more basic applications for Windows. While Microsoft recommends that the visually impaired purchase a full‐function screen reader for general computer use, Narrator is a significant piece of software for a number of reasons. Narrator is included with every copy of Microsoft Windows, providing a measure of access to Windows without the need to install additional software as long as the computer in use includes a sound card and speakers or headphones. Narrator can assist a blind person in installing a full‐function screen reader, assisting the user until his/her screen reader of choice is up and running. As well, because Narrator is a lightweight screen reader that requires minimal "hooks" into the operating system, Narrator can provide speech when a full‐function screen reader might be unable to do so such as during the process of updating hardware drivers. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 217 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com J. Carlton Collins, CPA ASA Research [email protected] 770.734.0950 J. Carlton Collins, CPA is a Certified Public Accountant with experience in technology, tax, auditing, accounting systems, financial reporting, and bond financing. He is an author, lecturer, and technology & accounting systems consultant. He has published more than two dozen books, two hundred articles, and thousands of web pages. As a public speaker, Mr. Collins has delivered more than 2,000 lectures in 44 states and 5 countries addressing more than 500,000 business professionals, including numerous keynote lectures at national and international conferences. Key awards include: "AICPA Lifetime Achievement Award", "Tom Radcliffe Outstanding Discussion Leader Award", "GSCPA Outstanding Discussion Leader Award", and "Accounting Technologies' Top Ten CPA Technologists Award". As a consultant, Mr. Collins has assisted 275+ large and small companies with the selection and implementation of accounting systems. Mr. Collins has a Bachelors degree in Accounting from the University of Georgia, is a 26 year member of the AICPA and the Georgia Society of CPAs, and is also a licensed realtor. At the University of Georgia Mr. Collins was elected President of the Phi Eta Sigma Honor Society, was initiated into the BIFTAD Honor Society, was a member of Alpha Tau Omega fraternity, and served three years in the Judicial Defender/Advocate program. At Glynn Academy High School Mr. Collins was Senior Class President, Class Valedictorian, and received a principle nomination to Annapolis Naval Academy. Mr. Collins has been married for 25 years and has two children. He devotes his leisure time to family, travel, tennis, fishing, snow skiing, and riding motorcycles (dirt and street). Mr. Collins is president of his home owners association, participates in the Gwinnett Clean and Beautiful program, and volunteers for Cooperative Ministries food drive. Selected Positions, Awards & Accomplishments: 1. 2008 and 2009 Chairman of the Southeast Accounting Show ‐ the south's largest CPA event. 2. Recipient of the 2008 Tom Radcliff Outstanding Discussion Leader Award. 3. Named “Top Ten CPA Technologists” by Accounting Technologies Magazine; Named “Top 100 Most Influential CPAs ” by Accounting Technologies Magazine in multiple years. 4. Has personally delivered over 1,500 technology lectures around the world. 5. Has published 80+ pages of accounting software articles in the Journal of Accountancy. 6. Recipient of the AICPA Lifetime Technical Contribution to the CPA Profession Award. 7. Recipient of the Outstanding Discussion Leader Award from the Georgia Society of CPAs. 8. Lead author for PPC's Guide to Installing Microcomputer Accounting Systems. 9. Has installed accounting systems for more than 200 companies. 10. Past Chairperson of the AICPA Technology Conference. 11. Has delivered keynote and session lectures at dozens of accounting software conferences including seven Microsoft Partner Conferences, five Sage Conferences, and multiple conferences for Epicor, Open Systems, Exact Software, Sage ACCPAC ERP, Dynamics.NAV, Dynamics. AX, SouthWare, Axapta . 12. Has provided consulting services to many computer companies (including Compaq, IBM, Microsoft, Apple, Novell, Peachtree, Epicor, Sage Software, Exact, ACCPAC, Intuit, Peachtree, Great Plains, and others). As an auditor Mr. Collins has audited businesses in the areas of health care, construction, distribution, automobile dealerships, insurance, manufacturing, and general business. Mr. Collins' tax experience includes corporate, individual, partnership, fiduciary, and estate tax planning work. In the area of finance, Mr. Collins has prepared feasibility studies and financial forecasts for nearly 300 projects seeking more than $3 billion in startup capital, including field work for 80 of those projects. Mr. Collins is familiar with bond issues, Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement, and conventional financing matters. As a consultant, Mr. Collins worked with the entire Microsoft Excel development team contributing more than 500 pages of design improvements ‐ many of which are found in Excel today. Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 218 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 219 High Tech Communications www.CarltonCollins.com High Tech Communications for CPAs Copyright April 2010, J. Carlton Collins, CPA (all rights reserved) 220