Download AlvariSTAR User Manual
Transcript
AlvariSTAR
User Manual
SW Version 4.7
June 2010
P/N 215668
Document History
Document History
Topic
Description
Date Issued
Version 4.0 is regarded as the first publication.
December 2008
Single platform for NMS and Local
CRAFT Utility
The manual covers both AlvariSTAR and
AlvariCRAFT. Unless otherwise stated, The
features are applicable to both applications.
Version 4.1, March 2009
Password Policy
New feature enabling to set a policy for all
passwords.
Version 4.1, March 2009
Watchdog
External application for monitoring the NMS
server, LDAP and database servers
Version 4.1, March 2009
Context Menus
New approach in accessing most of the
functions via right click menus instead of
buttons.
Version 4.5, September
2009
Dynamic Column Selection
Ability to select which columns are displayed
in tables and to pack columns in order to fit
into the available space.
Version 4.5, September
2009
Filters
Enhanced Filter Criteria Manager now allows
aggregating multiple selection criteria within
the same filter and using negated selection
criteria.
Version 4.5, September
2009
File Manager
New manager for handling files stored in the
database.
Version 4.5, September
2009
View Filters
Quickly switch between various types of
equipment that are displayed in the
Equipment Manager and the various types of
files that are displayed in the File Manager.
Version 4.5, September
2009
Summaries
Real time summary counts at the bottom of
the Equipment Manager and File Manager.
Version 4.5, September
2009
Task Creation
New wizard transforms task creation into a 3
step process.
Version 4.5, September
2009
Remote Access
Web Portal for launching any application in
StarSuite and ability to access the AlvariSTAR
server via the Java Web Start software
framework.
Version 4.5, September
2009
The Equipment Manager
Updated
Version 4.5,
October 2009
The Unified (All Network Elements)
View
Column structure updates
Version 4.7, June 2010
The Equipment Editor
Column structure updates
Version 4.7, June 2010
AlvariSTAR
ii
User Manual
Document History
Topic
Description
Date Issued
Discovery Settings Manager
Restructured
Version 4.7, June 2010
NBI Notifications Global Settings
New feature
Version 4.7, June 2010
Discovery Task
Renamed Range Discovery Task. Added
SNMP versions: v1, v2c, v3.
Version 4.7, June 2010
External Entities Mapping
New feature
Version 4.7, June 2010
User Domain Manager
New feature
Version 4.7, June 2010
Configuration Management
New chapter
Version 4.7, June 2010
Appendix C
New appendix describing how to connect the
NMS to an external LDAP server
Version 4.7, June 2010
Appendix D
New appendix describing how to use Google
Earth to view the network’s topography
Version 4.7, June 2010
Appendix E
New appendix describing SNMP version
compatibility for each supported device
Version 4.7, June 2010
AlvariSTAR
iii
User Manual
Legal Rights
Legal Rights
© Copyright 2010 Alvarion Ltd. All rights reserved.
The material contained herein is proprietary, privileged, and confidential and
owned by Alvarion or its third party licensors. No disclosure thereof shall be made
to third parties without the express written permission of Alvarion Ltd.
Alvarion Ltd. reserves the right to alter the equipment specifications and
descriptions in this publication without prior notice. No part of this publication
shall be deemed to be part of any contract or warranty unless specifically
incorporated by reference into such contract or warranty.
Trade Names
Alvarion®, BreezeCOM®, WALKair®, WALKnet®, BreezeNET®, BreezeACCESS®,
BreezeLINK®, BreezeMAX®, BreezeLITE®, BreezePHONE®, 4Motion® and/or other
products and/or services referenced here in are either registered trademarks,
trademarks or service marks of Alvarion Ltd.
All other names are or may be the trademarks of their respective owners.
"WiMAX Forum" is a registered trademark of the WiMAX Forum. "WiMAX," the
WiMAX Forum logo, "WiMAX Forum Certified,"and the WiMAX Forum Certified
logo are trademarks of the WiMAX Forum.
Statement of Conditions
The information contained in this manual is subject to change without notice.
Alvarion Ltd. shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or
consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of
this manual or equipment supplied with it.
Warranties and Disclaimers
All Alvarion Ltd. (“Alvarion”) products purchased from Alvarion or through any of
Alvarion's authorized resellers are subject to the following warranty and product
liability terms and conditions.
Exclusive Warranty
(a) Alvarion warrants that the Product hardware it supplies and the tangible
media on which any software is installed, under normal use and conditions, will
be free from significant defects in materials and workmanship for a period of
fourteen (14) months from the date of shipment of a given Product to Purchaser
(the “Warranty Period”). Alvarion will, at its sole option and as Purchaser's sole
remedy, repair or replace any defective Product in accordance with Alvarion'
standard R&R procedure.
AlvariSTAR
iv
User Manual
Legal Rights
(b) With respect to the Firmware, Alvarion warrants the correct functionality
according to the attached documentation, for a period of fourteen (14) month from
invoice date (the “Warranty Period”). During the Warranty Period, Alvarion may
release to its Customers firmware updates, which include additional performance
improvements and/or bug fixes, upon availability (the “Warranty”). Bug fixes,
temporary patches and/or workarounds may be supplied as Firmware updates.
Additional hardware, if required, to install or use Firmware updates must be
purchased by the Customer. Alvarion will be obligated to support solely the two (2)
most recent Software major releases.
ALVARION SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS TESTING
AND EXAMINATION DISCLOSE THAT THE ALLEGED DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT
DOES NOT EXIST OR WAS CAUSED BY PURCHASER'S OR ANY THIRD
PERSON'S MISUSE, NEGLIGENCE, IMPROPER INSTALLATION OR IMPROPER
TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED ATTEMPTS TO REPAIR, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE
BEYOND THE RANGE OF THE INTENDED USE, OR BY ACCIDENT, FIRE,
LIGHTNING OR OTHER HAZARD.
Disclaimer
(a) The Software is sold on an “AS IS” basis. Alvarion, its affiliates or its licensors
MAKE NO WARRANTIES, WHATSOEVER, WHETHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
WITH RESPECT TO THE SOFTWARE AND THE ACCOMPANYING
DOCUMENTATION. ALVARION SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ALL IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE AND NON-INFRINGEMENT WITH RESPECT TO THE SOFTWARE.
UNITS OF PRODUCT (INCLUDING ALL THE SOFTWARE) DELIVERED TO
PURCHASER HEREUNDER ARE NOT FAULT-TOLERANT AND ARE NOT
DESIGNED, MANUFACTURED OR INTENDED FOR USE OR RESALE IN
APPLICATIONS WHERE THE FAILURE, MALFUNCTION OR INACCURACY OF
PRODUCTS CARRIES A RISK OF DEATH OR BODILY INJURY OR SEVERE
PHYSICAL OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“HIGH RISK ACTIVITIES”). HIGH
RISK ACTIVITIES MAY INCLUDE, BUT ARE NOT LIMITED TO, USE AS PART OF
ON-LINE CONTROL SYSTEMS IN HAZARDOUS ENVIRONMENTS REQUIRING
FAIL-SAFE PERFORMANCE, SUCH AS IN THE OPERATION OF NUCLEAR
FACILITIES, AIRCRAFT NAVIGATION OR COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS, AIR
TRAFFIC CONTROL, LIFE SUPPORT MACHINES, WEAPONS SYSTEMS OR
OTHER APPLICATIONS REPRESENTING A SIMILAR DEGREE OF POTENTIAL
HAZARD. ALVARION SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY OF FITNESS FOR HIGH RISK ACTIVITIES.
(b) PURCHASER'S SOLE REMEDY FOR BREACH OF THE EXPRESS
WARRANTIES ABOVE SHALL BE REPLACEMENT OR REFUND OF THE
PURCHASE PRICE AS SPECIFIED ABOVE, AT ALVARION'S OPTION. TO THE
AlvariSTAR
v
User Manual
Legal Rights
FULLEST EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW, THE WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES SET
FORTH IN THIS AGREEMENT ARE EXCLUSIVE AND IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER
WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, EITHER IN FACT OR BY
OPERATION OF LAW, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO WARRANTIES, TERMS OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, SATISFACTORY QUALITY,
CORRESPONDENCE WITH DESCRIPTION, NON-INFRINGEMENT, AND
ACCURACY OF INFORMATION GENERATED. ALL OF WHICH ARE EXPRESSLY
DISCLAIMED. ALVARION' WARRANTIES HEREIN RUN ONLY TO PURCHASER,
AND ARE NOT EXTENDED TO ANY THIRD PARTIES. ALVARION NEITHER
ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER PERSON TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY
OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE OR USE OF ITS PRODUCTS.
Limitation of Liability
(a) ALVARION SHALL NOT BE LIABLE TO THE PURCHASER OR TO ANY THIRD
PARTY, FOR ANY LOSS OF PROFITS, LOSS OF USE, INTERRUPTION OF
BUSINESS OR FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, PUNITIVE OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, WHETHER ARISING UNDER
BREACH OF CONTRACT, TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), STRICT LIABILITY
OR OTHERWISE AND WHETHER BASED ON THIS AGREEMENT OR
OTHERWISE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
(b) TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, IN NO EVENT SHALL
THE LIABILITY FOR DAMAGES HEREUNDER OF ALVARION OR ITS EMPLOYEES
OR AGENTS EXCEED THE PURCHASE PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT BY
PURCHASER, NOR SHALL THE AGGREGATE LIABILITY FOR DAMAGES TO ALL
PARTIES REGARDING ANY PRODUCT EXCEED THE PURCHASE PRICE PAID
FOR THAT PRODUCT BY THAT PARTY (EXCEPT IN THE CASE OF A BREACH OF
A PARTY'S CONFIDENTIALITY OBLIGATIONS).
AlvariSTAR
vi
User Manual
Important Notice
Important Notice
This user manual is delivered subject to the following conditions and restrictions:
This manual contains proprietary information belonging to Alvarion Ltd. Such
information is supplied solely for the purpose of assisting properly authorized
users of the respective Alvarion products.
No part of its contents may be used for any other purpose, disclosed to any
person or firm or reproduced by any means, electronic and mechanical,
without the express prior written permission of Alvarion Ltd.
The text and graphics are for the purpose of illustration and reference only.
The specifications on which they are based are subject to change without
notice.
The software described in this document is furnished under a license. The
software may be used or copied only in accordance with the terms of that
license.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Corporate
and individual names and data used in examples herein are fictitious unless
otherwise noted.
Alvarion Ltd. reserves the right to alter the equipment specifications and
descriptions in this publication without prior notice. No part of this
publication shall be deemed to be part of any contract or warranty unless
specifically incorporated by reference into such contract or warranty.
The information contained herein is merely descriptive in nature, and does not
constitute an offer for the sale of the product described herein.
Any changes or modifications of equipment, including opening of the
equipment not expressly approved by Alvarion Ltd. will void equipment
warranty and any repair thereafter shall be charged for. It could also void the
user's authority to operate the equipment.
AlvariSTAR
vii
User Manual
About AlvariSTAR
About AlvariSTAR
AlvariSTAR is a comprehensive, Carrier-Class Network Management System
(NMS) for Broadband Wireless Access products-based networks. AlvariSTAR is
designed for today's most advanced service provider Network Operation Centers
(NOCs), providing the network OA&M staff and managers with all the network
surveillance, monitoring and configuration capabilities required in order to
effectively manage the network while keeping the resources and expenses at a
minimum.
AlvariSTAR provides the following network management functionality:
Equipment Management, allowing viewing of devices according to various
search criteria, access to devices' dependent features, such as device
configuration managers and maps, access to the Configuration Backup Task
for creating backup files for a selected device, exporting general information of
selected devices to a Commas Separated Value (CSV) file, and other tasks
according to the managed device family.
Single and Multiple Device Management, allowing comprehensive
configuration and management of devices.
Location Management, allowing definition and organization of hierarchical
locations and associating them with maps and other attributes.
Discovery Settings, allowing management of device discovery for identifying
and adding existing devices to the managed devices database.
Active Events, providing alerts and real-time updates of defined alarms.
Event History Management, providing the ability to query for alarms in specific
time intervals.
Event Template Management, allowing customization and management of
event templates according to specific preferences and needs.
Event Forwarding to other Network Management Systems.
Topology, providing Geographical hierarchical topology views for selected
objects.
AlvariSTAR
viii
User Manual
About AlvariSTAR
Task Management, allowing definition and scheduling of system-wide
background tasks, including:
»
Network Discovery, allowing to scan the network for new devices
»
Database Aging, allowing automation of database management tasks.
»
Range Discovery, allowing to scan a predefined range of IPs for new and
modified devices.
»
Additional product line dependent tasks according to the installed Device
Driver(s)
File Management, enabling to restore, import, and export configuration
backup files.
Contact Management, allowing definition of contact persons and attributes to
be associated with selected devices.
License, allowing to add and view the information about valid licenses for
managing devices.
Security Management, allowing management of users, user groups, functional
permissions and passwords.
Audit Logs, allowing viewing of logged events.
User Session Monitor, displays information on the currently logged in users
and enables sending messages to a logged in user.
Certain additional features are applicable only for certain product lines. For
information about these features refer to the applicable Device Driver Manual.
Embedded with the entire knowledge-base of WiMAX network operations, the
management system is a unique state-of-the-art power multiplier in the hands of
the service provider that enables the provisioning of satisfied customers.
AlvariSTAR dramatically extends the abilities of the service provider to provide a
rich portfolio of services and to support rapid customer base expansion.
NOTE
This manual describes the general features of the management system. To manage specific
product families, refer also to the applicable Device Driver Manual.
AlvariSTAR
ix
User Manual
About AlvariCRAFT
About AlvariCRAFT
AlvariCRAFT is a PC or Laptop based Graphical application based on the same
user interface available for AlvariSTAR. AlvariCRAFT is designed for field
technician use, enabling simple and intuitive Graphical Local Craft Terminal
(LCT) for managing and configuring a single device type in the field.
This utility simplifies the installation and maintenance of small size deployments
by easily enabling the change of settings or firmware upgrade for one modular
Base Station or Micro Base Station at a time, including the managed device's
components and associated SUs (if applicable).
The AlvariCRAFT utility includes all the functions of AlvariSTAR that are
applicable to the management of a single device.
AlvariSTAR
x
User Manual
About This Manual
About This Manual
This manual describes the AlvariSTAR management system (referred to as
Network Management System) and the AlvariCRAFT Local CRAFT Utility. The
manual describes the full functionality of the Carrier-class management system
and presents screen captures of the AlvariSTAR application. Unless otherwise
stated, the descriptions apply to both applications.
Limitations on AlvariCRAFT due to the single device restriction are noted in a Note
specific to the application, as follows:
LOCAL CRAFT NOTE
This feature is not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility.
This User Manual comprises the following chapters:
Chapter 1- Introduction - provides an overview of the AlvariSTAR and
AlvariCRAFT systems and their functionality.
Chapter 2 - Managed Network - describes how to access the management
functions for managing the system: Equipment Manager, Location Manager,
and Discovery Settings.
Chapter 3 - Fault Management - describes the tools for managing events
generated in the system: Active Events, Event History, Event Filter Manager,
Event Template Manager, Script Command Manager and Event Forwarding
NBI Manager
Chapter 5 - Administration - describes the administrative utilities: Task
Manager, File Manager, Contacts Manager and License Manager.
Chapter 4 - Configuration Management - describes features used for
integration with Google Earth: CPE Type Selector and File Generation
Parameters
Chapter 6 - Security Management - describes the utilities for managing the
user permissions and access rights for AlvariSTAR and AlvariCRAFT users:
AlvariSTAR
xi
User Manual
About This Manual
Audit Log Manager, User Manager, User Profile Manager, and User Session
Monitor.
Appendix A - Watchdog - describes the Watchdog application used for
monitoring the NMS, database and LDAP servers.
Appendix B - Remote Access - Describes the WebStart functionality.
Appendix C - Connecting to an External LDAP Server - Describe how to
connect AlvariSTAR to an LDAP server.
Appendix D - Google Earth Management - Describes how you can visualize the
network’s topography in Google Earth.
Appendix E - SNMP Compatibility - Describes SNMP version compatibility for
each supported device.
AlvariSTAR
xii
User Manual
Contents
Contents
Chapter 1 - Introduction .......................................................................... 1
1.1 Starting AlvariSTAR ...................................................................................................3
1.1.1 Post Installation Checklist ...................................................................................3
1.1.2 Quick Start ..........................................................................................................4
1.1.3 Starting the Client................................................................................................6
1.1.4 Logging In ...........................................................................................................6
1.1.5 Logging Out or Shutdown ...................................................................................7
1.1.6 Changing the Password ......................................................................................8
1.1.7 Suspended Accounts ..........................................................................................9
1.1.8 Application Server ...............................................................................................9
1.2 Starting AlvariCRAFT...............................................................................................10
1.3 The Main Window .....................................................................................................12
1.3.1 Main Menu ........................................................................................................12
1.3.2 Open Managers ................................................................................................13
1.3.3 Page Control Bar...............................................................................................13
1.3.4 Navigation Pane................................................................................................14
1.3.5 Management Functions.....................................................................................15
1.3.6 Hiding and Displaying the Navigation Pane ......................................................17
1.3.7 Status Bar .........................................................................................................17
1.4 The About Window...................................................................................................18
1.5 Conventions and Common Operations..................................................................20
1.5.1 Conventions ......................................................................................................20
1.5.2 Control Buttons .................................................................................................20
1.5.3 Context Menus ..................................................................................................21
1.5.4 Working with Tables..........................................................................................21
1.5.5 Manipulating the Displayed Information ............................................................23
Chapter 2 - Managed Network .............................................................. 27
2.1 Equipment Manager .................................................................................................29
2.1.1 Introduction to the Equipment Manager ............................................................29
AlvariSTAR
xiii
User Manual
Contents
2.1.2 The Unified (All Network Elements) View .........................................................30
2.1.3 The Equipment Editor .......................................................................................34
2.2 Location Manager.....................................................................................................37
2.2.1 Searching for a Location ...................................................................................39
2.2.2 Location Editor ..................................................................................................39
2.2.3 Coordinate Types..............................................................................................41
2.2.4 Location Map.....................................................................................................42
2.3 Discovery Settings Manager ...................................................................................45
2.3.1 Network Settings Window .................................................................................47
Chapter 3 - Fault Management.............................................................. 51
3.1 Introduction ..............................................................................................................53
3.2 Active Events............................................................................................................54
3.3 Event History ............................................................................................................57
3.3.1 Managing Alarms ..............................................................................................59
3.4 Event Filter Manager ................................................................................................74
3.4.1 Creating Event Filters........................................................................................76
3.4.2 Editing Event Filters ..........................................................................................82
3.4.3 Deleting Event Filters ........................................................................................83
3.4.4 Archiving Alarms ...............................................................................................83
3.5 Event Template Manager .........................................................................................84
3.5.1 Creating or Editing Event Templates ................................................................86
3.5.2 Deleting Event Templates .................................................................................96
3.6 Script Command Manager.......................................................................................97
3.6.1 Creating or Editing Commands .........................................................................99
3.6.2 Deleting Commands........................................................................................101
3.7 Event Forwarding NBI Manager ............................................................................102
3.7.1 Creating or Editing Event Forwarding NBI Interfaces .....................................104
3.7.2 Deleting Event Forwarding NBI Interfaces ......................................................106
3.7.3 Creating Event Forwarding NBI Interface Policies ..........................................106
3.7.4 NBI Notifications Global Settings ....................................................................114
AlvariSTAR
xiv
User Manual
Contents
Chapter 4 - Configuration Management .............................................. 116
4.1 CPE Types Selector ...............................................................................................118
4.2 File Generation Parameters...................................................................................120
Chapter 5 - Administration .................................................................. 121
5.1 Introduction ............................................................................................................123
5.2 Task Manager .........................................................................................................124
5.2.1 Using The Task Manager................................................................................124
5.2.2 The Task Scheduler ........................................................................................129
5.2.3 The Task Results Viewer ................................................................................131
5.2.4 Network Discovery Task .................................................................................133
5.2.5 Database Aging Tasks ....................................................................................134
5.2.6 Discovery Task................................................................................................136
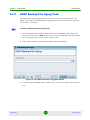
5.2.7 LDAP Backup/File Aging Task ........................................................................140
5.3 File Manager ...........................................................................................................141
5.4 Contact Manager ....................................................................................................143
5.4.1 Associating Devices with a Contact ................................................................145
5.4.2 Creating or Modifying a Contact......................................................................145
5.5 License Manager ....................................................................................................147
5.5.1 The License Manager .....................................................................................147
5.5.2 Adding Licenses..............................................................................................149
5.5.3 Activating Existing Licenses............................................................................149
5.5.4 Rescue License...............................................................................................149
5.5.5 Displaying Licensing Information ....................................................................150
Chapter 6 - Security Management ...................................................... 151
6.1 Overview .................................................................................................................153
6.2 Audit Log Manager.................................................................................................154
6.3 User Manager..........................................................................................................160
6.3.1 The User Manager Window ............................................................................160
AlvariSTAR
xv
User Manual
Contents
6.3.2 Adding or Modifying a User.............................................................................162
6.4 User Profile Manager .............................................................................................168
6.5 User Session Monitor ............................................................................................176
6.6 Password Policy.....................................................................................................179
6.7 External Entities Mapping .....................................................................................182
6.8 User Domain Manager ...........................................................................................185
Appendix A - Watchdog ...................................................................... 188
A.1 The Watchdog Application ....................................................................................190
Appendix B - Remote Access ............................................................. 192
B.1 WebStart..................................................................................................................194
B.2 The Web Portal .......................................................................................................195
Appendix C - Connecting to an External LDAP Server ...................... 196
C.1 The LDAP Server Configuration File ....................................................................198
C.2 Open LDAP Configuration.....................................................................................199
C.3 Active Directory Configuration .............................................................................200
Appendix D - Google Earth Management ........................................... 201
D.1 Connecting Google Earth to the NMS ..................................................................203
D.2 Viewing the Network Elements in Google Earth .................................................204
Appendix E - SNMP Compatibility ...................................................... 206
E.1 SNMP Version Compatibility .................................................................................208
AlvariSTAR
xvi
User Manual
Chapter
1
Introduction
Chapter 1 - Introduction
In This Chapter:
“Starting AlvariSTAR” on page 3
“Starting AlvariCRAFT” on page 10
“The About Window” on page 18
“The Main Window” on page 12
“Conventions and Common Operations” on page 20
AlvariSTAR
2
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1.1
Starting AlvariSTAR
Starting AlvariSTAR
This section describes the necessary steps to start the AlvariSTAR management
system. For a description of the AlvariCRAFT utility, go to Section 1.2.
The management system enforces security at the client level. To log in to the
application, you must have a valid user ID and password.
Before you can run this application your system must have running Application,
and Database Server. Typical installations implement the Application Server so it
runs in the background, even after you log out of the client. See the Installation
Manual for information about installing and configuring these required server
processes (called services in Windows, daemons in Solaris).
1.1.1
Post Installation Checklist
Before starting the client application, verify the following:
1.1.1.1
License
The default demo license is valid for 90 days and includes licenses for two
management system clients and a certain amount of managed devices. It does not
support licensed features.
To obtain a permanent license, contact your product reseller. To load and activate
licenses, see “License Manager” - Section 5.5.
1.1.1.2
Device Configuration
To discover and properly manage devices, certain parameters must first be
properly configured in the managed devices. For details refer to the relevant
Device Driver Manual.
1.1.1.3
SW Upgrade Files
Software Upgrade files for the managed devices need to be stored on the
Application Server in the management system firmware repository folder located
under <management system>\filesystem\firmware\<product-line>. The product
line name is device dependant (refer to the relevant Device Driver User Manual)
NOTE
The firmware repository folder is created automatically for certain device drivers. For other device
drivers it should be created manually.
Use forward slashes in UNIX systems.
AlvariSTAR
3
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1.1.1.4
Starting AlvariSTAR
SNMP Ports
Verify that the SNMP ports (161, 162) are not used by any other application
running on the computer. If Windows or any other SNMP Server is installed, open
the Windows Service Manager, stop the SNMP Services and disable it to ensure
that it will not start automatically the next time you restart the computer.
1.1.1.5
Security Enforcement
The Administrator should define users, user groups, passwords and functional
permissions (refer to Chapter 6).
1.1.2
Quick Start
The following is an overview that covers the basic steps for getting started with the
management process. Refer to the respective chapter in this manual or, when
applicable, in the relevant Device Driver Manual) for an in-depth explanation of
each step.
1
Design the equipment location hierarchy. Define locations and sub-locations
and associate them with maps if applicable. (Refer to Section 2.2.)
2
Define security policy and assign permissions to users/user profiles. (Refer to
Chapter 6 )
3
Open the Discovery Settings Application. Enter the necessary IP address
ranges, locations and SNMP parameters. Define all other applicable
parameters and initiate discovery. (Refer to Section 2.3 for information on
using the Discovery Settings application and Section 5.2.4 for information on
running the Network Discovery task for equipment discovery.)
4
After devices are discovered and stored in the database, you can fully use the
application to manage the system:
»
Use the Equipment Manager to view devices in the database according to
various search criteria. From the Equipment Manager you can access the
devices' dependent Configuration and Multiple Configuration managers
and topology maps. (Refer to the relevant Device Driver Manual.)
»
Use additional managers that may be applicable only for certain product
lines to manage different features and parameters that are product line
dependent.
AlvariSTAR
4
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Starting AlvariSTAR
»
Use the Location Manager to design and manage hierarchical locations and
associate them with maps. (Refer to Section 2.2.)
»
Use the Contact Manager to define contact persons and attributes to be
associated with selected devices. (Refer to Section 5.4.)
»
Use the Task Manager to define and schedule general system-wide tasks
and various additional tasks according to the managed product line. (Refer
to Section 5.2 and the relevant Device Driver Manual).
»
Use the Files Manager to restore, import, and export configuration backup
files generated via the Configuration Backup task (Refer to the relevant
Device Driver Manual).
»
Use the Database Aging Task to manage alarm records. (Refer to
Section 5.2.5.)
»
Use the License feature to view information on licensed vs. discovered
devices, enabling you to estimate when you need to update your license.
(Refer to Section 5.5.)
»
Use the User Session Monitor feature to identify other currently active
users and communicate with them. (Refer to Section 6.5.)
»
Use the Audit Log Manager to view logged events. (Refer to Section 6.2.)
»
Use Active Events to view alarms and other events in real time. (Refer to
Section 3.2.)
»
Use the Event History to query the database for events and alarms in
specific time intervals. (Refer to Section 3.3.)
»
Use the Event Forwarding NBI Manager to interface with other Network
Management Systems. (Refer to Section 3.7.)
»
Use the Script Command Manager to create script commands that can be
triggered by template-matched alarms.
5
Modify the threshold number of rows stored in the alarm table if necessary.
(Refer to “Database Aging Tasks” - Section 5.2.5.) By default 50000 rows are
displayed and the Database Aging task is scheduled to run every hour.
AlvariSTAR
5
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1.1.3
Starting AlvariSTAR
Starting the Client
To start the application:
From the Windows Start menu, select <Management System name> “Management
System”> Start Client. After the client application is started, the Login prompt
window will be displayed.
1.1.4
Logging In
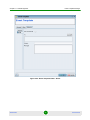
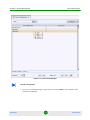
To log in, type a valid user name and password at the login prompt, as follows:
Default User Name
Default Passwords
admin
admin
manager
manager
observer
observer
By default, you have five attempts to enter the correct password before the system
aborts the login.
AlvariSTAR
6
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Starting AlvariSTAR
Figure 1-1: Login Prompt
1.1.5
Logging Out or Shutdown
Logging out keeps the application running but disable access to the client,
preventing unauthorized persons from using it. You may log in again without the
need to restart the client.
The Exit feature, however, shuts down the client application, while the Application
Server continues to run.
To log out of the system
1
From the Main Menu at the top of the window select System> Logout. A
confirmation message is displayed.
2
AlvariSTAR
Click OK to confirm.
7
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
3
Starting AlvariSTAR
Only the Main Menu of the client is displayed. Only the System and Help
menus are available.
To log in again after logging out
From the Main Menu at the top of the window select System > Login. The Login
prompt window will be displayed, allowing you (or another authorised user) to log
in.
To shut down the client:
1
From the main menu select System > Exit, or, use the X icon displayed on the
right upper corner of the main window, or use the Alt+F4 shortcut. A
confirmation message is displayed.
2
1.1.6
Click OK to confirm.
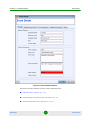
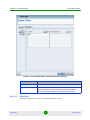
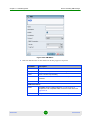
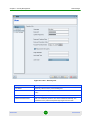
Changing the Password
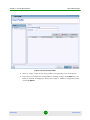
By default, there are no password constraints. By using Change Password, the
current logged-in users can change only their own password.
To change the password:
1
From the main menu, select System > Change Password. The Change
Password dialog is displayed.
AlvariSTAR
2
Enter the old password.
3
Enter the new password (8-32 characters). Confirm it.
4
Click OK to save the new password.
8
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Starting AlvariSTAR
Figure 1-2: Change Password Dialog
Passwords constraints are set from the Security Management > Password Policy
menu
The password policy also determines when the user receives a password
expiration warning.
1.1.7
Suspended Accounts
Users with a suspended account cannot access the system. An account can be
suspended by the administrator, or is blocked according to the Login Policy
settings set in the Password Policy window. The Login Attempts parameter sets
the number of unsuccessful login attempts before the user is locked out (default:
five attempts). The account can be re-activated by the system administrator.
Only the system administrator can activate suspended and blocked accounts. The
default admin user is never blocked.
To activate an account:
1.1.8
1
Open the User Manager window.
2
Select the suspended user and click Edit.
3
Select Security Info and change it to Active.
4
Click OK to apply the changes.
Application Server
The application server, which typically runs on a dedicated host, enables the
system to process incoming alarms and communicate with equipment and
AlvariSTAR
9
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Starting AlvariCRAFT
network devices. If the client application cannot connect to an application server,
a warning message appears and the client is not launched.
1.2
Starting AlvariCRAFT
To log in to the application, you must have a valid user ID and password.
To open AlvariCRAFT:
1
Double-click on the AlvariCRAFT icon or open it from the windows Start menu
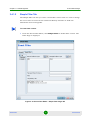
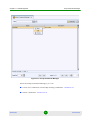
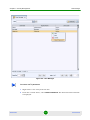
(Programs>AlvariCRAFT>Start Craft). The Network Interface Chooser opens.
Figure 1-3: Network Interface Chooser
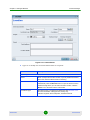
The Network Interface Chooser enables to select the IP address of the
computer on which the Local CRAFT Utility is installed. The Network Interface
Chooser includes the following fields:
AlvariSTAR
Field
Description
Network Interface
A list of the available network interface cards (NIC) installed.
State
The state of the selected network interface. Only network interfaces
that are UP are displayed.
MAC Address
The MAC Address of the selected NIC. For the local loopback NIC, no
MAC address is displayed.
IP Address
The IP address associated with the selected NIC.
10
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
AlvariSTAR
Starting AlvariCRAFT
Field
Description
Description
A read-only description of the selected NIC.
2
In the Network Interface Chooser, select a network interface from the list.
3
Click OK. The Main window opens.
11
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1.3
The Main Window
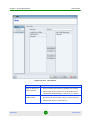
The Main Window
After logging on, the main window is displayed, providing access to all functions.
Opened Managers
Main Menu
Help Button
Separation Line
Work Area
Navigation Pane
Page Controls
Status Bar
Figure 1-4: The Main Window
1.3.1
Main Menu
The main menu contains all menus and their options, which provide access to the
management system functions. It mirrors all the functions available in the
Navigation Pane (see Section 1.3.4).
In addition, the Main Menu includes the following menus and options:
AlvariSTAR
12
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
The Main Window
Menu
Description
Help
Provides the following options:
About: Enables viewing details about installed system components
(see Section 1.4).
Help Contents: Opens the WebHelp contents window.
System
Provides the following options:
Login: Enables logging in to the client application. Applicable after
logging out (refer to Section 1.1.5) and in the management
system, also after time-out.
Logout: Enables logging out of the client application without
closing it. The application is still running and you may login again
(refer to Section 1.1.5).
Change Password: Opens the Change Password window
enabling to change the user’s password (refer to Section 1.1.6)
Exit: Enables shutting down the client application.
1.3.2
Open Managers
The Open Managers section displays all the currently open managers.
Click on an open manager name to switch to the window of this manager.
Click on the X sign of an open manager to close it.
1.3.3
Page Control Bar
The Page Control Bar is displayed at all times only for certain windows at the
bottom of the window. It contains quick access icons for some common
operations.
Figure 1-5: Page Control Bar
When the number of results in the manager exceeds the number defined in the
Page Size box, the results are divided into several pages. Use the following
controls to browse the various pages:
AlvariSTAR
13
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Icon
The Main Window
Description
Help - Opens the Online Help Navigator.
First/Previous - Cycles back to the first or previous page.
Next/Last - Cycles forward to the next or last page.
Go to Page - Specify the page number in the box to the right
Page Size - define the number of results to display in each page
1.3.4
Navigation Pane
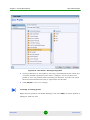
Figure 1-6: Navigation Pane
AlvariSTAR
14
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
The Main Window
Click on menu headings to expand that menu node (double click on the menu
heading or single-click on the + sign to its right), then click on the appropriate
item in that node to display the associated page.
1.3.5
Management Functions
The Navigation Pane and Main Menu provide access to all the management
functions. The Navigation Pane and Main Menu options are described below:
NOTE
Certain menus/menu options may be applicable only for certain product lines. The descriptions
below are only for menus/menu options that are common to all product lines. Refer to the relevant
Device Driver Manual for details on additional menus/menu options that are dependent on the
installed device driver(s) and the managed product line.
Node
Description
Managed Network
Provides the following options:
Equipment Manager - Opens the Equipment Manager window,
enabling to view equipment in the network and access the Equipment
Editor. Refer to Section 2.1 and the relevant Device Driver Manual.
Location Manager - Opens the Location Manager window, enabling to
define equipment locations and to associate maps and other features
with locations. Refer to Section 2.2.
Discovery Settings (not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility)- Opens
the Discovery Settings window, enabling to manage IP address ranges
or sub-nets and global SNMP Read and Write community pairs. Refer
to Section 2.3.
AlvariSTAR
15
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
The Main Window
Node
Description
Fault Management
The Fault Management allows you to manage alarms that occur in the
network. It displays information about each alarm and lets you
acknowledge received alarms. It also provides tools that help you
diagnose and correct alarms. The Fault Manager is divided into the
following sub-menus:
Active Events - Displays real time updates of new events and alarms
entering the system. Refer to Section 3.2.
Event History - Queries for alarms and events in the database,
according to specified time intervals. Refer to Section 3.3.
Event Filter Manager - Allows to create, edit and delete filters to the
Active Events/Event History windows. Refer to Section 3.4.
Event Template Manager - Allows to create, modify and delete event
templates. Refer to Section 3.5.
Script Command Manager - Allows to create, edit and delete script
commands. Refer to Section 3.6.
Event Forwarding NBI Manager (not applicable to the Local CRAFT
Utility) - Allows to connect to other management systems and to
forward traps related to this system. Refer to Section 3.7.
Administration
Provides the following sub-menus:
Task Manager - Enables to define, manage, schedule, run/abort
system-wide operations, such as Network Discovery (not applicable to
the Local CRAFT Utility), Database Aging, and product line dependent
tasks, etc. Refer to Section 5.2 and to the relevant Device Driver
Manual.
File Manager - Opens the File Manager window, enabling to manage
configuration backup and other types of files. Functionality depends on
the managed product line. Refer to Section 5.3 and to the relevant
Device Driver Manual.
Contact Manager - Opens the Contact Manager window, enabling to
organize and manage your contacts. Refer to Section 5.4
License Manager (not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility) - Enables
viewing information about valid licenses and summary details on the
currently managed device types, included in the license. Refer to
Section 5.5.
AlvariSTAR
16
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
The Main Window
Node
Description
Security Management
Provides the following sub-menus:
Audit Log Manager - Enables to view recorded events and export the
logged data to an external Comma Separated Value (CSV) file. Refer
to Section 6.2.
User Manager - Enables to create and manage users, and associate
information to them such as passwords, profile membership and
contact information. Refer to Section 6.3
User Profile Manager (not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility) Enables to create user profiles, edit them or delete profiles. Refer to
Section 6.4
User Session Monitor (not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility) Enables to view information on the currently logged in users and to
send messages to a logged in user. Refer to Section 6.5.
Password Policy (available only from the Main Menu) - enables to set
general policies for user passwords.
1.3.6
Hiding and Displaying the Navigation Pane
By default, both the Navigation Pane and Work Area are displayed. When hovering
the mouse over the separation bar between the Navigation Pane and Work Area,
the mouse pointer becomes a double-headed arrow (). You can change the size
of the Navigation Pane by dragging this arrow left/right.
You can hide the Navigation Pane to increase the size of the Work Area or hide the
Work area to increase the size of the Navigation Pane by clicking on the
arrowheads (
) located on the separation bar until reaching the required
display.
With the Navigation Pane hidden or maximized, if clicking the arrowhead does not
restore the display of both panes, manually drag the separation bar to restore the
display.
1.3.7
Status Bar
The Status Bar is displayed at the bottom of the main window, and contains the
following information:
Current logged user.
AlvariSTAR
17
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
The About Window
The IP address of the application server or the selected interface of the Local
CRAFT Utility machine.
The name of the currently open manager.
A progress bar is displayed every time a window is refreshed or a new window is
selected.
Figure 1-7: Status Bar
1.4
The About Window
The About window displays a list of all products installed and their software
version.
To open the About window, select Help > About in the Main Menu.
AlvariSTAR
18
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
The About Window
Figure 1-8: About Window
The version numbers of the management system and the installed product line
device driver(s) are in the format a.b.c.d, where a.b increases for major releases, c
increases for minor releases and d is an internal control number.
AlvariSTAR
19
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1.5
Conventions and Common Operations
Conventions and Common Operations
The following conventions and common operations appear throughout this
manual, unless otherwise specified.
1.5.1
Conventions
The phrase “Select Managed Network > Equipment Manager from the Main Menu
bar or the Navigation Pane” means you should do one of the following:
Click on the Managed Network menu in the Main Menu bar to expand it, then
click on Equipment Manager.
Click on the Managed Network node in the Navigation Pane to expand it (if it is
not already expanded), then click on Equipment Manager.
1.5.2
Control Buttons
A control button causes an immediate action. To activate a control button, click
on it. Certain control buttons only appear in selected windows. Others are
common to most windows. Equivalent functions to some control buttons are
available from the toolbar and main menu.
AlvariSTAR
Button
Description
Apply
Applies changes made in the window. Clicking the Apply button
maintains the window opened for the following transaction or
response delivery.
OK
Applies changes made in the window and closes the window.
Cancel
Closes the active window without taking any further action. Any
modifications made prior to clicking Cancel are ignored.
Refresh
Refreshes the window and displays the most updated information.
Save
Saves changes made in the dialog box.
Help
Displays the online help window.
Browse
The Browse button appears whenever the command’s completion
may need additional step. Clicking this button displays another
window that lets you select an entry for an adjacent field.
20
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Conventions and Common Operations
Button
Description
Clear
Clears adjacent fields. It appears next to a field with a Browse button
at the other end.
Retrieve
Displays all appropriate matches according to the selected filter. It can
also be used to refresh the display.
Some of the control buttons, such as Edit, Open, Import and Export may appear
grayed out for users without write permission.
1.5.3
Context Menus
When handling tables in the work area, most of the functions are accessible via
right click menus. The contents of these menus are context sensitive. Common
functions include:
New - Adds a new entry to the table
Delete - Removes an entry from the table
Edit - Changes the parameters of a particular entry
1.5.4
Working with Tables
All tables and lists allow resizing and rearranging the column display sequence. In
some pages, tables are used for displaying information and configuring and
managing multiple entities of the same type.
Color conventions:
»
Grayed-out cells are read-only.
»
In rows with modified parameter(s) all the details are colored blue.
»
The new lines added are green
»
The lines marked for deletion are red.
To modify the configuration of an existing entity:
AlvariSTAR
21
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1
Conventions and Common Operations
Double-click on the applicable cell
»
In a text-cell, edit the content.
»
In some cells a drop-down menu opens, enabling selection of the required
option.
2
Click on any other cell to apply the change to the selected cell. At this stage the
change only applies to the display.
3
1.5.4.1
Click Apply to apply the change to the device.
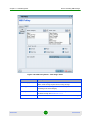
Dynamic Column Selection
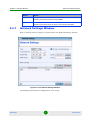
Some of the tables in the work area can be tuned to display only specific columns.
Tables that support Dynamic Column Selection have a small button located in the
top right corner as shown in Figure 1-9. Clicking this button displays a list of all
the columns that are available in the table. Check the columns that you wish to
display and uncheck the columns that you want to hide. The following additional
options are also available:
Horizontal Scroll - Displays/Hides the table’s horizontal scrollbar
Pack All Columns - When the table exceeds the width of the available work
area, this option attempts to fit it into the available space by reducing the
columns’ widths.
Pack Selected Column - Resizes the currently selected column to its minimum
width that still fits all its content.
AlvariSTAR
22
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Conventions and Common Operations
Figure 1-9: Dynamic Column Selection
Alternatively, you can select which columns to display/hide by right clicking the
table’s header and, from the list that displays, checking the corresponding column
names.
1.5.4.2
Sorting Tables
Click on any of the column headings to sort tables. Click again on a column
heading to toggle between ascending and descending sort order.
1.5.4.3
Resizing and Rearranging Columns
To resize a column, position the cursor on the border line between two columns
headings. The cursor changes into a double-headed arrow. Drag the cursor to the
left or to the right to increase or decrease the size of a column. To rearrange
column sequence, click a column header and drag it to the new desired position.
1.5.5
Manipulating the Displayed Information
1.5.5.1
Using Filters
Some of the tables support the filtering feature. Filters allow you to set up the
table so that it displays only rows that are relevant for your purposes. If a table
supports filters, the Filter control displays above it.
Figure 1-10: The Filter Control
AlvariSTAR
23
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Conventions and Common Operations
The following controls are available:
Button
1.5.5.1.1
Name
Description
Select Filter
Opens the Filter Criteria Manager which allows
you to define, edit and apply your filters.
Remove Filter
Removes the currently selected filter.
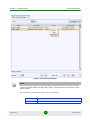
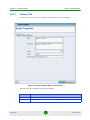
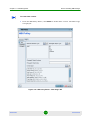
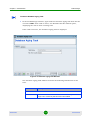
Filter Criteria Manager
Clicking the Select Filter button opens the Filter Criteria Manager (see
Figure 1-11). The Filter Criteria Manager contains a table that lists all the
available filters. Use the right-click menu to manage and select your filters.
Figure 1-11: Filter Criteria Manager
AlvariSTAR
24
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1.5.5.1.2
Conventions and Common Operations
Filter Criteria
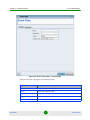
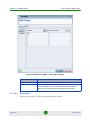
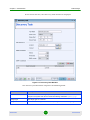
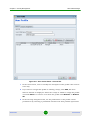
You define new filters or edit existing filters from the Filter Criteria window (see
Figure 1-12). This window is displayed whenever you select the New or Edit option
from the right-click menu inside the Filter Criteria Manager.
Figure 1-12: Filter Criteria
You define a selection criterion by specifying the values which are relevant for the
entries in a particular column. Then, press the Add button to include your
criterion into the filter criteria list. If you want to use multiple selection criteria,
use the above procedure to add additional entries to the list. All criteria in the list
are aggregated by applying the logical AND operator between them. This means
that only entries which fulfill each and every criterion in the list will be displayed
when the filter is applied.
AlvariSTAR
25
User Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Conventions and Common Operations
Once a selection criterion is added to the list, you can negate it by checking the
NOT checkbox. This is useful when it is easier to define entries that are to be
excluded from the selection than those which are to be included.
1.5.5.2
Limiting the Results Set
You can define the maximum number of results to be displayed in a list by
entering a number in the Page Size box or by using the up and down arrows to the
right of the number field. If the results set exceeds the defined number, it will be
divided into several pages. Click Refresh to refresh the displayed list. Refer to
Section 1.3.3 for details on navigating among pages.
AlvariSTAR
26
User Manual
Chapter
2
Managed Network
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
In This Chapter:
“Equipment Manager” on page 29
“Location Manager” on page 37
“Discovery Settings Manager” on page 45 - not applicable to the Local CRAFT
Utility
NOTE
This manual does not cover some topics, which are device driver dependant. Refer to the
applicable Device Manager Manual for information about the following features (if applicable):
GPS Chain manager
Network Maintenance
AlvariSTAR
28
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
2.1
Equipment Manager
Equipment Manager
This section includes:
“Introduction to the Equipment Manager”
“The Unified (All Network Elements) View”
“The Equipment Editor”
2.1.1
Introduction to the Equipment Manager
The Equipment Manager provides functionality and access to windows that
enables you to manage equipment in your network. Using the Equipment
Manager in conjunction with the right-click menu you can:
View devices that exist in the database according to various selection criteria.
View general information on the displayed devices
Add and Delete devices to/from the database
Edit the general properties of devices
Open the Configure window to configure a selected device
Apply licenses to selected equipment (not applicable to the Local CRAFT
Utility)
Open a Telnet session for a selected device (if supported by the specific device
type)
Open the Backup Configuration Task to backup the configuration of selected
devices (if applicable)
Export the general information of selected devices to a Commas Separated
Value (CSV) file.
Open a map display associated with a selected device, if applicable.
Perform additional operations according to the product line and type of
managed devices.
AlvariSTAR
29
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Equipment Manager
To open the Equipment Manager:
Select Managed Network > Equipment Manager from the Navigation Pane or menu
bar. The Equipment Manager window is displayed.
NOTE
Equipment Manager applications running on different NMS clients bound to the same server are
notified of the changes made by other clients. The equipment list will be automatically updated
whenever another client on the network modifies (adds, deletes or edits) equipment data.
The Equipment Manager can be configured to display only specific types of
network elements. This allows you to quickly switch between the various lines of
products that you need to manage, according to the installed Device Driver(s). For
this purpose, from the View drop menu at the top of the work area, select the
products type that you would like to be visible. The structure and functionality of
the Equipment Manager depend on the selected type of managed equipment.
Refer to the relevant Device Driver Manual for details on how to use the
Equipment Manager with the applicable devices.
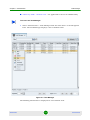
2.1.2
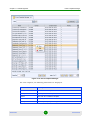
The Unified (All Network Elements) View
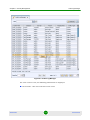
Selecting the All Network Elements option will display all the BTS units in the
database, as well as a summary count at the bottom of the work area. There are
two types of summaries you can switch between by right clicking:
Summary by NE Type - Lists counts for all types of BTS units.
Summary by State - Lists counts for units that are in the Unmanageable,
Unreachable, Unlicensed, Unknown, Unmanaged and Managed states.
The summaries are displayed in a ratio format. The first figure indicates the
filtered number of devices, while the second indicates the total number of devices.
For instance, if applying a filter excludes 2 devices from a total of 5, the ratio
displayed will be 3/5. If no filters are applied, both figures will indicate the total
number of devices. In our previous example, this would mean a ratio of 5/5.
The BTS equipment table for All Network Elements includes all the BTS objects
that exist in the database of the management system. This includes devices that
were discovered by the management system (using either Network Discovery Task
or the Range Discovery Task) and devices that were added manually to the
database (see New option below). The background color of the device’s icon is in
accordance with the device’s alarm status (the highest severity open alarms).
AlvariSTAR
30
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Equipment Manager
You can use the Filter option for viewing only devices that meet one or several
selection criteria.
The information displayed for each device (refreshed every 15 seconds) includes:
Parameter
Description
Name
The BTS Name configured in the device. Applicable only for devices
that are Up or that were reached previously.
NE Type
The device’s type.
Running SW Ver
The currently running SW version. Applicable only for devices that are
Up or that were reached previously.
IP Address
The IP address of the device. Applicable only for devices that are Up
or that were reached previously.
Location
The location of the device as defined in the database of the
management system, either automatically during discovery (based on
settings of discovery parameters) or manually using the Equipment
Editor.
Management Status
The management state of the device:
Managed - The equipment is answering to keep-alive/polling and
synchronization.
Down - Available only for CPEs. Equipment is reported as down.
Unreachable - A device that the management system is aware of
(exists in the database) but cannot be reached currently.
Unknown - This is typically a temporary status for a device that is
available in the database but has never been reached in the past
and its current status is unknown. After a short time its status
should change to one of the other options.
Unlicensed - If the number of devices of a certain type in the
database has reached the number of licenses for managing the
specific device type, additional devices of this type added to the
database will be presented as unlicensed. These devices cannot
be managed by the system. The License button in the Equipment
Manager will be available upon selecting unlicensed object(s),
allowing to install additional licenses.
Unmanageable - Equipment is reachable but cannot be managed
from various reasons: wrong SW version, synch errors, no route,
manual unmanage, etc.
Unmanaged - Operator does not want to manage an equipment,
although it is discovered.
AlvariSTAR
31
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Equipment Manager
Parameter
Description
Standby Status
This column indicates a device’s backup related behavior. The
following statuses are available:
Providing Service - The backup resource is providing service and
is backing up another resource.
Hot Standby - The resource is not providing service, but is
operating in synchronism with another resource that is to be
backed-up (e.g., a computer shadowing another computer). A
resource with a hot standby status will be immediately able to take
over the role of the resource being backed up, without the need
for initialization activity, and will contain the same information as
the resource to be backed up.
Cold Standby - The resource is to backup another resource, but is
not synchronized with that resource. A resource with a cold
standby status will not be immediately able to take over the role of
a resource being backed up, and will require some initialization
activity.
The available management options depend on the selected device type(s). Select
one or several entries and right-click to view the available management options.
The following options are available for all device types:
Option
Description
New
Adds a new equipment object to the database. Click to open the
Equipment Type selection dialog box. Select the type of equipment to
be added (available options depend on the installed Device Drivers)
and click OK. The Equipment Editor opens, allowing to enter general
information on the BTS to be added. For more details, see “The
Equipment Editor” on page 34.
NOTE: The New option is available when right-clicking anywhere in
the work area, without the need to select any existing entry.
Configure
Opens the Device Manager for the selected device. Not available if
two or more devices are selected or if the State of the selected device
is other than Up.
NOTE: You can also open the Device Manager by double-clicking on
the selected device.
Edit
AlvariSTAR
Opens the Equipment Editor for the selected equipment object(s),
allowing to edit general parameters. For multiple selected devices
you can edit only the Location and Contact parameters. For a single
device you can edit also some general SNMP parameters. For more
details, see “The Equipment Editor” on page 34.
32
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Equipment Manager
Option
Description
Delete
Deletes the selected equipment object(s) from the database. The
application prompts you for confirmation. You can always rediscover
deleted equipment.
License
Activated only when unlicensed equipment is selected. If the number
of devices of a certain type in the database has reached the number
of available licenses for managing the specific device type, additional
devices of this type will be presented as unlicensed. These devices
cannot be managed by the system. Select the License option to open
the License Manager, enabling to view the current status of available
licenses and add licenses if necessary.
Cut Through
Opens a Telnet session to the selected device. Not available if two or
more devices are selected or if the State of the selected device is
other than Up.
Open Map
Opens the location map, displaying the selected map for the
applicable location. Available only when a location is assigned to the
selected device. Not available if two or more devices are selected.
Open Alarms
Not available if two or more devices are selected or if the State is
other than Up. Opens the Open Alarms window, displaying the details
of currently active events,
Unmanage
Manually switch a device’s management status to Unmanaged
Manage
Attempt to revert a manually unmanaged device to its normal
management status.
Backup Configuration
Not available if two or more devices are selected or if the State is
other than Up. opens a Configuration Backup Task for the selected
device, where you can add additional devices to the task. Refer to the
Configuration Backup Task section in the relevant Device Driver
Manual.
Export
Not available if two or more devices are selected. Exports the general
information of the selected device to an external Comma Separated
Value (CSV) file. Opens the Exports Equipment dialog box in which
you can browse to the desired location, enter a file name, and click
Export. The information displayed for the selected device in the
Equipment Manager is exported.
Additional management options are available for a single device, according to the
specific product line of the selected entry. For details refer to the Equipment
Manager section in the relevant Device Driver Manual.
AlvariSTAR
33
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Equipment Manager
LOCAL CRAFT NOTE
The Equipment Manager in the Local CRAFT Utility enables managing a single BTS. There is an
exception for point-to-point equipment, allowing the user to discover both devices.
To manage a new device when a device already exists in the Equipment Manager, you must delete
the existing entity before adding the new one. Otherwise the new entity will be added with
Unlicensed State. To apply a License to the new entity, you must first delete the “older” one.
After performing the necessary changes, click Retrieve to update the display.
2.1.3
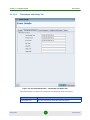
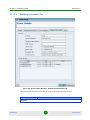
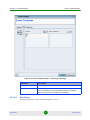
The Equipment Editor
The Equipment Editor enables editing NMS Reference (Location and Contact) and
SNMP parameters of a selected device. For multiple devices, it only enables editing
the NMS Reference (Location and Contact) parameters. It also enables defining the
parameters of a new device that you wish to add to the database.
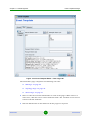
The Equipment Editor for all device types includes the following parameters:
Parameter
Description
General
Name
This field displays the network element’s name.
Location
The location associated with the device in the database of the management system
(optional). Click on the Browse icon to open the Select Location window and select a
location. Click the Eraser icon to clear the Location field.
Contact
The contact associated with the device in the database of the management system
(optional). Click on the Browse icon to open the Select Contact window and select a
contact. Click the Eraser icon to clear the Contact field.
Area Type
The type of environment the network element is located in. This feature is useful for
estimating and displaying the sector coverage in Google Earth (see Appendix D for
more information). The available options are:
Urban
Suburban
Rural
GPS Status
Indicates the GPS status for network elements which support GPS cards.
Latitude
Use this field to manually enter the network element’s latitude coordinate. Use positive
values for Northern latitudes and negative values for Southern latitudes.
Longitude
Use this field to manually enter the network element’s longitude coordinate. Use
positive values for Eastern longitudes and negative values for Western longitudes.
Altitude
Use this field to manually enter the network element’s altitude in meters.
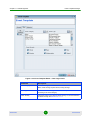
SNMP Parameters (applicable only for a single device editor)
AlvariSTAR
34
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Equipment Manager
Parameter
Description
Version
Indicates the SNMP protocol version used for communicating with the device. The
available options are:
v1
v2c
v3
For a complete list of all compatible SNMP versions for each device, see
Appendix E.
Agent Address
The device’s IP Address. Not configurable when editing the properties of an existing
object.
Port
The port number used by the device to communicate with the NMS. Not configurable
when editing the properties of an existing object.
Retries
The maximum number of retries for SNMP/TFTP communication with the Device.
The range is from 0 to 255.
The default is 2 retries.
Timeout(s)
The maximum time in seconds that the requesting process waits for a response from
the Device before attempting a retransmission (or aborting if the maximum number of
retries has been reached).
The available range is 1 to 3600 seconds.
The default is 15 seconds.
Read community (only
for SNMP v1 and v2c)
The Read community string (password) for SNMP get operations. This string is used
by the SNMP agent to allow/disallow SNMP read access.
The default Read community string in Base Station/Micro Base Station equipment is
public.
Write community (only for
SNMP v1 and v2c)
The Write community string (password) for SNMP set operations. This string is used
by the SNMP agent to allow/disallow SNMP write access. The Write community can
also be used for read (get) operations.
The default Write community string in Base Station/Micro Base Station equipment is
private.
Username (only for
SNMP v3)
AlvariSTAR
Username used for authentication
35
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Equipment Manager
Parameter
Description
Security Level (only for
SNMP v3)
Configures the authentication and privacy settings. The available options are:
NoAuth_NoPriv - Both authentication and privacy are disabled
Auth_NoPriv - Authentication is enabled and privacy is disabled
Auth_Priv - Both authentication and privacy are enabled
Authentication Algorithm
(only for SNMP v3)
Selects the hashing algorithm applied to the authentication password. The available
options are:
MD5 - Uses the Message-Digest algorithm 5
SHA - Uses the Secure Hash Algorithm
Authentication Password
(only for SNMP v3)
Password used for authentication.
Privacy Algorithm (only
for SNMP v3)
Encryption standard used for data transmission. The available options are:
AES - Uses the Advanced Encryption Standard
DES - Uses the Data Encryption Standard
Privacy Password (only
for SNMP v3)
AlvariSTAR
Encryption key used by the privacy algorithm
36
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
2.2
Location Manager
Location Manager
The Location Manager enables to specify information regarding the physical
location of managed equipment, to facilitate quick detection of managed objects
and to help drill down quickly when using maps to view specific equipment
components.
You can specify equipment locations within the Location Manager. Note that a
location can have a “Parent” Location, meaning that it belongs to a subset of
another location. For example, if network objects are on the third floor of a facility,
you can designate both the building and the specific floor as locations; the
building would be the parent of the floor. You may define multiple levels for
locations. In the current example, the city in which the building is located can be
defined as the parent location of the building, and so on.
To associate a single device with a location or several devices with a single
location, open the Equipment Editor for the device(s), click the Browse button
next to the Location field to open the Select Location window and select a location.
For further details, refer to Section 2.2.2.
To use the Location Manager:
1
Select Managed Network > Location Manager from the main menu or the
Navigation Pane. The Location Manager window is displayed.
AlvariSTAR
37
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
2
Location Manager
Select one or more locations from the list.
Figure 2-1: Location Manager
3
Use the following commands from the right click menu for various actions in
the Location Manager:
AlvariSTAR
Menu item
Action
New
Opens the Location Editor, through which you can define a new
location. Refer to Section 2.2.2, for more information
38
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Location Manager
Menu item
Action
Edit
Opens a Location Editor for a selected location, enabling you to
modify the definition of the Location. See Section 2.2.2 for more
information.
Delete
Enables to delete the selected location(s). When deleting a parent
location, the application also deletes its associated child locations. A
location associated with equipment cannot be deleted.
Add Child
Opens the Location Editor, through which you can define a new child
location that will be subordinate to the selected location. When
creating a child location, the name of the parent location field is
displayed in the Parent field.
Open Map
Opens the Location Map, displaying the selected location. See
Section 2.2.4 for more information.
2.2.1
Searching for a Location
To search for a specific location, enter the full name of the location (for example:
California) or part of the name (Ca) in the Name field. Only locations matching
that specification appear. Note that the filter is case-sensitive and the results are
displayed immediately.
2.2.2
Location Editor
The Location Editor enables to create a new location or modify details of an
existing location.
To create/modify a location:
1
In the Location Manager, right-click inside the work area and select New to
create a new location, or, to edit an existing location, right click a location from
the list and select Edit or double-click on the selected location. The Location
Editor is displayed.
AlvariSTAR
39
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Location Manager
Figure 2-2: Location Editor
2
Type in or modify the Location Editor fields as required:
Parameter
Description
General parameters
AlvariSTAR
Name
Enter a unique name for the Location, up to 32 printable characters.
This is the name that will be used for searching.
Parent
The parent of this location (the location to which this location is
subordinate). Click the Browser button to open the Select Location
window through which you can select a Parent Location. Click the
Eraser icon to clear the Parent Location field.
Coordinate Type
Specifies the way coordinates are designated; see Section 2.2.3
for more information. Valid types are: Country-City,
Latitude-Longitude, Area Code-prefix, Vertical-Horizontal.
40
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Location Manager
Parameter
Description
Coordinates
The coordinates of the location, using the Coordinate Type specified
above. Up to 80 printable characters.
Note that Coordinates do not relocate icons in geographic topology
maps; dragging icons does.
Images
Icon
Select an icon from the drop-down list to associate it with the location.
Available icons are: Building, Location.
Topology Image
Click the Browse button to open the Select Location window through
which you can select a map and associate it with the location. Click
the Eraser icon to clear the field. Click the Preview button to view the
associated map.
Depending on whether or not an image is assigned, the label
changes from "No image assigned" to "Image assigned".
Details
Postal Address
An optional field for entering the address of the location. A string of up
to 80 characters.
Location Details
An optional field for entering a description of the location. A string of
up to 80 characters.
3
2.2.3
Click Apply.
Coordinate Types
You can define locations using a variety of coordinate types, enabling accurate
definition of locations. The following are the default coordinate types:
Parameter
Description
Country-City
Country and city access codes.
Example: 049-071
Latitude-Longitude
Latitude and longitude.
Example: 38.57N, 121.47W
Area Code-Prefix
Area code and prefix.
Example: 916-939
Vertical-Horizontal
AlvariSTAR
Vertical / horizontal coordinates, developed by Bell
Systems.
41
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Location Manager
NOTE
Coordinates type and coordinates values are not used for displaying the location in geographic
topology. They are available for informational purposes only.
2.2.4
Location Map
The Location Map viewer displays a topology view of network devices and their
relationships. Clicking on the Open Map button opens the Location Map viewer
for the selected location, displaying its sub-locations and the equipment
associated with it. Associating a map with a location is optional; if no map is
associated with the location, the Location Map viewer will be empty. Each location
can either share a map with any other location or it can be associated with its own
map.
LOCAL CRAFT NOTE
In the Local CRAFT Utility, the Map displays only the licensed equipment and their associated SUs
(where applicable).
2.2.4.1
Defining Locations, Sub Locations and Maps
Primary (first level) locations have no parent locations. However, you can define
sub-locations (second level) whose “parents” are the primary locations. You may
continue and define third, fourth and fifth levels, where the parent location for
level N is a location in level N-1.
For each location you can also define a Geographical Map.
To define locations, sub locations, and/or maps:
1
Locations: From the Location Manager, click New to open the Location Editor.
Sub Locations: Select a location and click Add Child to open the Location
Editor with the selection location as the default parent location. Alternatively,
click New to open the Location Editor and select an existing node as the parent
in the Parent field.
2
AlvariSTAR
Define the Location Name.
42
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Location Manager
NOTE
For first level locations, the parent location field must be empty. For additional locations, a parent
location must be defined.
3
If you want to associate the location with a map, select the required map in the
Topology Image field.
NOTE
The required maps must be available (as *.jpg, *.gif, *.bmp, or *.png files) in the client station. The
file size is limited to 512 kb.
4
You can optionally define the Location Type, Icon and other details available in
the Location Editor.
5
2.2.4.2
You can associate equipment with locations. See Section 2.2.
Location Map Viewer Options
The Location Map viewer includes the following controls:
Parameter
Description
Up one level
Opens the next higher level of the topology map in the same
window. Disabled with in first level locations.
Display BreezeMAX SU
Check to display the associated SUs on the map. Only SUs
associated with the relevant location are displayed. If the serving
Base Station(s)devices are associated with the same location,
each of the displayed SU will be connected to the serving device.
Save
Saves the changes made to the map.
Cancel
Closes the Location Map viewer without saving.
The Location Map viewer provides a pop-up menu with the following options when
right-clicking on an equipment/location icon:
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Drill down
Opens the next lower level of the topology map in the same window.
Available only when right-clicking a location in the map, provided there is
a sub-location.
Configure
Available only for equipment with an Up state. Opens the Configuration
window, enabling to configure the selected device. You can also
double-click on the device icon on the map. Refer to the applicable Device
Manager Manual.
43
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Location Manager
Parameter
Description
Cut Through
Available only for equipment. Opens a Telnet session to the device.
Applicable only for devices that support this feature. (SUs do not support
Telnet.)
Open Alarms
Available only for equipment. Opens the Active Events window, enabling
to view the alarms (if any) associated with the selected device.
The background color of the device icon on the map is in accordance with the
alarm status of the device (the highest severity open alarms). For more
information, refer to “Alarm Severities” - Section 3.3.1.2.
Place a cursor on an icon to view its general details.
AlvariSTAR
44
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
2.3
Discovery Settings Manager
Discovery Settings Manager
LOCAL CRAFT NOTE
Not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility.
The Discovery Settings application enables to define the IP ranges/sub-nets in
which devices are expected to be discovered, and global SNMP Read and Write
community pairs. This defines the scope of your network and only devices within
this scope will be discovered. Up to 65535 IPs are supported.
To open the Discovery Settings Manager Application:
Select Managed Network > Discovery Settings Manager from the main menu or the
Navigation Pane.The Discovery Settings Manager displays the currently defined IP
address ranges/sub-nets (up to 65535 IPs) and other applicable information and
enables to add, edit, or remove a range.
AlvariSTAR
45
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Discovery Settings Manager
Figure 2-3: Discovery Settings Manager
Use the right click menu to perform the following available actions:
AlvariSTAR
Button
Action
New
Click to add a new entry to the table. This is done via the “Network
Settings Window”. Up to 65535 IPs are supported.
Edit
Click to edit an entry from the table. This is done via the “Network
Settings Window”.
Delete
Click to delete the selected Network IP Address Range entry.
46
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
2.3.1
Discovery Settings Manager
Button
Action
Import
Click to import an existing file (.xml or .nar) of IP address ranges settings.
Browse to the location of the file and click Open.
Export
Click to export the current IP Address Ranges table to an external file (.xml).
Browse to the location where the file is to be saved and click Save.
Network Settings Window
New or existing address ranges are edited inside the Network Settings window
Figure 2-4: The Network Settings Window
The following information is displayed for each range:
AlvariSTAR
47
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Discovery Settings Manager
Parameter
Description
Type
The type of range definition: IP Range or Subnet. Select from the drop-down
menu whether to define the range using IP Range (the first and last address in
the range) or Subnet (Network and Mask).
Start IP/Network
The first IP address in an IP Range or the Subnet address in a Subnet range
type.
End IP/Mask
The last IP address in an IP Range or the Subnet Mask in a Subnet range
type.
To minimize unnecessary traffic load in the network, avoid defining IP address
ranges that include too many “gaps”, e.g., non existing addresses.
Discovery
Check to enable periodical discovery, according to parameters defined in the
Task Manager. When unchecked, discovery is disabled.
Auto Discovery
Indicates whether Auto Discovery for the range is enabled or disabled. When
enabled, Discovery will be initiated whenever a trap is received from a device
in the range.
Location
The location defined for devices in the range. If a location is not defined, the
range will be used as the default location.
Contact
The contact defined for devices in the range.
SNMP Version
The SNMP protocol version used for communication by the discovered
devices. This can be either:
v1
v2c
v3
For a complete list of all compatible SNMP versions for each device see
Appendix E.
AlvariSTAR
48
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Discovery Settings Manager
Parameter
Description
SNMP Credentials
Use the Add and Remove buttons to populate the SNMP Credentials. The
type of credentials differ, depending on the SNMP version.
For SNMP v1 and v2c, fill in the read/write community table:
Read Community - SNMP Read community to be used by discovery when
accessing devices in the range. If unique communities are not defined, the
defined global Read communities will be used one after the other.
Write Community - The unique SNMP Write community to be used when
accessing discovered devices in the range. If unique communities are not
defined, the global Write community paired with the global Read
community that was used to discover devices in the range will be used
when accessing these devices.
For SNMP v3, the following credentials apply:
Username - Username used for authentication
Security Level - Authentication and privacy settings
»
NoAuth_NoPriv - Both authentication and
privacy are disabled
»
Auth_NoPriv - Authentication is enabled
and privacy is disabled
»
Auth_Priv - Both authentication and
privacy are enabled
Authentication Algorithm - Hashing algorithm applied to the authentication
password
»
MD5 - Message-Digest algorithm 5
»
SHA - Secure Hash Algorithm
Authentication Password - Password used for authentication
Privacy Algorithm - Encryption standard used for data transmission
»
AES - Uses the Advanced Encryption
Standard
»
DES - Uses the Data Encryption Standard
Privacy Password - Encryption key used by the privacy algorithm
AlvariSTAR
49
User Manual
Chapter 2 - Managed Network
Discovery Settings Manager
NOTE
Whenever possible, use unique SNMP community pairs for defined ranges rather than global
community pairs.The key for deciding which Write community to use is the IP range. Unique
community definitions enable to use the same Read community with several different Write
communities in different ranges, as well as to use the same Write community with several different
Read communities in different ranges. When using global community pairs, the Read community is
the key for deciding which Write community to use, meaning that the Read community should not
be used in more than one pair.
The Discovery process is based on the defined Read community. All future device management
actions will use the defined Write community. If a wrong Write community was defined, the device
will be discovered and displayed, but its status will be “Unknown” and it will not be possible to
manage it. The same is true for cases where the Write community in the device was changed (not
via the management system) after being discovered. In this case, the range must be updated with
the correct Write community, the device(s) must be deleted from the database, and the Discovery
process for the range should be re-initiated.
NOTE
When using global community pairs, the Read community is the key for deciding which Write
community to use. Each Read community should not be used more than once.
AlvariSTAR
50
User Manual
Chapter
3
Fault Management
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
In This Chapter:
“Introduction” on page 53
“Active Events” on page 54
“Event History” on page 57
“Event Filter Manager” on page 74
“Event Template Manager” on page 84
“Script Command Manager” on page 97
“Event Forwarding NBI Manager” on page 102 - not applicable to the Local
CRAFT Utility
AlvariSTAR
52
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.1
Introduction
Introduction
The Fault Management module provides network operators with the full fault
management capabilities required for rapid problem solving to ensure that the
network is up and running.
The Fault Management module comprises efficient tools for managing alarms
generated in the system. Information about each alarm is readily displayed,
helping operators diagnose and correct system failures. The Fault Management
tools allow you to acknowledge received alarms, clear, or forward them. You can
apply filters to display specific alarms or to display specific information about
each alarm according to your needs.
You can connect to other management systems and forward traps, apply
templates to automate the processing of alarms, and trigger external scripts.
The following Fault Management tools are available:
Active Events - Displays real time updates of new alarms entering the system,
color coded according to severity and allows to manage each alarm.
Event History - Enables to query the database for all events and alarms that
occurred in the system in specific time intervals, color coded according to
severity.
Event Filter Manager - Allows to create, edit and delete filters which are used
to display events in Active Events and Event History windows.
Event Template Manager - Allows to create, edit and delete templates to
automate the processing of alarms.
Script Command Manager- Allows to associate template-matched alarms with
external scripts.
Event Forwarding NBI Manager - Provides an interface where you can connect
to other management systems and effectively forward traps.
AlvariSTAR
53
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.2
Active Events
Active Events
The Active Events window displays real time updates of new alarms entering the
system, color coded according to severity. It allows you to manage and diagnose
alarms.
By default, only events that are categorized as alarms are displayed, and cleared
alarms are removed from the Active Events display and can only be viewed from
the Event History window. These can be either:
Manually cleared alarms
Alarms cleared by the automatic correlation rules
Alarms associated to a device that can no longer be managed by the system
Multiple occurrences of the same alarm (only one is visible in Active Events)
To change the default settings, see “Event Template Manager,” Section 3.5.
To open Active Events:
Select Fault Management > Active Events from the main menu or from the
Navigation Pane. The Active Events window is displayed.
AlvariSTAR
54
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Active Events
Figure 3-1: Active Events Window
When Active Events is launched, it opens in Listening mode. The display is
updated whenever an alarm is received or cleared.
To freeze the display such that the display of incoming alarms is suppressed, click
on the Freeze button. When in Freeze mode, the button label changes to
Unfreeze, enabling to return to the default state of displaying incoming alarms on
the fly.
The Active Events window is divided into the following main areas:
AlvariSTAR
55
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Active Events
Filter - allows you to filter out displayed alarms according to a custom filter or
according to severity. The displayed alarms change according to your
selection. Refer to Section 3.4 for information on the filtering options.
Alarm Table - displays general information about each alarm (see
Section 3.3.1.1). You can customize the information displayed in the table to
provide a more efficient view.
Counters - displays the distribution of the alarms, color coded according to
their severity, and a count of the number of active alarms meeting the filter
criteria out of the total number of active alarms. The format is x/y, where x is
the number of active alarms meeting the filter criteria per severity and y is the
total number of active alarms per severity.
Section 3.3.1 provides details on managing alarms in Active Events and Event
History. The following information is available:
“Alarm Table,” Section 3.3.1.1
“Alarm Severities,” Section 3.3.1.2
“Editing Event Filters,” Section 3.4.2
“Alarm Operations,” Section 3.3.1.4
AlvariSTAR
56
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.3
Event History
Event History
The Event History window displays a list of all events and alarms occurred in the
system, color-coded according to severity.
To open the Event History:
Select Fault Management > Event History from the main menu or from the
Navigation Pane. The Event History window is displayed:
Figure 3-2: Event History Window
To display newly received alarms or to updated the display of cleared alarms, click
on the Refresh button.
The Event History window is divided into the following main areas:
AlvariSTAR
57
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event History
Counters - displays the list of severities, color coded according to pre-defined
settings, and a count of active alarms distributed according to severity. The
format is x/y, where x is the number of active alarms meeting the filter criteria
per severity and y is the total number of active alarms per severity.
Alarm Table - displays general information about each event or alarm (see
Section 3.3.1.1). You can customize the information displayed in the table to
provide a more efficient view. You can also define the maximum number of
alarms displayed in the table (see Section 3.3.1.1.1).
Filter - allows you to filter out displayed alarms according to a custom filter or
for a range of dates that the event occurred. By default the alarms are
displayed for 10 days, but the range can be changed. Click on the calendar
icon to change the date and use the up/down arrows to change the time from
and until when to display events. The default time displayed is the real time of
the system. If Now is checked, alarms will be displayed from the time selected
until the present time.
Page Size - allows you to limit the number of displayed alarms.
Page x of y - a read only display of the number of the page displayed. You can
browse through the multiple screen displays using the right/left arrows.
Section 3.3.1 provides details on managing alarms in Active Events and Event
History. The following information is available:
“Alarm Table,” Section 3.3.1.1
“Alarm Severities,” Section 3.3.1.2
“Event Details Window,” Section 3.3.1.3
“Alarm Operations,” Section 3.3.1.4
AlvariSTAR
58
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.3.1
Event History
Managing Alarms
The following paragraphs describe how to manage alarms using Active Events and
Event History.
3.3.1.1
Alarm Table
The Alarms Table presents general information about each alarm occurred in the
system. You can change the order of the columns by dragging the columns title to
the desired location. The following describes the available attributes (columns) in
alphabetic order.
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Acked By
The user who acknowledged the alarm.
Ack Time
The date and time the alarm was acknowledged.
Alias
A user defined name for the equipment.
Cleared By
The user who cleared the alarm.
Clear Time
The date and time that the alarm was cleared.
Location
The location of the equipment at the source of the alarm.
Equipment
The name of the equipment at the source of the alarm.
Equipment Type
The type of equipment at the source of the alarm.
Event Category
The category classification of the event. The event categories are:
Alarm, State Change, System Event, Config Change
Event Name
The name of the alarm. For SNMP traps, the name is the trap OID. If
the name is blank when received by the application, the alarm takes
the name of the event template used for processing.
Event Time
The time and date the event occurred.
Event Type
The classification type of the alarm. Event types vary according to the
event category.
Last Update Time
The date and time the network element last updated the alarm.
Managed Object
The name of the equipment associated with the alarm. If the object
name is unknown, NotFound appears. An identification of a
component of the network element for which the alarm occurred. For
example a port on a router would be a managed object instance.
IP Address
The IP address of the mediation agent reporting this alarm.
Receive Time
The time the alarm was received by a mediation agent.
Severity
The severity of the alarm. Refer to Section 3.3.1.2
59
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event History
Event Category
Event Type
Alarm
All
Other
Communications Alarm
Quality of Service Alarm
Processing Error Alarm
Equipment Alarm
Environmental Alarm
Integrity Violation
Operational Violation
Physical Violation
Security Violation
Time Domain Violation
State Change
All
State Or Status Change
System Event
All
System Event
Software Download
Backup Configuration File
Maintenance
Telnet Session
Config Change
All
Config Change
Entity Added
Entity Changed
Entity Removed
3.3.1.1.1
Limiting the Number of Events from the Database
You can change the maximum number of events recorded in the database by
changing the value of the Max Row Count field in the Database Aging Task Editor
(Section 5.2.5). If the number of alarms exceeds 150% from the maximum number
of alarms, older alarms will be deleted. If your Secondary Storage is set up as
CSV, they will be saved to the following folder:
<Management_System>/filesystem/archive
AlvariSTAR
60
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.3.1.1.2
Event History
Customizing Views in Active Events / Event History
You can make changes to a view by adjusting columns in the Alarm Table
The following are the available options for customizing the view:
Sort columns - Click on the column header of the column according to which
you want to sort the table. An icon appears on the header, indicating sorting in
ascending/descending order. Only the following columns can be sorted:
Severity, Event Name, Received Time, Equipment, IP Address, Managed
Object, Alias, and Location.
NOTE
Column sorting is not available in Active Events.
Move Columns - Click the column header of the column you want to move and
drag it to its new location.
Resize Columns - Click the right margin of the column header you want to
resize and drag to resize the column. The column margin is located between
the column headers.
You can also Configure which alarms will appear in the Alarm Table, using the
Event Filter Manager (see Section 3.4).
3.3.1.2
Alarm Severities
The management system is delivered with a set of default alarm severity
definitions, each with its own default color.
The default severity definitions are:
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Critical
A service-halting condition occurs, requiring immediate corrective
action. The equipment is completely out of service and you must
restore its capability.
Major
A service-affecting condition has developed and corrective action is
required. There is severe degradation in the equipment’s capability
and you must restore its full capability.
Minor
A non-service-affecting fault condition exists and corrective action
should be taken in order to prevent a more serious fault. The detected
alarm condition is not currently degrading the capacity of the
equipment.
61
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.3.1.3
Event History
Parameter
Description
Warning
A potential or impending service-affecting fault could occur, and no
significant effects have yet been felt. Action should be taken to further
diagnose and correct the problem to prevent it from becoming a more
serious service-affecting fault. The detected alarm condition does not
currently pose a problem, but may degrade the capacity of the
equipment if you do not take corrective action.
Cleared
The problem is corrected, and the correlated alarm is cleared from
the Alarm Table.
Other
All other types of events/alarms.
Indeterminate
Indicates an alarm for which the perceived severity is uncertain, due
to any cause.
Event Details Window
The Event Tables in Active Events/Event History provide a simplified display,
summarizing each alarm. The Event Details window, however, presents all the
information associated with a selected alarm.
To open the Event Detail Information window:
From the Active Events/Event History window, select an alarm from the table,
right-click and select Event Details from the Alarm pop up menu, or double-click
on the alarm.
An example of the Event Details window is displayed below:
AlvariSTAR
62
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event History
Figure 3-3: Event Details Window
The Event Details window consists of the following tabs:
“General Tab,” Section 3.3.1.3.1
“Timestamps and Status Tab,” Section 3.3.1.3.2
“Event Parameters Tab,” Section 3.3.1.3.3
AlvariSTAR
63
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event History
“Additional Information Tab,” Section 3.3.1.3.4
“Notes Tab,” Section 3.3.1.3.5
3.3.1.3.1
General Tab
The General tab displays the following alarm attributes:
Parameter
Description
Network Element
Equipment Name
The name of the equipment.
Equipment Type
The type of equipment: Base Station, Micro Base Station, SU, NPU,
AU.
Managed Object
The name of the equipment associated with the alarm. If the object
name is unknown, NotFound appears.
Alias
A user defined name for the equipment
Location Name
The physical location of the equipment.
General Information
AlvariSTAR
Event Category
The category classification of the event. The event categories are:
Alarm, State Change, System Event, Config Change
Event Type
The classification type of the alarm. Event types vary according to the
event category.
Event Name
The name of the alarm. For SNMP traps, the name is the trap OID. If
the name is blank when received by the application, the alarm takes
the name of the event template used for processing.
Event Description
An optional text description of the alarm as defined in the related
event template.
Event Severity
The severity of the alarm.
Object Severity
The alarm severity of the object associated with the alarm.
64
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.3.1.3.2
Event History
Timestamps and Status Tab
Figure 3-4: Event Details Window - Timestamps and Status Tab
The Timestamps and Status tab displays the following alarm attributes:
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Last Update Time
The date and time the Alarm Table was last updated.
65
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
AlvariSTAR
Event History
Parameter
Description
Receive Time
The time a mediation agent received the alarm.
Event Time
The time that the event actually occurred.
Ack Time
The date and time the alarm was acknowledged.
Acked By
The user who acknowledged the alarm.
Clear Time
The date and time that the alarm was cleared.
Cleared By
The user who cleared the alarm.
66
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.3.1.3.3
Event History
Event Parameters Tab
Figure 3-5: Event Details Window - Event Parameters Tab
The Event Parameters tab displays the following alarm attributes:
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Event Severity
The severity of the alarm.
67
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
AlvariSTAR
Event History
Parameter
Description
Object Severity
The alarm severity of the object associated with the alarm.
Probable Cause
The probable cause of the alarm.
Specific Problem
The specific problem that caused the alarm.
Cleared By
The user who cleared the alarm.
Clear Time
The date and time that the alarm was cleared.
Clear Cause
The reason the alarm was cleared.
68
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.3.1.3.4
Event History
Additional Information Tab
Figure 3-6: Event Details Window - Additional Information Tab
The Additional Information tab displays the following alarm attributes:
Parameter
Description
Protocol
AlvariSTAR
69
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event History
Parameter
Description
Protocol
The protocol used for the alarm. The current version supports SNMP
only.
Source IP Address
The IP address of the object or device that sent the alarm. For Q3,
the source is the TNS name of the device or object.
Mediation Agent Address
The IP address of the mediation agent that received the trap.
SNMP Version
The SNMP version number
Generic Trap
The generic trap code. For Q3, it indicates an enterprise specific trap.
Possible values: 0,1,2,3,4,6
Specific Trap
The specific trap code as defined in the MIB, used only if Generic trap
is 6.
Enterprise OID
The SNMP Object Identification number. For SNMP v1, the OID is the
enterprise value from the SNMP PDU. For SNMP v2c, the OID is the
SNMP trap OID. For Q3, the OID is the Q3 Alarm Enterprise OID—
1.3.6.1.4.1.231.7.1.3.1.1.5.204.
System Up Time
Seconds elapsed since the object or device last rebooted. For Q3, it
is seconds elapsed since the Q3 Listener/Parser last rebooted.
Variable Bindings - Displays a list of the variable bindings for the selected alarm
AlvariSTAR
Name
The name of the variable as it appears in the MIB.
OID
The variable’s Object Identification.
Value
The value for the variable set in the MIB.
70
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.3.1.3.5
Event History
Notes Tab
Figure 3-7: Event Details Window - Notes Tab
AlvariSTAR
71
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event History
The Notes tab displays the following information about the alarm:
3.3.1.4
Parameter
Description
Event Advisor
Displays a text description of the alarm and sometimes proposes a
remedy. For example, “The device has received an improperly
authorized protocol message. The message has been discarded.”
The default message displayed in the Advisor page comes from the
trap’s MIB, but the message can be edited in the Event Template
Editor Advisor page (see Section 3.5.1.3.1). The Advisor
message is the default message for any e-mails sent about the alarm.
Proposed Repair Actions
The proposed remedy for the Alarm. The remedy comes from the
trap’s MIB.
General Notes
Enables the operator to provide additional information about the
selected alarm, such as steps already taken to correct the problem.
The note is stored with the alarm.
Alarm Operations
The system provides many alarm management features allowing you to diagnose,
troubleshoot, process, and clear alarms.
All general alarm operations are available via the context menu.
To manage alarms:
Select an alarm from the table and right-click on it to display the context
menu.The following are the displayed items:
Action
Description
Acknowledge Alarm
Acknowledges the selected open alarm(s). The current date and time
appear in the Ack Time field, and the name of the currently logged-on
user appears in the Ack By field.
Available for events that were set in the Event Template Manager to
require acknowledgement and for alarms. This status can be
changed, using an event template. See Section 3.5.1 for additional
information.
Unacknowledge Alarm
Unacknowledges previously acknowledged selected alarm(s), and
clears the entries in the Ack By and Ack Time fields.
Available for the current user if the alarm was previously
acknowledged by the current user.
AlvariSTAR
72
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event History
Action
Description
Clear Alarm
Clears only open selected alarm(s). Alarms’ status changes from
open to cleared. The status of the alarm changes from open to
cleared, but the alarm remains in the table.
Available if the Event type of a selected entity is Alarm and is not
acknowledged automatically by correlation mechanism.
Event Details
Displays detailed information about the selected alarm. See
Section 3.3.1.3 for additional information.
Event Advisor
Displays a text description of the alarm and sometimes proposes a
remedy.
Clearing Event
Opens the Event Details window of the event that cleared the alarm.
Equipment Details
Opens the Configuration Manager for the selected equipment.
Cut Through
Opens a Telnet session to the device. Applicable only for devices that
support this feature.
Topology Map
Displays the Location Map centered on the equipment associated
with the selected alarm.
Available only when the device has a location associated with it.
AlvariSTAR
Export
Exports the selected alarm(s) and creates a comma delimited text file
that can be imported into other programs (for example, a
spreadsheet).
Print Preview
Displays a preview of the Event History of the selected alarm(s)
before printing.
Print
Prints the Event History of the selected alarm(s).
73
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.4
Event Filter Manager
Event Filter Manager
The Event Filter Manager lets you create, edit and delete filters which are used to
display events in the Active Events and Event History windows. When using
pre-defined filters, specific alarm types are displayed, allowing you to control
alarms more efficiently.
To open the Event Filter Manager:
1
Select Fault Management > Event Filter Manager from the main menu or from
the Navigation Pane.
AlvariSTAR
74
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Filter Manager
Figure 3-8: Event Filter Manager
NOTE
You cannot apply an event filter to the Alarm Tables in the Active Events or Event History windows
from the Event Filter Manager. To apply a filter, select a Custom Filter in the Active Events or Event
History windows.
For each filter, the following information is displayed:
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Name
The name of the filter
75
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
2
3.4.1
Event Filter Manager
Parameter
Description
Description
A description of the filter.
Owner
The user who created the filter.
Creation Date
The filter’s date of creation.
From the Event Filter Manager you can:
»
Create new event filters - see Section 3.4.1
»
Modify existing event filters - see Section 3.4.2
»
Delete event filters - see Section 3.4.3
Creating Event Filters
To create a new event filter:
1
From the Event Filter Manager window (Figure 3-8), right click and select New
to define a new event filter. The Event Filter Editor window is displayed.
The Event Filter Editor window comprises the following main pages:
3.4.1.1
»
“General Tab” on page 76
»
“Simple Filter Tab” on page 78
2
Enter the relevant information in each of the pages.
3
Click OK to confirm your choices and save them to the database.
General Tab
In the General Tab, you can add general information on the filter.
AlvariSTAR
76
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Filter Manager
Figure 3-9: Event Filter Editor - General Page
The General Tab comprises the following fields:
Parameter
Description
General Event Template Settings
AlvariSTAR
Name
The name of the event filter.
Description
An optional description of the filter’s purpose.
Owner
A read only display of the user who created the template.
Creation Date
A read only display of the creation date of the template.
77
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.4.1.2
Event Filter Manager
Simple Filter Tab
The Simple Filter tab lets you enter custom filter criteria that are used to change
the event views in Active Events and Event History windows to make the
information more manageable.
To create filter criteria:
1
From the Event Filter Editor, click Simple Filter to define filter criteria. The
Filter Page is displayed:
Figure 3-10: Event Filter Editor - Simple Filter Page: NE
AlvariSTAR
78
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Filter Manager
The main Simple Filter page comprises the following pages:
2
»
“NE Tab” on page 79
»
“Topology Page” on page 79
»
“Event Tab” on page 80
Enter the relevant information in each of the pages. When there is a select
icon, click the icon to select elements from a list. Click the eraser icon to
remove selected elements.
3
3.4.1.2.1
Click the OK button to confirm your choices and save them to the database
NE Tab
The NE page (Figure 3-10) lets you enter the following filter criteria:
3.4.1.2.2
Parameter
Description
Network Element Type
Select the type of the network element from which the alarm
originated from.
Managed Object Type
Select the type of managed object from which the alarm originated.
Managed Object
Instance
Enter a specific instance name of the object where the alarm
originated.
Alias
A user defined name for the managed object.
Trap Name / OID
Select the trap name or OID Selector of the alarm. For SNMP traps,
the name of the trap is OID.
Topology Page
The Topology Page lets you select the following filter criteria about the equipment
and at a particular location:
AlvariSTAR
79
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Filter Manager
Figure 3-11: Event Filter Editor - Simple Filter Tab: Topology
3.4.1.2.3
Parameter
Description
Locations
Select the physical location of the equipment.
Network Elements
Select the network element from which the alarm originated. This
option is available only if the user selected at least one Network
Element Type which is different from "NMS" (in the NE page).
Event Tab
The Event page lets you select the following filter criteria:
AlvariSTAR
80
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Filter Manager
Figure 3-12: Event Filter Editor - Simple Filter Tab: Event
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Event Category
Select the category classification of the event. Possible values are:
All, Alarm, State Change, System Event, Config Change
Event Type
Select the classification type of the event. The possible values differ
according to the event category.
Event Severity
Check the boxes for the relevant alarm severity. For more information
on alarm severity see Section 3.3.1.2.
Event Status
Check Acknowledged to display only acknowledged alarms, Cleared
to only display cleared alarms or both to display all alarms
81
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.4.2
Event Filter Manager
Parameter
Description
User Classifier
Possible values are: None, Service Affecting
Editing Event Filters
To edit an existing event filter:
1
From the Event Filter Manager Window (Figure 3-8), right click an existing
filter from the list and select Edit. The Event Filter Editor window is displayed:
Figure 3-13: Event Filter Editor
AlvariSTAR
82
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Filter Manager
The Editing Event Filter window comprises the following main pages:
3.4.3
»
“General Tab” on page 76
»
“Simple Filter Tab” on page 78
2
Edit the information in the fields on all the pages as required.
3
Click OK to confirm your choices and save them to the database.
Deleting Event Filters
To delete an Event Filter:
1
In the Event Filter Manager window (Figure 3-8), right click the filter to remove
and select Delete. A confirmation message is displayed.
2
3.4.4
Click Yes to confirm the deletion.
Archiving Alarms
To ensure your database does not fill up with alarms, you can archive them via
the Database Aging task. See Section 5.2.5 for further details.
AlvariSTAR
83
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.5
Event Template Manager
Event Template Manager
Event Templates determine how the system processes different types of messages
sent by managed network objects. These templates can even trigger external
scripts (see Section 3.6). The system’s messages(alarms)typically indicate a
change in the operational status of the object, like a device failure or a system
reset. Event templates match each incoming message with specific actions. Device
drivers often install their own templates.
To open the Event Template Manager:
Select Fault Management > Event Template Manager from the main menu or from
the Navigation Pane. The Event Template Manager window is displayed:
AlvariSTAR
84
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Template Manager
Figure 3-14: Event Template Manager
For each template, the following information is displayed:
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Name
The name of the template.
Description
A description of the template.
Owner
The user who created the template.
Creation Date
The template’s date of creation.
Priority
The template’s priority. The range is 1~99999.
85
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Template Manager
From the Event Template Manager you can:
Create new event templates and modify existing templates - Section 3.5.1
Delete event templates - Section 3.5.2
3.5.1
Creating or Editing Event Templates
To create or edit an event template:
1
In the Event Template Manager window (Figure 3-14), right click and select
New to define a new event template, or select an existing template from the list
and click Edit. The Event Template Editor window is displayed:
The Event Template Editor window comprises the following main pages:
AlvariSTAR
»
“General Tab” on page 87
»
“Filter Tab” on page 88
»
“Behavior Tab” on page 93
2
Enter the relevant information in each of the pages.
3
Click OK to confirm your choices and save them to the database.
86
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.5.1.1
Event Template Manager
General Tab
In the General tab, you can add general information on the template.
Figure 3-15: Event Template Editor - General Tab
The General tab comprises the following fields:
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Name
The name of the event template.
Description
An optional description of the template’s purpose.
87
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.5.1.2
Event Template Manager
Parameter
Description
Priority
A numerical ranking for this template. The template priority field determines
which template processes an alarm if the alarm matches more than one
template. The smaller the number defining a template’s priority, the higher the
priority the template is. The range is: 0~999999.
Owner
A read only display of the user who created the template.
Creation Date
A read only display of the creation date of the template.
Filter Tab
The Filter tab lets you edit Filter Criteria. This filter information matches, or finds,
an event template for each alarm received by Fault Management. The first
template that matches the received alarm controls the processing of that alarm.
Fault Management’s fault processing logic uses the filtering information provided
in the Event Template, along with the templates’ priority, to determine which
template to use for a given alarm.
NOTE
The smaller the number defining a template’s priority, the higher the priority.
For every alarm received, Fault Management scans each template, in order of
priority (high to low). Fault Management selects the first template that matches on
each of the filterable fields for alarm processing.
If a template does not define a field (with either a null or empty value, or set to
“All”) then Fault Management does not use the field in the comparison. Empty or
“All” in a filterable template field means that the field matches anything.
Therefore, Fault Management uses only fields that have non-empty or non-“All”
values in any comparison.
To create filter criteria:
1
From the Event Template Editor, click Filter to define filter criteria. The Filter
tab is displayed:
AlvariSTAR
88
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Template Manager
Figure 3-16: Event Template Editor - Filter Page: NE
The main Filter page comprises the following sub-tabs:
2
»
“NE Page” on page 90
»
“Topology Page” on page 90
»
“Event Page” on page 91
Enter or edit the relevant information in each of the pages. When there is a
select icon, click the icon to select elements from a list. Click the eraser icon to
remove selected elements.
3
AlvariSTAR
Edit the information in the fields on all the pages as required.
89
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
4
3.5.1.2.1
Event Template Manager
Click OK to confirm your choices and save them to the database.
NE Page
The NE page (Figure 3-16) lets you enter the following filter criteria about the
network elements and managed objects from which the alarm originates:
3.5.1.2.2
Parameter
Description
Network Element Type
Select the type of the network element from which the alarm
originates.
Managed Object Type
Select the type of managed object from which the alarm originates.
Managed Object
Instance
Enter a specific instance name of the object where the alarm
originated.
Managed Object Alias
A user defined name for the managed object
Event Name
Select the name of the alarm.
Topology Page
The Topology Page lets you select the following filter criteria about the equipment
at a specific location:
AlvariSTAR
90
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Template Manager
Figure 3-17: Event Template Editor - Filter Page: Topology
3.5.1.2.3
Parameter
Description
Locations
Select the physical location of the equipment.
Network Elements
Select the network element from which the alarm originates. This
option is available only if the user selected at least one Network
Element Type different from NMS (on the NE page).
Event Page
The Event page lets select the following filter criteria:
AlvariSTAR
91
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Template Manager
Figure 3-18: Event Template Editor - Filter Page: Event
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Event Category
Select the category classification of the event. Possible values are:
Alarm, State Change, System Event, Config Change
Event Type
Select the classification type of the event. The possible values differ
according to the event category.
Event Severity
Check the boxes for the relevant alarm severity. For more information
on alarm severity see Section 3.3.1.2.
92
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.5.1.3
Event Template Manager
Behavior Tab
The Behavior tab provides parameters that determine how Fault Management
processes matching alarms.
Figure 3-19: Event Template Editor - Behavior Tab
The main Behavior page comprises the following sub-tabs:
“Actions Page” on page 94
“Email Page” on page 94- not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility
AlvariSTAR
93
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.5.1.3.1
Event Template Manager
Actions Page
The Actions page contains the following parameters:
Parameter
Description
Script Command
Initiates an external script. Browse for the script command name by
clicking the command (...) button. When you click this button, the
Command Selector is displayed.
See Section 3.6 for information about how to add commands to this
selector. Click the eraser icon to remove selected scripts from this
field.
3.5.1.3.2
User Classifier
Select the User Classifier. Possible values: None, Service Affecting
Alarm Severity
Select the severity level of the alarm. Once Fault Management
selects the template, before actually processing the alarm, this field
overrides the severity of the alarm as it was received from mediation.
Possible values are: No Change, Cleared, Indeterminate, Warning,
Minor, Major, Critical
Requires Acknowledge
Check to require that the associated event is acknowledged
Advisor Message
Enter a text description of the event.
Email Page
LOCAL CRAFT NOTE
The Email page is not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility.
Use the Email page to enter a message that appears in emails when the template
acts and define a list of recipients to be notified. This presupposes email functions
within the environment where your host is installed.
AlvariSTAR
94
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Template Manager
Figure 3-20: Event Template Editor - Email
AlvariSTAR
95
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Template Manager
The Email page contains the following parameters:
3.5.2
Parameter
Description
Auto Send Email
Check to automatically send a defined email message to the specified
recipient(s) whenever the associated event occurs.
To
Select the recipient for this email message from the list.
Subject
Enter the subject line of the email message.
Message
Enter an email message.
Deleting Event Templates
To delete an Event Template:
1
In the Event Template Manager window (Figure 3-14), right click the template
to remove and select Delete. A confirmation message is displayed.
2
AlvariSTAR
Click Yes to confirm the deletion.
96
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.6
Script Command Manager
Script Command Manager
Template-matched alarms can trigger external scripts. These script commands
can even have parameters that come from values in the EventInfo alarm’s
attributes, or other assigned constants. The Script Command Manager lists
available script commands. You can create, edit and delete script commands.
To open the Script Command Manager:
Select Fault Management > Script Command Manager from the main menu or from
the Navigation Pane. The Script Command Manager window is displayed:
AlvariSTAR
97
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Script Command Manager
Figure 3-21: Script Command Manager
From the Script Command Manager, you can:
Create new commands and modify existing commands - Section 3.6.1
Delete commands - Section 3.6.2
AlvariSTAR
98
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.6.1
Script Command Manager
Creating or Editing Commands
To create or edit a command:
1
In the Script Command Manager, right click and select New to define a new
command. The Command Editor window is displayed:
Figure 3-22: Command Editor
2
AlvariSTAR
Configure your script with the following fields:
99
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Parameter
Script Command Manager
Description
Command Information
Command Name
A unique text identifier.
Description
A text description
Command Details
Script Name
The name of the script to run
Script Path
The location of the script. Describe either a Windows or UNIX path.
Command Argument
Argument Option
Enter a text value
Argument Type
Possible values are: Constant, Event Property
Argument Value
If Argument Type = Constant, this is a text field
If Argument Type = Event Property then select from a list of possible
attributes
Text Qualifier
Select whether this parameter needs double, single quotes, or no
qualifier. When you select quotes, the parameter looks like this: -a
“surrounded by quotes”.
Command Line
This section of the screen displays the script command as you
assemble it. Click the Add button on the right to assemble the
complete script command. Added parameters always appear last on
the list in this area, but you can use the arrow keys to re-arrange their
order, and the Delete button to remove parameters (but not the
script). Delete All removes everything.
3
Click Add to assemble the complete script command. Added parameters
always appear last on the list, but you can use the arrow keys to re-arrange
their order, or use the Delete button to remove parameters (not the script).
Delete All removes everything.
AlvariSTAR
4
Click the Up or Down buttons to arrange the order of parameters.
5
Click OK to add your command script to the list of available scripts.
100
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.6.2
Script Command Manager
Deleting Commands
To delete a command:
1
In the Script Command Manager window (Figure 3-21), right click the
command to remove and, from the context menu click Delete. A confirmation
message is displayed.
2
AlvariSTAR
Click Yes to confirm the deletion.
101
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.7
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
LOCAL CRAFT NOTE
The Event Forwarding NBI Manager is not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility.
The Event Forwarding NBI Manager provides an interface where you can connect
to other management systems, and effectively forward traps. Fault Management
uses these definitions to enable it to forward notifications to those systems.
Event Forwarding NBI systems include any EMS system (a system receiving
information from Fault Management), for example: Billing Management Systems,
Support Management Systems, Network Management Systems, and Customer
Service Systems.
To open the Event Forwarding NBI Manager:
Select Fault Management > Event Forwarding NBI Manager from the main menu
or from the Navigation Pane.
AlvariSTAR
102
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
Figure 3-23: Event Forwarding NBI Manager
For each filter, the following information is displayed:
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Name
The name of the filter.
Description
A description of the filter.
IP Address
The IP address of the higher manager
Protocol
The protocol governing the network management.
Event Forwarding
The event forwarding status.
103
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
From the Event Forwarding NBI Manager you can:
Create or modify Event Forwarding NBI interfaces - Section 3.7.1
Delete Event Forwarding NBI interfaces - Section 3.7.2
Create and modify Event Forwarding NBI interface policies - Section 3.7.3
Set up status notifications sent by the NMS Server for synchronisation Section 3.7.4
NOTE
It is mandatory to define at least one policy for a Event Forwarding NBI interface in order to activate
trap forwarding. Provided that the Event Forwarding NBI is enabled in the NBI Editor, if no policy
has been defined, or if the policy is not enabled, the Event Forwarding NBI interface appears gray in
the display, indicating that an action must be taken.
3.7.1
Creating or Editing Event Forwarding NBI
Interfaces
To create a new Event Forwarding NBI interface:
1
Right click inside the Event Forwarding NBI Manager window (Figure 3-23)
and select New to define a new Event Forwarding NBI interface, or right click
an entry from the list and select Edit. The NBI Editor window is displayed:
AlvariSTAR
104
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
Figure 3-24: NBI Editor
2
Edit the information in the fields on all the pages as required.
Parameter
Description
Name
The name for the northbound interface.
Description
An optional description of the Event Forwarding NBI interface.
Enable
Check to enable trap forwarding
IP Address
The IP address of the remote host to which the traps will be
forwarded.
Protocol
SNMP
SNMP Parameters
AlvariSTAR
Version
The SNMP version. Possible values are: v1, v2c or v3. For a
complete list of all compatible SNMP versions for each device see
Appendix E.
Trap Port
The port number to use to communicate with the system.
105
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
NOTE
The port configured in the NBI editor must match the port your system uses to communicate.
Typically, SNMP devices use port 161 to receive set/get requests and port 162 to receive traps. So,
typically you must configure Fault Management to forward traps to an OSS/SNMP client with a
destination port of 162
3
3.7.2
Click OK to confirm your choices and save them to the database.
Deleting Event Forwarding NBI Interfaces
To delete an NBI:
1
In the Event Forwarding NBI Manager window (Figure 3-23), right click the
filter to remove and select Delete. A confirmation message is displayed.
2
3.7.3
Click Yes to confirm the deletion.
Creating Event Forwarding NBI Interface
Policies
Once you have defined the IP address to which to forward traps, the policy
determines which traps to forward and when. At least one policy must be defined
for a specific Event Forwarding NBI interface in order to activate trap forwarding.
The policy manager displays the current policies defined for the specific interface
To open the NBI Policy List:
From the Event Forwarding NBI Manager window (Figure 3-23), right click an
existing NBI from the list and select Policy. The NBI Policy List is displayed:
AlvariSTAR
106
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
Figure 3-25: NBI Policy List
For each NBI Policy, the following information is displayed:
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Name
The name of the policy.
Description
A description of the policy.
Status
The policy status
107
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
From the NBI Policy list you can:
Create or modify NBI policies - Section 3.7.3.1
Delete NBI policies - Section 3.7.3.2
3.7.3.1
Creating or Modifying NBI Policies
To create or modify an NBI policy:
1
Right click inside the NBI Policy window (Figure 3-25), and select New to
define a new NBI policy, or right click an entry from the list and click Edit. The
NBI Policy Editor window is displayed (Figure 3-26).
The NBI Policy Editor window comprises the following main pages:
3.7.3.1.1
»
“General Page” on page 108
»
“Filter Tab” on page 109
2
Enter the relevant information in each of the pages.
3
Click OK to confirm your choices and save them to the database.
General Page
In the General page, you can add general information on the policy.
AlvariSTAR
108
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
Figure 3-26: NBI Policy Editor - General Page
The General page comprises the following fields:
3.7.3.1.2
Parameter
Description
Name
The name of the NBI policy.
Description
An optional description of the policy.
Enabled
Check to enable the policy.
Filter Tab
The Filter tab lets you associate a filter with the NBI policy.
AlvariSTAR
109
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
To create filter criteria:
1
From the NBI Policy Editor, click Filter to define filter criteria. The Filter Page
is displayed:
Figure 3-27: NBI Policy Editor - Filter Page: NE
AlvariSTAR
110
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
The main Filter page comprises the following sub-tabs:
2
»
“NE Page” on page 111
»
“Topology Page” on page 111
»
“Event Page” on page 112
Enter the relevant information in each of the pages. When there is a select
icon, click the icon to select elements from a list. Click the eraser icon to
remove selected elements.
3
3.7.3.1.2.1
Click the OK button to confirm your choices and save them to the database
NE Page
The NE page (Figure 3-27) lets you enter the following filter criteria:
3.7.3.1.2.2
Parameter
Description
Network Element Type
Select the type of the network element from which the alarm
originated from.
Managed Object Type
Select the type of managed object from which the alarm originated.
Managed Object
Instance
Enter a specific instance name of the object where the alarm
originated.
Managed Object Alias
A user defined name for the managed object.
Event Name
Select the name of the alarm.
Topology Page
The Topology Page lets you select the following filter criteria:
AlvariSTAR
111
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
Figure 3-28: NBI Policy Editor - Filter Page: Topology
3.7.3.1.2.3
Parameter
Description
Locations
Select the physical location of the equipment.
Network Elements
Select the network element from which the alarm originated. This
option is available only if the user selected at least one Network
Element Type which is different from "NMS" (in the NE page).
Event Page
The Event page lets you select the following filter criteria:
AlvariSTAR
112
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
Figure 3-29: NBI Policy Editor - Filter Page: Event
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Event Category
Select the category classification of the event. Possible values are:
Alarm, State Change, System Event, Config Change
Event Type
Select the classification type of the event. The possible values differ
according to the event category.
Severity
Check the boxes for the relevant alarm severity. For more information
on alarm severity see Section 3.3.1.2.
User Classifier
Select the User Classifier. Possible values: None, Service Affecting
113
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
3.7.3.2
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
Deleting NBI Policies
To delete an NBI policy:
1
In the Event Forwarding NBI Manager window (Figure 3-23), right click the
policy to remove and select Delete. A confirmation message is displayed.
2
3.7.4
Click Yes to confirm the deletion.
NBI Notifications Global Settings
The NBI Notifications Global Settings configures the synchronization notifications
sent by the NMS to the OSS.
Figure 3-30: NBI Notifications Global Settings
The following settings are available:
Parameter
Description
Notifications
Keep Alive
AlvariSTAR
Sends keep alive notifications at predefined time intervals as long as
the NMS server is active. Check to enable, uncheck to disable.
114
User Manual
Chapter 3 - Fault Management
Event Forwarding NBI Manager
Parameter
Description
Interval (minutes)
Defines the time interval (in minutes) between successive keep alive
notifications. Use the text box to enter the desired value.
Server Started
Sends a notification message when the server has started up. Check
to enable, uncheck to disable.
Server Shutdown
Sends a notification message when the server is shutting down.
Check to enable, uncheck to disable.
Event Types
Send Original Traps
Select this option to forward traps in their original format, just as they
are received from the device.
Send NMS Events
Select this option if you want the sent traps to include all the relevant
information stored in the fault management database.
NOTE
In order to enable synchronization with the NMS, the following RW parameters must be configured
on the OSS/SNMP client:
Parameter
Description
sendOperationalAlarms
Enables/Disables alarm synchronization. The following values
apply:
0 - Synchronization disabled
1 - Synchronization enabled
2 - Synchronization based on a custom time interval
3 - Synchronization based on a custom SeqNo interval
opAlarmsCustomIntervalStart
Interval start for custom time/SeqNo interval based
synchronization
opAlarmsCustomIntervalEnd
Interval end for custom time/SeqNo interval based
synchronization
NOTE
The OSS/SNMP client uses the 16162 port to send synchronization request to the NMS.
AlvariSTAR
115
User Manual
Chapter
4
Configuration Management
Chapter 4 - Configuration Management
In This Chapter:
This chapter describes functionalities used by the NMS to support integration
with Google Earth (see Appendix D for more information about Google Earth
integration). These features are:
“CPE Types Selector” on page 118
“File Generation Parameters” on page 120
AlvariSTAR
117
User Manual
Chapter 4 - Configuration Management
4.1
CPE Types Selector
CPE Types Selector
The CPE Types Selector allows users to indicate the frequency bands, power and
antenna gains used by the deployed CPEs. Based on this information, sector
coverage representations can be estimated and displayed in Google Earth.
To open the CPE Types Selector:
Select Configuration Management > CPE Types Selector from the main menu. The
CPE Types Selector window opens.
Figure 4-1: CPE Types Selector
Select one or more CPE types that are deployed:
Use the > button to add the currently selected available CPE type to the Active
CPE Types list
AlvariSTAR
118
User Manual
Chapter 4 - Configuration Management
CPE Types Selector
Use the >> button to add all currently available CPE types to the Active CPE
Types list
Use the < button to remove the currently selected active CPE type from the list
Use the << button to remove all the CPE types that are currently active from
the list
AlvariSTAR
119
User Manual
Chapter 4 - Configuration Management
4.2
File Generation Parameters
File Generation Parameters
The NMS can be configured to generate a file containing information about the
network elements’ locations. This file uses the Keyhole Markup Language (.kml)
format, which is compatible with Google Earth, allowing it to display the network’s
topography.
To open the File Generation Parameters:
Select Configuration Management > File Generation Parameters from the main
menu. The File Generation Parameters window opens.
Figure 4-2: File Generation Parameters
The following parameters can be configured:
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
File Generation Enabled
Check to generate the .kml file, and uncheck if you don’t want the file
to be generated. The feature is enabled by default. If you don’t plan to
use Google Earth you may disable it.
File Generation Interval
Enter how often (in minutes) the .kml file is updated. The default value
is 5 minutes.
120
User Manual
Chapter
5
Administration
Chapter 5 - Administration
In This Chapter:
“Introduction” on page 123
“Task Manager” on page 124
“File Manager” on page 141
“Contact Manager” on page 143
“License Manager” on page 147 - not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility
AlvariSTAR
122
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
5.1
Introduction
Introduction
The Administration node in the Navigation Pane comprises the following
system-wide utilities:
Task Manager - enables to manage system-wide tasks, such as SW upgrade,
Network Discovery (not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility), PM collection,
etc. See Section 5.2.
File Manager - enables to manage files that are stored in the database. These
files and functionality of the manager are product line dependent. For details
refer to the relevant Device Driver Manual. Refer to Section 5.3.
Contact Manager - enables to organize and manage your contacts. Refer to
Section 5.4
License Manager (not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility) - enables to view
information about valid licenses. See Section 5.5.
AlvariSTAR
123
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
5.2
Task Manager
Task Manager
This section includes:
“Using The Task Manager” on page 124
“The Task Scheduler” on page 129
“The Task Results Viewer” on page 131
“Network Discovery Task” on page 133 - not applicable to the Local CRAFT
Utility
“Database Aging Tasks” on page 134
“Discovery Task” on page 136 - not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility
5.2.1
Using The Task Manager
Tasks are operations that are performed on a large number of system entities
(such as equipment, services, etc.). They run in the background, allowing the
network administrators to continue managing the network while they run. After a
task has completed, or upon termination of a task, a report is issued.
The Task Manager displays information on defined tasks and enables to create
new tasks, edit, schedule, run or delete existing tasks. If there is any error in the
parameters definition such as a missing parameter, contradicting definitions or a
non-valid value, the relevant error message(s) will be displayed at the top section
of the window, and a red border around the relevant entries will indicate the
parameters that should be corrected. The Task Manager also enables to abort
running tasks and to view reports on completed and aborted tasks.
As tasks availability and functionality differ depending on the configured device
driver, refer to the relevant Device Driver Manual for a detailed description of
performing these tasks.
The following are the common available types of tasks:
“Network Discovery Task” - Section 5.2.4 - not applicable to the Local CRAFT
Utility
“Database Aging Tasks” - Section 5.2.5
AlvariSTAR
124
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
“Discovery Task” - Section 5.2.6 - not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility
To access the Task Manager:
1
Select Administration > Task Manager from the main menu or the Navigation
Pane. The Task Manager displays a list of defined tasks.
Figure 5-1: Task Manager
The following information is displayed for each defined task:
AlvariSTAR
125
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
Parameter
Description
Name
A unique name of the task.
Created by
The user name of the task creator.
Modified by
The name of the user who last modified the task.
Volatile
Describing if the task’s behavior varies unpredictably. This type of
tasks is not saved in the database. It can be run only once.
Type
The type of task. The available task types are:
Network Discovery Task (not applicable to the Local
CRAFT Utility)
Database Aging Task
Range Discovery Task (not applicable to the Local CRAFT
Utility)
Additional tasks according to the installed device driver(s).
State
The current state of the task: Active, Inactive, Waiting, Stopping.
Last Run
The date and time the last time the task was run.
Last Run Result
The result of the task’s last run: Completed/Completed with
errors/Aborted/Never run.
Next Run
The date and time the next time the task is scheduled to run, or Not
Scheduled.
2
AlvariSTAR
The following controls are available in the Task Manager’s context menu:
126
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
Control
Description
New
Adds a new task to the Task list. When selected, it opens the Task
Wizard. The wizard has three steps:
Edit
1
Create New Task - Define the task’s name, description, type and
the network equipment to which it applies.
2
Configure Task - Define the specific task parameters. This step is
customized based on the type of task and network equipment.
3
Finish Task - Choose how to use the task once you are finished
defining it:
»
Run it immediately (Run Now)
»
Don’t run it (None)
»
Schedule it to be run later (Schedule)
For an Inactive Task: Opens the Task Editor for the selected
Inactive task, allowing to edit the task parameters. Not available if
more than one task is selected. From the Task Editor, you can
also run the task by clicking Run.
For Active Task: Opens the Runtime Results window displaying
the task’s progress.
Delete
Deletes the selected task from the database. Right click the task to
remove and select Delete. The application prompts you for
confirmation.
Not available for active tasks and for system tasks (Network
Discovery Task and Database Aging Tasks).
Scheduled tasks cannot be deleted. To delete a scheduled task, you
need to first clear the schedule (see below).
Run
Manually executes the task. While the task is running, the state
changes from Inactive to Active. The option is unavailable for
currently running tasks. The Run button is also available in each of
the task windows. If there are more than 20 active tasks, some of the
tasks may change from Inactive to Waiting.
When attempting to run a task which affects equipment that is not part
of the user’s visibility domain, a meaningful message will be
displayed in the task report. For more information about domain
management, see “User Domain Manager” on page 185.
AlvariSTAR
127
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
Control
Description
Abort
Aborts the selected running task. Available for running tasks only.
Upon selecting the Abort option, a confirmation message is
displayed. Click Yes to abort the task. The task’s State changes to
Inactive and the Last Run Result to Aborted.
Schedule
Opens the Schedule Editor, enabling to schedule the activation of the
task. See Section 5.2.2.
Unschedule
Clears the schedule for the selected task. Active only for scheduled
tasks.
Report
Opens the Task Report window, enabling to view a report of the last
execution of the selected task. Not available for tasks that were never
run.
The Report window can also be accessed from each task editor. The
Report button in the task editors is inactive while the task is running
and will become active only after the task has completed.
You can save the report to the file system by clicking the Save As
button in the Task Report window. The system will prompt you to save
large reports. You can print the report directly from the report window.
Not available for tasks that were never run.
History
Opens the Task Results window, displaying a list of all past
activations of the selected task and their results.
Not available for tasks that were never run.
When editing tasks, the following general controls are available:
Click
To:
OK
Save the changes and close the task window
Cancel
Close the window without saving
Run
Execute the task
Abort
Stop the task
View Report
Open the scan report (see Section 5.2.3)
Schedule
Set a time to run the task (see Section 5.2.2)
Additional task status information may appear at the bottom of the task window.
For example: Completed, Never Run, or Inactive
AlvariSTAR
128
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
5.2.2
Task Manager
The Task Scheduler
Tasks can be scheduled to run once, or at predefined recurrence intervals.
Examples of recurring tasks include Network Discovery and Database Aging.
To schedule a task:
1
In the Task Manager window, right click a task from the list and select
Schedule. Alternatively, you can schedule a task during task creation, or
while editing a task, by clicking on the scheduler icon at the bottom left of the
task window. The Schedule Editor opens.
Figure 5-2: Schedule Editor
AlvariSTAR
129
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
The Schedule Editor includes the following parameters:
Parameter
Description
Start
The start time for the task. Select one of the following options:
Now
On - set a specific start date and time. You can highlight the value
to change (month, day, year) and click on the up/down arrows to
change the value, or you can pick a specific date using the
calendar icon. You can also type in the date and time as follows:
MMMM DD, YYYY HH:MM AM/PM.
Recurrence
Set the recurrence interval between each task execution. Available
intervals include:
None - no recurrence (default)
Minutely - specify the number of minutes. (the range is 1-1,440)
Hourly - specify the number of hours. (the range is 1-96).
Daily - specify the number of days. (the range is 1-60)
Weekly - select one of the following options:
»
Recur every - enter the number of weeks between task
executions (the range is 1-20)
»
Day - specify the day of the week (Sunday to Saturday) and
the number of weeks between task executions (the range is
1-20).
Monthly - select one of the following options:
AlvariSTAR
»
Recur every - enter the number of months between task
executions (the range is 1-36)
»
Day - specify the day in the month (1-31) and the number of
months between task executions (the range is 1-36).
130
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
Parameter
Description
End
The end time for a recurring task (only). Select one of the following
options:
Never - enable tasks to be executed indefinitely
After N occurrences (where N is a number between 1-65,000) set the number of occurrences after which the task’s scheduling
will be cleared.
On - set an end date and time. You can highlight the value to
change (month, day, year) and click on the up/down arrows to
change the value, or you can pick a specific date using the
calendar icon. You can also type in the date and time as follows:
MMMM DD, YYYY HH:MM AM/PM.
5.2.3
2
Set the Start and End time and optionally select a recurrence interval.
3
Click OK to apply the schedule for the selected task.
The Task Results Viewer
The Task Results window displays a list of all past activations of the task selected
in the Task Manager window and their results. Not available for tasks that were
never run.
To use the Task Results window:
1
In the Task Manager window, right click a task from the list and select History
from the context menu. The Task Results window is displayed.
AlvariSTAR
131
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
Figure 5-3: Task Results Window
The Task Results window displays the following information for each listed
activation:
2
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Start
The start time of the activation.
End
The end time of the activation.
Result
The result of the activation.
Use the Task Results controls as required:
Action
Description
View
Displays the task results.
Save
Enables to save the task results to an external file. Click and
browse to a location in the file system, enter a name for the
file and click Save.
Delete
Deletes the selected task.
132
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
5.2.4
Task Manager
Action
Description
Close
Closes the Task Results window.
Network Discovery Task
LOCAL CRAFT NOTE
The Network Discovery Task is not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility.
The Network Discovery task is a system task that scans the entire network for
new devices. The scope of the network is defined in the Discovery Settings window
(see Section 2.3). The Network Discovery task can only be modified, not deleted.
To edit the Network Discovery Task
1
In the Task Manager window, right click the Network Discovery task from the
list and select Edit, or double-click the task’s entry. If the task is Active, the
Runtime Results window opens, displaying the status of the running task.
Figure 5-4: Network Discovery Task - Runtime Results
If the task is Inactive, the Network Discovery Task is displayed.
AlvariSTAR
133
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
Figure 5-5: Network Discovery Task Window
2
You can modify the SNMP Parameters of the Network Discovery Task as
required (the Discovery Settings are read-only and can be modified only in the
Discovery Settings manager):
Parameter
Description
Retries
The maximum number of retries for SNMP communication.
The range is from 0 to 255.
Timeout
The maximum time in seconds that the requesting process waits for a
response before attempting a retransmission (or aborting if the
maximum number of retries has been reached).
The available range is 1 to 3,600 seconds.
3
5.2.5
Use the Editor controls as required.
Database Aging Tasks
The Database Aging tasks set the maximum number of alarms shown in the Event
History (Section 3.3) and Audit Log (Section 6.2) and automate database
management tasks. Database Aging tasks are system tasks and can only be
modified, not deleted.
AlvariSTAR
134
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
To edit the Database Aging Task:
1
In the Task Manager window, right click the Database Aging task from the list
and select Edit. If the task is Active, the Runtime Results window opens,
displaying the status of the running task.
If the task is Inactive, the Database Aging Task is displayed.
Figure 5-6: Database Aging Task Window
The Database Aging Task window includes the following information in two
tabs:
Parameter
Description
Criteria tab
Table Name
AlvariSTAR
The name of the table. Possible values are Event History and Audit
Logs. This is a read only field and cannot be modified
135
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
Parameter
Description
Max Row Count
The maximum number of alarms in the database.
Note: When the number of alarms exceeds the value entered in the
Max Row Count field by 25%, an alarm is sent. When the number of
alarms exceeds the value entered in the Max Row Count field by
50%, the oldest alarms are deleted so that the total number of alarms
in the database equals the value defined in the Max Row Count field.
Actions tab
5.2.6
Secondary
Storage
File type of the archived records. Possible values are: None, CSV
Destination
A disk location for archiving. The default location is:
<Management_System>/filesystem/archive.
Discovery Task
LOCAL CRAFT NOTE
The Discovery Task is not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility.
The Discovery Task enables to scan a predefined range of IPs for new and modified
devices.
To open the Range Discovery Task window:
1
In the Task Manager window:
»
Right click and select New. The Task Wizard opens.
»
In the Task Wizard, select Discovery Task in the Category field, fill in the
rest of the fields according to your preferences and click Next to proceed to
the Discovery Task configuration window described below.
»
After you configure all your settings, proceed to the third step of the wizard
to finalize your task creation.
OR
»
Right click an existing Discovery task from the list and select Edit, or
double-click the task’s entry. If the task is Active, the Runtime Result
window is displayed, displaying the status of the running task.
AlvariSTAR
136
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
If the task is Inactive, the Discovery Task window is displayed.
Figure 5-7: Discovery Task Window
The Discovery Task window comprises the following fields:
Parameter
Description
Task Name
The name of the task. A string of up to 128 printable characters. The name must be
unique in the system and cannot include the following characters: /,\,?,<,>,:,*,^,|,"
Range Type
The range type: IP or Subnet.
Range Start
The first IP in the range or the base IP, depending on the selected Range Type.
AlvariSTAR
137
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
Parameter
Description
Range End/Subnet Mask
The last IP in the range or the subnet mask, depending on the selected Range Type.
Location
An optional field for defining a location for devices in the range. Select from the
available locations. Newly discovered devices will be automatically associated with the
defined location. Devices already in the database will not be affected.
Contact
An optional field for defining a contact for devices in the range. Select from the
available contacts. Newly discovered devices will be automatically associated with the
defined contact. Devices already in the database will not be affected.
Retries
The maximum number of retries for SNMP communication.
The range is from 0 to 255.
Timeout(s)
The maximum time in seconds that the requesting process waits for a response before
attempting a retransmission (or aborting if the maximum number of retries has been
reached).
The available range is 1 to 3,600 seconds.
SNMP Version
The SNMP protocol version used by the devices the NMS is attempting to discover.
The available options are:
v1
v2c
v3
For a complete list of all compatible SNMP versions for each device, see
Appendix E.
AlvariSTAR
138
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Task Manager
Parameter
Description
SNMP Credentials
Use the Add and Remove buttons to populate the SNMP Credentials. The type of
credentials differ, depending on the SNMP version.
For SNMP v1 and v2c, fill in the read/write community table:
Read Community - SNMP Read community to be used by discovery when
accessing devices in the range. If unique communities are not defined, the defined
global Read communities will be used one after the other.
Write Community - The unique SNMP Write community to be used when
accessing discovered devices in the range. If unique communities are not defined,
the global Write community paired with the global Read community that was used
to discover devices in the range will be used when accessing these devices.
For SNMP v3, the following credentials apply:
Username - Username used for authentication
Security Level - Authentication and privacy settings
»
NoAuth_NoPriv - Both authentication and
privacy are disabled
»
Auth_NoPriv - Authentication is enabled and
privacy is disabled
»
Auth_Priv - Both authentication and privacy are
enabled
Authentication Algorithm - Hashing algorithm applied to the authentication
password
»
MD5 - Message-Digest algorithm 5
»
SHA - Secure Hash Algorithm
Authentication Password - Password used for authentication
Privacy Algorithm - Encryption standard used for data transmission
»
AES - Uses the Advanced Encryption Standard
»
DES - Uses the Data Encryption Standard
Privacy Password - Encryption key used by the privacy algorithm
AlvariSTAR
139
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
5.2.7
Task Manager
LDAP Backup/File Aging Task
The LDAP Backup/File Aging task is used to set up the backup frequency for
LDAP credentials. LDAP Backup/File Aging tasks are system tasks and can only
be modified, not deleted.
To edit the LDAP Backup/File Aging Task:
1
In the Task Manager window, right click the LDAP Backup/File Aging task
from the list and select Edit. If the task is Active, the Runtime Results window
opens, displaying the status of the running task.
2
If the task is Inactive, the Database Aging Task is displayed.
Figure 5-8: The LDAP Backup/File Aging Edit Window
3
Use the Days Threshold field to indicate how often the backup task should be
run.
AlvariSTAR
140
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
5.3
File Manager
File Manager
The File Manager allows users to manage different types of files stored in the
database such as backup configuration files and performance collection files.
Figure 5-9: File Manager
For detailed information about each type of file that is supported for a particular
equipment, check the File Manager related section of the corresponding device
driver manual. In general, you can use the right click menu to import, export or
delete various files from the client file system. Depending on the file type,
AlvariSTAR
141
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
File Manager
additional options may be available in the context menu, such as initiating a
restore configuration task for configuration backup files.
You can display only specific types of files by selecting the corresponding setting
from the View drop menu at the top of the working area. When doing so, the table
header will change so that only the columns that are relevant for that particular
file type are shown. If you choose the All Files option, an additional summary
section will be displayed at the bottom of the Working Area. You can switch
between two types of summaries by right clicking on the section and selecting the
corresponding option from the context menu:
Summary by File Category - File counts for performance, configuration,
logging and other file categories.
Summary by File Type - File counts for various types of files according to the
installed Device Drivers.
AlvariSTAR
142
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
5.4
Contact Manager
Contact Manager
The Contact Manager enables to organize and manage your contacts. Each device
can be associated with a contact.
To open the Contact Manager:
1
Select Administration > Contact Manager from the main menu or the
Navigation Pane. The Contact Manager displays a list of available contacts.
AlvariSTAR
143
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
Contact Manager
Figure 5-10: Contact Manager
2
Use the following controls in the right click menu of the Contact Manager
window:
AlvariSTAR
Button
Description
New
Opens the Contact Editor window, enabling to create new contacts.
Edit
Opens the Contact Editor window, enabling to modify the selected
contact.
144
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
5.4.1
Contact Manager
Button
Description
Delete
Deletes the selected contact(s) from the Contact Manager window
and from the database. Contacts that are associated with equipment
cannot be deleted.
Associating Devices with a Contact
To associate devices with a contact:
Open the Equipment Editor of the device. Click the Browse button next to the
Contact field to open the Select Contact window and select a contact.
5.4.2
Creating or Modifying a Contact
To create/modify a contact:
1
From the Contact Manager window, right click and select New to create a new
contact. To modify an existing Contact, select a contact from the list and click
Edit, or double-click on the selected contact.
Figure 5-11: The Contact Editor
AlvariSTAR
145
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
2
3
Contact Manager
Configure the following parameters:
Parameter
Description
Contact ID
A unique identifier for this contact. Up to 80 printable characters.
First Name
Optional. The contact’s first name. Up to 80 printable characters.
Last Name
Optional. The contact’s last name. Up to 80 printable characters.
Company
Optional. The contact’s company name. Up to 80 printable
characters.
Contact Icon
Optional. Select from the drop-down list an icon to represent this
contact: Contact/Group.
Address
Optional. The contact’s address. Up to 80 printable characters.
Phone Number
Optional. The contact’s phone number. Up to 80 printable characters.
Mobile Number
Optional. The contact’s mobile number. Up to 80 printable characters.
Email
Optional. The contact’s e-mail address. Up to 80 printable characters.
Fax Number
Optional. The contact’s fax number. Up to 80 printable characters.
Click OK, to save and close the contact, or click Cancel to close the window
without saving the changes.
AlvariSTAR
146
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
5.5
License Manager
License Manager
LOCAL CRAFT NOTE
The License Manager is not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility.
This section includes:
“The License Manager” on page 147
“Adding Licenses” on page 149
“Activating Existing Licenses” on page 149
“Rescue License” on page 149
“Displaying Licensing Information” on page 150
5.5.1
The License Manager
The License Manager displays information about valid licenses for managing
different device types, summary details on the currently managed device types,
and server information included in the license.
To access the License Manager window:
Select Administration > License Manager from the main menu or the Navigation
Pane.
AlvariSTAR
147
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
License Manager
Figure 5-12: License Manager
The License Manager displays the following information for each licensed device
type: <Name> (#) used: #
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Name
The device type.
(#)
The number of licensed devices of the applicable type.
used: #
The number of managed devices. The number increases whenever a
new device is discovered.
148
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
License Manager
When the number of discovered devices (Managed Devices) reaches the number of
Licensed Devices, additional discovered devices will be ignored.
Unlicensed devices will be marked in Equipment Manager with an exclamation
icon.
When considering future expansion plans, the number of licensed devices
compared with the number of managed devices of each type, will indicate whether
there is a need for an updated license.
5.5.2
Adding Licenses
Before adding a license, make sure that the file obtained from the supplier is
available.
To add licenses:
From the right click menu, select Add and browse to the location of the license
file. Select the file and click Open. The new licenses are displayed on the list.
Alternatively, save the license file in the /<Management_System>/file
system/license folder. The next time the server will be restarted, the new license
will also be added.
5.5.3
Activating Existing Licenses
The new license added to the system needs to be activated in order to enable the
system to manage the required devices.
To activate a license:
Right click the required license and select Activate.
NOTE
Activating a license will deactivate all other licenses.
5.5.4
Rescue License
The NMS comes with a default license called Rescue. This license is activated
automatically if there is no other license currently active. It allows the user to
login and add a new valid license. This prevents the user from being locked out of
the application if the current license expires.
AlvariSTAR
149
User Manual
Chapter 5 - Administration
5.5.5
License Manager
Displaying Licensing Information
To display licensing information:
From the right click menu, select Licensing Information. The Server Information
window is displayed showing the Server IP and MAC Addresses.
Figure 5-13: Server Information Window
AlvariSTAR
150
User Manual
Chapter
6
Security Management
Chapter 6 - Security Management
In This Chapter:
“Overview” on page 153
“Audit Log Manager” on page 154
“User Manager” on page 160
“User Profile Manager” on page 168
“User Session Monitor” on page 176 - not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility
“Password Policy” on page 179
“External Entities Mapping” on page 182
“User Domain Manager” on page 185
AlvariSTAR
152
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
6.1
Overview
Overview
In the Security Management menu you can define and manage user permissions
and access rights for users of the management system. The access level you
assign to users determines the management functions that the user can access.
The menu provides access to the following windows:
Audit Log Manager - Enables to view recorded events and export the logged
data to an external Comma Separated Value (CSV) file. Refer to Section 6.2.
User Manager - Enables to create and manage users, and associate
information with each user. Refer to Section 6.3.
User Profile Manager - Enables to create and manage user profiles, which
contain the default access right definitions for all users assigned to that user
group. Refer to Section 6.4.
User Session Monitor (not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility) - Enables to
display information on the currently logged in users and to send messages to a
logged in user. Refer to Section 6.5.
Password Policy - Enables to set policies for user passwords. These policies
govern the security measures applied to user’s attempts to log in.
NOTE
All security changes will be visible to the user only after logging out and logging back into the
system.
AlvariSTAR
153
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
6.2
Audit Log Manager
Audit Log Manager
The management system provides a logging service that records messages to the
database upon the occurrence of pre-specified events. These messages can
include event date and time, event type, error messages and other important
information according to the recorded event. The Audit Log Manager enables to
view recorded events and export the logged data to an external Comma Separated
Value (CSV) file.
To open the Audit Log Manager:
Select Security Management > Audit Logs from the main menu or the Navigation
Pane. The Audit Log Manager displays a list of all logged records.
AlvariSTAR
154
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
Audit Log Manager
Figure 6-1: Audit Log Manager
For each audit record, the following information is displayed:
Event Time - The date and time of the event
AlvariSTAR
155
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
Audit Log Manager
Category - The category of the event:
»
Equipment Manager
»
Event Filter Manager
»
Event Template Manager
»
Licence
»
NBI Manager
»
NBI Policy Manager
»
Script Command Manager
»
Security
»
System
»
Task Manager
»
User Manager
»
User Profile Manager
User ID - The user who initiated the action. System User ID indicates a system
initiated action.
AlvariSTAR
156
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
Audit Log Manager
The action performed:
AlvariSTAR
»
Change Password
»
Entity Change
»
Entity Create
»
Entity Delete
»
Equipment Create
»
Equipment Delete
»
Licence Activated
»
License Expired
»
License Imported
»
System Shutdown
»
System Startup
»
Task Abort
»
Task Create
»
Task Delete
»
Task Finish
»
Task Start
»
Task Schedule
»
Task Unschedule
»
Task Update
»
User Login
»
User Logout
157
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
Audit Log Manager
Target Entity - The element which is the target of an action, (for example: the
"entity delete" action that for which the target is a user named "aa"):
AlvariSTAR
»
Event History DAP
»
User of any type
»
Audit Log DAP
»
Task Names
»
License Names
»
Filter Names
»
Device Names
158
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
Audit Log Manager
Entity Type - The entity associated with the event.
»
Database Aging Task
»
Event Filter
»
Event Template
»
License
»
NBI
»
NBI Policy
»
Network Discovery Task
»
Performance Collection Task
»
Script Command
»
Security
»
Range Discovery Task
»
System
»
User
»
User Profile
»
Additional entities according to the installed Device Driver(s)
To export the information of selected audit records:
Right click the desired entry and select Export. In the window that opens, browse
to the desired location, enter a file name and type, and click Save.
AlvariSTAR
159
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
6.3
User Manager
User Manager
The User Manager enables to create and manage users, and associate information
to them such as passwords, profile membership and contact information. You can
filter the display to show a select subset of users.
6.3.1
The User Manager Window
The User Manager displays the User Name, Display name, and status (Active or
Suspended, Password Expired and Activation Waiting) for each user.
To access the User Manager window:
Select Security Management > User Manager. The User Manager window is
displayed.
AlvariSTAR
160
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Manager
Figure 6-2: User Manager
To reset a user’s password:
1
Right click a user entry from the list.
2
From the context menu, select Reset Password. The Reset Password window
is displayed.
AlvariSTAR
161
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Manager
Figure 6-3: Reset Password Window
3
6.3.2
Enter and confirm the new password.
Adding or Modifying a User
You can add new users or edit existing ones by modifying their properties.
You can set the User Profiles to associate with a user (see Section 6.4 for
information about how to create the profiles). As you grant permissions to defined
profiles, you can grant or deny users access to certain functions based on their
profile associations.
To create a new user:
1
From the right click menu, select New to display the User Editor.
2
Enter the appropriate information for the General section. Most of the
information associated with a user is optional. However, the Username entries
required.
AlvariSTAR
162
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Manager
Figure 6-4: User Editor - General
NOTE
The Username must be unique; if it matches an existing Username, the application generates an
error. The Username you enter here is displayed in the User Manager window and in all relevant
reports.
3
AlvariSTAR
Click Next and enter the required information for the Security Info section:
163
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Manager
Figure 6-5: User - Security Info
Parameter
Description
User Name
Read-only. Taken from the previous dialog box.
Password
Password is mandatory. The password must adhere to the Password
Policy.
Confirm Password
Re-enter the password.
Password Creation Date
Date you created the password. The date is added automatically. The
countdown for the password expiration age begins from this date.
AlvariSTAR
164
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Manager
Parameter
Description
Password Expiration Date
Specify a date when the password will expire. The default is three months.
Account Activation Date
The date when this account becomes effective. This field lets you create
accounts in advance. The accounts remain with Activation Waiting status
until the first login of the user after the Effective Date.
Specify an Effective Date by entering the date directly in the text field, in the
proper format (by default: month/day/year). You can also click the
Calendar button and select a date from the calendar graphic display.
Password Never Expires
When selected, the user’s password will not expire, regardless of the
password policy.
Login Attempts
Number of attempts to login until the system is locked
Last Login Time
Time that the user last logged in
User State
Active or Activation Waiting
4
Click Next and set the user profile in the User Profile section. Use the controls
in this section to assign profiles to or remove assignments from the current
user:
AlvariSTAR
165
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Manager
Figure 6-6: User - User Profile
To
Do This:
Assign or remove one
profile to the user
1
Select a profile from the left pane (Available User Profiles)
2
Click the right-arrow (>) button to move the profile into the
right pane (Profile Membership), or left-arrow (<) to remove.
1
Ctrl+click to select multiple items or click on one item and
Shift-click on another to select a range of consecutive items
2
Click the right-arrow (>) or left-arrow (<).
Assign or remove
multiple profiles
AlvariSTAR
166
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Manager
To
Do This:
Assign or remove all
profiles to the user
Click the double-right-arrow (>>) or double-left-arrow (<<) button
Click Finish. The new user is added to the list.
To edit an existing user entry:
1
Right-click an entry from the list and select Edit. A three-tab User Editor
appears, open to the General tab.
2
Modify the information as required in the General, Security Info and User
Profile tabs. For more information, see the steps in “To create a new user:” .
3
Click OK to apply the changes.
4
Click Delete to remove the entry.
In addition to these entries, you may want to associate the user with a Profile.
This confers a predetermined set of permissions to the user. See Section 6.4 for
more information.
AlvariSTAR
167
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
6.4
User Profile Manager
User Profile Manager
The User Profile Manager lets you create user profiles, edit them or delete profiles.
You can associate individual users with profiles and grant permissions to users
based on their association with a profile.
Only profiles that have no users can be deleted. Default profiles and users cannot
be deleted or modified.
By default, several user profiles with one user defined in each profile are provided
when you install your application. The following are the defaults:
»
Administrators (admin)
»
Observers
»
Managers
To access the User Profile Manager
Select Security Management > User Profile Manager from the main menu or the
Navigation Pane. The User Manager window is displayed, showing the profile
names and how many users share those profiles.
AlvariSTAR
168
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Profile Manager
Figure 6-7: User Profile Manager
To add a new profile:
1
In the User Profile Manager, right click and select New.A User Profile editor
window is displayed.
AlvariSTAR
169
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Profile Manager
Figure 6-8: User Profile Editor
2
3
Enter a unique name for the new profile and optionally add a description.
If you want to assign that new profile to existing user(s), click Add; The User
Selector window is displayed. Select the user(s) to which to assign the profile
and click Select.
AlvariSTAR
170
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Profile Manager
Figure 6-9: User Selector
4
AlvariSTAR
Click Next; The Security Assignment window is displayed.
171
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Profile Manager
Figure 6-10: User Profile - Security Assignment
5
Grant permissions to the profile by selecting a predefined function check-box
and then possible operations (edit, delete, configure, and so on) that each
profile or user can perform when exercising the function. To select all, check
the Functional Permissions and/or Operations check-boxes.
6
Click Finish to save your settings.
To modify an existing profile:
Right click the profile in the Profile Manager, and select Edit; An editor window is
displayed, with two tabs.
AlvariSTAR
172
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Profile Manager
Figure 6-11: User Profile Editor - General Tab
7
In the General tab, enter or modify the description of the profile. The name is
read-only.
8
If you want to assign that profile to existing user(s), click Add; The User
Selector window is displayed. Select the user(s) to which to assign the profile
and click Select. To remove users from the profile click Remove or Remove
All.
9
In the Security Assignment tab, set the permissions to the profile: Grant
permissions by selecting a predefined function and then possible operations
AlvariSTAR
173
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Profile Manager
(delete, edit, configure, and so on) that each profile or user can perform when
exercising the function. To select all, check the Functional Permissions and/or
Operations check-boxes.
Figure 6-12: User Profile Editor - Security Assignment Tab
10 Click OK to save your settings.
To delete a profile:
AlvariSTAR
174
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Profile Manager
Right click the profile to remove and select Delete. Default profiles cannot be
deleted.
AlvariSTAR
175
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
6.5
User Session Monitor
User Session Monitor
LOCAL CRAFT NOTE
The User Session Monitor is not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility.
The User Session Monitor window displays information on the currently logged in
users and enables sending messages to a logged in user. Users with Administrator
rights can terminate the application of other users.
To open the User Monitor:
1
Select Security Management > User Session Monitor from main menu or the
Navigation Pane. The User Session Monitor displays a list the Current Logged
In Users with the User Name, IP addresses with correlation to server and client
IPs, and login time for each of the currently logged in users.
AlvariSTAR
176
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Session Monitor
Figure 6-13: User Session Monitor Window
2
Use the following options available in the User Session Monitor right click
menu:
AlvariSTAR
Button
Description
Send Message
Select after right clicking one of the logged in users to open the
Sending Message window, enabling you to send a text message to
the selected user.
177
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
AlvariSTAR
User Session Monitor
Button
Description
Kill
Select to terminate the application of the selected user(s). Only an
Administrator can perform this operation to terminate applications of
users with lower permission levels.
178
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
6.6
Password Policy
Password Policy
The Password Policy editor enables to set policies for user passwords, such as
required length, required characters, expiration policy.
To open the Password Policy Editor:
Select Security Management > Password Policy from the main menu. The
Password Policy Editor opens.
Figure 6-14: Password Policy Editor
The Password Policy Editor includes the following parameters:
AlvariSTAR
179
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
Password Policy
Parameter
Description
Minimum Password Length
Sets the minimum length of accepted passwords.
Any password with less than the set minimum will be
rejected.
Value range: 1 - 32.
Maximum Password Length
The maximum length allowed for a password. The
maximum length is pre-set to 32 characters and
cannot be changed.
Character Setting Rules
Lower Cases
When checked, a new password will be required to
include at least one lower case character.
Upper Cases
When checked, a new password will be required to
include at least one upper case character.
Numbers
When checked, a new password will be required to
include at least one digit.
Special Characters
When checked, a new password will be required to
include at least one special character, e.g. <, >, /, *,
&, ^, $, #, !.
Login and Expiration
Login Attempts
The number of allowed erroneous login attempts
before the application is closed and the user is
blocked.
This parameter can be configured for a selected user
from the User Manager. In case of contradiction, the
parameter set in the User Manager overrides the
general policy for the specific user.
Value range: 3 - 20
Password Expiration Age
The time in months before the user is required to
change the password.
This parameter can be configured for a selected user
from the User Manager. In case of contradiction, the
parameter set in the User Manager overrides the
general policy for the specific user.
From the User Manager you can set the password
expiration policy for a selected user to never expire.
Value range: 1 - 12
AlvariSTAR
180
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
Password Policy
Parameter
Description
Password Expiration Warning
The number of days before a user password expires
during which a message requiring to change the
password is displayed. The message is displayed at
every login until the password expiration age is
reached.
Value range: 1 - 14
Password History
The number of old passwords for the system to keep
a record. The user will not be able to repeat a used
password if it was used in a cycle within the set
range.
Value range: 0 - 10
Inactivity Session Timeout
The number of minutes with no user activity, after
which the user is logged out. The user will be
required to log in again to continue working.
Not applicable to the Local CRAFT Utility
Value range: 0 - 100
NOTE
All password policy parameters except Inactivity Session Timeout do not apply to external users.
AlvariSTAR
181
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
6.7
External Entities Mapping
External Entities Mapping
If you are using an LDAP server for user account management, you can map
existing LDAP entities to specific user profiles defined in the NMS. For this
purpose, you must set up a connection between the NMS server and the external
LDAP server. See Appendix C for details on how to do this.
NOTE
The external LDAP connection is disabled by default. If you want to enable it, follow these steps:
1
Go to <NMS_Installation_Path>\jboss\server\nms\deploy\bwanms.sar\conf
2
Edit the appserver.properties file
3
Look for the com.bwanms.backend.security.externalLDAPEnabled entry
4
Change its value from false to true
5
Restart the NMS server
To open External Entities Mapping:
Select Security Management > External Entities Mapping from the main menu. The
External Entities Mapping window opens.
NOTE
The External Entities Mapping is available only to users with “New” operations enabled for the “User
Manager” functional permission. For more information about setting functional permissions, see
“User Profile Manager” on page 168.
AlvariSTAR
182
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
External Entities Mapping
Figure 6-15: External Entities Mapping
AlvariSTAR
Parameter
Description
Global Default User Profile
Use this drop box to allocate a default user profile to
entities defined in the LDAP server that are not
explicitly mapped to any user profile.
183
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
External Entities Mapping
Parameter
Description
External Entity Type
Select an entity from the LDAP server that you wish
to map to one or multiple user profiles. You can either
choose:
A group of users, or
A specific user (in which case the group(s) it
belongs to will be displayed below, in the Member
of text box).
User Profiles
Select one or more user profiles you wish to map to
the external entity.
Use the > button to map individual user profiles
that are available
Use the >> button to map all the user profiles that
are available
Use the < button to unmap individual user profiles
that have been previously mapped
Use the << button to unmap all the user profiles
that have been previously mapped
When you are done defining a mapping rule, click Add to confirm it. The rule will
be visible in the mapping table.
To remove an active rule, select it from the mapping table and click Remove.
AlvariSTAR
184
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
6.8
User Domain Manager
User Domain Manager
The User Domain Manager is used to allocate location visibility domains to each
user that is not an administrator (administrators are always able to see all
network elements in every location). A domain is a group of Network Elements
that are located in one or multiple areas. Therefore, domains are defined by
selecting specific locations that have been previously defined in the Location
Manager.
NOTE
The User Domain Manager is enabled by default. If you want to disable it, follow these steps:
1
Go to <NMS_Installation_Path>\jboss\server\nms\deploy\bwanms.sar\conf
2
Edit the appserver.properties file
3
Look for the com.bwanms.backend.domainmanagement.disable entry
4
Change its value from false to true
5
Restart the NMS server
By default, users are not assigned to any domain, thus being able to see all
network elements. A user who is assigned to a domain, can only view and manage
the network elements and related objects inside that domain or the ones that have
no domain associated. The following features are impacted:
Equipment Manager
»
Only equipment in the current users’s domain and equipment not
associated to any domain is visible
»
All counters are computed according to the visible equipment
»
Equipment selectors implement domain based filtering
File Manager
AlvariSTAR
»
Only files pertaining to equipment in the current user’s domain are visible
»
Backup/restore tasks are limited to the applicable domain
»
Imported files are visible to all users
185
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Domain Manager
Active Events/Event History
»
Only events pertaining to equipment in the current user’s domain are
visible
»
All counters are computed according to the visible equipment
Task Manager
»
All tasks are displayed, but edit and run operations only work for
equipment in the current user’s domain
Location Manager
»
All locations are displayed, but only locations associated to the current
user’s domain can be edited
To open the User Domain Manager:
Select Security Management > User Domain Manager from the main menu. The
User Domain Manager opens.
NOTE
The User Domain Manager is available only to users with administrator privileges.
AlvariSTAR
186
User Manual
Chapter 6 - Security Management
User Domain Manager
Figure 6-16: User Domain Manager
The User Domain Manager includes the following parameters:
Parameter
Description
User
Use the drop box to select a user you want to assign
a domain.
Administrators are not available.
Assigned Locations
Use the location tree to check the locations you want
to be assigned to the user’s domain.
Once you have defined a domain for a specific user, click the Save button to
enable it. You can then switch to another user and start another domain
definition process.
Clicking the Revert button resets the currently selected user’s domain to the
previously saved setting.
AlvariSTAR
187
User Manual
Appendix
A
Watchdog
Appendix A - Watchdog
In This Appendix:
“The Watchdog Application” on page 190
AlvariSTAR
189
User Manual
Appendix A - Watchdog
A.1
The Watchdog Application
The Watchdog Application
Watchdog is an external application for monitoring the NMS server, LDAP and
database servers (providing they reside on the same machine as the NMS). The
NMS watchdog service is started when the NMS server is started.
In case the server or LDAP are down, Watchdog will try to restart them. The
monitoring information and the actions involved in restarting the NMS server or
LDAP are written in the watchdog.log file. The log is saved daily to
<Management System Root>\<NMS installation
folder>\watchdog\watchdog.log.YYYY-MM-DD
Watchdog can be configured from the watchdog.properties file located in
<Management System Root>\<NMS installation folder>\watchdog.
Watchdog logs can be automatically deleted by configuring the following two
parameters (in red text) in the log4j.xml file located in
<Management System Root>\<NMS installation folder>\watchdog.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<?xml version=”1.0” encoding=”UTF-8” ?>
<!DOCTYPE log4j:configuration SYSTEM “log4j.dtd”>
<log4j:configuration xmlns:log4j=”http://jakarta.apache.org/log4j/”>
<appender name=”LOG_SHRINK”
class=”com.bwanms.watchdogcommon.SizeShrinkAppender”>
<param name=”File” value=”${nms.root}/watchdog/log/dummy.log”/>
<param name=”MaxFileSize” value=”10KB”/>
<param name=”MaxBackupIndex” value=”1”/>
<param name=”RetainsDays” value=”10”/>
<!-- max log files size (ex.: 10KB, 20MB, 3GB, 100) -->
<param name=”MaxFilesSize” value=”10MB”/>
<layout class=”org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout”>
<param name=”ConversionPattern” value=”%d %-5r %-5p [%c{2}] (%t:%x) %m%n”/>
</layout>
</appender>
<appender name=”FILE” class=”org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender”>
AlvariSTAR
190
User Manual
Appendix A - Watchdog
The Watchdog Application
<param name=”File”
value=”${nms.root}/watchdog/log/watchdog.log” />
<!-- Rollover at midnight each day -->
<param name=”DatePattern” value=”’.’yyyy-MM-dd”/>
<layout class=”org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout”>
<param name=”ConversionPattern” value=”%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %c{1} - %m%n”/>
</layout>
</appender>
<appender name=”stdout” class=”org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender”>
<layout class=”org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout”>
<param name=”ConversionPattern” value=”%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %c{1} %m%n”/>
</layout>
<filter class=”org.apache.log4j.varia.LevelRangeFilter”>
<param name=”LevelMin” value=”INFO” />
<param name=”LevelMax” value=”INFO” />
</filter>
</appender>
<root>
<priority value=”INFO” />
<appender-ref ref=”FILE”/>
<appender-ref ref=”LOG_SHRINK”/>
<appender-ref ref=”stdout”/>
</root>
</log4j:configuration>
AlvariSTAR
191
User Manual
Appendix
B
Remote Access
Appendix B - Remote Access
In This Appendix:
This appendix describes the alternative of accessing the NMS server via the Java
Web Start software framework, without using the NMS client:
“WebStart” on page 194
“The Web Portal” on page 195
AlvariSTAR
193
User Manual
Appendix B - Remote Access
B.1
WebStart
WebStart
You can access the NMS directly using Java Web Start, by employing the following
procedure:
1
Open a browser and type the following URL:
http://<NMS IP address>:8080/webstart
2
The Download NMS Client page opens, allowing you to download a .jnlp file.
3
Once the download is complete, run it to start your application remotely.
NOTE
The Java Network Launching Protocol (JNLP) is part of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). You
need JRE 1.6 or higher in order to run the .jnlp file.
AlvariSTAR
194
User Manual
Appendix B - Remote Access
B.2
The Web Portal
The Web Portal
The NMS server also runs a web portal that allows users to quickly access all the
applications in StarSuite which are installed. To access the web portal:
1
Open a web browser and type the following URL:
http://<NMS IP address>:8080/starsuite
The Web Portal interface is displayed
Figure B-1: The Web Portal
2
Click the desired application logo to launch it.
Selecting the NMS launcher, will take you directly to the Download NMS Client
page, from where you can proceed as described above.
AlvariSTAR
195
User Manual
Appendix
C
Connecting to an External LDAP
Server
Appendix C - Connecting to an External LDAP Server
In This Appendix:
This appendix describes how to set up a connection to a typical LDAP server:
“The LDAP Server Configuration File” on page 198
“Open LDAP Configuration” on page 199
“Active Directory Configuration” on page 200
AlvariSTAR
197
User Manual
Appendix C - Connecting to an External LDAP Server
C.1
The LDAP Server Configuration File
The LDAP Server Configuration File
To set up the parameters for connecting to an external LDAP server:
1
Go to <NMS path>\jboss\server\nms\deploy\bwanms.sar\conf
2
Open the external-ldap.properties file.
3
Edit the LDIF entries in this file, so that they apply to the corresponding LDAP
server.
See “Open LDAP Configuration” on page 199 and “Active Directory Configuration”
on page 200 for examples on how to configure the external-ldap.properties file.
AlvariSTAR
198
User Manual
Appendix C - Connecting to an External LDAP Server
C.2
Open LDAP Configuration
Open LDAP Configuration
The example below illustrates a typical configuration for connecting to an Open
LDAP server (installed by default from the Solaris CD).
java.naming.factory.initial =
com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory
java.naming.provider.url = ldap://192.168.10.171:10389
java.naming.security.authentication = simple
rootDN = cn=Directory Manager
rootPW = nssecret
ldapSuffix = dc=testing,dc=ldap
principalCNPrefix = ou=
principalCN = People
principalDNPrefix = cn=
groupCNPrefix = ou=
groupCN = Groups
groupDNPrefix = cn=
userObjectClass = inetOrgPerson
groupObjectClass = groupofUniqueNames
usernameAttribute = cn
#accountNameAttribute = sAMAccountName
groupNameAttribute = cn
groupDescriptionAttribute = description
groupMembersAttribute = uniquemember
AlvariSTAR
199
User Manual
Appendix C - Connecting to an External LDAP Server
C.3
Active Directory Configuration
Active Directory Configuration
The example below illustrates a typical configuration for connecting to an Active
Directory server.
java.naming.factory.initial =
com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory
java.naming.provider.url = ldap://192.168.10.120:389
java.naming.security.authentication = simple
rootDN = cn=Administrator,cn=Users,dc=nms,dc=local
rootPW = alpha
ldapSuffix = dc=nms,dc=local
principalCNPrefix = cn=
principalCN = Users
principalDNPrefix = cn=
groupCNPrefix = cn=
groupCN = Users
groupDNPrefix = cn=
userObjectClass = organizationalPerson
groupObjectClass = group
usernameAttribute = cn
accountNameAttribute = sAMAccountName
groupNameAttribute = cn
groupDescriptionAttribute = description
groupMembersAttribute = member
AlvariSTAR
200
User Manual
Appendix
D
Google Earth Management
Appendix D - Google Earth Management
In This Appendix:
The following sections describe how you can visualize your network elements in
Google Earth:
“Connecting Google Earth to the NMS” on page 203
“Viewing the Network Elements in Google Earth” on page 204
AlvariSTAR
202
User Manual
Appendix D - Google Earth Management
D.1
Connecting Google Earth to the NMS
Connecting Google Earth to the NMS
The NMS server maintains information regarding the network elements’ locations
in a Keyhole Markup Language based (.kml) file. By linking to this file, Google
Earth can use the information within to display your network’s topography. For
this purpose you need a computer with:
Google Earth installed
Access to the Internet
Access to the NMS server
NOTE
It is not required for the NMS server itself to run on a computer with Internet access.
To populate Google Earth with the network elements defined in the NMS:
1
Open Google Earth
2
Go to Add > Network Link.
3
In the New Network Link window that opens, type the following path in the
Link field:
http://<NMS path>:8080/bwanmsws/load.kml
4
Fill in the remaining Google Earth options according to your preferences and
click OK when done.
AlvariSTAR
203
User Manual
Appendix D - Google Earth Management
D.2
Viewing the Network Elements in Google Earth
Viewing the Network Elements in
Google Earth
Once Google Earth is synchronized with the NMS server, all viewable network
elements will be displayed in the My Places section. The following network
elements are visible in Google Earth:
Network elements supporting GPS cards or the Chain Manager feature
Network elements with latitude/longitude coordinates defined in Equipment
Editor
Figure D-1: Network Elements Displayed in Google Earth
AlvariSTAR
204
User Manual
Appendix D - Google Earth Management
Viewing the Network Elements in Google Earth
When clicking on a network element, either in My Places or on the map, a callout
containing information on the network element is displayed. The displayed
information includes:
Name, IP address, Type, Software version, Management status, Operational
state - As displayed in Equipment Manager
Alarm status - The network element’s highest order alarm currently displayed
in the Active Events manager. This alarm’s color code will also determine the
network element’s icon color.
Where applicable, sector coverage information is also displayed by highlighting
the covered area on the map.
AlvariSTAR
205
User Manual
Appendix
E
SNMP Compatibility
Appendix E - SNMP Compatibility
In This Appendix:
This appendix lists the SNMP versions supported by each device
AlvariSTAR
207
User Manual
Appendix E - SNMP Compatibility
E.1
SNMP Version Compatibility
SNMP Version Compatibility
Each device managed by AlvariSTAR may supports one or more SNMP versions:
Table E-1: SNMP Compatibility for Each Device
Device Driver
SNMP v1
SNMP v2C
SNMP v3
4Motion
-
X
-
BreezeMAX FDD/TDD
X
-
-
BreezeMAX DM
X
-
-
BreezeACCESS Family
X
-
-
BreezeMAX Extreme
-
X
-
BNB 300
X (only read)
-
X
Outdoor Cabinet
X
-
-
AAA Server
X
X
X
AlvariSTAR
208
User Manual